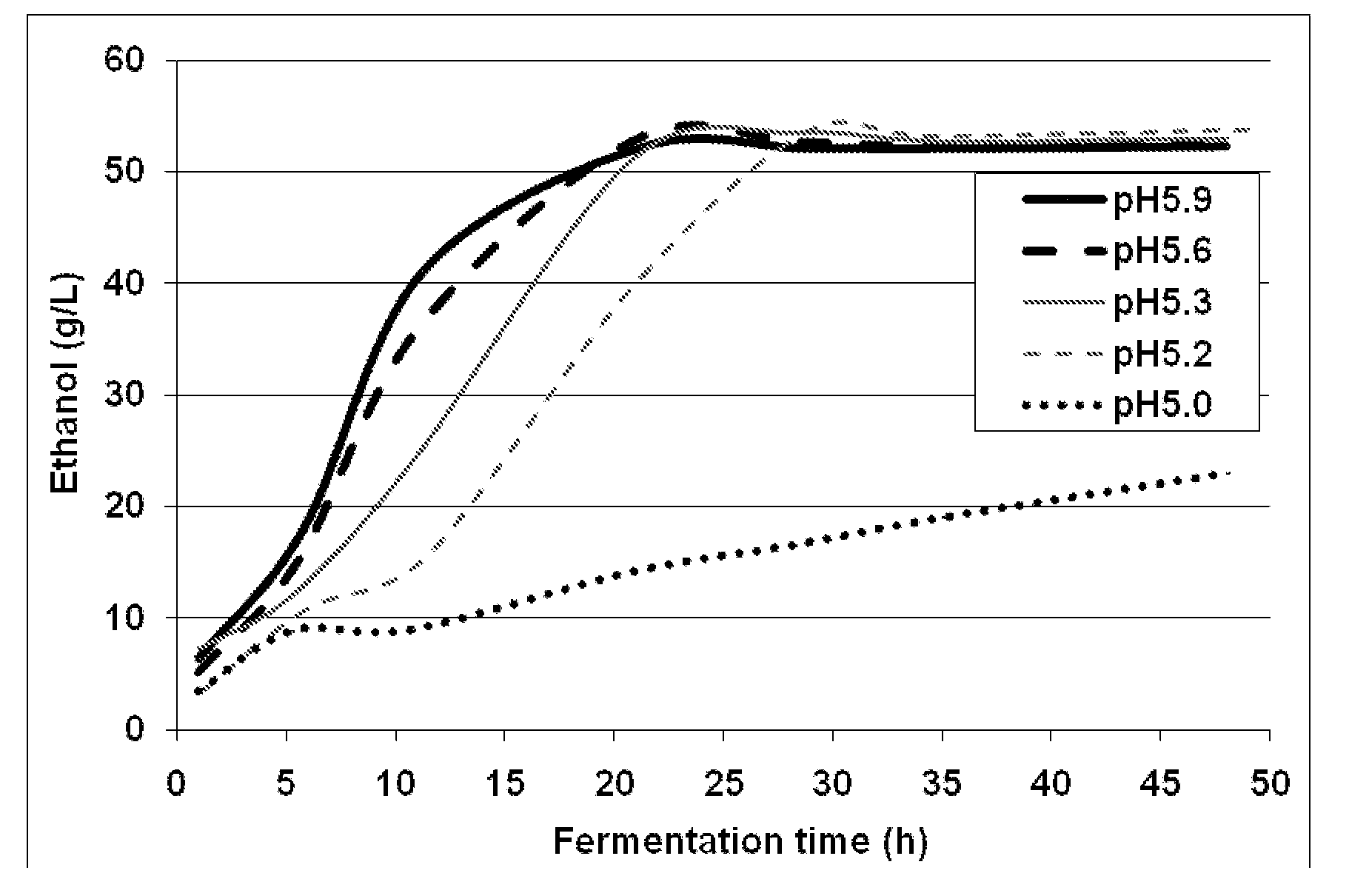
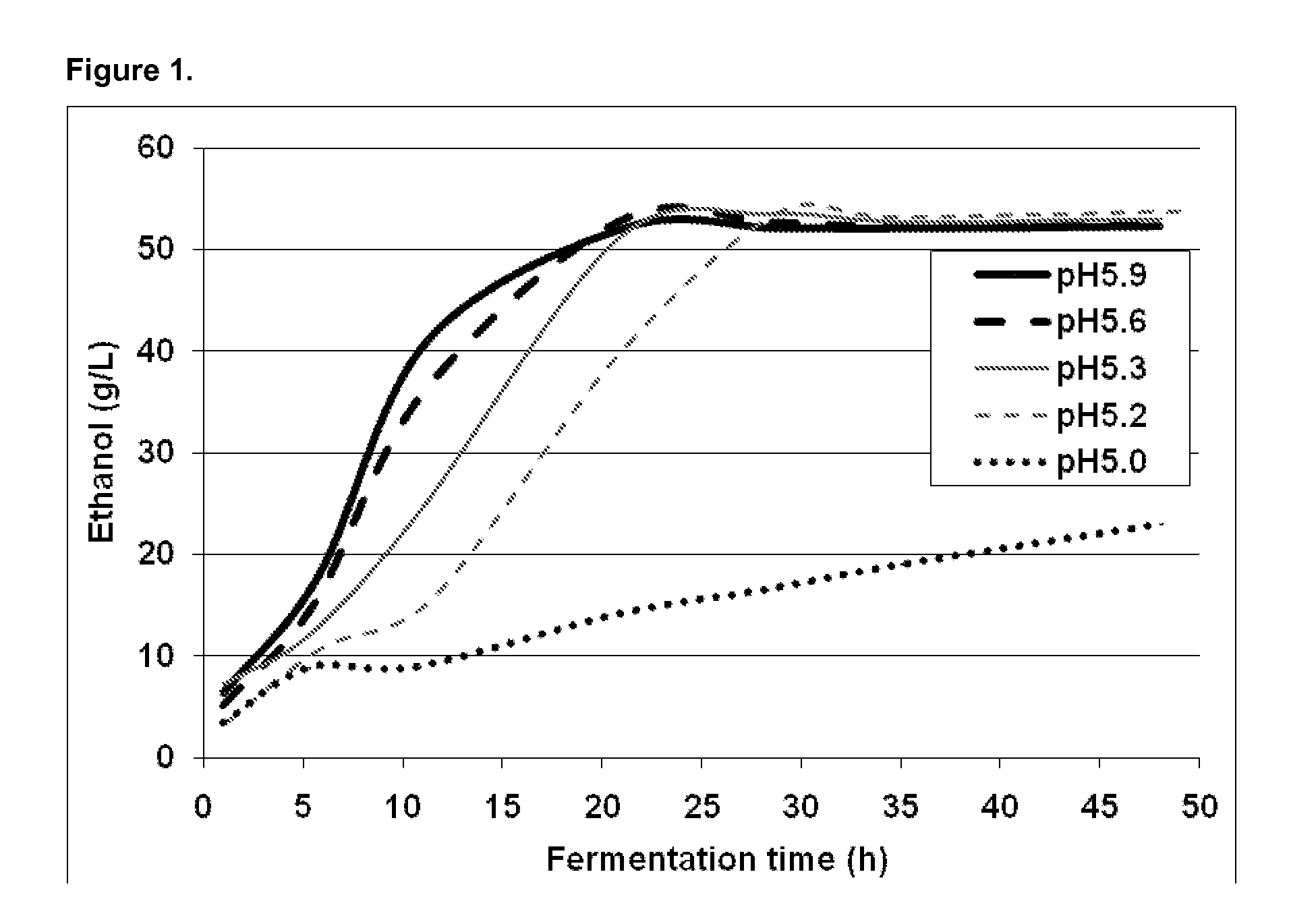
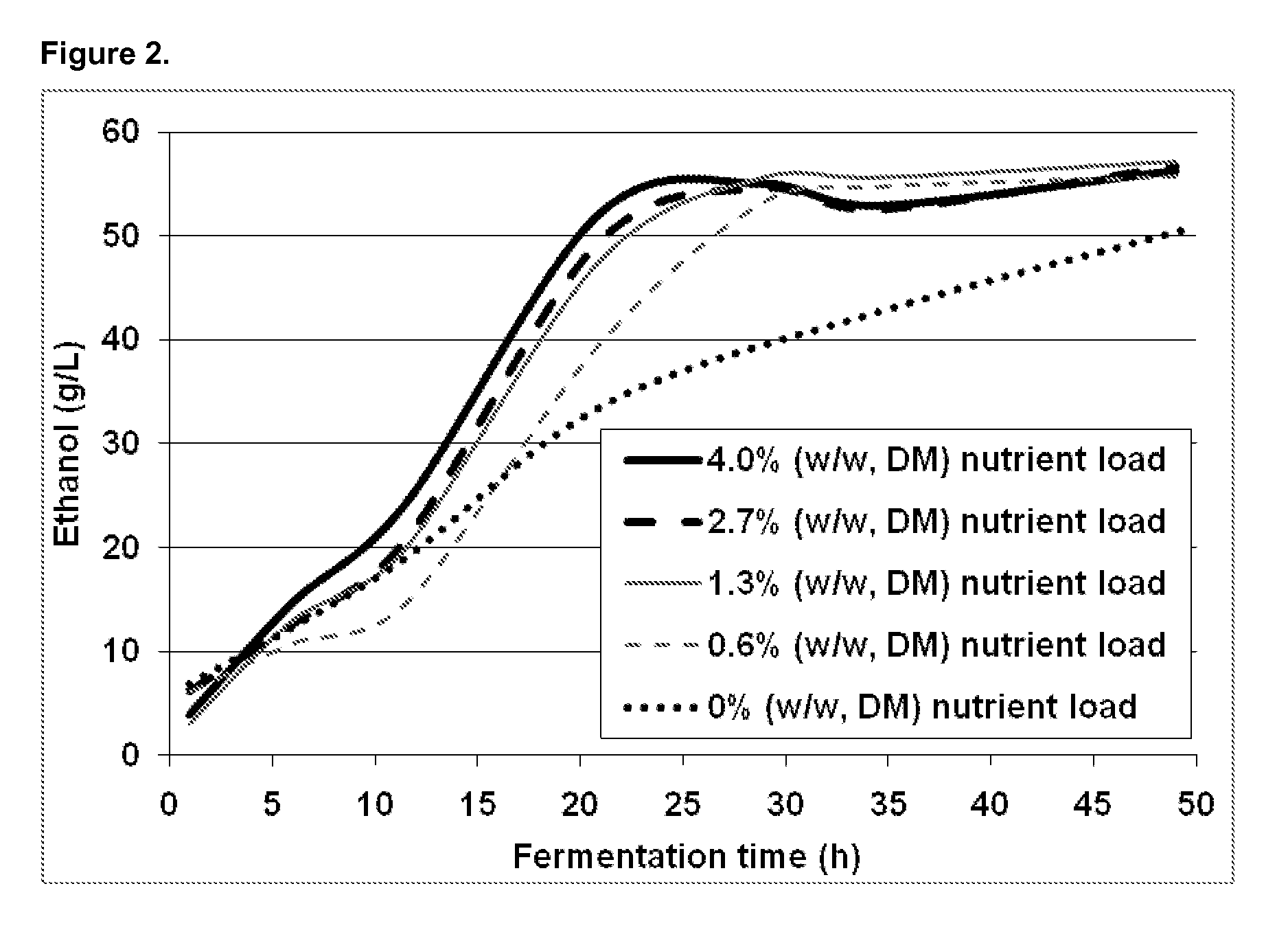
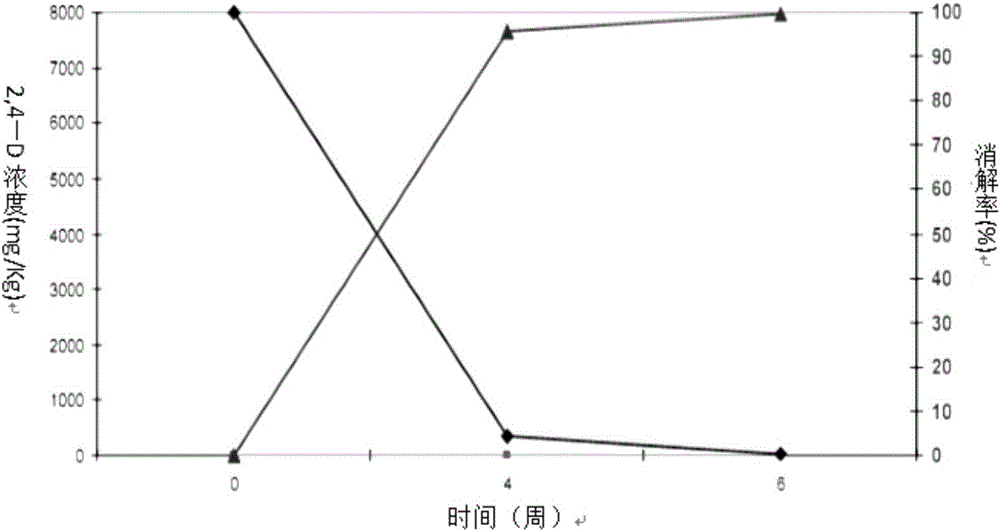
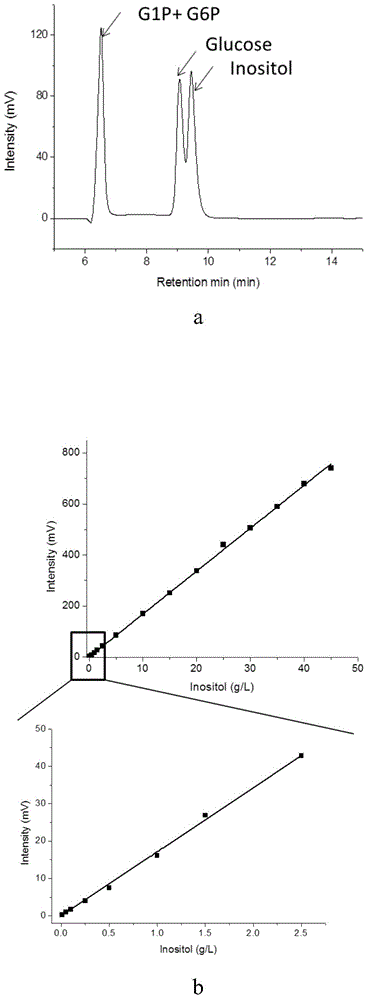
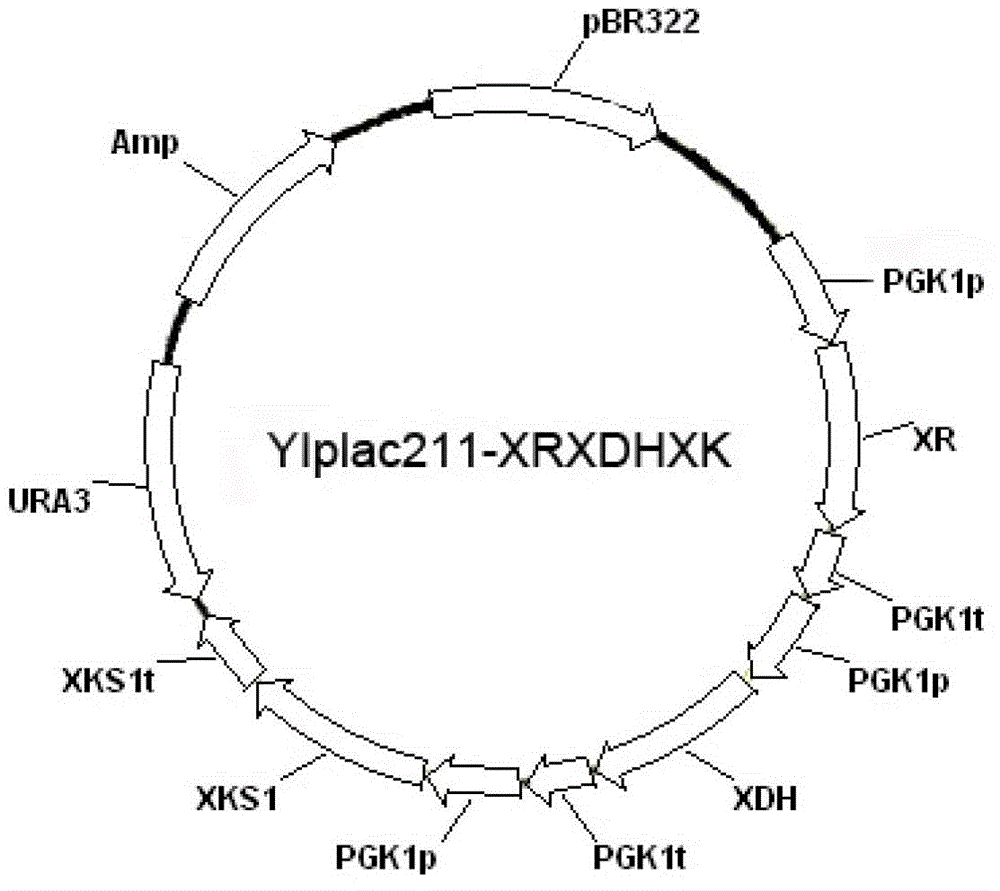
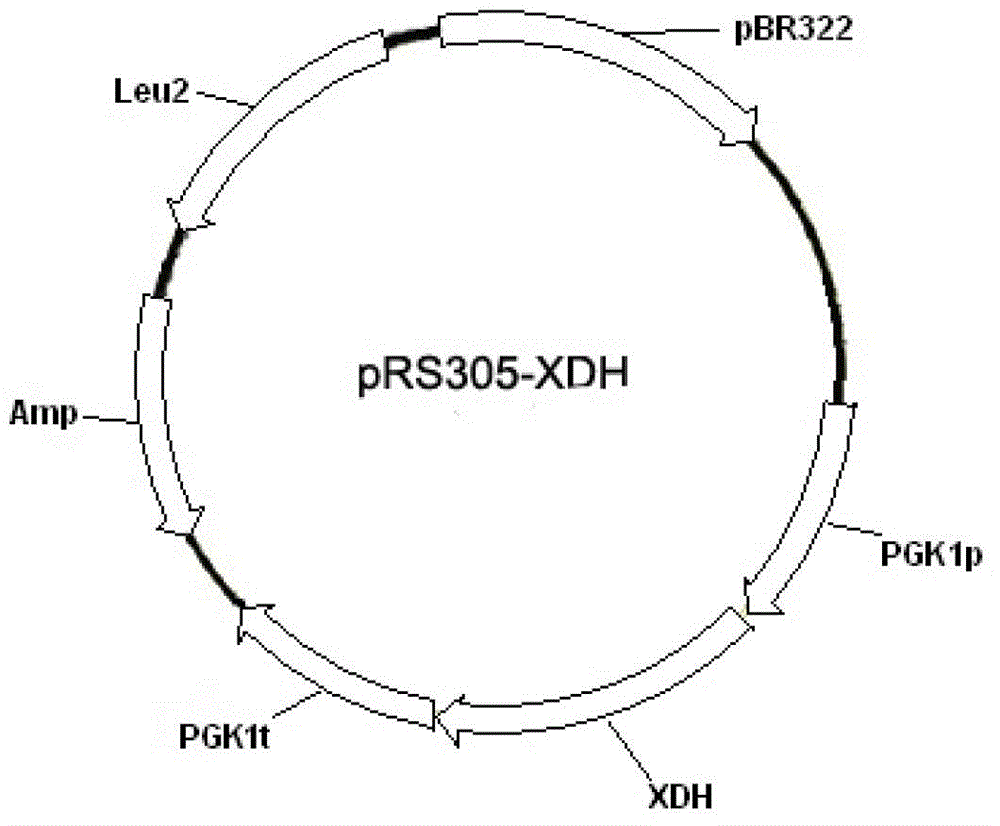
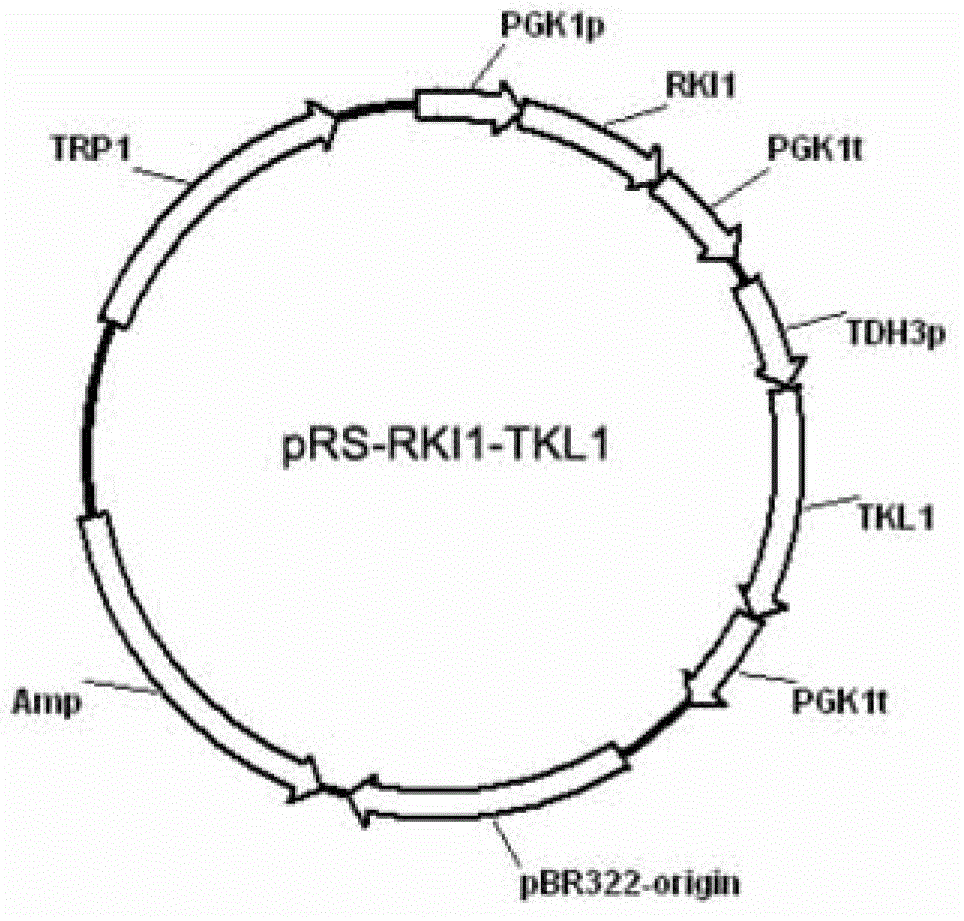
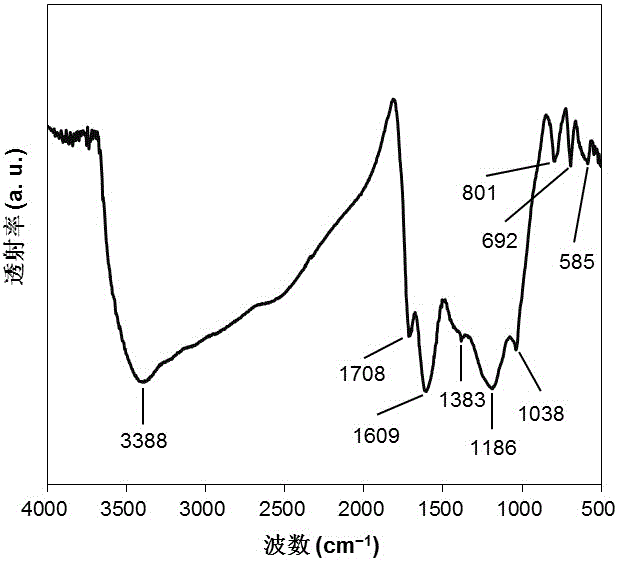
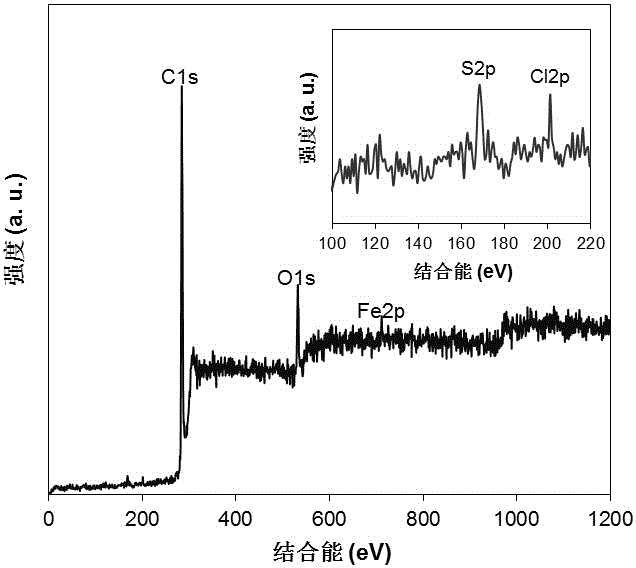
Patents
Literature
463 results about "Cellulose hydrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Hydrolysis of cellulose, an organic compound used to make all sorts of things from paper to biofuels, results a split in the chemical bonds between cellobiose and cellulase. The cellobiose can then be further hydrolyzed to create glucose.
