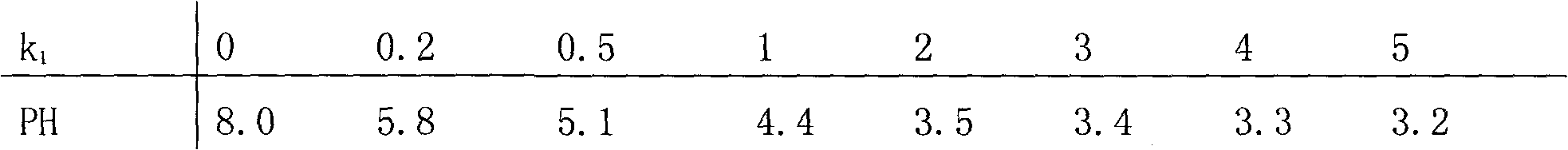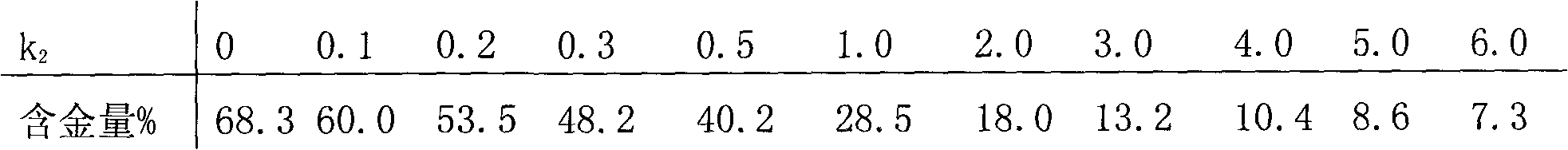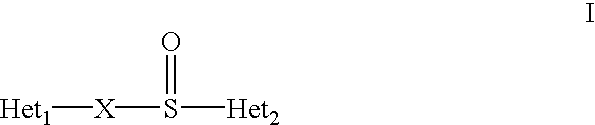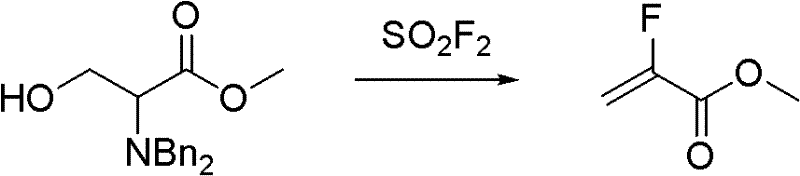Patents
Literature
597 results about "Kainite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Kainite (/ˈkaɪnaɪt/ or /ˈkeɪnaɪt/) (KMg(SO₄)Cl·3H₂O) is an evaporite mineral in the class of "Sulfates (selenates, etc.) with additional anions, with H₂O" according to the Nickel-Strunz classification. It is a hydrated potassium-magnesium sulfate-chloride, naturally occurring in irregular granular masses or as crystalline coatings in cavities or fissures. This mineral is dull and soft, and is colored white, yellowish, grey, reddish, or blue to violet. Its name is derived from Greek καινος [kainos] ("(hitherto) unknown"), as it was the first mineral discovered that contained both sulfate and chloride as anions. Kainite forms monoclinic crystals.
Non-phosphorus compound scale and corrosion inhibitor for treatment of circulating cooling water
ActiveCN1621362AEasy to useIncrease the concentration factorScale removal and water softeningPhosphateTungstate
The composite phosphate-free scale inhibiting corrosion inhibitor for treating circular cooling water consists of scale inhibitor and corrosion inhibitor. The scale inhibitor consists of one or several of PASP, PVA, oxidized starch, polyacrylic acid, acrylic acid / acrylate copolymer and acrylic acid / acrylate copolymer with sulfo radical. The corrosion inhibitor consists of one or several of sodium salt / potassium salt / ammonium salt of organic salt, sodium / potassium / ammonium borate, nitrous organic matter, soluble molybdenate, soluble tungstate, soluble nitrate, soluble nitrite and soluble zinc salt. The composite scale inhibiting corrosion inhibitor has excellent scale inhibiting and corrosion inhibiting performance, is environment friendly, and is especially the treatment of hard circulation water with high calcium and high alkali content.
Owner:BEIJING YANHUA XINGYE TECH DEV +1
Dispersible potash pellets
ActiveUS20070180877A1Alkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersWater dispersibleSulfate
A water-dispersible particle is provided that includes a sulfate or phosphate of potash in an amount ranging from 5% to 99.9% by weight of the total dry weight of the particle. A binder component is present in an amount from 1% to 95% by weight. The sulfate or phosphate of potash and the binder component on that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces.A process for making a water-dispersible particle includes mechanical aggregation of a sulfate or phosphate of potash into a pellet. A binder component is present in the particle in an amount ranging from 1% to 95% by weight. The sulfate or phosphate of potash and the binder component are present in a form such that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces. The pellet is then dried and ready to be applied.
Owner:THE ANDERSONS
Potassium glyphosate formulations
InactiveUS7049270B2Improve weed control effectImprove compatibilityBiocideCationic surface-active compoundsChemical compositionEmulsion
A herbicidal composition is provided comprising an aqueous solution of N-phosphonomethylglycine, predominantly in the form of the potassium salt thereof, at a concentration of at least 300 g a.e. / l of the composition; and a surfactant component in solution or stable suspension, emulsion, or dispersion in the water, comprising one or more surfactants in a total amount of about 20 to about 300 g / l of the composition, wherein the composition has a viscosity of less than about 250 centipoise at 0° C. or a Gardner color value less than 10.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Potassium salt of (s)-omeprazole
The present invention relates to a novel form of 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)-methyl]sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole, known under the generic name omeprazole. More specifically, it relates to a novel crystalline form of the potassium salt of the (S)-enantiomer of 5-methoxy-2-[[(4-methoxy-3,5-dimethyl-2-pyridinyl)methyl]sulfinyl]-1H-benzimidazole. The present invention also relates to processes for preparing such a form of the potassium salt of (S)-omeprazole and pharmaceutical compositions containing it.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Dispersible potash pellets
ActiveUS7789932B2Alkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersWater dispersibleSulfate
