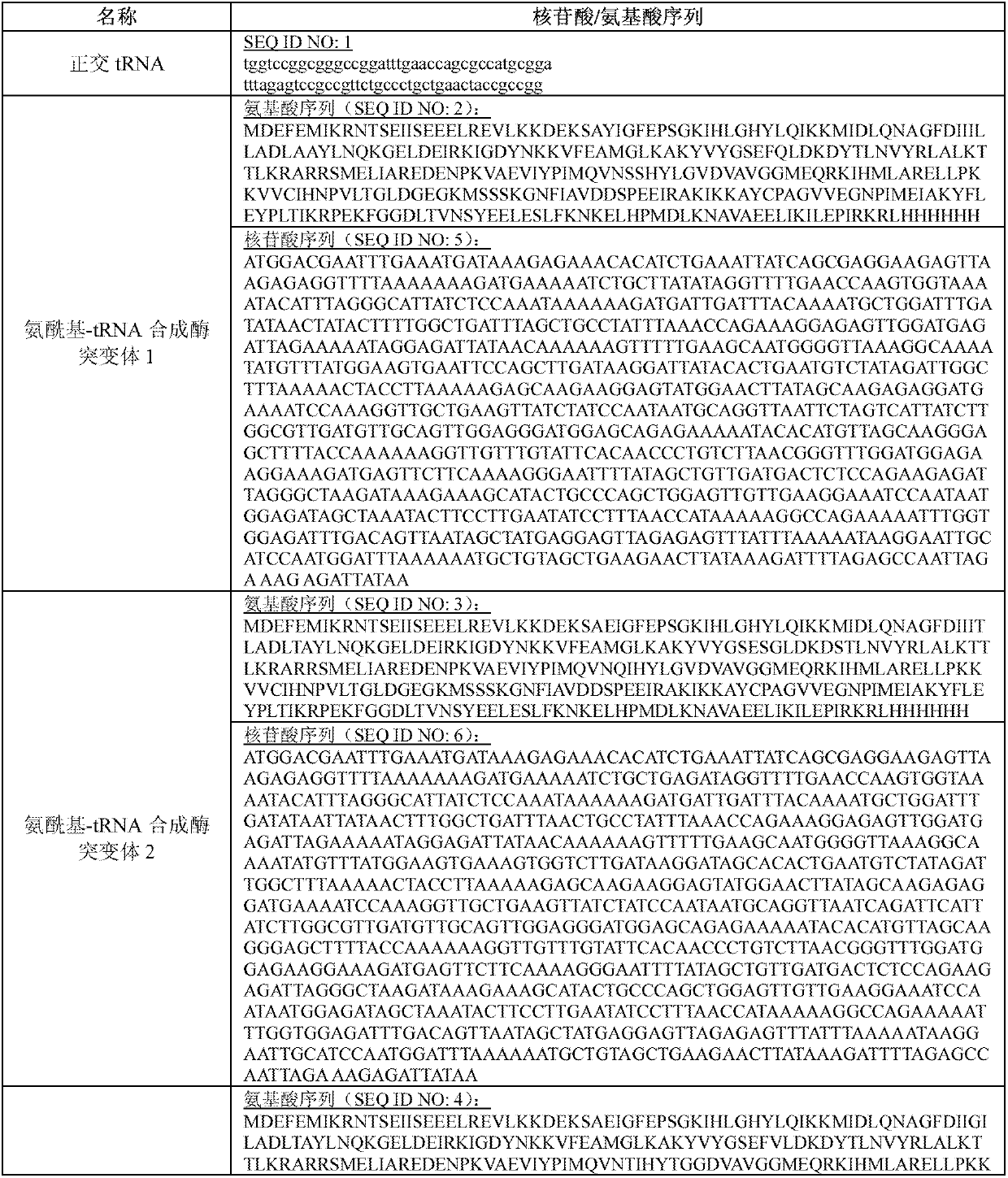
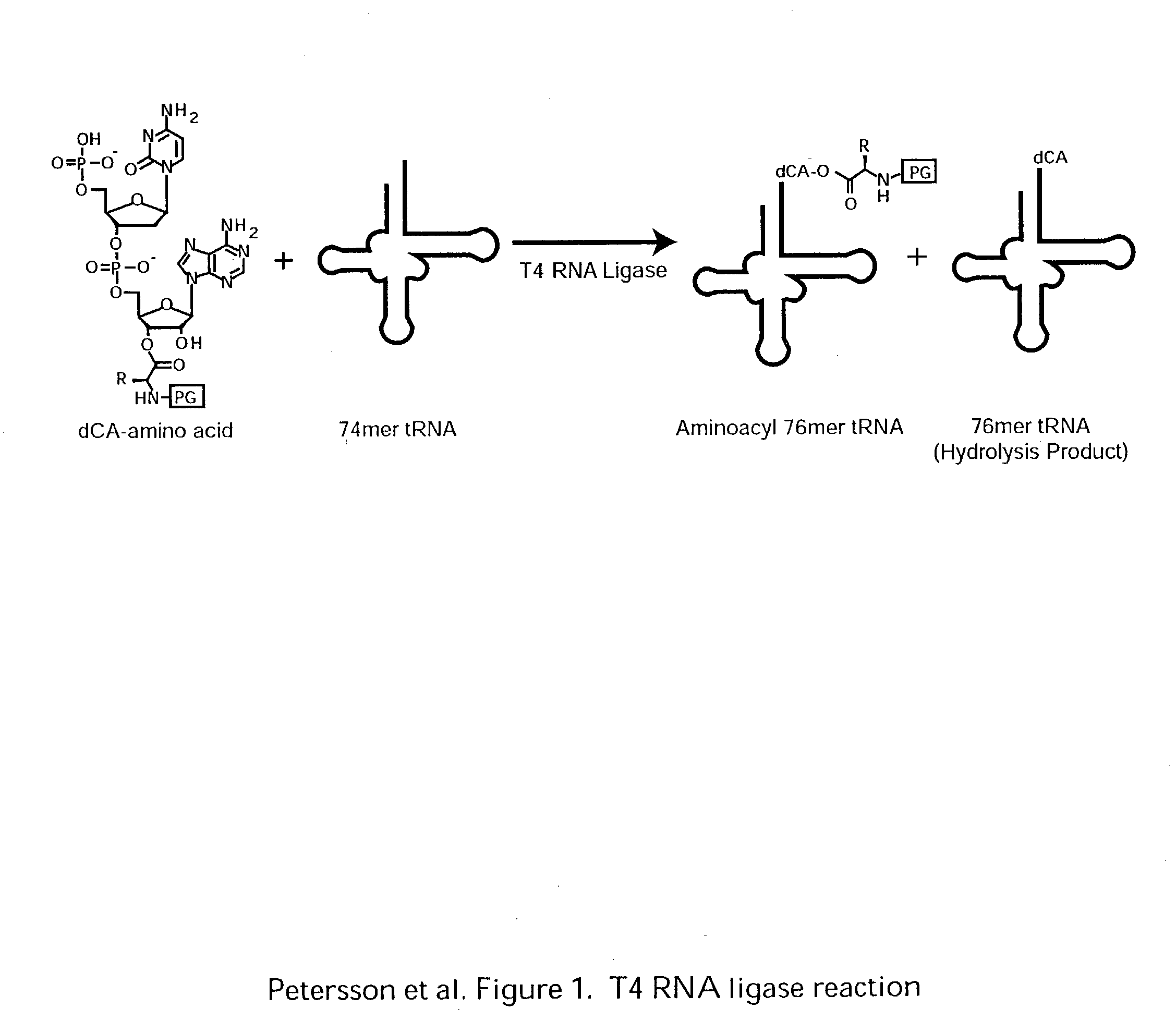
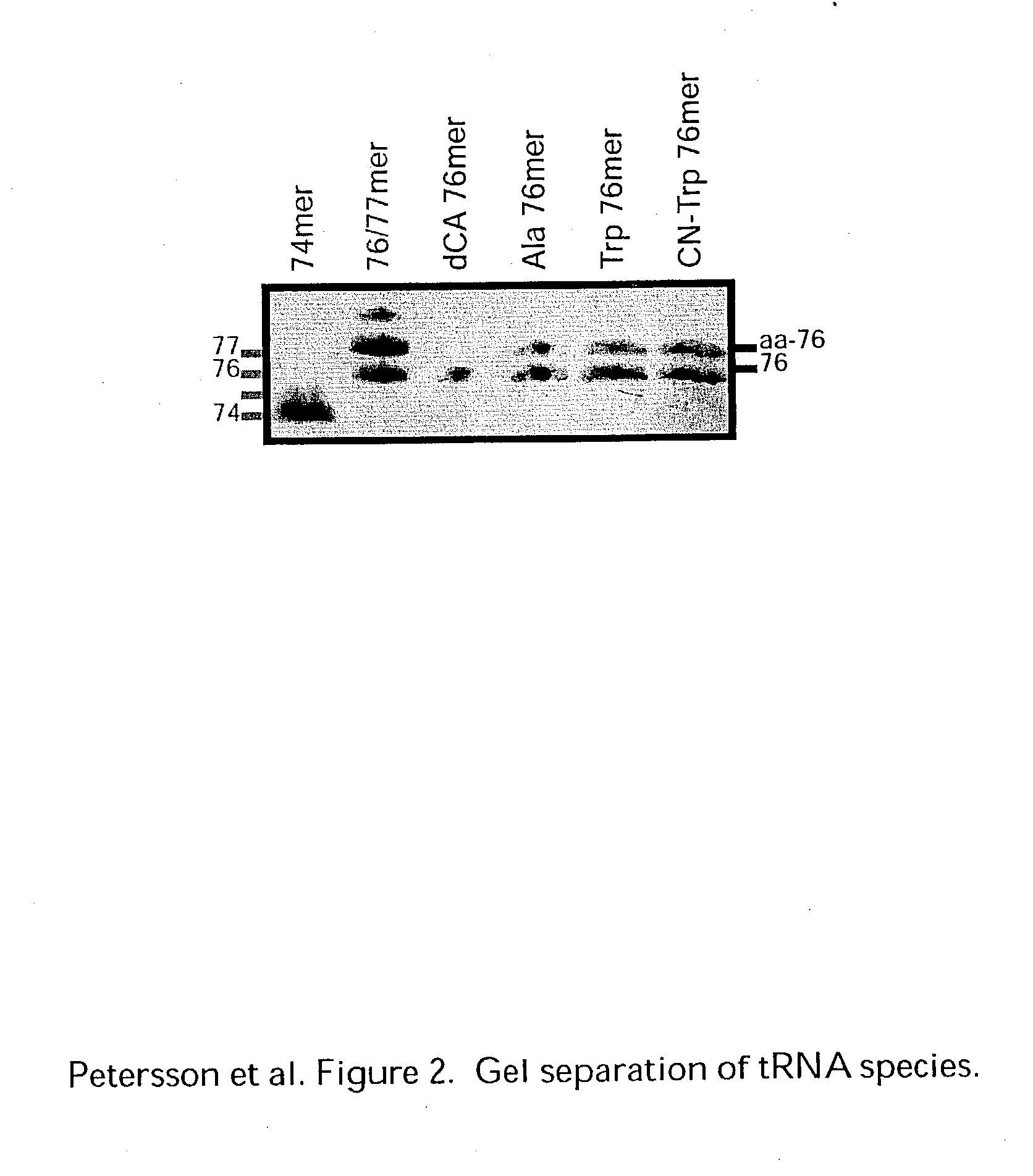
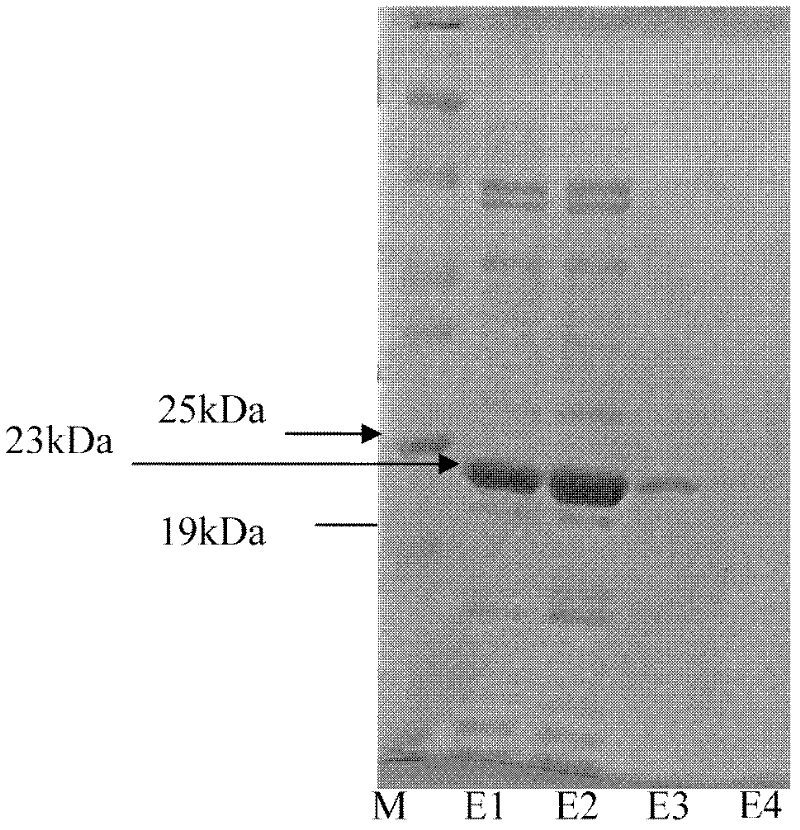
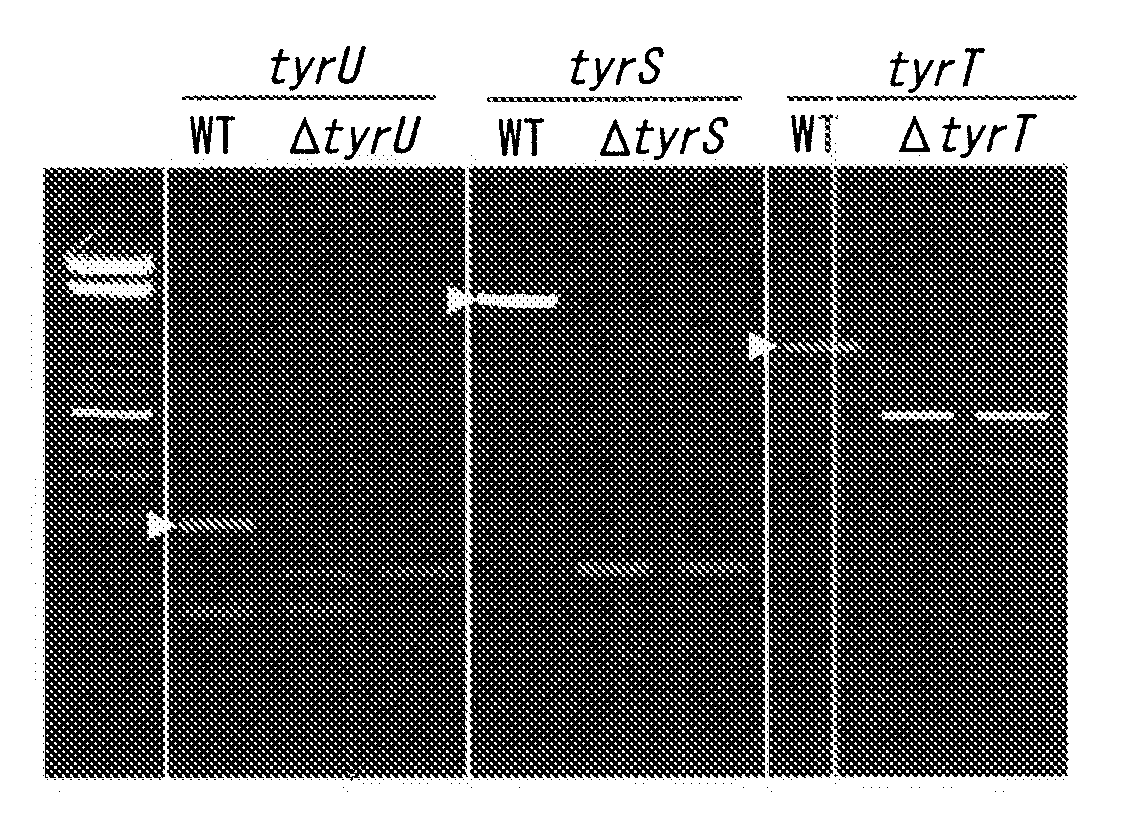
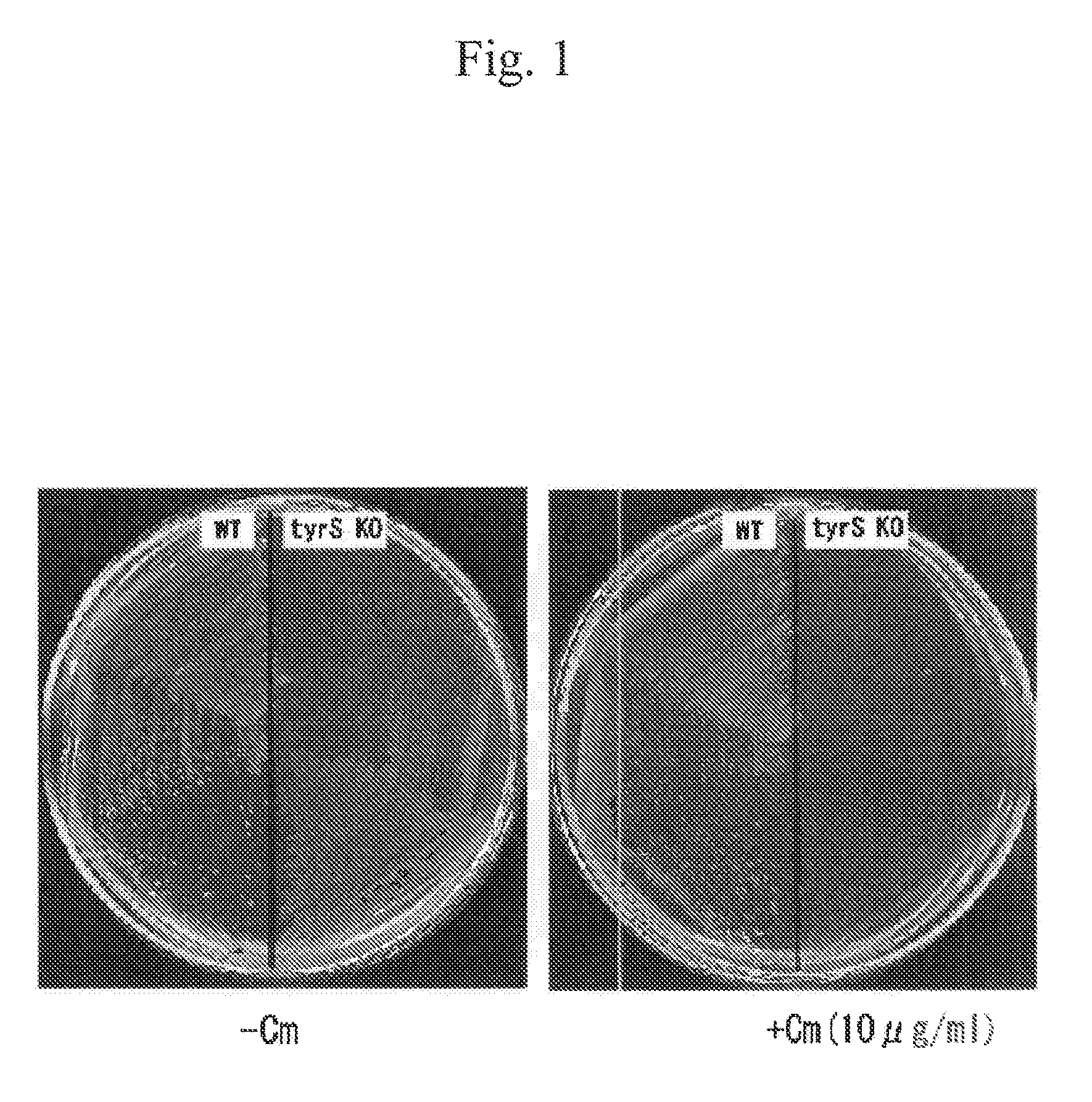
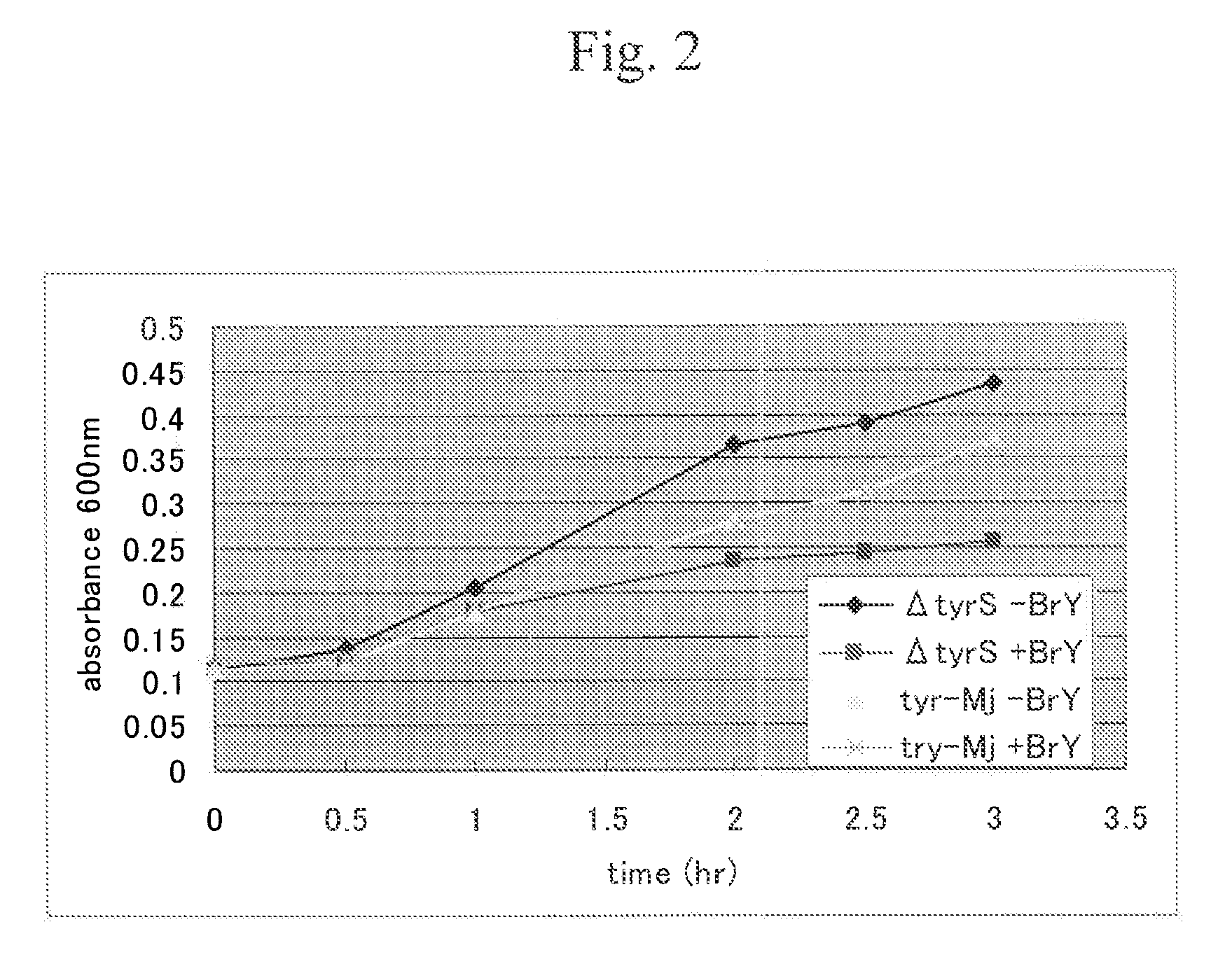
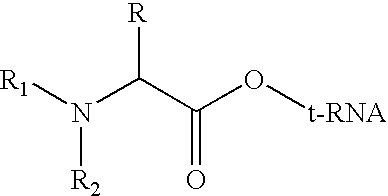
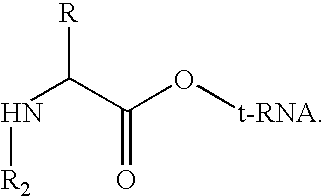
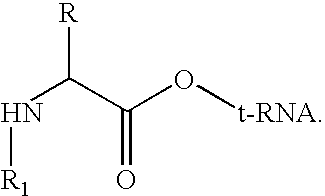
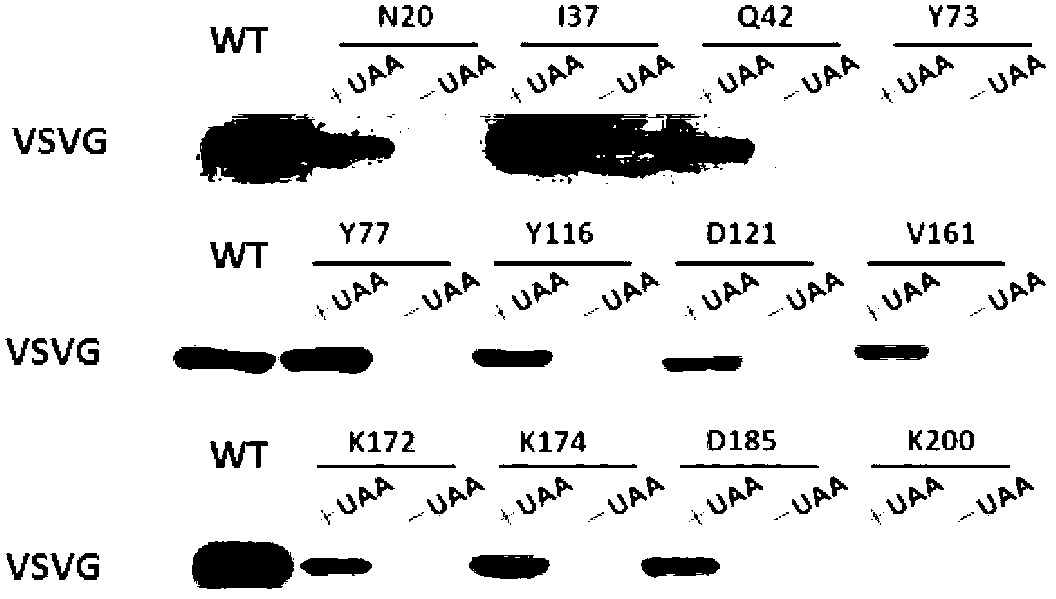Patents
Literature
41 results about "Aminoacyl-tRNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
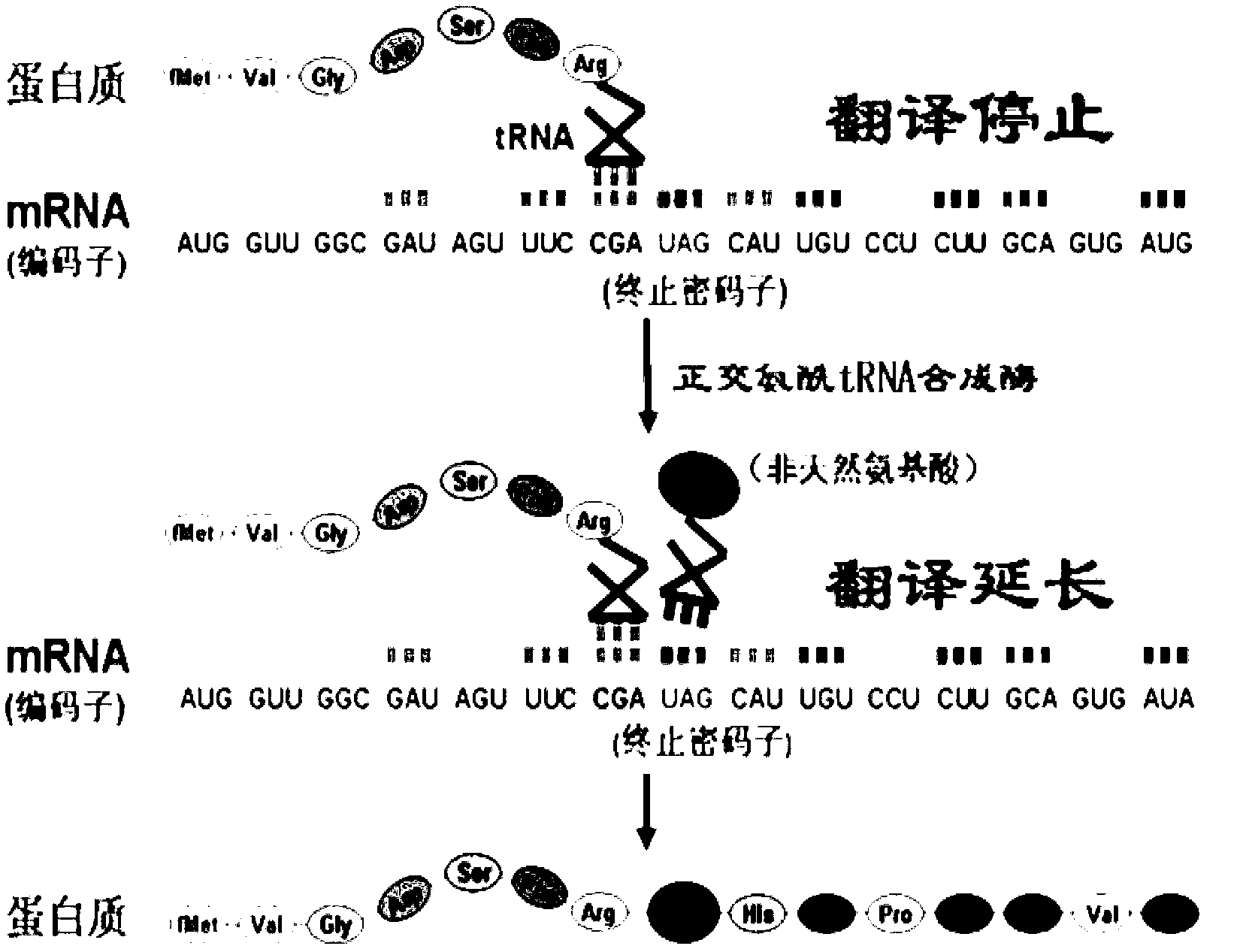
