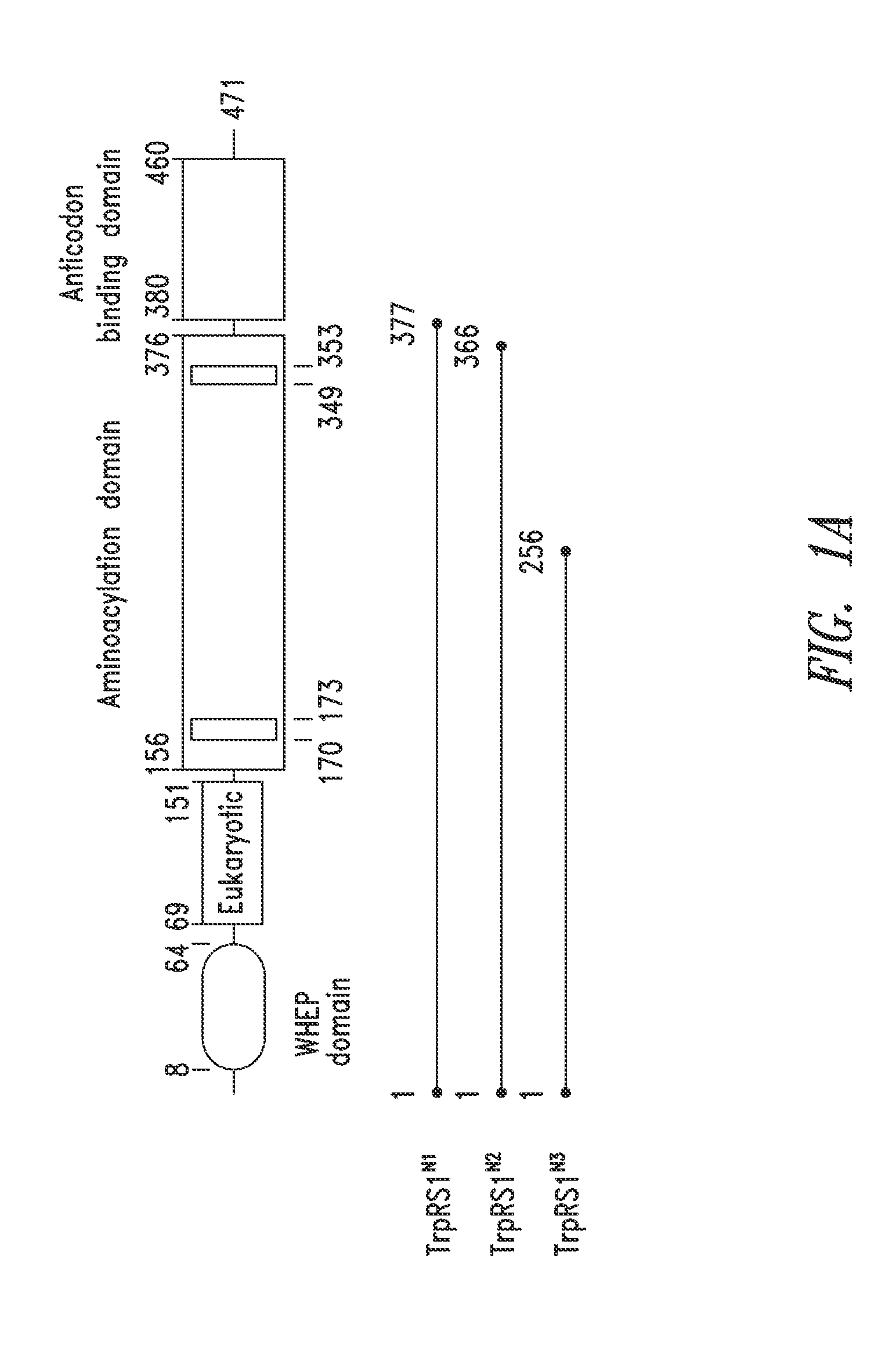
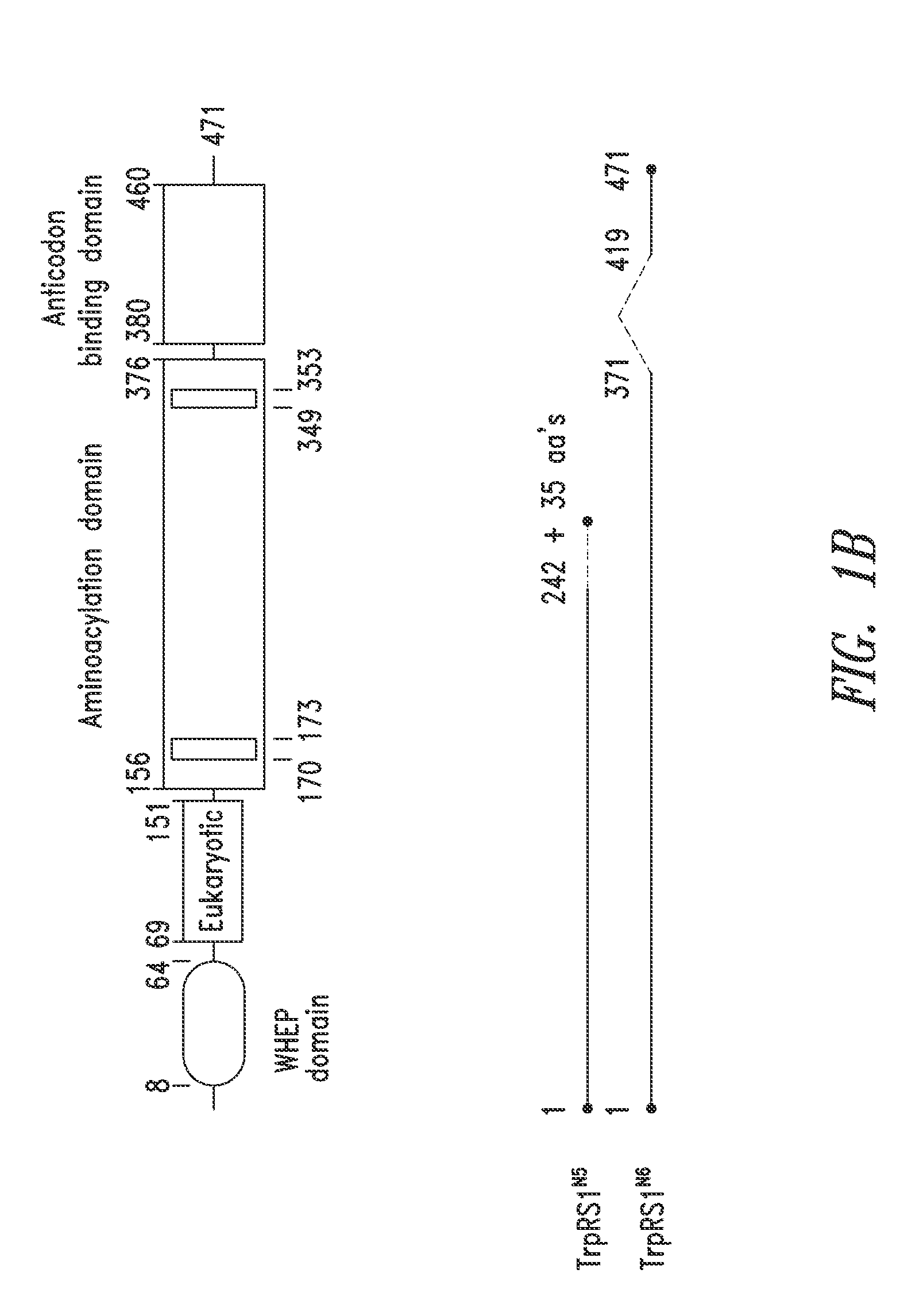
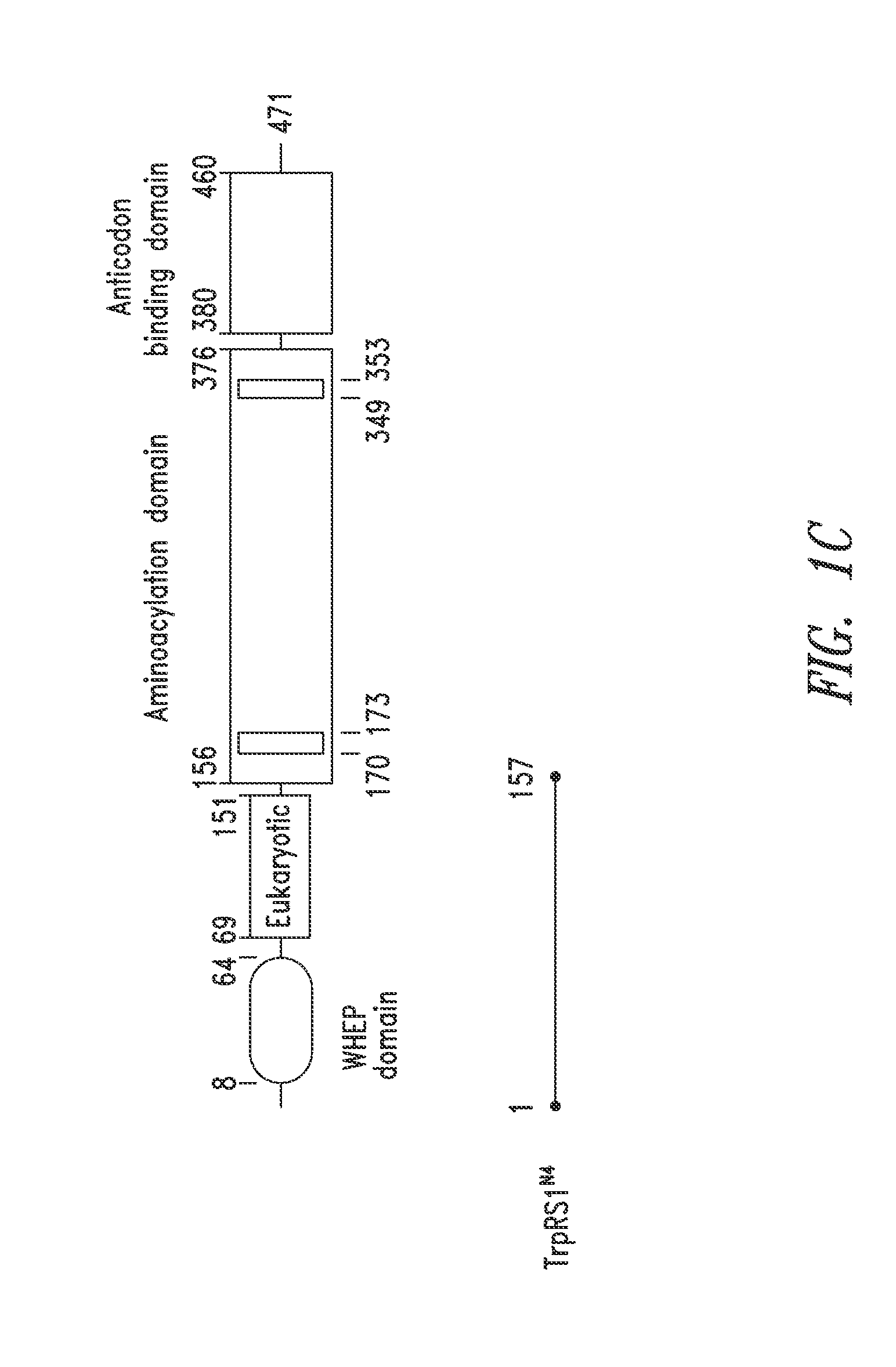
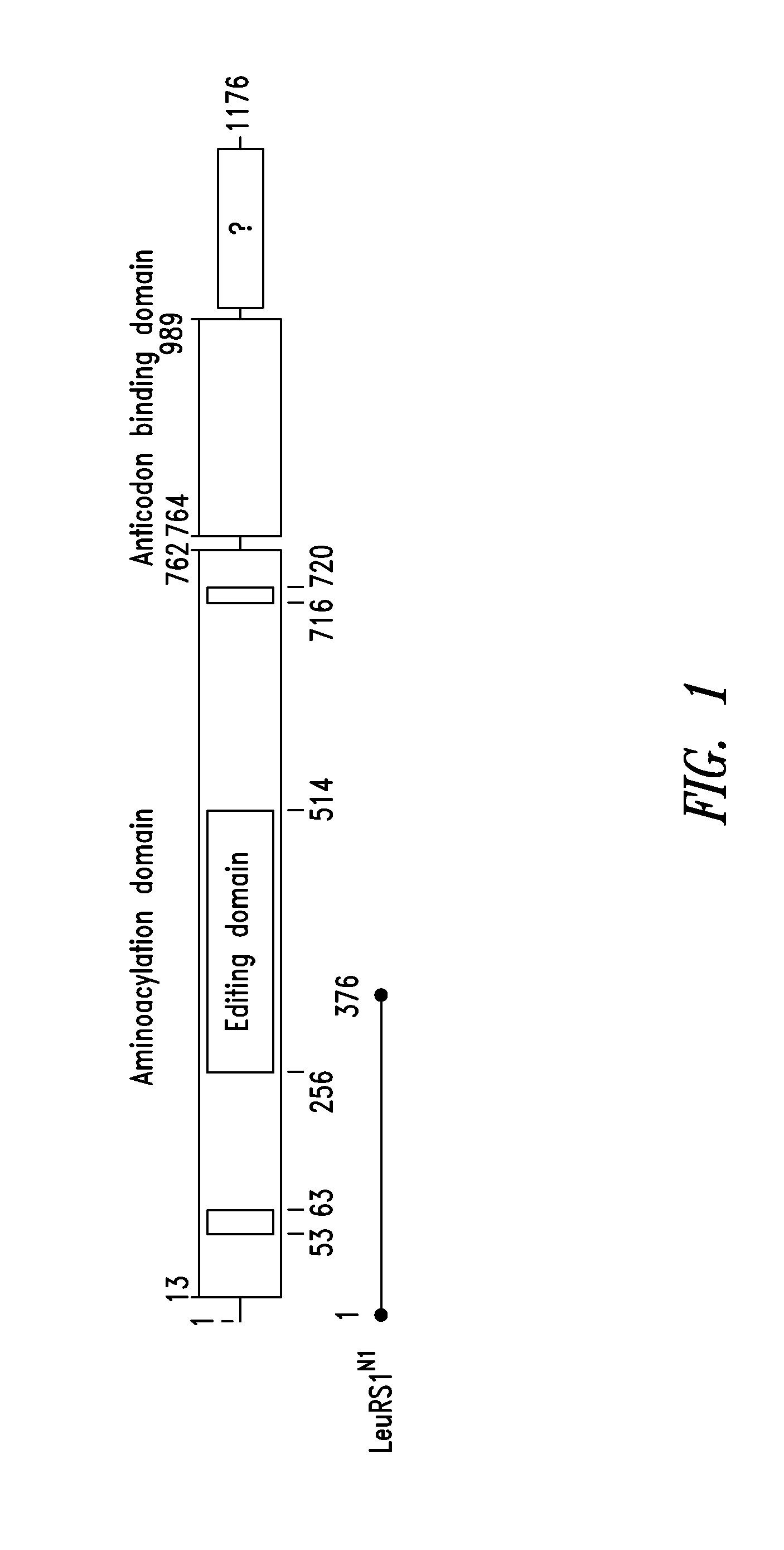
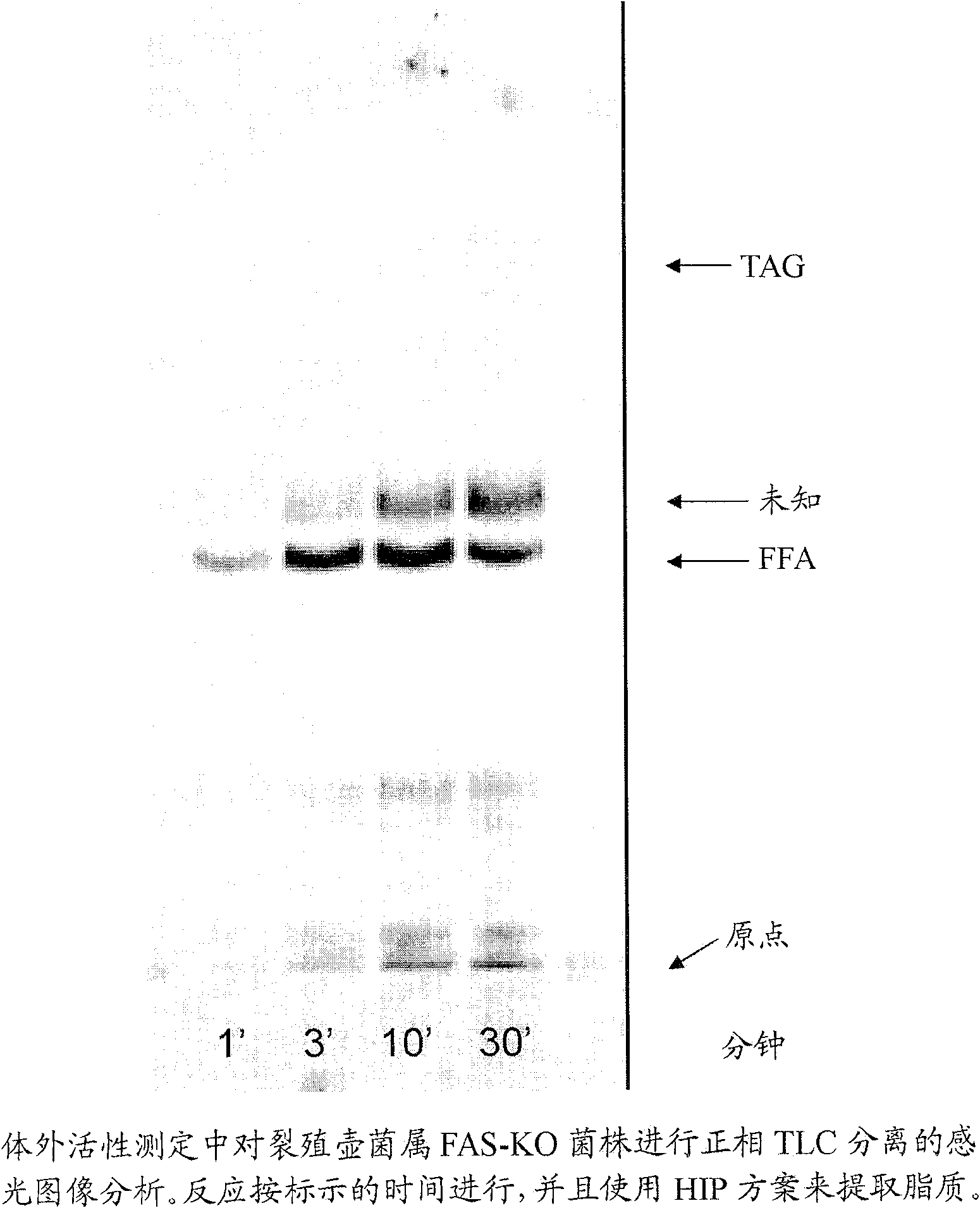
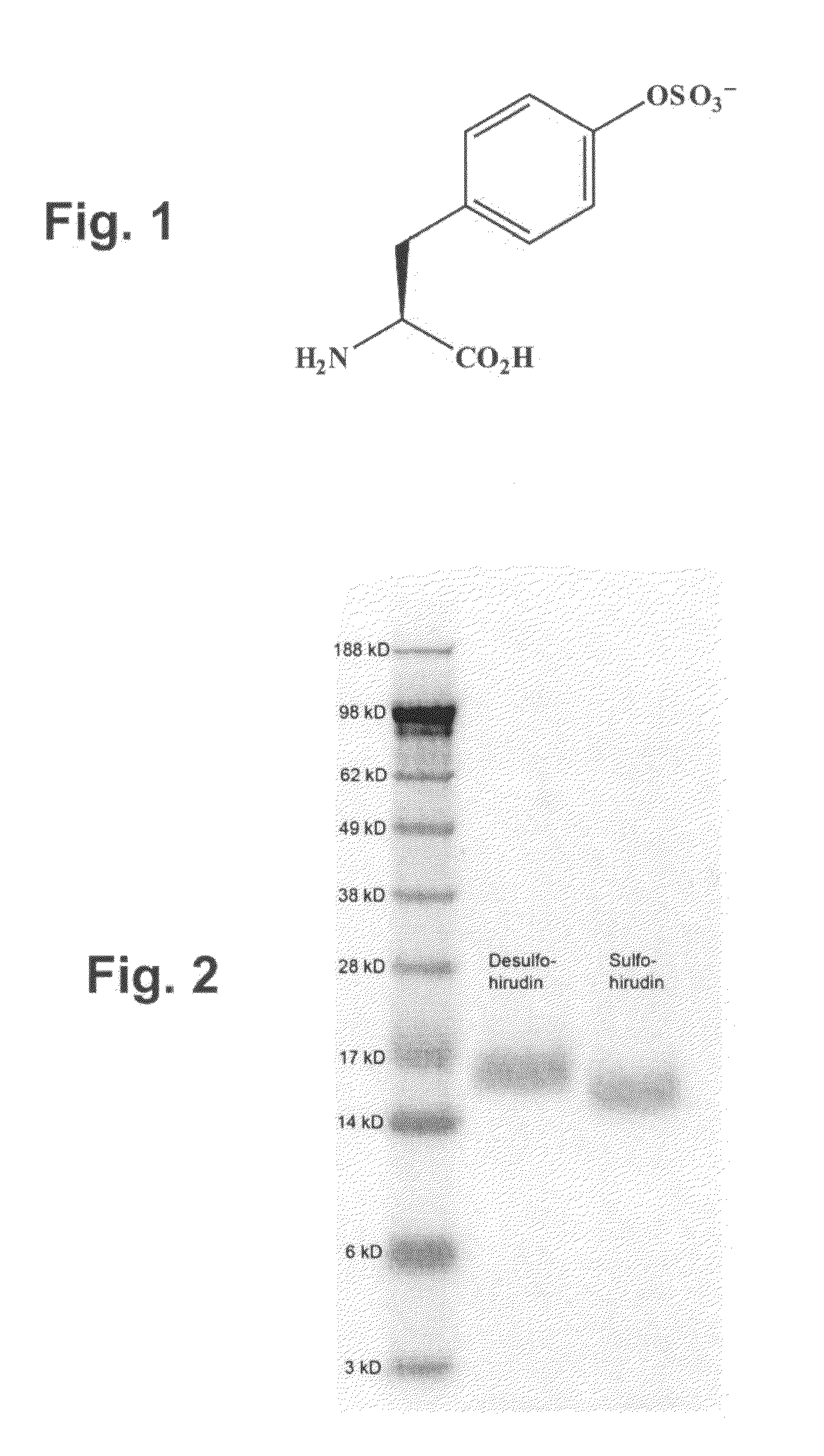
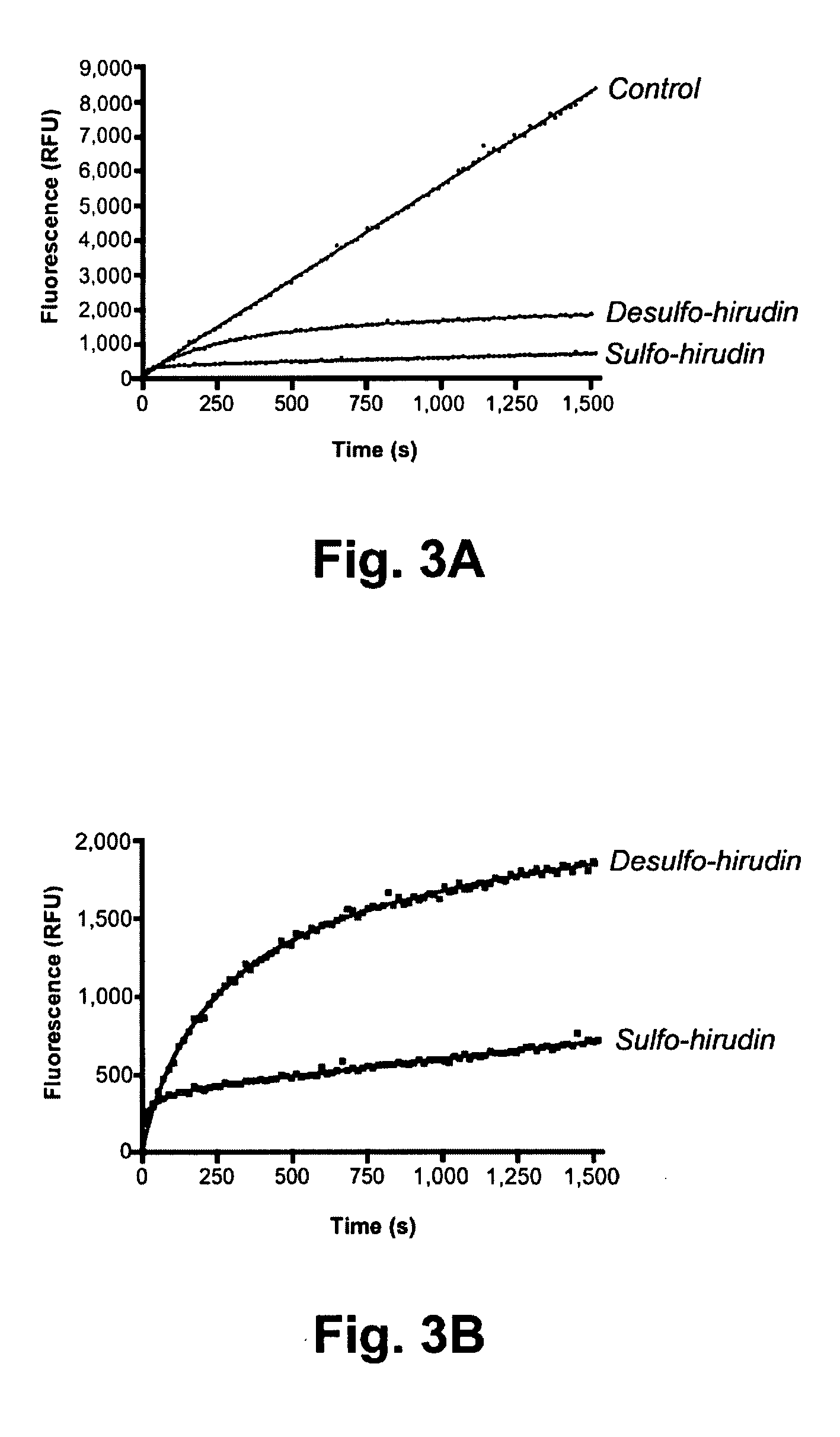
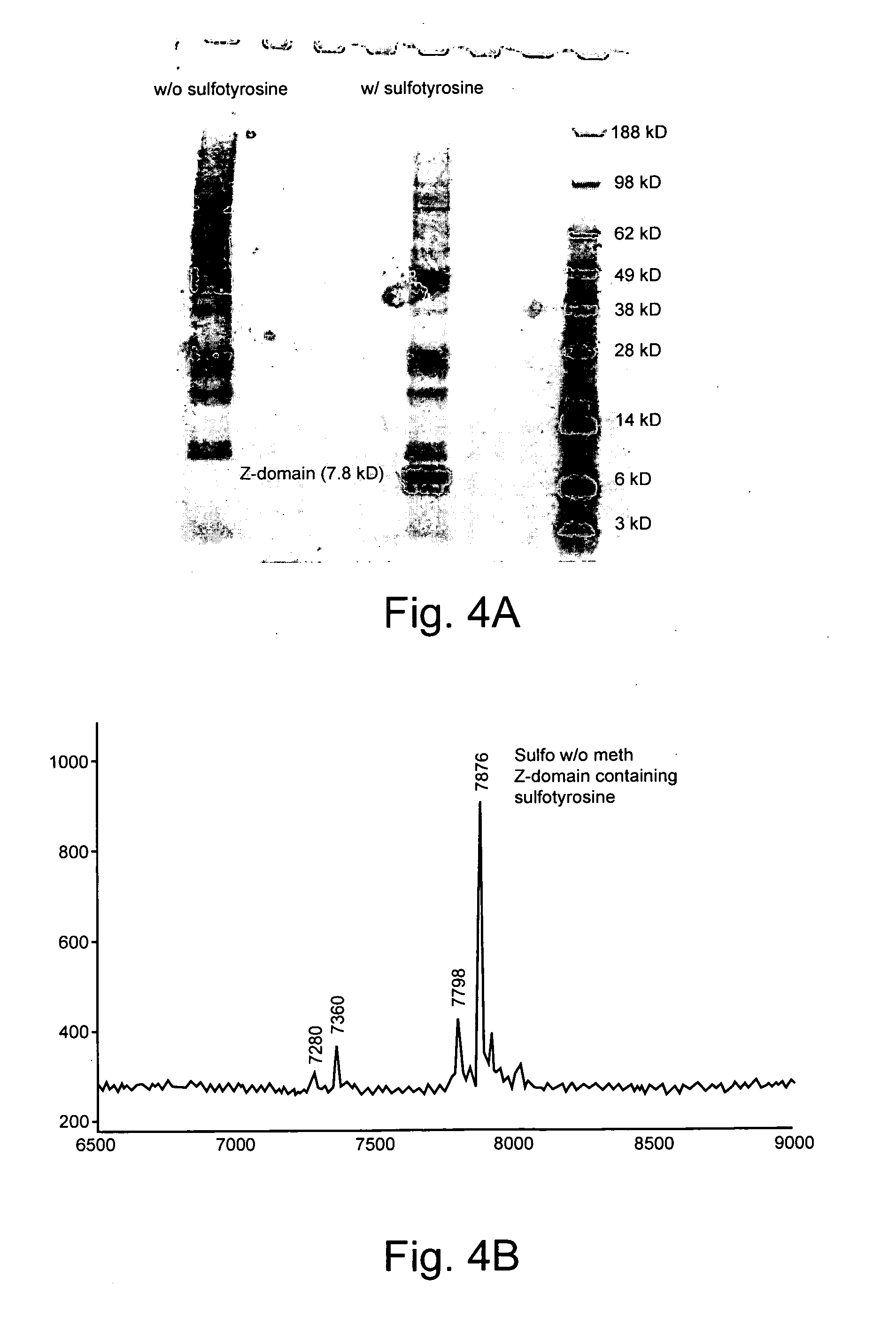
Patents
Literature
592 results about "Synthetic enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An artificial enzyme is a synthetic, organic molecule or ion that recreate some function of an enzyme. The area promises to deliver catalysis at rates and selectivity observed in many enzymes.
