Patents
Literature
67 results about "Polyhalite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
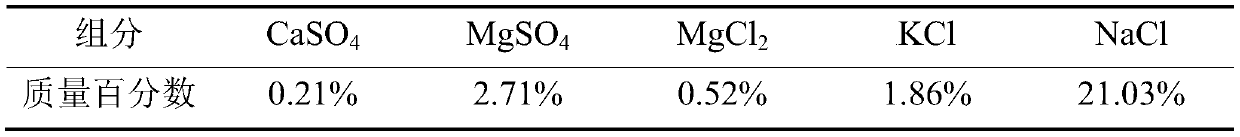
Polyhalite is an evaporite mineral, a hydrated sulfate of potassium, calcium and magnesium with formula: K₂Ca₂Mg(SO₄)₄·2H₂O. Polyhalite crystallizes in the triclinic system, although crystals are very rare. The normal habit is massive to fibrous. It is typically colorless, white to gray, although it may be brick red due to iron oxide inclusions. It has a Mohs hardness of 3.5 and a specific gravity of 2.8.
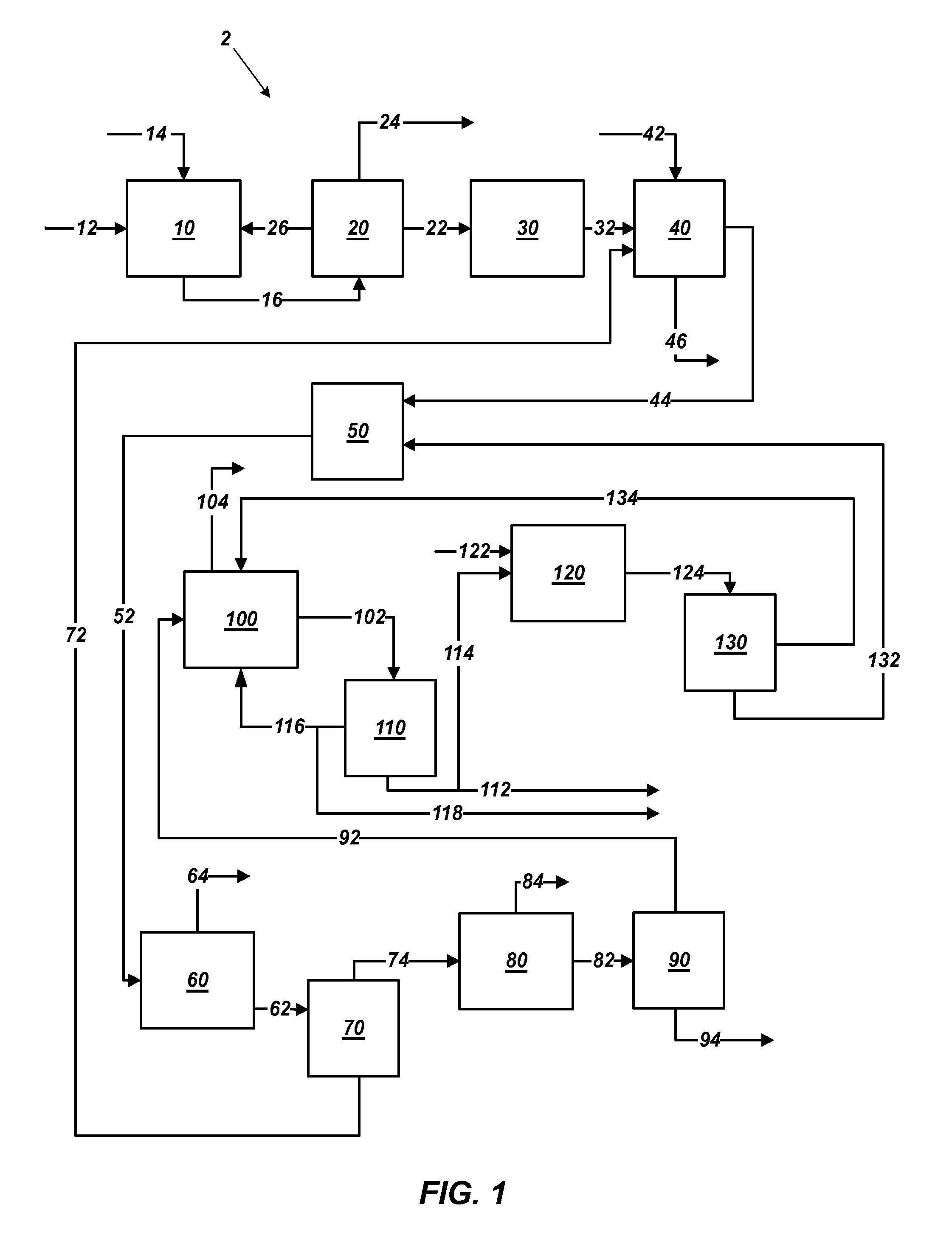
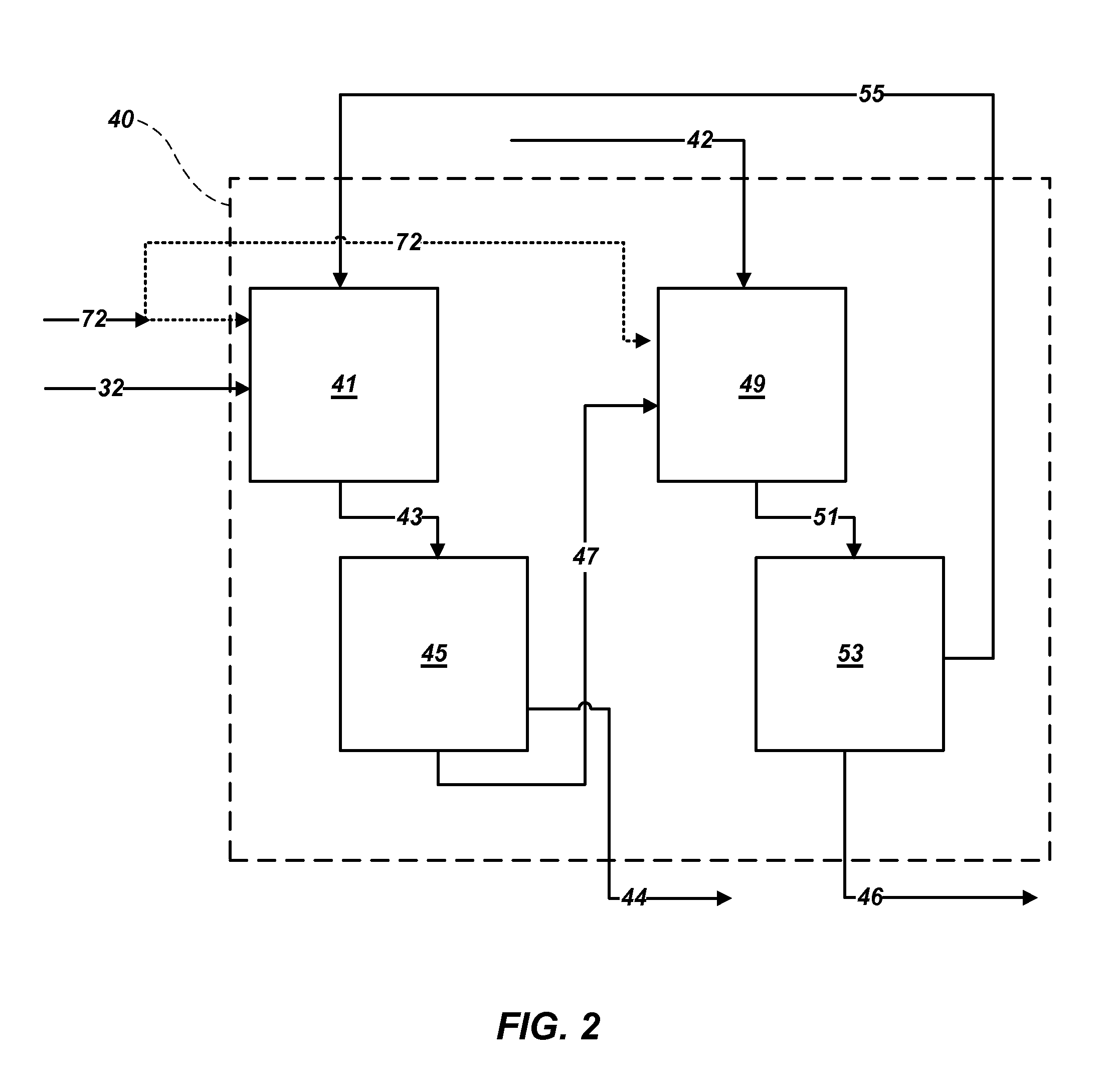
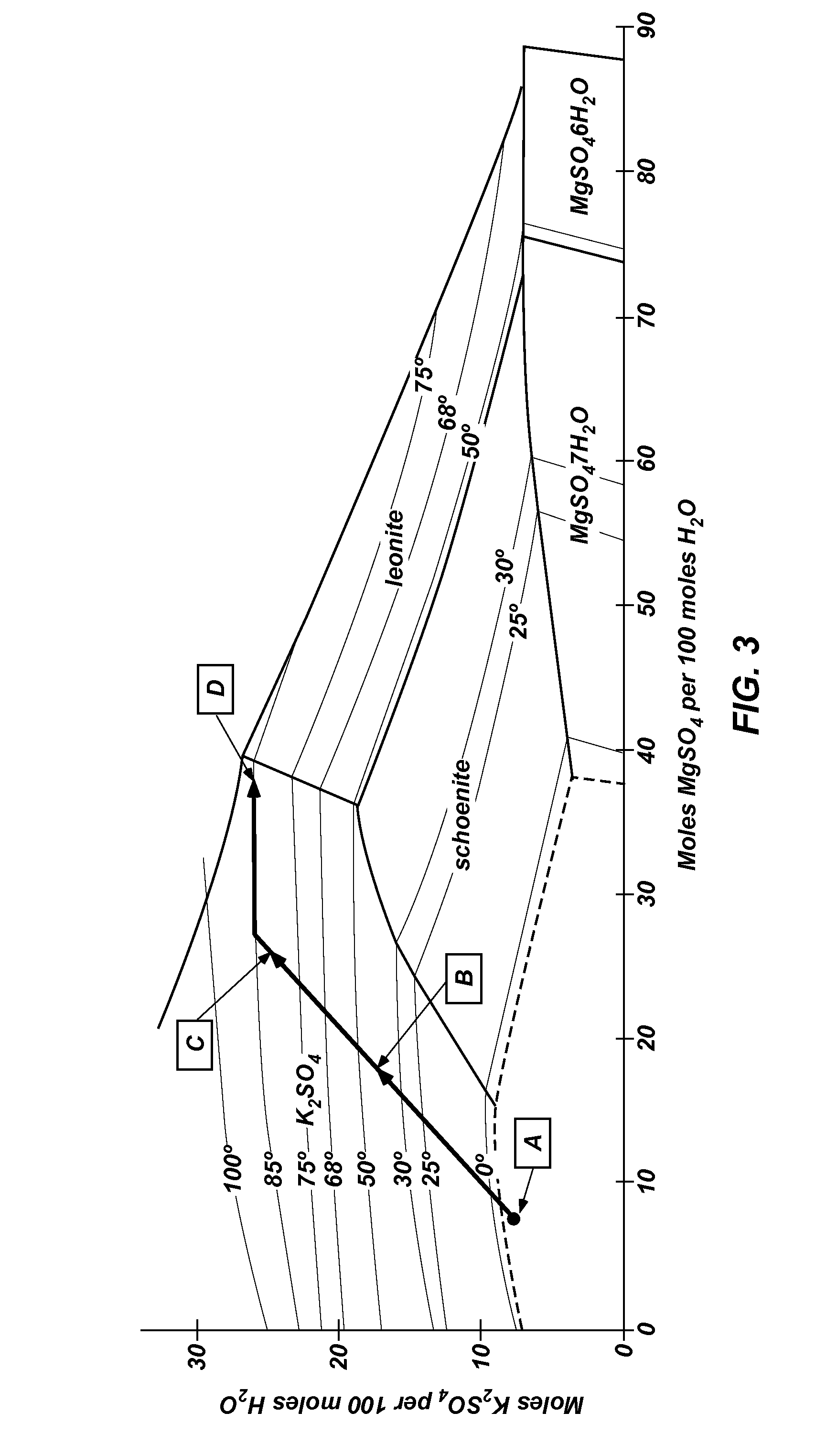
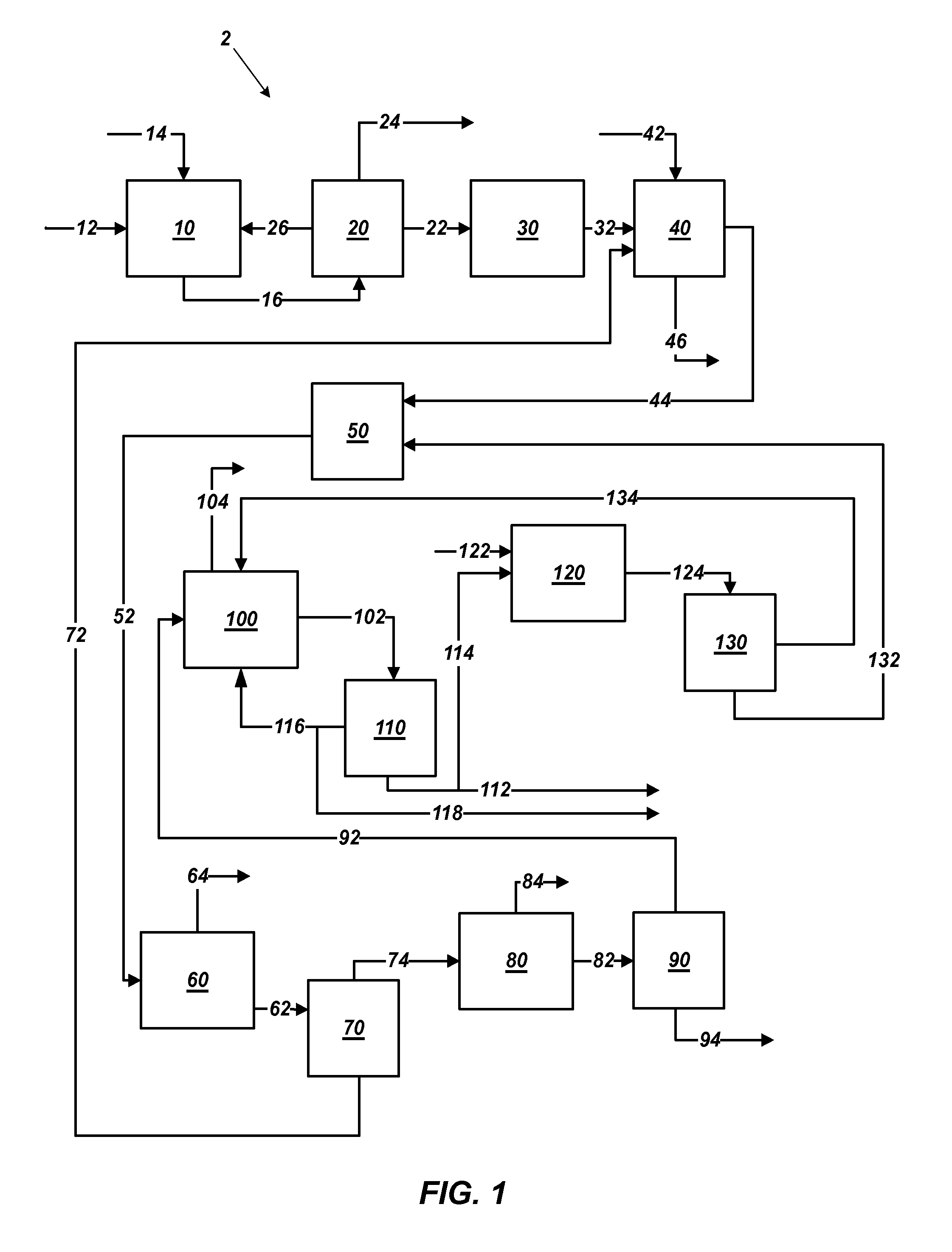
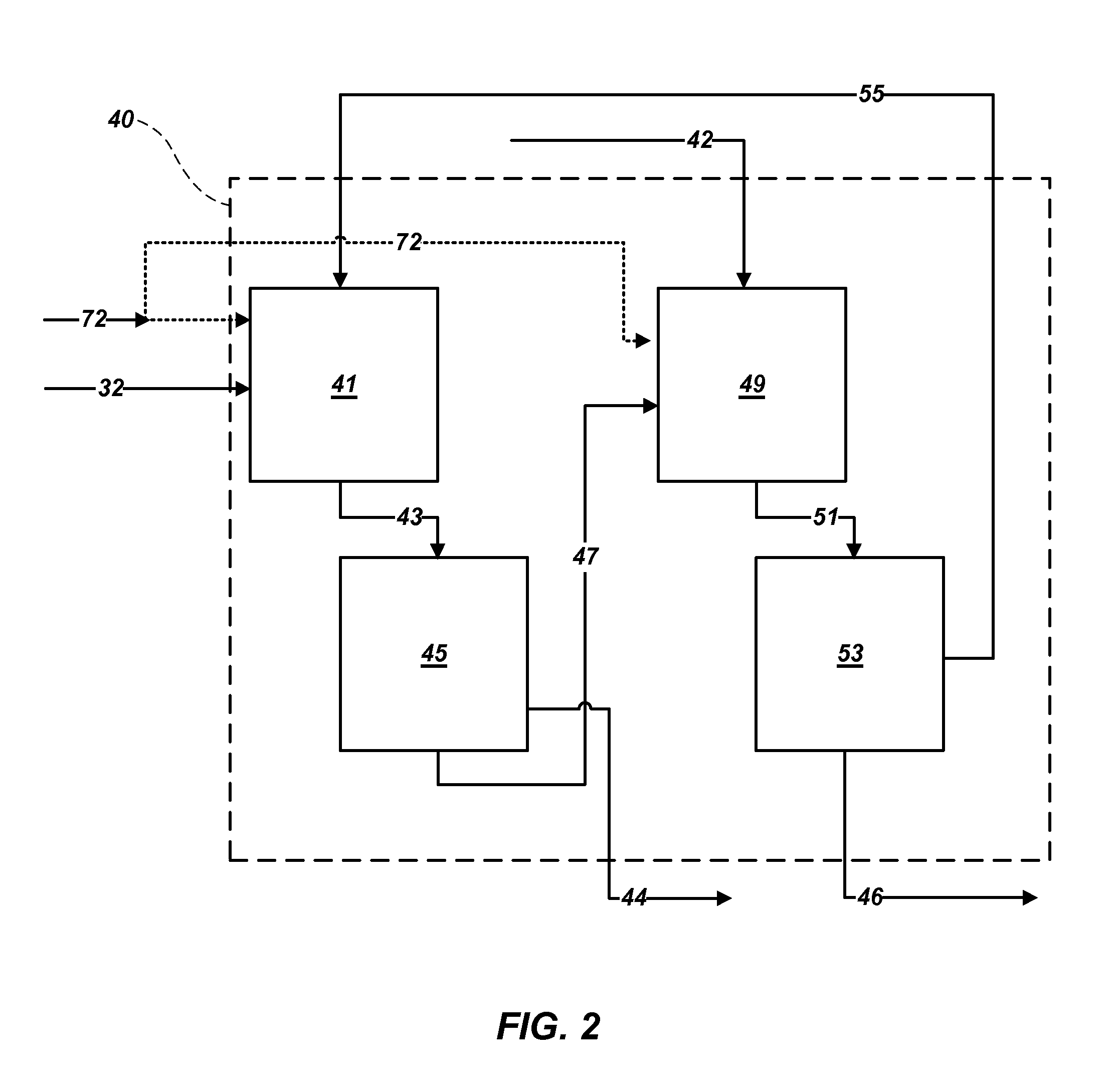
Methods of processing polyhalite ore, methods of producing potassium sulfate, and related systems
ActiveUS20130121900A1Improve concentrationLimit economic riskSolution crystallizationCrystallization by component evaporationWater solublePotassium sulfate
Methods of forming potassium sulfate include calcining polyhalite ore particles to convert the polyhalite ore particles to a water-soluble composition. At least a portion of the water-soluble composition is dissolved in an aqueous medium to form an aqueous solution comprising K+, Mg2+, and SO42− ions and a calcium-containing solid. The calcium-containing solid is separated from the aqueous solution to form a filtrate comprising