Method for photochemical degradation of sulfonamide in water by using freshwater algae
A freshwater algae, photochemical technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, light water/sewage treatment, oxidized water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve the problems of metal catalytic media entry, not much, aquatic animals and plants harm, etc., to save operation effect of cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
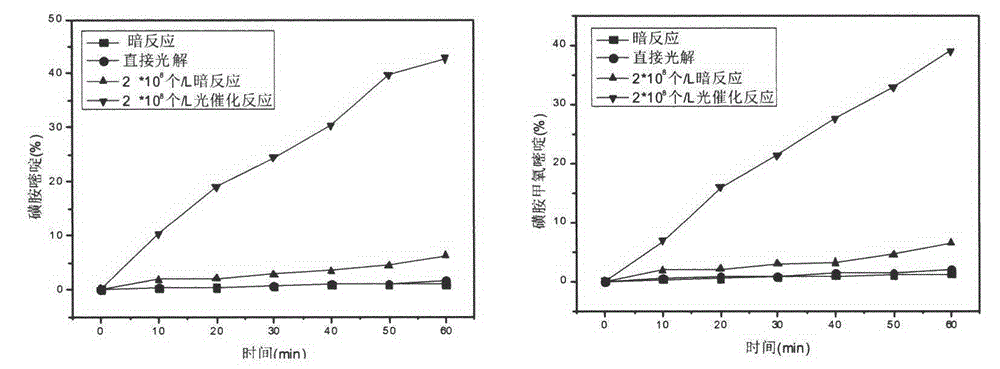
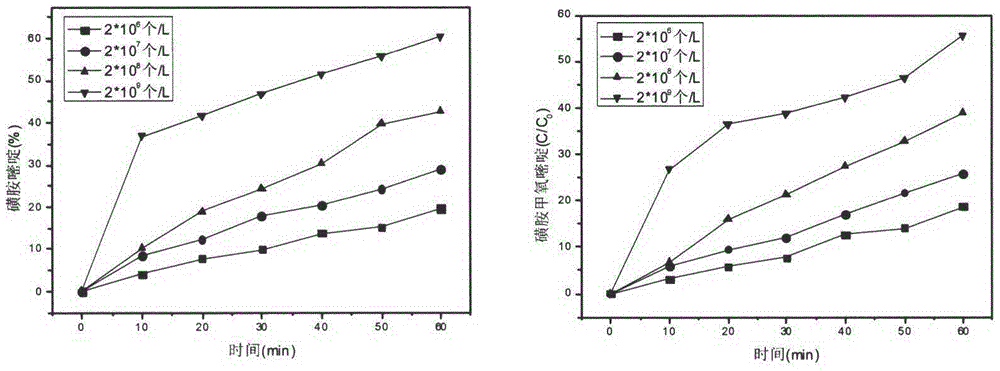
Embodiment 1
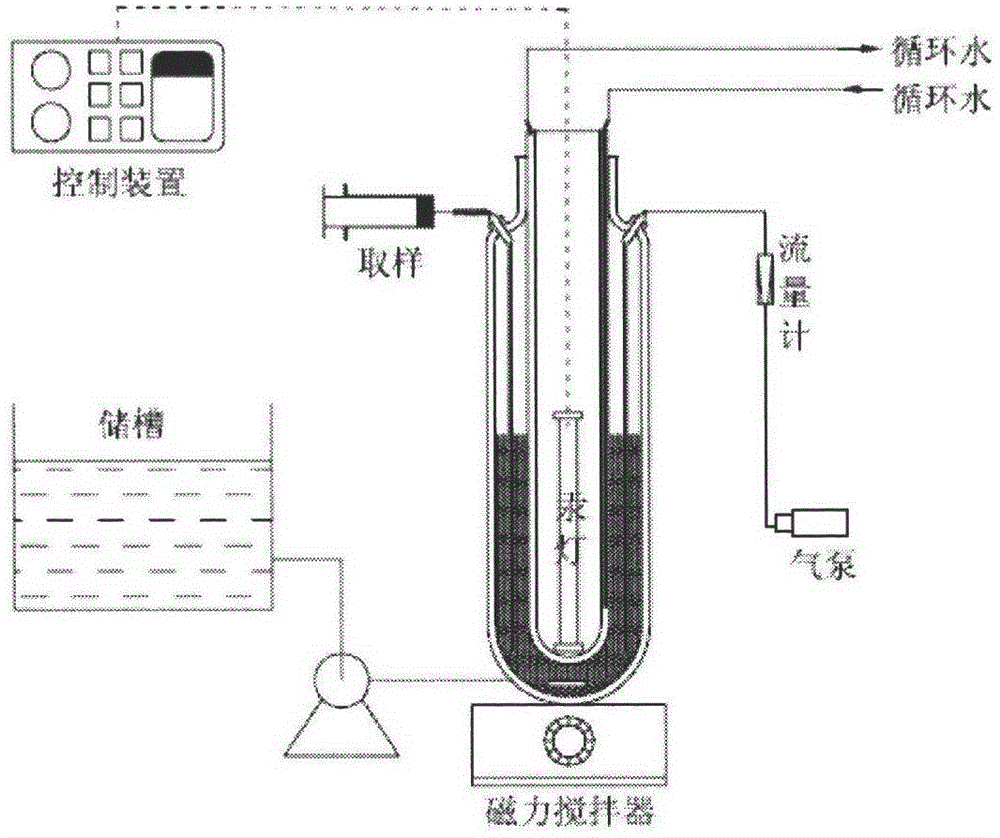
[0026] Fill 3L of sulfadiazine wastewater in the storage tank (length 20cm, width 20cm, height 15cm), adjust the pH value to about 6, add a certain amount of algae (2 × 10 9 algae cells / L), turn on the constant flow pump to make the wastewater to be treated enter the reactor at a flow rate of 0.3L / min.
[0027] Step 1 Turn on the circulating water pump to maintain the jacket water circulation of the quartz reactor, the circulating water flow rate is 1L / min, and the aqueous solution in the reactor is maintained at room temperature (about 25°C).
[0028] Step 2 Turn on the air pump and adjust the rotameter connected to the reactor to be constant at 0.5 L / min.
[0029] Step 3: Turn on the control system, set the reaction time, alarm at intervals of 10 minutes to prompt sampling test, and then turn on the magnetic stirrer to stir the wastewater to be treated, and set the speed to 100 rpm.
[0030] After step 4 system is stable 1-2min, open the mercury lamp (power is 25W) in the r...
Embodiment 2
[0034] The storage tank (length 20cm, width 20cm, height 15cm) is equipped with 3L of sulfamethoxine wastewater, the pH value is adjusted to about 6, and a certain amount of algae (2 × 10 9 algae cells / L), turn on the constant flow pump to make the wastewater to be treated enter the reactor at a flow rate of 0.3L / min.
[0035] Step 1 Turn on the circulating water pump to maintain the jacket water circulation of the quartz reactor, the circulating water flow rate is 1L / min, and the aqueous solution in the reactor is maintained at room temperature (about 25°C).
[0036] Step 2 Turn on the air pump and adjust the rotameter connected to the reactor to be constant at 0.5 L / min.
[0037] Step 3: Turn on the control system, set the reaction time, alarm at intervals of 10 minutes to prompt sampling test, and then turn on the magnetic stirrer to stir the wastewater to be treated, and set the speed to 100 rpm.
[0038] Step 4: After the system is stable for 1-2 minutes, turn on the mer...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com