Patents
Literature
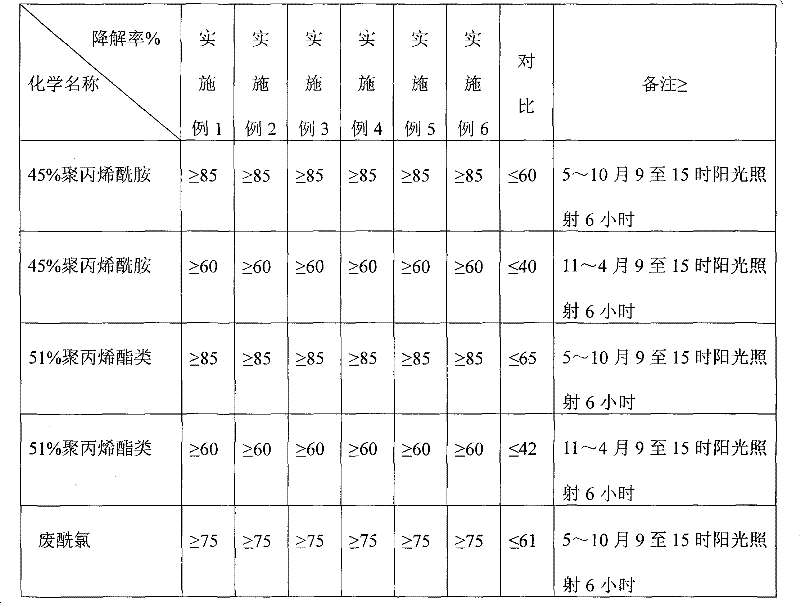
36 results about "Photochemical degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
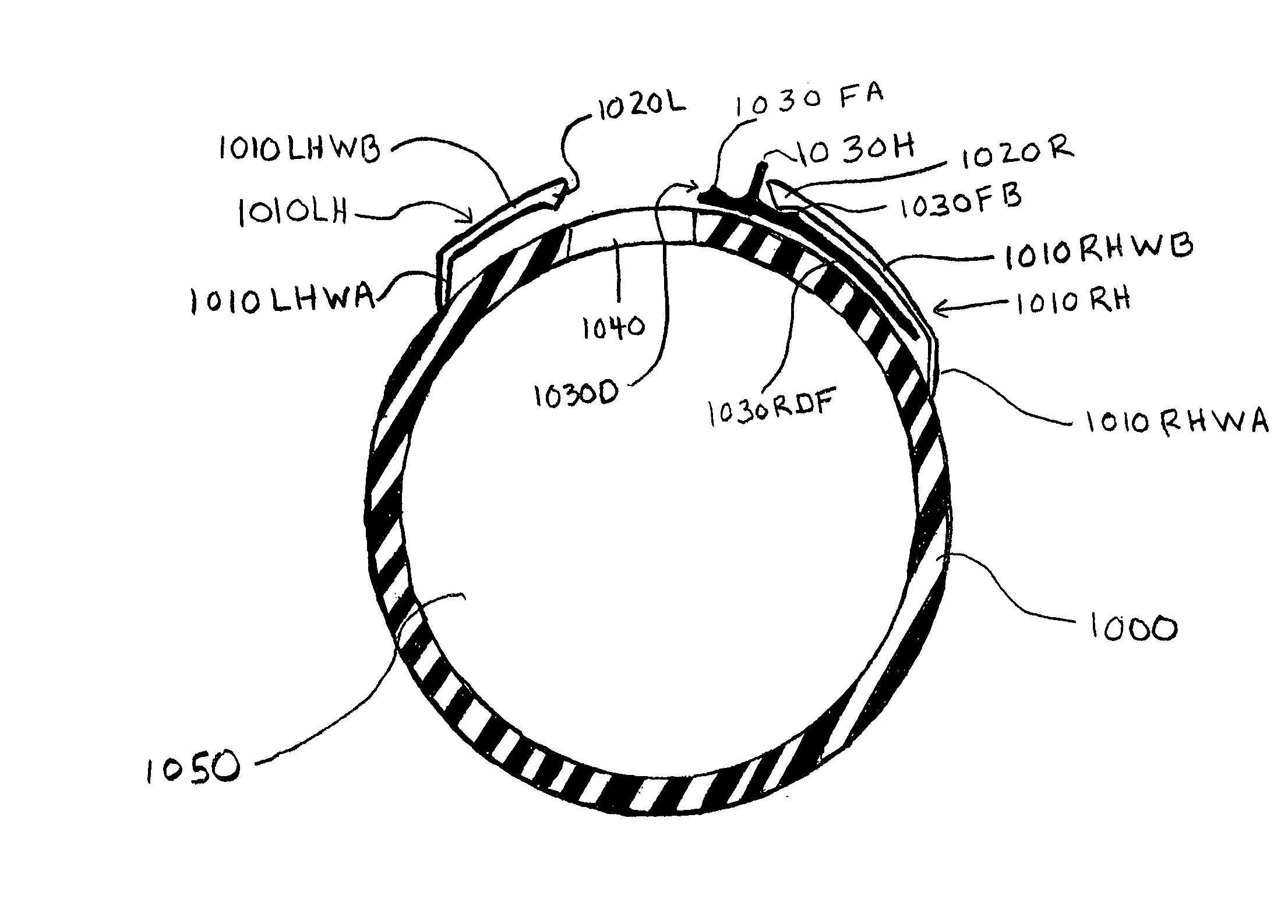
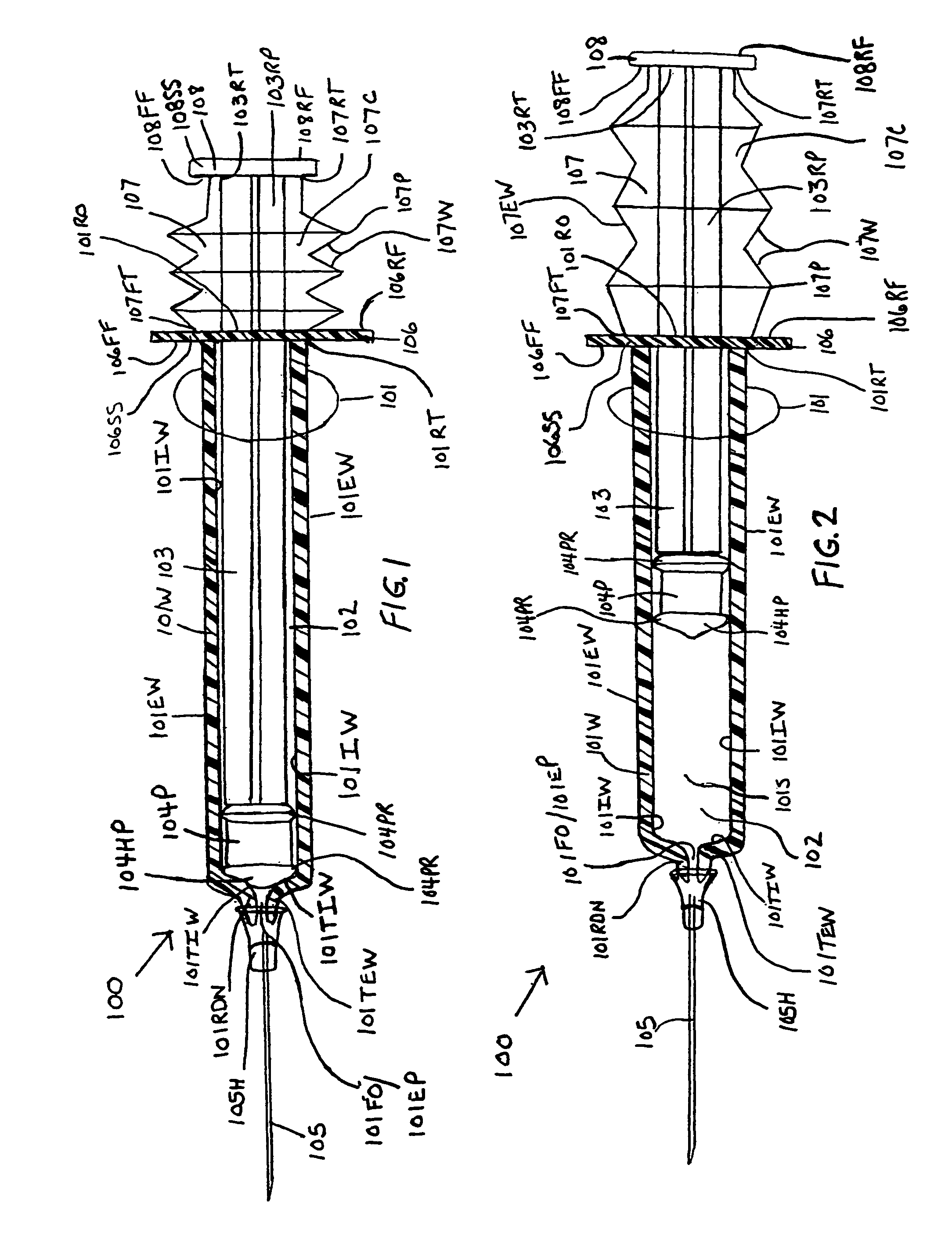
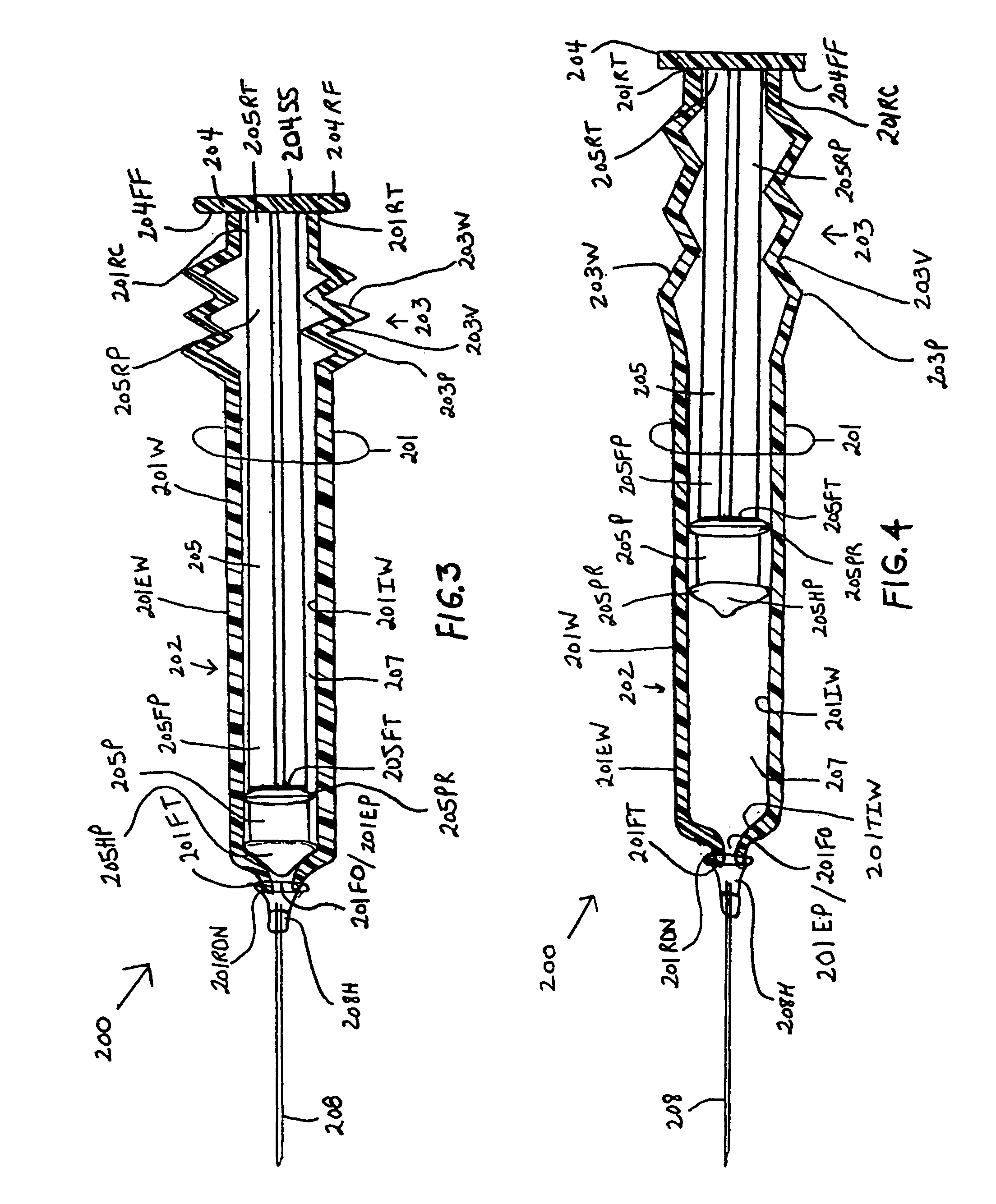
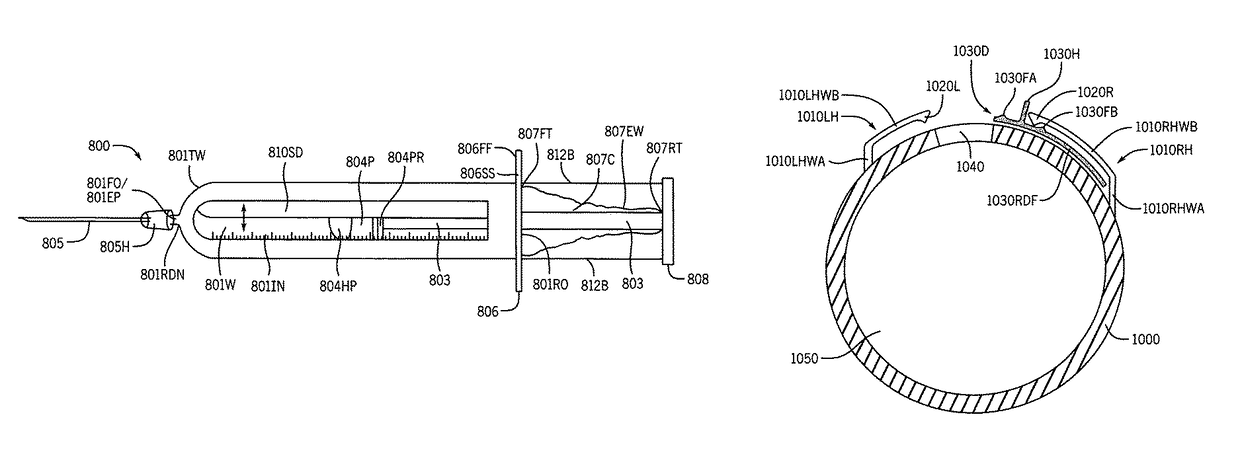
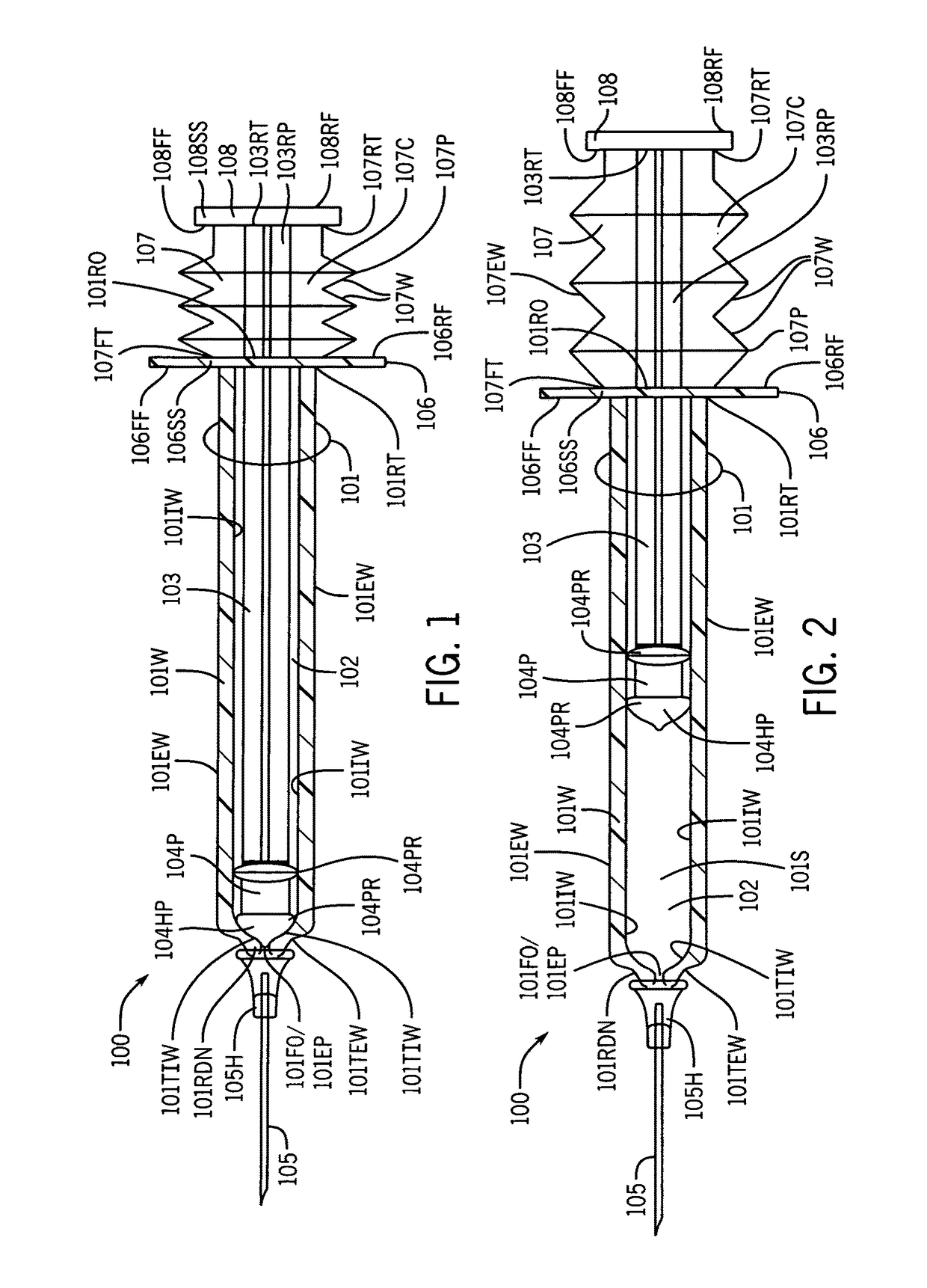
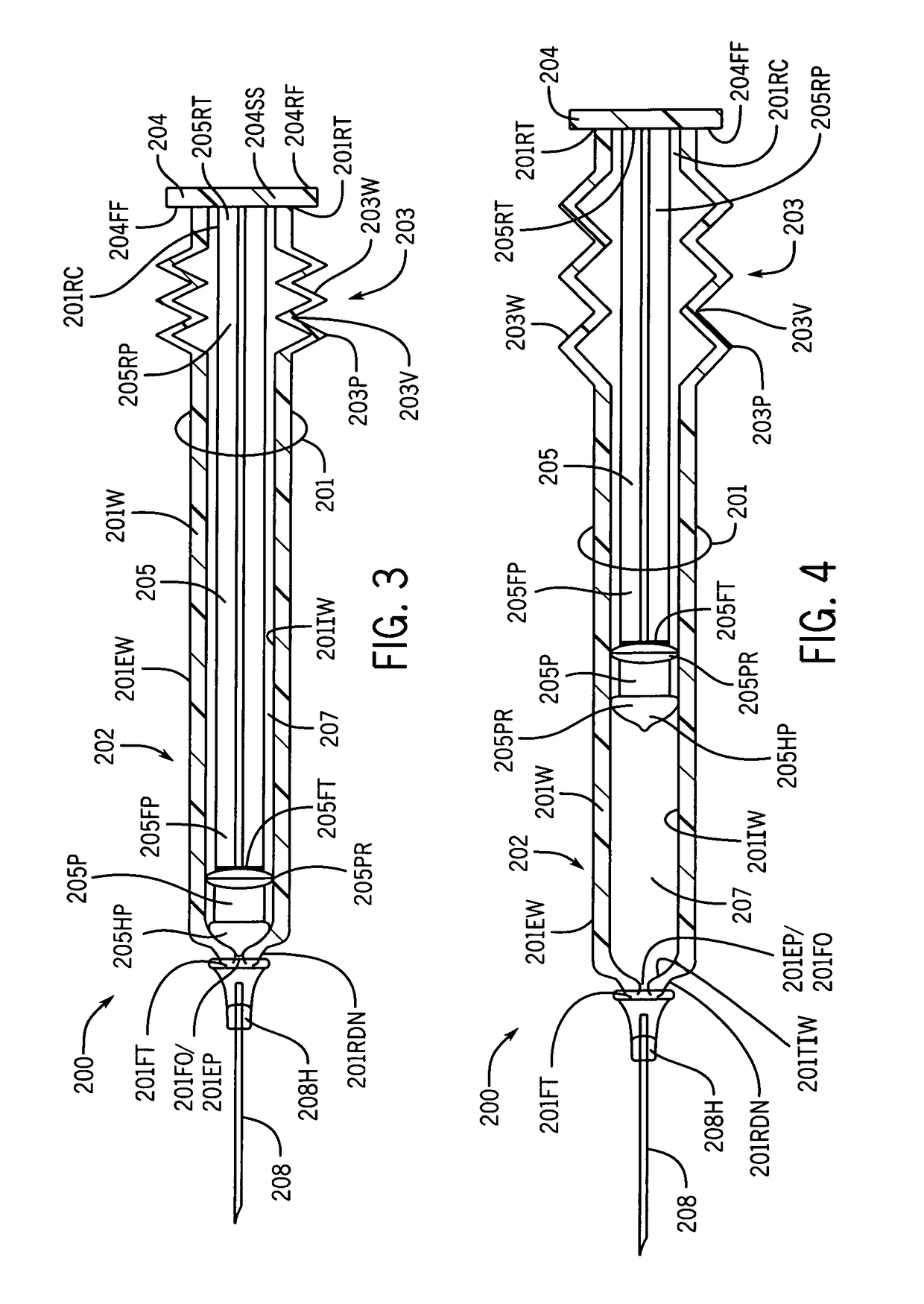
Syringe with inspection window
InactiveUS8777906B1Avoid accidental separationLimited extentInfusion syringesMedical devicesPhotochemical degradationBiomedical engineering
Syringes and methods of using are described which protect materials within the syringe barrel cavity from contaminants and photo-chemical degradation. A syringe is provided having an inspection window for viewing medications or other materials within the cavity of a syringe barrel. The syringe barrel and other syringe components may be colored, opaque, darkened, amber, tinted; or the syringe barrel may have applied thereto polarizing