K+, Mg2+, and SO42− ions. A potassium-containing salt is dissolved in the filtrate to increase the concentration of K+ and SO42− ions to from a concentrated liquor, and K2SO4 is crystallized from the concentrated liquor. A system for processing polyhalite ore includes a countercurrent leaching apparatus, a first mix tank, an evaporator, and at least one crystallizer.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL POTASH CORP USA
Organic leaf fertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105439762AReduce pestsReduce diseaseCalcareous fertilisersExcrement fertilisersInsect pestWillow bark
The invention discloses an organic leaf fertilizer and a preparation method of the organic leaf fertilizer. The organic leaf fertilizer is prepared from the following raw materials in terms of parts by weight: 44-46 parts of urine, 14-16 parts of rhizobium astragalus, 20-22 parts of rape pollen, 13-15 parts of maize seeds, 8-10 parts of withered flowers, 12-14 parts of bleeding sap, 5-7 parts of brown sugar, 13-15 parts of willow bark, 2-4 parts of gibberella, 11-13 parts of stonewort, 6-8 parts of calcium hydroxide, 12-14 parts of pistia stratiotes, 7-9 parts of tea seed cakes, 3-5 parts of collophanite and 1-3 parts of polyhalite. The organic leaf fertilizer has the advantages of quickness in fertilizer efficiency, good fertility, insect pest resistance and capability of significantly increasing crop yield.