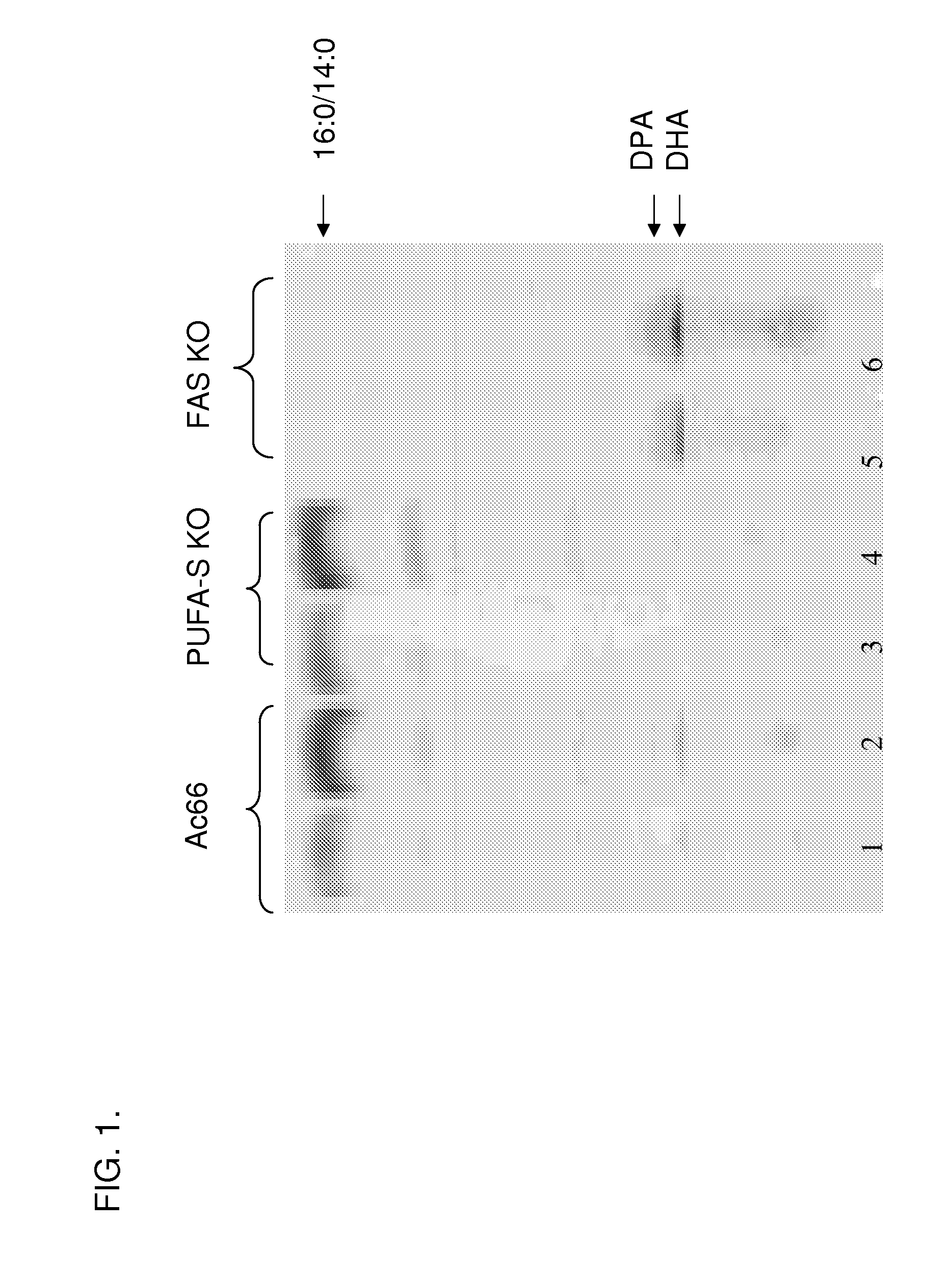
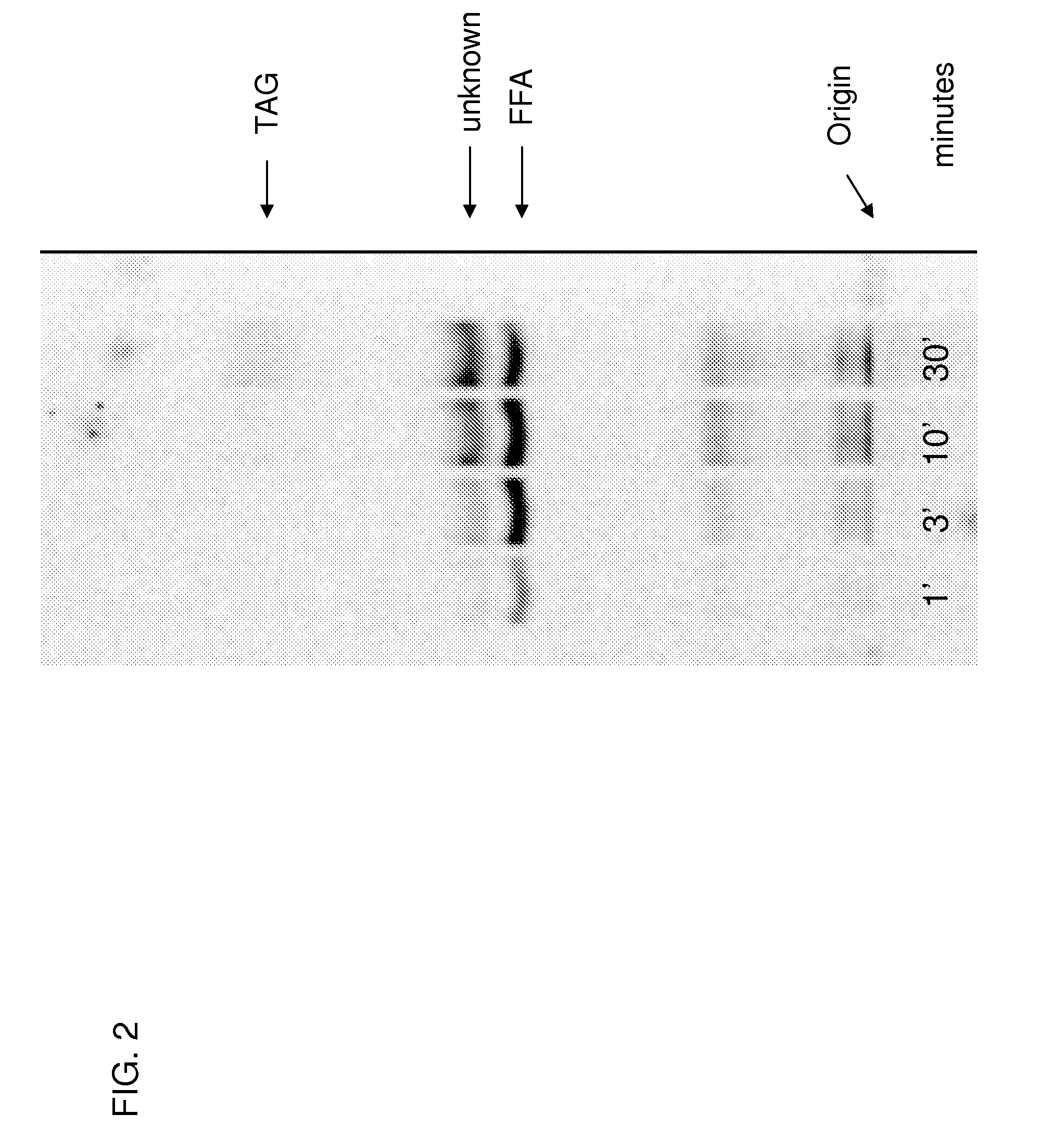
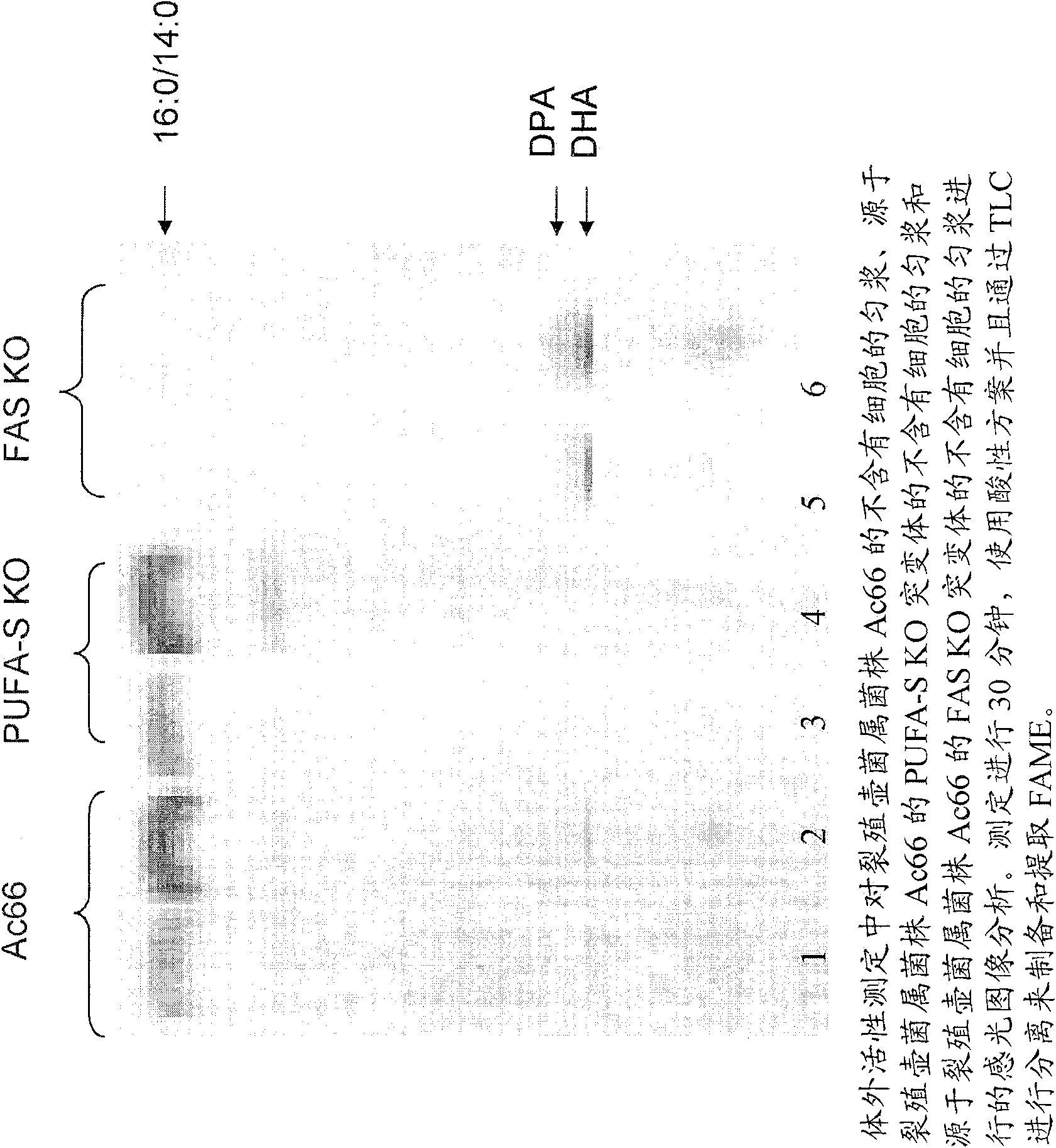
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
ActiveUS20070270494A1Improve the level ofReduce competitionAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHeterologousAcyl-CoA synthetase
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or to increase the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils obtained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Unnatural reactive amino acid genetic code additions
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
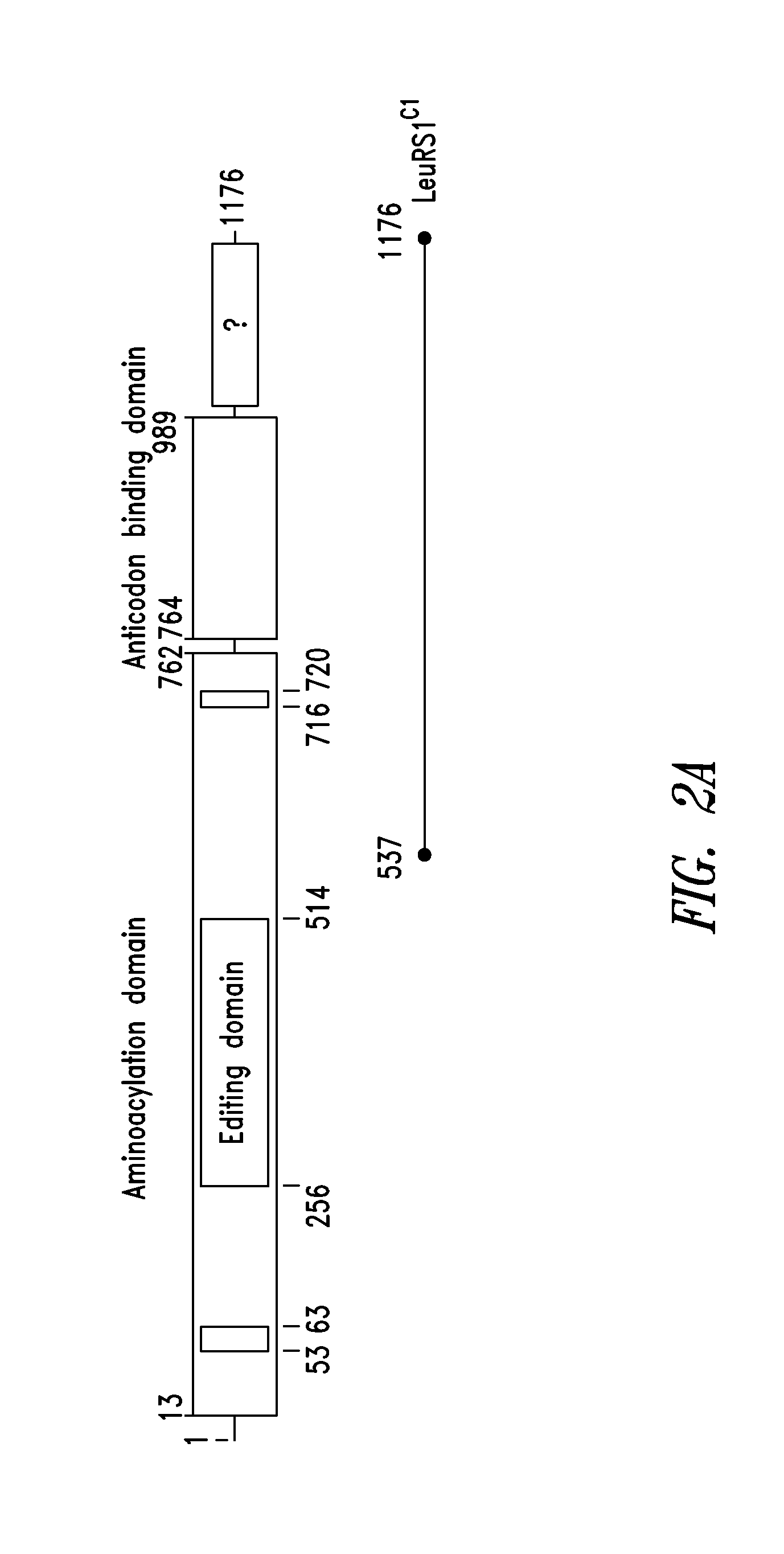
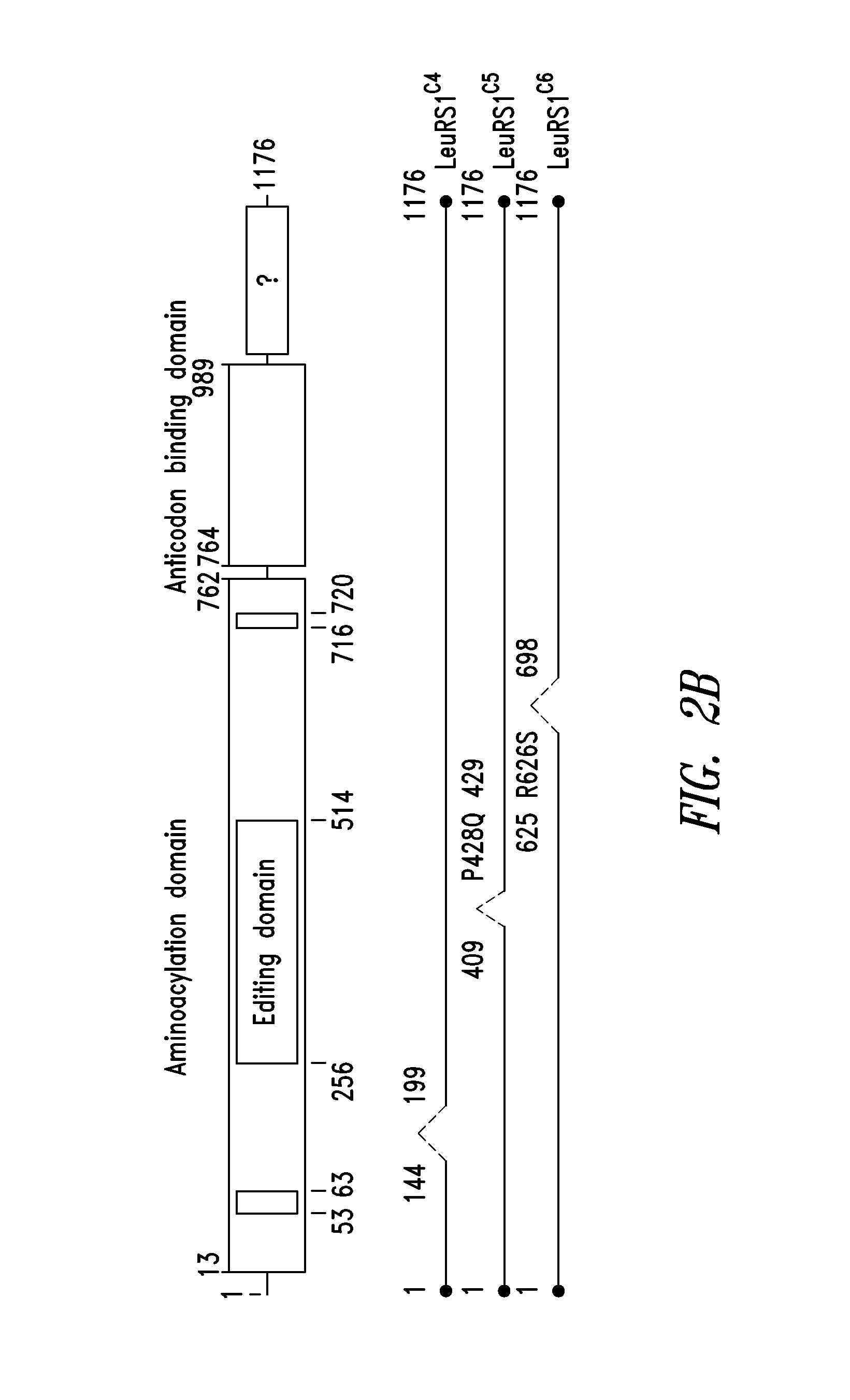
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of tryptophanyl-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130330312A1Nervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAminoacyl-tRNA synthetasesNucleotide
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of leucyl-trna synthetases
ActiveUS20130209434A1Altering abilityImprove purification effectNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideProtein Fragment
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
Methods for treating pain
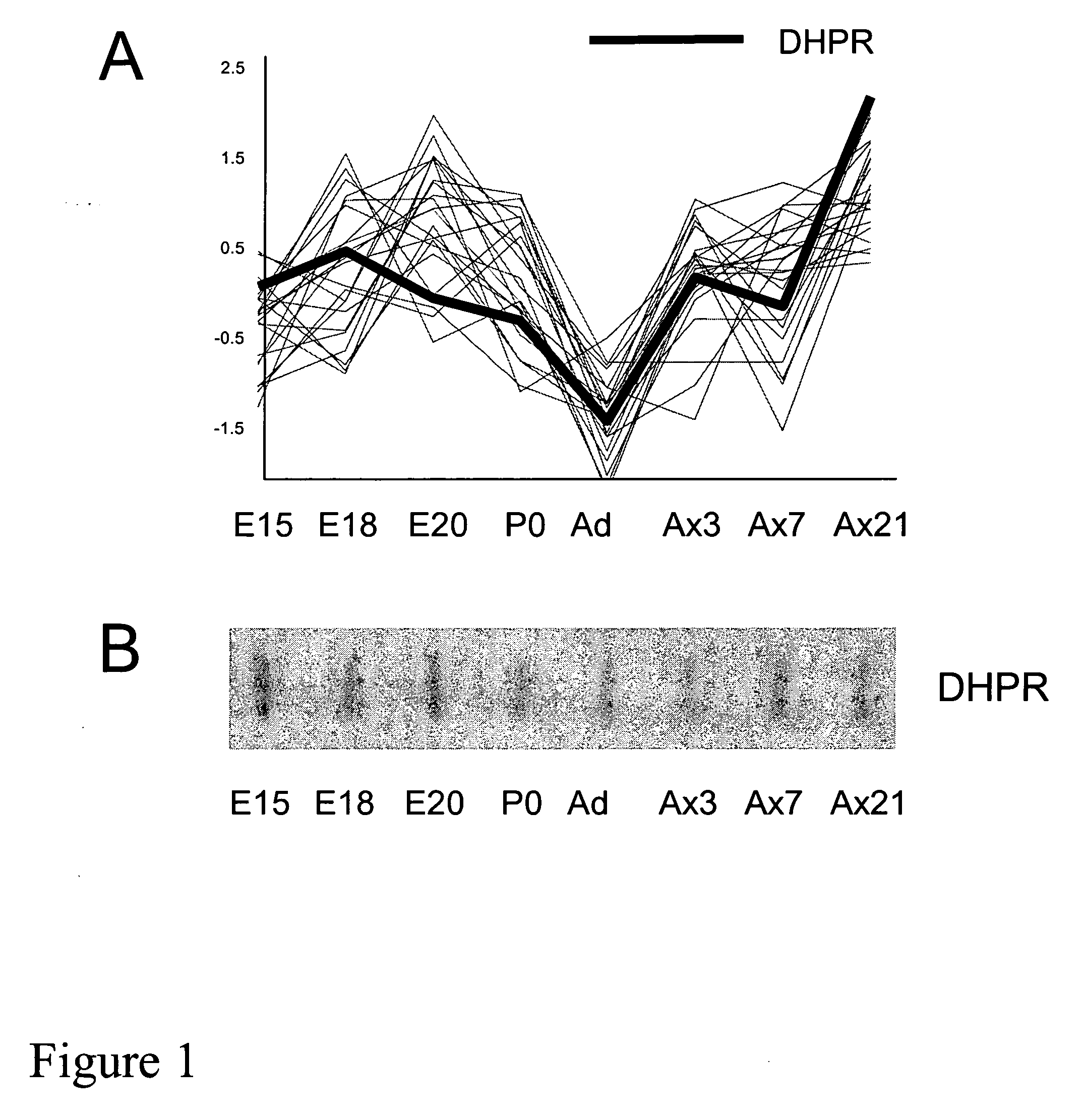
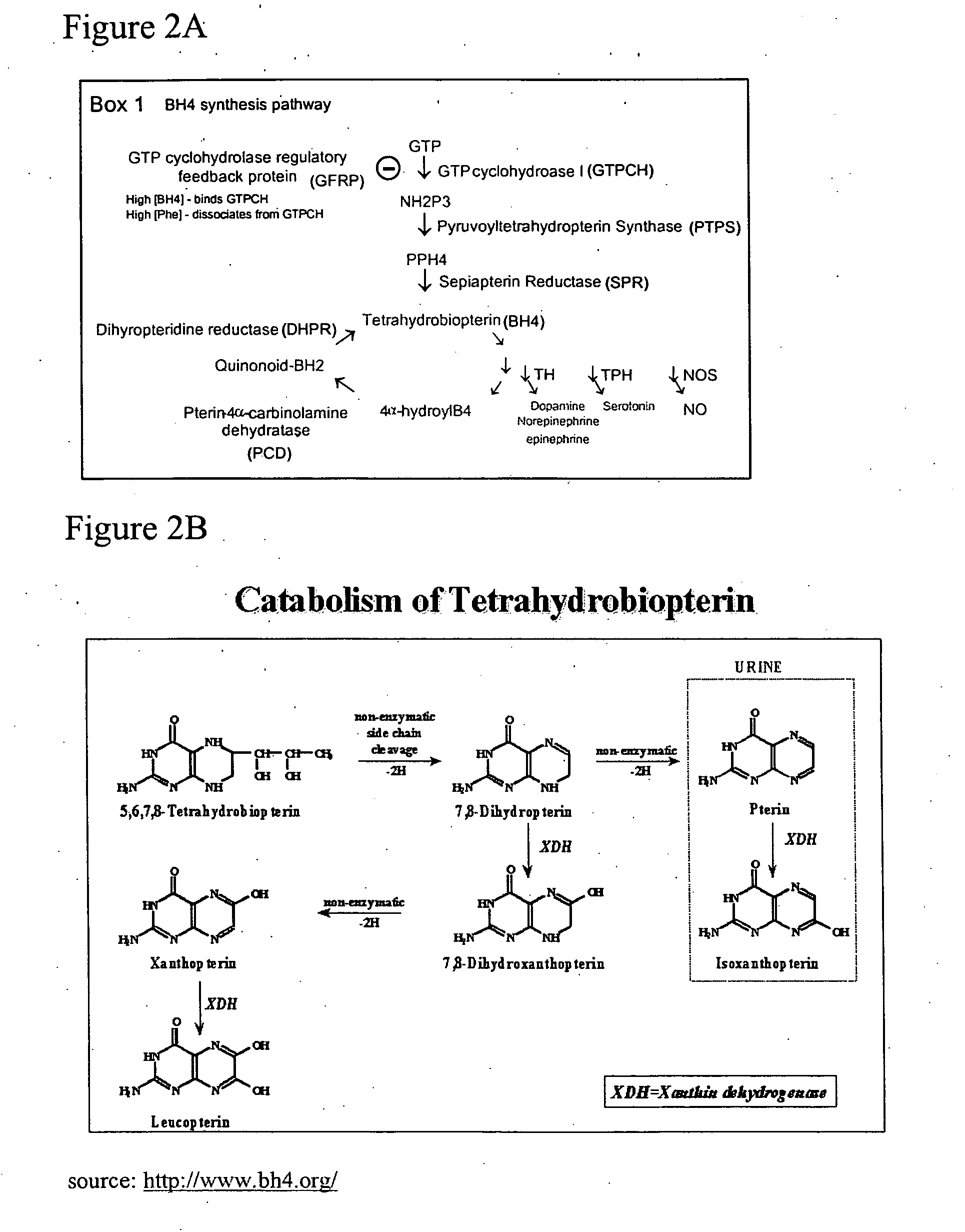
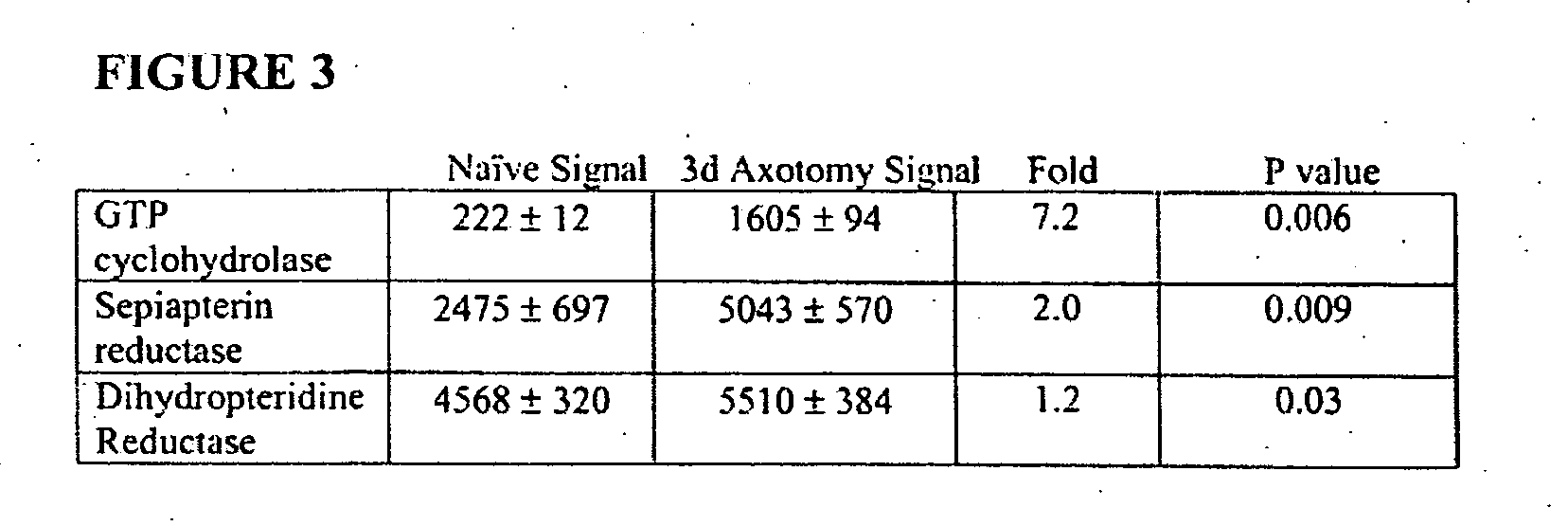
InactiveUS20050197341A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced activityBiocideNervous disorderGtp cyclohydrolaseMetabolite
The present invention features methods and compositions for preventing, reducing, or treating a traumatic, metabolic or toxic peripheral nerve lesion or pain including, for example, neuropathic pain, inflammatory and nociceptive pain by administering to a mammal in need thereof a compound that reduces the expression or activity of BH4. According to this invention, this reduction may be achieved by reducing the enzyme activity of any of the BH4 synthetic enzymes, such as GTP cyclohydrolase (GTPCH), sepiapterin reductase (SPR), or dihydropteridine reductase (DHPR); by antagonizing the cofactor function of BH4 on BH4-dependent enzymes; or by blocking BH4 binding to membrane bound receptors. The compounds of the invention may be administered alone or in combination with a second therapeutic agent. The invention also provides methods for diagnosing pain or a peripheral nerve lesion in a mammal by measuring the levels of BH4 or its metabolites in biological sample. Alternatively, pain or a peripheral nerve lesion may be diagnosed by measuring the levels or activity of any one of the BH4 synthetic enzymes in tissue samples of a mammal. Also disclosed are screening methods that make use of BH4 or BH4 synthetic enzymes, BH4-dependent enzymes, and BH4-binding receptors for the identification of novel therapeutics for the treatment, prevention, or reduction of pain.