Aminoacyl-tRNA (also aa-tRNA or charged tRNA) is tRNA to which its cognated amino acid is chemically bonded (charged). The aa-tRNA, along with some elongation factors, deliver the amino acid to the ribosome for incorporation into the polypeptide chain that is being produced. A specific cognate amino acid is charged or aminoacylated to each tRNA by aminoacyl tRNA synthetase. This matching is crucial, since it ensures that only the particular amino acid matching the anticodon of the tRNA, and in turn matching the codon of the mRNA, is used in protein synthesis.
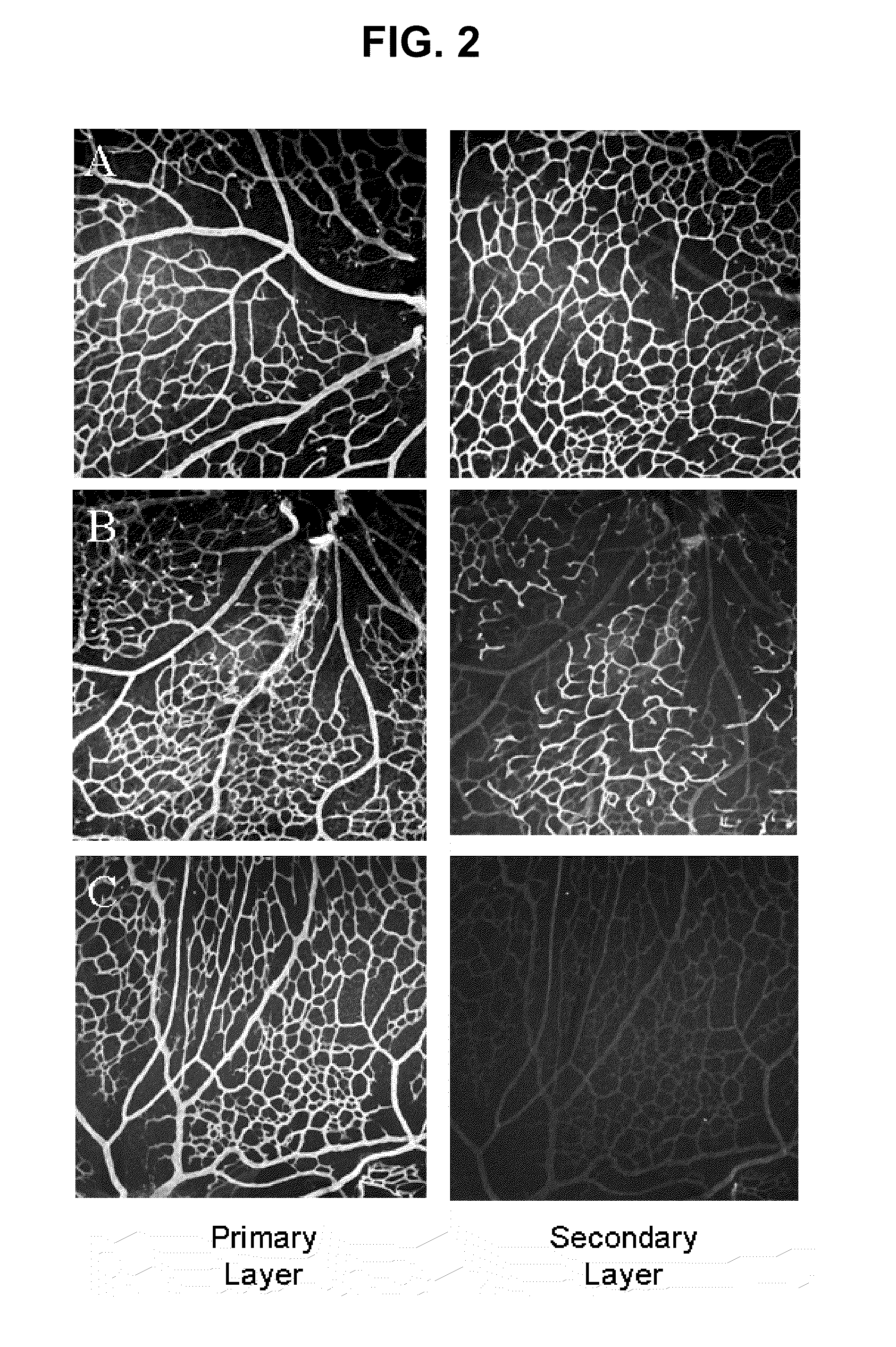
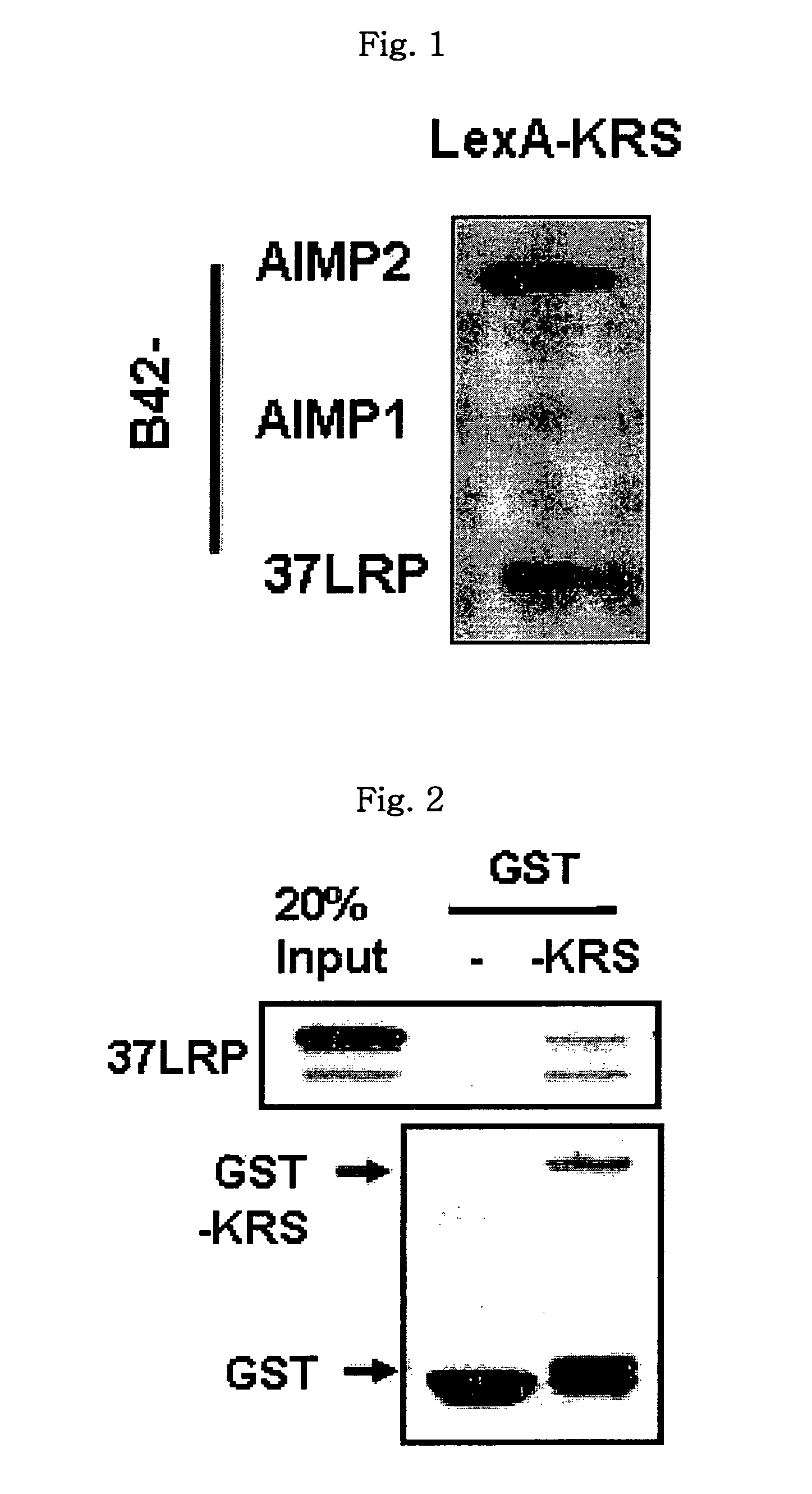
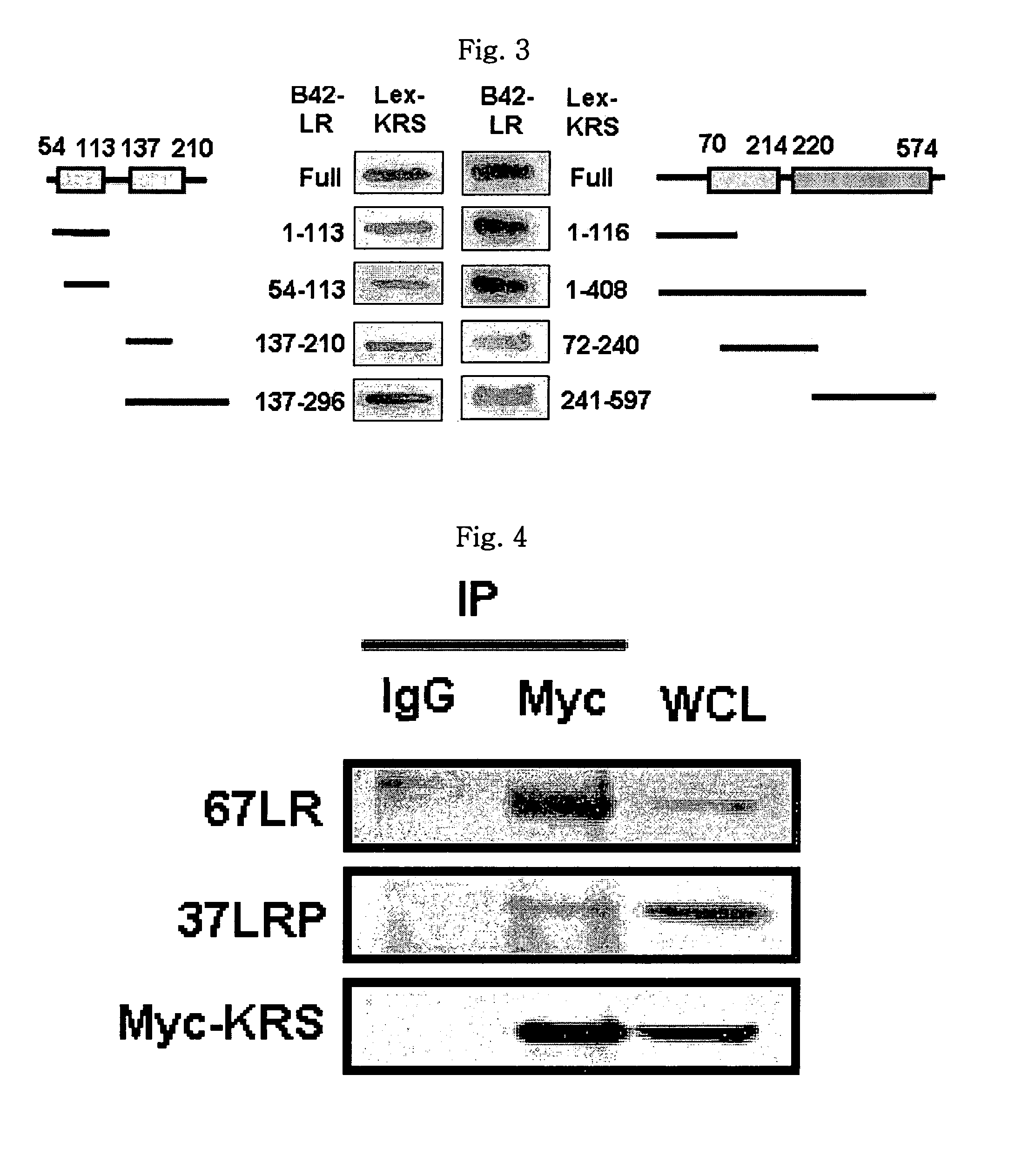
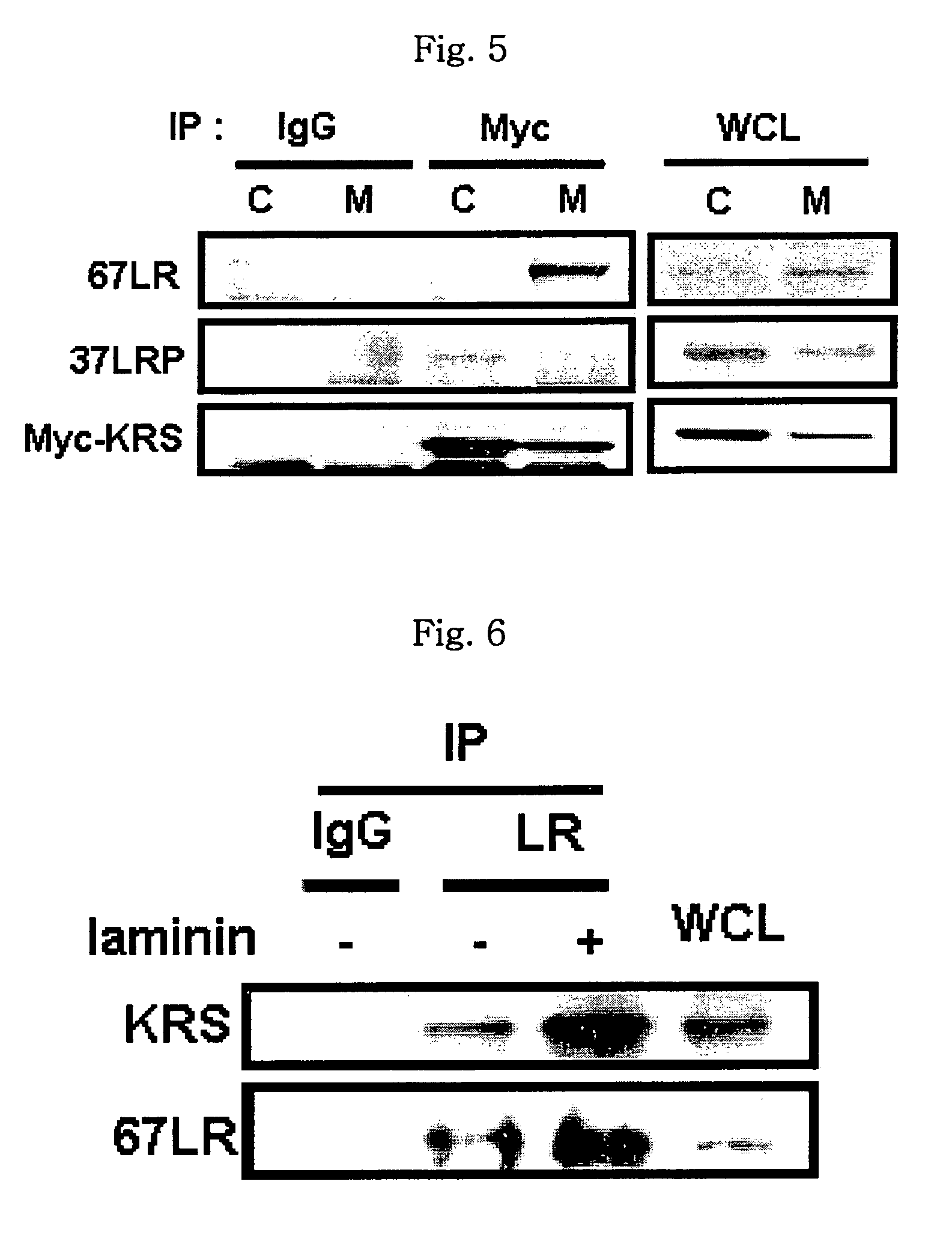
