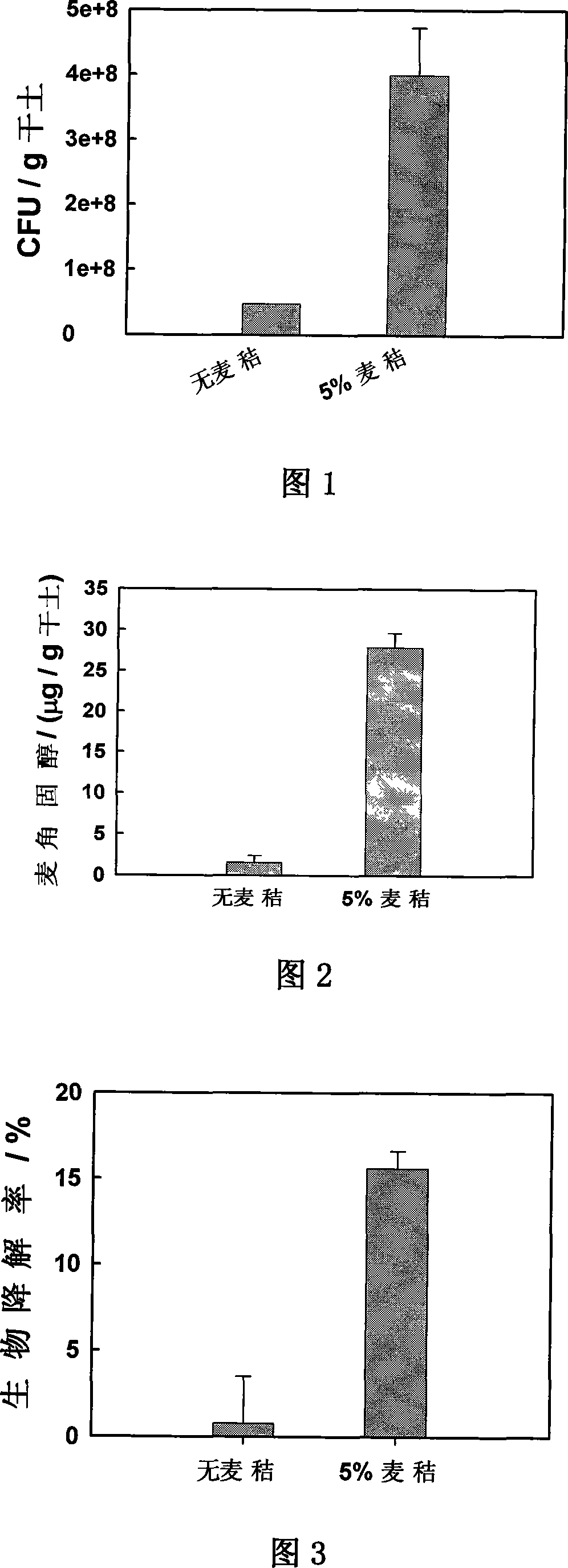
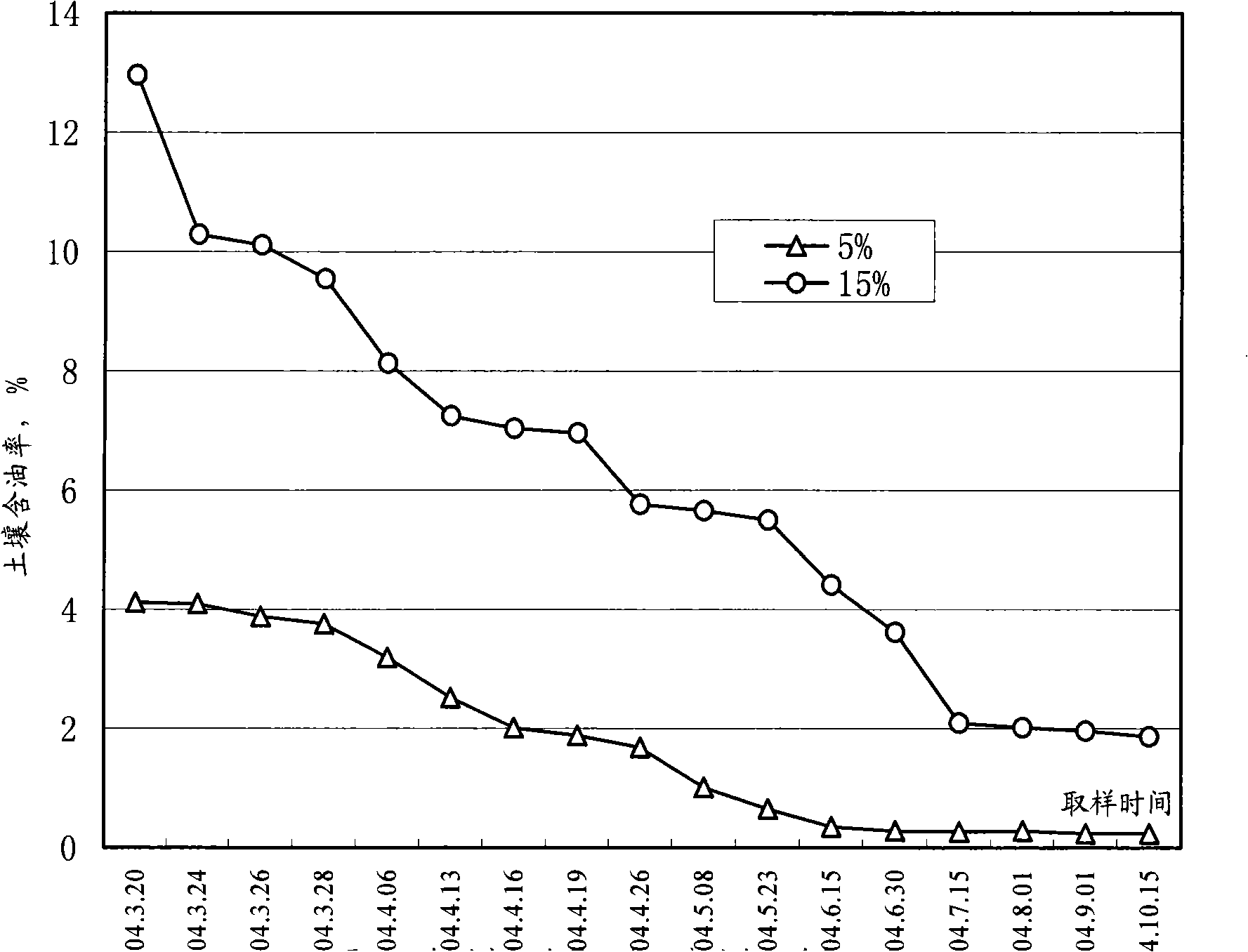
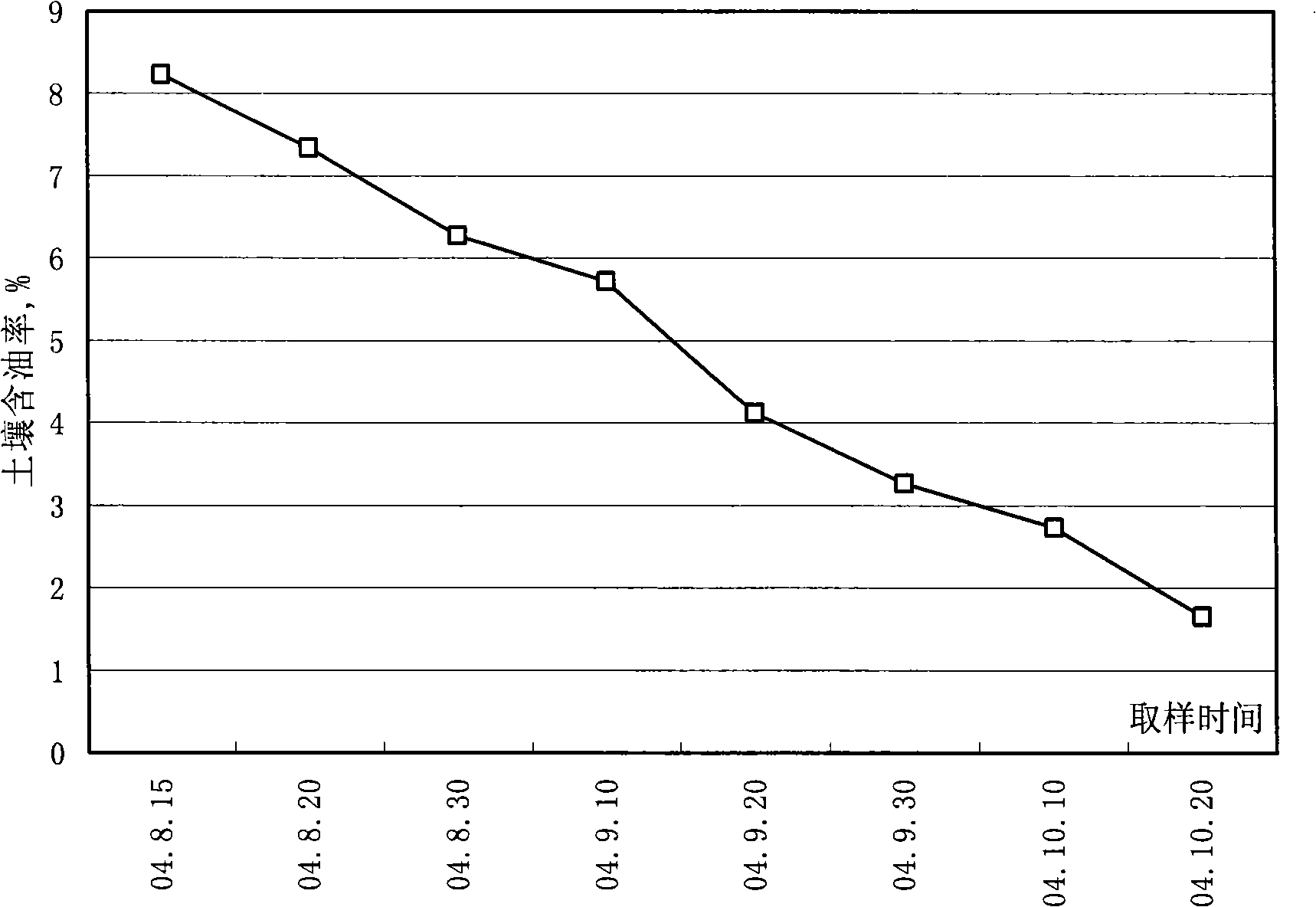
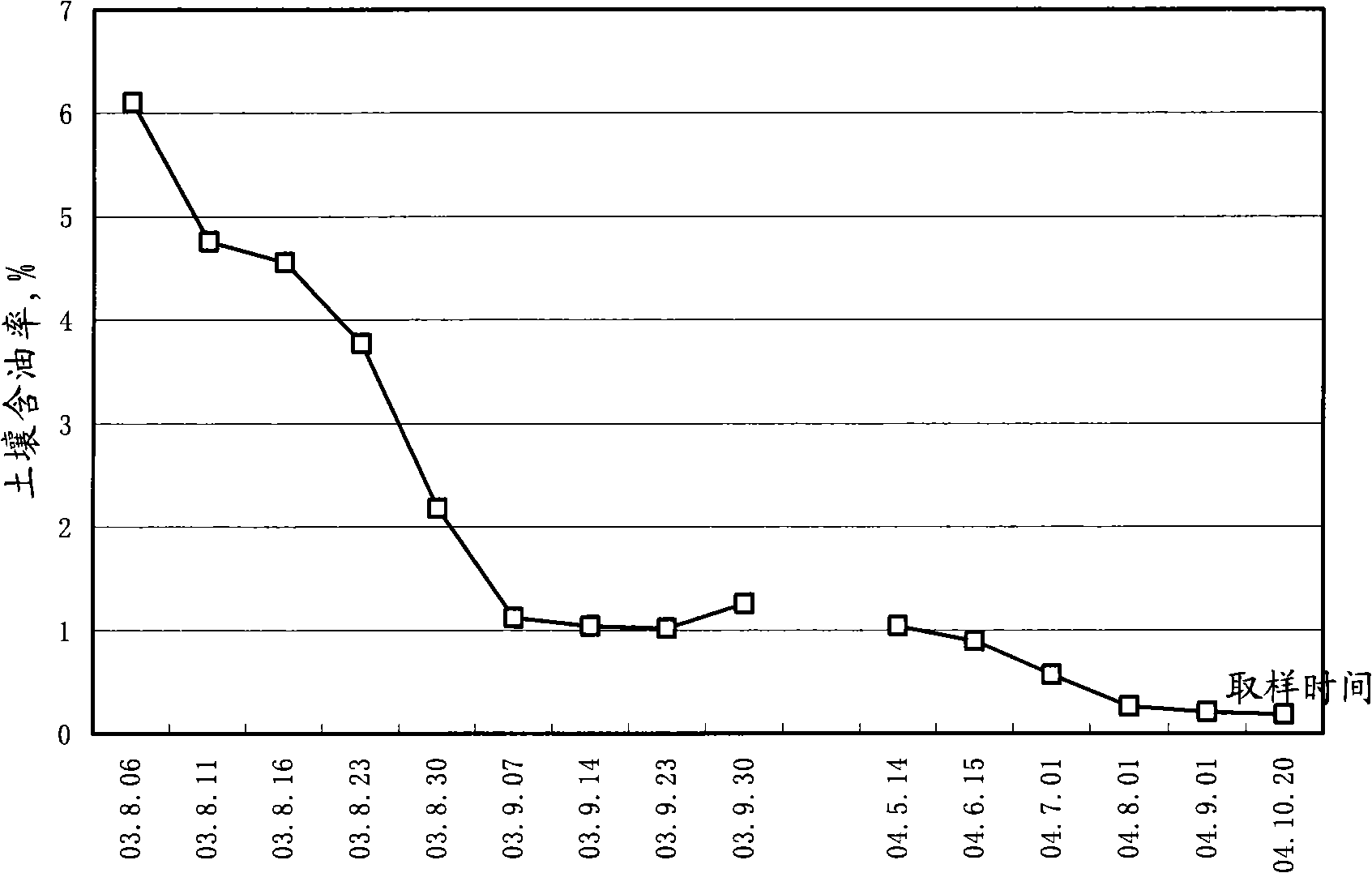
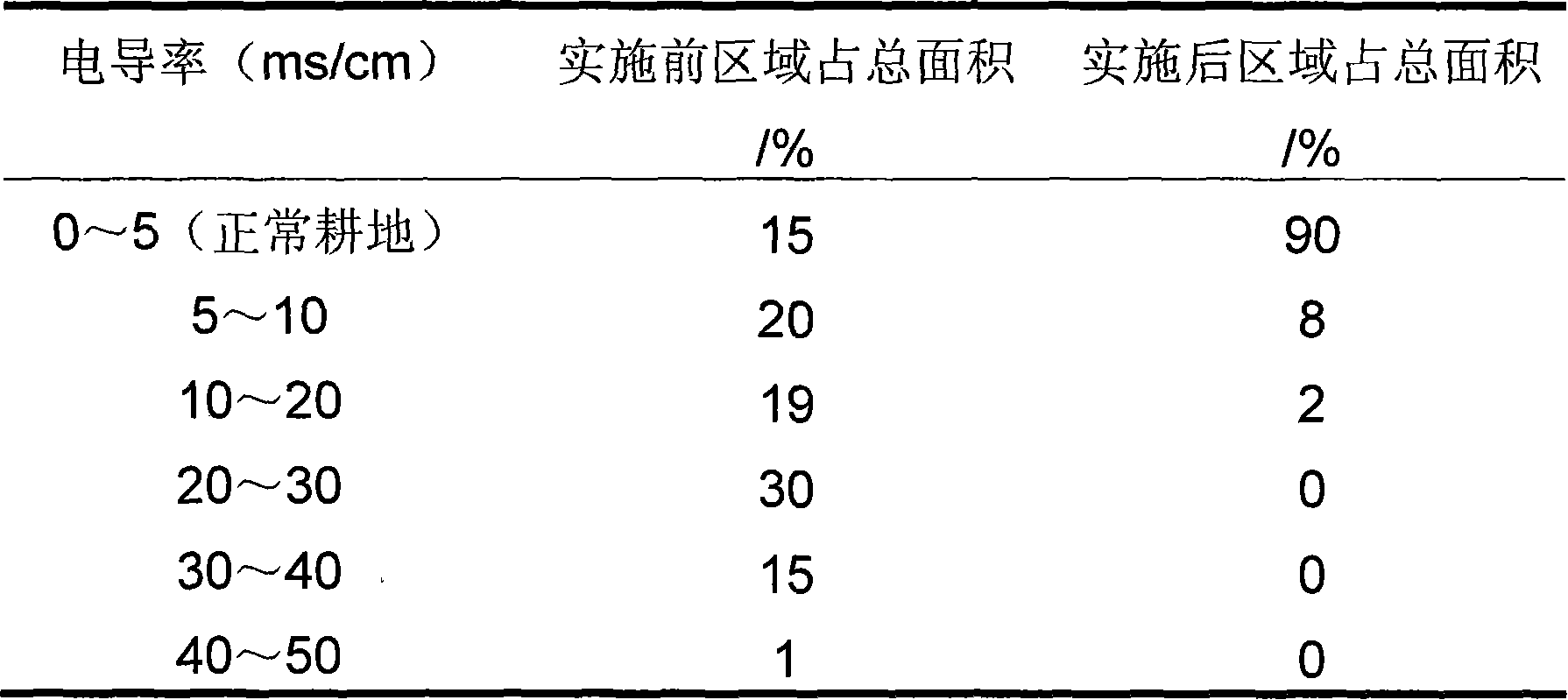
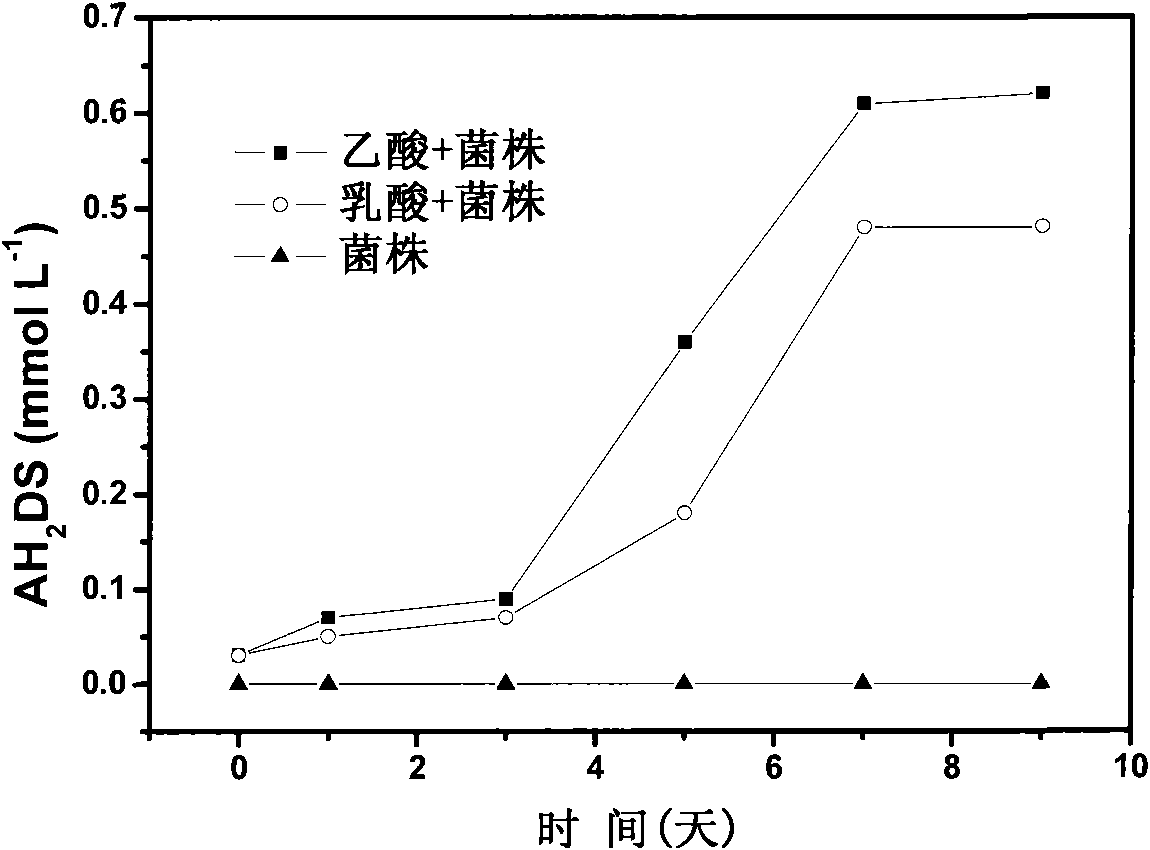
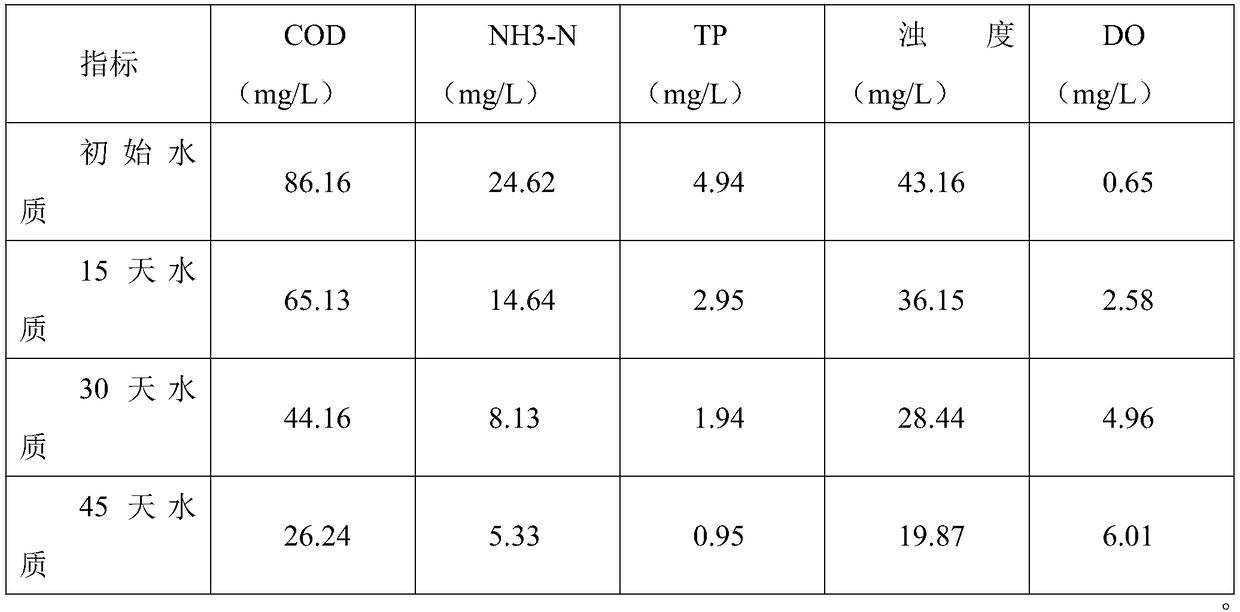
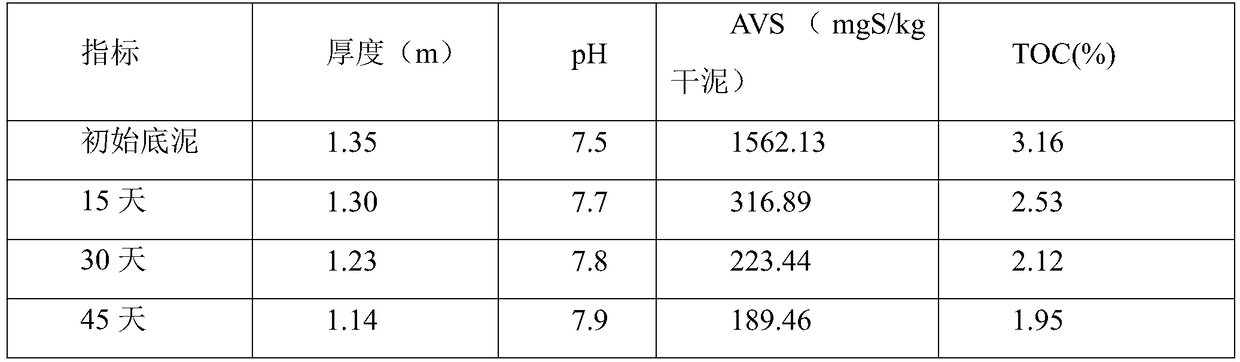
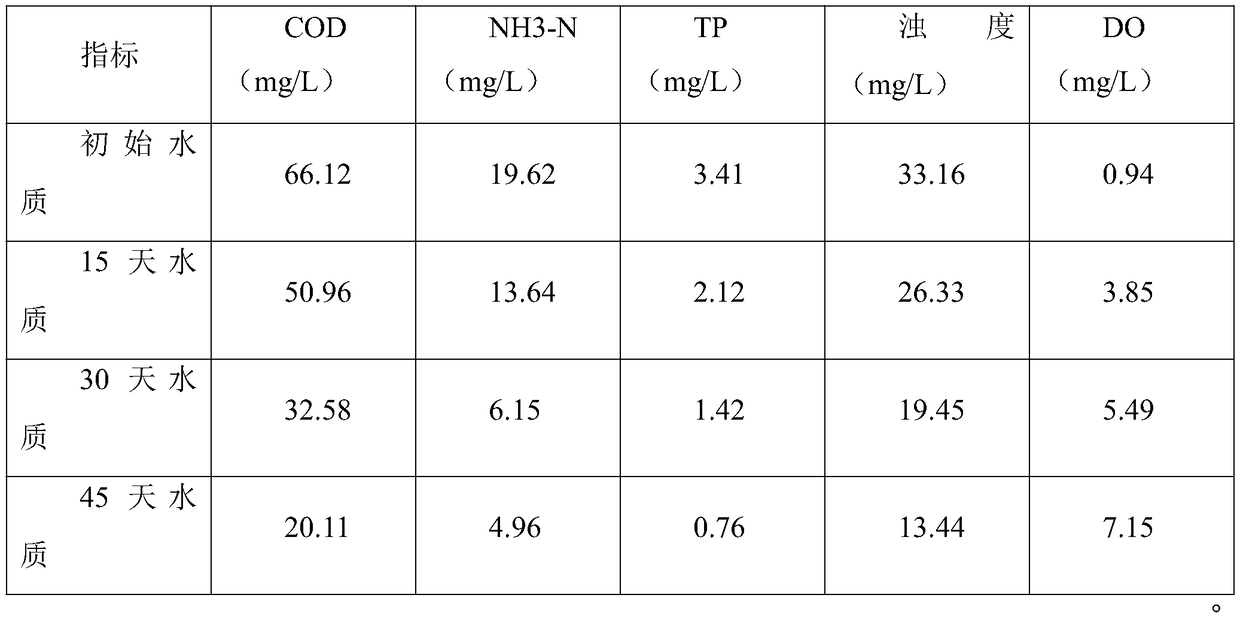
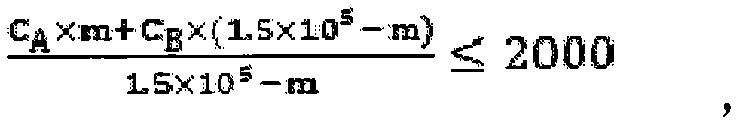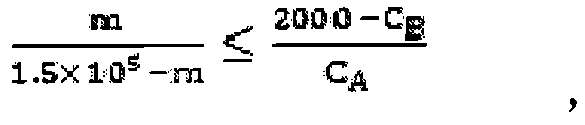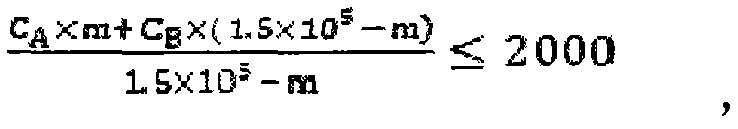Patents
Literature
102 results about "In situ bioremediation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bioremediation is the process of decontaminating polluted sites through the usage of either endogenous or external microorganism. In situ is a term utilized within a variety of fields meaning "on site" and refers to the location of an event. Within the context of bioremediation, in situ indicates that the location of the bioremediation has occurred at the site of contamination without the translocation of the polluted materials. Bioremediation is used to neutralize pollutants including Hydrocarbons, chlorinated compounds, nitrates, toxic metals and other pollutants through a variety of chemical mechanisms. Microorganism used in the process of bioremediation can either be implanted or cultivated within the site through the application of fertilizers and other nutrients. Common polluted sites targeted by bioremediation are groundwater/aquifers and polluted soils. Aquatic ecosystems affected by oil spills have also shown improvement through the application of bioremediation. The most notable cases being the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in 2010 and the Exxon Valdez oil spill in 1989. Two variations of bioremediation exist defined by the location where the process occurs. Ex situ bioremediation occurs at a location separate from the contaminated site and involves the translocation of the contaminated material. In situ occurs within the site of contamination In situ bioremediation can further be categorized by the metabolism occurring, aerobic and anaerobic, and by the level of human involvement.
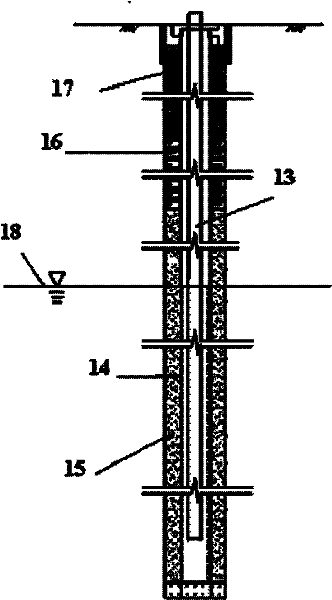
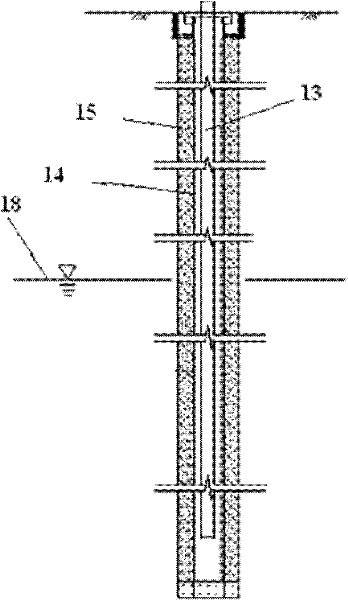
In-situ biological repairing method for biomass intensified petroleum contaminative soil
ActiveCN101104177APromote accumulationIncrease intakeFungiBacteriaBiomass degradationIn situ bioremediation
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Microorganism product for repairing soil polluted by petroleum and products produced thereby and repair method
InactiveCN101301657ASolve the problem of long-term storageAdapt to biodegradationFungiBacteriaBiotechnologySolarisation
The invention provides a micro-organism restoration product and a restoration method used for soils polluted by petroleum and petroleum products. The micro-organism restoration product consists of degrading bacteria of hydrocarbon, biological nutrient, biology surfactant and soil activator; the four components are singly stored; in the micro-organism restoration method, the four matters are added according to a certain proportion and steps and mixed at the same time so as to complete the inoculation of biology restoration; subsequently, diluent