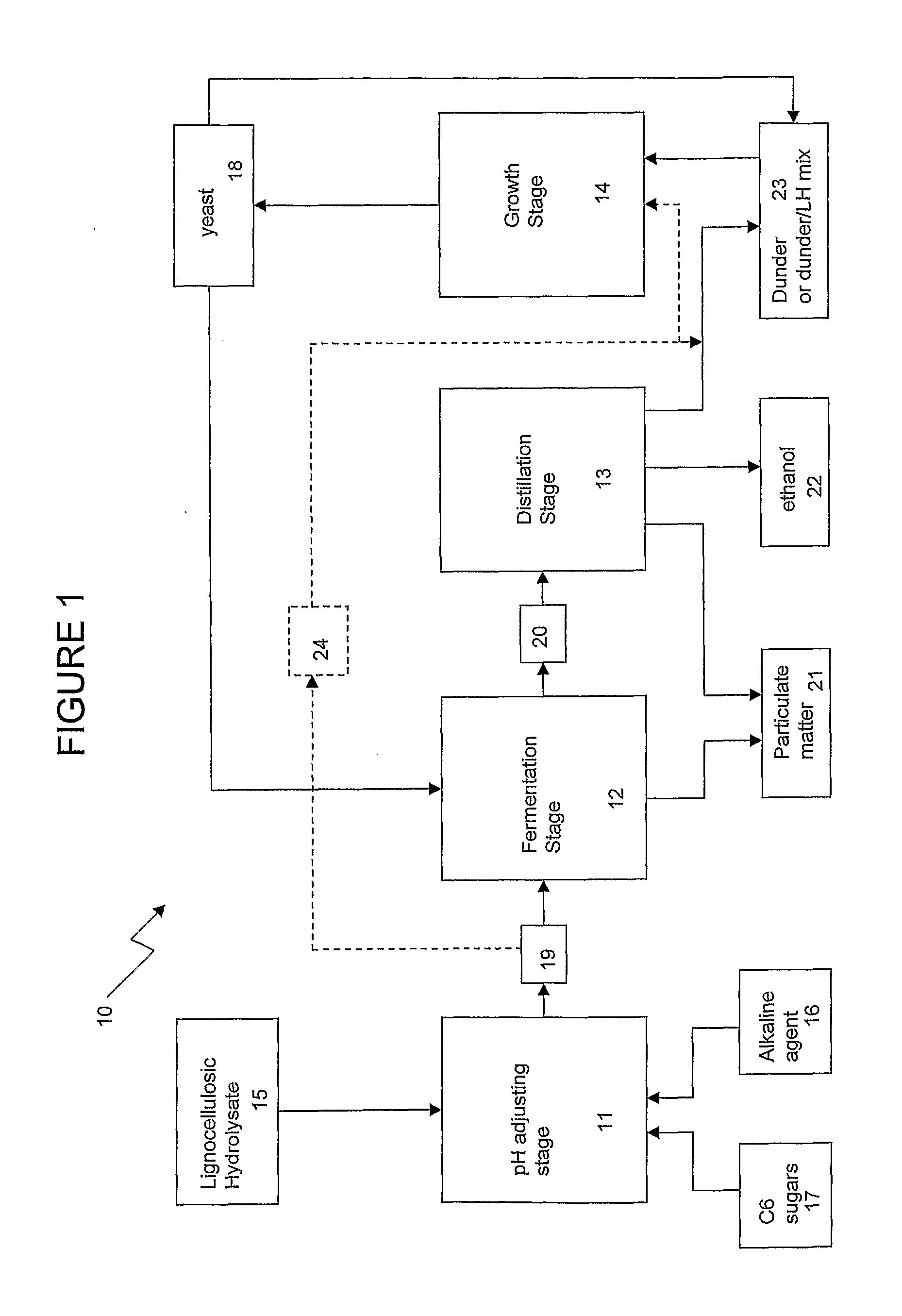
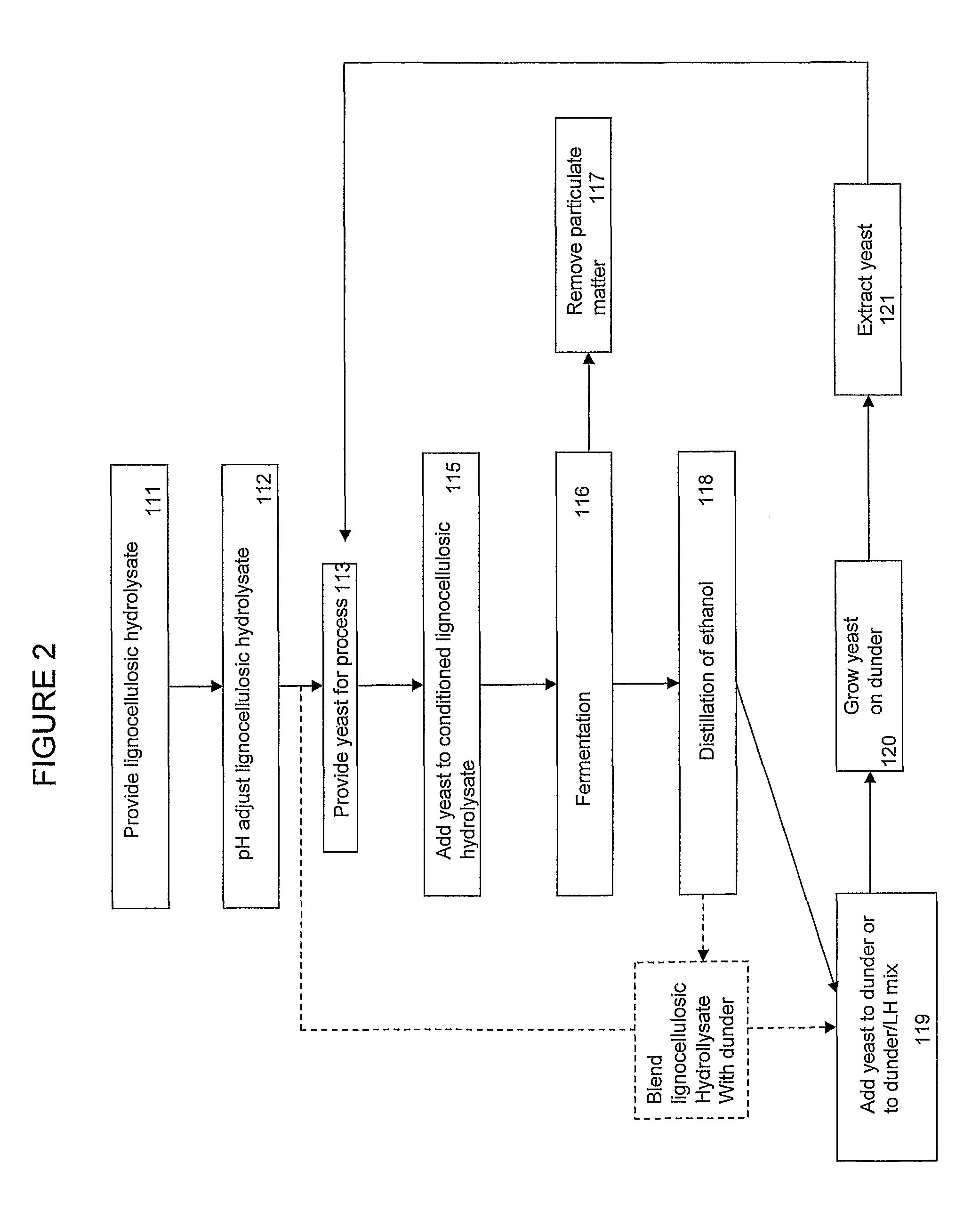
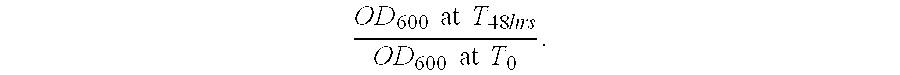Method of producing yeast biomass
a technology of saccharomyces yeast and biomass, which is applied in the field of producing saccharomyces yeast, can solve the problems of unsuitable growth of waste streams, and achieve the effect of reducing the biological oxygen demand of a substra
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Growth of Saccharomyces Strain NMI V08 / 013,411 and Saccharomyces Strain V09 / 005,064 Using Xylose as a Sole Carbon Source in Minimal Mineral Medium
[0166]Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain V08 / 013,411 was deposited at the National Measurement Institute, 51-65 Clarke Street, South Melbourne, Victoria, 3205, Australia under the Budapest Treaty on 23 May 2008 under accession number V08 / 013,411.
[0167]Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain V09 / 005,064 was deposited at the National Measurement Institute, 1 / 153 Bertie Street, Port Melbourne, Victoria, 3207, Australia, under the Budapest Treaty on 18 Feb. 2009 under accession number V09 / 005,064.
[0168]Saccharomyces yeast strain ER, which is representative of Saccharomyces yeast used for industrial starch-to-ethanol production, was isolated using standard microbiological procedures from a pack of “Ethanol Red” dry alcohol yeast which is commercially available from Fermentis, BP 3029-137 rue Gabriel Péri, F-59703 Marcq-en-Baroeul Cedex France (batch numbe...
example 2
Preparation of Lignocellulosic Hydrolysates
[0170]Washed lignocellulosic biomass was dried to <5% moisture at 90-120° C. and reduced to <1.5 mm using a hammer-mill to produce dry milled biomass.
[0171]Sulphuric acid was mixed at a level of 55.2 mg sulphuric acid per gram of dry biomass, into the dry milled biomass in order to produce a 25% w / w solid / water mash.
