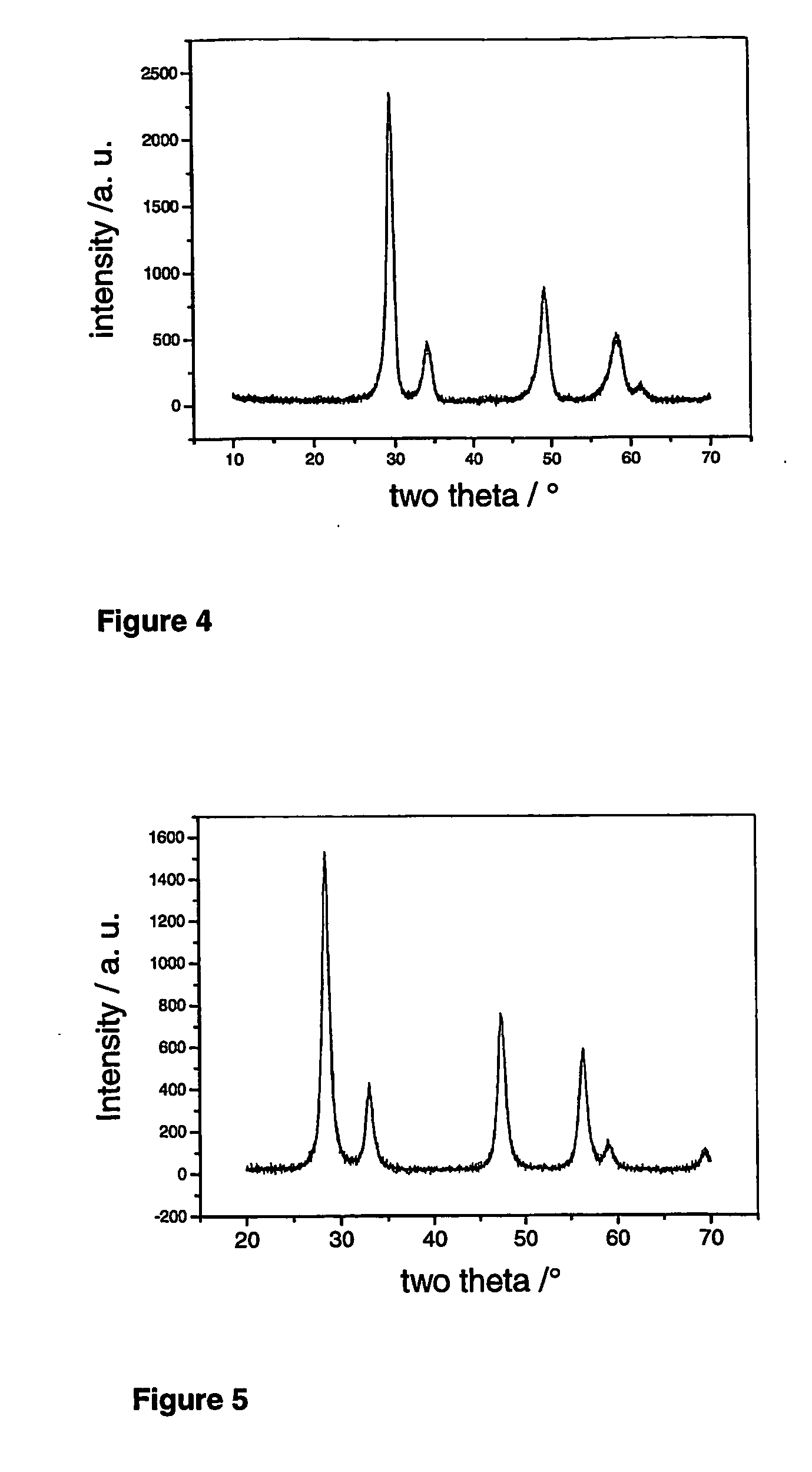
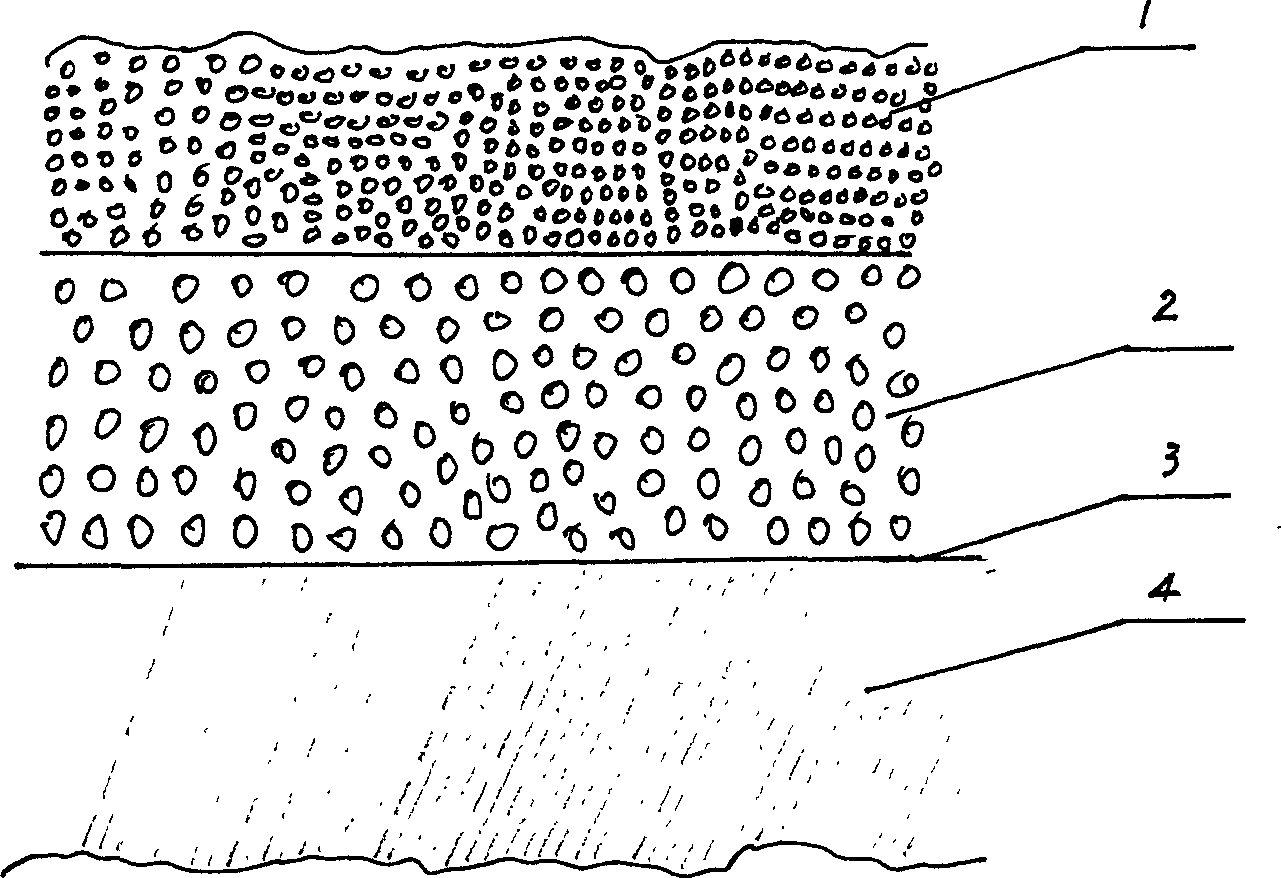
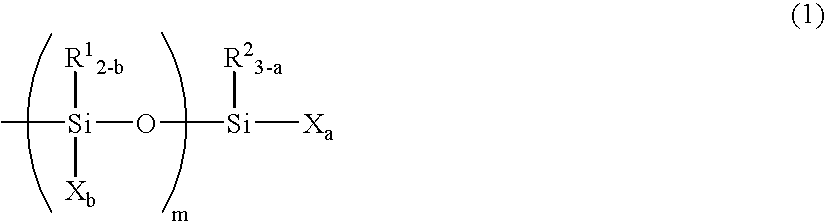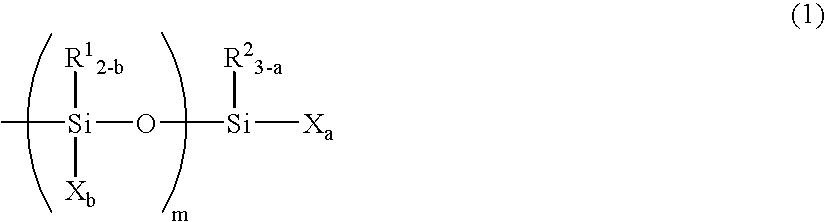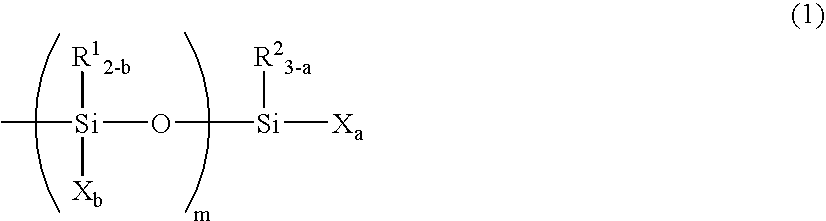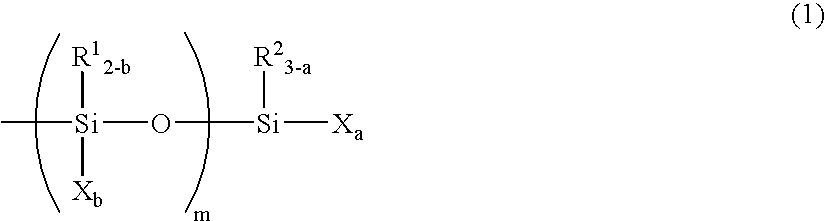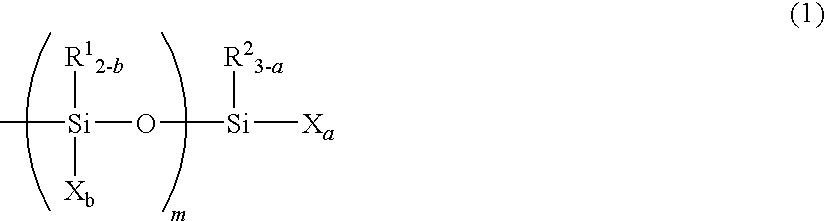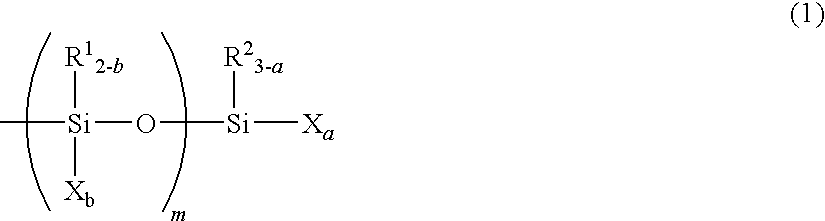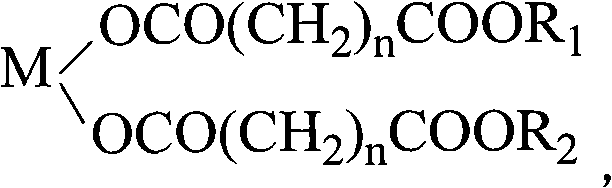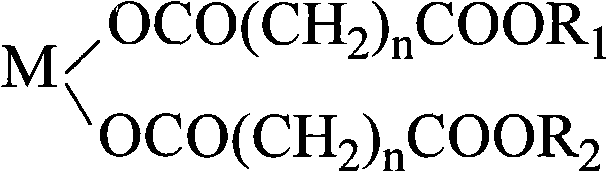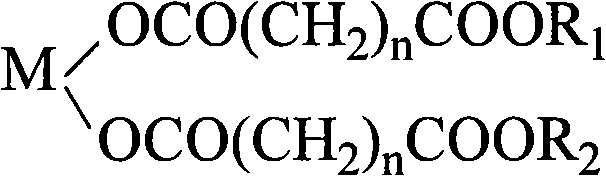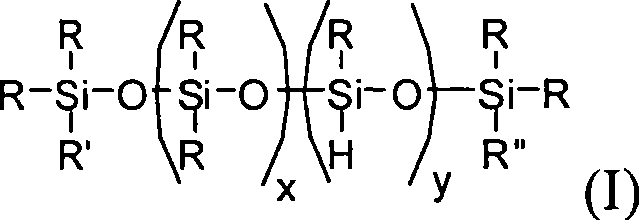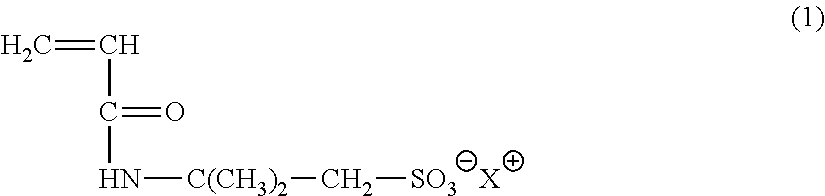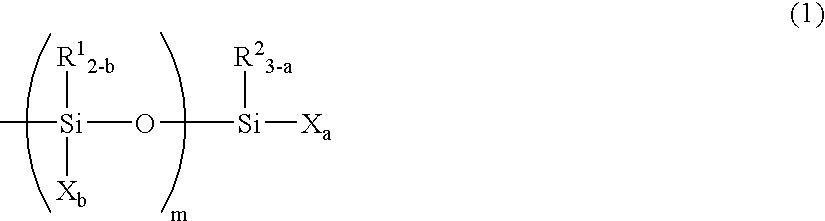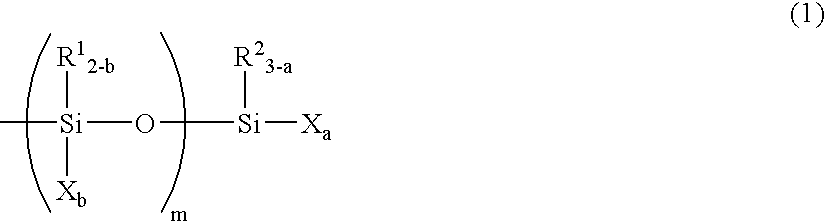Patents
Literature
122 results about "Metallacarboxylic acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A metallacarboxylic acid is a metal complex with the ligand CO₂H. These compounds are intermediates in reactions that involve carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide, these species are intermediates in the water gas shift reaction. Metallacarboxylic acids are also called hydroxycarbonyls.
Curable composition
InactiveUS20050171315A1Small in curing variationSatisfactory in curabilityOther chemical processesCarboxylic acidMetallacarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a curable composition which has a high recovery ratio, a high creep resistance, a practical curability and a storage stability. The present invention relates to a curable composition comprising a reactive silicon group-containing organic polymer (A) and a carboxylic acid (B), (I) wherein the composition comprises, as the carboxylic acid (B), a carboxylic acid (C) in which the carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon atom; and / or (II) wherein the composition comprises a metal carboxylate (D) formed between a carboxylic acid in which the carbon atom adjacent to the carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon atom and a metal atom of 208 or less in atomic weight.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Curable Composition
The present invention has its object to provide a curable composition which has good curability and adhesiveness while containing an organotin-free catalyst. The present invention provides a one package curable composition which comprises (A) a polyoxyalkylene polymer having a silicon-containing group capable of crosslinking by forming a siloxane bond, (B) a (meth)acrylic ester polymer having a silicon-containing group capable of crosslinking by forming a siloxane bond and compatible with the component (A), and (C) (c1) a carboxylic acid of which the carbon atom adjacent to a carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon, and / or (c2) a metal carboxylate of which the carbon atom adjacent to a carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Metal delivery system for nanoparticle manufacture
ActiveUS20060229197A1Improve productivityWell mixedRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMolten spray coating2-Ethylhexanoic acidMetallacarboxylic acid
Described is a method for the production of pure or mixed metal oxides, wherein at least one metal precursor that is a metal carboxylate with a mean carbon value per carboxylate group of at least 3, e.g. the 2-ethyl hexanoic acid salt, is formed into droplets and e.g. flame oxidized. The method is performed at viscosities prior to droplet formation of usually less than 40 mPa s, obtained by heating and / or addition of one or more low viscosity solvents with adequately high enthalpy.
Owner:ETH ZURICH THE SHORT NAME OF EID GENOSSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH
Environmental protection weeping plastic track
InactiveCN1552999AOvercome disadvantagesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesGround pavingsPolyurethane adhesiveWaste rubber