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Methods and compositions for directed microwave chemistry
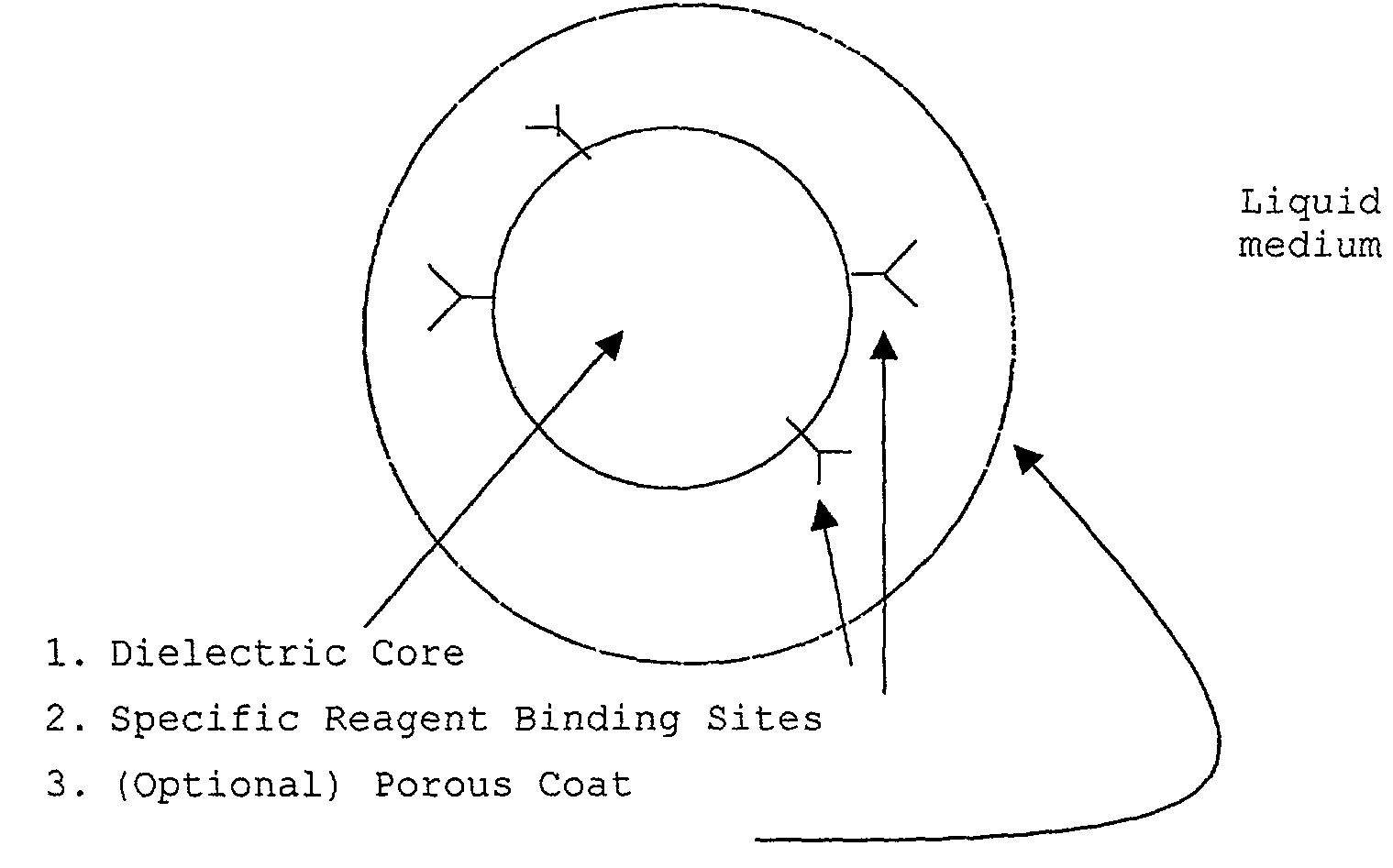
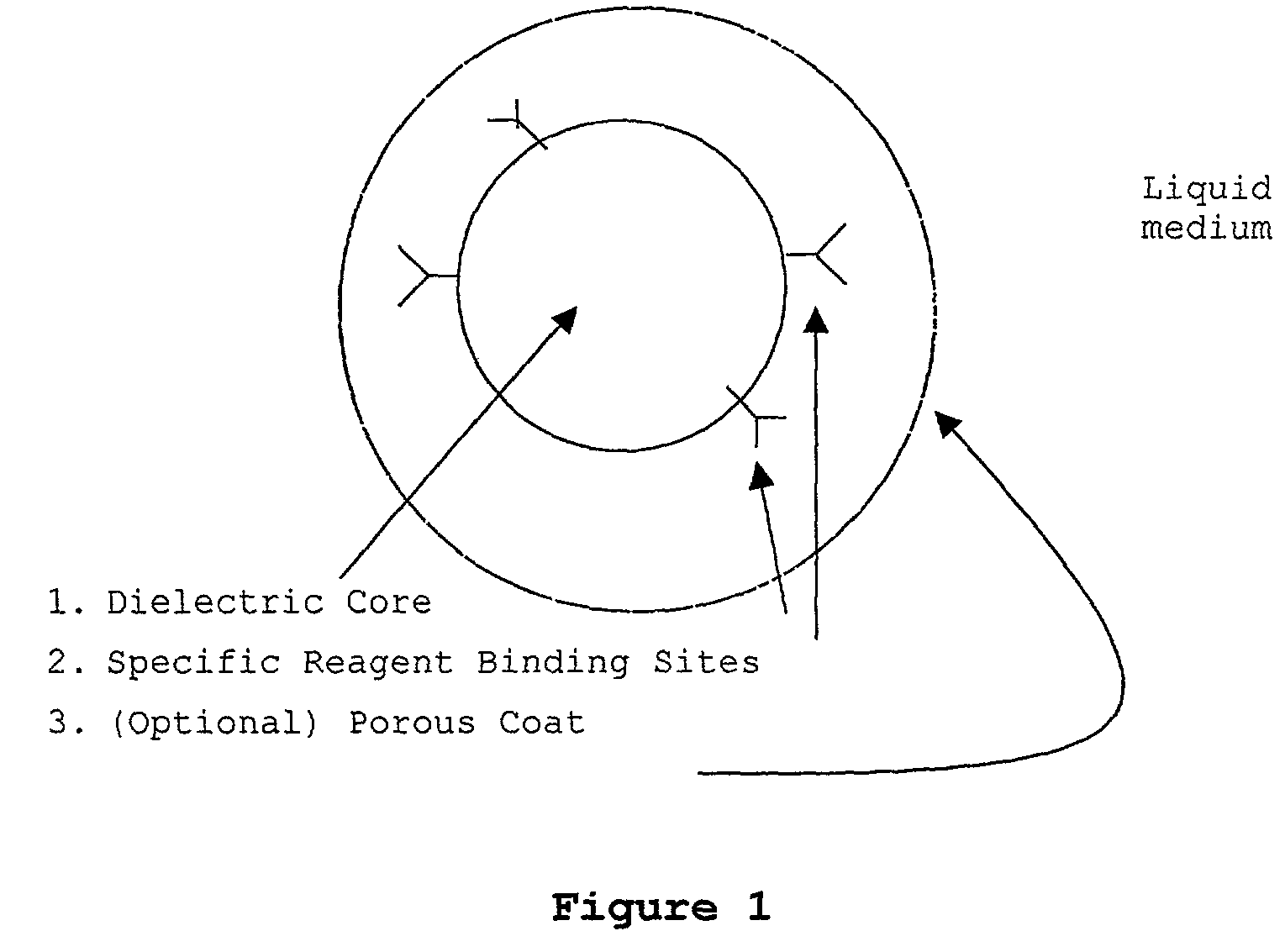
InactiveUS7351590B2Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsArtificial enzymeChemical measurement
The present invention concerns a novel means by which specific chosen reactions can be accelerated through the use of a new type of artificial enzyme. The invention allows specific reactions to occur at an accelerated rate, even in the presence of other non-chosen molecules, which may be very similar in structure to the chosen reactant. The reactions may be stoichiometric or catalytic.
Owner:MILESTONE SRL
Pluripotent therapeutic compositions and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090274660A1Reduce riskReduce significant riskBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSelf-healingAnticarcinogen
Synthetic Stem Cell-like Tissue Healing and Regeneration Medication with Anti-inflammatory, Protein Synthesis, Enzyme Deficiency Activation and Genetic Therapy, and Anti-cancer Agent derived from a series of inventions that include these products of Biomolecular Engineering, Drug Discovery from a Biologic Periodic Table of Applied Biochemistry and Biophysics. Tissue has a self healing effect promoting tissue healing and tissue regeneration. Not only does it maintain good health but also it has been observed that the patient's blood is withdrawn from the patient and applied to the ulcer has healing qualities. Cartilage placed in a wound promotes and accelerates wound healing. The anabolic biochemical and biophysical equivalent of tissue has been found in these embodiments to have the same pharmacologic qualities, when devoid of genetic DNA mismatch and other catabolic factors including the catabolic effects of microorganism overgrowth that lacks pro-biotic qualities. The healing efficacy of these tissue components gives us further appreciation of the protective action of human tissue over and above and other than the immune protective system or perhaps an integral component part of the immune system.
