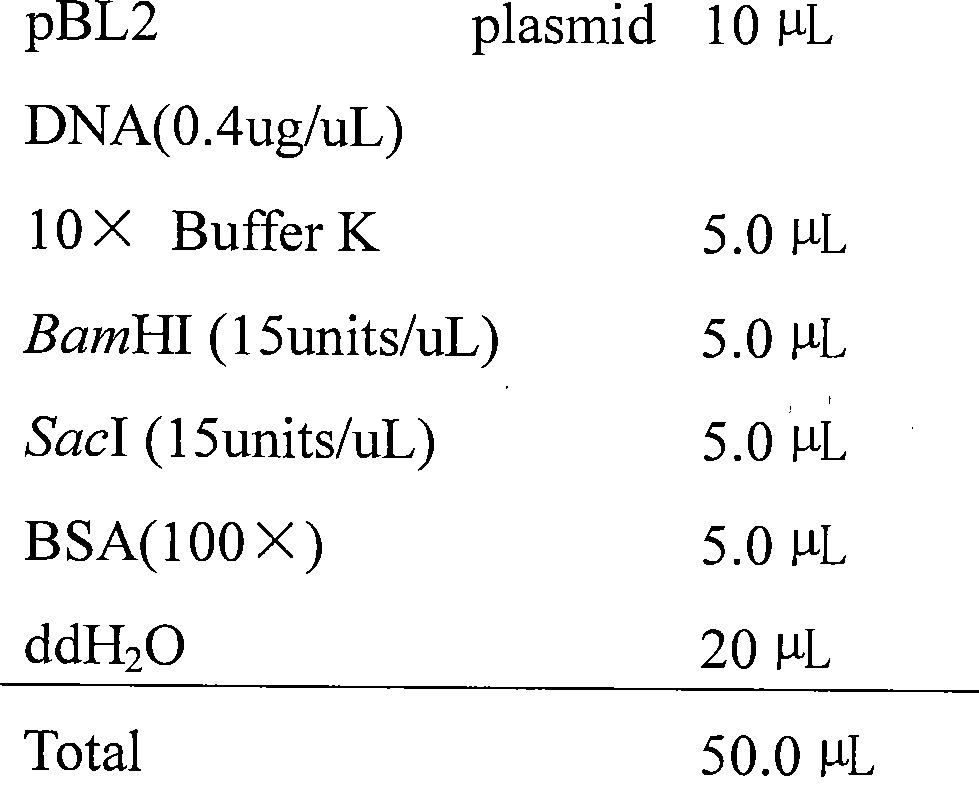Patents
Literature
39 results about "RNA blotting" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
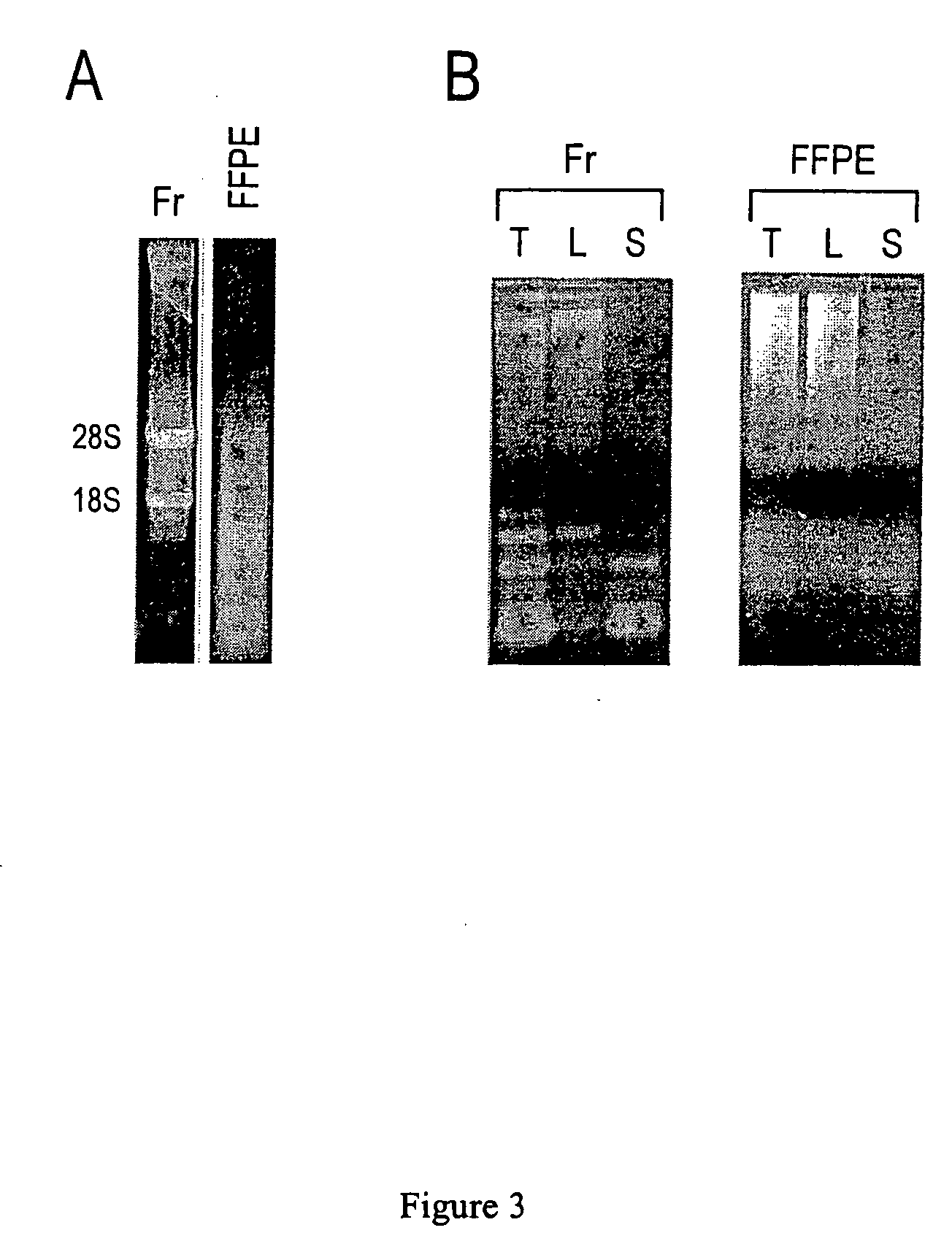
Flow diagram outlining the general procedure for RNA detection by northern blotting. The northern blot, or RNA blot, is a technique used in molecular biology research to study gene expression by detection of RNA (or isolated mRNA) in a sample.
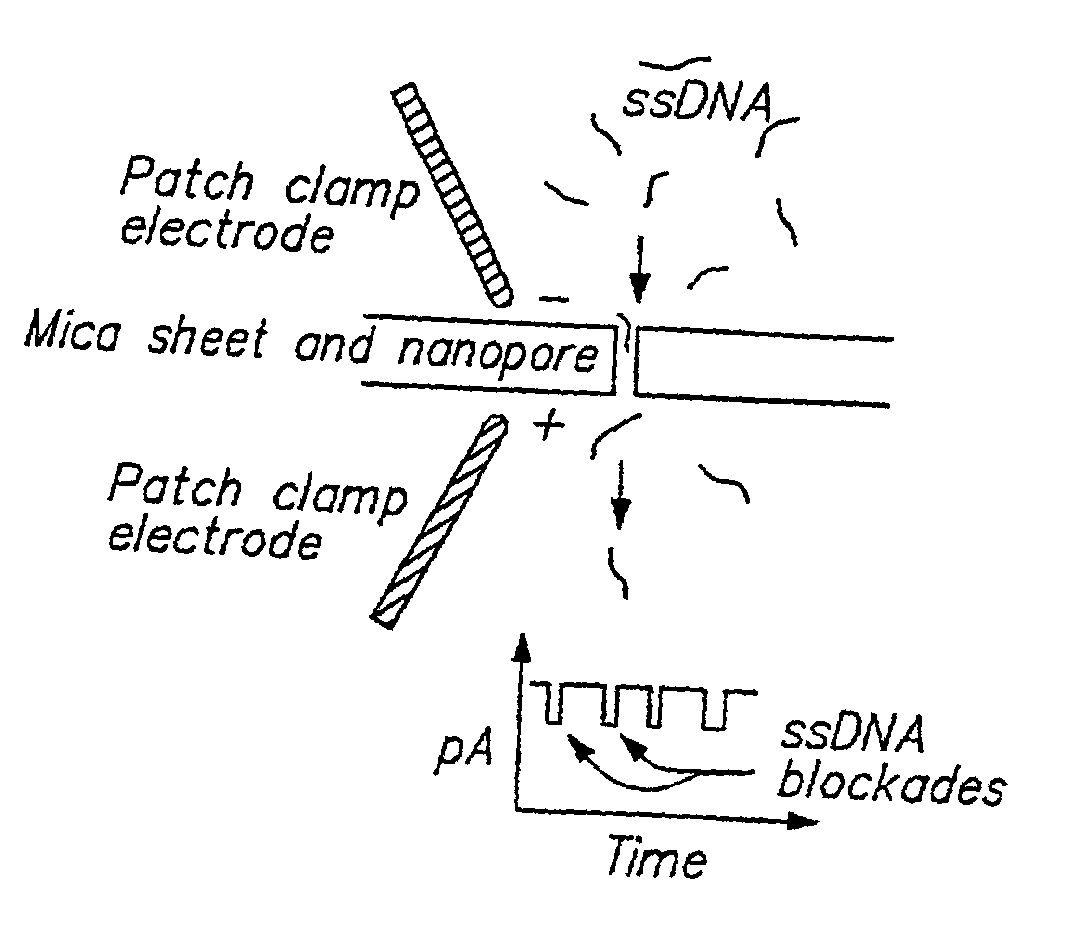
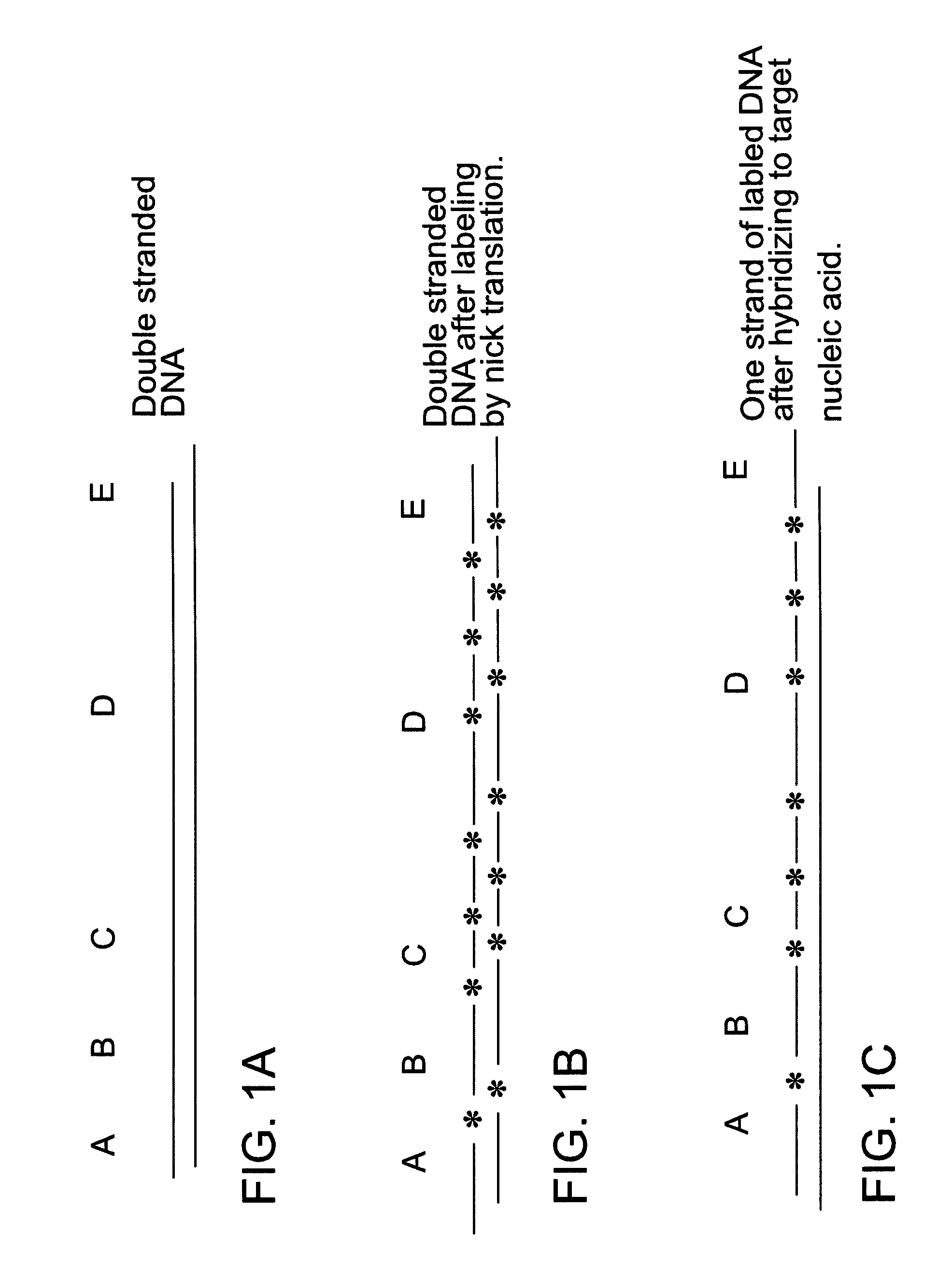
Methods of determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample
InactiveUS6428959B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRNA blottingAssay
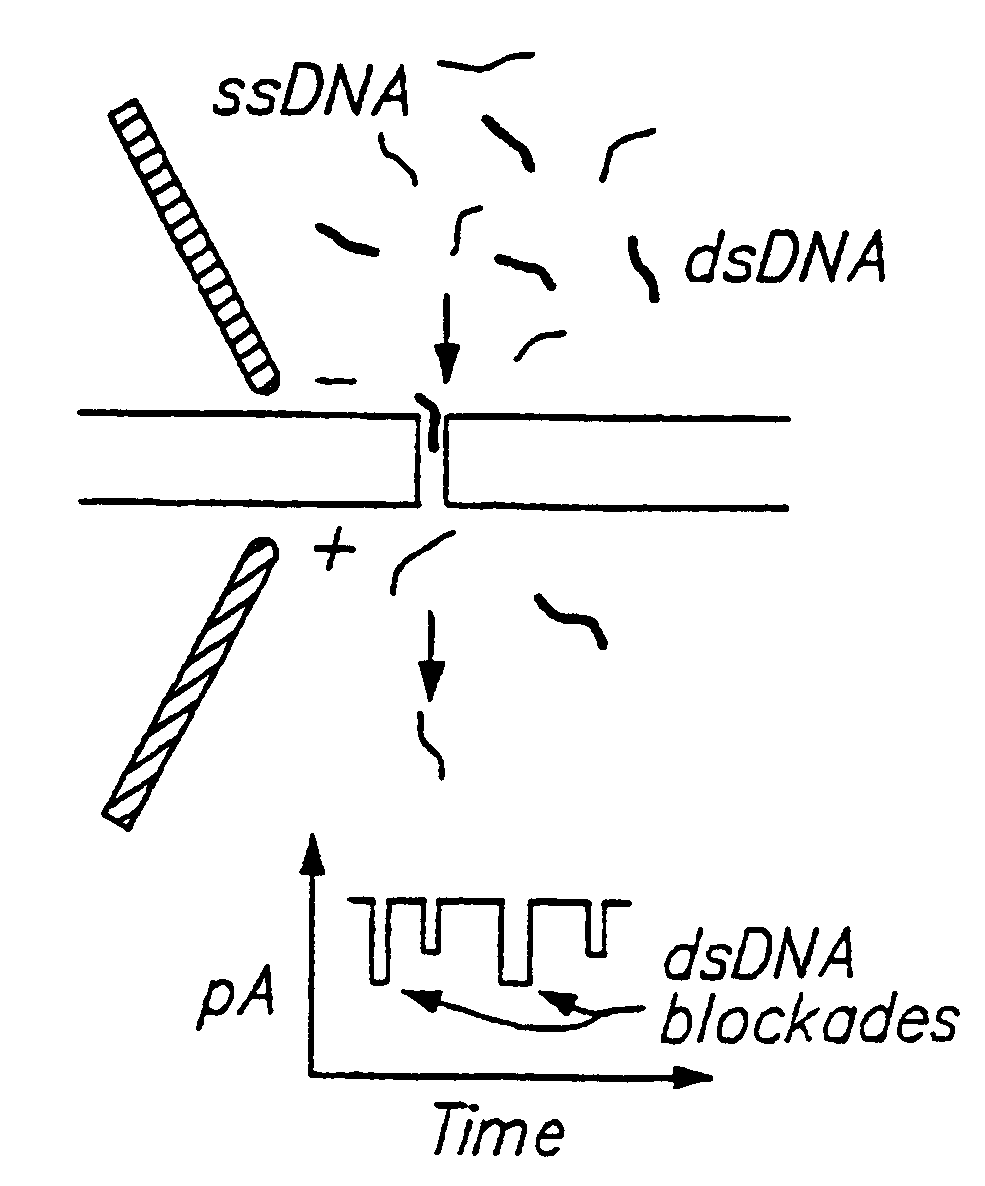
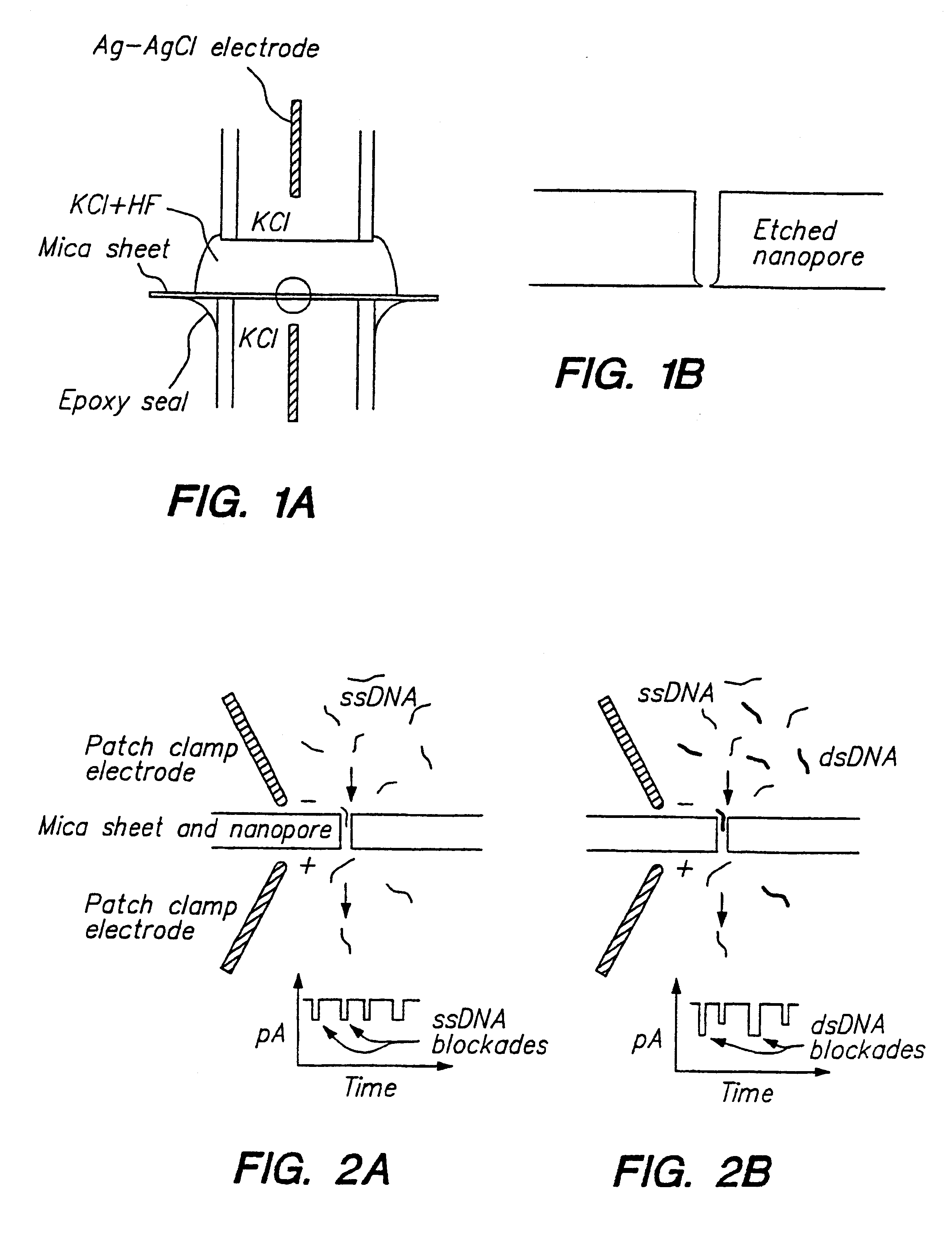
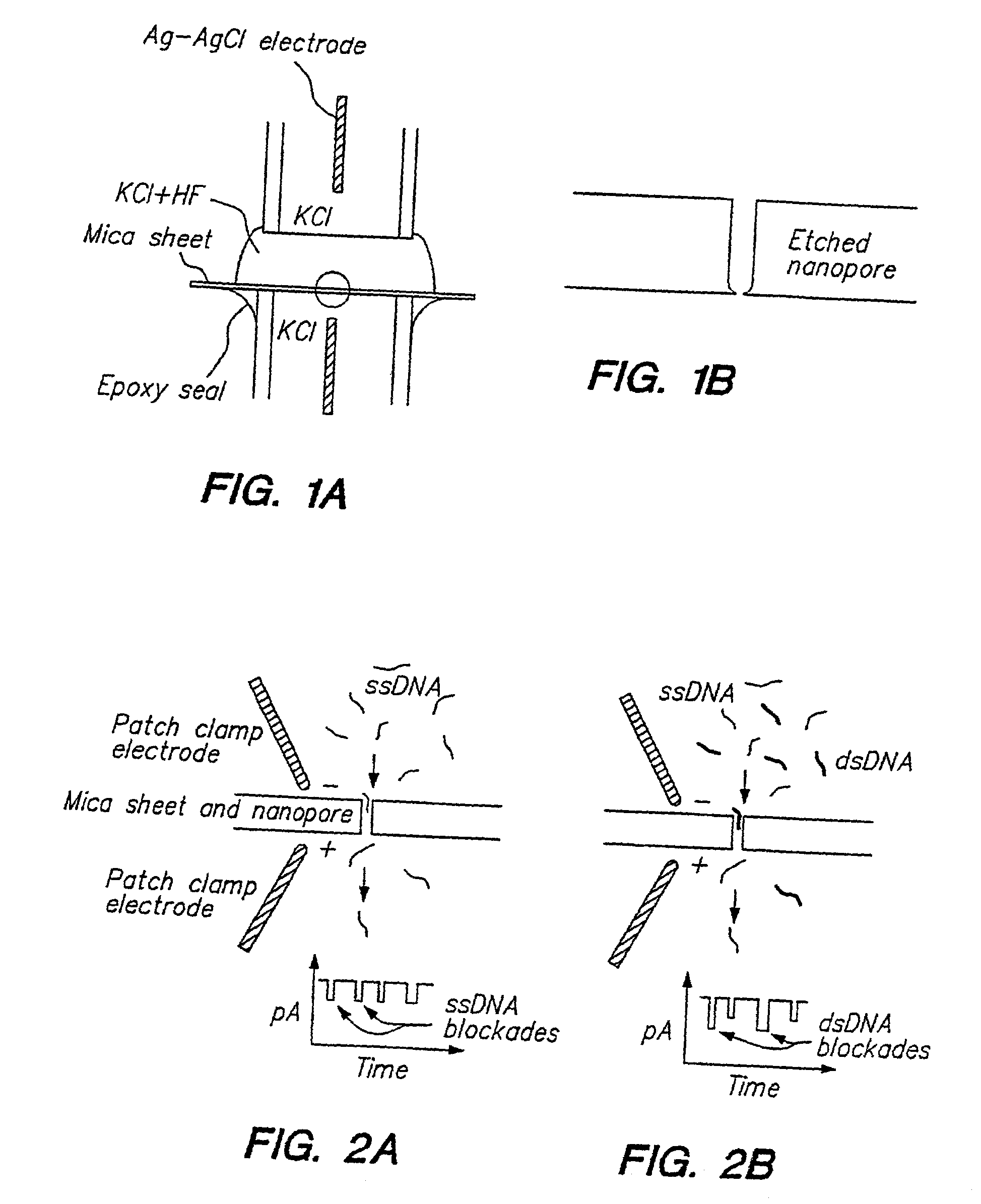
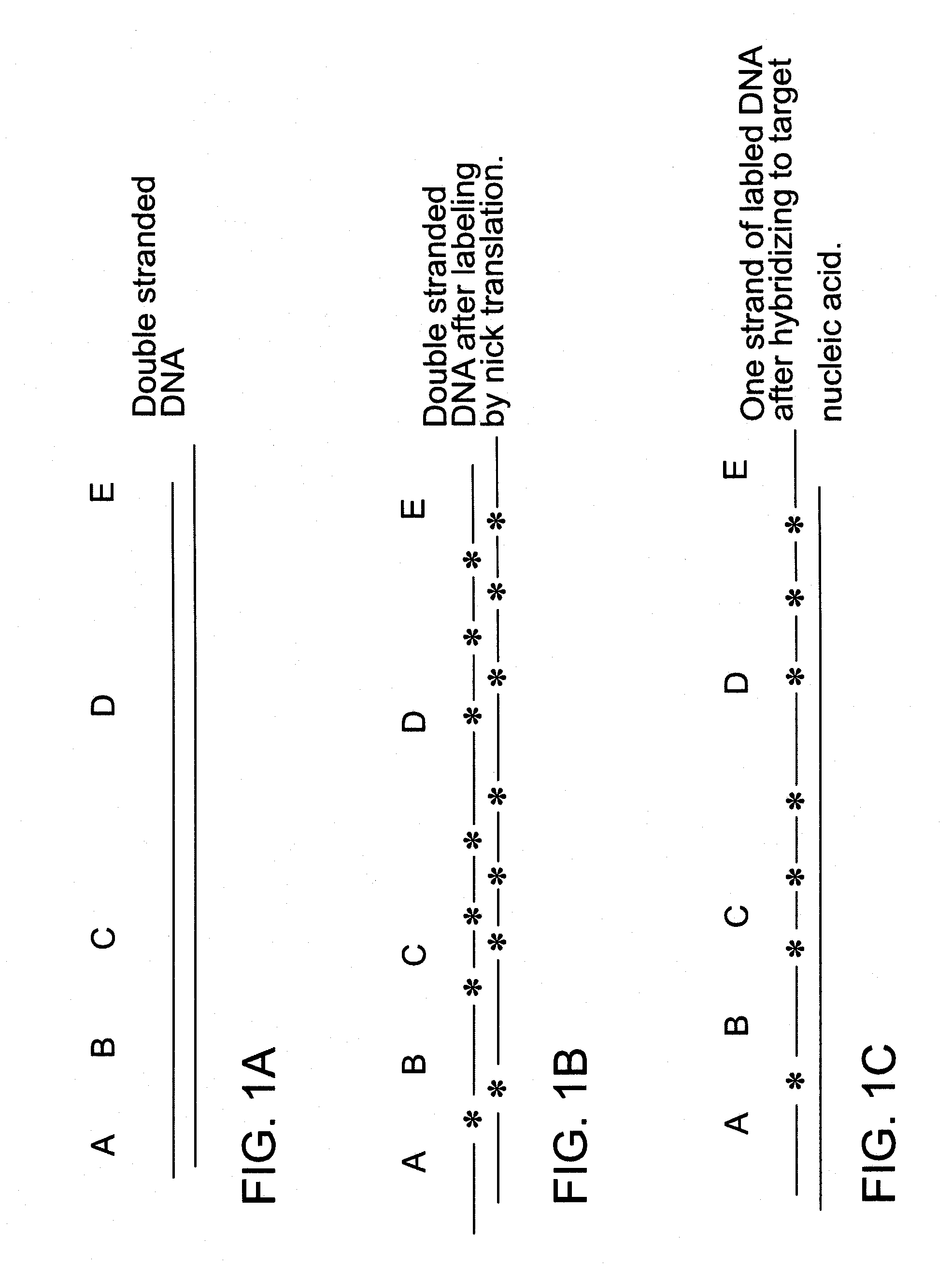
Methods for determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample are provided. In the subject methods, nucleic acids present in a fluid sample are translocated through a nanopore, e.g. by application of an electric field to the fluid sample. The current amplitude through the nanopore is monitored during the translocation process and changes in the amplitude are related to the passage of single- or double-stranded molecules through the nanopore. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the detection of the presence of double-stranded nucleic acids in a sample is desired, e.g. in hybridization assays, such as Northern blot assays, Southern blot assays, array based hybridization assays, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Novel microarray techniques for nucleic acid expression analyses
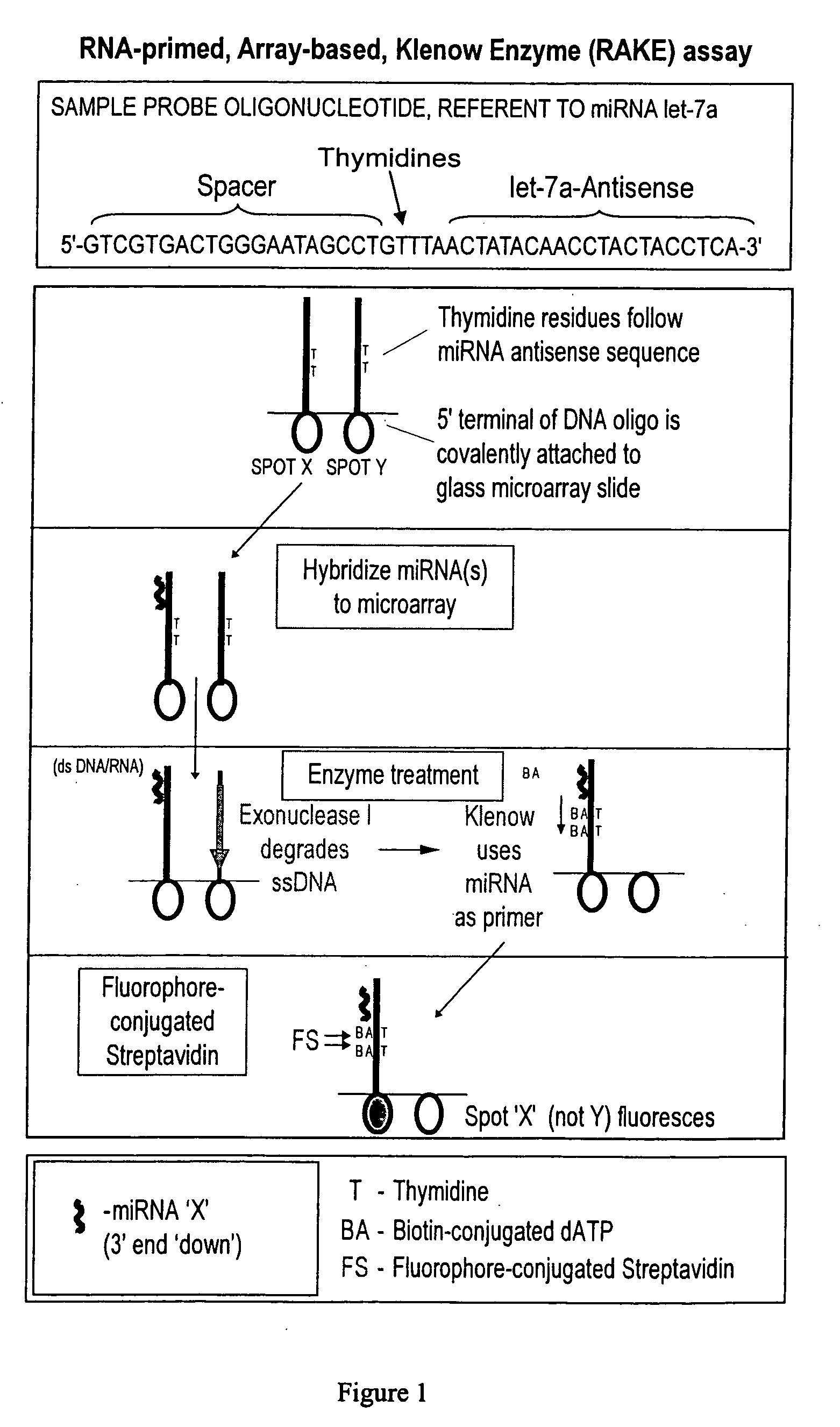
ActiveUS20060078925A1Eliminate biasConvenient experimentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMiRNA GeneExonuclease I
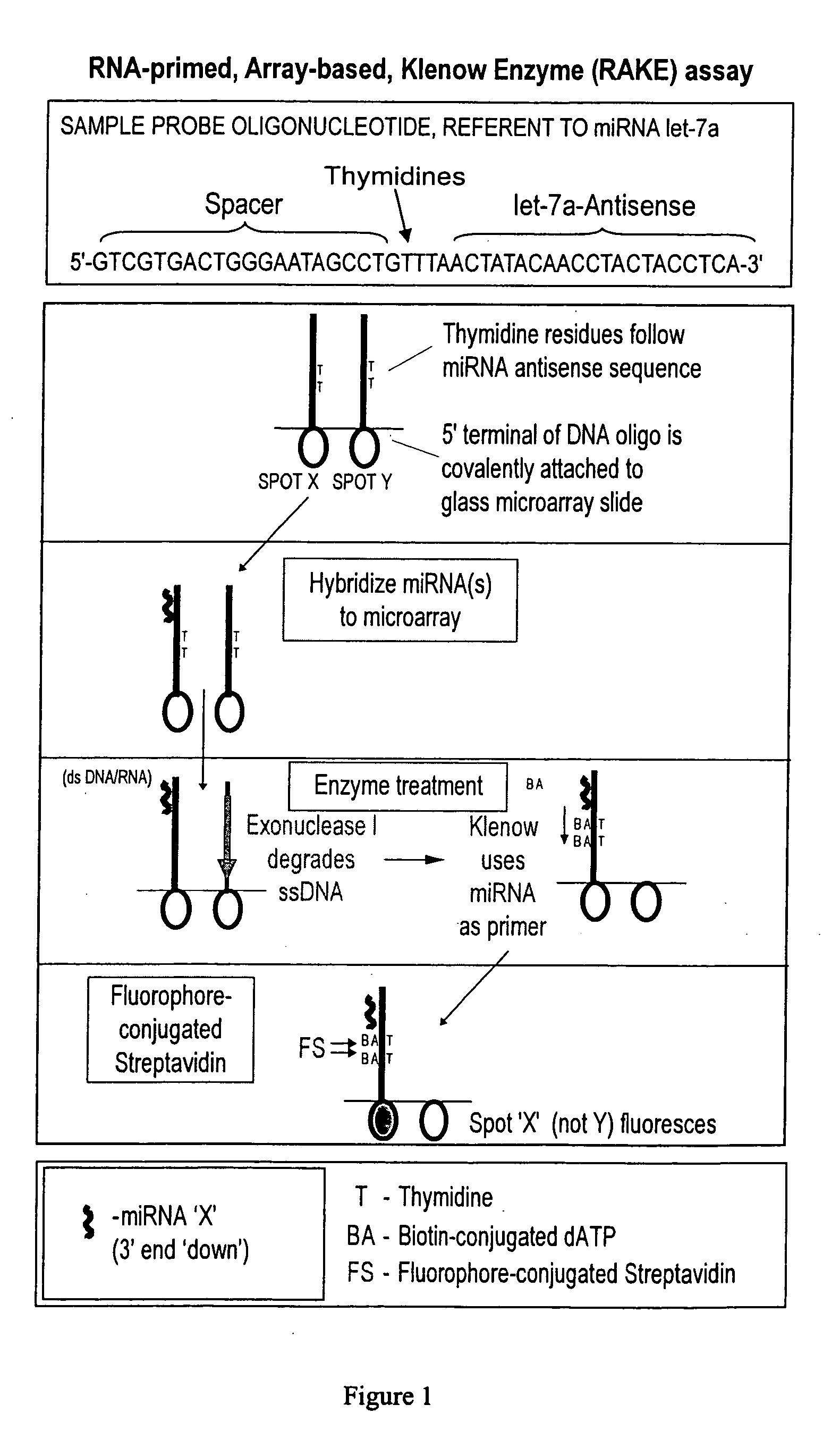
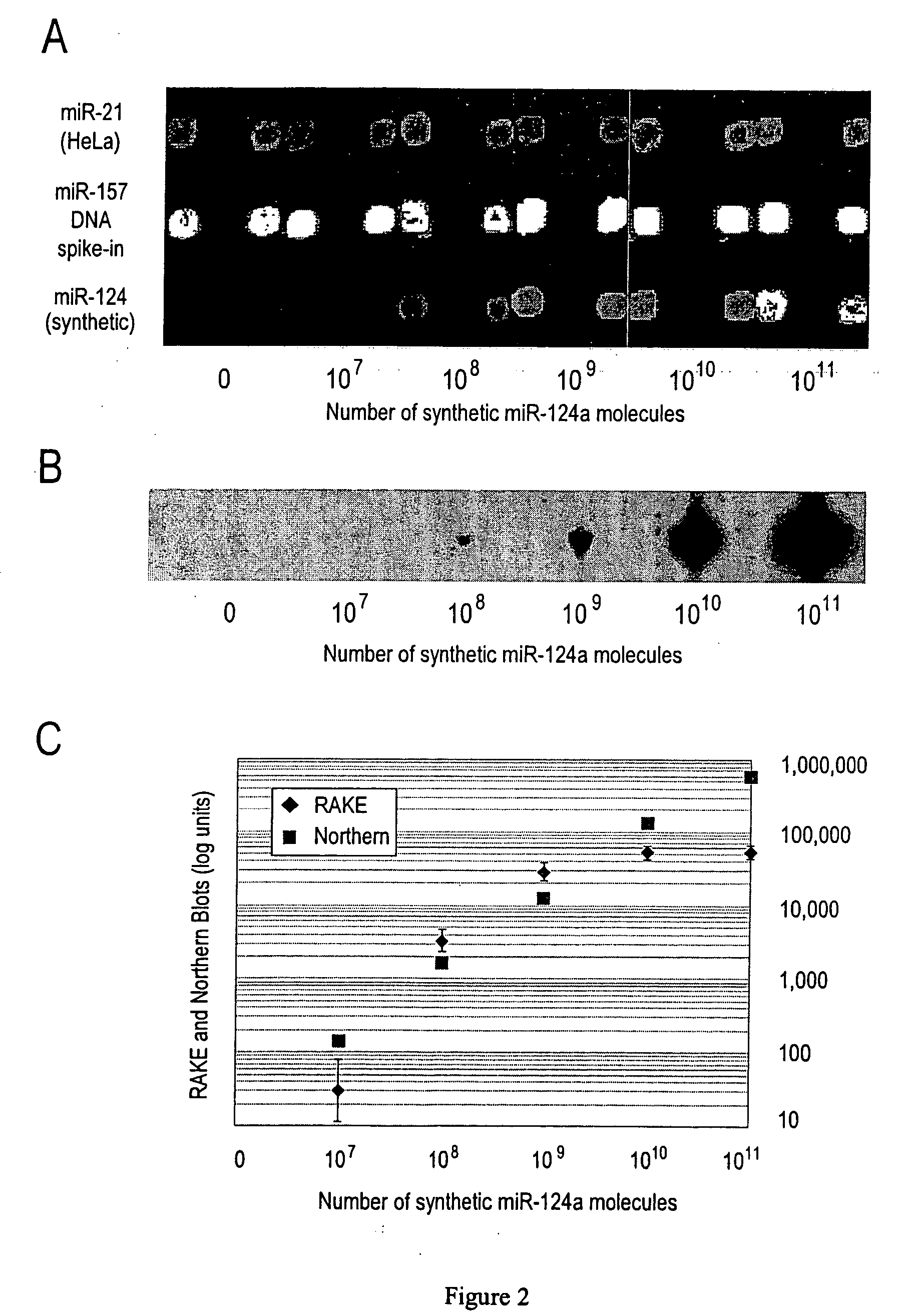
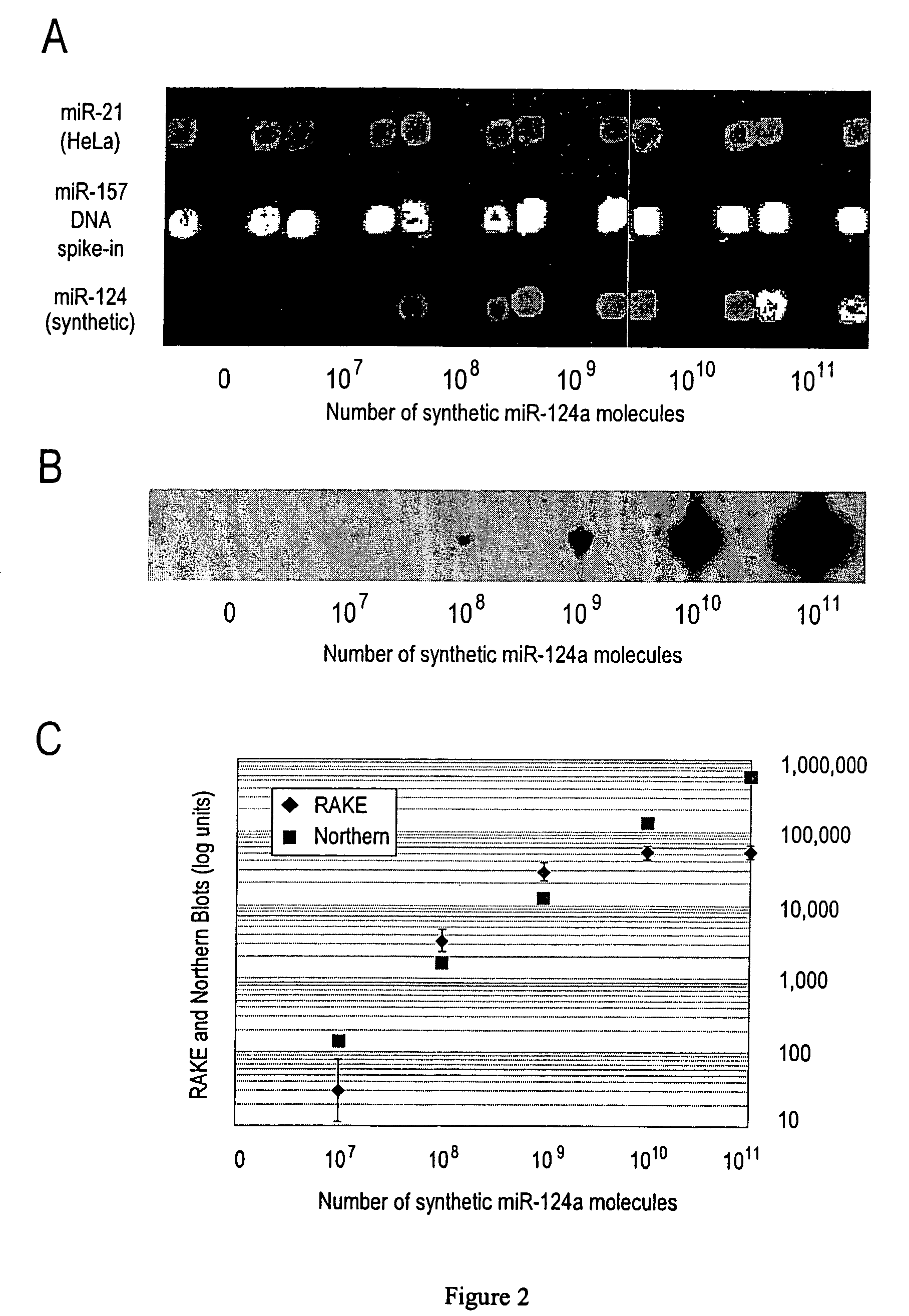
Provided are DNA microarray techniques that allow hybridization without RNA amplification, without using cDNA, and without labeling the nucleic acid prior to hybridization. Referred to as the Double-stranded Exonuclease Protection (DEP) assay, the technique permits the sample RNA to be used directly for hybridization, without manipulation in any way. Further provided is a microarray technique for high-throughput miRNA gene expression analyses, termed the RNA-primed, Array-based, Klenow Enzyme (RAKE) assay. The RAKE assay is a sensitive and specific technique for assessing single-stranded DNA and RNA targets, and offers specific advantages over Northern blots.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase from Hevea brasiliensis and rubber producing method using the same