An environment protective and water penetrative plastic trick involves a polymer material, consisting of adhesive, pigment for spraying adhesive, catalyst for carboxylic salt, black waste rubber granules, and color EPDM granules. It is constructed by: making mono-component polyurethane as primary agent to bind recovered rubber granules; mixing with catalyst and stirring uniformly; mechanically spreading; curing at atmosphere - 70 deg.C to form a plastic layer with thickness of 4 - 10mm; and then spreading well-mixed polyurethane adhesive, color EPMD granules and catalyst to form a top plastic layer, finally curing to form the said trick with a plastic layer and a cement substrate. The construction are not only available for tricks, but also for other pavements with low cost, high strength, large extension rate, and good penetration. It can be constructed mechanically and effectively with good flatness.
Owner:上海康达新材料科技有限公司
Curable composition
InactiveUS7550547B2Small in curing variationSatisfactory in curabilityOther chemical processesCarboxylic acidMetallacarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a curable composition which has a high recovery ratio, a high creep resistance, a practical curability and storage stability. The present invention relates to a curable composition comprising a reactive silicon group containing organic polymer (A) and a carboxylic acid (B), wherein the composition comprises (I), as the carboxylic acid (B), a carboxylic acid (C) in which the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon atoms and / or the composition comprises (II) a metal carboxylate (D) formed between a carboxylic acid in which the carbon atoms adjacent to the carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon atoms and a metal atom of 208 or less in atomic weight.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
PVC heat stabilizer of metal carboxylate of pentaerythritol ester and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101768288AThermally stableEasy to processOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationCarboxylic acidMetallacarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a PVC heat stabilizer of metal carboxylate of pentaerythritol ester and a preparation method thereof. The heat stabilizer has the following structure: M is Ca2+, Mg2+ or Zn2+, n is equal to 3-8, and R1 and R2 are -CH2C(CH2OH)2CH2OCH2C(CH2OH)3 or -CH2C(CH2OH)3; the heat stabilizer is formed as follows: salt forming reaction is carried out on one carboxylic acid group of dicarboxylic acid and oxides or hydroxides of zinc, calcium and magnesium, and esterification reaction is carried out on the other carboxylic acid group of the dicarboxylic acid and pentaerythritol or dipentaerythritol. The heat stabilizer is solid which can be melted, is white powder after being grinded, and has excellent heat stabilization for PVC.
Owner:BELIKE CHEM
Coatings for metal cutting tools
InactiveUS7211292B1Prolong lifeLow costPretreated surfacesEfficient propulsion technologiesCarboxylic saltCarboxylic acid
The method is disclosed for coating or impregnating a metal cutting tool with a metal oxide. The method includes the steps of applying a liquid metal carboxylate composition, or a solution thereof, to a substrate material, and exposing the metal cutting tool to an environment that will cause vaporization or dissipation of any excess carboxylic acids in the liquid metal carboxylate composition and conversion of the metal carboxylates to metal oxides.
Owner:C 3 INTL
Production method for ethylene-based ionomer and ethylene-based ionomer
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a production method for a novel ethylene-based ionomer exhibiting exceptionally excellent break elongation, breaking stress, and strain hardening and a high melting point, as well as excellent mechanical properties and heat resistance. This invention pertains to an ethylene-based ionomer production method characterized by including a heating and conversion step in which a specific ethylene / unsaturated carboxylic acid ester copolymer is heated and an ester group in the copolymer is converted to a metal-containing carboxylic acid salt containing a metal ion from group 1, group 2 or group 12 of the periodic table.