Owner:IMMUNOPATH PROFILE INC A CORP OF PA
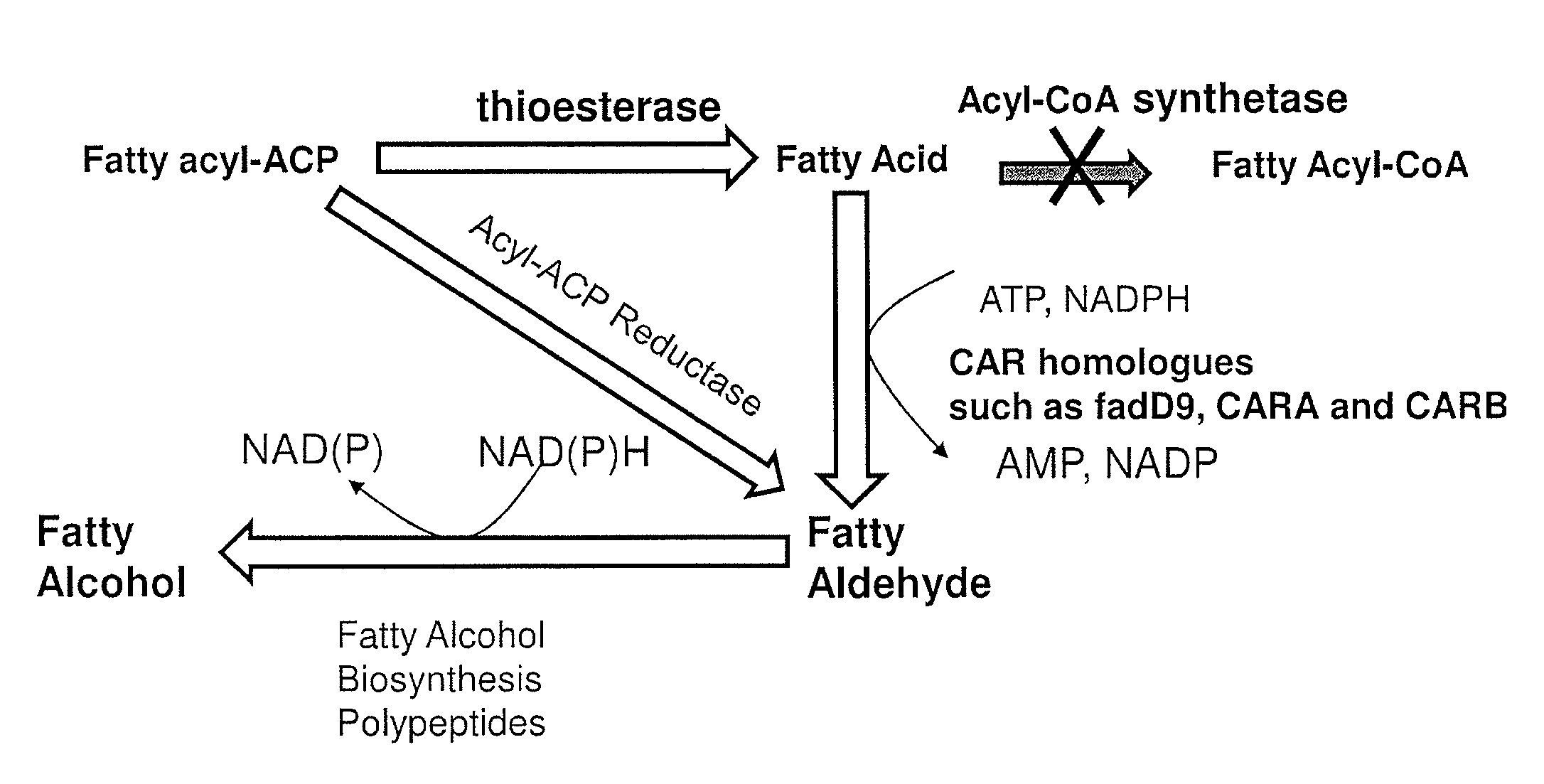
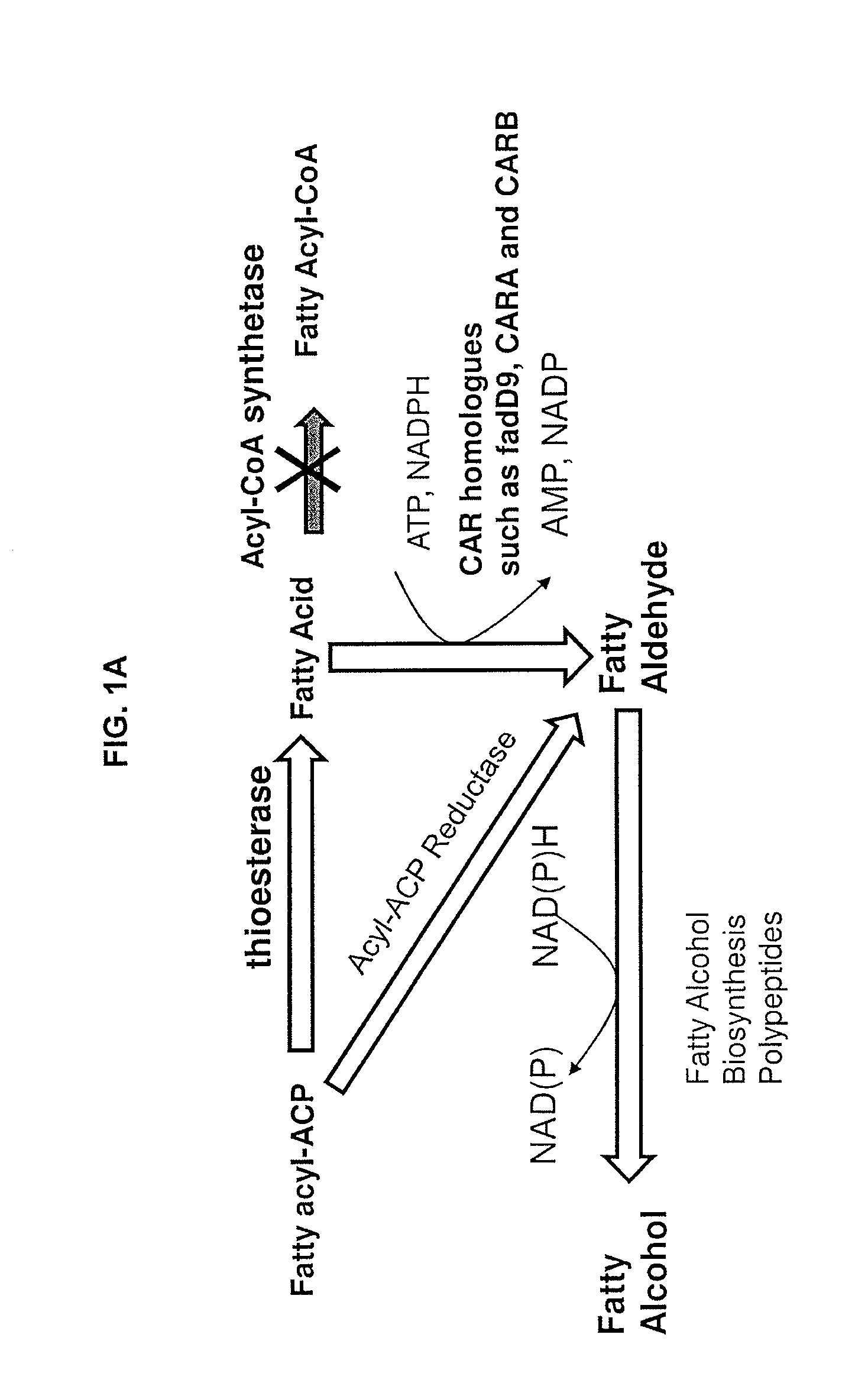
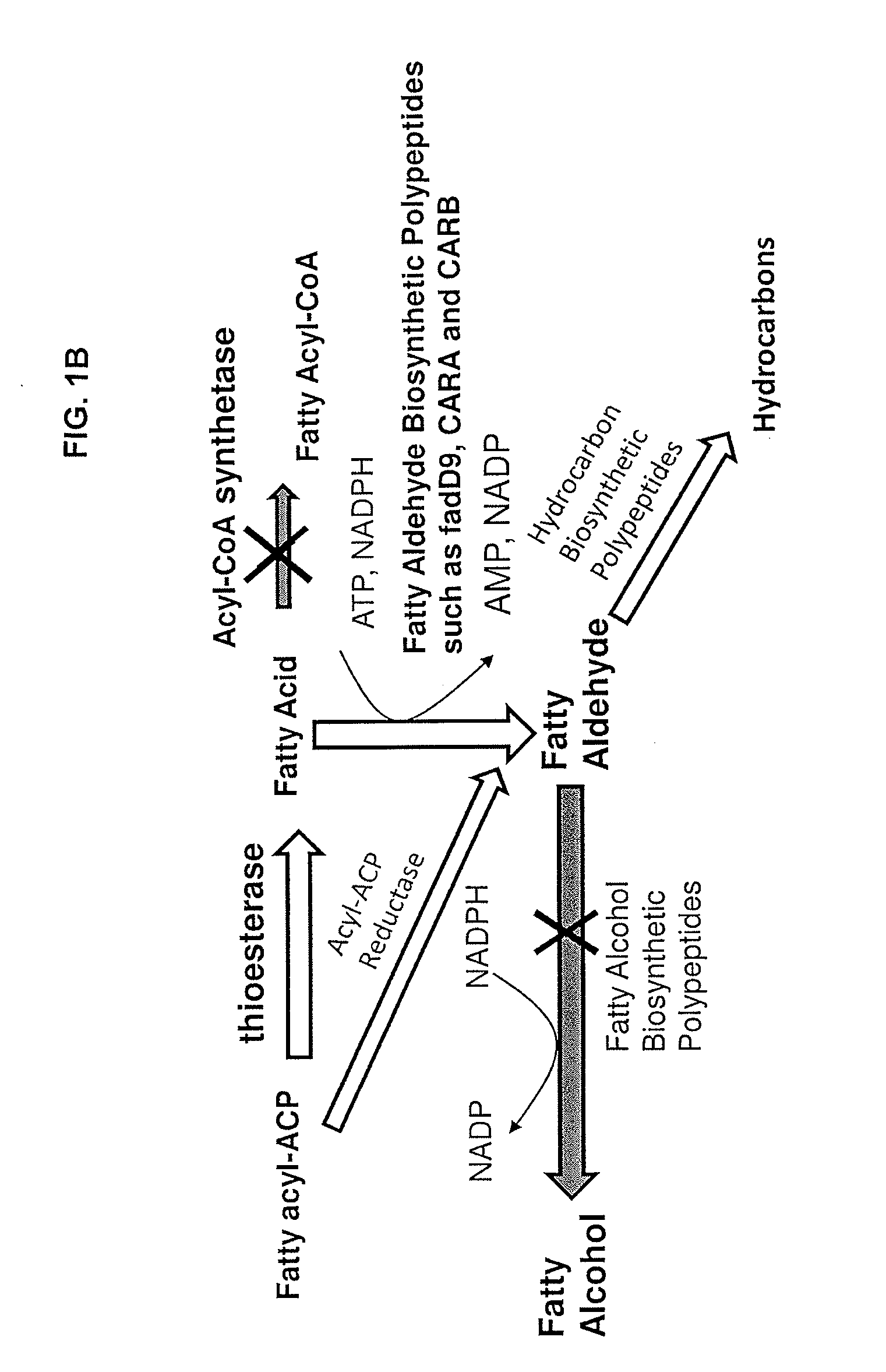
Methods and compositions related to fatty alcohol biosynthetic enzymes
InactiveUS20110250663A1High potencyOrganic chemistryMicroorganismsFatty alcoholFatty acid derivatives
Compositions and methods for producing fatty acid derivatives using recombinant microorganisms are described herein.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC +1
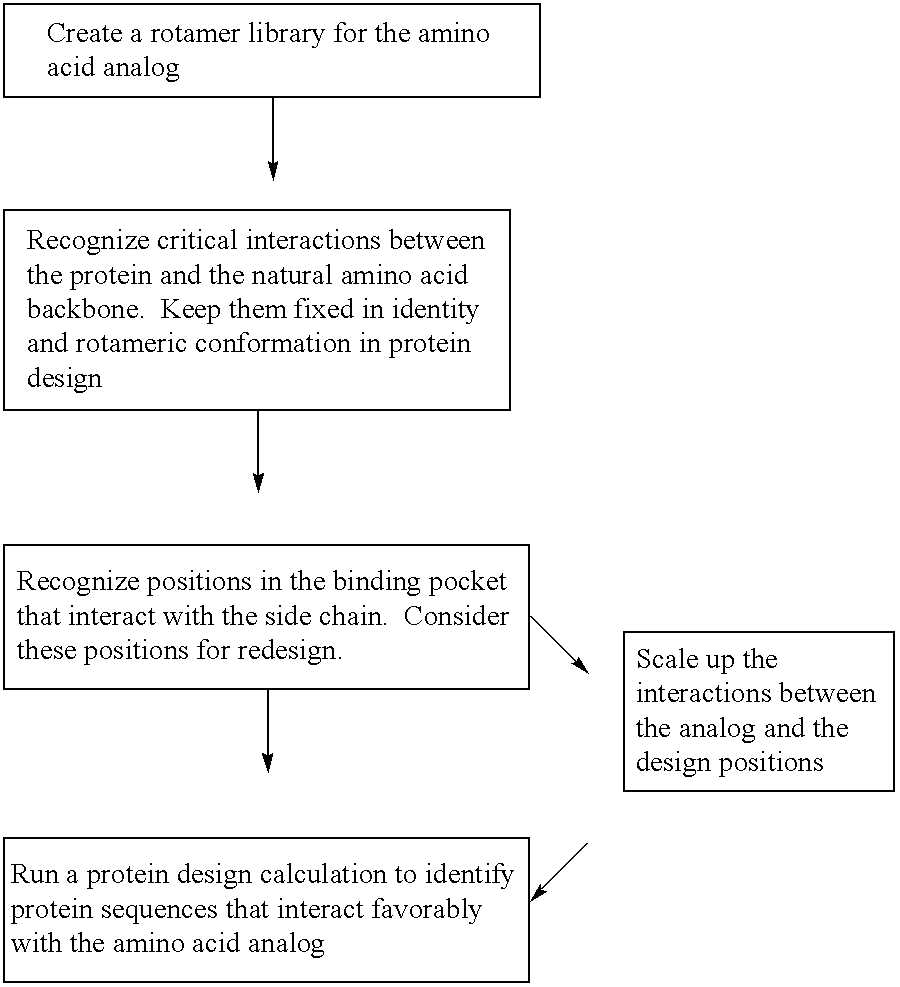
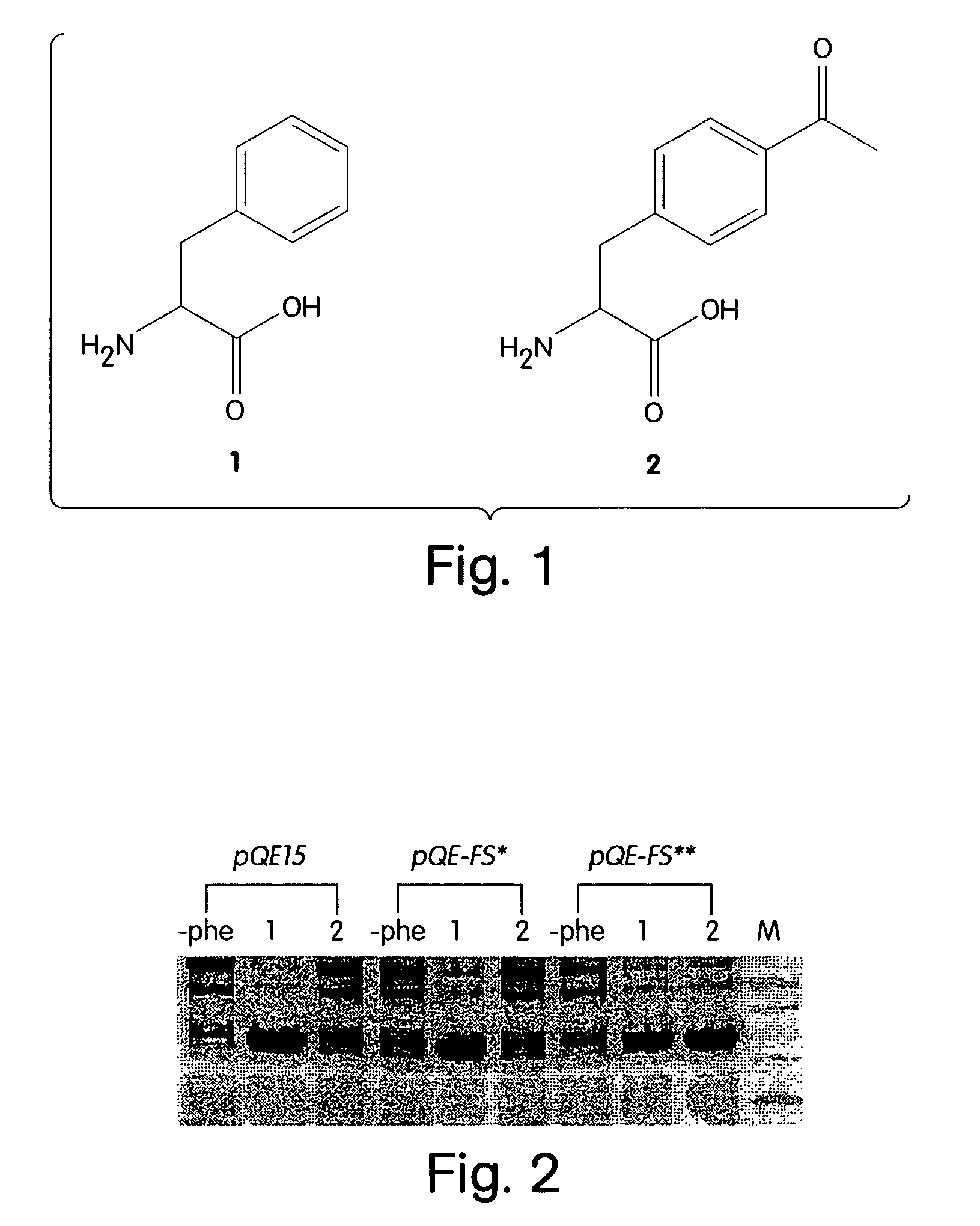
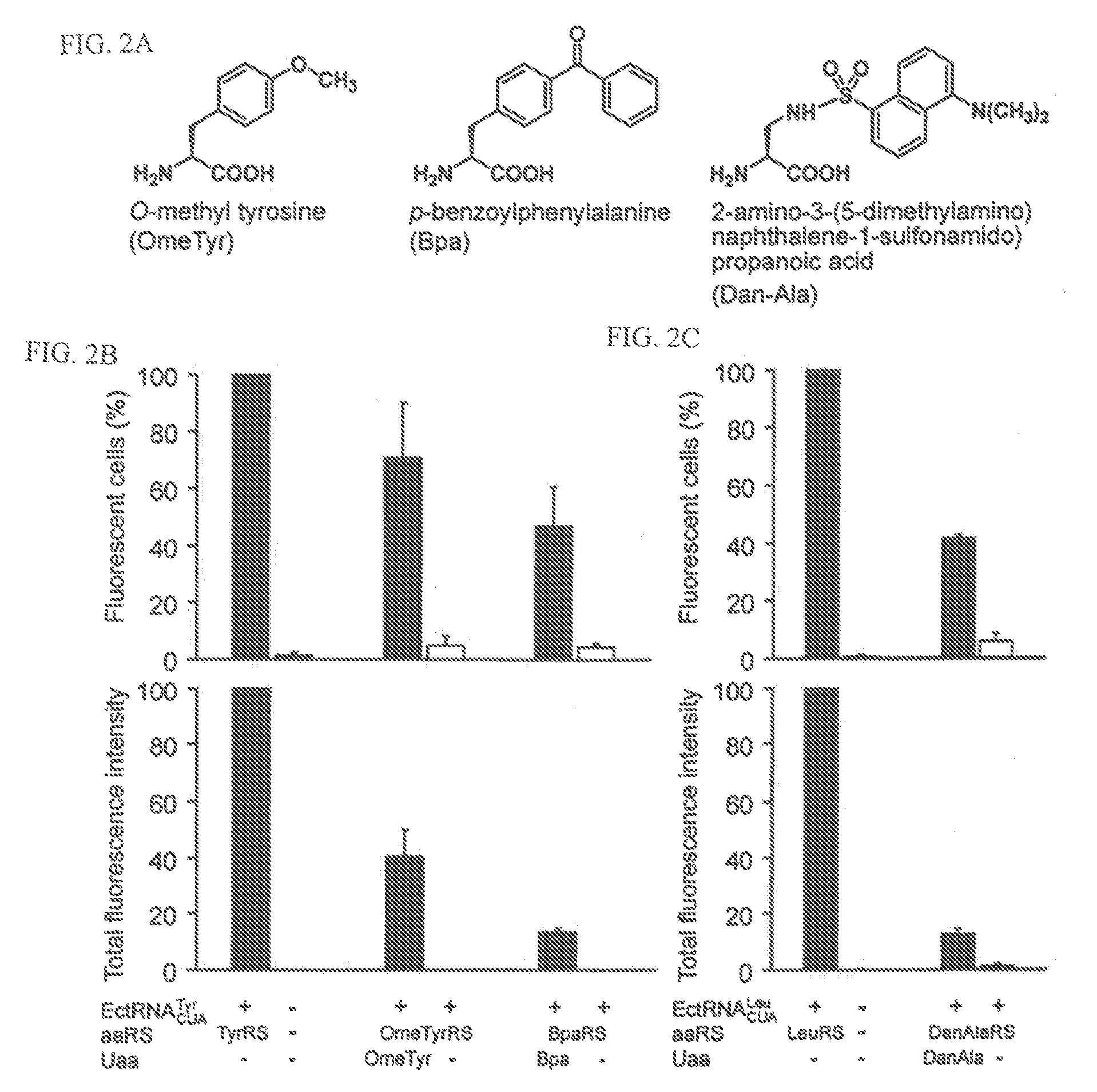
Computational method for designing enzymes for incorporation of non natural amino acids into proteins
The instant invention provides methods, reagents, and computational tools for designing non-natural substrate analogs for enzymes, especially for designing unnatural amino acid analogs for aminoacyl tRNA Synthetases (AARSs), such as the Phe tRNA Synthetase. The instant invention also provides methods to incorporate unnatural amino acid analogs, especially those with interesting functional groups, into protein products to generate proteins of modified or novel functions.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods and compositions for directed microwave chemistry
InactiveUS20020197645A1Facilitate decision-makingReduce chanceImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsArtificial enzymeChemical measurement
The present invention concerns a novel means by which specific chosen reactions can be accelerated through the use of a new type of artificial enzyme. The invention allows specific reactions to occur at an accelerated rate, even in the presence of other non-chosen molecules, which may be very similar in structure to the chosen reactant. The reactions may be stoichiometric or catalytic.
Owner:MILESTONE SRL
Kit for Treatment of Cancer
InactiveUS20080287541A1Effective treatmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRate limiting enzymeAdduct
The present invention relates to a kit for the treatment of cancer comprising (a) a container for containing a first compound (i) or a precursor thereof, said first compound or precursor being a compound that oxidizes glutathione (GSH); (b) a container for containing a second compound (ii) or a precursor thereof, said second compound or precursor being a compound that forms an adduct or conjugate with GSH; (c) a container for containing a third compound (iii) or a precursor thereof, said third compound or precursor being a compound that inhibits the rate-limiting enzyme of GSH biosynthesis, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (GCS); and (d) a container for containing a fourth compound (iv) or a precursor thereof, said fourth compound or precursor being a compound that inhibits the enzyme responsible for the conversion of GSSG to GSH, glutathione reductase (GR).