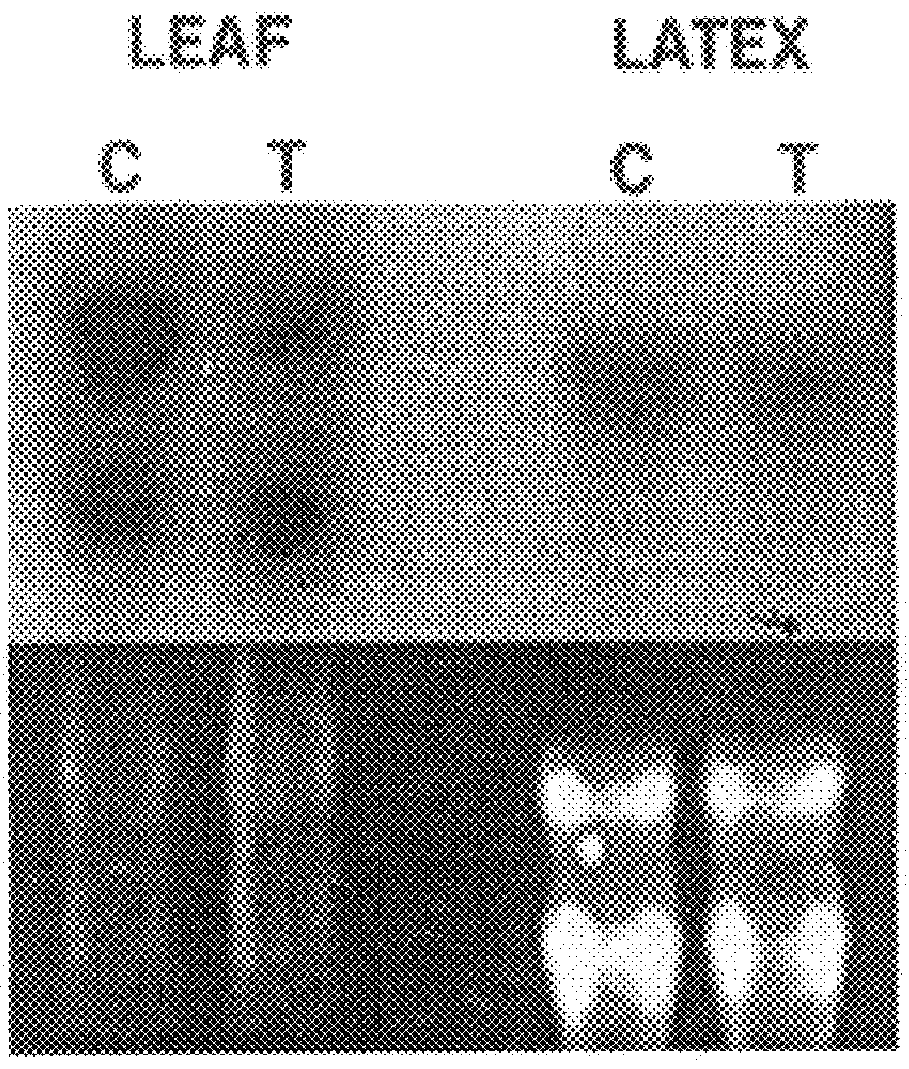
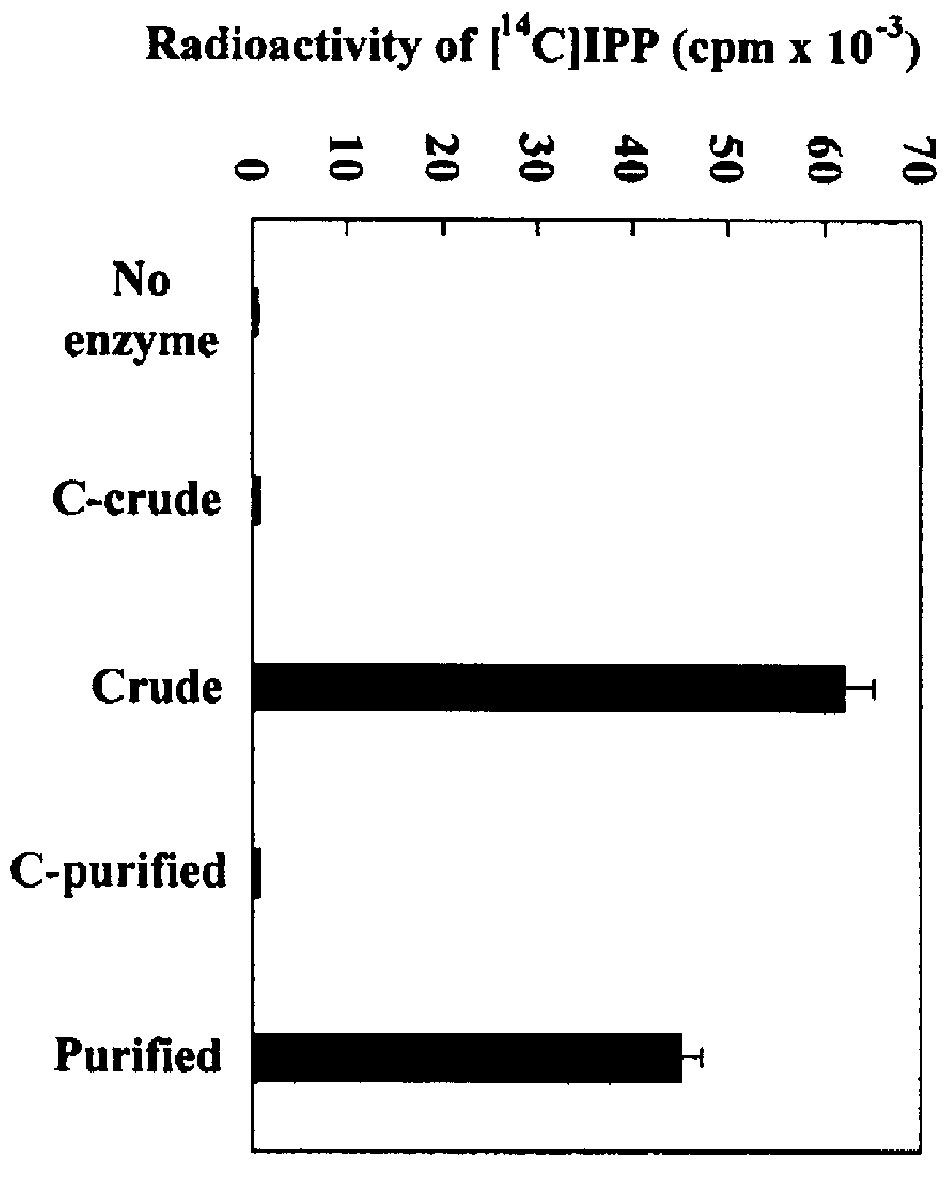
The present invention cloned a cDNA clone encoding isopentenyl diphosphate (hereafter "IPP") isomerase (EC 5.3.3.2) from a cDNA library of Hevea brasiliensis latex. The clone has a continuous open reading frame encoding a peptide of 234 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 26.7 kDa. The deduced protein is acidic with an isoelectric point of 4.7 and shows high sequence identity with other IPP isomerases. The recombinant protein expressed in Escherichia coli showed IPP isomerase activity. In vitro rubber biosynthesis assays using washed rubber particle (WRP) deprived of initiating allylic diphosphates were performed with the addition of IPP isomerase in the reaction mixture. Results revealed that the recombinant IPP isomerase is catalytically active in catalyzing the conversion of IPP to DMAPP, a key activation step of the basic five-carbon isoprene unit in rubber biosynthesis. Southern analysis indicated that the IPP isomerase is encoded by two genes in Hevea rubber tree. In Northern blot analysis, two different sizes of transcripts (1.2 and 0.6 kb) were detected from leaf tissues while only one hybridizing band (1.0 kb) was detected from latex. Analyses of RNA extracted from extruded latex and leaf tissues of the trees wounded with nails showed that wounding did not change the transcript level of IPP isomerase.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
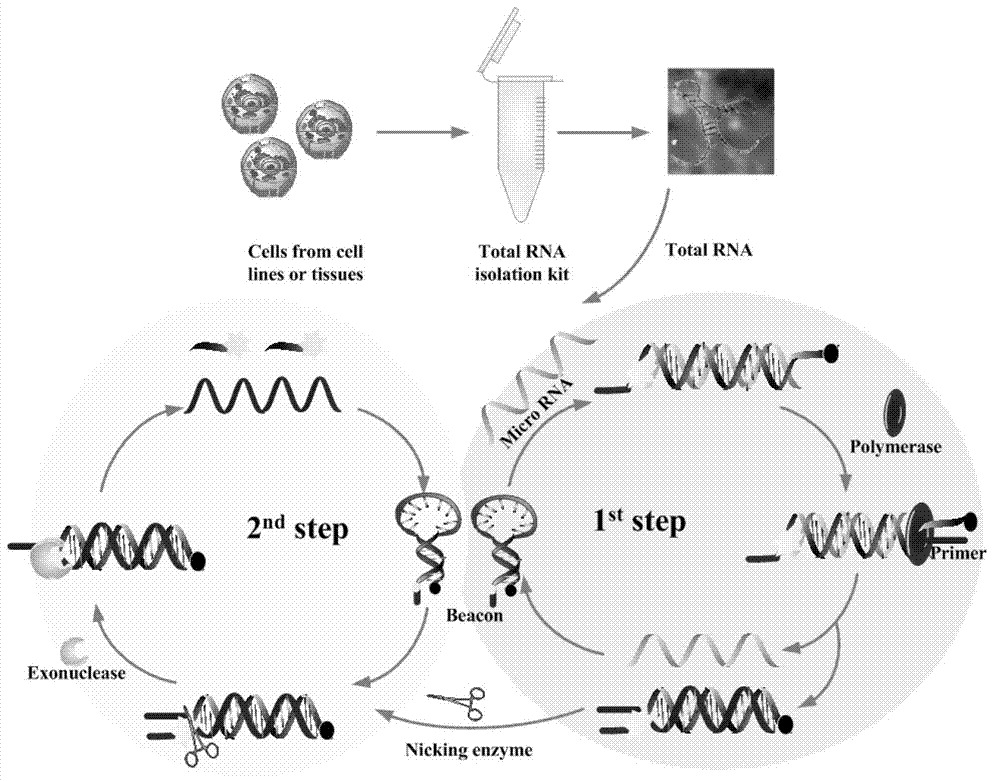
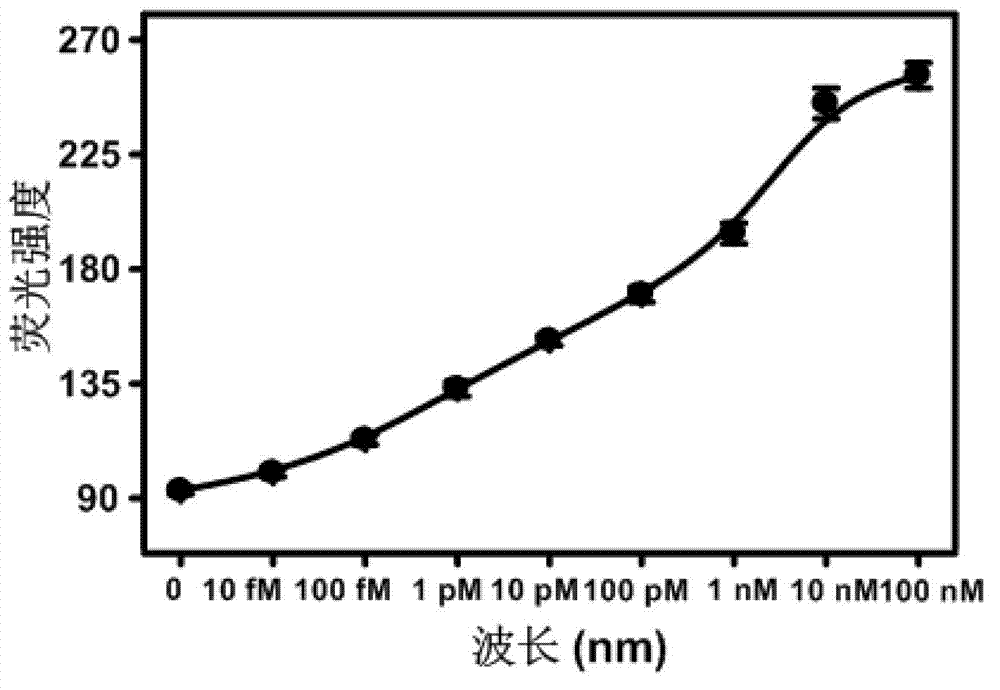
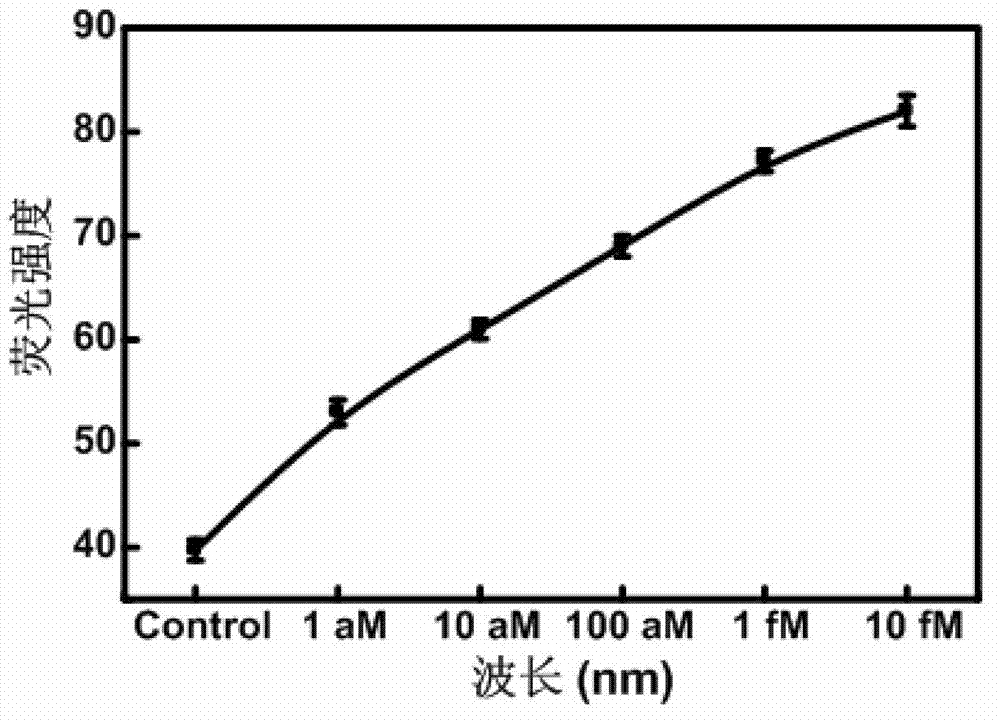
Testing method and kit for secondary circulation amplification of microRNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid)
InactiveCN103088128AHigh sensitivitySimple designMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence designRNA blotting
The invention provides a testing method and a kit for secondary circulation amplification of microRNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid). According to the detection method provided by the invention, a secondary circulation amplification reaction can be finished by only a single operation, the sensitivity is high, and nine RNA chains in a 15-microliter reaction system can be detected; the design is simple, the compounding and modifying of nanometer materials are not related; the noise is low, so that the sensitivity, specificity and generality are increased; compared with a conventional Northern blot assay method and a conventional microarray assay method, the required sample amount is little, and the specificity is excellent; compared with a real-time