A water-dispersible particle is provided that includes a sulfate or phosphate of potash in an amount ranging from 5% to 99.9% by weight of the total dry weight of the particle. A binder component is present in an amount from 1% to 95% by weight. The sulfate or phosphate of potash and the binder component on that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces.A process for making a water-dispersible particle includes mechanical aggregation of a sulfate or phosphate of potash into a pellet. A binder component is present in the particle in an amount ranging from 1% to 95% by weight. The sulfate or phosphate of potash and the binder component are present in a form such that contact with water causes particle dispersion into more than 100 pieces. The pellet is then dried and ready to be applied.
Owner:THE ANDERSONS
Catalyst for preparing mixing alcohol with low carbon from synthesis gas and its preparing method
InactiveCN1431049AGuaranteed stabilityGuaranteed lifeOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHigh resistanceMANGANESE ACETATE
A catalyst for preparing low-carbon alcohol mixture from synthetic gas contains Mo (2-40 %), Ni (4-10%), Mn (0.1-5.0%), K (5-15%), S (20-40%) and bentone, and is prepared through reaction of ammoniumsulfide solution or hydrogen sulfide gas on ammonium molybdate, adding concentrated acetic acid, thermal stirring, cooling for deposition, adding deionized water for dissolving doposit to obtain solution of ammonium thiomolybdate, dropping the solution along with the mixed solution of nickel acetate and manganese acetate in acetic acid to form black deposit, filtering, washing, baking, mixing with bentone, and tabletting. Its advantages are high resistance to S and no carbon deposit.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
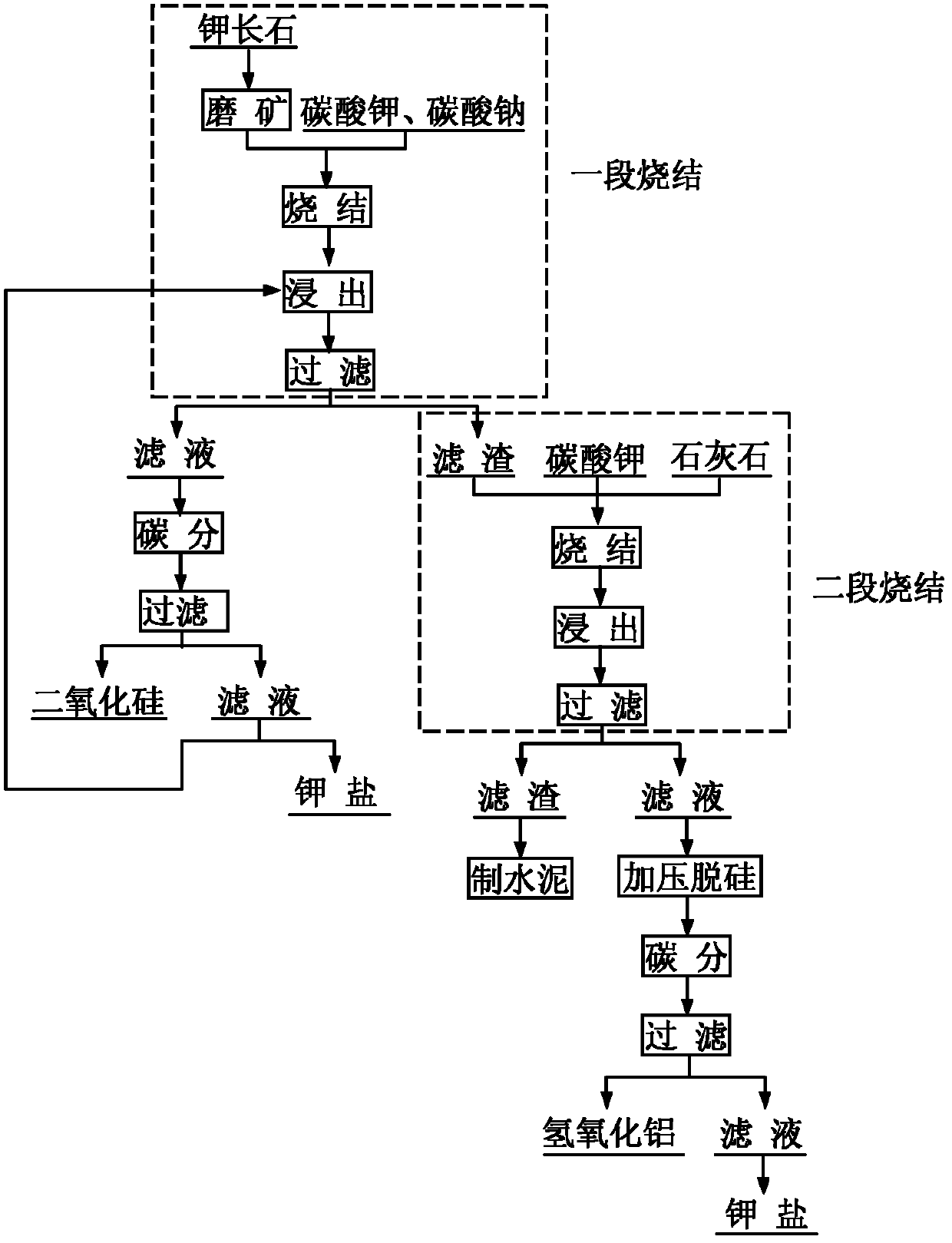
New process for comprehensively utilizing potassium feldspar
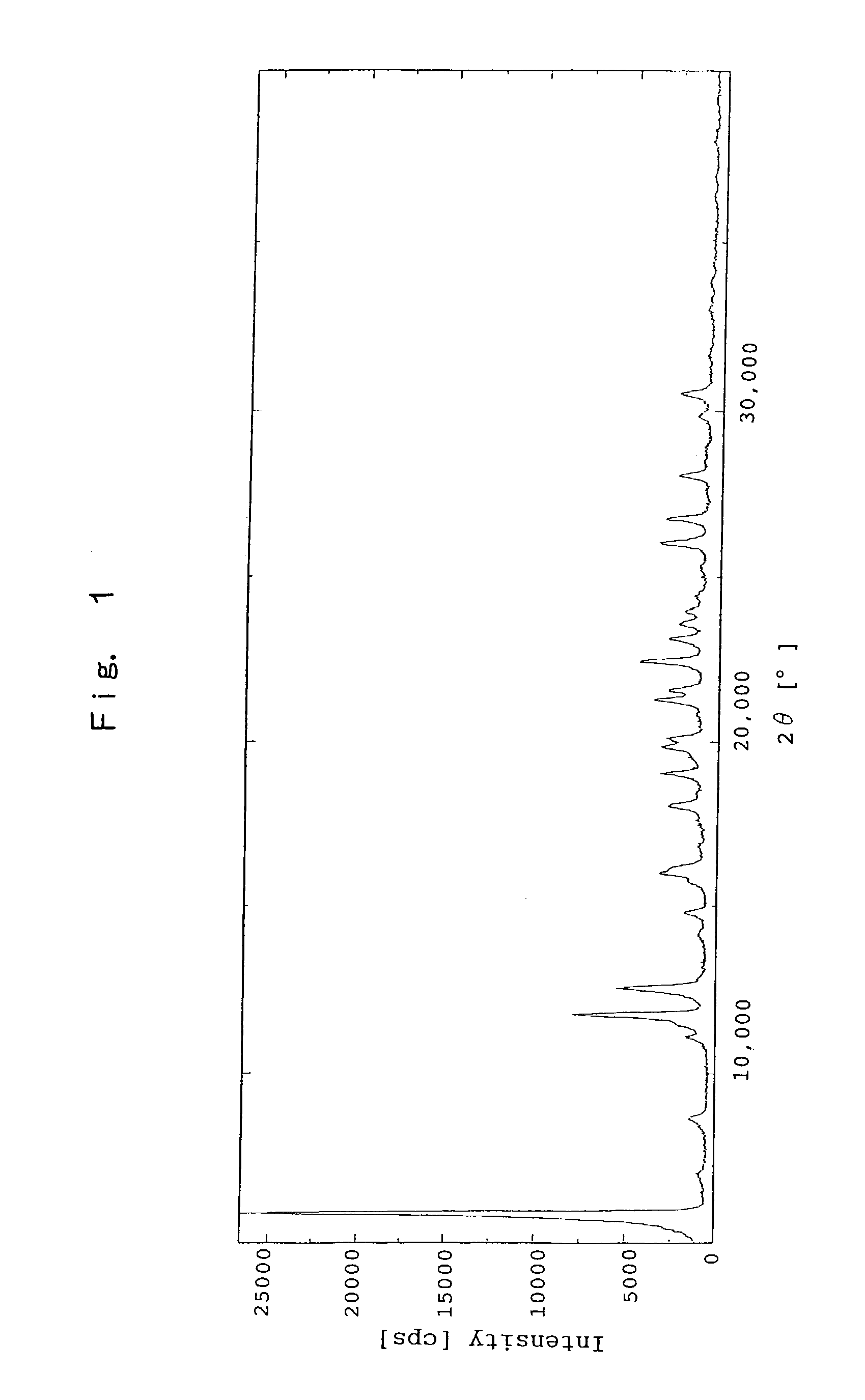
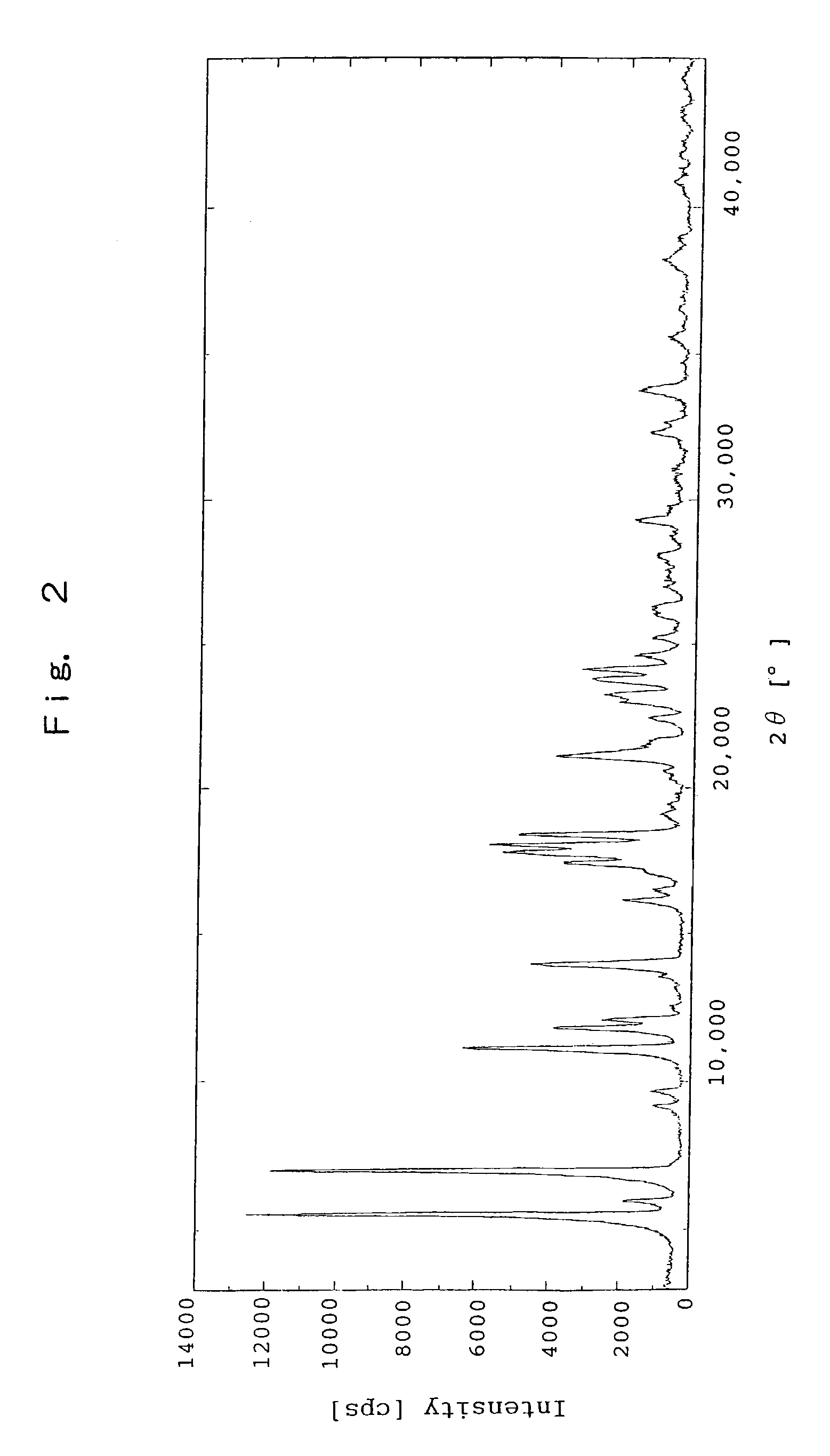
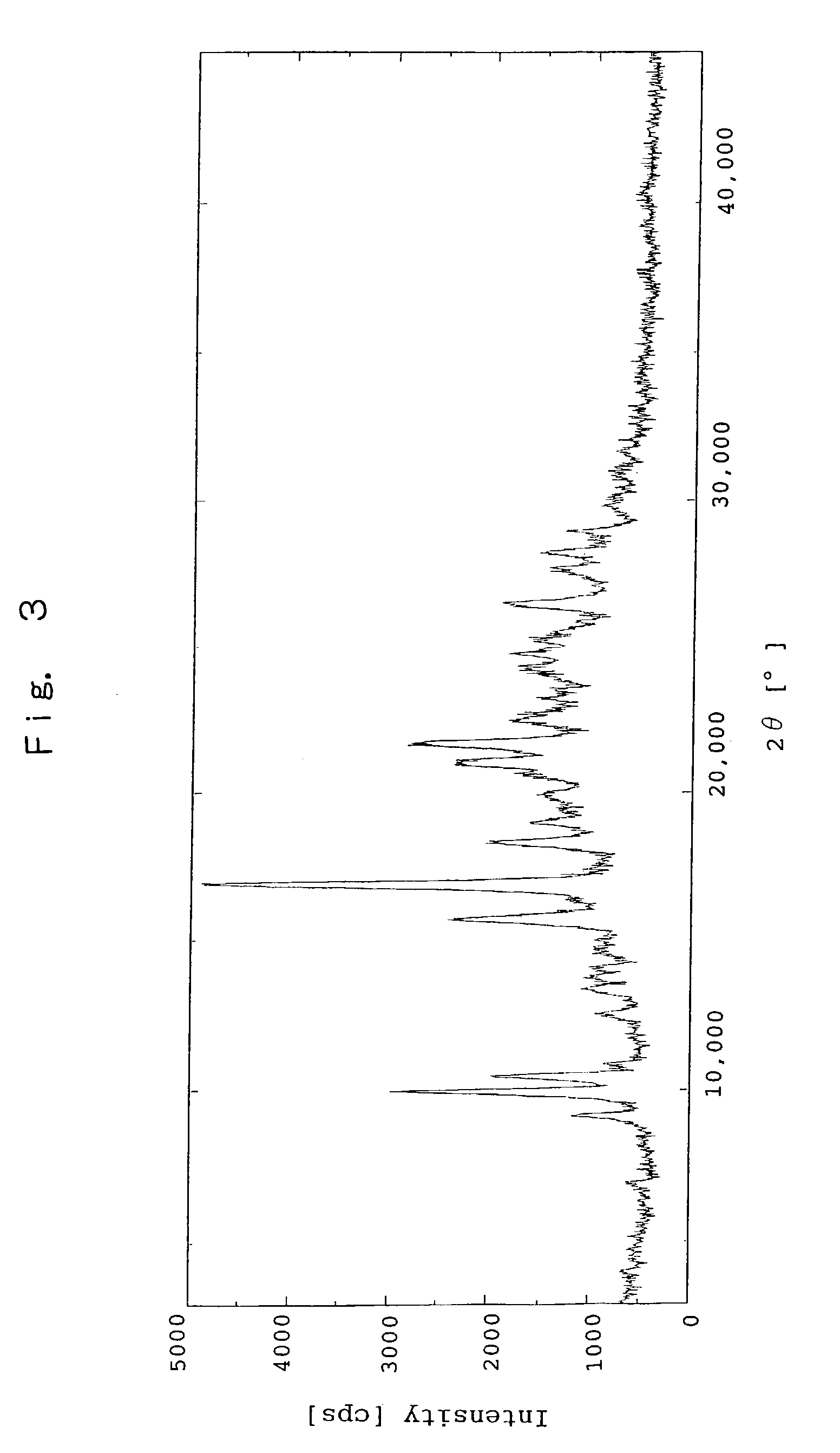
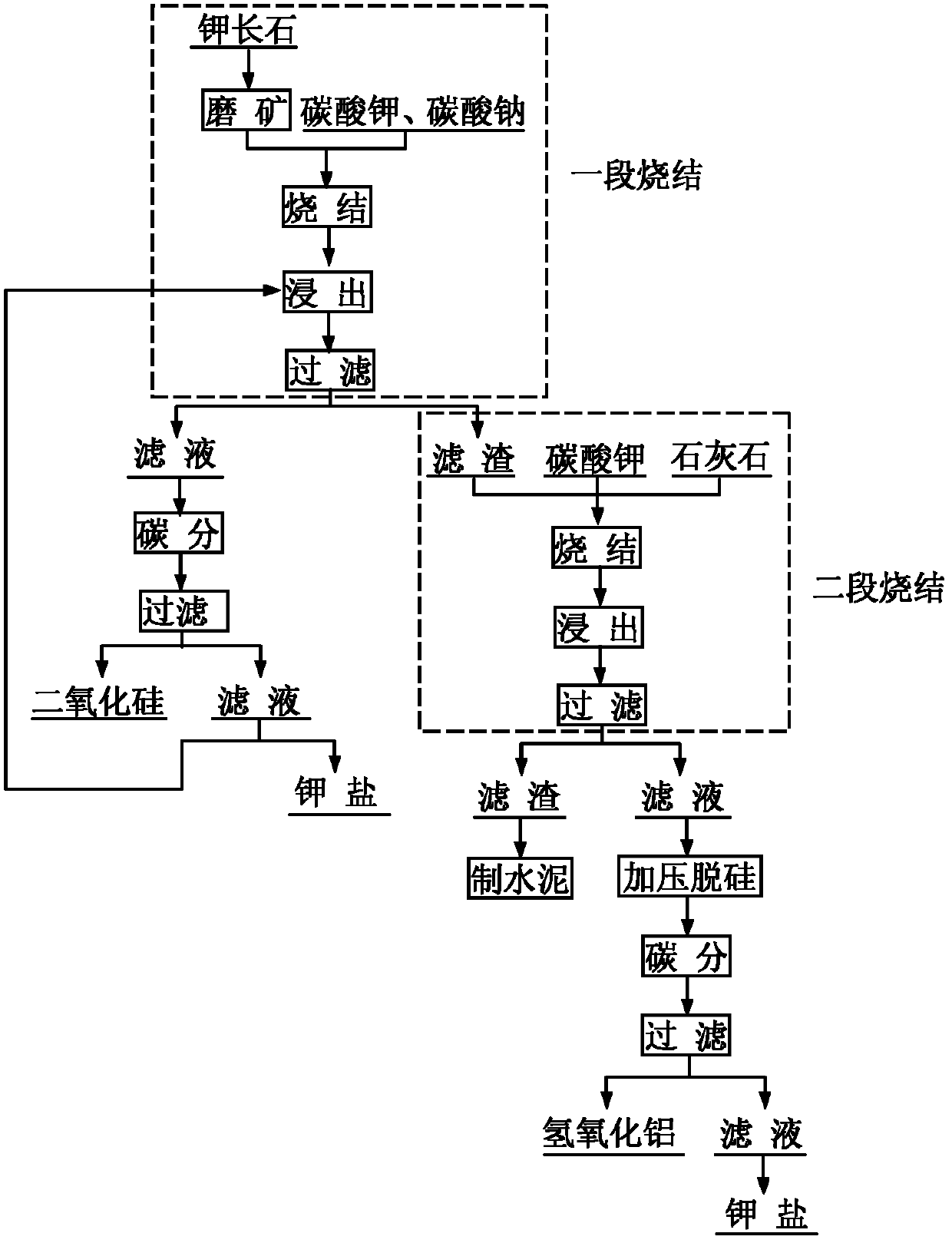
InactiveCN102557050AMaximize the value of silicon resourcesResource value maximizationSilicaCement productionDecompositionFiltration
The invention discloses a new process for comprehensively utilizing potassium feldspar. The new process comprises the following steps of: performing primary sintering on the potassium feldspar added with potassium carbonate or sodium carbonate, leaching the sintering clinker in a mixed solution of potassium hydroxide and potassium carbonate, and filtering, wherein the obtained filter residue is araw material for secondary sintering, the obtained filtrate is subjected to carbon decomposition and filtration, partial silicon dioxide is recovered from filter residue for producing white carbon black, part of the filtrate is used for producing potassium salt and part of the filtrate returns to the primary leaching procedure; and performing secondary sintering, namely sintering primary sintering clinker leaching residue added with limestone and potassium carbonate, leaching the sintering clink in a mixed solution of potassium hydroxide and potassium carbonate, and filtering, wherein filter residue is taken as a cement production raw material, filtrate is added with calcium oxide for pressure desilication treatment, a solution subjected to desilication is subjected to carbon decomposition and filtration, and aluminum hydroxide is recovered from filter residue for producing diversified alumina. In the process of primary sintering and secondary sintering, the filtrate subjected to carbon decomposition and filtration is subjected to desilication, concentration and other processes, and the potassium carbonate can be recovered. By the process, the potassium feldspar value resource canbe utilized maximally, the potassium carbonate can be recycled, and environment is protected.
Owner:KUNMING METALLURGY INST
Gold potassium citrate for gold plating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101781784ALow toxicityPH value is stableLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingChemical compositionCITRATE ESTER
The invention relates to gold potassium citrate for gold plating and a preparation method thereof. The gold potassium citrate is used to substitute for gold potassium cyanide in acidic and neutral gold plating technology. The problem that the product coverage area is too wide when gold citrate is used in the gold plating technology is solved. The technical scheme is that the gold potassium citrate is the mixed crystal of gold potassium cyanide and citric acid potassium salt and the chemical composition of the gold potassium citrate is KAu (CN)2 (K3C6H5O7. k1C6H8O7) k2, wherein KAu (CN)2 is gold potassium cyanide, K3C6H5O7.k1C6H8O7 is citric acid potassium salt which is mixed by potassium citrate K3C6H5O7 and citric acid C6H8O7, k1 is the molar ratio of potassium citrate to citric acid, is more than or equal to zero and is less than or equal to three, and k2 is the molar ratio of citric acid potassium salt to gold potassium cyanide, is more than or equal to one point three and is less than five. The method is mainly suitable for the acidic and neutral gold plating technology.
