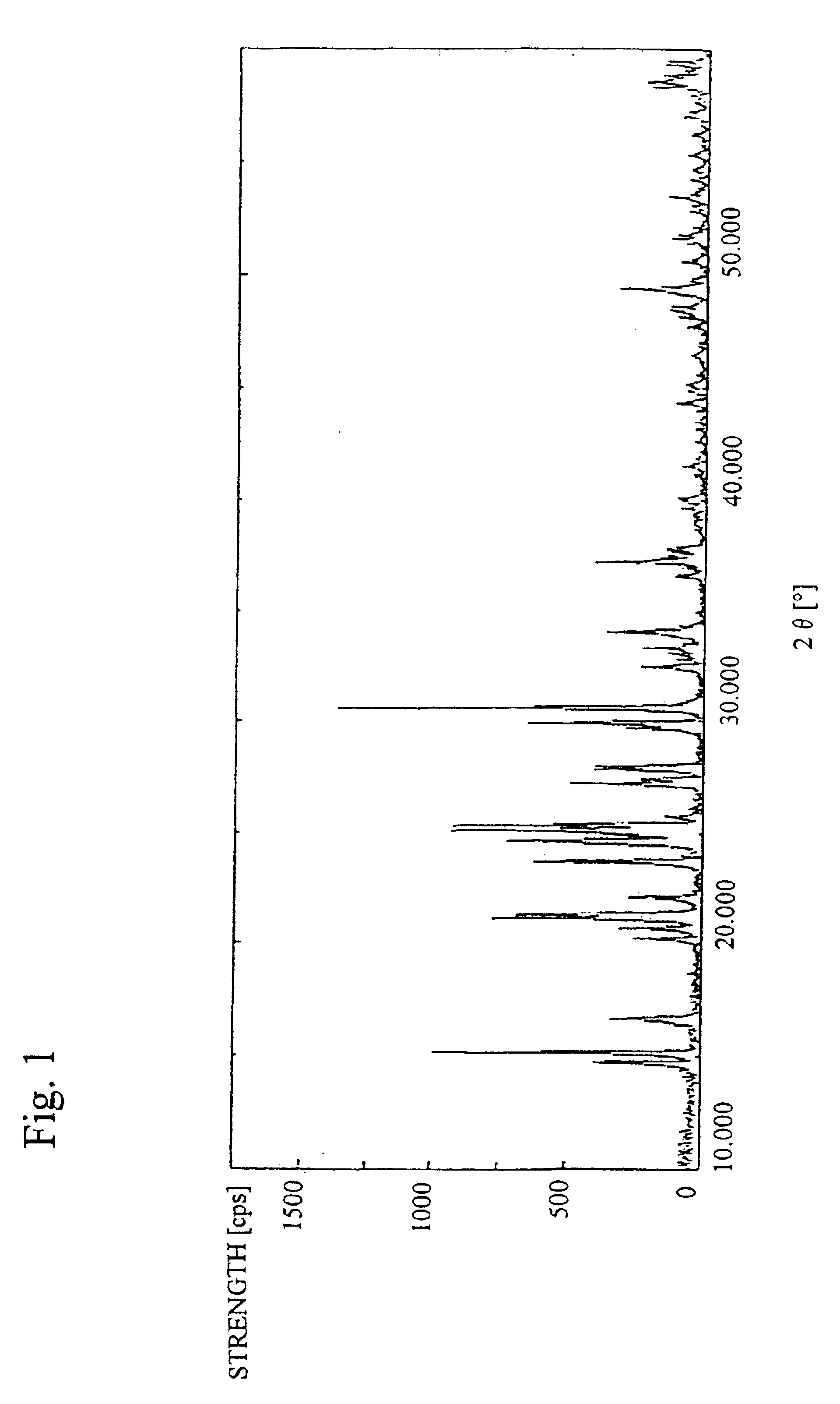
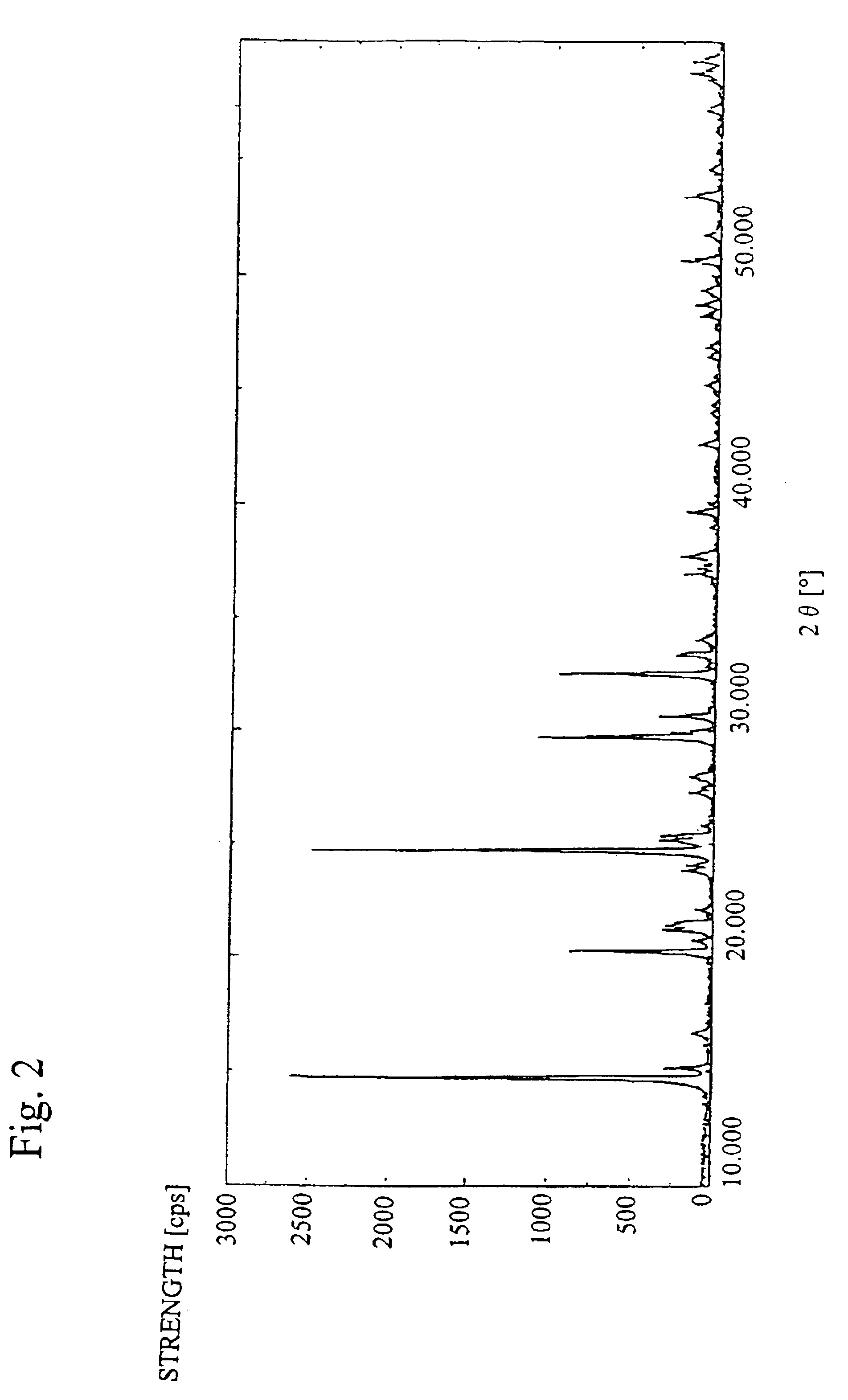
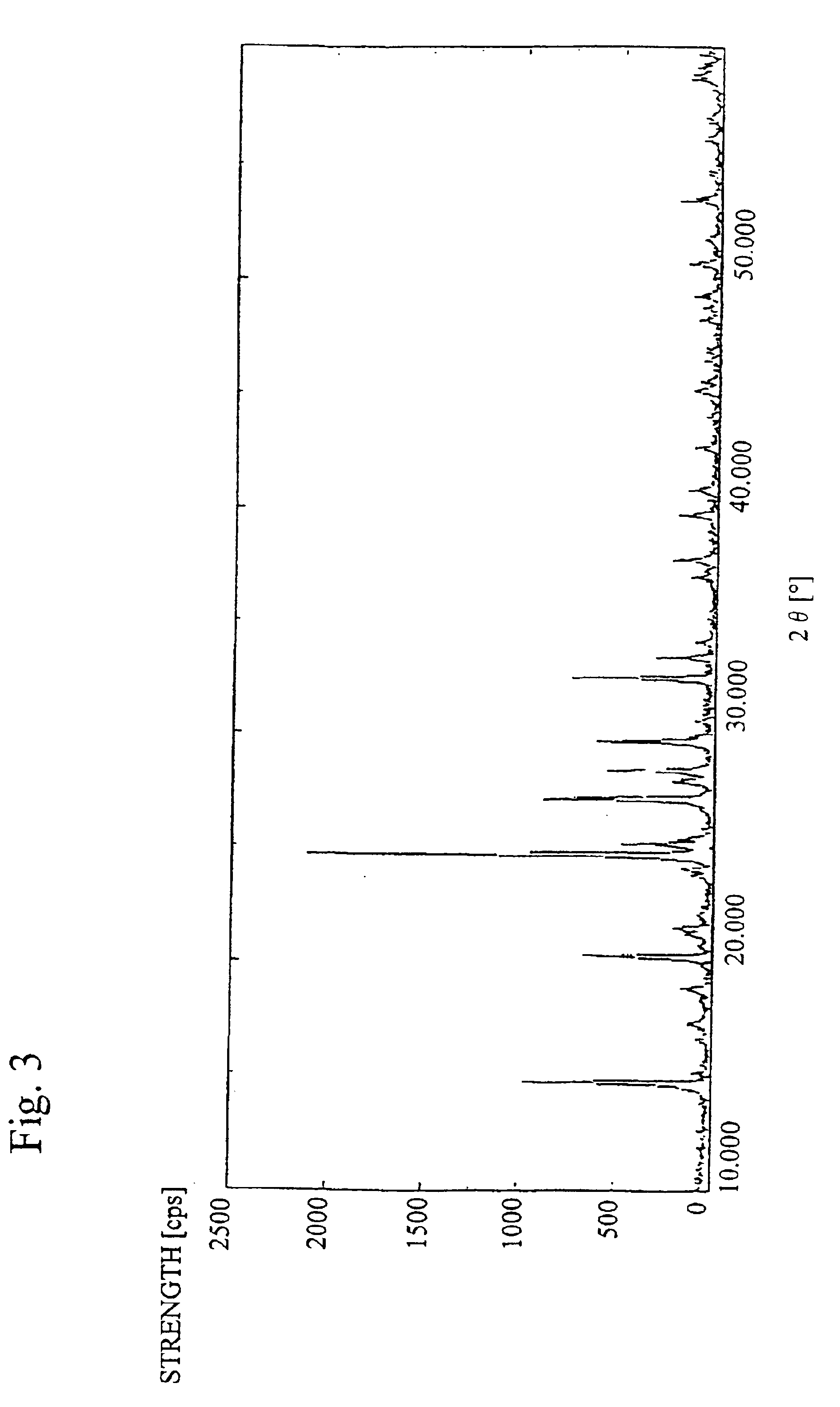
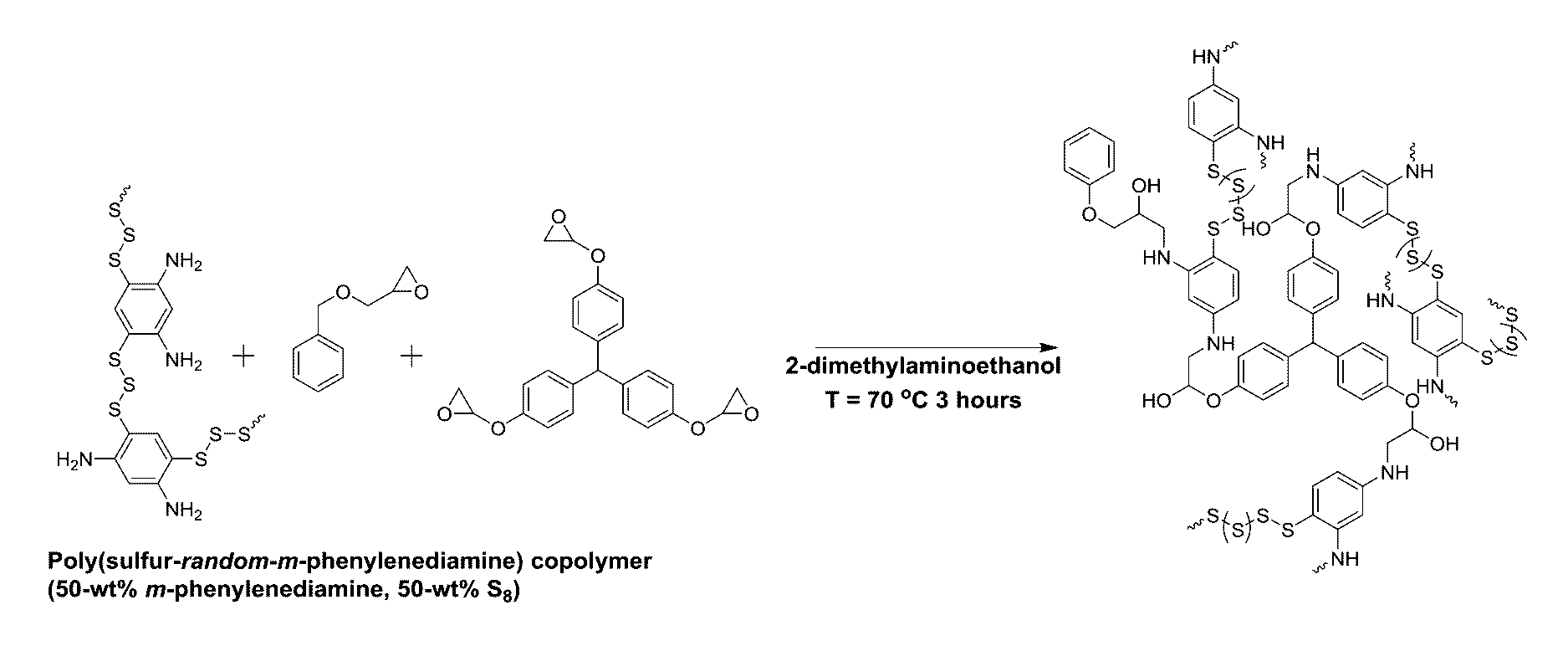
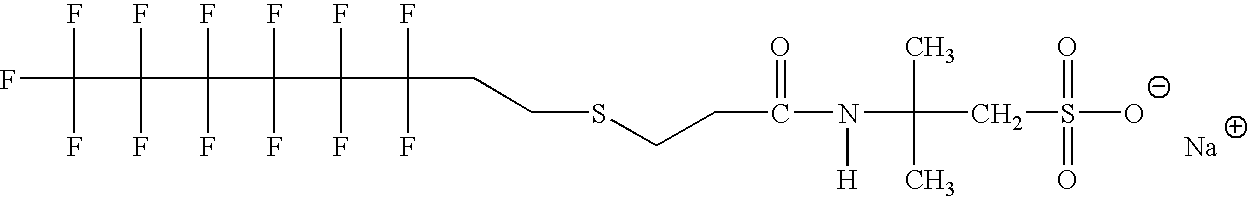
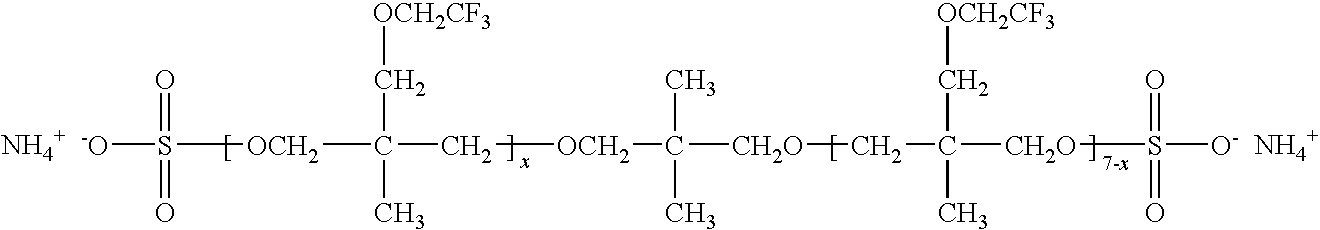
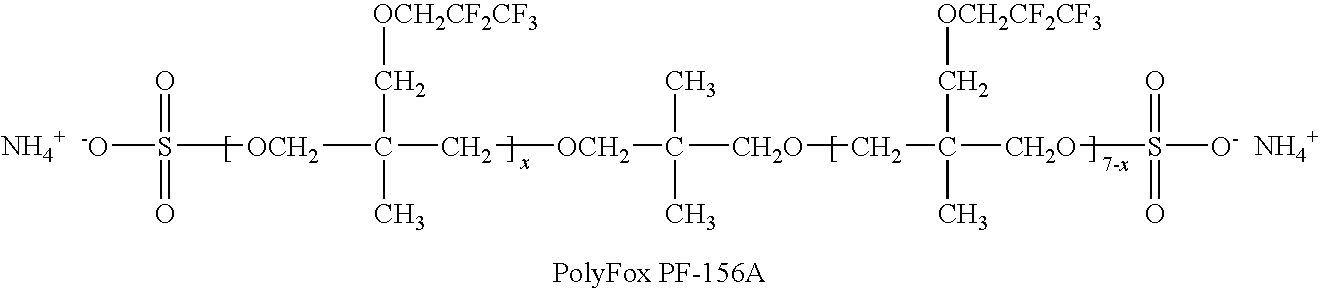
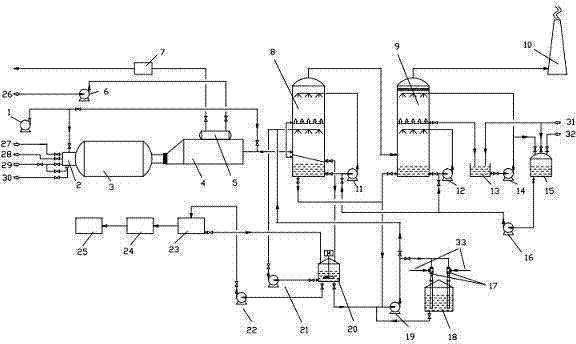
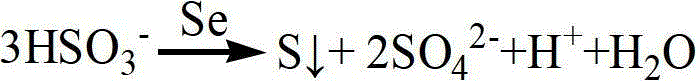Patents
Literature
187results about "Sulfate preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Process for preparing multicomponent liquid glucose and lignose while effectively hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass
InactiveCN101285106ASimple recycling processNot volatileSulfate preparationLignin derivativesLiquid glucoseFiltration
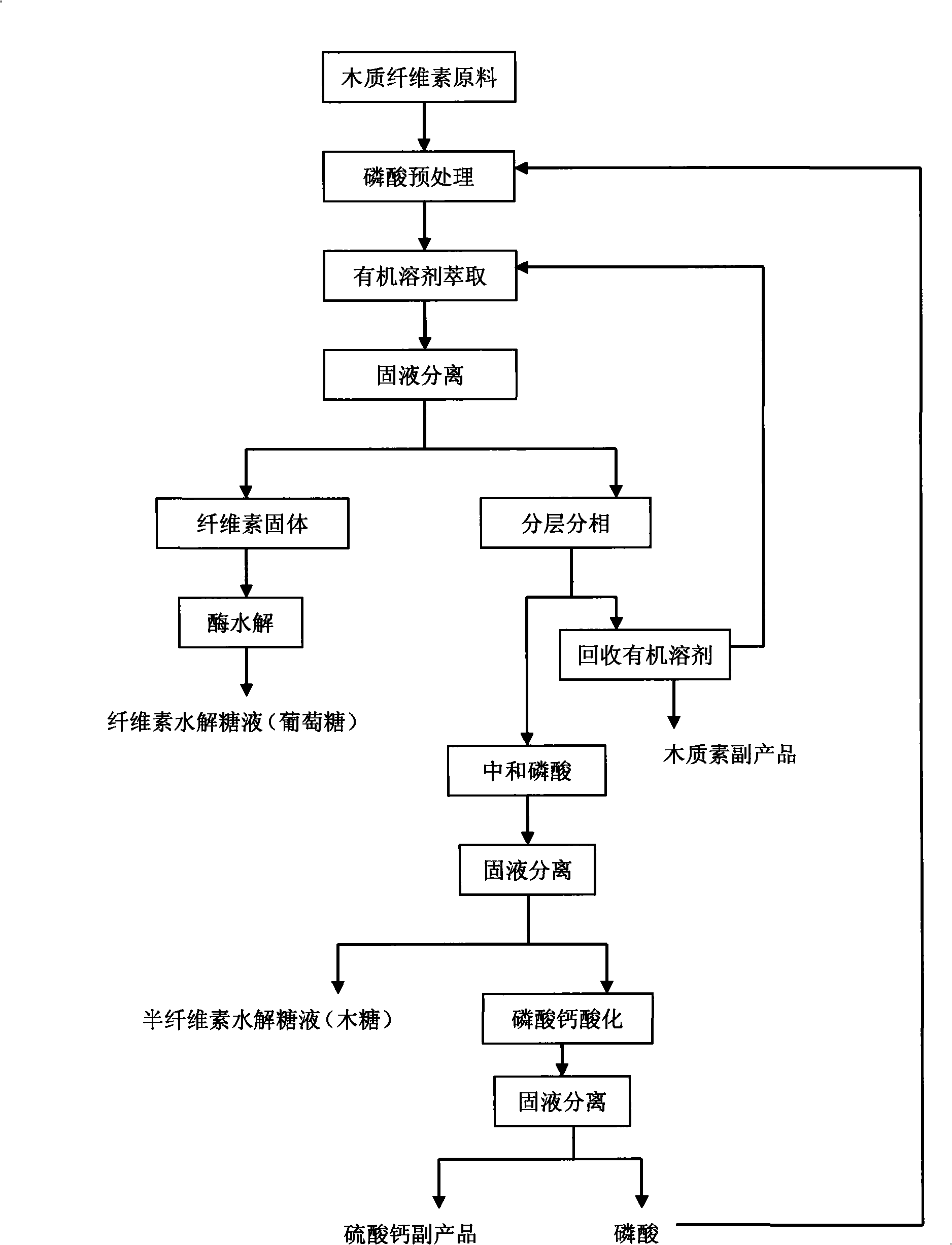
The invention discloses a method for efficiently hydrolyzing lignocellulosic biomass and synchronously preparing multi-component liquid glucose and lignin. The method comprises the steps that: the lignocellulosic biomass through physical crushing is added with phosphoric acid to perform acid hydrolysis; then organic solvent is added to extract the lignin, the layering and the phase separation are performed, then the lignin is extracted out while the organic solvent is reclaimed under the condition of pressure reduction and distillation; phosphoric acid can be reclaimed through steps such as neutralization, filtration, acidification and so on, hemicellulose hydrolyzed liquid glucose is obtained at the same time; and the remained cellulose undergoes the zymohydrolysis to prepare cellulosic hydrolyzed liquid glucose. The method can separate lignin, hemicellulose and cellulose, remarkably decreases the degree of crystallinity of the cellulose hydrolyzed by phosphoric acid, and remarkably improves the zymohydrolysis efficiency; and the prepared hydrolyzed liquid glucose does not contain fermentation inhibitors. The method has mild treatment conditions, simple process and less side reactions; the phosphoric acid and the organic solvent can both be reclaimed and circularly used; and the method is environment-friendly, and has broad social and economic benefits.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Regenerative recovery of sulfur dioxide from effluent gases
ActiveUS20120107209A1Improve energy efficiencySpeed up the processGas treatmentSulfur-dioxide/sulfurous-acidOrganic acidSulfate
This invention relates to processes for selective removal of contaminants from effluent gases. A sulfur dioxide absorption / desorption process for selective removal and recovery of sulfur dioxide from effluent gases utilizes a buffered aqueous absorption solution comprising weak inorganic or organic acids or salts thereof, to selectively absorb sulfur dioxide from the effluent gas. Absorbed sulfur dioxide is subsequently stripped to regenerate the absorption solution and produce a sulfur dioxide-enriched gas. A process for simultaneous removal of sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides (NOx) from effluent gases and recovery of sulfur dioxide utilizes a buffered aqueous absorption solution including a metal chelate to absorb sulfur dioxide and NOx from the gas and subsequently reducing absorbed NOx to form nitrogen. A process to control sulfate salt contaminant concentration in the absorption solution involves partial crystallization and removal of sulfate salt crystals.