Owner:夏勇
Methods of processing polyhalite ore, methods of producing potassium sulfate, and related systems
ActiveUS8551429B2Limit economic riskLess energyChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesAlkali metal oxides/hydroxidesWater solublePotassium sulfate
Methods of forming potassium sulfate include calcining polyhalite ore particles to convert the polyhalite ore particles to a water-soluble composition. At least a portion of the water-soluble composition is dissolved in an aqueous medium to form an aqueous solution comprising K+, Mg2+, and SO42− ions and a calcium-containing solid. The calcium-containing solid is separated from the aqueous solution to form a filtrate comprising K+, Mg2+, and SO42− ions. A potassium-containing salt is dissolved in the filtrate to increase the concentration of K+ and SO42− ions to from a concentrated liquor, and K2SO4 is crystallized from the concentrated liquor. A system for processing polyhalite ore includes a countercurrent leaching apparatus, a first mix tank, an evaporator, and at least one crystallizer.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL POTASH CORP USA
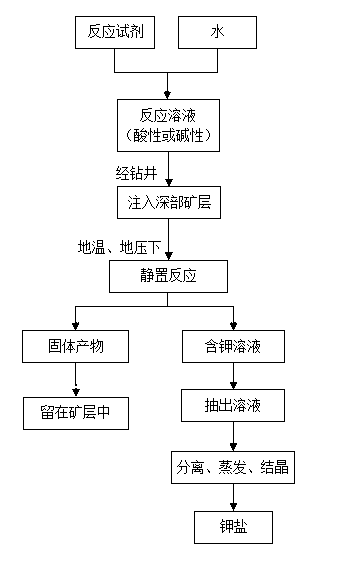
Method for preparing water-soluble sylvite from deep polyhalite in in-situ reaction mode
ActiveCN103321615ASolve development problemsAchieving a breakthrough in the development and utilization of technologyFluid removalEnvironmental engineeringAqueous solubility
The invention relates to a method for preparing water-soluble sylvite from a deep polyhalite seam in an in-situ reaction mode. The method for preparing the water-soluble sylvite from deep polyhalite in the in-situ reaction mode is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) preparing a reaction solution with certain concentration; (2) filling the reaction solution into the deep polyhalite seam, and enabling the reaction solution to contact with polyhalite; (3) standing and reacting, prompting the reaction solution to react with the polyhalite by using conditions of earth temperature and earth pressure, so as to generate water-soluble sylvite, and dissolving the water-soluble sylvite into a water solution so as to form a potassium-containing solution; (4) pulling out the potassium-containing solution from the seam; (5) filtering the potassium-containing solution and preparing the sylvite. By using the method, water-soluble sylvite is prepared from deep polyhalite in situ in large scale, the process is simple, the cost is low, the energy is saved and the environment is protected.
Owner:SICHUAN BESTRED MINING
Process using polyhalite extraction mother liquor to produce potassium sulfate
ActiveCN105668594AIncrease productionIncrease added valueProductsReagentsCalcium hydroxidePotassium ions
The invention relates to a process using polyhalite extraction mother liquor to produce potassium sulfate.The process includes the steps of firstly, feeding ammonia gas into the polyhalite polyhalite extraction mother liquor to regulate pH to 10.0-12.0 so as to obtain Mg(OH)2 slurry; secondly, feeding CO2 until the pH is 7.5-8.0 to obtain carbonized mother liquor; thirdly, performing pyrolysis and solid-liquid separation to obtain MgCO3.3H2O solid salt and mother liquor after pyrolysis and separation; fourthly, adding calcium oxide slurry or calcium hydroxide slurry into the mother liquor after pyrolysis and separation, heating, stirring, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain mother liquor after causticization separation; fifthly, performing forcible evaporation, and crystalizing to separate out potassium sulfate.The K2O content of the potassium sulfate obtained by the process reaches up to 51.9%, potassium ion yield reaches up to 91.7%, byproducts such as high-purity magnesium oxide and gypsum can be coproduced, and the process is simple in process flow, simple in needed equipment, easy in industrial production and low in cost.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Polyhalite mining method
InactiveCN104847358AAchieve miningPrevent collapseUnderground miningFluid removalSalt lakeDetonation
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
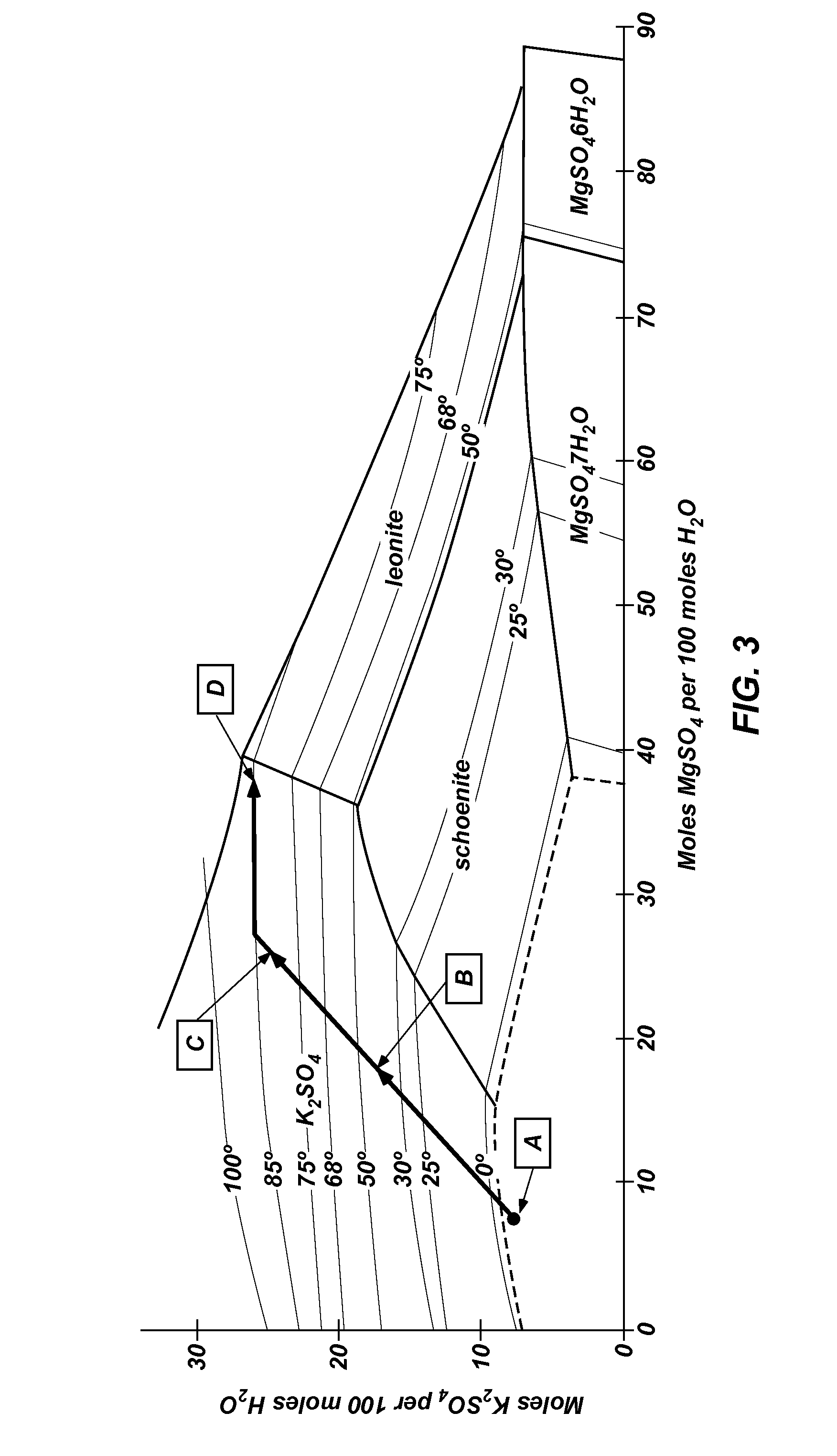
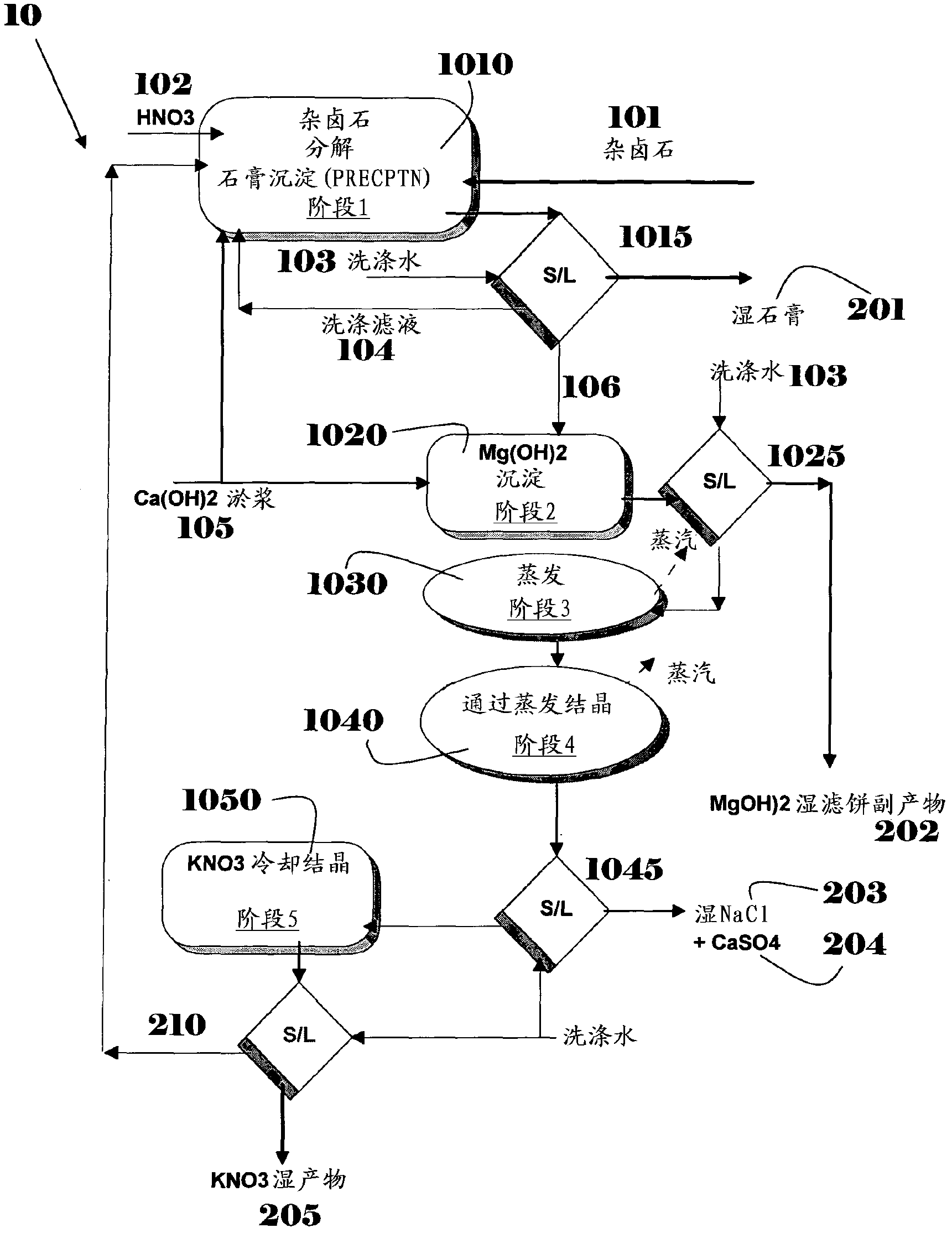
Polyhalite IMI process for KNO3 production
ActiveCN102869609ACalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesAlkali metal nitrate preparationSulfatePolyhalite
A process for producing KNO3 from polyhalite is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, the process comprises steps of (a) contacting polyhalite with HNO3; (b) adding Ca(OH)2 to the solution, thereby precipitating as CaSO4 at least part of the sulfate present in said solution; (c) precipitating as Mg(OH)2 at least part of the Mg2+ remaining in said solution by further addition of Ca(OH)2 to the remaining solution; (d) concentrating the solution, thereby precipitating as a sulfate compound at least part of the sulfate remaining in solution; (e) separating at least part of the NaCl from the solution remaining; and (f) crystallizing as solid KNO3 at least part of the K+ and NO3- contained in the solution. The process enables direct conversion of polyhalite to KNO3 of purity exceeding 98.5% and that is essentially free of magnesium and sulfate impurities.
Owner:ICL EUROPE COOPERATIEF U A
Process for leaching dissoluble potassium from polyhalite
InactiveCN105648239AIncrease concentrationSave the cost of evaporation and concentrationProcess efficiency improvementPolyhaliteLeaching rate