Owner:JAPAN POLYETHYLENE CORP +1
Flame synthesis of metal salt nanoparticles, in particular calcium and phosphate comprising nanoparticles
InactiveUS20070196259A1Increase chanceCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesMaterial nanotechnologyBiocompatibility TestingMetallacarboxylic acid
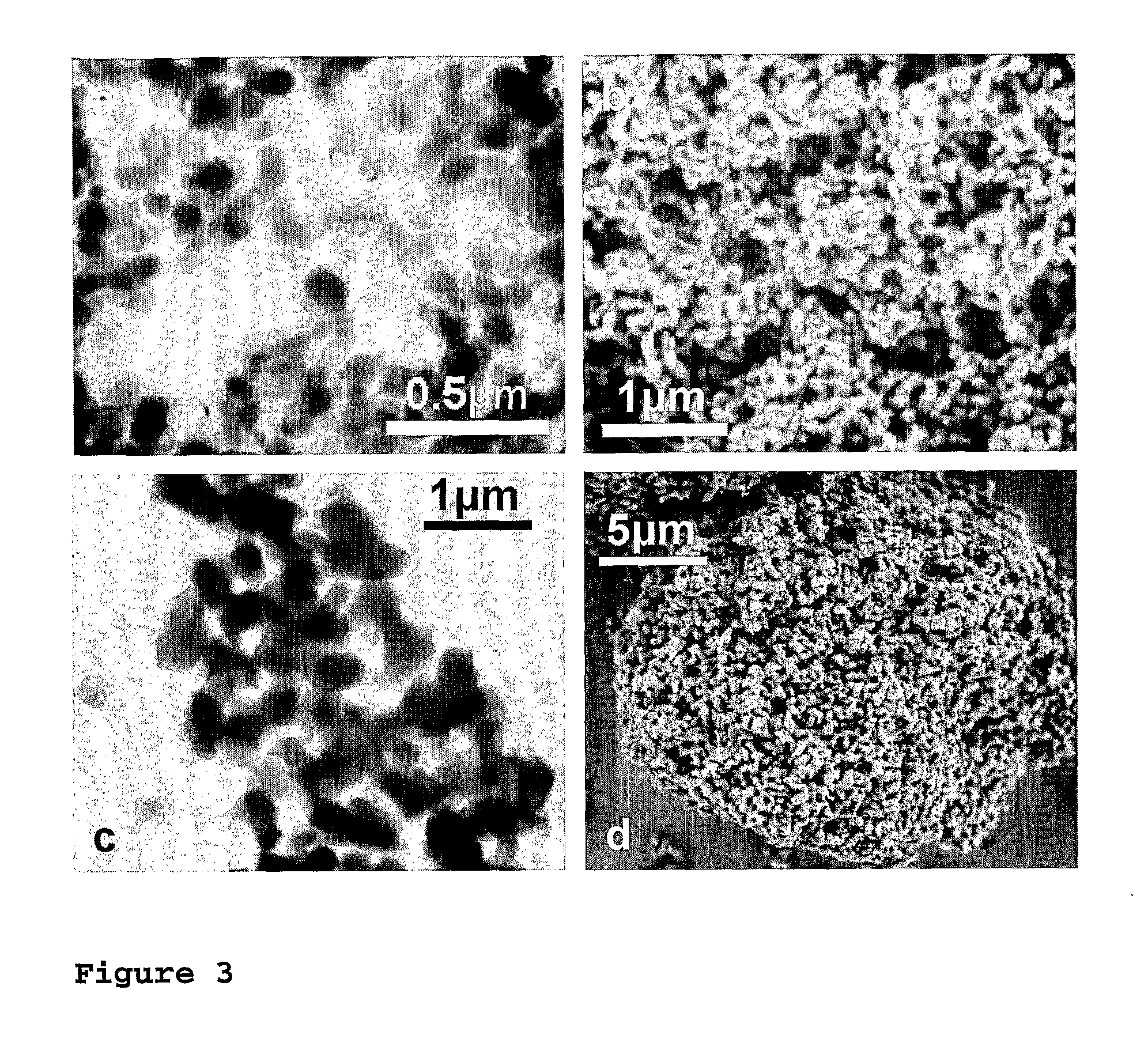
Described is a method for the production of metal salts, wherein the cationic metal is preferably selected from Group I to IV metals and mixtures thereof and the anionic group is selected from phosphates, silicates, sulfates, carbonates, hydroxides, fluorides and mixtures thereof, and wherein said method comprises forming a mixture of at least one metal source that is a metal carboxylate with a mean carbon value per carboxylate group of at least 3 and at least one anion source into droplets and oxiding said droplets in a high temperature environment, preferably a flame. This method is especially suited for the production of calcium phosphate biomaterials such as hydroxyapatite (HAp,Cal0(P04)6(OH)2) and tricalcium phosphate (TCP,Ca3(P04)2) that exhibit excellent biocompatibility and osteoconductivity and therefore are widely used for reparation of bony or periodontal defects, coating of metallic implants and bone space fillers.
Owner:EIDENGOSSICHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH
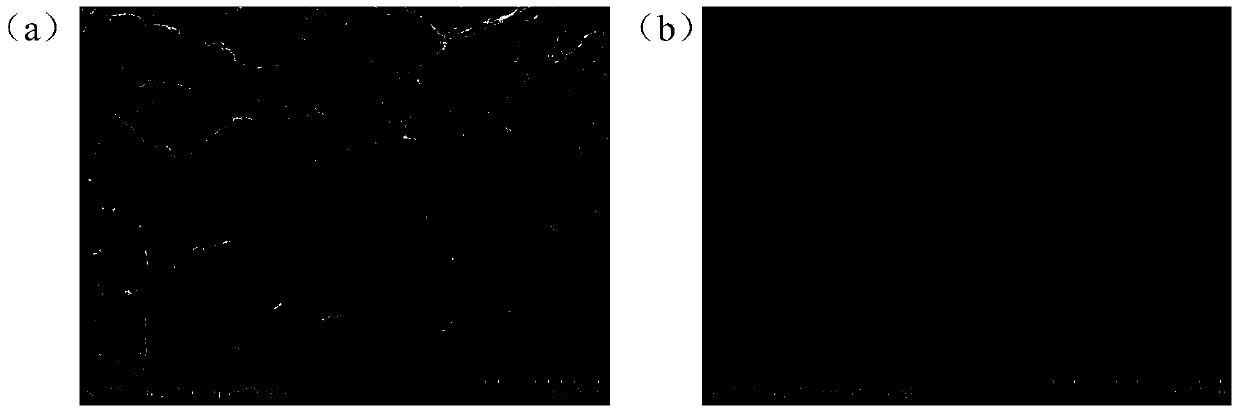
Metal nanoparticles stabilized with a carboxylic acid-organoamine complex
InactiveCN101450387AImprove stabilityExtended storage timeMaterial nanotechnologyMetal-working apparatusCarboxylic saltOrganic group
Metal nanoparticles with a stabilizer complex of a carboxylic acid-amine on a surface thereof are formed by reducing a metal carboxylate in the presence of an organoamine and a reducing agent compound. The metal carboxylate may include a carboxyl group having at least four carbon atoms, and the amine may include an organo group having from 1 to about 20 carbon atoms.
Owner:XEROX CORP
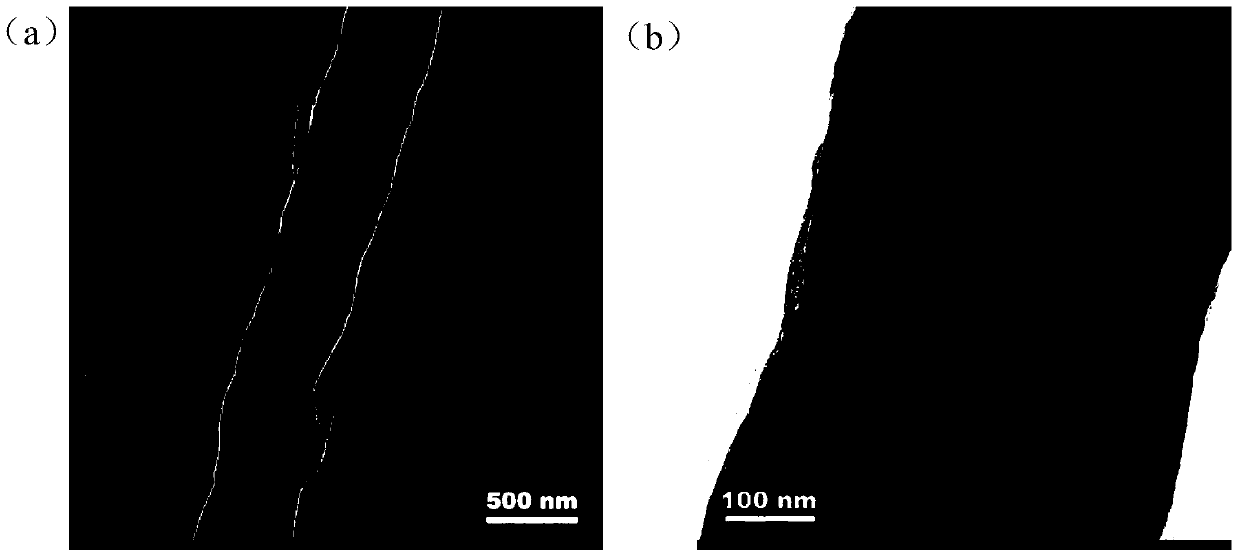
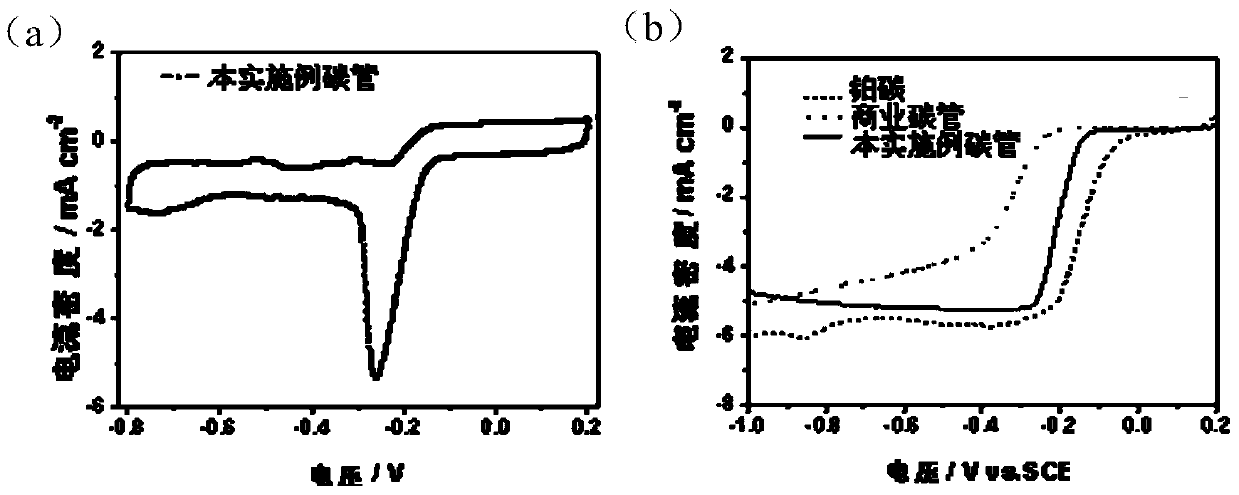
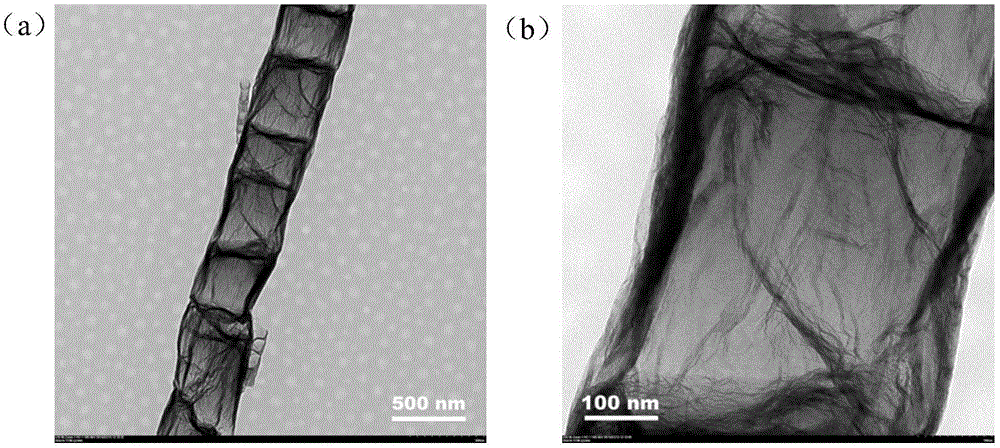
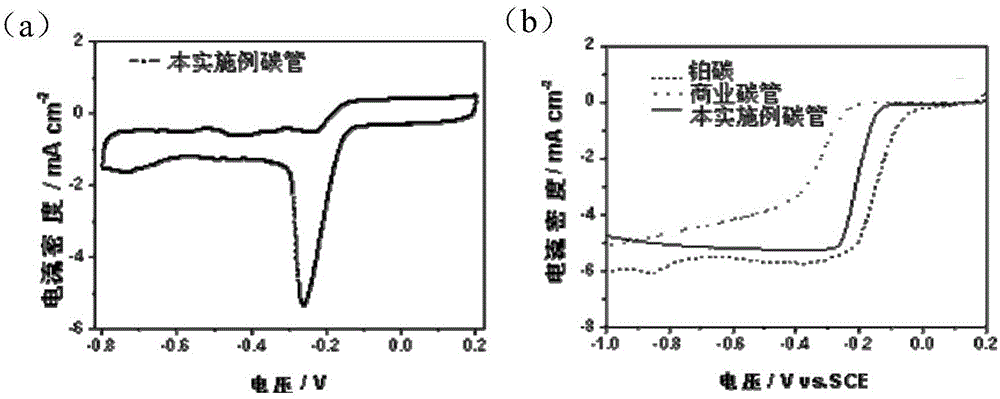
Preparation method and product of nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube
ActiveCN104176724AWide variety of sourcesEvenly distributedMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical chemistryNitrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method and a product of a nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing calcination on a precursor under a nitrogen atmosphere, and performing acid treatment after calcination to obtain the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube, wherein the precursor is a compound of carboxylate of organic amine and metal carboxylate; the carboxylate of organic amine is melamine carboxylate or dicyanodiamide; the length of the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube is more than 5 microns, and the tube diameter of the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube is 50-500 nanometers. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, is wide in raw material source and strong in sustainability, can be used for obtaining the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tubes which are uniformly distributed in a large area range, and is expected to achieve large-scale production; and the modification on surface functional groups can be completed in one step by virtue of calcination without implementing subsequent complex modification processes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
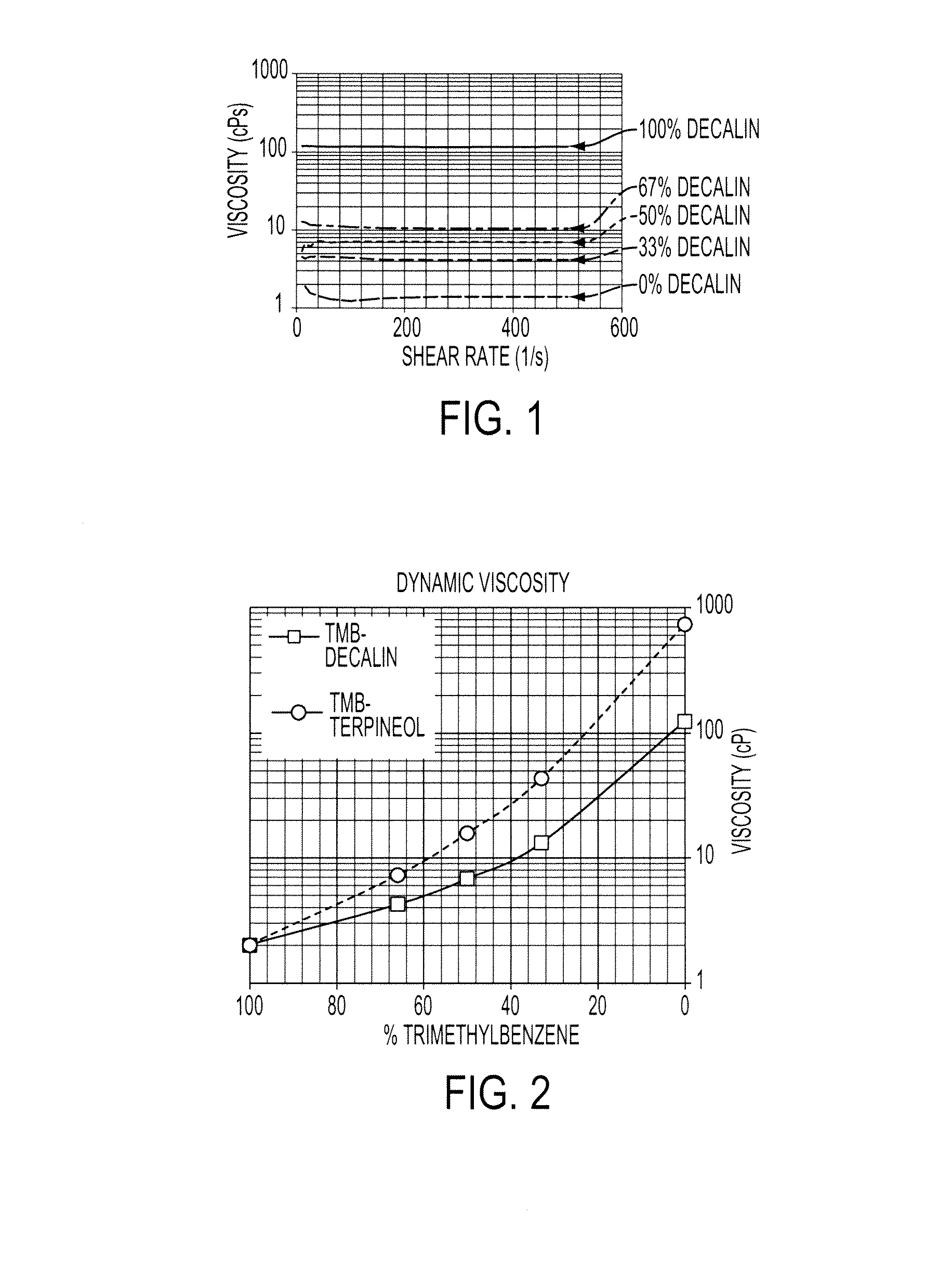
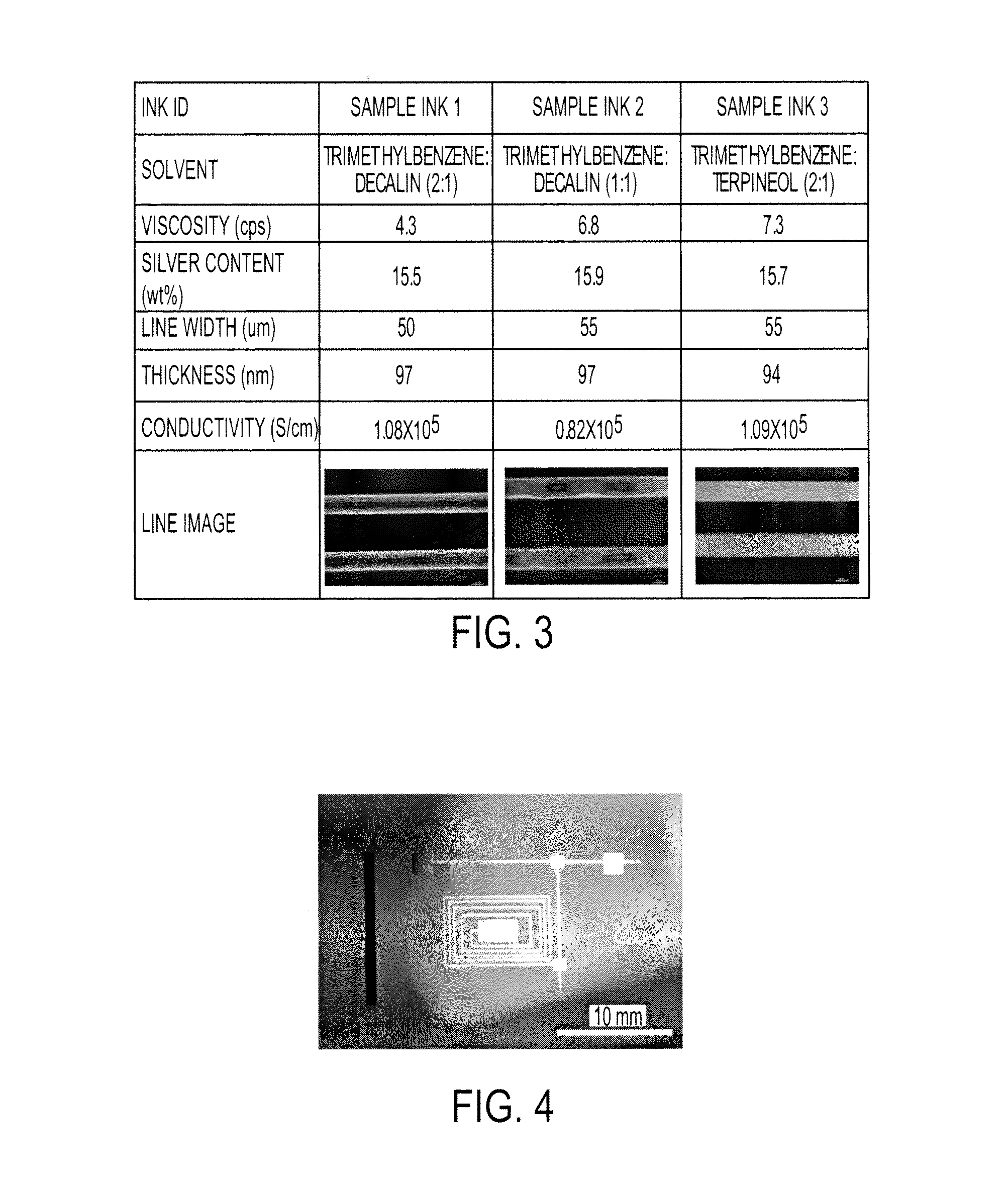
Conductive compositions comprising metal carboxylates
ActiveUS20150132476A1Low viscosityHigh viscosityDuplicating/marking methodsConductive materialScreen printingCarboxylic acid
A conductive composition that comprises a branched metal carboxylate and one or more solvents. The solvents may be an aromatic hydrocarbon solvent. In embodiments, the branched metal carboxylate is a silver carboxylate. The conductive composition may be used in forming conductive features on a substrate, including by inkjet printing, screen printing or offset printing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Mixed base phenates and sulfonates
InactiveUS20070060485A1Synergistic anti-wear propertiesImprove anti-wear performanceBiocideOrganic chemistryMetal sulfateCarboxylate
A lubricant composition. The lubricant composition includes (a) a phenate, a sulfonate, or both; and (b) a base composition wherein the base composition is (i) a metal carbonate and a metal sulfate, (ii) a metal sulfate and a metal phosphate; (iii) a metal sulfate and a metal carboxylate; (iv) a metal phosphate and a metal carboxylate; or (v) three-way or four-way combination of a metal sulfate, a metal carboxylate, a metal phosphate, and a metal carbonate; and (c) a lubricating oil or a grease.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Coatings for metal casting parts
InactiveUS7718221B2Improve the immunityReduce capacityPretreated surfacesEfficient propulsion technologiesCarboxylic saltVaporization
The method is disclosed for coating or impregnating a metal tool with a metal oxide to render the metal part more resistant to liquid metal attack or micro-welds. The method includes the steps of applying a liquid metal carboxylate composition, or a solution thereof, to a substrate material, and exposing the substrate to an environment that will cause vaporization or dissipation of any excess carboxylic acids in the liquid metal carboxylate composition while the metal carboxylates are being converted to metal oxides.
