Process for preparing multicomponent liquid glucose and lignose while effectively hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass
A technology for lignocellulosic and sugar hydrolysis, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of low solvent recovery rate, inability to remove lignin, immature technology, etc., achieve extensive economic and social benefits, promote sustainable development, The effect of reducing environmental pollution
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
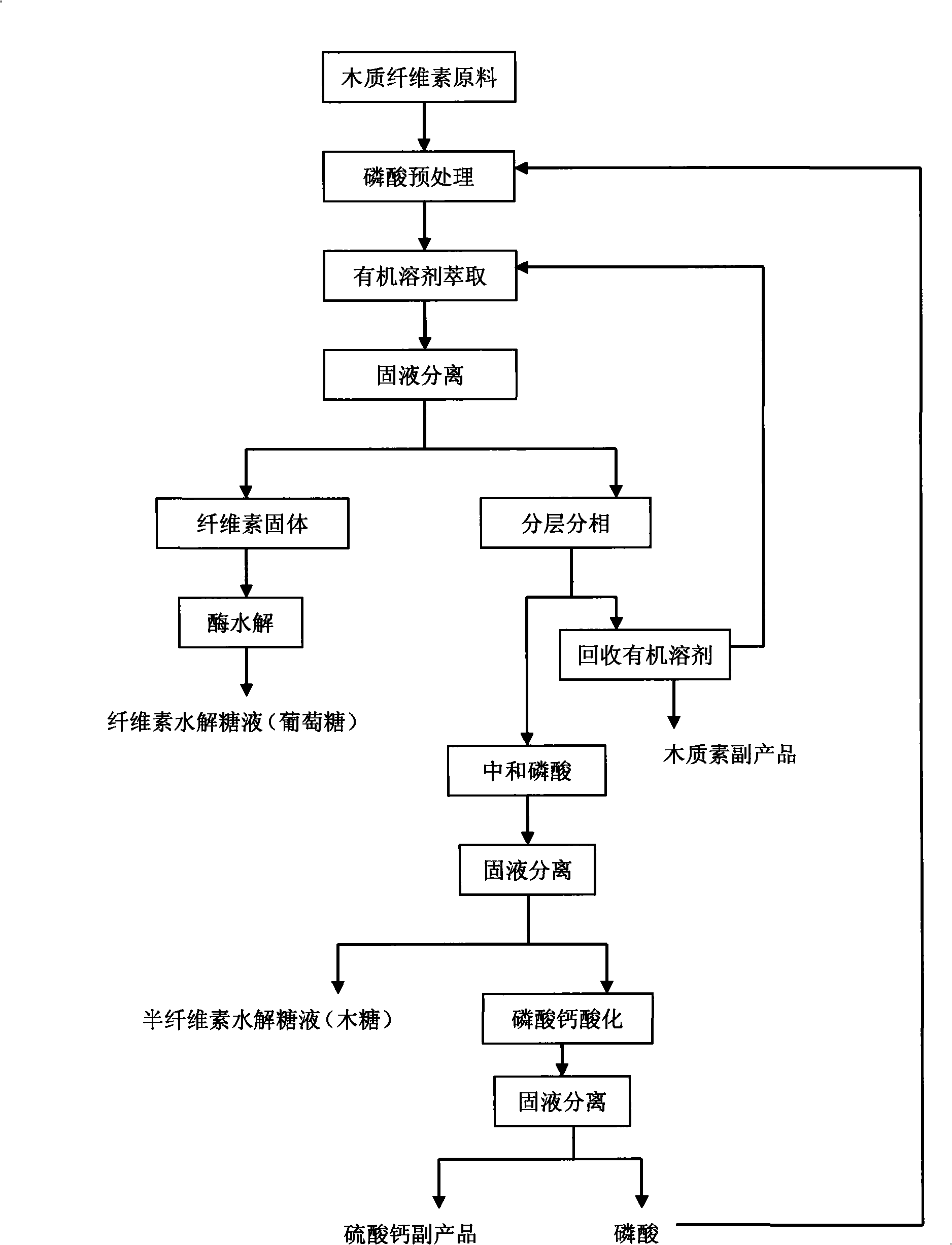
[0028] Get the dry corn stalks, grind them to 40 mesh through mechanical grinding, get 5g corn stalk powder (24.7% of cellulose content, 20.1% of hemicellulose, 15.6% of lignin), add 85% phosphoric acid, the solid-liquid content is 12.5% (w / v), the reaction solution was stirred and hydrolyzed at 50°C for 60 minutes, cooled to 30°C, added 50mL propyl acetate (10%w / v) and stirred for 10min, filtered, and the filter cake was washed with propyl acetate (10%w / v) v) Washing 3 times, merging the washing liquid and the filtrate, separating the layers, distilling the organic phase under reduced pressure to reclaim the extractant, the recovery rate of propyl acetate is 92%, and the lignin solid is precipitated, and centrifuged to obtain 0.73g of lignin ( Purity 96%), lignin removal rate 89.8%.
[0029] Use hot water to wash the cellulose solid, combine the washing liquid with the water phase after oil-water separation, add calcium carbonate to the solution for reaction, filter and se...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Get the dried corncob, grind it to 60 orders through mechanical grinding, get 5g corncob powder (29.8% of cellulose content, 32.4% of hemicellulose, 18.3% of lignin), add 80% phosphoric acid, solid-liquid content is 20% ( w / v), the reaction solution was stirred and hydrolyzed at 60°C for 30 minutes, cooled to 20°C, added ethyl acetate (20% w / v) and stirred and extracted for 30 minutes, filtered, the filter cake was washed 3 times with ethyl acetate, and combined The filtrate was separated and the organic phase was distilled under reduced pressure. The recovery rate of ethyl acetate was 95%. The precipitated lignin solid was filtered and dried to obtain 0.94 g of lignin (purity 95%), and the lignin removal rate was 97.4%.
[0034] Wash the cellulose solid with hot water, combine the washing liquid with the water phase separated from water and oil, add calcium carbonate to the solution for reaction, filter and separate the calcium phosphate precipitate from the hemicellul...
Embodiment 3
[0038] Get dry bagasse, through mechanical crushing to 20 orders, get 5g bagasse particles (cellulose content 38.2%, hemicellulose 22.5%, lignin 19.8%), add 50% phosphoric acid, solid-liquid content is 25% (w / v), the reaction solution was stirred and hydrolyzed at 40°C for 40 minutes, cooled to 30°C, added ethyl formate (30% w / v) and stirred and extracted for 20 minutes, filtered, the filter cake was washed twice with ethyl formate, and combined The filtrate was separated and the organic phase was distilled under reduced pressure. The recovery rate of ethyl formate was 85%. The precipitated lignin solid was centrifuged and dried to obtain 1.02 g of lignin (purity 93%), and the lignin removal rate was 96%.
[0039] Wash the cellulose solid with hot water, combine the washing liquid with the water phase after water and oil separation, add calcium hydroxide to the solution for reaction, filter and separate the calcium phosphate precipitate from the hemicellulose hydrolyzed sugar...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com