quantitative PRC (Polymerase Chain Reaction), the method is a thermostatic reaction, so that the test can be realized on a normal fluorescence instrument, the use range of the method is enlarged, and the sequence design is simple and convenient; and the miRNA in a level of a single breast cancer cell can be detected. The technique disclosed by the invention can be used for designing diagnostic kits and devices for tumor.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods of determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample
InactiveUS20020137089A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsRNA blottingAssay
Methods for determining the presence of double stranded nucleic acids in a sample are provided. In the subject methods, nucleic acids present in a fluid sample are translocated through a nanopore, e.g. by application of an electric field to the fluid sample. The current amplitude through the nanopore is monitored during the translocation process and changes in the amplitude are related to the passage of single- or double-stranded molecules through the nanopore. The subject methods find use in a variety of applications in which the detection of the presence of double-stranded nucleic acids in a sample is desired, e.g. in hybridization assays, such as Northern blot assays, Southern blot assays, array based hybridization assays, etc.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Methods for separation and immuno-detection of biomolecules, and apparatus related thereto
InactiveUS8470541B1Evaluating efficacyOptimize patient therapyElectrophoretic profilingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansClinical settingsRadioactive agent
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, methods and apparatus for immunoblotting separated biomolecules, and methods for the use of biomolecules processed via the methods and apparatus of the present invention, including use in a clinical setting. The methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel comprises vertical agarose gel electrophoresis in the first dimension, and the electrophoresis of a novel non-denaturing 3-35% concave gradient polyacrylamide gel in the second dimension. This novel gel can be cast in a modified gel caster that can facilitate the pouring of multiple gels simultaneously. The methods and apparatus for immunblotting are useful with any type of immunoblotting, including Western blot, Northern blot, and Southern blot analyses. These methods and apparatus provide safe, efficient and cost-effective immunoblots, while facilitating the reduction of exposure to toxic or radioactive materials, as well as the disposal of those materials.