Method for controlling cancer metastasis or cancer cell migration by modulating the cellular level of lysyl trna synthetase
ActiveUS20110189195A1Promote migrationCancer metastasisOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBreast cancer metastasisDisease
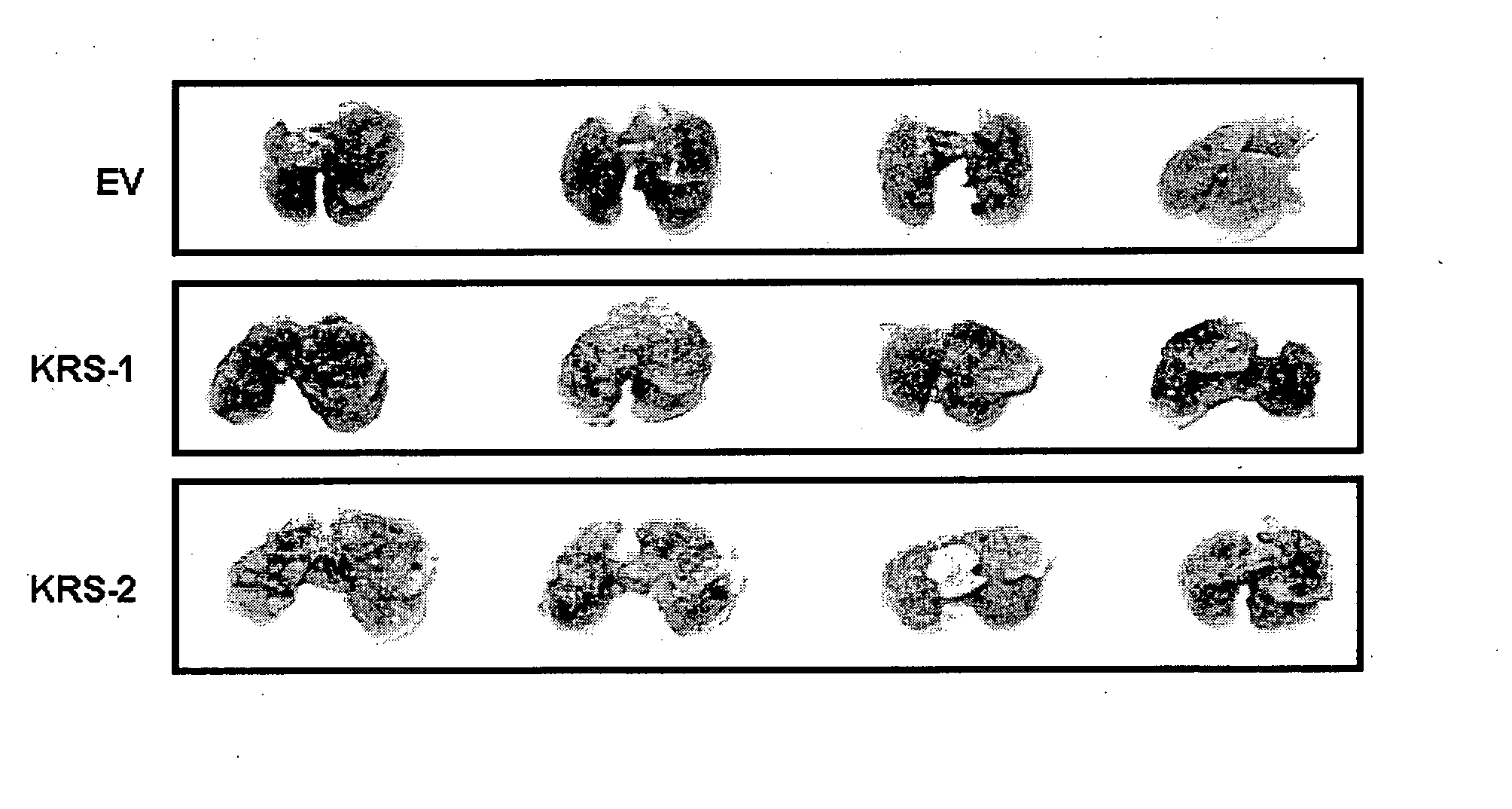
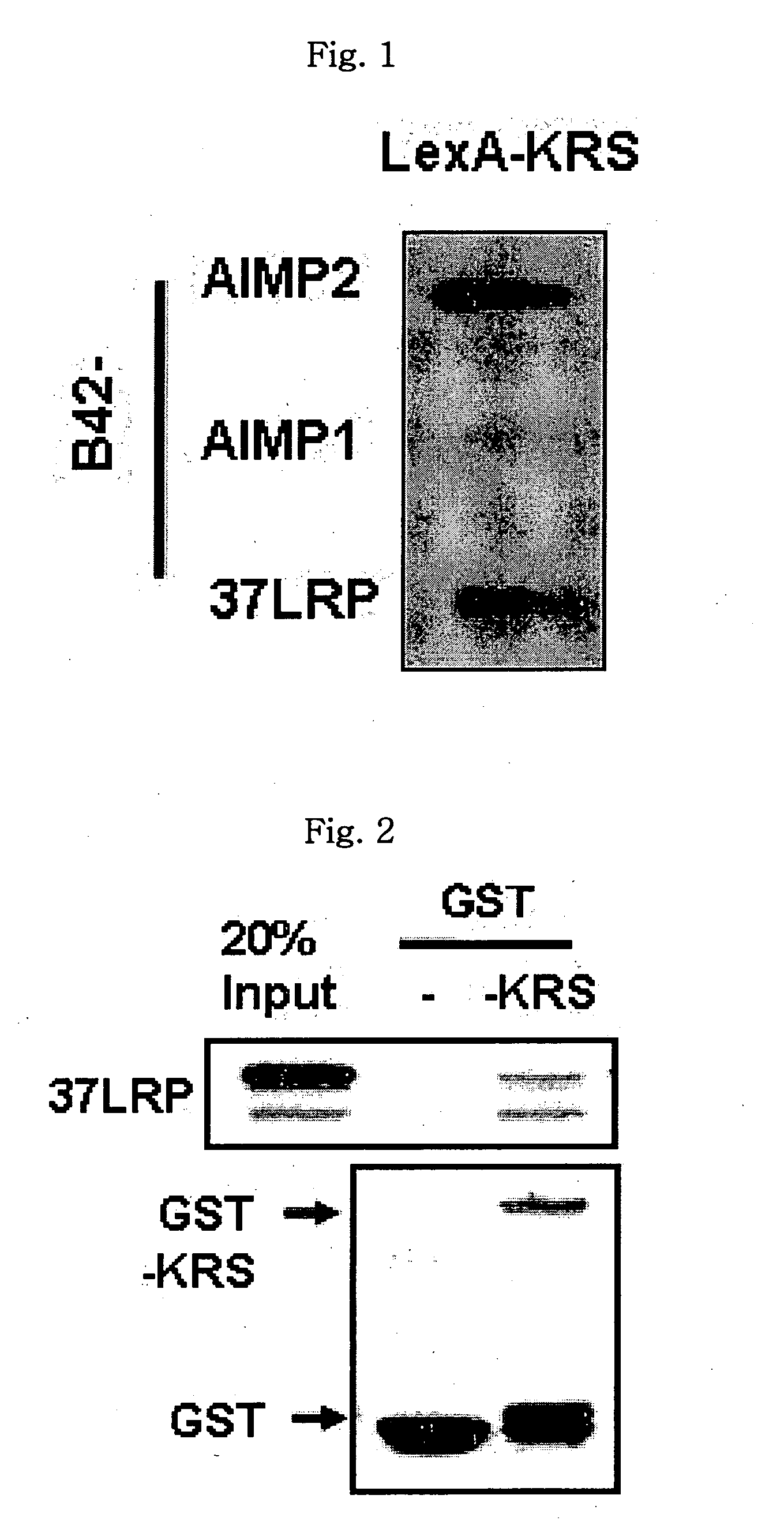
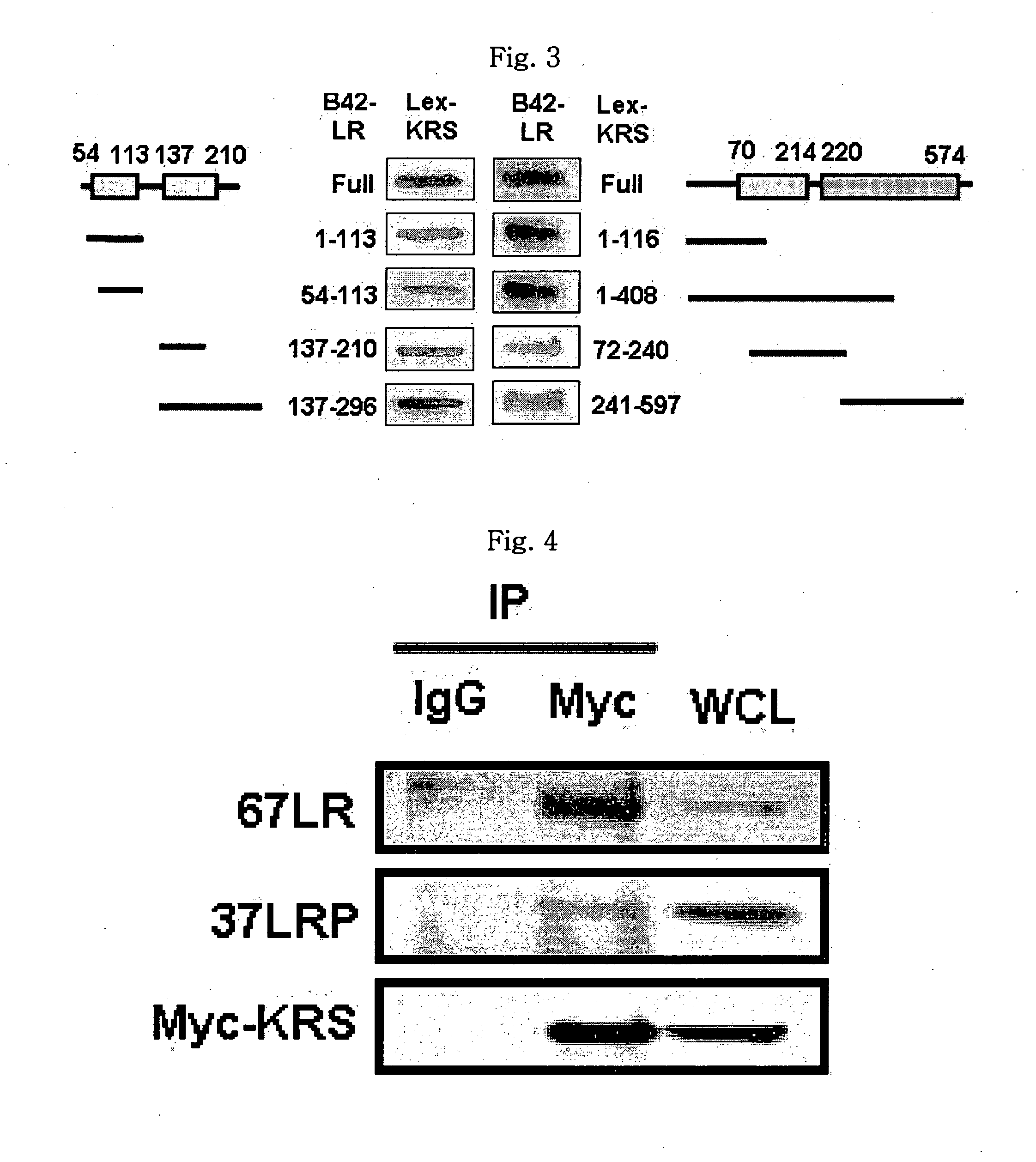
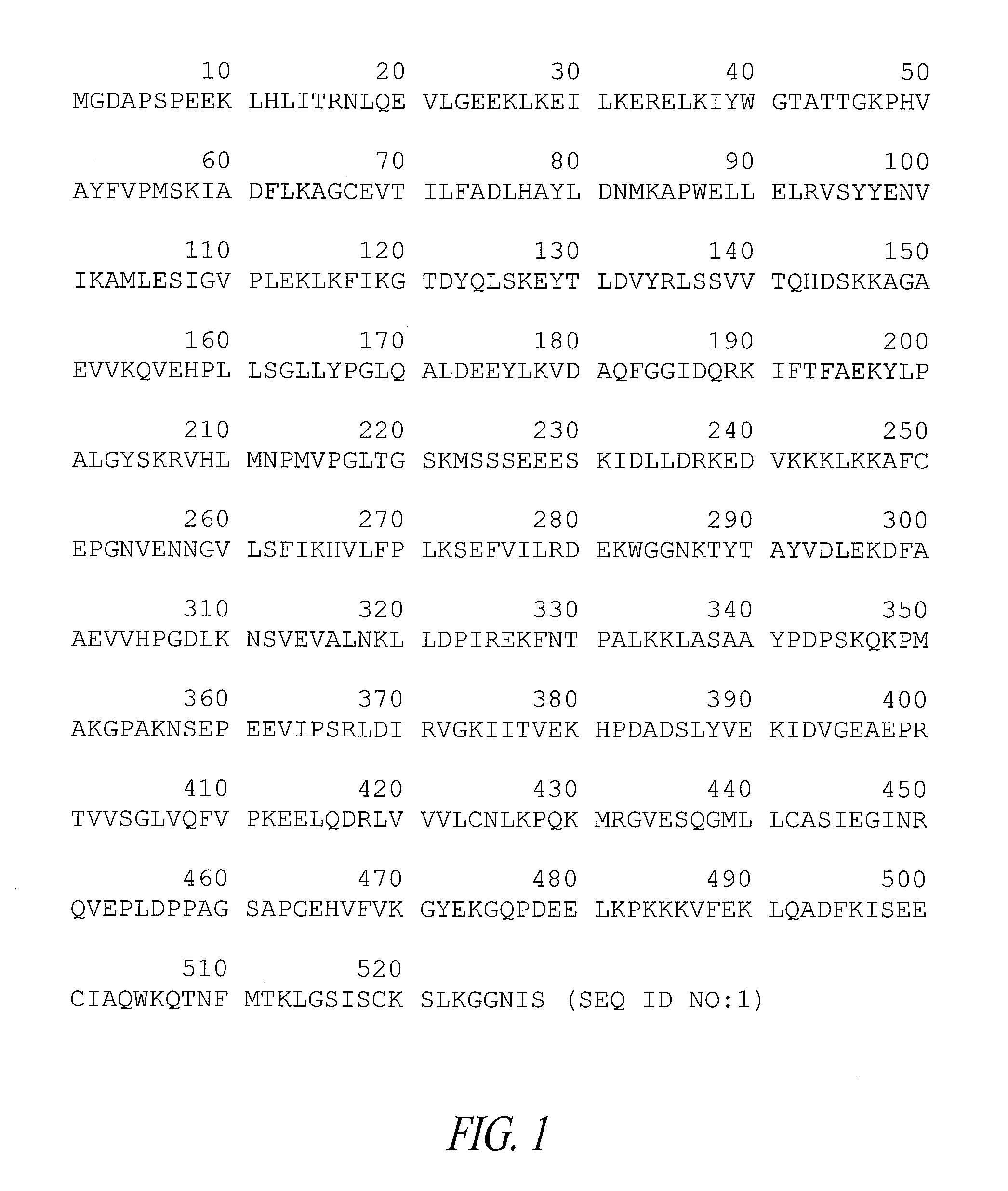
The present invention relates to a novel function of lysyl tRNA synthetase (KRS) which enhances tumor cell migration and affects cancer metastasis via KRS's interaction with laminin receptor (67LR) by its translocation to membrane. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for modulating cancer metastasis or migration, which comprises regulating intracellular levels of KRS; a composition for preventing or treating cancer; use of expression vector for inhibiting the expression of KRS; a method for preventing or treating cancer; use of an agent for inhibiting an activity of KRS; a method for screening an agent which modulates cancer metastasis or migration; and a method for screening an agent which inhibits the interaction of KRS with 67LR, by said novel function. Thus, KRS can modulate cancer metastasis or migration and furthermore, can modulate intra-cellular metabolism related to 67LR. The interaction between KRS and 67LR can be used effectively in treating, preventing and / or diagnosing of various diseases or disorders related to the interaction.
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT
Thrombopoietic activity of tyrosyl-trna synthetase polypeptides
InactiveUS20100092434A1Reduce lung inflammationReduce inflammationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsTyrosyl-tRNA SynthetaseIncreased Thrombopoiesis
Thrombopoietic compositions are provided comprising tyrosyl tRNA synthetase polypeptides, including truncations and / or variants thereof. Also provided are methods of using such compositions in the treatment of conditions that benefit from increased thrombopoiesis, such as thrombocytopenia.