of the biological nutrient and the soil surfactant are sprayed periodically, meanwhile, water is supplemented and the plowing and oxygen solarisation of the soil are carried out till that the required indexes are achieved. The micro-organism restoration method and the micro-organism restoration product of the invention solidify the degrading bacteria on wheat bran, solve the problem of long-term storage of the miro-organism, and can obtain the required micro-organism with the activation can be obtained by activating the micro-organism by warm water when in use; the method can adopt in-situ biological restoration or ex-situ biological restoration.
Owner:TIANJIN RUIFENGYUAN BIOREMEDICTION
Preparation and use method of microbial immobilized material for remedying polluted soil
InactiveCN101372688AHigh affinityHigh immobilization efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationOn/in organic carrierHectareIn situ bioremediation
The invention discloses a method for preparing and using a microbial immobilized material for repairing contaminated soil. The method comprises the following steps: (1) after being dried by air, the waste biomass raw material is pulverized or ground into 1-20mm of particles; (2) the biomass particles are carbonized and sterilized at the temperature of 150-450 DEG C and under limited oxygen condition for 0.5-6 hours to prepare a carrier material; (3) the carrier material is put into bacterium suspension for enrichment culture according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 0.5-2mL / g, then the microbial immobilized material is produced; (4) the produced microbial immobilized material is added to organic contaminated soil according to the proportion of 1-500 tons per hectare soil, 0-30cm of topsoil is ploughed to cause the microbial immobilized material to be mixed evenly in the soil, simultaneously, the contaminated soil is biologically repaired and safe agricultural products are produced. The method has the advantages that the carrier material contains abundant lignin structures, carbon and nutrient elements, which provides more suitable matrix for microbial growth; and the immobilized material has strong affinity, high immobilization efficiency, strong adsorption capacity and good resistance against the pollutants in the environment; and the immobilized material is a soil fertilizer, and is suitable for large-scale in-situ biological repair of the contaminated soil.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Compositions for removing hydrocarbons and halogenated hydrocarbons from contaminated environments
InactiveCN1668535AReduce concentrationLow costOther chemical processesWater treatment compoundsSorbentSulfate
The invention provides a bioremediation composition for in situ bioremediation of soil and / or groundwater contaminated with hydrocarbons, comprising an adsorbent capable of adsorbing said hydrocarbons, a mixture of facultative anaerobes capable of metabolizing said hydrocarbon under sulfate-reduction conditions, a sulfate-containing compound that releases sulfate over a period of time, and a nutrient system for promoting growth of said anaerobes, wherein said nutrient system includes a sulfide scavenging agent.
