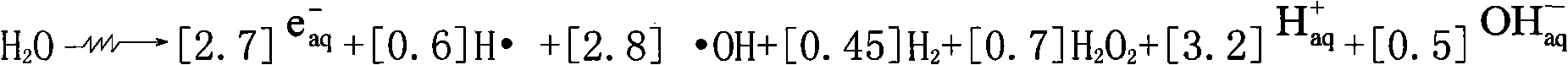Patents
Literature
58 results about "Residual lignin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The residual lignin extracted by acid hydrolysis has less etherified units and more free phenolic functions than that of the enzymatic hydrolysis. It contains some unsaturated structures but no carbohydrate contaminants.
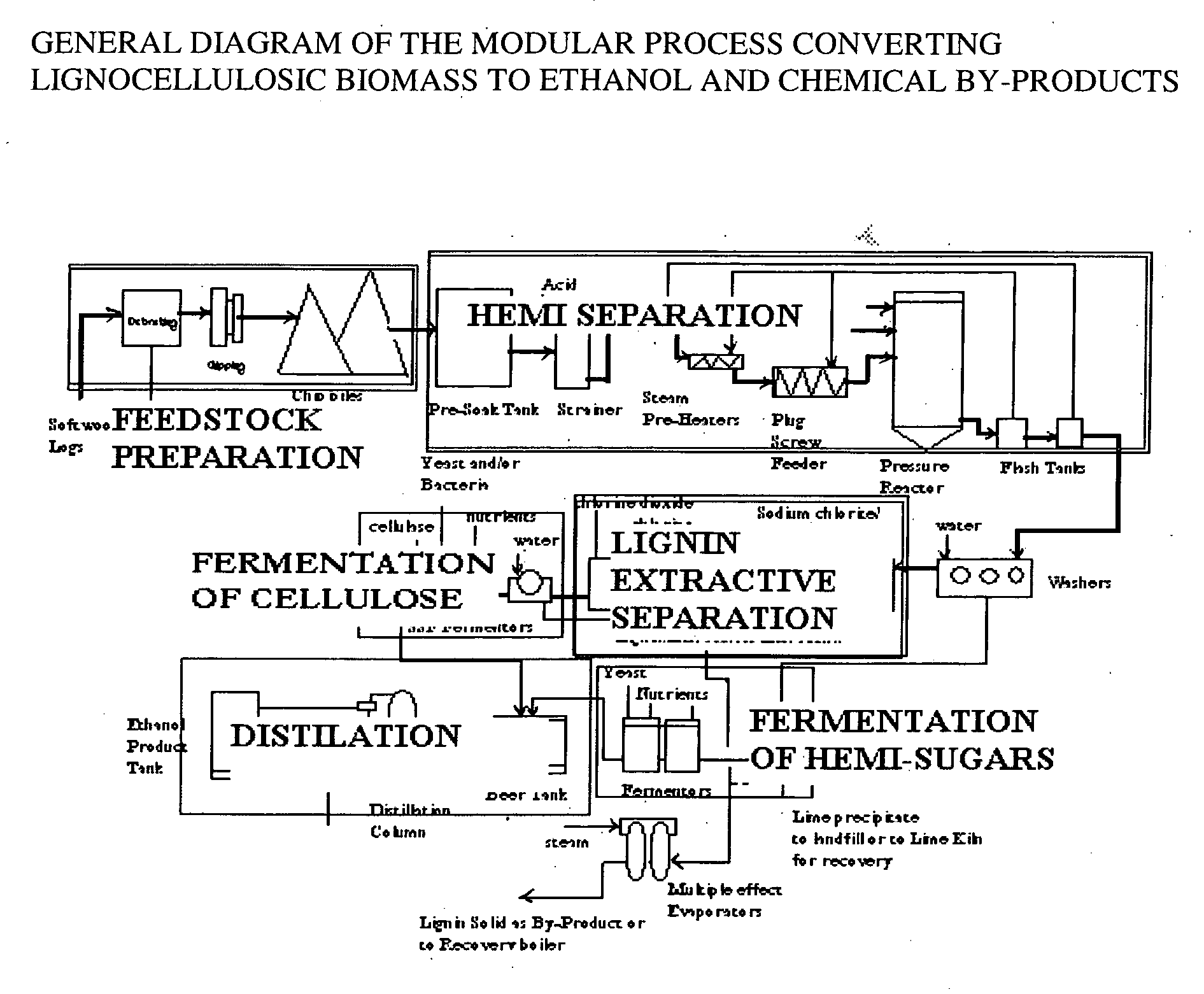
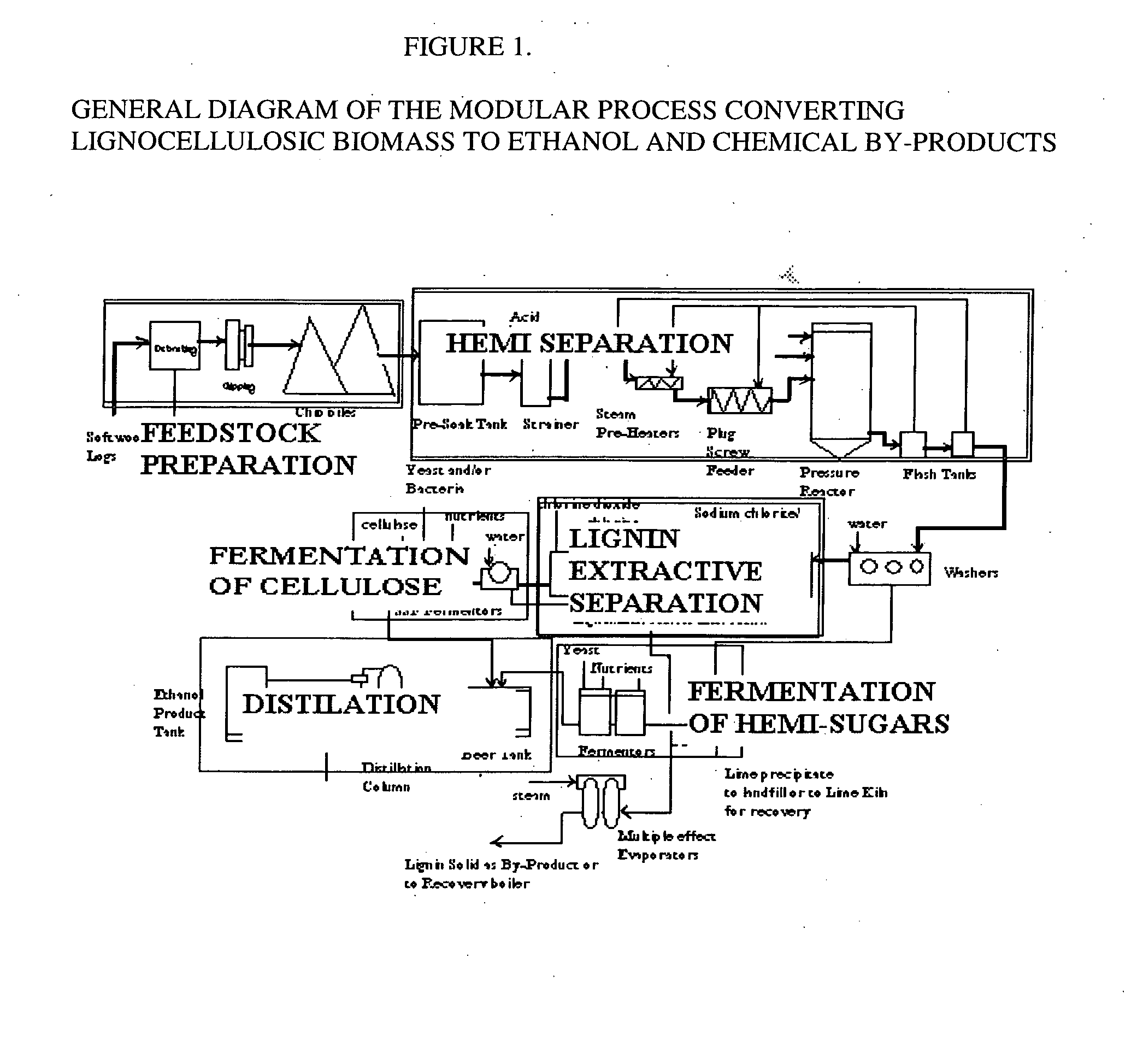
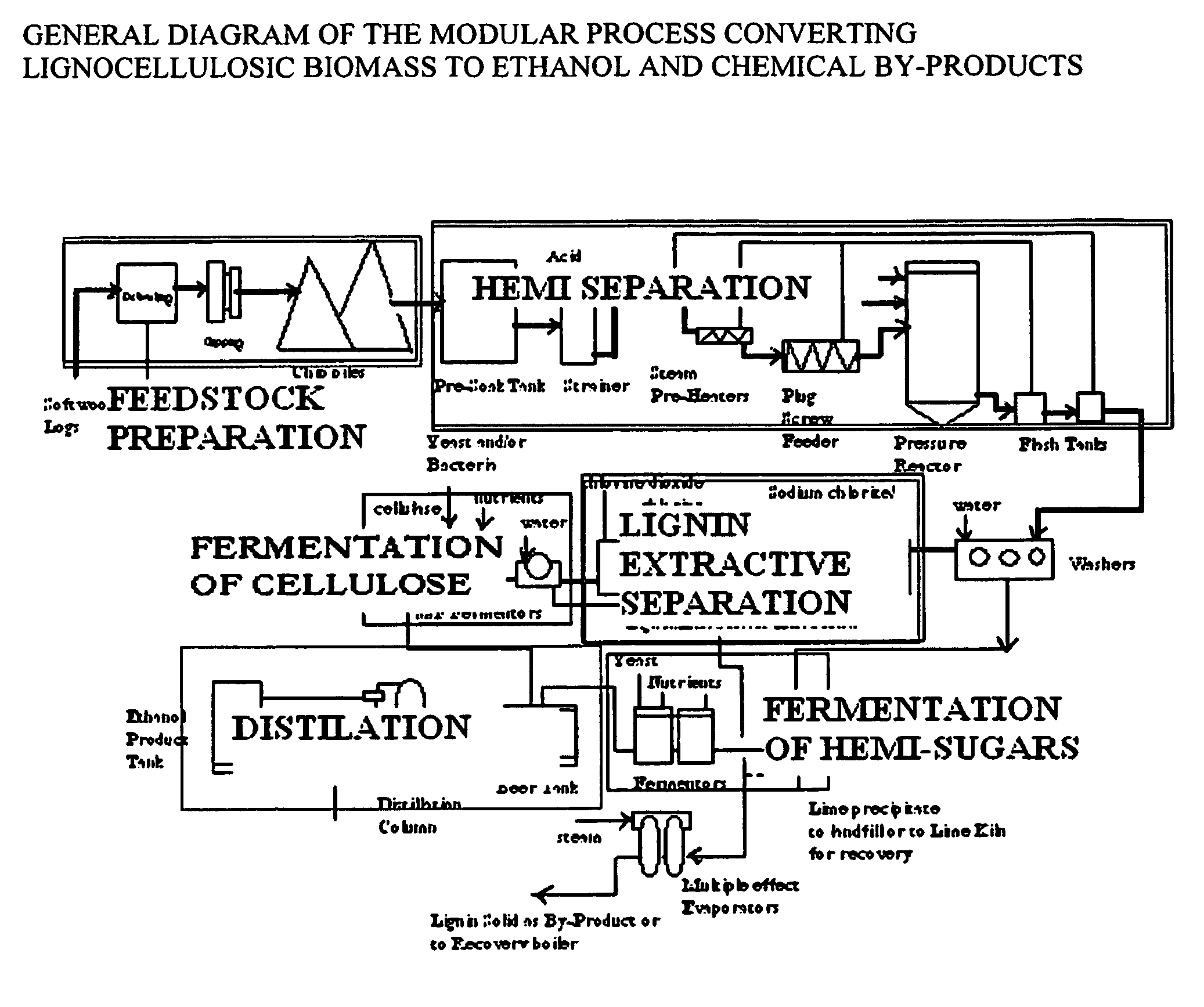
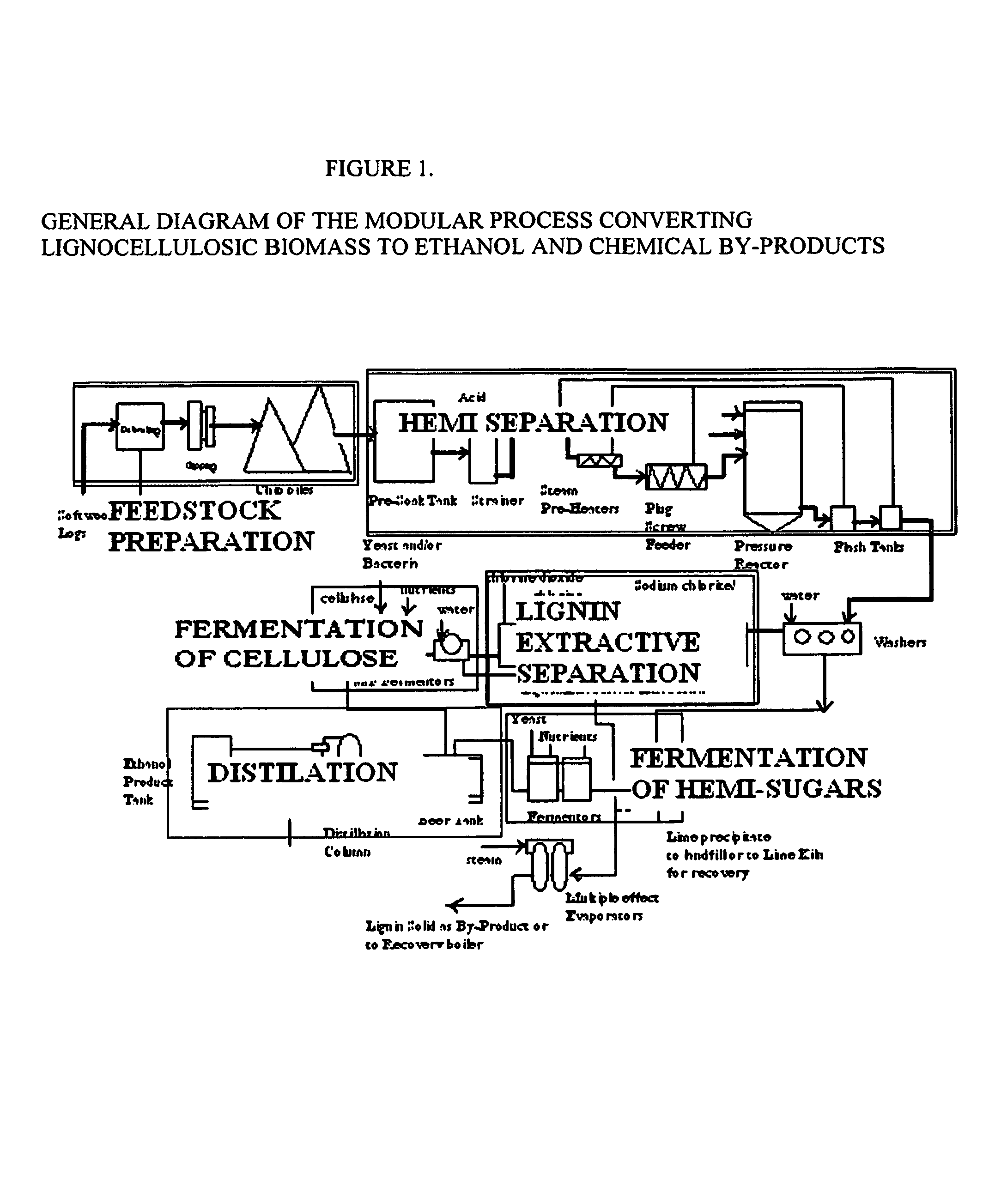
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS20080057555A1Robust and cost-effectiveImprove responseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentButanediol
A continuous and modular process converts lignocellulosic materials for the production of ethanol principally and / or chemicals such as methanol, butanediol, propanediol, hydrocarbon fuel, etc. Renewable lignocellulosic biomass such as but not all inclusive hardwoods (gum, beech, oak, sweet gum, poplar, eucalyptus, etc.), soft woods (pines, firs, spruce, etc.), corn stovers, straws, grasses, recycled papers, waste products from pulp and paper mills, etc can be used as feedstock. The process is designed to be modular and the feed entry point can be selected to adapt to different biomass feedstock. Lignocellulosic biomass such as hardwood and softwood are subjected to chemical / pressure treatment stages using potent and selective chemicals such as sodium chlorite / acetic acid (anhydrous) and chlorine / chlorine dioxide to separate the main components—lignin, cellulose (glucose) and hemicelluloses (xylose, arabinose, galactose)—into three process streams. The separated carbohydrates are further subjected to washing, cleaning, neutralization, and / or mild hydrolysis and subsequently fermented to produce ethanol. Residual lignin and extractives remained with the cellulose are removed by chemical treatment