Owner:MECS
Device and process for recycling and treating hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas
InactiveCN103301732AReach the purpose of recyclingDispersed particle separationEnergy inputHigh heatSulfur dioxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical waste gas treatment, and mainly relates to a device and a process for recycling and treating hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas. The process for recycling and treating hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas comprises the following steps of: igniting and completely burning the hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas into sulfur dioxide-rich high-temperature flue gas, recycling much heat and adjusting the temperature of the flue gas by cold air, and enabling the flue gas to enter an adsorption tower; completely absorbing the sulfur dioxide in the flue gas by utilizing an alkaline solution, removing less alkaline solution and sulfite contained in the flue gas absorbed by the alkaline solution, and exhausting the demisted pure flue gas to the atmosphere. The sulfite, which is generated by absorbing sulfur dioxide by the alkaline solution, is oxidized, concentrated, crystallized and dried to obtain side product sulfate.
Owner:义马煤业集团煤生化高科技工程有限公司 +1
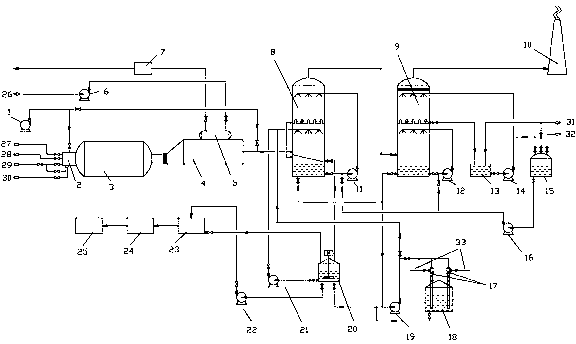
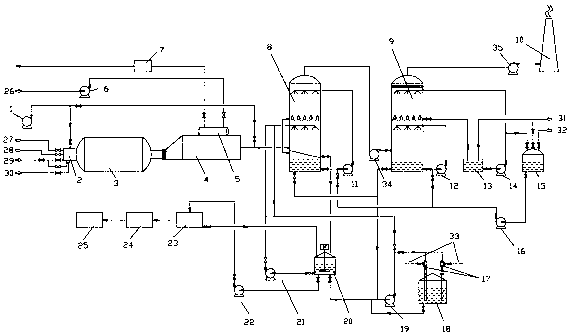
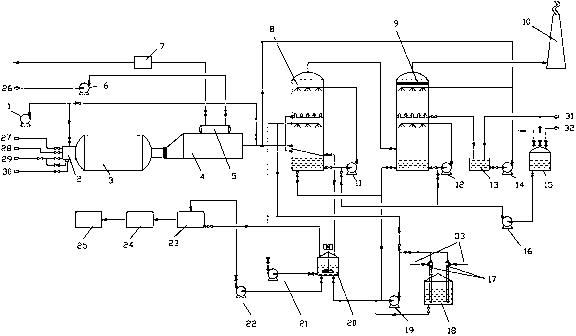
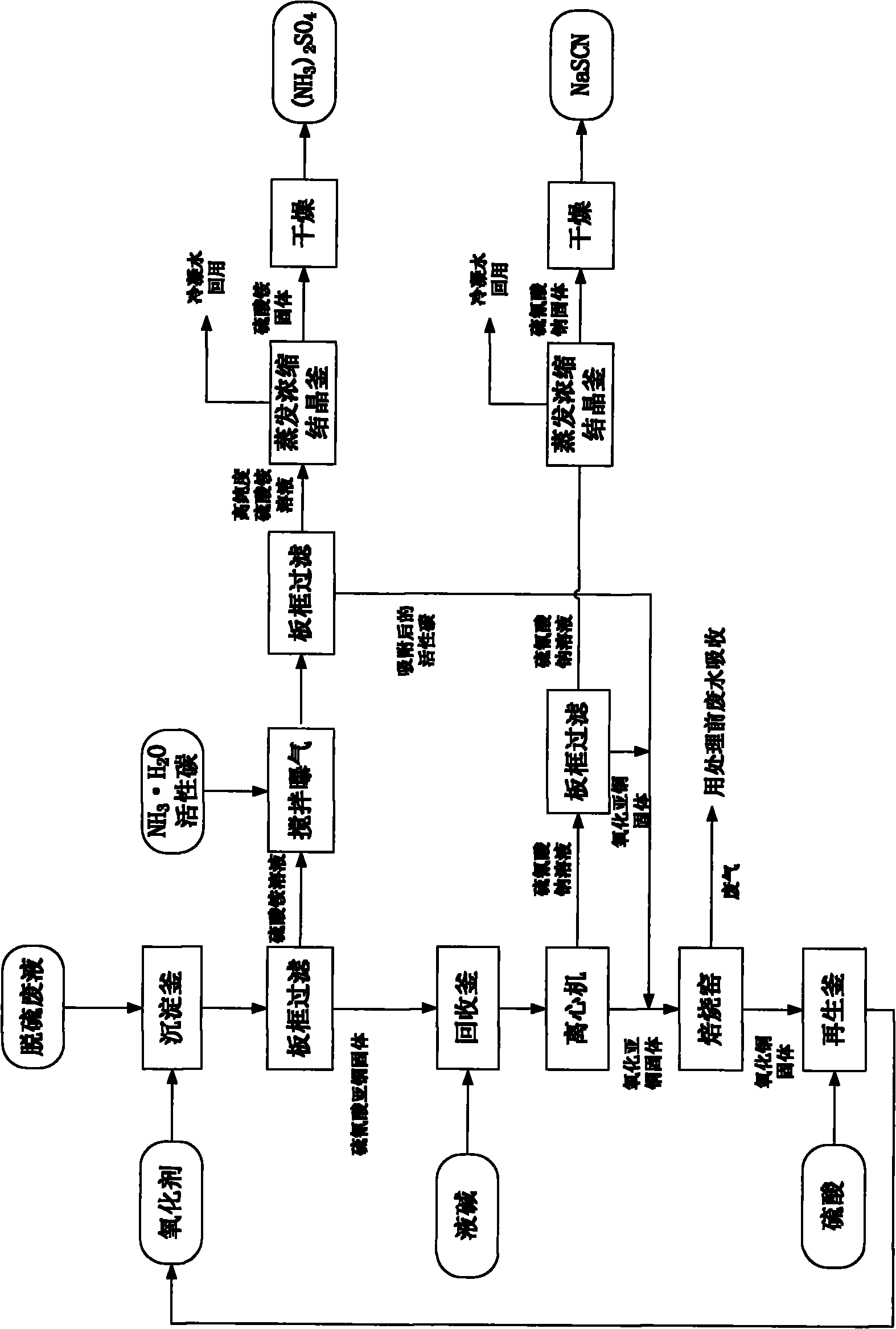
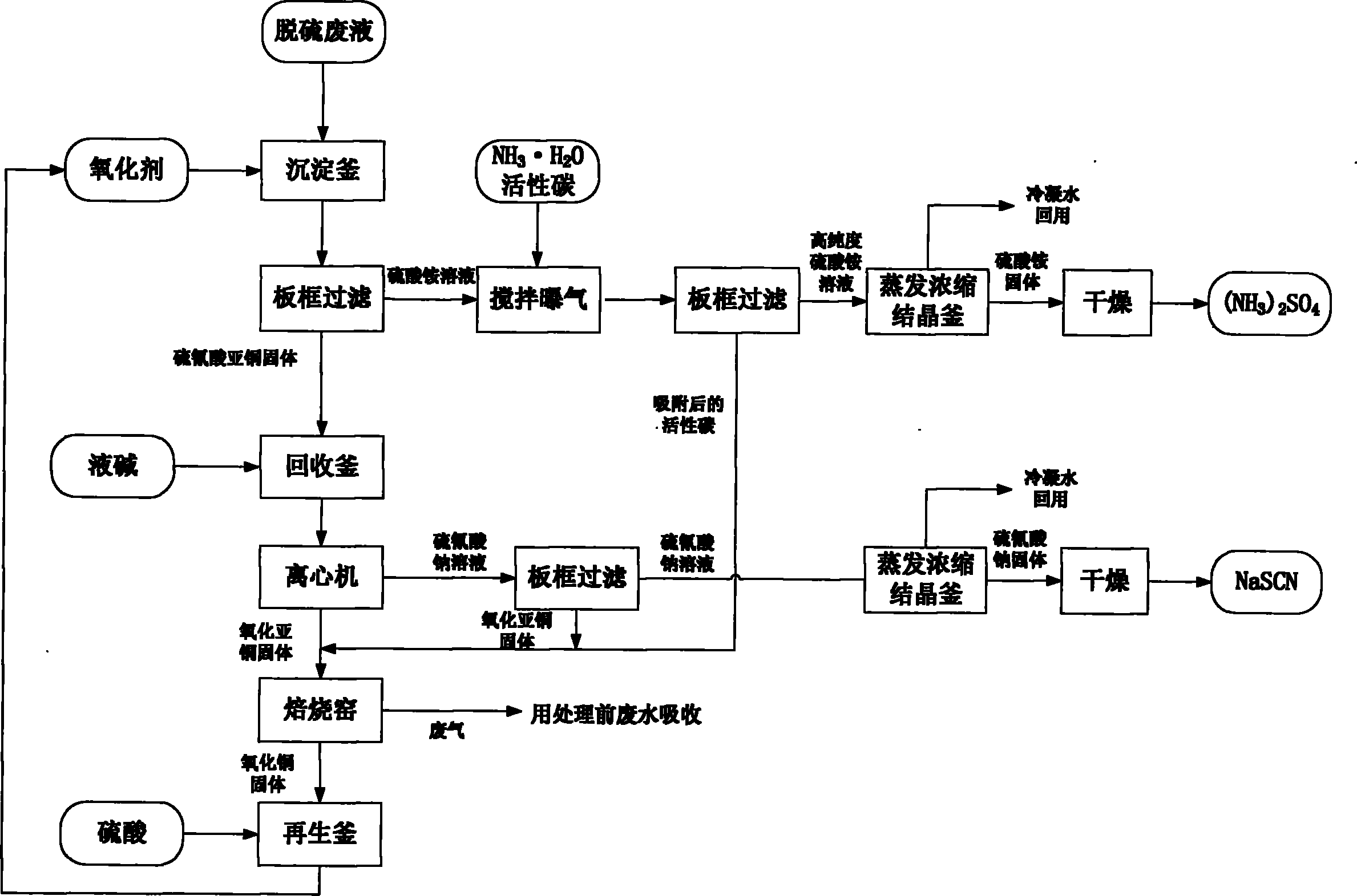
Method for preparing thiocyanate and sulfate by utilizing desulfuration waste liquor in coking plant
ActiveCN101985359AReduce consumptionReduce lossesThiocyanic acidSulfate preparationActivated carbonSulfate
The invention relates to a method for preparing thiocyanate and sulfate by utilizing desulfuration waste liquor in a coking plant, which comprises the following steps of: preparing saturated solution of copper sulfate, mixing the saturated solution with desulfuration waste liquor, and heating and stirring; performing solid-liquid separation to obtain a solid and sulfate liquid; adding aqueous alkali into the solid, heating at the temperature of between 50 and 98 DEG C, and stirring and reacting for 10 to 120 minutes; performing solid-liquid separation on slurry obtained by heating; concentrating the obtained liquid, and freezing for crystallizing and drying to obtain a high-purity thiocyanate product; calcining the obtained solid, adding solution of sulfuric acid, and stirring to produce the copper sulfate for circular use; adding activated carbon into the sulfate liquid, and aerating and oxidizing to purify sulfate; and concentrating the sulfate, and crystallizing and drying to obtain a high-purity sulfate product. The method solves the problem of pollution of the desulfuration waste liquor to the environment, and simultaneously, pollutants can become value products through the production of the high-purity thiocyanate product and the high-purity sulfate product.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
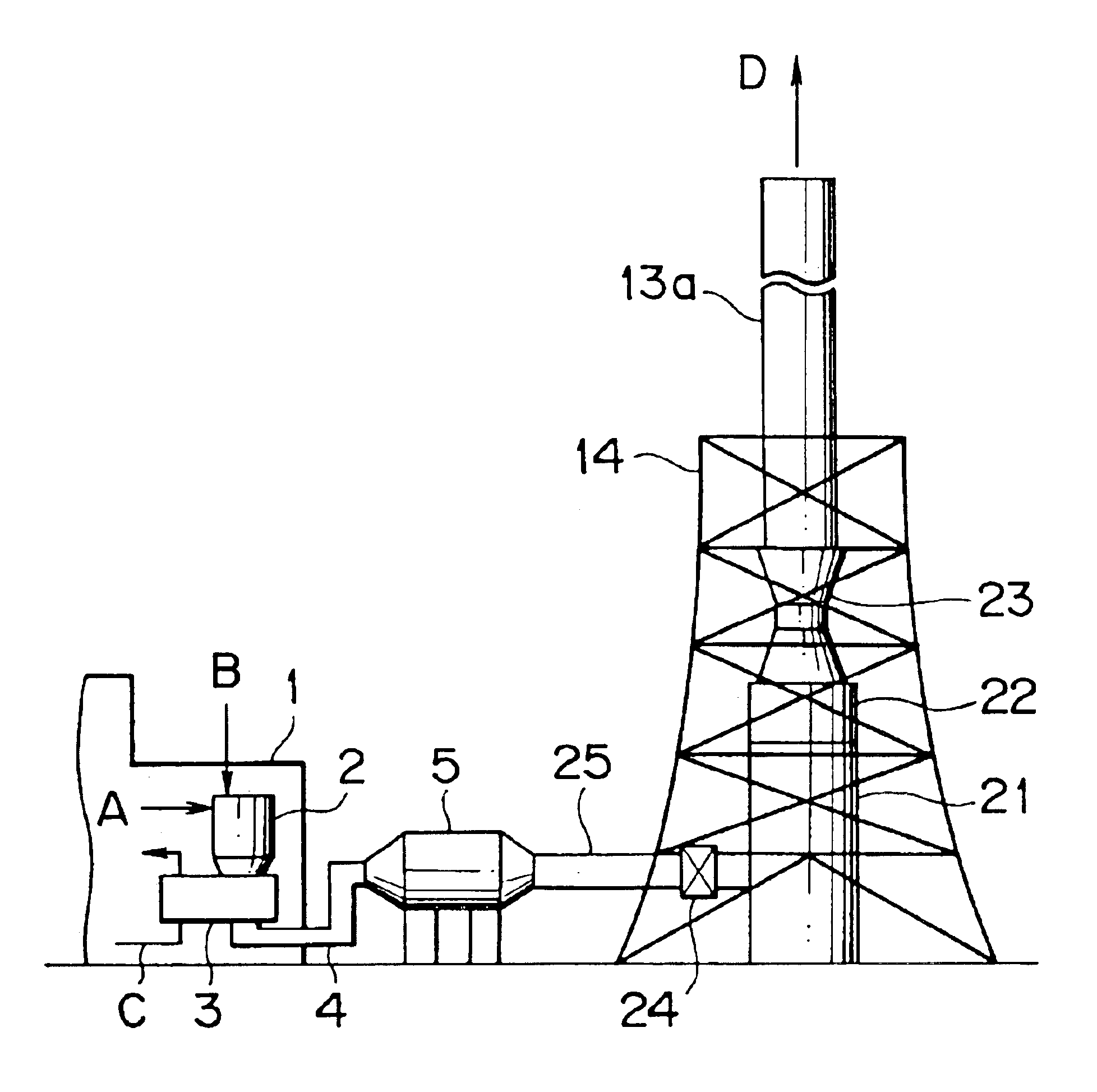
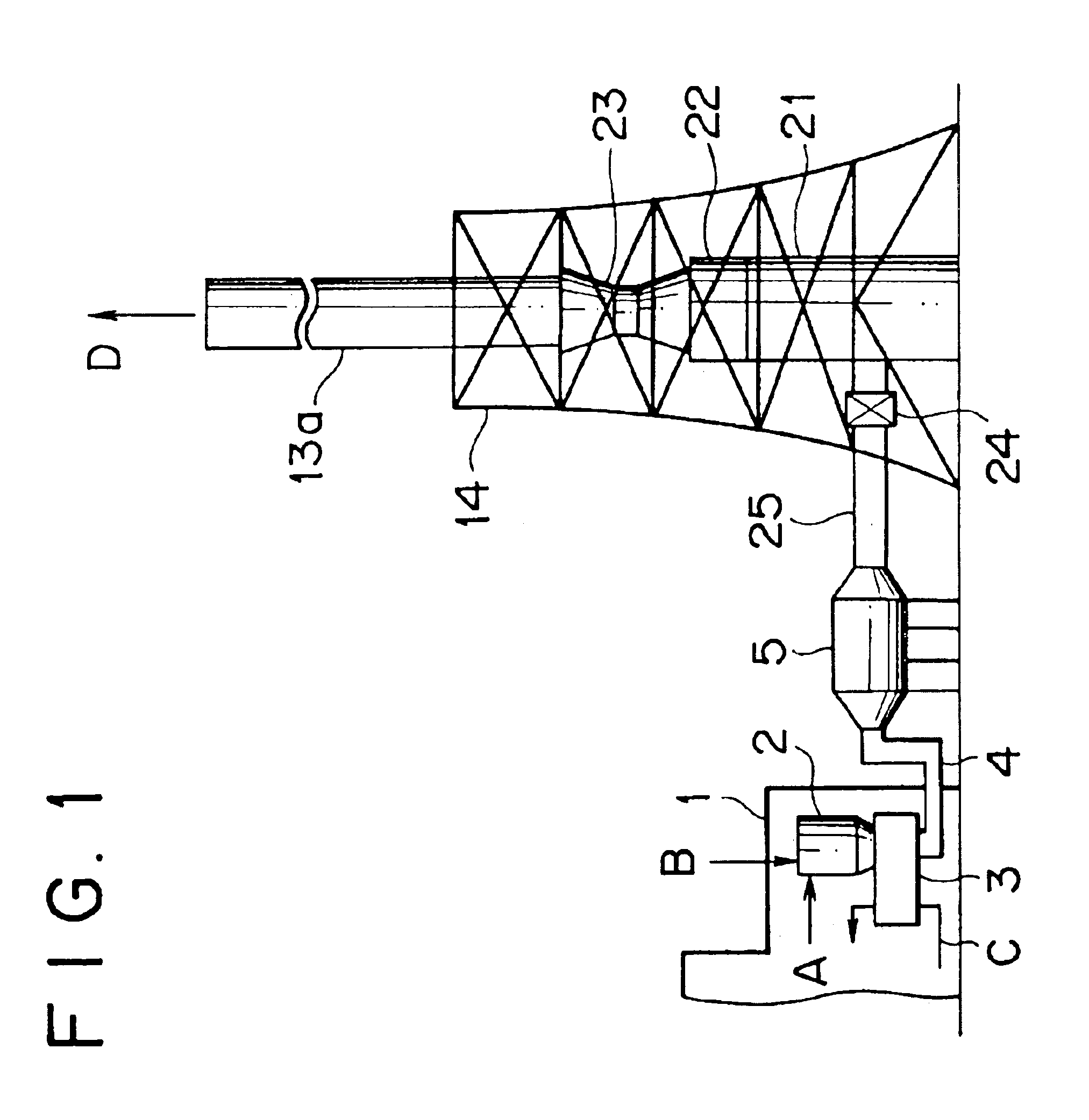
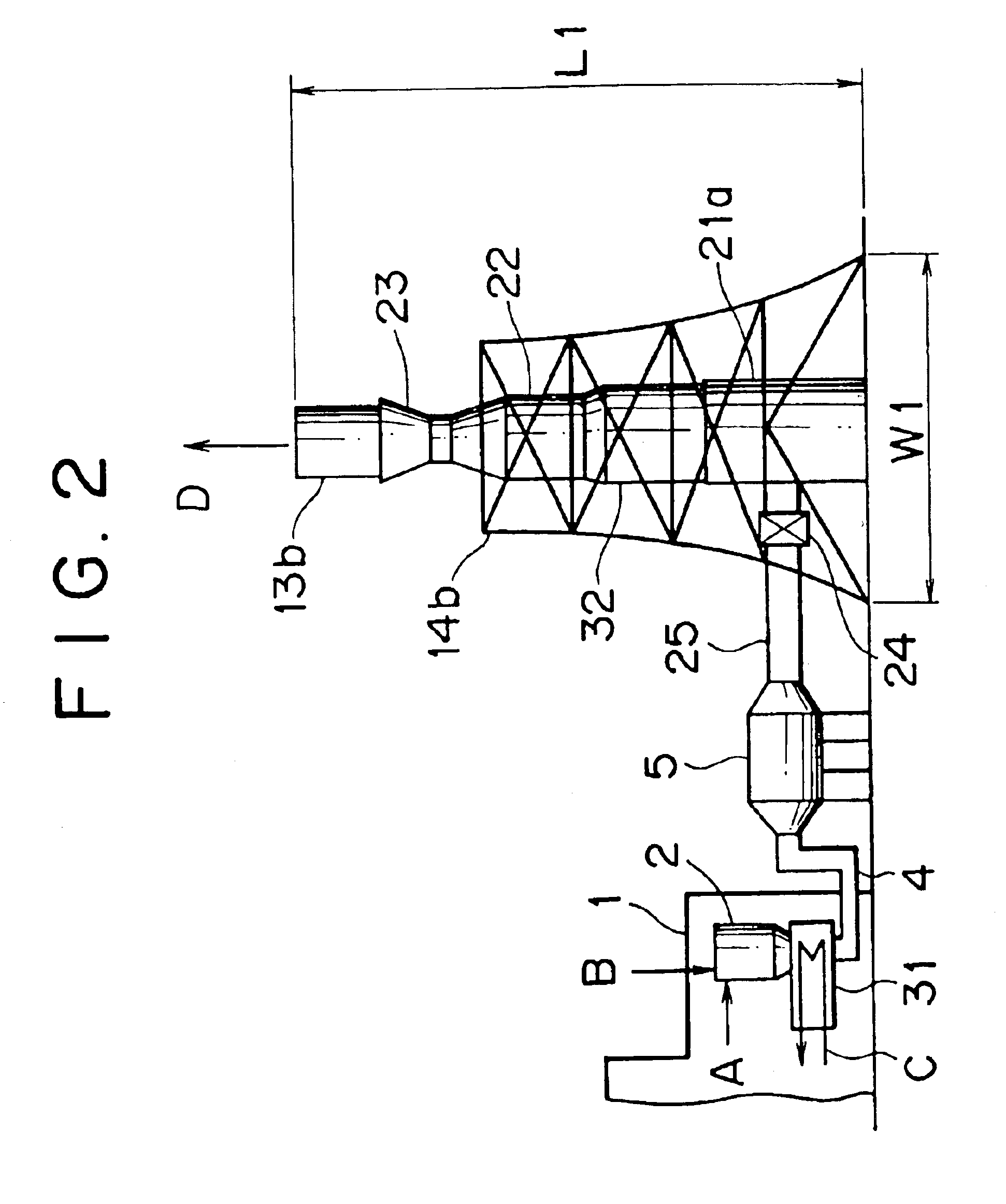
Flue gas treating system and process
In a flue gas treating system, an absorption tower (21), a reheating section (22) and a fan (23) are arranged in line on a vertical axis so as to function as at least a part of a stack for emitting the treated flue gas into the atmosphere. Moreover, in a flue gas treating process, the amount of ammonia injected in the denitration step (a denitrator (2)) and / or the amount of ammonia at a point downstream of the denitration step are determined so as to be on such an excessive level that ammonia or ammonium salt will remain in the flue gas introduced into the desulfurization step (absorption tower (21)). Thus, the size and cost of the equipment can be reduced.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Modified vanadium compound, producing method thereof, redox flow battery electrolyte composite and redox flow battery electrolyte producing method