The invention discloses a process for leaching dissoluble potassium from polyhalite. The process comprises the following steps of firstly, grinding ores: crushing polyhalite ores, and grinding the ores to be smaller than or equal to 80 meshes to obtain an ore ground product; secondly, roasting: roasting the ore ground product at the temperature of 350 to 500DEG C for 20 to 90 minutes to obtain a roasted product; thirdly, performing acid leaching: adding an acid solution into the roasted product according to the sold-liquid ratio of 1:0.8 to 10, and leaching at the temperature of 25 to 100DEG C for 20 to 120 minutes to obtain a polyhalite ore pulp; and fourthly, performing solid-liquid separation: performing solid-liquid separation on the polyhalite ore pulp to obtain a dissoluble potassium solution. The K<+> concentration in the obtained dissoluble potassium can reach as high as 8.10 weight percent; the dissoluble potassium solution can be repeatedly leached, so that the evaporation and concentration cost at later stage is reduced; the leaching rate of potassium can reach as high as 95.5 percent, and the leaching cycle is only 1 to 2 hours. The process disclosed by the invention is simple; raw materials of the leaching solution are wide in source and are low in cost; an obtained acid leaching mother solution can be recycled.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Crop universal base fertilizer containing secondary and minor elements and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105084983AMeet normal growth needsStrong stress resistanceFertilizer mixturesMinor elementPhosphate
The invention discloses a crop universal base fertilizer containing secondary and minor elements and a preparation method thereof. The base fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 18-24 parts of urea, 30-35 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 45-50 parts of polyhalite, 0.4-0.6 part of boric fertilizer and 0.8-1.0 part of zinc fertilizer. The boric fertilizer is sodium borate, and the zinc fertilizer is white vitriol. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out physical crushing, screening and metering on the obtained raw materials, proportionally and thoroughly mixing in a stirrer to obtain a product, and carrying out metered packaging to obtain the finished product. The fertilizer contains the nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium, and also contains rich calcium, magnesium and other secondary and minor elements. When being used as a base fertilizer, the fertilizer can satisfy the demands for nutrients in the whole crop growth period, enhance the stress tolerance and immunity and increase the crop yield.
Owner:HEFENGRUI SUZHOU AGRI TECH DEV CO LTD
Technology for extracting potassium and removing sodium from high-sodium polyhalite ore
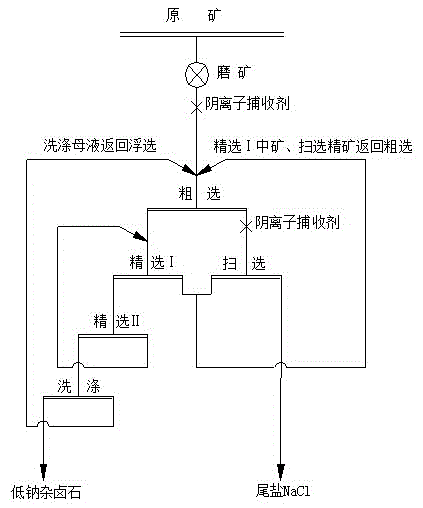
InactiveCN104998748AReduce water consumptionReduce manufacturing costFlotationWet separationPotassiumPolyhalite
A technology for extracting potassium and removing sodium from high-sodium polyhalite ore includes the following steps that firstly, the high-sodium polyhalite ore is ground; secondly, flotation mother liquor returns to a closed technological process in the sequence of one-time roughing, two-time concentration, one-time scavenging, returning of middlings in concentration I and scavenged concentrate to roughing, and returning of middlings in the concentration II to concentration I, wherein 100-200 g / ton anionic collectors are added in the roughing process, flotation time ranges from 3 minutes to 5 minutes, 50-100 g / ton anionic collectors are added in the scavenging process, flotation time ranges from 2 minutes to 3 minutes, no collectors are added in the process of the two-time concentration, flotation time ranges from 3 minutes to 5 minutes, and flotation concentrate can be obtained; and thirdly, the flotation concentrate is washed and filtered, and low-sodium polyhalite is obtained. The technology is reasonable in process; the flotation technology is mature and reliable; the process and the reagent rule are simple; the technology is low in investment, easy to operate, low in energy and water consumption and low in comprehensive production cost; and large-scale industrial production can be achieved easily.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Method for determining chloride ion content in polyhalite
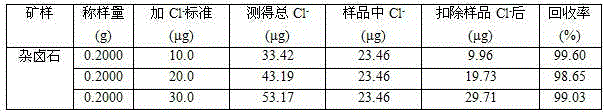
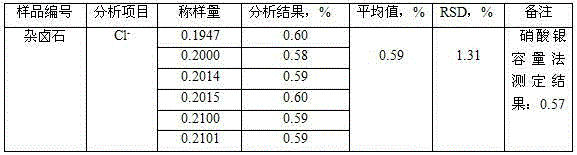
InactiveCN104807767AThe measurement results are accurate and reliableWide applicabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsIon contentTest sample
The invention discloses an analysis method for chloride ion content in polyhalite. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a polyhalite test sample with acid; reacting chloride ions with mercuric thiocyanate in an acid medium to displace thiocyanate ions out; generating a red complex with iron III ions in ferric salt added into a solution; measuring the light absorption value of the complex in a test solution at the 460-nanometer position of a spectrophotometer in order to calculate the content of chloride ions in the polyhalite. For the content determination of chloride ions less than 1 percent in the polyhalite, the method is simple, convenient, reasonable, rapid and accurate; moreover, results are stable, and the precision is high.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Method of preparing potassium-magnesium fertilizer
InactiveCN108585960AAvoid chemical reactionsImprove uniformityMagnesium fertilisersPotassium fertilisersEvaporationWater immersion
The invention discloses a method of preparing a potassium-magnesium fertilizer. The method comprises the following steps of by taking polyhalite and potash feldspar as raw materials, crushing the rawmaterials into powder, then replenishing magnesium sulfate, and performing calcination, water immersion, filtering and evaporation to prepare the potassium-magnesium fertilizer. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that, firstly, by adopting the polyhalite and the potash feldspar as raw materials, the raw materials are available, the cost is low, potassium-bearing minerals which widely exist in China are fully utilized to replace brine, and the technical problem of shortage of agricultural potassium resources in China is solved; secondly, by fully utilizing potassium andmagnesium elements in the raw materials and combining with external the magnesium sulfate for further replenishment of the magnesium elements, the produced potassium-magnesium fertilizer provides thepotassium and magnesium elements required for growth of crops and is good in fertilizer efficiency; and thirdly, the preparation method is simple and is low in production requirement and production cost and liable in popularization use.