Owner:张东山
Method for producing potassium salt and sodium salt by using waste incineration fly ash
ActiveCN110040748AHigh purityEfficient use ofAlkali metal halide purificationTechnical gradeSodium salt
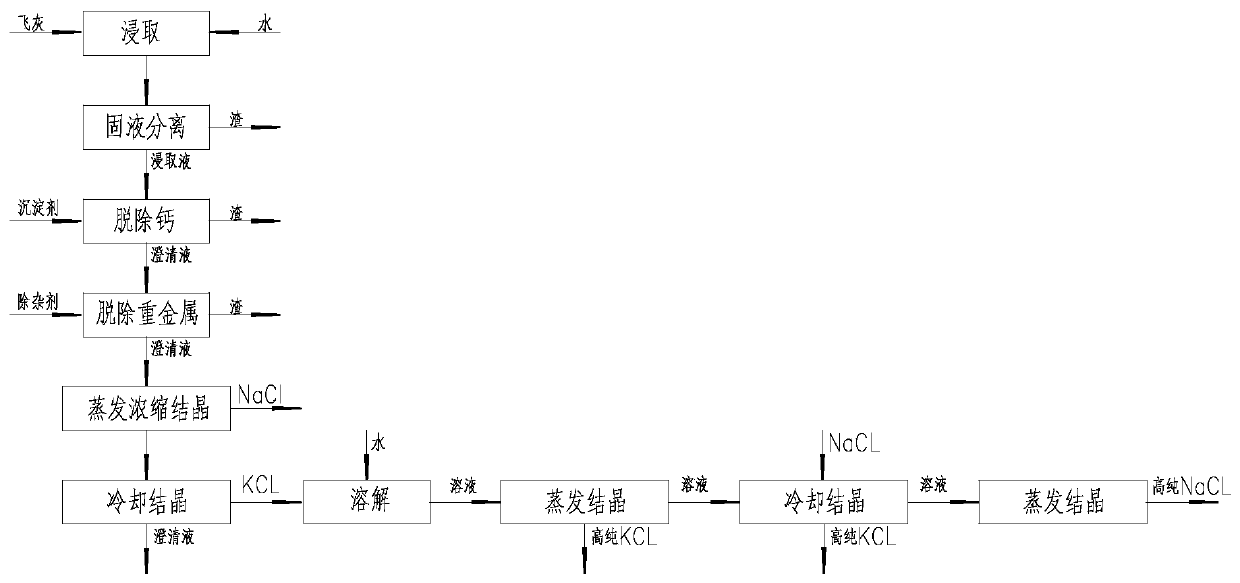
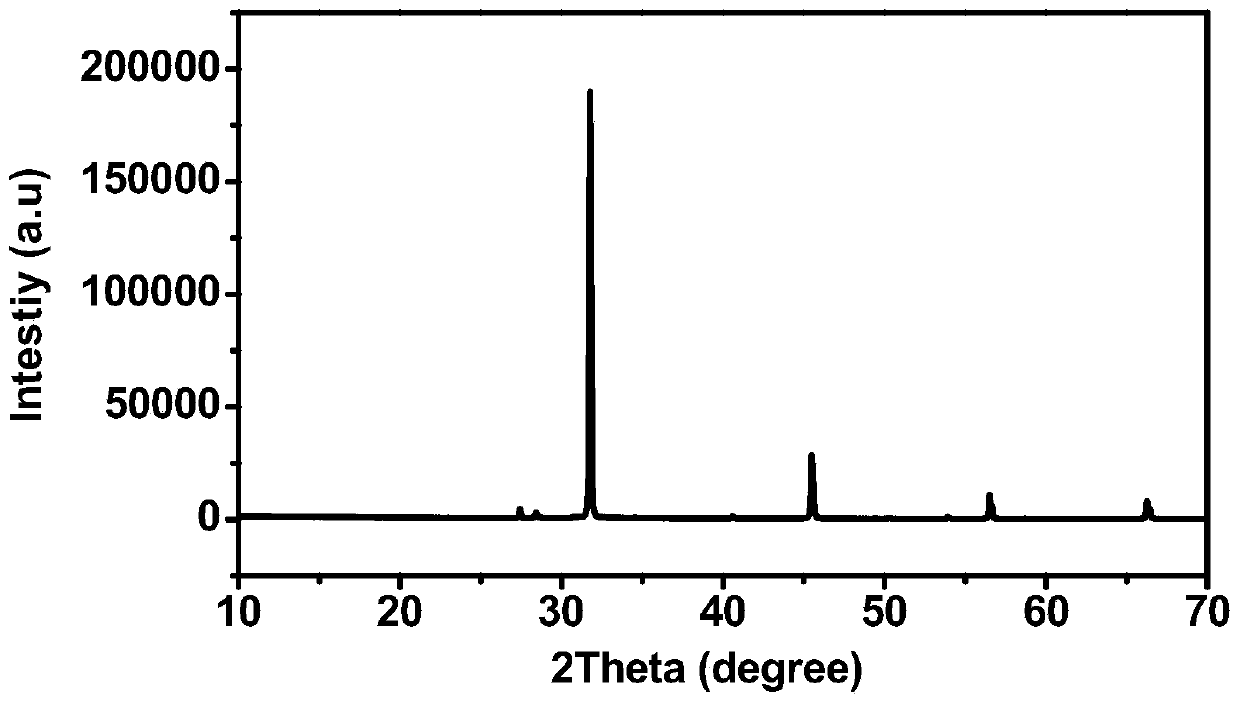
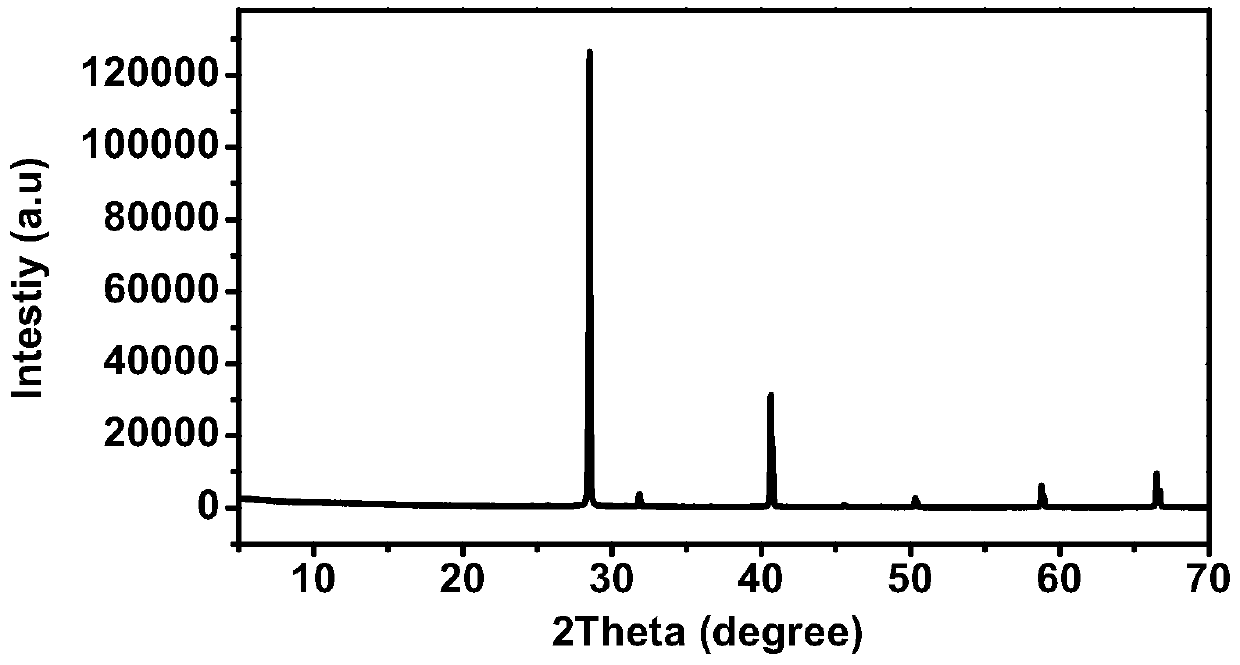
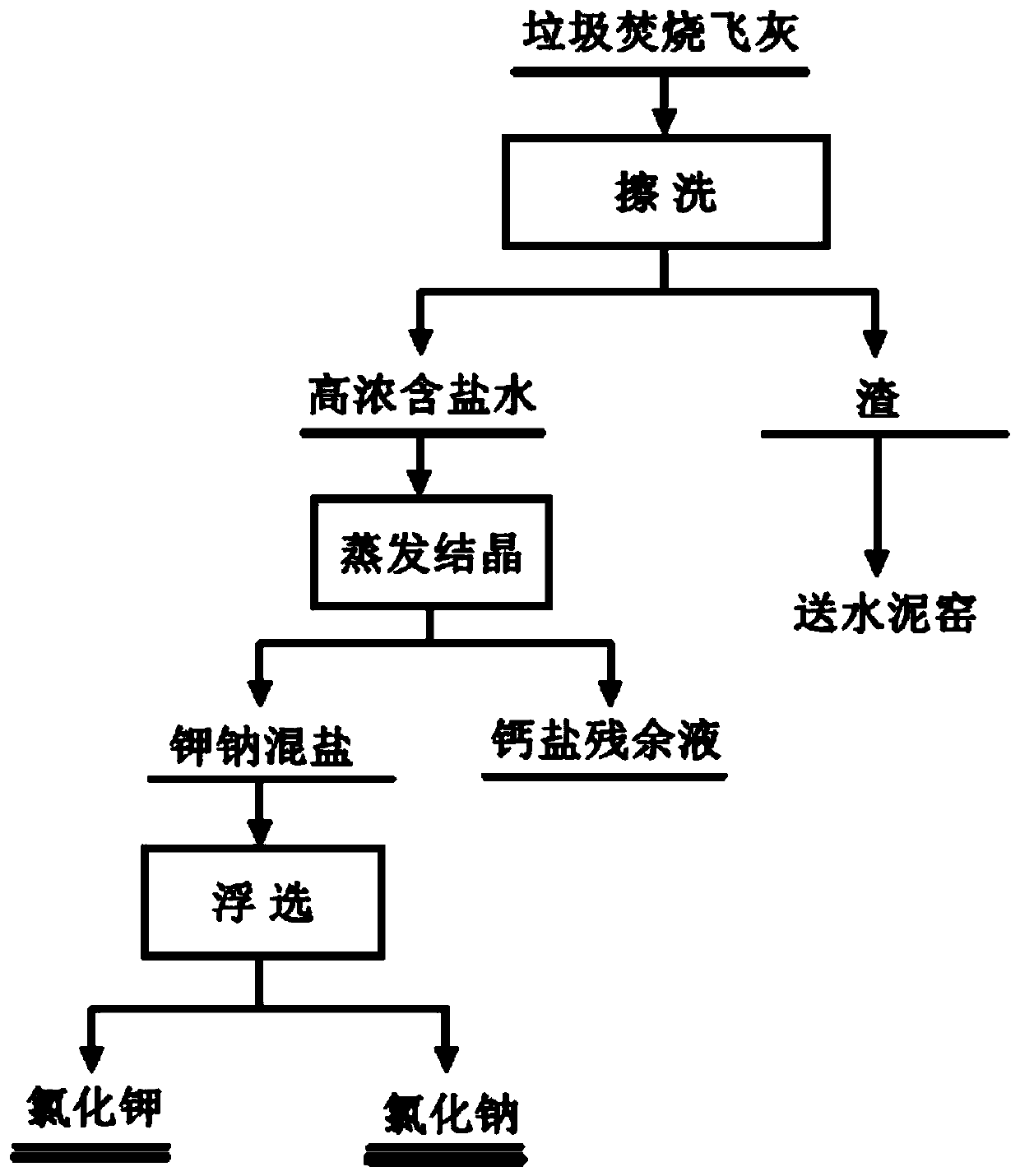
The invention discloses a method for producing potassium salt and sodium salt by using waste incineration fly ash, comprising the following steps: extracting waste incineration fly ash with water to obtain an extract; removing calcium ions and heavy metal impurities in the extract, and adjusting the pH of the solution to 6-8; heating and evaporating to concentrate the solution obtained in the previous step until crystallization, immediately filtering to obtain crystals sodium chloride, and naturally cooling the filtrate to room temperature for crystallization to obtain crystals crude potassiumchloride; dissolving the crude potassium chloride in water with a mass ratio of the crude potassium chloride to water is 1:1-1:1.9, heating and evaporating the solution until crystallization, and immediately separating the solid and liquid to get crystals pure potassium chloride and filtrate; and supplementing sodium chloride into the filtrate obtained in the previous step, cooling for crystallization, and filtering to obtain crystals pure potassium chloride. The invention can separate sodium salt and potassium salt in fly ash washing wastewater, and obtain high purity or industrial grade ofsodium chloride and potassium chloride crystals.
Owner:SINOMA INT ENG
Steam hot aerosol fire-extinguishing composite and application method and fire extinguishing device thereof
ActiveCN101554520AWide variety of sourcesLess corrosiveFire rescueFire extinguisherSodium bicarbonateEpoxy
The invention provides a steam hot aerosol fire-extinguishing composite which contains 30-80wt percent of oxidant, 10-60wt percent of fuel additive and 2-30wt percent of cohesion solidification molding auxiliary agent. The oxidant can be one or more of the following substances: potassium salt, strontium salt, ammonium salt, magnesium salt, nitrocellulose and nitroglycerin; the fuel additive can be one or more of the following substances: azos, azoles, amino-guanidine nitrate, sodium bicarbonate, melamine, cyanoguanidine, carbamide, hexamine, triaminoguanidine nitrate, olefin, saccharose, aluminium powder, magnesite powder and magnesium-aluminium alloy power; the cohesion solidification molding auxiliary agent can be one or more of the following substances: phenol formaldehyde resin, ethoxyline resin, glycidyl azide, urethane rubber, hydroxyl-terminated polybutadiene, polyisobutylene, acetyl tributyl citrate, carboxymethyl cellulose, polyvinyl alcohol phenolic resin and acrylic resin. The invention also provides a fire extinguishing method and a fire extinguishing device adopting the composite. The invention has strong fire extinguishing capacity and fewer hazardous materials and can be applied to different places.