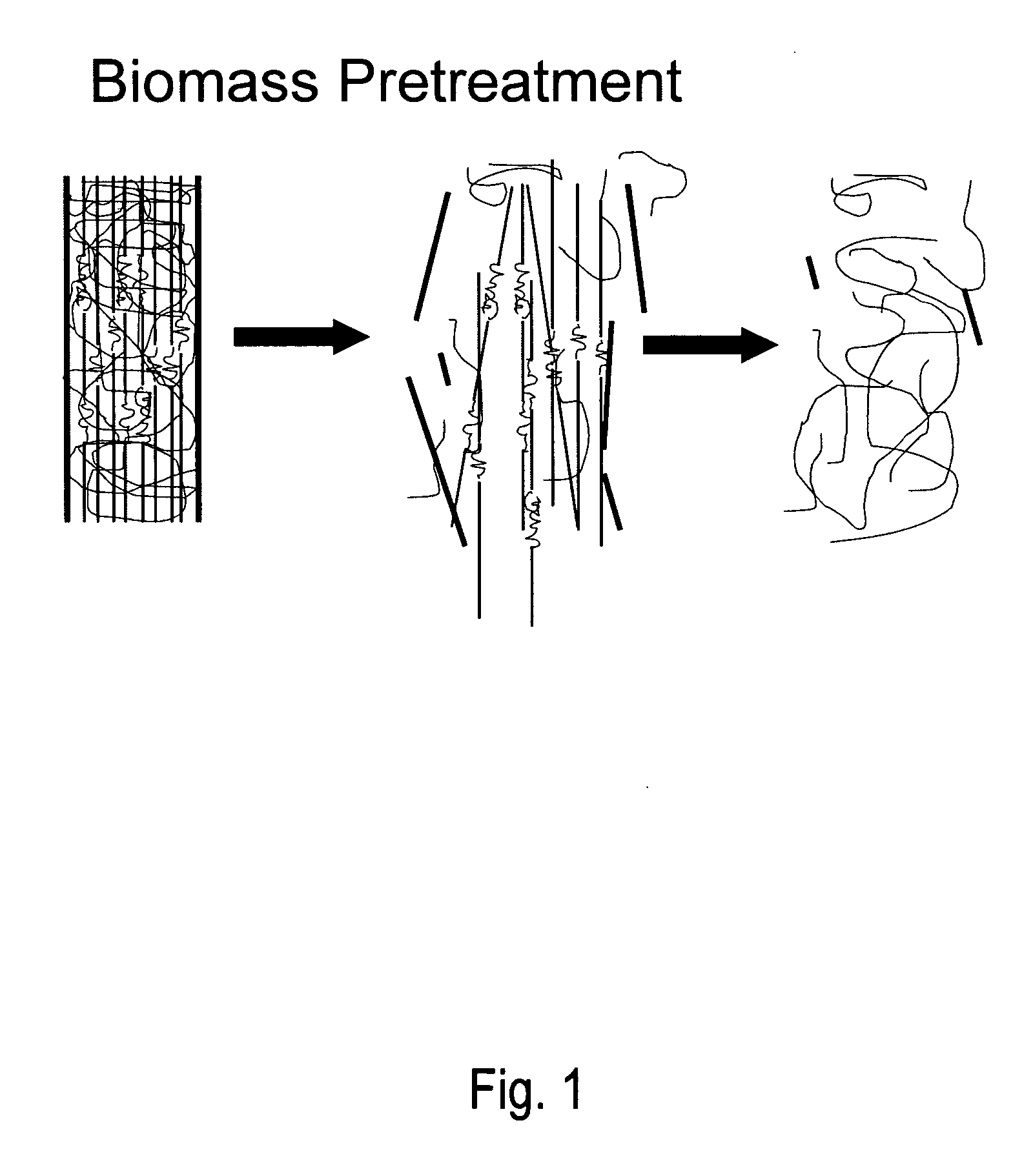
Biomass pretreatment
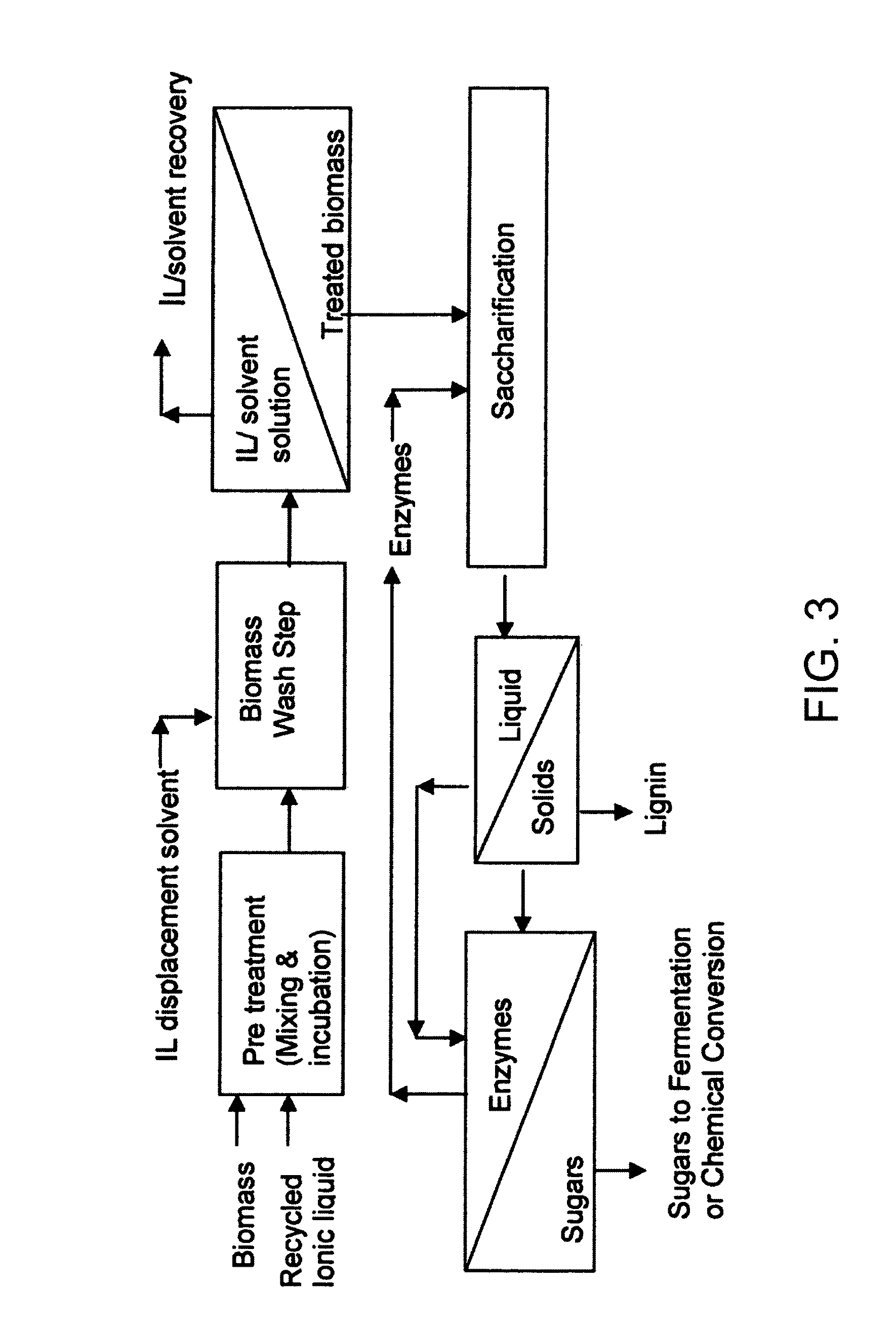
A method for lignocellulose conversion to sugar with improvements in yield and rate of sugar production has been developed by using ionic liquid pretreatment. This new pretreatment strategy substantially improves the efficiency (in terms of yield and reaction rates) of saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass. Cellulose and hemicellulose, when hydrolyzed into their sugars, can be converted into ethanol fuel through well established fermentation technologies. These sugars also form the feedstocks for production of variety of chemicals and polymers. The complex structure of biomass requires proper pretreatment to enable efficient saccharification of cellulose and hemicellulose components to their constituent sugars. Current pretreatment approaches suffer from slow reaction rates of cellulose hydrolysis (by using the enzyme cellulase) and low yields.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO +1
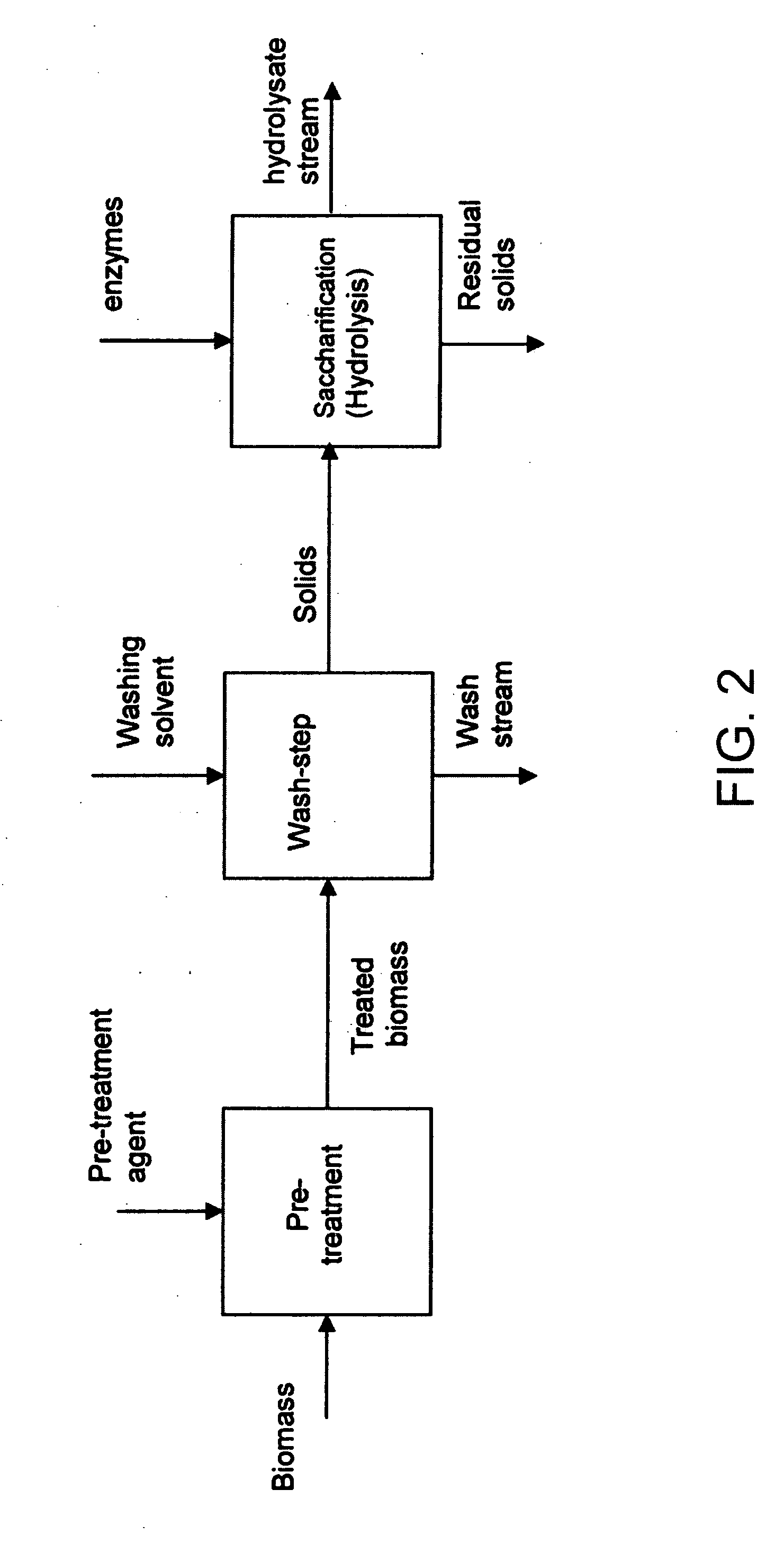
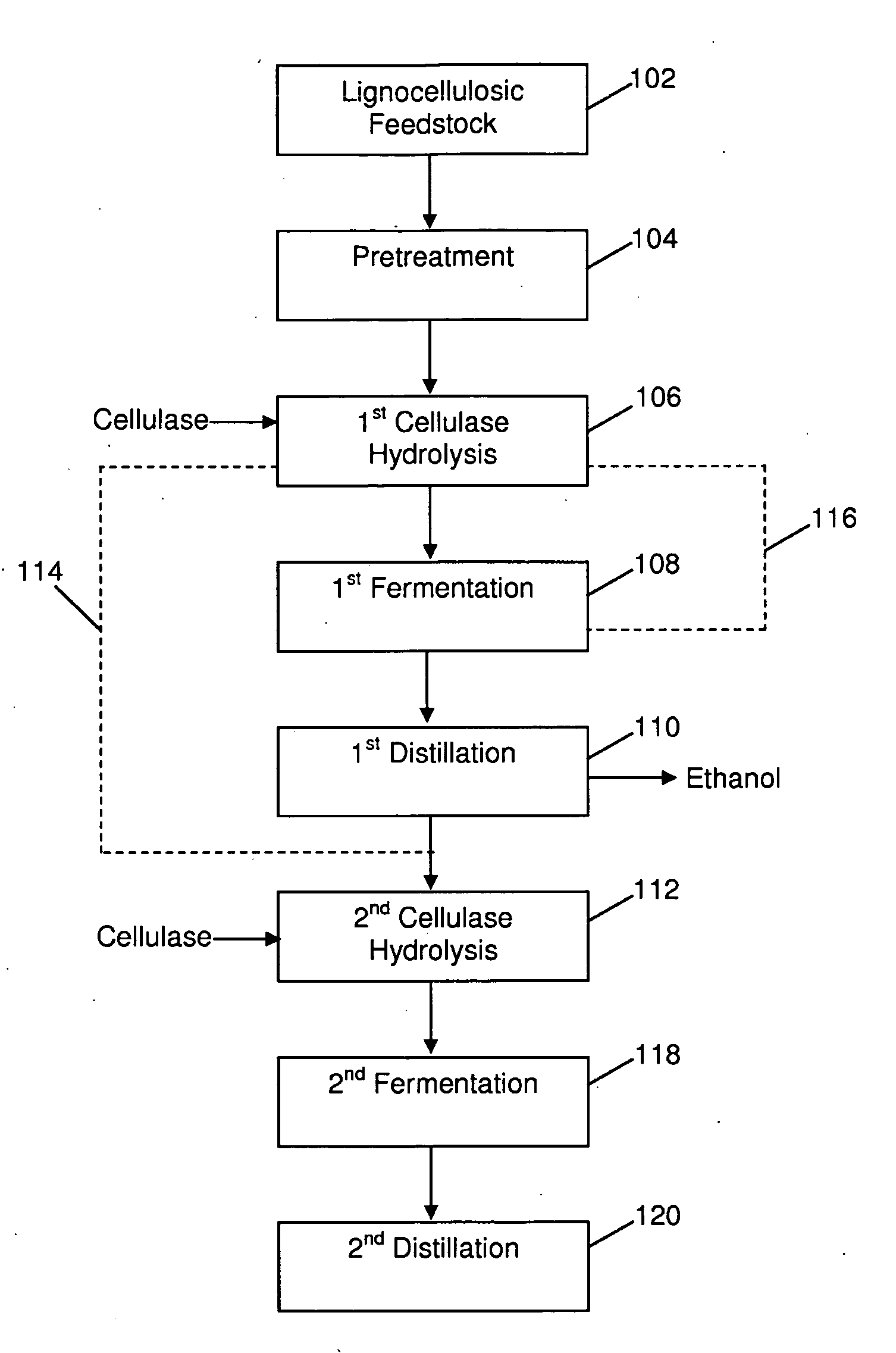
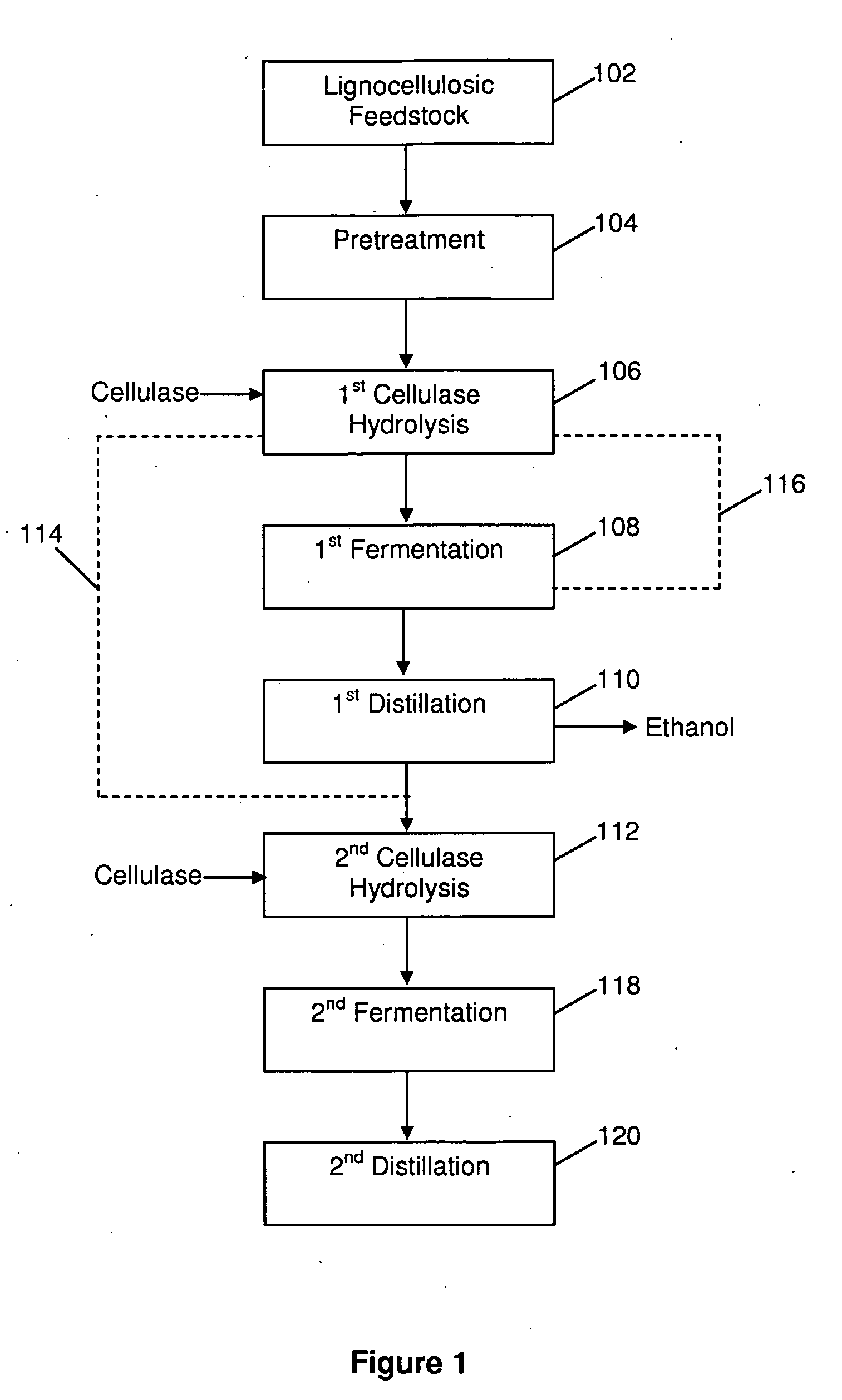
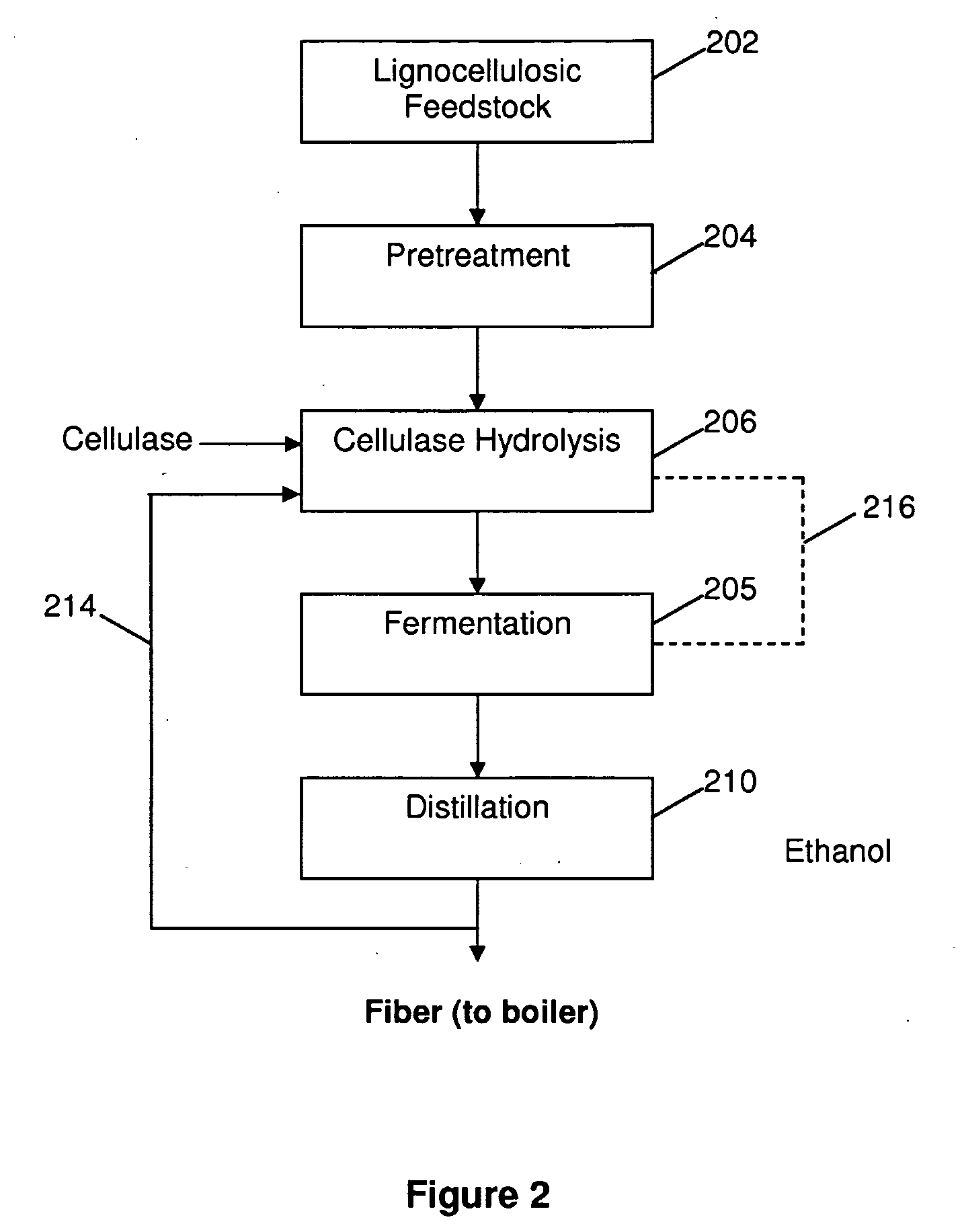
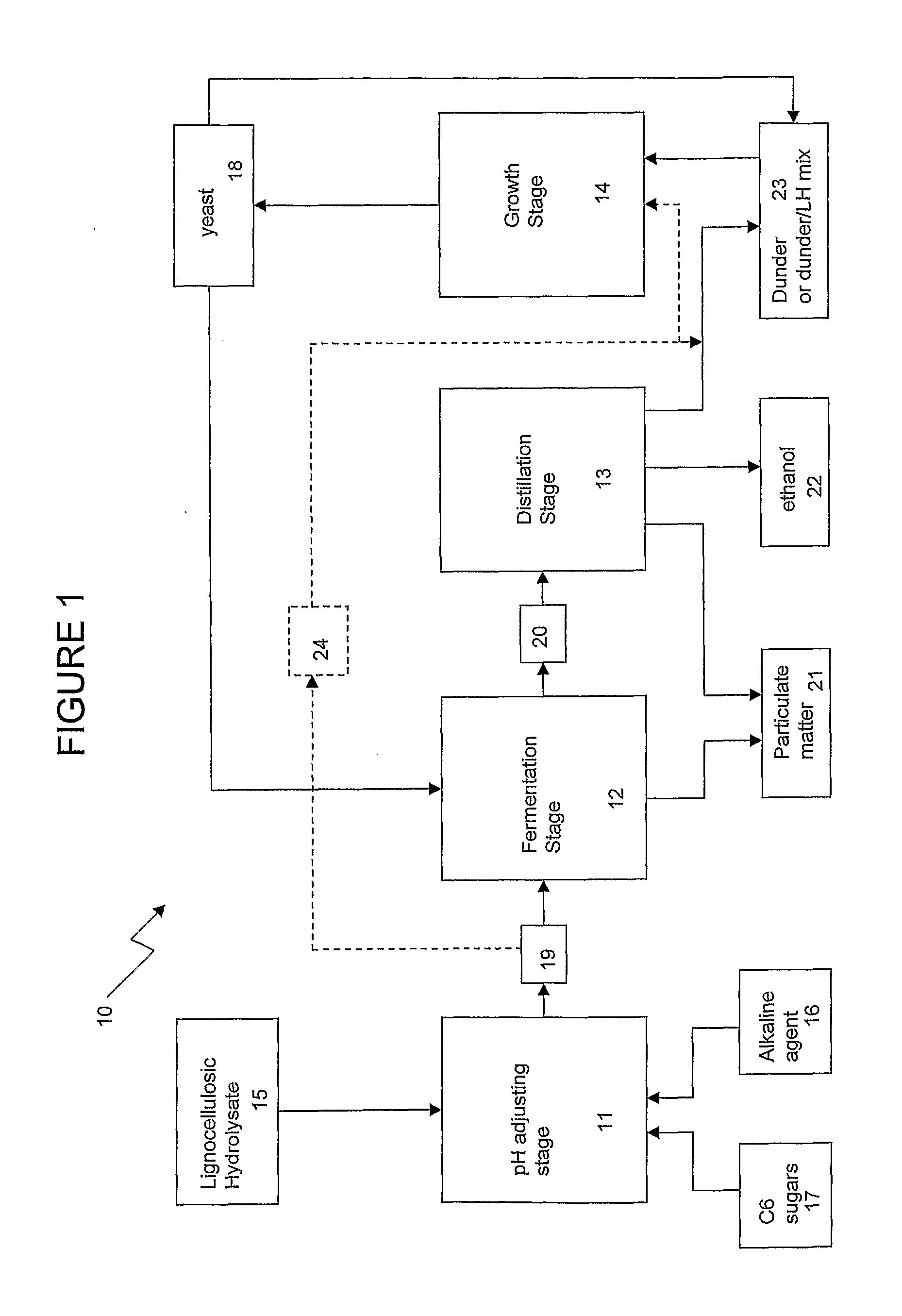
Method for the production of alcohol from a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock
ActiveUS20090035826A1Increase volumeIncrease productionFermented solutions distillation/rectificationBiofuelsAlcoholSlurry
A process for the production of glucose from a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock is provided. The method comprises enzymatically hydrolyzing the pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock with cellulase enzymes to produce a hydrolyzate slurry comprising glucose and unhydrolyzed cellulose and fermenting the hydrolyzate slurry in a fermentation reaction to produce a fermentation broth comprising alcohol. A process stream is obtained comprising unhydrolyzed cellulose, which is then subjected to a denaturing step, preferably comprising exposing the unhydrolyzed cellulose to elevated temperatures, thereby producing a heat-treated stream comprising the unhydrolyzed cellulose. The heat-treated stream comprising unhydrolyzed cellulose is then further hydrolyzed with cellulase enzymes to hydrolyze the cellulose to glucose.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
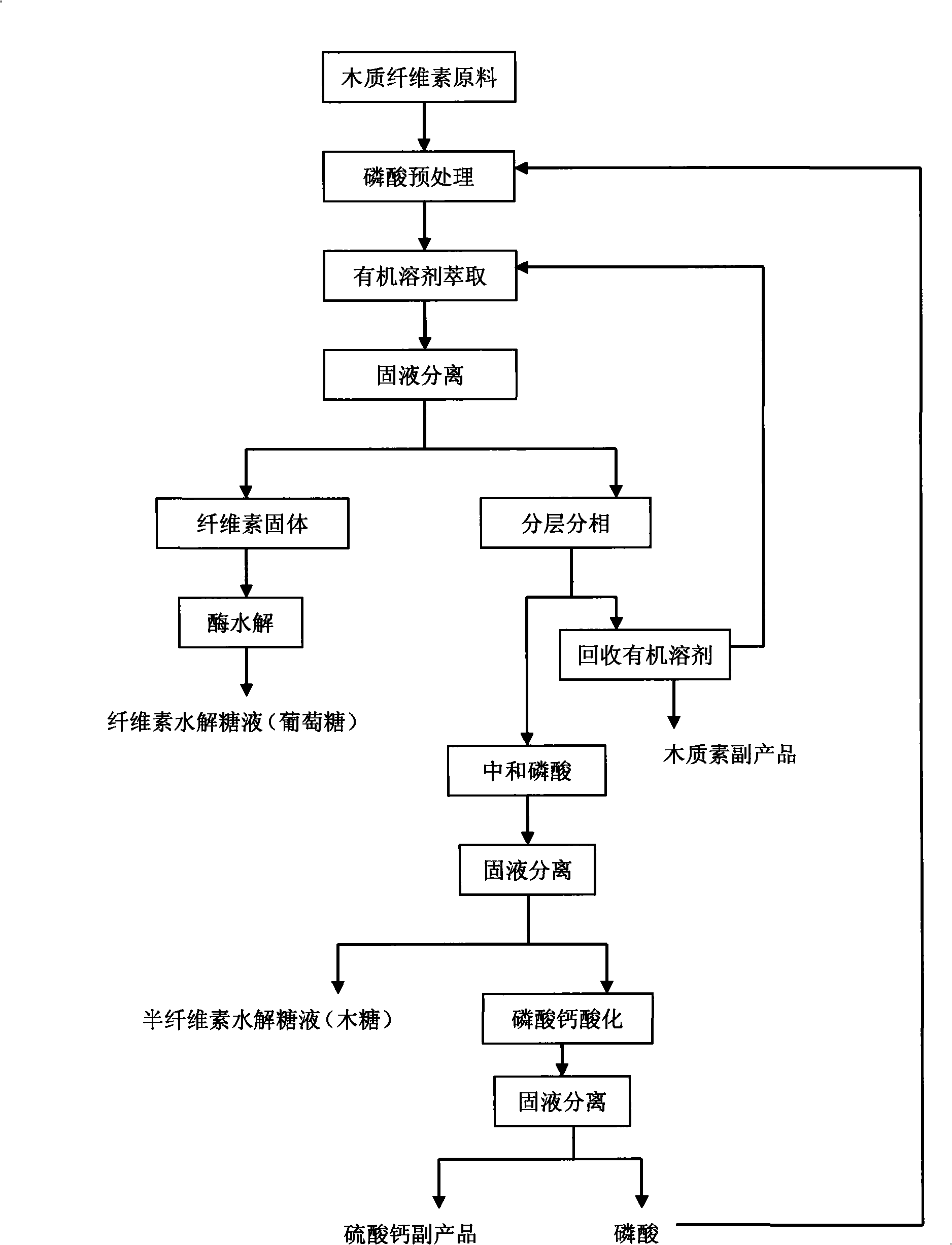
Process for preparing multicomponent liquid glucose and lignose while effectively hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveCN101285106ASimple recycling processNot volatileSulfate preparationLignin derivativesLiquid glucoseFiltration
The invention discloses a method for efficiently hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass and synchronously preparing multi-component liquid glucose and lignin. The method comprises the steps that: the lignocellulosic biomass through physical crushing is added with phosphoric acid to perform acid hydrolysis; then organic solvent is added to extract the lignin, the layering and the phase separation are performed, then the lignin is extracted out while the organic solvent is reclaimed under the condition of pressure reduction and distillation; phosphoric acid can be reclaimed through steps such as neutralization, filtration, acidification and so on, hemicellulose hydrolyzed liquid glucose is obtained at the same time; and the remained cellulose undergoes the zymohydrolysis to prepare cellulosic hydrolyzed liquid glucose. The method can separate lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose, remarkably decreases the degree of crystallinity of the cellulose hydrolyzed by phosphoric acid, and remarkably improves the zymohydrolysis efficiency; and the prepared hydrolyzed liquid glucose does not contain fermentation inhibitors. The method has mild treatment conditions, simple process and less side reactions; the phosphoric acid and the organic solvent can both be reclaimed and circularly used; and the method is environment-friendly, and has broad social and economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Biomass pretreatment