InactiveUS6872376B2Improve solubilityEasy to prepareCell electrodesRegenerative fuel cellsVanadium CompoundsSulfate
Owner:THE KANSAI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
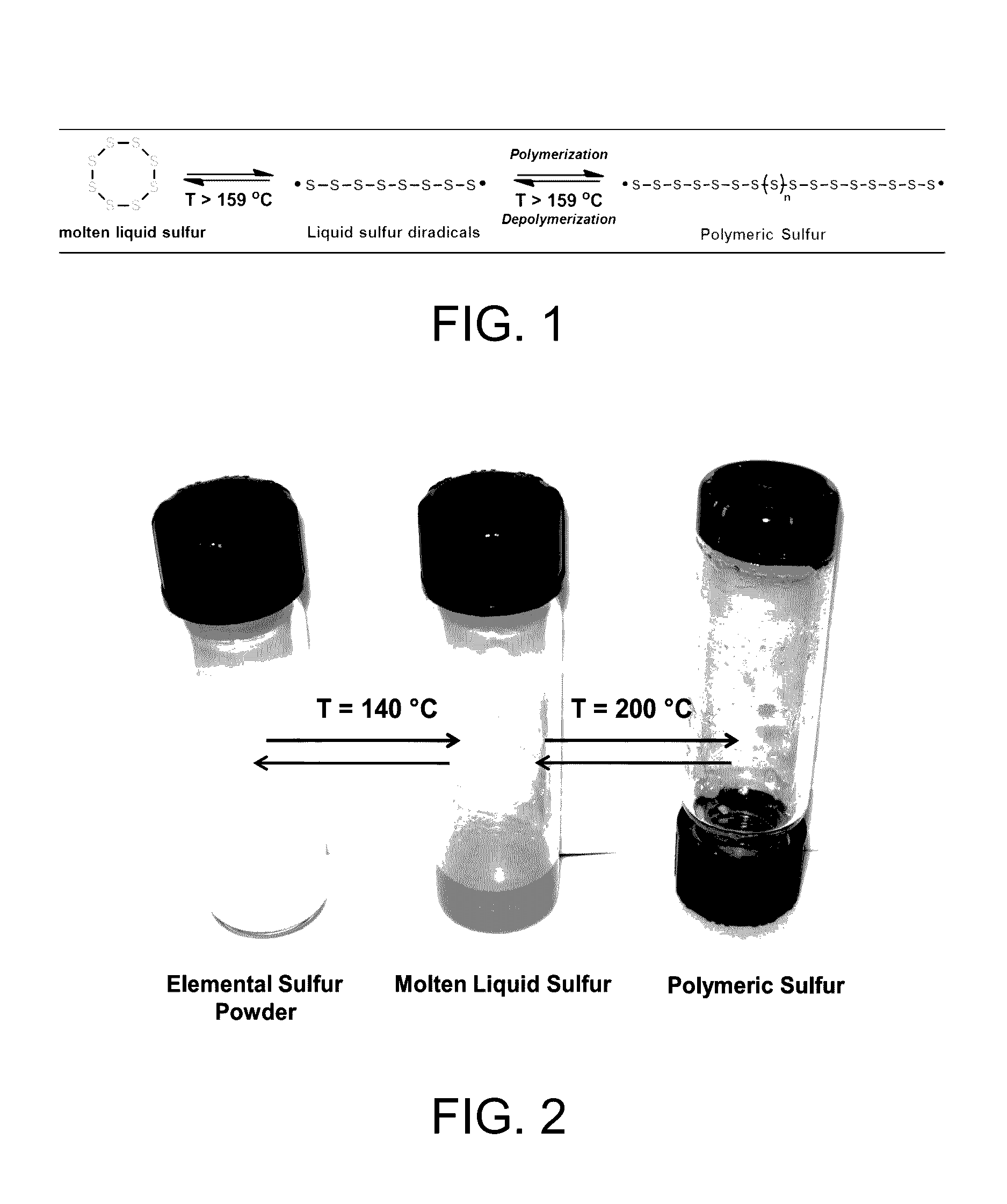
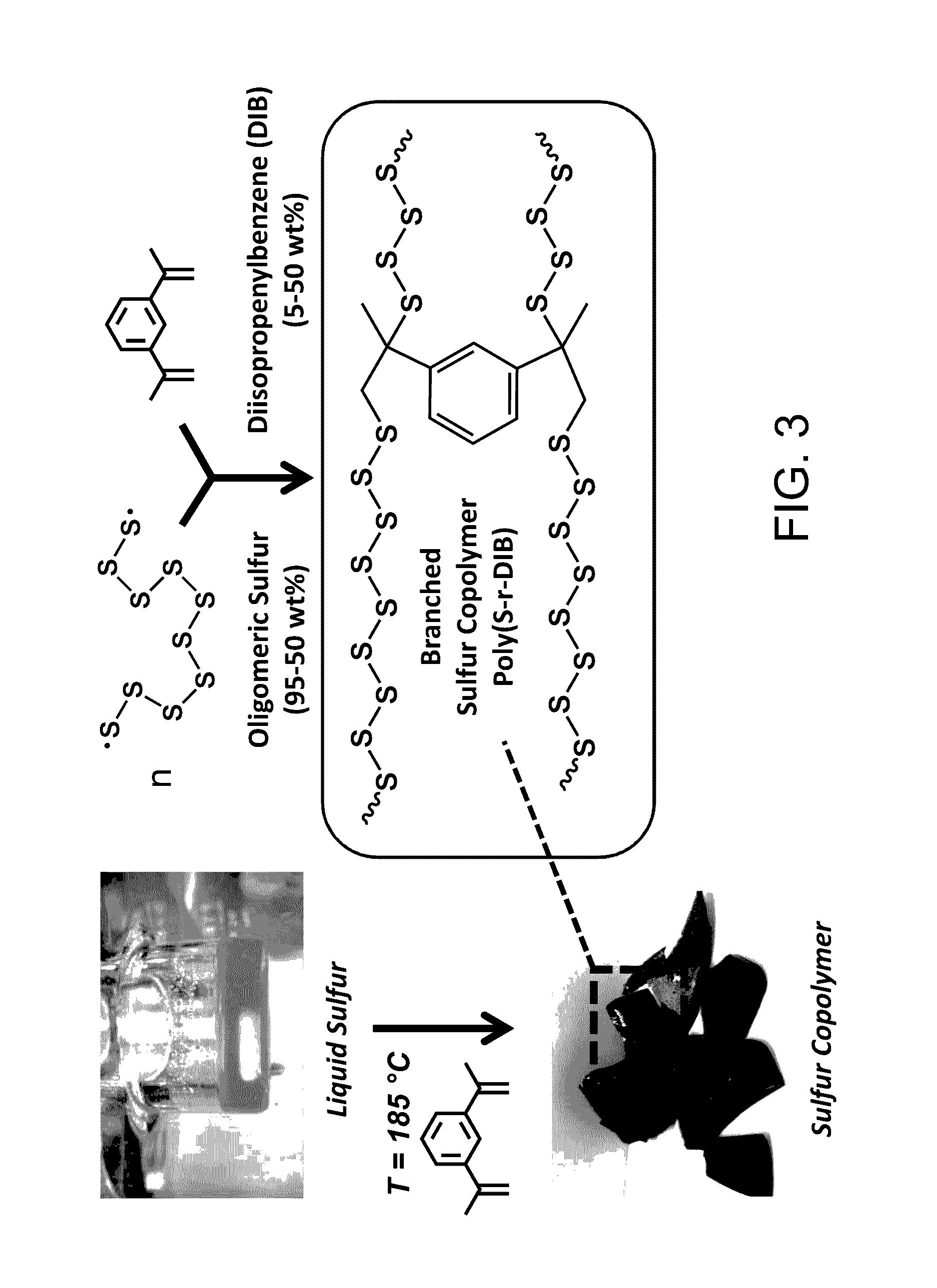
Sulfur composites and polymeric materials from elemental sulfur
ActiveUS9567439B1Increase heightSimple materialBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCeramic compositeSulfide
Sulfur composites and polymeric materials having a high sulfur content and prepared from elemental sulfur as the primary chemical feedstock. The sulfur copolymers are prepared by the polymerization of elemental sulfur with one or more monomers of amines, thiols, sulfides, alkynylly unsaturated monomers, nitrones, aldehydes, ketones, thiiranes, ethylenically unsaturated monomers, or epoxides. The sulfur copolymers may be further dispersed with metal or ceramic composites or copolymerized with elemental carbon, photoactive organic chromophores, or reactive and solubilizing / biocompatible moieties. The sulfur composites and polymeric materials feature the ability self-healing through thermal reformation. Applications utilizing the sulfur composites and polymeric materials may include electrochemical cells, optics, H2S donors and antimicrobial materials.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
Production of silver sulfate grains using organo-sulfate or organo-sulfonate additives
ActiveUS7261867B1Uniform morphologyUniform sizePigmenting treatmentCosmetic preparationsOrganic sulfonic acidSulfonate
An aqueous precipitation process for the preparation of particles comprising primarily silver sulfate, comprising reacting an aqueous soluble silver salt and an aqueous soluble source of inorganic sulfate ion in an agitated precipitation reactor vessel and precipitating particles comprising primarily silver sulfate, wherein the reaction and precipitation are performed in the presence of an aqueous soluble organo-sulfate or organo-sulfonate additive compound, the amount of additive being a minor molar percentage, relative to the molar amount of silver sulfate precipitated, and effective to result in precipitation of particles comprising primarily silver sulfate having a mean grain size of less than 50 micrometers.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Scavenger for aldehyde(s) and a manufacturing method of a woody panel using the same
InactiveUS20090130474A1Ease of evaluationImprove trapping efficiencyOrganic chemistrySulfate/bisulfate preparationScavengerRoom temperature
Regarding the scavenger for aldehyde(s) used at the time of manufacturing a woody panel using woody materials and formaldehyde-based binders, the scavenger for aldehyde(s) without lowering of trapping properly even when a surface of said woody panel is sanded and having an excellent trapping property of trapping formaldehyde is provided. Further, the method of manufacturing a woody panel using a scavenger for aldehyde(s) and a woody panel are provided.At least one kind of compound for trapping aldehyde(s) being solid at a room temperature is included and said compound for trapping aldehyde(s) is defined to be a powdery scavenger for aldehyde(s) having a property of generating acidic gas, in particular, sulfurous acid gas by heating and said compound for trapping aldehyde(s) is added to a binder or woody materials followed by a hot press, thereby manufacturing a woody panel.