Owner:JIANGXI TSINGHUA IND CO LTD
Process for recovery of sulphate of potash
ActiveUS7041268B2Eliminate needMaximize recoveryChemical industrySulfate preparationPhysical chemistryCarnallite
The present invention is directed to a novel integrated process for the recovery of sulphate of potash (SOP) from sulphate rich bittern. The process requires bittern and lime as raw materials. Kainite type mixed salt is obtained by fractional crystallization of the bittern, and is converted to schoenite which is subsequently reacted with muriate of potash (MOP) for its conversion to SOP. End liquor from kainite to schoenite conversion (SEL) is desulphated and supplemented with MgCl2 using end bittern generated in the process of making carnallite. Decomposed carnallite liquor produced is reacted with hydrated lime for preparing CaCl2 solution and high purity Mg(OH)2 having low boron content. It is shown that the liquid streams containing potash are recycled in the process, and the recovery of potash in the form of SOP is quantitative.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
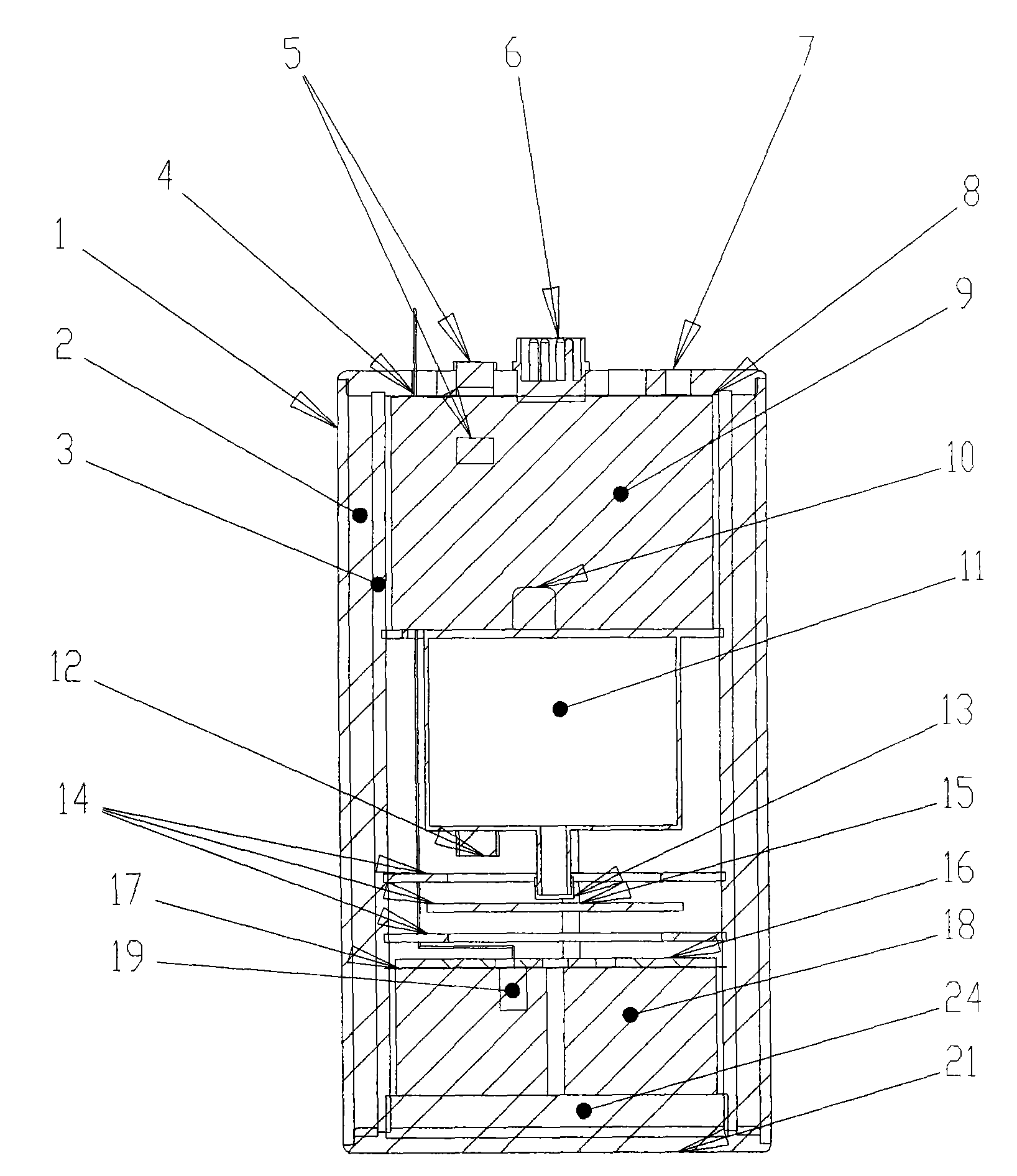
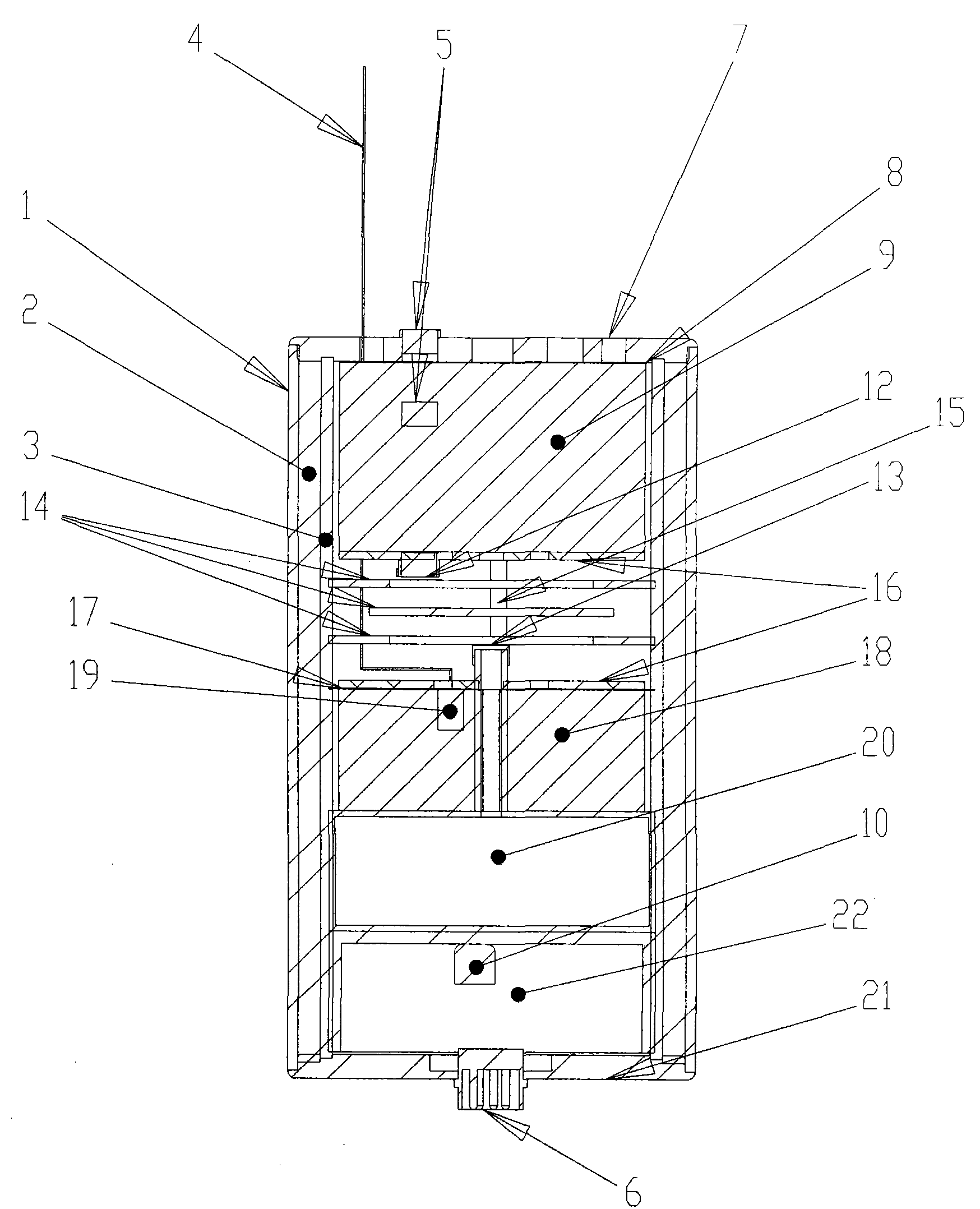
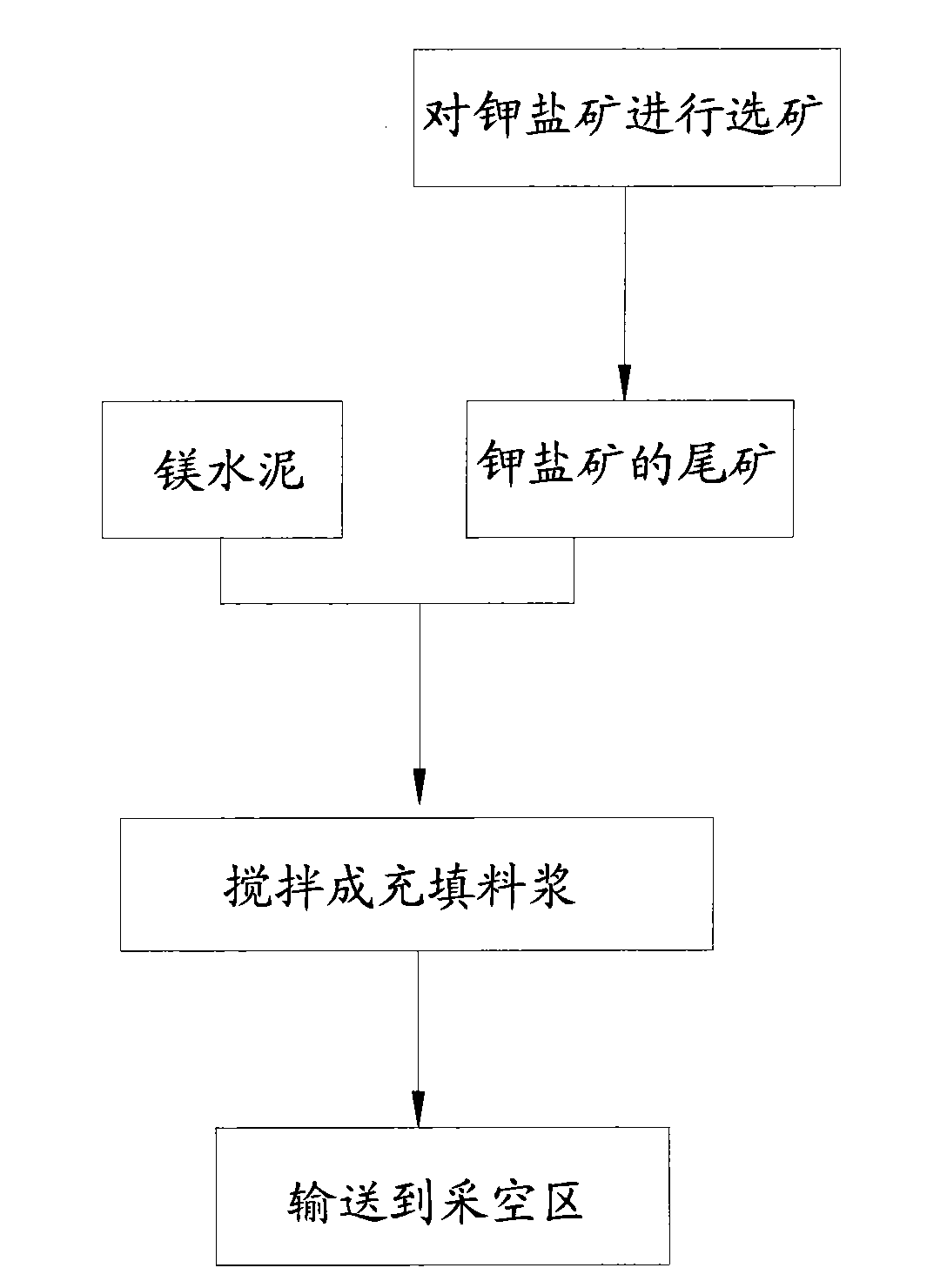
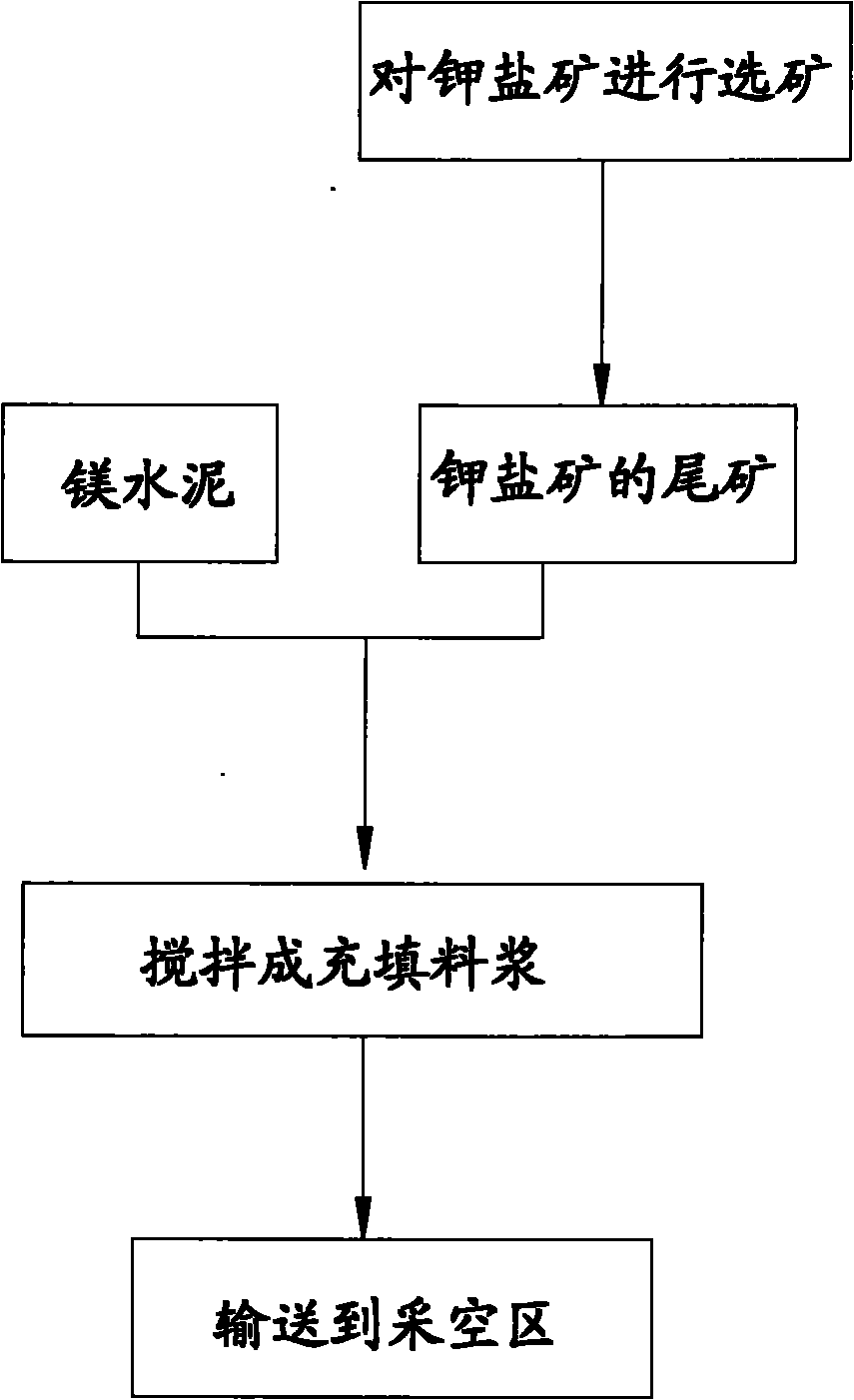
Potash salt ore goaf filling method
ActiveCN101864988AHigh filling strengthSolid waste managementMaterial fill-upMagnesium saltWater soluble
The invention discloses a potash salt ore goaf filling method, including the following steps: potash salt ore is subject to mineral separation, so as to obtain potash salt ore tailing; magnesium cement and the potash salt ore tailing are mixed and stirred into filling pulp; and the filling pulp is conveyed to potash salt ore goaf. According to the potash salt ore goaf filling process of the invention, pulp made by mixing magnesium cement and tailing is taken as filling main material, as the magnesium cement is mainly magnesium oxide, magnesium oxide water soluble magnesium salt is taken as gelling material, then water is added for blending, and air hardening gelled body, thus meeting the strength requirement of goaf filing.