ActiveUS8030030B2Improvement in yield and rateImprove efficiencyHydrolasesBiofuelsPretreatment methodReaction rate
A method for lignocellulose conversion to sugar with improvements in yield and rate of sugar production has been developed by using ionic liquid pretreatment. This new pretreatment strategy substantially improves the efficiency (in terms of yield and reaction rates) of saccharification of lignocellulosic biomass. Cellulose and hemicellulose, when hydrolyzed into their sugars, can be converted into ethanol fuel through well established fermentation technologies. These sugars also form the feedstocks for production of variety of chemicals and polymers. The complex structure of biomass requires proper pretreatment to enable efficient saccharification of cellulose and hemicellulose components to their constituent sugars. Current pretreatment approaches suffer from slow reaction rates of cellulose hydrolysis (by using the enzyme cellulase) and low yields.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF TOLEDO +1
Lignocellulose acid/alkali coupling pretreatment method
InactiveCN102153763ARealize the separation of all componentsHigh purity of componentsFermentationSaccharides productionSolid componentPretreatment method
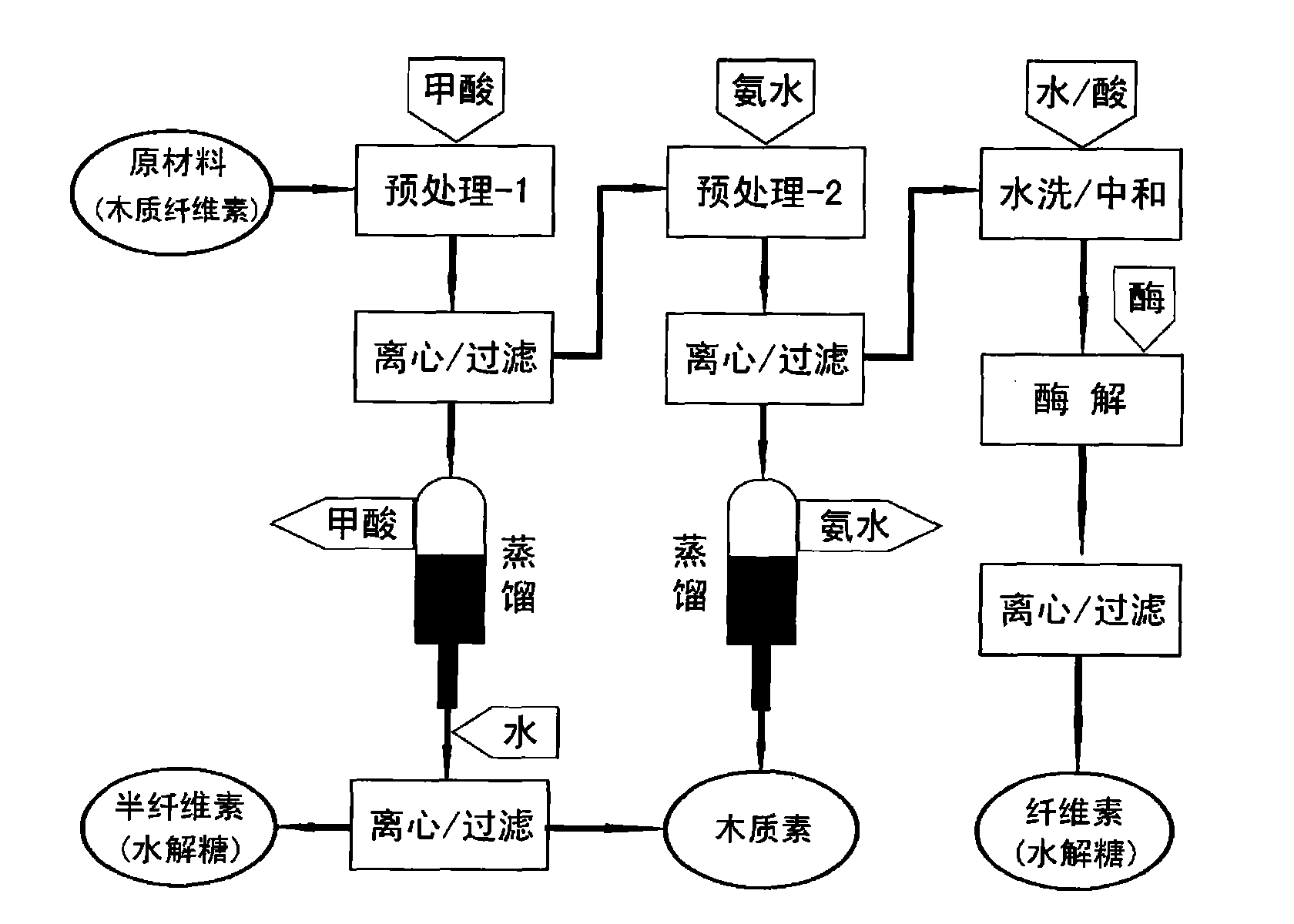
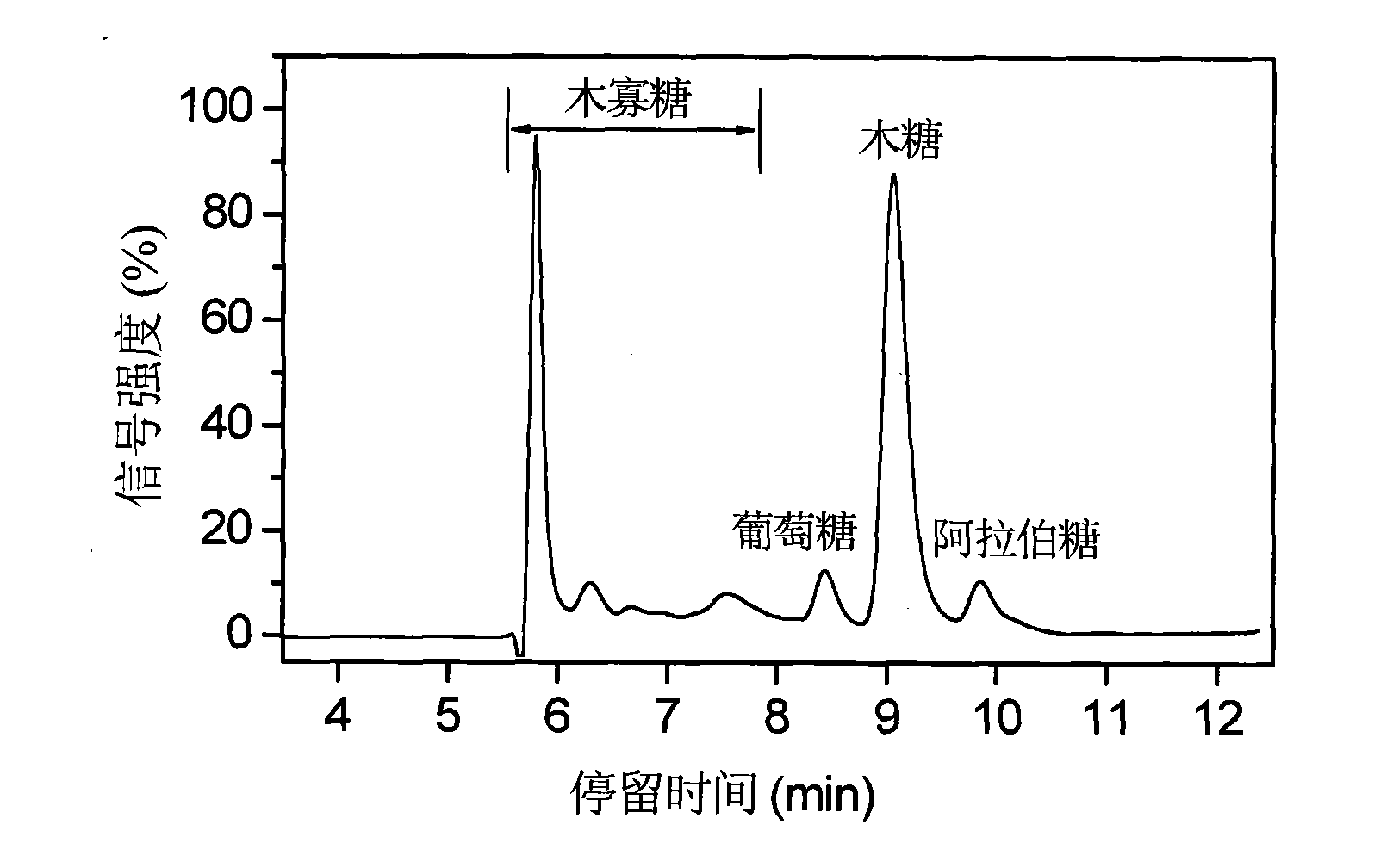
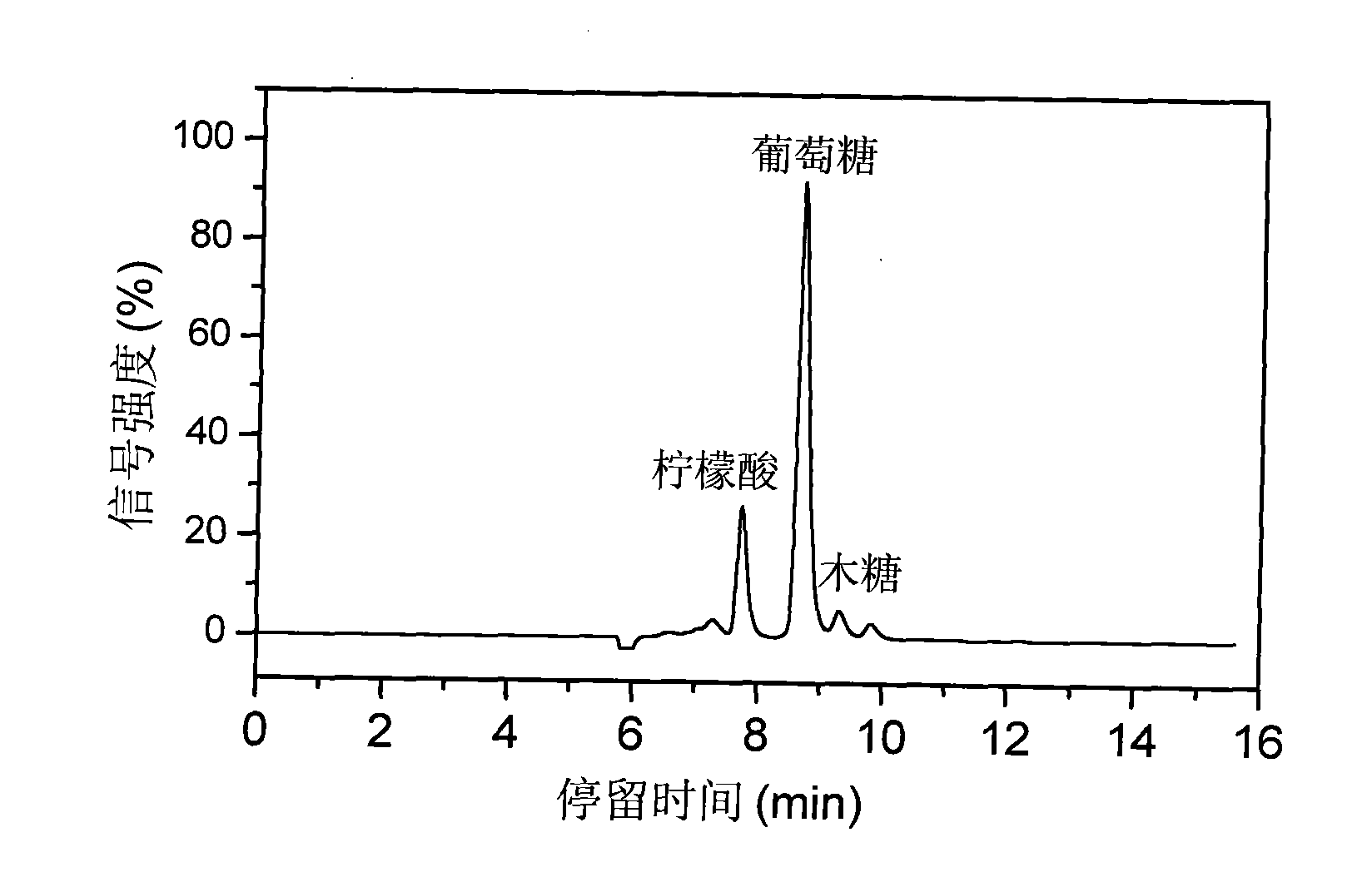
The invention relates to a lignocellulose acid / alkali coupling pretreatment method. Lignocellulose is separated into cellulose, hemicellulose and lignin by acid / alkali coupling pretreatment; and simultaneously, lignocellulose components are separated and subjected to high-efficiency enzymolysis and saccharification. The method comprises the steps of lignocellulose pretreatment, component separation, cellulose enzymolysis, solvent recovery and the like. The lignocellulose material is pretreated by formic acid or dilute sulphuric acid and is then subjected to solid-liquid separation, wherein the liquid component is used for recovering hemicellulose hydrolyzed sugar and part of lignin; and the solid component is further treated by ammonia water or a sodium hydroxide solution and is then subjected to solid-liquid separation, the liquid component is used for recovering lignin, and the solid component (cellulose) is subjected to enzymolysis and saccharification. By converting the lignocellulose into cellulose hydrolyzed sugar (glucose), hemicellulose hydrolyzed sugar (xylose and xylooligosaccharide) and lignin, the invention provides a basis for full-biomass utilization and develops a green process route for recovering the pretreatment solvent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Process for alcoholic fermentation of lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveUS20100159552A1Lower cost of capitalReduce operating costsBiofuelsFermentationCelluloseHydrolysate
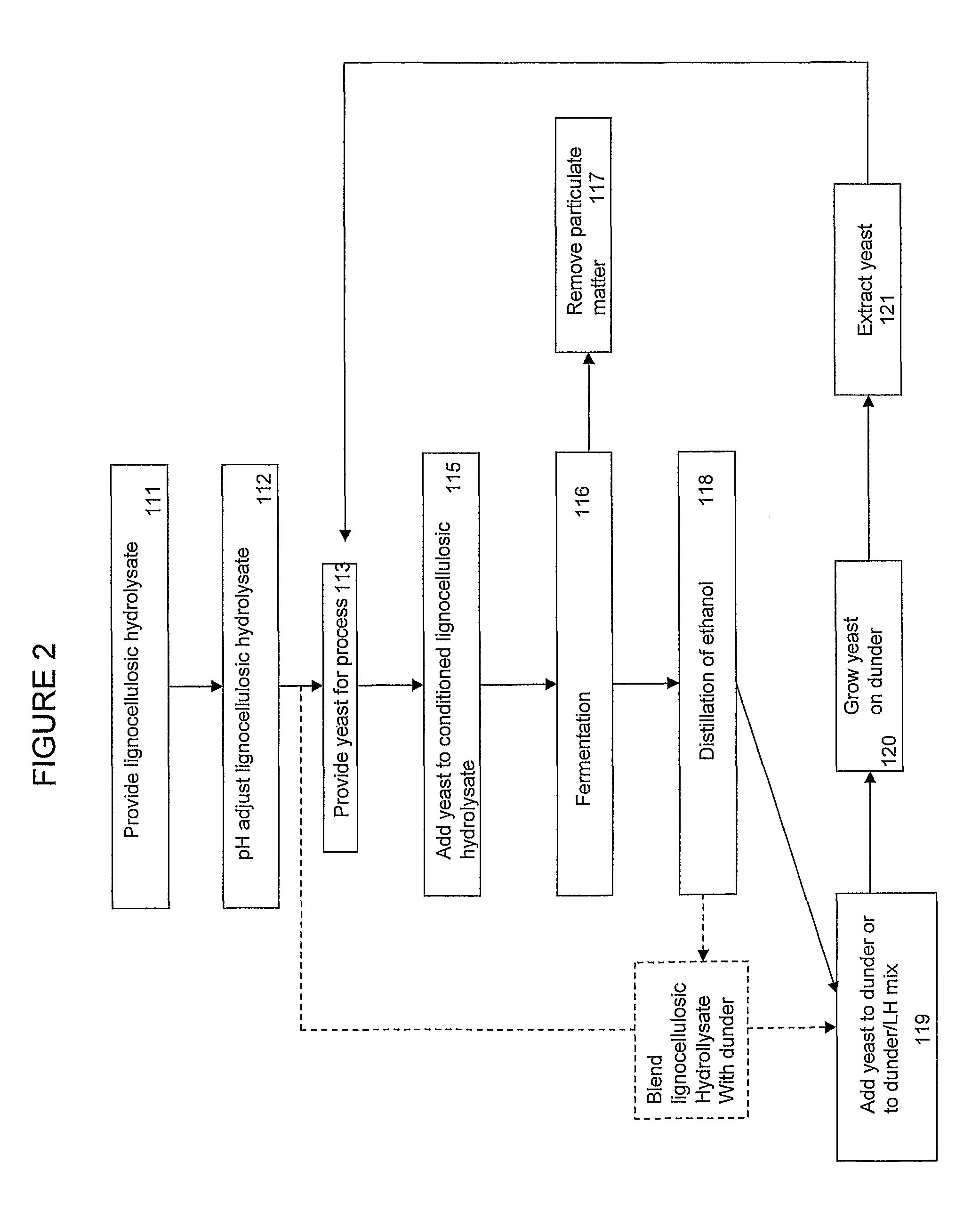
A process for the production of ethanol wherein a hydrolyzed lignocellulosic biomass is fermented in the presence of a stillage residue. The fermentation of cellulosic hydrolysates is improved by adding prior to and / or during fermentation a stillage residue side stream from a corn starch-to-ethanol process as a nutrient source for the yeast organisms used in the fermentation. Stillage residues from the grain dry mill ethanol producing process, including the whole stillage, wet cake, thin stillage, and / or syrup are added to assist as a nitrogen and nutrient source for the fermentive processes. The stillage residue is produced by any grain-to-ethanol process.