Owner:BOSTON HEART DIAGNOSTICS
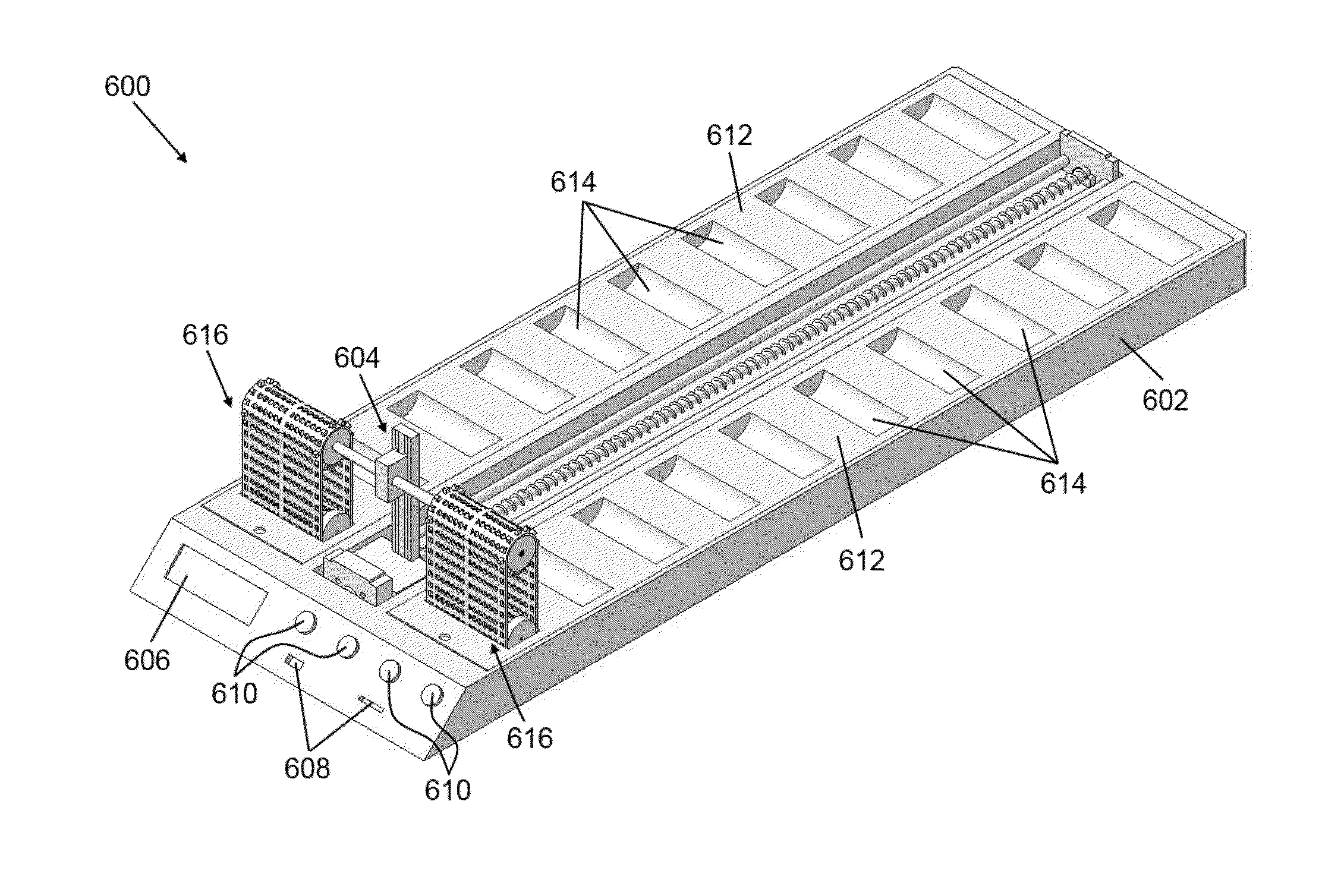
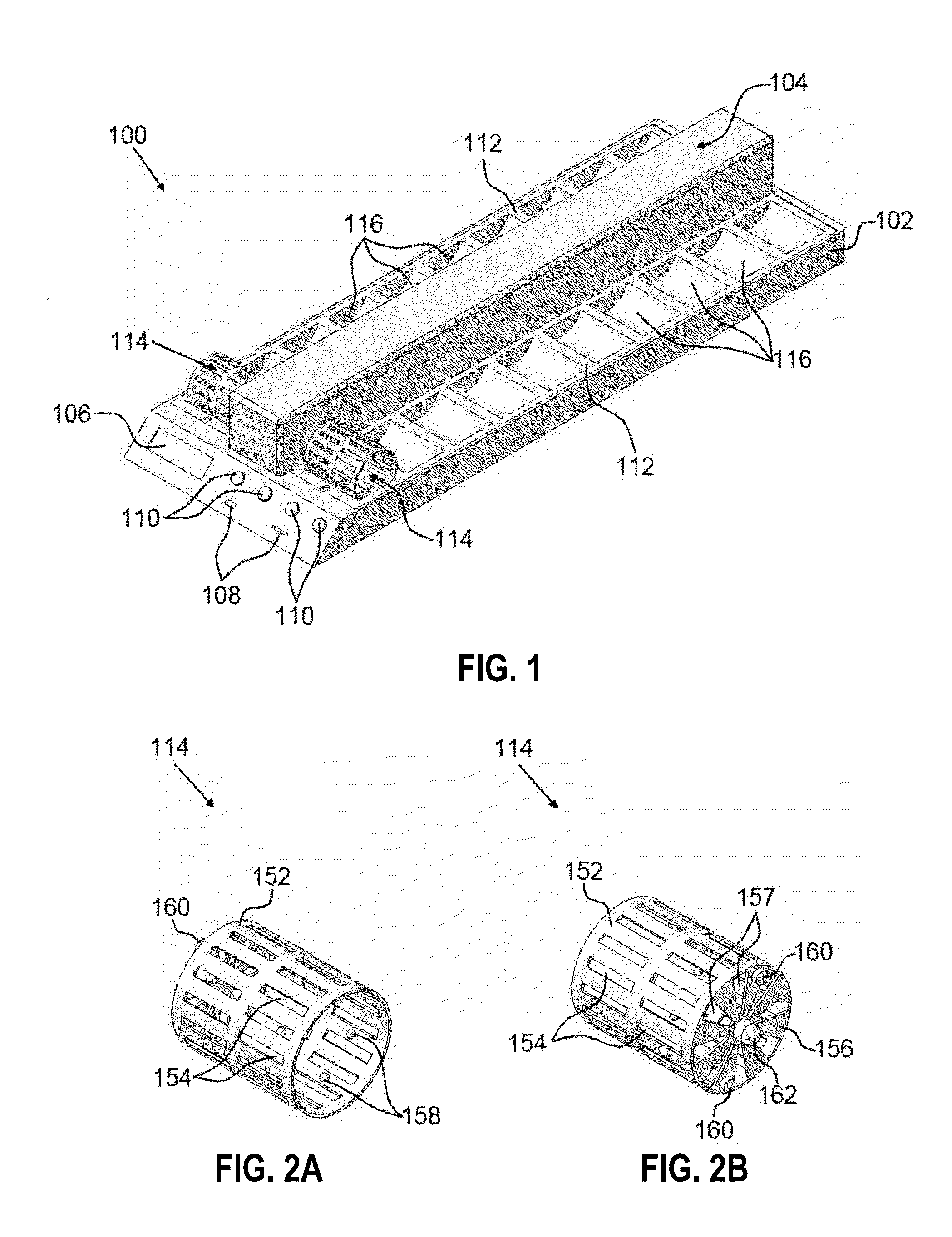
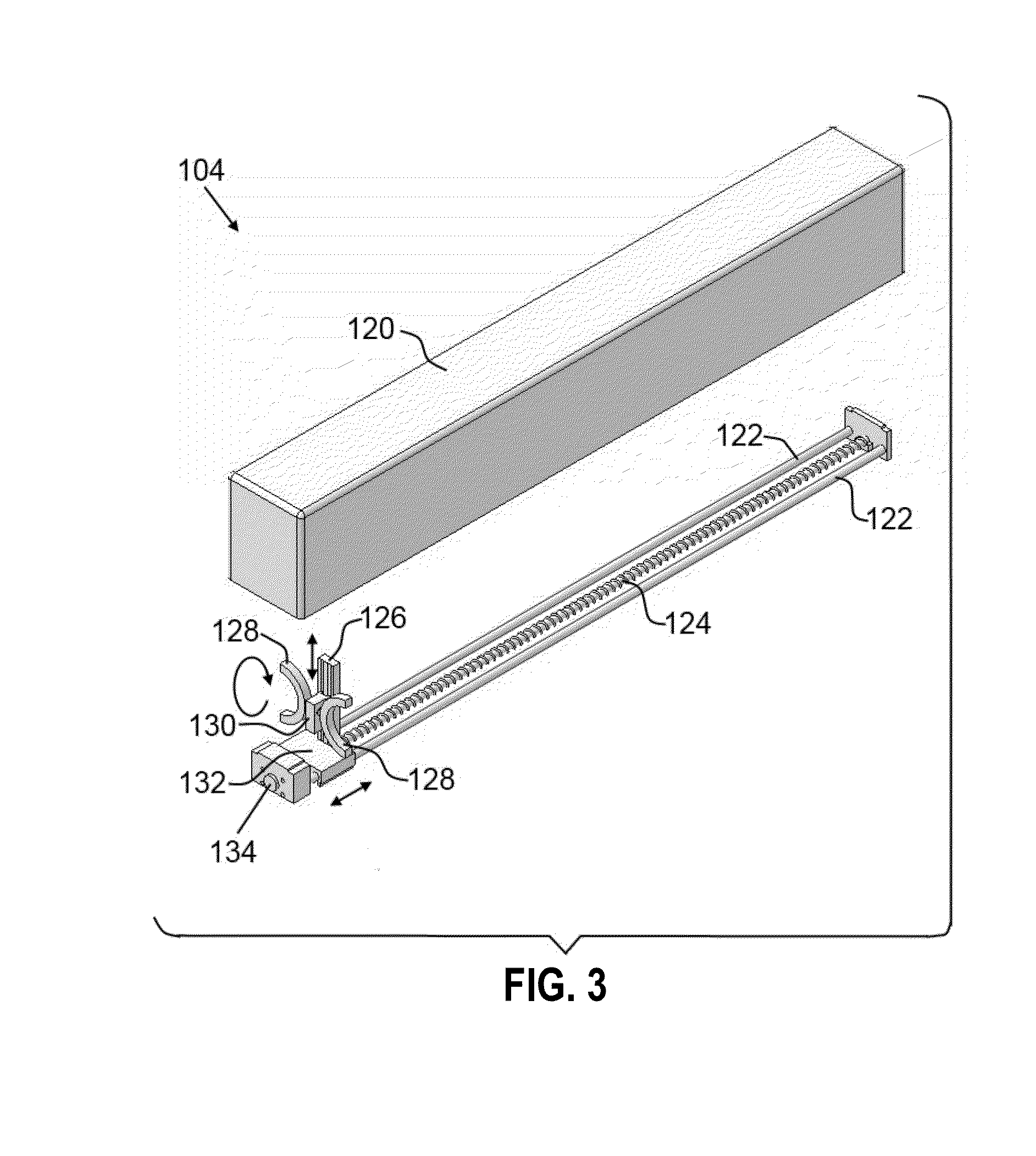
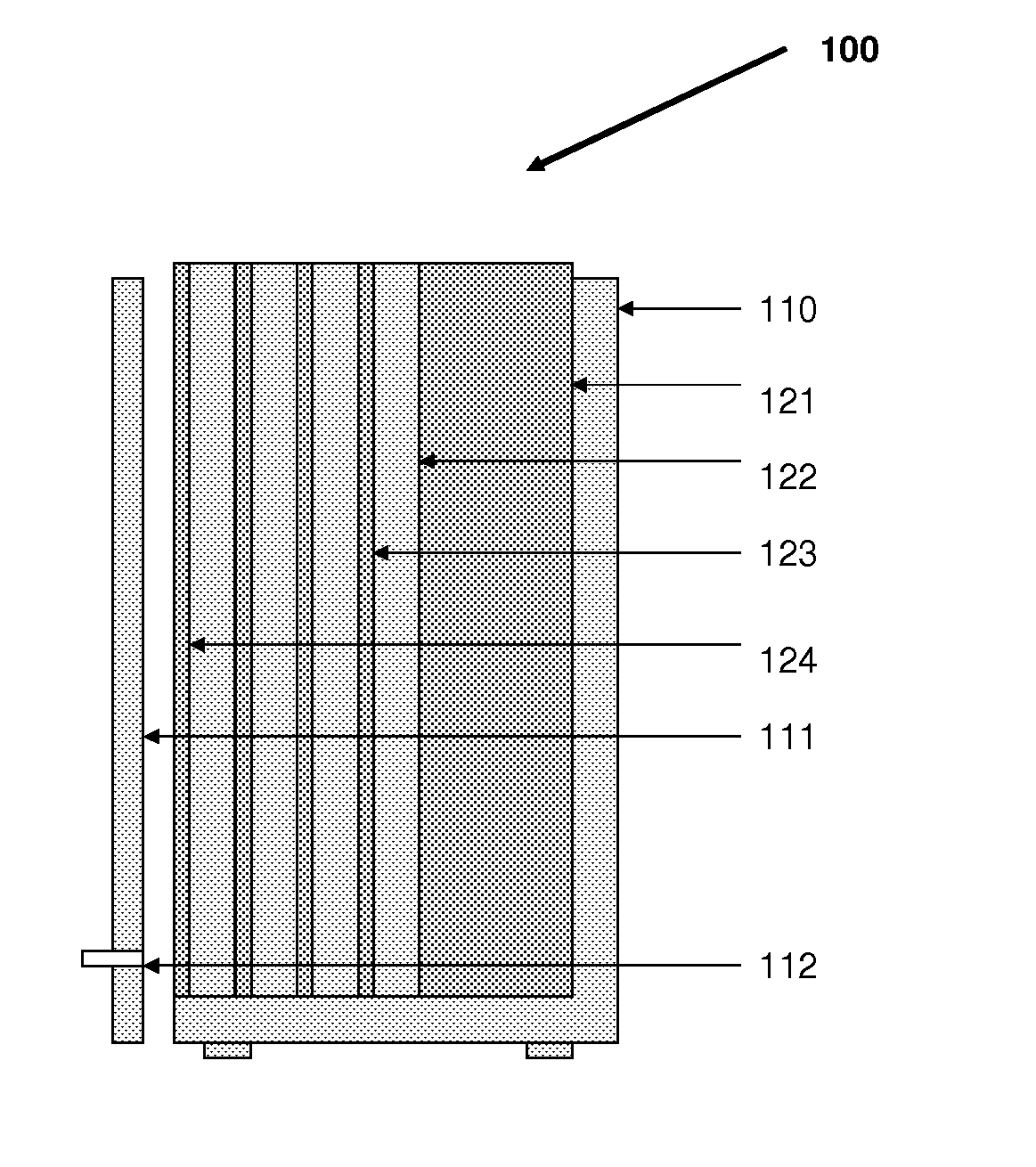
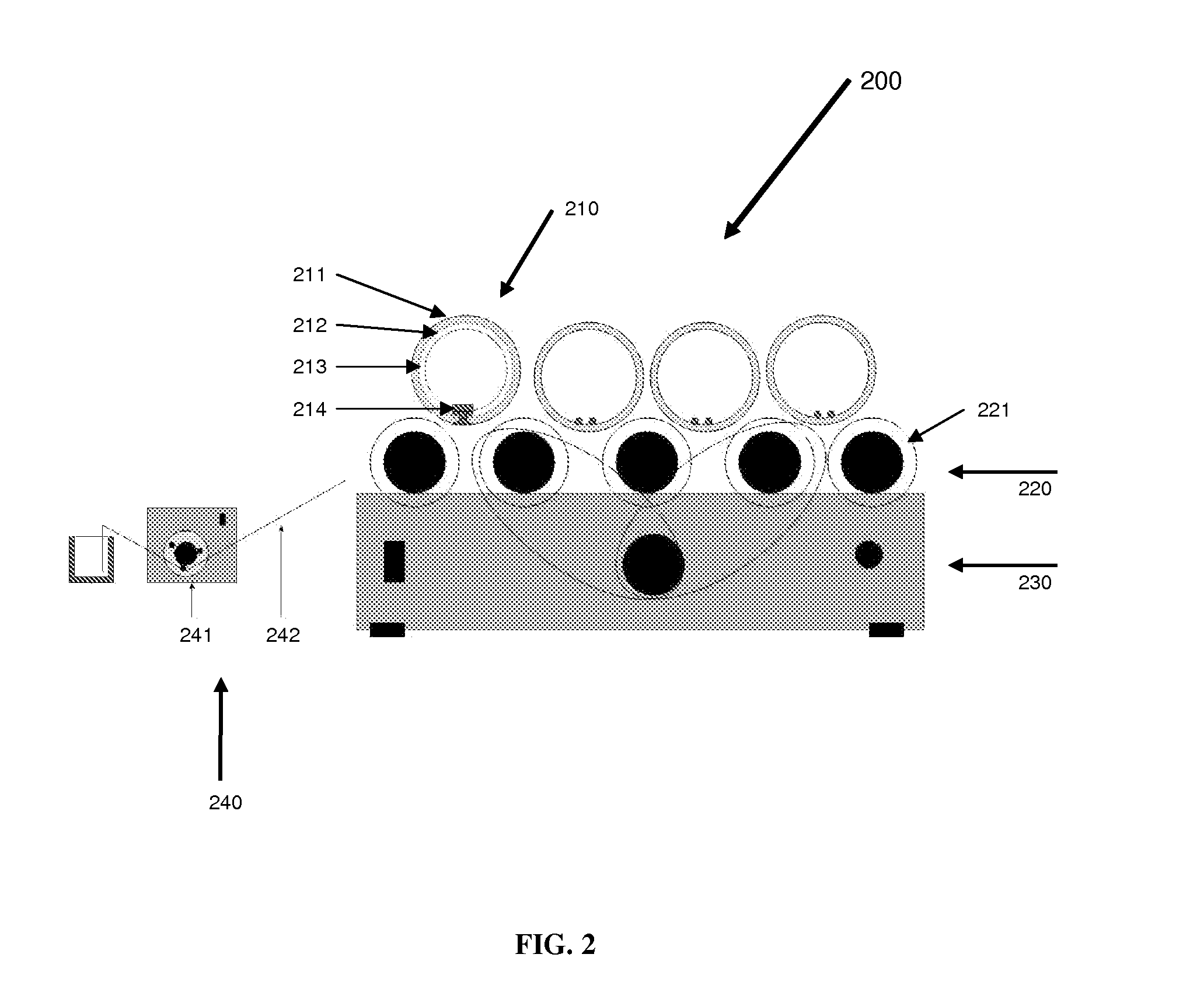
Apparatus for processing biological samples and method thereof
ActiveUS20130203072A1Avoid cloggingShorten the timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsComputer scienceAutomatic processing
The present invention provides devices, apparatuses and methods for automated processing of biological samples. This invention provides automated devices and automated methods of sequentially treating a biological sample with processing fluids in more than one washing basin. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of western blot processing. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of Southern blot processing. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of northern blot processing. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of staining biomolecules on solid supports. In some embodiments, the invention provides automated devices and automated methods of nucleic acid separation and isolation.