filters; or materials having light polarizing properties can be used to manufacture the syringe barrel and other syringe components of the syringe to cancel particular components of light.
Owner:GRAY ROBIN SCOTT
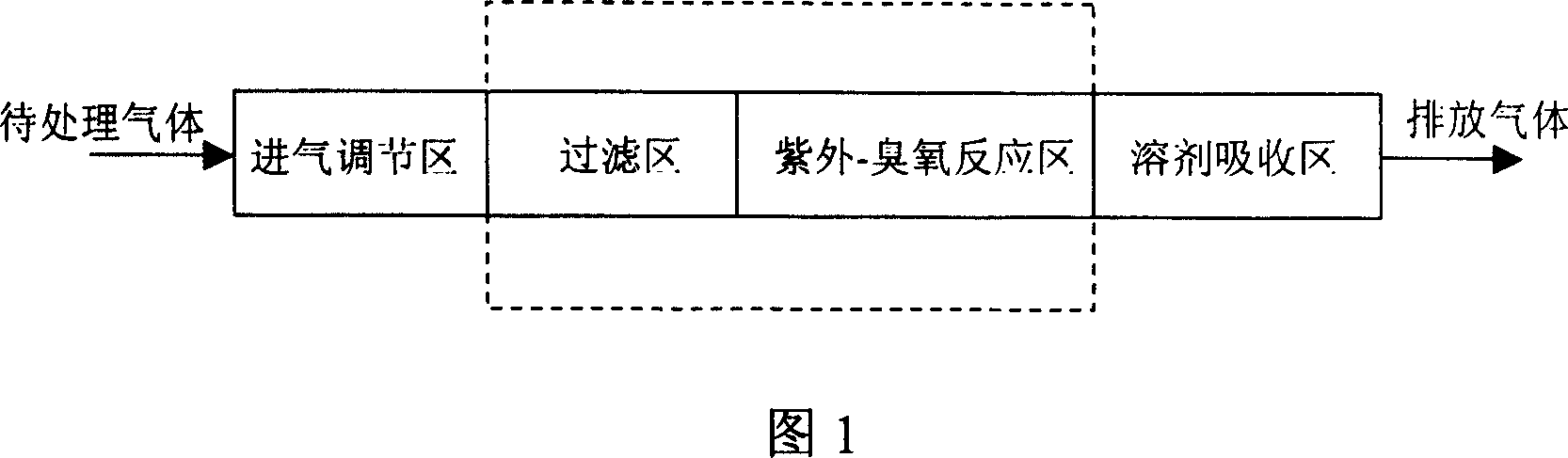
Method and apparatus for photochemical degradation of organic gas
InactiveCN1951544AAchieve degradationSynergistic effect, strong oxidation abilityDispersed particle separationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesPhotochemical degradationSolvent based
The invention relates to a method for using photochemistry method to degrade organic gas. Wherein, it uses ozone, ultraviolet or ozone-ultraviolet to oxidize the organic gas; the processed gas is filtered with particles; then enters into ultraviolet-ozone reaction area, to be radiated and reacted with ozone; then passes the solvent absorber to be purified, and discharged at gas outlet. The invention can effectively degrade organic gas as triphenylamine, without pollution.