Owner:GREENFIELD SPECIALTY ALCOHOLS
Composite microbial flora and enzyme product thereof, and method of applying composite microbial flora and enzyme product thereof in soil restoration
InactiveCN105176866AReduce the amount of applicationNo pollutionAgriculture tools and machinesFungiPhytaseFlora
The invention provides a composite microbial flora and an enzyme product thereof, and a method of applying the composite microbial flora and the enzyme product thereof in soil restoration. The composite microbial flora is composed of a microbial flora and a bioactive enzyme, wherein the microbial flora is composed of bacillus subtilis, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus amyloliquefaciens, pediococcus pentosaceus, pichia farinose and pediococcus acidilactici, and the bioactive enzyme is composed of phytase, protein hydrolase, cellulose hydrolase and urease. Compared with the prior art, an effective microbial community and a microecological environment are constructed to realize biological catalysis and improve the content of organic matters and beneficial microbial flora in soil, and thus, the fertility of the soil is improved; biochemical degradation rate of soil pollutant can be substantially accelerated, digestion and biodegradation of the pollutant can be accelerated, and final inertial products like carbon dioxide, water and nitrogen are obtained; and toxic intermediate produced in the process of biochemical degradation can be rapidly removed, odor is eliminated, and emission of organic volatile matters (VOC) is reduced.
Owner:TERRABIOTA BEIJING AGRI SCI & TECH
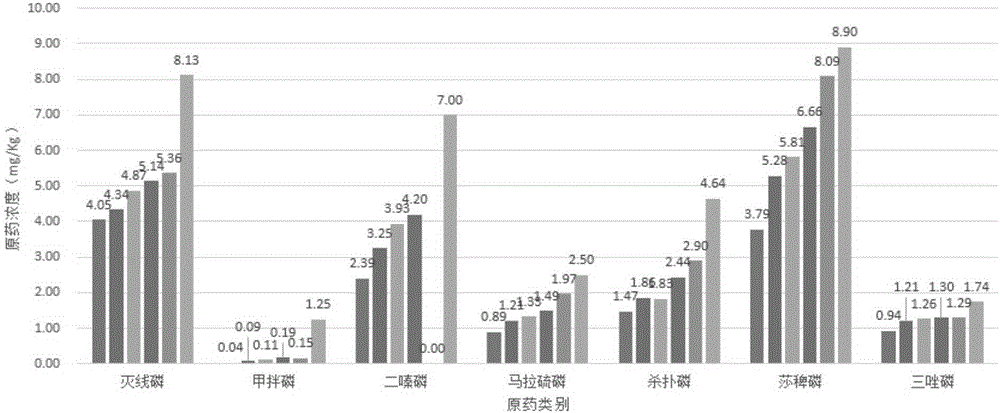
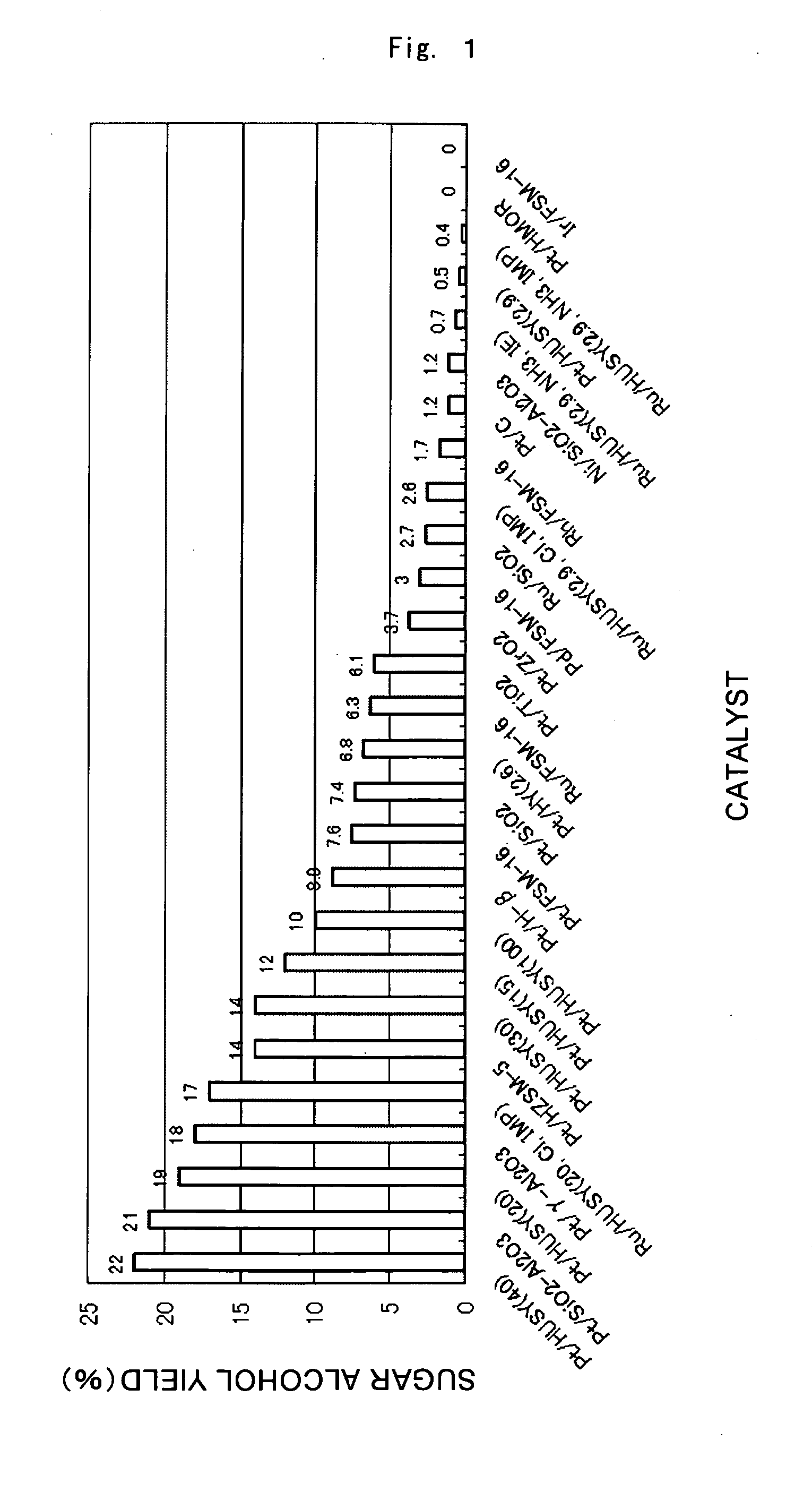
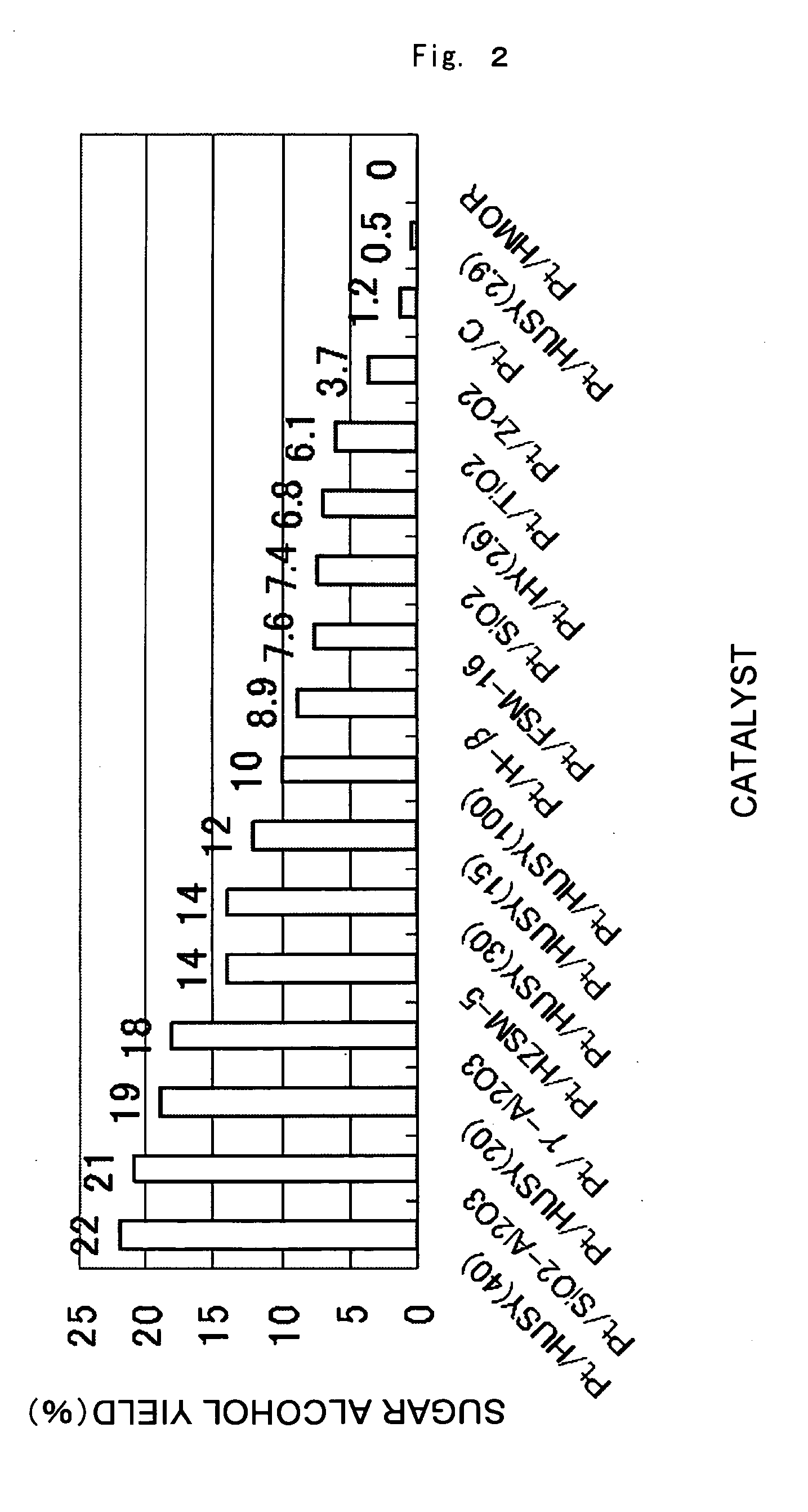
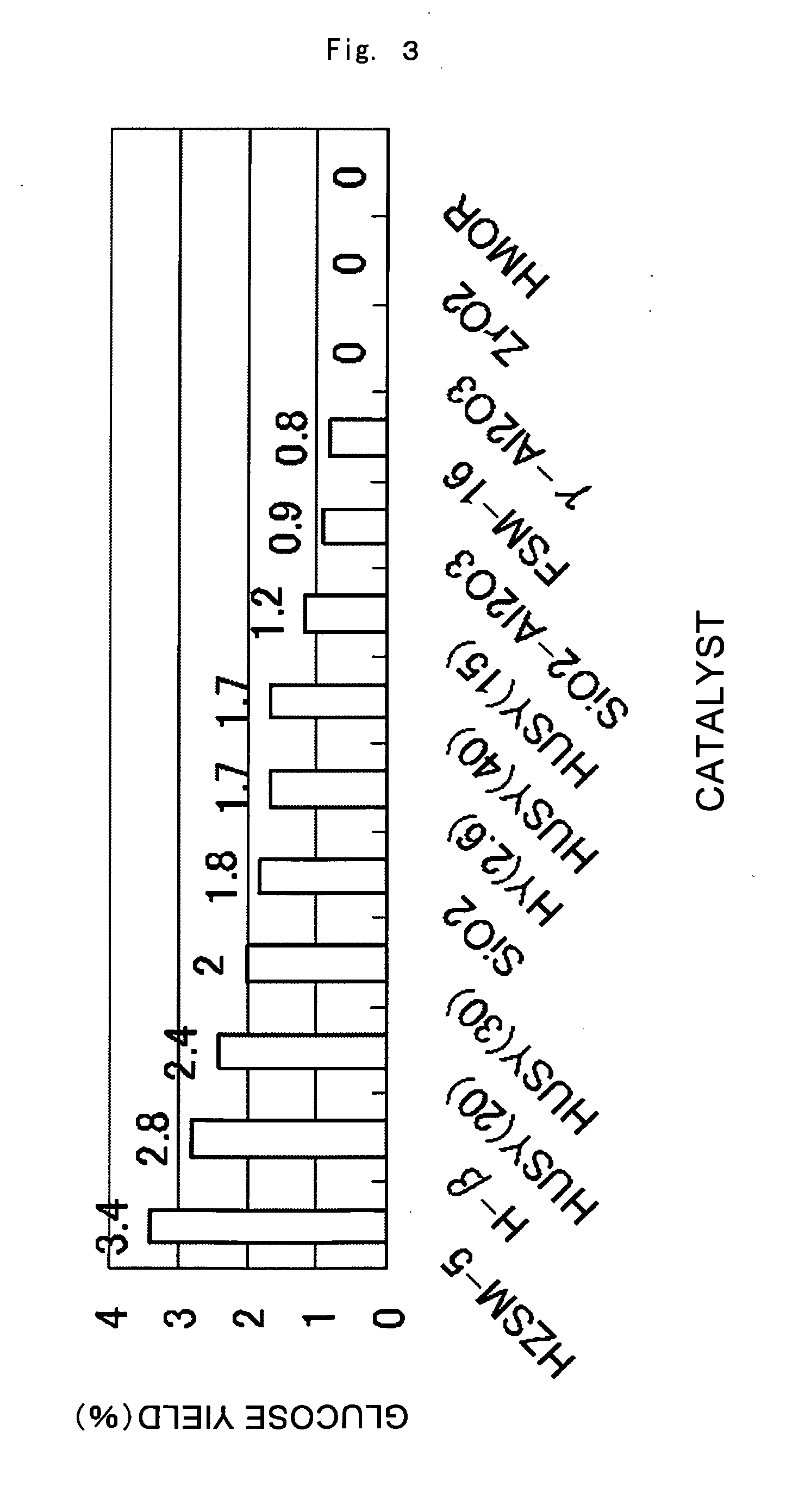
Catalyst for Cellulose Hydrolysis and/or Reduction of Cellulose Hydrolysis Products and Method of Producing Sugar Alcohols From Cellulose
A catalyst for cellulose hydrolysis and / or the reduction of hydrolysis products, in which a transition metal of group 8 to 11 is supported on a solid support. A method of producing sugar alcohols comprising: hydrolyzing cellulose in the presence of the catalyst in a hydrogen-containing atmosphere with pressurization; and reducing the hydrolysis product of cellulose. Provided are a catalyst for use in the production of sugar alcohols by the hydrolysis and hydrogenation of cellulose that affords easy separation of catalyst and product, and that does not require pH adjustment, acid or alkali neutralization, or activation of the catalyst during reuse, and a method of producing sugar alcohols from cellulose employing this catalyst.