Owner:C 3 INTL
Polylactic-acid-based isotactic compound crosslinking copolymer and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102432852AReduce usageSolve the shortcomings of easy discoloration and easy degradation during processingLactideEnd-group
The invention belongs to the technical field of preparation of polylactic acid, and particularly relates to polylactic-acid-based isotactic compound crosslinking copolymer and a preparation method thereof. The copolymer is multi-branched polyether-D(L)-polylactic acid-L(D)-polylactic acid copolymer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: under the action of a catalyst, the multi-branched polyether introduces open-loop polymerization reaction of D-lactide or L-lactide and prepolymer is obtained; under the condition of no water or the protection of inert gases, the prepolymer reacts with end-group activating agent metallic carboxylate or metal alkoxide, and after drying, white solid is obtained; the white solid introduces open-loop polymerization reaction with the D-lactide or L-lactide; and the polylactic-acid-based isotactic compound crosslinking copolymer is obtained. The isotactic compound crosslinking copolymer can form a physical-crosslinking mesh structure, is endowed with a shape memory function of thermoplasticity of the material and has the advantages of high toughness and heat resistance and wide application prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
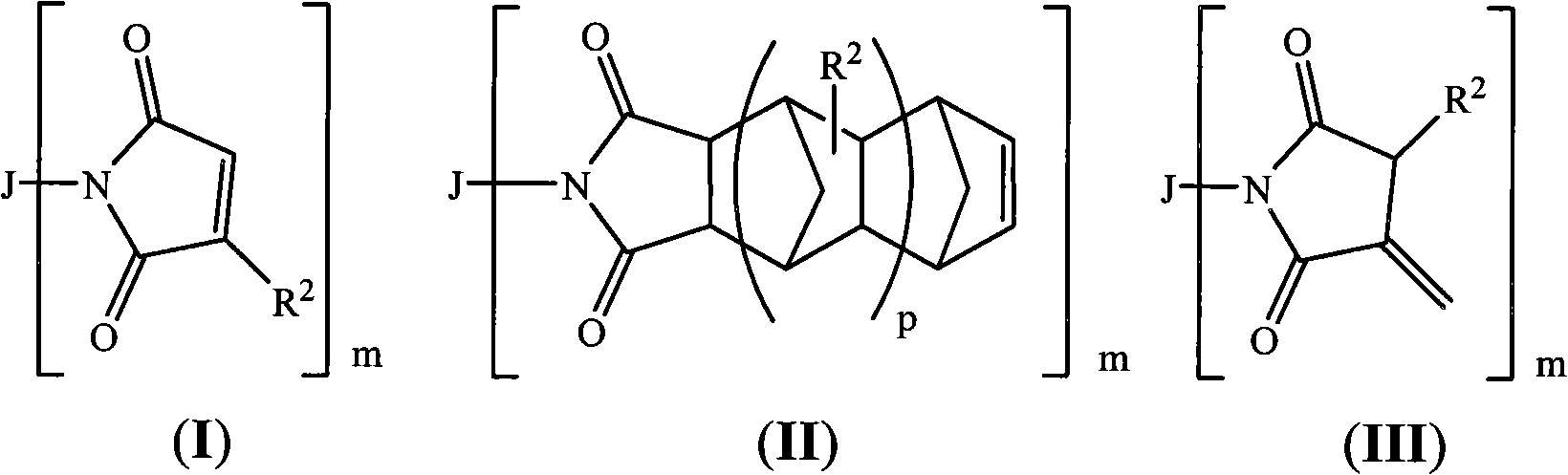
Low temperature curing compositions
The present invention relates to thermosetting resin compositions that include maleimide-, nadimide- or itaconimide-containing compounds and a metal / carboxylate complex and a peroxide, which is curable at a low temperature at relative short period of time, such as less than about 100 DEG C, for instance 55-70 DEG C, over a period of time of about 30 to 90 minutes. The invention further provides methods of preparing such compositions, methods of applying such compositions to substrate surfaces, and packages and assemblies prepared therewith for connecting microelectronic circuitry.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Method for producing branched polyorganosiloxane
InactiveCN101362823AEasy to processEasy to handleTransportation and packagingMixingOrganic groupCarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method for organic branched polysiloxane, in particular to a preparation method for branched siloxane containing an R-SiO3 / 2 unit, wherein R is an organic group, and linear polysiloxane containing silicon hydride in a polymer chain reacts under the condition that no hydroxyl functional organic compound is existent in the presence of ammonium or metal carboxylate as a catalyst. The invention also relates to application of siloxane obtained by the preparation method to prepare polyurethane foam and antifoaming agent products.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Environment protection type polyurethane non-particle spray coating material for play ground layer and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN101245223AImprove mechanical propertiesOvercome injuryGround pavingsPolyurea/polyurethane coatingsEpoxyCalcium bicarbonate
The invention discloses an environmental-friendly type polyurethane non particle spraying material used in stadium ground layer, which is formed by the mixing of component A and component B; wherein, the weight proportion of component A and component B is 1:3; the component A is obtained by mixing diphenylmethane diisocyanate and polyether glycol according to certain proportion; the component B is obtained by mixing polyether-tribasic alcohol, polyether glycol, dry process montmorillonite clay, 3, 5-methyl-sulfide base tolylene diamine, trimethylolpropane, epoxy resin, two-octyl, silica dioxide powder, calcium bicarbonate, organobentonite, iron oxide red or tartrazine-phthalo green mixture and metal carbonyl carboxylate according to certain proportion. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the material, which includes the steps: first preparing the component A and the component B respectively in specific condition, and mixing and stirring the component A and the component B to obtain the material of the invention. As the material of the invention contains no TDI and MOCA, the polyurethane non particle spraying material has no toxicity and safety hidden danger, and is an environmental-friendly material.