Owner:FUJIAN NEWLAND ENTECH CO LTD
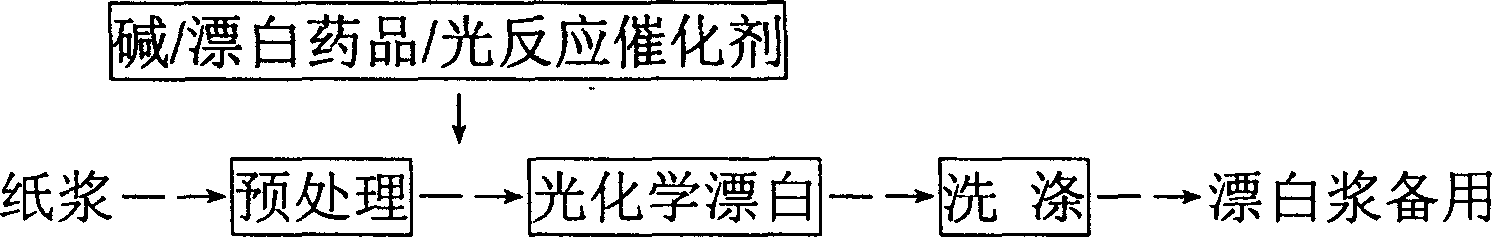
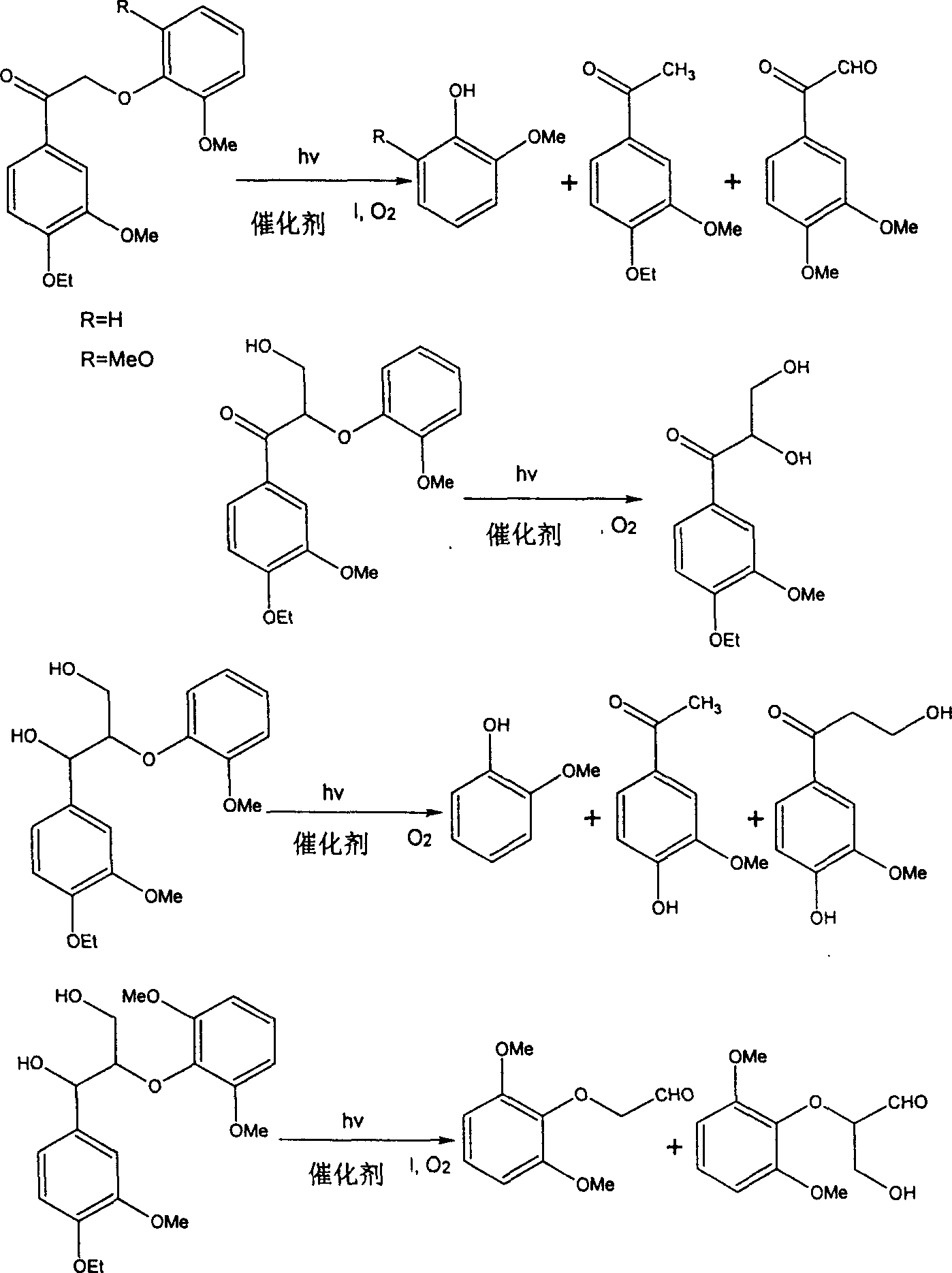
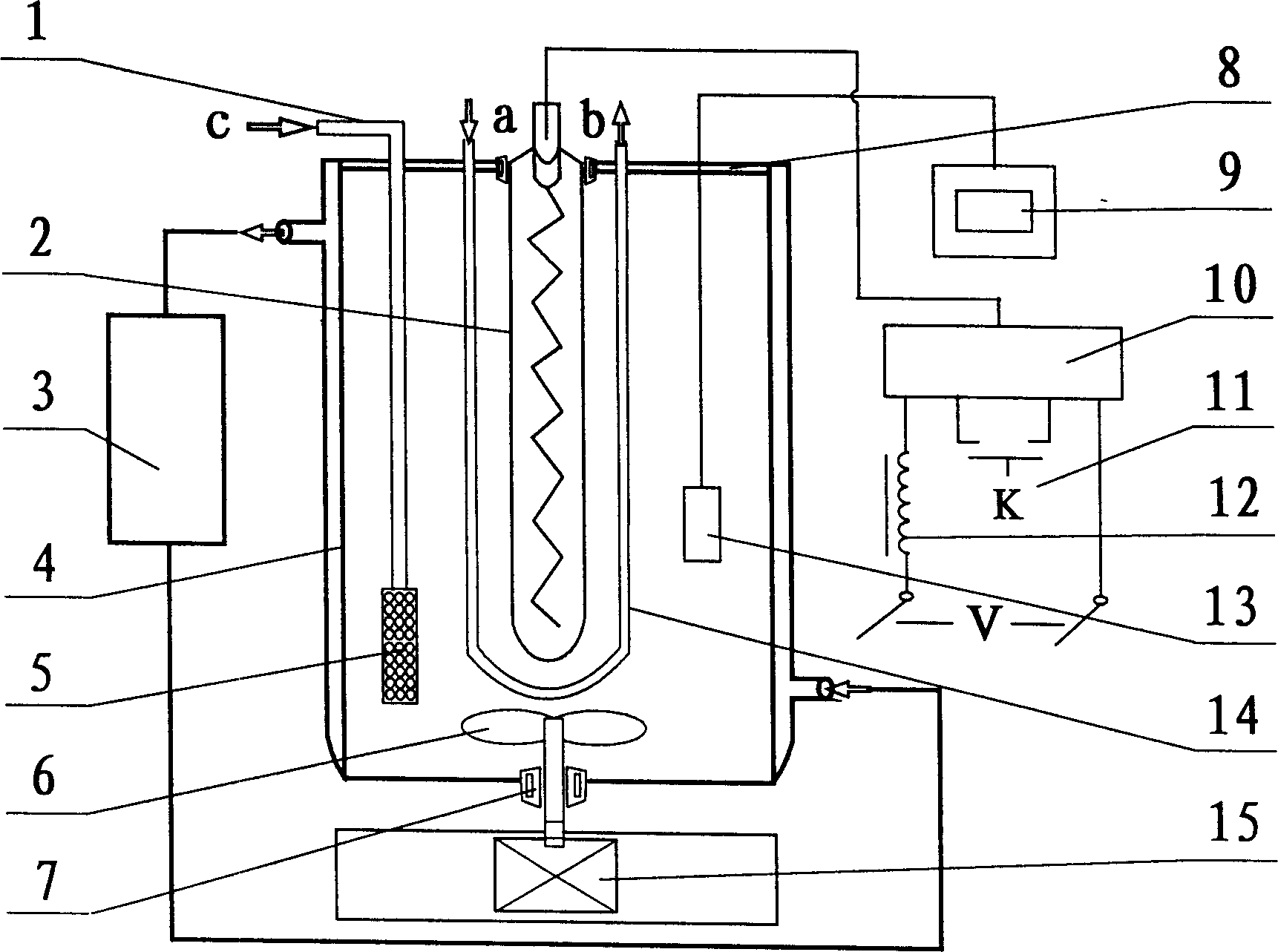
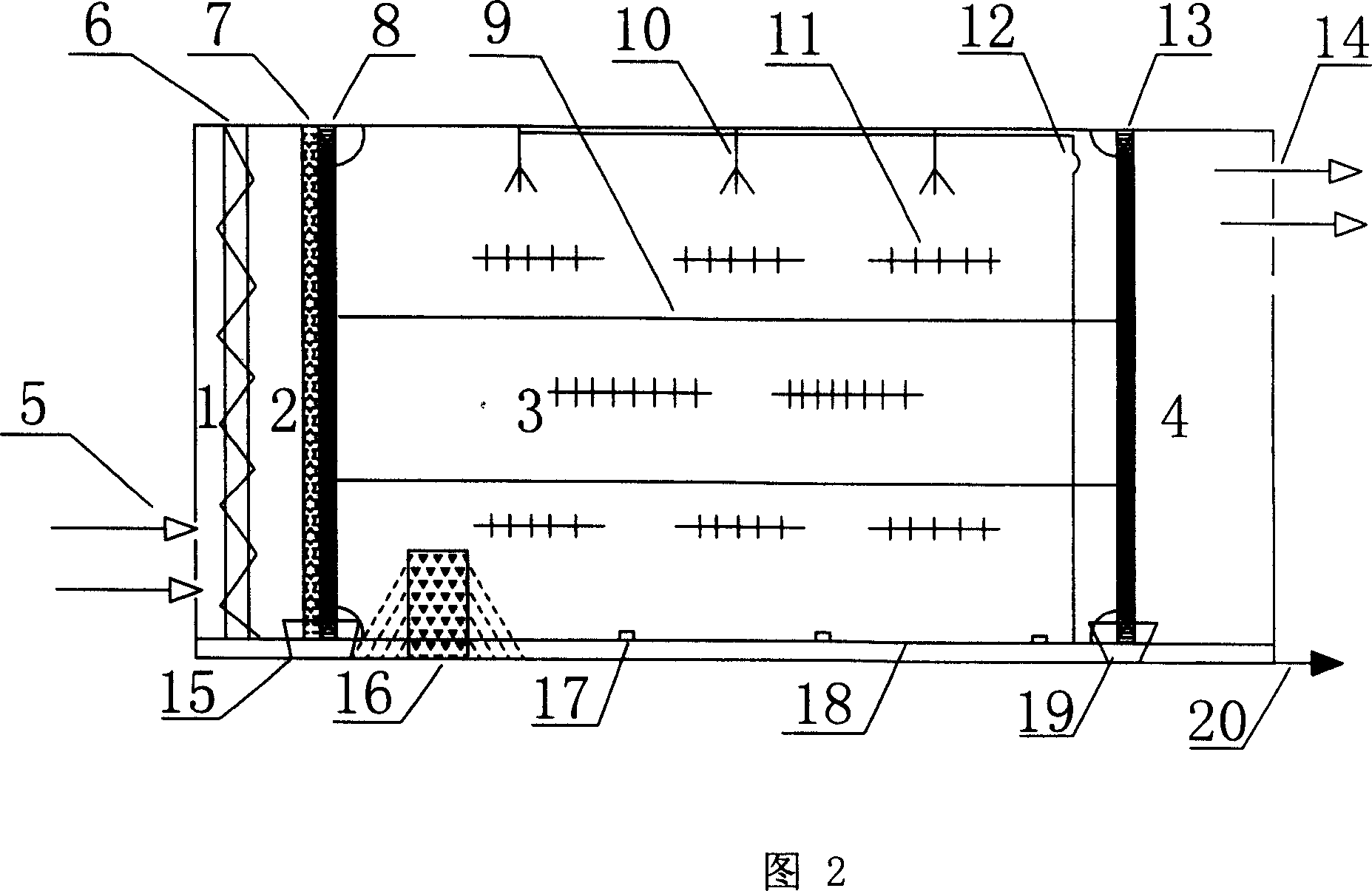
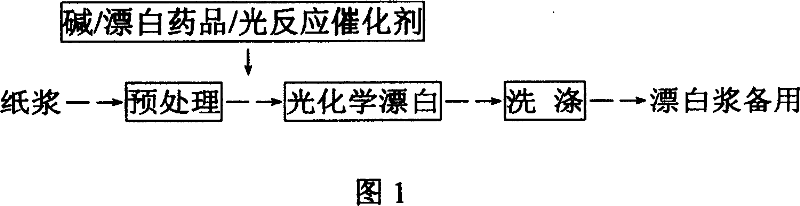
Photochemical paper pulp bleaching method and device
InactiveCN1554826AHigh whitenessHigh degree of delignificationPulp bleachingPlant fibrePhotochemical degradation
Based on photochemical principle, plant fiber pulp after being pre-treated is irradiated with light, and in alkali environment and under the aid of introduced oxygen or air and photobleaching catalyst, the residual lignin in pulp is degraded via photochemical reaction into leached out fragments and thus eliminated, resulting in high whiteness pulp. During the bleaching process, different shielding agent may be added to shield partial light selectively to protect the physical strength of pulp. The bleaching process is environment friendly, and has less corrosion to the apparatus and simple operation.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
In-situ bioremediation preparation and remediation method for chlorothalonil contaminated soil
ActiveCN106591166ASolve serious dangerAddressing food safetyFungiBacteriaPhotochemical degradationIn situ bioremediation
Relating to the soil remediation field, the invention discloses a preparation for in-situ remediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil. The preparation contains fungi and / or bacteria with chlorothalonil degradation ability. The fungi can be at least one of Aspergillus niger, rhizomucor variabilis and Cunninghamella bertholletiae, and the bacteria can be at least one of Burkholderia zhejiangensis, pseudomonas aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. According to the invention, the provided preparation is employed for in-situ bioremediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil, not only overcomes the problems that photochemical degradation is easily limited by illumination conditions and can easily cause secondary chemical reagent pollution to arable land, at the same time makes full use of fungi and / or bacteria for catabolism of chlorothalonil residual in soil, thus solving the problem that high residual chlorothalonil in soil severely endangers food safety. At the same time, the micro-ecology of soil is improved, so that soil can recover farming ability more rapidly. Also, the method is low in cost, thus having broad application prospects.
Owner:粮华生物科技(北京)有限公司
Ultraviolet degradation method for soil polluted by polycyclic hydrocarbon
InactiveCN101168164AHigh speedImprove efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationPhotochemical degradationFiltration
The invention relates to degradation of soil polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, specifically an ultraviolet light degradation method of soil polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, namely treating soil polluted by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon with ultraviolet light illumination. The method is specifically that spreading out polluted soil in a ware, and placing the two in an ultraviolet light illumination box for illumination degradation. The illumination conditions in the illumination box are ultraviolet light illumination wavelength 210-365nm, distance of sample to light source 5-20cm, light intensity 500-10000mu w / cm 2, temperature 25-35 DEG C, humidity in draft control box 30-50%, and illumination time 2-50 days, which is easy to operate. The invention is simple in treatment of removing polluted soil, low in cost, high in speed and efficiency. What is needed is only to conduct simple treatment of air dehydration to polluted soil and filtration, then to place a device with paved polluted soil under an ultraviolet light source for illuminating. The invention belongs to chemical degradation, and causes no secondary pollution, which is an environment-friendly method of treating polluted soil.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
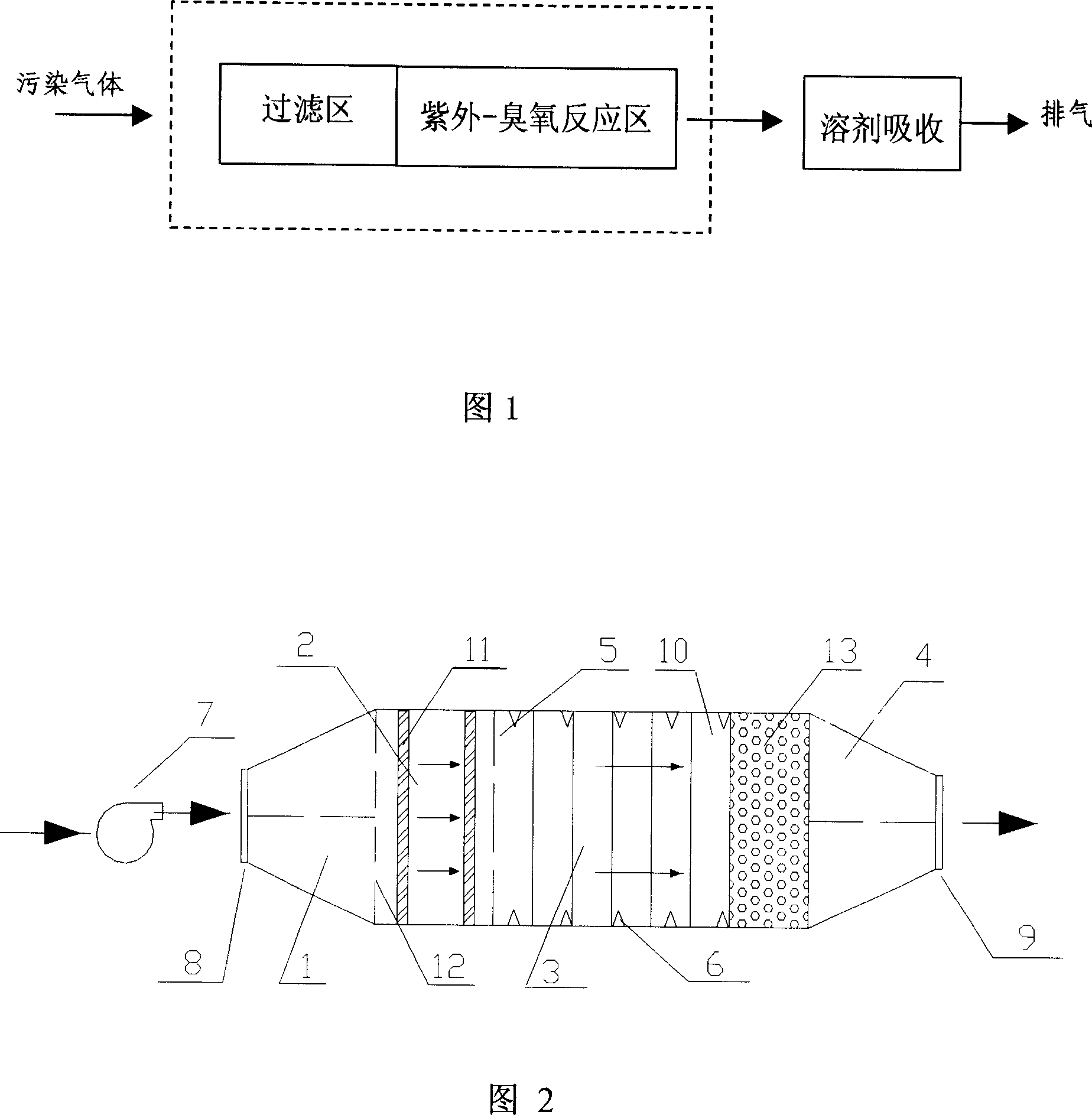
Device for photochemical degradating pollution gas
InactiveCN101053758AAchieve degradationStrong oxidation abilityDispersed particle separationEnergy based chemical/physical/physico-chemical processesBenzenePhotochemical degradation
The invention provides a device for optics degradating dusty gas, comprising a container used as a reactor characterized in that: the reactor is composed of an air inlet control zone, a filter zone, a UV-ozone reacting zone and a solution absorbing zone, wherein they need not be connected by conduit, the UV-ozone reacting zone is at least mounted with a ultraviolet light cluster each comprising at least one ultraviolet light tube, there is ozone in the UV-ozone reacting zone when the device runs, and the tail gas is completely purified by solution absorbing unit to discharge from the exhaust port after air inlet controlled. The invention can be used for the treatment of the dusty gas like 'three-benzene' discharged by the plant of shoes and furnishings, for the treatment of the exhaust gas with fetid smell discharged by effluent treatment plant, tannery, culturing plant and pharmaceutical factory, and also for the pollution gas discharged by other factories.