Owner:IPPOSHA OIL INDS
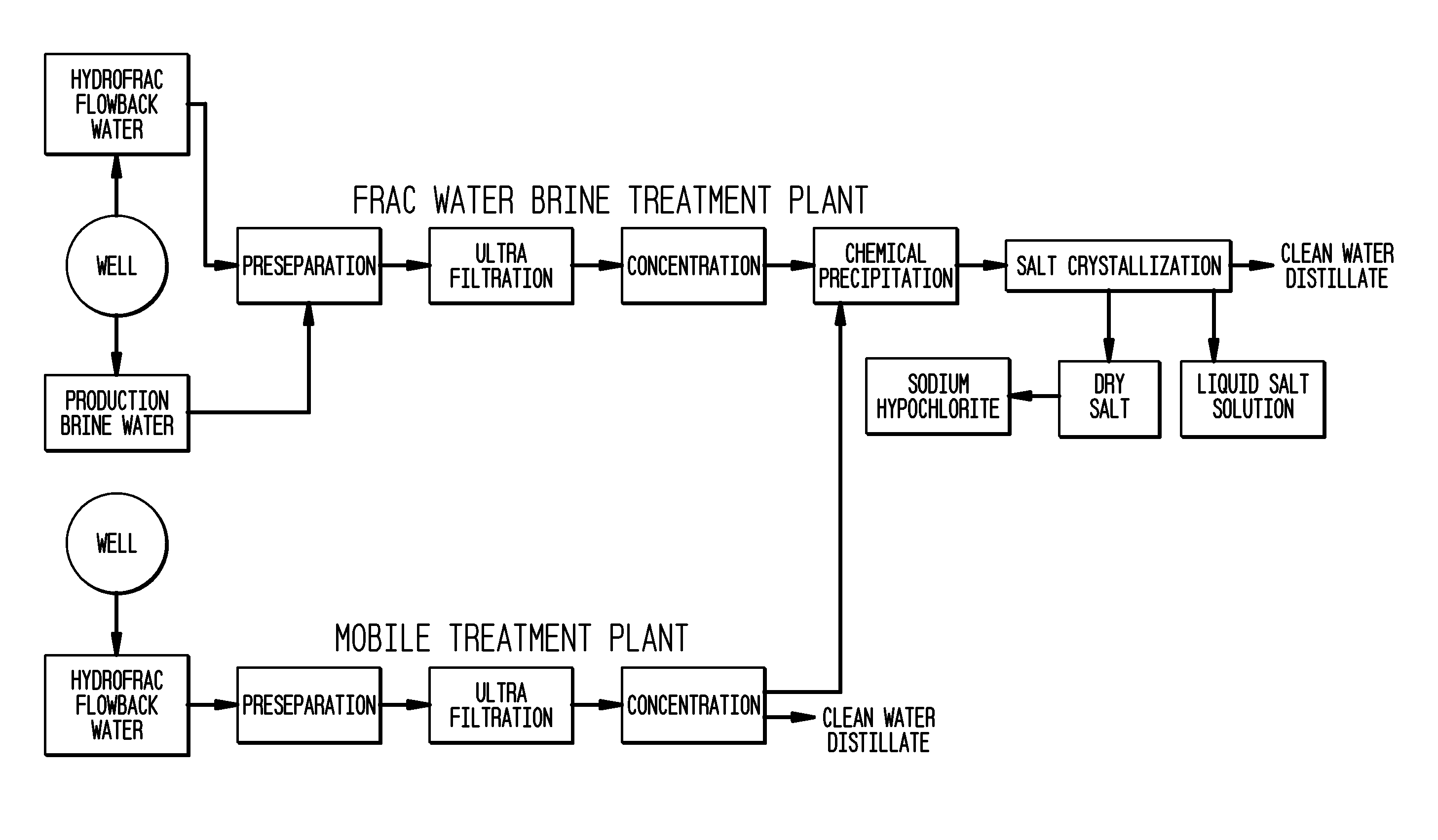
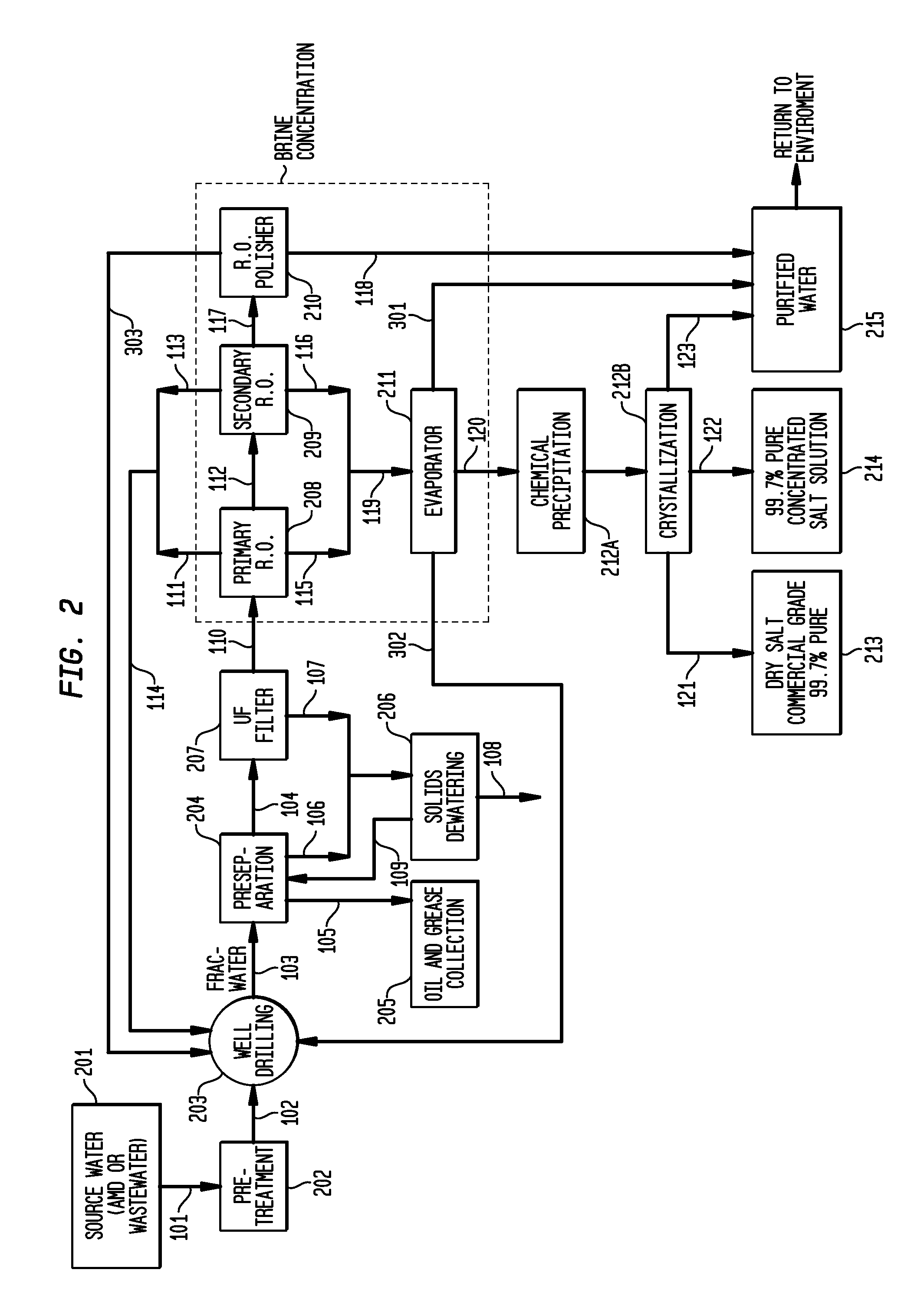
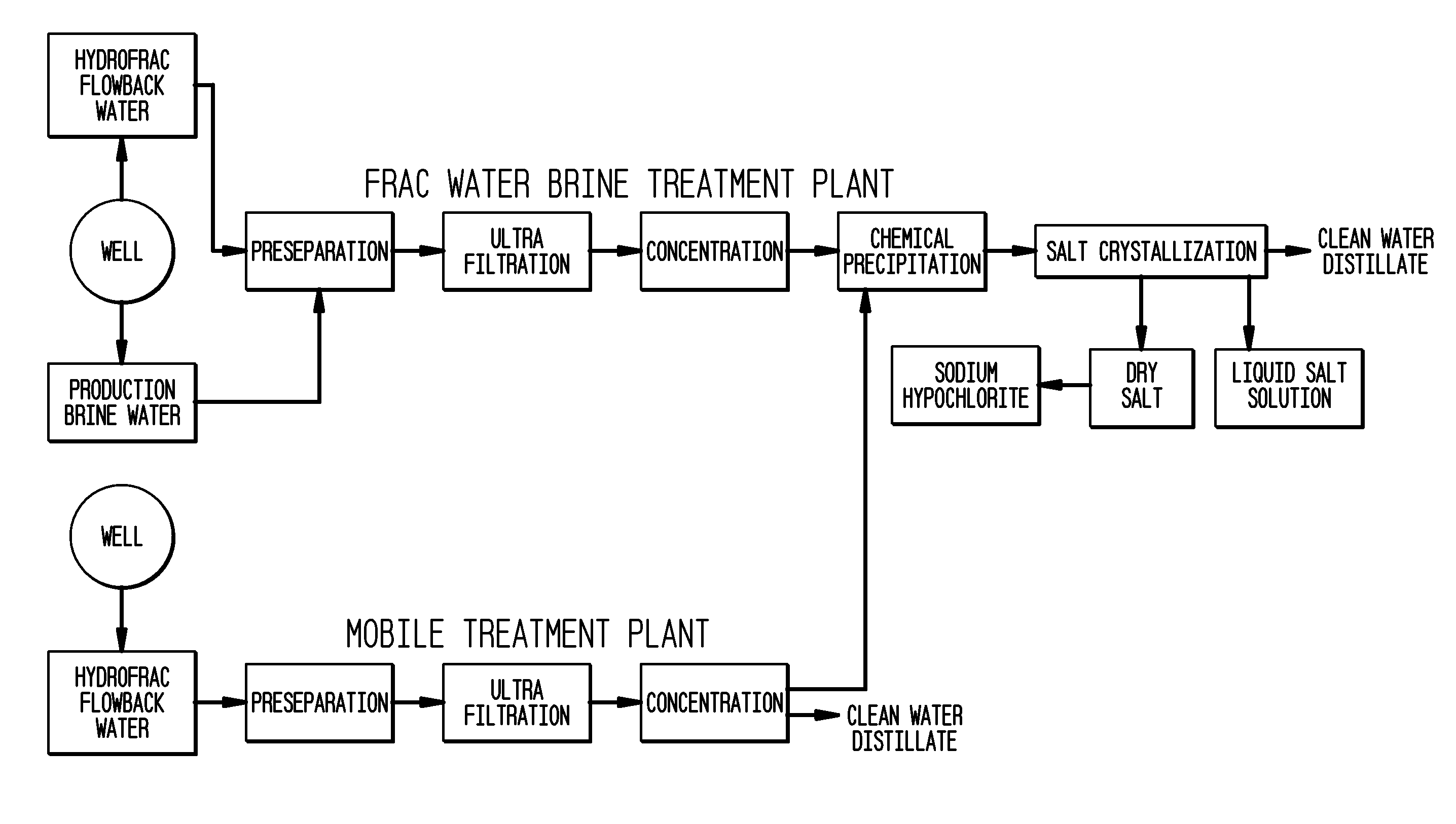
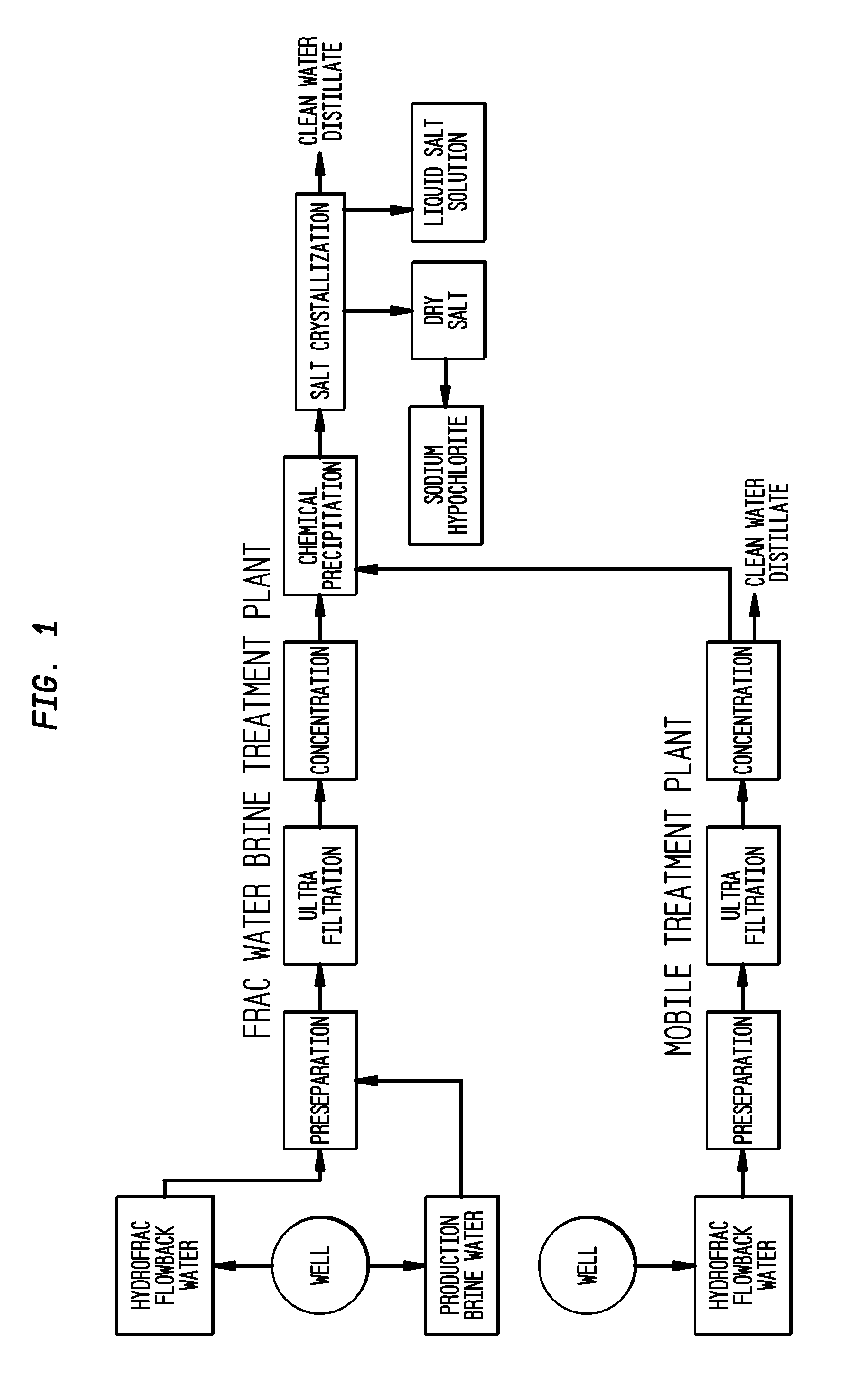
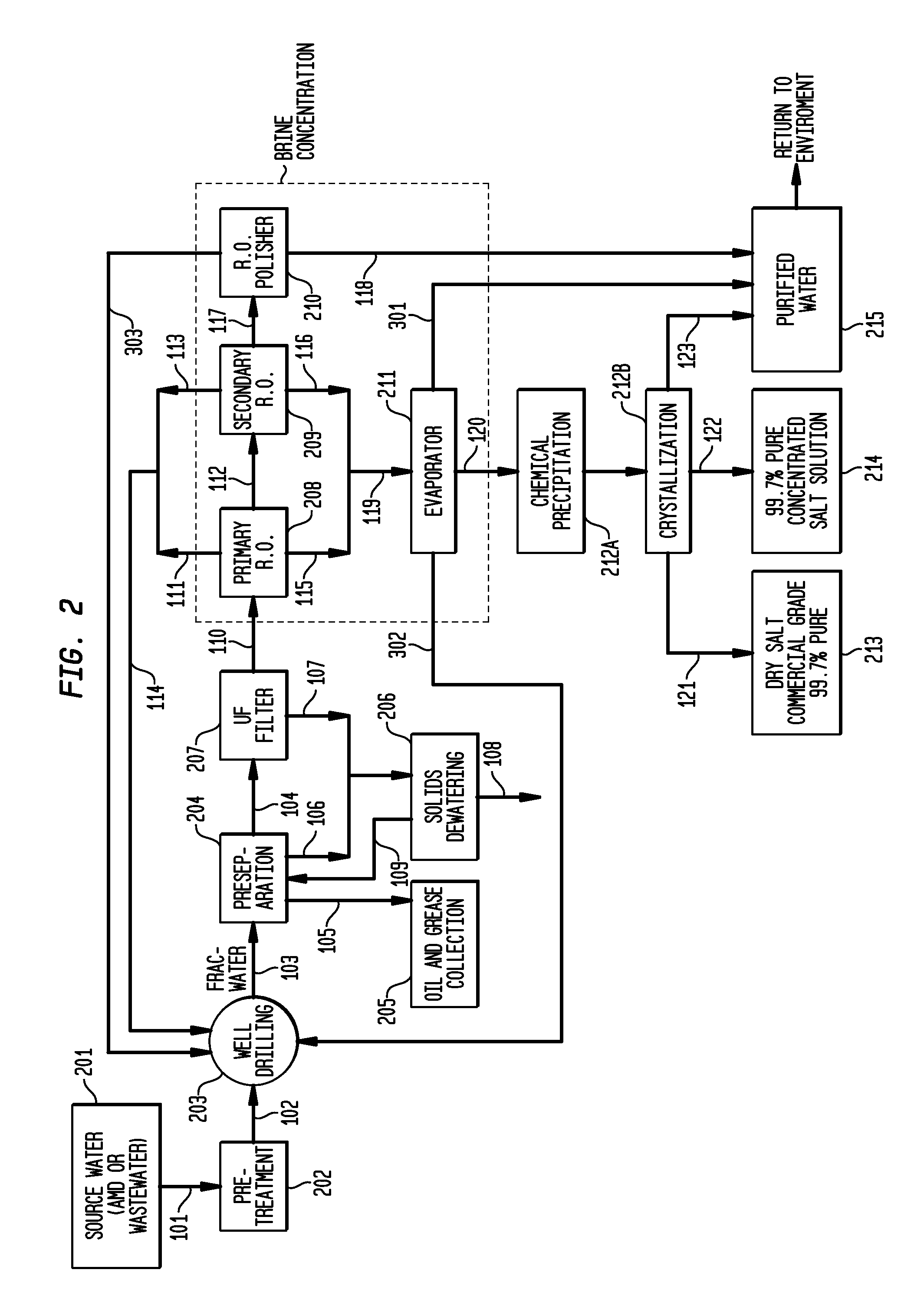
Method of making pure salt from FRAC-water/wastewater
ActiveUS8158097B2Yield maximizationQuality improvementCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesWater useParticulates
The present invention relates to a method for making pure salt comprises recapturing post-drilling flowback water from hydro-fracturing; removing oil from the flowback water; filtering the flowback water using an ultra filter with a pore size of about 0.1 microns or less to remove solid particulates and large organic molecules, such as benzene, ethylbenzene, toluene, and xylene, from the water; concentrating the flowback water to produce a brine that contains from about 15 wt % to about 40 wt % of salt relative to the total weight of the flowback brine; performing one or more chemical precipitation process using an effective amount of reagents to precipitate out the desired high quality commercial products, such as, barium sulfate, strontium carbonate, calcium carbonate; and crystallizing the chemically treated and concentrated flowback brine to produce greater than 99.5% pure salt products, such as sodium and calcium chloride.