Owner:CHINA ENFI ENGINEERING CORPORATION
Process for recovery of sulphate of potash
ActiveUS20050220698A1Minimize effluent generationEnhance potash recoveryEnergy inputSulfate preparationDecompositionCarnallite
A novel integrated process for the recovery of sulphate of potash (SOP) from sulphate rich bittern is disclosed. The process requires only bittern and lime as raw materials. Kainite type mixed salt is obtained by fractional crystallization of the bittern, Kainite is converted to schoenite with simultaneous removal of NaCl by processing it with water and end liquor obtained from reaction of schoenite with MOP for its conversion to SOP. The end liquor from kainite to schoenite conversion (SEL) is used for the recovery of MOP. SEL is desulphated and supplemented with MgCl2 using end bittern generated in the process of making carnallite. The carnallite is decomposed to get crude potash which in turn processed to get MOP. The carnallite decomposed liquor produced in the decomposition of carnallite is reacted with hydrated lime for preparing CaCl2 solution and high purity Mg(OH)2 having low boron content, The CaCl2 solution is used for desulphatation of SEL producing high purity gypsum as a byproduct. It is shown that the liquid steams containing potash are recycled in the process, the recovery of potash in the form of SOP is quantitative.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Low foam laundry liquid
ActiveCN101993791AImprove cleanlinessEasy to rinseNon-ionic surface-active compoundsDetergent compounding agentsWater savingCoconut oil
The invention relates to a low foam laundry liquid which is composed of the following components in percentage by weight: 5-7% of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate, 6-10% of fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether (3) sodium sulfate (70%), 1-3% of coconut oil acid diethanolamine (1:1.5), 4-6% of fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether (EO=6-12), 1-2% of C12-18 fatty acid potassium or amine salt and the balance of water. The detergency of the laundry liquid of the invention is in accord with the standard of the Class B in QB / T1224-2007, and the laundry liquid can efficiently reduce foams. The invention has the advantages of favorable rinsing effect, water saving, energy saving and high cleanness of rinsed clothes.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOAP FACTORY
Method for preparing potash manure (kali salt) from potassium-rich rock using hydrothermal chemical reaction
InactiveCN1508092AHigh potassium dissolution rateSimplified separation and purification processAlkali metal carbonatesAlkali metal sulfites/sulfatesChemical reactionLiquid ratio
The method for preparing potash fertilizer (kaili salt) by using potassium-rich rock through the process of hydrothermal chemical reaction is characterized by that its adopted alkaline raw material can be lime or light-burned magnesia or dolomite lime and gypsum, and said method includes the following steps: coarse-crushing and medium crushing the above-mentioned raw materials to below 3 mm; according to the ratio of that potassium-rich rock; lime or light-burned magnesia or dolomite lime; gypsum is 1:0.8-1:0.2-0.25 feeding the above-mentioned raw materials into vibration grinding machine and grinding them to below 200 meshes, uniformly mixing them, conveying obtained mixture material into storage tank device, adding water, regulating solid-liquid ratio to 1:1-3, stirring and mixing, transferring said material into high-pressure reactor, introducing high-pressure steam, making hydrothermal reaction at 130-250 deg.C constant temperature for 5-24 hr. so as to obtain the invented prdouct.
Owner:ZHONGKE JIANCHENG MINERAL TECH BEIJING
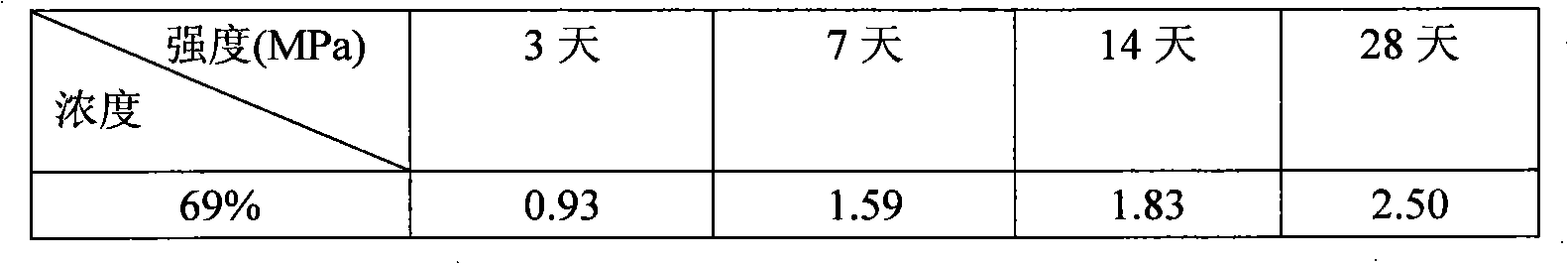
Process for preparing sodium potassium silicate solution by predesiliconizing potassium-rich rock
InactiveCN101798095ARaise the ratioReduce consumptionAluminium silicatesAlkali metal silicatesWater insolubleSlag
The invention discloses a process for preparing a sodium potassium silicate solution by predesiliconizing potassium-rich rock. The process comprises the following steps of: crushing and homogenizing potassium-rich rock to prepare potash feldspar powder; grinding the potash feldspar powder and an alkali solution together to prepare original ore pulp; carrying out a constant temperature reaction of the original ore pulp in a reaction at 180-250 DEG C for 1-4h to obtain reaction slurry; and diluting, filtering and reversely washing the reaction slurry to prepare a sodium potassium silicate solution and an Al-rich hydrated sodium aluminum filter cake. The sodium potassium silicate solution can be used as a raw material for preparing inorganic silicon compounds and sylvite products, and the Al-rich hydrated sodium aluminum filter cake is further processed to extract alumina therein. The process solves the problems of great silicon-calcium slag castoff emission and scaled production restriction existing in the potassium-extracting process from water-insoluble potassium ore.
Owner:昊青薪材(北京)技术有限公司
Method for producing phosphoric acid and soluble potassium salt by phosphorus ore and potash feldspar
InactiveCN101585521AReduce consumptionReduce external heating energyCement productionPhosphoric acidSlagPhosphor
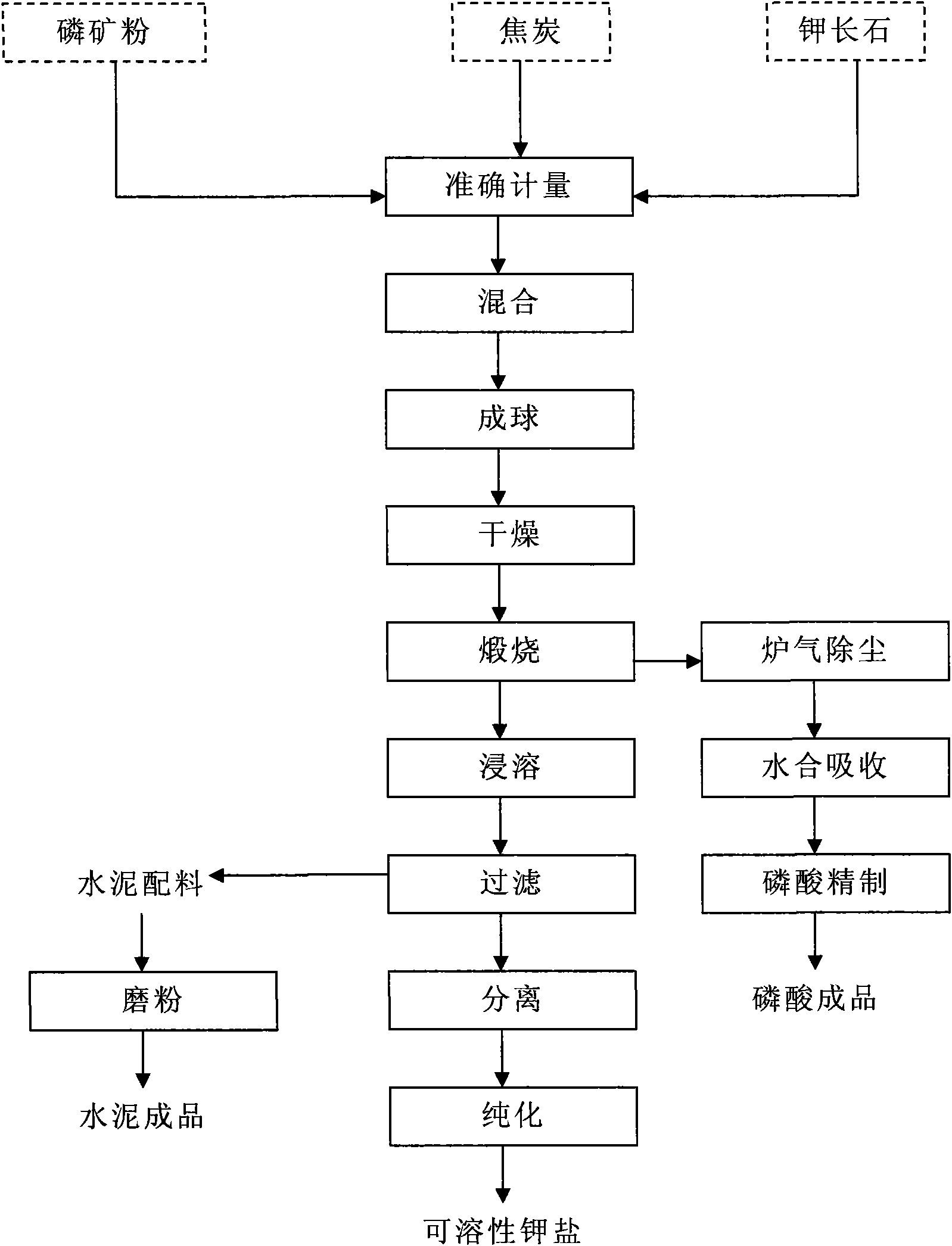