steps to enhance the fermentations of cellulose. Pre-hydrolysate after neutralization to neutralize and remove toxic components such as acetic acid, furfural, phenolics, etc. containing (xylose, arabinose, galactose) and hexoses (glucose) can be either separately or together with the purified cellulosic fraction fermented to produce ethanol. Approximately 100 gallons of ethanol, suitable to be used as a fuel, can be produced from one dried ton of wood. Significant amount of lignin are separated as a by-product and can be converted to hydrocarbon fuel, surfactant, drilling aid, or can be incinerated for generation of power and steam.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
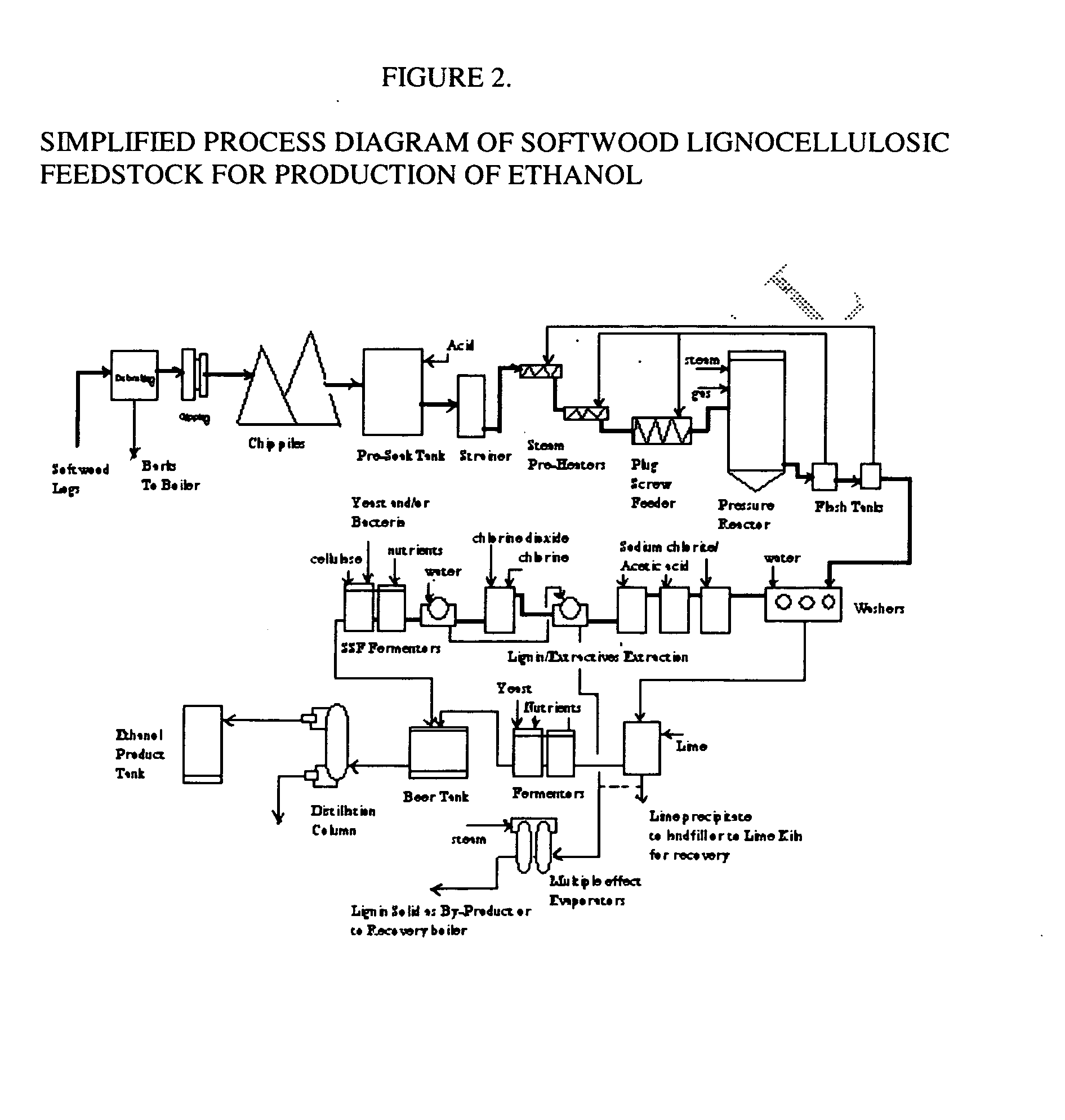
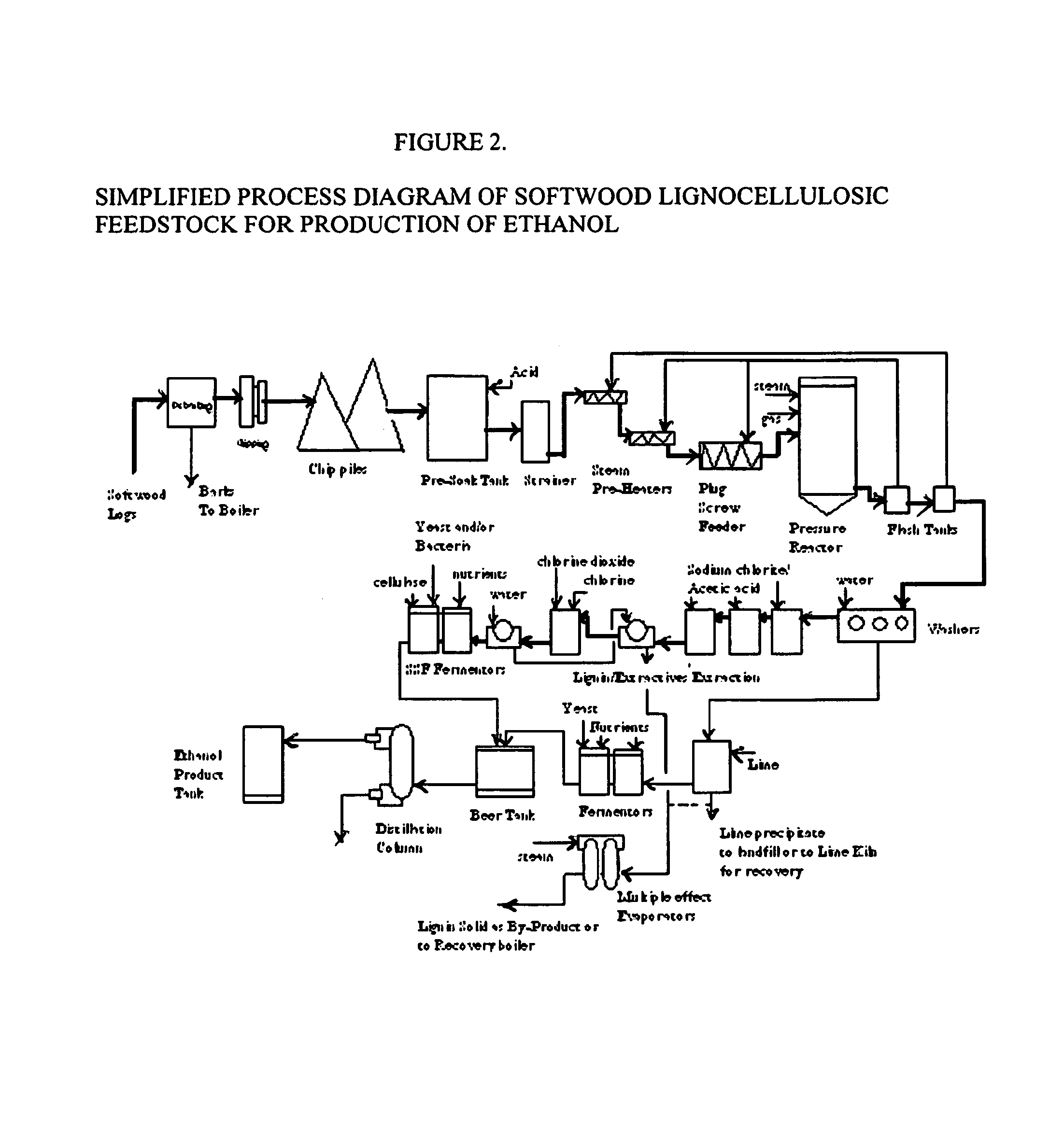
Integrated process for separation of lignocellulosic components to fermentable sugars for production of ethanol and chemicals
InactiveUS7666637B2Robust and cost-effectiveImproving biological reactivity of celluloseChemical industryBiofuelsChemical treatmentHydrolysate
The invented process separates main components in lignocellulosic biomass, specifically hardwoods, softwoods into lignin and fractions of high purity sugars which are used for ethanol production. The invented process comprises of treatment stages at high temperature and high pressure with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid. Residual lignin and extractives in the cellulosic solid fraction are selectively removed by chemical treatments of sodium chlorite, anhydrous acetic acid, chlorine and chlorine dioxide to enhance the purity and biological conversion of cellulose to ethanol. The pre-hydrolysate generated from the acid treatment stage, containing xylose, arabinose, galactose, glucose and the purified cellulosic fraction are enzymatically hydrolyzed and fermented to produce ethanol. Significant amount of lignin from the process is recovered as a by-product.