Owner:FRACPURE HLDG
Process for recovery of sulphate of potash
ActiveUS7041268B2Eliminate needMaximize recoveryChemical industrySulfate preparationPhysical chemistryCarnallite
The present invention is directed to a novel integrated process for the recovery of sulphate of potash (SOP) from sulphate rich bittern. The process requires bittern and lime as raw materials. Kainite type mixed salt is obtained by fractional crystallization of the bittern, and is converted to schoenite which is subsequently reacted with muriate of potash (MOP) for its conversion to SOP. End liquor from kainite to schoenite conversion (SEL) is desulphated and supplemented with MgCl2 using end bittern generated in the process of making carnallite. Decomposed carnallite liquor produced is reacted with hydrated lime for preparing CaCl2 solution and high purity Mg(OH)2 having low boron content. It is shown that the liquid streams containing potash are recycled in the process, and the recovery of potash in the form of SOP is quantitative.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Process for recovery of sulphate of potash
ActiveUS20050220698A1Minimize effluent generationEnhance potash recoveryEnergy inputSulfate preparationDecompositionCarnallite
A novel integrated process for the recovery of sulphate of potash (SOP) from sulphate rich bittern is disclosed. The process requires only bittern and lime as raw materials. Kainite type mixed salt is obtained by fractional crystallization of the bittern, Kainite is converted to schoenite with simultaneous removal of NaCl by processing it with water and end liquor obtained from reaction of schoenite with MOP for its conversion to SOP. The end liquor from kainite to schoenite conversion (SEL) is used for the recovery of MOP. SEL is desulphated and supplemented with MgCl2 using end bittern generated in the process of making carnallite. The carnallite is decomposed to get crude potash which in turn processed to get MOP. The carnallite decomposed liquor produced in the decomposition of carnallite is reacted with hydrated lime for preparing CaCl2 solution and high purity Mg(OH)2 having low boron content, The CaCl2 solution is used for desulphatation of SEL producing high purity gypsum as a byproduct. It is shown that the liquid steams containing potash are recycled in the process, the recovery of potash in the form of SOP is quantitative.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
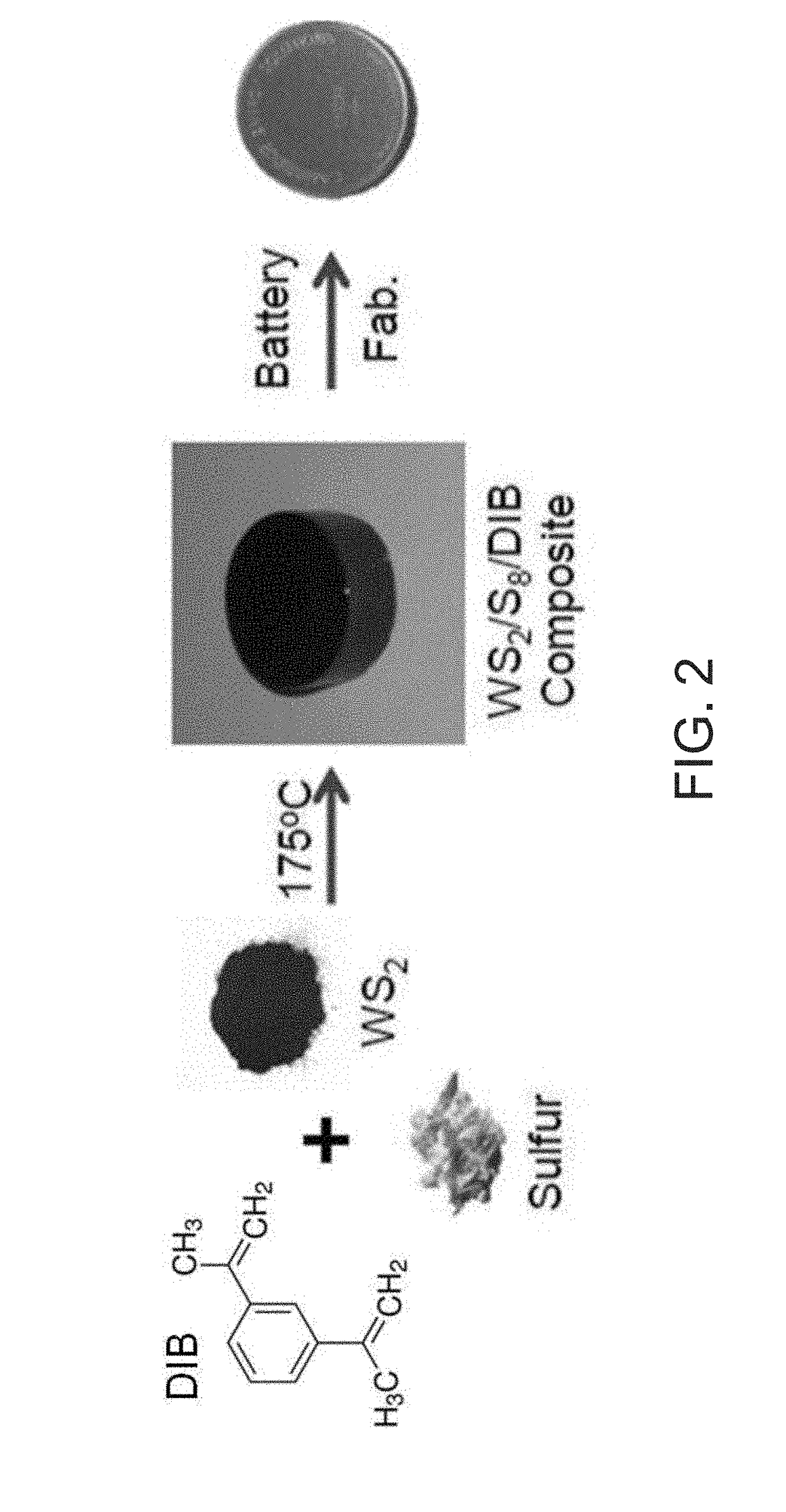
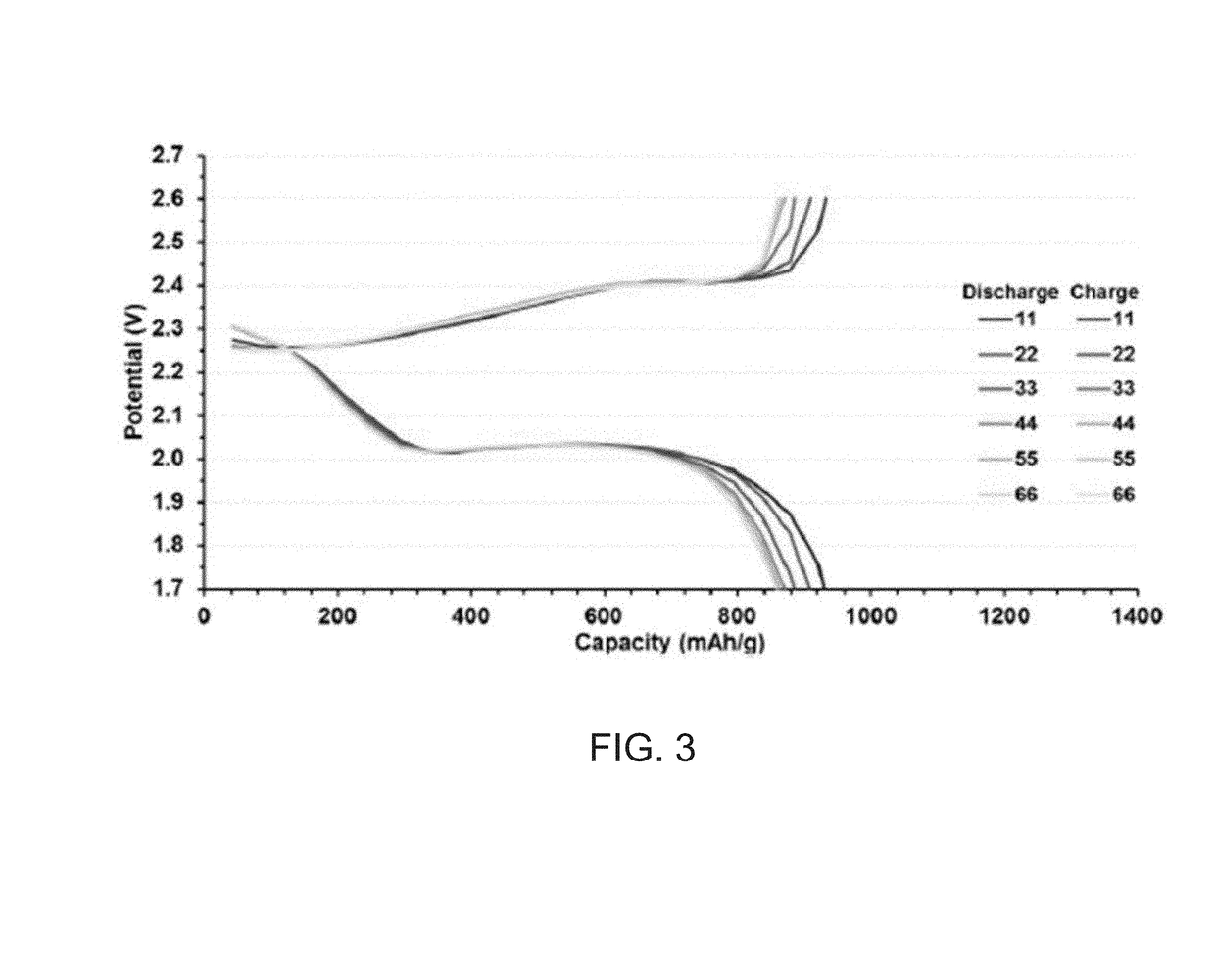
CATHODE MATERIALS FOR Li-S BATTERIES
ActiveUS20180079865A1Improves Li-S battery performanceMaintain good propertiesBiocideOrganic active ingredientsElectrical batteryElectrochemical cell
Compositions and methods of producing composite materials for use as a cathode in electrochemical cells. Elemental sulfur is mixed with tungsten sulfide (WS2) to form a composite mixture. Organic comonomers may be added to the composite mixture. The composite mixture is reacted to form the composite material. Electrochemical cells with cathodes containing the composite material demonstrated improved battery performance.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
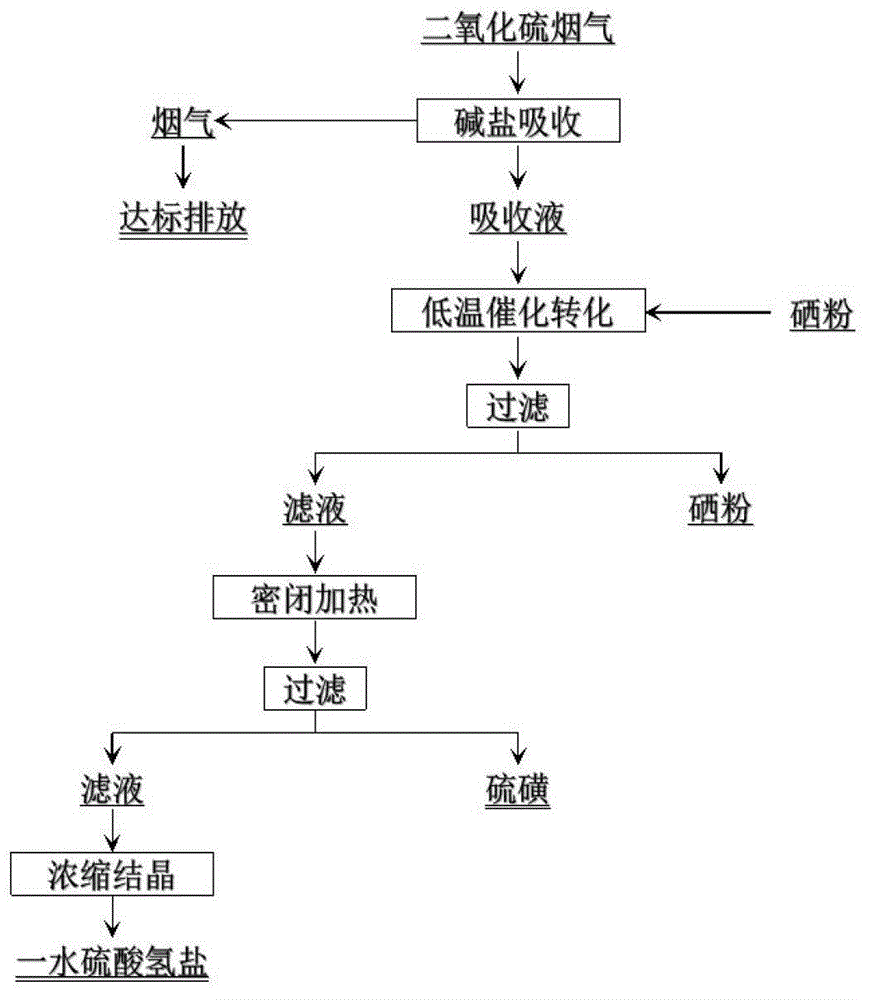
Method of sulfur recovery through sulfur dioxide flue gas cleaning and catalyzing and application of catalyst
ActiveCN102910590AHigh purityEffective absorptionSulfur preparation/purificationSulfate preparationFlue gasEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method of sulfur recovery through sulfur dioxide flue gas cleaning and catalyzing and the application of a catalyst. The technical steps are shown as the following figure, and the method concretely comprises the following steps: absorbing sulfur dioxide flue gas through alkali liquor, adding elementary selenium powder catalyst into obtained absorption liquid containing hydrosulphite, adding the elementary selenium powder catalyst and the absorption liquid into a closed container to be conducted to catalyzing, so as to produce elementary sulfur precipitate, adding sulphuric acid into the liquid after the sulfur precipitate is filtered and separated, concentrating and crystallizing, and obtaining hydrosulfate crystal after filtering. The method overcomes the deficiency of low concentration sulfur dioxide flue gas treatment in the prior art, adopts the elementary selenium as the catalyst, provides an efficiently absorbed sulfur recovery, adopts the mode of recovering elementary sulfur through two-stage low temperature sulfur-containing absorption liquid catalyzing and converting, is simple and environmentally friendly and high in economic benefit, and belongs to the field of resource and environment protection.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
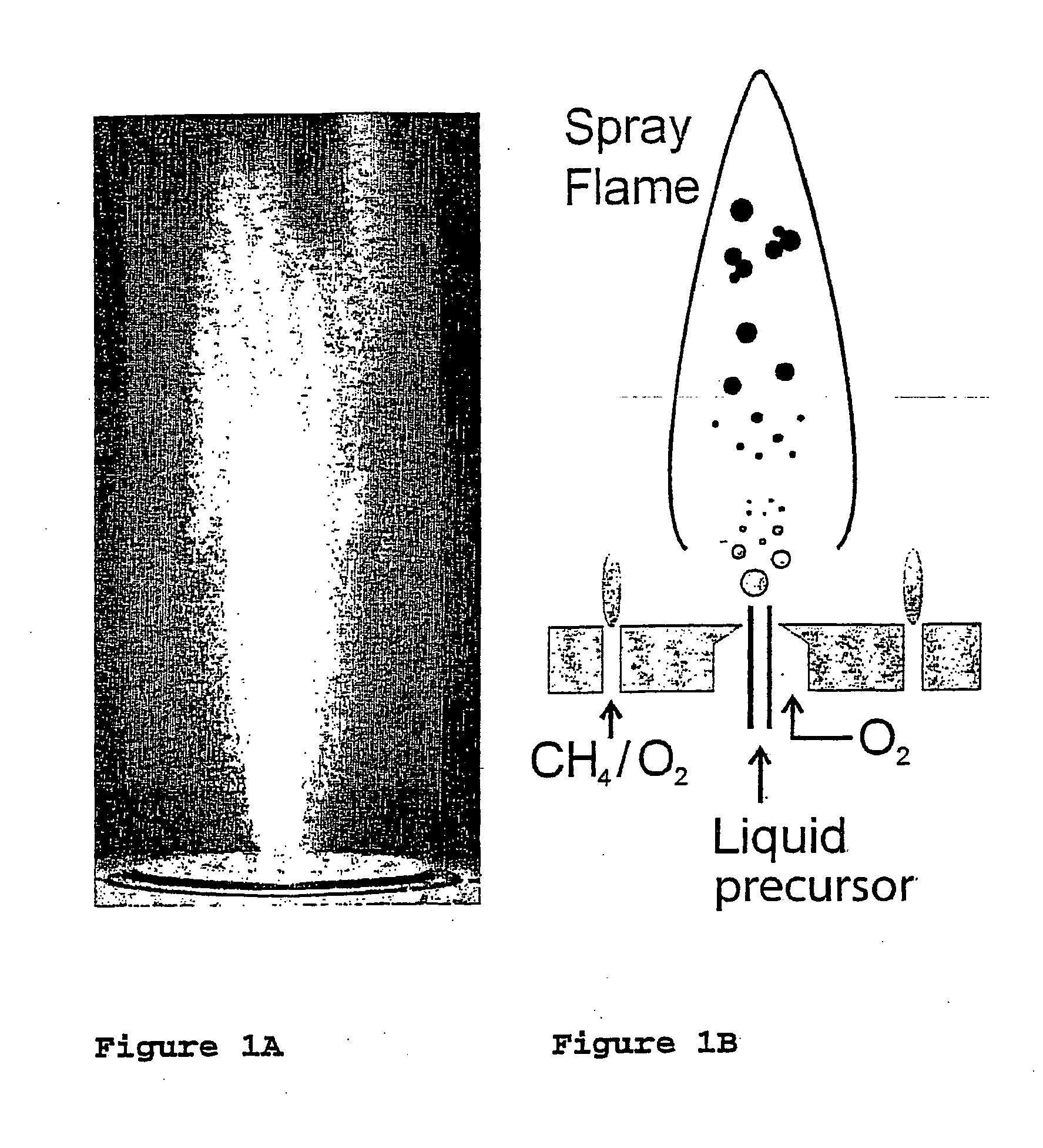
Flame synthesis of metal salt nanoparticles, in particular calcium and phosphate comprising nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070196259A1Increase chanceCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesMaterial nanotechnologyBiocompatibility TestingMetallacarboxylic acid
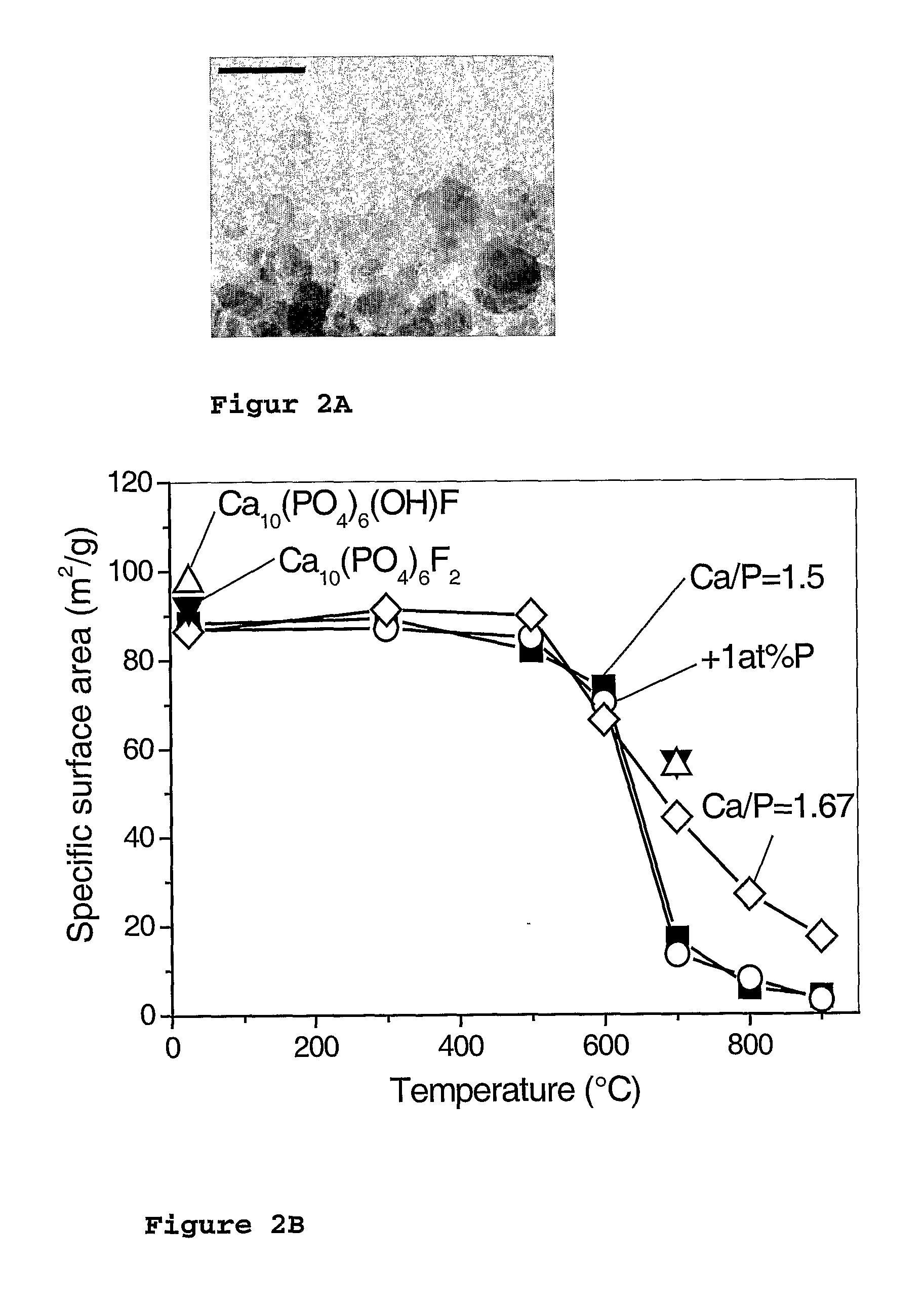
Described is a method for the production of metal salts, wherein the cationic metal is preferably selected from Group I to IV metals and mixtures thereof and the anionic group is selected from phosphates, silicates, sulfates, carbonates, hydroxides, fluorides and mixtures thereof, and wherein said method comprises forming a mixture of at least one metal source that is a metal carboxylate with a mean carbon value per carboxylate group of at least 3 and at least one anion source into droplets and oxiding said droplets in a high temperature environment, preferably a flame. This method is especially suited for the production of calcium phosphate biomaterials such as hydroxyapatite (HAp,Cal0(P04)6(OH)2) and tricalcium phosphate (TCP,Ca3(P04)2) that exhibit excellent biocompatibility and osteoconductivity and therefore are widely used for reparation of bony or periodontal defects, coating of metallic implants and bone space fillers.