Owner:SICHUAN AOHAI SPORTS ENG
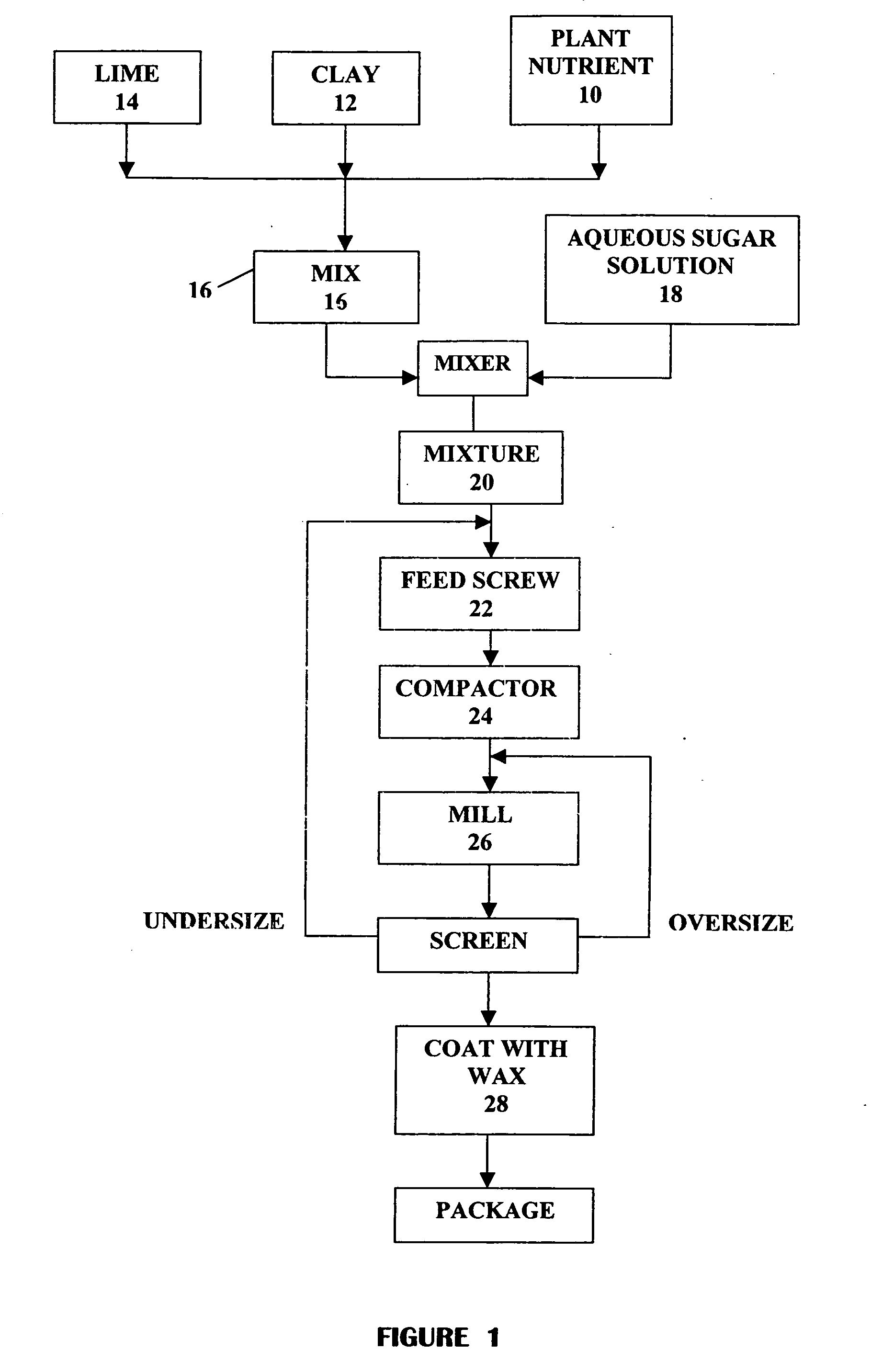
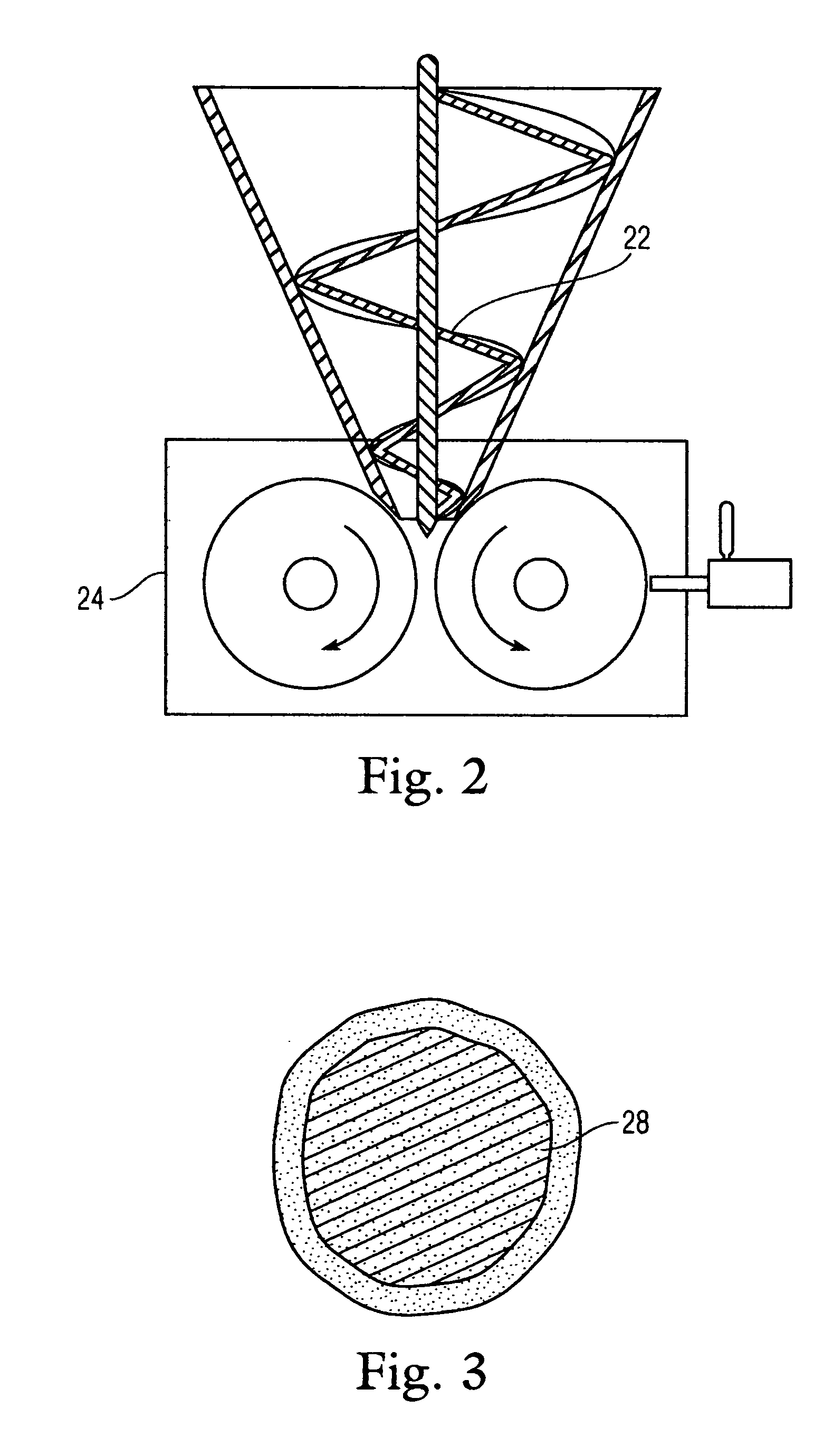
Plant nutrient and method of making
InactiveUS20050126238A1Aid in dispersionAid in availabilityCalcareous fertilisersClimate change adaptationWaxWater dispersible
Soil and water dispersable plant nutrients in the form of metal carboxylates (sucrates) are formed from the combination of metal oxides and saccharides. A method of preparing granular metal carboxylates (sucrates) is provided. Metal oxides, lime, clay and aqueous beet sugar extract are combined and fed through a roll press compactor with 100 tons of pressure which elevates the material temperature to approximately 170° F., driving the reaction to completion. The compacted metal carboxylates (sucrates) are milled, screened, and wax coated.
Owner:QC CORP
A kind of environment-friendly metal carboxylate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102276441AEasy to makeEasy to operateCarboxylic acid salt preparationCarboxylic saltCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses an environment-friendly metal carboxylate and a preparation method thereof. The metal carboxylate has the following structure: CH3(CH2)nCOO-M-OOC(CH2)nCH3, wherein M is Zn2+, Mg2+, n=10 ~16; Salt formation reaction is carried out by linear saturated monocarboxylic acid and zinc, magnesium oxide or hydroxide powder under the action of a catalyst. The metal carboxylate is a meltable solid, which can be prepared after crushing. A powdery, environmentally friendly metal carboxylate product. The invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, strong operability, energy saving, high product purity, environmental protection and compliance with the requirements of ROHS directive, EU REACH regulation and EN71-3 standard.