Owner:TIAN FENG +2
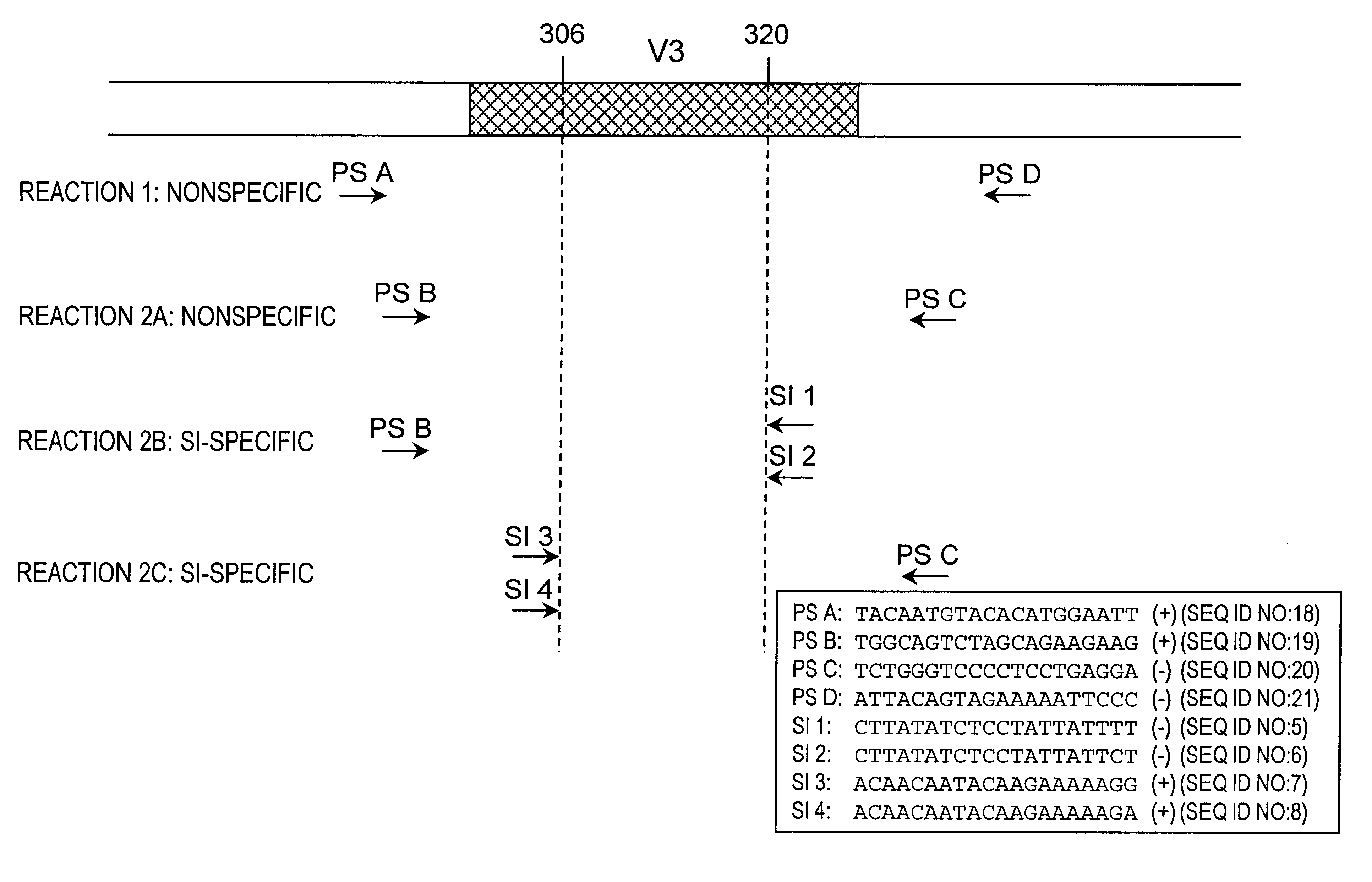
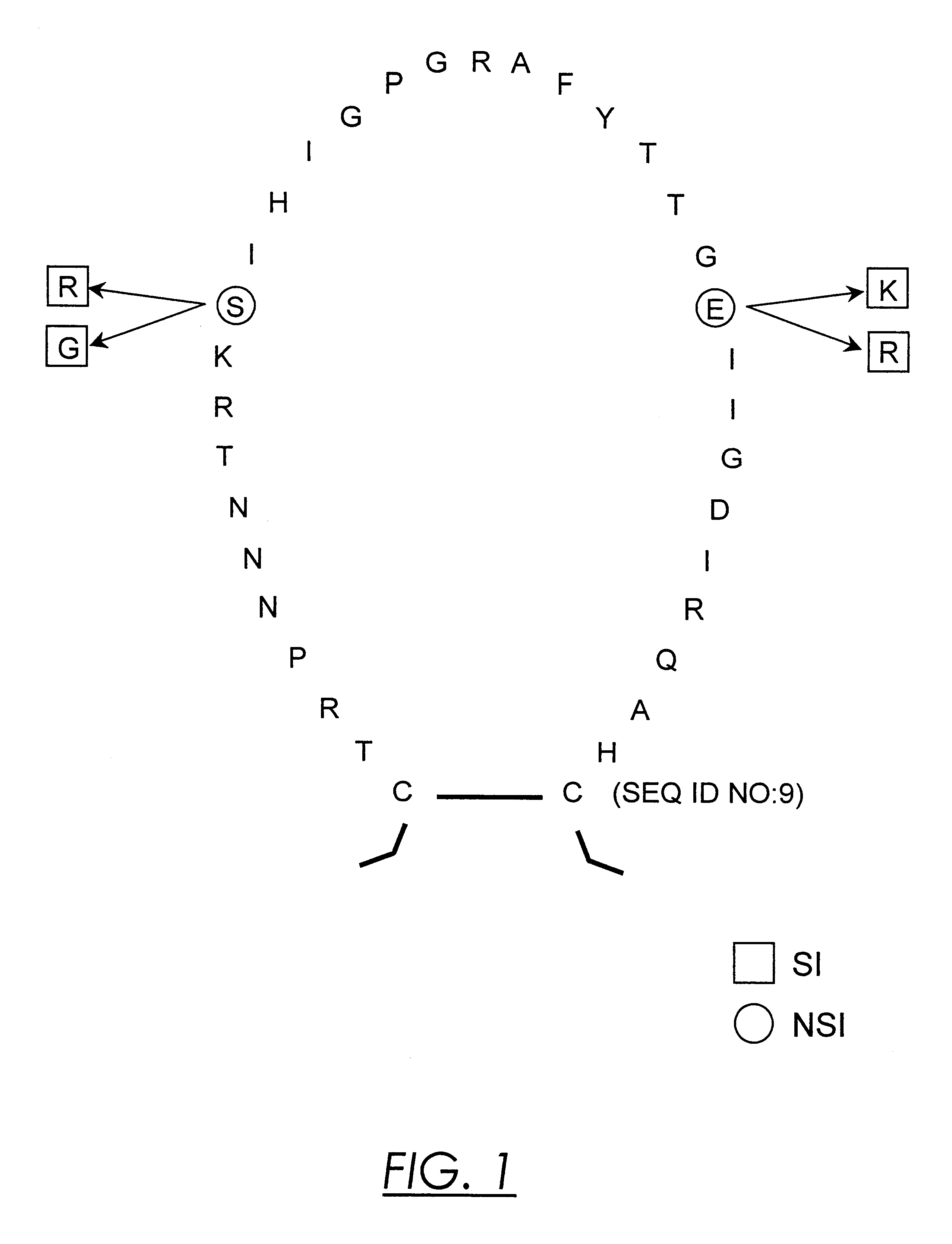
Nucleic acids and methods for the discrimination between syncytium inducing and non syncytium inducing variants of the human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS6379881B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeteroduplexImmunodeficiency virus
This invention is in the area of molecular biology / virology and presents oligonucleotides with nucleotide-sequences specific for SI HIV-1 strains. These oligonucleotides may be used for in vitro determination of biological phenotype of HIV-1 strain in biological material from HIV-infected individuals by a number of techniques such as Southern and Northern blot analysis, PCR, NASBA, in situ hybridization, branched DNA hybridization, heteroduplex tracing hybridization and liquid hybridizations. HIV-1 phenotyping may i.e. be used as a diagnostic marker for disease progression or for testing efficacy of antiviral therapy.
Owner:AKZO NOBEL NV +1
Methods for separation and immuno-detection of biomolecules, and apparatus related thereto
InactiveUS20130248370A1Safe and efficient and cost-effectiveEfficient and cost-effectiveCellsFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesClinical settingsRadioactive agent
Disclosed are methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel electrophoresis, methods and apparatus for immunoblotting separated biomolecules, and methods for the use of biomolecules processed via the methods and apparatus of the present invention, including use in a clinical setting. The methods and apparatus for separation of biomolecules via two-dimensional gel comprises vertical agarose gel electrophoresis in the first dimension, and the electrophoresis of a novel non-denaturing 3-35% concave gradient polyacrylamide gel in the second dimension. This novel gel can be cast in a modified gel caster that can facilitate the pouring of multiple gels simultaneously. The methods and apparatus for immunblotting are useful with any type of immunoblotting, including Western blot, Northern blot, and Southern blot analyses. These methods and apparatus provide safe, efficient and cost-effective immunoblots, while facilitating the reduction of exposure to toxic or radioactive materials, as well as the disposal of those materials.
Owner:BOSTON HEART DIAGNOSTICS
Artificial genes for use as controls in gene expression analysis systems
InactiveUS20060115851A1Easy to analyze and useSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA blottingPositive control
Method of producing universal controls for use in gene expression analysis systems such as macroarrays, real-time PCR, northern blots, SAGE and microarrays. The controls are generated either from near-random sequence of DNA, or from intergenic or intronic regions of a genome. Twenty-three specific control sequences are also disclosed. Also presented are methods of using these controls, including as negative controls, positive controls, and as calibrators of a gene expression analysis system.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE SV CORP
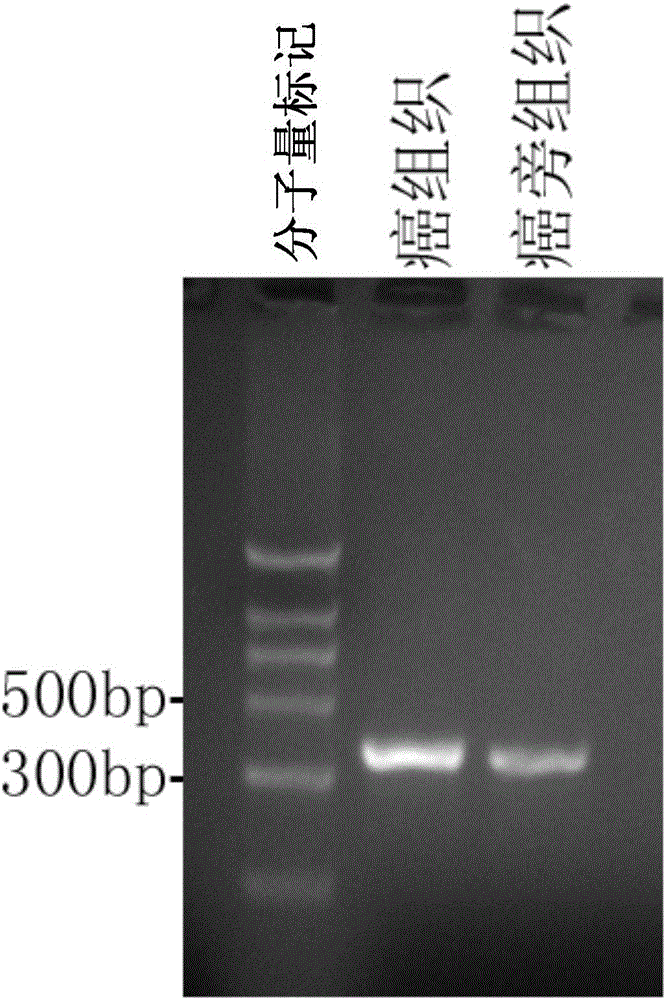
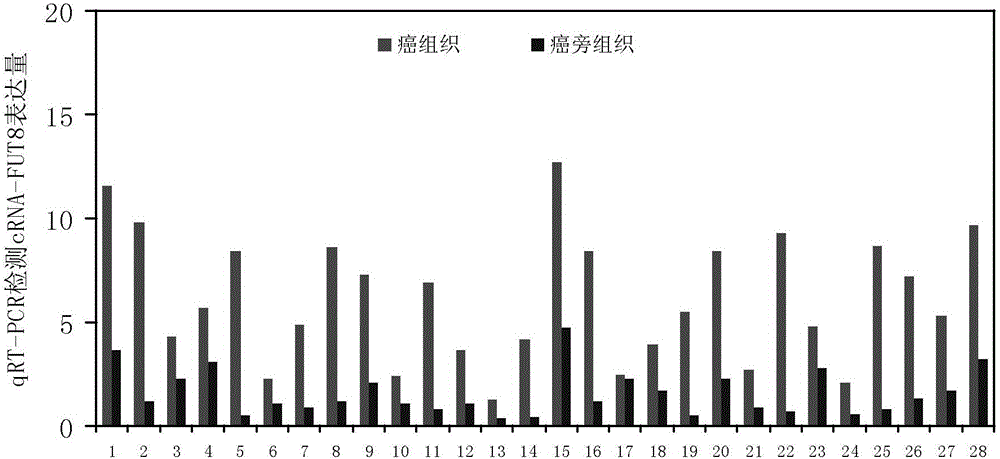
cRNA-FUT8 detection applied to hepatocellular carcinoma screening and application thereof
InactiveCN105802964AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationLymphatic SpreadHepatocellular carcinoma
The invention mainly relates to cRNA-FUT8 detection applied to hepatocellular carcinoma screening and application thereof. A specific method comprises the steps that a gene chip technique is utilized to carry out cRNA-FUT8 expression profile differential analysis on carcinoma para-carcinoma tissue cells to screen out an obvious high-expression circular RNA, cRNA-FUT8, in a hepatocellular carcinoma tissue of a person. Compared with a para-carcinoma normal tissue, the circular RNA has obvious high expression in the hepatocellular carcinoma tissue of the person. Furthermore, a real-time quantitative PCR, Northern Blot experiment further proves that the expression quantity of the cRNA-FUT8 in the hepatocellular carcinoma tissue of the person is obviously higher than that in the normal tissue. The new-researched cRNA-FUT8 can provide a novel view for a research on a relapsing and metastasis mechanism of the hepatocellular carcinoma and also provides a new evaluating index and a new intervening target spot for diagnosing, preventing and curing the hepatocellular carcinoma.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
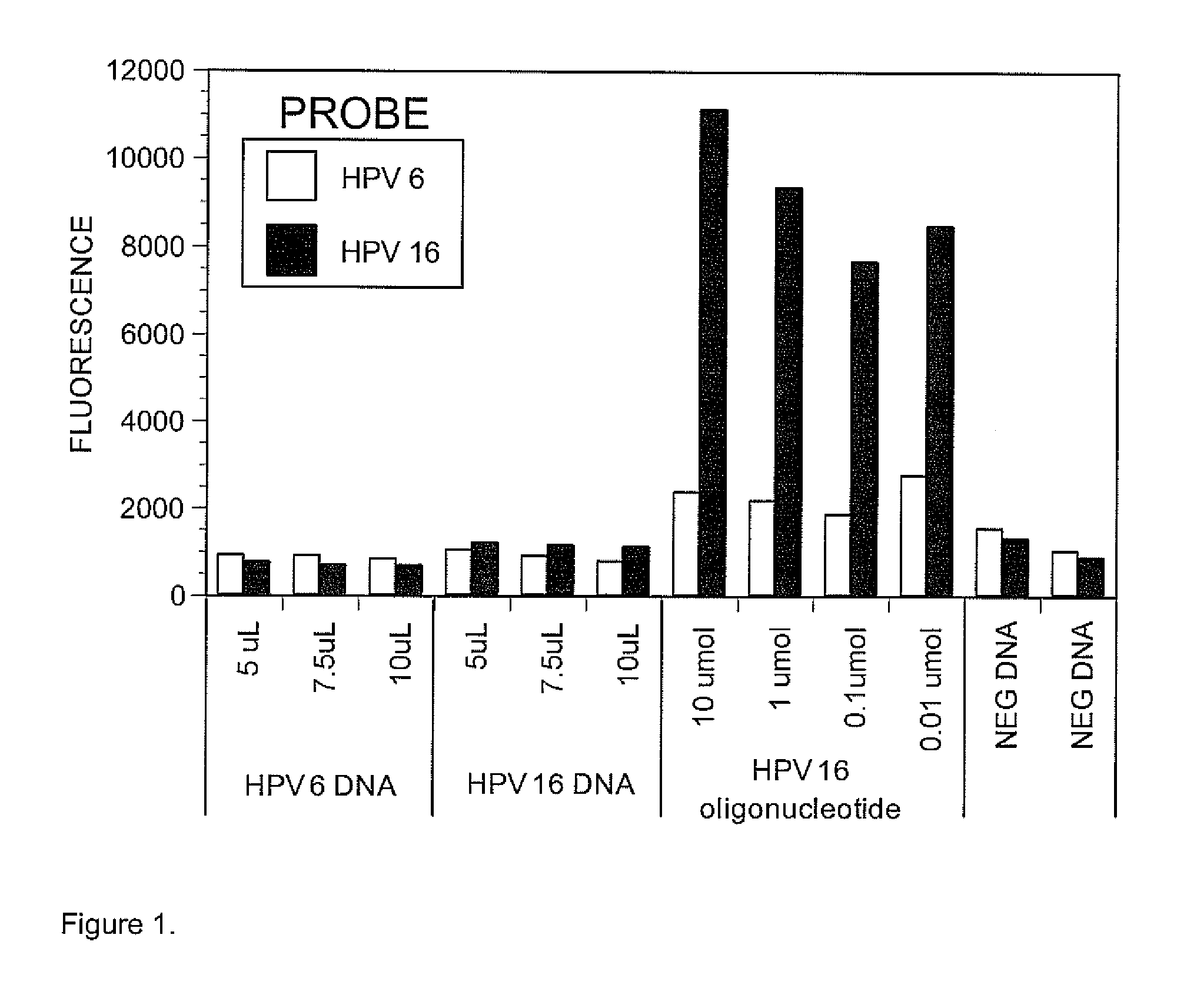
Set of Probes for the Detection and Typing of 46 Human Papillomavirus Mucosal Types
InactiveUS20130143751A1Accurate prevalence resultImprove automationNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman papillomavirusNorthern blot
We have developed a set of probes to detect and identify 46 types of mucosal human papillomaviruses (HPV). These probes recognize the variable region comprised between the 2 conserved regions of the published GP5+ / GP6+ set of PCR primers. The example described in this application, called NML Luminex genotyping method, uses a multiplex assay based on nested PCR amplification and the Luminex xMAP technology. The 46 probes have been shown to hybridize, as intended, to the DNA derived from the following HPV types: 6, 11, 13, 16, 18, 26, 30, 31, 32, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 43, 44, 45, 51, 52, 53, 54, 56, 58, 59, 61, 62, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 74, 81, 82, 83, 84, 85, 86, 87, 89, 90, 91 and 97. The hybridization of each probe is specific for each type without any cross hybridization among types and it is sensitive enough to allow detection of PCR products for genotyping of HPV DNA contained in clinical samples. We also present a validation of the NML Luminex method against direct sequencing of HPV types and against the Roche Linear Array, a leading commercial method for HPV genotyping. The probes described here are suitable for use in other assays based on hybridization with labelled target HPV DNA, including, but not limited to, Southern and Northern blots, reverse line blot hybridization, DNA microarray, or ELISA.