Owner:FUJIAN NEWLAND ENTECH CO LTD
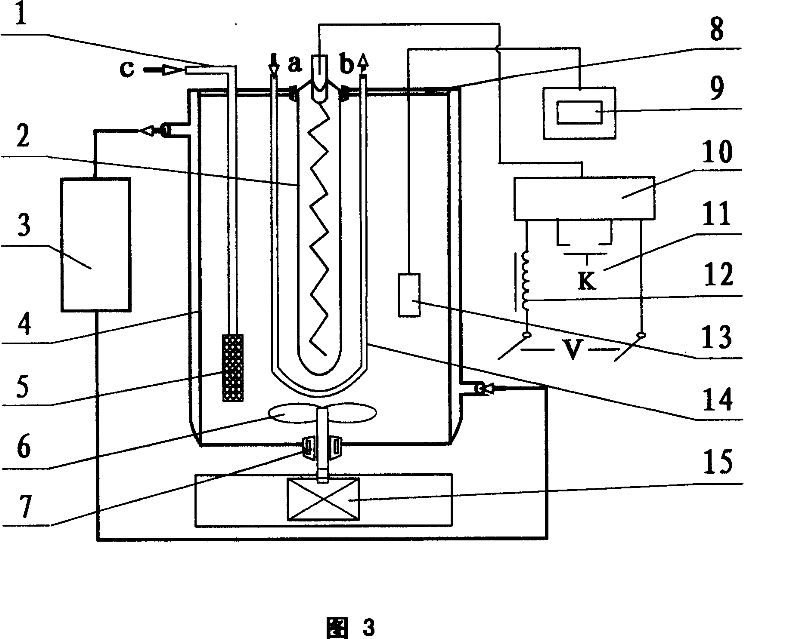
Capacity expansion method of wastewater photochemical degradation reactor combining titanium dioxide catalyst
InactiveCN102849821AExpansion design volumeNo need to worry about temperature rise effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationMicrowavePhotochemical degradation
The invention relates to a capacity expansion method of wastewater photochemical degradation reactor combining titanium dioxide catalyst, which belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. The prior art has the problems of nonideal microwave energy utilization, small single pot wastewater treating capacity and the like, and the method aims at solving the problems. The method comprises the main steps that an electrodeless ultraviolet lamp is further wrapped in a quartz tube through a cage-shaped microwave restraint made of metal material; a waveguide tube is communicated with the cavity of the microwave restraint; the waveguide tube is positioned inside the reactor, so that microwave weak irradiation air space or microwave zero irradiation air space is established between the outer wall of the cage-shaped microwave restraint and the inner wall of the reactor; the method further comprises the step of extending and expanding the size of the microwave weak irradiation air space or the microwave zero irradiation air space inside the reactor in the three-dimensional direction; and the problems are solved through the main steps, and the reactor is allowed to be greatly expanded through the method.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Photo-biodegradable and antibacterial plastic and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses photo-biodegradable and antibacterial plastic and a preparation method thereof and relates to the technical field of plastic preparation. The photo-biodegradable and antibacterial plastic is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 20 to 30 parts of polyethylene, 15 to 25 parts of calcium carbonate, 15 to 25 parts of modified starch, 5 to 15 parts of maltodextrin, 5 to 15 parts of wood fibers, 1 to 10 parts of gelatin, 1 to 5 parts of glycerol, 2 to 10 parts of diphenylcyclopropenone, 1 to 7 parts of iron carbamate disulfide, 1 to 5 parts of nano titanium dioxide, 8 to 16 parts of polyhydroxyalkanoate, 1 to 3 parts of sodium diacetate, 1 to 5 parts of sodium lignosulfonate, 2 to 12 parts of acetyl tributyl citrate and 2 to 10 parts of oxidized polyethylene wax. The polyethylene plastic disclosed by the invention has a photo-biodegradable effect; especially, biological degradation and photochemical degradation have a synergetic effect and thedegradation rate is high; meanwhile, the photo-biodegradable and antibacterial plastic has an antibacterial effect and is suitable for producing and manufacturing various plastic products.
Owner:李君
Syringe with inspection window
InactiveUS9764094B1Avoid separationReduce the possibilityInfusion syringesMedical devicesPhotochemical degradationBiomedical engineering
Owner:GRAY ROBIN SCOTT
Device and method for degradating organic pollutant in tea by photo chermistry
InactiveCN1561771AEliminate organic pollutantsKeep the shape of the productPre-extraction tea treatmentIsotope separationPhotochemical degradationUltraviolet lights
An apparatus for photochemically degradating the organic pollutants in tea is composed of a reacting container with tea inlet and outlet, blowing inlet, oxygen inlet, atomizing nozzle and exhaust port, and an ultraviolet light source consisting of light-source tubes. Its method is also disclosed.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
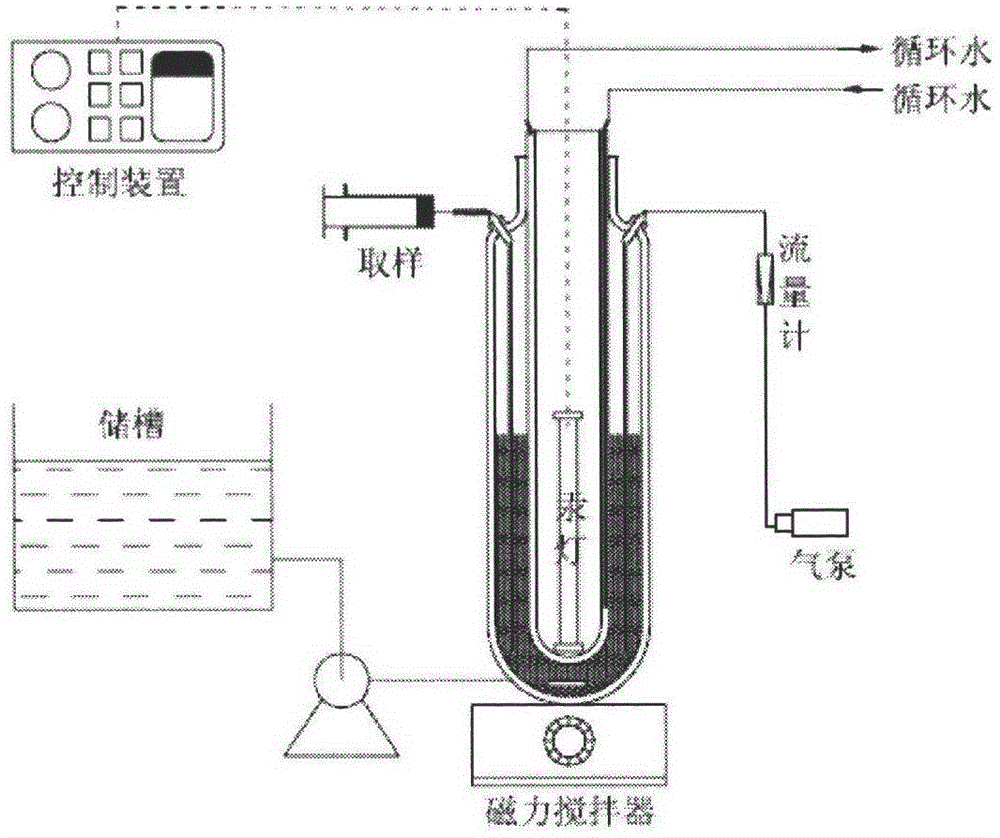
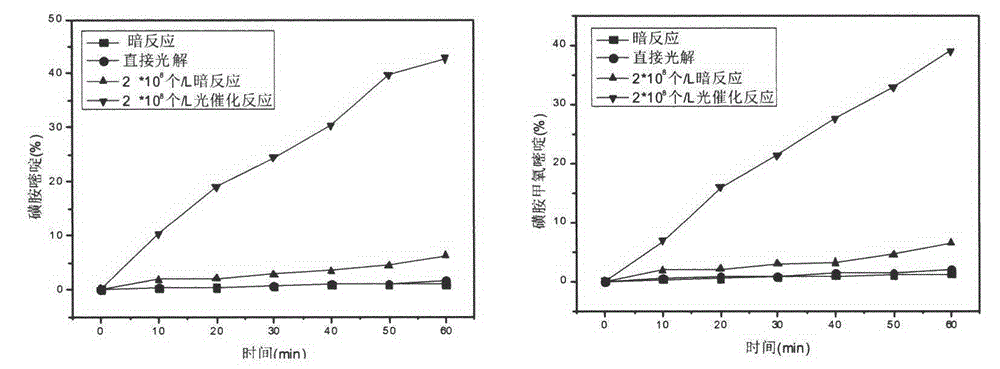
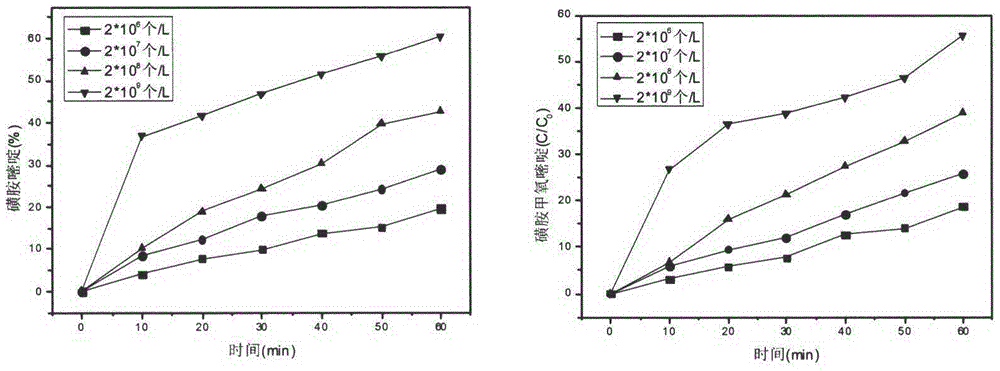
Method for photochemical degradation of sulfonamide in water by using freshwater algae
InactiveCN104556292ANo secondary pollutionNo secondary treatmentWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater contaminantsFreshwater algaeFresh water organism
The invention relates to a method for photochemical degradation of sulfonamide in water by using freshwater algae. A sulfonamide in water is degraded by utilizing active oxygen produced by the freshwater algae. The specific implementation method is as follows: wastewater to be treated is introduced into a reactor in a circulating way, and the active oxygen matter produced by light radiation on the freshwater algae is used for degrading the sulfonamide when the ventilatory capacity is 0.5L / min and the pH value is 6 at certain alga concentration and temperature. The reaction time is prolonged, the concentration of the sulfonamide is reduced, and the effluent which meets the requirements can be finally achieved.