The invention is a method for producing phosphoric acid and soluble potassium salt by phosphorus ore and potash feldspar, characterized in that, the method comprises: selecting phosphorus ore containing P2O5 15-30% and potash feldspar containing K2O 10-18% to mix with coke; crushing, ball milling, balling by adding water and drying; calcining for 10-30 minutes under temperature of 1100-1400DEG C; then soaking the calcined product in 1-5% citric acid solution for 12 hours, wherein, the soaking temperature is between room temperature and 60 DEG C; crystallizing and purifying the separated filtering solution; obtaining the soluble potassium salt; P2O5 in the phosphorus ore is reduced into phosphor vapor to be volatilized, the phosphor vapor above the material layer can be oxidized into P2O5 gas by the air introduced into the furnace, in the hydration apparatus, P2O5 gas can be absorbed to obtain the phosphoric acid. the invention solves the problems of waste slag and waste gas emissions during producing phosphoric acid, also alleviates the existing state that in our country, the soluble kalium resources are depended on importation, the method of the invention is economical and environment-protecting.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
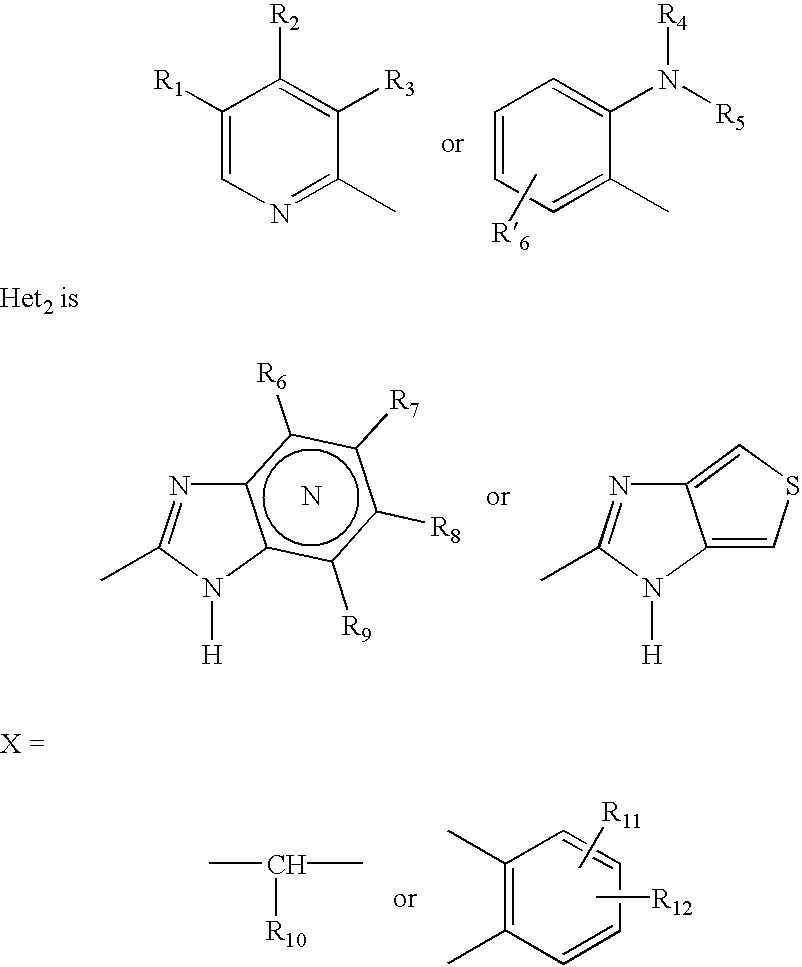
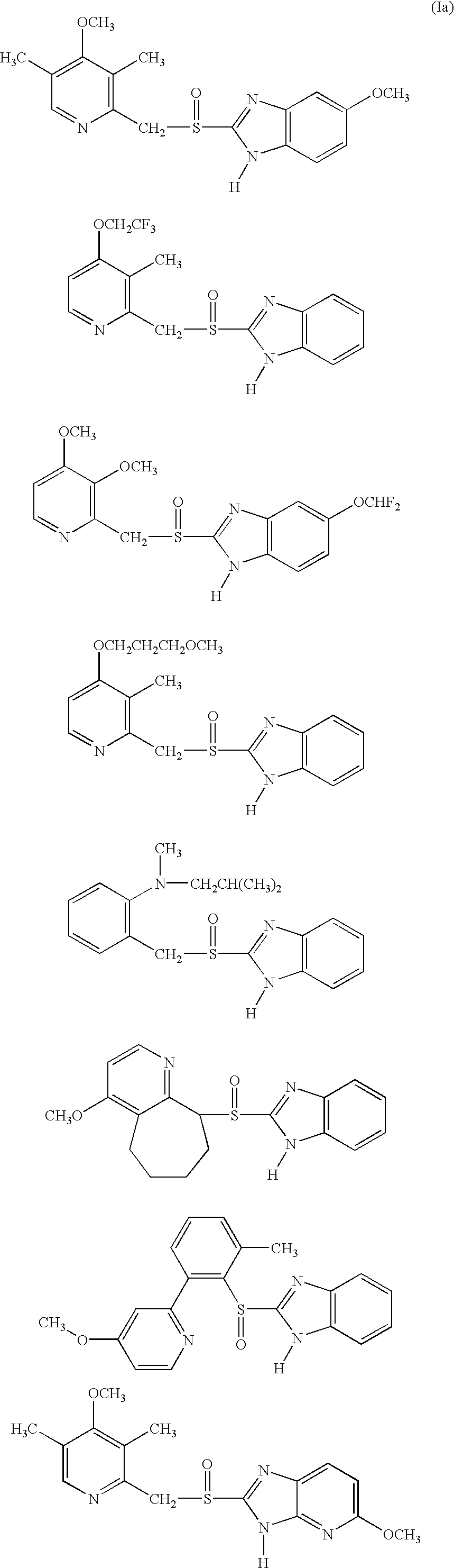
Formulation of substituted benzimidazoles
The present invention relates to stable liquid formulations that comprise a water free or almost water free, polyethylene glycol solution of sodium or potassium salt of a H<+>, K<+>-ATPase inhibitor of Formula I or a sodium or potassium salt of one single enantiomer thereof. Alternatively, the sodium or potassium salt of the H<+>, K<+>-ATPase inhibitor may be formed in situ in the polyethylene glycol solution by adding sodium or potassium hydroxide together and the active compound. The invention is also directed to the preparation of the claimed formulation, use of the stable liquid formulations in medicine and in the treatment of gastrointestinal diseases.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Preparation method of catalyst for preparing propylene by virtue of propane dehydrogenation
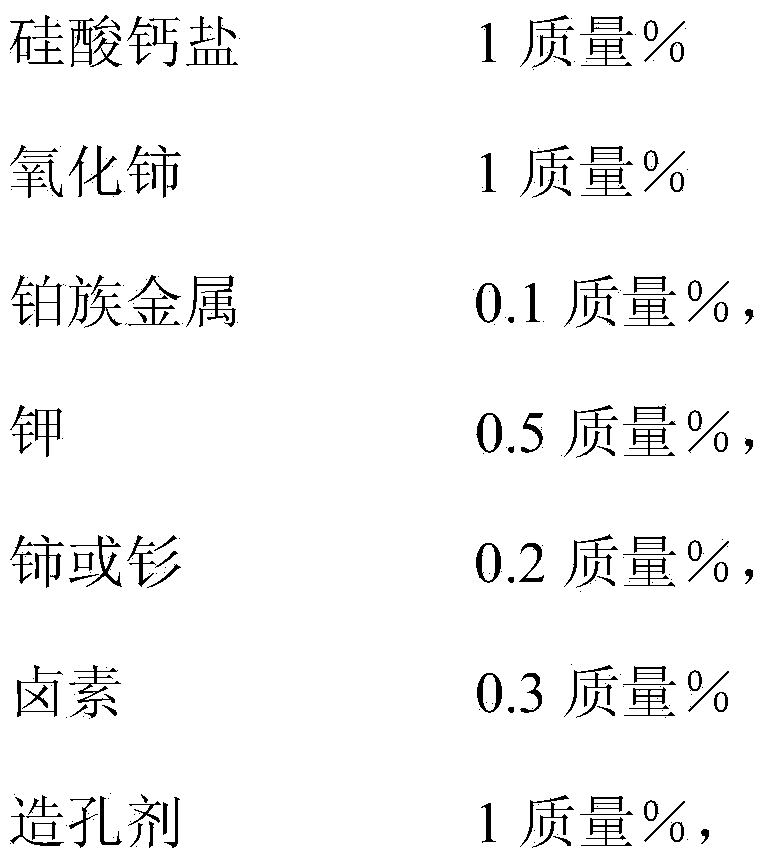
InactiveCN104368364AAvoid it happening againAvoid Contaminated SituationsPhysical/chemical process catalystsHydrocarbonsCalcium silicateHydrogen halide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a catalyst for preparing propylene by virtue of propane dehydrogenation. The catalyst comprises an aluminum oxide carrier and active components with the following contents in percentage by mass calculated based on the carrier: 1-3% of calcium silicate salt, 1-3% of cerium oxide, 0.1-2.0% of a platinum group metal, 0.5-5.0% of potassium, 0.2-5.0% of cerium or samarium, 0.3-10% of halogen, 1-5% of a pore forming agent and the balance of impurities, wherein the molar ratio of cerium or samarium to the platinum group metal is 7:8; the platinum group metal is platinum; and halogen is chlorine. The preparation method comprises the following steps: soaking, drying and roasting the aluminum oxide carrier by using a soluble compound solution of cerium or samarium and a calcium silicate salt solution, then soaking, drying and roasting by using a solution containing compounds of the platinum group metal and hydrogen halide, and then soaking, drying and roasting by using a potassium salt solution; and then mixing cerium oxide and the pore forming agent with corresponding amounts, and roasting for 3 hours at 600 DEG C to obtain the catalyst for preparing propylene by virtue of propane dehydrogenation.
Owner:华玉叶
Method for recovering and separating potassium salt and sodium salt from waste incineration fly ash
InactiveCN110589856AImprove the dissolution rate of soluble saltsReduce consumptionCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesAlkali metal chloridesHigh concentrationFiltration
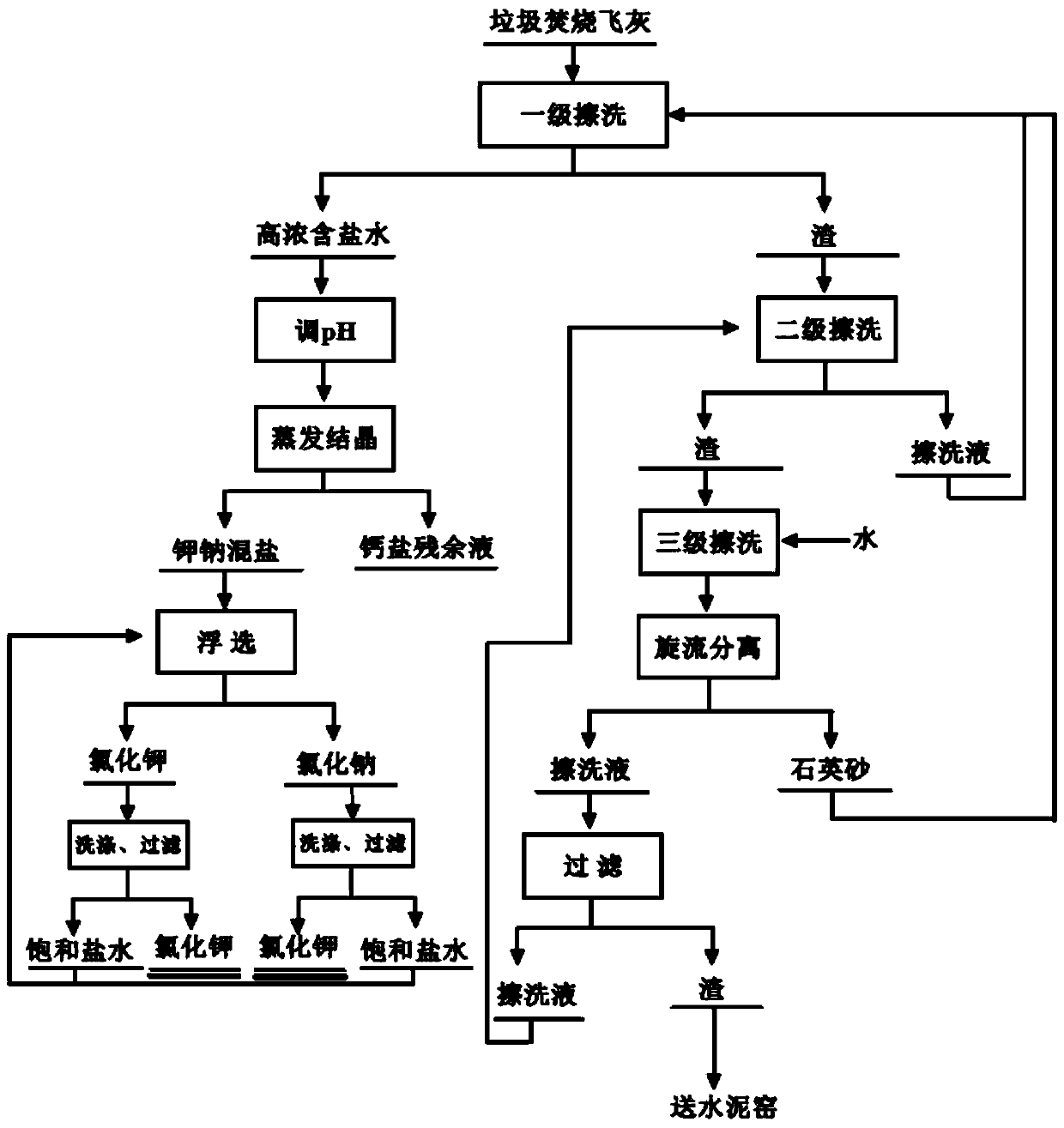
The invention relates to a method for recovering and separating a potassium salt and a sodium salt from waste incineration fly ash, which comprises the following steps of: extracting the potassium salt, the sodium salt and a calcium salt from the waste incineration fly ash by quartz sand and water to obtain high-concentration salt-containing water, separating the quartz sand from the fly ash, returning the quartz sand for continue use; adjusting the pH value of the high-concentration salt-containing water to 5-7 with an acid, and conducting evaporating and concentrating to obtain potassium andsodium mixed salts and a residual calcium chloride saturated solution; conducting flotation separation on the potassium and sodium mixed salts in saturated potassium chloride and sodium chloride solutions, and conducting filtration, so as to obtain a foam product, namely potassium chloride, and tailings slurry, namely sodium chloride; respectively conducting stirring washing on the potassium chloride and sodium chloride obtained by flotation through corresponding saturated salt water, and conducting filtering to obtain industrial grade potassium chloride and sodium chloride products, whereina washing solution is a saturated potassium chloride and sodium chloride mixed solution and is returned to the flotation procedure as a supplement solution of a flotation medium. The method effectively separates soluble salts in the fly ash: potassium chloride, sodium chloride and calcium chloride without decalcification to obtain high purity or industrial grade potassium chloride and sodium chloride products; and the efficiency-cost ratio of the treatment process is greatly improved.