Owner:NGUYEN XUAN NGHINH
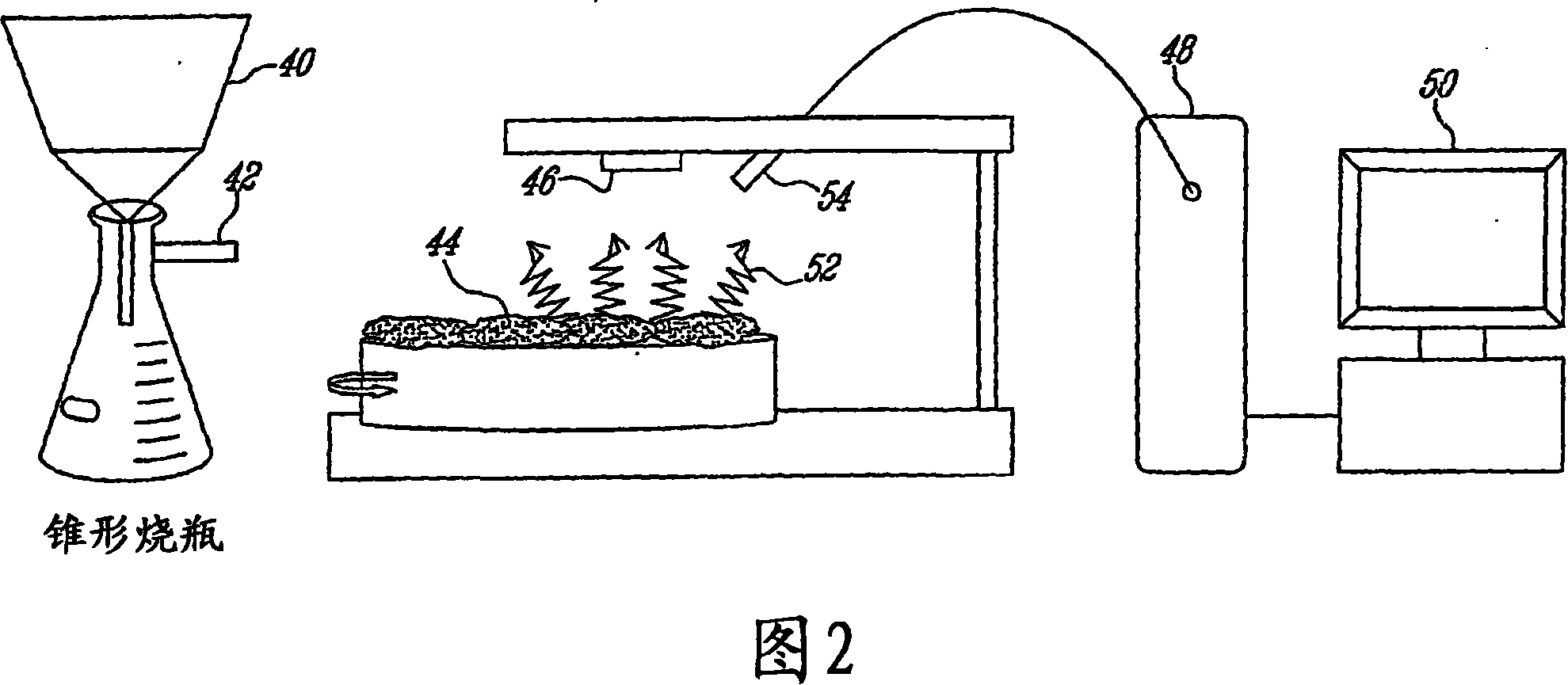
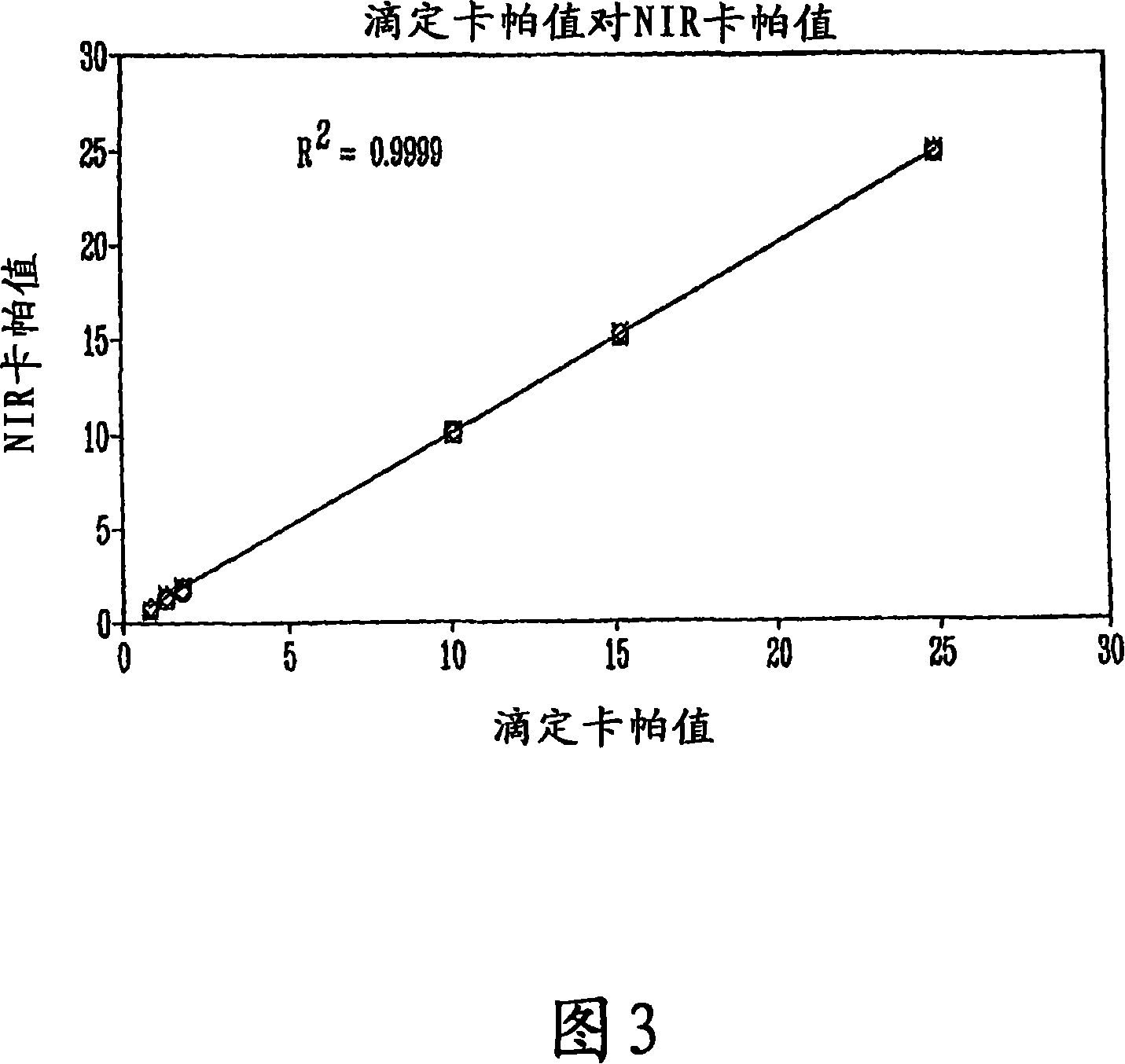
Method for determining chemical pulp Kappa number with visible-near infrared spectrometry
ActiveUS20060196622A1Overcomes shortcomingCellulosic pulp after-treatmentRadiation pyrometryContinuous measurementPresent method
A method for the determination of cellulosic-fibre properties, such as, but not limited to, residual lignin content of chemical pulp, with the aid of a spectroscopic technique obtained over a range covering the visible and the near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, comprising the steps of obtaining a sample from the process line, minimally removing some excess water, exposing the fibres in the sample to a large beam light source, optionally moving the sample at a constant speed, and acquiring the spectral data over a pre-determined length of time, and correlating the spectrum to a previously determined calibration so as to determine the Kappa number. Alternatively, as an arrangement for process control, along with other varying configurations, the instant invention includes the mounting of the excitation light source and fibre-optic probe along the various locations of the kraft cooking and bleaching process, such as 1) at the drum brownstock washers and 2) throughout the bleach plant deckers, located just before the doctored blade, the probe being connected to a fast scanning spectrometer, via fibre optic cables, with a computer sequencing spectral acquisition and correlating the spectrum against a predetermined calibration, and logging the results. The process configuration, with the use of the instant invention, overcomes all limitations of prior art, including sampling hardware and sample preparation, and provides true online Kappa number determinations of the order of seconds, as compared to current state of the art Kappa analyzers which require 10 to 15 minutes per analysis. The present method is capable of measuring residual lignin content of chemical pulps with varying consistency, accounts for species effects to provide species insensitivity and can provide analysis in less than 10 seconds. The method can provide true online continuous measurement of Kappa number for feedforward and feedback control of the bleaching, paper machine and kraft cooking processes.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass
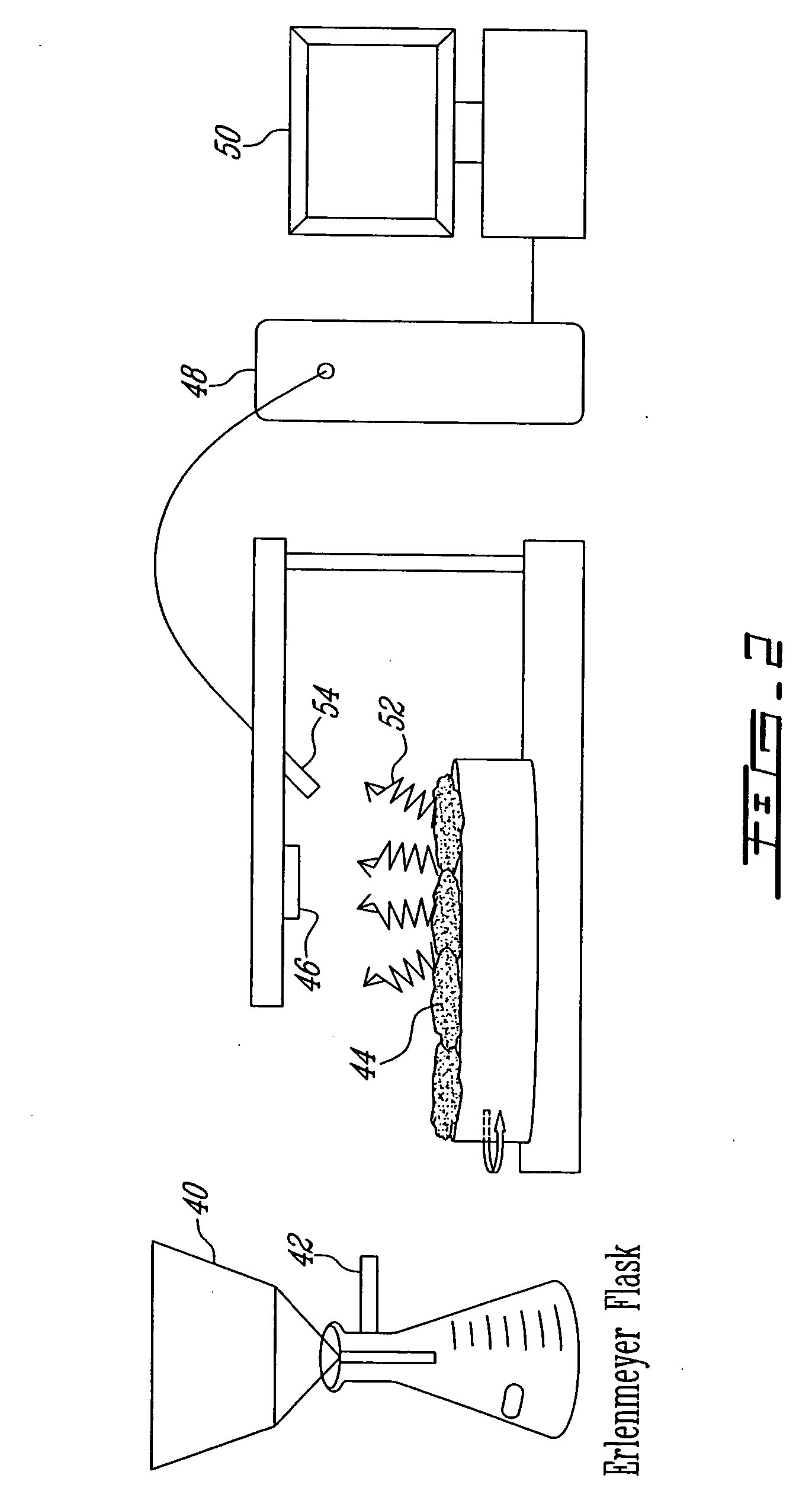
ActiveUS20130252302A1Efficient and low-cost processingPrevent degradationBiofuelsSucrose extraction by chemical meansFiltrationIon exchange
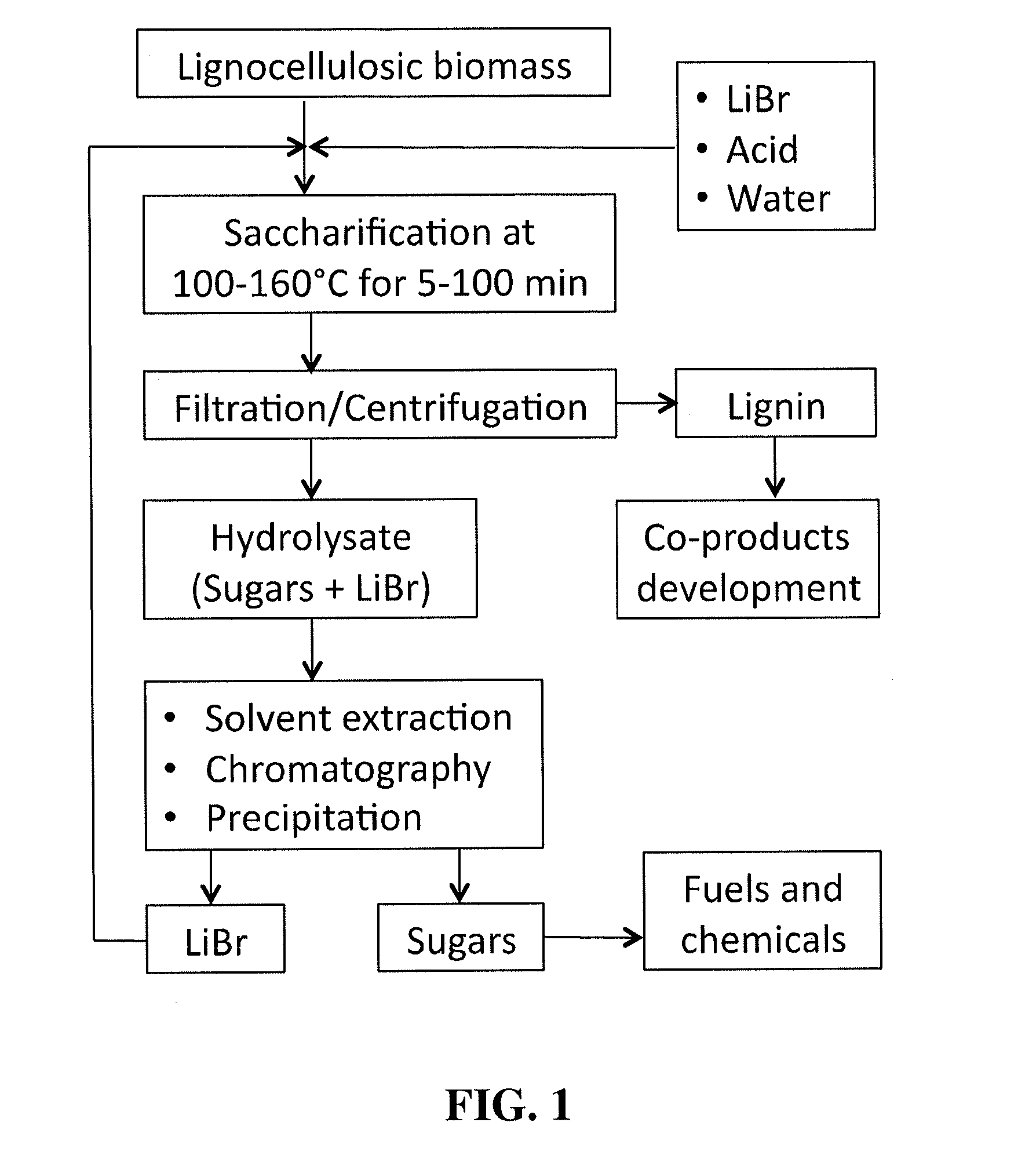
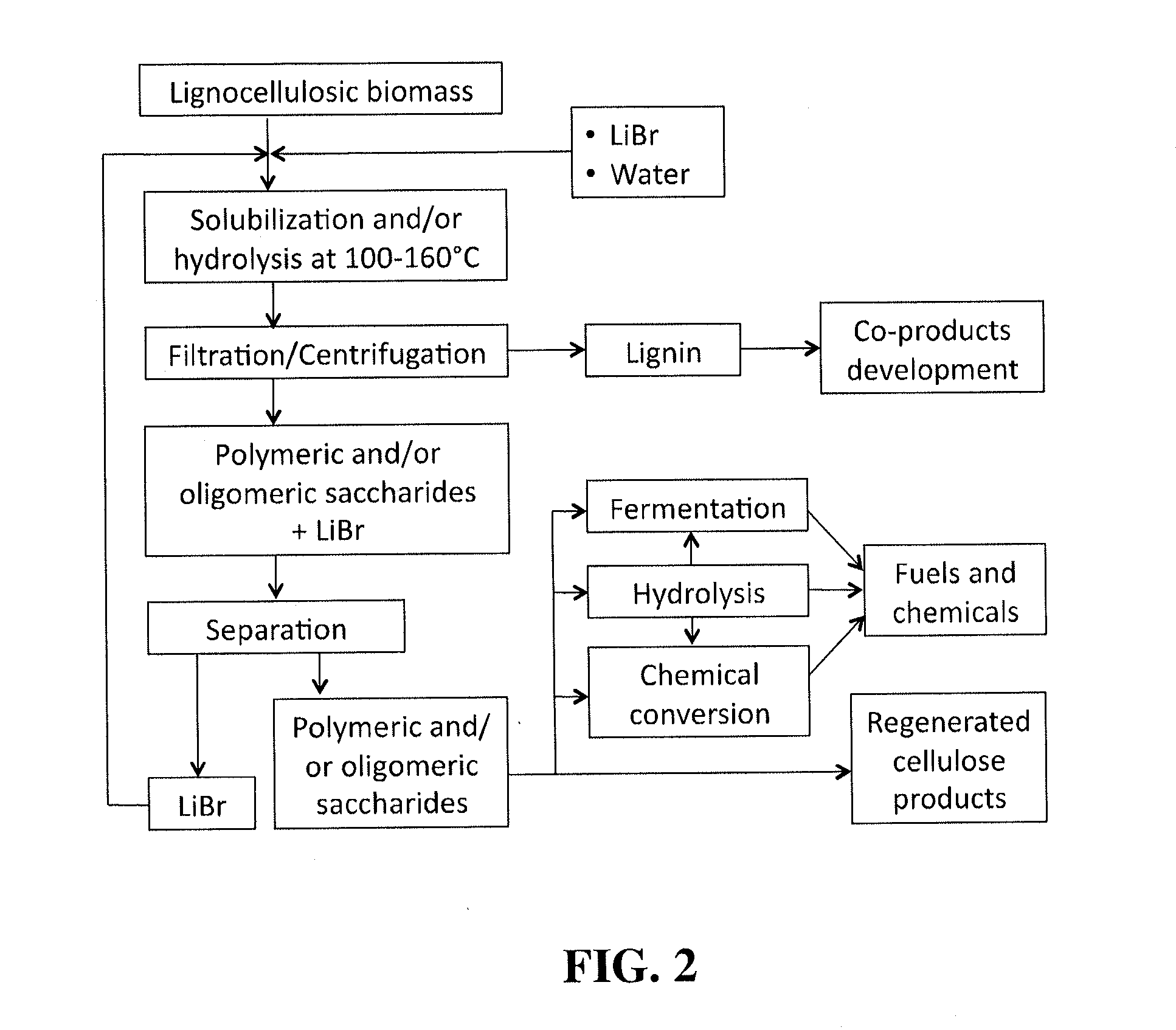
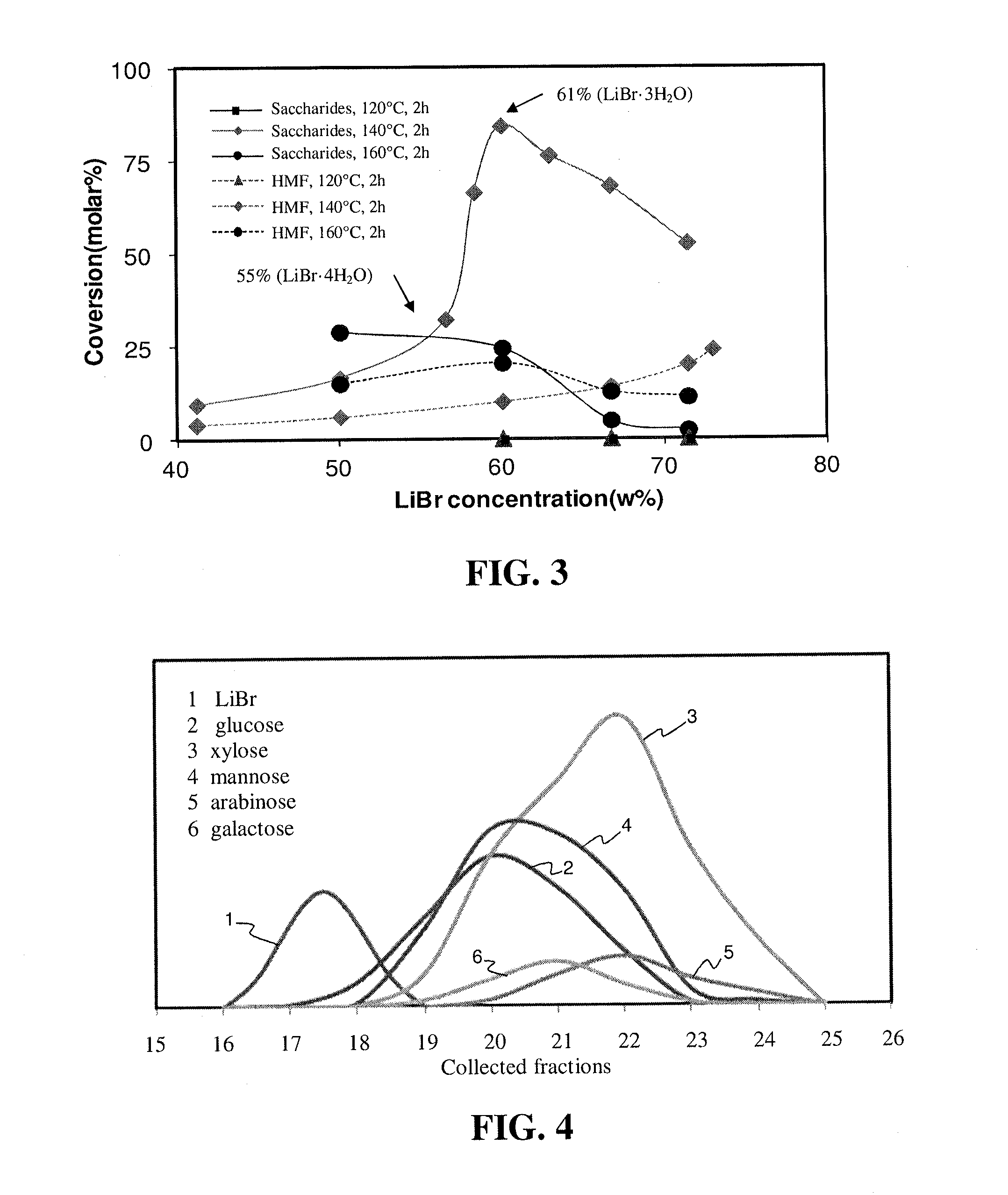
An efficient process for saccharifying lignocellulosic biomass in concentrated aqueous solutions of certain bromine salts, particularly LiBr and CaBr2. Real lignocellulose biomass, such as corn stover, switchgrass, waste paper, hardwood, and softwood, can be hydrolyzed without the need for any prior pretreatment. Complete saccharification of both cellulose and hemicellulose is achieved within 5-200 min at temperatures ranging from about 100 to about 160° C. Residual lignin is readily separated from product sugars by filtration or centrifugation and can be used to prepare beneficial coproducts. The bromine salt can be recovered and separated from product sugars (predominantly monosaccharides) by any art-known method and in particular solvent extraction, anti-solvent precipitation, ion-exclusion chromatography and / or ion-exchange chromatography can be employed. Hydrolysis product containing sugars can be employed for in fermentation for the production of value added products or useful fuels.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for preparing natural color bamboo pulp fiber household paper
InactiveCN103882758AIncrease brightnessCompact structureNatural cellulose pulp/paperPaper-making machinesCrude fibreFiber