Owner:EIDENGOSSICHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH
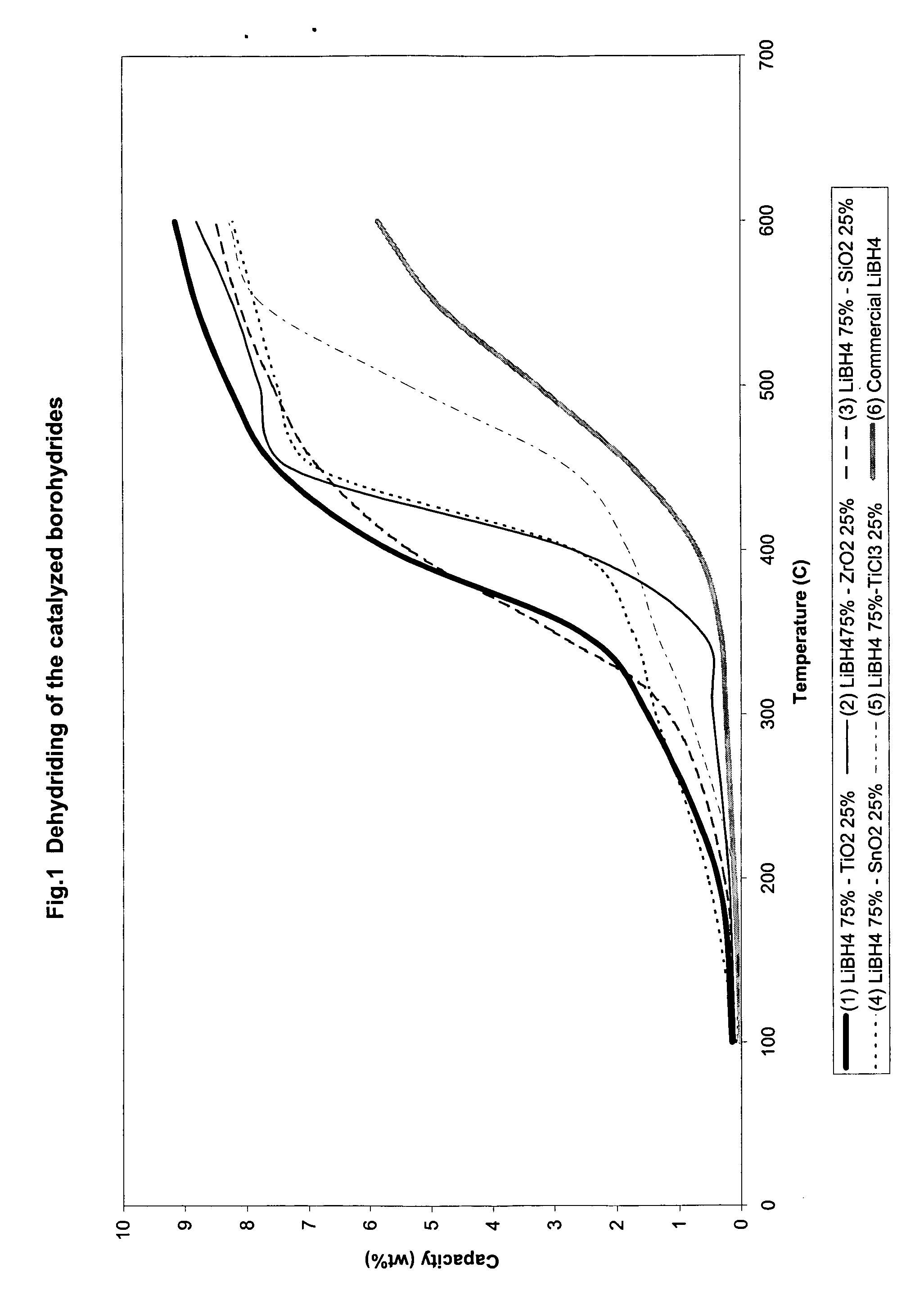
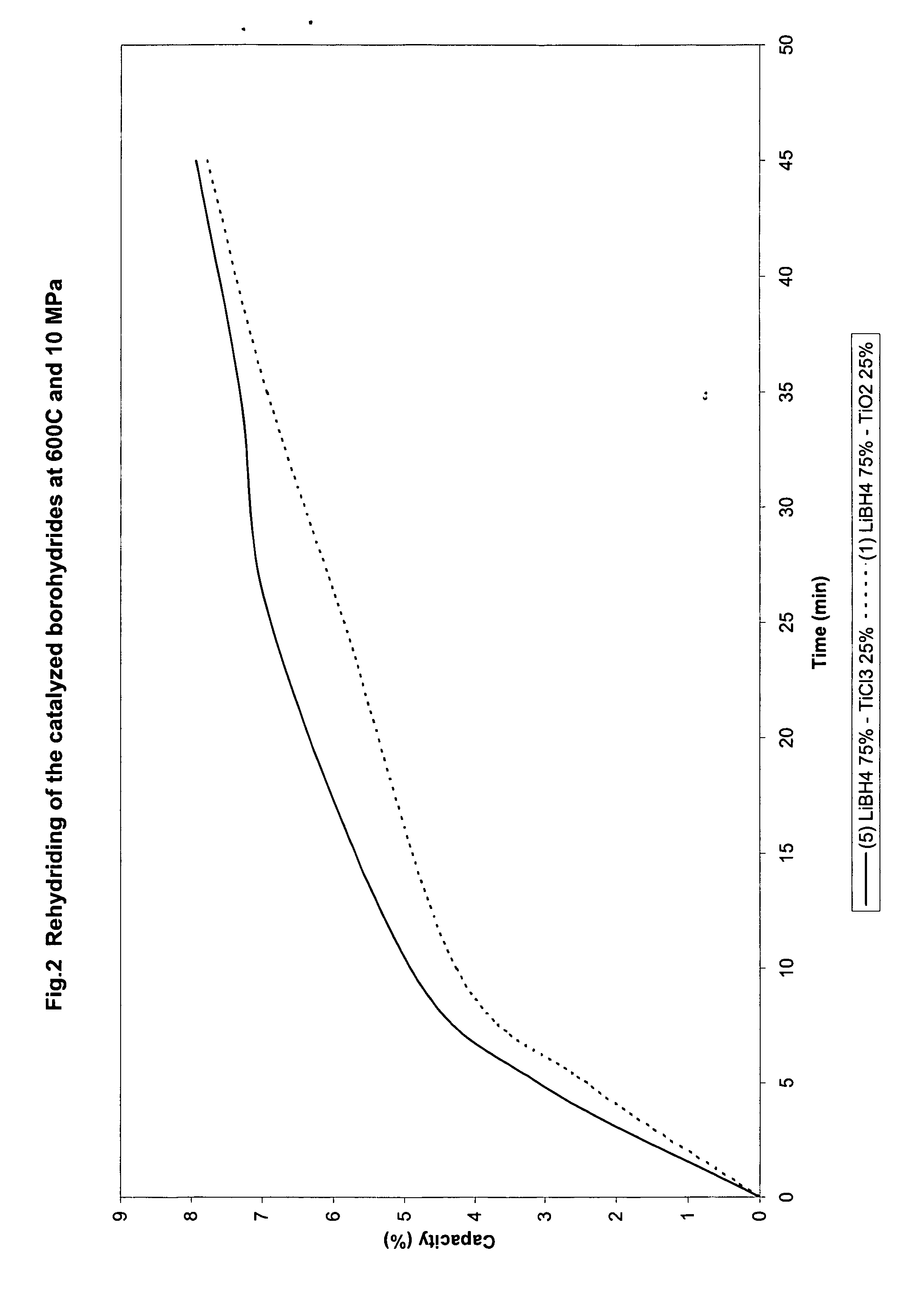
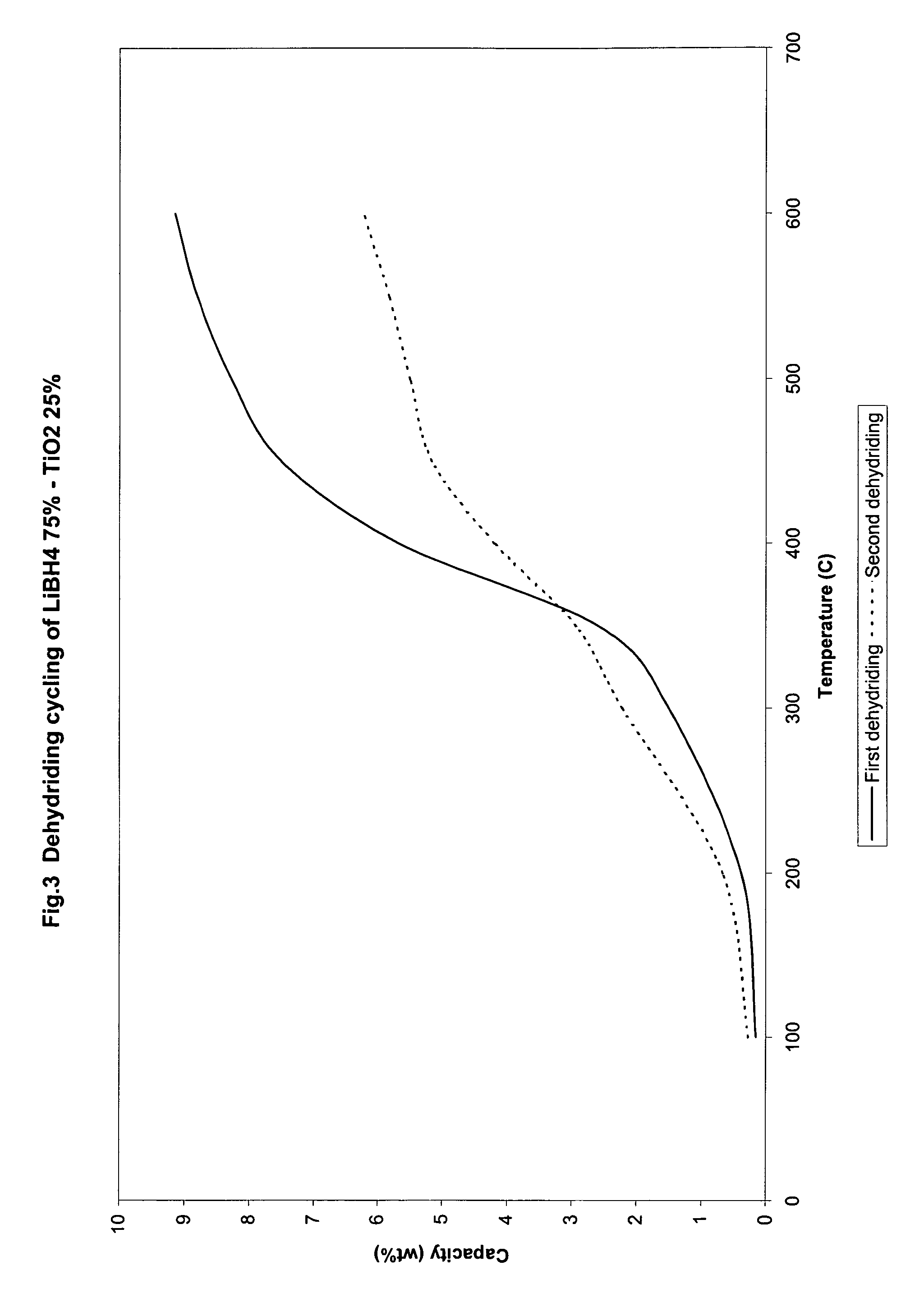
Catalyzed borohydrides for hydrogen storage
InactiveUS20060046930A1Reduce the temperatureOther chemical processesMonoborane/diborane hydridesChlorideTitanium
A hydrogen storage material and process is provided in which alkali borohydride materials are created which contain effective amounts of catalyst(s) which include transition metal oxides, halides, and chlorides of titanium, zirconium, tin, and combinations of the various catalysts. When the catalysts are added to an alkali borodydride such as a lithium borohydride, the initial hydrogen release point of the resulting mixture is substantially lowered. Additionally, the hydrogen storage material may be rehydrided with weight percent values of hydrogen at least about 9 percent.
Owner:SAVANNAH RIVER NUCLEAR SOLUTIONS
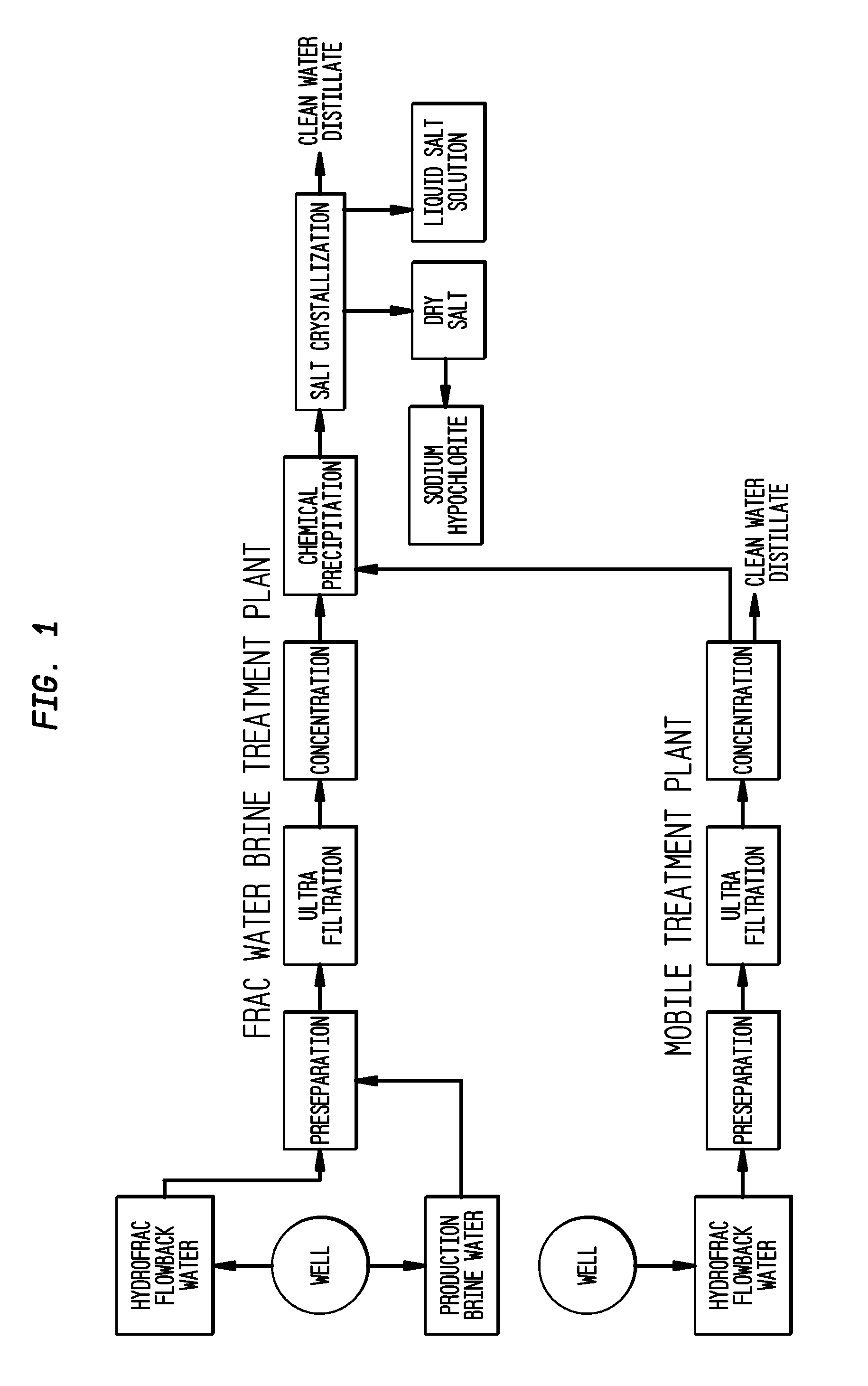
Method of making pure salt from frac-water/wastewater
ActiveUS20110104038A1Easy to produceQuality improvementCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesParticulatesWater use
The present invention relates to a method for making pure salt comprises recapturing post-drilling flowback water from hydro-fracturing; removing oil from the flowback water; filtering the flowback water using an ultra filter with a pore size of about 0.1 microns or less to remove solid particulates and large organic molecules, such as benzene, ethylbenzene, toluene, and xylene, from the water; concentrating the flowback water to produce a brine that contains from about 15 wt % to about 40 wt % of salt relative to the total weight of the flowback brine; performing one or more chemical precipitation process using an effective amount of reagents to precipitate out the desired high quality commercial products, such as, barium sulfate, strontium carbonate, calcium carbonate; and crystallizing the chemically treated and concentrated flowback brine to produce greater than 99.5% pure salt products, such as sodium and calcium chloride.