Owner:SEVERINI ALBERTO +1
Methods for producing nucleic acid hybridization probes that amplify hybridization signal by promoting network formation
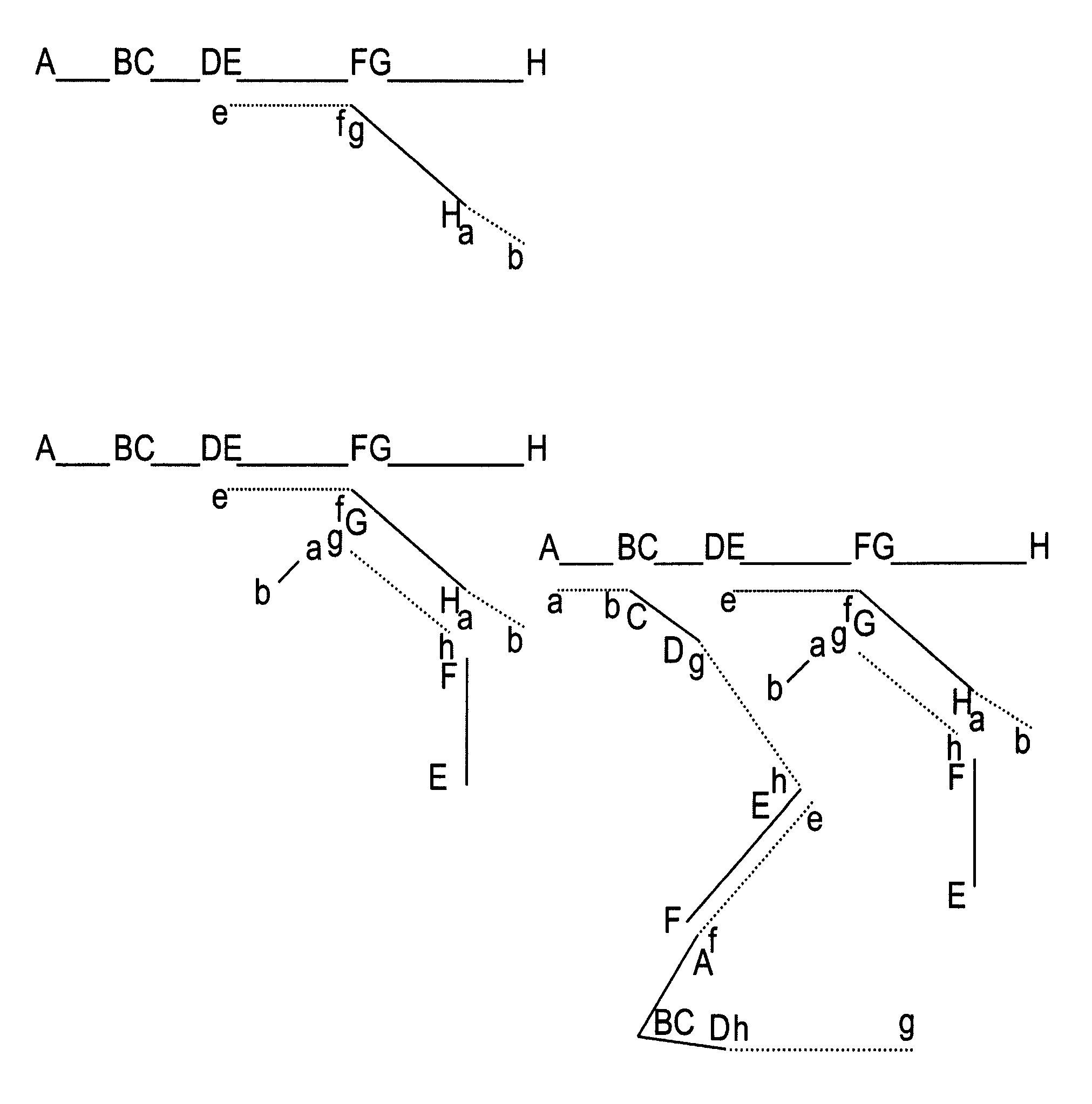
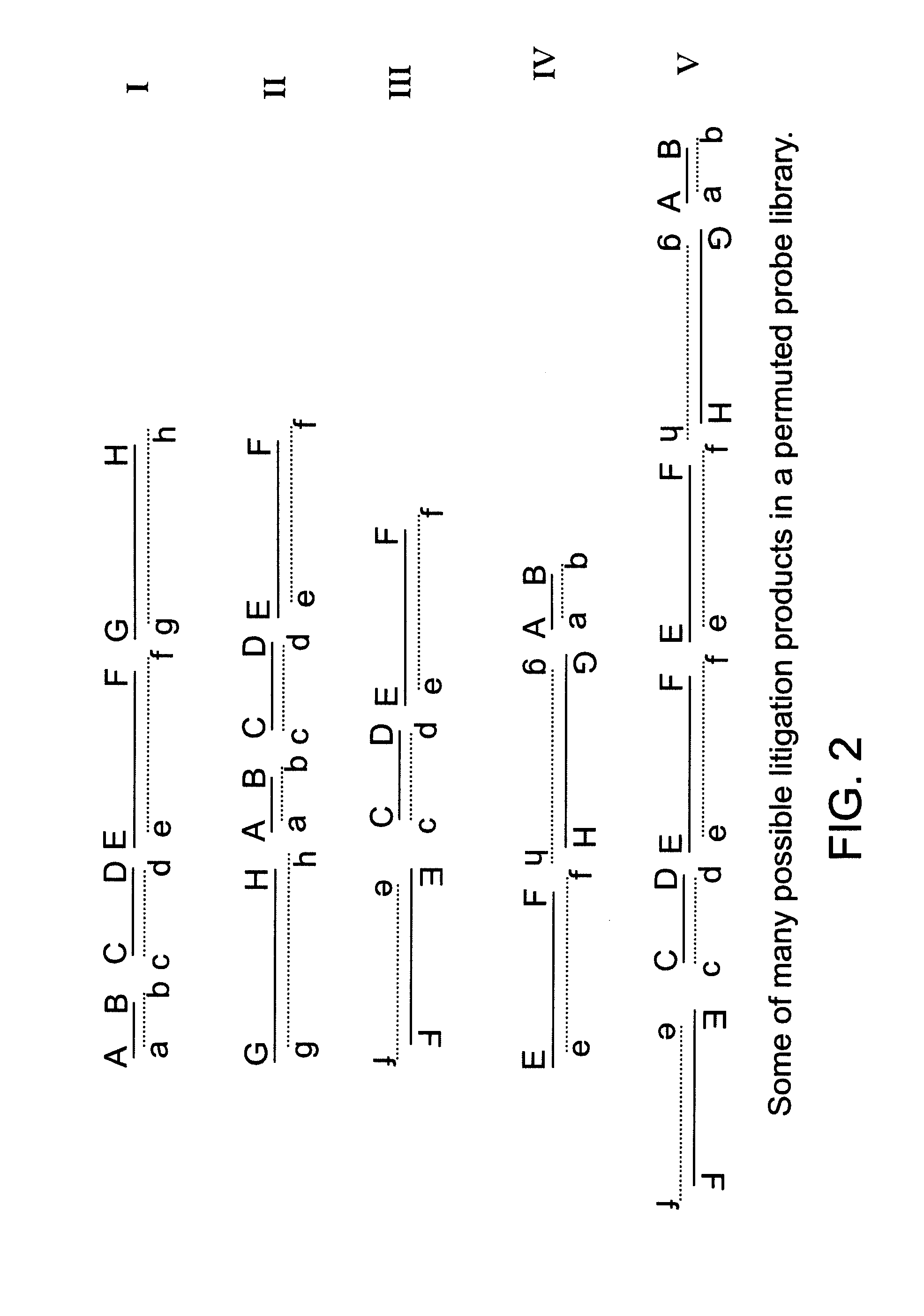
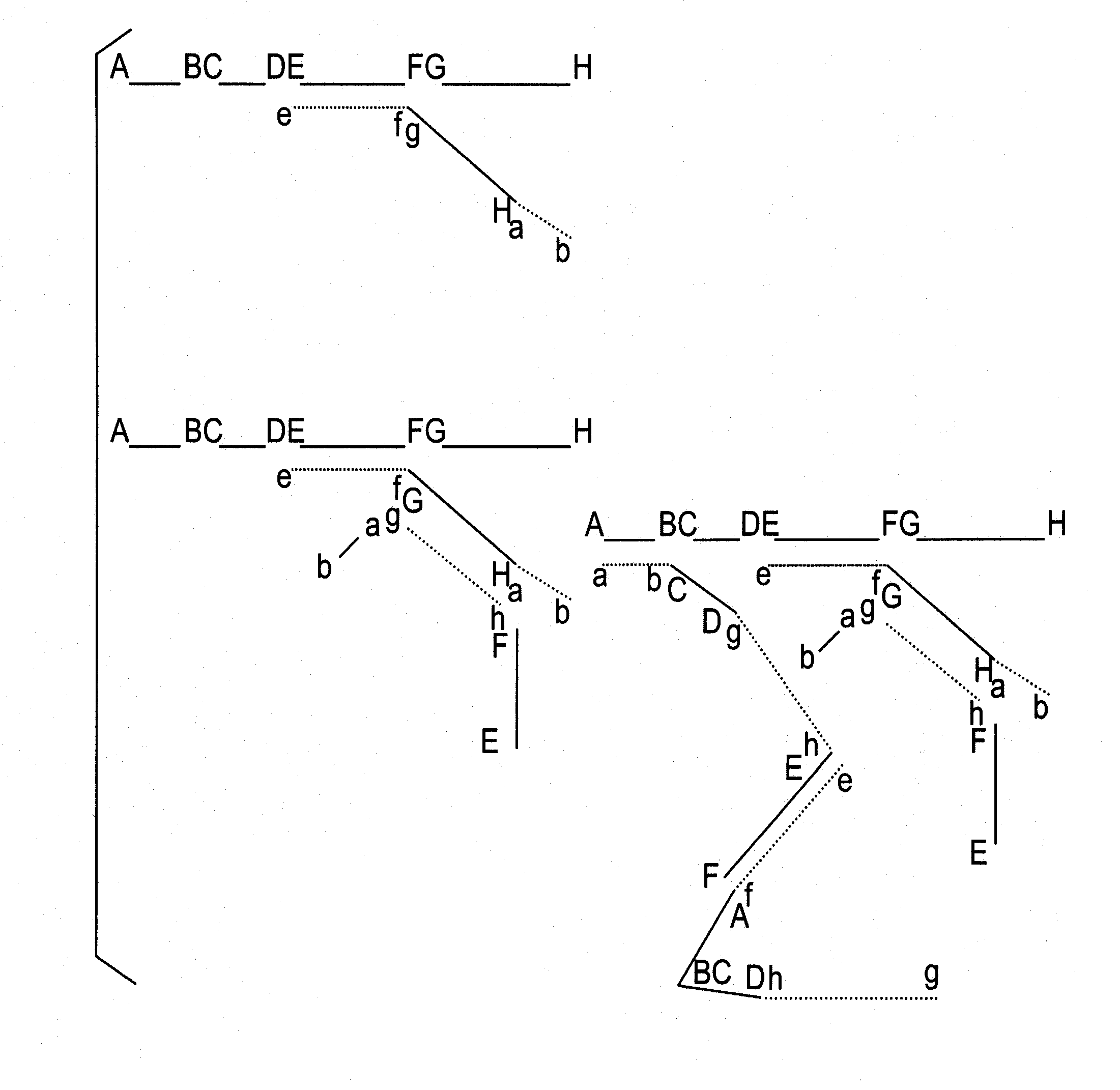
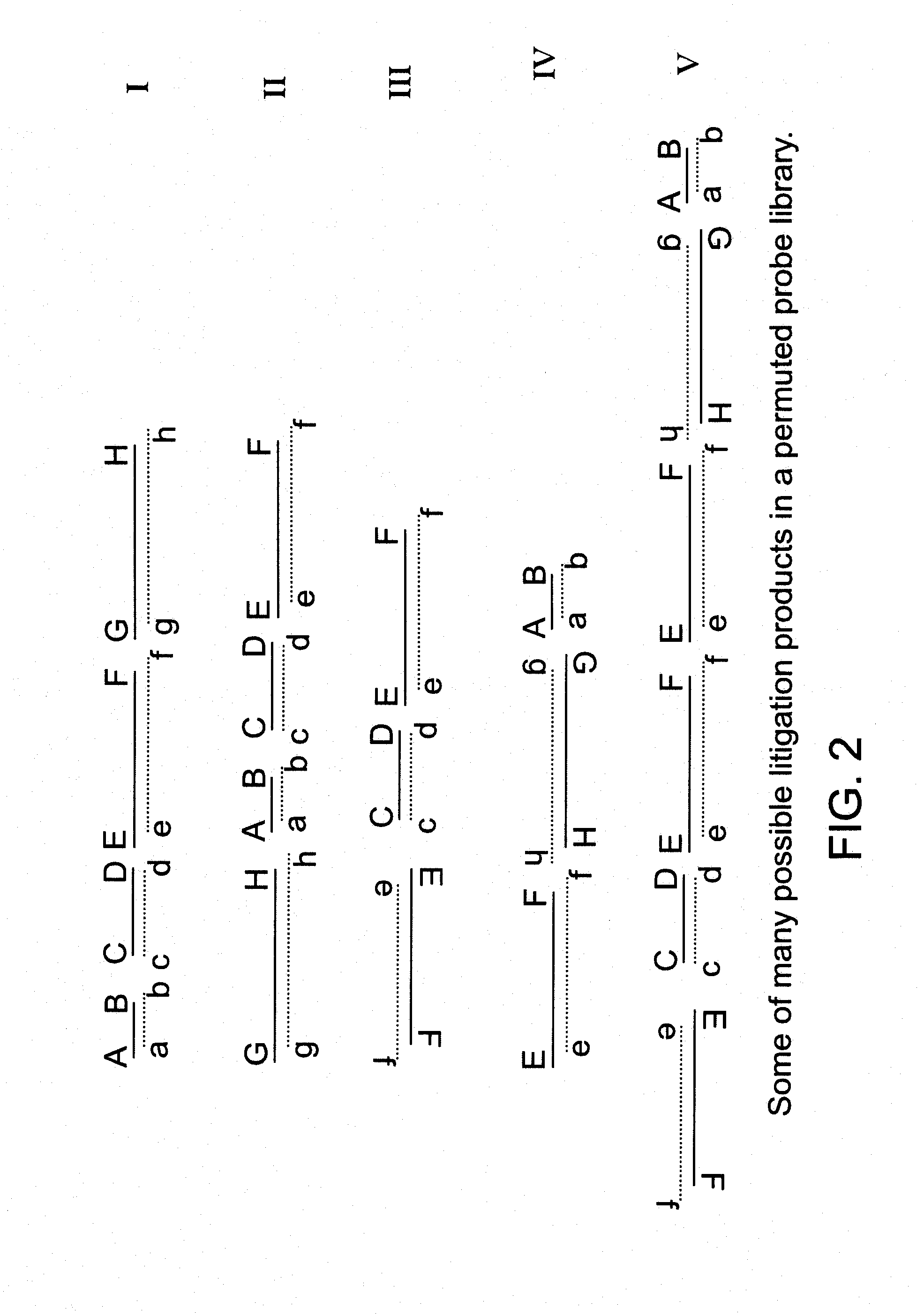
This invention describes methods for the generation of nucleic acid probes that improve the sensitivity of hybridization assays. The sensitivity increase results from structural modifications of nucleic acids that promote network formation during hybridization with the result that a single target molecule becomes attached to a complex of many probe molecules. The structural modification involves fragmentation of the probe nucleic acid followed by joining the fragments together such that their order and orientation and number is altered from the original probe molecule. The result is the generation of permuted probe libraries. Probes made according to this invention can be used in many kinds of hybridization assays including Southern blots. Northern blots. Dot blots. Nucleic acid Array hybridization, ‘in situ’ hybridization with fluorescent or other labels (FISH) and various kinds of sandwich hybridization assays.