Owner:BELIKE CHEM
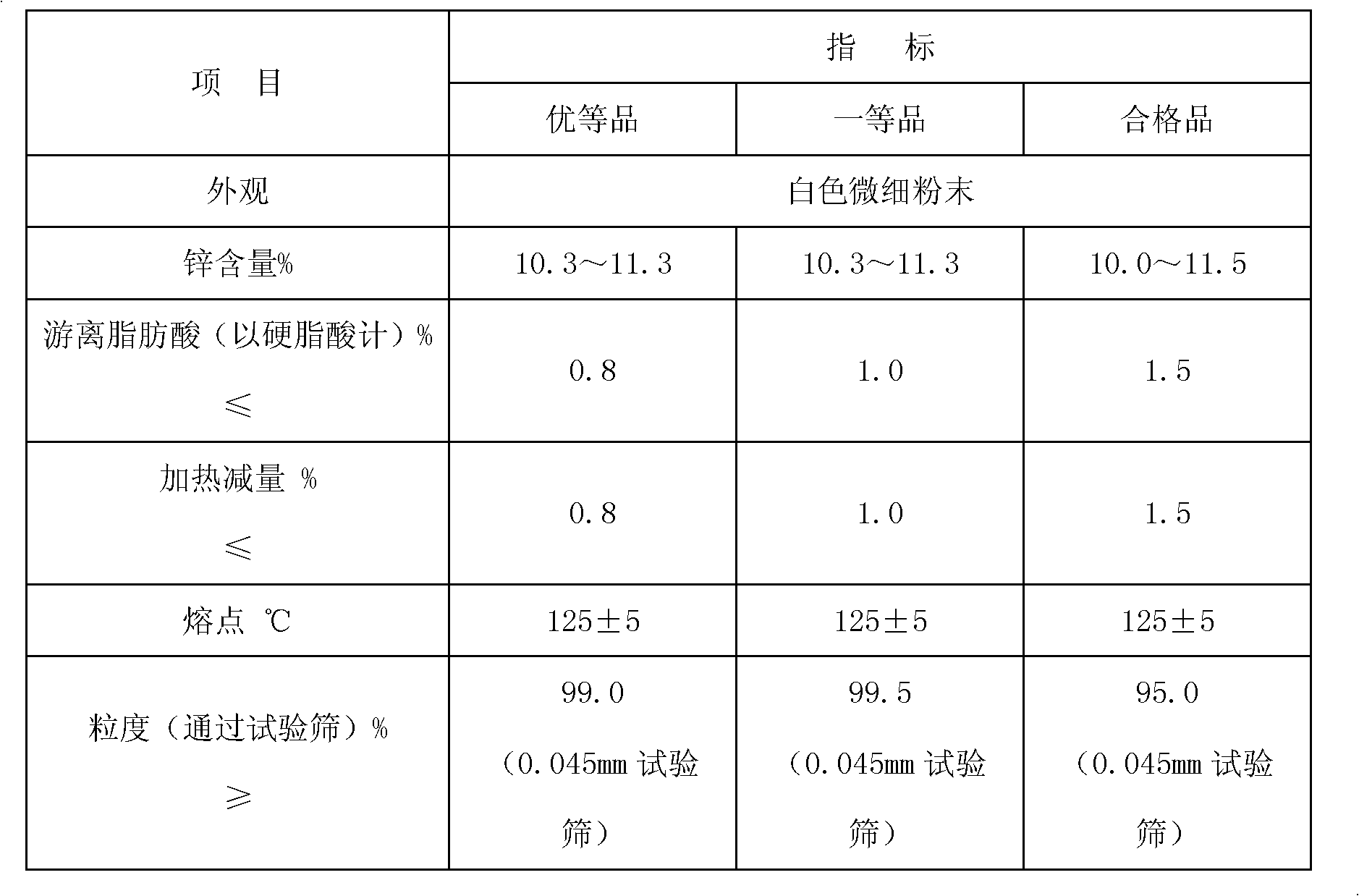
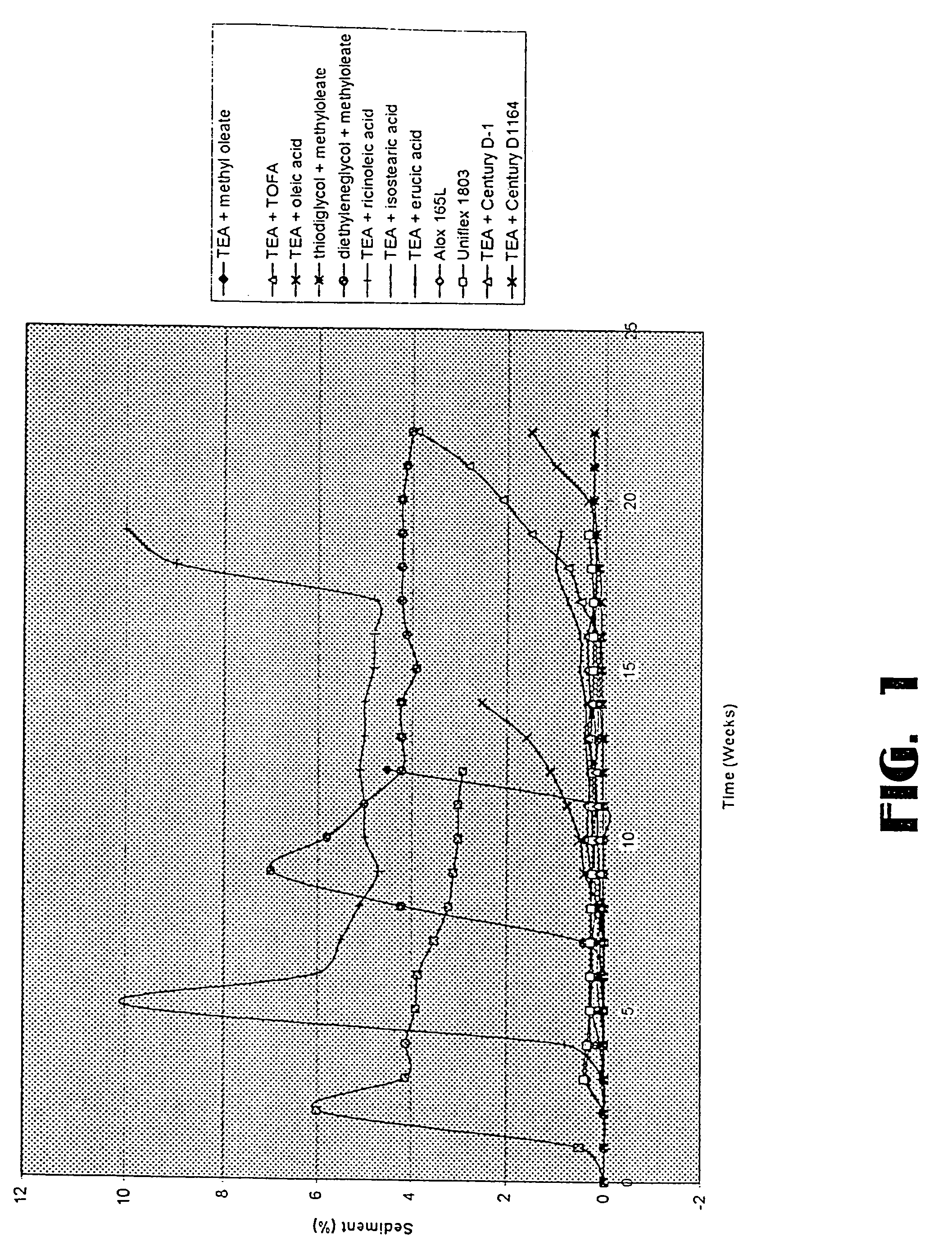
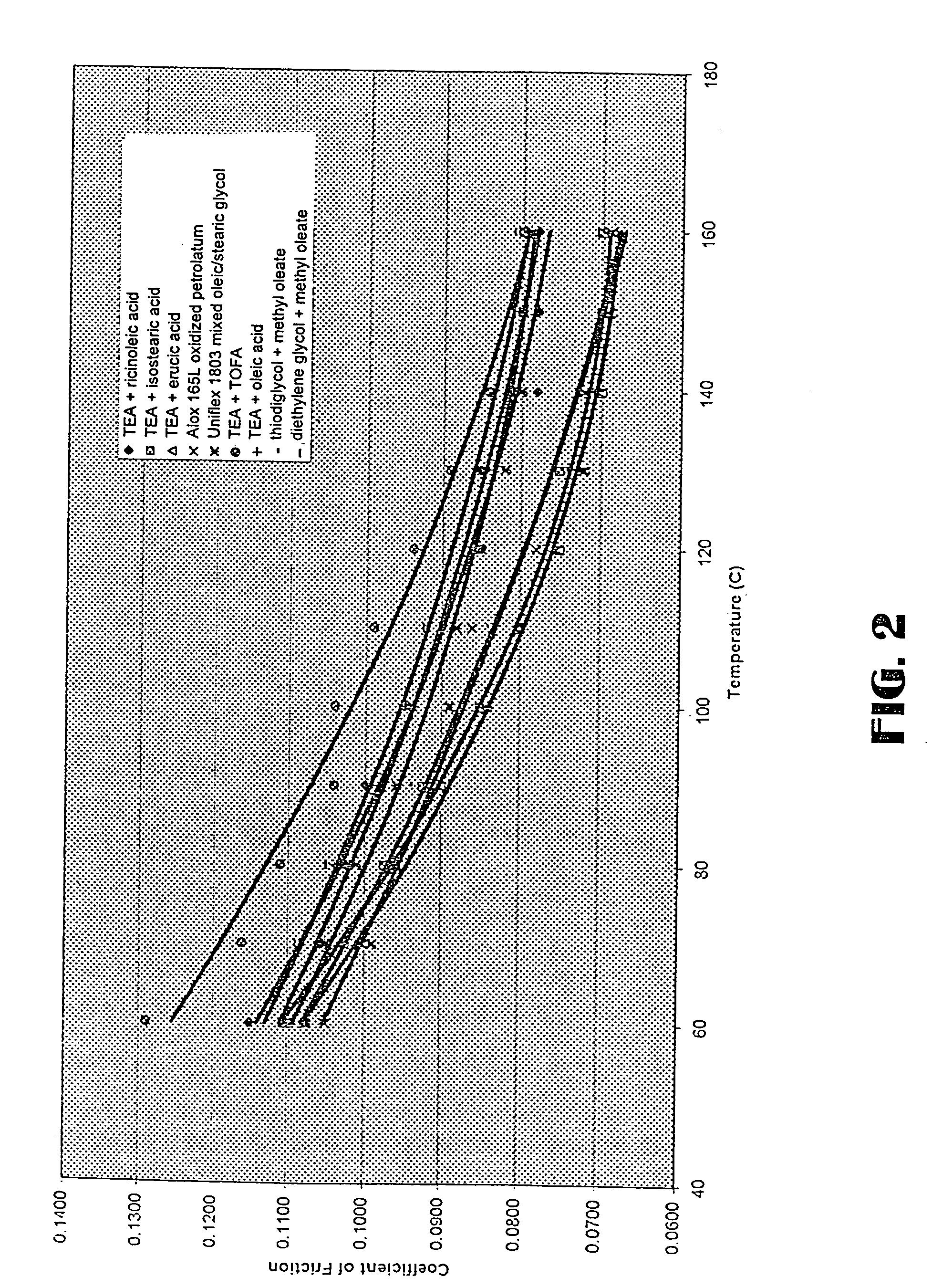
Low sediment friction modifiers
InactiveUS20050124510A1Improve the lubrication effectAvoid excessive sedimentationLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAdditivesSulfonateAlkaline earth metal
An additive mixture for lubricant oils includes an overbased alkaline earth metal sulfonate, and at least one friction modifier selected from the group consisting of an overbased alkaline earth carboxylate, the reaction product of an alkanolamine with a fatty acid or a fatty acid ester and the reaction product of thiodiglycol or a dialkylene glycol with a fatty acid or a fatty acid ester. The additive mixture, when combined with a lubricant stock, provides a lubricant composition characterized by less sedimentation during storage.