The invention relates to a method for preparing natural color bamboo pulp fiber household paper. The method includes the steps that firstly, digesting is conducted, natural clustered bamboo chips are placed in a specially-made digesting container, NaOH and Na2S are added to the container, and then steaming is conducted on the bamboo chips; secondly, large bulks of undigested bamboo chips, undigested bamboo joints, undigested crude fibers, gravels in raw materials and the like are removed through a screening and purifying device, black liquor in crude pulp is extracted through a pulp washing device, and then bamboo pulp fibers are primarily obtained; thirdly, the oxygen delignification working process is conducted on the obtained bamboo pulp fibers to further remove residual lignin in the bamboo pulp fibers, the bamboo pulp fibers are completely washed through the pulp washing device, and eventually natural color bamboo fibers are obtained; fourthly, the natural color bamboo fibers are pulped, pulp is placed in a pulp mixing pool, and coniferous long fibers are mixed into the pulp mixing pool; fifthly, additives are added to the pulp generated in the fourth step according to different products; sixthly, the pulp is fully stirred; seventhly, the mixed natural color bamboo pulp is online diluted and then processed through a purification system to further remove impurities; eventually, pulp is placed on a screen, paper is manufactured with the pulp, a layer of wet paper sheet is formed and processed, and then natural color bamboo pulp fiber household paper body paper is obtained. The method has the advantages that the prepared paper is greener, more environmentally friendly and healthier.
Owner:SHAONENG GRP SHAOGUAN NANXIONG ZHUJI PAPER IND CO LTD
Preparation method of magnetic biomimetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst
InactiveCN105149007ALow priceReduce manufacturing costOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGlucose productionPtru catalystSolid acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic biomimetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst. Enzymatically decomposed residual lignin serves as a starting raw material, a chlorine-containing compound serves as a dopant, and the magnetic biomimetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst is obtained after pretreatment, dipping, evaporation, carbonization and sulfonation are performed in sequence. The obtained catalyst further contains a chlorine group (-Cl) besides a carboxyl group (-COOH), phenolic hydroxyl (Ph-OH) and a sulfonic group (-SO3H) and can improve cellulose adsorption ability and enhance the cellulose hydrolysis capacity, the raw materials are low in price, the manufacturing cost is low, the high efficiency of inorganic acid hydrolysis, adsorption directionality of cellulose enzyme and recycling of magnetic solid acid are effectively coupled, and the preparation method has important practical significance on development of a green environmentally-friendly cellulose hydrolysis technology.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Method for digesting a biomass comprising lignin together with cellulose and/or hemicellulose
ActiveUS20110201096A1Low costLower the volumeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAlkaneEther
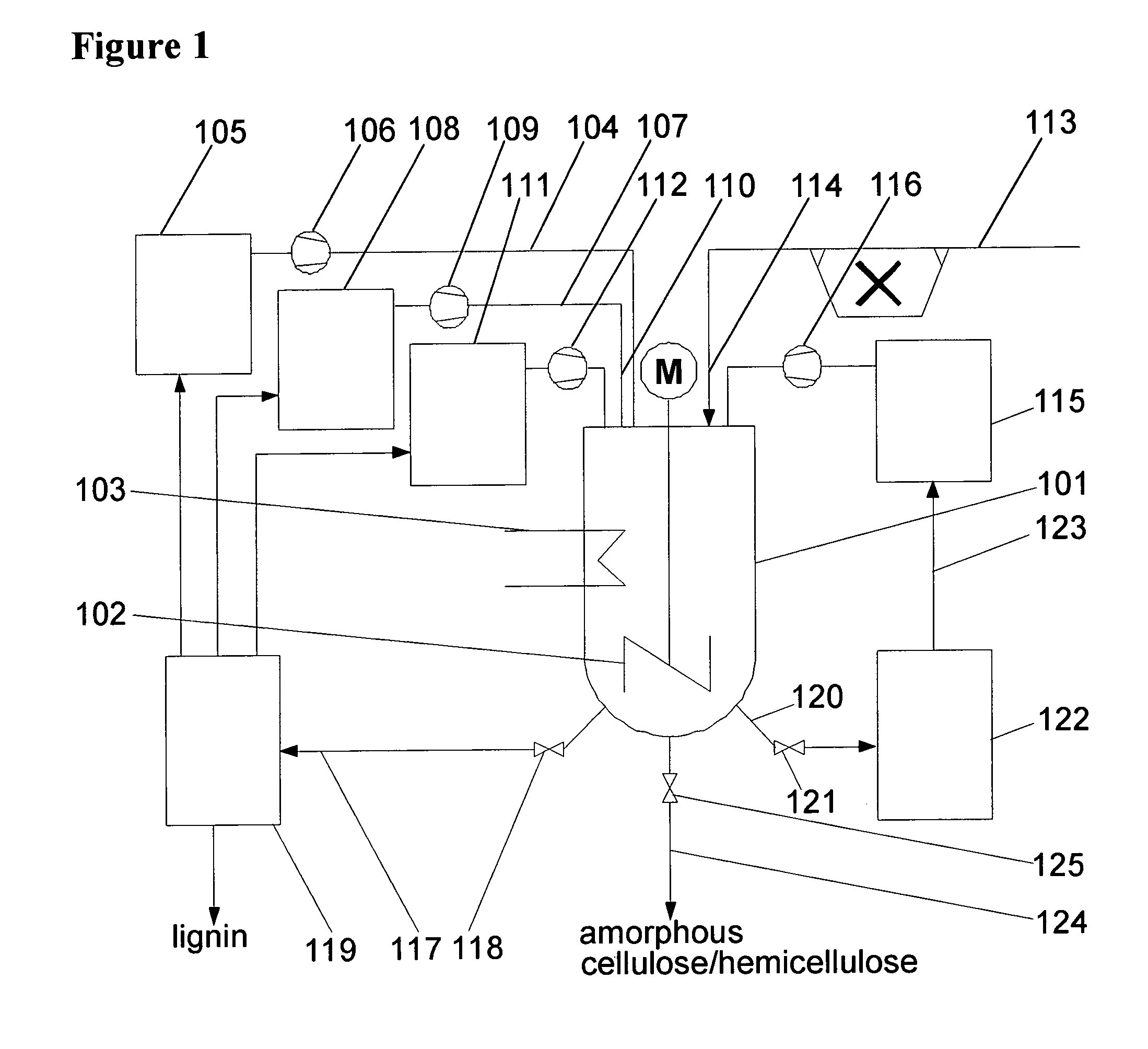
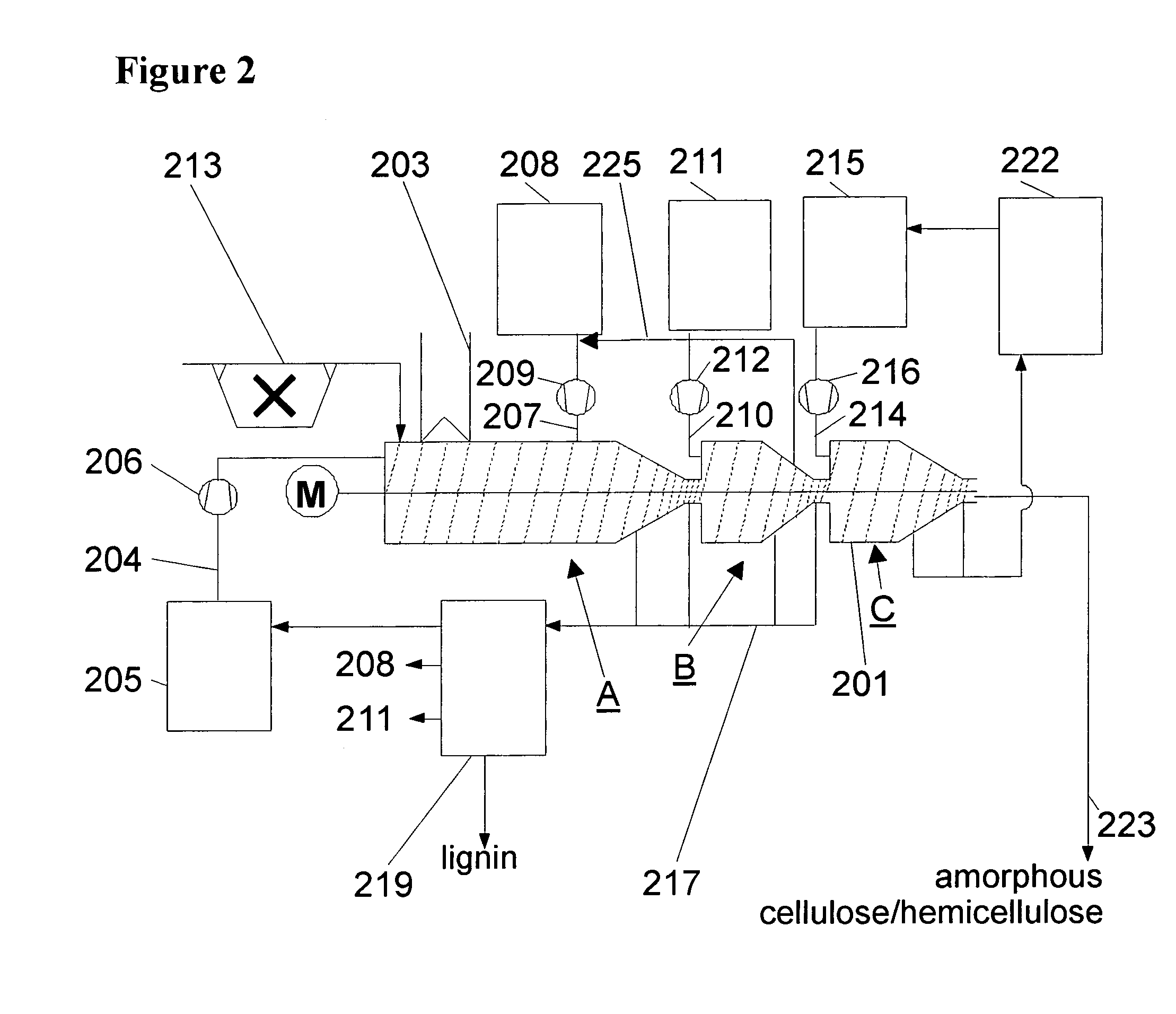
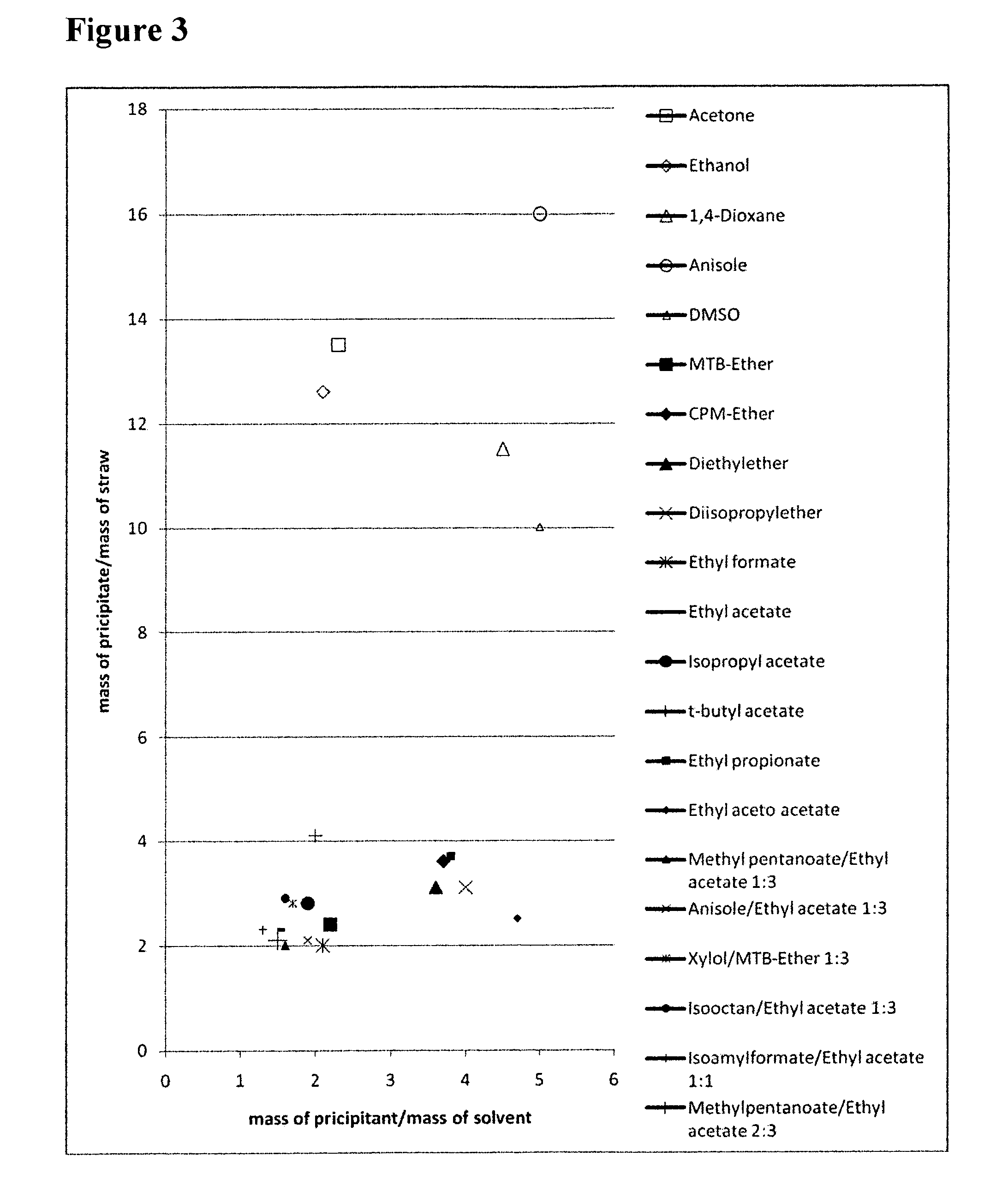
The invention relates to a method for digesting a biomass comprising, lignin, cellulose, and hemicellulose, comprising the steps of: (a) contacting the biomass with a first solvent for dissolving the cellulose and / or the hemicellulose, (b) contacting the dissolved cellulose and / or hemicellulose with a precipitant for forming a precipitate comprising cellulose and / or hemicellulose and residual lignin, wherein the precipitant is selected from the group consisting of alkanes, ethers, and esters; and (c) contacting the precipitate with a second solvent for removing residual lignin from the precipitate. The invention further relates to an apparatus for performing such a method.
Owner:MAXBIOGAS
Process for preparing wheatgrass cellulose with low pollution
The invention relates to a process for preparing wheatgrass cellulose with low pollution. The process comprises the following steps: putting wheatgrass into an ethanol water solution, dissolving mostof lignin and hemicellulose in the wheatgrass at high temperature, then dispersing the wheatgrass into water, adding MgSO4, introducing oxygen, filtering after further removing the lignin and part ofthe hemicellulose under a heating condition, washing a cellulose crude product, introducing ozone, removing the residual lignin and the residual hemicellulose to obtain a cellulose product; finally, filtering, washing the cellulose product, adding alkali, regulating the pH value to 8-12, adding H2O2, carrying out heat processing, filtering, washing to obtain a pure cellulose product after being refined. The invention adopts a low-pollution ethanol method to decompose the raw material of the wheatgrass, separates and refines the cellulose in the wheatgrass by a process adopting pollution-free chemical reagents, such as the oxygen, the ozone, the H2O2 and the like, to carry out subsequent processing, relieves the emergent shortage problem of common cellulose resources, such as wood, cotton and the like, and also makes full use of the agricultural waste of wheat straw resource.