Owner:RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF TSINGHUA UNIVERSITY IN SHENZHEN
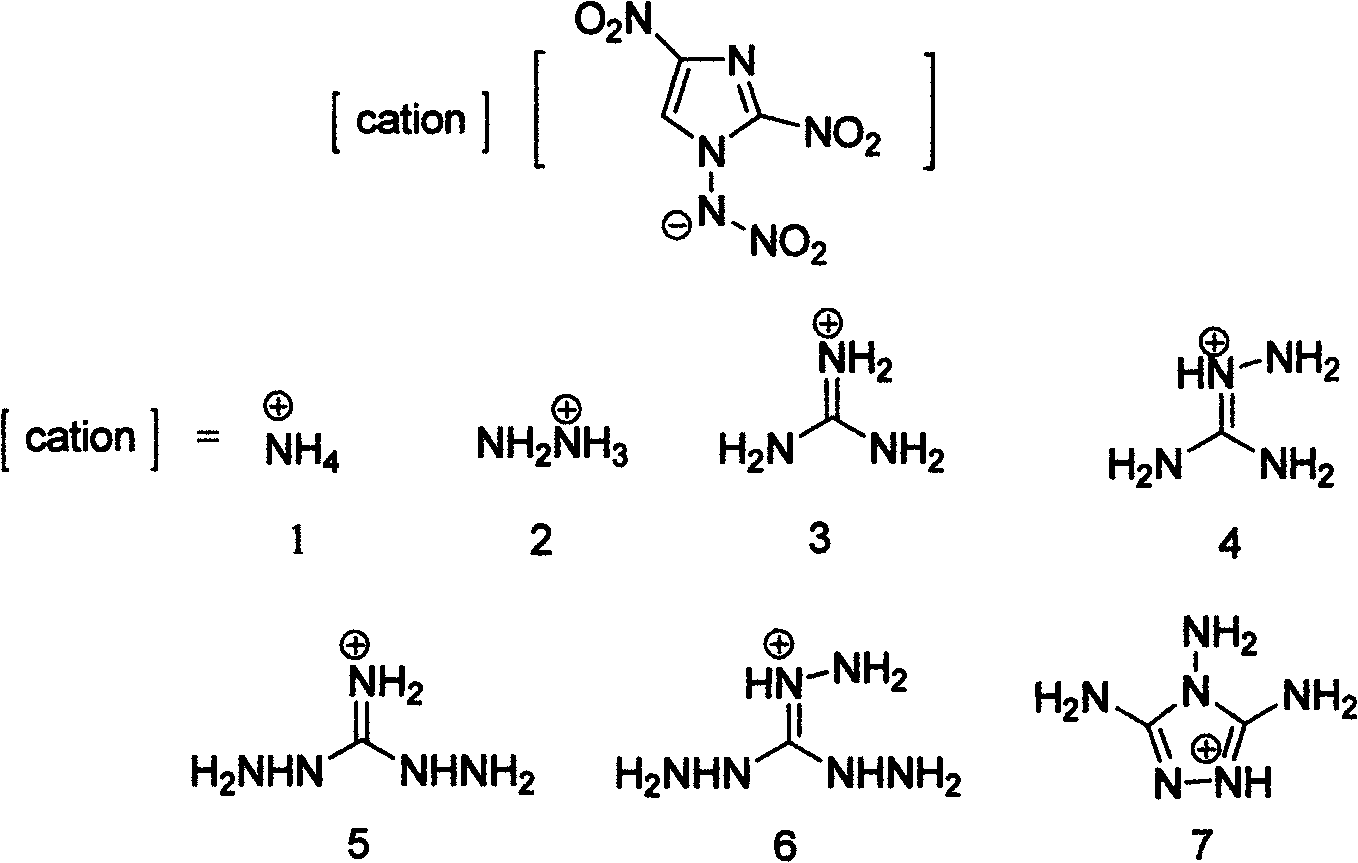
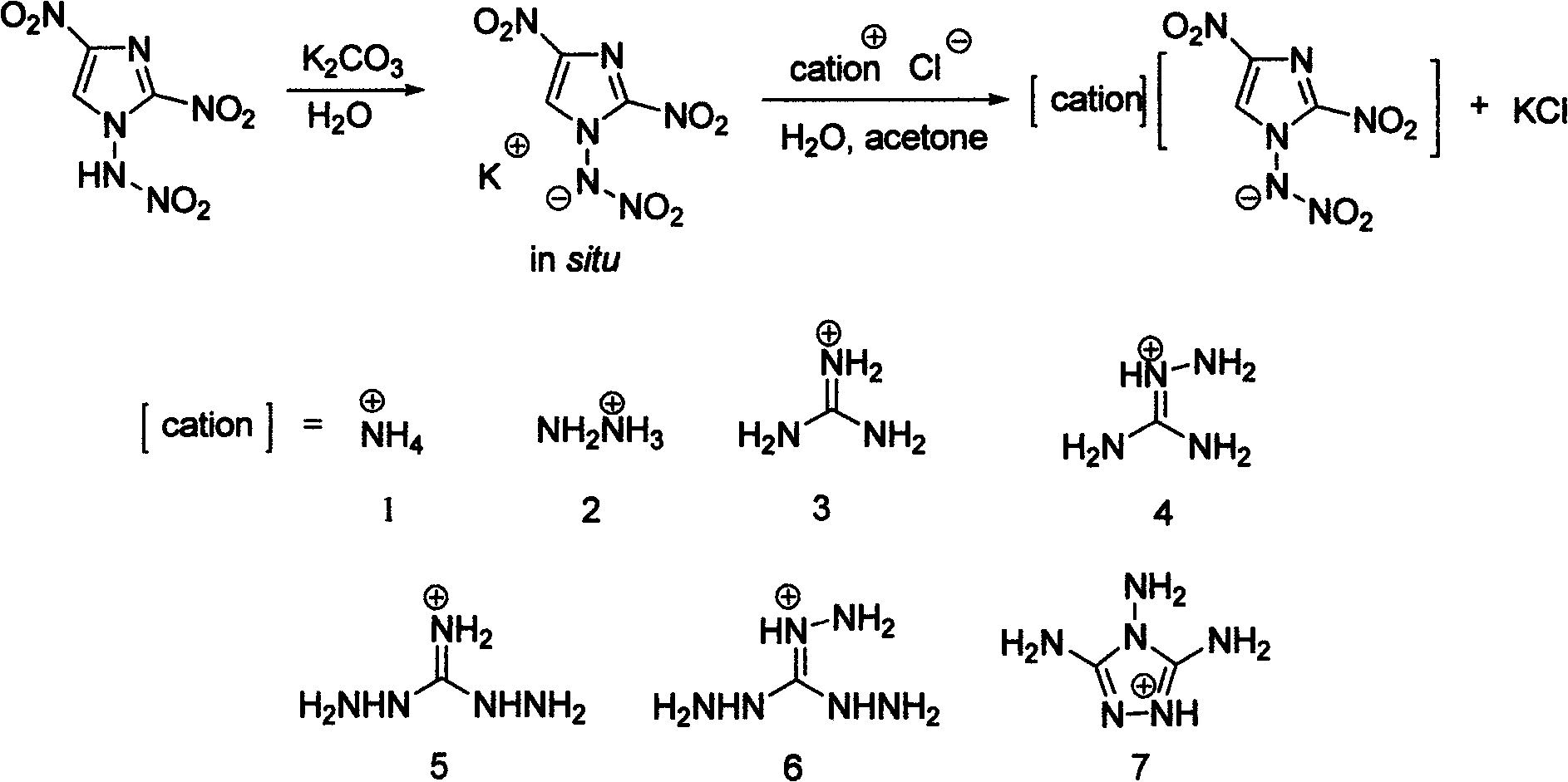
Energetic ion salts of 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe and preparation method thereof
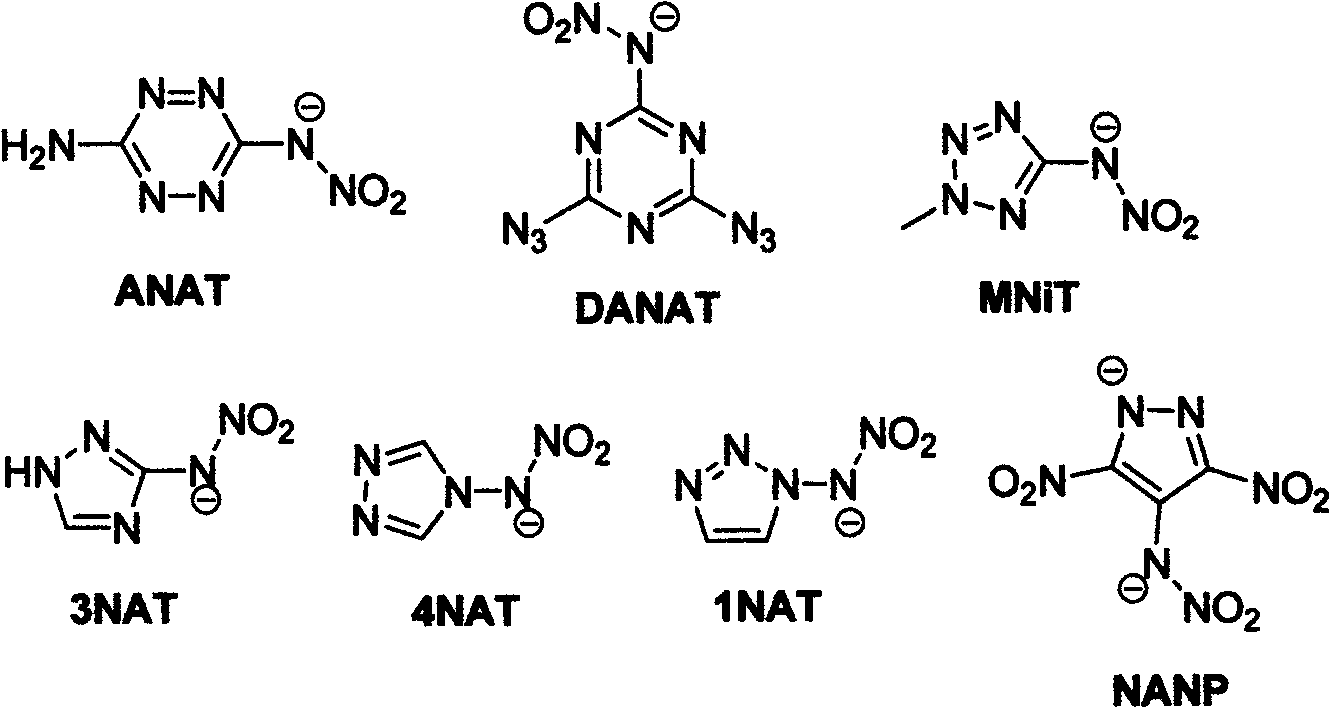
InactiveCN103483264AExcellent detonation speed and pressure performanceThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationNitroimidazoleHydrazine compound
The invention discloses energetic ion salts of 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of energetic materials. The synthetic method is as follows: dissolving the 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe in deionized water to obtain a pale yellow clear liquid, adding with stirring 0.5 time molar equivalent of potassium carbonate at room temperature for in-situ generation of 1-nitramine-2, 4-dimetridazloe potassium salt, then adding one time molar equivalent of ammonium chloride, hydrazine hydrochloride, guanidine hydrochloride, monoaminoguanidine hydrochloride, diaminoguanidine hydrochloride, triaminoguanidine hydrochloride and 3, 4, 5-triamino-1, 2, 4-triazole hydrochloride, stirring to precipitate a pale yellow solid precipitate, after about 1 hour of reaction, filtering the pale yellow precipitate, further recrystallizing a coarse product by use of an acetone and diethyl ether mixed solvent to obtain a pure product. The synthetic method of the invention is simple, mild in condition and high in yield, and is environmental friendly due to using of the deionized water as a solvent. The density of involved seven salts is 1.70-1.93g cm<-3>, the detonation velocity calculated by EXPLO software is between 8370 and 9209 m s<-1>, the detonation pressure is between 29.3 and 40.5 GPa, the actually measured impact sensitivity is 4-40J, the detonation performance is excellent, and the energetic ion salts are potential energetic materials.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for preparing solid glyphosate potassium salt
ActiveCN101186622ASimple methodEase of industrial productionBiocideGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsGlyphosateReaction temperature
The invention provides a preparation method of glyphosate potassium salt solid wet product or relative raw pesticide, which comprises mixing solid glyphosate with some water, to be added and reacted with alkali containing potassium cation, controlling the reaction temperature, cooling, crystallizing and drying to obtain glyphosate potassium salt drug. The invention further provides a preparation method of glyphosate potassium salt raw pesticide, which comprises that solid glyphosate is mixed some water, to be added and reacted with alkali containing potassium cation, the reaction mixture is directly dried to obtain glyphosate potassium salt raw pesticide. The invention further provides a high-content soluble solid glyphosate potassium salt. The inventive glyphosate potassium salt raw pesticide, compared with other glyphosate potassium salts, has better weeding speed and rain resistance in same conditions, while the potassium ions on leaf and in soil can be effectively absorbed by plantto feed potassium fertilizer. And the invention has simple package, storage and transmission of prepared glyphosate potassium salt raw pesticide, to reduce cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG XINAN CHEM INDAL GROUP
Heavy metal polluted soil plant repair method
InactiveCN1640565ALarge biomassImprove enrichment capacityContaminated soil reclamationEthylenediaminePhytoremediation
The present invention discloses a method for repairing soil contaminated by heavy metal by utilizing plant. Said method is characterized by that in the soil contaminated by heavy metal the maize can be planted, before harvest at least two additives selected from editic acid or its sodium salt or its potassium salt (EDTA), nitrilotriacetic acid or its sodium salt or its potassium salt (NTA) and citric aid or its sodium salt or its potassium salt (CA) can be applied, and then the aerial part of maize can be harvested so as to attain the goal of repairing soil contaminated by heavy metal.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for mining and machining water-soluble potassium salt mine
InactiveCN102251759APromote recoveryReduce collapseMagnesium chloridesFluid removalSodium saltPollution
The invention discloses a method for mining and machining a water-soluble potassium salt mine. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, exploiting the potassium salt mine by adopting a well drilling water soluble method; evaporating and crystallizing the exploited brine to sequentially precipitate a sodium salt and a potassium salt; refrigerating and crystallizing the residual feed liquid to further precipitate potassium chloride; and respectively filtering and drying the precipitated sodium salt and potassium salt to obtain finished sodium salt and potassium salt, wherein a part of mother liquor after the sodium salt and potassium salt are precipitated is used for preparing magnesium chloride, and the other part is used for preparing magnesium oxide. The method disclosed by the invention is particularly suitable for the exploitation of a potassium mine having the defects of complicated geological and hydrologic conditions, over-shallow or over-deep burial, poor quality and high carnallite content, can reduce ground collapse, improves the exploitation rate, can prepare a potassium fertilizer in a large scale and has the advantages of low energy consumption and little pollution and waste discharge.