Owner:张军伟 +2
Photochemical degradable sol composition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102039194AImprove efficiencyLow costOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSesquioxidePhotochemical degradation
The invention provides a photochemical degradable sol composition and a preparation method thereof. The composition comprises the following components in part by weight: 50 parts of water, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of photographic gelatin, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of span 80, 40 to 50 parts of nano anatase titanium white powder, 4 to 8 parts of nano rutile titanium white powder, 5 to 15 parts of mixed light absorbing cyanine dye, 0.5 to 1 part of bismuth nitrate, 0.5 to 1 part of cerous chloride and 1 to 3 parts of nano iron sesquioxide. The degradable sol composition integrates photochemistry, catalysis technology and nano chemistry; sunlight serving as inexhaustible natural resource can be fully utilized and combined with non selectively of modern advanced photochemistry, catalysis technology and nano chemistry on organic waste degradation and oxidation effects; and the method has low cost, is simple and convenient to operate, and is suitable for developing medium and small enterprises.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGSHENG NEW MATERIALS
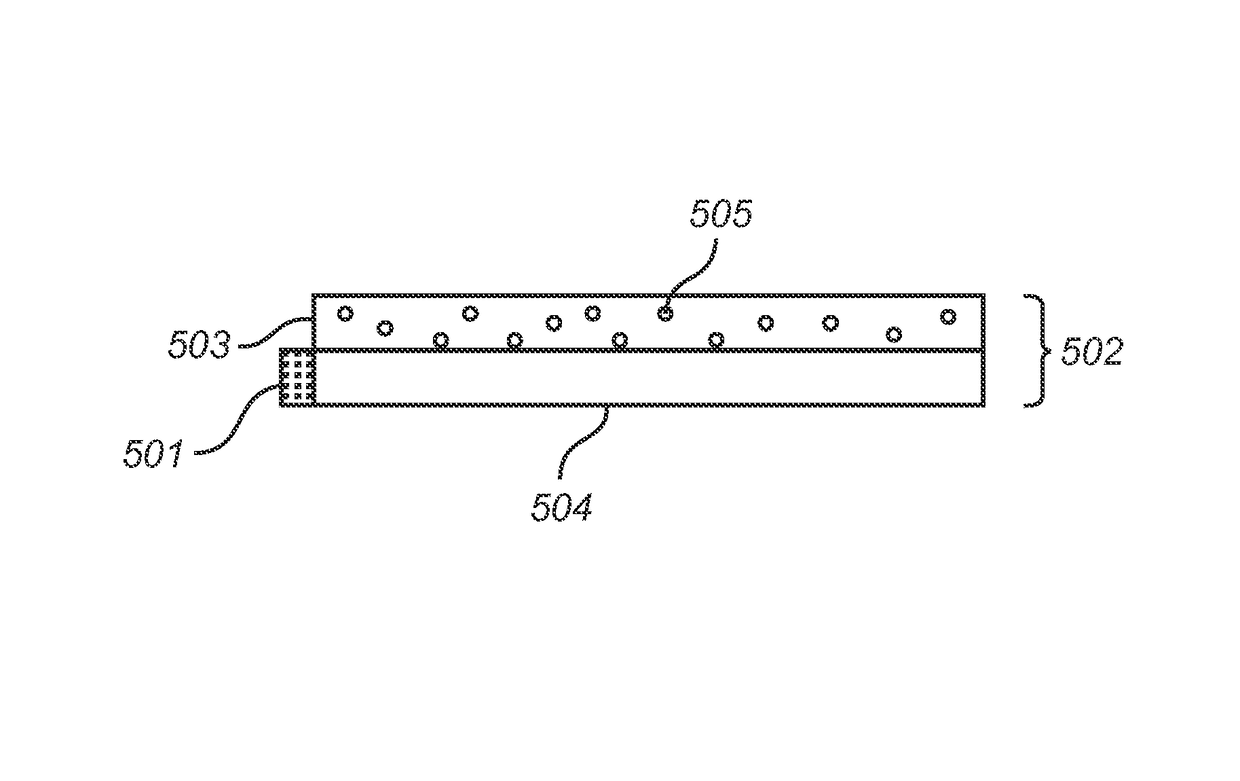
Stabilized wavelength converting element
ActiveUS20150219290A1Good dimensional stabilityImprove stabilityPoint-like light sourceElectroluminescent light sourcesPhosphorPhotochemical degradation
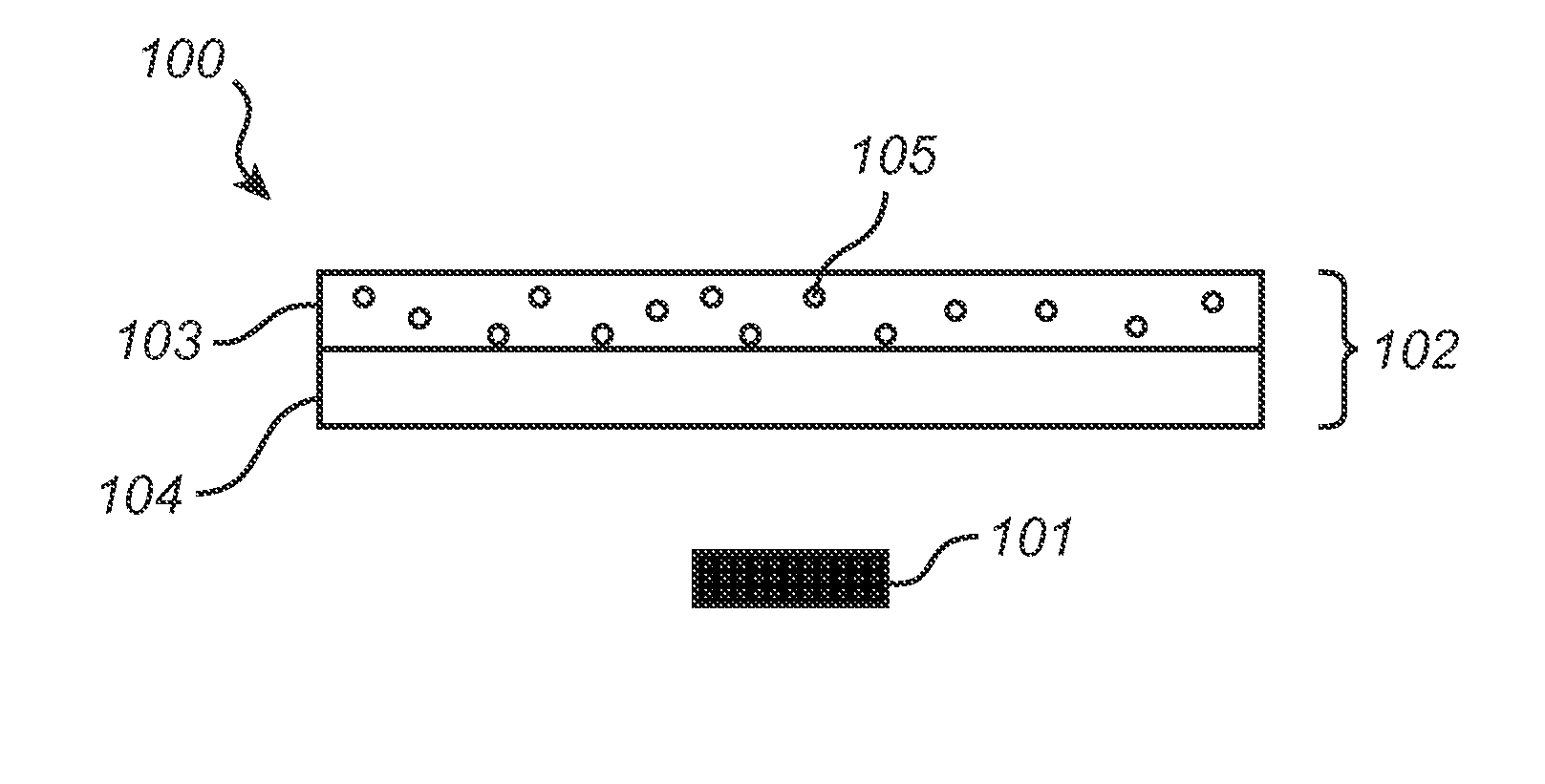
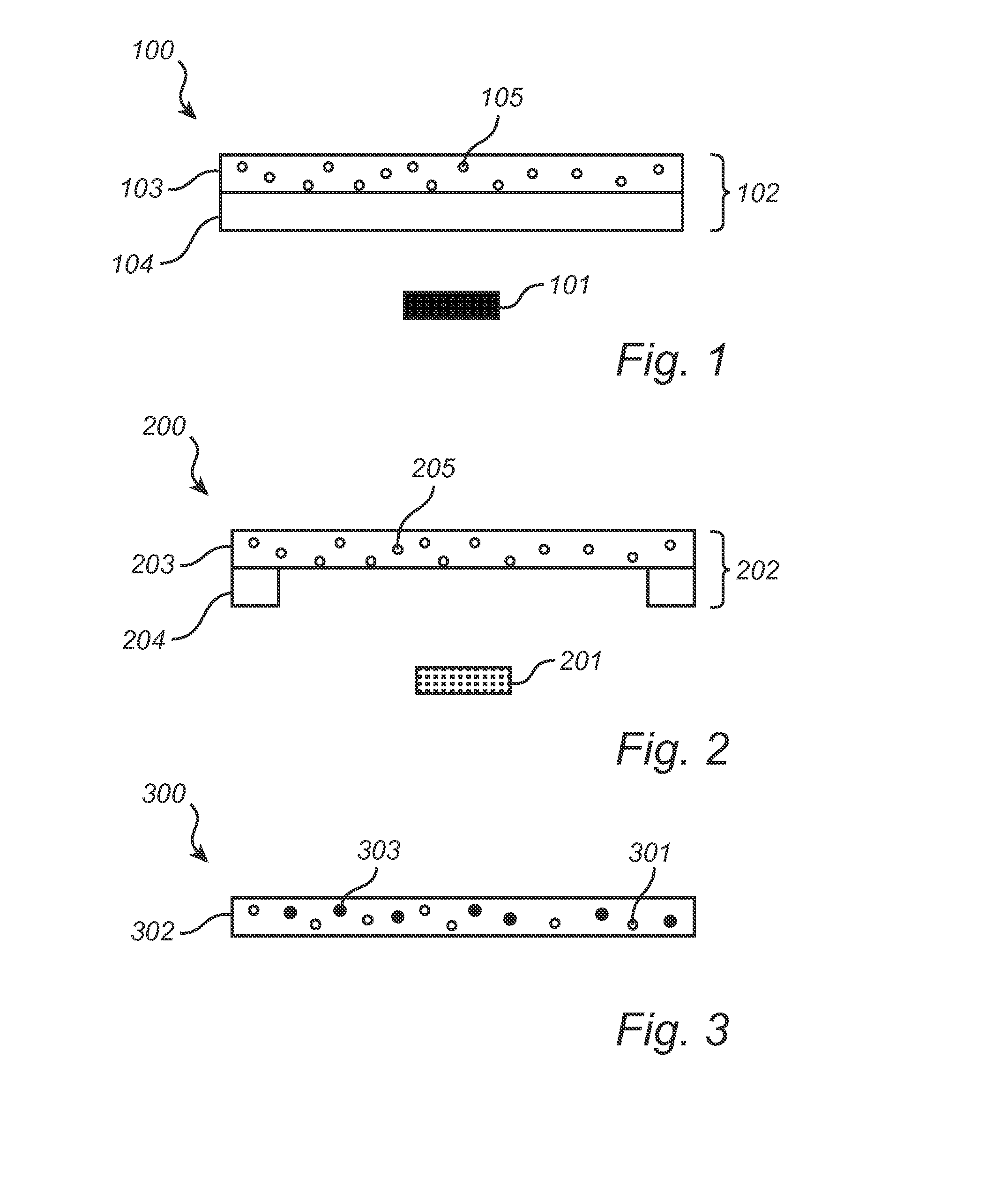
A wavelength converting member (102) is provided, comprising a wavelength converting layer (103) comprising an organic wavelength converting compound (105) distributed in a matrix comprising an amorphous or semi-crystalline aromatic polyester wherein the aromatic polyester molecules are predominantly in a randomly oriented state, said wavelength converting member further comprising at least one support element (104). By avoiding uniaxial or biaxial orientation of the polyester matrix, the organic wavelength converting compound (organic phosphor) is well protected against photo-chemical degradation. The support element ensures the dimensional stability of the polyester matrix at temperature above the glass transition temperature
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
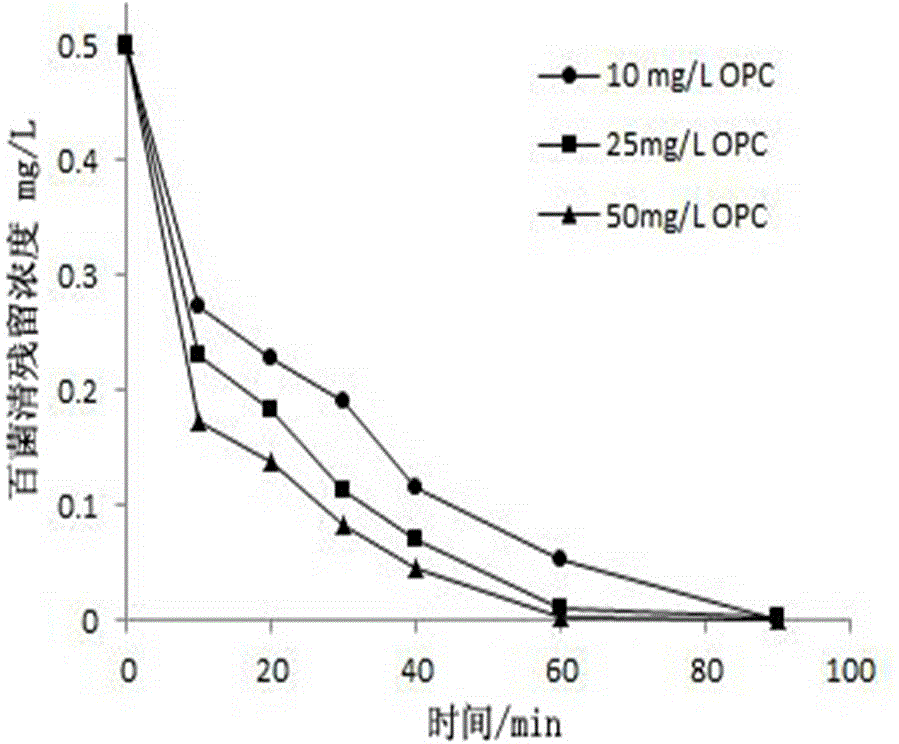
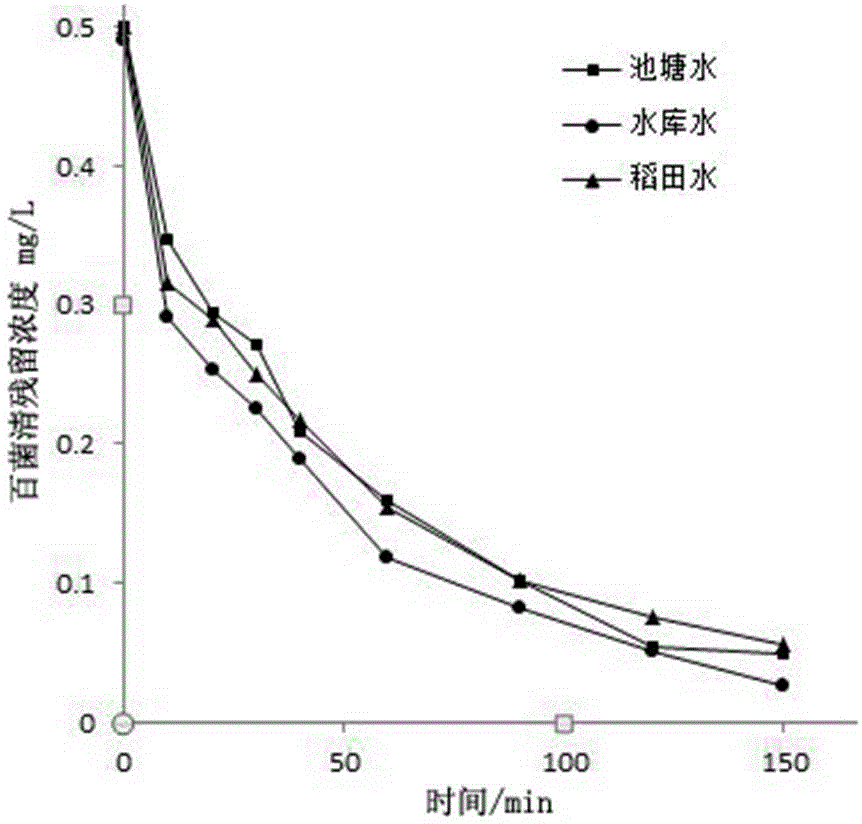
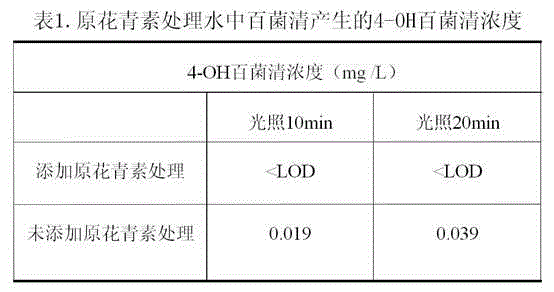
Method for treating chlorothalonil in water by utilizing oligomeric proantho cyanidins extracted from natural plants
ActiveCN104787837APromote clear photochemical degradationPromote dechlorination degradationWater/sewage treatment by irradiationEnergy based wastewater treatmentMetabolitePhotochemical degradation
The invention relates to a method for treating chlorothalonil in water by utilizing oligomeric proantho cyanidins (OPC) extracted from natural plants. Under a condition that the light intensity is 84,000-93,000 lx, chlorothalonil is dissolved into an aqueous solution or directly put into a to-be-treated water body, the addition amount of chlorothalonil is 10-50 mg / L, the illumination time is controlled to be 10-20 minutes, wastewater treatment is performed, the removal rate of chlorothalonil is 32-70%, and a highly toxic metabolite, namely 4-OH chlorothalonil is not generated. A photosensitive degradation effect of OPC on chlorothalonil promotes dechlorination degradation of chlorothalonil, and the reducibility of OPC under the lighting condition promotes photochemical degradation of chlorothalonil in the aqueous solution; at the same time, a photolysis pathway of chlorothalonil is changed, thereby effectively avoiding generation of the highly toxic metabolite, namely 4-OH chlorothalonil.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Wastewater photochemical degradation reactor capacity expanding method for simultaneously reinforcing internal cycle of liquid
InactiveCN103086467AExpansion design volumeNo need to worry about temperature rise effectWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationMicrowavePhotochemical degradation
The invention relates to a wastewater photochemical degradation reactor capacity expanding method for simultaneously reinforcing the internal cycle of a liquid belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. A scheme in the invention aims to solve problems comprising unsatisfactory microwave energy utilization condition, small wastewater throughput of the single tank of a reactor, insufficient internal liquid cycle intensity and the like in the prior art. The scheme mainly comprises the following steps: wrapping an electrodeless ultraviolet lamp with a metal cage in a quartz tube, communicating a waveguide tube with the inner cavity of the metal cage, positioning the quartz tube in the reactor, and constructing a microwave weak-irradiation airspace or a microwave zero-irradiation airspace between the outer wall of the metal cage and the inner wall of the reactor; arranging a horn-shaped member used for guiding and reinforcing the liquid flow cycle by means of rising ozone-containing bubbles just under the quartz tube; and extending and expanding the size of the microwave weak-irradiation airspace or the microwave zero-irradiation airspace in the reactor in a three-dimensional direction.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Stabilized wavelength converting element
ActiveUS9803809B2Good dimensional stabilityImprove stabilityElectroluminescent light sourcesLuminescent compositionsVitrificationPhotochemical degradation
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Method for photochemically degrading ciprofloxacin in water by using limnetic algae
InactiveCN103951066ANo secondary treatmentRealize semi-automationBiological water/sewage treatmentMaterial DegradationPhotochemical degradation
The invention discloses a method for photochemically degrading ciprofloxacin in water by using limnetic algae. Ciprofloxacin in water is degraded by means of oxidization of hydroxyl radicals generated by the limnetic algae. The method is concretely implemented as follows: circularly introducing wastewater to be treated to a reactor, and optically radiating the limnetic algae to generate hydroxyl radical substances to degrade ciprofloxacin at a certain alga concentration and temperature and under the conditions that the ventilation is 0.5L / min and the pH value is equal to 6. The reaction time is prolonged, the concentration of ciprofloxacin is reduced, and finally, the outer drainage meeting the requirement can be realized.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for photochemical degradation of phosphorus-containing wastewater
ActiveCN106186175AAvoid generatingEliminate the effects ofWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsHigh concentrationPhotochemical degradation
The invention discloses a method for photochemical degradation of phosphorous-containing wastewater, and aims to degrade organic matters and precipitate and remove phosphorus in phosphorus-containing wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: using peroxide as an oxidant, carbohydrate as an initiator, ferrous ion as a catalyst, ferrous ion complexing organic matter hydroxyacetic acid as a stabilizer, and soluble aluminum salt or calcium salt as a phosphate precipitant; and performing UV photo-oxidative degradation under a weak acidity condition of pH 2-6. In the method provided by the invention, the peroxide is decomposed through a UV-induced Fenton reaction to generate free radicals and the catalyst in a complexing state is used at the same time to eliminate the poisoning of phosphate radicals to the catalyst, thereby realizing the rapid degradation of high-concentration organic wastewater containing a large amount of phosphate radicals. The method has the advantages of simple steps, no need of heating or pressing, and easy control, uses the cheap stabilizer, realizes the degradation process under mild conditions, and is a phosphorus-containing wastewater degradation method featured with huge potential, environmental protection, high efficiency and economy.