Owner:HOKKAIDO UNIVERSITY
Production of alcohol from mixed bacterial population degradable fermented bastose substance
InactiveCN1896254AReduce degradationShorten the fermentation cycleBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesAlcohol productionCellulose degradation
Production of alcohol from mixed microbial pool degradable and fermented lignocellulose substance is carried out by crushing lignocellulose substance, soaking with H2SO4, bursting by steam, solid-liquid separating, adding nutritive liquid into solid-phase substance, sterilizing, adding distiller's yeast and cellulose degrading microbe into saccharifying fermentative substrate, degradation saccharifying-fermenting synchronously, distilling and rectifying to obtain final product. It is simple, has short saccharifying and fermenting period, higher raw material utilization rate and more alcohol yield and no feedback inhibition function.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
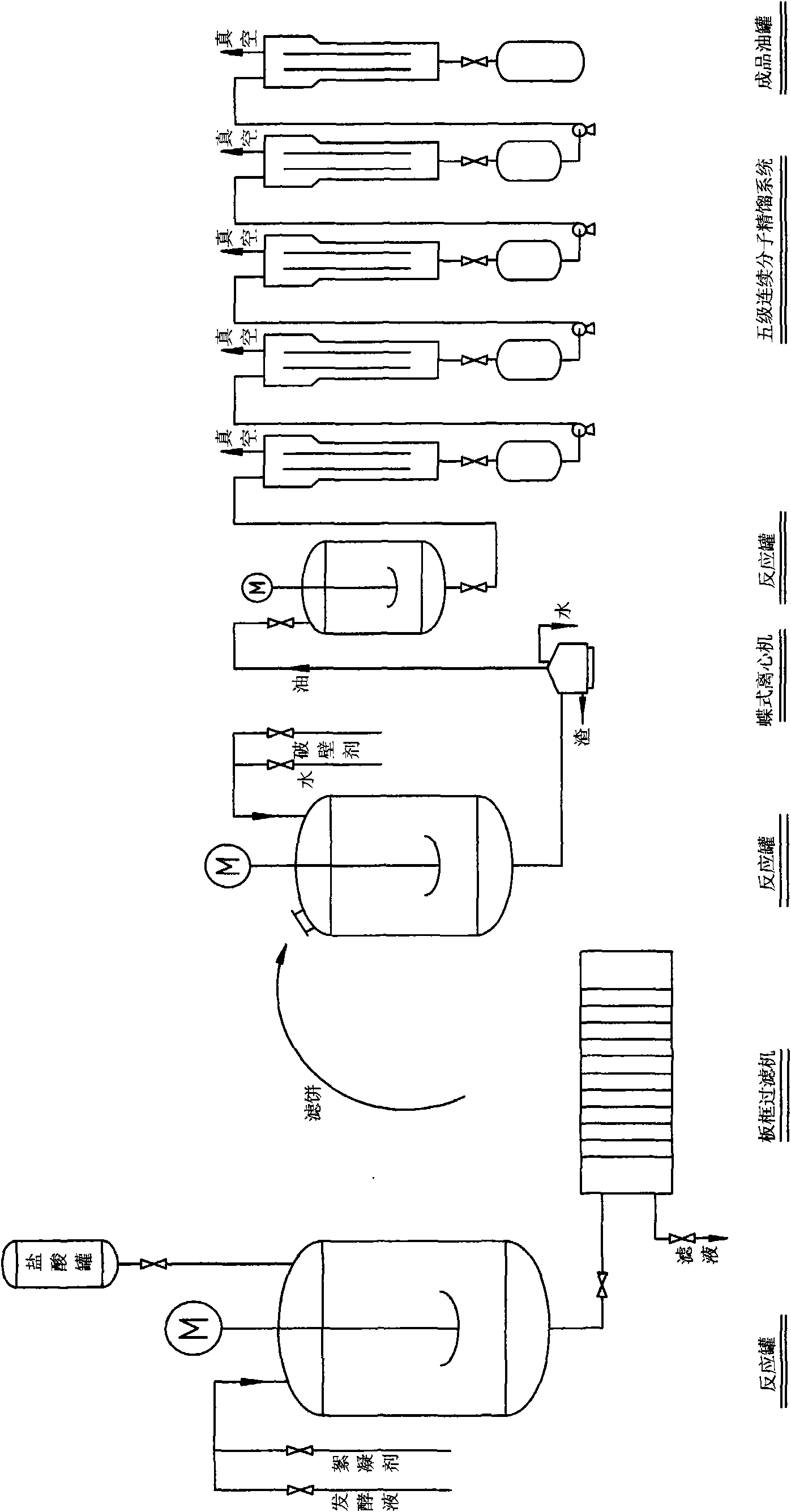
Method of extracting DHA unsaturated fatty acid from dino flagellate fermentation liquor
ActiveCN101585759AReduce usageAchieve decolorizationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationCelluloseFlagellate
The invention discloses a method of extracting DHA unsaturated fatty acid from dino flagellate fermentation liquor; the method comprises the main processes of: firstly adjusting pH value of dino flagellate fermentation liquor by using hydrochloric acid solution, taking non-residual monomer polyacrylamide as flocculant for flocculating; filtering by flocculating frame to obtain filter cake; breaking the filter cake by broken liquid prepared by adding water in compound cellulose hydrolase; after breaking, using centrifugal machine to realize three-phase separation of residue, aqueous phase and oil phase, repeating 2 to 5 times until no oil phase existing, combining the oil phase and washing, that is DHA crude oil; the crude oil entering into five class continuous molecular to distill, thereby obtaining unsaturated fatty acid having 40-50% of DHA. The invention uses high speed centrifuge with rotation rate being 8000 to 12000 rpm to separate to directly obtain crude oil, avoids the use of organic solvent; the refining of the crude oil utilizes five class molecular distillation, which can effectively achieve the effects of decolorization, deacidification and deodorization. The invention has low process cost and is environment-friendly.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA KINGDOMWAY PHARMA LTD +1
Cellulose Ester and Production Method Thereof
ActiveUS20090043088A1Good optical performanceImprove optical isotropySugar derivativesProjectorsOptical propertyChemical composition
A cellulose ester and film thereof useful for remarkably improving optical properties such as optical isotropy are provided. The cellulose ester is adjusted so that the degree of substitution is from 2.90 to 2.965, the total of degrees of substitution at 2- and 3-positions is not less than 1.97, and the half height width of chemical composition expressed in degree of substitution is not more than 0.09. Such a cellulose ester maybe produced by a method for producing a cellulose ester, which comprises (i) an acylating step for acylating a cellulose with an acylating agent in the presence of a sulfuric acid catalyst, and (ii) a hydrolyzing step for hydrolyzing the acylated product in the presence of a sulfuric acid catalyst, and in which the acylation carried out with from 1.40 to 2.0 molar equivalents of the acylating agent relative to 1 mol of a hydroxyl group in the cellulose in the presence of 6.5 to 9.5 parts by weight of the sulfuric acid catalyst relative to 100 parts by weight of the cellulose in the acylating step (i).
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Method of producing yeast biomass
InactiveUS20110183394A1Reduces biological oxygen demandReducing chemical and biological oxygen demandFungiBiofuelsCelluloseYeast biomass
The invention relates to use of a substrate comprising C5 compound-containing material, in the growth of Saccharomyces yeast or the production of a product of Saccharomyces yeast, wherein the C5 compound-containing material is: (a) C5 compound-containing material obtained from lignocellulosic hydrolysate; (b) C5 compound-containing material obtained from fermentation of lignocellulosic hydrolysate; or (c) a mixture of (a) and (b). The invention also relates to a method of producing Saccharomyces yeast biomass or a product of Saccharomyces yeast using the substrate, and to methods of producing ethanol comprising incubating Saccharomyces yeast produced by the use or method. The invention further relates to strains of Saccharomyces yeast suitable for the use or methods.
Owner:MICROBIOGEN PTY LTD
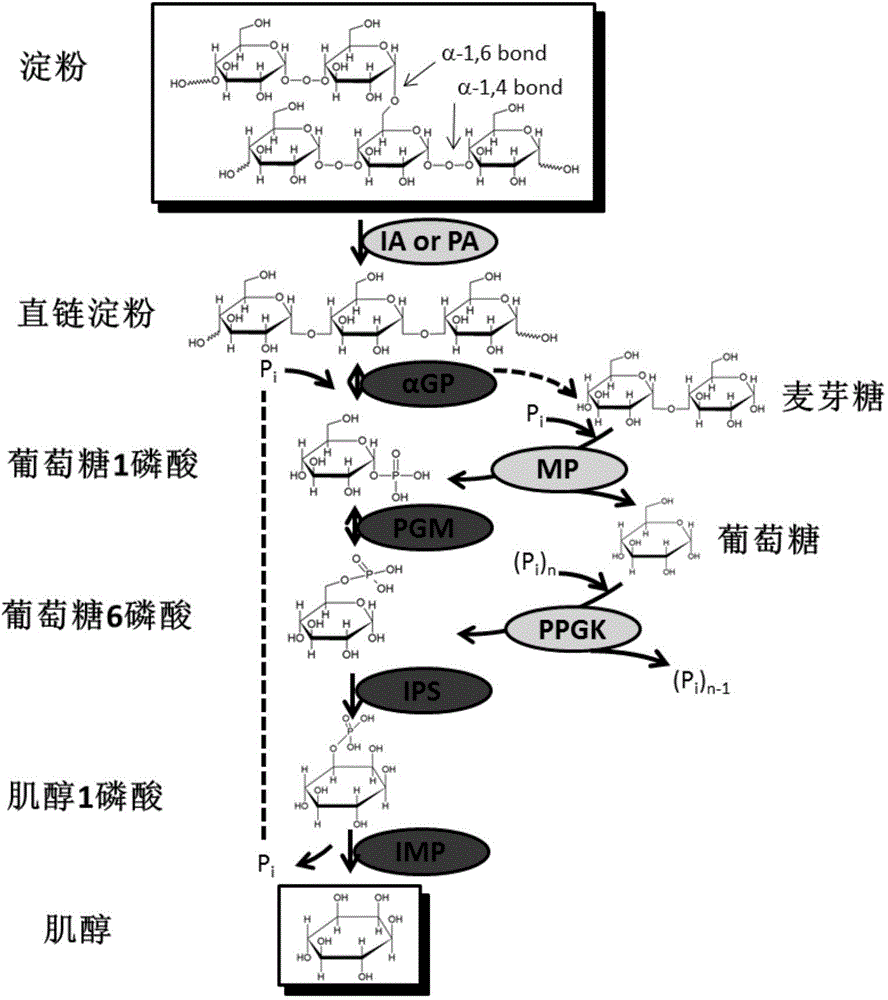
Inositol preparing method
ActiveCN106148425AIncrease profitReduce separation costsHydrolasesFermentationProcess optimizationCellulose
The invention discloses an inositol preparing method and belongs to the field of enzymatic preparation of inositol. According to the method, starch, cellulose or derivatives thereof are used as substrates and converted into inositol in a multi-enzyme reaction system through in-vitro multi-enzyme efficient catalysis. By conducting process optimization, adding enzymes capable of promoting starch or cellulose hydrolysis and utilizing the enzyme of the byproduct glucose, the multi-enzyme reaction system is established, and raw material conversion efficiency and inositol yield are improved remarkably. By the adoption of the method, raw material conversion rate is high, inositol yield is high, steps are simple, production cost is low, influence on the environment is small, and large-scale production of inositol can be achieved.
Owner:CHENGDU BOHAODA BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Recombinant yeast strain capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose and application thereof
The invention discloses a recombinant yeast strain (Saccharomyces cerevisiae)) capable of efficiently metabolizing xylose, which is named SyBE005. The recombinant yeast strain has been collected in Common Microorganism Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, the collection number is CGMCC No.6634, and the recombinant yeast strain has the capacity of efficiently metabolizing xylose to produce ethanol. The recombinant yeast strain SyBE005 can effectively ferment xylose to generate ethanol. The ethanol yield reaches 64% of the theoretical yield, and the yield of the byproduct xylitol is lower than 12%; and thus, the recombinant yeast strain can efficiently convert xylose into ethanol, and is an excellent strain utilizing cellulose hydrolysate.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
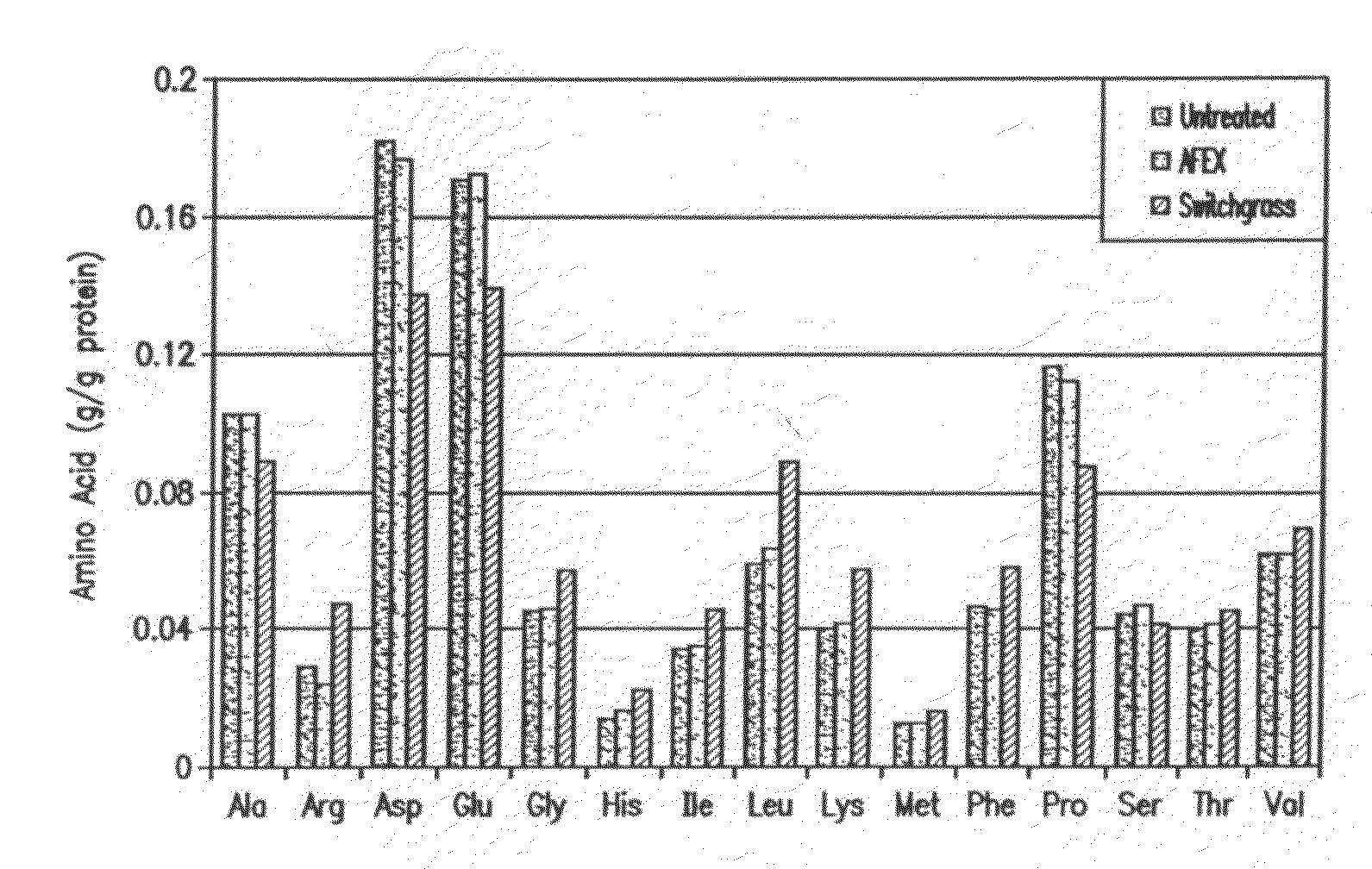
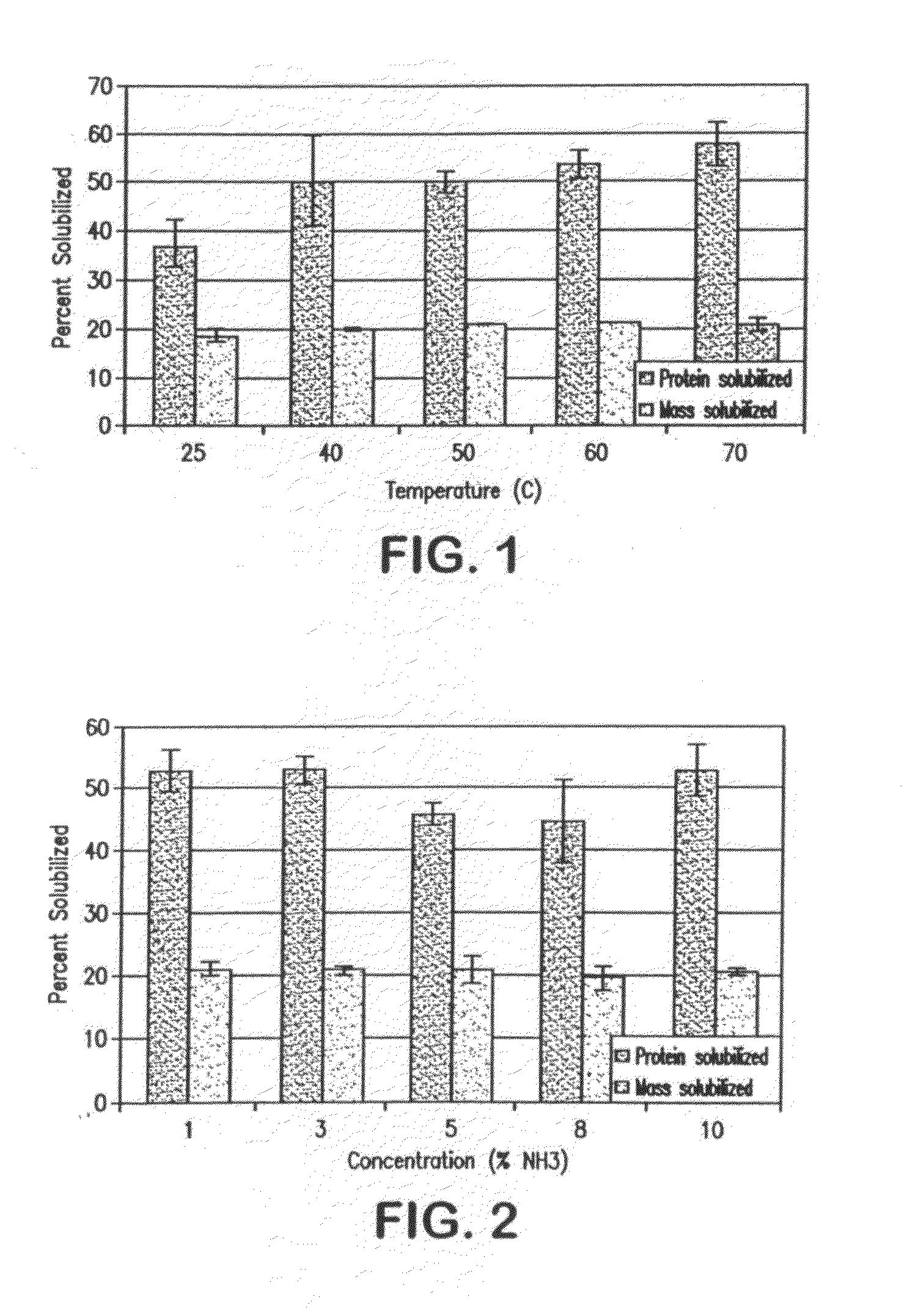
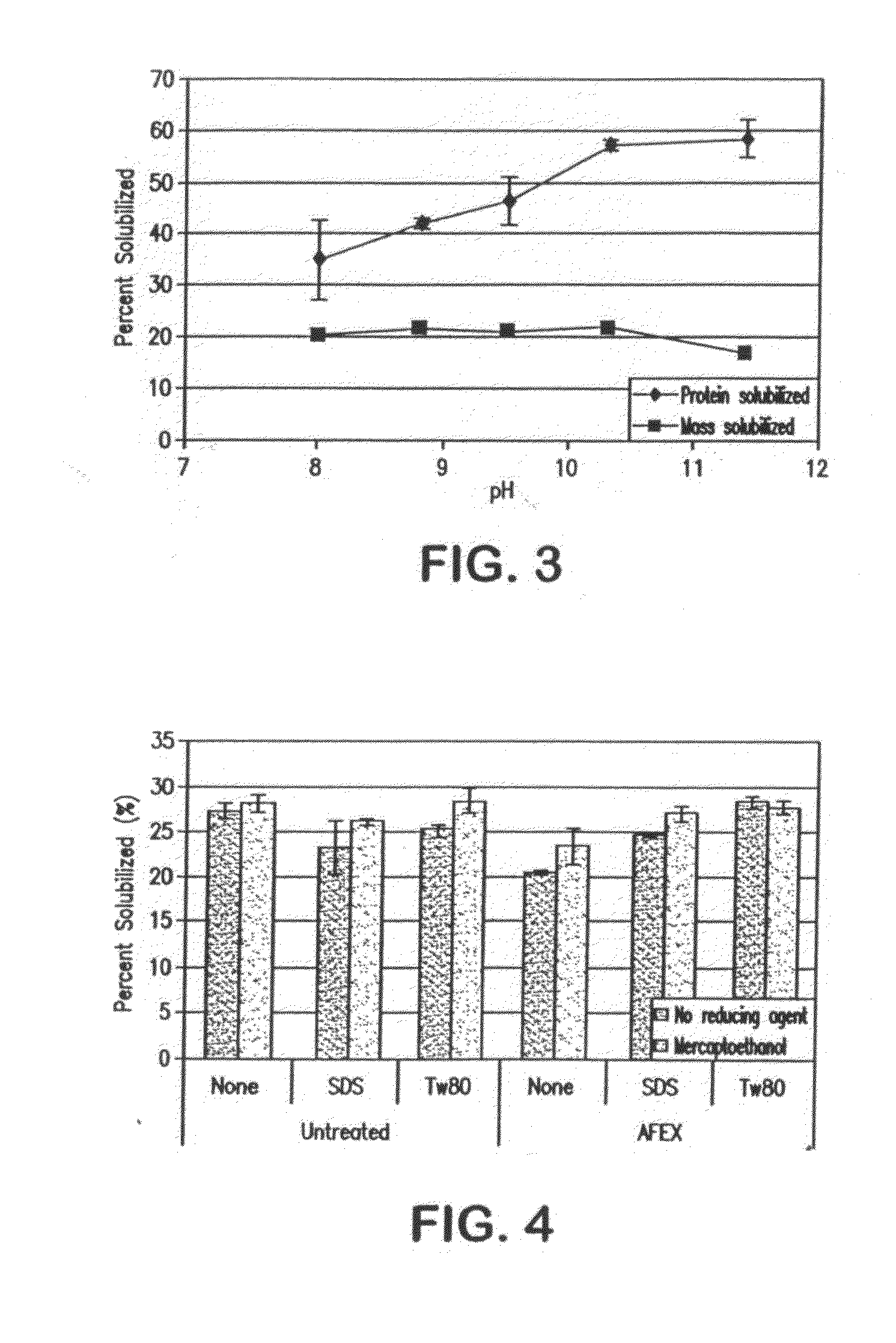
Separation of Proteins from Grasses Integrated with Ammonia Fiber Explosion (AFEX) Pretreatment and Cellulose Hydrolysis
A process for extracting an aqueous ammonium hydroxide solution from a plant biomass after an Ammonia Fiber Explosion (AFEX) process step, is described. The proteins can be separated before or after a hydrolysis of sugar precursors (carbohydrates) from the biomass to produce sugars for fermentation to produce ethanol. The proteins are useful as animal feeds because of their amino acid food values.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Method for promoting hydrolysis of lignocellulose
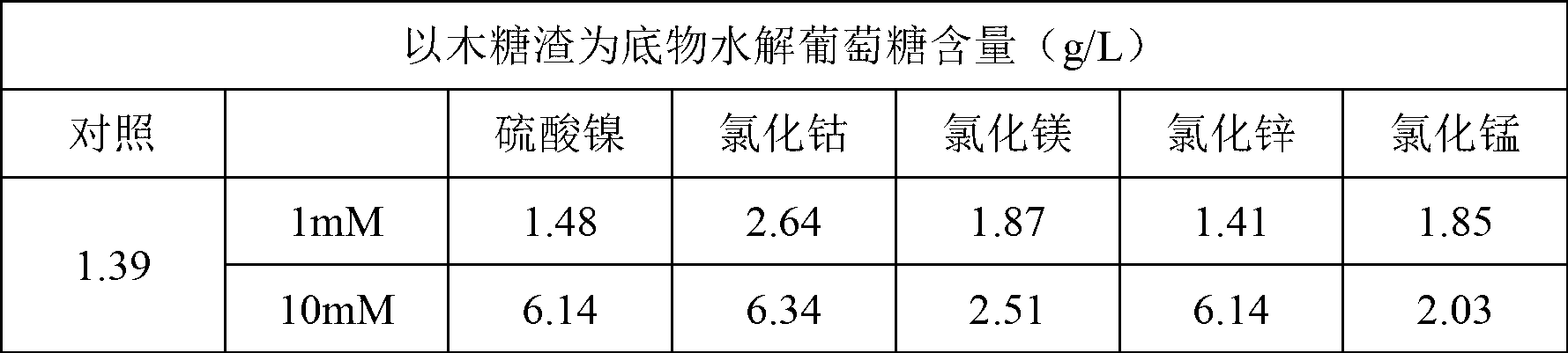
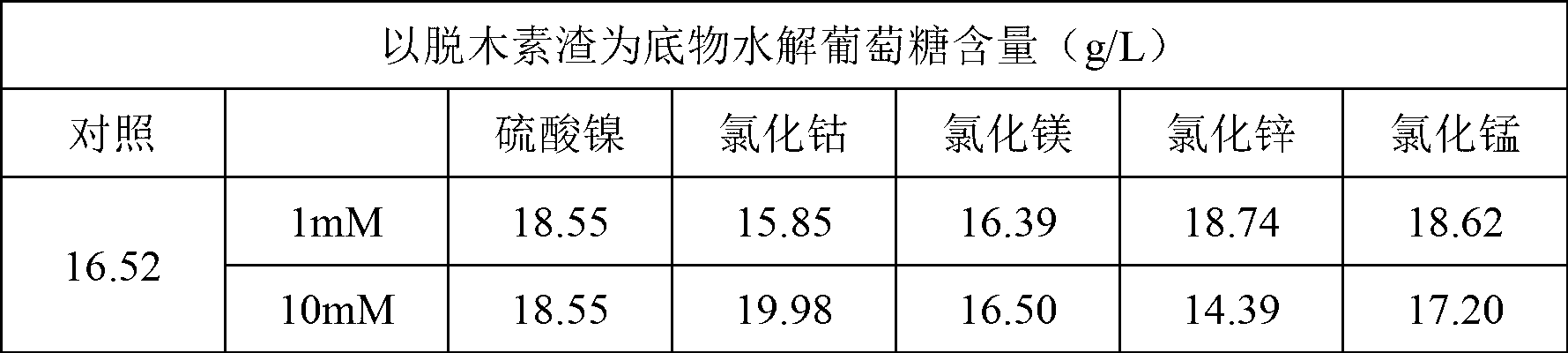
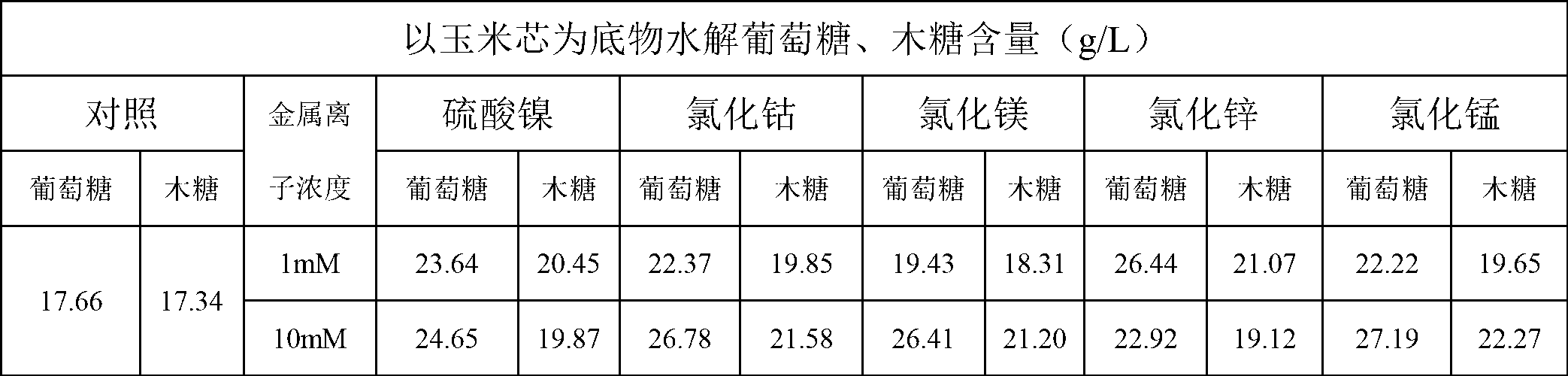
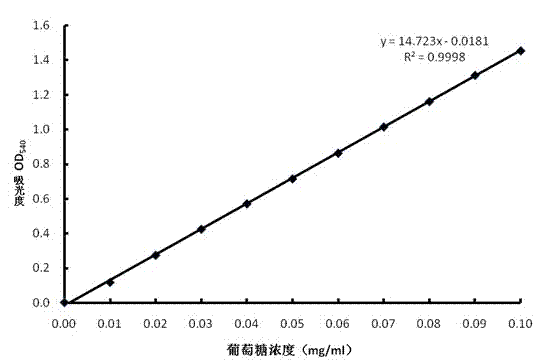
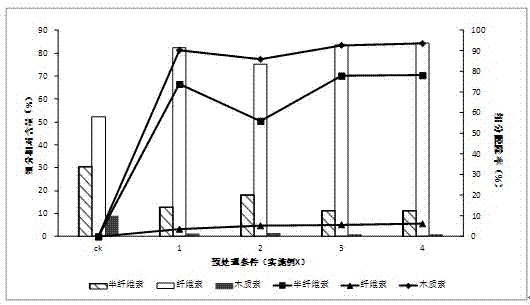
The invention discloses a method for promoting hydrolysis of lignocelluloses. According to the method, metal ions such as nickel, cobalt, magnesium, zinc, manganese and the like are added in the processes of saccharifying and hydrolyzing the lignocelluloses so as to improve the enzyme activity of the ligno-cellulase and hemicellulase, thereby further improving the hydrolysis efficiency of the ligno-cellulase. Proved by experiments, the hydrolysis efficiency of glucan can be improved by 4.5 times by adding the metal ions. According to the method, the operation is simple, the metal ions can be recycled, the investment cost is low, the usage range is wide, the pollution does not exist, the hydrolysis efficiency of the cellulose is obviously improved, and the method can be widely applied in the process of hydrolyzing the lignocelluloses and in the fields of manufacturing and developing biomass energy.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV +1
Bagasse pretreatment method
InactiveCN103205473AIncrease hydrolysis rateIncrease contentFermentationPretreatment methodHemicellulose
The invention discloses a bagasse pretreatment method. The bagasse pretreatment method comprises the following steps of: drying, crushing and screening the bagasse, then pretreating the bagasse by using sodium hydroxide and hydrogen peroxide to obtain the pretreated bagasse. According to the pretreated bagasse material, the maximum removal rates of the hemicellulose and lignin respectively reach 78.18 percent and 94.56 percent, the maximum enzyme hydrolysis rate of the cellulose is 64.37 percent, and the enzymolysis efficiency is improved by 60.67 percent compared with that of untreated raw bagasse. Therefore, the pretreatment method breaks through wrapping of the hemicellulose and lignin to the cellulose, the hydrolysis rate of the cellulose is increased, the enzymolysis resistance property of the bagasse is improved, the obtained bagasse material can be used for converting high added value products, such as ethanol through microbial fermentation after being subjected to enzymolysis, and thus biomass resources, such as bagasse are effectively utilized.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Biological agent for organic waste composting and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102250769AWith hydrolysis functionShorten composting timeFungiBacteriaSludgeNitrifying bacteria
Owner:江苏新奇环保有限公司
Separation of tropical candiyeast strain and production of xylitol
ActiveCN1982460AHighlight substantiveSignificant progressMicroorganism based processesGenetic engineeringFiberHydrolysate
Separation of tropical moniliasis strain and production of xylitol are disclosed. The process is carried out by amplification culturing to obtain seed liquid, preparing hemicellulose hydrolyte culture medium, circulating and reutilizing. It has excellent sugar-tolerance and mithridatism. It could be used above time times.