Owner:REMEDIATION PROD INC
In situ biological restoring method of petroleum polluted soil
ActiveCN1785539AHigh biological activityPromote degradationContaminated soil reclamationPlastic mulchIn situ bioremediation
An in-situ biologic repairing method for the soil polluted by petroleum features that after the fungus-bacteria mixed liquid, soil improver, organic fertilizer and inorganic nutrients are applied to the polluted soil, the soil is irrigated, ploughed, and covered by plastic film.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for preparing magnetic microbe immobilizing material for soil pollution repair and application thereof
InactiveCN101629172AStrong adsorption capacityHas a locking effectContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesBiomassEnvironmental chemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing a magnetic microbe immobilizing material for soil pollution repair and an application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) drying, pulverizing and sieving waste biomass in 20-100 meshes; (2) charging the sieved biomass into 0.1 mol / L of iron salt solution, dropwise adding 3-6 mol / L of NaOH solution during stirring till the pH value is 9 to 10; filtering, drying and carbonizing sediments with limited oxygen at 100-400 DEG C for 1 hour to 4 hours to prepare a carrier material; (3) injecting bacterial suspension according to the solid-to-liquid ratio of 1-10mL / g and adding sodium alginate; (4) dropwise adding the mixed suspension into 2-5 percent of CaCl2 solution to prepare a particle with the diameter of 1 mm to 2 mm; breeding the particle to prepare a magnetic microbe immobilizing material; and (5) charging the prepared material into polluted soil according to 2-20 ton / hectare and plowing 0 cm to 30 cm of soil in the surface layer, after 3 to 12 months, recovering by magnetic separation, activating and recycling. The invention has the advantages of magnetic material and controllable particle parameter, can be recovered by magnetic separation after use and is suitable for in-situ biological repair and heterotopic slurry reaction vessel repair of the polluted soil.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for treating eutrophication water body by herbaceous plant waterborne planting
InactiveCN101125711APromote growthGrow fastCultivating equipmentsSoilless cultivationComing outSprouted Seeds
The invention discloses a water cultivation method of herbs to treat eutrophic water, comprising the steps: PVC plastic tubes are taken as a frame, a nylon net is bound on the frame to form a floating bed; seeds of grass species are soaked for accelerating germination at a room temperature of 28-32 DEG C, the seeds after germination are sowed in a seedling bed formed by a PE membrane with even eyelets to keep the moisture content and temperature, facilitating the germinated seeds to take root and grow; the seedling bed is put on the floating bed that floats in the eutrophic water after the roots of the grass species grow into three-leaf seedlings and come out through the eyelets of the PE membrane, then nutrient salts of nitrogen and phosphors, etc. in the water body are absorbed by the herbs, meanwhile, allelochemicals are secreted to inhibit the propagation of algae, so as to realize in-situ bioremediation of the eutrophic water and promote feed production when improving the water quality. The whole treating method realizes a good circulation system between 'environment-plant-animal-human'.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
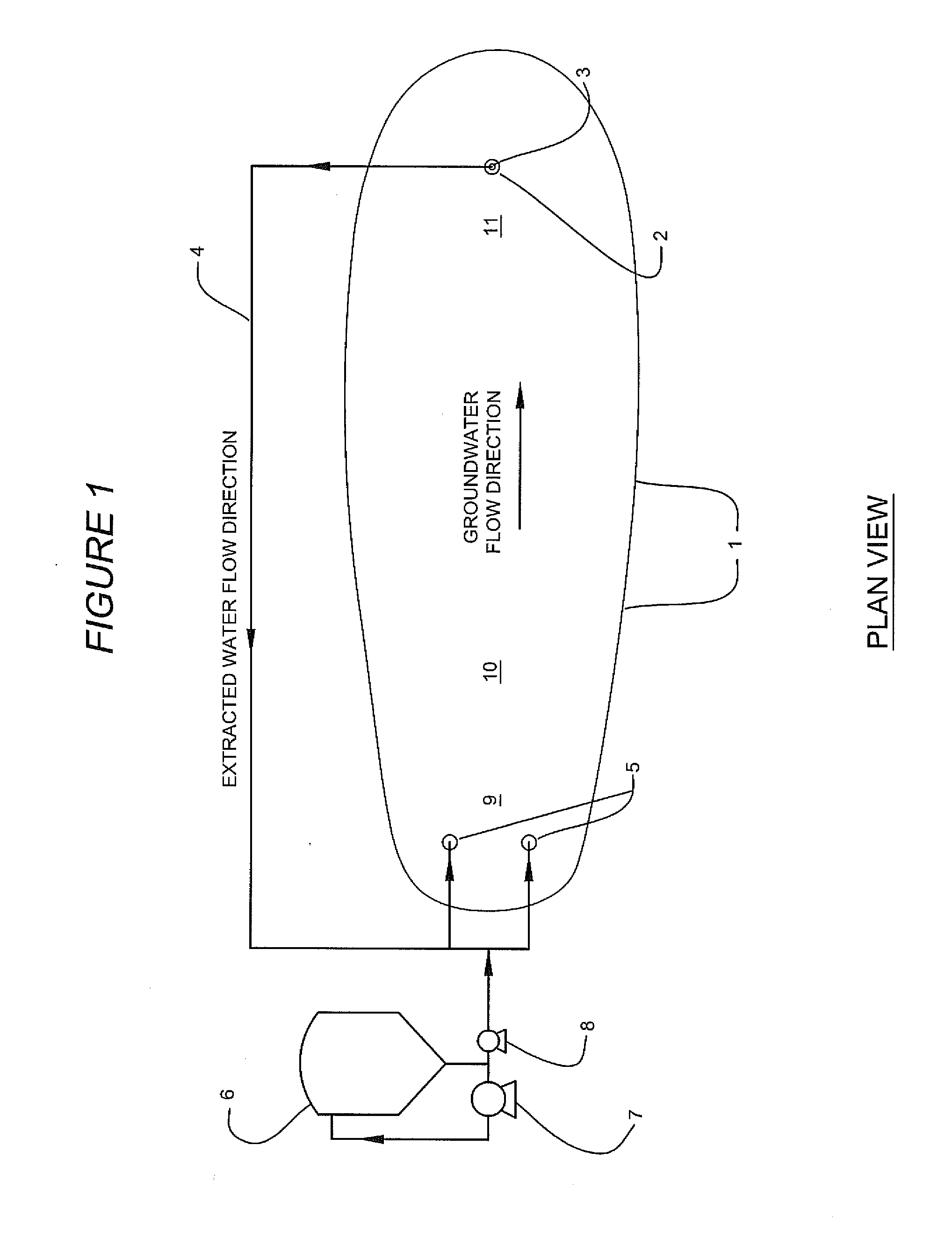
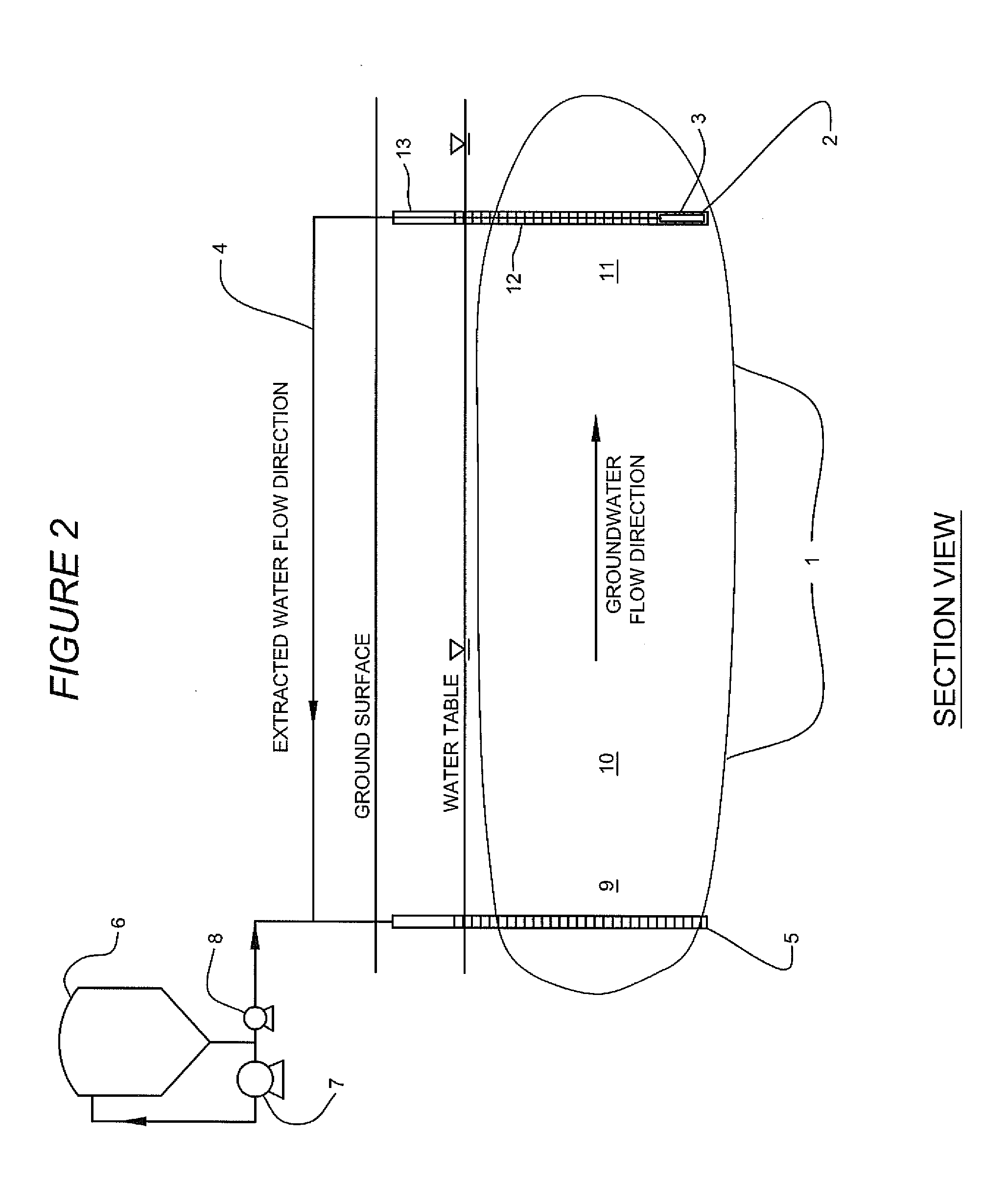
Method for in-situ bioremediation of pollution caused by chlorohydrocarbon of underwater
InactiveCN102976490AReliable in situ repairMaintain securityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesElectron donorIn situ bioremediation
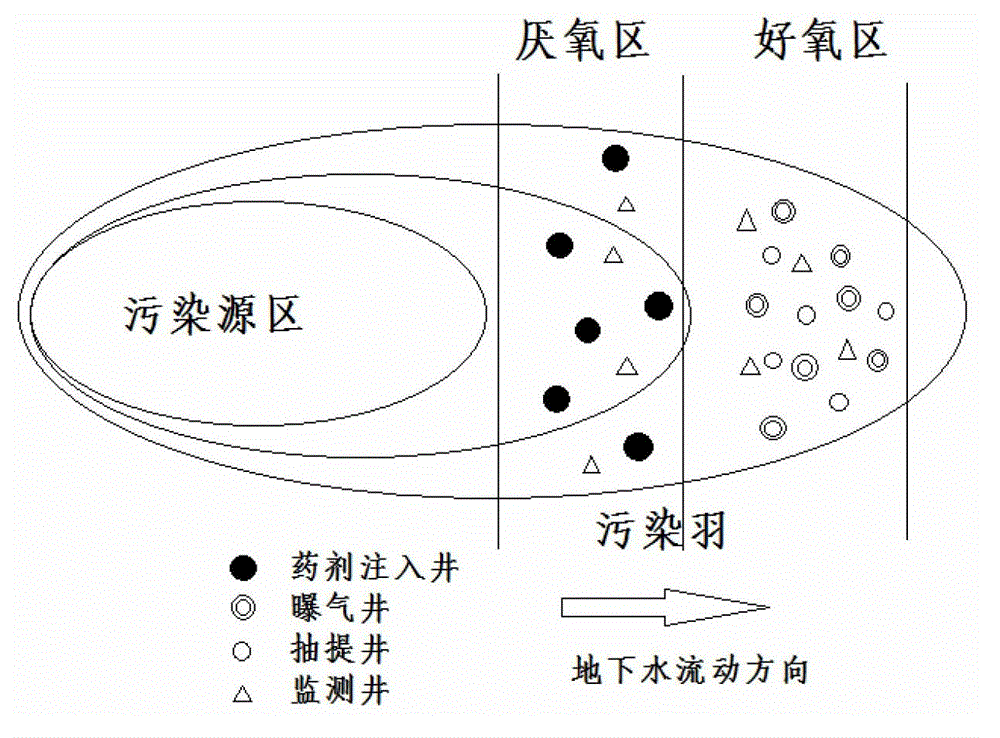
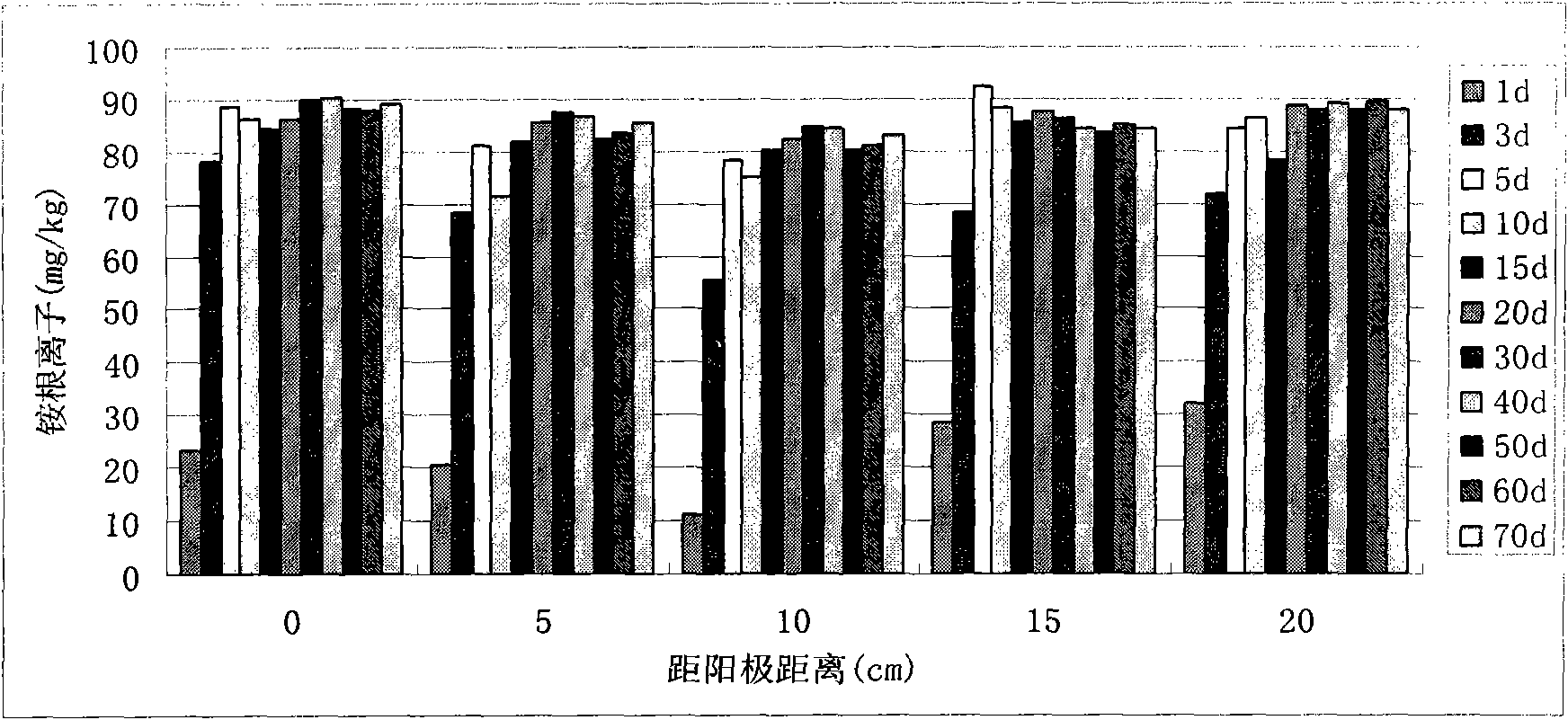
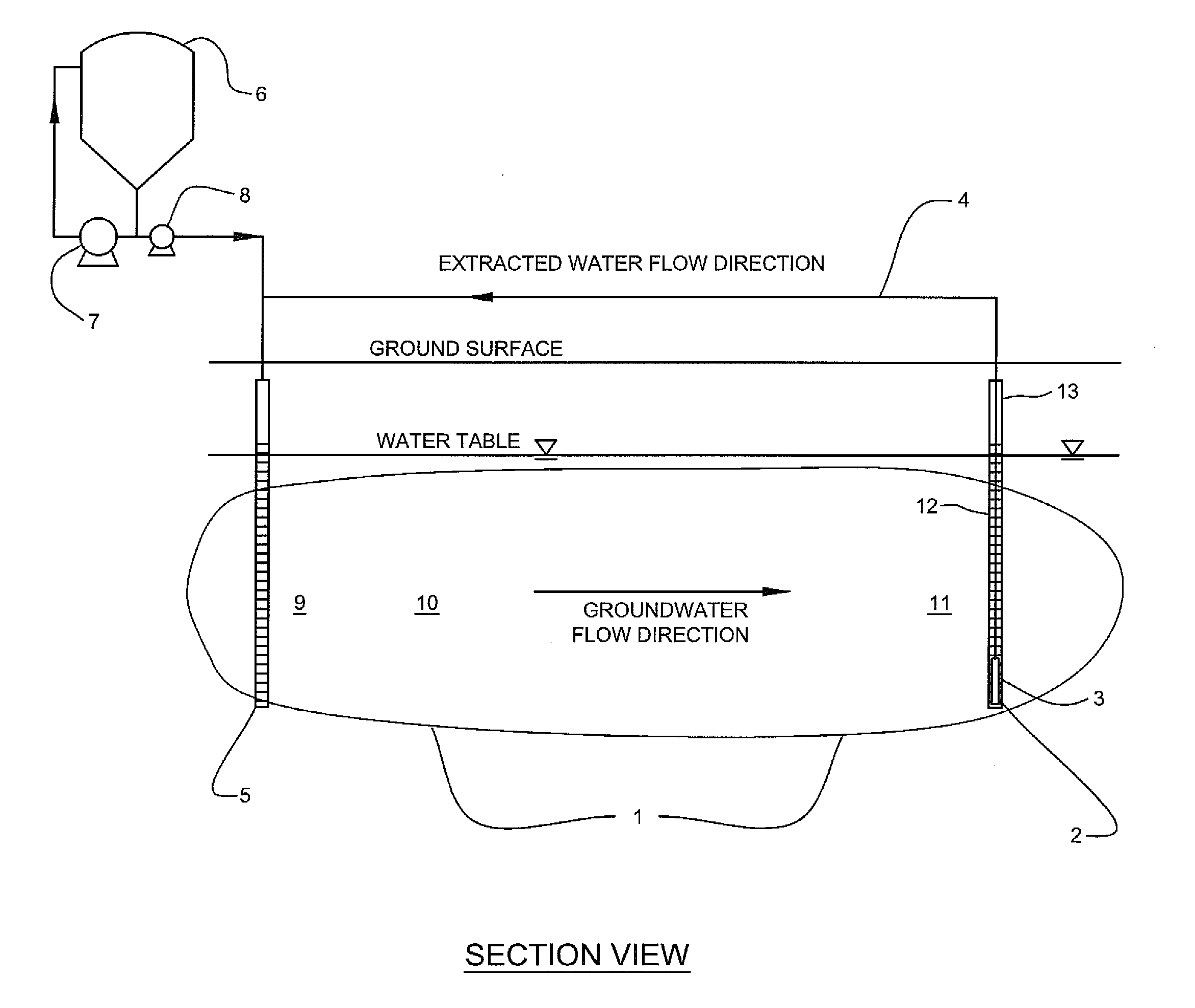
The invention discloses a method for in-situ bioremediation of pollution caused by chlorohydrocarbon of underwater, which specifically comprises a coupling process of anaerobic reductive dechlorination and aerobiotic oxydative degradation. An anaerobic reaction area and an aerobiotic reaction area are established in the front and back of a chlorohydrocarbon pollution area along the flowing direction of underwater in a zone of saturation. Poly-chlorohydrocarbon (trichloro or tetrachloro) in the anaerobic reaction area is quickly reduced and dechlorinated to low chlorohydrocarbon (monochloro or bichloro), the low chlorohydrocarbon is transferred to the aerobiotic reaction area and oxidized and degraded to products such as carbon dioxide. The anaerobic reaction area is realized by providing electron donor materials, a deoxidant and a reducer through the injection of an injection well, while the aerobiotic area is realized by aeration toward underground water.