Owner:NINGBO SUNNY NOVEL MATERIAL TECH
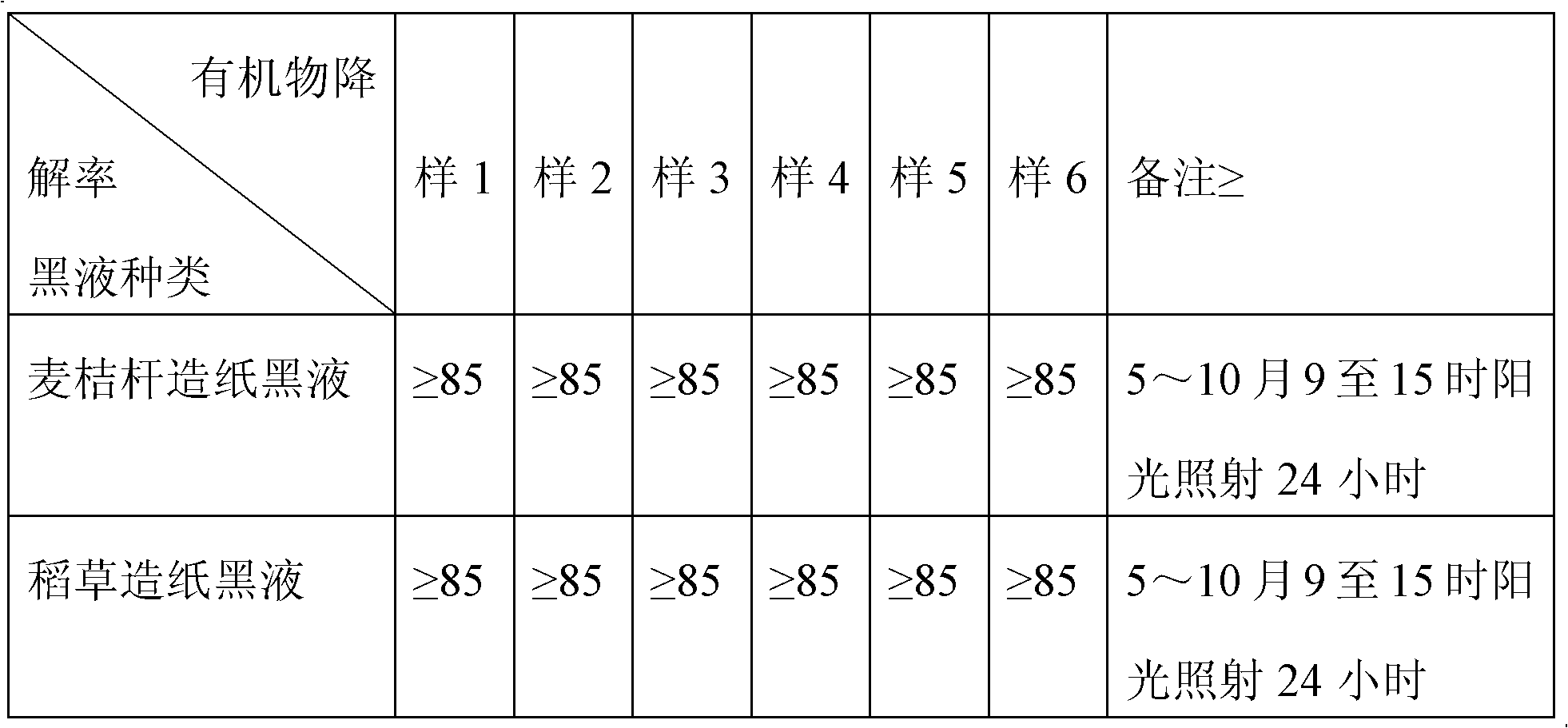
Photochemical degradation agent for treating paper making paper making black liquor and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102631950AImprove efficiencyReduce consumptionWater/sewage treatment by irradiationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPhotochemical degradationSilanes
The invention provides a photochemical degradation agent for treating paper making paper making black liquor and a preparation method thereof. The photochemical degradation agent comprises the following components in parts by weight: 40-60 parts of nano anatase titanium white, 3-6 parts of 3-methylacryloyloxypropyltrimethoxy silane, 5-15 parts of visible light absorber, 1-3 parts of bismuth nitrate, 1-3 parts of cerous chloride, 3-6 parts of nano ferric oxide and 1-3 parts of nano copper oxide. The photochemical degradation agent for treating organic matters in paper making black liquor integrates photochemistry, catalytic technology and nano chemistry, and can treat the organic matters in the black liquor through photochemical degradation by fully utilizing the inexhaustible natural resource sunlight and combining advanced photochemistry, catalytic technology and nano technology at present; and thus, the invention is very suitable for high-efficiency low-consumption environmental management in China. The technique and preparation method, which have the advantage of low cost and are simple to operate, are more suitable for medium and small paper making enterprises in development.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGSHENG NEW MATERIALS
Internal-liquid-circulation-reinforced high-treatment-capacity reactor for wastewater photochemical degradation
InactiveCN103112922ANo need to worry about temperature rise effectExpansion design volumeWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisHigh absorptionMicrowave
The invention relates to an internal-liquid-circulation-reinforced high-treatment-capacity reactor for wastewater photochemical degradation, belonging to the technical field of wastewater treatment The existing electrodeless ultraviolet catalytic degradation technique for organic-substance-containing industrial wastewater has the problems of inutile energy dissipation due to high absorption amount of microwave energy by the wastewater water body, overlow single-tank wastewater treatment capacity of the reactor, insufficient internal liquid circulation strength and the like. The scheme provided by the invention aims to solve the problems above. According to the scheme provided by the invention, an electrodeless ultraviolet lamp is arranged in a metal cage-shaped photopermeable microwave restriction device into which microwaves are introduced, so that inutile dissipation is inhibited by restricting the microwaves; meanwhile, in the structure, an ultraviolet-permeable quartz tube for gas-liquid isolation is arranged between the microwave restriction device and the wastewater body; and a flared component for reinforcing liquid circulation is arranged right below the quartz tube. The scheme provided by the invention totally solves the problems above.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method of dissolubility iron salt induction photochemical degradation total fluorination substituted compound
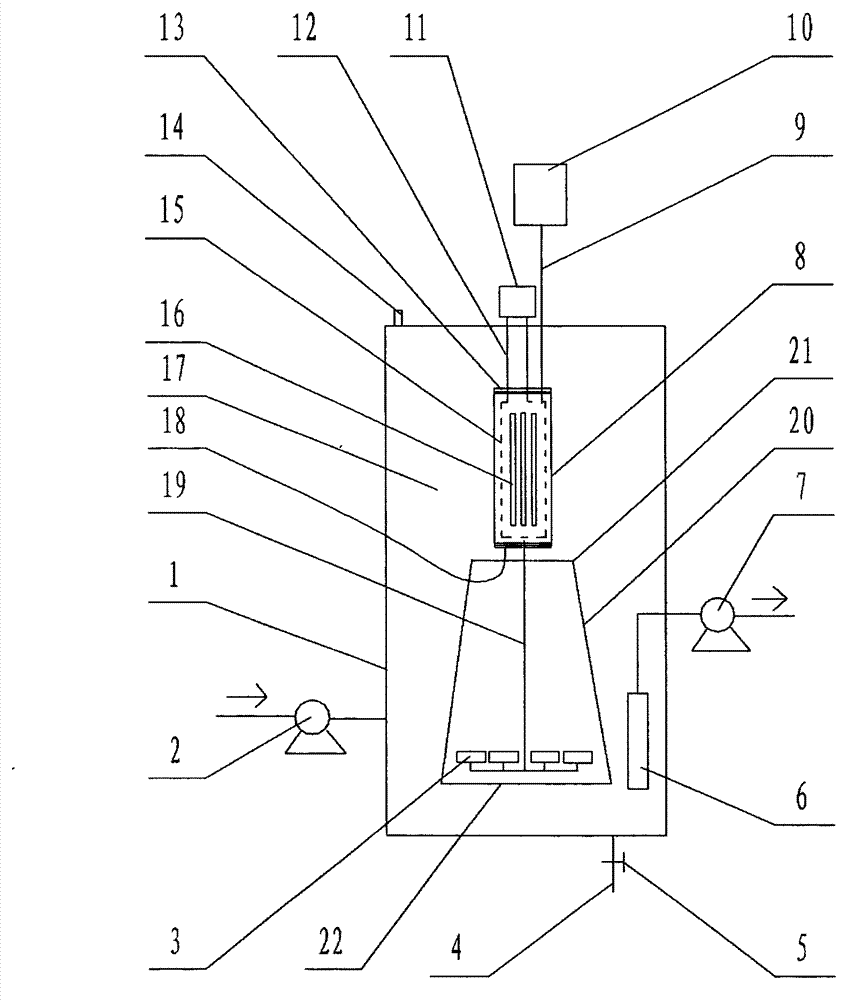
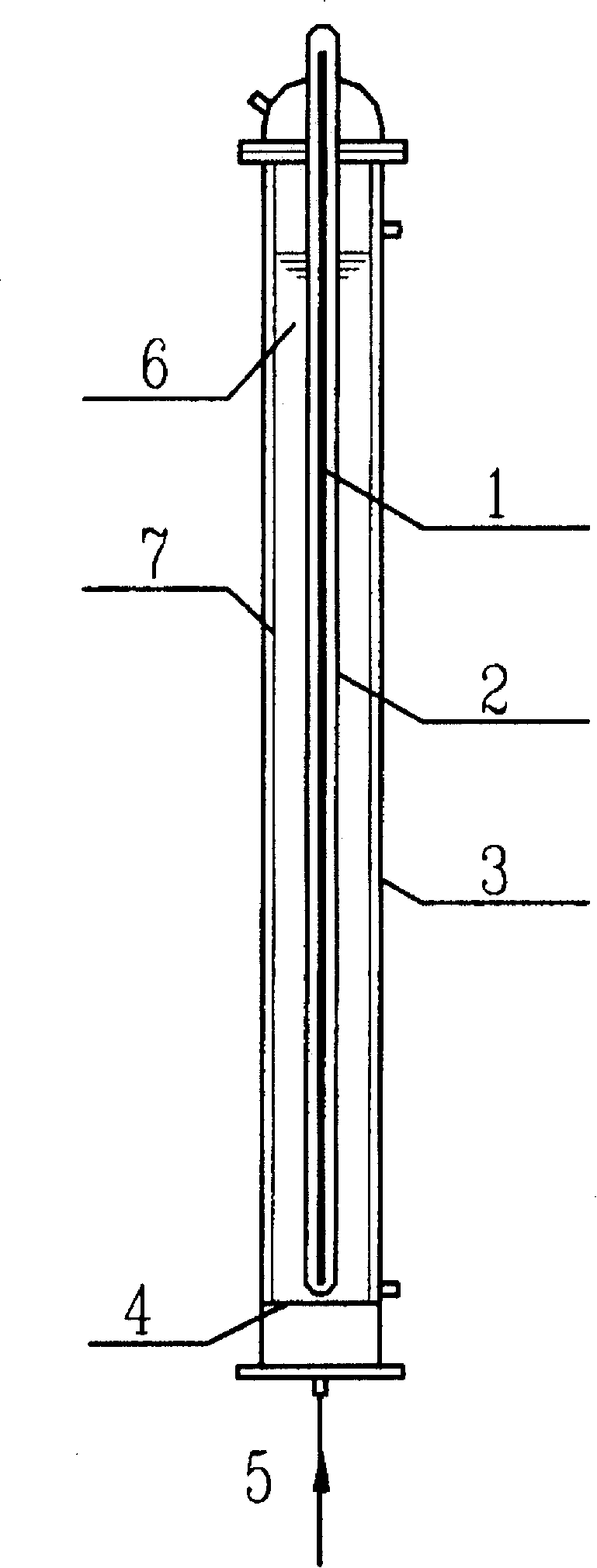
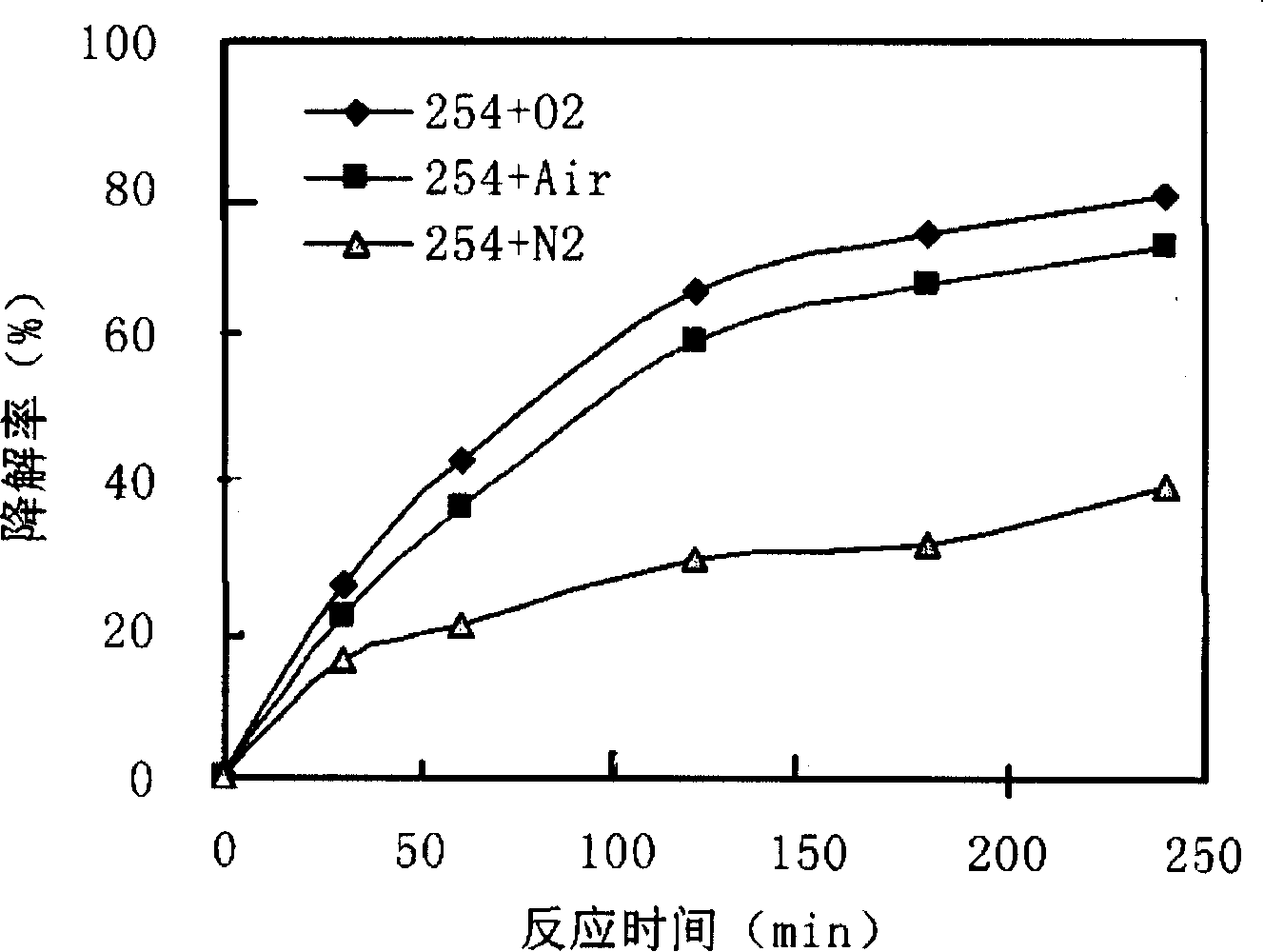
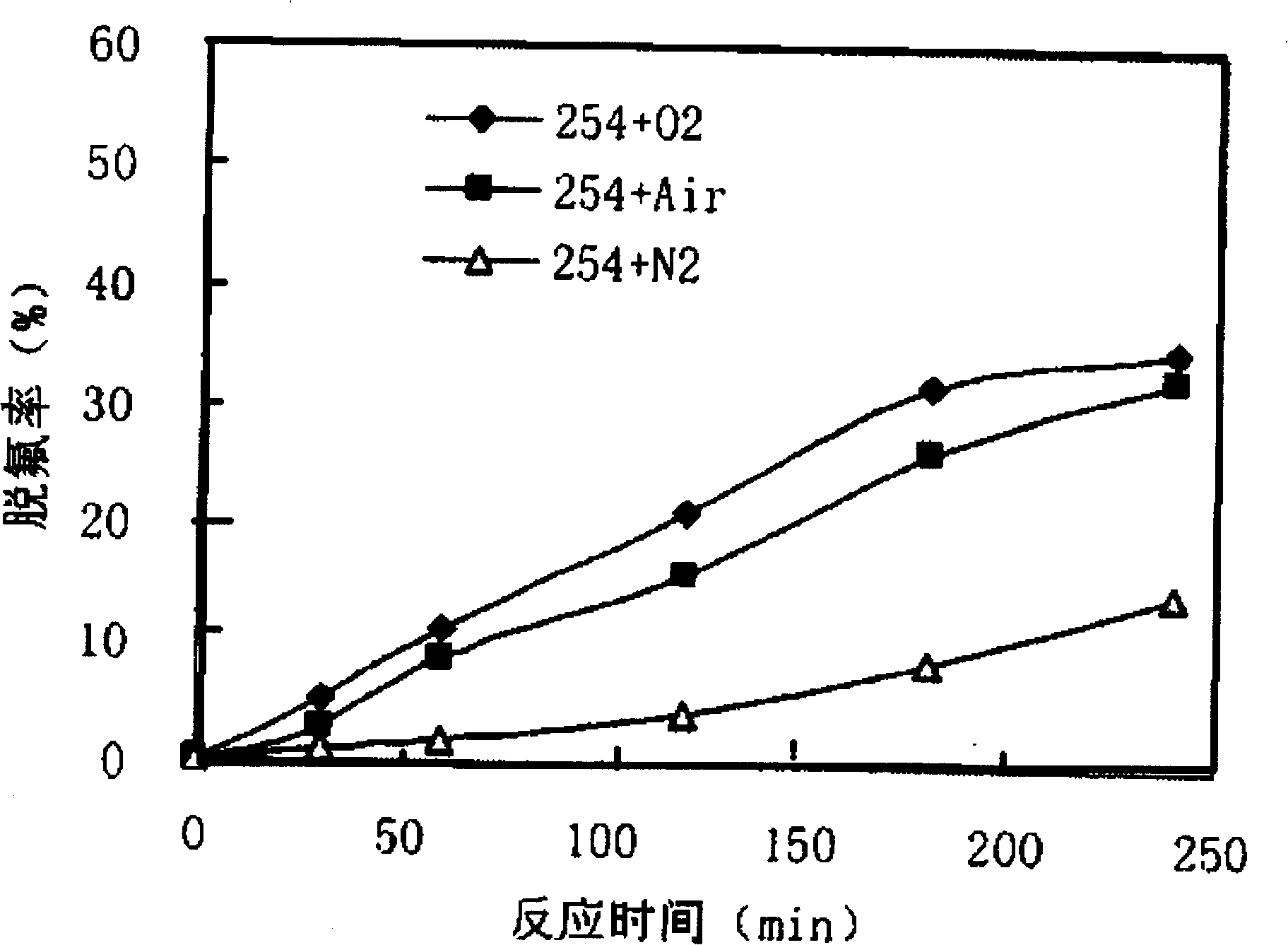