Owner:UNIV FOR SCI & TECH ZHENGZHOU
Process for preparing potassic-magnesian fertilizer by using polyhalite
InactiveCN106380233AWide variety of sourcesSimple processPotassium fertilisersEvaporationPotassium sulfate
The invention provides a process for preparing a potassic-magnesian fertilizer by using the polyhalite. The process comprises the steps of (1) grinding ores: grinding the polyhalite till 85wt% of the polyhalite are over 100 meshes in size; (2) washing: washing with water to remove the sodium chloride in the polyhalite; (3) roasting: roasting washed minerals at a high temperature; (4) leaching: leaching to extract potassium and magnesium in the polyhalite; (5) solid-liquid separation: subjecting the ore pulp obtained through the leaching step to solid-liquid separation so as to obtain a mother liquor containing potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate; (6) evaporation: evaporating and crystallizing the mother liquor to obtain a potassium-magnesium fertilizer product. The process is simple, wide in source of raw materials and low in cost, wherein the sodium chloride in the polyhalite can be effectively removed. Meanwhile, the leaching rate of K+ is high and the water consumption of leaching is reduced. The concentration of K+ in the leaching mother liquor is high, and the energy consumption of the subsequent evaporation and crystallization step is reduced. The potassium-magnesium fertilizer product obtained after the evaporation step meets the requirements of first-class products specified in GB / T20937-2007.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Method for exploitation and utilization of polyhalite-halite accompanying mineral deposit
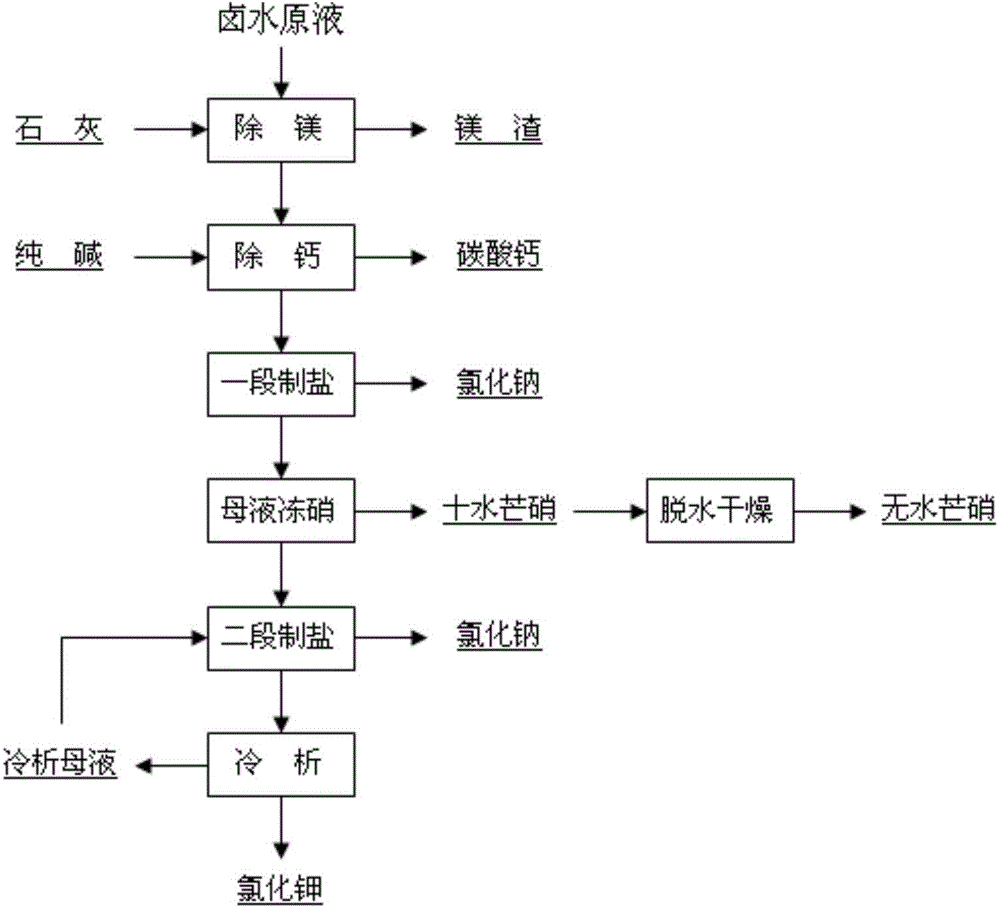
ActiveCN103601218AHigh yieldHigh purityAlkali metal chloridesAlkali metal sulfites/sulfatesEmulsionPotassium ions
The invention provides a method for exploitation and utilization of a polyhalite-halite accompanying mineral deposit. The method comprises the steps of injecting fresh water into the polyhalite-halite accompanying mineral deposit to leach out a brine stock solution of which the sodium ion concentration is more than 79g / L and the potassium ion concentration is more than 4g / L; enabling the brine stock solution to react with a lime emulsion, filtering and then adding a sodium carbonate solution to obtain purified brine; concentrating the purified brine by evaporating, and controlling the concentration of sulfate ions to be more than 20g / L to obtain crude sodium chloride and concentrated brine; freezing the concentrated brine to obtain coarse nitrate and a frozen nitrate stock solution; concentrating the frozen nitrate stock solution through vacuum evaporation, and controlling the potassium ion concentration to be more than 80g / L to obtain crude sodium chloride and a salt manufacturing stock solution; cooling the salt manufacturing stock solution to obtain crude potassium chloride and a separated potassium stock solution. The method provided by the invention is reasonable in process and ensures that the accompanying mineral deposit is subjected to maximized utilization. The method is simple in operation, low in cost and high in yield, and not only reduces the exploitation cost of polyhalite, but also realizes the comprehensive utilization of resources.
Owner:DAZHOU HENGCHENG ENERGY GROUP
Method for preparing nitrogen, sulfur and potassium from polyhalite
InactiveCN107082668AImprove fertilizer efficiencyGood water solubilityAmmonium salt fertilisersMagnesiaSolubilityDecomposition
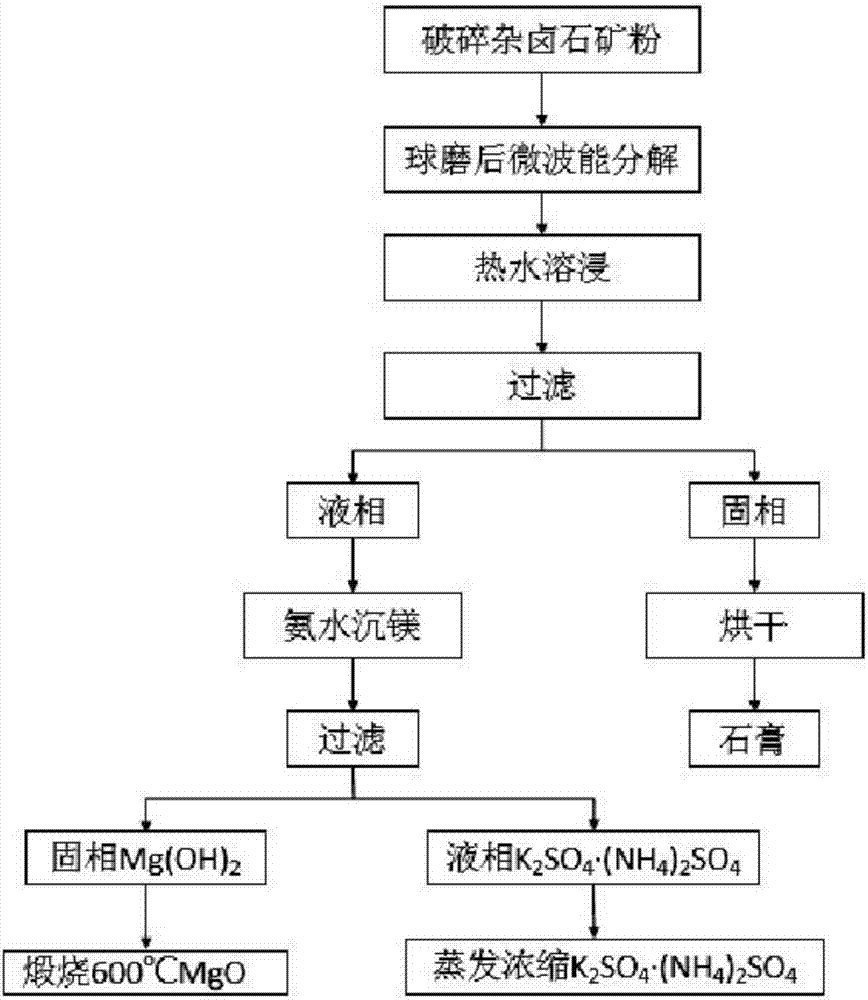
The invention discloses a method for preparing nitrogen, sulfur and potassium from polyhalite. The method comprises the following steps: crushing polyhalite ore powder and carrying out microwave-energy decomposition; subjecting the polyhalite ore powder having undergone microwave-energy decomposition to leaching with a hot solution and carrying out solid-liquid separation so as to obtain liquid-phase K2SO4, a MgSO4 solution and solid-phase CaSO4; subjecting K2SO4 and the MgSO4 solution to ammonia water precipitation so as to remove magnesium and carrying out filtering for separation so as to obtain solid Mg(OH)2 and liquid-phase K2SO4.(NH4)2SO4; calcining Mg(OH)2 at a temperature of 600 DEG C so as to obtain a MgO lightweight product; and subjecting liquid-phase K2SO4.(NH4)2SO4 to evaporative concentration and crystallization so as to obtain a K2SO4.(NH4)2SO4 product. Nitrogen-sulfur-potassium three-component fertilizer prepared in the invention has high fertilizer efficiency and good water solubility, can be rapidly absorbed by plants and is applicable to economic crops. The preparation method is simple in process flow, low in energy consumption, clean, environment friendly and low in production cost; and calcium, magnesium and potassium in polyhalite are overally recycled.