Owner:TIANJIN ECOLOGY CITY ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
In-situ bioremediation preparation and remediation method for heavy metal contaminated soil
InactiveCN106590685ATake advantage ofSolve serious dangerAgriculture tools and machinesContaminated soil reclamationBacillus licheniformisIn situ bioremediation
The invention relates to the field of soil remediation and discloses an in-situ bioremediation preparation for heavy metal contaminated soil. The preparation contains fungi and / or bacteria with heavy metal degrading abilities, the fungi refer to at least one of aspergillus niger, rhizomucor variabilis and grey cunninghamella, and the bacteria refer to at least one of bacillus amyloliquefaciens, bacillus licheniformis and bacillus simplex. By using the preparation for in-situ bioremediation of the heavy metal contaminated soil, the problems that the soil needs to move by using a moving method and secondary chemical agent pollution of the cultivated land is easily caused by using a decomposition method can be overcome, at the same time, residual heavy metals in the soil obtained after catabolism through the fungi and / or bacteria can also be fully used, the problem that high residual heavy metals in the soil seriously endanger food safety is solved, the soil micro-ecology is improved, the cultivated ability of soil is more quickly recovered, and the method is relatively low in cost and has broad application prospects.
Owner:粮华生物科技(北京)有限公司
Biology in situ renovation method for biomass strengthen mix contaminated soil of stone oil-salt
InactiveCN101172286AImprove repair efficiencyImprove physiological and biochemical characteristicsFungiBacteriaBiomass degradationIn situ bioremediation
The invention discloses an in situ biological repairing method of biomass strengthening petroleum -salt-mixed contaminated soil, which is to add biomass degradation agent into biomass, and then the biomass degradation agent is plowed and landfilled under plough horizon, water logging and salt washing are utilized to reduce soil salt content, and then petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent is added to degrade petroleum hydrocarbon, The invention utilizes the biomass to interdict capillary salt uprise phenomenon possibly generated; carbohydrate substance generated by biomass degradation can be taken as a good quality carbon source of the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent, so as to accelerate the growth of the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent; lignin generated by the biological degradation can absorb petroleum hydrocarbon pollutant, to prevent being diffused in the water logging and salt washing, bio surfactant generated by microorganism in the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent can accelerate the digestion of the petroleum hydrocarbon pollutant and further be converted into carbon dioxide and water by the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation bacteria agent biology. The efficiency of the degradative petroleum hydrocarbon pollutant of the invention method is high, and the speed is quick.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Oxygen releasing material for permeable reactive barrier aerobic biodegradation of groundwater
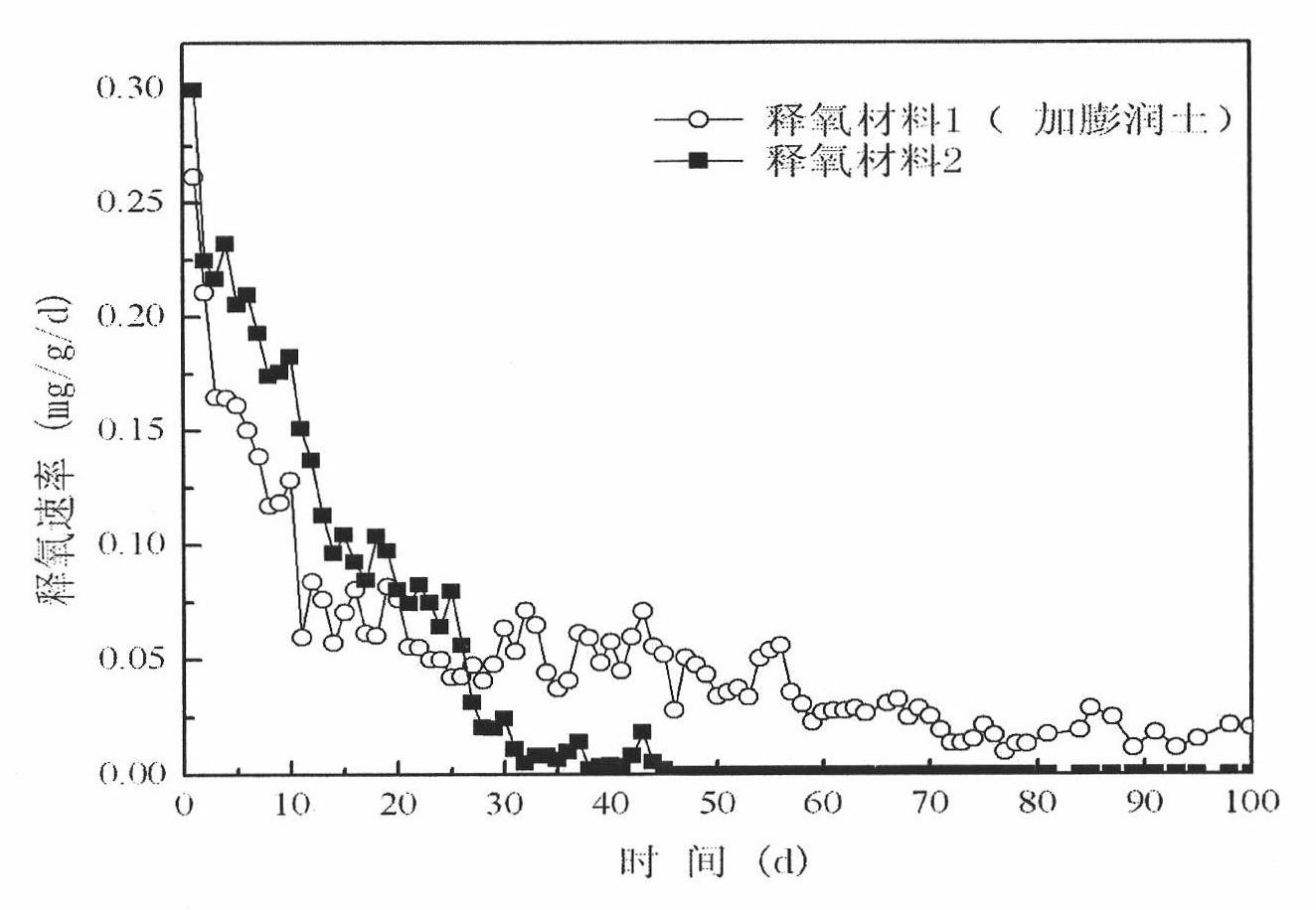
InactiveCN101921018AInitial oxygen contentSlow oxygen release rateSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentIn situ bioremediationEnvironmental engineering
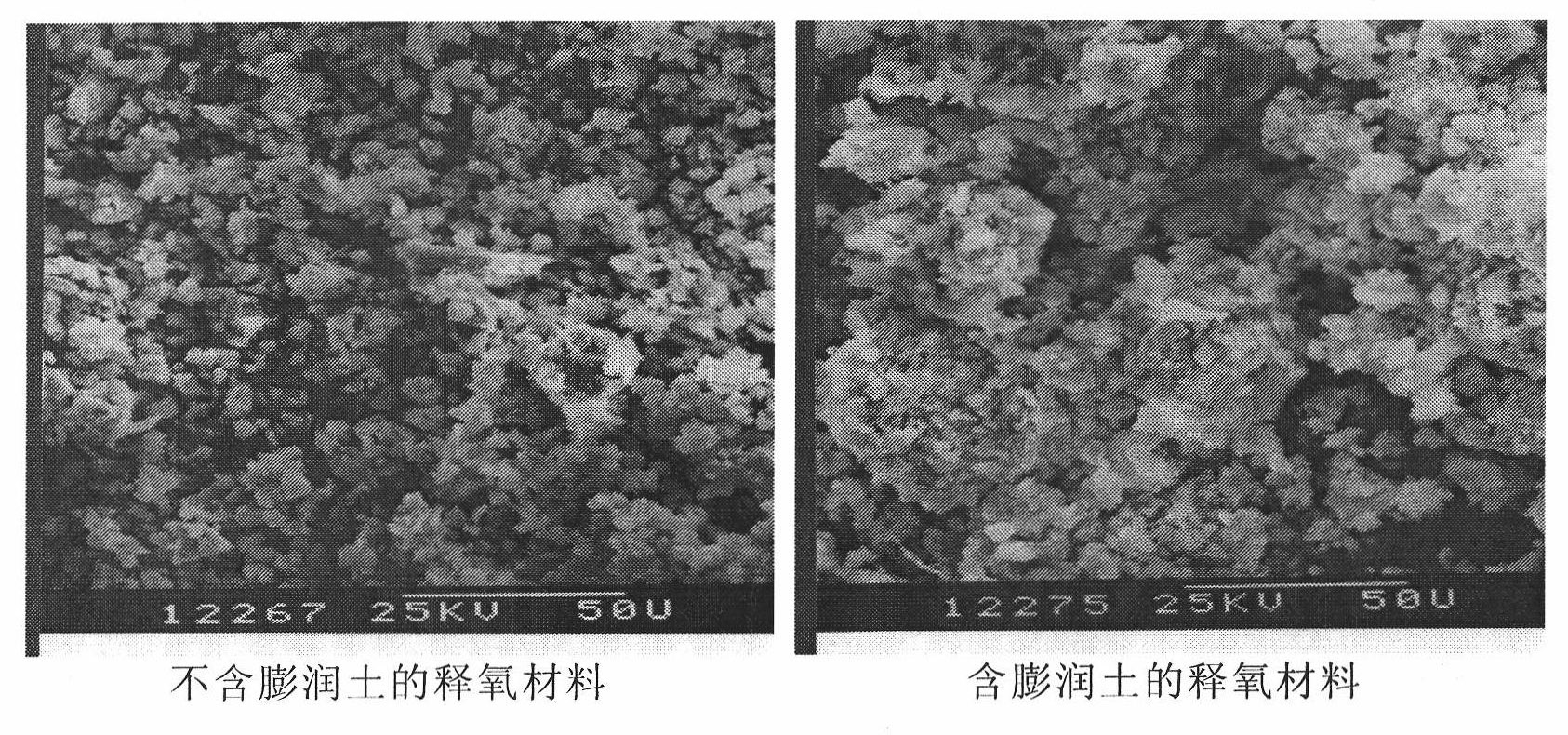
The invention relates to an oxygen releasing material for permeable reactive barrier aerobic biodegradation of groundwater, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 5-20% of oxygen releasing compound, 5-20% of bentonite and the balance of coagulant. The oxygen releasing material added with the bentonite has the advantages of large oxygen releasing amount, long oxygen releasing time, low cost and easy preparation; and moreover, the used materials are all natural and easy to obtain and do not cause secondary pollution to the groundwater environment, thereby remarkably improving the in situ bioremediation technology of the contaminated groundwater.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF WATER +1
Novel electrokinetic intensified technology and process for biologically remedying polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon polluted soil
InactiveCN102463254AImprove repair efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationIn situ bioremediationVoltage gradient
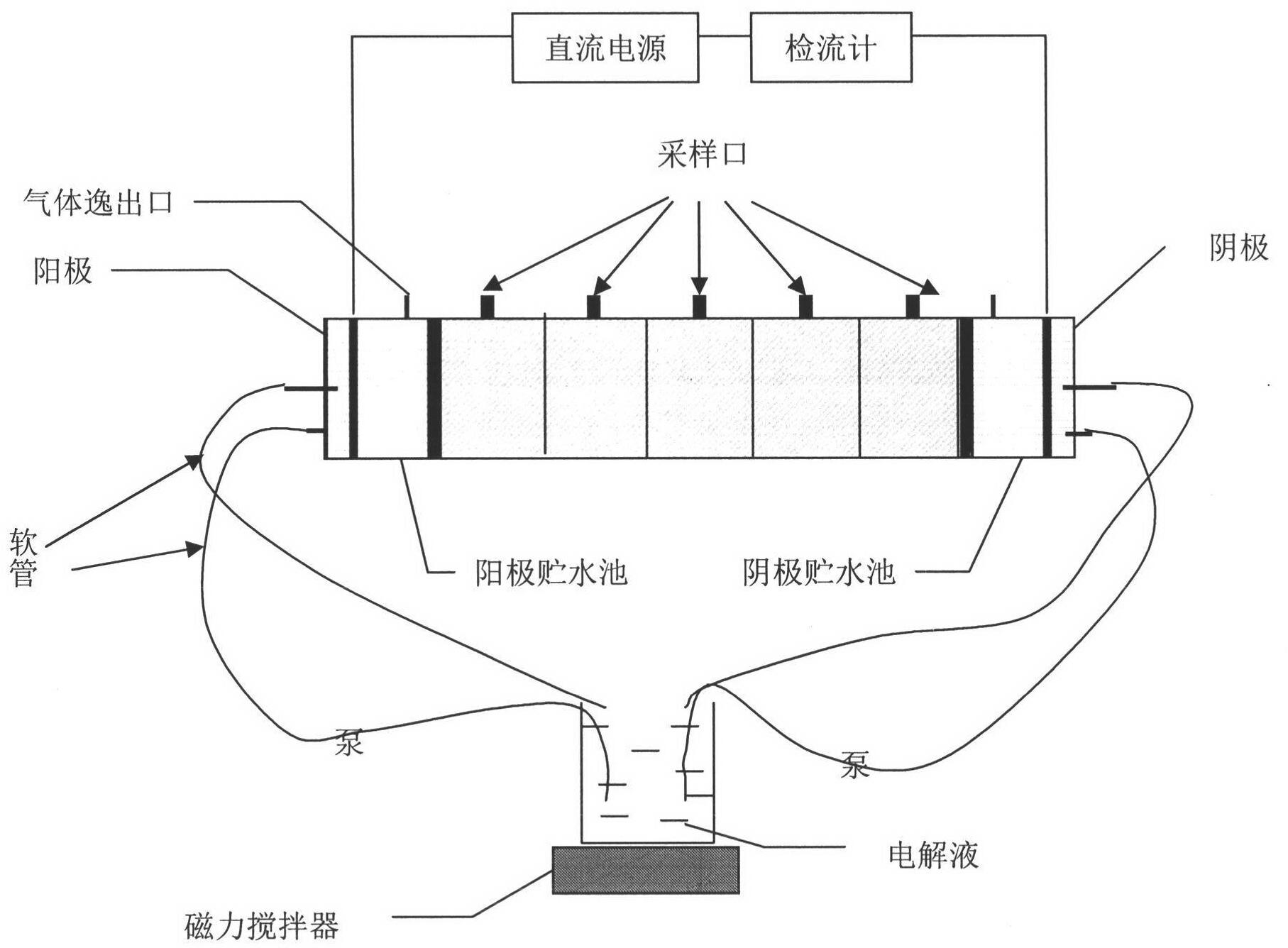
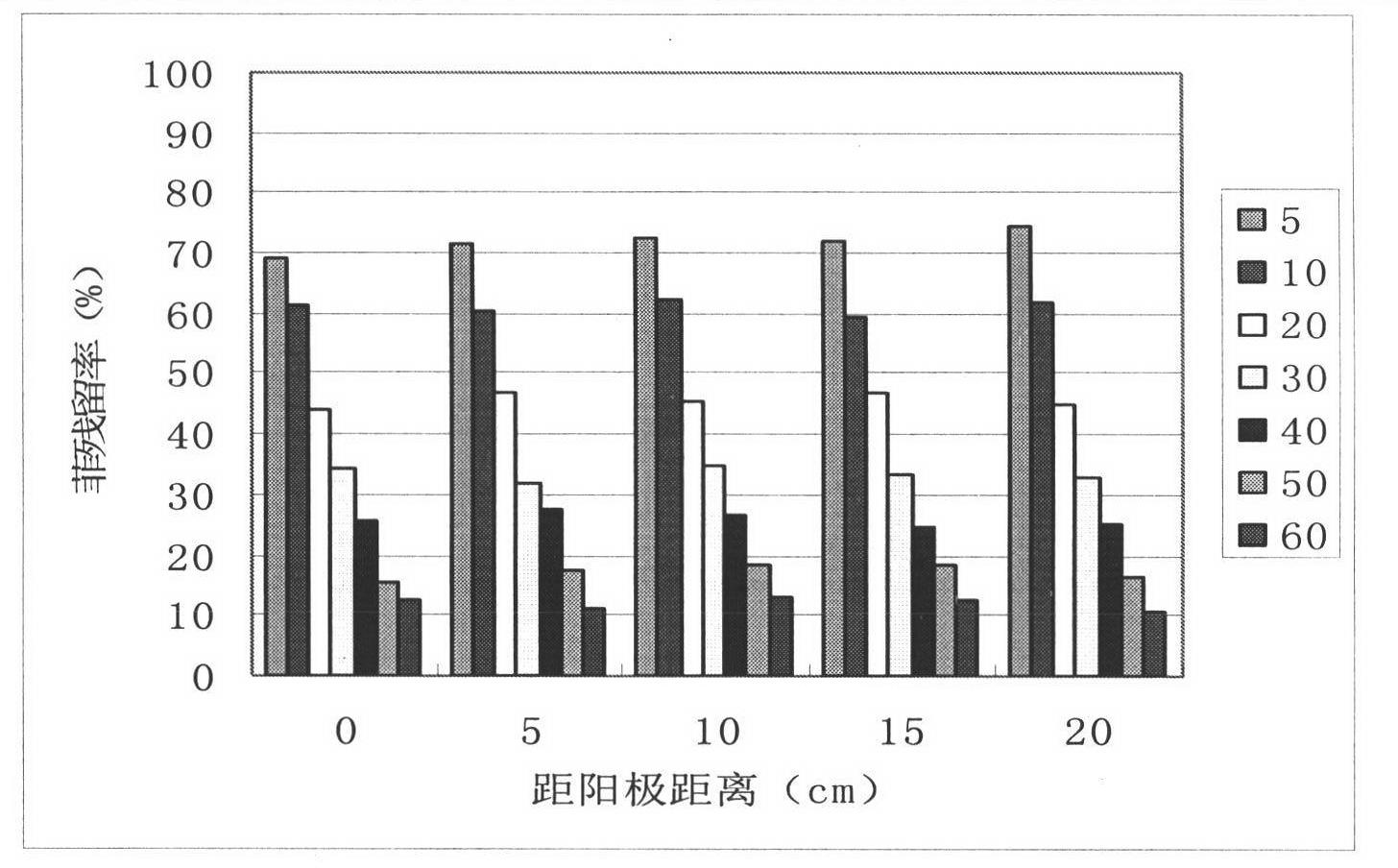
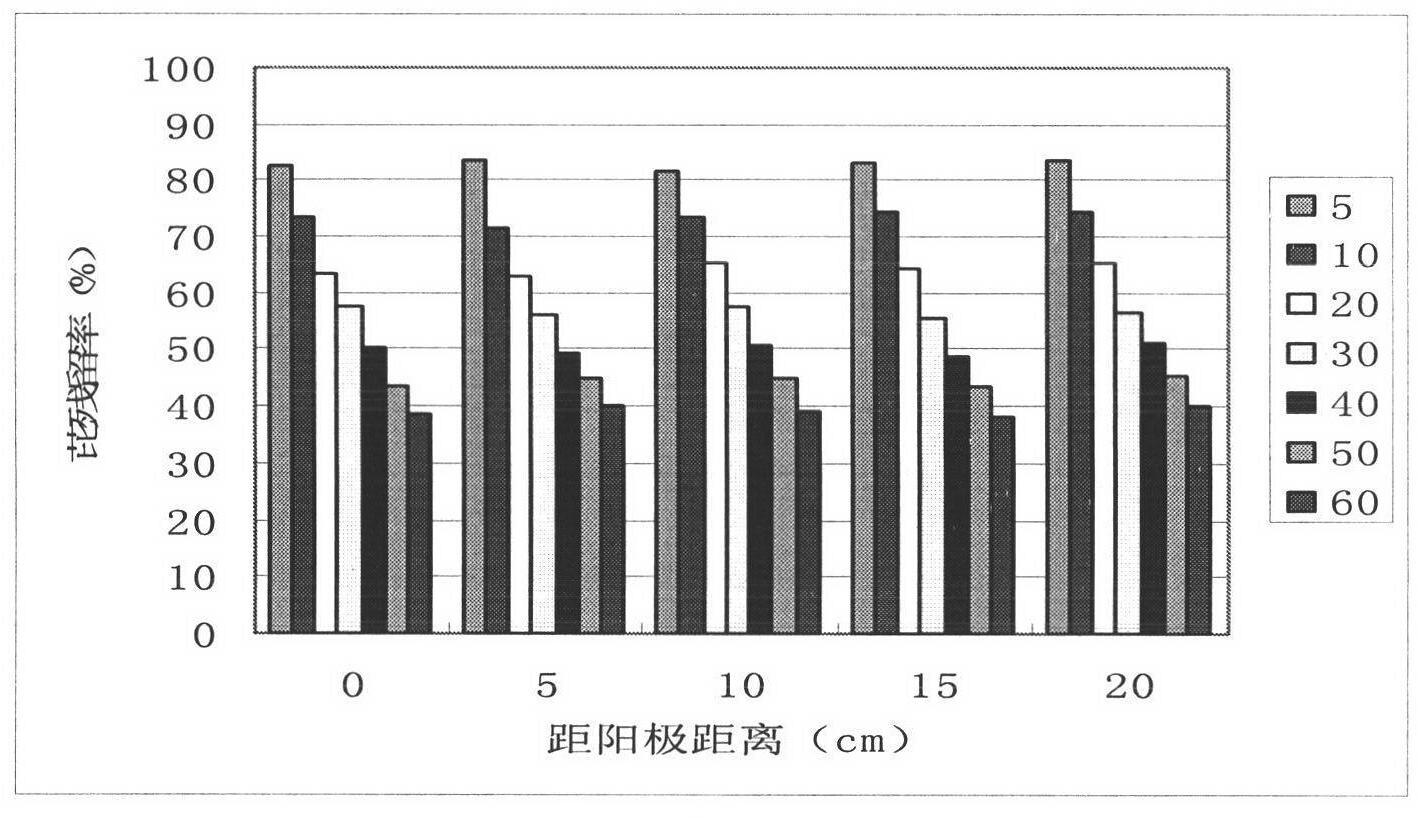
The invention discloses a novel electrokinetic intensified technology and process for biologically remedying polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon polluted soil, which successfully introduces nutrients and microorganisms into a reaction zone to degrade target pollutant, provides advantages for in situ bioremediation of the soil polluted by organic pollutant, and promotes research on electrokinetic remediation and in situ bioremediation. The process is the combined application of electrode switch and electrolyte mixture circulation of two electrodes in electrokinetic remediation; when the voltage gradient is 1 V / cm, the electrokinetic intensified remedying test is performed by adopting a motion manner of periodically changing electric field direction, when the electrode switch time is 12 h, the electrolyte is bacterium suspension (comprising nutrients), the pH value is 7.3, and the flow speed of the circular electrolyte is 800 ml / h. Test result indicates that the nutrients and the microorganisms can be introduced into the zone to be remedied by the novel electrokinetic intensified biologically remedying process, the target pollutant can be degraded, and the problems of easiness in change of soil pH value and nonuniform distribution of nutrients in conventional electrokinetic remediation are solved, and the bioremediation efficiency is increased by 55%, thus providing advantages to the in situ bioremediation of the soil polluted by organic pollutant, and effectively improving the bioremediation efficiency.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Soil remediation method for treating heavy metal pollutants