Owner:REDOXIA ISRAEL
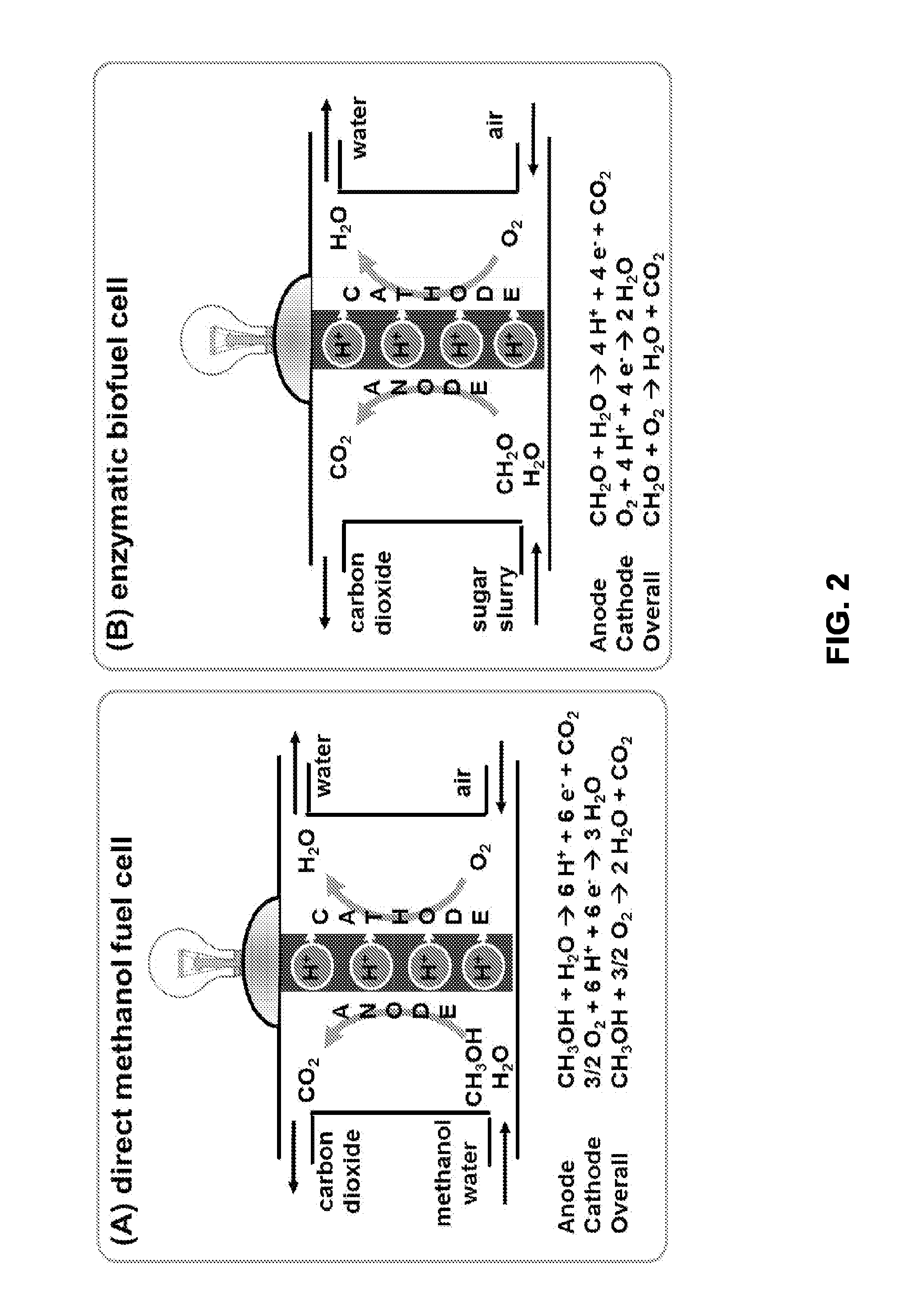
Complete Oxidation of Sugars to Electricity by Using Cell-Free Synthetic Enzymatic Pathways
ActiveUS20160028101A1High densityHigh energy storage densityBiochemical fuel cellsElectricityCell free
The present invention is in the field of bioelectricity. The present invention provides energy generating systems, methods, and devices that are capable of converting chemical energy stored in sugars into useful electricity.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
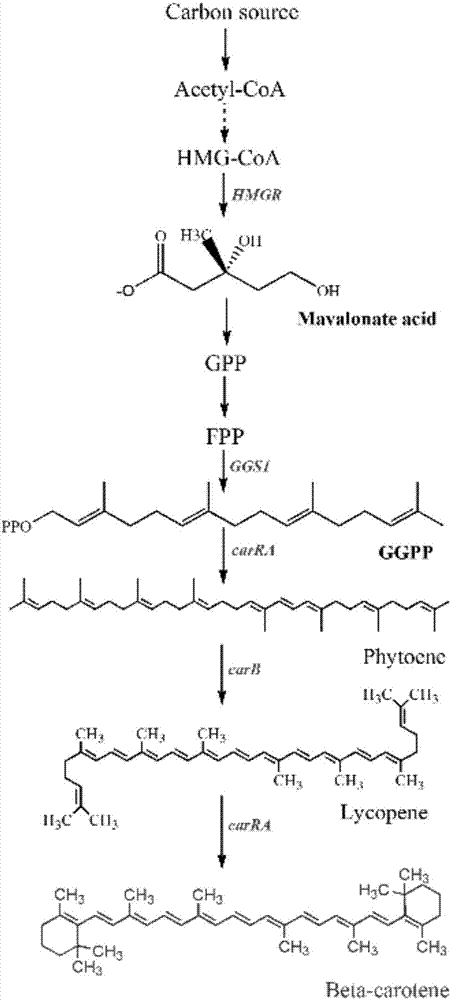
Genes encoding carotenoid compounds
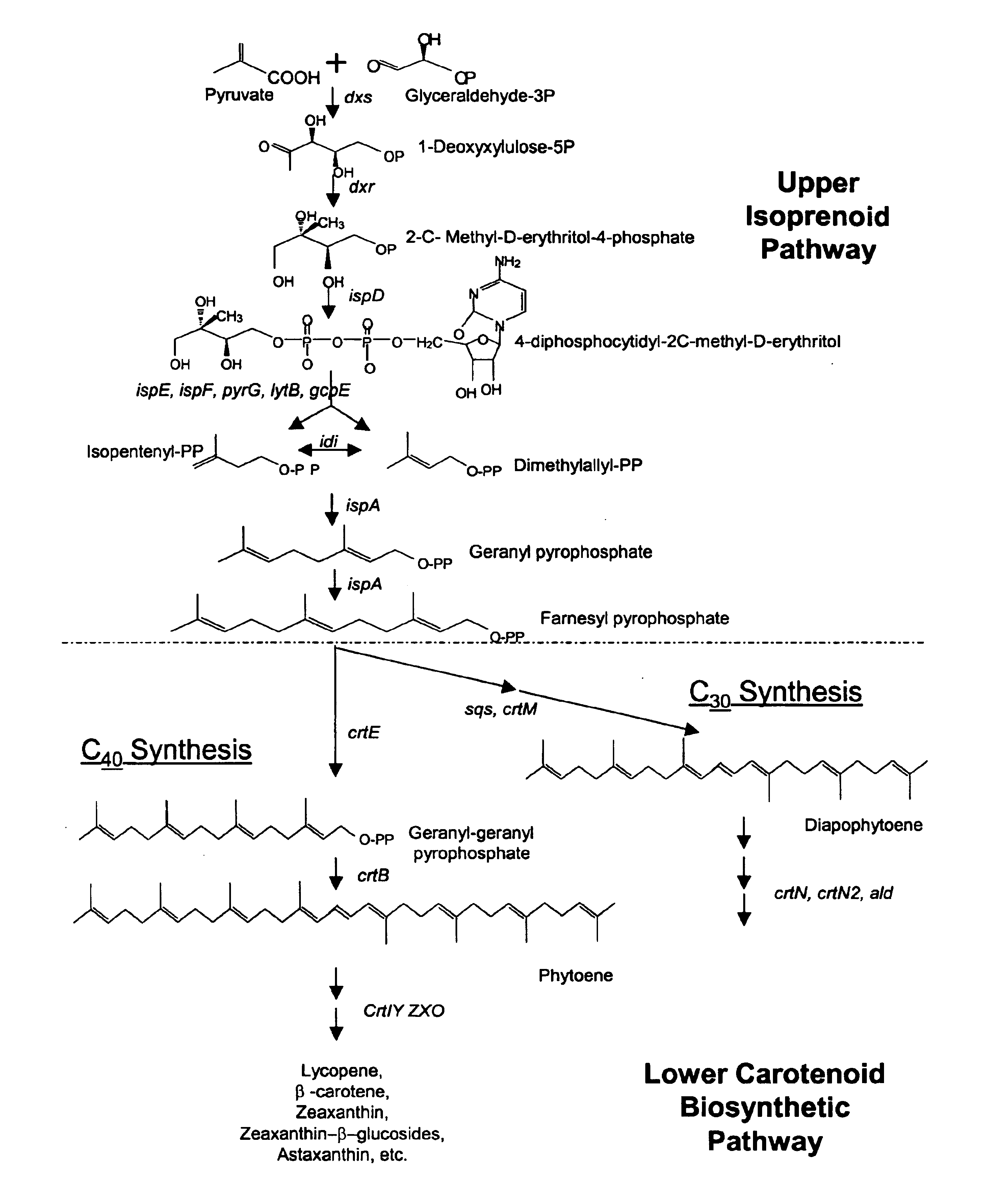
A unique carotenogenic biosynthetic gene cluster has been isolated from Panteoa agglomerans strain DC404, wherein the genetic organization of the cluster is crtE-idi-crtY-crtI-crtB-crtZ. The genes contained within this cluster encode geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate (GGPP) synthetase (CrtE), isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase (Idi), lycopene cyclase (CrtY), phytoene desaturase (CrtI), phytoene synthase (CrtB), and β-carotene hydroxylase (CrtZ). The gene cluster, genes and their products are useful for the conversion of farnesyl pyrophosphate to carotenoids. Vectors containing those DNA segments, host cells containing the vectors and methods for producing those enzymes by recombinant DNA technology in transformed host organisms are disclosed.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Genetically encoded fluorescent coumarin amino acids
InactiveUS20080044886A1Retain biological activityBacteriaTissue cultureBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
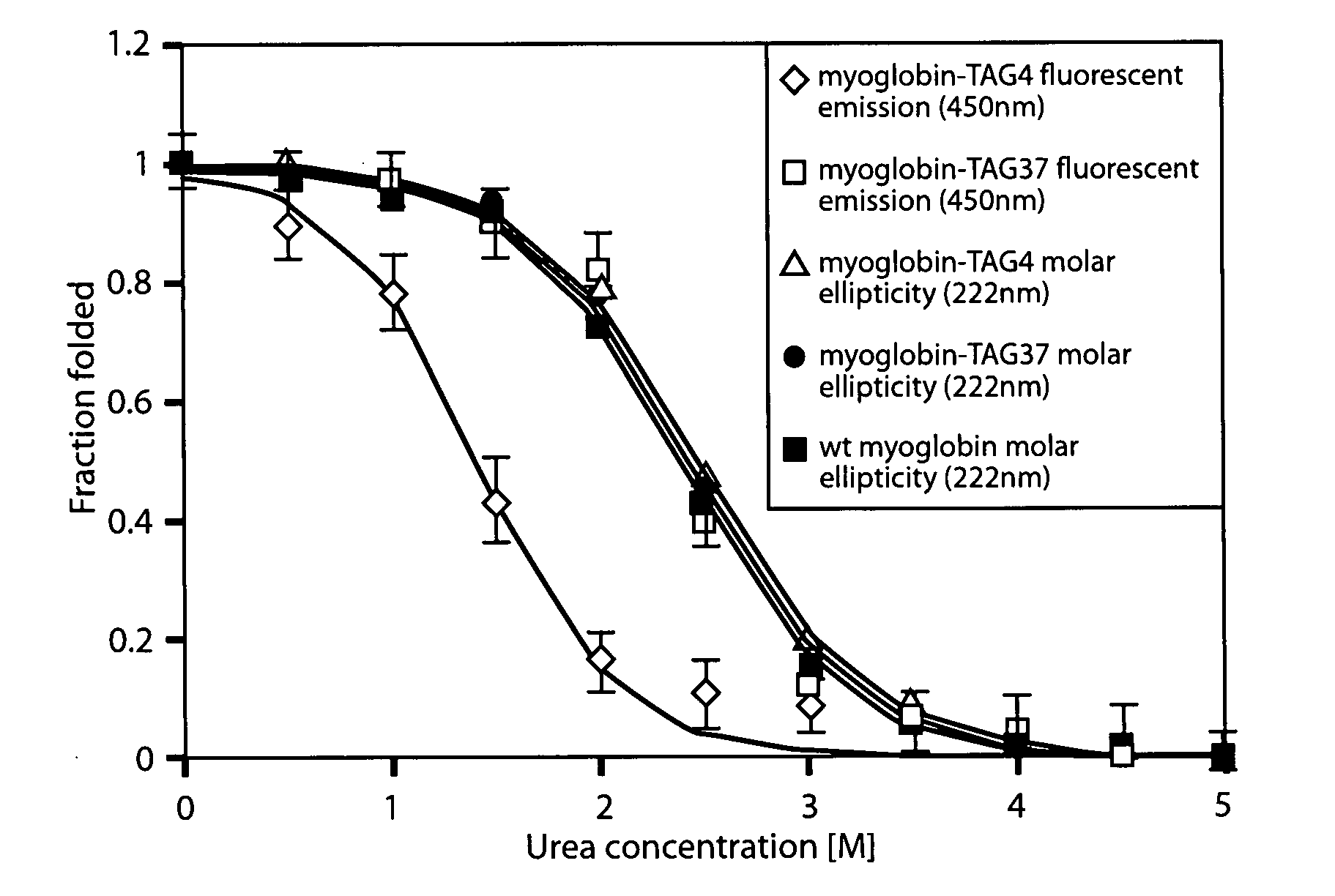
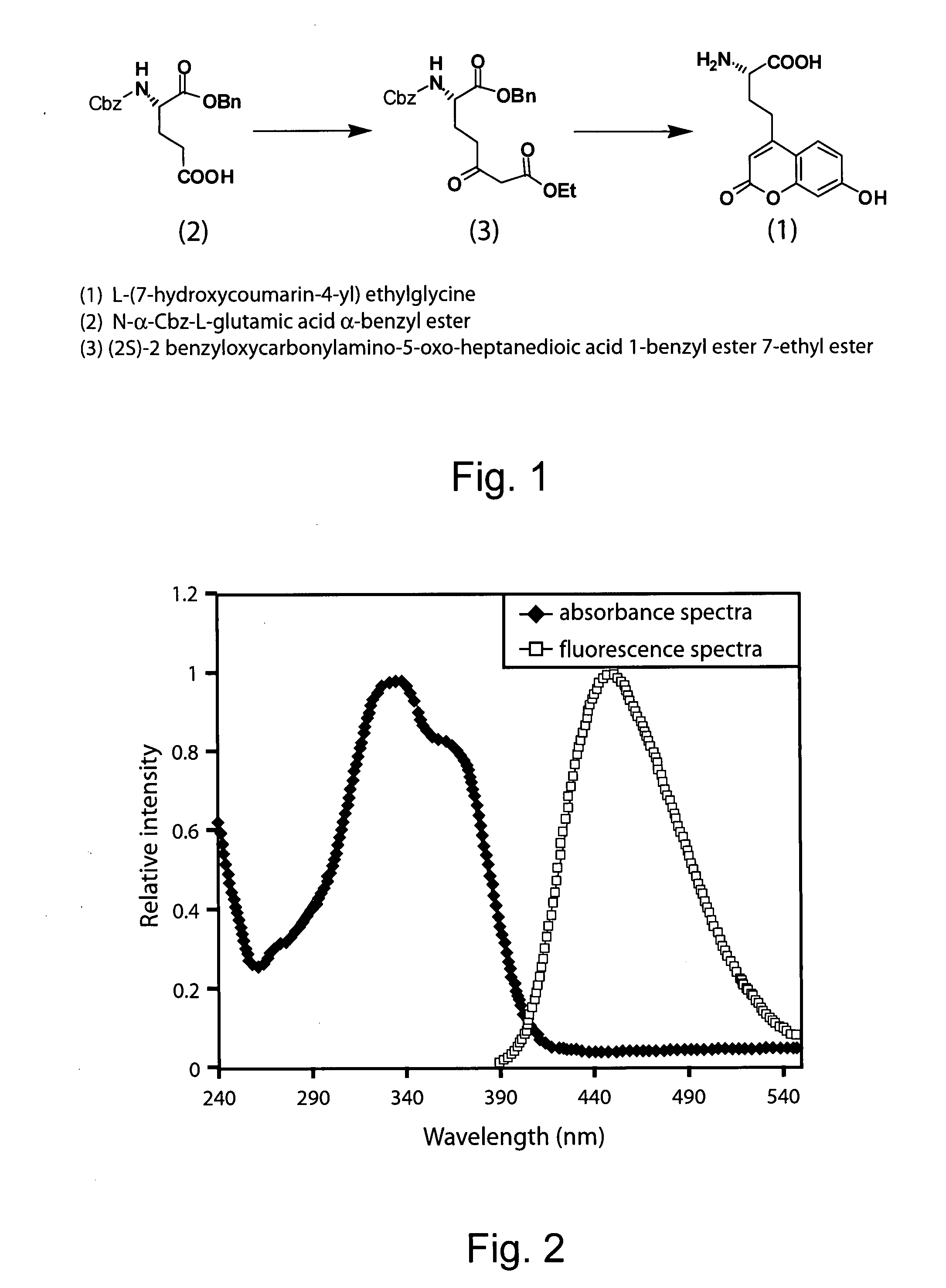
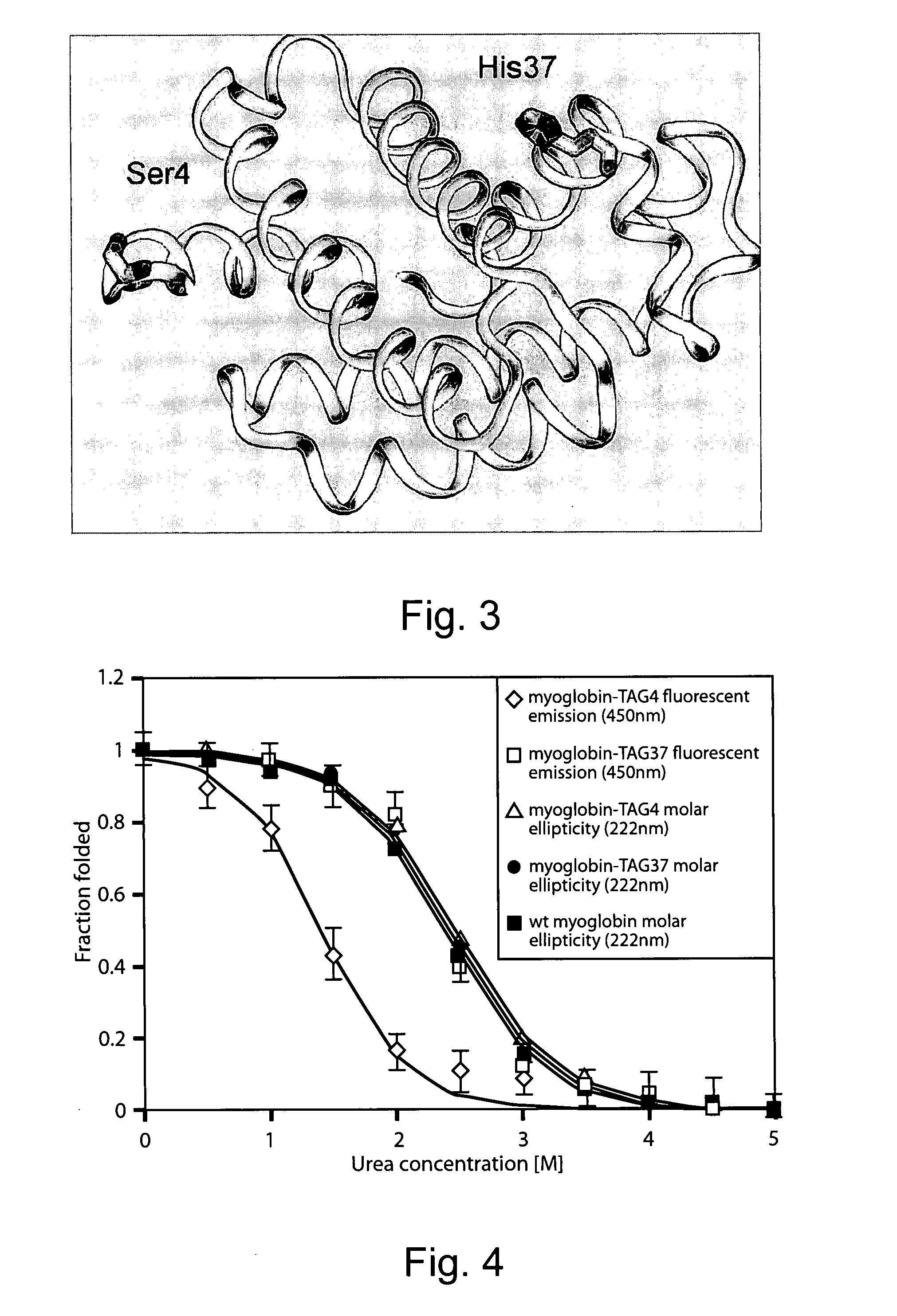
The invention relates to orthogonal pairs of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that can incorporate the coumarin unnatural amino acid L-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl) ethylglycine into proteins produced in eubacterial host cells such as E. coli. The invention provides, for example but not limited to, novel orthogonal synthetases, methods for identifying and making the novel synthetases, methods for producing proteins containing the unnatural amino acid L-(7-hydroxycoumarin-4-yl)ethylglycine and related translation systems.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Construction and application of polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01
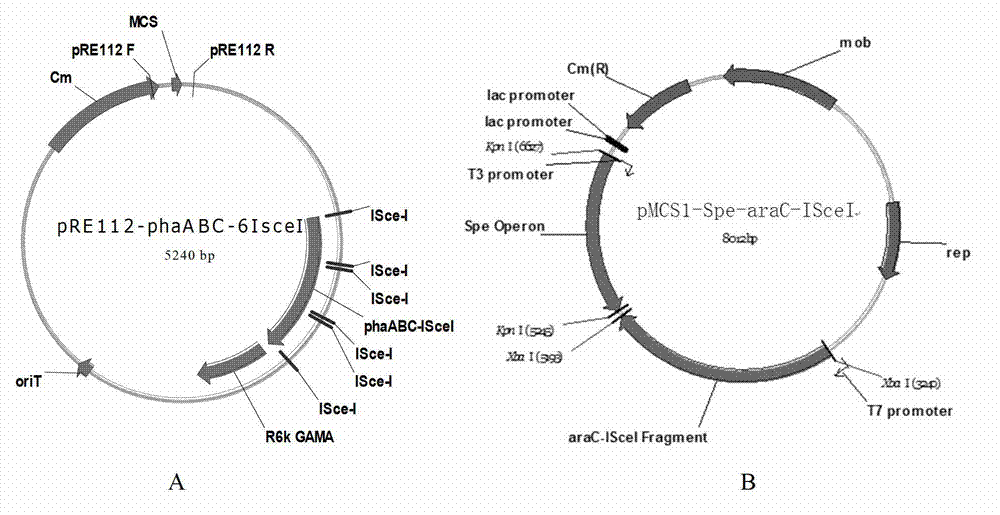
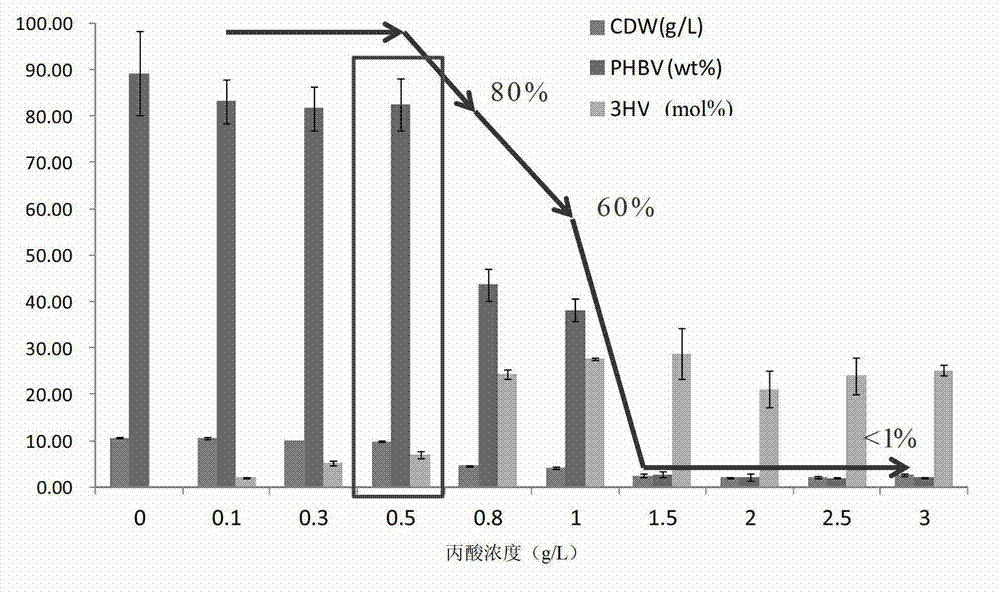
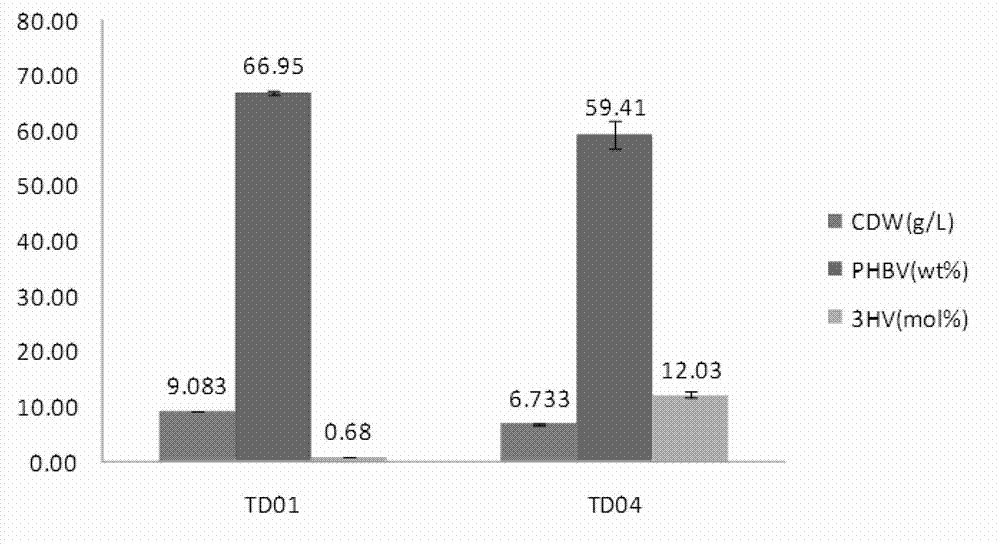
ActiveCN102816729AGood characterIncrease the molar ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnology3-Hydroxypentanoic acid
The invention discloses construction and application of a polygene knockout strain of Halomonas sp. TD01. The invention provides a recombinant strain which is obtained by inactivating one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid in the Halomonas sp. TD01 used for producing polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA). The one or more genes related to metabolic pathways of propionic acid are at least one selected from the group consisting of a coding gene for 2-methylcitrate synthetase, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 1, a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 2 and a coding gene for PHA digestive enzyme 3. According to results of experiments in the invention, molecular modification is carried out on the Halomonas sp. TD01 to knock out 2-methylcitrate synthetase PrpC and three PHA digestive enzymes so as to obtain the novel recombinant strain, poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) (PHBV) with more excellent material performance can be highly efficiently produced by utilizing propionic acid, and the proportion of 3-hydroxyvaleric acid monomers in the produced PHBV and the conversion rate of the substrate propionic acid are substantially improved.
Owner:BLUEPHA CO LTD
Polyunsaturated fatty acid production in heterologous organisms using pufa polyketide synthase systems
InactiveCN101573451AImprove the level ofReduce competitionMicrobiological testing/measurementAcyl Coenzyme A SynthetasesBiotechnology
Disclosed are novel acyl-CoA synthetases and novel acyltransferases, nucleic acid molecules encoding the same, recombinant nucleic acid molecules and recombinant host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules, genetically modified organisms (microorganisms and plants) comprising the same, and methods of making and using the same. Also disclosed are genetically modified organisms (e.g., plants, microorganisms) that have been genetically modified to express a PKS-like system for the production of PUFAs (a PUFA PKS system or PUFA synthase), wherein the organisms have been modified to express an acyl-CoA synthetase, to express an acyl transferase, to delete or inactivate a fatty acid synthase (FAS) expressed by the organism, to reduce competition for malonyl CoA with the PUFA synthase or toincrease the level of malonyl CoA in the organism, and in one aspect, to inhibit KASII or KASIII. Additional modifications, and methods to make and use such organisms, in addition to PUFAs and oils o btained from such organisms, are disclosed, alone with various products including such PUFAs and oils.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Genetically programmed expression of selectively sulfated proteins in eubacteria
The invention relates to orthogonal pairs of tRNAs and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases that can incorporate the unnatural amino acid sulfotyrosine into proteins produced in eubacterial host cells such as E. coli. The invention provides, for example but not limited to, novel orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases, polynucleotides encoding the novel synthetase molecules, methods for identifying and making the novel synthetases, methods for producing proteins containing the unnatural amino acid sulfotyrosine and translation systems.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Transgenic high tryptophan plants
The present invention provides resistance to amino acid analogues of tryptophan and / or modification of tryptophan content in plants by introducing and expressing an isolated DNA fragment encoding anthranilate synthase in plant cells Methods. Also provided are transgenic plants transformed with the isolated DNA fragment encoding an anthranilate synthase, as well as human or animal food, seeds and progeny derived from these plants.