Owner:四川省冶金地质勘查局六0五队
Method for preparing potassium sulfate by using polyhalite
ActiveCN106379917AWide variety of sourcesSimple processAlkali metal sulfites/sulfatesEvaporationPotassium sulfate
The invention provides a method for preparing potassium sulfate by using polyhalite. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) grinding ores: grinding the polyhalite till 90wt% of the polyhalite are over 150 meshes in size; (2) washing: washing with water to remove the sodium chloride in the polyhalite; (3) roasting: roasting washed minerals at a high temperature; (4) leaching: leaching to extract potassium in the polyhalite; (5) solid-liquid separation: subjecting the ore pulp obtained through the leaching step to solid-liquid separation so as to obtain a mother liquor containing K+; (6) conversion: evaporating the mother liquor, adding potassium chloride and a potassium mixed salt, preparing potassium sulfate through the conversion method, and filtering to obtain a potassium sulfate product and the mother liquor; (7) evaporation: continuously evaporating the mother liquor, filtering to obtain a potassium mixed salt, and returning the potassium mixed salt to the conversion process. According to the method, the potassium sulfate is prepared by using the polyhalite. The process is simple, wide in source of raw materials and low in cost, wherein the sodium chloride in the polyhalite can be effectively removed. Meanwhile, the leaching rate of K+ is high and the water consumption of leaching is reduced. The concentration of K+ in the leaching mother liquor is high, and the energy consumption of the subsequent evaporation and crystallization step is reduced. Obtained potassium sulfate products are high in purity.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
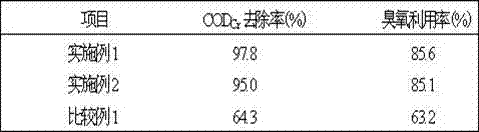
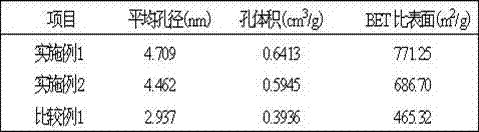
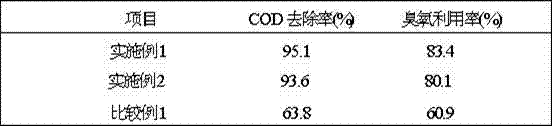
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107159209AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesCatalyst activation/preparationUltrasound - actionSodium Bentonite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of environmentally-friendly and chemical catalysts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking medical stone, wollastonite, bentonite, polyhalite, magnesia spinel and olivinite as carriers, reaming the carriers with lithium hypochlorite and bis(acetylacetone) beryllium, then adding octadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride serving as a surfactant for activation treatment under ultrasonic action, putting the activated carriers into a hydrothermal reaction kettle for hydrothermal reaction together with borax and potassium sulfate which serve as composite mineralizers, isopropyl scandium oxide (III), holmium oxalate hydrate, thulium trifluoromethane sulfonate (III) and lutetium carbonate hydrate which serve as catalytic active auxiliary precursors and a dicyclopentadienyl titanium cyclo-replaced salicylic acid complex, molybdenum L-aspartate, potassium dithiocyanoargentate (I) and diammineplatinum(II) dichloride which serve as catalytic active center component precursors under the action of N-cetyl dimethyl-N'-trimethyl-propyl ammonia dichloride serving as an emulsifier, drying a reaction product to remove water, and firing the reaction product in a muffle furnace, thus obtaining the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Glass micro-bead for use in PP reflection film and method for preparing same
The present invention discloses a glass micro-bead for use in a PP reflection film and a method for preparing same. The glass micro-bead is prepared using the following raw materials based on part by weight: 24 to 42 parts of chabazite, 36 to 54 parts of silica fume, 18 to 36 parts of tridymite, 15 to 30 parts of illite, 22 to 44 parts of polyhalite, 26 to 48 parts of gibbsite, 45 to 60 parts of ceramic waste, 14 to 26 parts of sodium nitrate,12 to 16 parts of dipropylene glycol methyl ether acetat, 10 to 15 parts of ammonium polyacryloyldimethyl taurate, 3 to 6 parts of Jojoba acid polyoxypropylene ester, 4 to 8 parts of Acrylic ester of stearic acid ester, and 14 to 18 parts of additive. The glass micro-beads prepared according to the present invention have high qualification rate, good quality, stable properties, high inverse reflection coefficient, good reflection effect, excellent weather resistance, corrosion resistance and thermal resistance, good durability and wide application prospect.
Owner:HEFEI DINGLIANG OPTICAL TECH
Polyhalite leaching agent and application thereof
InactiveCN107686890ASolve drainage problemsEffective for leachingProcess efficiency improvementChemical industryFresh water
The invention relates to the technical field of the salt chemical industry, in particular to a polyhalite leaching agent and an application thereof. The polyhalite leaching agent comprises oil field water and an acid chemical reagent. The volume ratio of the acid chemical reagent to the oil field water is 1:10-20. The oil field water is used as the leaching agent for leaching mining of polyhalite.The leaching agent can effectively leach the polyhalite. In the leaching process, the acid chemical reagent is added, and the leaching rate of K+ can be increased. Further, as the oil field water isadopted as the leaching agent, on one hand, the problem of a serious lack of fresh water resources required for leaching in polyhalite ore deposit areas is solved, and on the other hand, dual mining and utilization of oil field water and polyhalite is achieved, and the trouble of draining of oil fields is solved.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting polyhalite from polyhalite ore containing gangue minerals
ActiveCN108714481BEffective separation and extractionSeparation and extraction are stable and effectiveDifferential sedimentationFlotationSlurryPolyhalite
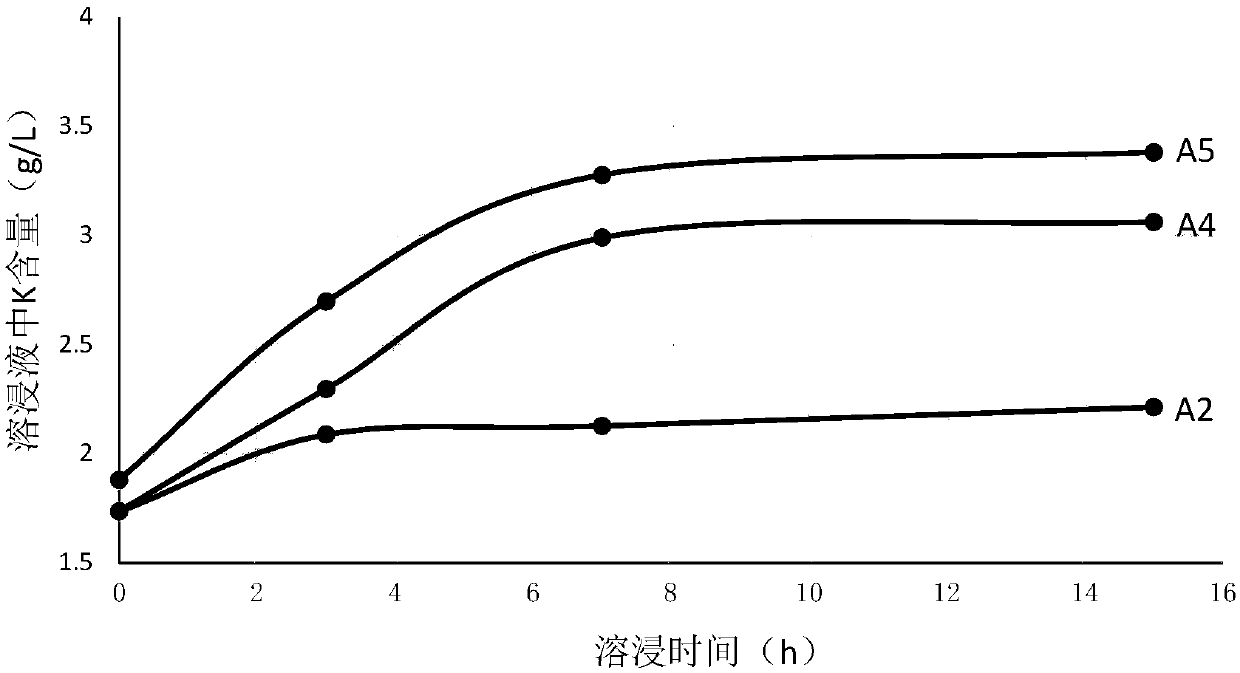
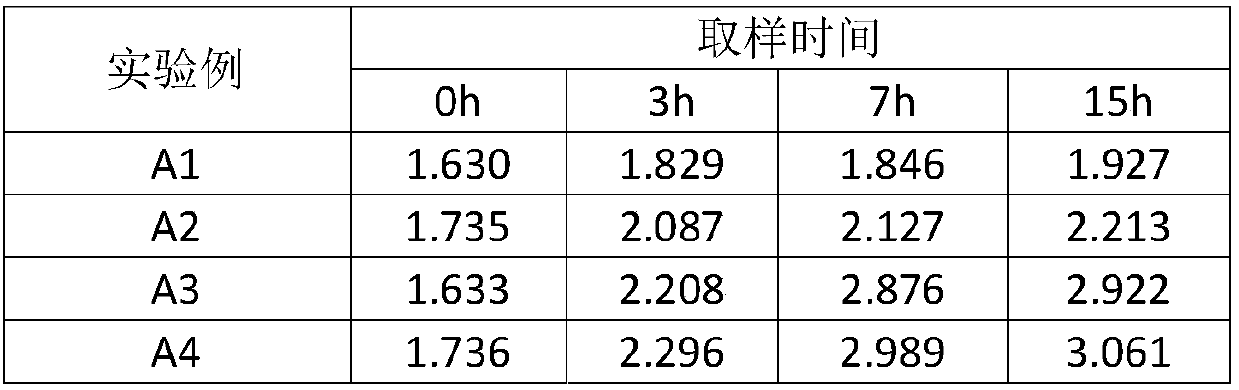
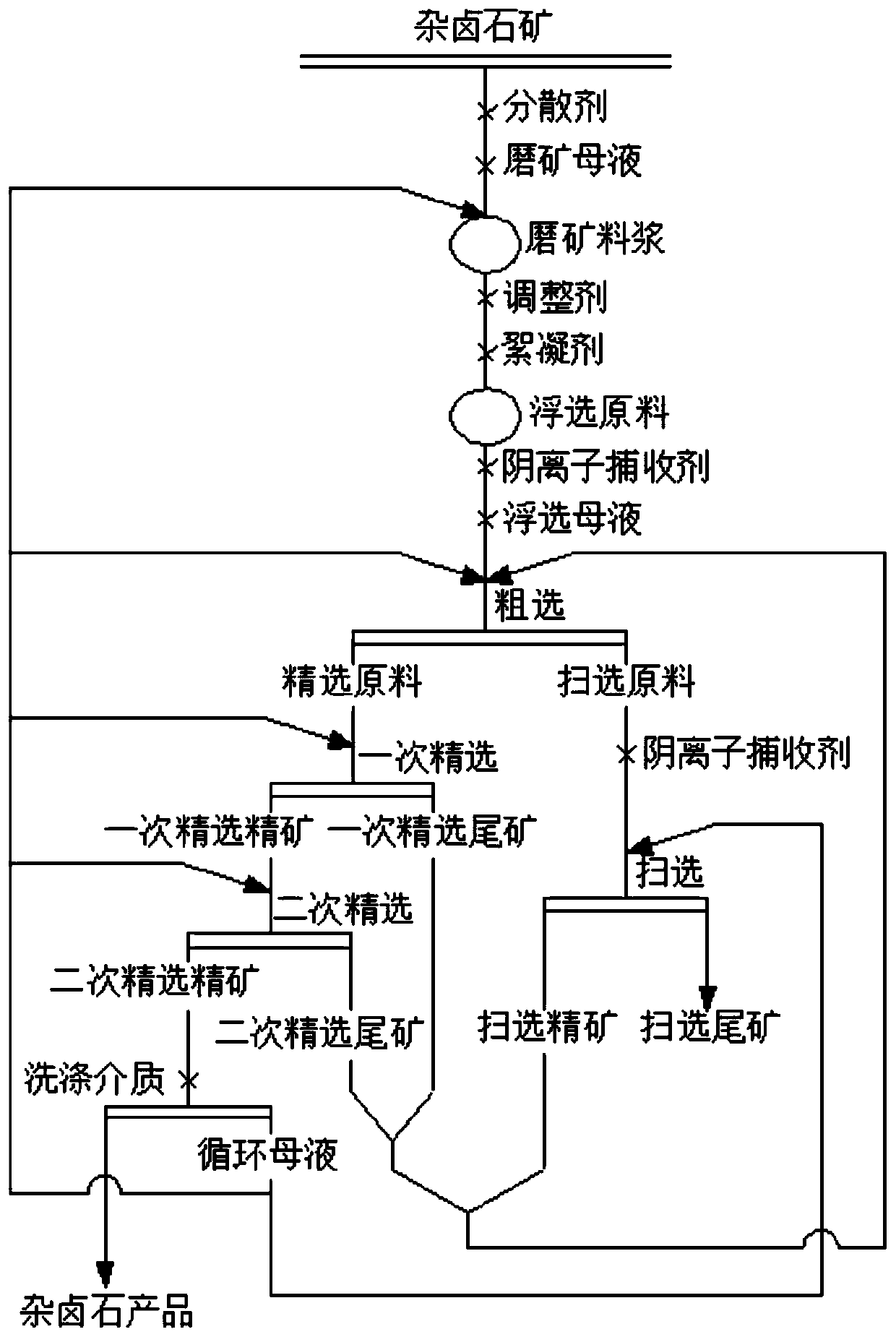
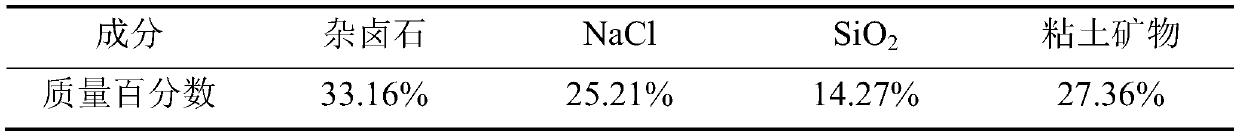
The invention discloses a method for extracting polyhalite from polyhalite ore containing gangue mineral. The method comprises the steps that firstly, polyhalite ore containing gangue minerals containing halite and silicate and / or scrap salt is ground, a dispersing agent and ore grinding mother liquor are added, and ore grinding slurry is obtained; secondly, an adjusting agent and a flocculating agent are added in the ore grinding slurry, and a flotation raw material is obtained; thirdly, the flotation raw material is subjected to roughing in flotation mother liquor, and a selected raw material and a scavenging raw material are obtained; fourthly, the selected raw material is sequentially subjected to primary selection and secondary selection, secondary selected concentrates are obtained,the scavenging raw material is subjected to scavenging, and scavenging tailings are obtained; and fifthly, the flotation mother liquor and washing mother liquor are mixed to serve as a washing medium,solid-liquid separation is conducted after the secondary selected concentrates are washed, and polyhalite products are obtained. The method is suitable for separating and extracting the polyhalite from the polyhalite ore containing gangue minerals containing the silicate and / or the scrap salt and the like, and a technical scheme for utilizing the polyhalite in other types of polyhalite ore is further provided.