ActiveCN101947539BReduce the amount requiredNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationPollution soilSoil remediation
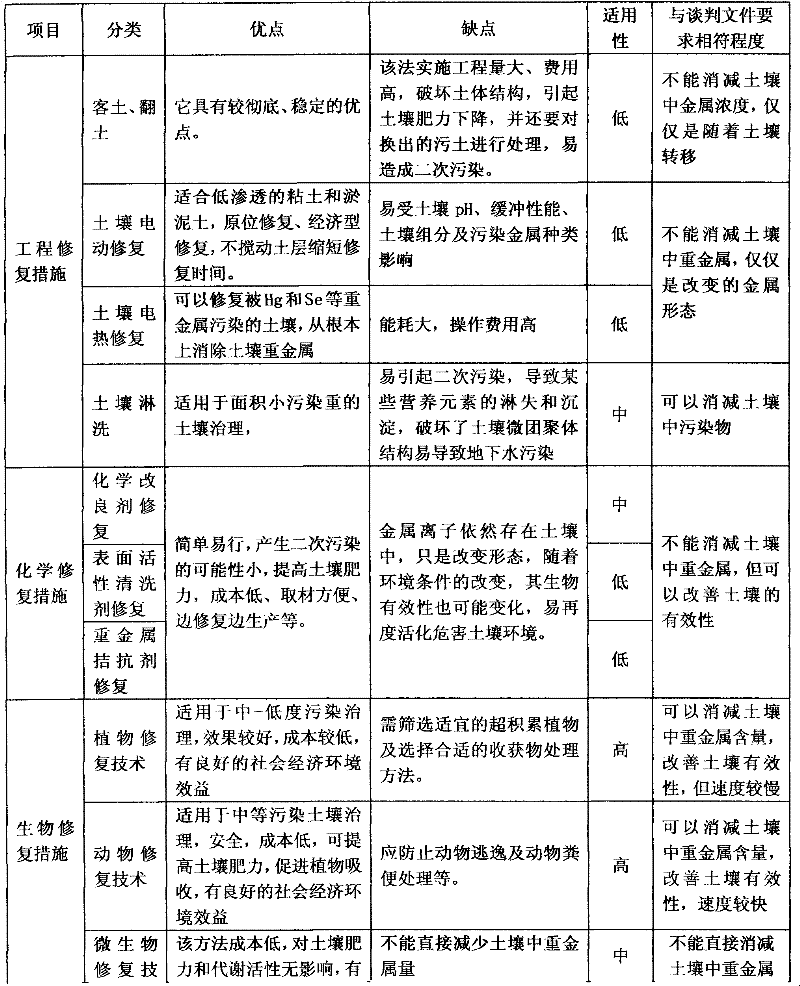
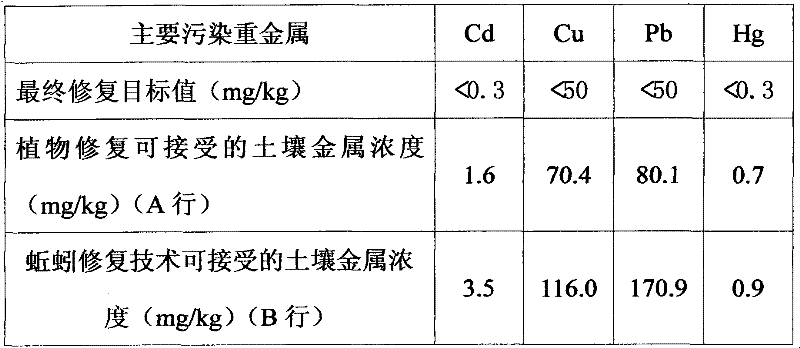
The invention relates to a soil remediation method for treating heavy metal pollutants. The soil is divided into three classes according to the heavy metal content in the soil, namely, heavily contaminated soil, moderately contaminated soil and lightly contaminated soil. The soil remediation method for the heavily contaminated soil comprises the steps of chemical leaching, earthworm enrichment remediation and phytoremediation; the soil remediation method for the moderately contaminated soil comprises the steps of earthworm enrichment remediation and phytoremediation; and the soil remediation method for the lightly contaminated soil is phytoremediation. The invention combines the animal / plant enhanced composite remediation, realizes in-situ bioremediation of the soil successfully and has obvious effect without causing secondary pollution to the soil.
Owner:浙江博世华环保科技有限公司
Novel process and technology for strengthening electric remediation and bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil by using surfactant
InactiveCN102652955AImprove efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationIn situ bioremediationVoltage gradient
The invention discloses a novel process and technology for strengthening electric remediation and bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil by using a surfactant, and provides the novel process for strengthening the electric remediation and the bioremediation of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil by using the surfactant, and parameters of the process, which effectively improves the efficiency of the slightly soluble organic pollutant in the bioremediation, and propels the researches on the electric remediation and in-situ bioremediation. According to the process provided by the invention, electrolytes of two electrodes are mixed and circulated, and the surfactant and microorganisms are added in the electrolytes for electric injection. A test for strengthening the electric remediation and the bioremediation by using the surfactant is carried out in conditions as follows: a voltage gradient is 1 V / cm; the electrolytes are bacterium suspension (containing nutrients) and the surfactant; a pH value is 7.3; and the flow velocity of the circulating electrolytes is 800 ml / h. Shown by a test result, the novel process for strengthening the electric remediation and the bioremediation by using the surfactant can effectively improve a degradation speed of the contaminated soil in China and Philippines, improves a degradation speed of pyrene and benzopyrene, and solves the problem that the acid-base variation of a pH value of the soil is easy to occur in the traditional electric remediation and bioremediation.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Mixed substrates for anaerobic bioremediation in aquifers
InactiveUS20120305479A1Low costEasy injectionWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsInorganic compoundCarboxylic salt
A method for the in-situ biological remediation of groundwater contaminated with halogenated organic compounds, heavy metals, various inorganic compounds, nitrate, and other compounds which can be reduced into less harmful by-products under anaerobic conditions through the application and distribution of a water-soluble microbial substrate mixture consisting of alcohol, carboxylates, and glycerol in an alkaline solution. The method delivers and distributes a substrate mixture into impacted groundwater zones using different mixture proportions based on aquifer conditions so as to optimize distribution in the aquifer. Acclimated microbes and nutrients are also added as needed.
Owner:INNOVATIVE ENG SOLUTIONS
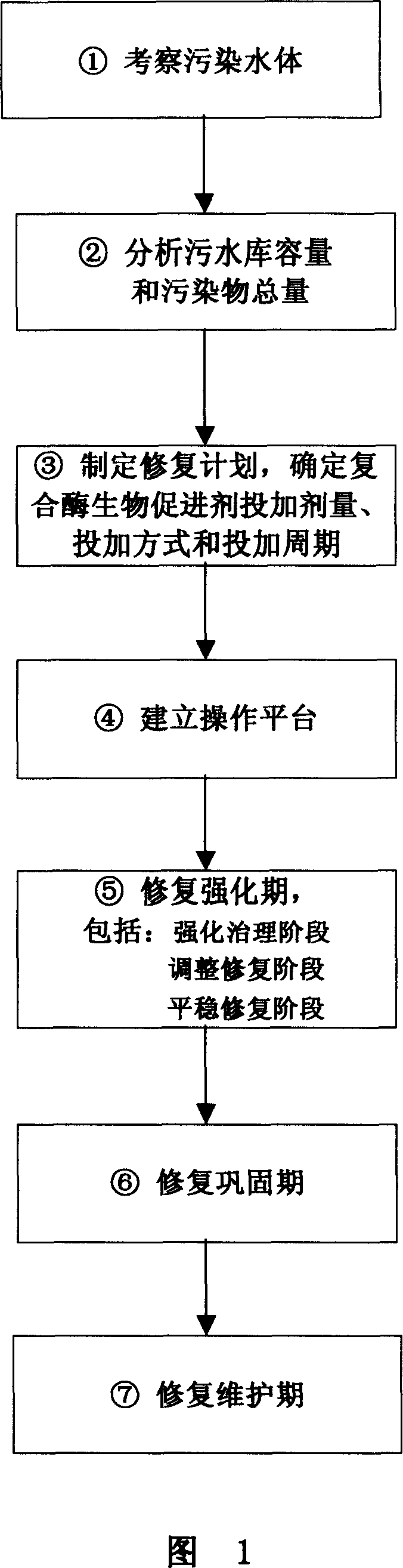
In-situ biologically repairing method of polluted water body with composite enzyme biopromoter
ActiveCN1974436ARestoring the natural ecological environmentImprove water qualityTreatment using aerobic processesSustainable biological treatmentEcological environmentEutrophication
The in-situ biological repairing method of polluted water body with composite enzyme biopromoter is to throw composite enzyme biopromoter in the amount and mode determined based on pollutant quantity to the polluted water body. The work flow includes the steps of: examining the polluted water body, analyzing the polluted water amount and total pollutant amount, determining the repair plan, establishing operation platform, and repairing the water body in different stages. The present invention has the advantages of restoring water self-cleaning capacity, restoring the natural ecological environment, low ecological risk and simple operation, and is suitable for treatment on different kinds of polluted water bodies.