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determining chemical pulp kappa number with visible-near infrared spectrometry
A method for the determination of a cellulosic-fibre property, namely, residual lignin content or Kappa number of chemical pulp, with the aid of a spectroscopic technique obtained over a range covering the visible and the near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum, comprising exposing the wet fibres to a light source covering a range in the visible region of 350 nm to 750 nm and a range in the near-infrared of 1100 nm to 2400 nm, reflecting light from the wet fibres, establishing a spectrum, comparing the spectrum with a known spectrum of the property and evaluating the comparison; the method has particular utility in a pulp manufacture line; an apparatus is described for carrying out the method.
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
Method for extracting xylooligosaccharides, lignin and glucose from walnut shell
The invention discloses a method for extracting xylooligosaccharides, lignin and glucose from walnut shell; the method comprises the specific steps of crushing walnut shell to obtain walnut shell powder; adding the walnut shell powder into acidic electrolyzed water for cooking, and filtering to remove cooking liquor to obtain cooked walnut shell powder; charging the cooked walnut shell powder into a steam blasting device, introducing steam until a certain pressure is reached, holding the pressure for a period of time, and allowing instant blasting; adding xylanase to allow enzymatic hydrolysis, and separating residue and liquid after enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain enzymatic liquid and residue, wherein the enzymatic liquid incudes walnut shell hemicellulose limiting degradation products, xylooligosaccharides and xylose; adding alkaline electrolyzed water into the residue, cooking, dissolving to obtain residual lignin, and adding cellulase into the residue to perform enzymatic hydrolysis to obtain glucose. The method can produce products of high added value, xylooligosaccharides yield is > / =80%, lignin dissolution rate is > / =75%, and final glucose yield is > / =85%; solid waste is effectively treated and turned into wealth.
Owner:陕西兆信生物科技有限公司
Bamboo alpha-pulp for viscose and production method thereof
InactiveCN101736427AUniform oxidationGuaranteed responseArtificial filaments from viscoseMultistage pulping processSulfateHemicellulose
The invention discloses a bamboo alpha-pulp for viscose and a production method thereof. Main quality indexes of a bamboo pulp finished product are that: the degree of polymerization is 500 to 600 DP, alpha cellulose is more than or equal to 92 percent, ash is less than or equal to 0.20 percent, iron is less than or equal to 30 ppm, and the reaction performance is less than or equal to 200s. The production method comprises the following steps: preparing materials, stewing, bleaching, acidating and pulping. The stewing method adopts two-time different processes. The primary stewing adopts a sulfate method and the secondary stewing adopts a pure caustic soda method. The primary stewing can effectively dissolve the lignin in bamboo chips, remove the alkaline lignin and alkali soluble impurities through multistage washing, and reduce the pollution. The secondary stewing further removes hemicellulose and residual lignin, purifies the alpha cellulose, and guarantees that the reaction performance of the bamboo alpha-pulp can totally pass. The production method greatly improves the content of the alpha cellulose and reaction performance passing speed of the bamboo alpha-pulp, reduces the discharge of the stewing waste liquor, and provides a basis for further improving the yield and quality of bamboo fibers in chemical fiber production.