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107159195AImprove adsorption capacityBurning at high temperature makes the organic matter completely carbonized and strong adsorptionOther chemical processesCatalyst activation/preparationSodium BentoniteCalcite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of environmentally-friendly and chemical catalysts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking medical stone, wollastonite, dolomite, calcite, bentonite and polyhalite as carriers, reaming the carriers with lithium hypochlorite and bis(acetylacetone) beryllium, then adding myristyl tributyl ammonia chloride serving as a surfactant for activation treatment through ultrasonic waves, putting the activated carriers into a hydrothermal reaction kettle for hydrothermal reaction together with borax and potassium sulfate which serve as composite mineralizers, isopropyl scandium oxide (III), tri(4,4,4-trifluoro-1-(2-thiophene)-1,3-butanedione) europium, tri(6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptafluoro-2,2-dimethyl-3,5-octene diketone) dysprosium (III), tri(trifluoromethane sulfonylamine) ytterbium which serve as catalytic active auxiliary precursors and a dicyclopentadienyl titanium cyclo-replaced salicylic acid complex, zinc lactate, zirconium ammonium carbonate and tetraammine dichloropalladium (II) which serve as catalytic active center component precursors under the action of N-dodecyl dimethyl-N'-trimethyl-2-hydroxypropyl ammonia dichloride serving as an emulsifier, drying a reaction product to remove water, and firing the reaction product in a muffle furnace, thus obtaining the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107029743AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesUltrasound - actionSodium Bentonite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection and chemical catalysts. The preparation method includes the steps: taking attapulgite, diopside, bentonite, polyhalite, fly ash and coal gangue as carriers; broaching the carriers by lithium hypochlorite and beryllium bis(acetylacetonate); adding the surfactant trioctylmethylammonium chloride to perform activating under the action of ultrasonic wave; performing hydrothermal reaction on the carriers with composite mineralizing agents including borax and potassium sulfate, catalytic active aid precursors including praseodymium tri(3-trifluoroacetyl-D-camphor) (III), neodymium 1,1,1-trifluoroacetyl acetone, thulium trifluoromethanesulfonate (III) and lutetium carbonate hydrate, and catalytic active center precursors including ferrous fumarate, nickel citrate, zinc lactate and iridium dihydrate tetrachloride in a hydrothermal reactor under the action of the emulsifier, N-hexadecyldimethyl-N'-trimethyl-propyl ammonium dichloride; drying for removing water and firing in a muffle furnace to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107051452AImprove bindingHigh activityCatalyst carriersWater contaminantsUltrasound - actionLithium hypochlorite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst and belongs to the technical field of environment protection and chemical catalysts. The preparation method includes: using medical stone, wollastonite, bentonite, polyhalite, fluorite and glauberite as the carriers, using lithium hypochlorite and bis(acetylacetone) beryllium to perform pore expansion on the carriers, adding surfactant chlorinated octadecyl trimethyl ammonium to activate the carriers under ultrasonic action, allowing the carriers to have hydrothermal reaction with compound mineralizer including borax and potassium sulfate, catalytic activity promoter precursors including scandium(III) isopropoxide, holmium oxalate decahydrate, tri[N, N-bis(trimethyl silane) amine] erbium and thulium(III) trifluoromethane sulfonate, and catalytic activity central precursors including titanocene ring substituted salicylic acid complex, L-aspartic acid molybdenum, K[Ag(SCN)2] and hexanitroso rhodium trisodium in a hydrothermal reaction kettle under the effect of an emulsifier tri(cetyl) methyl ammonium bromide, drying to remove moisture, and burning in a muffle furnace to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107008404AImprove bindingEnhanced anti-toxicityCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesSodium BentoniteUltrasound - action
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst and belongs to the technical field of environmental-friendly and chemical engineering catalysts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking erionite, garnet, diatom pure, kyanite, bentonite and polyhalite as a carrier, after chambering and modifying the carrier through lithium hypochlorite and di(acetylacetone) beryllium, adding a surfactant dodecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride for surface activating treatment under the action of ultrasonic waves; then performing a reaction on the ultrasonic surface activated carrier in a hydrothermal reaction kettle and a compound mineralizer borax and potassium sulfate and catalytic active auxiliary agent precursors isoproscandium oxide (III), a tri(hexafluoroacetyl acetone) yttrium (III) dihydrate, tri(3-trifluoro acetyl-D-camphor) praseodymium (III) and thulium trifluoromethanesulfonate (III); and performing a hydrothermal reaction with catalytic active central compound precursors a titanocene ring substituted salicylic acid complex, vanadium isonicotinoyl hydrazone pyruvate, cupric glutamate and dichlorotetraaminopalladium under the action of an emulsifier N-dodecyl dimethyl-N'-dodecyl-2-hydroxypropyl ammonium dichloride, drying a reaction product to remove water, and firing the reaction product in a muffle furnace to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A kind of technology that prepares potassium sulfate with polyhalite
ActiveCN106379917BWide variety of sourcesSimple processAlkali metal sulfites/sulfatesEvaporationPotassium sulfate
The invention provides a method for preparing potassium sulfate by using polyhalite. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) grinding ores: grinding the polyhalite till 90wt% of the polyhalite are over 150 meshes in size; (2) washing: washing with water to remove the sodium chloride in the polyhalite; (3) roasting: roasting washed minerals at a high temperature; (4) leaching: leaching to extract potassium in the polyhalite; (5) solid-liquid separation: subjecting the ore pulp obtained through the leaching step to solid-liquid separation so as to obtain a mother liquor containing K+; (6) conversion: evaporating the mother liquor, adding potassium chloride and a potassium mixed salt, preparing potassium sulfate through the conversion method, and filtering to obtain a potassium sulfate product and the mother liquor; (7) evaporation: continuously evaporating the mother liquor, filtering to obtain a potassium mixed salt, and returning the potassium mixed salt to the conversion process. According to the method, the potassium sulfate is prepared by using the polyhalite. The process is simple, wide in source of raw materials and low in cost, wherein the sodium chloride in the polyhalite can be effectively removed. Meanwhile, the leaching rate of K+ is high and the water consumption of leaching is reduced. The concentration of K+ in the leaching mother liquor is high, and the energy consumption of the subsequent evaporation and crystallization step is reduced. Obtained potassium sulfate products are high in purity.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
A kind of technology of preparing potassium sulfate and potassium magnesium fertilizer with polyhalite
ActiveCN106276980BWide variety of sourcesSimple processAlkali metal sulfite/sulfate purificationProcess efficiency improvementEvaporationPolyhalite