Owner:福建光宇环保科技有限公司 +1
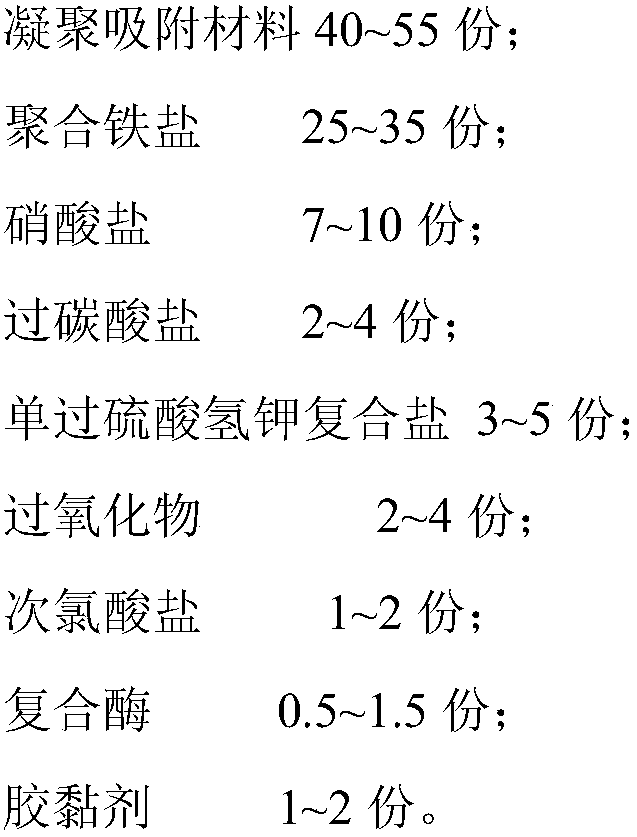
Integrated in-situ remediation and treatment medicament of surface black and odorous water and bottom mud as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107555498ARealize integrated in situ repairBreed fastSludge treatmentWater/sewage treatmentHypochloriteAdhesive
The invention discloses an integrated in-situ remediation and treatment medicament of surface black and odorous water and bottom mud. The integrated in-situ remediation and treatment medicament is prepared from an agglomeration and adsorption material, polymeric ferric salt, nitrate, oxidants, complex enzymes, adhesives and the like, wherein the oxidants are selected from at least one of percarbonates, potassium monopersulfate compound salts, peroxides and hypochlorite. The medicament is applied to integrated remediation of the surface black and odorous water and the bottom mud; compound chemicals are added into the medicament, so that the dissolved oxygen in the water and the bottom mud can be increased; an ecosystem of microorganisms can be activated and restored; the in-situ biologicalremediation and degradation effects can be enhanced; the self-purification capacity of the water is improved; the yield of the bottom mud is reduced; meanwhile, the efficiency of removing nitrogen andphosphorus is improved; the medicament has long-term stability, is free of secondary pollution, and has good application prospects.
Owner:AEROSPACE KAITIAN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
Oxidant-scavenging compound for anaerobic treatment
InactiveUS20050239189A1Less disruptiveDecreasing time to site closureFungiSolid waste disposalYeastStimulant
The present invention provides a mixture for use as a biological stimulant in in-situ bioremediation via enhanced reductive dehalogenation. The mixture is primarily a mixture of Lactose and Brewer's Yeast for use as an electron donor in the bioremediation process.
Owner:SCHAFFNER I RICHARD
Systems and methods for microbial reductive dechlorination of environmental contaminants
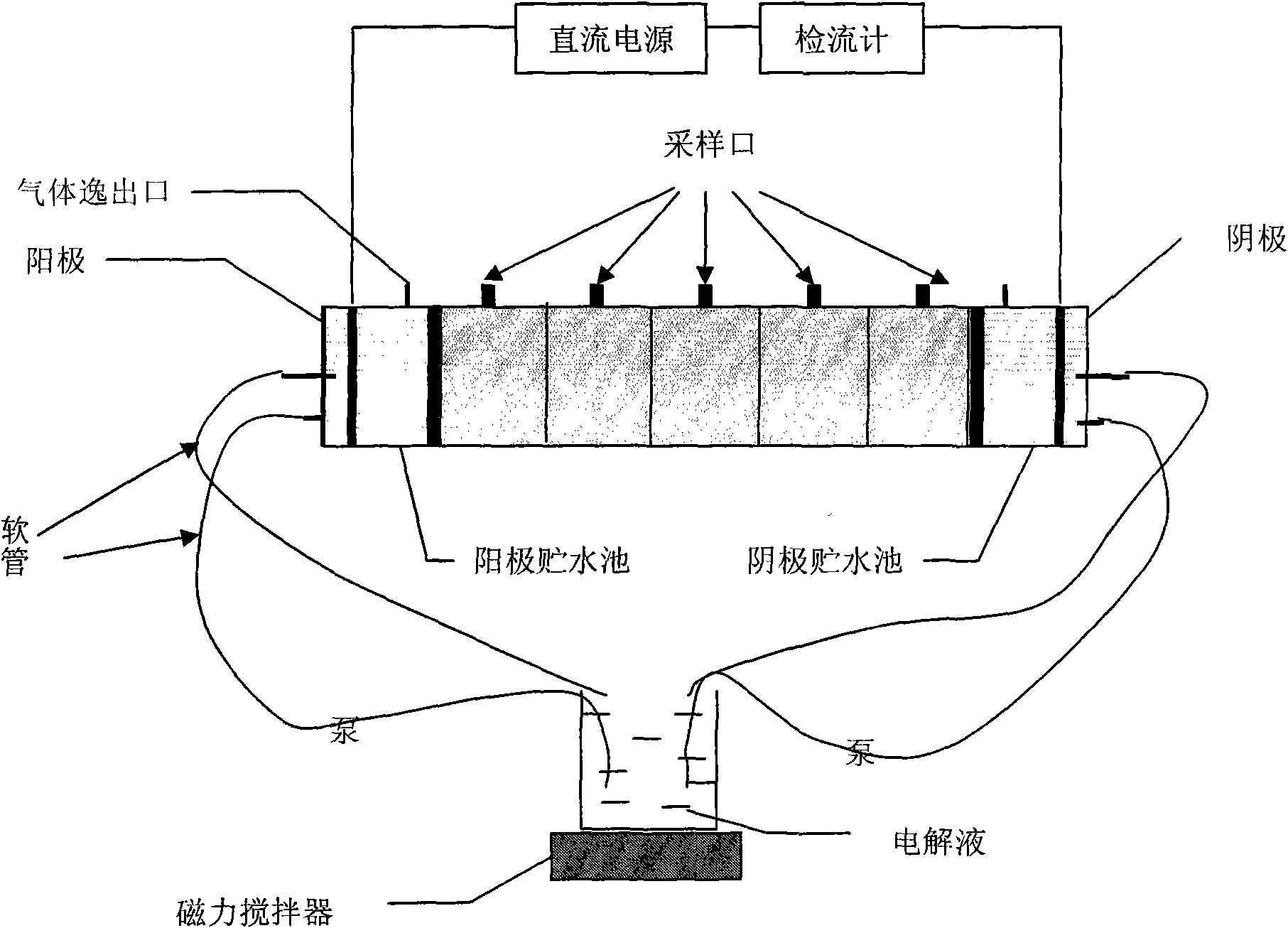
ActiveUS20100059436A1Improve solubilityHigh activityWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOther chemical processesMicroorganismIn situ bioremediation
In preferred embodiments, bioremediation systems are provided that comprise electricigenic microbes that use electrons provided directly from the anode of an electrical bioremediation system to carry out reductive dehalogenation of halogenated hydrocarbon contaminants, including chlorinated solvents. The present invention also provides methods of performing in situ bioremediation of halogenated solvents in groundwater or soil through the use of the provided systems.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS +1
Steady state anaerobic denitrifying consortium for application in in-situ bioremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated sites and enhanced oil recovery
InactiveUS20100216217A1Stable stateEnhanced overall recoveryBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicrobial enhanced oil recoveryIn situ bioremediation
Enriched steady state microbial consortiums for microbial enhanced oil recovery and in situ bioremediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated sites, under anaerobic denitrifying conditions, are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Environmental bioremediation using shell as an electron donor
InactiveUS7138059B2Low costImprove efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationSeparation devicesParticulatesElectron donor
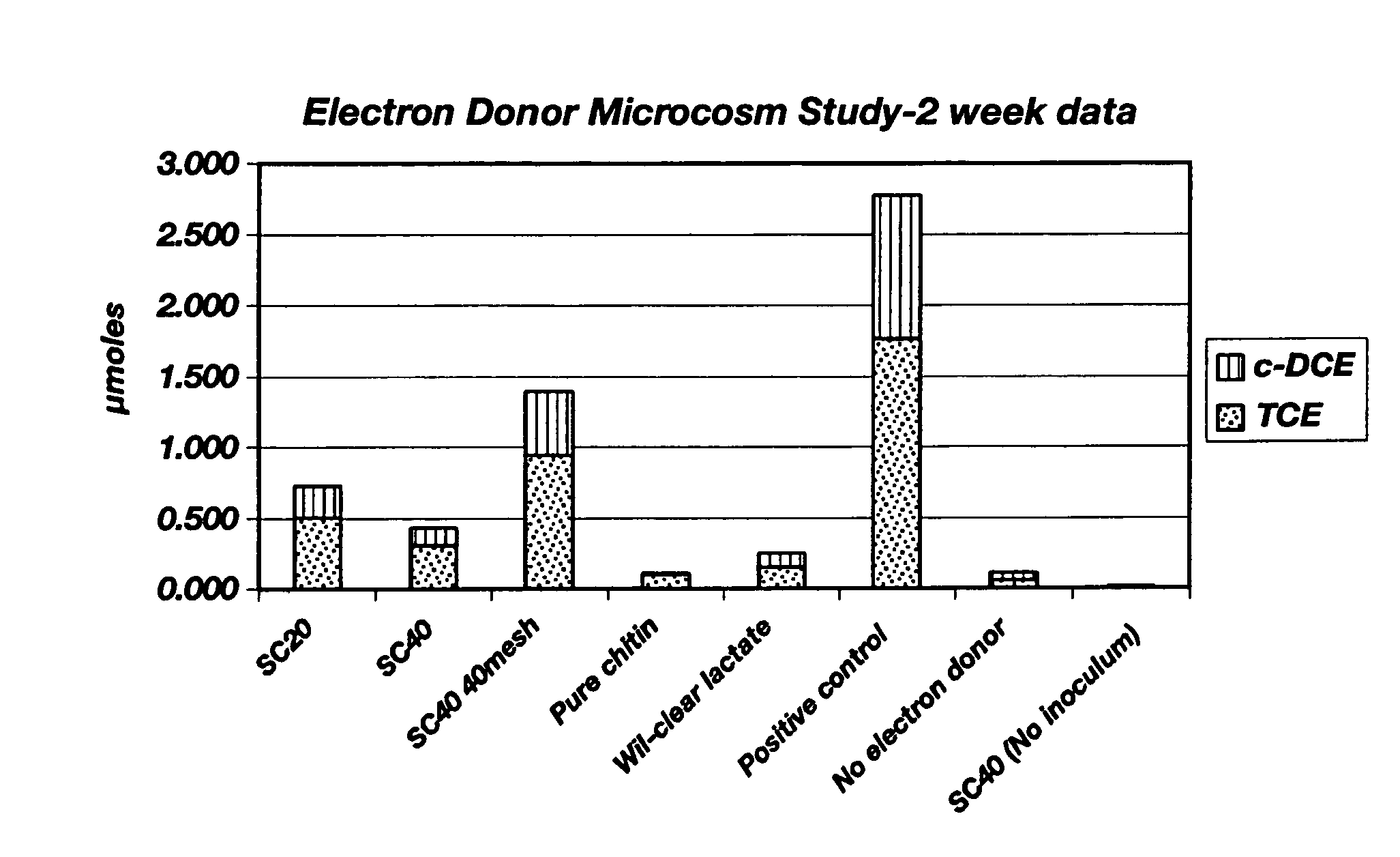
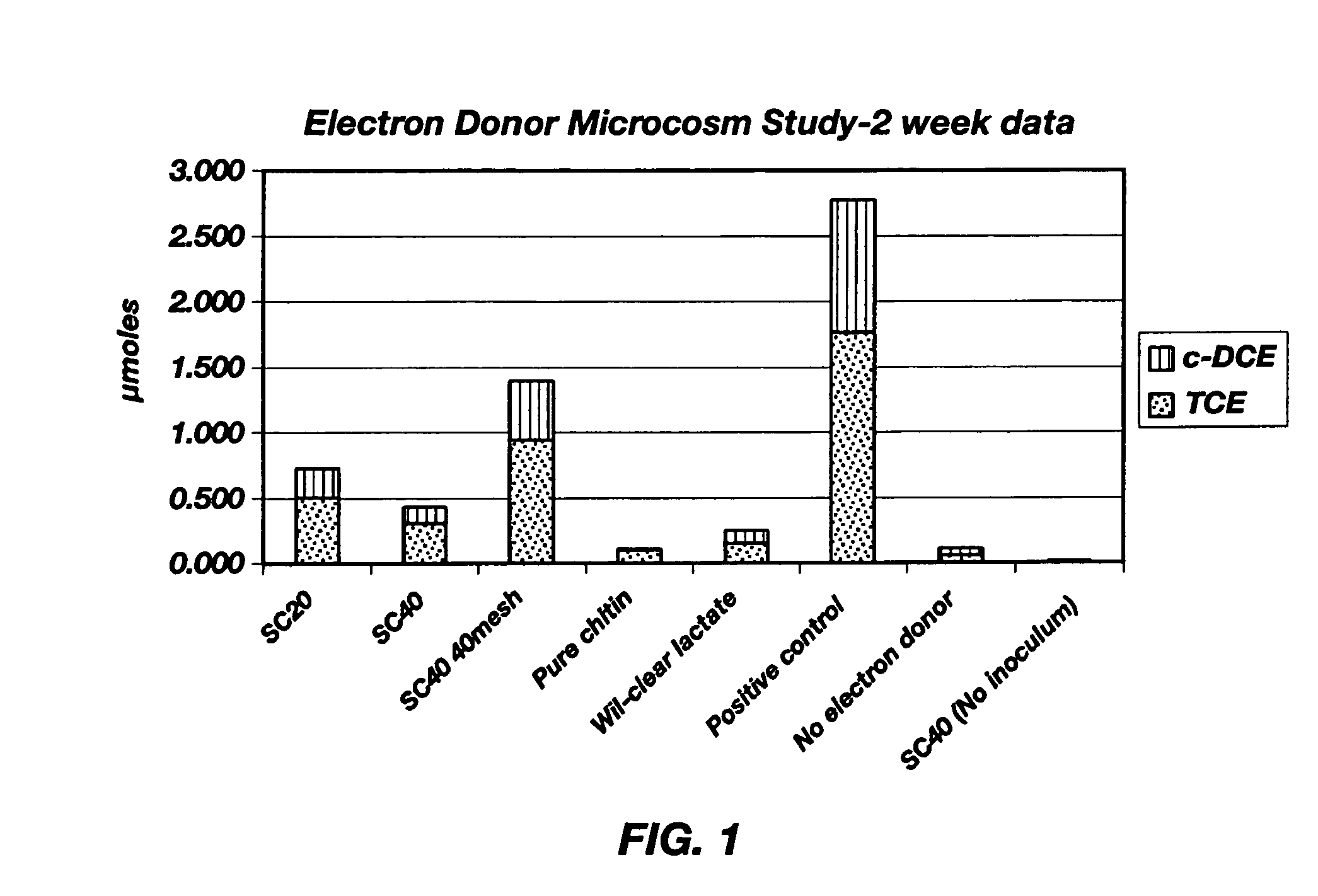
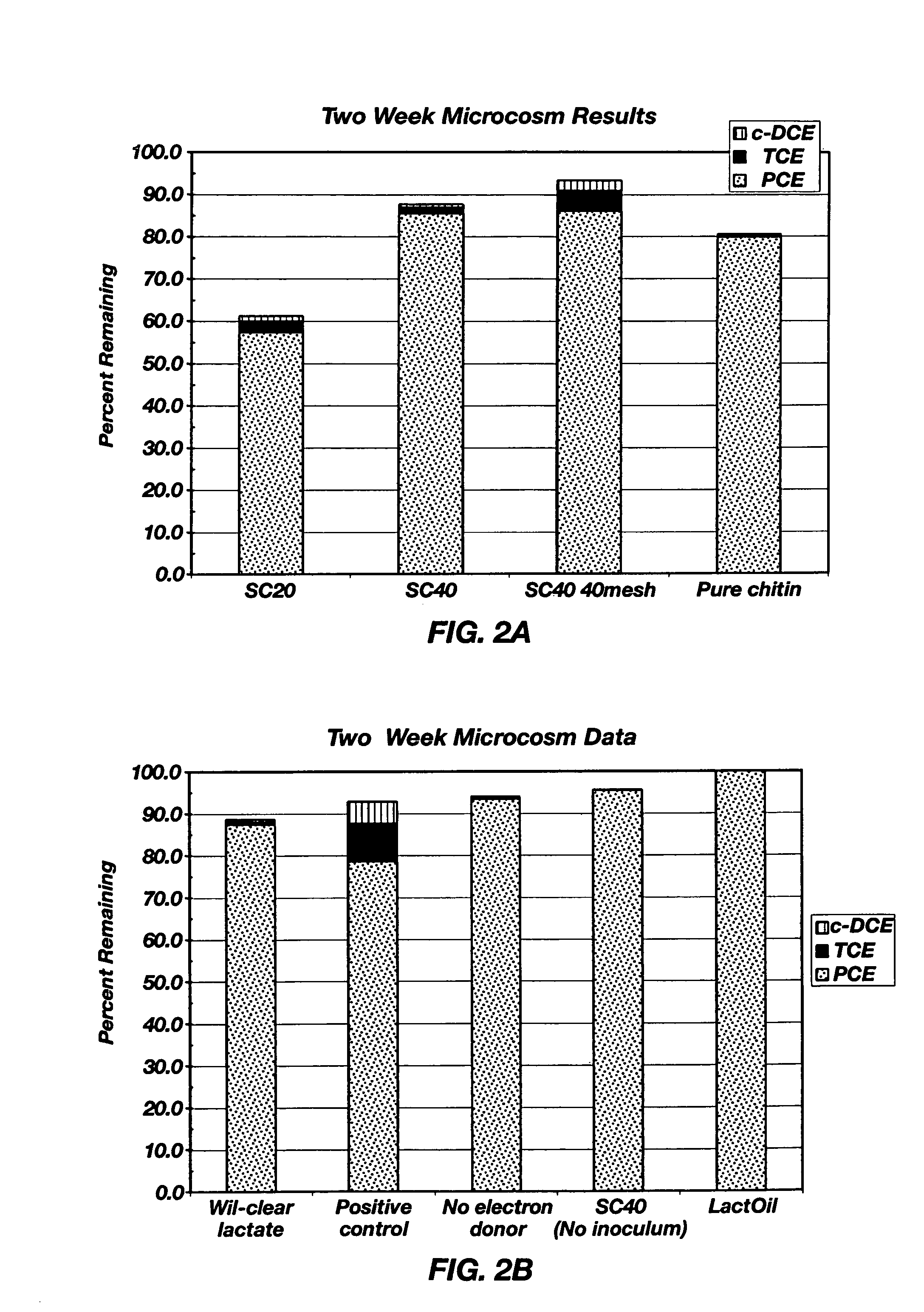
A method for in situ bioremediation of contaminants in the environment is described. The method includes adding an electron donor to ground water in an amount sufficient for a microbe in the ground water to use the electron donor for reducing the contaminant into an innocuous derivative thereof. Illustratively, the electron donor contains about 0.1 to 75% by weight of chitin, such as crustacean shell, partially deproteinized crustacean shell, ground mushrooms, or a fungal fermentation broth. The chitinous electron donor can be added to the ground water as a particulate solid or aqueous slurry.
