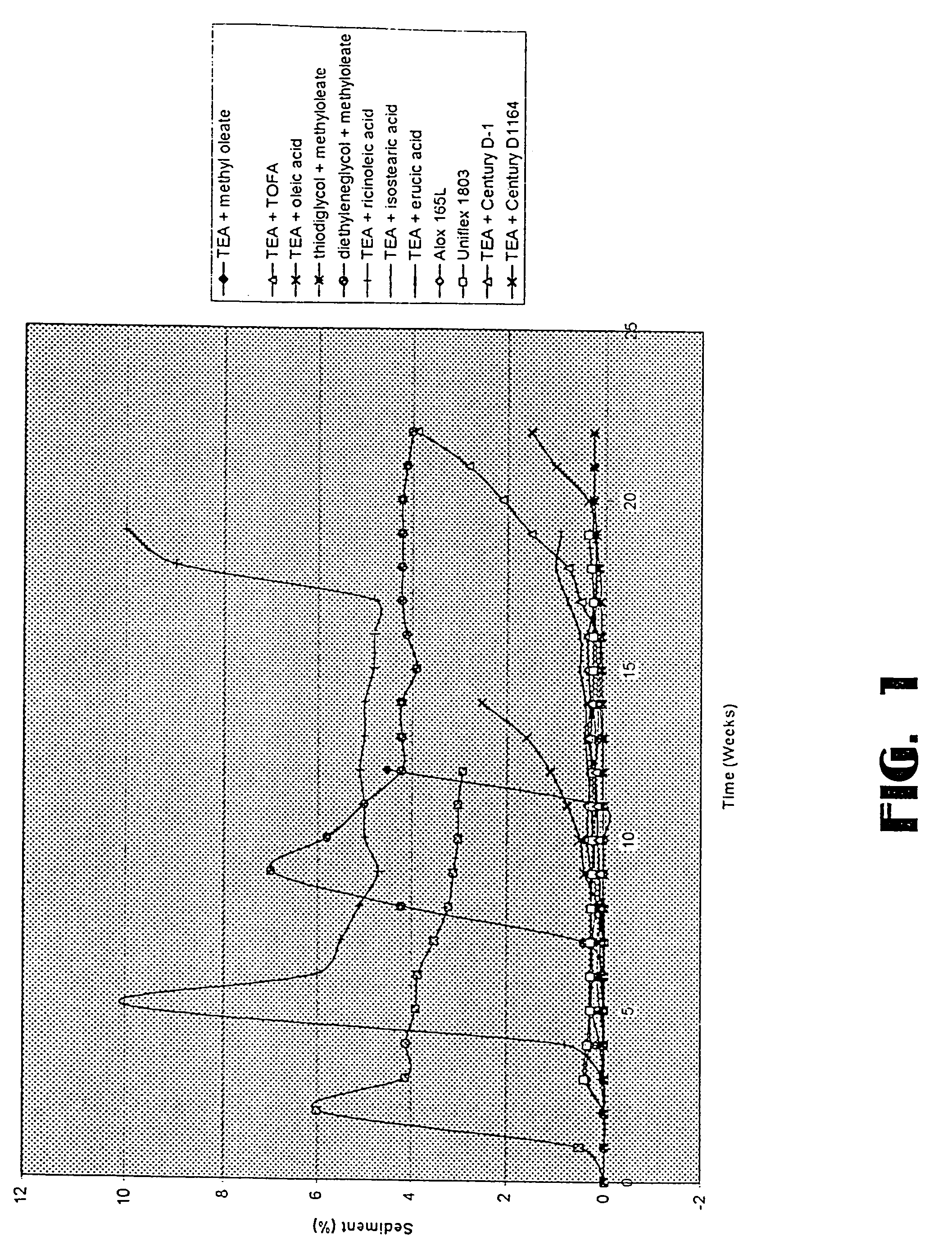
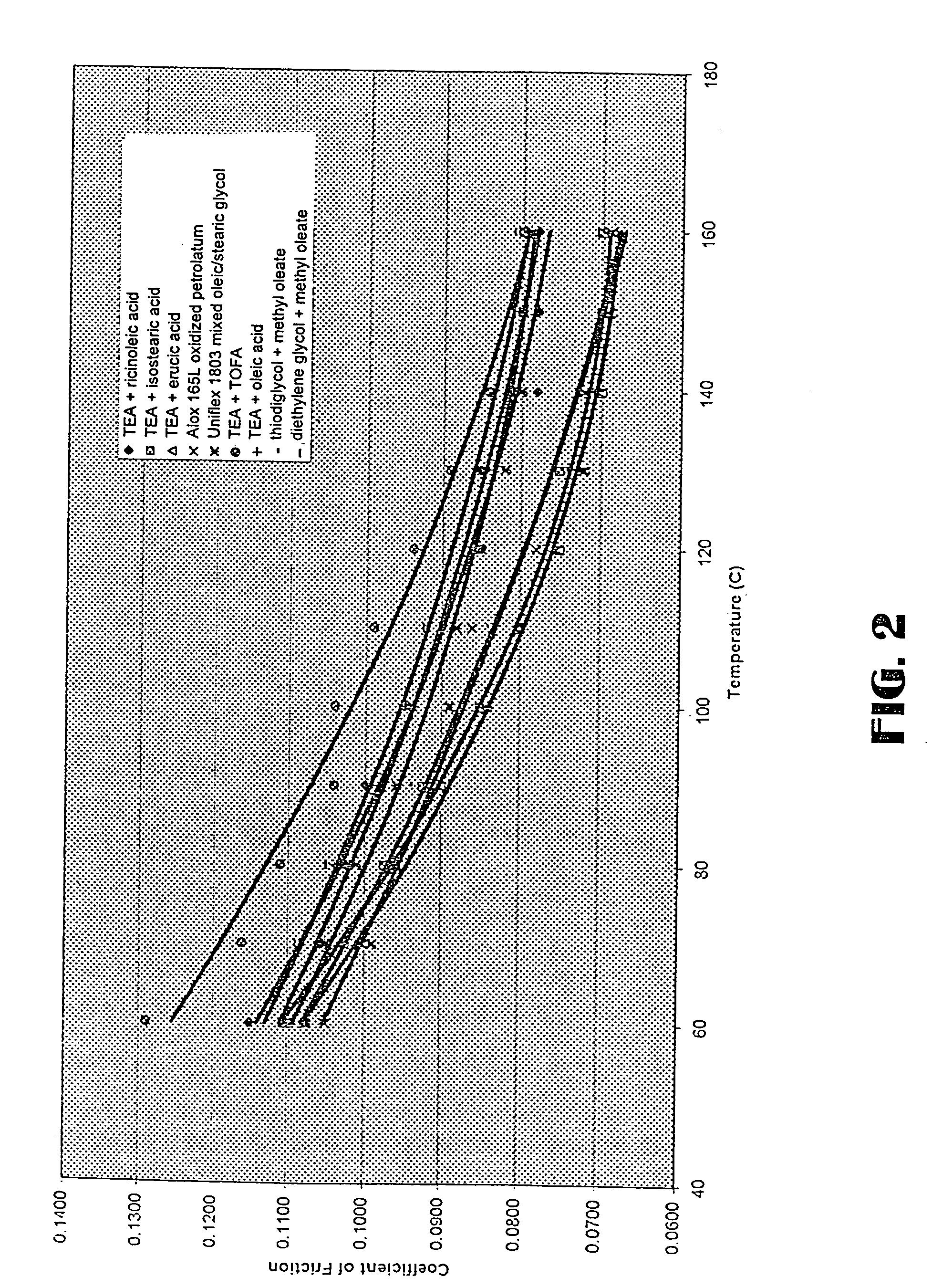
Low sediment friction modifiers
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
examples 1-8
[0027] These examples are directed to a study of the sedimentation characteristics of various blends of overbased calcium sulfonate and selected friction modifiers. Two types of overbased calcium sulfonates were individually tested. Calcinate™ C300CS is a crystalline overbased calcium sulfonate having TBN of about 300 and a particle size of from about 50 nm to about 100 nm, and is available from Crompton Corporation. Calcinate™ C400CLR is an amorphous overbased calcium sulfonate available from Crompton Corporation having TBN of about 400 and a particle size of no more than about 30 nm. Overbased calcium sulfonates were present in 10% concentrations. The friction modifier included glycerol mono oleate (“GMO”). Polyisobutylene succinic anhydride (“PIBSA”) having a molecular weight of about 1,050, was present in Examples 3, 4, and 7 as a dispersant. The friction modifier was present in 1% concentrations when employed. The lubricant oil stock was a severely hydrotreated naphthenic oil a...
examples 9 to 16
[0030] Sedimentation experiments were conducted in the same manner as in Examples 1-8 except that the friction modifiers tested were an oxidized petroleum fraction available under the designation Alox 165L from Lubrizol, an overbased calcium oleate, designated herein as “OCO”, and GMO. The friction modifiers, when employed, were each present in 0.5% concentration. Examples 10 and 14 did not employ any friction modifiers.