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC
Peptide Library Production Method, Peptide Library, and Screening Method
ActiveUS20140018257A1High affinityStrong specificityPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsCell freeAminoacyl-tRNA
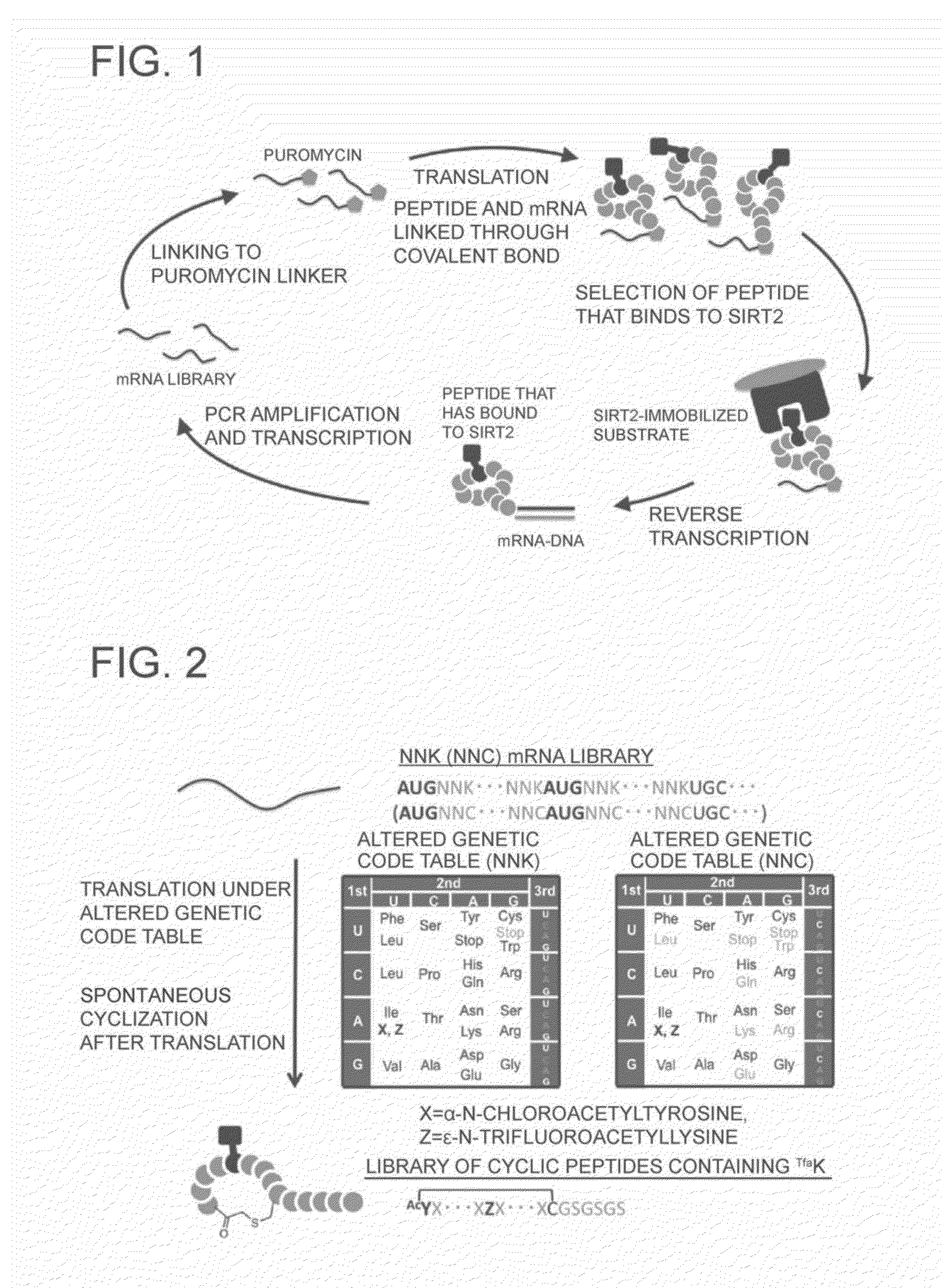
Object is to provide a method of constructing a library of peptides having, at a desired position in the random sequence of each peptide, an amino acid having a portion capable of binding to a target. The invention provides a method of producing a library of peptides having, at a designated position in the random sequence of each peptide, a special amino acid having a portion capable of binding to a target, including (i) preparing a library of mRNAs having, in the mRNA sequence coding for a random amino acid sequence, a base sequence having an altered codon encoding the special amino acid, (ii) preparing an aminoacyl tRNA with the special amino acid linked to a tRNA encoded by the altered codon, and (iii) translating the mRNAs by using a cell-free translation system containing the aminoacyl tRNA to obtain a library of peptides having, in the random sequence thereof, a predetermined special amino acid.
Owner:THE UNIV OF TOKYO
Viromembrane protein with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration, preparation method and applications of viromembrane protein
ActiveCN102838663AAvoid dissociationSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaViral Membrane ProteinsUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses viromembrane protein with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration, a preparation method and applications of the viromembrane protein. Amber codon TAG is introduced to the specific site of envelope protein G (VSV G) gene of vesicular stomatitis virus, unnatural amino acid DiZPK with photo-crosslinking property is introduced to the specific site of VSV G by utilizing the orthorhombic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-tRNA through site-specific mutagenesis. In the interaction process of virus and host cells, the DiZPK photo-crosslinking reaction is triggered by 365nm ultraviolet light, the covalent bond is formed between the VSV G and interacting protein, the interaction dissociation can be avoided, and the powerful measure is provided for the research of the interaction of the virus and protein of the host cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
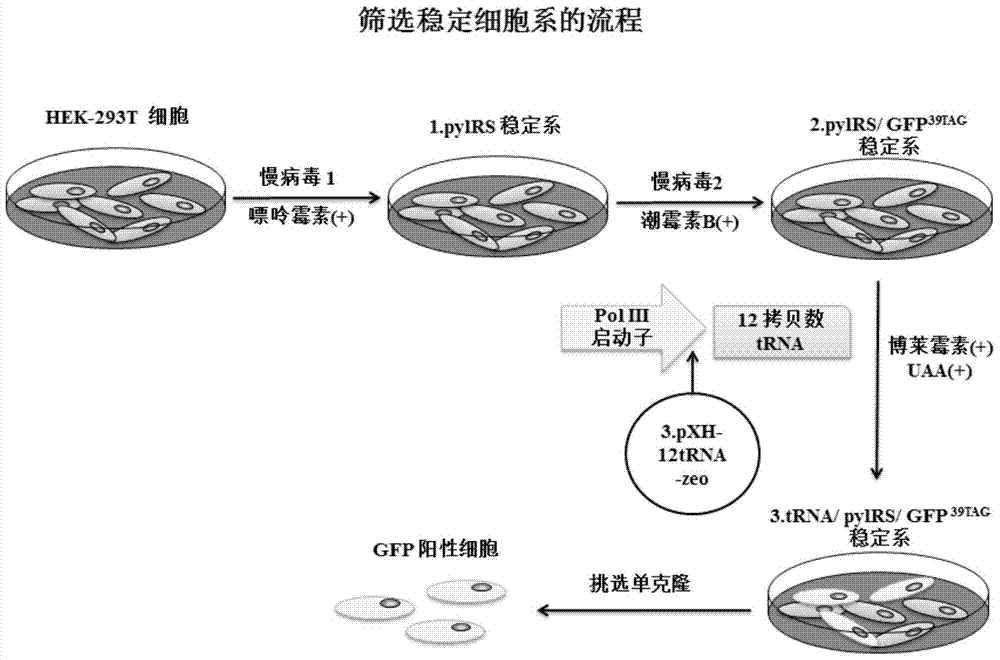
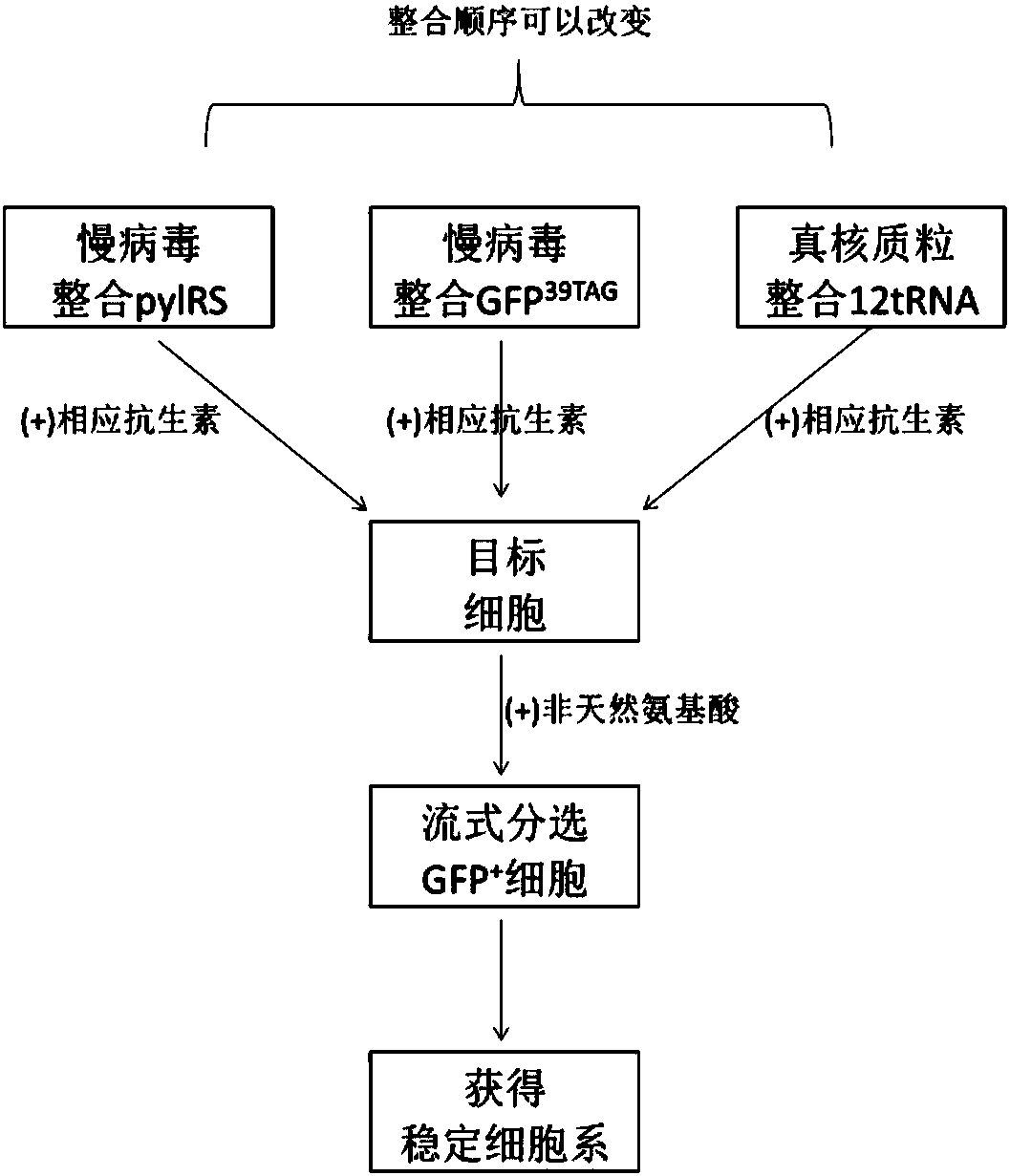
Building of stable cell line carrying orthogonal tRNA/arginyl tRNA synthetase
The invention relates to a building method of a stable cell line carrying orthogonal tRNA / arginyl tRNA synthetase. On the basis of a gene codon expansion technology, a pair of orthogonal tRNA / arginyl tRNA synthetase is used for introducing unnatural amino acid into a fixed point of protein. The invention also relates to a building method of double lentiviral vectors, a building method of a multi-copy-number tRNA carrying carrier and a method for stably integrating the orthogonal tRNA / arginyl tRNA synthetase gene into the cell genome through double lentiviral stable transduction and plasmid stable transfection. The invention further relates to application of the stable cell line, such as the purpose of expressing the target protein containingunnatural amino acid.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Innovative discovery of therapeutic, diagnostic, and antibody compositions related to protein fragments of isoleucyl tRNA synthetases
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC +1
N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN103667202AValid markEfficient expressionBacteriaHaemoglobins/myoglobinsProtein targetAminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
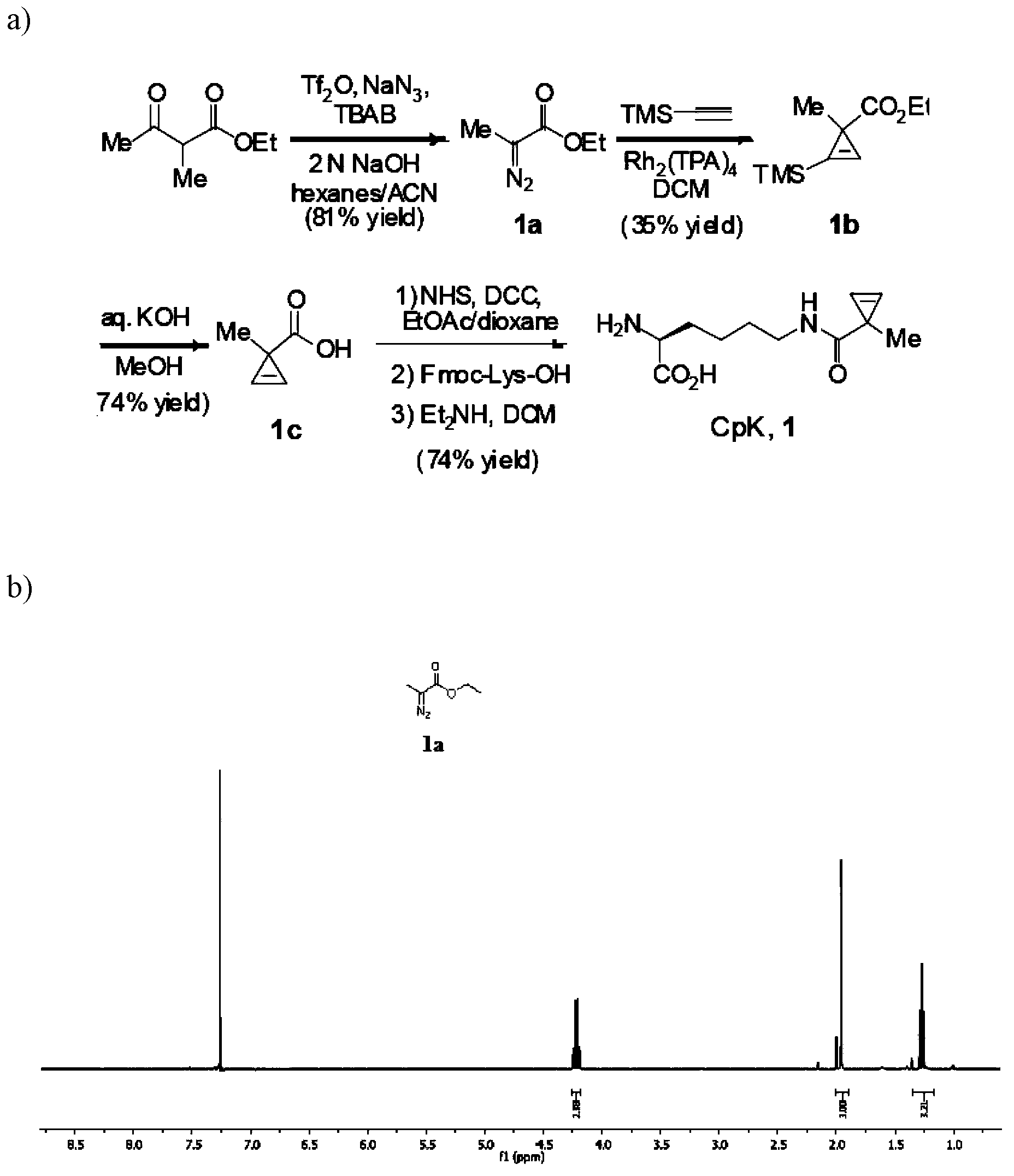
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) synthetase mutant containing an amino acid sequence selected from groups consisting of amino acids shown by SEQ ID NO:4 and conservative variants thereof. The invention provides a CpK (short for N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine) translation system for fixed point specific insertion of N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine in a target protein through pairing of orthogonal tRNA and orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, and a method for fixed point specific insertion of CpK in the target protein by using the translation system. The CpK translation system comprises (i) N<epsilon>-(1-methylcyclopropyl-2-acrylamide)-lysine, (ii) the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, (iii) the orthogonal tRNA and (iv) a nucleic acid for coding the target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase is used for realizing aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA preferentially by using CpK, and the nucleic acid contains at least one selective codon specifically identified by the orthogonal tRNA. The invention also relates to an application of a mutant protein for fixed point specific insertion of CpK in protein labeling through a light click reaction with a tetrazole compound.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
3-chlorinated tyrosine translation system and application thereof
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) synthetase mutant, wherein the amino acid sequence contained therein is selected from a group composed of the amino acids shown by the SEQ ID No. 2, 3 and 4 and the conservative mutants thereof. The invention provides a 3-chlorinated tyrosine translation system doping 3-chlorinated tyrosine into the target protein by use of the orthogonal tRNA, orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and the pairing thereof, and a method for doping the 3-chlorinated tyrosine into the target protein by use of the translation system. The 3-chlorinated tyrosine translation system comprises (i) 3-chlorinated tyrosine, (ii) orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, (iii) orthogonal tRNA and (iv) nucleic acid coding the target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase performs aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA by use of the 3-chlorinated tyrosine by priority; and the nucleic acid contains at least one selection coder for specificity identification of the orthogonal tRNA.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Thrombopoietic activity of tyrosyl-trna synthetase polypeptides
ActiveUS20140255375A1Increased platelet formationReduce development riskPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticTyrosyl-tRNA SynthetaseIncreased Thrombopoiesis
Thrombopoietic compositions are provided comprising tyrosyl tRNA synthetase polypeptides, including truncations and / or variants thereof. Also provided are methods of using such compositions in the treatment of conditions that benefit from increased thrombopoiesis, such as thrombocytopenia.