Owner:FRACPURE HLDG
Methods for recovering at least one metallic element from ore
ActiveUS7323150B2Reduce and eliminate needEasy extractionCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesSolvent extractionSulfateSolvent
Owner:CABOT SPECIALTY FLUIDS
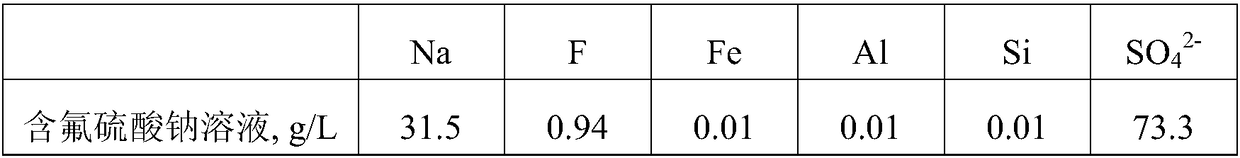
Method for removing fluorine from sulfate solution
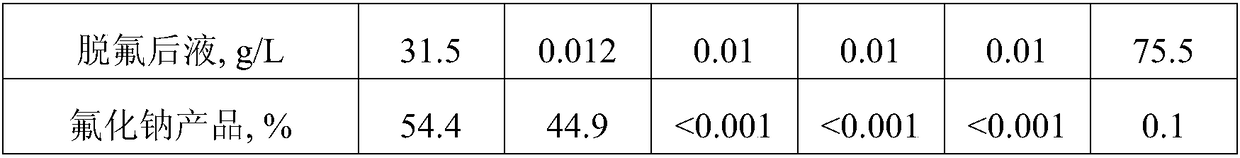
InactiveCN108373140AMeet the requirements of fluorineSimple processPhotography auxillary processesSulfate preparationSodium fluorideSolubility
The invention provides a method for removing fluorine from a sulfate solution. The method comprises the following steps: enabling a fluorine-containing sulfate solution to be in contact with calciumsulfate; controlling the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) of the solution to be 1.5 to 9.5 and transforming the fluorine into calcium fluoride; carrying out liquid-solid separation to obtain a fluorine-removed solution and fluorine-containing filtering dreg; transforming the fluorine-containing filtering dreg to recycle a sodium fluoride crystal; utilizing the fluorine-removed solution for direct industrial production, so as to extract valuable metal. By utilizing the difference of solubility of CaF2 and CaSO4 in a water solution, calcium sulfate is in contact with the fluorine-containing sulfate solution; the fluorine is transformed into calcium fluoride and is removed through the liquid-solid separation; in a treated sulfate solution, the content of F is less than or equal to 20mg / L; then a transformation agent is added to separate and recycle fluorine in fluorine-removing dreg by utilizing the difference of the solubility of the CaF2 and the CaSO3 in the water solution, so that recycling of the CaSO4 in a technological process is realized. The removal of the fluorine in the sulfate solution is realized and requirements, on the fluorine in material liquid, by industrial production are met; the production of fluorine-containing solid wastes is avoided. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple technology, convenience for operation, cleanness and environment protection, economical and high efficiency and the like and is suitable for industrial application of the removal of the fluorine in the sulfate solution.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +1
Process for the isolation and purification of zirconium peroxosulfate and uses thereof
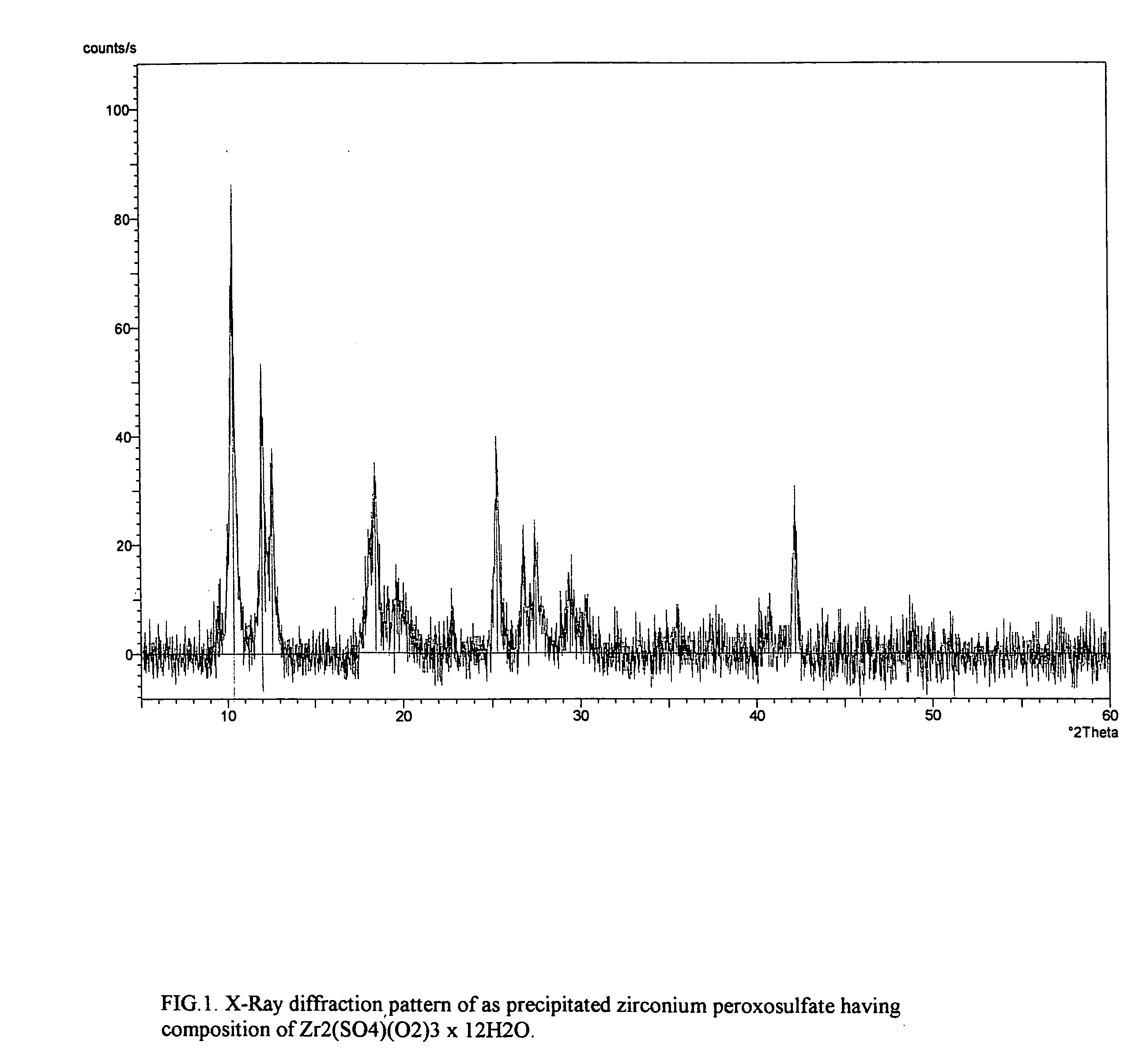
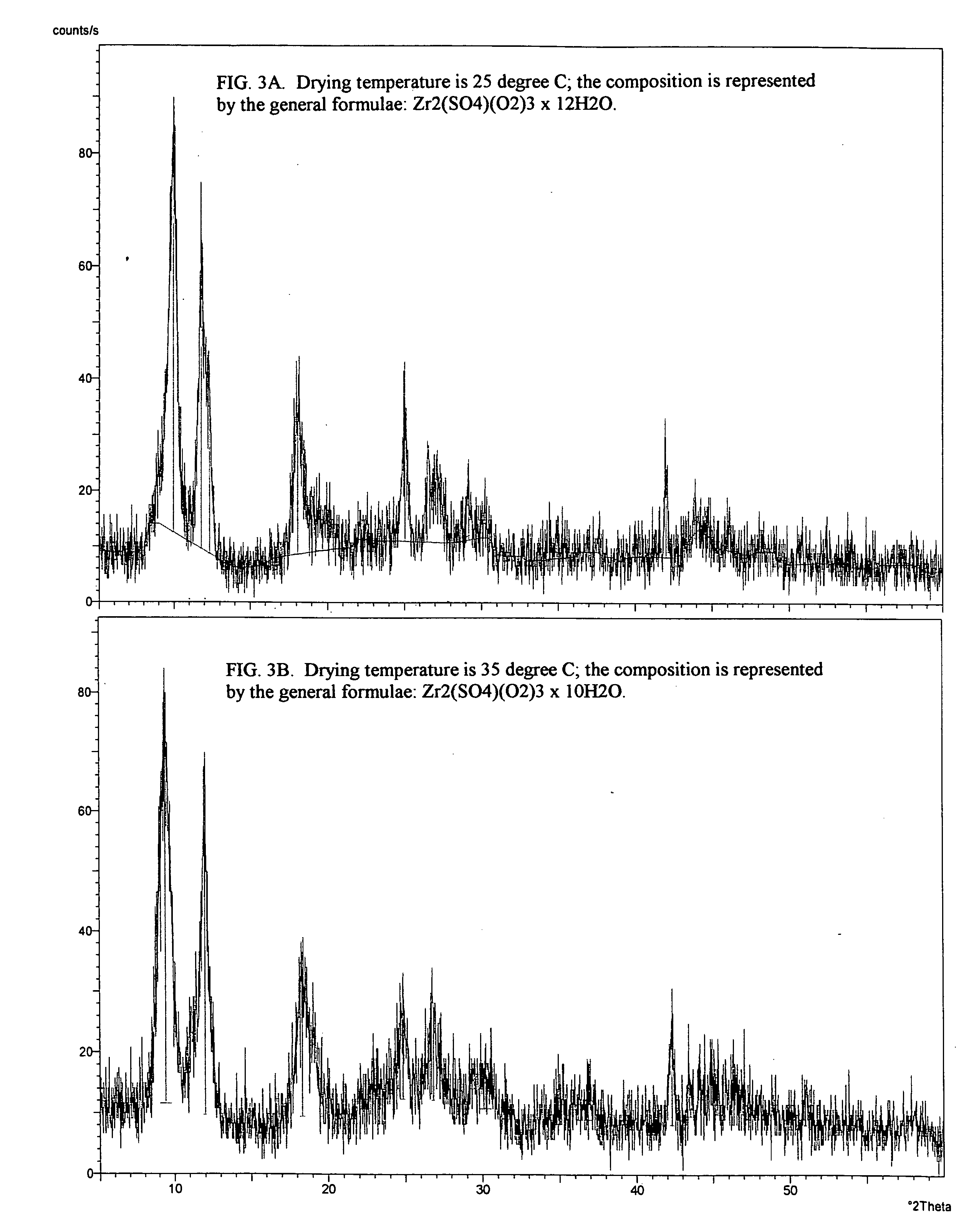
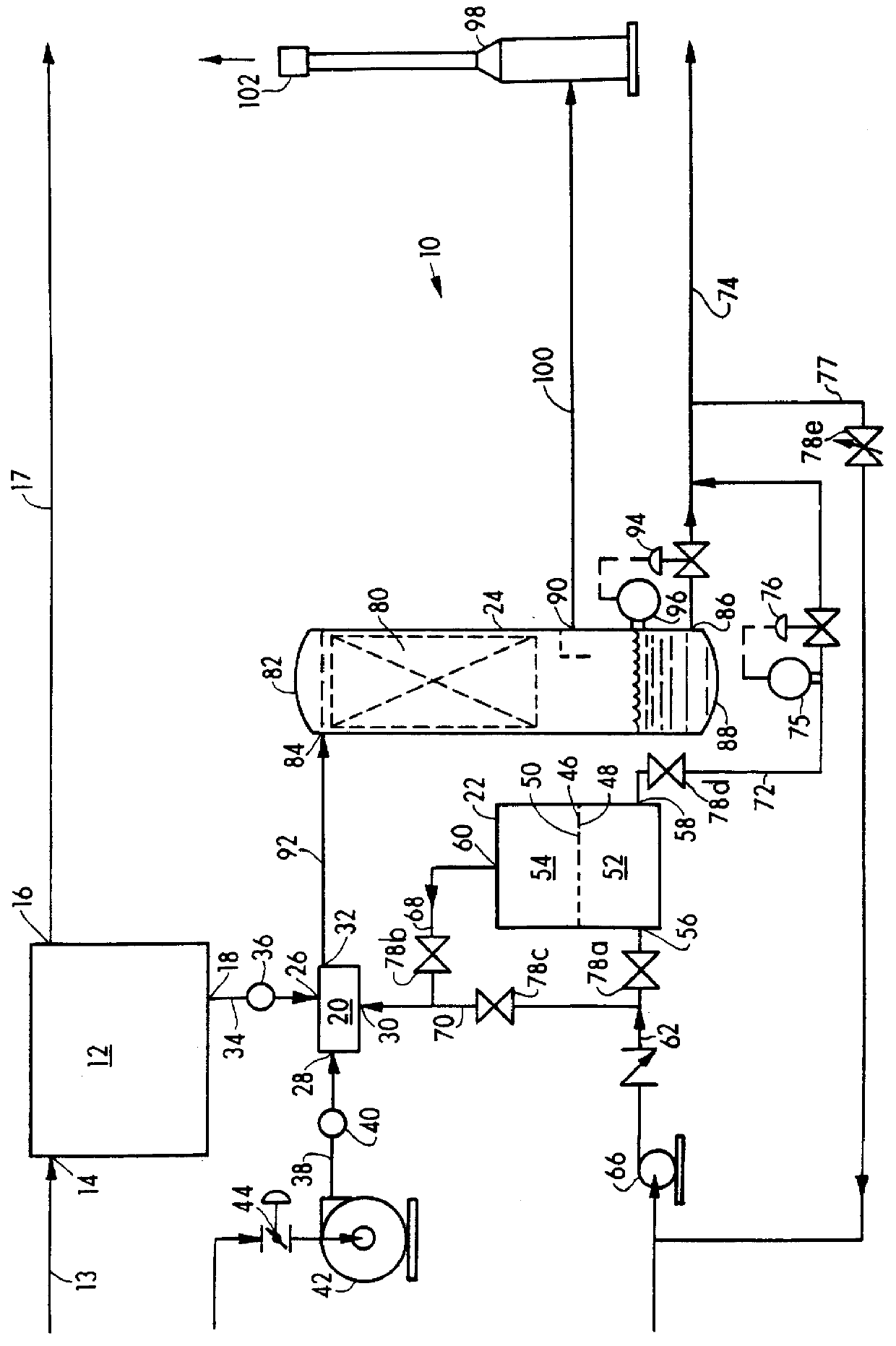
InactiveUS20050180911A1High degreeShort processing timePeroxyhydrates/peroxyacidsSulfate preparationPurification methodsZirconium compounds
Provided is a process for isolating zirconium peroxosulfate and its use, either as is or to prepare high purity zirconium compounds including powders of zirconium dioxide and stabilized zirconia. The process is based on precipitating a peroxide compound from an acidic peroxide solution of zirconium and provides a simple, economical method for producing the zirconium peroxosulfate powder and its derivatives with degree of zirconium recovery more than 99%. This process further provides an effective method for the separation and purification of zirconium from a variety of elements and / or naturally occurring ores.
Owner:BELOV VLADIMIR +1
Disposal of hydrogen sulfide gas by conversion to sulfate ions in an aqueous solution
A process is provided for disposing of hydrogen sulfide contained in a gas stream, wherein a first gas feed stream having a hydrogen sulfide gas component, a second gas feed stream having an oxygen gas component, and an aqueous liquid feed stream are combined to form a reaction mixture. The aqueous liquid feed stream may be water available in remote oilfield locales, such as produced water, or sea water. The aqueous liquid feed stream may include a significant concentration of preexisting sulfate ions, in which case it is generally desirable to remove the preexisting sulfate ions using membrane separation before mixing the aqueous liquid feed stream with the first and second gas feed streams. The resultant low sulfate liquid may further comprise one or more of the following dissolved ions: Na+,K+, Mg2+, Cl-, Br-, HCO3-. The reaction mixture is contacted with a catalyst, which is preferably an activated carbon, capable of inducing catalytic oxidation of the hydrogen sulfide gas component to produce sulfate ions. Oxidation of the reaction mixture results in a product mixture substantially free of elemental sulfur and having an aqueous liquid product stream which retains the produced sulfate ions in solution and a gas product stream which is substantially free of hydrogen sulfide. The gas product stream is separated from the aqueous liquid product stream and the two streams are separately disposed. The gas product stream is conventionally disposed by discharge into the atmosphere. The aqueous liquid product stream is conventionally disposed by discharge to the environment.
Owner:MARATHON OIL CO
Production process of aluminium iron sulfate polymer as composite water purifying agent
InactiveCN1337356AReduce manufacturing costSimple processSulfate preparationWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationIron sulfateCleansing Agents
The production process of compound water-cleaning agent aluminium iron polysulfate uses the iron oxide contained offscum produced after production of sulfuric acid in sulfuric acid plant as raw material, and adopting the folloiwng steps: according to the chemometric, adding water, offscum and sulfuric acid into reactor in turn to make reaction, then adding isometric water to make dilution, and discharging diluted reactant into settling tank, adding small quantity of flocculant to make natural settling and solid-liquid separation, pumping said clear liquor into polymerization container, addingH2O2 and making it and the clear liquor to implement quick oxidation and polymerization to obtain the invention finished product liquor, evaporating and dewatering to obtain its natural crystal, thenbreaking it into granular or powdered material to obtain the invented solid aluminium iron polysulfate. It can obtain good sewage treatment effect.
Owner:邓中杰
Production of silver sulfate grains using a fluorinated additive
InactiveUS20090258984A1Uniform morphologyUniform sizePigmenting treatmentCosmetic preparationsMicrometerWater soluble
An aqueous precipitation process for the preparation of particles comprising primarily silver sulfate, comprising reacting an aqueous soluble silver salt and an aqueous soluble source of inorganic sulfate ion in an agitated precipitation reactor vessel and precipitating particles comprising primarily silver sulfate, wherein the reaction and precipitation are performed in the presence of an aqueous soluble fluorinated additive, the amount of additive being a minor molar percentage, relative to the molar amount of silver sulfate precipitated, and effective to result in precipitation of particles comprising primarily silver sulfate having a mean grain-size of less than 50 micrometers.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Device and process for recycling and treating hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas
InactiveCN103301732BReach the purpose of recyclingDispersed particle separationEnergy inputCold airFlue gas
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical waste gas treatment, and mainly relates to a device and a process for recycling and treating hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas. The process for recycling and treating hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas comprises the following steps of: igniting and completely burning the hydrogen sulfide-containing chemical acid waste gas into sulfur dioxide-rich high-temperature flue gas, recycling much heat and adjusting the temperature of the flue gas by cold air, and enabling the flue gas to enter an adsorption tower; completely absorbing the sulfur dioxide in the flue gas by utilizing an alkaline solution, removing less alkaline solution and sulfite contained in the flue gas absorbed by the alkaline solution, and exhausting the demisted pure flue gas to the atmosphere. The sulfite, which is generated by absorbing sulfur dioxide by the alkaline solution, is oxidized, concentrated, crystallized and dried to obtain side product sulfate.
Owner:义马煤业集团煤生化高科技工程有限公司 +1
Antibacterial and antifungal protection for ink jet image
InactiveUS20130189499A1Effective in providing antibacterialEffective in antifungal protectionBiocideDecorative surface effectsColor imageSolvent
A method of forming a clear ink jet coating or a colored ink jet image on a substrate is disclosed. The coating or colored image provides antibacterial and antifungal protection. The method includes providing a source of ink jet ink having a mixture of solvent and a silver salt biocide including a silver sulfate biocide having a concentration range of 0.0005 to 0.5 weight %, applying the clear ink or colored ink in an image wise fashion to a substrate, and fixing the clear or colored ink to the substrate whereby an effective coating or image article is formed that provides antibacterial and antifungal protection.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Regeneration of cupric etchants and recovery of copper sulfate
InactiveUS7175819B2Easy to useLower requirementBiocideChlorine/hydrogen-chloride purificationDistillationCopper chloride
Spent, acidic solutions comprising cupric chloride and hyrdrochloric acid from the copper etching process are regenerated by a process in which the acid is subjected to distillation with sulfuric acid. In one embodiment, the process comprises (a) providing a spent etchant comprising at least about 10% by weight chloride and at least about 5% dissolved copper; (b) adding at least about 2 moles of sulfuric acid per mole of dissolved copper to the spent etching solution, thereby converting copper chloride into hydrochloric acid and precipitated copper sulfate; (c) distilling the mixture from step (b) to vaporize at least a portion of the hydrochloric acid; (d) condensing at least a portion of the vaporized hydrochloric acid; (e) separating at least a portion of the precipitated copper sulfate from the residual liquid, wherein said residual liquid comprises sulfuric acid; and (f) reusing at least a portion of the residual liquid as a sulfuric acid source in step (b).