Owner:唐传生物科技(厦门)有限公司
Method for preparing plant hemicellulose hydrolysis liquid and method for extracting xylose and gum sugar
InactiveCN101880329AAchieve mass productionSolve the capacity problem of popular applicationChemical recyclingHigh concentrationLiquid ratio
The invention provides a method for preparing plant hemicellulose hydrolysis liquid and a method for extracting xylose or gum sugar. The method for preparing the hemicellulose hydrolysis liquid comprises the steps of soaking, acid liquid pretreatment, heating hydrolysis, washing and the like. The problems of low sugar liquid concentration and large acid liquid reclaiming amount caused by a large liquid ratio when flowing water is boiled are solved by adopting a flowing water-free wet material boiling method; and on the other hand, reduction of sugar liquid concentration and dilution of acid liquid caused by changing water vapor into condensed water during directly heating the water vapor and preserving the heat are also avoided by adopting an indirect heating mode in a heat preservation boiling process so as to obtain high-concentration sugar liquid and reduce the concentration of the acid liquid used at initial soaking.
Owner:陈培豪
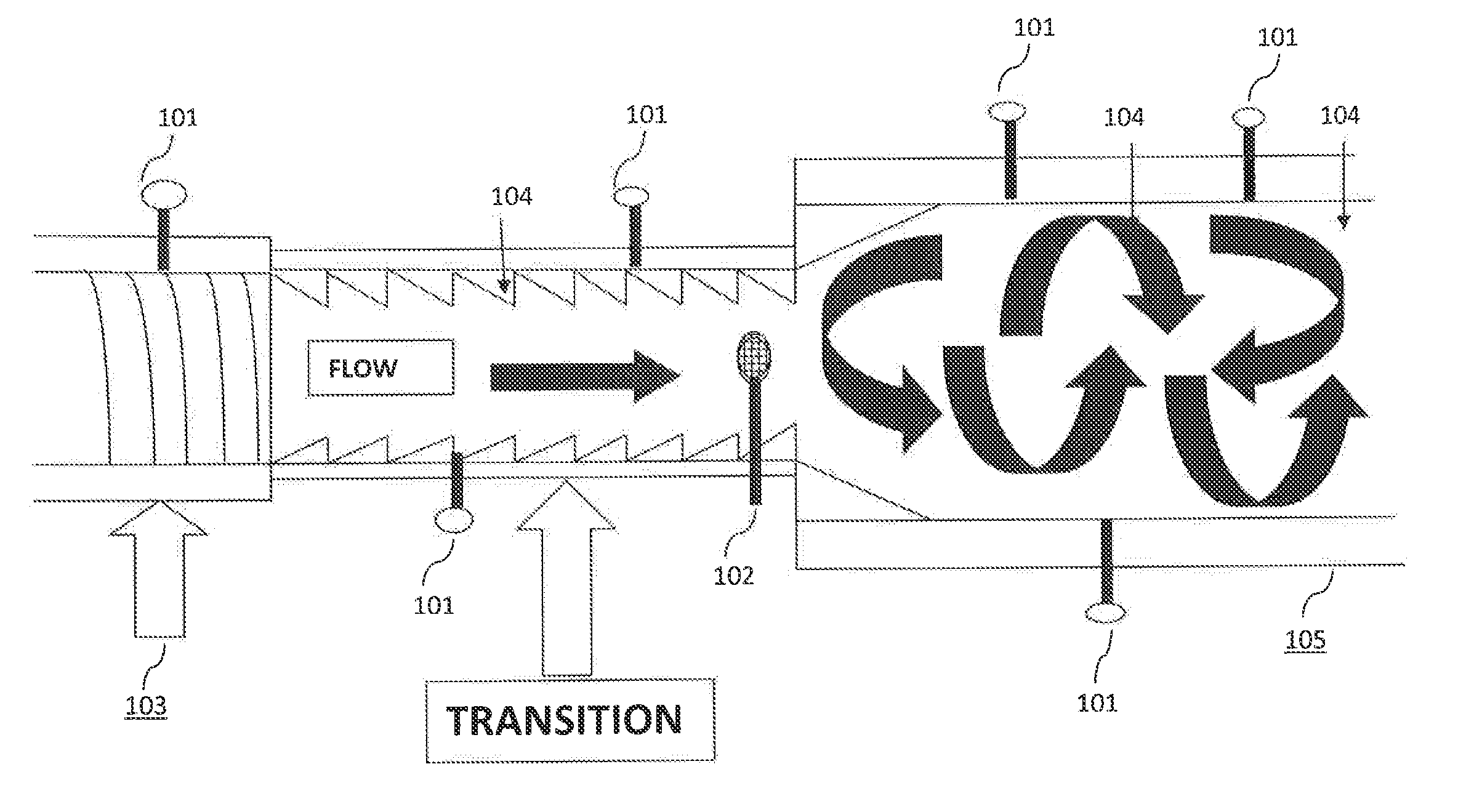
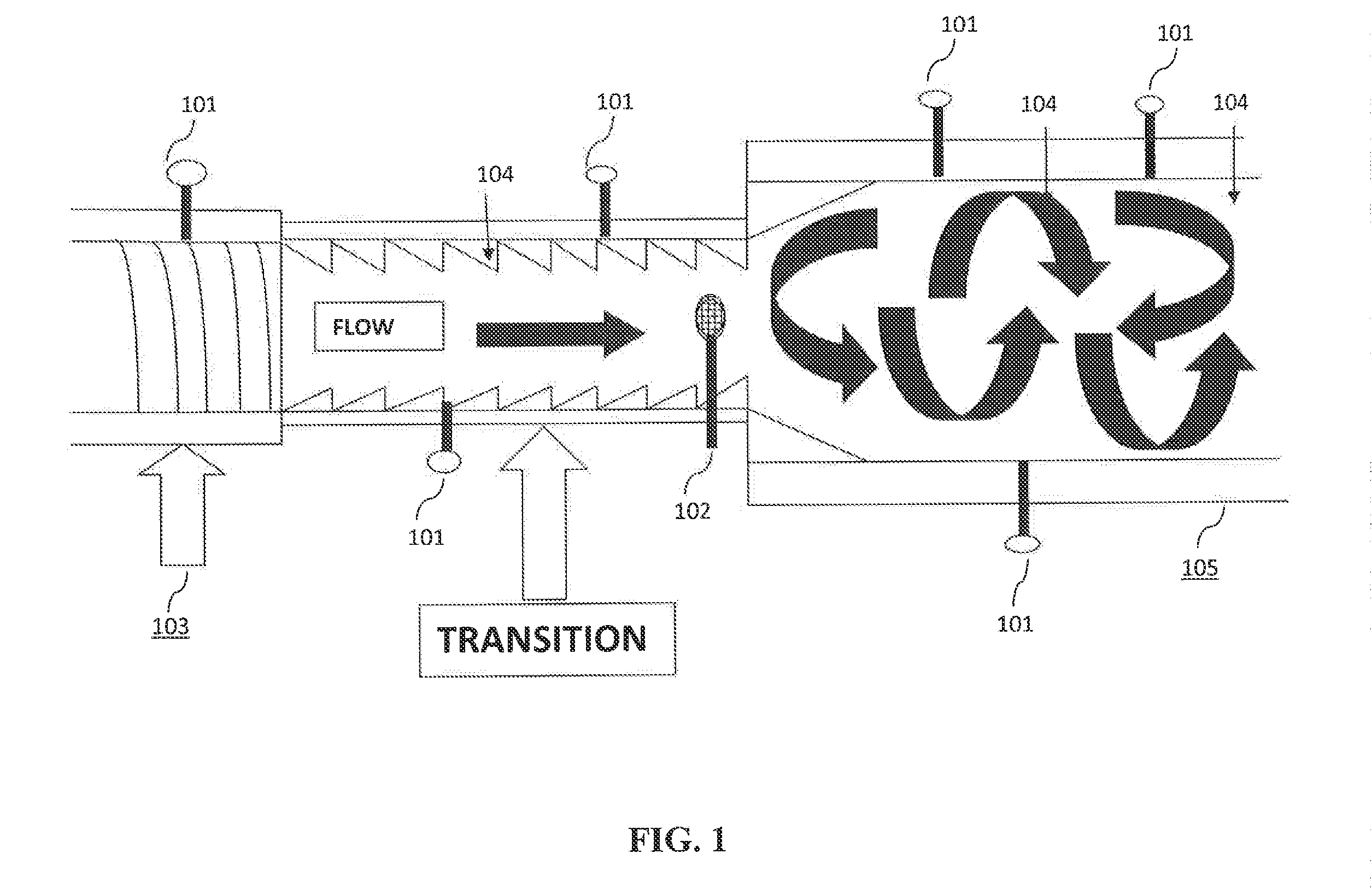
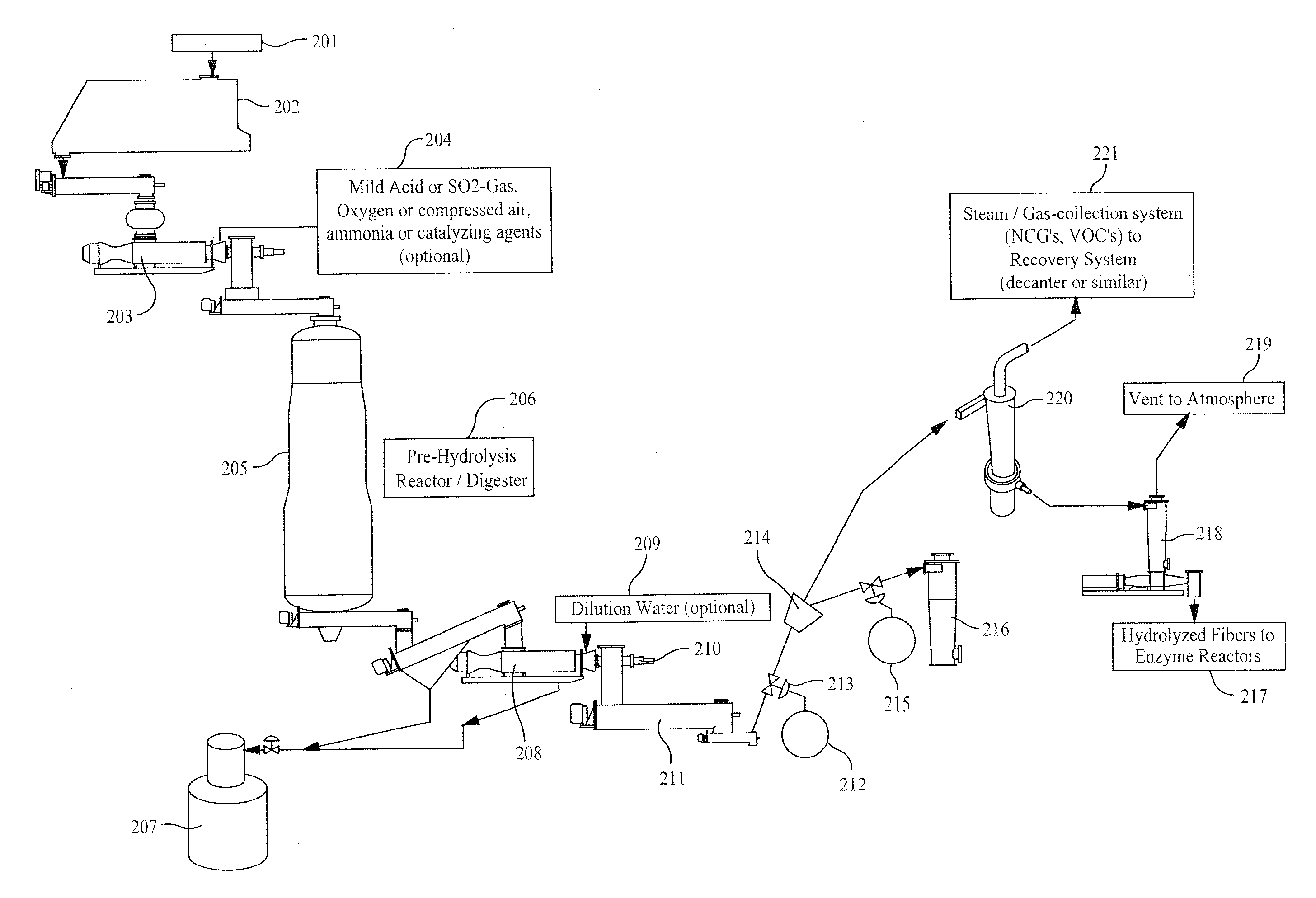
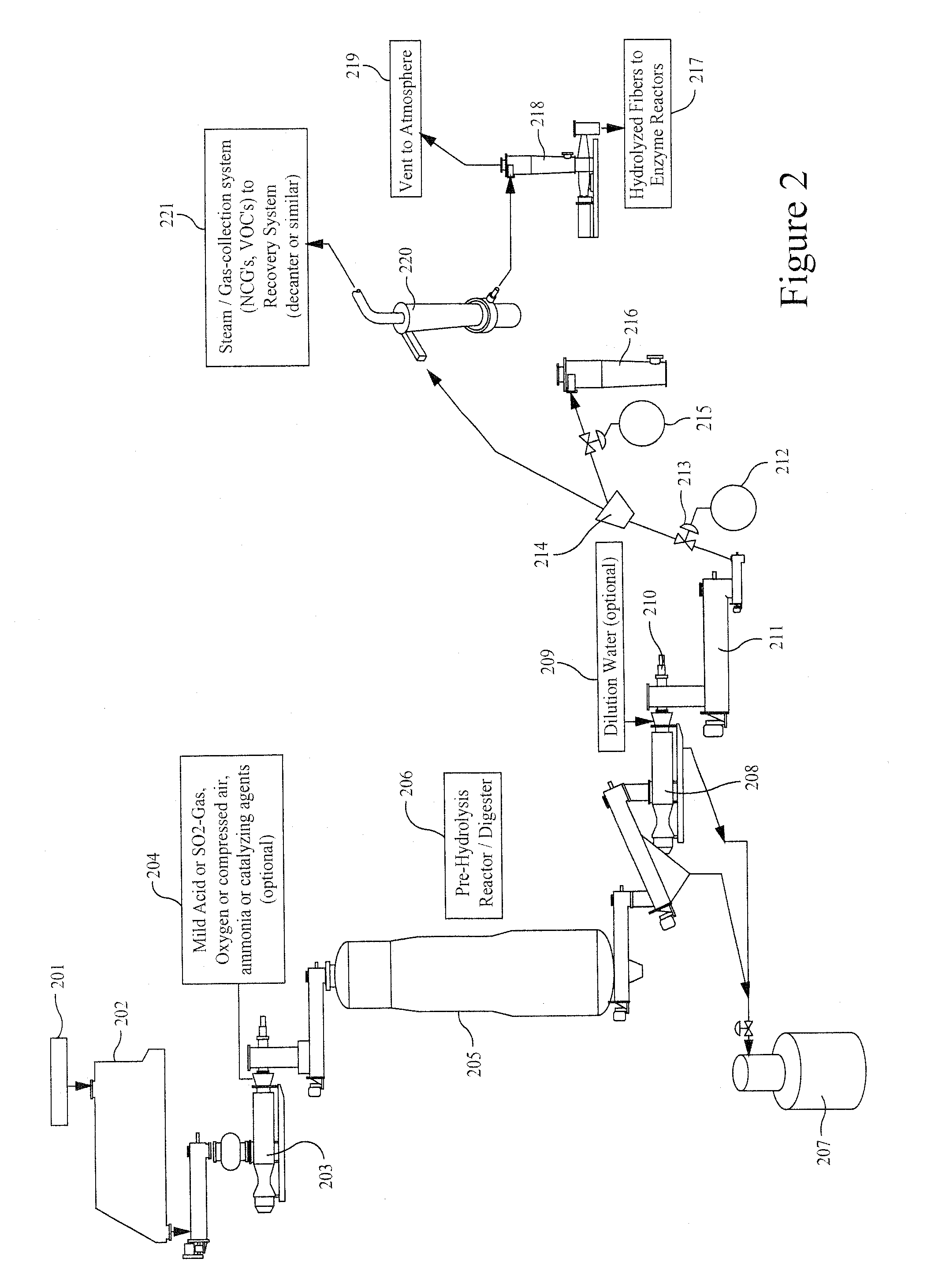
Continuous hydrolyzation method for cellulose series biomass and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN101343292AAvoid degradationImprove hydrolysis effectSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationCelluloseHydrolysate
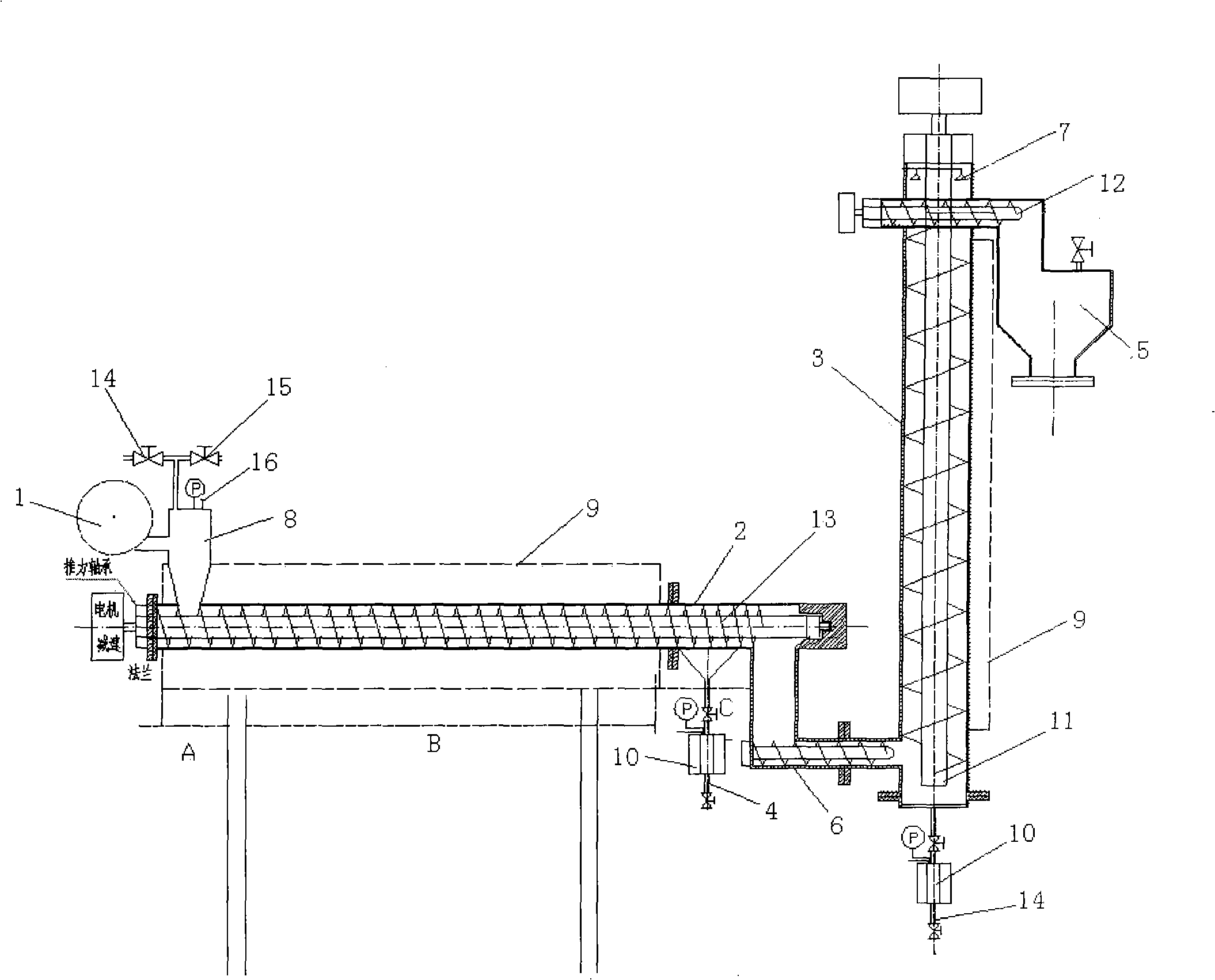
The invention discloses a method for hydrolyzing cellulosic biomass continually, which is characterized in that solid biomass material mixed with water is conveyed into a horizontal type plug flow reactor, and a variable pitch spiral pushing rod is arranged inside the horizontal type plug flow reactor; at the same time, reaction solution is conveyed into the reactor, and the mixture is pushed by the variable pitch spiral pushing rod to advance so that the solid and the liquid are separated from each other; the solid residue is conveyed into a vertical countercurrent bed, then is conveyed upward by a constant pitch vertical spiral pushing rod, and at the same time is conveyed into the reaction solution from the upper part of a vertical countercurrent reactor; and finally, the solid residue is collected at the upper part of the vertical countercurrent reactor, and cellulosic hydrolysate is collected at the lower part of the vertical countercurrent reactor. The invention also comprises a device for realizing the method. The device comprises a continuous feeding air lock system, a horizontal type plug flow reactor and a vertical countercurrent reactor, wherein, a variable pitch spiral pushing rod is arranged inside the horizontal type plug flow reactor; the variable pitch spiral pushing rod comprises a feeding section, a principal reaction section and a pressing section; the feeding section is communicated with the continuous feeding air lock system; and the horizontal type plug flow reactor is communicated with the vertical countercurrent reactor by means of a residue conveying device.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY CONVERSION - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for pretreating and hydrolyzing microcrystalline cellulose
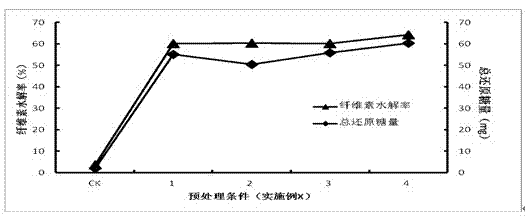
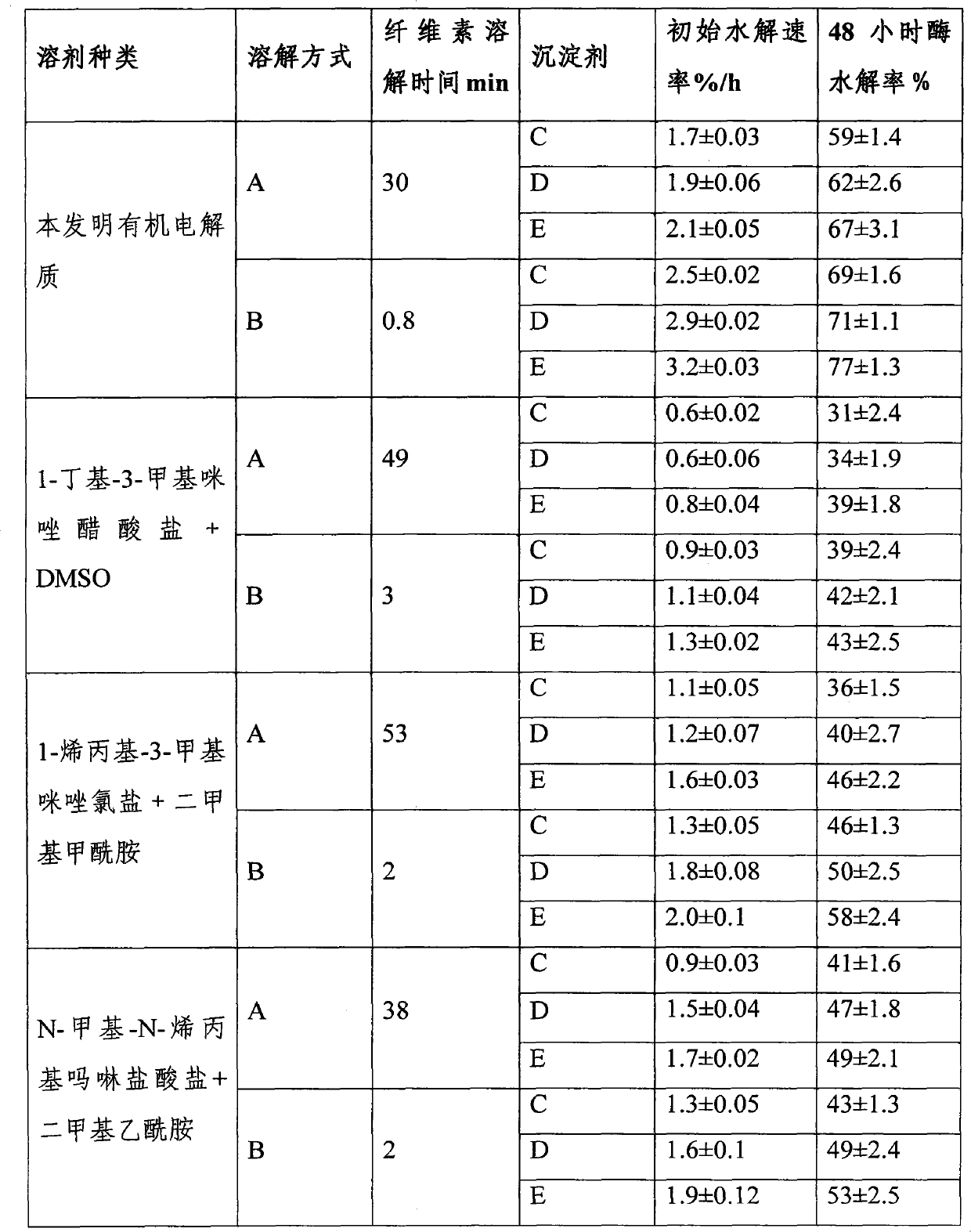
The invention aims to provide a method for dissolving and pretreating microcrystalline cellulose by an organic electrolyte in the technical field of green chemical and biomass new energy production. The method is economic and efficient, can be used for quickly dissolving the microcrystalline cellulose, and has small pollution on the environment, and the organic electrolyte can be recycled repeatedly. The initial hydrolysis rate of the treated regenerated cellulose can be raised by 5-6 times, and the 72-hour hydrolysis rate is raised by 6-8 times. The method mainly consists of four steps of organic electrolyte preparation, cellulose dissolution regeneration, cellulose hydrolysis and organic electrolyte recovery and recycling.