InactiveCN101199884ALow toxicityReduce concentrationChemical protectionSolubilityPhotochemical degradation
The invention discloses a method of dissolved ferric salt inducing photochemical degradation of total fluorine substitution compound, belonging to the technical field of photochemical degradation of fluorine-containing organic compound in environmental protection. Under the atmosphere of air, oxygen and nitrogen, the mixed solution of total fluorine substitution compound and dissolved ferric salt in the reactor produces the decomposition reaction under the light-source irradiation for 100 to 300 minutes, so that the fluorine atom turns into the fluorine ion. The method which is easy to apply can react under the normal temperature and normal pressure, without complex equipment and strict reaction condition. The toxicity of the decomposition product is reduced, so that other subsequent methods can be easily adopted for further disposal. In addition, in the reaction, the concentration of the dissolvable ferric salt is reduced and the total fluorine is degraded into the harmless substance to avoid the pollution of the total fluorine compound to the environment.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Organic matter polluted wastewater photochemical degradation reactor single-tank throughput expansion method
InactiveCN103086463AExpansion design volumeIncrease throughputWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater/sewage treatment by oxidationMicrowavePhotochemical degradation
The invention relates to an organic matter polluted wastewater photochemical degradation reactor single-tank throughput expansion method, and belongs to the technical field of wastewater treatment. A scheme adopted in the invention aims to completely solve the problems comprising unsatisfactory microwave energy utilization condition, small reactor single-tank throughput, insufficient internal liquid circulation intensity and the like in the prior art. The scheme mainly comprises the following steps: wrapping an electrodeless ultraviolet lamp with a metal cage in a quartz tube, communicating a waveguide tube with the inner cavity of the metal cage, and constructing a microwave weak-irradiation air space or a microwave zero-irradiation air space between the outer wall of the metal cage and the inner wall of a reactor; placing the quartz tube in the upper portion area in the wider cavity tube of a hanging vertical upside-down horn-shaped member positioned in the reactor in a hidden manner; and extending and expanding the dimension of the microwave weak-irradiation air space or the microwave zero-irradiation air space in the reactor in a three-dimensional direction. The method provided by the invention comprehensively solves the series of problems.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
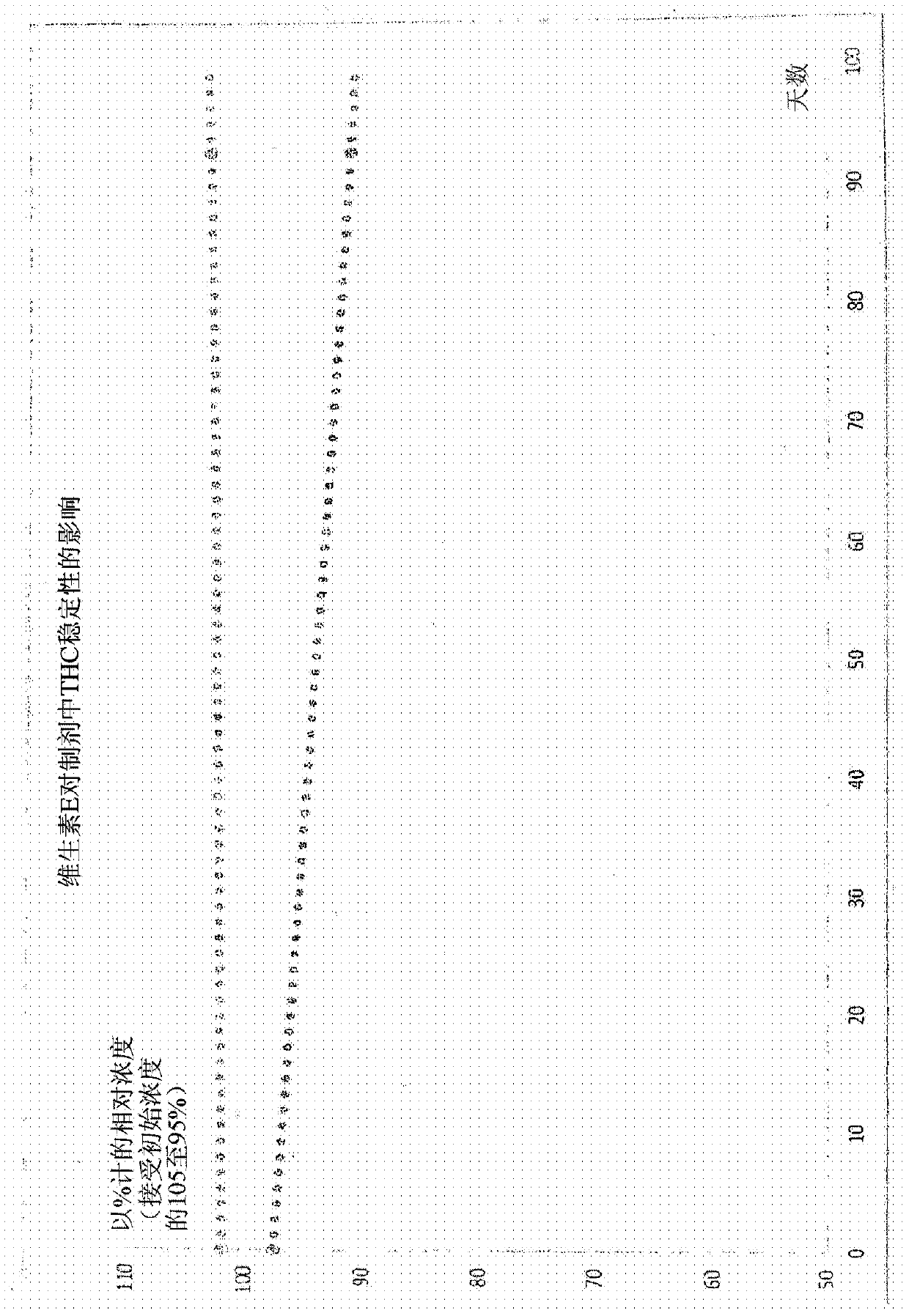
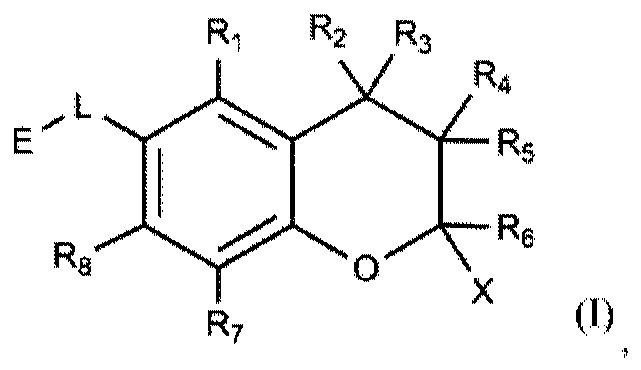
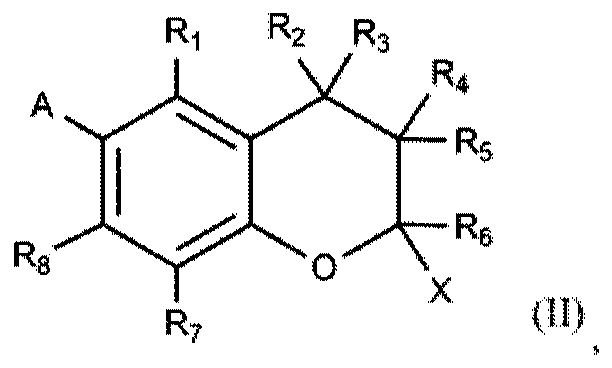
Stable cannabinoid compositions
InactiveCN111246844AHydroxy compound active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPhotochemical degradationSynthetic cannabinoids
A composition comprising a cannabinoid, in particular a phytocannabinoid or a synthetic cannabinoid, where the cannabinoid is stabilised against oxidation and / or photochemical degradation, characterized in that the composition comprises a micellar solution of composite micelles in an aqueous solution and where the composite micelles encapsulate the cannabinoid.