Owner:TANGSHAN SANYOU GRP DONGGUANG PULP CO LTD
Comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass
ActiveCN111395025AAvoid damageWon't happenFinely-divided material pretreatmentCellulose material pulpingFiberDepolymerization
The invention discloses a comprehensive utilization method of lignocellulose biomass. According to the method, a lignocellulose raw material is pretreated by p-toluenesulfonic acid to realize efficient conversion and utilization of each component after component separation; a lignin-containing biomass-based hydrogel is prepared from a fiber material containing residual lignin by virtue of a dissolution-regeneration method; the hemicellulose and the cellulose degradation product can be converted into furfural through a hydrolysis method; and lignin is prepared into a lignin depolymerization product which can be used as an aviation fuel precursor through hydrogenization depolymerization. According to the comprehensive utilization method of the lignocellulose biomass, all components of lignocellulose can be utilized in a high-valued mode, the loss is small in the high-valued utilization process, the yield is high, the preparation process is simple, and harmful pollutants cannot be discharged into air.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for determining chemical pulp kappa number with visible-near infrared spectrometry
Owner:FPINNOVATIONS INC
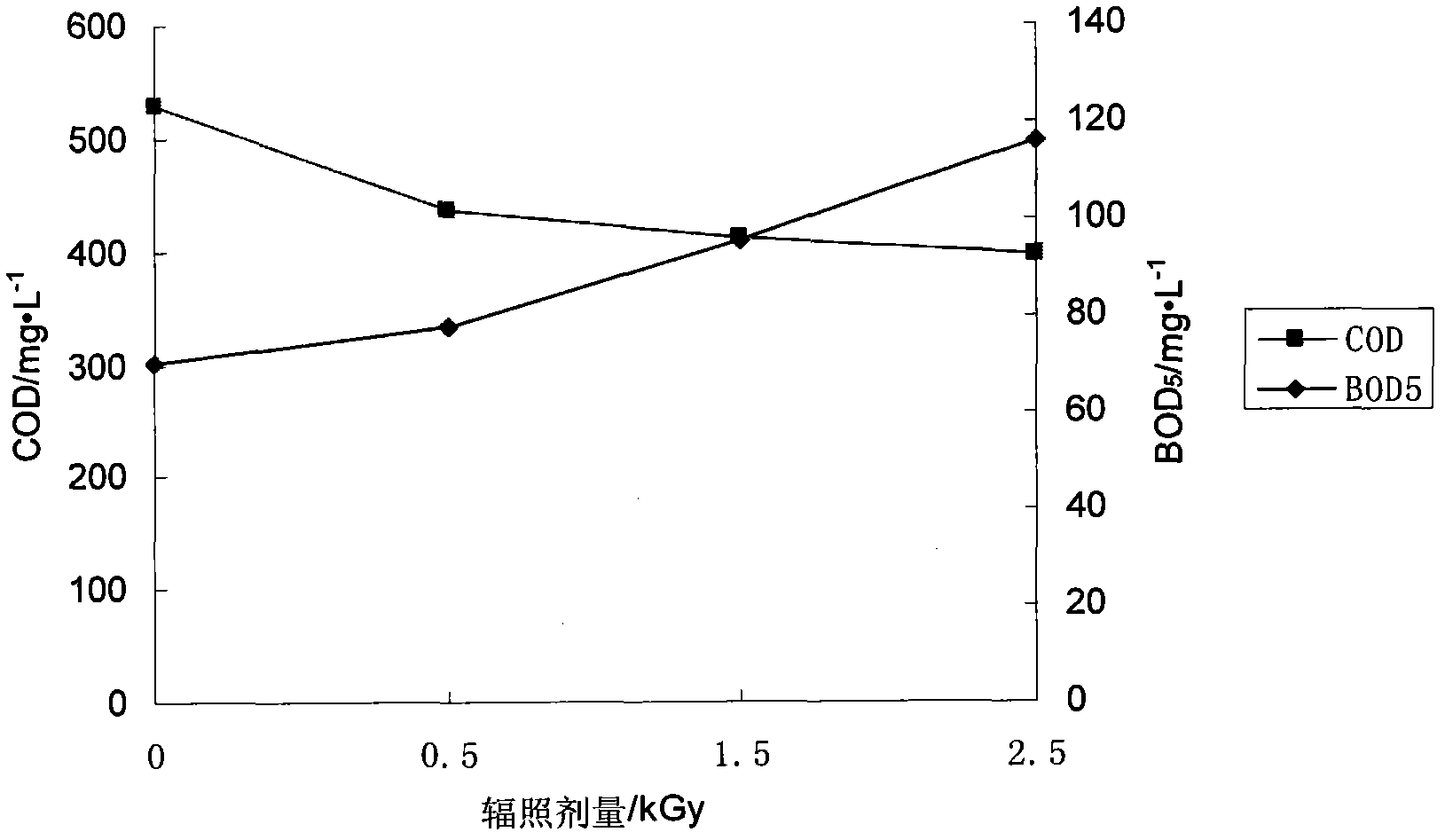
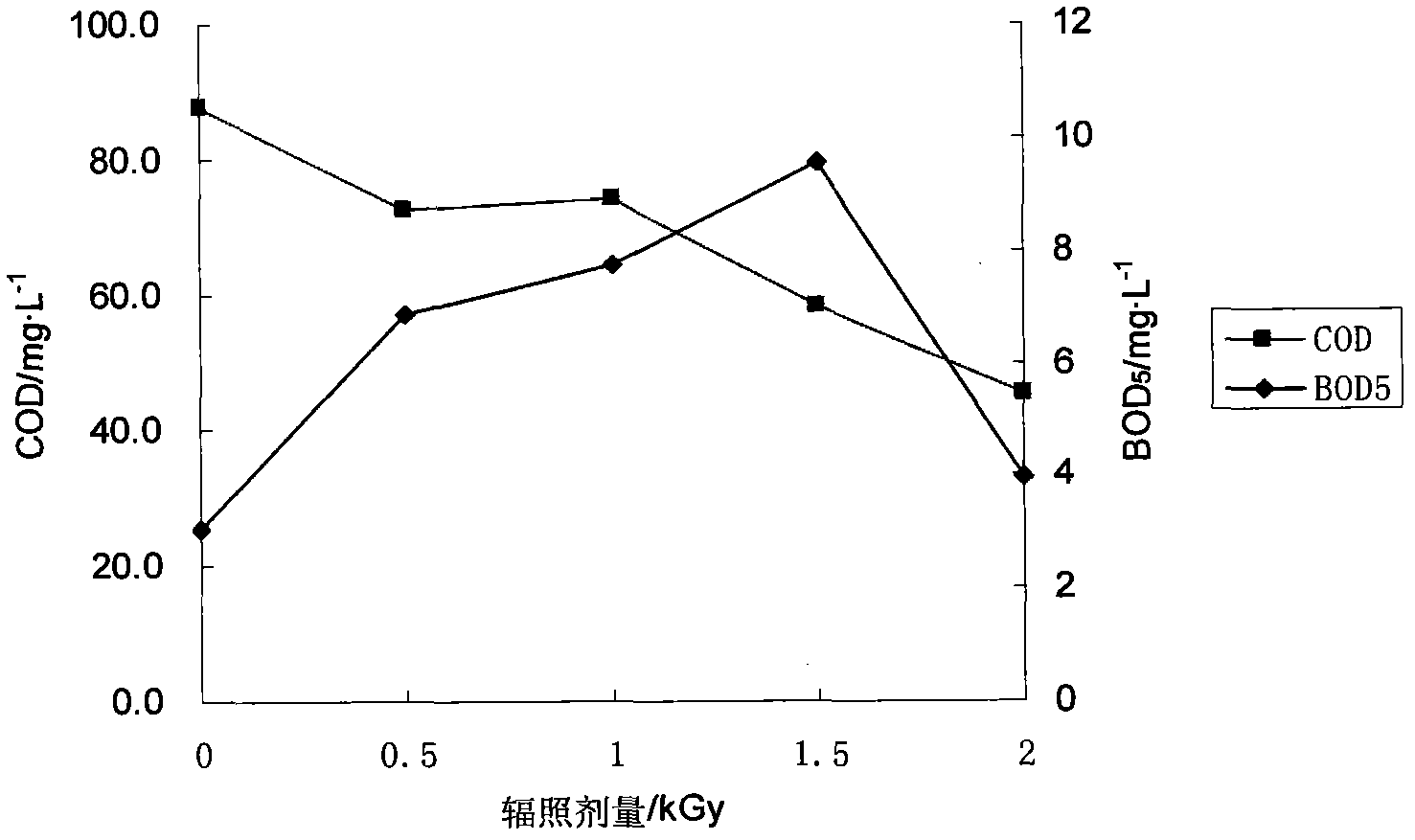
Method for improving biodegradability of papermaking wastewater by using combined process of coagulation and irradiation
InactiveCN102107975AImprove biodegradabilityImprove economyMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from plant processingCelluloseNuclear technology
The invention discloses a method for improving the biodegradability of papermaking wastewater by using a combined process of coagulation and irradiation in the field of nuclear technology application and environment protection. The method comprises the following steps: the papermaking wastewater is treated by adopting a method combining coagulation and ionizing radiation; and firstly, most organic matters with cutoff molecular weights above 3000 kDa in the papermaking wastewater are removed by utilizing a coagulation and sedimentation process, and then toxic and difficultly biodegraded matters in the waste water, such as residual lignin, cellulose, aromatic compounds, and the like, are transformed to non-toxic / low-toxic and easily biodegraded matters through ionizing radiation, thereby improving the biodegradability of the papermaking wastewater. By adopting the combined process of coagulation and irradiation, difficultly biodegraded organic matters can be removed, and the radiation dose can be reduced to the maximum extent, thereby improving the economical efficiency of ionizing radiation treatment of the papermaking wastewater.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for reducing AOX forming amount in chlorine dioxide bleaching process of bagasse pulp
The invention relates to a method for reducing an AOX forming amount in a chlorine dioxide bleaching process of a bagasse pulp. The method is characterized by mainly including the following steps: (1) high temperature acid pretreatment section; (2) biological enzyme pretreatment section; and (3) chlorine dioxide bleaching section. According to the present invention, high temperature acid pretreatment on the unbleached bagasse pulp is mainly to remove the hexenuronic acid in theunbleached pulp, and the use of biological enzyme is to remove the semi-cellulose on the fiber surface and to expose more residual lignin, so as to ensure the less usage of chlorine dioxide in the chlorine dioxide bleaching process, and reduce the AOX generated in the bleaching process. After high temperature acid pretreatment and enzyme pretreatment on the bagasse pulp, the usage amount of chlorine dioxide is saved by 15%-30%, and the forming amount of AOX is reduced by 20%-40%.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Method for removing lignin through biological treatment of plant fibrous material hydrolysate
The invention relates to a method for removing lignin through biological treatment of plant fibrous material hydrolysate. According to the method, horse radish peroxidase treatment and then cationic polymer flocculation treatment are performed on the plant fibrous material hydrolysate, horse radish peroxidase treatment can ensure that low molecular weight dissolved lignin in the hydrolysate is polymerized into macromolecular lignin, and a part of lignin is removed through precipitation; after the lignin is subjected to horse radish peroxidase treatment, even if the part of the lignin which isnot separated out through precipitation is easier to remove in the subsequent cationic polymer flocculation treatment because of polymerization and increasing of molecular weight, and then cationic polymer treatment is adopted, so that residual lignin is further removed. The method can greatly improve the total removal rate of lignin through the combination of horse radish peroxidase treatment andcationic polymer treatment, and meanwhile can further obviously reduce the loss of sugar during the cationic polymer treatment.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
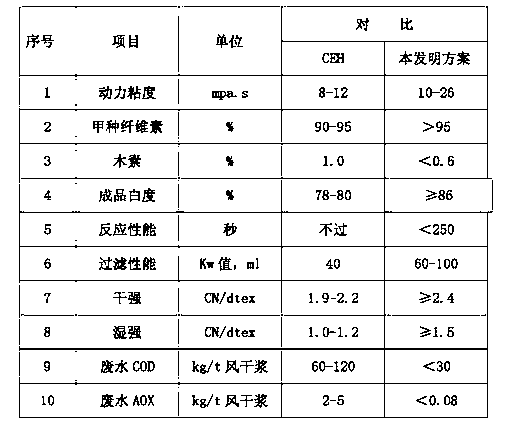
Bleaching method for preparing high quality low pollution bamboo wood dissolving slurry
ActiveCN102995478AHigh whitenessHigh strengthCellulosic pulp after-treatmentChlorine dioxidePulp and paper industry
The invention relates to a bleaching method for preparing a high quality low pollution bamboo wood dissolving slurry, which comprises the following steps: 1) removing parenchyma cells, employing a sieve method or a slurry washing method for removing parenchyma cells; 2) performing an oxidation reaction to remove a transition metal compound, removing boiled residual lignin in the unbleached slurry, performing ozone bleaching on washed slurry; 3) refining alkali in a reinforced mode; 4) bleaching chlorine dioxide; and 5) processing by acidifying at high temperature. According to the invention, delignification step by step, dynamic viscosity adjusting, whiteness enhancement, fine fiber generation reduction, and reaction capability activation are carried out on unbleached bamboo wood dissolving slurry, on the basis of increasing fiber strength, whiteness and filtering quality, the pollution load of the bleaching waste water is reduced, the bamboo wood dissolving slurry with high product quality and low environmental pollution is prepared, and provides a high quality raw material for producing the viscose fiber.
Owner:四川天竹竹资源开发有限公司
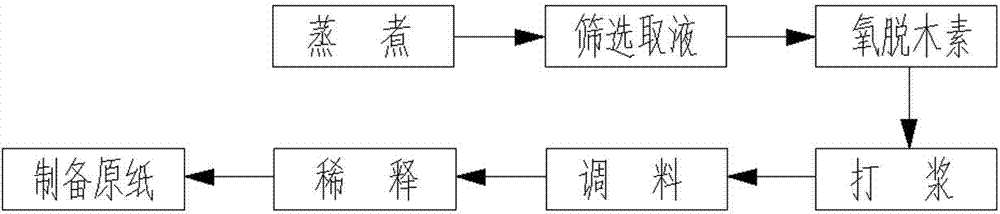
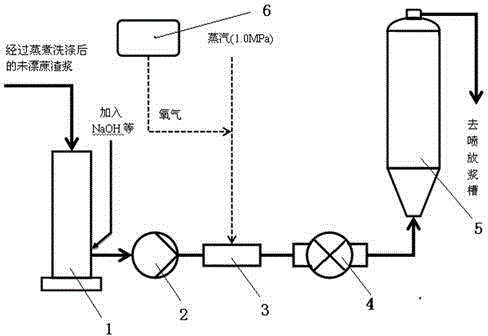
Method and device for oxygen delignification for bagasse pulping
The invention discloses a method and a device for oxygen delignification for bagasse pulping. According to the method, the oxygen delignification procedure is added between the cooking and bleaching of the conventional bagasse pulping process, cooked bagasse pulp is treated by the washing procedure at a washing section, the pulp enters a vertical pipe of a medium-consistency pump through a pulp outlet screw of a pulp washer, a certain amount of NaOH is added on the vertical pipe, then the pulp is conveyed by the medium-consistency pump, enters a steam feeding device where steam and oxygen are added, is mixed uniformly in a mixer and enters an oxygen delignification tower for delignification reaction, and finally the pulp after reaction is filtered and washed to enter a subsequent bleaching section. Based on the method and the technological conditions, residual lignin in the cooked bagasse pulp can be effectively removed, the consumption of chemicals at the bleaching section is reduced, the pollution load of waste water is greatly reduced, and meanwhile, the bagasse pulp has high yield and quality.