Owner:JRW BIOREMEDIATION +1
Ectopic-in-situ combined bioremediation method of high-concentration petroleum contaminated soil
ActiveCN104759459AImprove in situ repair efficiencyReduce concentrationContaminated soil reclamationHigh concentrationIn situ remediation
The invention relates to an ectopic-in-situ combined bioremediation method of high-concentration petroleum contaminated soil, and belongs to the technical field of contaminated soil remediation. The ectopic-in-situ combined bioremediation method comprises the following steps: firstly, high-concentration petroleum contaminated soil is subjected to ectopic biological piling, so that the concentration of petroleum hydrocarbon in soil is reduced greatly; then a certain amount of the piled materials are returned to the field, so that the concentration of petroleum hydrocarbon in soil after field return is less than 2000mg.kg<1-> to meet the in-situ remediation requirement; finally, the remediation requirement is achieved after in-situ remediation. The ectopic-in-situ combined bioremediation method is combined skillfully so as to achieve the economical and efficient remediation effect.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Comprehensive heavy metal contaminated soil remediation method
ActiveCN104289504AEasy to fixThe repair was successfully implementedContaminated soil reclamationPaulowniaPaulownia coreana
The invention discloses a comprehensive heavy metal contaminated soil remediation method. A comprehensive phytoremediation technology combining woody fast-growing tree paulownia elongate with an obvious effect of fixing multiple heavy metals such as Cu, Pb, Cd and Zn and herbaceous plant Elsholtzia splendens with hyperaccumulating effect and high growth speed on Cu2+ is adopted, and an auxiliary animal (earthworm) restoration technology is used, so that the highest effect of eliminating heavy metal pollution of soil is achieved, in situ bioremediation of the soil is successfully realized, pollutants are effectively prevented from directly entering a food chain, and secondary pollution of the soil is avoided. The comprehensive heavy metal contaminated soil remediation method disclosed by the invention is environment-friendly, low in cost and easy to popularize in large area, has an obvious effect of remediating the heavy metal contaminated soil and can improve the fertility of the heavy metal contaminated soil.
Owner:武汉文科生态环境有限公司
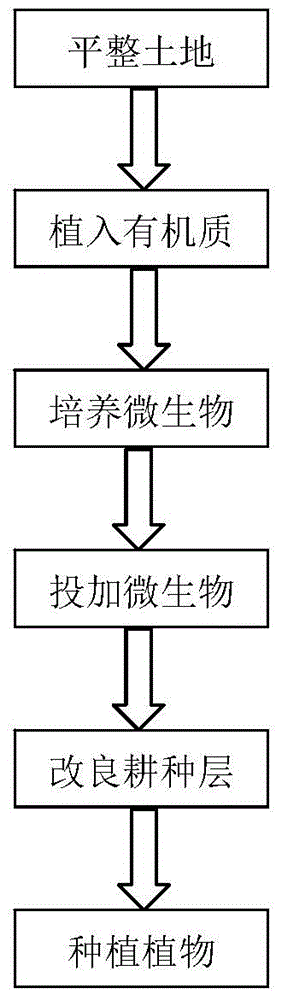
In-situ bioremediation method for soils polluted by nitrocompounds
ActiveCN104907330AEfficient degradationReduce leaching toxicityContaminated soil reclamationNitro compoundNitrobenzene
The invention provides an in-situ bioremediation method for soils polluted by nitrocompounds. The method mainly carries out in-situ remediation treatment of nitrocompounds in polluted soil through combined action of nitrocompound dominant degradation bacteria and plants with strong tolerance. The method comprises the following steps: land leveling, organic matter implantation, culture and adding of microorganisms, improvement of farming layer soil and cultivation and conservation of plants. Pollutants in soil can be degraded rapidly, leaching toxicity of soil can be lowered greatly, the soil remediation cycle is shortened, the remediation cost is low, secondary pollution cannot be generated, the method is simple and practicable, fertility of pollution place soil can be raised, and the method is suitable for in-situ remediation of pollution places with various scales. The method can be suitable for in-situ bioremediation of soils polluted by TNT waste water, DNT waste water, MNT waste water, nitrobenzene waste water, phenyl amine waste water.
Owner:BEIJING FENGZELVYUAN ENVIRONMENT TECH
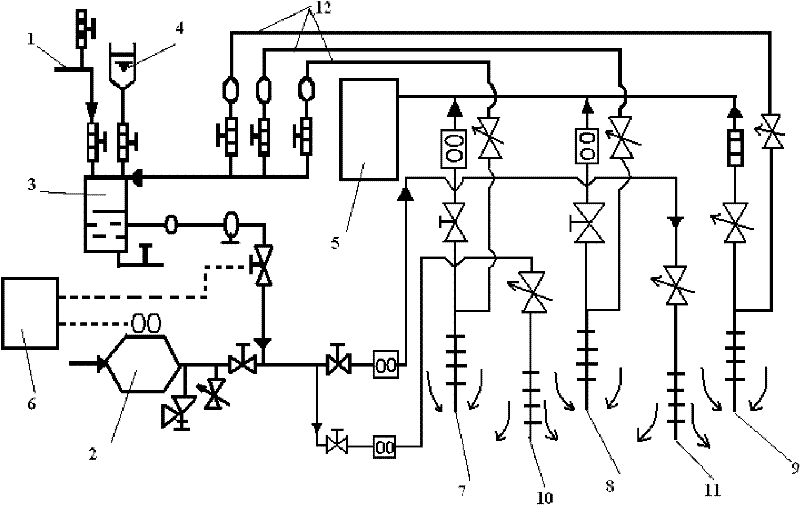
Reinjecting twin-well pneumatic shatter auxiliary restoration system and method of underground oil pollution
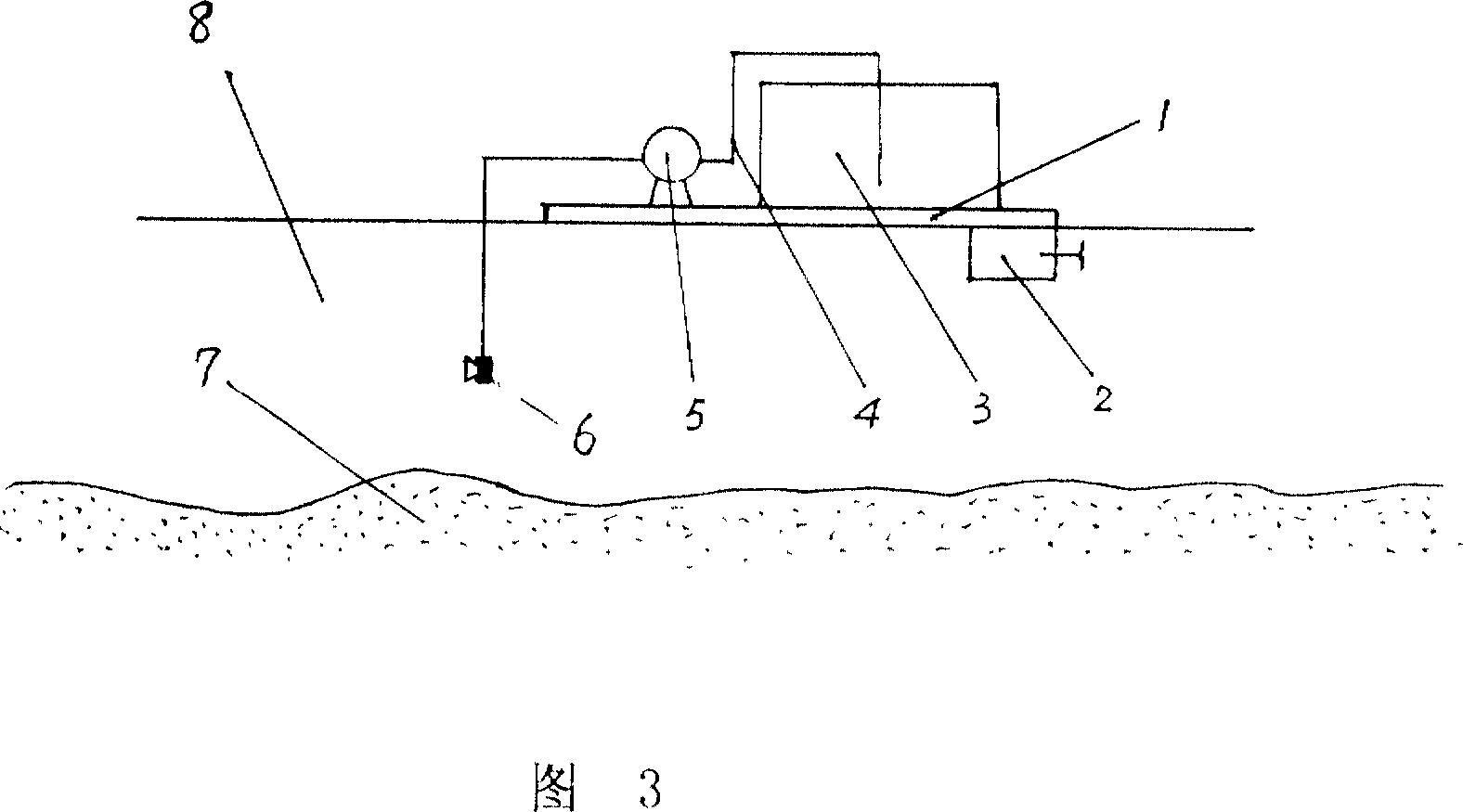
InactiveCN102225429AImprove in situImprove efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationAutomatic controlIn situ bioremediation
The invention discloses a reinjecting twin-well pneumatic shatter auxiliary restoration system and method of underground oil pollution, belonging to the technical field of auxiliary restoration of oil pollution. The system is composed of an indoor part and an outdoor part, wherein, the indoor part comprises a pneumatic shatter unit, a preparation and storing unit for a bacteria liquid, a nutrition adding unit, a reinjecting pipeline of the bacteria liquid, a biphase suction unit and a control unit, and the outdoor part comprises an injecting / shattering well and a seeping well. The in situ bioremediation of the underground oil pollution is realized by utilizing the steps of pneumatic shattering, injecting bacterium, maintaining pressure, reinjecting aeration, pausing and cycling of the system provided by the invention. The system has the advantages of short process flow, compact structure, simple operation and complete realization of automatic control.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
In-situ bioremediation preparation and remediation method for chlorothalonil contaminated soil
ActiveCN106591166ASolve serious dangerAddressing food safetyFungiBacteriaPhotochemical degradationIn situ bioremediation
Relating to the soil remediation field, the invention discloses a preparation for in-situ remediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil. The preparation contains fungi and / or bacteria with chlorothalonil degradation ability. The fungi can be at least one of Aspergillus niger, rhizomucor variabilis and Cunninghamella bertholletiae, and the bacteria can be at least one of Burkholderia zhejiangensis, pseudomonas aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. According to the invention, the provided preparation is employed for in-situ bioremediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil, not only overcomes the problems that photochemical degradation is easily limited by illumination conditions and can easily cause secondary chemical reagent pollution to arable land, at the same time makes full use of fungi and / or bacteria for catabolism of chlorothalonil residual in soil, thus solving the problem that high residual chlorothalonil in soil severely endangers food safety. At the same time, the micro-ecology of soil is improved, so that soil can recover farming ability more rapidly. Also, the method is low in cost, thus having broad application prospects.
Owner:粮华生物科技(北京)有限公司
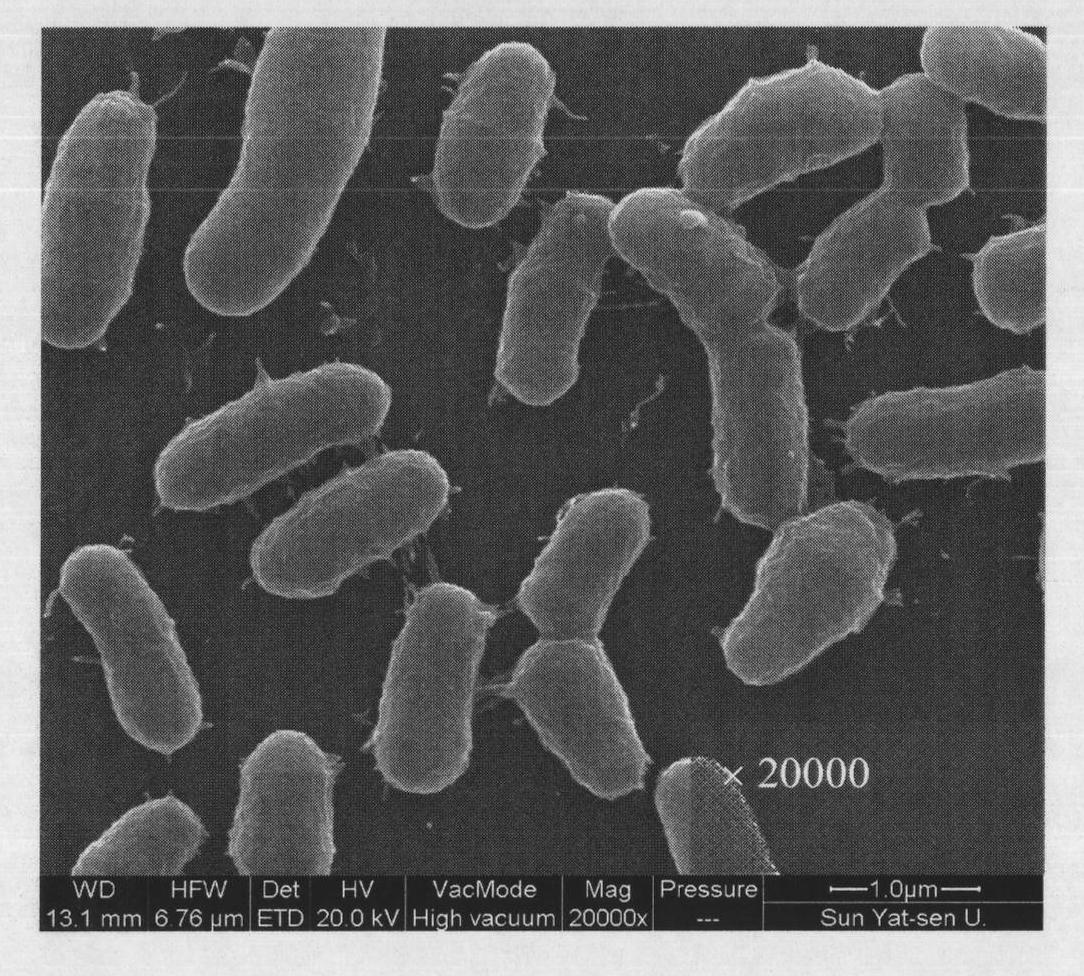
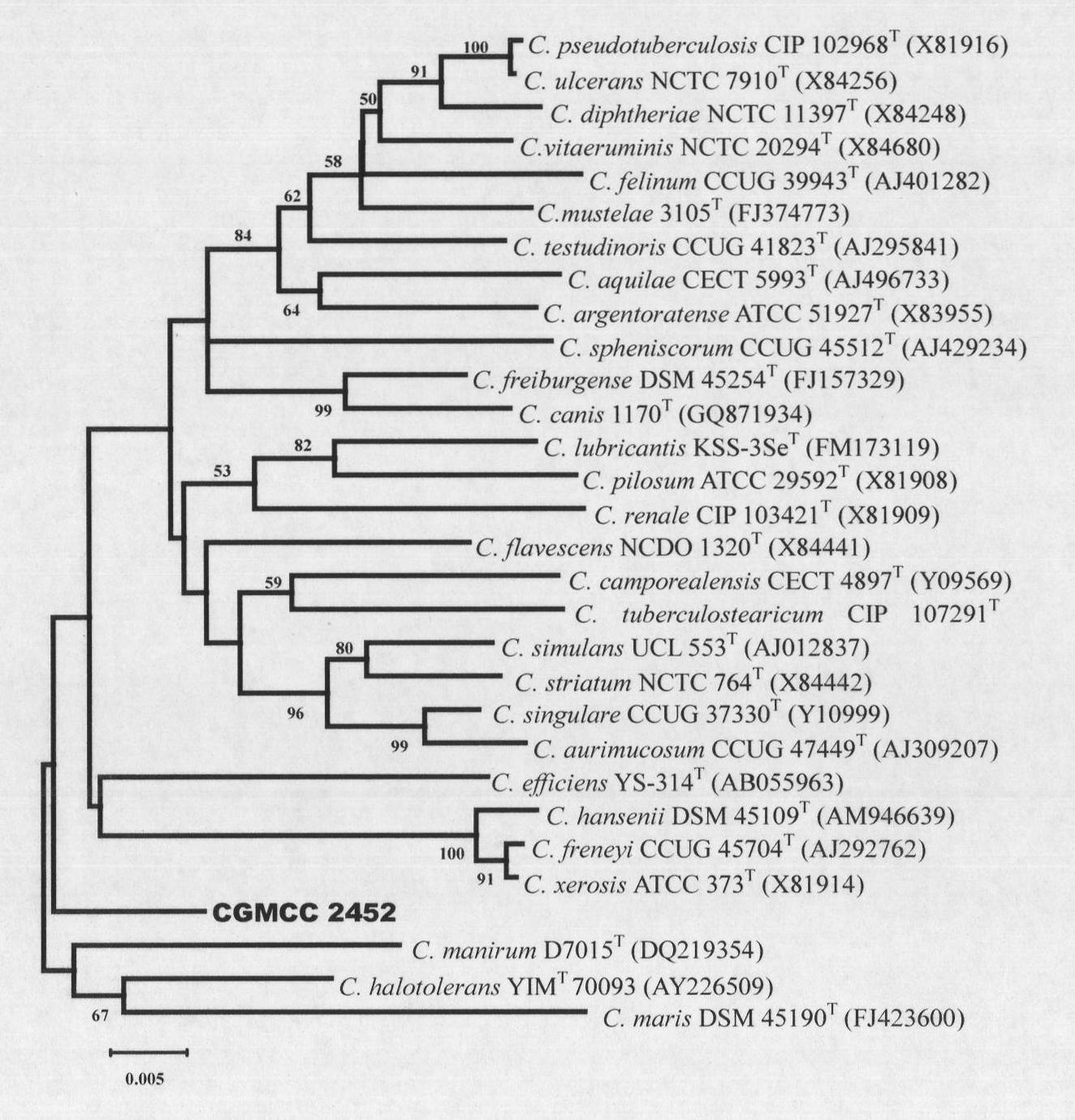
Corynebacterium humireducens and application thereof
InactiveCN101892180AUtilize a broad spectrumEfficient reduction abilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHigh concentrationSludge
The invention discloses corynebacterium humireducens and an application thereof. The corynebacterium humireducens is obtained by separating and purifying anolyte of a sludge microbe fuel cell, and is preserved in the ordinary microbe centre of the China Microbe Culture Preservation Management Committee on April 14, 2008 with the preservation number of CGMCC No.2452. The corynebacterium humireducens has wide utilization spectrum of electron donor under the anaerobic condition, has efficient humus reduction capability and electrogenesis capability under the alkaline condition, can be widely applied to in-situ microbe restoration of organic pollutants, microbe fuel cell generating technology or recycling processing of high-concentration organic wastes.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Solid composite biological preparation for in-situ repairing and treatment on black and odorous water body bottom mud and preparation method of solid composite biological preparation
InactiveCN108658404AImprove processing efficiencyAdaptableBiological sludge treatmentIn situ bioremediationBiology
The invention discloses a solid composite biological preparation for in-situ repairing and treatment on black and odorous water body bottom mud and a preparation method of the solid composite biological preparation. The solid composite biological preparation is characterized by comprising the following materials in parts by weight: 15-30 parts of a biological composite enzyme, 15-30 parts of a composite microorganism bacterial liquid, 10-15 parts of a microorganism growth promoter, 1-5 parts of a protection agent and 20-40 parts of dry powder aids. By adopting the solid composite biological preparation disclosed by the invention, due to physical, chemical and biological functions of the components upon bottom mud, the bottom mud can be greatly reduced, and the problem of black and odorouswater bodies can be remarkably alleviated; meanwhile, in-situ biological repairing and degradation functions can be activated and intensified, the self cleaning capability of the bottom mud is improved, and the bottom mud can be further reduced. The solid composite biological preparation has the advantages of being wide in raw material source, high in treatment efficiency, good in adaptability, low in cost, low in production and operation cost, and the like.