[0172]The acidified solid / water mash was transferred to an autoclavable plastic drum, covered with aluminium foil and placed within a 100 L pressure vessel. The temperature of the pressure vessel was maintained at 130 degrees C., 23 psi / 160 kPa for 90 minutes. The vessel was then depressurised to allow atmospheric pressure to be reached within 3 minutes.
[0173]The resulting hydrolyzed mash was fed into a manual screw press and dewatered. The moisture content of the pressed mash was 60-65%. Hydrolysate is liquid from the hydrolysed mash.
[0174]The hot liquor (the ‘hydrolysate’) had a pH of 0.8 to 1.5, and was continuously stirred. ...
example 3
High Density Inoculation of Lignocellulosic Hydrolysate Facilitates Rapid Fermentation
[0179]Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains ER and NMI V08 / 013,411 were grown in sucrose-minimal medium and harvested as described in Myers et al. (1997) Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 63: 145-150, to provide yeast biomass for inoculum.
[0180]One hundred milliliters of pH adjusted hydrolyzate liquor was buffered by addition of 1% tri-sodium citrate to pH 5.0. Citrate buffering was used to help maintain subsequent culture pH within a suitable range for yeast growth. pH control in culturing and fermentation could also be achieved by titration with other common acids and bases. Sixteen percent (weight per volume) D-glucose was dissolved into the hydrolyzate liquor for conversion to ethanol. The glucose was added to the hydrolyzate liquor in order to mimic the hexoses that would have been available for yeast to utilize if hydrolysed cellulose or other hexose-rich materials were employed. The buffere...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com