Transcription factors participating in regulating and controlling synthesis of bitter principles of cucumis melo and application of transcription factors
A transcription factor, a technology encoding a transcription factor, applied in the field of transcription factors involved in the regulation of melon bitterin synthesis, can solve the problems that the gene has not been cloned and the molecular mechanism is unclear
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Mining and acquisition of transcription factors regulating the synthesis of cucurbitacin E in melon
[0039] 1. Mining of candidate genes
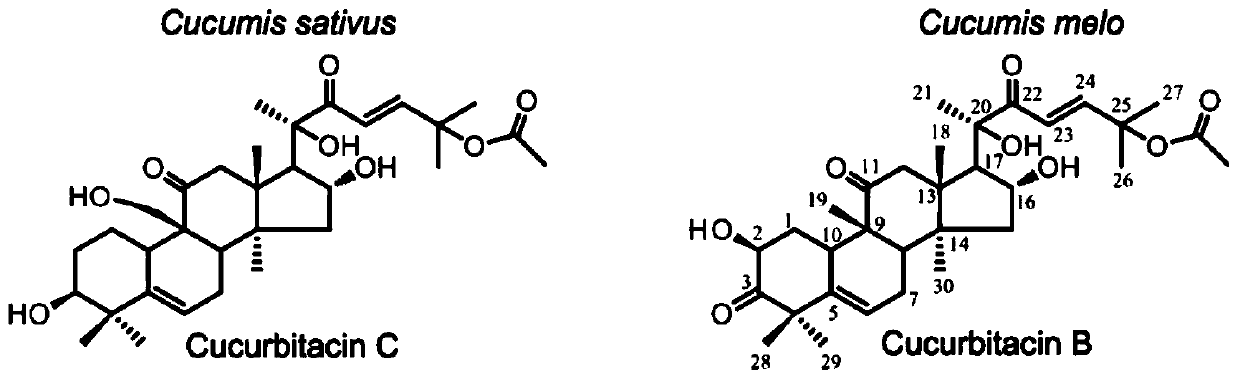
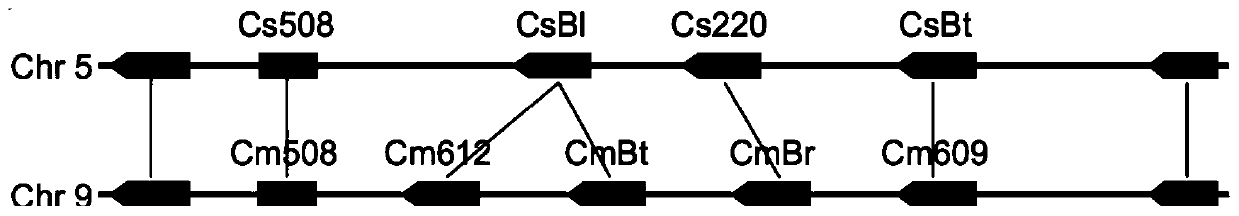
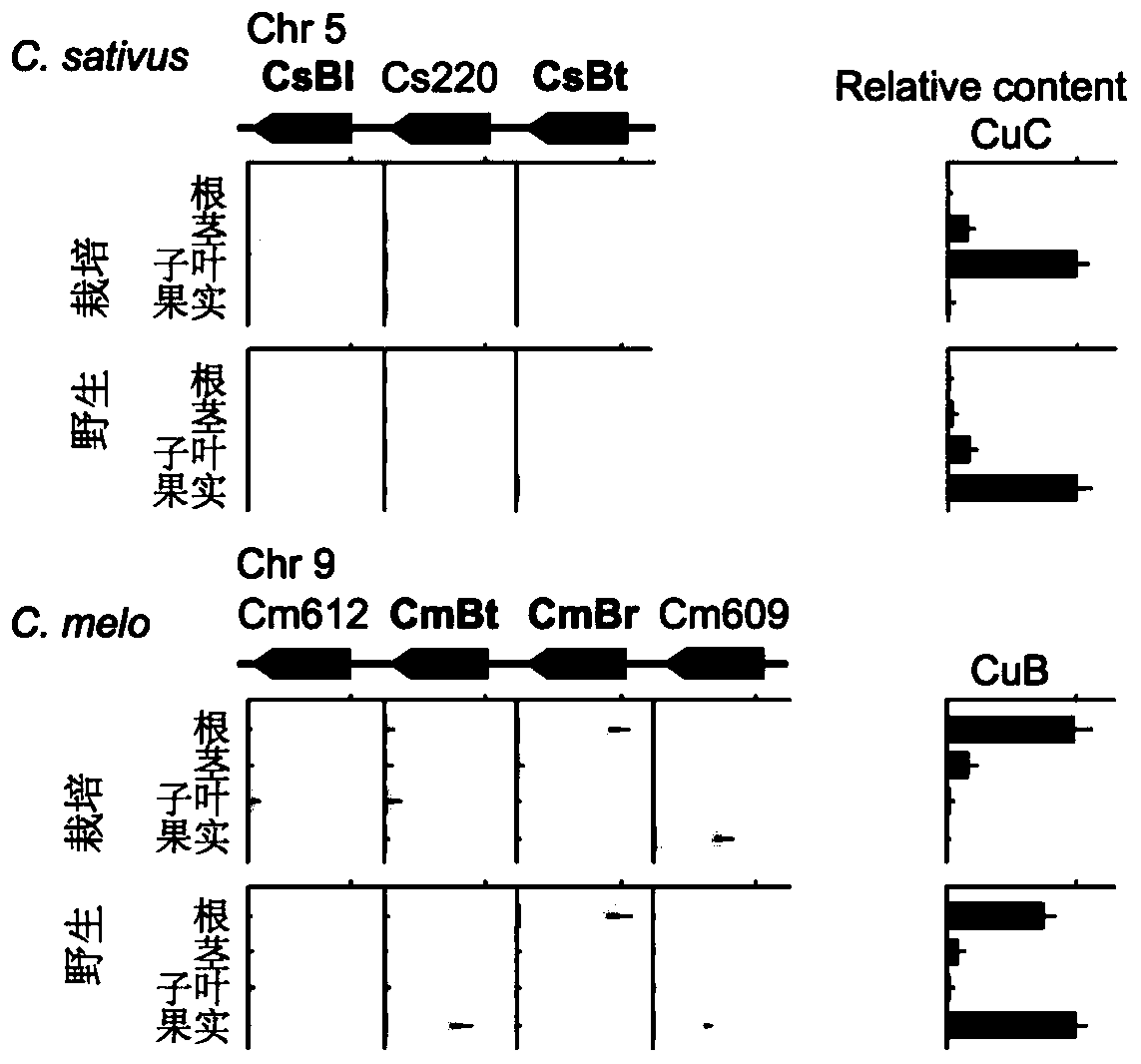
[0040] Through comparison, it was found that the bitter cucurbitacin B in melon and the bitter cucurbitacin C in cucumber have very similar structures ( figure 1 ), so it is speculated that its synthesis mechanism should be relatively similar, so we used comparative genomics to find a gene cluster similar to the regulation of cucumber bitterness synthesis in the melon genome ( figure 2 ), the gene cluster is composed of 4 bHLH-type transcription factors, and the gene expression analysis by fluorescent quantitative PCR shows that the gene CmBr is specifically expressed in roots, and the CmBt gene is specifically expressed in wild fruits, and the expression trend of the two genes It is consistent with the content of bitterin in each tissue of melon ( image 3), we speculated that the CmBr gene should control the synthesis...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2 Using the Agrobacterium-mediated transient expression method to verify the function of the transcription factor controlling the bitterness of melon
[0051] Since the stable muskmelon transgenic system is immature, the muskmelon cotyledon transient expression system was established in this example to further verify the functions of CmBr and CmBt.
[0052] The CmBr and CmBt genes were constructed on the binary vector pBIN-Plus. They were respectively introduced into Agrobacterium EA105 by chemical transformation. Cultivate Agrobacterium containing the target gene to OD 600 About 1.0, then diluted to OD with injection buffer 600 About 0.4, use a syringe without a needle to inject Agrobacterium into the cotyledons of melon seedlings about 10 days old. After one week, the leaves were collected, the compounds in the leaves were extracted with methanol, and then UPLC-Q-TOF (Agilent) detection and related expression analysis were performed. The results are as foll...
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3 Melon CmBt gene belongs to domestication gene
[0054] In the previous studies on the synthesis, regulation and domestication of cucumber bittern, it was found that the transcription factor Bt, which controls the bitterness of cucumber fruit, is a domestication gene. Through the analysis of the nucleic acid diversity of wild and cultivated muskmelon materials, it was found that the CmBt gene of muskmelon is located in the domestication area, so there is a phenomenon of cooperative domestication of bitterness in Cucurbitaceae plants ( Figure 8 ).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com