Owner:CHEMTURA CORP
Lignin-based bimetallic functionalized carbon material as well as preparation method and application thereof
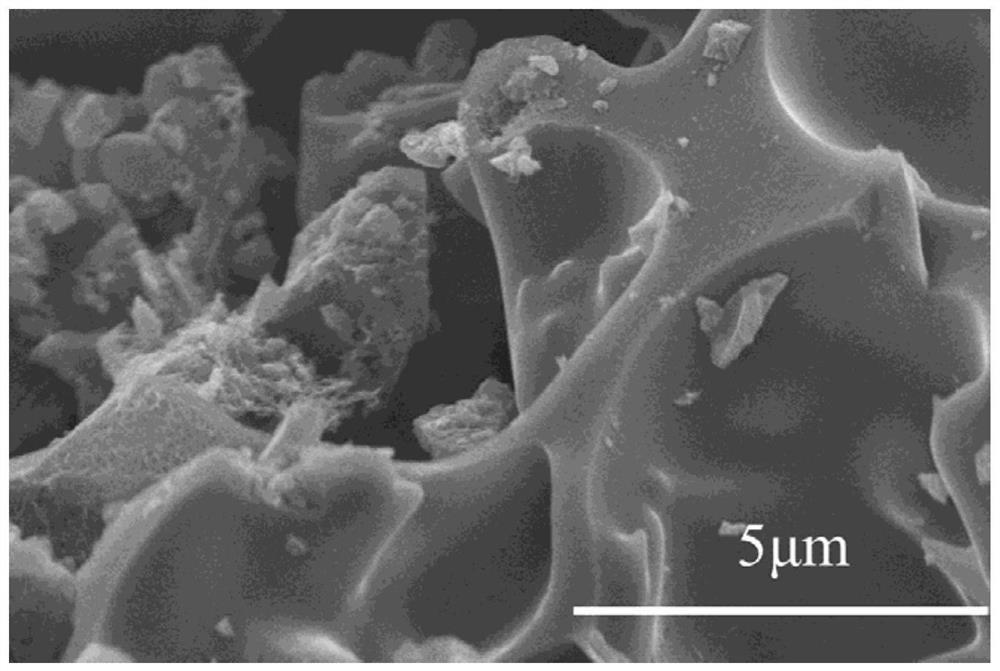
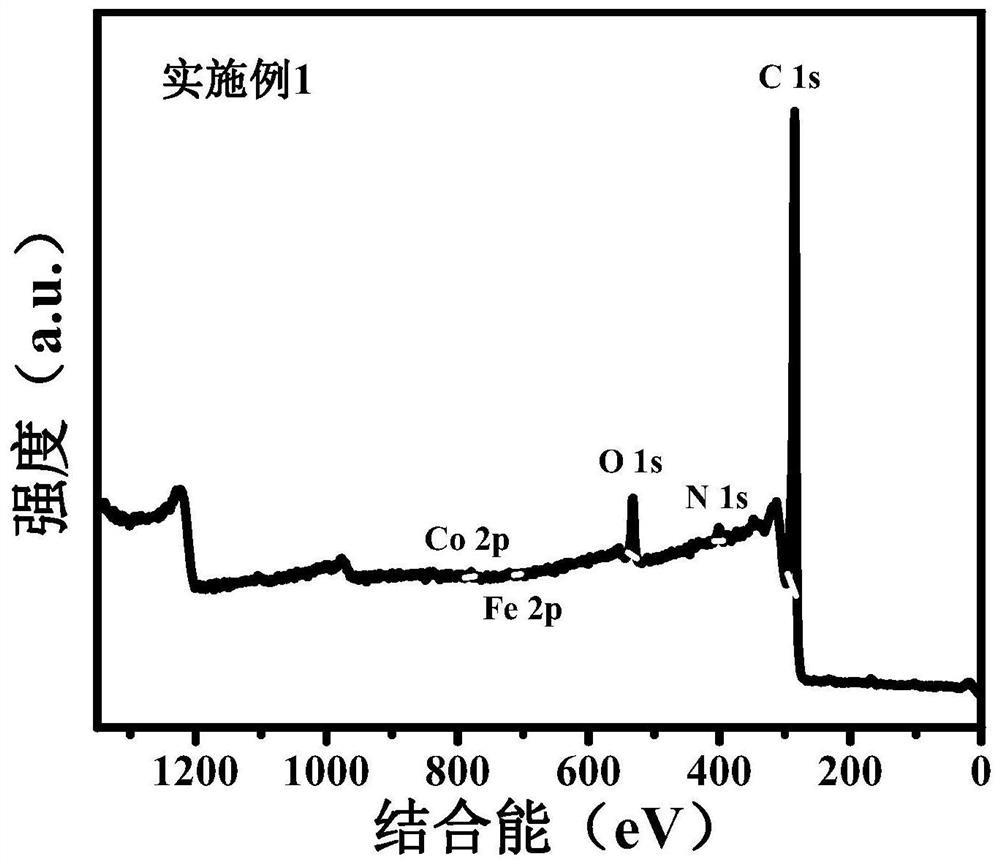
ActiveCN112044461AHigh metal contentShort preparation timeCatalyst activation/preparationElectrodesCarbonizationEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomass materials and discloses a lignin-based bimetallic functionalized carbon material as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The invention provides the preparation method of the lignin-based metal functionalized carbon material. The method carrying out carboxylation modification on lignin, coordinating with transition metal to form a metal carboxylated lignin-based supramolecular precursor, co-doping with nonmetal heteroatoms, and carrying out high-temperature carbonization. The method comprises the following steps: S1, coordinating and combining carboxylated lignin with an iron and cobalt metal salt solution to obtain a bimetal carboxylated lignin-based supramolecular precursor; and S2, carrying out non-metal doping andhigh-temperature carbonization treatment on the metal lignin-based supramolecular precursor to obtain the modified lignin-based metal functionalized carbon material. An electrocatalytic oxygen evolution electrode prepared from the carboxylated lignin-based metal functionalized carbon material prepared by the preparation method disclosed by the invention shows excellent catalytic activity.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Permanent resist, permanent resist-laminated substrate and process for producing the same
InactiveUS20040253540A1Increase flexibilityIncrease resistancePhotosensitive materialsPhotosensitive material processingPolymer scienceAlkaline earth metal
A permanent resist obtained by at least photoexposure and alkali development of a photosensitive resin composition, the permanent resist containing a metal carboxylate group, or a carboxyl group (a carboxyl anhydride group is also included among a carboxyl group according to the invention) and a metal carboxylate group, wherein an alkaline earth metal carboxylate group constitutes at least 30 mole percent of the total of a carboxyl group and a metal carboxylate group.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD
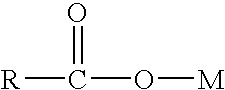
Composition and method for scavenging sulfides and mercaptans
This invention relates to a composition comprising 1.) a metal carboxylate, wherein the metal M is selected from the group consisting of Ag, Cn, Hg, Pb, Sn, Ni, Co, Ca, Fe, Zn and Mn, those metals being present as ions in a +2 or +3 charge state, and wherein the carboxylate anion is derived from a hydrocarbyl monocarboxylic acid having 5 to 20 carbon atoms, or a mixture of such acids, 2.) a solvent selected from the group consisting of water, glycol ethers having from 4 to 15 carbon atoms, alkyl alcohols having from 1 to 10 carbons, and aromatic hydrocarbon solvents having from 6 to 30 carbons, and 3.) an emulsion breaker which is a polymeric nonionic surfactant.
Owner:CLARIANT INT LTD
Method for the production on metal carboxylates and the metal aminoate or metal hydroxy analogue methionate derivatives thereof, and use of same as growth promoters in animal feed
ActiveUS20070259954A1Improves production parameterImprove bioavailabilityBiocideOrganic compound preparationMetallacarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
A method of production of metal carboxylates and of their metal carboxylate-aminoate or metal carboxylate-methioninate hydroxy analog derivatives, and their use as growth promoters in animal nutrition. It comprises mixing stoichiometric quantities of formic or butyric acid and oxide and of the dry basic salt of divalent metal, the oxide or hydroxide of Zn2+ or Cu2+, to give an exothermic reaction, without addiction of solvents, giving rise to a dry carboxylate of divalent metal that is easy to use. It also describes the use of a stage of mixing with metal aminoates or hydroxy analogs of methionine in the process, for forming either a carboxylate-aminoate of divalent metal or a carboxylate-methioninate hydroxy analog of divalent metal, products that are finally obtained in a dry form that is easy to use. Finally it describes the use of the compounds that can be obtained in the feeding of monogastric animals for improving the productivity, the bioavailability of the metals, and achieve a reduction of their emission to the environment, owing to the growth-promoting effect that they all display.
Owner:NOREL ANIMAL NUTRITION USA INC
Metal delivery system for nanoparticle manufacture
InactiveUS8007758B2Add featureImprove homogeneityRare earth metal oxides/hydroxidesMolten spray coating2-Ethylhexanoic acidCarboxylic salt
Described is a method for the production of pure or mixed metal oxides, wherein at least one metal precursor that is a metal carboxylate with a mean carbon value per carboxylate group of at least 3, e.g. the 2-ethyl hexanoic acid salt, is formed into droplets and e.g. flame oxidized. The method is performed at viscosities prior to droplet formation of usually less than 40 mPa s, obtained by heating and / or addition of one or more low viscosity solvents with adequately high enthalpy.
Owner:ETH ZURICH THE SHORT NAME OF EID GENOSSISCHE TECHN HOCHSCHULE ZURICH
Single-Component Curable Composition
The present invention has its object to provide a one package curable composition which contains an organotin-free catalyst and therefore has good curability and adhesiveness. The present invention provides a one package curable composition which comprises (A) an organic polymer having a silicon-containing group capable of crosslinking by forming a siloxane bond, (B)(b1) a carboxylic acid of which the carbon atom adjacent to a carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon, and / or (b2) a metal carboxylate of which the carbon atom adjacent to a carbonyl group is a quaternary carbon, and (C) a surface-treated ground calcium carbonate.
Owner:KANEKA CORP
A kind of preparation method and product of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube
ActiveCN104176724BWide variety of sourcesEvenly distributedMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical chemistryNitrogen atmosphere
The invention discloses a preparation method and a product of a nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing calcination on a precursor under a nitrogen atmosphere, and performing acid treatment after calcination to obtain the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube, wherein the precursor is a compound of carboxylate of organic amine and metal carboxylate; the carboxylate of organic amine is melamine carboxylate or dicyanodiamide; the length of the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube is more than 5 microns, and the tube diameter of the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tube is 50-500 nanometers. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, is wide in raw material source and strong in sustainability, can be used for obtaining the nitrogen-doped carbon nano-tubes which are uniformly distributed in a large area range, and is expected to achieve large-scale production; and the modification on surface functional groups can be completed in one step by virtue of calcination without implementing subsequent complex modification processes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nano particle grafted stereoblock polylactic acid, preparation method and application of nano particle grafted stereoblock polylactic acid
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Overbased metal carboxylate calcite-containing greases
InactiveUS20080274923A1Organic compound preparationLiquid carbonaceous fuelsAlkaline earth metalPolyol
Grease precursors of overbased alkaline earth metal carboxylates are prepared by reacting an alkaline earth metal base and a carboxylic acid in the presence of a hydrocarbon liquid, a polyol and an alcohol. The resulting grease precursor has amorphous calcium carbonate and a calcite content of greater than 10% by weight. At least one converting agent is added to the grease precursor containing elevated levels of calcite. This mixture is heated followed by the removal of water to form calcite-containing greases having a calcite content greater than 12.5% by weight.
Owner:OMG AMERICAS INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com