Owner:PHIBRO TECH
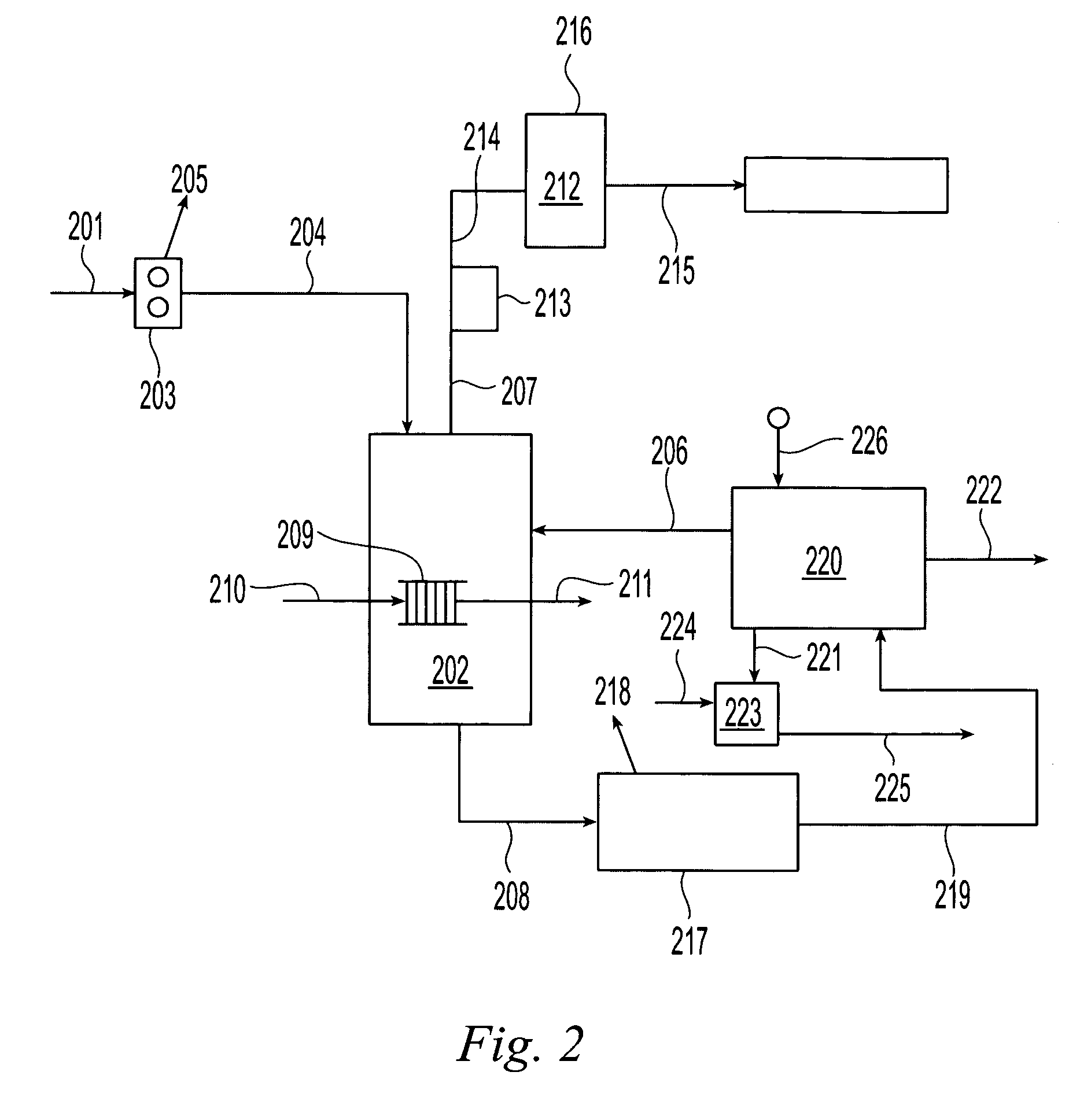
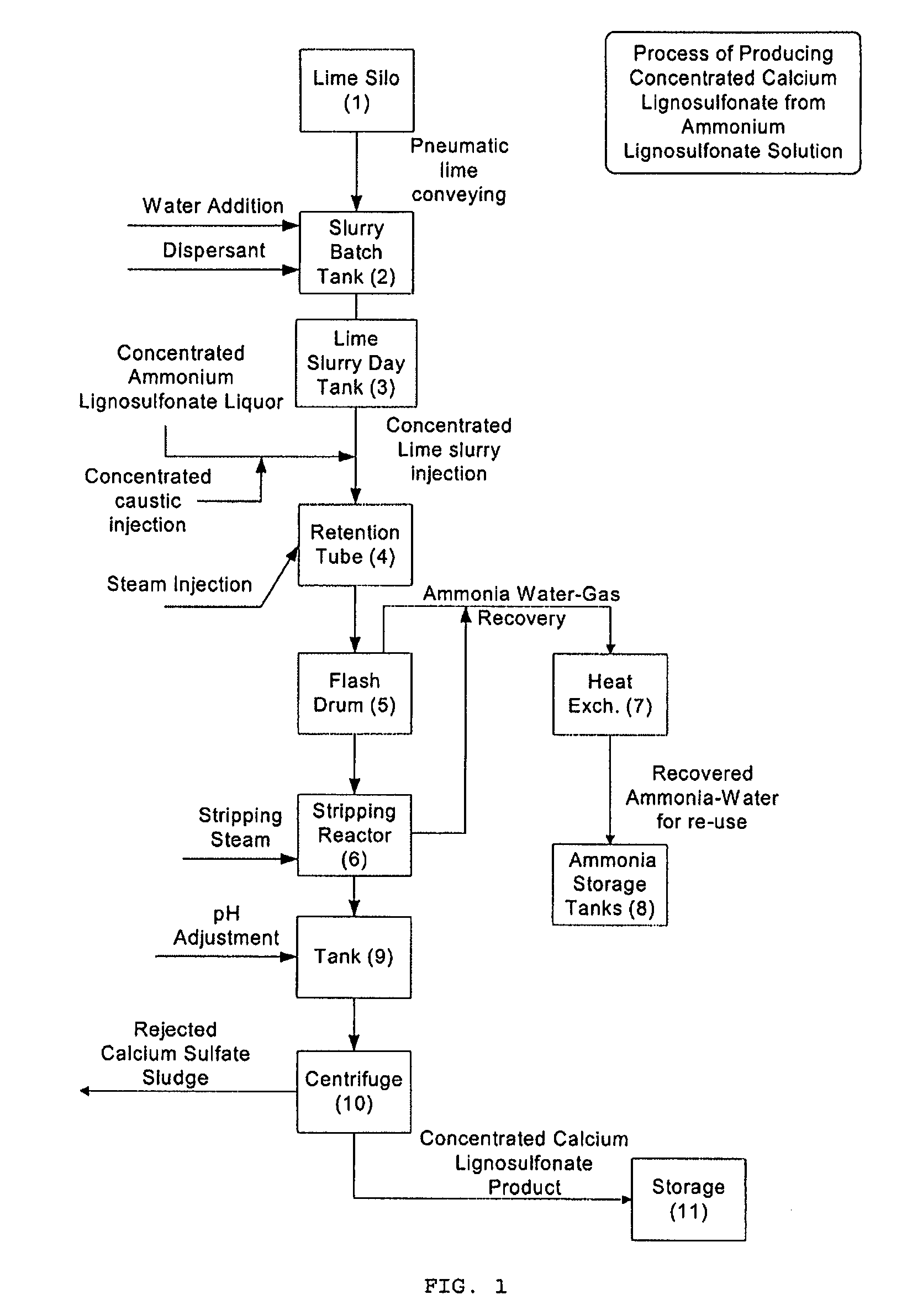
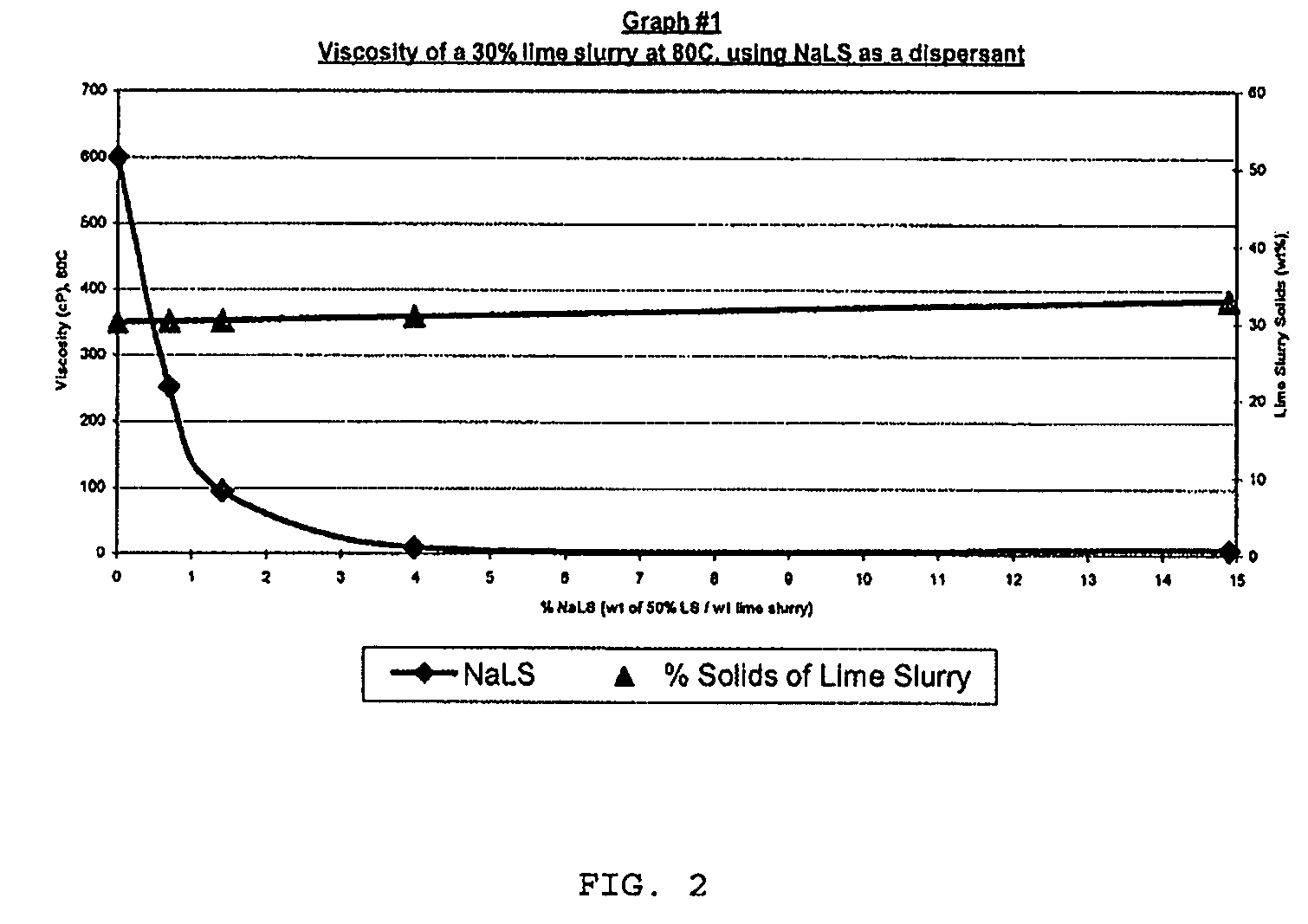
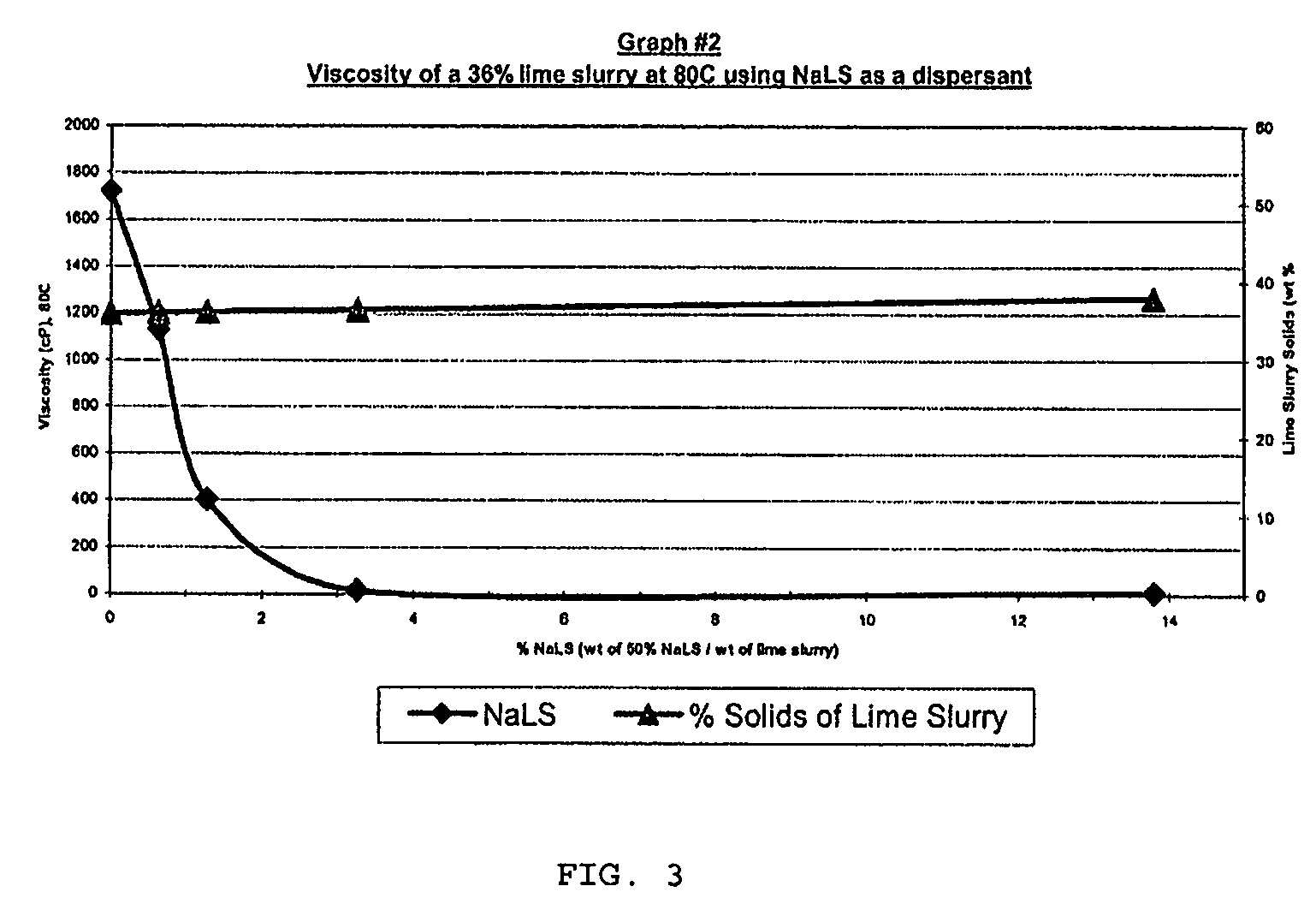
Higher than 30% concentration lime slurries, preparation and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080206126A1Reduced final product viscosityEliminate processingNon-fibrous pulp additionNatural cellulose pulp/paperCalcium hydroxideSulfate
The present invention relates to a composition comprising water, more than 30% w / w of calcium hydroxide, and >0.2% w / w dispersant. A process for preparing such a composition is also disclosed. The composition which can be in the form of a 45-55% concentration lime slurry is particularly useful for converting concentrated ammonium lignosulfonate into calcium lignosulfonate, for converting ammonium lignosulfonate into low sulfate calcium, potassium, sodium, or magnesium lignosulfonate and mixtures thereof, for removing soluble sulfate from concentrated sodium, potassium, ammonium or magnesium lignosulfonate or for treating a weak liquor obtained from the pulp and paper industry.
Owner:TEMBEC INC
Method for treating sulfides in waste streams
ActiveUS20170073257A1Non toxicWaste water treatment from quariesWater treatment compoundsWaste streamWastewater
A method for treating sulfide in an aqueous fluid comprises contacting the fluid with an oxidizer in the presence of a sulfur dye or sulfurized vat dye. In one embodiment, the method comprises treating sulfide contaminated water by contacting the contaminated water with air in the presence of a sulfur dye or a sulfurized vat dye. The method is useful for remediating industrial, agricultural, and municipal waste water.
Owner:BILL ARCHER LLC
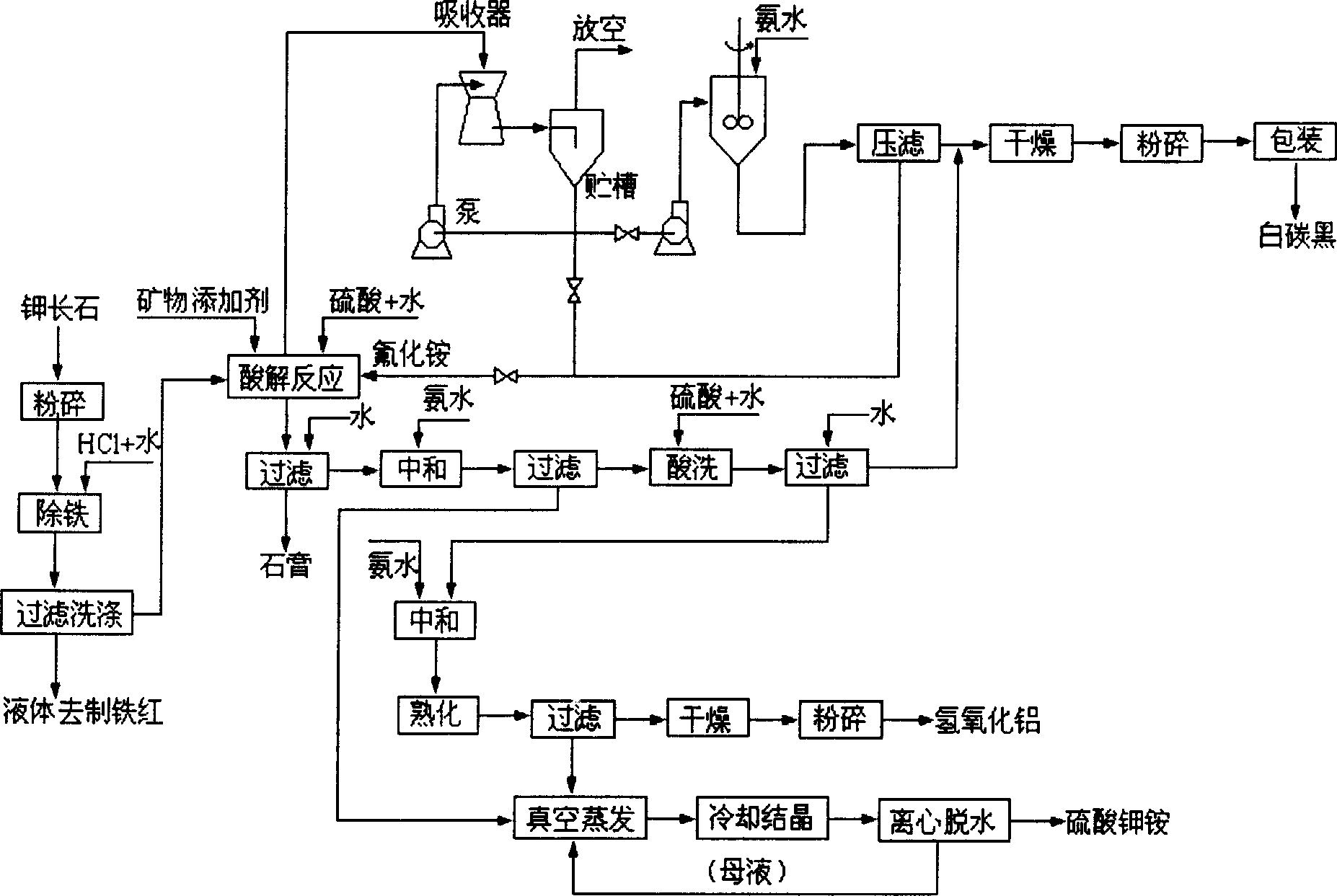
Method for decomposing potash feldspar ore by low temperature wet process
InactiveCN1850624ATake advantage ofEmission reductionIron oxides/hydroxidesCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesResource utilizationFire retardant
The invention relates to a potassium feldspar decomposing method, namely a potassium feldspar low-temperature and wet decomposing method, characterized in that it comprises the steps of: 1) crushing potassium feldspar into <=200 meshes, adding in hydrochloric acid and water and obtaining mother solution A and filter cake A; and preparing ferric oxide red with the mother solution A; 2) mixing the filter cake A with fluoride mineral additive and water, adding pulp into a reactor, reacting and producing escaping SiF4 gas and preparing white carbon black; adding water to reaction product in the reactor, filtering and obtaining filtrate C and CaSO4 2H2O; 3) regulating the filtrate C with ammonia and obtaining filter cake D and mother solution D; preparing potassium ammonium sulphate with the mother solution D; 4) pulping the filter cake D with water and adding in sulphuric acid, filtering and obtaining filter cake E and filtrate E, mixing the filter cake E uniformly with SiO2 nH2O prepared in the step 2) and preparing white carbon black; 5) adding ammonia to the filtrate E and obtaining filter cake F and filtrate F, and preparing the filter cake F into fire retardant aluminum hydroxide. And the method has characters of a whole low-temperature course, low production cost, and full resources utilization.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Process for conversion of waste fluid streams from chemical processing plants to beneficiary agriculture products
The present invention is directed to the conversion of gas streams comprising ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and water in the form of liquids or gases that are generated by petroleum refineries and coke ovens to beneficiary agriculture products, by forming ammonium sulfide and then converting the ammonium sulfide, using sulfuric acid, to pure ammonium sulfate.
Owner:TESSENDERLO KERLEY INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com