[0031] As can been seen from the results the amorphous overbased calcium sulfonate Calcinate™ C400CLR (Examples 13-16) was characterized by very low sedimentation percentages (typically about 0.001 to about 0.005) as opposed to the sedimentation percentages (0.11 to 0.50) for the Calcinate™ C300CS (Examples 9-12).
[0032] The results of these experiments are set forth in Table 2.
TABLE 2Example910111213141516C300CS 10% 10% 10% 10%————C400CLR———— 10% 10% 10% 10%Alox 16520.5%———0.5%———OCO——0.5%———0.5%—GMO———0.5%———0.5%Hyprene H10089.5% 9089.589.589.59089.589.5% Sedime...
examples 17 to 28
[0033] Sedimentation experiments were conducted in a manner similar to Examples 9 to 16, except that the friction modifiers tested were OCO (overbased calcium oleate), Alox 302 (oxygenated petroleum fraction), an overbased barium tallate having 3% -10% barium and designated herein as “OBT”, an overbased calcium tallate having 4%-10% calcium and designated herein as “OCT”, and GMO (glycerol mono oleate). Examples 22 and 28 did not employ any friction modifier.
[0034] As can be seen, the amorphous overbased calcium sulfonate Calcinate™ C400CLR (Example 23-28) is characterized by much lower percentages of sedimentation as opposed to the sedimentation percentages for the crystalline overbased calcium sulfonate Calcinate™ C300CS (Examples 17-22).
[0035] The results of these experiments are set forth in Table 3
TABLE 3Example171819202122232425262728C300CS 10% 10% 10% 10% 10% 10%——————C400CLR—————— 10% 10% 10% 10% 10% 10%OCO0.5%—————0.5%—————Alox 302—0.5%—————0.5%————OBT——0.5%—————0.5%———...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com