Owner:CHINA LIGHT IND NANNING DESIGN ENG
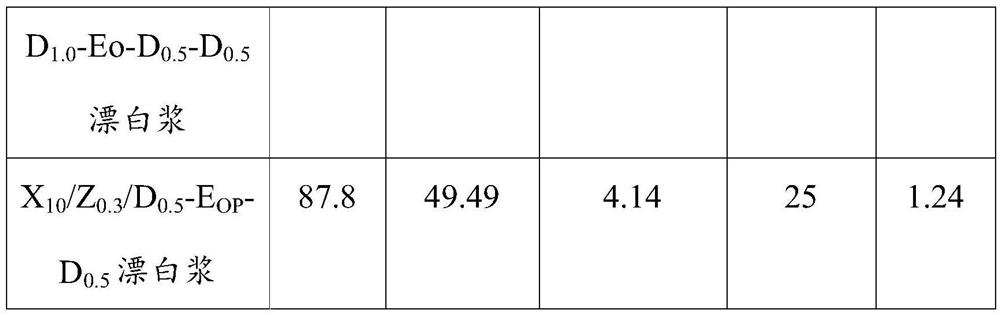
Sulfate wood pulp short-sequence ECF bleaching process X/Z/D-EOP-D or X/D/Z-EOP-D
PendingCN111979818AHigh whitenessHigh strengthPulp bleachingPulping with inorganic basesChlorine dioxidePapermaking
The invention belongs to the technical field of papermaking, and relates to a sulfate wood pulp short-sequence ECF bleaching process X / Z / D-EOP-D or X / D / Z-EOP-D. The process comprises the following steps: (1) sequential bleaching (X / Z / D or X / D / Z): carrying out X / Z / D or X / D / Z sequential bleaching on sulfate wood pulp subjected to oxygen delignification to obtain semi-bleached paper pulp; (2) enhanced alkali extraction (EOP): carrying out hydrogen peroxide and oxygen enhanced alkali extraction treatment on the sequentially bleached paper pulp to further dissolve out residual lignin in the pulp; and (3) supplementary bleaching (D): carrying out chlorine dioxide supplementary bleaching on the paper pulp to obtain fully bleached paper pulp (88% ISO). Through the above bleaching treatment, the paper pulp with high whiteness and strength index is obtained. Compared with a traditional D-EO-D-D bleaching sequence, X / Z / D-EOP-D or X / D / Z-EOP-D bleaching sequence reduces one chlorine dioxide bleaching section, and under the condition that the final whiteness is the same, the chlorine dioxide consumption is reduced by 30% or above, and the water consumption is reduced by 20% or above.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for bioenzyme-assisted chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp
The invention relates to a method for bioenzyme-assisted chlorine dioxide bleaching of bagasse pulp. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing hemicellulase pretreatment; (2) performing ligninase pretreatment; (3) performing chlorine dioxide bleaching. According to the method, hexenuronic acid and hemicellulose in unbleached bagasse pulp are removed through the hemicellulase pretreatment of the unbleached bagasse pulp, so that more residual lignin is exposed; lignin exposed on the fiber surface is removed by using ligninase, so that less chlorine dioxide is used in a chlorine dioxide bleaching section and AOX (adsorbable organic halogen) generated in the bleaching process is reduced; after the bagasse pulp is subjected to bioenzyme pretreatment, the consumption of chlorine dioxide is saved by 30%-50% and the forming amount of AOX is reduced by 40%-60%.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
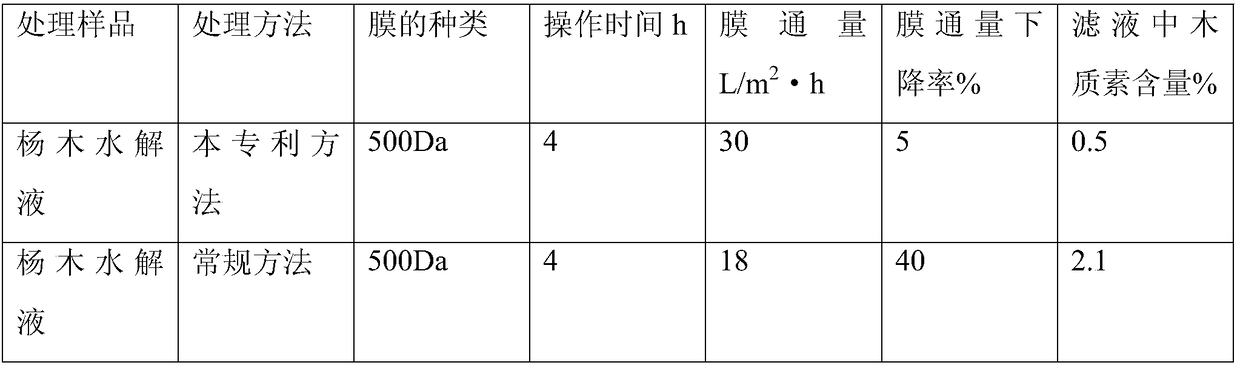
Method for refining high-temperature wood hydrolyzate
Owner:CHENGDU LIANJIE MEMBRANE TECH
Pretreatment method for promoting efficient utilization of biomass
ActiveCN111304262AAvoid damageHigh molecular weightBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesCelluloseFiber
The invention discloses a pretreatment method for promoting efficient utilization of biomass. The pretreatment method comprises the steps of mixing lignocellulose raw material with a p-toluenesulfonicacid solution, heating, stirring at a constant temperature at a fixed stirring speed for a certain period of time, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a solid material which is a fibersample containing residual lignin; washing the fiber sample with residual lignin by using distilled water until p-toluenesulfonic acid is completely cleaned, and then sequentially carrying out short-time ultrasonic treatment and freeze drying to obtain a fully defibering fiber material. The lignocellulose raw material is pretreated under mild conditions, the loss of each component is small, and the obtained lignin can be subjected to high-value utilization; moreover, short-time ultrasonic pretreatment is carried out on the separated fiber sample, so that the cellulose structure becomes more loose, and the fiber material with the loose structure is large in contact area, more sufficient in enzymolysis, better in fermentation and higher in ethanol yield during enzymolysis.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Solvent and method for dissolving plants
InactiveCN106220870AEffective dissolutionAvoid recycling difficultiesBulk chemical productionFiltrationAgricultural residue
The invention discloses a solvent and method for dissolving plants. The solvent is prepared by mixing an imidazole ionic liquid and a polar aprotic solvent. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out high temperature alkali cooking on the plants, removing a filtrate containing hemicelluloses after filtration, and carrying out water washing on filter residues to be neutral to obtain a blend of lignin and cellulose; dissolving the blend of the lignin and cellulose in the solvent to dissolve the plants. The solvent provided by the invention can efficiently dissolve wood and agricultural residues at a lower temperature. The hemicelluloses are low in molecular weights, soluble in water and bad in performances, and have great influences on mechanical properties of the final product, thus firstly, the high temperature alkali cooking is carried out on the plants to remove the hemicelluloses, and then the residual lignin and cellulose are directly dissolved. The solvent is adopted for directly dissolving plant resources of the wood, the agricultural residues and the like; the cellulose, lignin and hemicelluloses are not required to be separated, so that biomass resources can be directly used.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
Wastewater recycling process for waste paper pulping and manufacturing bobbin paper
ActiveCN103420542ASimple processEasy to operate and manageMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from plant processingBobbinBiological activated carbon
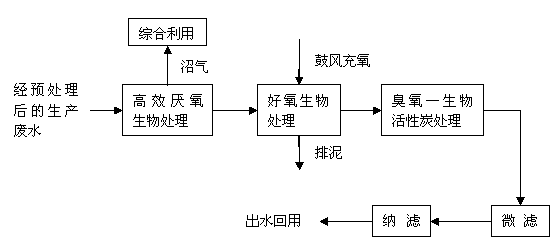
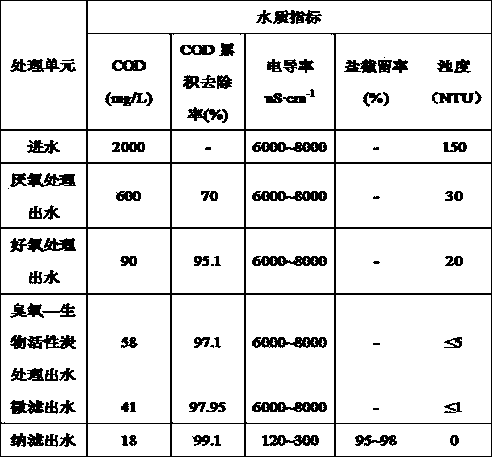
The invention provides a wastewater recycling process for waste paper pulping and manufacturing bobbin paper. The wastewater recycling process is characterized in that waste water is sequentially subjected to high-efficient anaerobic organism processing, aerobic organism processing, ozone-biological activated carbon processing and microfiltration and nanofiltration processing, and water after processing is recycled. Refractory organics such as residual lignin in the wastewater can be effectively removed, COD removal rate is more than 98 percent, and Ca2+ and Mg2+ removal rates are also high and are respectively larger than 75 percent and 85 percent.
Owner:山东绿泉环保科技股份有限公司
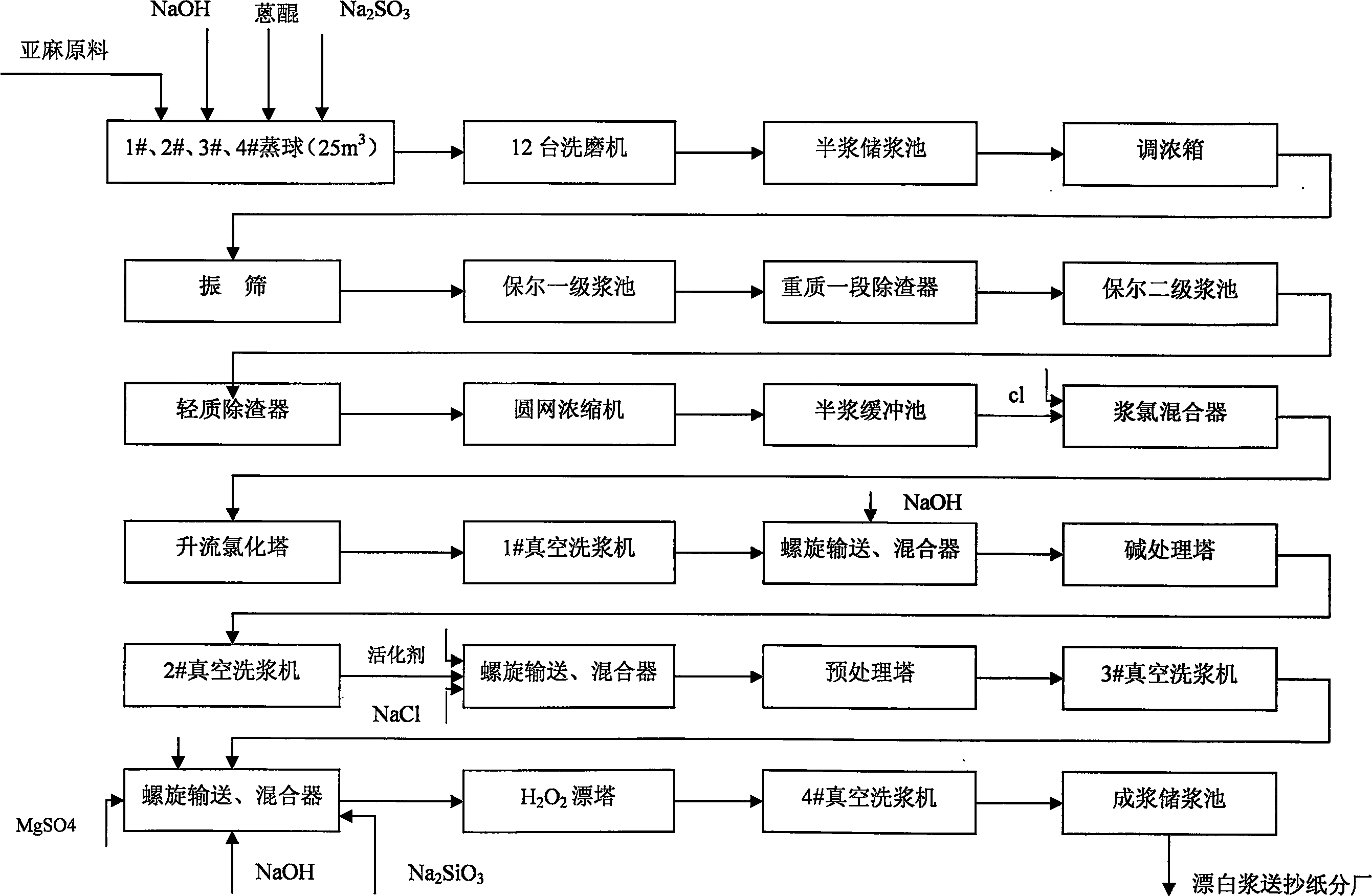
Method for consecutive blanching flax paper pulp in high whiteness through multiple stage
InactiveCN1873090AHigh removal rateLower the activation energy of the reactionPulp bleachingBleaching agents additionBiological activationHydrogen peroxide
A continuous multisection bleaching method of high whiteness flax paper pulp applies bleaching process as chlorinating-alkali treatment-activation pretreatment-hydrogen peroxide bleaching. In the method, bleaching whiteness value of single hydrogen peroxide bleaching section can be increased by 20-30% ISO.