Owner:CHINA NAT OFFSHORE OIL CORP +2
Potassium leach-out exploitation method from mamanite ore
InactiveCN1766138AThe solution mining method is simpleReduce the impactProcess efficiency improvementEarth surfaceAqueous solution
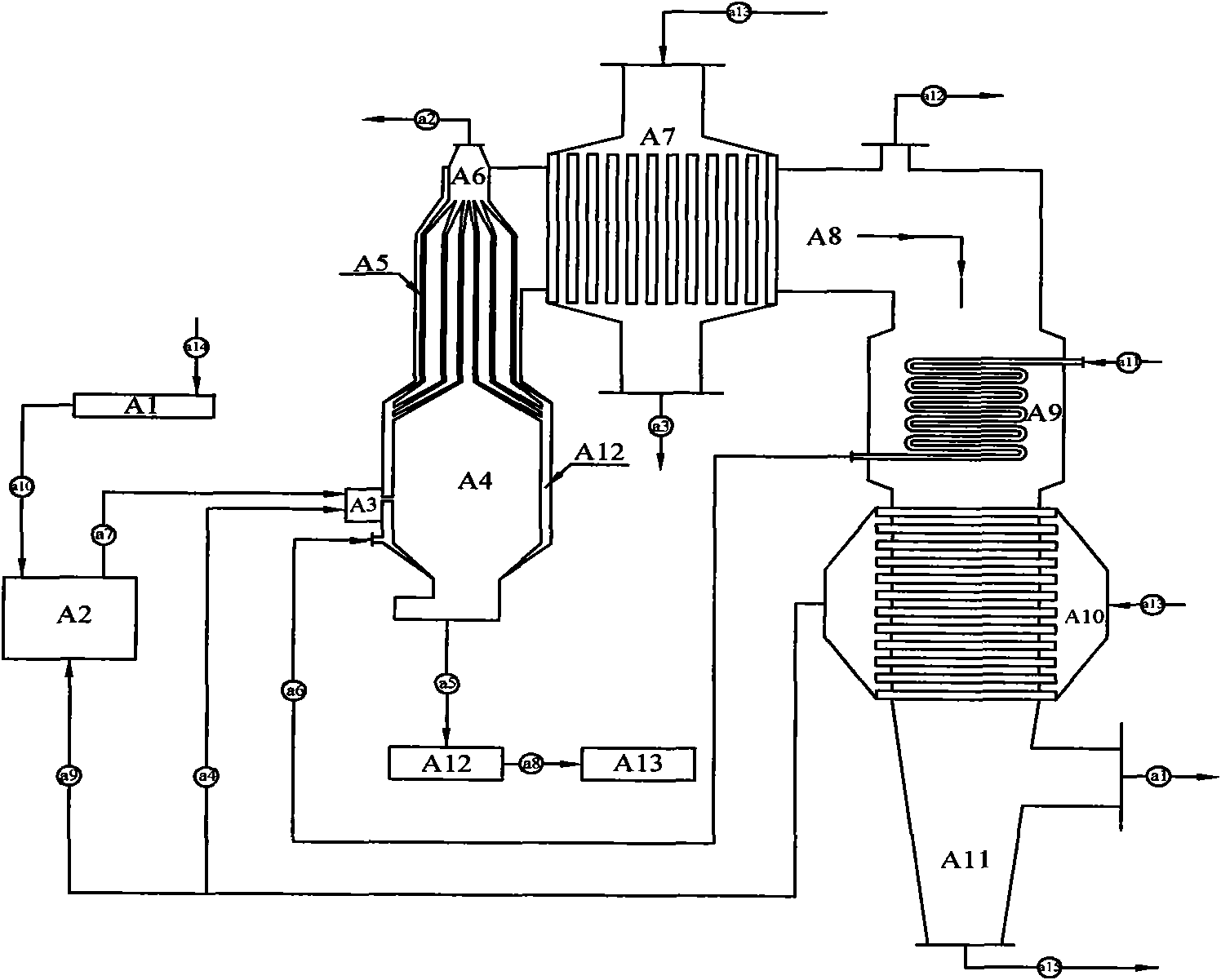
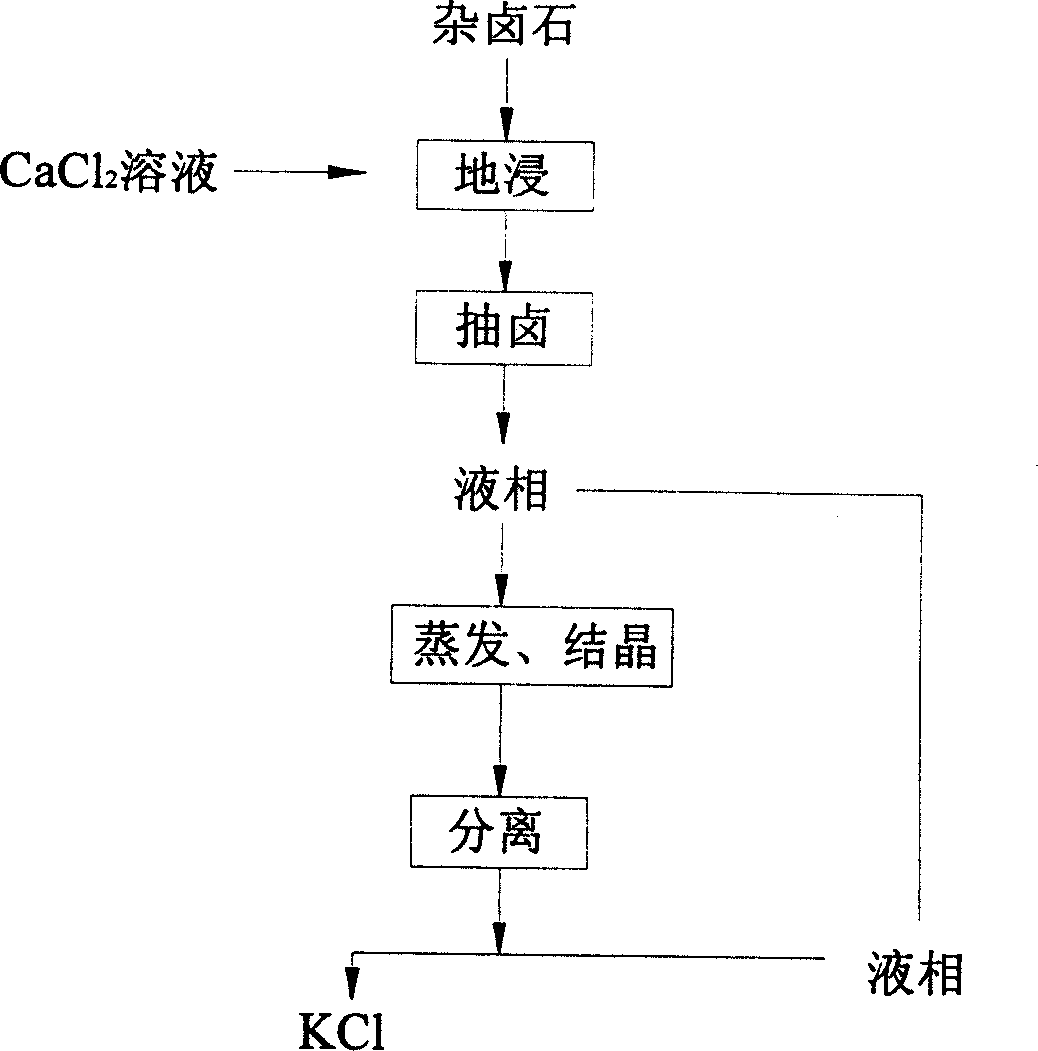
The leach mining method for kalium in polyhalite comprises: after leaching treatment to broken ore, recovering leaching liquid contained Ca2+ and / or Ba2+, and / or at least one from CO32-, HCO3-, PO43-, HPO42-, and SiO32-, while preferring CaCl2 liquid. This method fits to deep buried ore and ground or superficial layer ore with extraction rate more than 80%.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
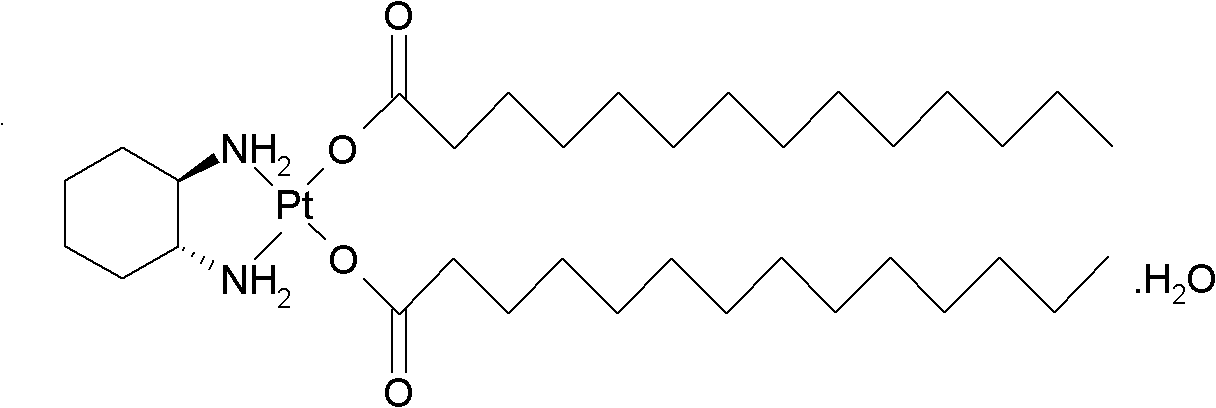
Preparation method of meter platinum
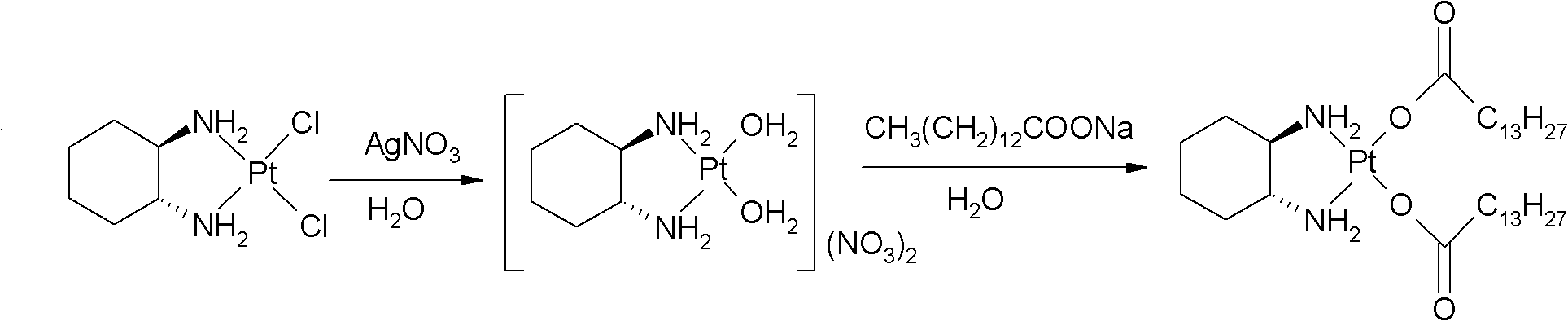
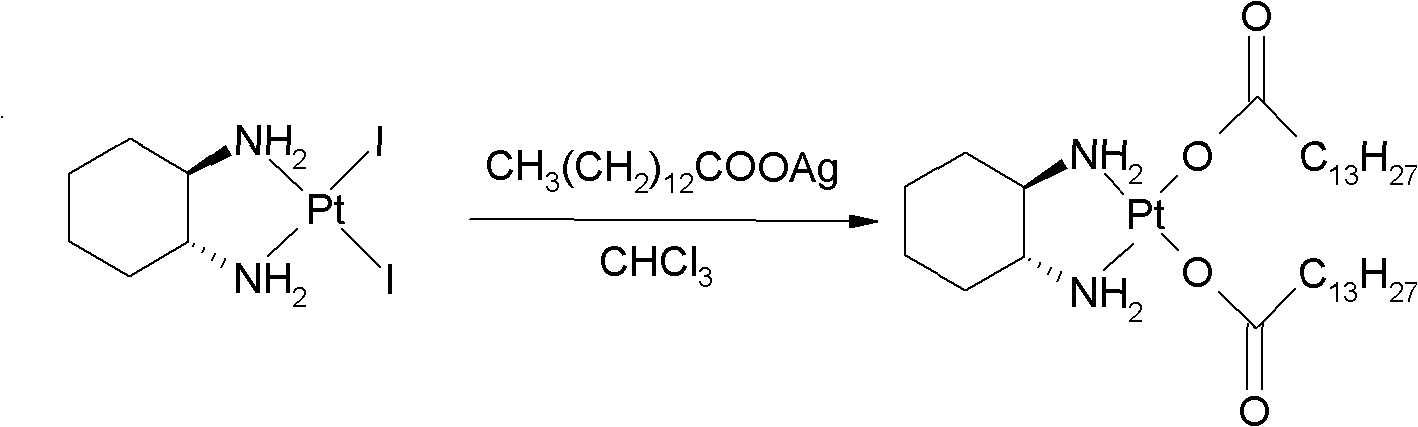
The invention relates to a preparation method of meter platinum, including that dinitric acid cis-((1R, 2R)-1, 2-diaminocyclohexane-dihydrate) platinum (II) and myristate react in solvent; wherein the solvent is composed of alkyl alcohol and water, the alkyl alcohol is methyl alcohol, ethyl alcohol, propyl alcohol or isopropyl alcohol, the myristate is sodium salt, kali salt or ammonium salt of myristic acid, reaction temperature is 20-80 DEG C, and the mass ratio of dinitric acid cis-((1R, 2R)-1, 2-diaminocyclohexane-dihydrate) platinum (II) and water is 1: 10-100. The volume ratio of water and alkyl alcohol is 1: 0.5-2 preferentially, and 1:1 more preferentially. The preparation method has simple steps, reaction medium can dissolve myristate, thus reaction can be effectively carried out and the method can be applied to industrialized production.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Synthesis method of methyl-alpha-fluoroacrylate and analogues thereof
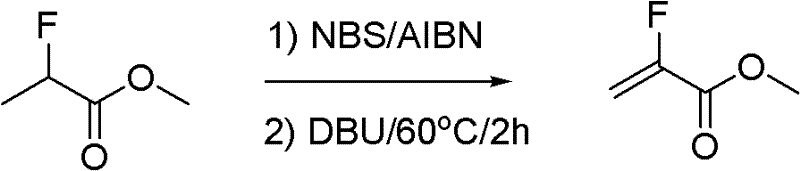
InactiveCN102211998ALow costReduce manufacturing costOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationSynthesis methodsSolvent
The invention relates to a synthesis method of methyl-alpha-fluoroacrylate and analogues thereof. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, based on methyl fluoroacrylate and dimethyl oxalate serving as raw materials, dissolving the raw materials in a solvent, and adding base for carrying out condensation reaction so as to generate sodium enolate or potassium enolate intermediate; and step 2, reacting sodium enolate or potassium enolate intermediate with paraformaldehyde or trioxane in the solvent so as to generate methyl-alpha-fluoroacrylate. According to the invention, cheap methyl fluoroacrylate and dimethyl oxalate are used as the raw materials, and the low-cost solvent and other reactants are selected, thus the method has the advantages of low preparation cost and high yield and can be suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:RADIANT PHARMA & TECH
Potassium sodium dehydroandroandrographolide succinates and their preparations
InactiveCN1557812AHigh purityImprove solubilityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsSide effectSuccinates
The present invention relates to one kind of sodium-potassium andrographolide-semisuccinate and its preparations. On the basis of potassium andrographolide-semisuccinate, which is not enough stable and is likely to produce precipitate and negative effect, sodium-potassium andrographolide-semisuccinate is developed and has relatively high stability and less side effect. The sodium-potassium andrographolide-semisuccinate is prepared into injection, powder for injection and other forms.
Owner:YAOPHARMA CO LTD
Tilmisartan salt and its prepn
InactiveCN1548421AHigh dissolution rateEasy to manufactureOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryAlkaline earth metalOrganic solvent
The Tilmisartan salt of the present invention is salt formed with Tilmisartan and alkali metal, alkali earth metal, pharmaceutically acceptable amine, amino acid. It may be sodium salt, potassium salt, calcium salt, magnesium salt and amine salt, preferably sodium salt, potassium salt or tert-butyl amine salt. The preparation of Tilmisartan salt includes the following steps: reaction between Tilmisartan and organic alkali, inorganic alkali, arginine or lysine in organic solvent or water to produce target product, and collecting Tilmisartan salt. The Tilmisartan salt may be used to replace available Tilmisartan.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com