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Design of artificial genes for use as controls in gene expression analysis systems
Method of producing controls for use in gene expression analysis systems such as macroarrays, real-time PCR, northern blots, SAGE and microarrays. The controls are generated either from near-random sequence of DNA, or from inter- or intragenic regions of a genome. Ten specific control sequences are also disclosed. Also presented are methods of using these controls, including as negative controls, positive controls, and as calibrators of a gene expression analysis system.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE SV CORP
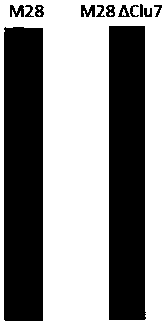
Small RNA (ribonucleic acid) related to virulence of Brucella and application of small RNA in preparation of weak virulence Brucella
ActiveCN109593761ADownregulation of virulenceUnderstand the pathogenic mechanismAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBALB/cRNA blotting
The invention discloses a small RNA (ribonucleic acid) related to virulence of Brucella and application of the small RNA in preparation of the weak virulence Brucella. The application Northern blot proves an sRNA Clu7 exists in a virulent Brucella strain M28, a sRNA defective strain M28 delta Clu7 is constructed by adopting a homologous recombination method, and the affection of the sRNA on the virulence of the M28 is evaluated by taking a mouse macrophage RAW264.7 and a Balb / c mouse as models. A result shows that the replication capability and the survival capability of the virulent strain M28 in the mouse macrophage RAW264.7 and the mouse can be remarkably reduced after deficiency of the sRNA. When in a fifth week of inoculation, the M28 delta Clu7 is completely eliminated from a body ofthe mouse, and the virulence of the M28 delta Clu7 is remarkably lowered in comparison with the M28. A mouse virulence attacking protection experiment shows that the protection effect that the mouseresists the infection of the virulent strain M28 by the immune M28 delta Clu7 can reach the protection force of a vaccine strain M5-90. The results indicate that the sRNA Clu7 has a significant decisive effect on the virulence of the Brucella. The small RNA has a significant promoting effect on a mechanism of disclosing the virulence of the Brucella. According to the small RNA, a novel technical means is provided for research and development of a novel candidate vaccine strain of the Brucella.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Therapeutical effect of atabrine and substitutes thereof on hepatitis B
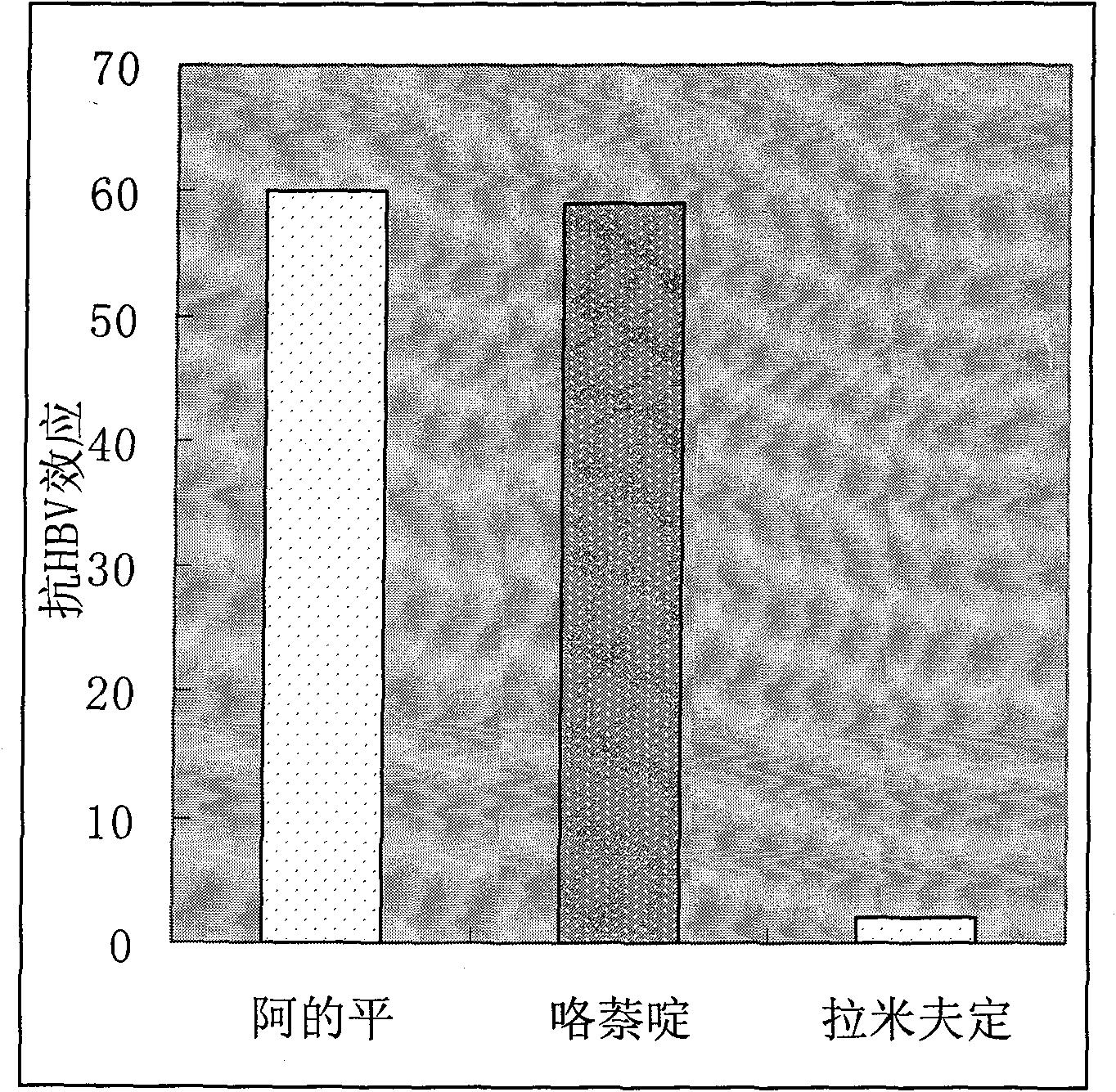
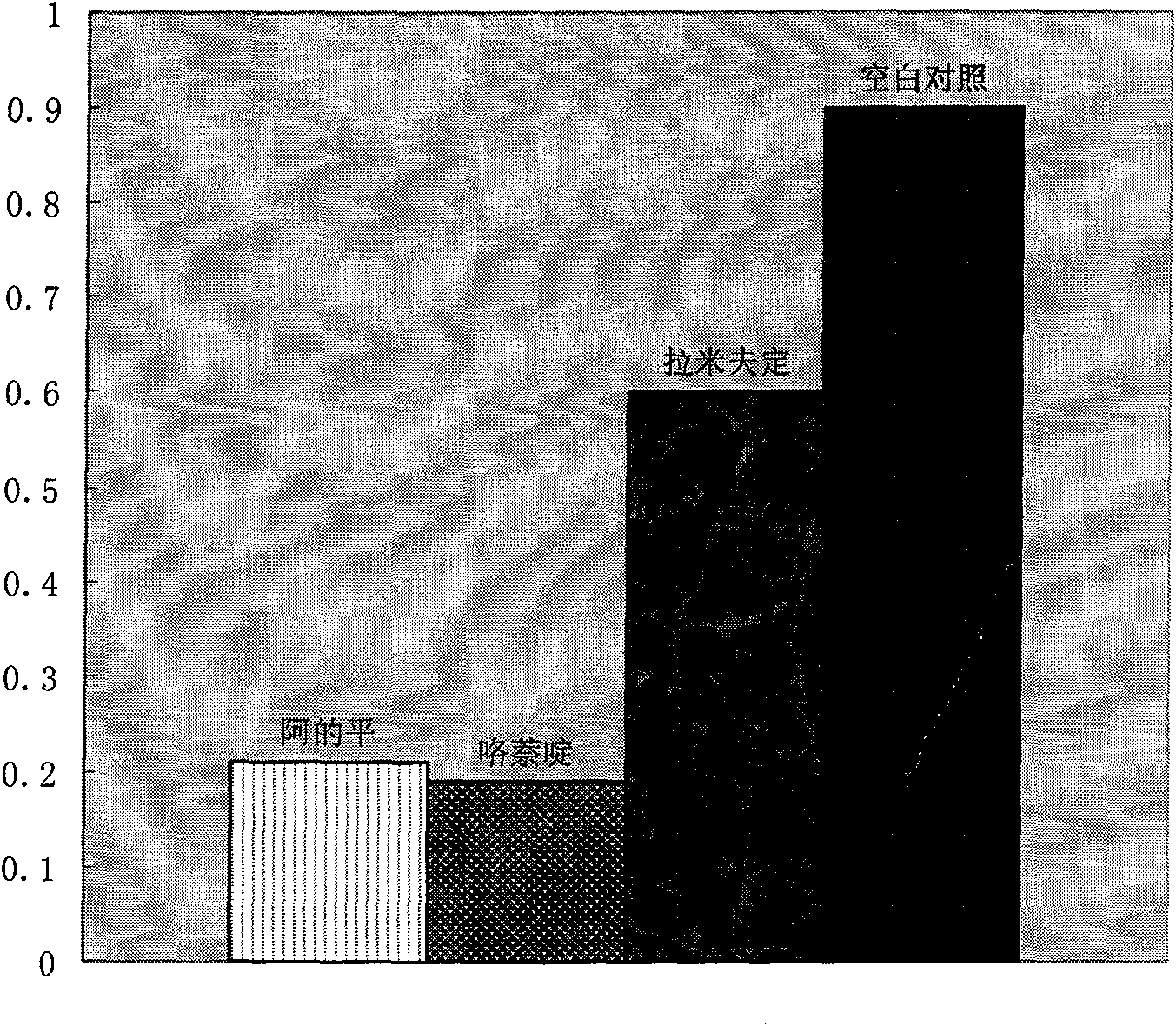
InactiveCN101856355ALower titerInhibition killOrganic active ingredientsAntiviralsAntigenNorthern blot
Owner:蔡荣 +3
Plant expression vector for specific expression of resveratrol in fruit
InactiveCN101440377AVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationRNA blottingAgglutinin
The invention relates to a plant expression vector for specifically expressing resveratrol in fruit. The vector utilizes an agglutinin genetic promoter specifically expressed in banana fruit to replace combination type 35S promoter on a plant expression vector pBI121, and utilizes grape resveratrol synthetic enzyme gene to replace gus gene on the pBI121. By an agricultural bacillus dip method, the vector is subjected to tomato conversion, PCR detection and Southern blot detection to prove that exogenous gene is successfully inserted in tomato genome; and the RT-PCR detection and the Northern blot detection prove that the agglutinin genetic promoter drives the resveratrol synthetic enzyme gene to make specific expression in tomato fruit. The obtaining of the promoter provides useful tools for specifically expressing the resveratrol in fruit, particularly lays a foundation for utilizing the vector to culture new fruit varieties with health care function. Therefore, the promoter has important application values on trans-genetic research in the future.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI +1
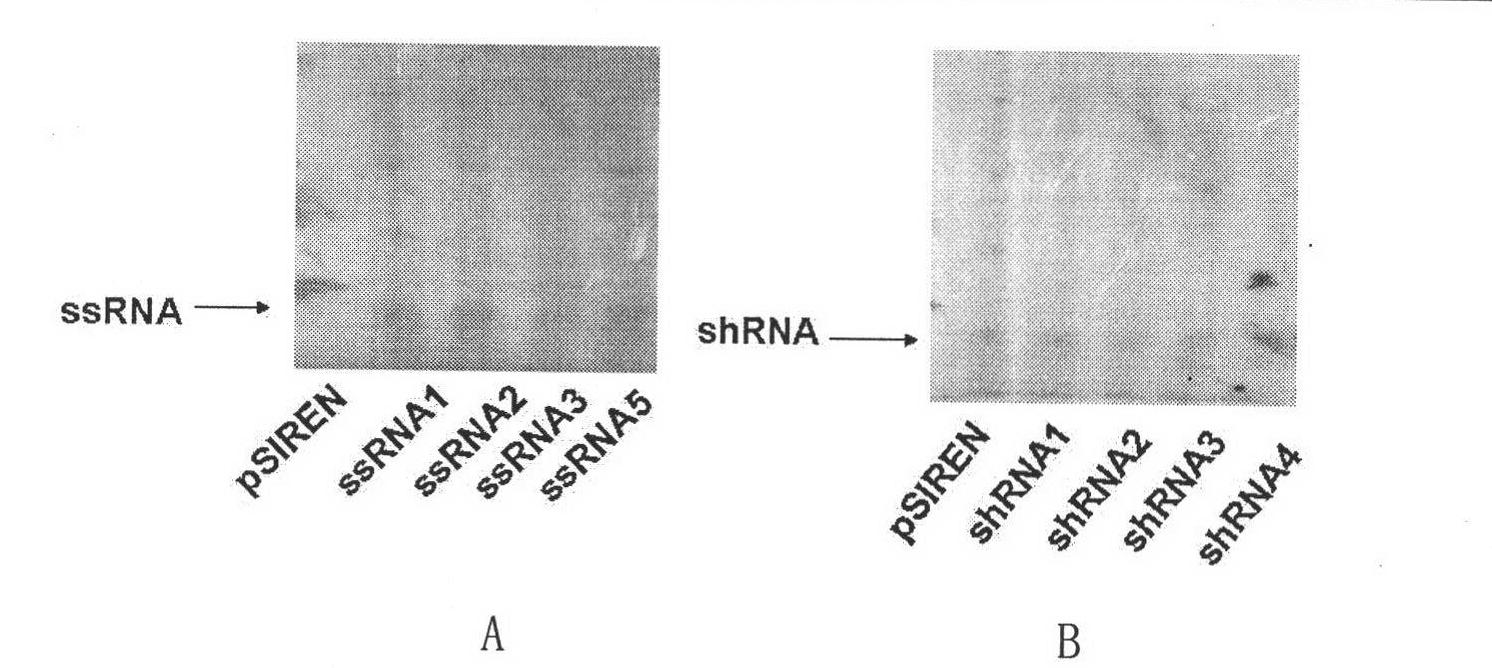
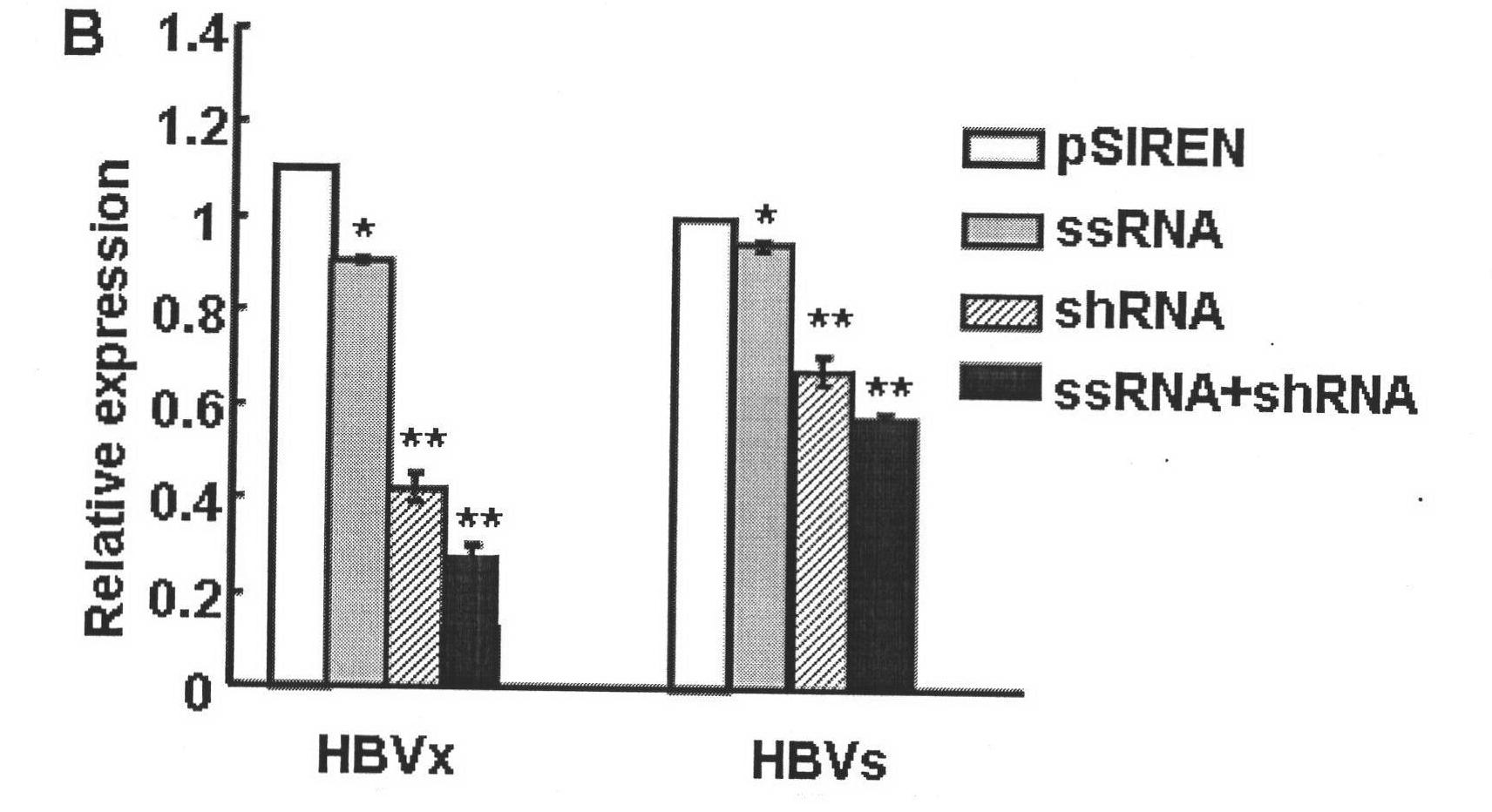
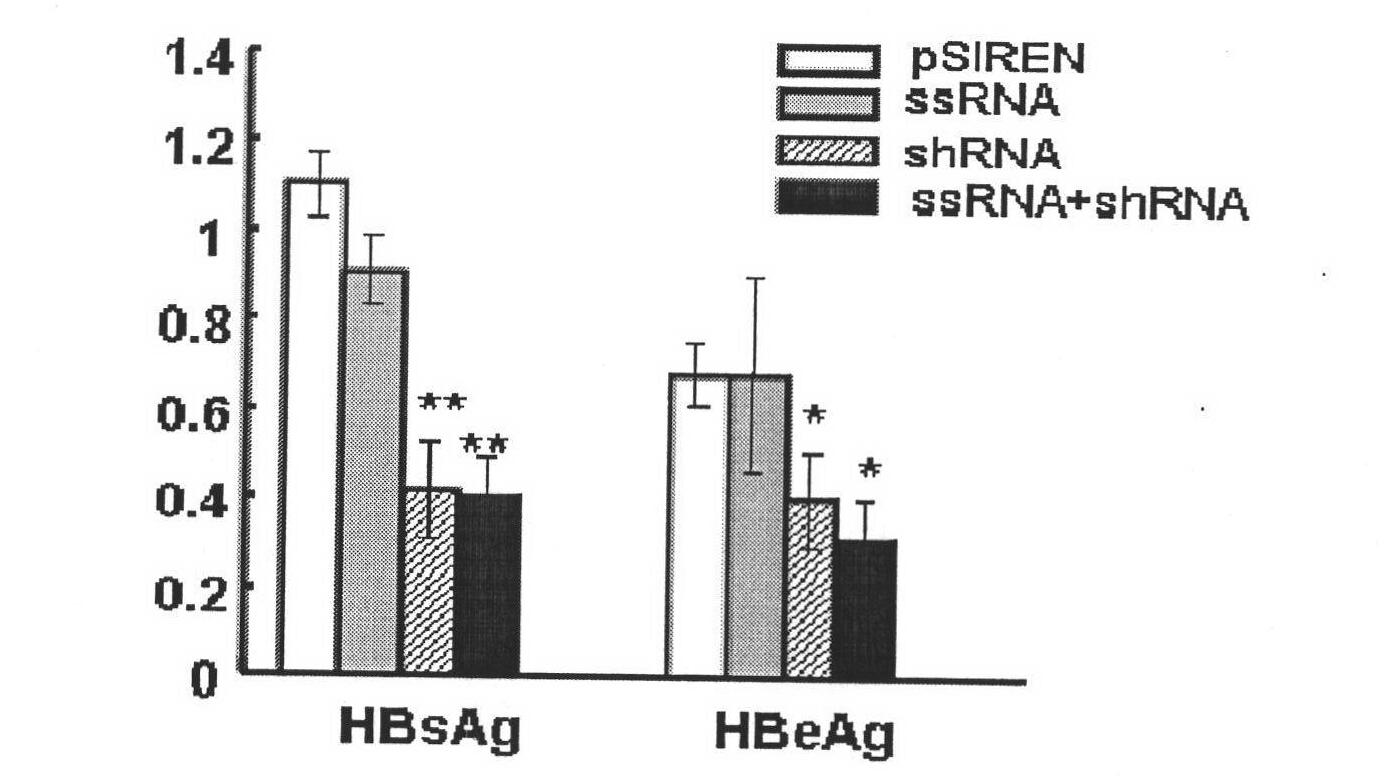
Dual expression vector for immunostimulatory RNA and HBV target gene silence RNA, construction and application thereof
InactiveCN101979595AEnhanced inhibitory effectGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemAntigenRNA blotting
The invention discloses a dual expression vector for immunostimulatory RNA and HBV target gene silence RNA. The dual expression vector is a recombinant vector consists of a DNA sequence of transcription shRNA, the DNA sequence of transcription ssRNA and pTZU6+1 vector; and the sequence of the dual expression vector is shown as seq.1. By transfecting HepG2.2.15 cells by using the dual expression vector for the immunostimulatory RNA and the HBV target gene silence RNA of the invention, the vector can be expressed in cells by Northern blot identification; by transfecting the HepG2.2.15 cells, the vector can regulate the expression of HBV down by detecting after 24 hours; and by transfecting the HepG2.2.15 cells, the vector can regulate the HBV antigenic content and the intracellular antigen content in supernatant liquid down by detecting after 24 hours. Thus, the dual expression vector for the immunostimulatory RNA and the HBV target gene silence RNA of the invention can be used as an anti-HBV medicament.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Whole blood RNA quick lysate and application
PendingCN110804609AReduce extraction timeImprove integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationSodium acetateRNA extraction
The invention provides whole blood RNA quick lysate which does not need erythrocyte pyrolysis firstly, and an RNA extraction method. According to the method, the usage of toxic reagents is reduced toa large extent, RNA extraction steps are simplified, and RNA obtained through purification is good in integrity and high in purity and can be directly used for various molecular biology experiment ofRT-PCR, Northern blot, Dot blot and the like. Every 1000ml by volume of the whole blood RNA quick lysate disclosed by the invention consists of the following components by dosage of 0.2M-4M of guanidine thiocyanate, 0.2M-3M of ammonium thiocyanate, 0.01M-0.2M of anhydrous sodium acetate, 0.05M-0.3M of glacial acetic acid, 0.1%-2%(W / V) of sodium lauroyl sarcosine, 0.02M-0.3M of sodium chloride, 1%-15%(V / V) of glycerine, 10%-75% (V / V) of a water saturation phenol solution, and the balance DEPC treating water.
Owner:杭州联科生物技术股份有限公司
Mycobacterium Avium Subspecies Paratuberculosis (Map) Diagnostic Test
InactiveUS20100021897A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA blottingMycobacterium Infections
The subject invention provides PCR primers and other nucleic acid sequences derived from Mycobacterium avium genes (IS1311 (Genbank accession # U16276), F57 (Accession # X70277) and ISMav2 (Accession # AF286339); these accession numbers and their respective descriptions are hereby incorporated by reference in their entirety and are provided in SEQ ID NOs: 5, 7 and 213). Additionally, the subject invention also provides methods of identifying animals or individuals infected with Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis (MAP). Non-limiting examples of identifying such animals or individuals include various nucleic hybridization techniques such as, and not limited to, Northern blots, Southern blots and PCR techniques.