Owner:RENESSEN +1
Recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacterium
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacterium. The construction method comprises the following steps: respectively constructing superstrong gene expression modules of protein phytoene synthetase / lycopene cyclase coded by beta-carotene synthetic genes optimized by codons, phytoene dehydrogenase, protein geranyl diphosphate synthase coded by MAV (micro aerial vehicle) pathway genes and 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; assembling the gene expression modules in vitro, so as to obtain four plasmids of the gene expression modules, integrating the plasmids into a host bacteria genome which does not produce beta-carotene and screening orange single colonies, so as to obtain the recombinant bacterium for producing beta-carotene. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention is adopted for producing beta-carotene by fermental cultivation, and the yield of beta-carotene can reach 26.03mg / g DCW. Therefore, the recombinant bacterium has high performance of producing beta-carotene.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
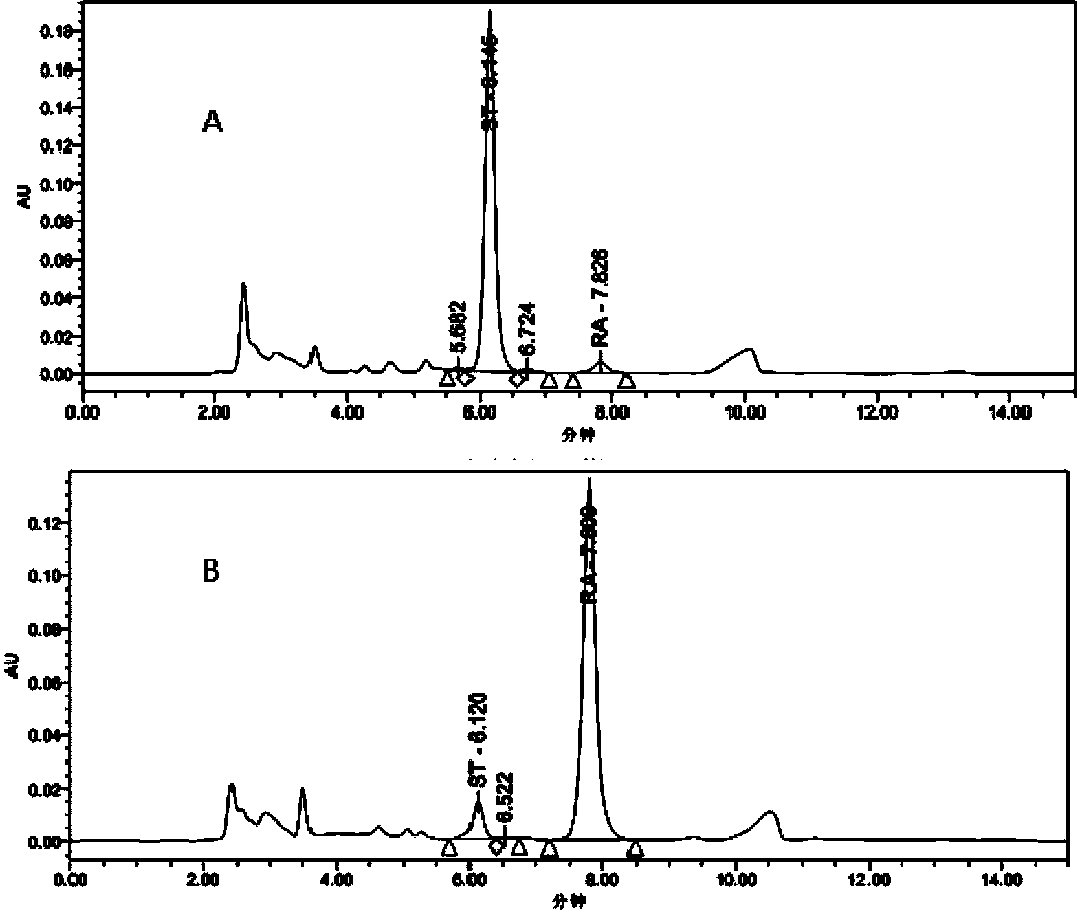
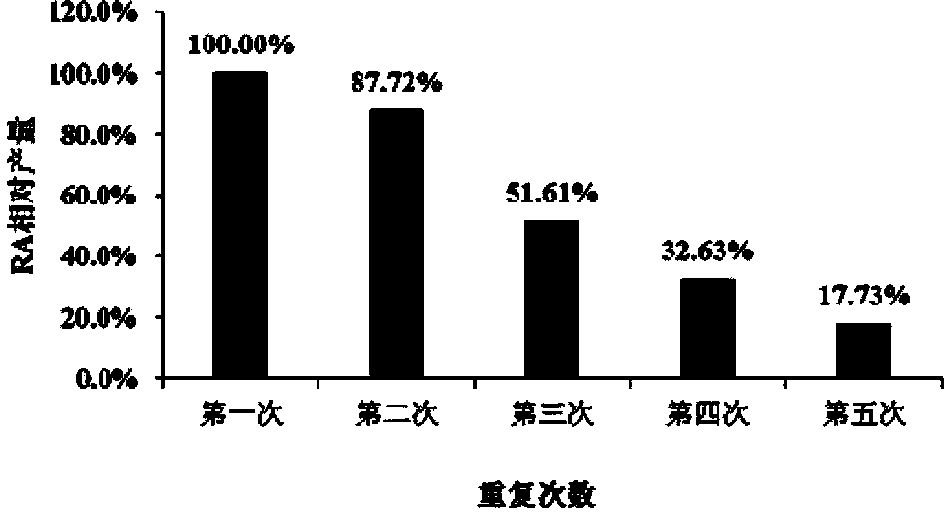
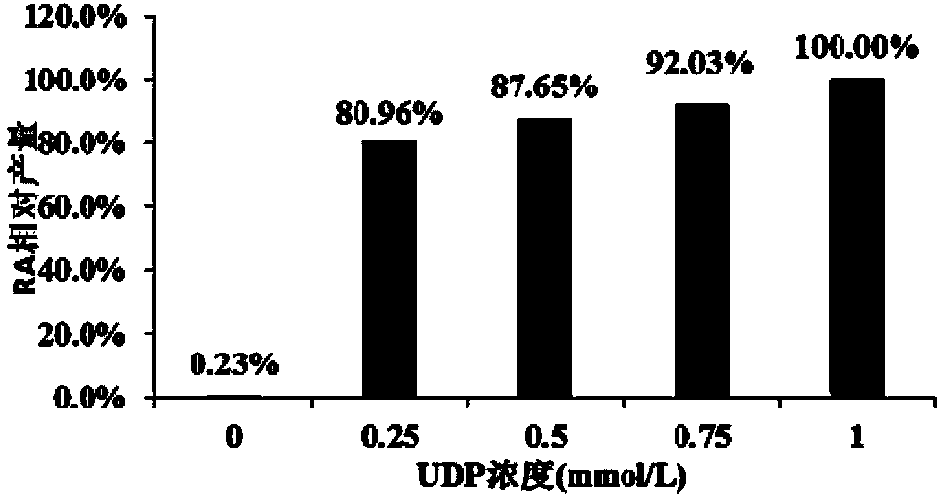
Recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium and application thereof to synthesis of RA (rebaudioside A)
ActiveCN104232496AIncrease usageHigh synthesis efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesSucrose synthetasePtru catalyst
The invention discloses a recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium and a method for using the recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium as a whole-cell catalyst for synthesizing RA (rebaudioside A). The recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium is obtained through conversion of pichia pastoris after linearization of an expression vector containing exogenous DNA as follows: the DNA sequence for coding sucrose synthetase Sus1 is represented by SEQ ID NO.3, and the DNA sequence for coding UDP-glycosyl transferase UGT76G1 is represented by SEQ ID NO.4. The intracellular expression of the Sus1 and the surface expression of the UGT76G1 are realized by the aid of the recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium, and the recombinant pichia pastoris engineering bacterium is used as the whole-cell catalyst and can be effectively used for synthesizing the RA, so that the synthetic efficiency of the RA is improved, the raw material utilization rate is increased, the production cost is reduced, and a new industrial way is opened for production and processing of the RA.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KANGLINNAI BIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Programmable molecular manipulating processes
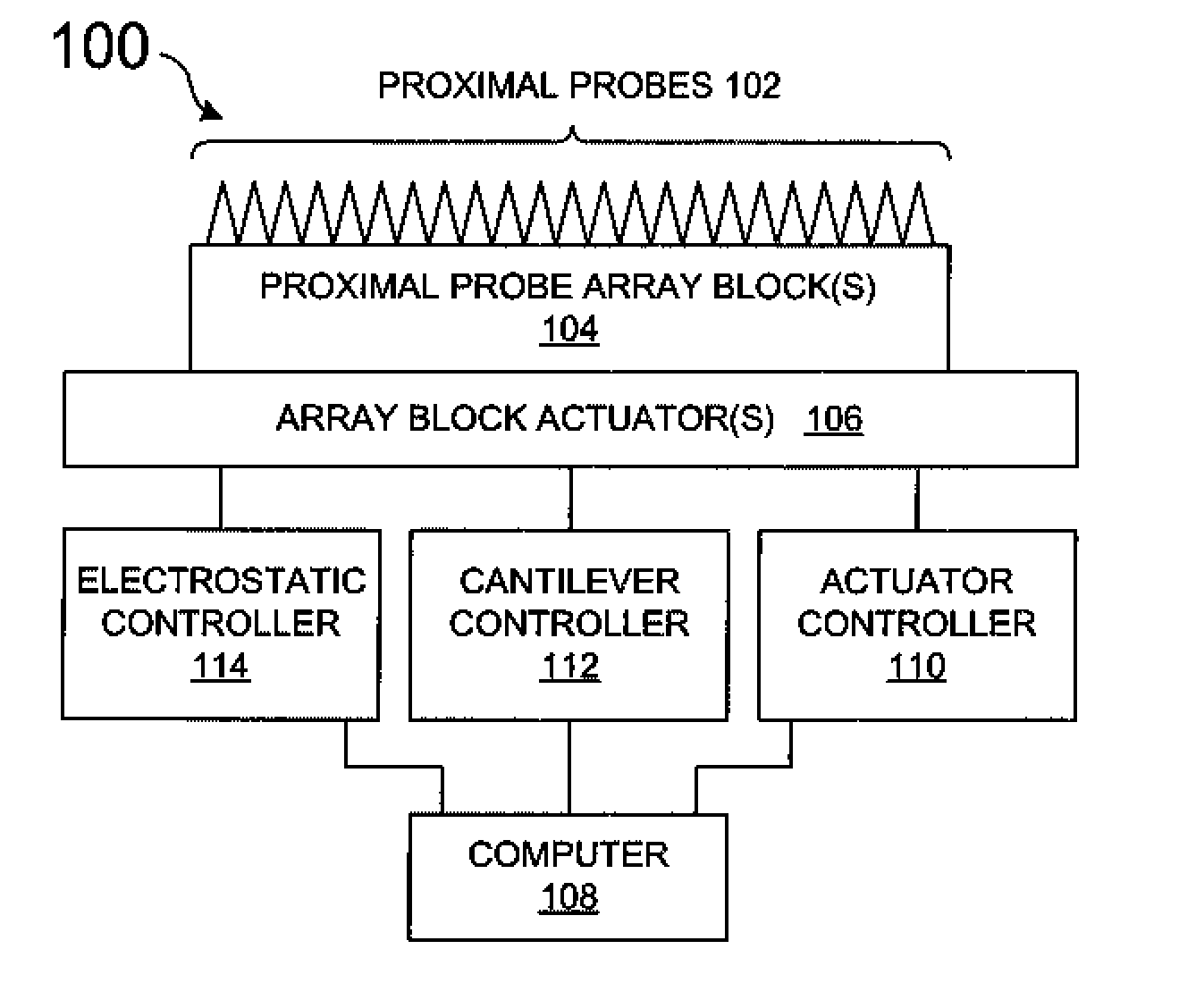
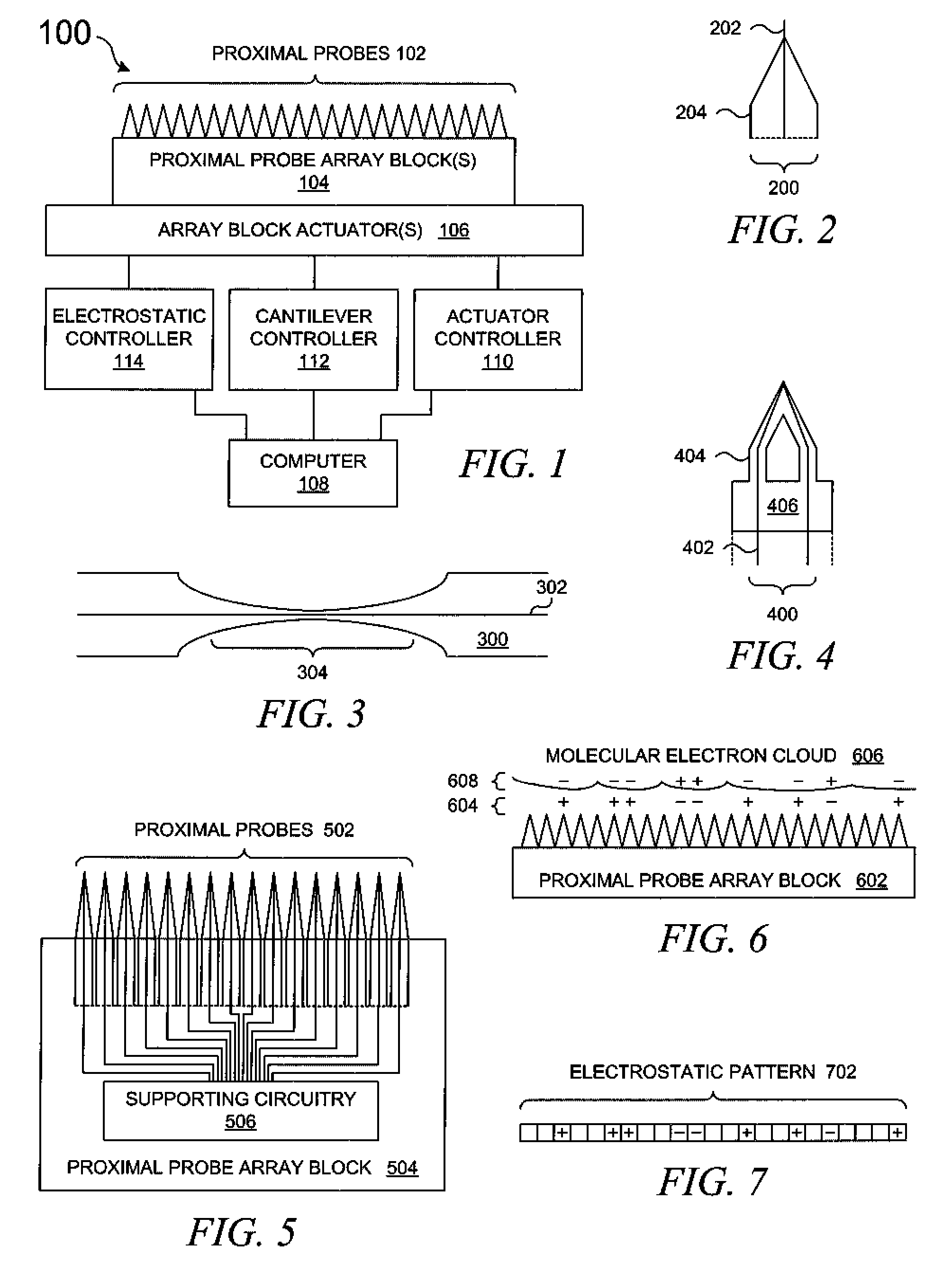
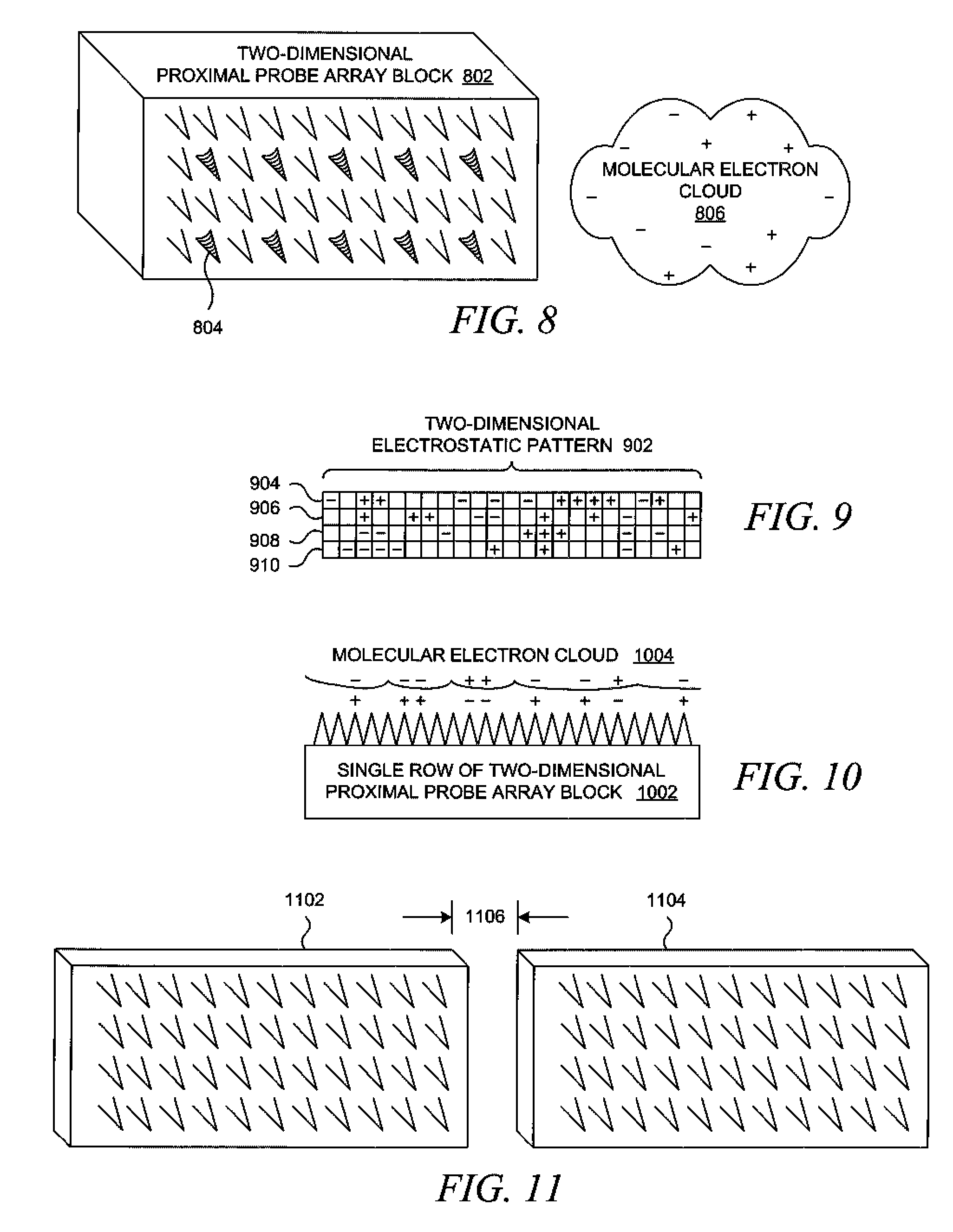
InactiveUS7326923B2Material nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureChemical reactionSynthetic enzyme
A system manipulates molecules using a set of proximal probes such as those used in atomic force microscopes. An electrostatic pattern is placed on a set of proximal probes such that each proximal probe may exert an electrostatic force. A molecule is captured using those electrostatic forces, after which the molecule can be manipulated while the molecule remains captured by the proximal probes. The electrostatic pattern can be modified such that the molecule moves and / or rotates over the set of proximal probes while the molecule remains captured by the set of proximal probes. The electrostatic pattern can be used to bend or split the molecule while the molecule remains captured by the set of proximal probes, thereby allowing the system to engage the molecule in chemical reactions, e.g., to act as a synthetic catalyst or a synthetic enzyme.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method for producing lacto-n-biose i and galacto-n-biose
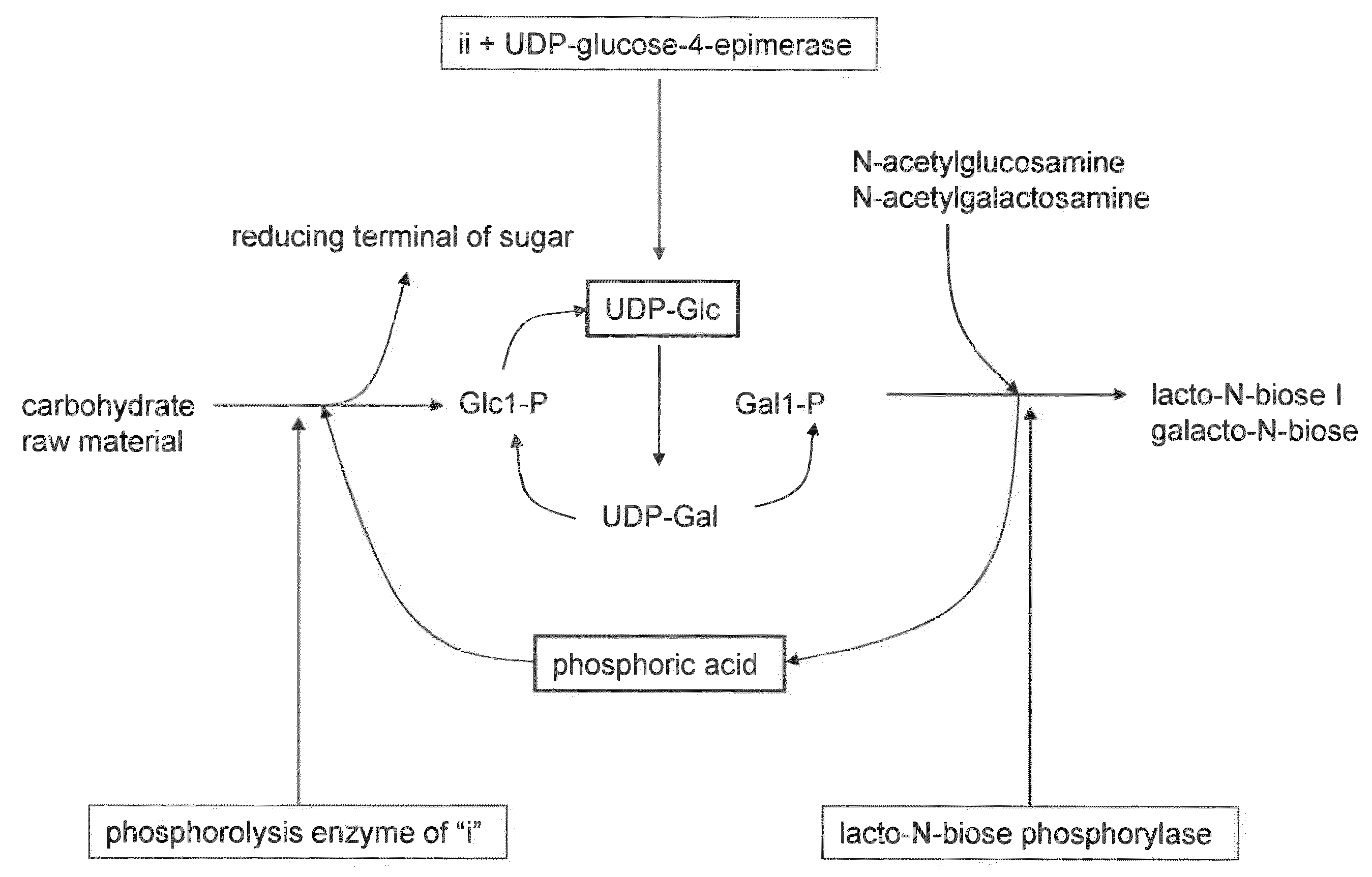
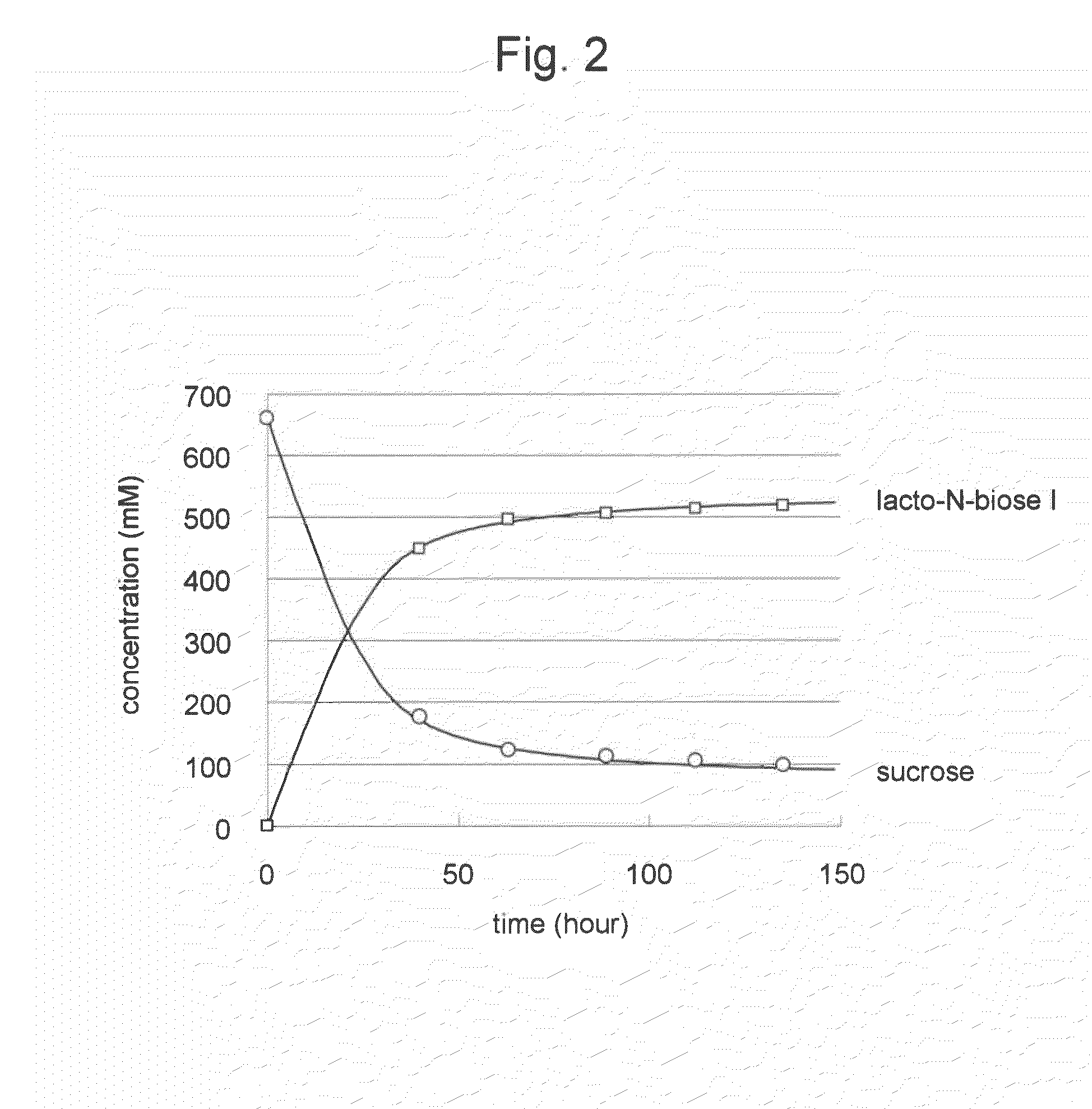
ActiveUS20100120096A1Easily and conveniently carry-outGood value for moneyImmobilised enzymesHydrolasesO-Phosphoric AcidPhosphorylation
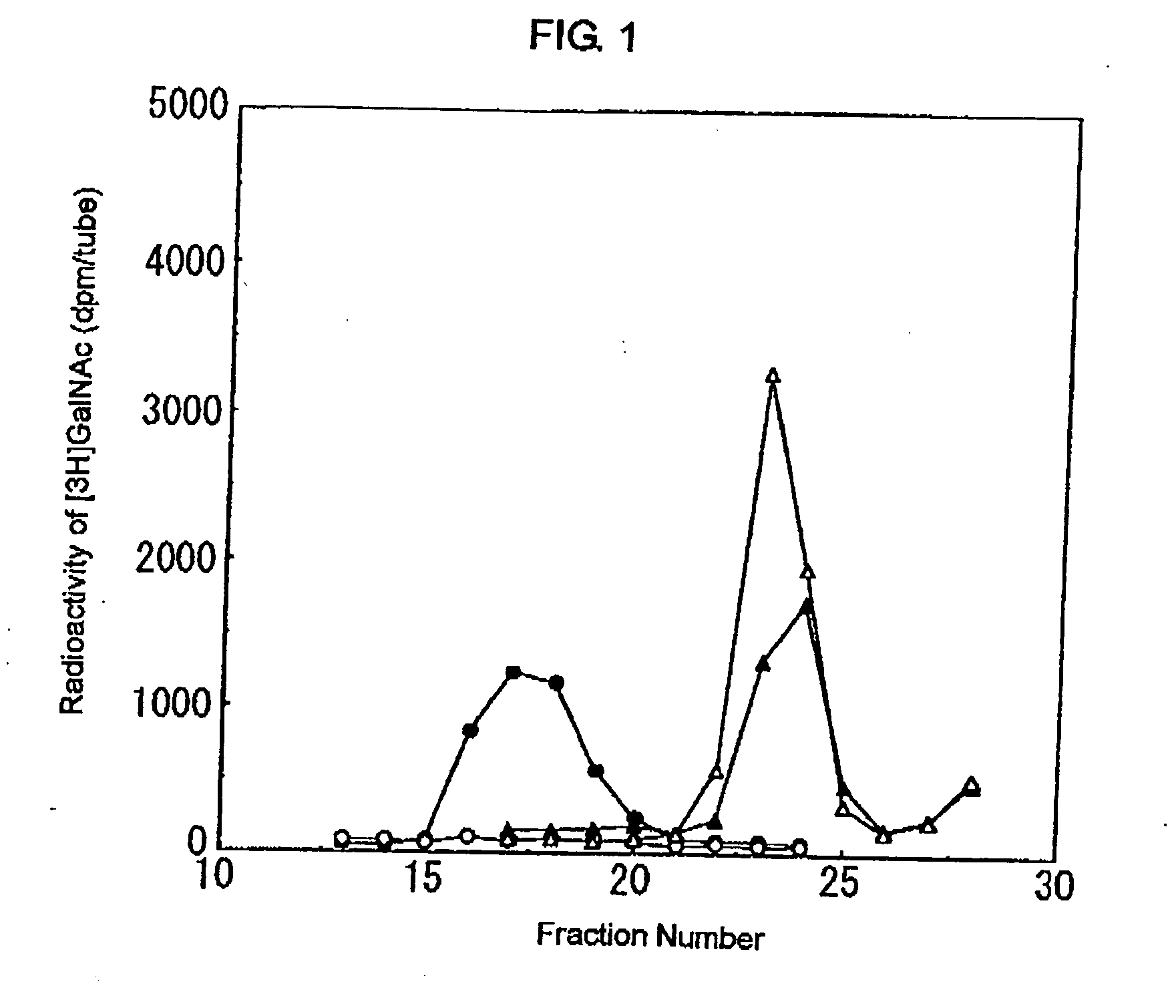
A method for producing lacto-N-biose I and galacto-N-biose inexpensively and conveniently is provided. The method for producing lacto-N-biose I or galacto-N-biose, characterized in that the method comprises causing: (i) a combination of a carbohydrate raw material with an enzyme that catalyzes phosphorolysis of the carbohydrate raw material to give a-glucose-1-phosphate; and (ii) a combination of an enzyme that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate to UDP-glucose and an enzyme that converts UDP-galactose to galactose-1-phosphate with their cofactors, and / or a combination of an enzyme (UDP-Gly synthase) that converts α-glucose-1-phosphate and UDP-galactose to UDP-glucose and α-galactose-1-phosphate, respectively, with its cofactor(s) to act in the presence of N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine, phosphoric acid, lacto-N-biose phosphorylase (EC 2.4.1.211), and UDP-glucose-4-epimerase (EC 5.1.3.2).