Owner:ATYR PHARM INC
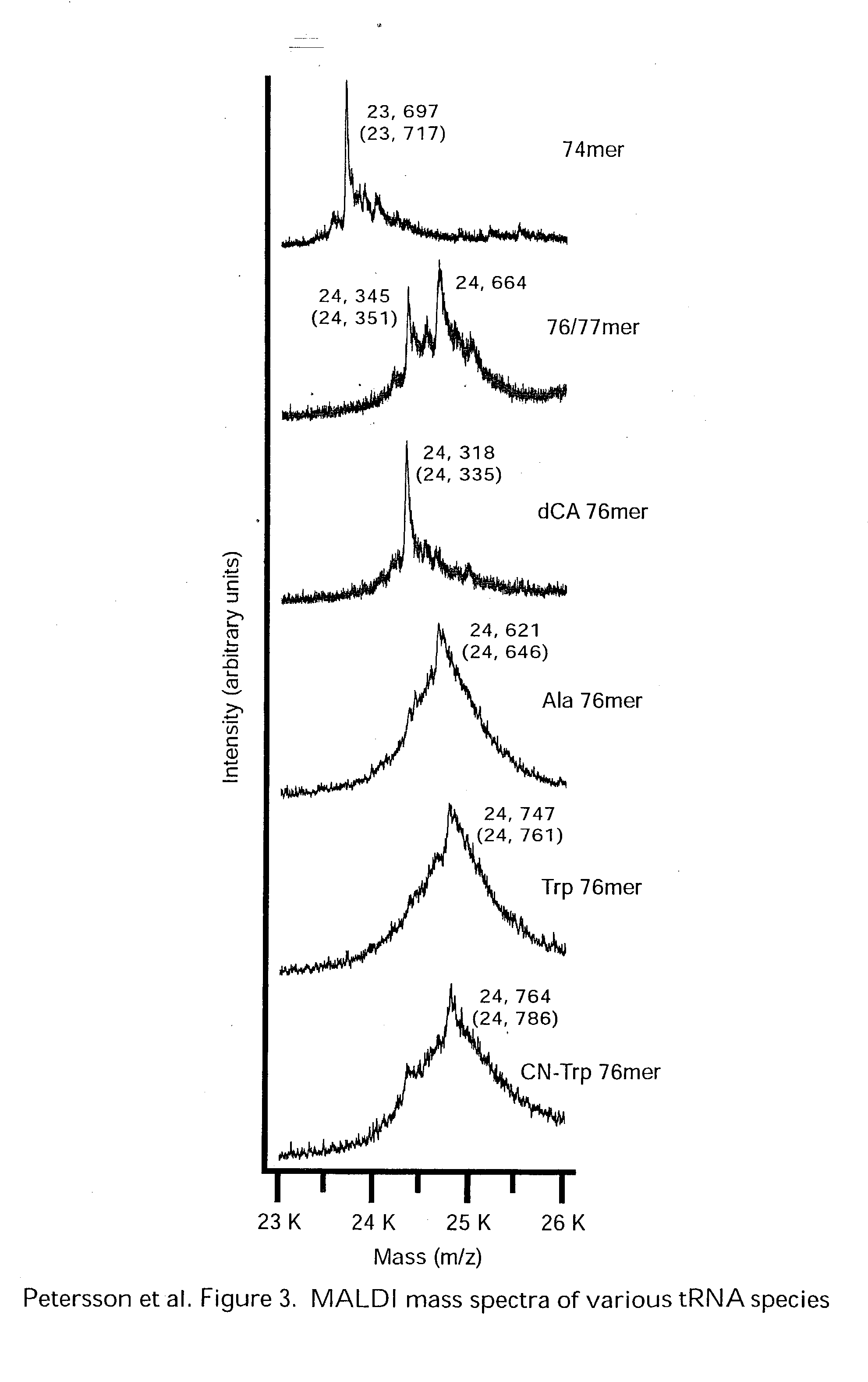
Methods for evaluation of in vitro aminoacyl tRNA production using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20050074759A1Less timeLess materialTime-of-flight spectrometersSamples introduction/extractionSide chainProtein structure
The present invention relates to a new use for matrix-assisted laser desorption / ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Specifically, the present invention provides a new method for evaluating the aminoacylation state of tRNAs, which are useful for site-directed mutagenesis of both sidechain and backbone protein structures. Further, the present invention useful for the generation of novel peptides, polypeptides, and proteins that may be used in drug design and screening, and in the design of small molecule agonists or antagonists for receptors, enzymes and other proteins and molecules involved in various disease states. Additionally, the present invention is useful in the field of tRNA aminoacylation, particularly in the design of synthetases.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
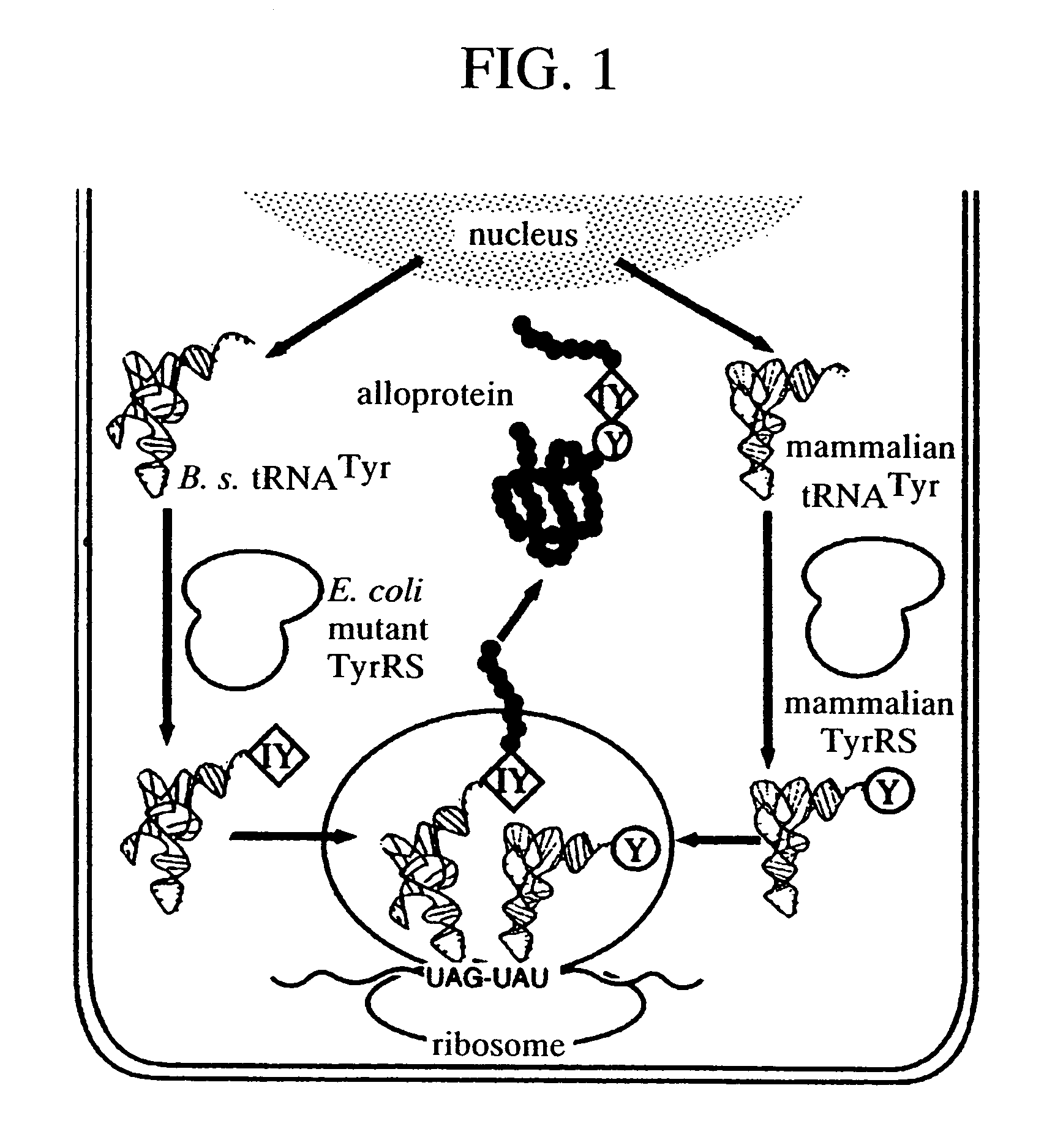
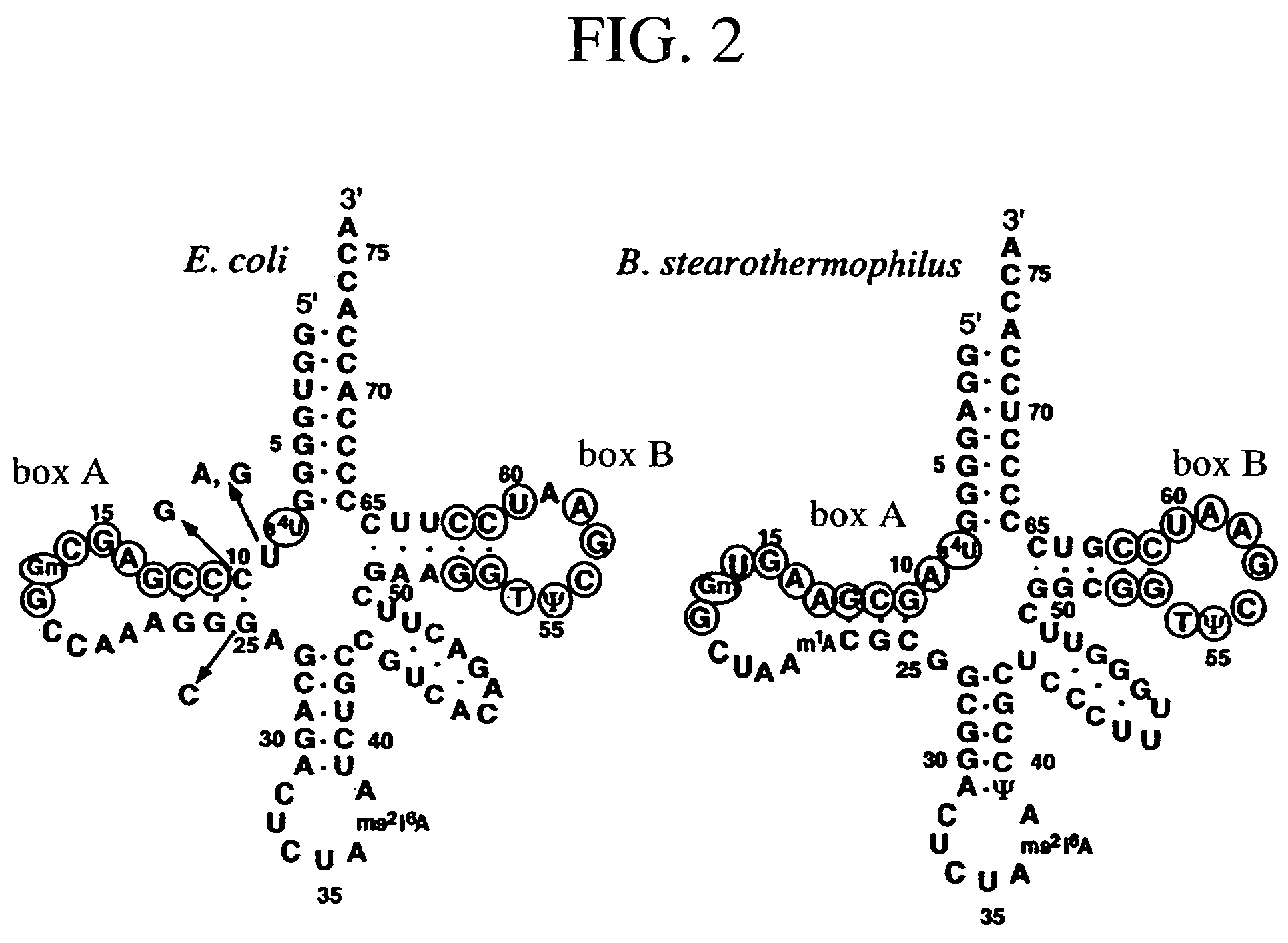
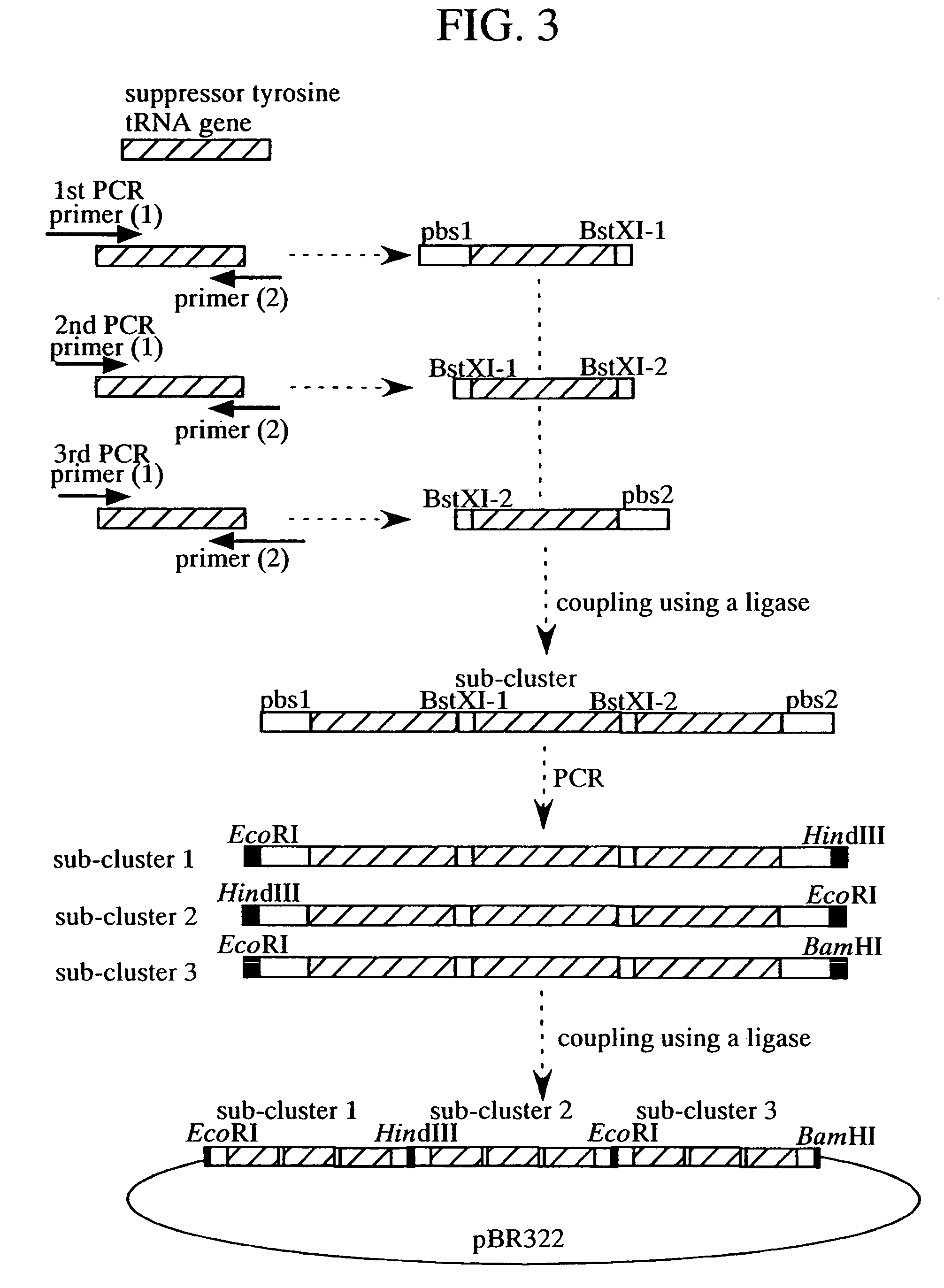
Method of expressing proteins comprising non-naturally-occurring amino acids
A method of expressing a protein having an unnatural amino acid integrated thereinto comprising expressing (A) a mutant tyrosyl tRNA synthase that is derived from Escherichia coli-origin tyrosyl tRNA synthase and has an elevated specificity for an unnatural tyrosine derivative compared with the specificity for tyrosine, (B) a suppressor tRNA originating in an eubacterium belonging to the genus Bacillus, Mycoplasma or Staphylococcus which is capable of binding to the above tyrosine derivative in the presence of the above mutant TyrRS, and (C) a desired protein gene having a nonsense mutation at a desired site in animal cells to thereby incorporate the above tyrosine derivative into the nonsense mutation site in the above protein.
Owner:RIKEN
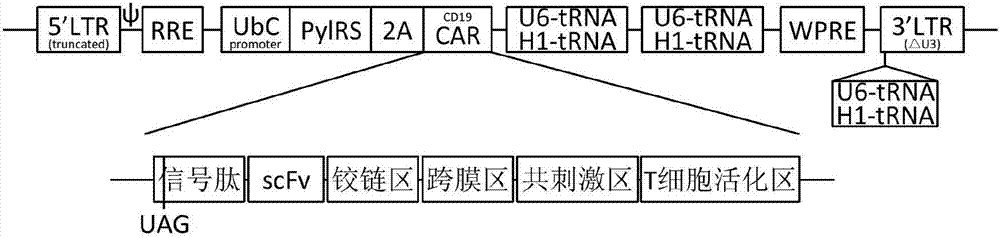
Regulation and control method of expression in chimeric antigen receptor
ActiveCN107099546AImprove securityImprove controllabilityVectorsFermentationAntigenAntigen receptors
The invention discloses a regulation and control method of expression in a chimeric antigen receptor. An expression system enables coexpression of the chimeric antigen receptor, unnatural amino acid is coded to the corresponding UAG orthogonal unnatural amino acid arginyl tRNA and tRNA pair, the nonsense codon UAG is introduced into an amino acid sequence of the chimeric antigen receptor for coding the unnatural amino acid, the expression system is lack of the unnatural amino acid, the chimeric antigen receptor cannot be expressed, and when the expression system adds the unnatural amino acid, the chimeric antigen receptor can be completely expressed. The recombinant chimeric antigen receptor having unnatural amino acid-dependence keeps targeting and killing efficiency on CAR-T, and increases the controlling performance on two specific characters, a control switch is selected as a micromolecular compound, and the method provides an important approach for increasing the safety for cancer clinical treatment for CAR-T.
