Device and method for degradating organic pollutant in tea by photo chermistry
A technology of organic pollutants and photochemistry, applied in the field of photochemistry and environmental photochemistry application research, can solve problems affecting foreign exchange earnings from tea exports, soil environment, water environment pollution, refractory degradation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
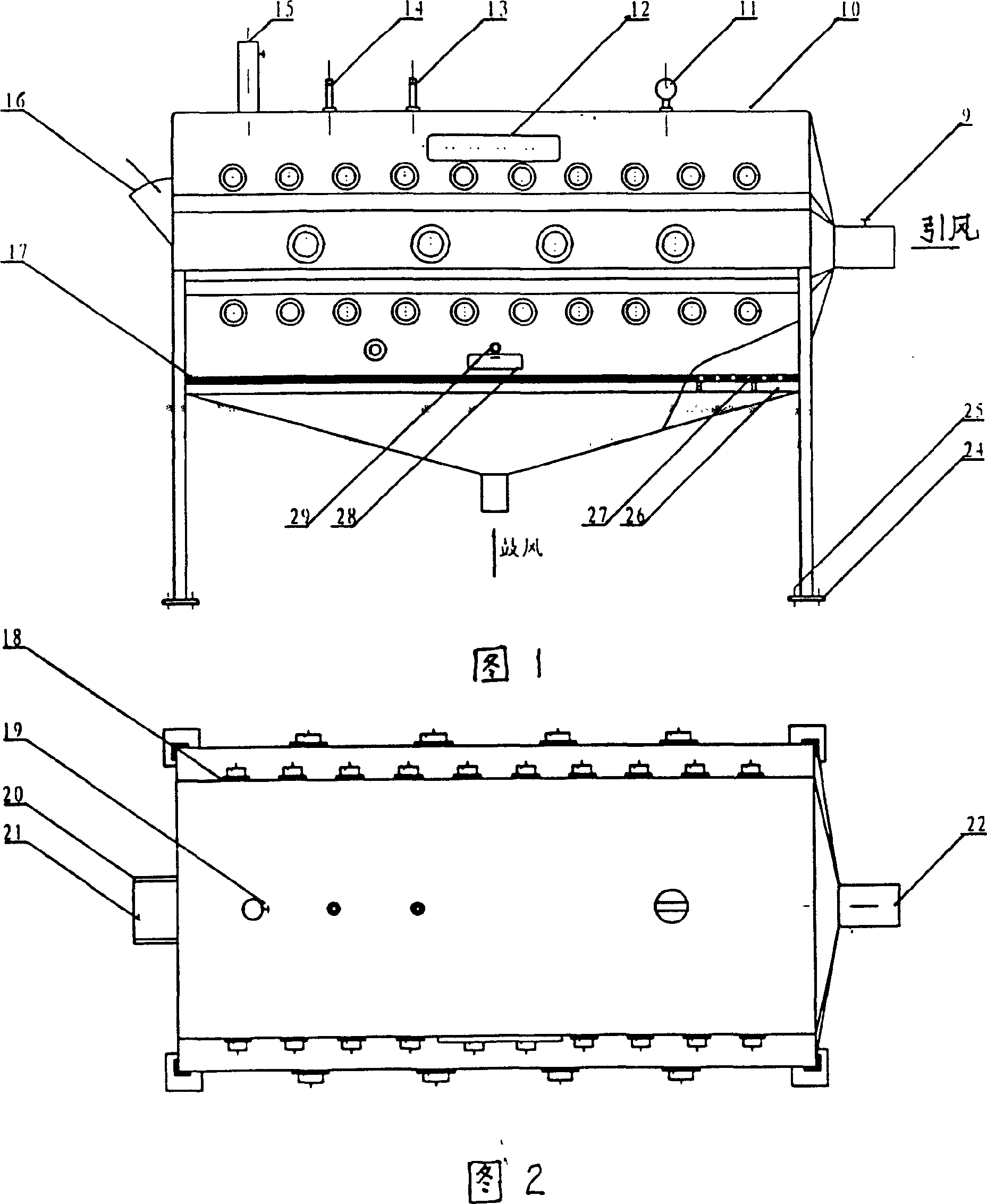
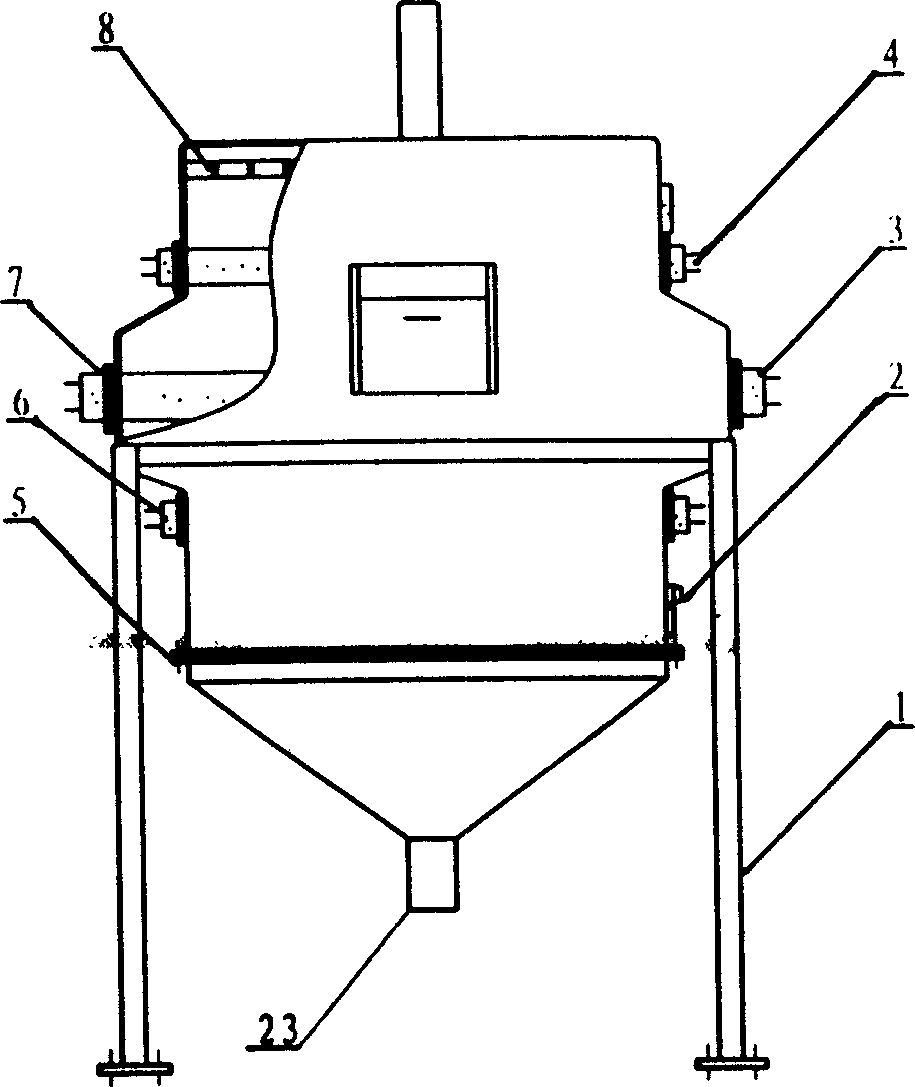
[0034] Pick 80.0kg of Sichuan Leshan fresh tea and send it to the degradation equipment. Light up UV light source groups 3, 4, and 6. The power of UV light source tubes in UV light source group 3 is 300W, and the power of UV light source tubes in UV light source groups Be 40W, make the operating temperature in the reactor 10 be controlled at 25 ℃, relative humidity is 605%, open the exhaust port 5, turn on the blower, blow into the reactor 10 by the blast port 23 and be the air of 0.2Mpa pressure, the air Through the air splitter 26 and the hole bed 27, the tea leaves are suspended up and down in the reactor 10. At the same time, oxygen is intermittently input through the oxygen delivery nozzle 2, and the oxygen delivery rate is 1.8 l / min. Or spray water mist intermittently. After 10 minutes of photochemical reaction, the total amount of residual pesticides in the original tea leaves was changed from 28 mg / kg to 0.02 mg / kg.
Embodiment 2
[0036] Pick 80.0kg of Anhui Qimen fresh tea and send it into the degradation equipment, operate according to the working conditions and methods of Example 1, the result is: the total amount of residual pesticide in the original tea leaves is 23mg / kg, after 5min of photochemical reaction, the residual pesticide The amount is 0.03 mg / kg.
Embodiment 3
[0038] 60kg of fresh tea from Longjing, Hangzhou, Zhejiang, was sent into the degradation equipment, and the working conditions and methods were operated according to Example 1. The result was that the total amount of residual pesticides in the original tea leaves was 12 mg / kg. After 10 min of photochemical reaction, the total amount of pesticides remained The amount is 0.03mg / kg.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com