Owner:NAT AGRI & FOOD RES ORG
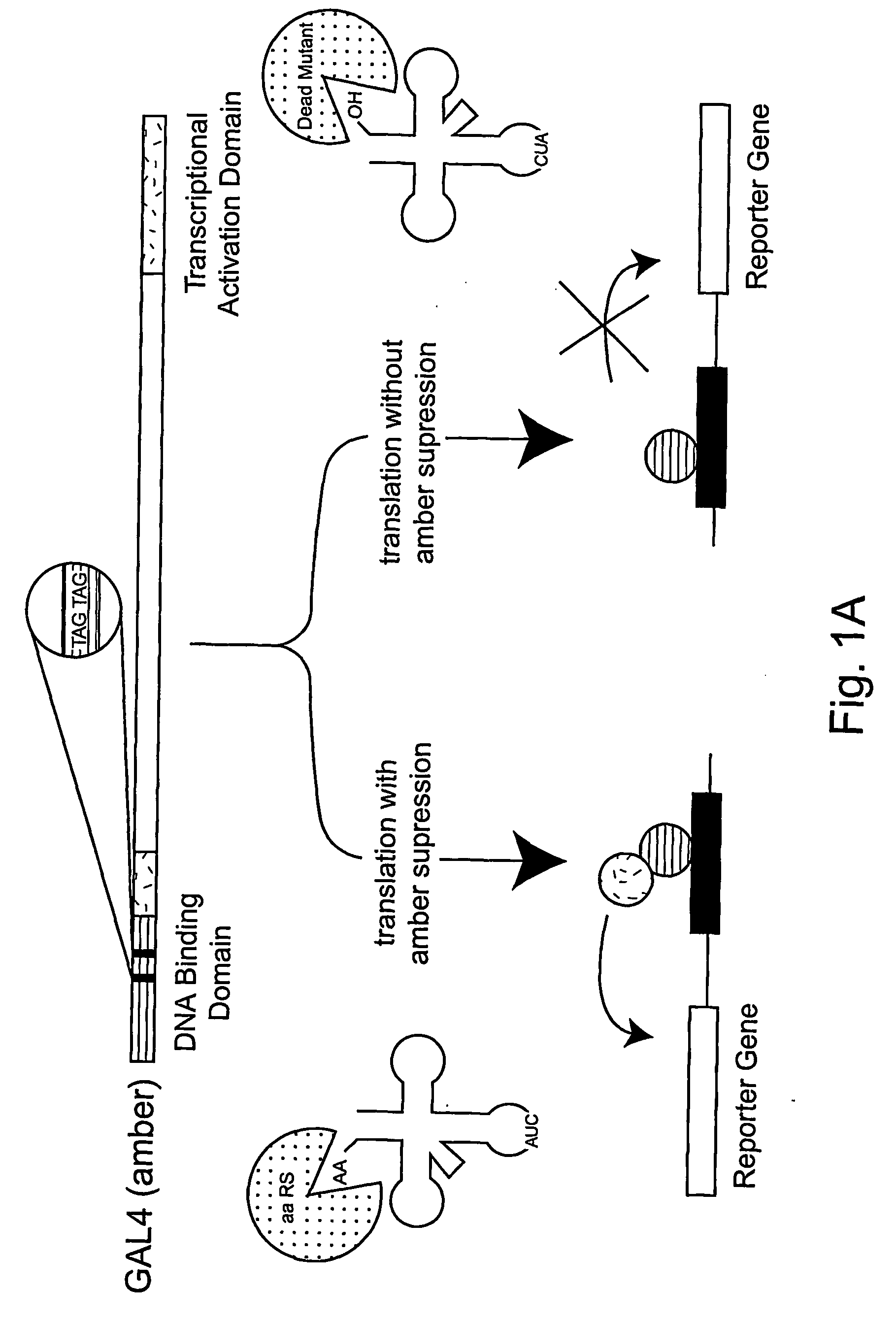
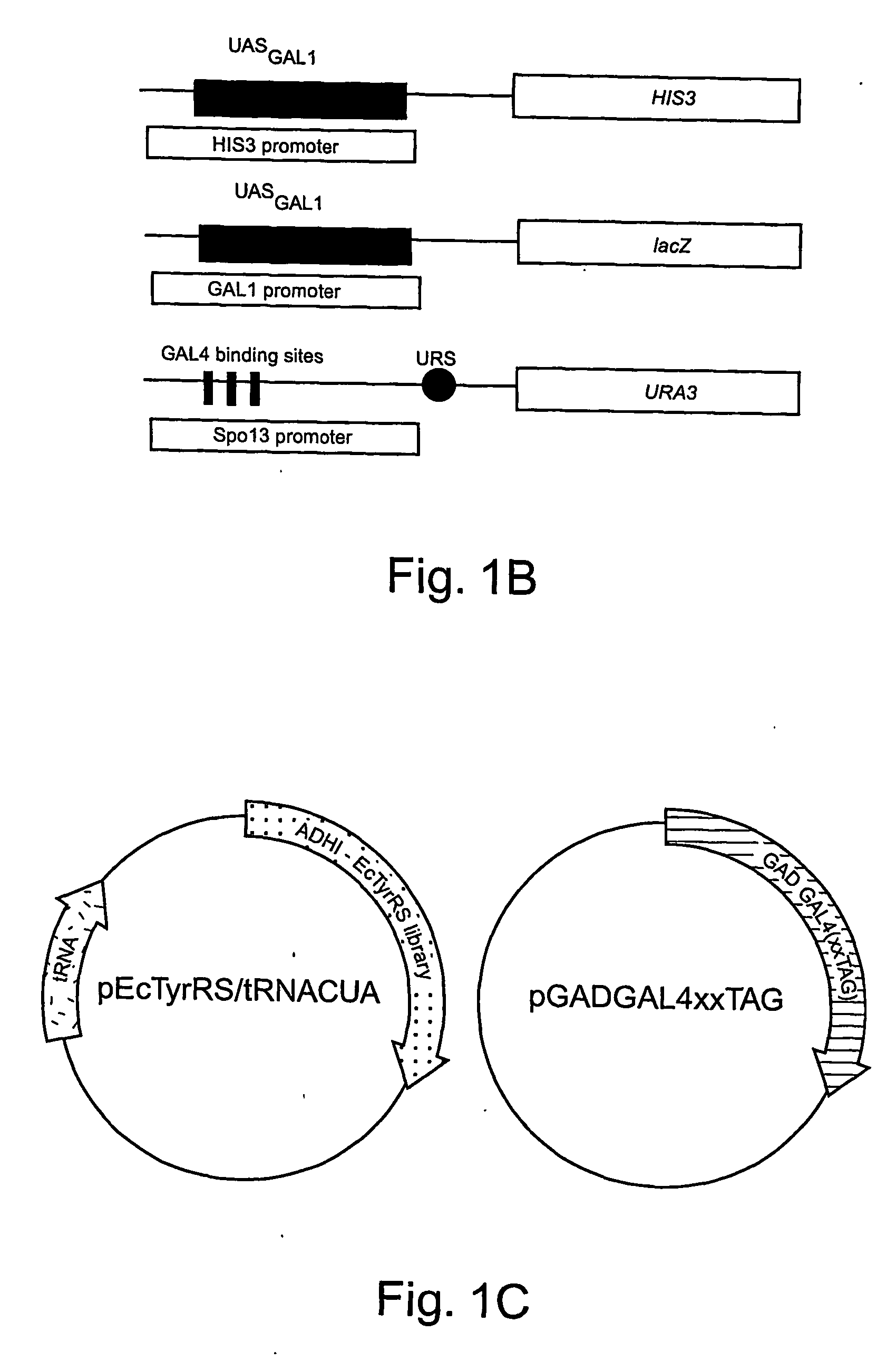
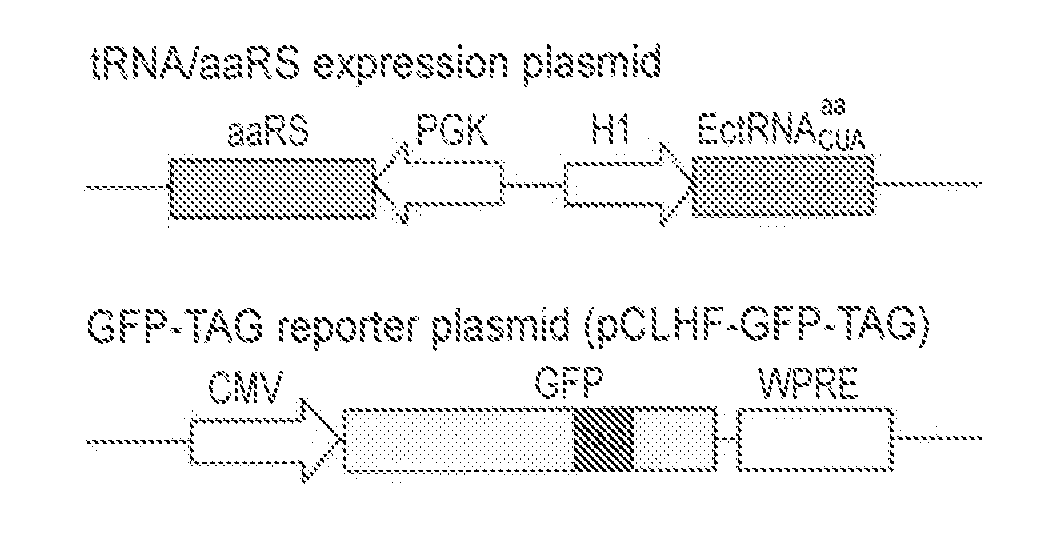
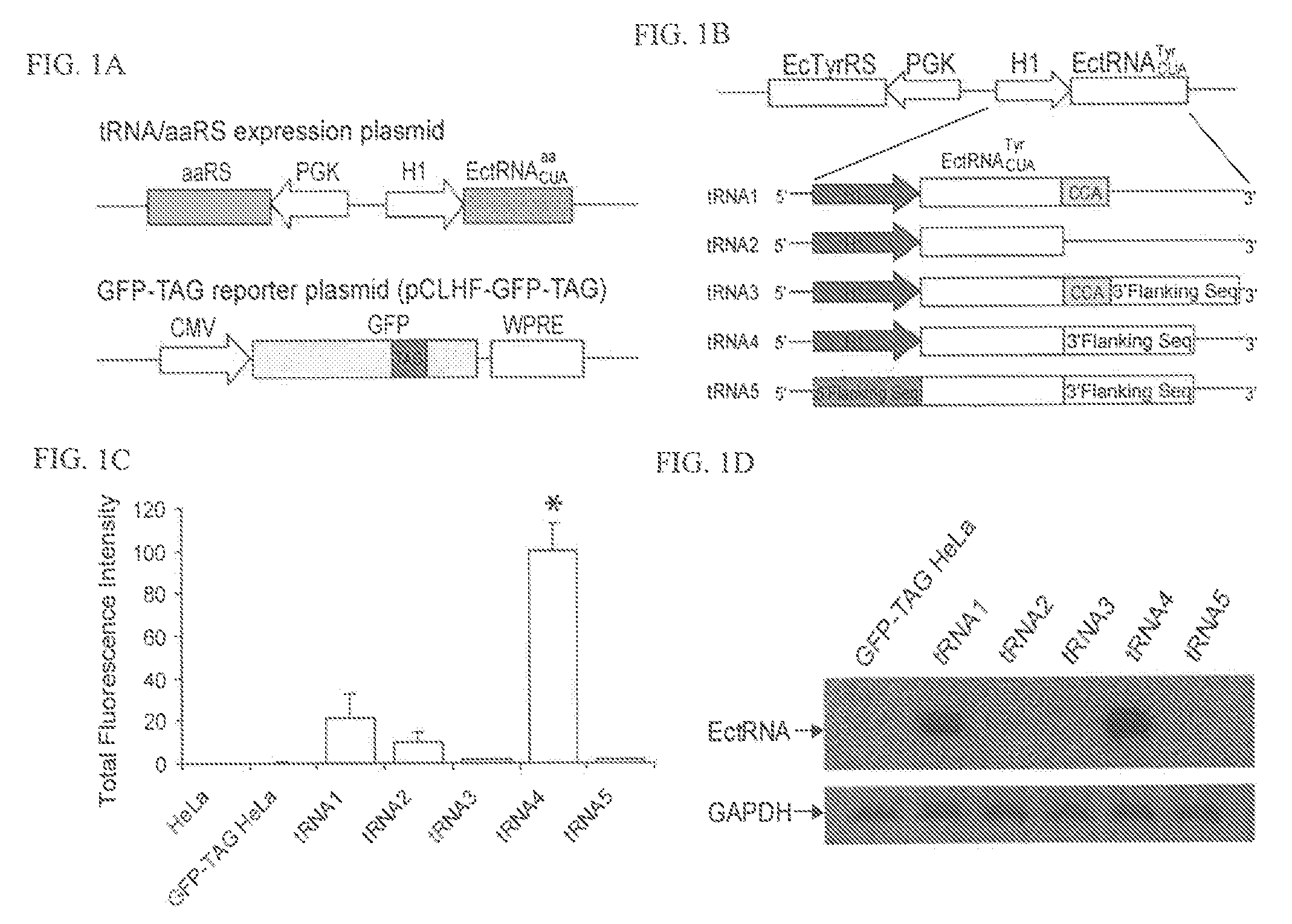
METHODS OF GENETICALLY ENCODING UNNATURAL AMINO ACIDS IN EUKARYOTIC CELLS USING ORTHOGONAL tRNA/SYNTHETASE PAIRS
InactiveUS20080254540A1Improve efficiencyMicroorganismsHybrid cell preparationMRNA DecayMammalian cell
This disclosure concerns compositions and methods for genetically encoding and expressing prokaryotic tRNAs in eukaryotic cells. In some embodiments, the disclosure concerns methods and compositions for expressing unnatural amino acids in eukaryotic cells using orthogonal tRNA / synthetase pairs. In certain embodiments, the methods involve expressing prokaryotic tRNA / synthetase pairs in eukaryotic cells, for instance mammalian cells or yeast cells (such as those that are NMD-deficient), under the control of a pol III promoter, for instance a type-3 pol III promoter or an internal leader promoter. Also provided are cell lines that are NMD-deficient and methods of increasing the efficiency of UAA incorporation in a cell that include de-activating the NMD pathway in the cell. Also provided are methods increasing the efficiency of incorporation of an unnatural amino acid in a cell by disrupting a Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay—(NMD) pathway in the cell.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Transformant that produces copolymerized PHA containing 3HH unit, and method for producing said PHA
ActiveUS10829793B2High composition proportionBacteriaOxidoreductasesMicroorganismAcyl CoA dehydrogenase
Owner:KANEKA CORP
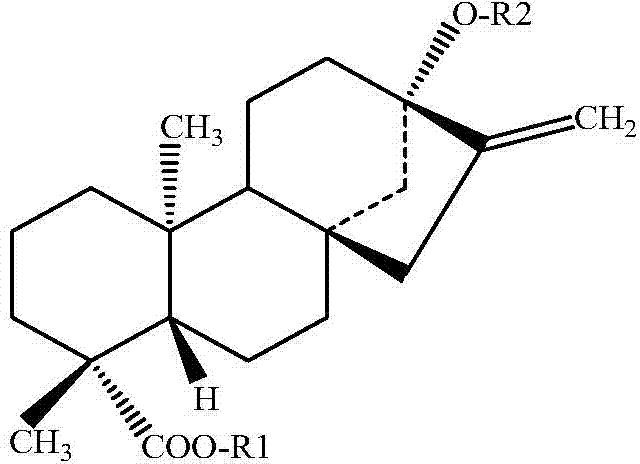
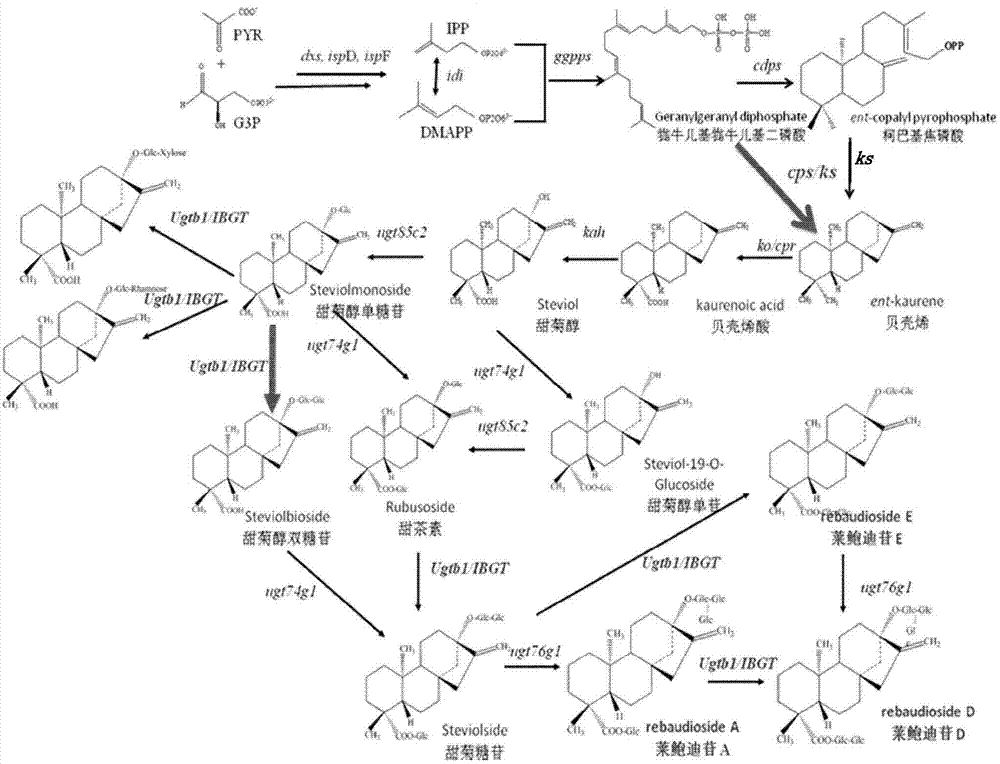
Method for producing stevioside compounds by using microorganisms
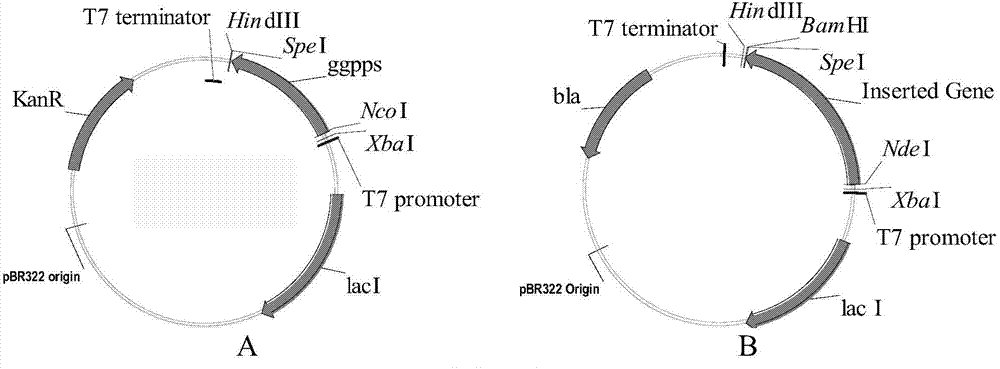
The invention relates to a method for producing stevioside compounds by using microorganisms. According to the present invention, the key enzymes for heterologous biosynthesis of the stevioside compounds are disclosed in the first time, wherein the applied enzymes comprise GGPPS, one selected from a CDPS and KS mixture and CPS / KS, KO, CPR, kaurenoic acid-13alpha-hydroxylase, UGT85C2 glycosyltransferase and UGTB1 / IBGT glycosyltransferase, and further optionally comprise UGT74G1 glycosyltransferase and / or UGT76G1 glycosyltransferase so as to carry out heterologous biosynthesis of the stevioside compounds.