Owner:MUDANJIANG HENGFENG PAPER CO LTD
Preparation method of self-adhesive and water-stable paper straw
ActiveCN113580668AWide variety of sourcesRich reservesPaper/cardboard articlesWood treatment detailsAdhesiveAqueous solution
The invention discloses a preparation method of a self-adhesive and water-stable paper straw. The preparation method comprises the following steps of preparing paper pulp from biomass softened in a mixed aqueous solution of nitric acid and hydrogen peroxide, then preparing the paper pulp into a wet paper sheet, cutting the wet paper sheet into a rectangle or a square, rolling the paper sheet into a wet paper tube, and air-drying the wet paper tube; and carrying out heat treatment on the air-dried paper tube to vitrify residual lignin so as to prepare the paper straw. By means of the preparation method, the structure of the paper straw prepared by the method does not collapse after being soaked in water for more than 2 weeks, and the paper straw is completely degraded within two months after being buried in humid soil. The method is simple and convenient in process, adopted chemical reagents are easy to obtain and low in cost, the prepared paper straw has high water stability and natural degradability, and the paper straw is formed in a self-adhesion manner, free of chemical additives, green, safe and wide in application prospect in the fields of medium-and-high-end drinks, catering and the like.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
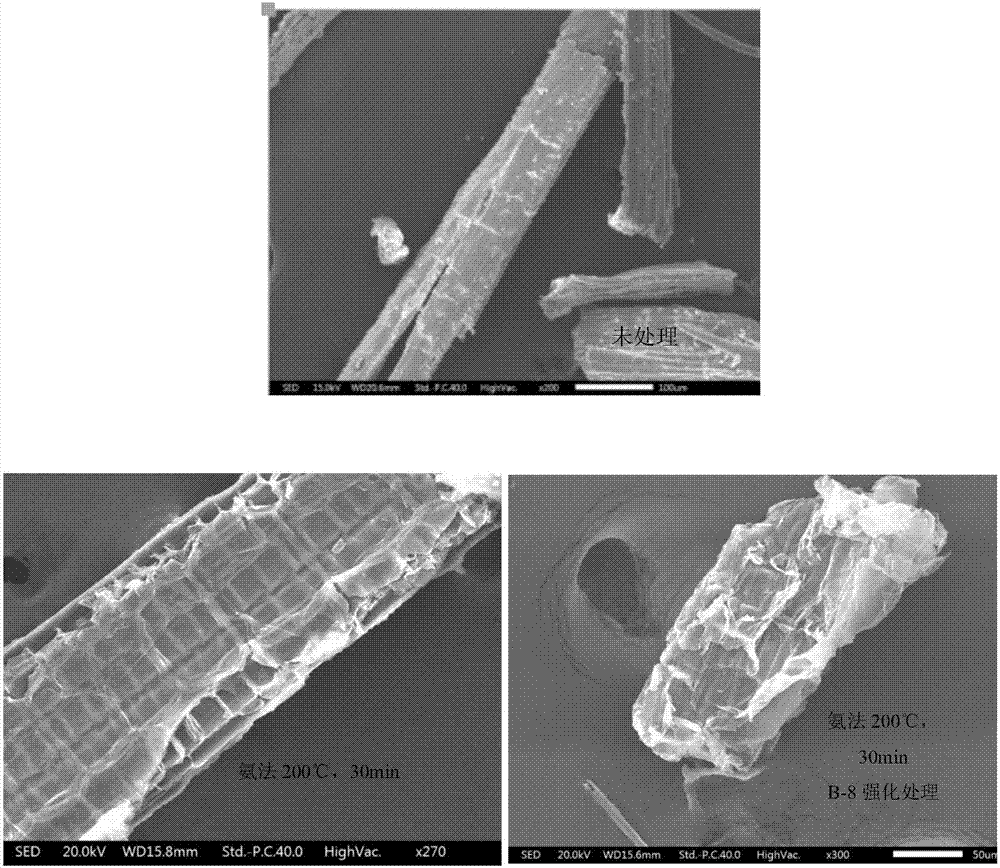
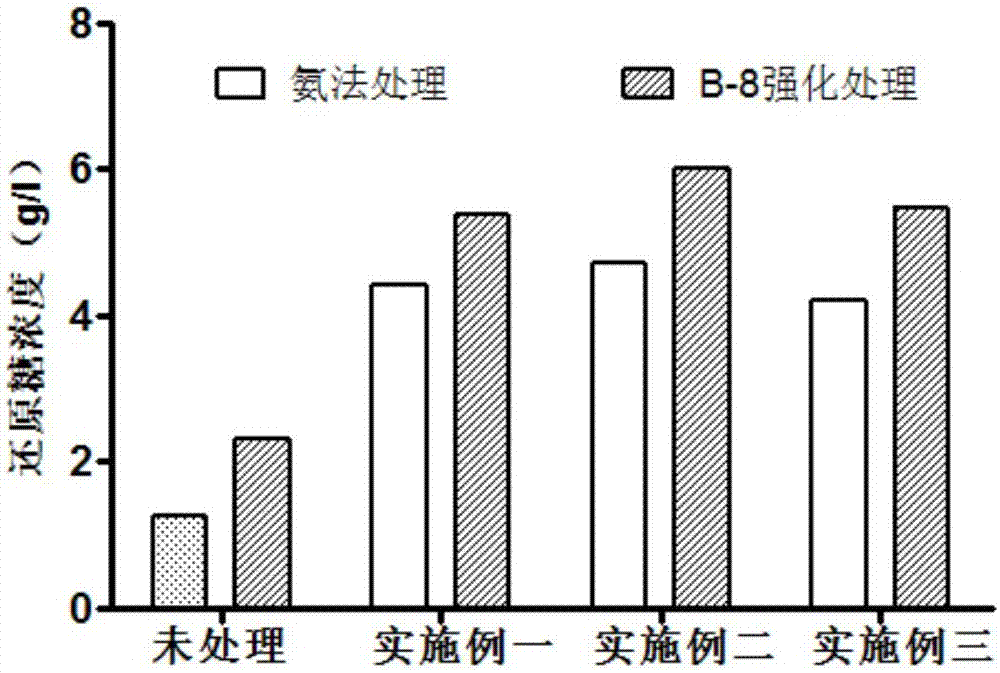
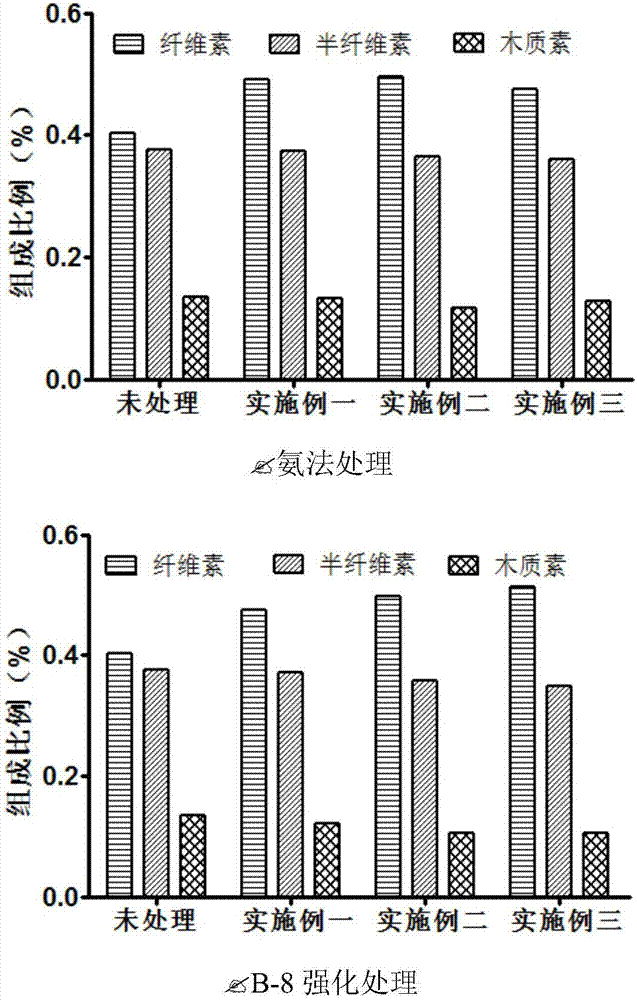
Method for strengthening ammonia pretreatment of waste biomass by means of lignin-degrading bacteria
ActiveCN107058427AIncreased accessible surfaceImprove enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseCupriavidus basilensis
The invention discloses a method for strengthening the ammonia pretreatment of waste biomass by means of lignin-degrading bacteria. Particularly, on the basis of the ammonia pretreatment of the waste biomass, the lignin-degrading bacteria, namely Cupriavidus basilensis B-8, with the preservation number of CGMCC No.4240 are used, residual lignin in the waste biomass is further removed by improving culturing conditions, and the cellulose accessible surface is improved in the enzymolysis and saccharification processes. By using the method, the enzymolysis efficiency of the pretreatment of a single ammonia method is improved by about 30%, and the method has the advantages of being short in treatment time, simple in operation, small in secondary pollution, low in cost and the like.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
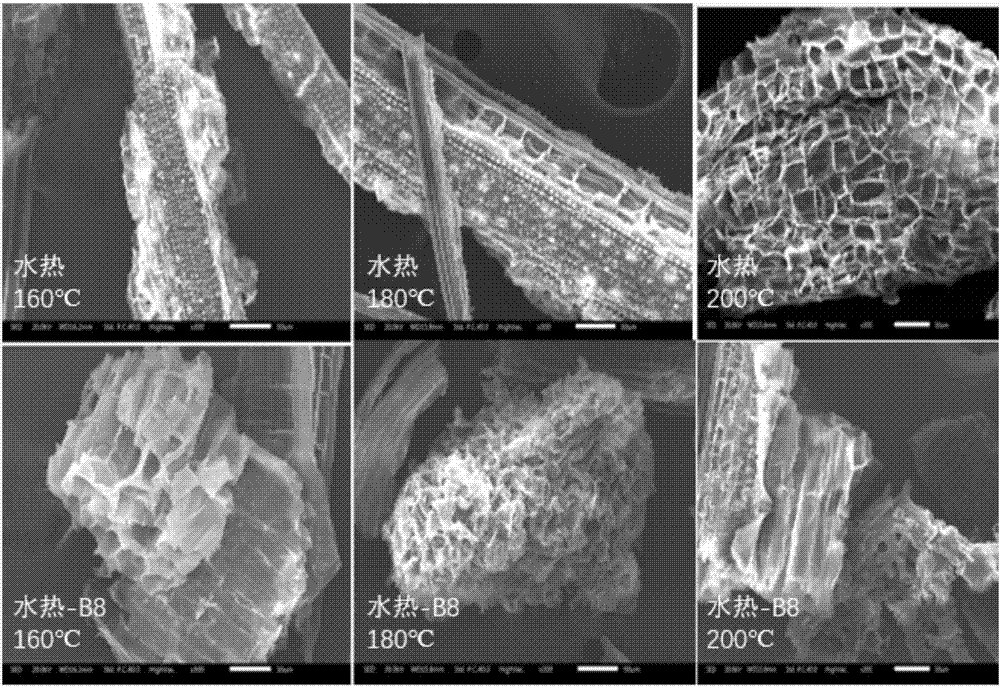
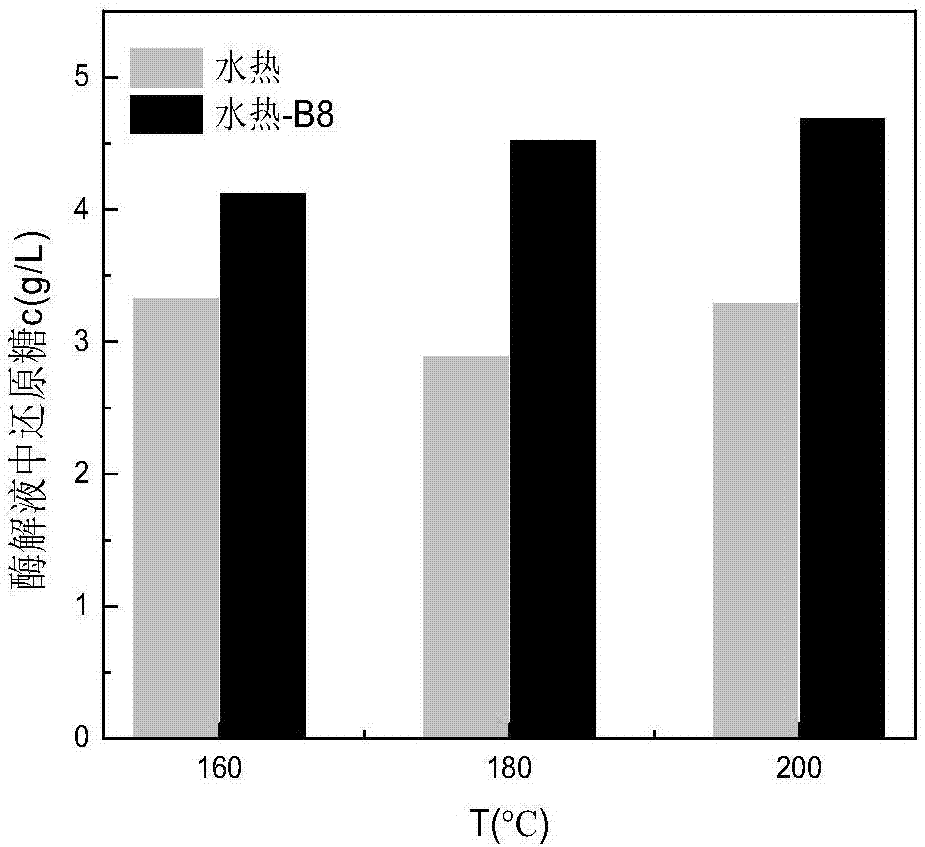
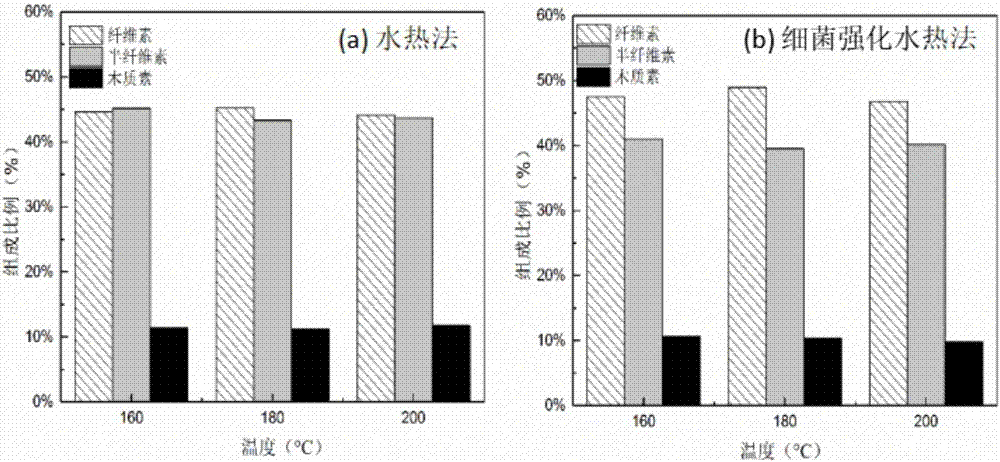
Method for enhancing waste biomass hydro-thermal pretreatment by using lignin degrading bacteria
ActiveCN107513545AImprove stabilityLoose structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationEnzymatic hydrolysisCupriavidus basilensis
The invention discloses a method for enhancing waste biomass hydro-thermal pretreatment by using lignin degrading bacteria, and concreatly relates to a method that based on pretreatment of waste biomass by a hydrothermal method, the lignin degrading bacteria (Cupriavidus basilensis B-8, a preservation number is CGMCC No.4240) is used, the culture condition is improved, and the residual lignin in the waste biomass is removed, and the accessible surfaces while enzymatic hydrolysis and saccharification can be greatly increased. The enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency for hydrothermal method pretreatment is increased by about 56%, and the method has the advantages of short processing time, simple operation, no secondary pollution, and low cost.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for extracting cellulose from tobacco waste based on water-alcohol oxidation process
ActiveCN102733217AHigh purityHigh crystallinityPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPre treatmentHemicellulose
The invention relates to a chemical extraction method of agricultural waste, particularly a method for extracting cellulose from tobacco waste based on water-alcohol oxidation process, comprising the following steps: crushing the tobacco waste, putting the crushed waste in water to boil for no less than 20 min and dewatering to obtain a pretreatment material; adding an alcoholic solution having the volume of 5-70 times of the volume of the tobacco waste in the obtained pretreatment material, reacting for at least 30min at 80-100 DEG C, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain filter residues, wherein the volume percentage of the alcoholic solution is 20-90 %, and the filter residues are crude cellulose. The method has the advantages of simple process, energy saving and environmental protection, and the purposes of removing residual lignin, extracting residual hemicellulose and soluble substance can be achieved by using reductant-oxidants to process the tobacco raw material. By using the water-alcohol oxidation process to process tobacco cellulose first and using the reductant-oxidant solution to oxidize and then extracting, the extraction efficiency is raised about by 150% compared with using the water-alcohol oxidation process along, thus the extraction efficiency is greatly raised.
Owner:CHONGQING HENGYUAN JINTONG TECH
Method for filtering sugar solution by using lignin
The invention discloses a sugar liquid filtering method of lignin, which is characterized by the following: adopting lignin to replace filter soil as filter aid and sugar residual precoating; reaching low-adhesivity for sugar residual protein; filtering conveniently; avoiding utility value reduced by residual lignin.
Owner:SHANDONG XIWANG SUGAR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com