Owner:XISHUANGBANNA TROPICAL BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
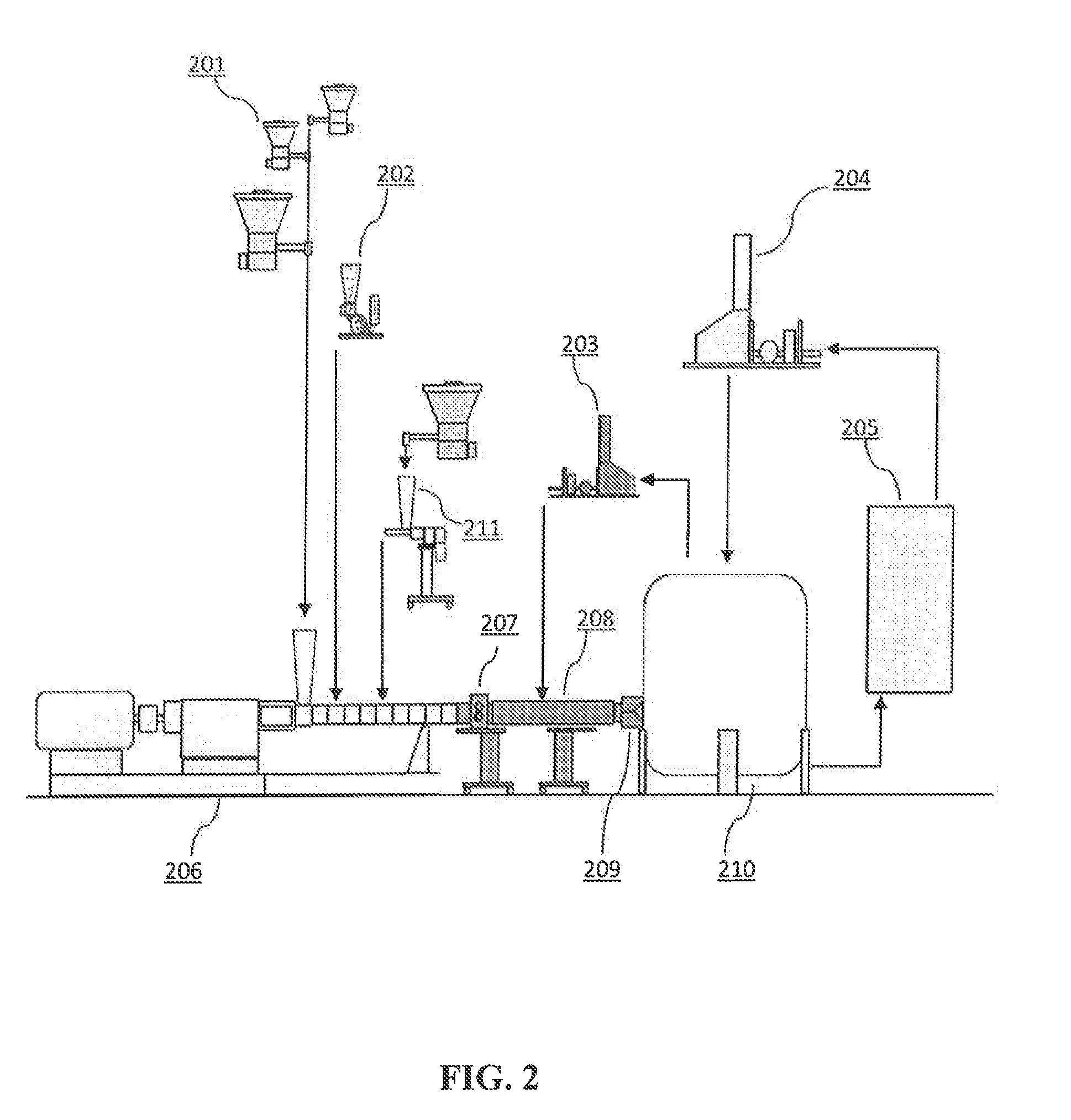
Continuous cellulostic pre-treatment and bio-mass processing by reactive extrusion
ActiveUS20120125324A1Increased ethanol productionExpand accessPressurized chemical processBiofuelsCelluloseCell wall
Cellulosic materials are treated with Supercritical Carbon Dioxide in an extruder. Machine configuration and operating parameters are strictly controlled in a manner to enhance the ability of Supercritical CO2 to enter into the cells. This results in a controlled deterioration of the ceil walls, increasing the reactivity of cellulose and also enhancing the rate and the extern of cellulose hydrolysis. This precisely controlled combination of pressure, shear & temperature accelerates the penetration of carbon dioxide molecules into the crystalline structures, thus more glucose is produced from cellulosic materials after the cell is destructurized as compared to those without the pretreatment increasing glucose yield by as much as 50%. Concurrent saccharification and fermentation tests also show the increase in the available carbon source from the cellulosic materials for fermentation to produce ethanol. As the system operates at low temperature, it will not cause degradation of sugars such as those treated with the high-temperatures involved in many systems discussed.
Owner:FISK DONALD L
Method for producing ethanol by high-efficiency simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation
InactiveCN102251010AReduce pollutionNo pollution in the processBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesEthanol yieldHemicellulose
The invention discloses a method for producing ethanol by high-efficiency simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation, which comprises the following steps: pretreating; concentrating and detoxifying; preparing yeast seed solution; performing simultaneous saccharification and cofermentation; and distilling / rectifying. When the method provided by the invention is used, the inhibition action of a monosaccharide component formed by hydrolysis of cellulose on cellulose is relieved, the enzymolysis saccharification efficiency and fermentation yield are improved, the recovery rate of hemicelluloses in bagasse is about 60 percent, the cellulose recovery rate is about 86 percent, and the total ethanol yield of dry bagasse can reach about 20 percent.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YOURUI BIOSCI
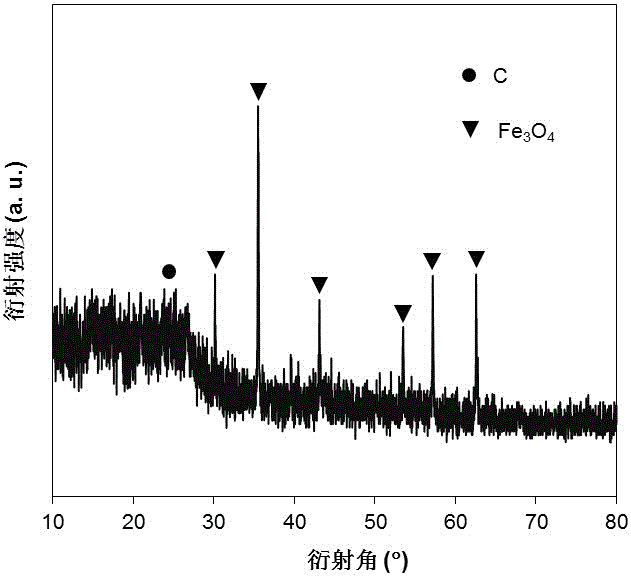
Preparation method of magnetic biomimetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst
InactiveCN105149007ALow priceReduce manufacturing costOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsGlucose productionPtru catalystSolid acid
The invention discloses a preparation method of a magnetic biomimetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst. Enzymatically decomposed residual lignin serves as a starting raw material, a chlorine-containing compound serves as a dopant, and the magnetic biomimetic carbon-based solid acid catalyst is obtained after pretreatment, dipping, evaporation, carbonization and sulfonation are performed in sequence. The obtained catalyst further contains a chlorine group (-Cl) besides a carboxyl group (-COOH), phenolic hydroxyl (Ph-OH) and a sulfonic group (-SO3H) and can improve cellulose adsorption ability and enhance the cellulose hydrolysis capacity, the raw materials are low in price, the manufacturing cost is low, the high efficiency of inorganic acid hydrolysis, adsorption directionality of cellulose enzyme and recycling of magnetic solid acid are effectively coupled, and the preparation method has important practical significance on development of a green environmentally-friendly cellulose hydrolysis technology.