Owner:SICHUAN INGIA BIOSYNTHETIC CO LTD
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-arginine and construction method and application thereof
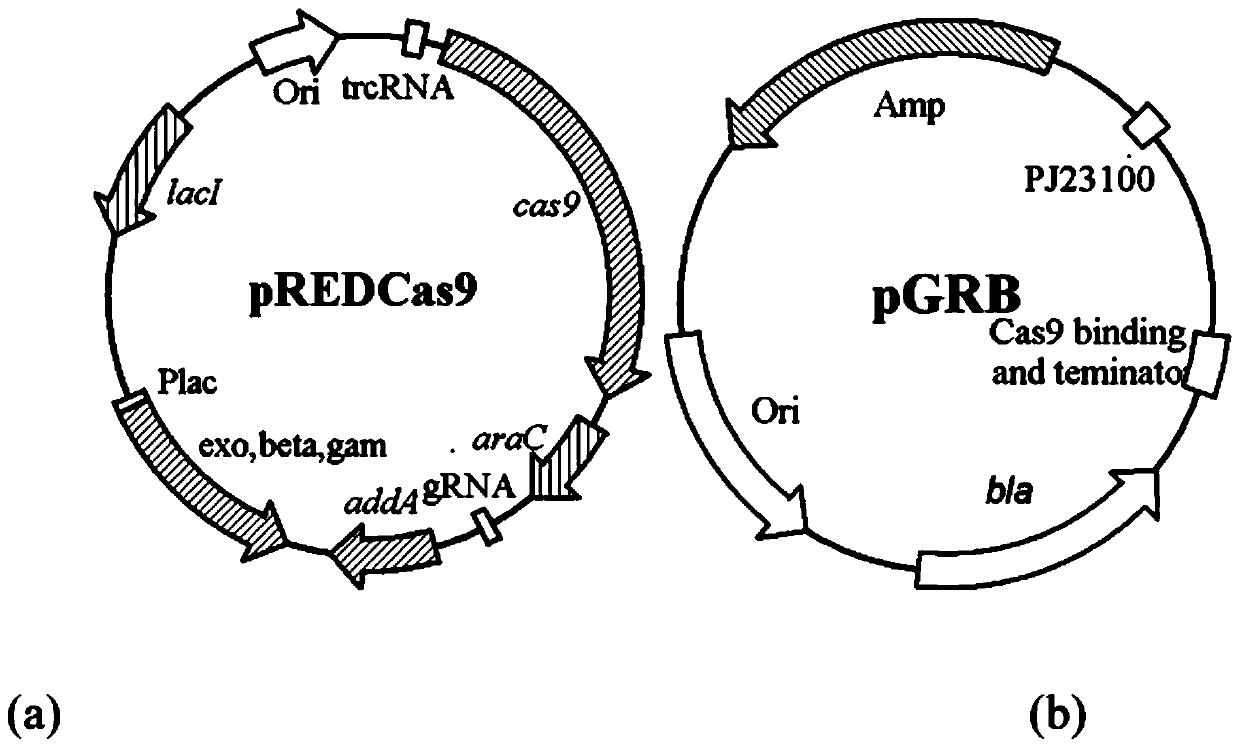
ActiveCN110964683AShorten the growth cycleClear genetic backgroundBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliCarbamyl Phosphate
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-arginine and a construction method and application thereof. According to the invention, a gene for encoding carbamyl phosphate synthetase and a gene for encoding L-arginine biosynthetic pathway enzyme are integrated in escherichia coli; a synthetic route of arginine in escherichia coli and metabolic flux related to argininein a whole amino acid metabolic network are analyzed and reconstructed to obtain genetically engineered bacteria which are clear in genetic background, do not carry plasmids, are not mutated and canstably and efficiently produce L-arginine; and the genetically engineered bacteria have good L-arginine production capacity.
Owner:NINGXIA EPPEN BIOTECH
Chondroitin systhetase and nucleic acid coding for the enzyme
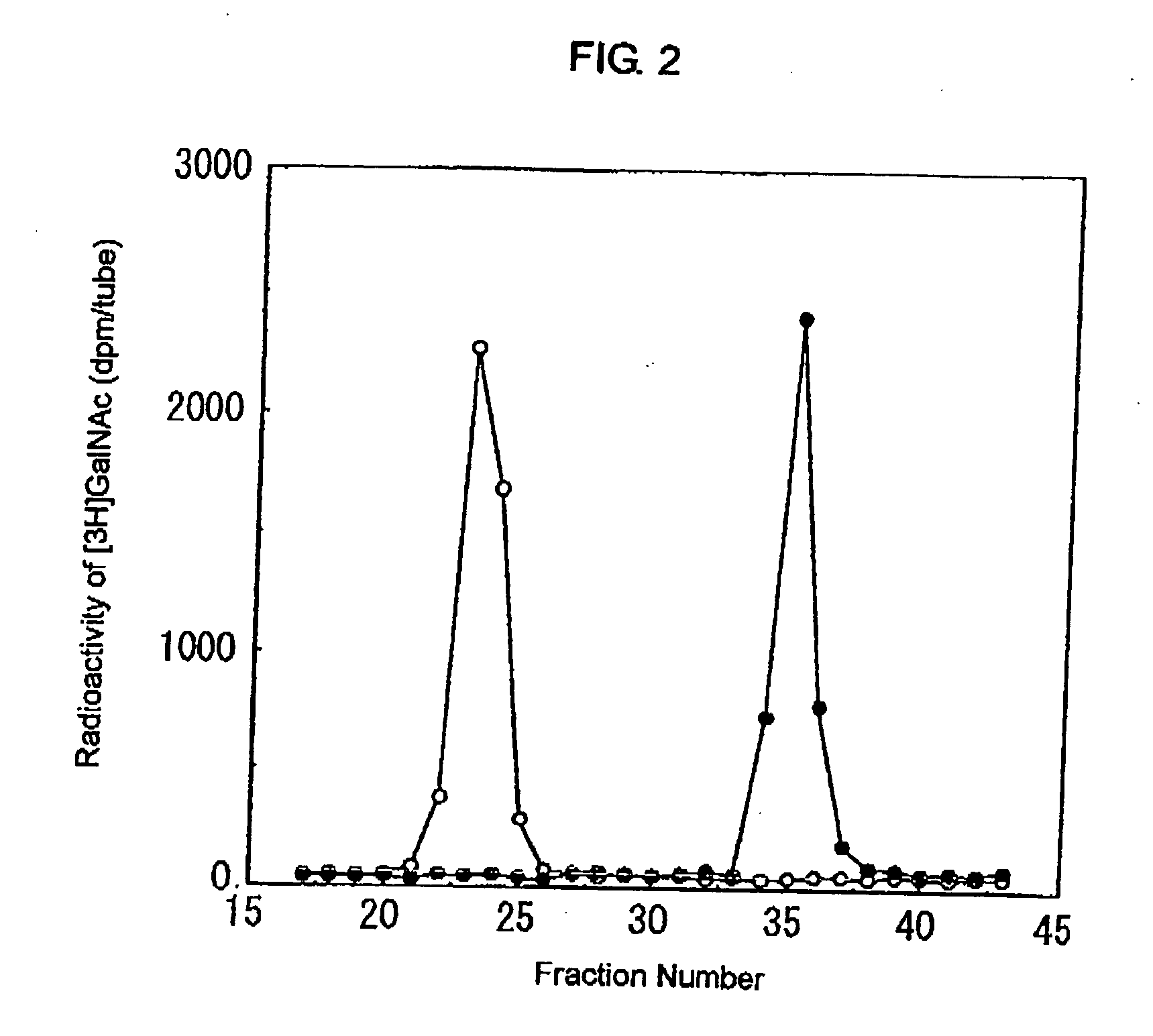
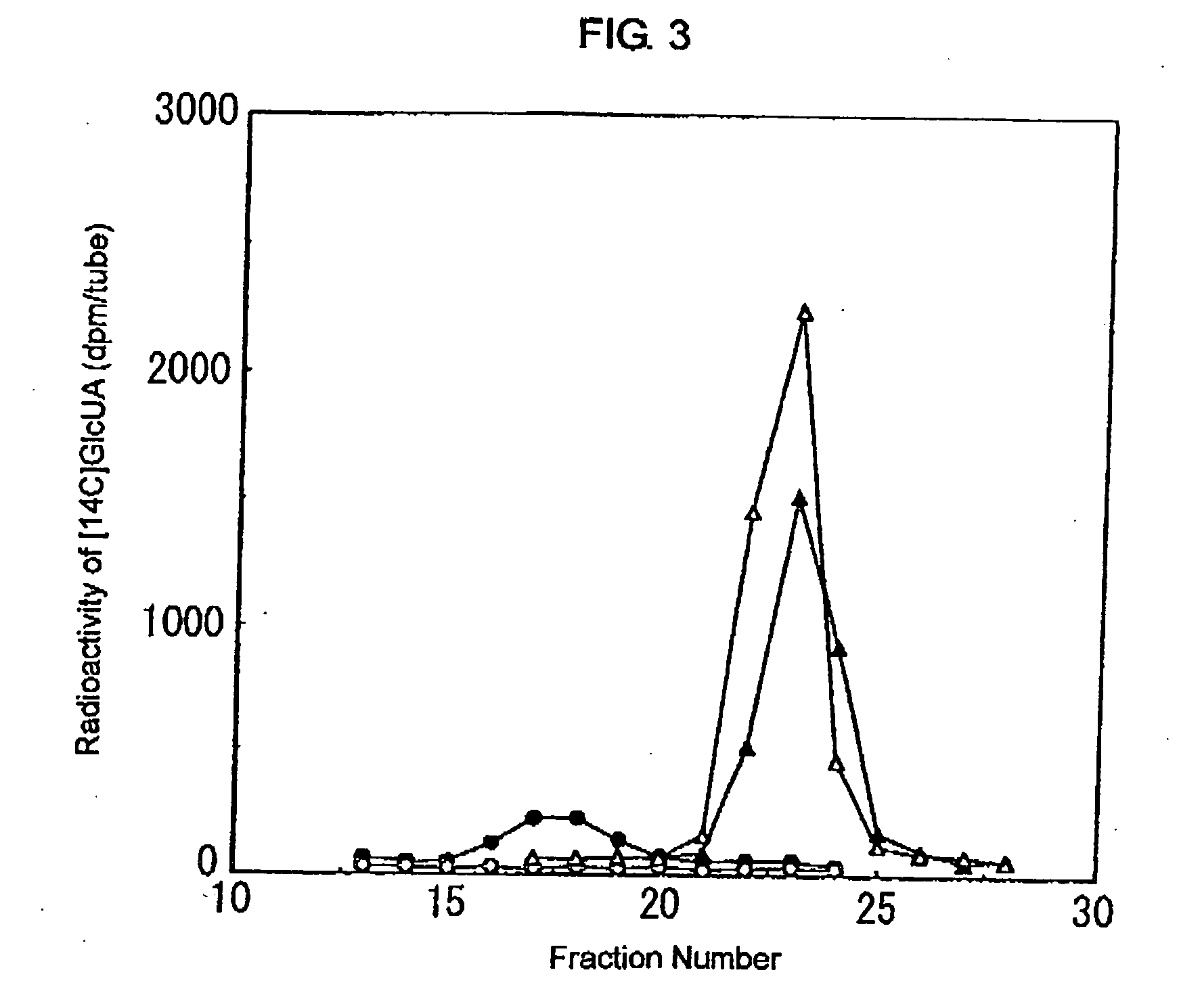
A human-derived novel chondroitin synthase, which is an enzyme for synthesizing a fundamental backbone of chondroitin and has both glucuronic acid transferring activity and N-acetylgalactosamine transferring activity.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD +1
Silk functional fiber preparation method
InactiveCN101187160ASolve usabilityResolve separabilityAnimal fibresChemical LinkageArtificial enzyme
The invention relates to a process for preparing silk functional fabric, which grafts the cyclodextrin onto the silk fiber through the chemical bond to obtain the silk functional fabric product with cyclodextrin solid chirality hydrophobic cavity, wherein the process can be used for preparing fabric with aromatic and medical health care functions and also can be used in the fields of molecule identification, waste water purification, artificial enzyme system forming and pharmaceutical slow releasing.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
Gene for coding glutamine dipeptide biosynthetic enzyme and application thereof
ActiveCN106754985AImprove conversion efficiencyResolve separabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliDipeptide
The invention discloses a gene for coding a glutamine dipeptide biosynthetic enzyme and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses an amino acid sequence coded by the gene, and provides a recombinant vector containing the gene, recombinant escherichia coli, and a method for performing biotransformation to synthesize the glutamine dipeptide by using the gene. The gene and the application of a recombinant bacterial strain of the gene have the advantages of high mol conversion rate, high reaction speed, easy separation, low cost and the like. In the synthesis method, the maximum mol conversion rate of the glutamine dipeptide can reach 83.3 percent; meanwhile, the thalli can be applied to the catalytic synthesis of the glutamine dipeptide again after the circulation recovery; in addition, the catalytic activity is stable. Therefore high market competitive power and application values are realized; a foundation is laid for the industrial production of the glutamine dipeptide.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
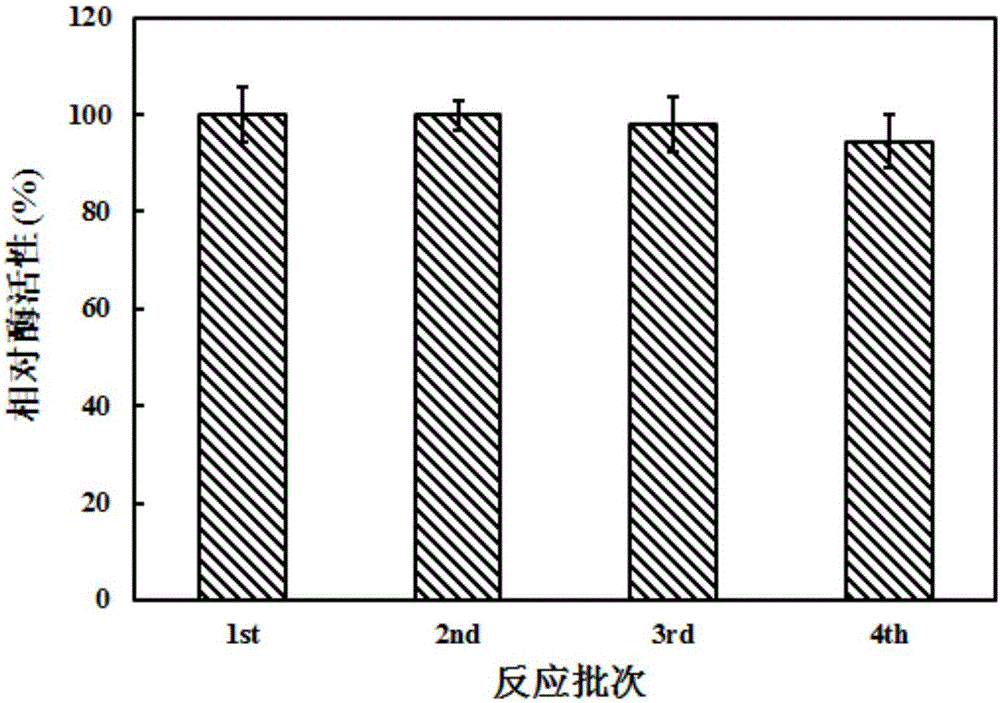
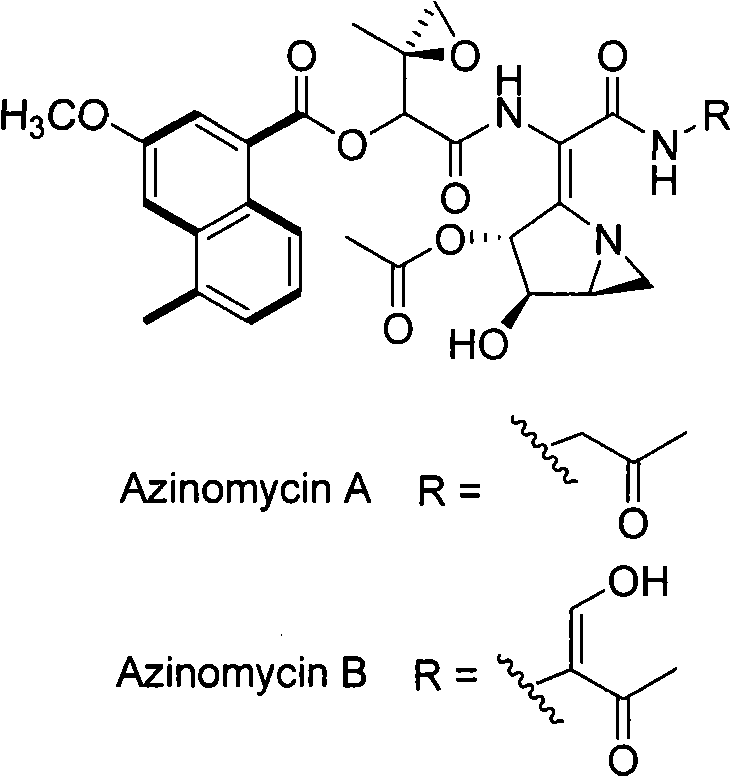
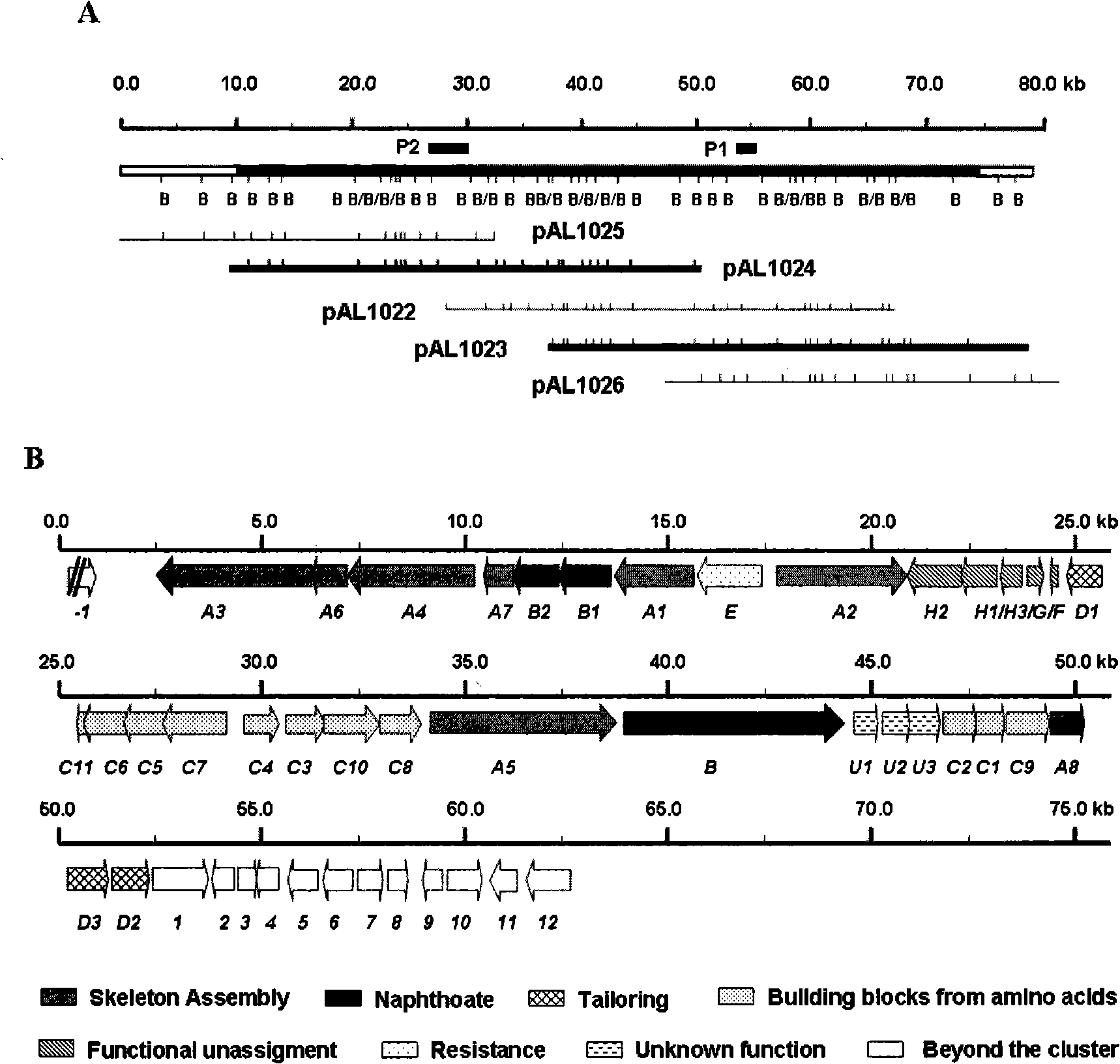
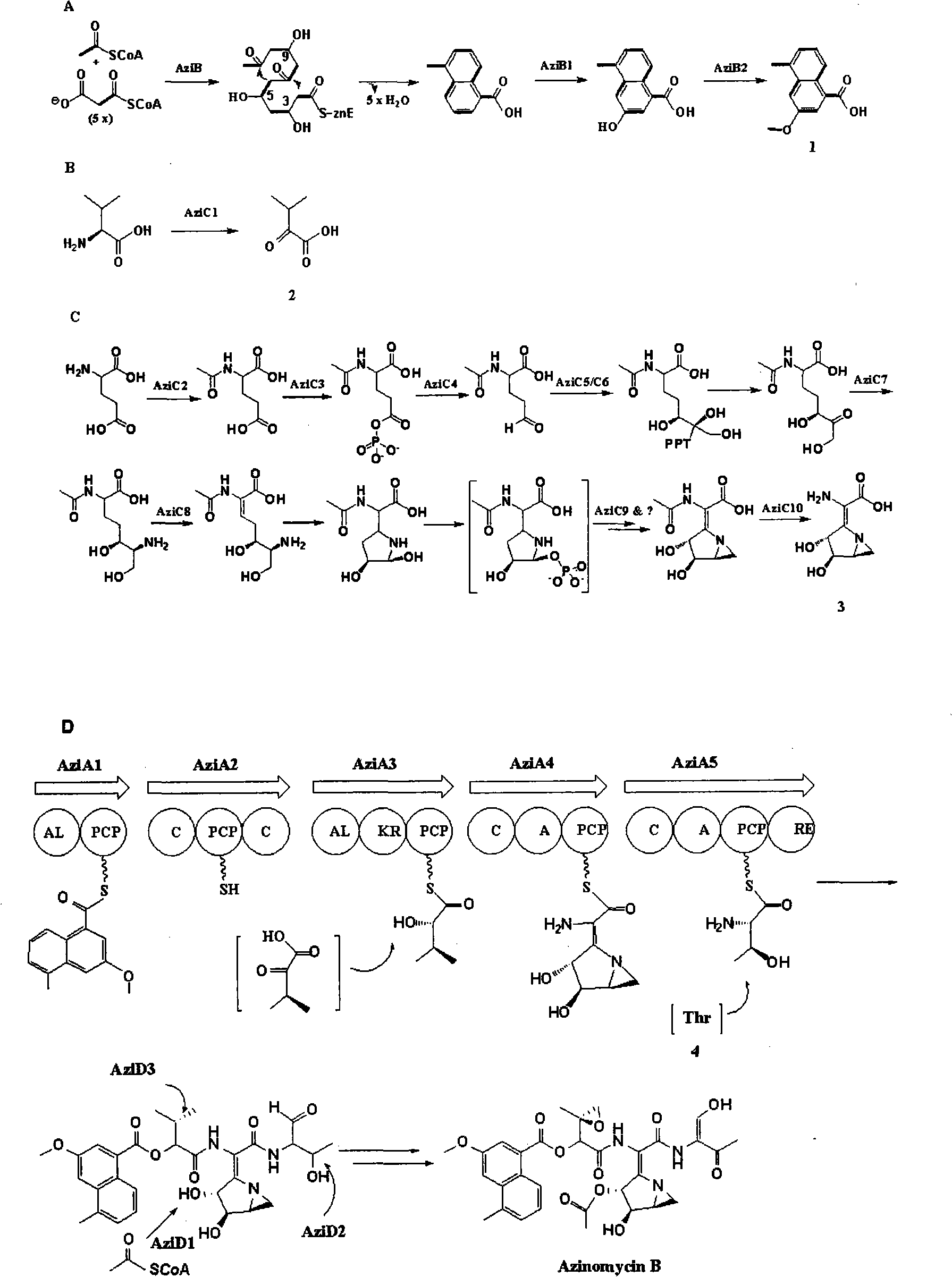
Biological synthesis gene cluster for Azintamide
InactiveCN101275141AUnderstanding Biosynthetic MechanismsFermentationPlant genotype modificationHeterologousEnzyme Gene
The present invention provides cloning sequencing, analyzing, function research of a biosynthesis gene cluster of an antibiotic-Azinomycin B having antitumor activity produced by streptomyces, and its application. The whole gene cluster includes 34 genes: one repeatedly using I type polyketide synthase gene; two naphthalene ring modification enzyme genes; 8 non-ribosomal polypeptide skeleton synthesis and modification enzyme genes; 11 non-natural amino acid structure unit synthase genes; 1 resistance gene; 3 post modification enzyme genes and 8 genes which functions are not determined. The genetic operation of the biosynthesis gene breaks the synthesis of Azinomycin B; the precursor compound is produced by the heterologous expression of synthesis gene and modification gene of naphthalene ring. The gene of the invention and the protein can be used for searching and finding compound or gene, protein applied in medical, industry or agriculture.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ORGANIC CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com