Owner:WILLIAMS JOSEPH ELLIOT +2
Extraction method for total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of apple tissues
The invention discloses an extraction method for total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of apple tissues. The method comprises the following steps: grinding the apple tissues by liquid nitrogen to obtain powder; adding lysate and shaking uniformly; completely cracking a sample in a water bath; centrifuging and adding phenol-chloroform with the same volume into supernatant; centrifuging and adding LiCl into the supernatant; centrifuging to obtain an RNA sediment; dissolving the RNA sediment by DEPC (Diethylpyrocarbonate)-treated ddH2O; adding sodium acetate and absolute ethyl alcohol; centrifuging and washing by ethanol to obtain a sediment; and drying the sediment at room temperature to obtain the total RNA of the apple tissues. According to the method, the purity of the extracted RNA is high and the pollution to DNA is not caused; the integrity is good; the operation method is simple, convenient and rapid; the obtained RNA can be used for operation including molecular cloning, Northern blot, Real-time PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Kit and method for detecting microRNA (ribonucleic acid)-122
InactiveCN103361420AImprove detection efficiencyAdvanced Cascade Amplification EfficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementNatural stateNorthern blot
The invention discloses a kit and method for detecting microRNA (ribonucleic acid)-122. The kit comprises asymmetrical hairpin probes shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with traditional RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction), northern blot and other technologies, the kit has the prominent advantages that (1) the kit carries out liquid-phase hybridization reaction, is closer to the natural state of molecular reaction, solves the problem of high steric hindrance of solid-phase hybridization, and improves the hybridization reaction efficiency; (2) the kit has high detection efficiency and high detection speed, and the traditional nucleic acid detection technology usually needs a few hours and even a dozen hours while the technology carries out molecular recognition and cascade signal amplification simultaneously, can complete nucleic acid detection within ten minutes and does not need to carry out RT-PCR on samples in advance; and (3) the reaction system is simple, dispenses with enzyme reaction and is low in cost.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
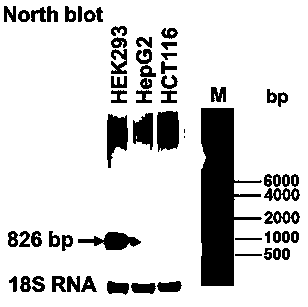
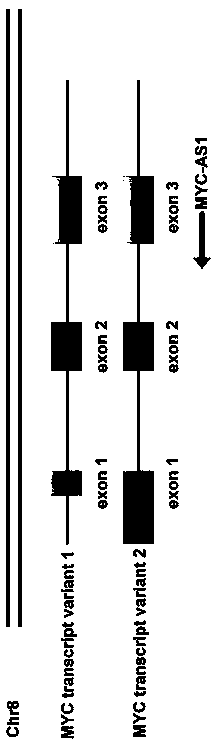
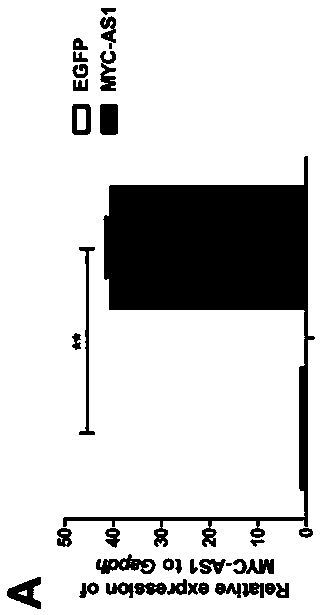
Long-chain non-coding RNA MYC-AS1 expression Northern blot detection primer and kit
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology, and particularly relates to a long-chain non-coding RNA MYC-AS1 expression Northern blot detection primer and a kit. The sequences of the primers are shown as SEQ ID NO. 8 and SEQ ID NO. 9. The invention further provides an MYC-AS1 expression Northernblot detection kit, a method and a basis are provided for analysis of an MYC-AS1 expressionlaw, and the MYC-AS1 expression Northernblot detection kit can be used for detecting the expression situation of oncogenes in a tumor sample in clinical medicine.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
A method for detection of miRNAs using Digoxigenin-labeled EDC cross-linking and bridging
Owner:JILIN UNIV
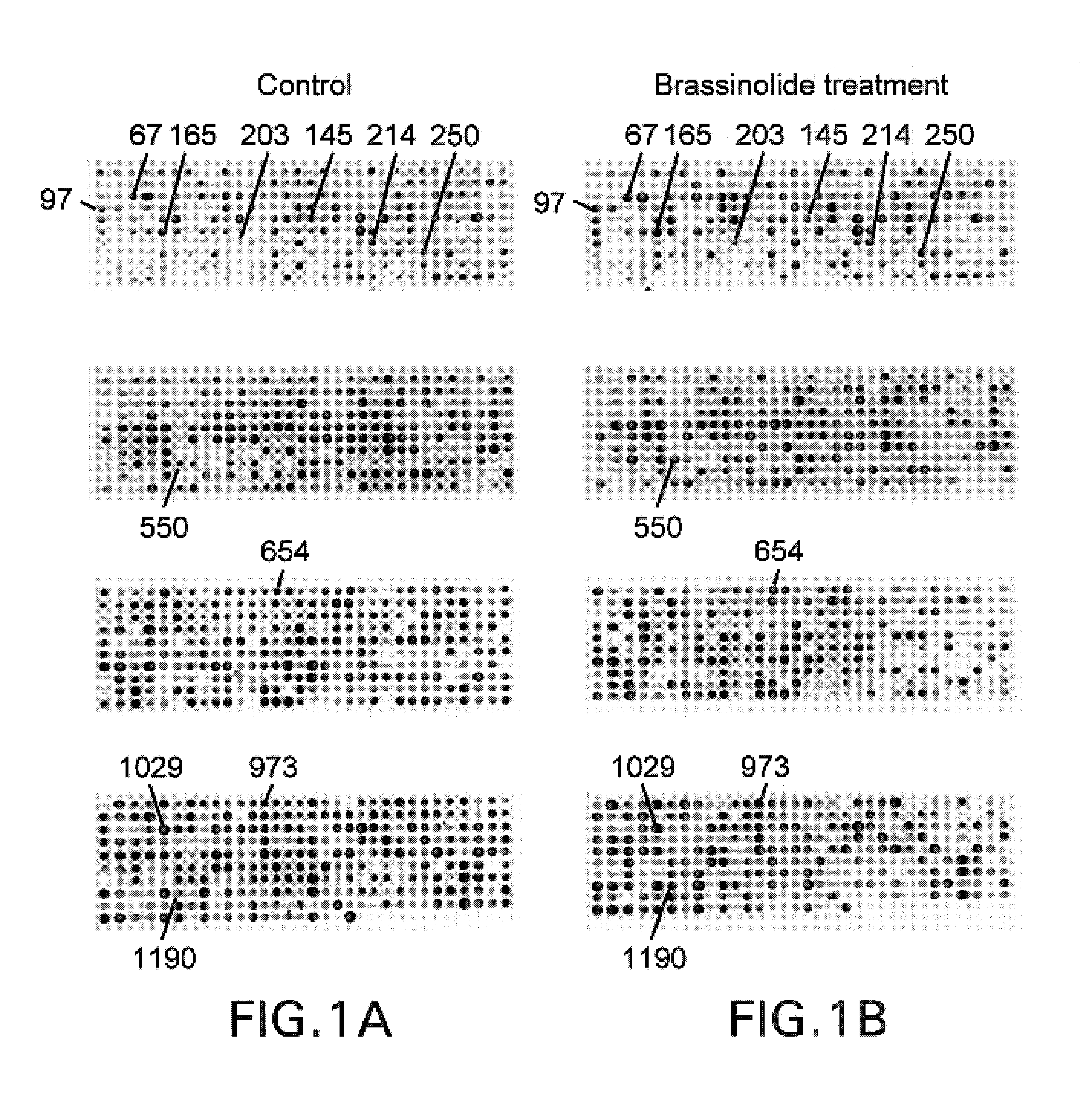
Plant brassinolide responsive genes and use thereof
InactiveUS7132524B2Promote plant growthSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesPlant hormoneRice plants
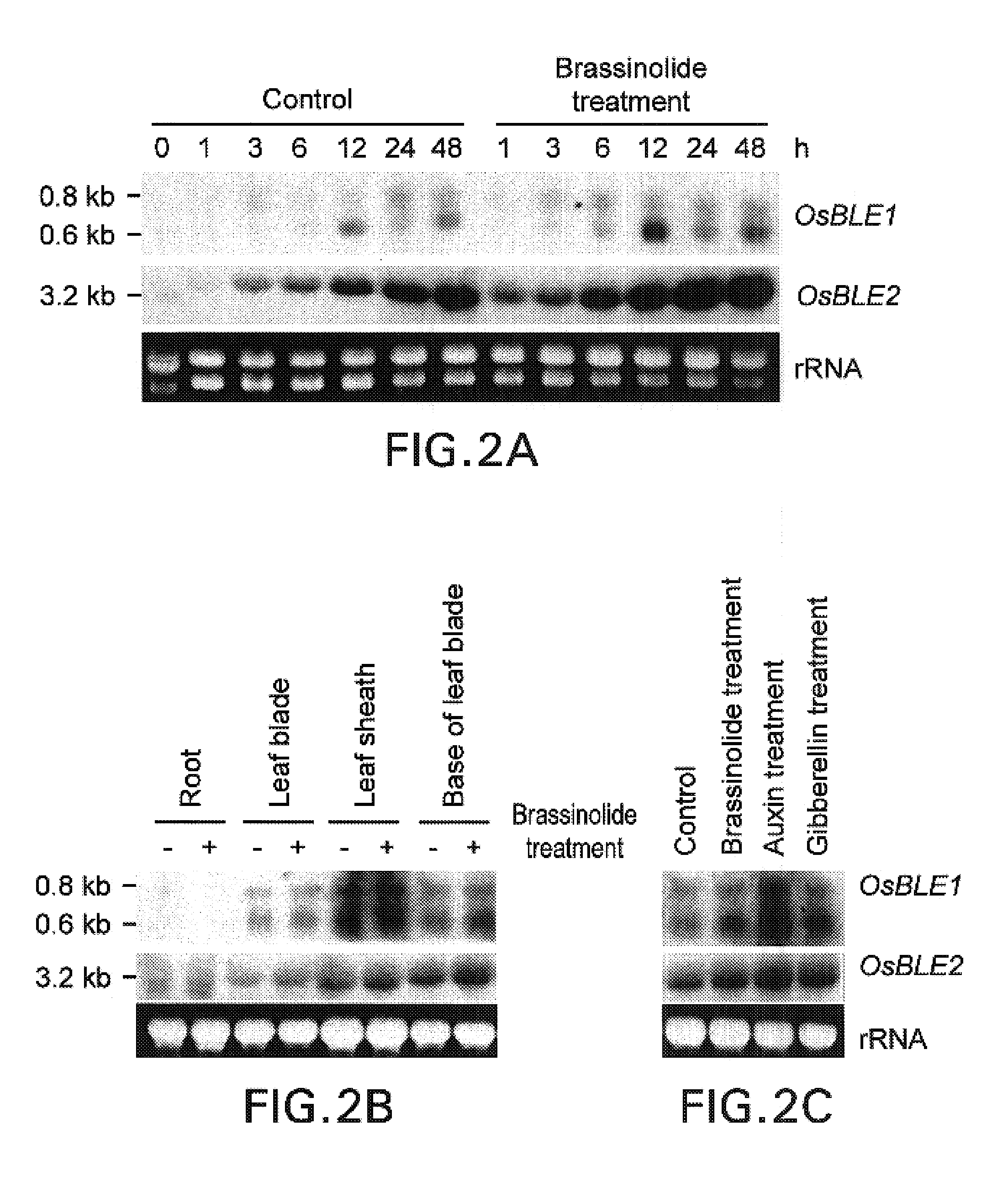
The objective of the present invention is to isolate and identify genes responsive to plant hormones, such as, brassinolide, and to provide these genes and their use. The present inventors found two novel genes (referred to as OsBLE1 gene and OsBLE2 gene) whose expressions are markedly increased by brassinolide and auxin, using DNA microarray techniques and Northern blotting. Transformed rice plants were produced using Agrobacterium EHA101 which comprise antisense polynucleotide against OsBLE1 and OsBLE2 under the control of the CaMV35S promoter in a binary vector pIG121-Hm. As a result, the transformed rice plants exhibited inhibition in stem and leaf growth as compared with controls which carried the vector alone.
Owner:INC ADMINISTRATIVE AGENCY NAT AGRI & BIO ORIENTED RES ORG +1
Method for detecting gastric cancer by detecting VLDLR gene
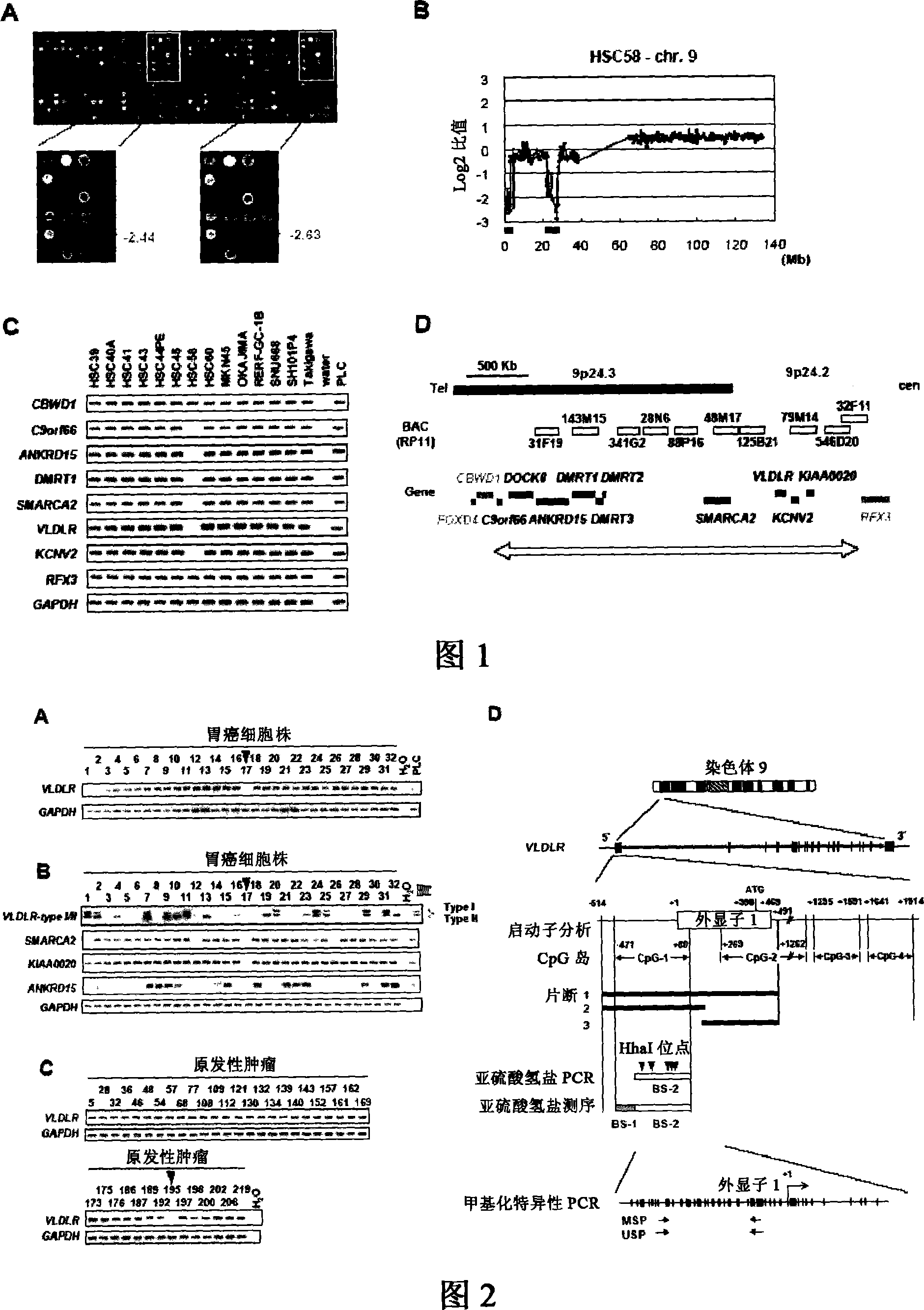
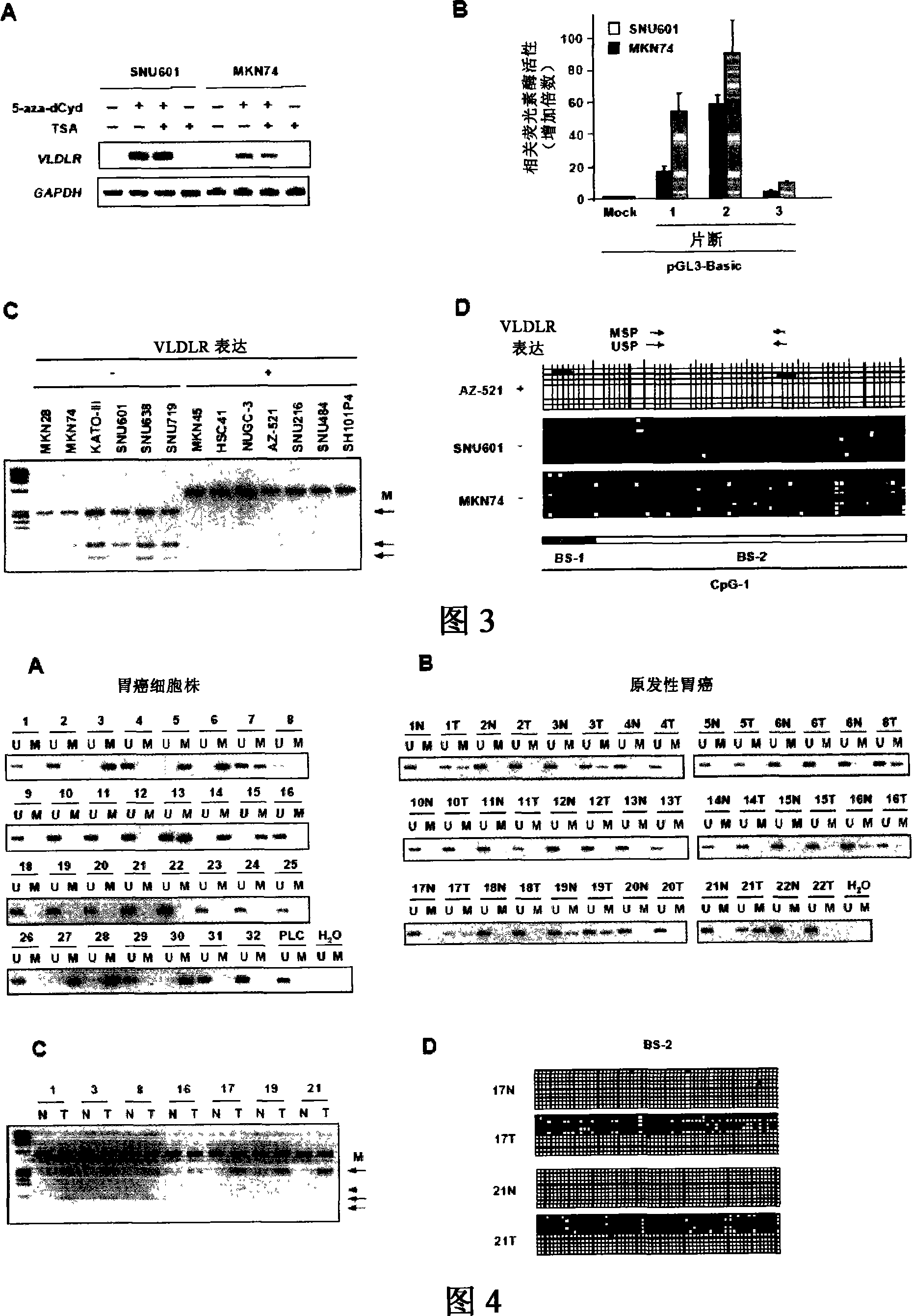
InactiveCN101092650AAccurately grasp the signs of cancerAccurately grasp the progress of cancer developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementReal-Time PCRsRNA blotting
The method for detecting gastric cancer comprises detecting canceration of gastric tissue cell by detecting the inactivation of the human VLDLR (VLDL receptor) gene in the gastric tissue cell by (homozygote) deletion, methylation of CpG island, etc. A DNA chip method, a Southern blot method, a Northern blot method, a real time RT-PCR method, an FISH method, a CGH method, etc., may be cited as the detecting means.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Methods for producing nucleic acid hybridization probes that amplify hybridization signal by promoting network formation
InactiveUS20100279304A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA blottingNucleic Acid Probes
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
Method for quickly extracting low molecular weight RNA of plant
The invention discloses a method for quickly extracting low molecular weight RNA of plant. After cells are disrupted, genomic DNA and high molecular weight RNA form a DNA-protein complex and a RNA-protein complex with protein respectively; and the DNA-protein complex and the RNA-protein complex are insoluble in acid and low-salt environment, and can be removed and extracted through acid and phenol. The low molecular weight RNA stays in supernatant solution, and can be recovered through the precipitation of ethanol or isopropanol. The method is quick and efficient, and can recover the low molecular weight RNA only by one-step precipitation after phenol extraction. The low molecular weight RNA extracted by the method has high purity, and can be used for the cloning of the low molecular weight RNA and the detection of Northern blot hybridization. The method has simple and quick experimental process, and is suitable for the extraction of the low molecular weight RNA of various plant tissues.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Microarray techniques for nucleic acid expression analyses
ActiveUS9145582B2Eliminate biasConvenient experimentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationMiRNA GeneNorthern blot
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Kit and method for detecting microRNA (ribonucleic acid)-155
InactiveCN103361421BQuick checkOvercome the problem of large steric hindranceMicrobiological testing/measurementNatural stateNorthern blot
The invention discloses a kit and method for detecting microRNA (ribonucleic acid)-155. The kit comprises asymmetrical hairpin probes shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. Compared with traditional RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction), northern blot and other technologies, the kit has the prominent advantages that (1) the kit carries out liquid-phase hybridization reaction, is closer to the natural state of molecular reaction, solves the problem of high steric hindrance of solid-phase hybridization, and improves the hybridization reaction efficiency; (2) the kit has high detection efficiency and high detection speed, and the traditional nucleic acid detection technology usually needs a few hours and even a dozen hours while the technology carries out molecular recognition and cascade signal amplification simultaneously, can complete nucleic acid detection within ten minutes and does not need to carry out RT-PCR on samples in advance; and (3) the reaction system is simple, dispenses with enzyme reaction and is low in cost.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF THIRD MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY OF PLA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com