Owner:HUNAN JINLV ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION CO LTD +1
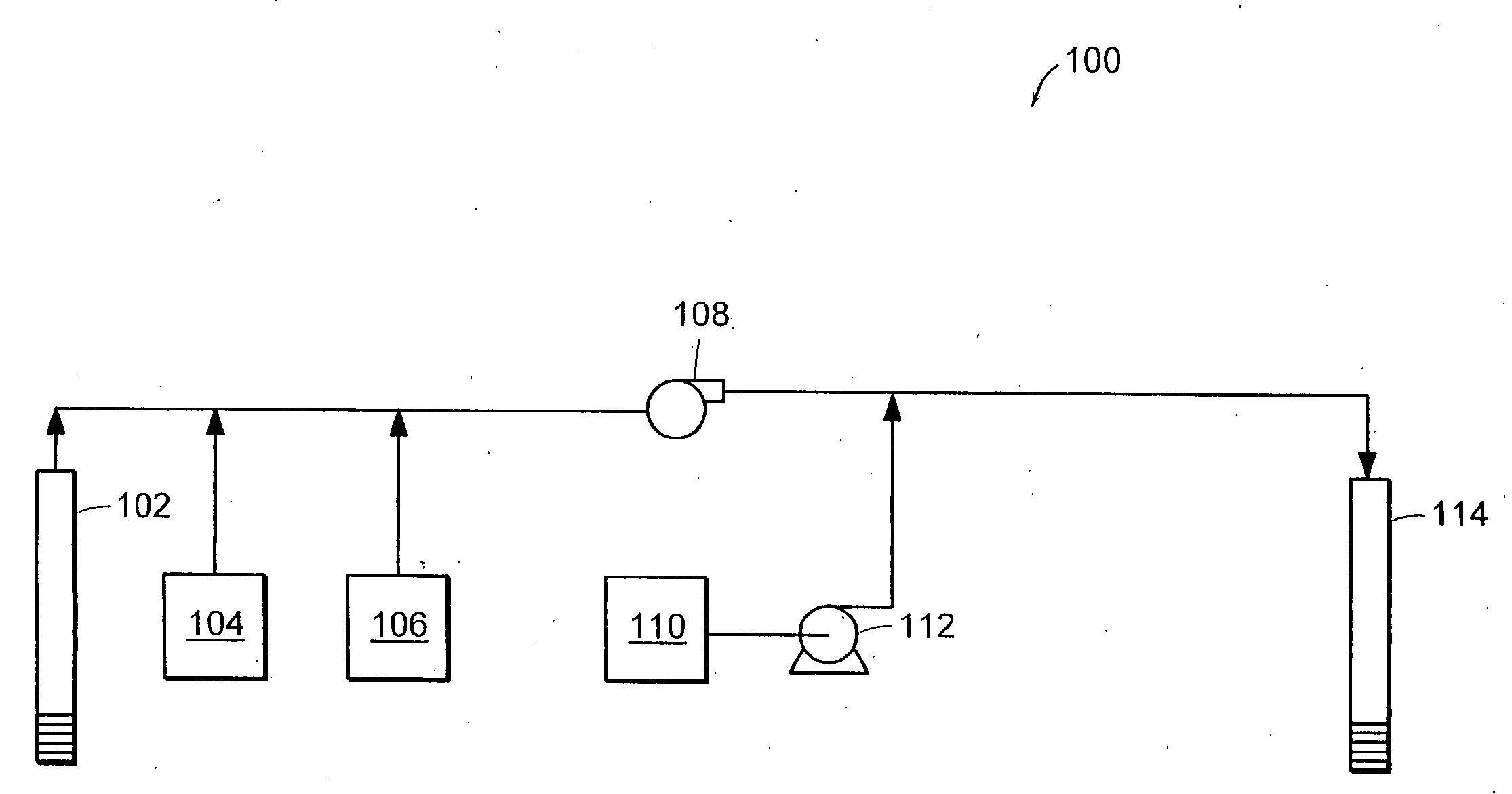
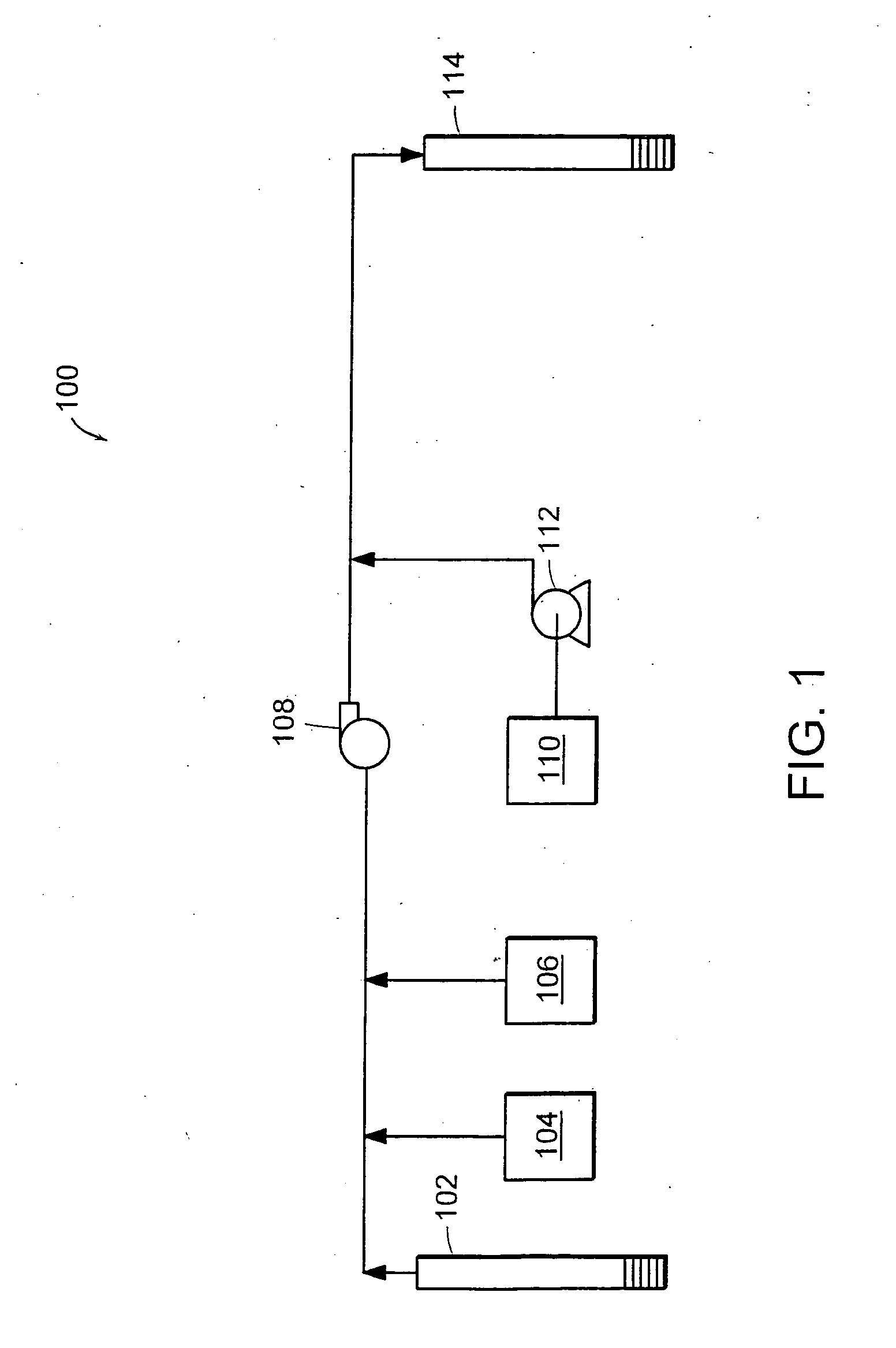
Process for in situ bioremediation of subsurface contaminants
InactiveUS20060263869A1Eliminate needReduce riskSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationHydrogenMulti pollutant
This invention includes methods of stimulating anaerobic degradation of subsurface contaminants. The methods include vaporizing a liquid electron donor to form a treating gas. The treating gas or hydrogen is directed to a subsurface site that includes one or more contaminants, thereby stimulating anaerobic degradation of the subsurface contaminants.
Owner:CDM SMITH
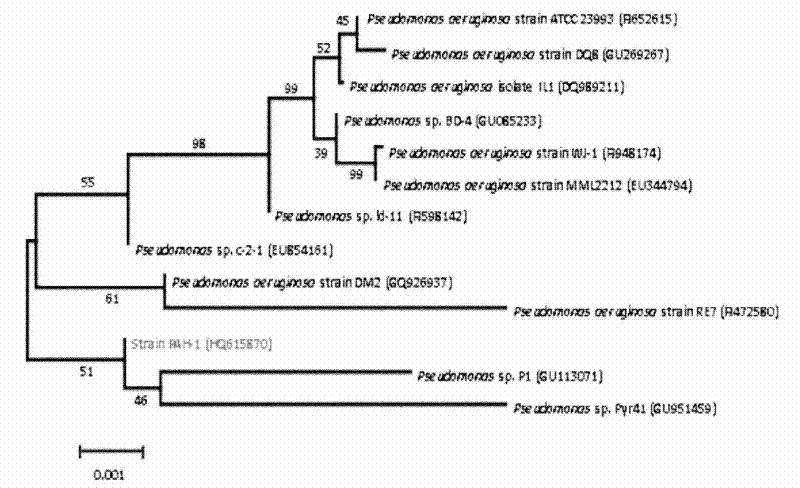
A strain of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and its isolation method and application
InactiveCN102296037AIncreased degradation rateBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationHuminIn situ bioremediation
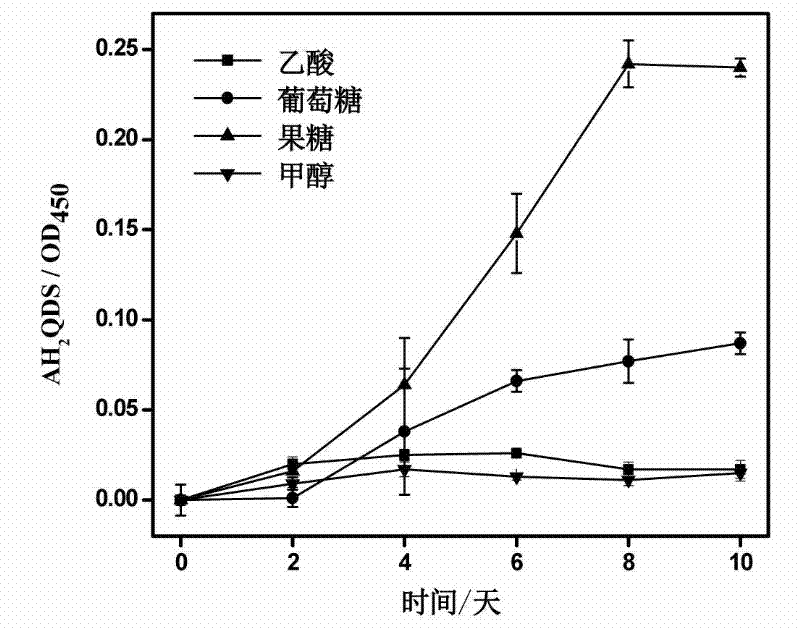
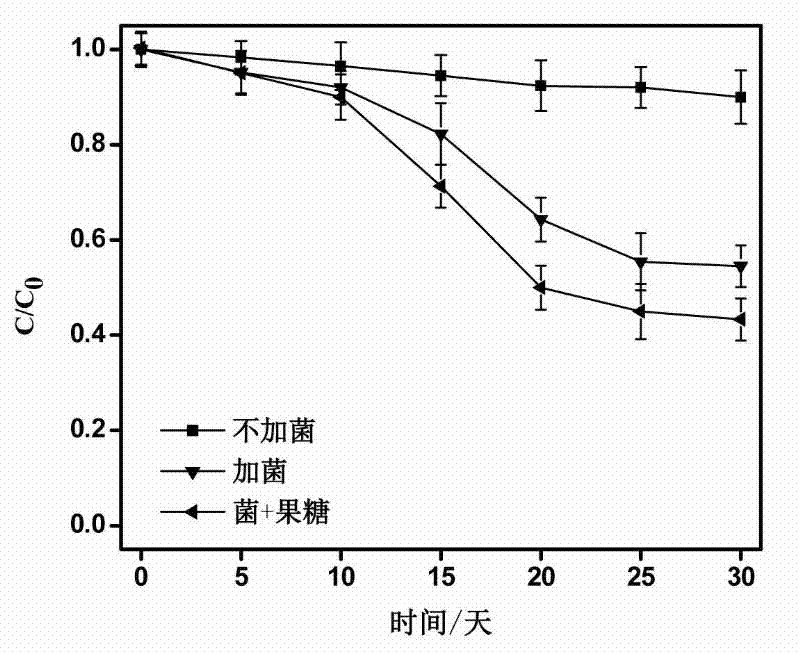
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain PAH-1 capable of degrading PAHs, and its preservation number is CGMCC No.4773. Pseudomonas aeruginosa of the present invention can use humus as an electron acceptor under anaerobic conditions to oxidize and degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, and can significantly improve the degradation rate of phenanthrene under glucose or fructose and phenanthrene co-metabolism conditions, and can be widely used in mild In situ bioremediation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon contaminated soil.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF ECO ENVIRONMENT & SOIL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com