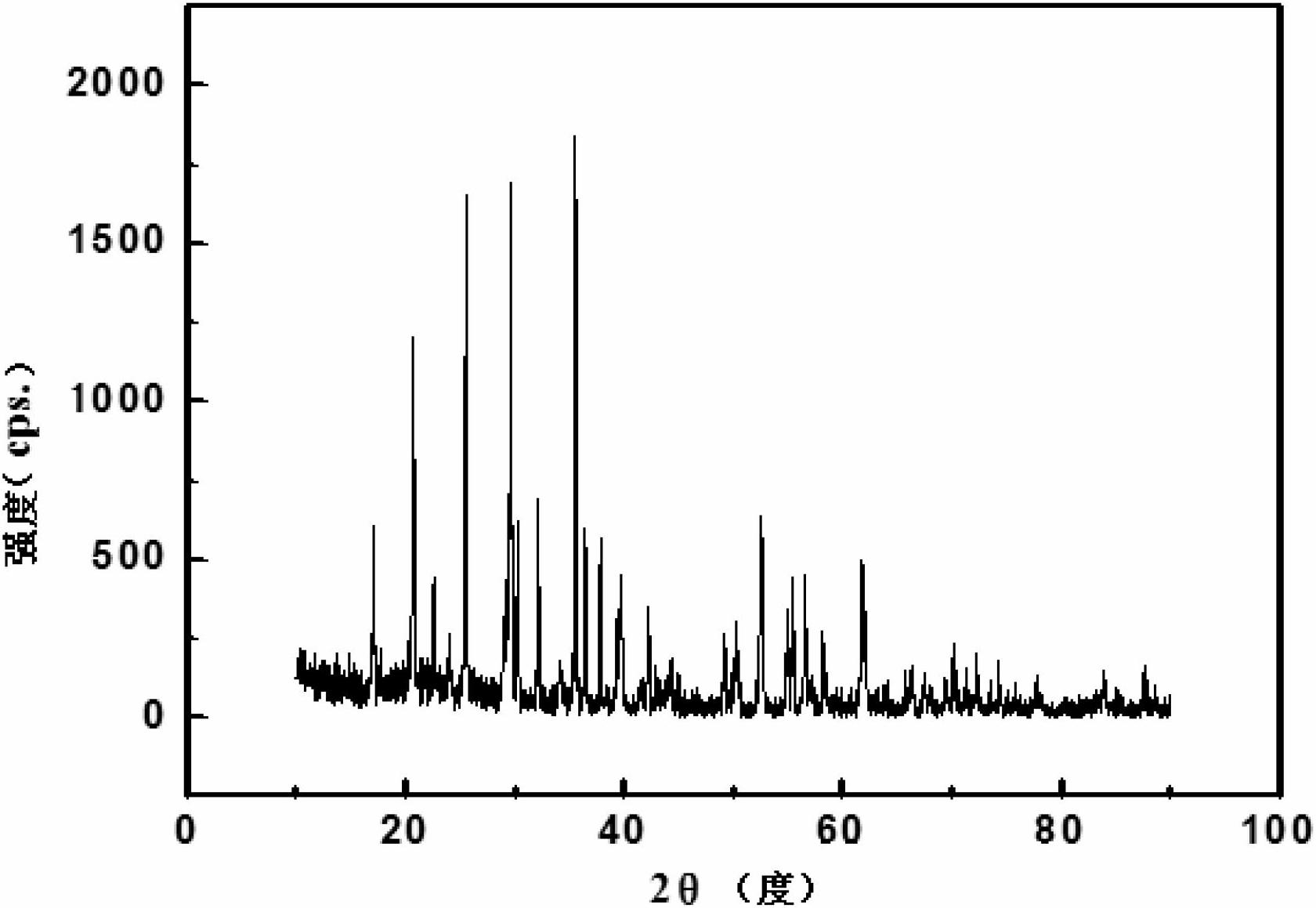
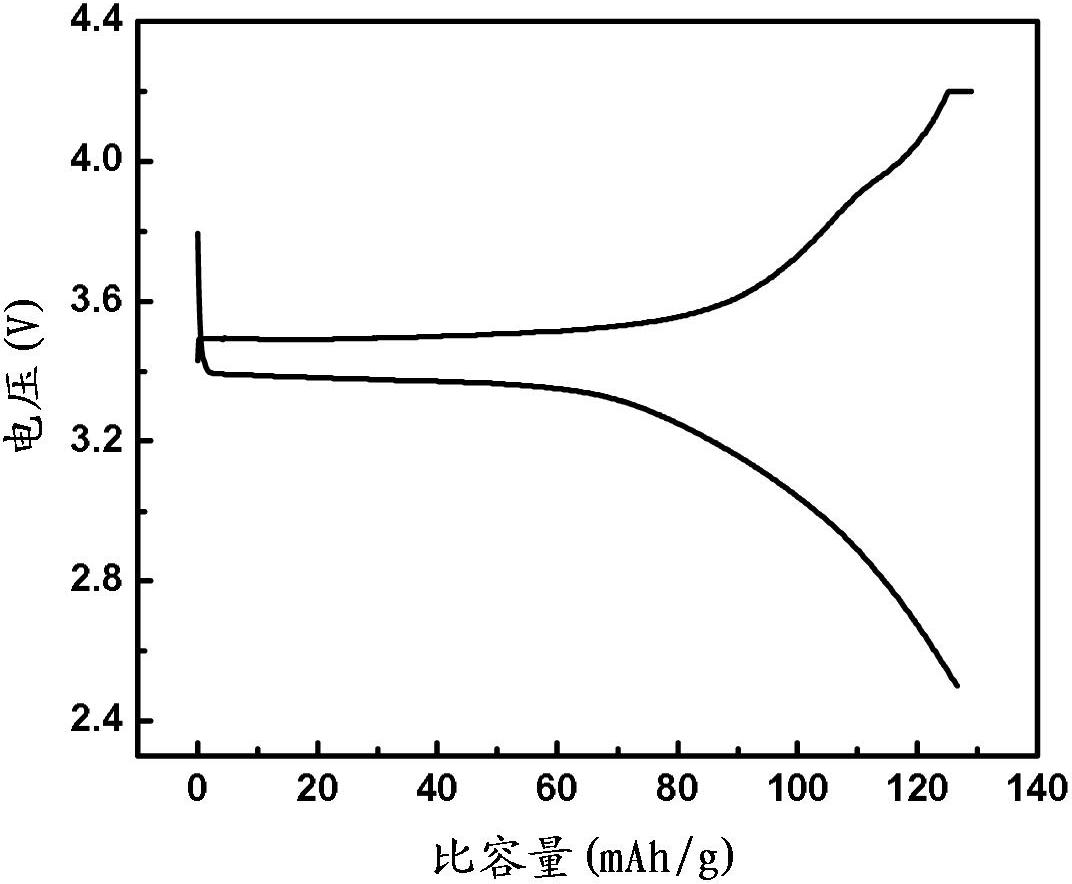
Method for recycling waste lithium iron phosphate batteries
A technology of lithium iron phosphate battery and recycling method, which is applied in the direction of battery recycling, waste collector recycling, recycling technology, etc., can solve the problems of high price, poor safety, unfriendly environment, etc., and achieve low production cost, quick effect, The effect of good electrochemical performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0022] Specific implementation mode one: the recycling method of waste lithium iron phosphate battery in this implementation mode is as follows:
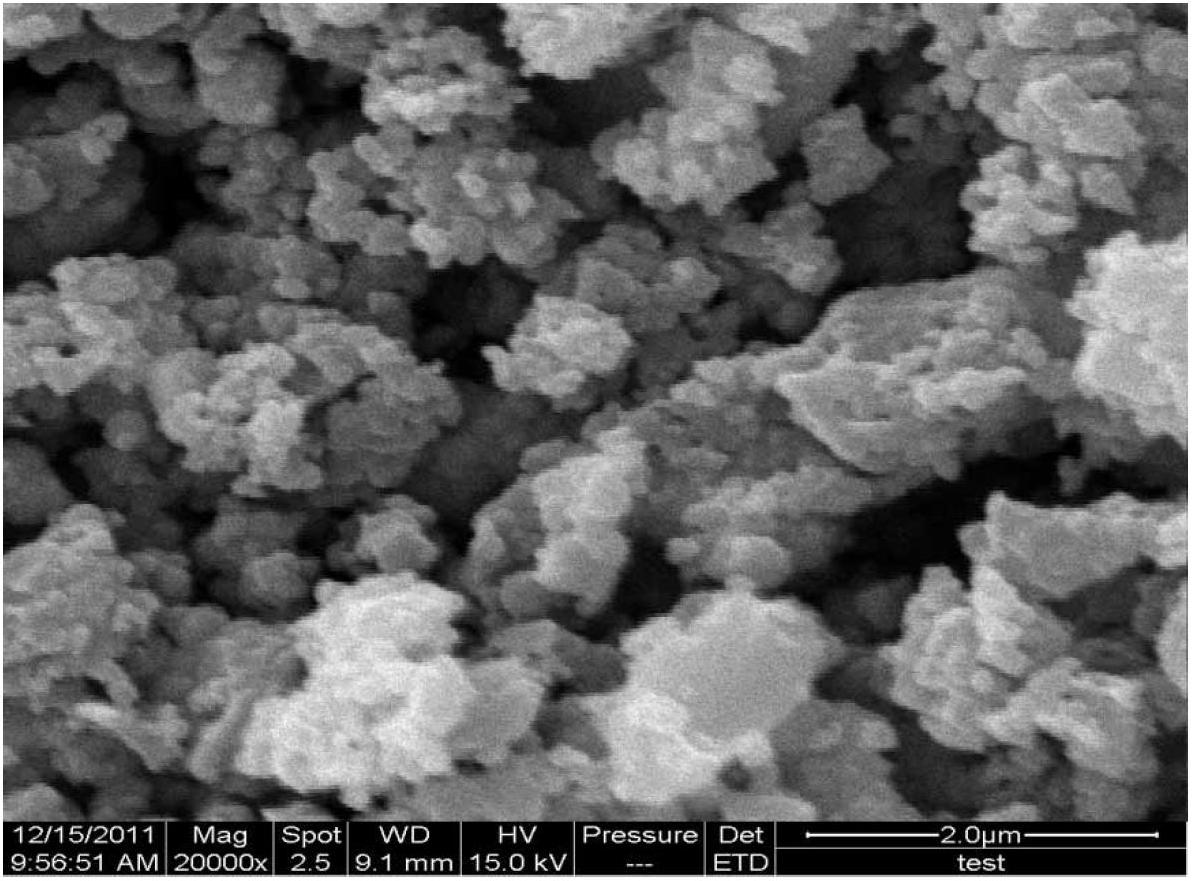
[0023] 1. Remove the residual power of the waste lithium iron phosphate battery, take out the battery cell and crush it into cell fragments, soak the cell fragments in sodium hydroxide solution and stir them, and perform ultrasonic oscillation while stirring, then filter, wash and dry And vibrating sieving, the pure aluminum, pure copper and diaphragm obtained on the sieve, among which the aluminum and copper are recovered through smelting, and the mixed powder is obtained under the sieve;
[0024] 2. Wash the mixed powder with acid solution for 1 to 3 minutes, and then dry;
[0025] 3. Heat-treat the mixed powder processed in step 2 at a temperature of 150°C to 450°C for 2h to 8h;
[0026] 4. Detect the mixed powder treated in step 3. According to the content of lithium, iron, phosphorus and carbon, adjust the lithium, iron, lithi...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0035] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that the inert gas described in step 5 is argon or argon-hydrogen mixed gas, and the hydrogen in the argon-hydrogen mixed gas accounts for 5% to 50% of the total volume of the argon-hydrogen mixed gas. %. Others are the same as in the first embodiment.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0036] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that the concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution in step 1 is 0.4 mol / L. Others are the same as in the first or second embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com