Owner:SOLMIC BIOTECH GMBH
A method for photochemical degradation of phosphorus-containing wastewater
ActiveCN106186175BAvoid generatingEliminate the effects ofWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsHigh concentrationPhotochemical degradation
The invention discloses a method for photochemical degradation of phosphorous-containing wastewater, and aims to degrade organic matters and precipitate and remove phosphorus in phosphorus-containing wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: using peroxide as an oxidant, carbohydrate as an initiator, ferrous ion as a catalyst, ferrous ion complexing organic matter hydroxyacetic acid as a stabilizer, and soluble aluminum salt or calcium salt as a phosphate precipitant; and performing UV photo-oxidative degradation under a weak acidity condition of pH 2-6. In the method provided by the invention, the peroxide is decomposed through a UV-induced Fenton reaction to generate free radicals and the catalyst in a complexing state is used at the same time to eliminate the poisoning of phosphate radicals to the catalyst, thereby realizing the rapid degradation of high-concentration organic wastewater containing a large amount of phosphate radicals. The method has the advantages of simple steps, no need of heating or pressing, and easy control, uses the cheap stabilizer, realizes the degradation process under mild conditions, and is a phosphorus-containing wastewater degradation method featured with huge potential, environmental protection, high efficiency and economy.
Owner:NINGBO SUNNY NOVEL MATERIAL TECH
Photochemical paper pulp bleaching method and device
InactiveCN100338303CHigh degree of delignificationEasy to operatePulp bleachingPlant fibrePhotochemical degradation
Based on photochemical principle, plant fiber pulp after being pre-treated is irradiated with light, and in alkali environment and under the aid of introduced oxygen or air and photobleaching catalyst, the residual lignin in pulp is degraded via photochemical reaction into leached out fragments and thus eliminated, resulting in high whiteness pulp. During the bleaching process, different shielding agent may be added to shield partial light selectively to protect the physical strength of pulp. The bleaching process is environment friendly, and has less corrosion to the apparatus and simple operation.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
In-situ bioremediation preparation and remediation method of chlorothalonil-contaminated soil
ActiveCN106591166BAddressing food safetyImprove MicroecologyFungiBacteriaPhotochemical degradationIn situ bioremediation
Relating to the soil remediation field, the invention discloses a preparation for in-situ remediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil. The preparation contains fungi and / or bacteria with chlorothalonil degradation ability. The fungi can be at least one of Aspergillus niger, rhizomucor variabilis and Cunninghamella bertholletiae, and the bacteria can be at least one of Burkholderia zhejiangensis, pseudomonas aeruginosa and Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. According to the invention, the provided preparation is employed for in-situ bioremediation of chlorothalonil contaminated soil, not only overcomes the problems that photochemical degradation is easily limited by illumination conditions and can easily cause secondary chemical reagent pollution to arable land, at the same time makes full use of fungi and / or bacteria for catabolism of chlorothalonil residual in soil, thus solving the problem that high residual chlorothalonil in soil severely endangers food safety. At the same time, the micro-ecology of soil is improved, so that soil can recover farming ability more rapidly. Also, the method is low in cost, thus having broad application prospects.
Owner:粮华生物科技(北京)有限公司
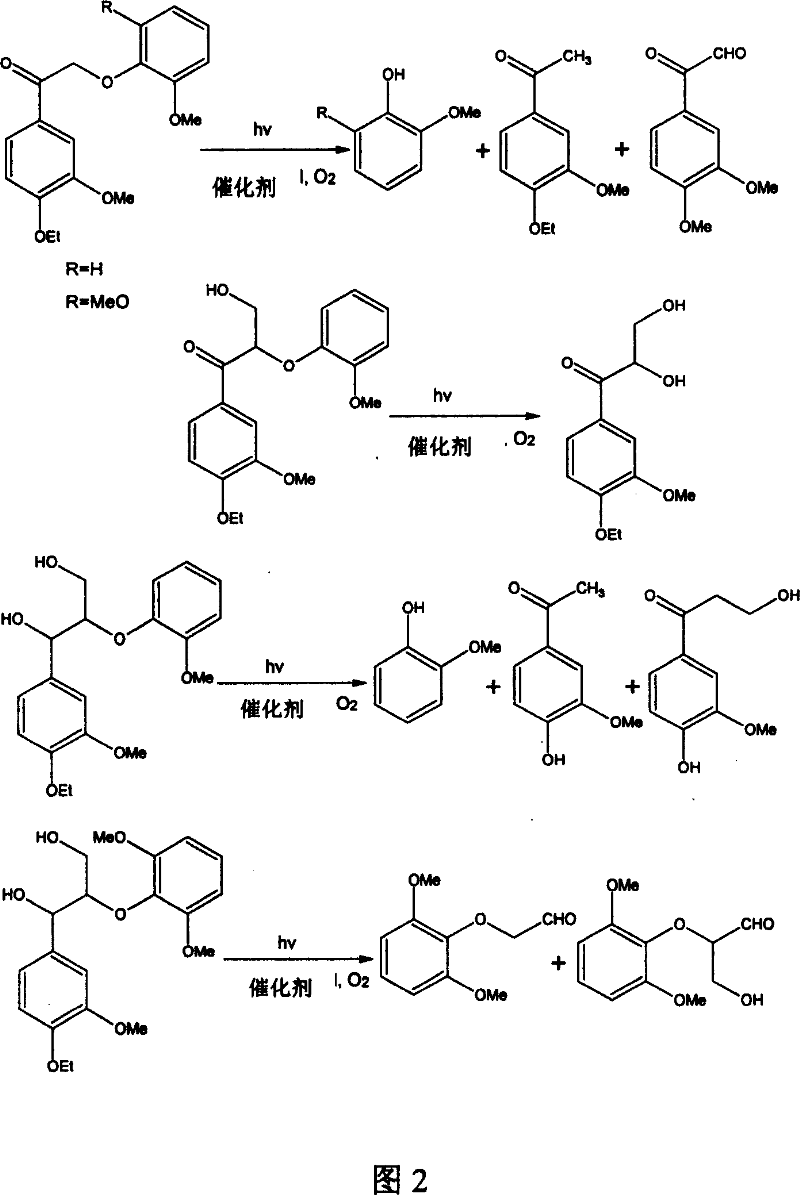
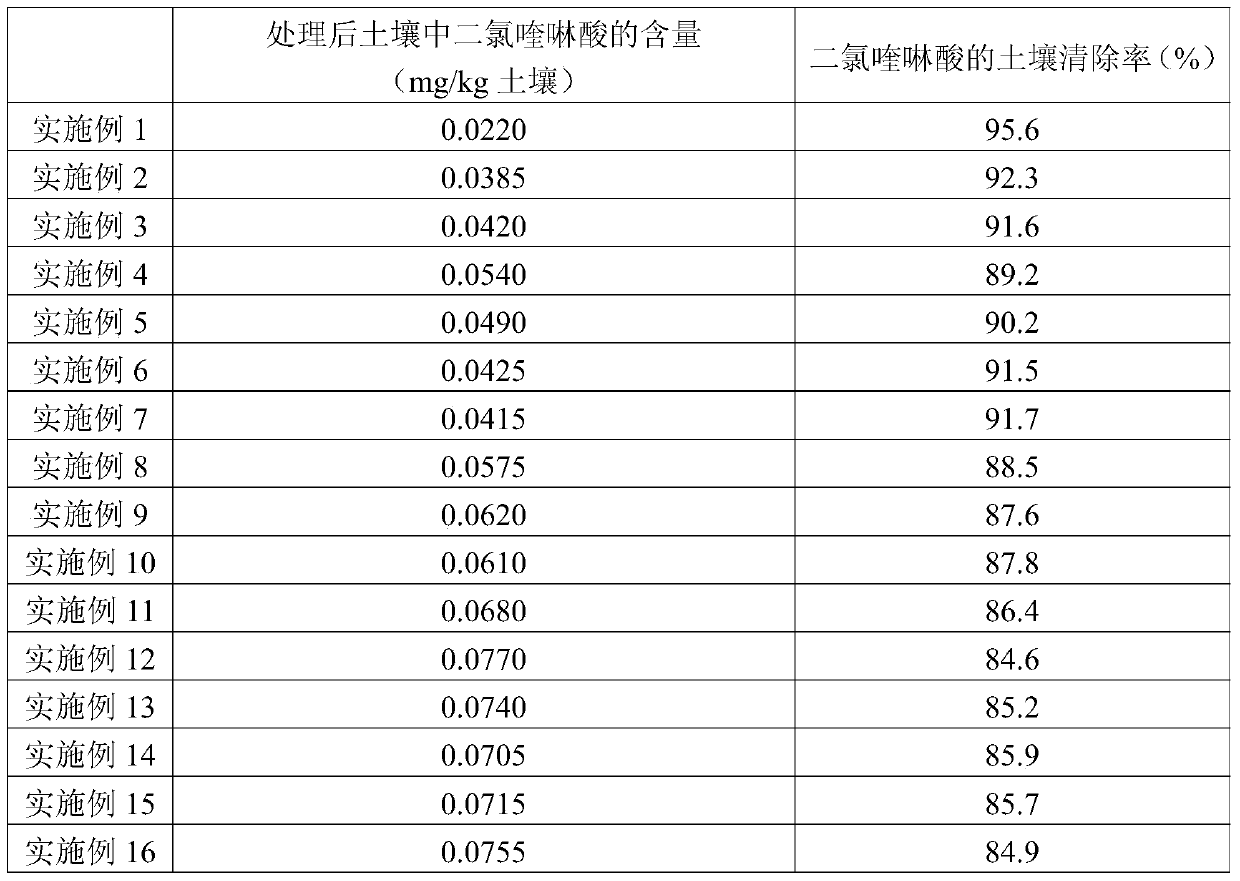
In-situ bioremediation preparation and remediation method of quinclorac-contaminated soil
ActiveCN106591165BAddressing food safetyImprove MicroecologyFungiBacteriaDecompositionPhotochemical degradation
The present invention relates to the field of soil remediation, and discloses an in-situ remediation preparation for quinclorac contaminated soil, the in-situ remediation preparation for quinclorac contaminated soil comprises fungi and / or bacteria with quinclorac degrading capability; the fungi are at least one of Aspergillus niger, rhizomucor variabilis and cunninghamella bertholletiae, and the bacteria are at least one of Pseudomonas denitrificans, Burkholderia caribensis and Serratia marcescens. The in-situ remediation preparation is used for in-situ bioremediation of the quinclorac contaminated soil, the problems that photochemical degradation method is vulnerable to the restriction of light conditions and secondary chemical reagent pollution of farmlands is easy to cause are overcome, the fungi and / or the bacteria are fully used for decomposition metabolism of residual quinclorac in the soil, the problems that the highly residual quinclorac in the soil seriously endanger food safety can be overcome, the micro-ecology of the soil is improved, the farming ability of the soil is faster to recover, and the method is low cost, and has broad application prospects.
Owner:粮华生物科技(北京)有限公司
Photochemical degradable sol composition and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102039194BImprove efficiencyLow costOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSesquioxidePhotochemical degradation
The invention provides a photochemical degradable sol composition and a preparation method thereof. The composition comprises the following components in part by weight: 50 parts of water, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of photographic gelatin, 0.5 to 1.5 parts of span 80, 40 to 50 parts of nano anatase titanium white powder, 4 to 8 parts of nano rutile titanium white powder, 5 to 15 parts of mixed light absorbing cyanine dye, 0.5 to 1 part of bismuth nitrate, 0.5 to 1 part of cerous chloride and 1 to 3 parts of nano iron sesquioxide. The degradable sol composition integrates photochemistry, catalysis technology and nano chemistry; sunlight serving as inexhaustible natural resource can be fully utilized and combined with non selectively of modern advanced photochemistry, catalysis technology and nano chemistry on organic waste degradation and oxidation effects; and the method has low cost, is simple and convenient to operate, and is suitable for developing medium and small enterprises.
Owner:SHANGHAI DONGSHENG NEW MATERIALS
Co-used iron-carbon micro-electrolysis and photo degradation two-section perfluoro octanoic acid degradation method
InactiveCN104773884AEfficient degradationEffective defluorinationWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentOctanoic AcidsElectrolysis
The invention discloses a co-used iron-carbon micro-electrolysis and photo degradation two-section perfluoro octanoic acid degradation method. The method comprises the following steps: (a) active carbon pretreatment: soaking active carbon in a perfluoro octanoic acid solution to be processed for 24 hours, washing the active carbon by ultrapure water, and drying the active carbon for later use; (b) adding the perfluoro octanoic acid water solution to be processed in to an iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor, adding iron powder and processed active carbon simultaneously, controlling the primary pH value of the reactions at a range of 2 to 4, carrying out reactions at a room temperature under stirring for one hour, and discharging the effluent; (c) subjecting the effluent to suction filtering, then introducing the effluent into a photo degradation reactor, adding H2O2 as the oxidant at the same time, controlling the pH value in a range of 2 to 4, installing an ultraviolet lamp; carrying out reactions at a constant temperature under stirring for 3 to 5 hours, and finally discharging the effluent. The provided method is simple, the two-section cooperative system fully utilizes the functions of the electrolysis and photo degradation, and the fluorine is effectively removed from PFOA.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com