A process for preparing potassium sulfate and potassium-magnesium fertilizer from polyhalite includes the following steps of 1, ore grinding, wherein polyhalite is subjected to ore grinding until the content of 120-mesh ground polyhalite is 85wt% or above; 2, washing, wherein sodium chloride in polyhalite is washed away with water; 3, roasting, wherein the washed ore is roasted at a high temperature; 4, leaching, wherein potassium and magnesium in polyhalite are leached; 5, solid-liquid separation, wherein ore pulp obtained through leaching is subjected to solid-liquid separation, and mother liquor containing potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate can be obtained; 6, evaporation, wherein the mother liquor is evaporated to separate out potassium sulfate, filtering separation is carried out to obtain a potassium sulfate product, the mother liquor continues to be evaporated to a certain concentration, and filtering separation is carried out to obtain a potassium-magnesium fertilizer product. The process is simple, the raw material source is wide, and the cost is low; sodium chloride in polyhalite can be effectively removed, the K+ leaching rate is high, the water consumption for leaching is small, the K+ concentration in the leaching mother liquor is high, the energy consumption for evaporative crystallization at the later stage is lowered, the K+ utilization rate is high, and the product grade is high.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst preparation method
InactiveCN107051508AImprove stabilityHigh activityCatalyst carriersWater contaminantsPtru catalystUltrasound - action
The invention belongs to the technical field of environment protection and chemical catalysts and relates to an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst preparation method. The preparation method includes: taking porous mineral materials including perlite, albite, bentonite, polyhalite, basalt and bloedite as carriers; subjecting the carriers to lithium hypochlorite and bis(acetylacetone)beryllium broaching modification; adding surfactant nonylphenol biquaternary ammonium salt for surface activation under the action of ultrasonic waves; subjecting the carriers subjected to ultrasonic surface activation to hydrothermal reaction, with a complex mineralizer composed of borax and potassium sulfate, catalytic activity auxiliary agent precursors including1,1,1-neodymium trifluoroacetylacetonate, tri(6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptafluoro-2,2-dimethyl-3,5-octenyldiketone)dysprosium (III), tris[N,N-bis(trimethylsilane)amine]erbium and tri(trifluoromethanesulfonimide)ytterbium rare earth metal organic compounds and catalytic activity central component precursors including normal transition metal organic compounds namely cobalt gluconate and nickel citrate and precious metal compounds namely potassium dithiocyanoargentate (I) and tetraammine dichloropalladium, in a hydrothermal reactor under the action of trimethylamino glycolate ammonium iodide palmitate serving as an emulsifying agent; drying reaction products to remove moisture, and firing in a muffle furnace at a certain temperature to obtain an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107051540AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst carriersWater contaminantsUltrasound - actionLithium hypochlorite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst and belongs to the technical field of environment protection and chemical catalysts. The preparation method includes: using medical stone, wollastonite, bentonite, polyhalite, basalt and blodite as the carriers, using lithium hypochlorite and bis(acetylacetone) beryllium to perform pore expansion on the carriers, adding chlorinated octadecyl trimethyl ammonium to activate the carriers under ultrasonic action, allowing the carriers to have hydrothermal reaction with compound mineralizer including borax and potassium sulfate, catalytic activity promoter precursors including scandium(III) isopropoxide, holmium oxalate decahydrate, tri[N, N-bis(trimethyl silane) amine] erbium and tri(trifluoromethane sulfonimide) ytterbium, and catalytic activity central component precursors including titanocene ring substituted salicylic acid complex, L-aspartic acid molybdenum, K[Ag(SCN)2] and tetraammine dichloropalladium(II) in a hydrothermal reaction kettle under the effect of di(octadecyl) lauryl methyl ammonium bromide, drying to remove moisture, and burning in a muffle furnace to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for solid catalyst for ozone heterogeneous oxidization
InactiveCN107008391AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesUltrasound - actionCerium
The invention relates to a preparation method for a solid catalyst for ozone heterogeneous oxidization and belongs to the technical field of an environment-friendly and chemical catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking gamma-aluminum oxide, barite, activated carbon, carnallite, bentonite and polyhalite as a carrier; modifying the carrier by broaching with lithium hypochlorite and bis(acetylacetone) beryllium, and then adding surfactant bidecalkyl dimethyl ammonium chloride and performing surface activating treatment under the effect of ultrasonic wave; performing hydrothermal reaction on the carrier, a compound mineralizer including borax and potassium sulphate, catalytic activated assistant precursors, including 4(2, 2, 6, 6, 6-tetramethyl-3, 5-heptanedione) cerium (IV), 1,1,1-trifluoroacetylacetone neodymium, tricyclopentadiene promethium and tri(4,4,4-trifluoro-1-(2-thiophene)-1,3-butanedione) europium and catalytic active core component precursors, including manganese lysine, cupric glutamate and potassium dicyanoargentate and dichlorodiamminoplatinum in a hydrothermal reaction kettle under the effect of chlorinated methyl acryloyl ethyltrimethylammonium chloride used as an emulsifier; drying and dewatering the reaction product; burning in a muffle furnace under a certain temperature, thereby acquiring the solid catalyst for ozone heterogeneous oxidization.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidized solid catalyst
InactiveCN107020097AImprove adsorption capacityBurning at high temperature makes the organic matter completely carbonized and strong adsorptionCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesUltrasound - actionSodium Bentonite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidized solid catalyst, and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection and chemical catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking maifanite, wollastonite, bentonite, polyhalite, hydrotalcite and alunite as carriers, performing lithium hypochlorite and bis(acetylacetonato) beryllium reaming, adding octadecyl trimethyl ammonium chloride to perform activating treatment under an ultrasonic effect; and then enabling the active carriers to perform hydrothermal reaction with the compound mineralizing agent borax and potassium sulfate, catalytic active promoter precursors scandium isopropoxide (III), holmium oxalate decahydrate, erbium tris[bis(trimethylsilyl)amide], lutetium carbonate hydrate, catalytic active center precursors titanocene ring substituted salicylic complex, L-aspartic acid molybdenum, potassium dithiocyanatesilver (I), dipotassium hexachloroosmium under the effect of the emulsifier N-dodecyl dimethyl-N'-dodecyl-dimethyl-2-hydroxypropyl ammonium dichloride, drying to remove the moisture, firing in a muffle furnace to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidized solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com