Owner:HUAIYIN TEACHERS COLLEGE
Integrated treatment method for high-salinity and high-concentration refractory organic wastewater resulted from cellulose ether production
ActiveCN106746198ASolve processingSolve the costTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationExisting Treatment
The invention discloses an integrated treatment method for high-salinity and high-concentration refractory organic wastewater resulted from cellulose ether production. The method comprises the steps of (1) carrying out pretreatment on to-be-treated wastewater through coagulating sedimentation and fenton reaction in sequence; (2) carrying out biochemical treatment on fenton reaction effluent through cellulase hydrolysis, anaerobic treatment, first-stage contact oxidation and second-stage contact oxidation in sequence, feeding cellulose to carry out degradation, anaerobic treatment, first-stage contact oxidation and second-stage contact oxidation processes on the wastewater in the cellulose hydrolysis process, adding a salt-tolerant fungicide of producing the cellulose ether to carry out strengthened treatment on the wastewater; and (3) carrying out deep treatment on second-stage contact oxidation effluent through the fenton reaction and finally discharging the effluent. Compared with an existing treatment method, the integrated technology has the characteristics of being high in pertinence, economic and environment-friendly; and problems that the wastewater is high in salinity, high in concentration and refractory are solved for enterprises that produce the cellulose ether.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL SCI RES & DESIGN INST OF ZHEJIANG PROVINCE
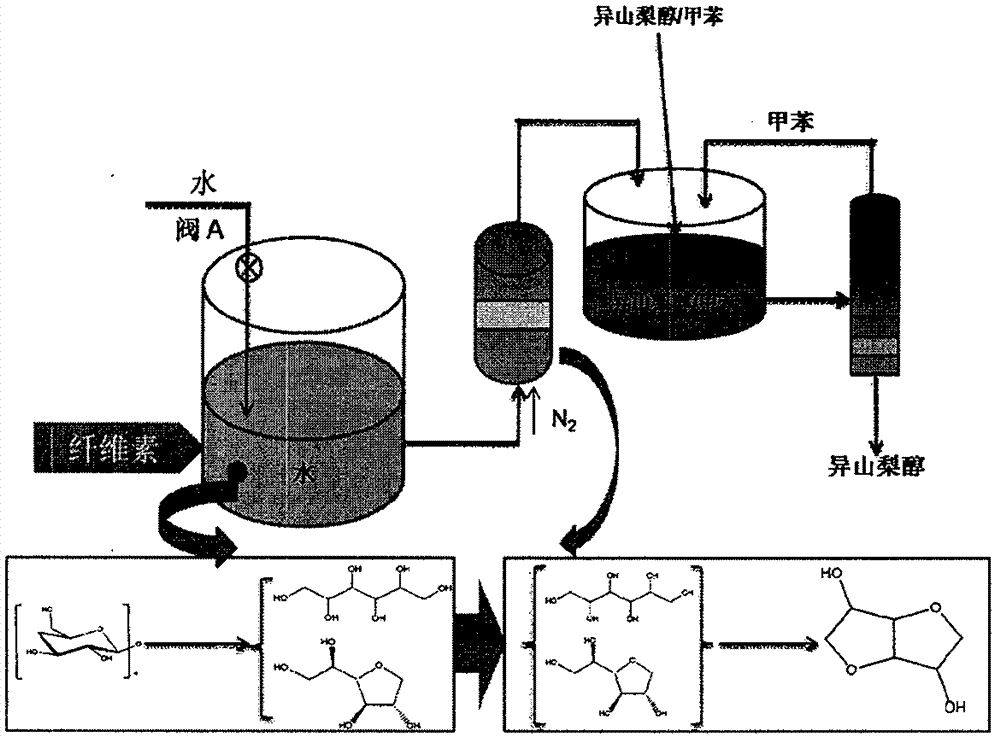
New method for preparing isosorbide through cellulose
InactiveCN103159775APrevent oxidationSimple purification processOrganic chemistryCellulosePtru catalyst
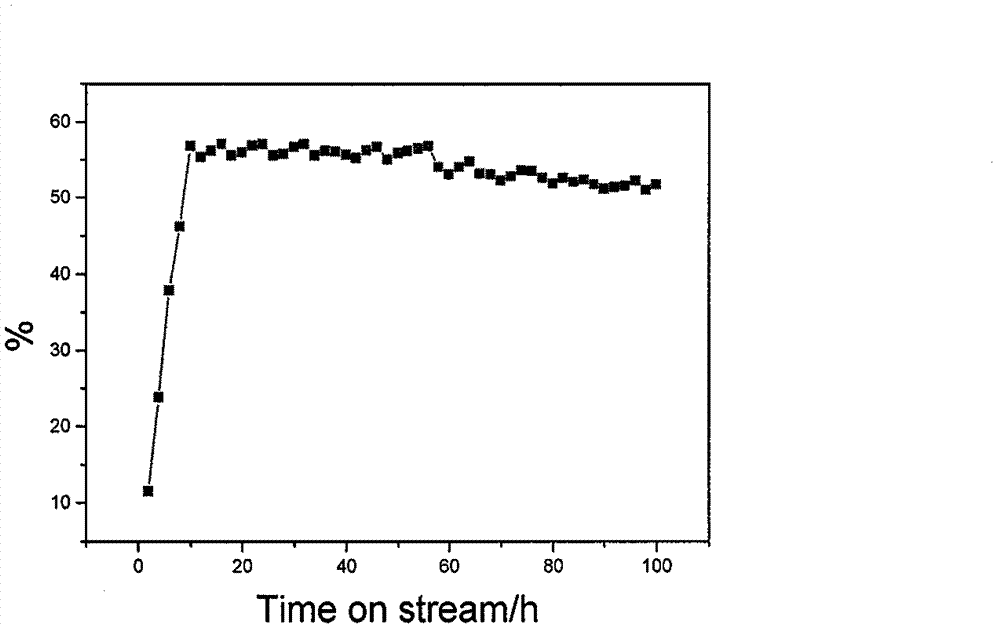
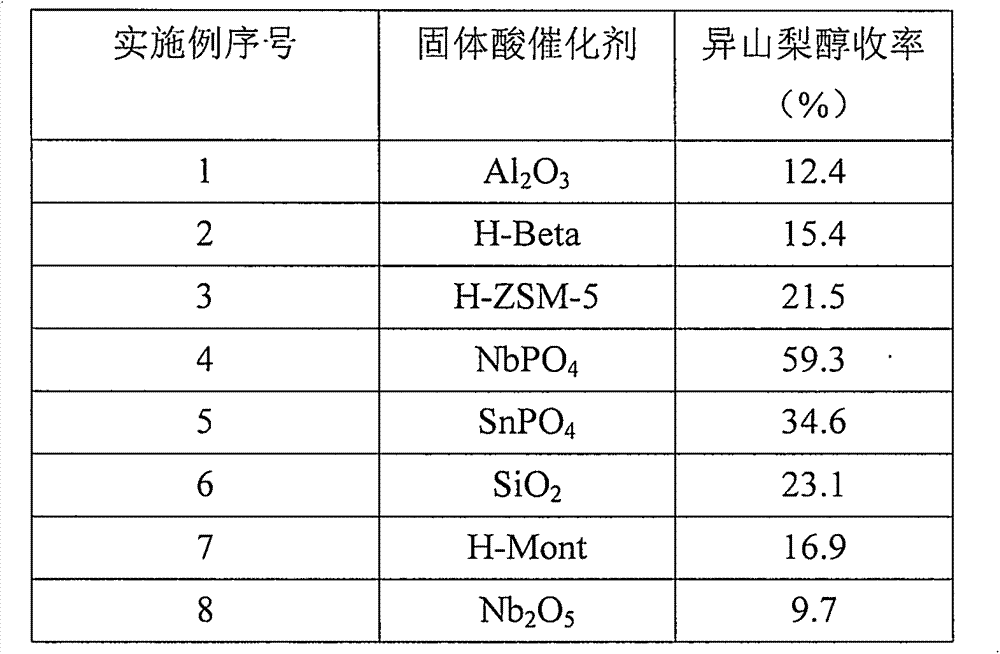
The invention relates to a method for preparing isosorbide through cellulose, and belongs to the preparation field of synthesizing renewable energy sources and chemicals by utilizing of biomasses. The method comprises a step of hydrolyzing the cellulose under a dual-function catalyst of metal-solid acid and adding hydrogen to obtain reaction liquid containing sorbitol, and a step of catalyzing and dehydrating the reaction liquid containing the sorbitol through the solid acid to obtain the isosorbide. According to the method, liquid acid does not need to be added, the reaction liquid containing the sorbitol does not need to be separated and purified, wherein the reaction liquid is obtained by hydrolyzing the cellulose and adding the hydrogen. The method has the advantages that raw material is the cellulose which is abundant, low in cost and environment-friendly, the yield of the isosorbide reaches up to 56.3%, the catalyst is easy to separate and recycle, a very valuable new channel is provided for transferring the cellulose into high value-added chemicals, and the method has a good industrialization application prospect.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Graphite-like g-C3N4/montmorillonite composite material and application thereof in cellulose hydrolysis
InactiveCN106799250AReaction conditions are easy to controlReaction condition controlPhysical/chemical process catalystsGlucose productionCelluloseNitrogen
The invention discloses a graphite-like g-C3N4 / montmorillonite composite material and an application thereof in cellulose hydrolysis. The g-C3N4 / montmorillonite composite material is prepared through the following steps of (1) mixing montmorillonite and deionized water and then stirring evenly to obtain a mixture for later use; (2) adding a nitrogen-containing compound to the mixture obtained in the step (1), carrying out exchange adsorption to obtain homogenate; (3) washing the homogenate prepared in the step (2) for multiple times and carrying out centrifugal separation; (4) drying lower solid obtained through centrifugal separation at 50-120 DEG C for 5-24h; and (5) grinding solid dried in the step (4) into powder, heating the powder in a nitrogen atmosphere to 200-800 DEG C, roasting at constant temperature for 1-10h, and naturally cooling after roasting is completed to obtain the product graphite-like g-C3N4 / montmorillonite composite material. The invention provides an application of the graphite-like g-C3N4 / montmorillonite composite material as a catalyst in cellulose hydrolysis. The graphite-like g-C3N4 / montmorillonite composite material has good catalytic performance.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
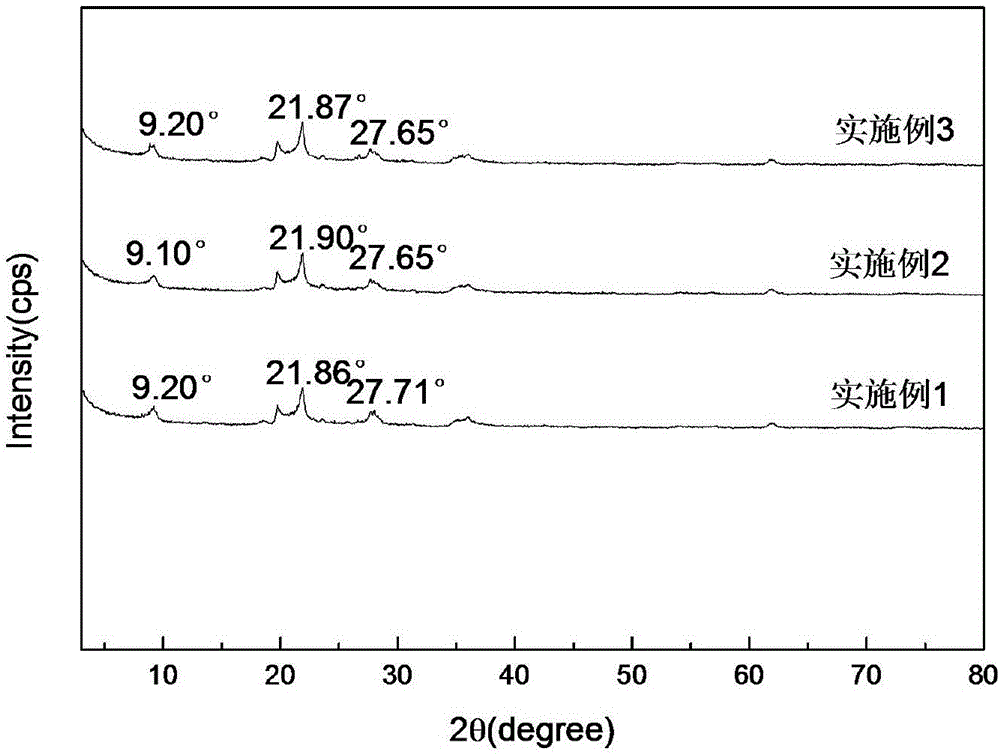
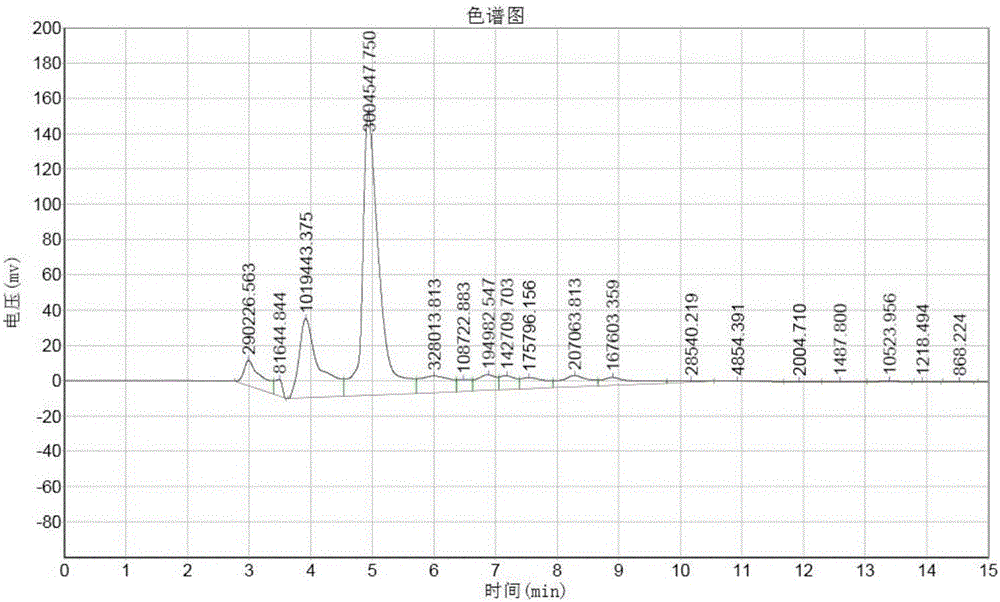
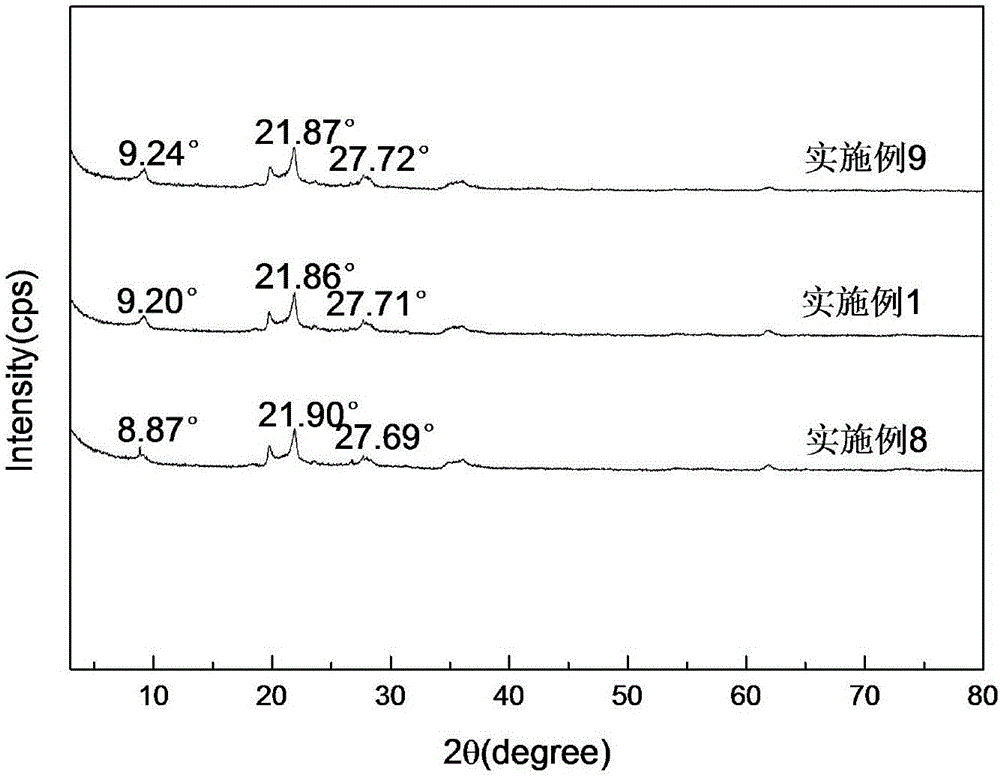
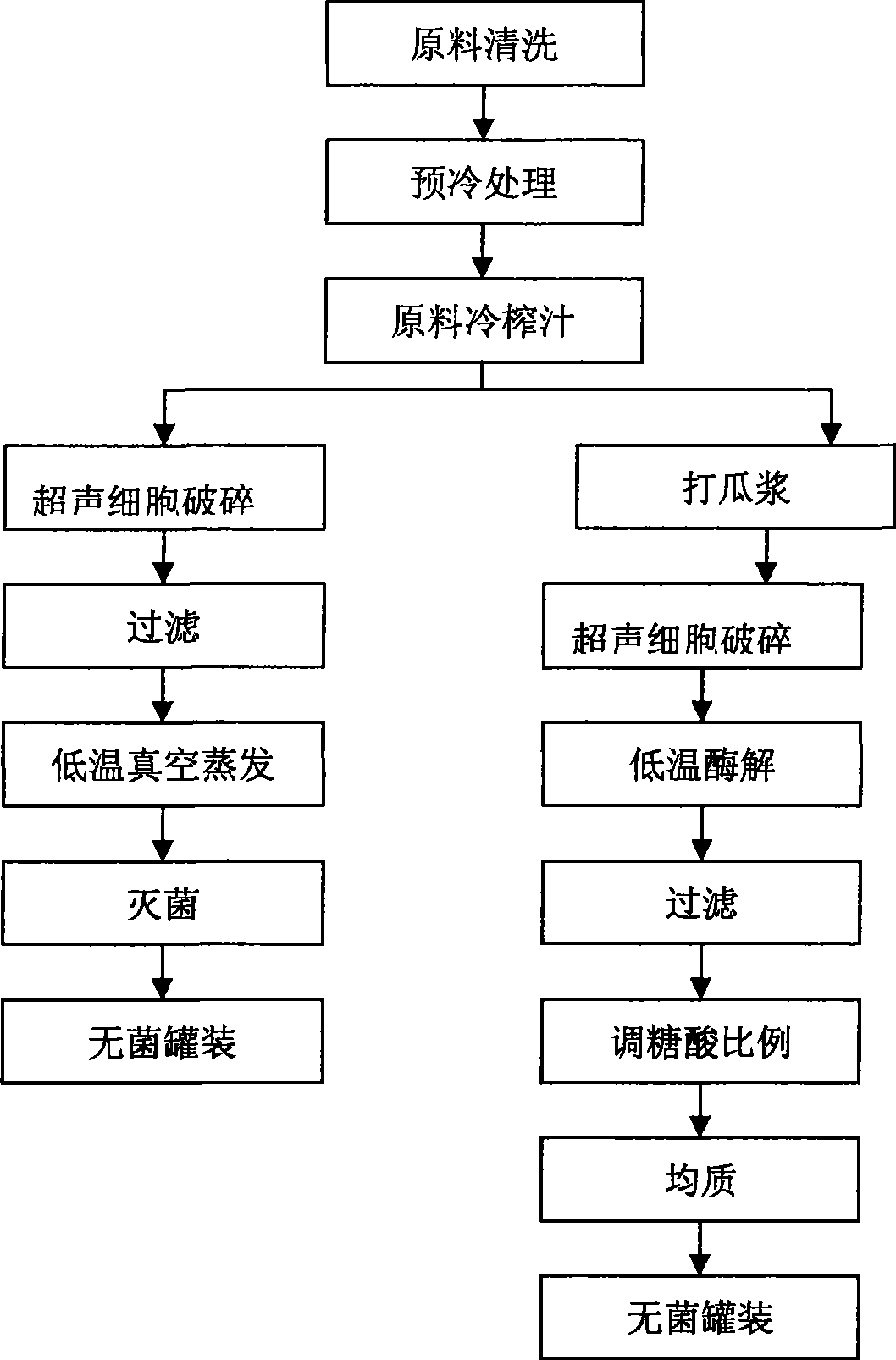
Method for processing watermelon water and watermelon juice by combining ultrasonic and ultrahigh pressure
The invention relates to a method for processing watermelon water and watermelon juice by combining ultrasonic and ultrahigh pressure, and belongs to the field of food beverage and producing and processing method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) watermelon water: cleaning and pre-cooling a fresh watermelon raw material; crushing the watermelon and taking out pulp, and adding Vc and citric acid into the pulp for cold-pressing juice; carrying out broken wall treatment by ultrasonic; then evaporating the mixture by vacuum at low temperature to obtain the watermelon water; sterilizing the watermelon water by adopting ultraviolet and ultrahigh pressure combined sterilizing technology; and finally carrying out sterile canning; and (2) watermelon juice: cleaning and pre-cooling a fresh watermelon raw material; crushing the watermelon and taking out pulp, and adding Vc and citric acid into the pulp for cold-pressing juice; carrying out broken wall treatment by ultrasonic; adding pectase and cellulolytic enzyme into the mixture to carry out low temperature enzymolysis; homogenizing the mixture twice; adding sucrose or honey into the mixture to adjust taste; sterilizing the mixture by ultrahigh pressure; and carrying out sterile canning. The product has the natural character flavor of the watermelon, can obviously improve the utilization rate of the watermelon, reduce resource waste, and increase the economic benefit of the watermelon industry.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
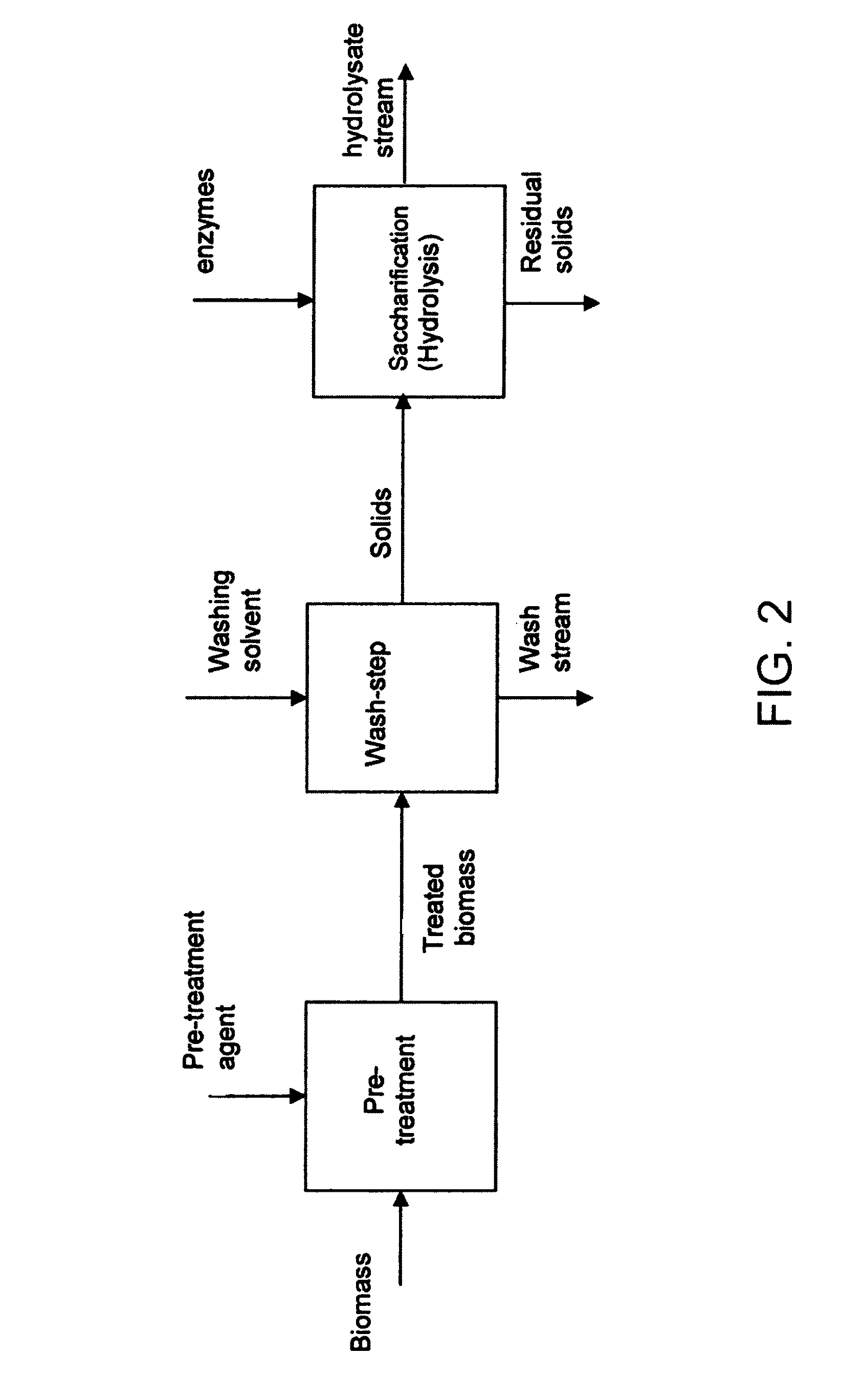
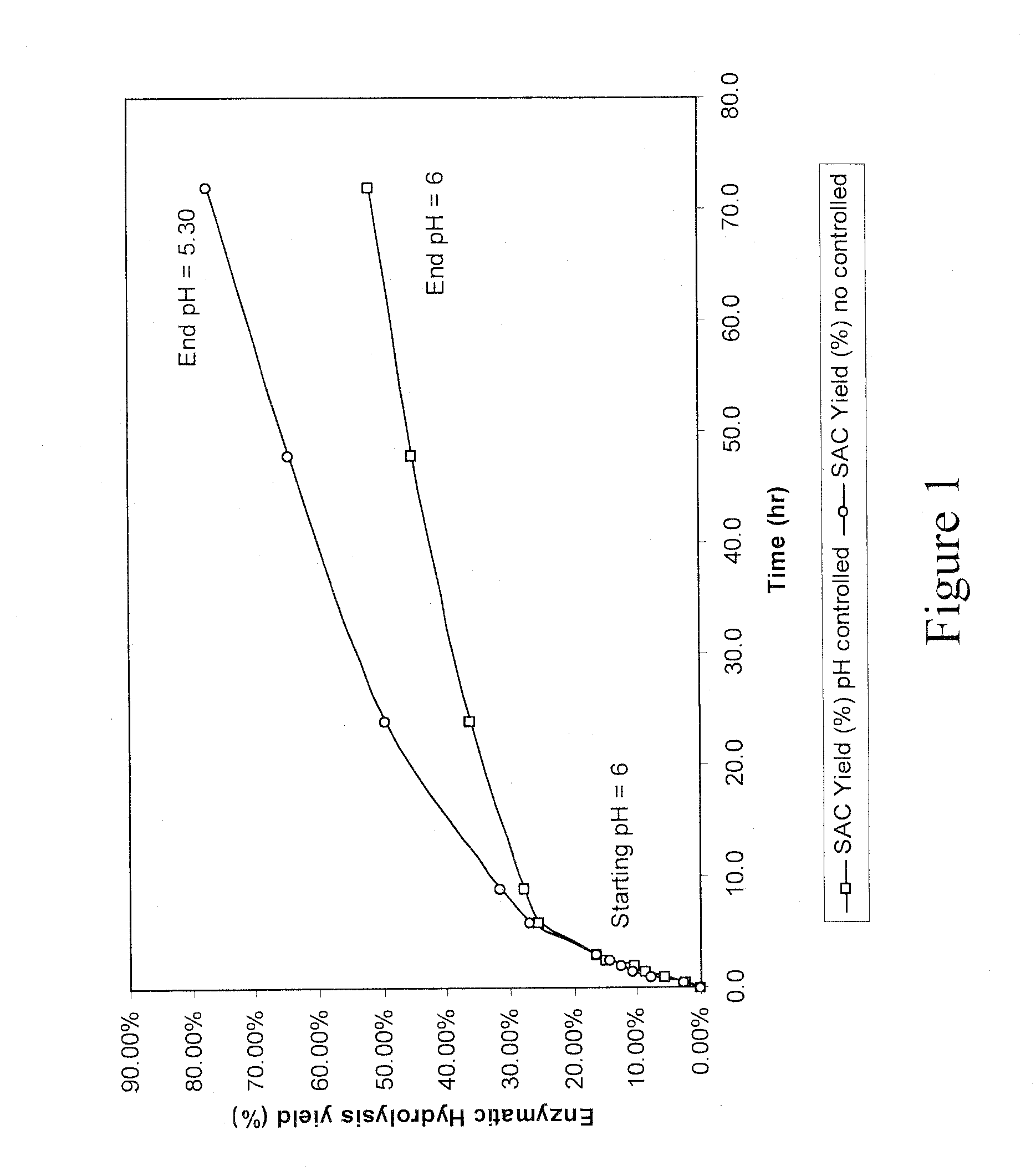
Enzymatic hydrolysis of pre-treated biomass
This disclosure relates to a method for performing high solids saccharification comprising by (a) providing a cellulosic biomass; (b) pretreating the cellulosic biomass in a pretreatment process to produce a pretreated cellulosic biomass; (c) adjusting said pretreated cellulosic biomass to a solids concentration of 6% to 35% w / w and a starting pH of between 5-7; and (d) hydrolyzing the pretreated biomass with at least one aqueous hydrolyzing liquid comprising at least one enzyme selected from the group consisting of a cellulase, a saccharification enzyme, and a combination thereof for a period of time, to hydrolyze at least a part of the pretreated cellulosic biomass to a cellulosic hydrolysate, said cellulosic hydrolysate comprising fermentable sugars.
Owner:ANDRITZ INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com