Owner:胜武(北京)生物科技有限公司
Preparation method of mutant of double-carbonyl reductase containing D-amino acid
InactiveCN102517241AUniversally applicableLow priceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesProtein targetADAMTS Proteins
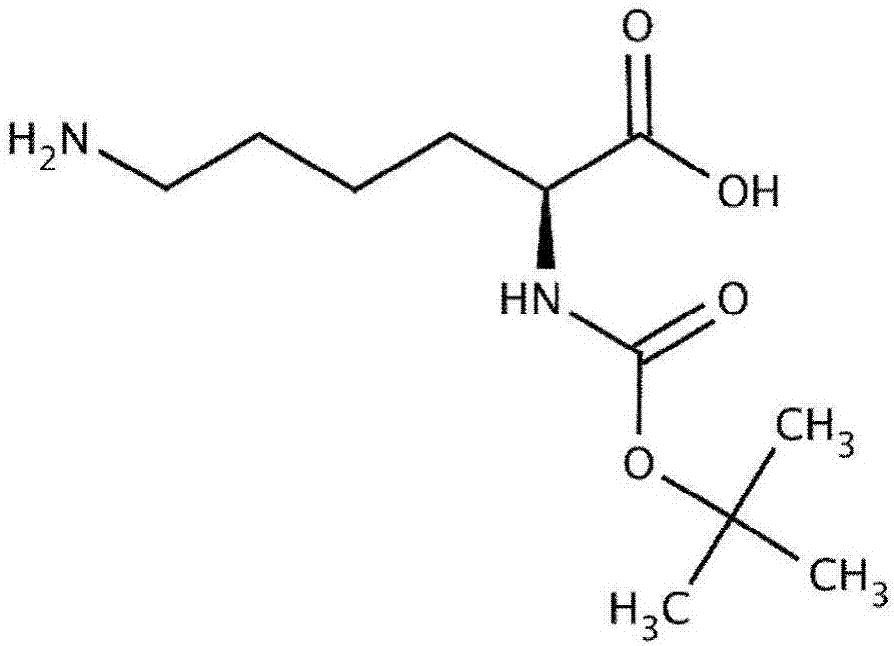
The invention discloses a preparation method of protein and polypeptide containing D-lysine. According to the invention, an expression gene of a target protein is introduced into a specific enzyme-digested multiple cloning site of an expression plasmid, and a target site of the expression gene is mutated into a TAG codon; a sequence of ph aminoacyl tRNA synthetase is introduced into another specific enzyme-digested multiple cloning site of the expression plasmid, such that a recombinant plasmid is obtained; a pAC-ph delta-AK3 plasmid is prepared; the pAC-ph delta-AK3 plasmid and the recombinant plasmid are cotransfected into a host, such that an expression system is obtained; D-lysine is added into a cultivation medium, and is used for inducing the expression system to express a target protein; the protein is purified, such that the target protein is obtained. According to the invention, a characteristic that lysyl tRNA synthetase and inhibitory type tRNA molecule pair originated frompyrococcushorikoshii can specifically select amber codon TAG is adopted, and D-lysine is introduced in a set position in double-carbonyl reductase. The introduction rate is close to 100%. The method has wide application values.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Construction of stable cell line carrying orthogonal tRNA/aminoacyl tRNA synthetase
InactiveCN109295100AAchieve stable expressionStable expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetically modified cellsAminoacyl-tRNA synthetasesAminoacyl-tRNA
The present invention relates to a method for constructing a stable cell line carrying an orthogonal tRNA / aminoacyl tRNA synthetase, and the method stably integrates an orthogonal tRNA / aminoacyl tRNAsynthetase gene into cell genomes by double lentiviral stable transduction and plasmid stable transfection. The invention further relates to the stable cell line obtained by the method and the use ofthe stable cell line in the expression of a protein containing non-natural amino acids, and by utilizing unique reactive groups on the non-natural amino acids, the purpose of high-efficiency and specific protein modification can be achieved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
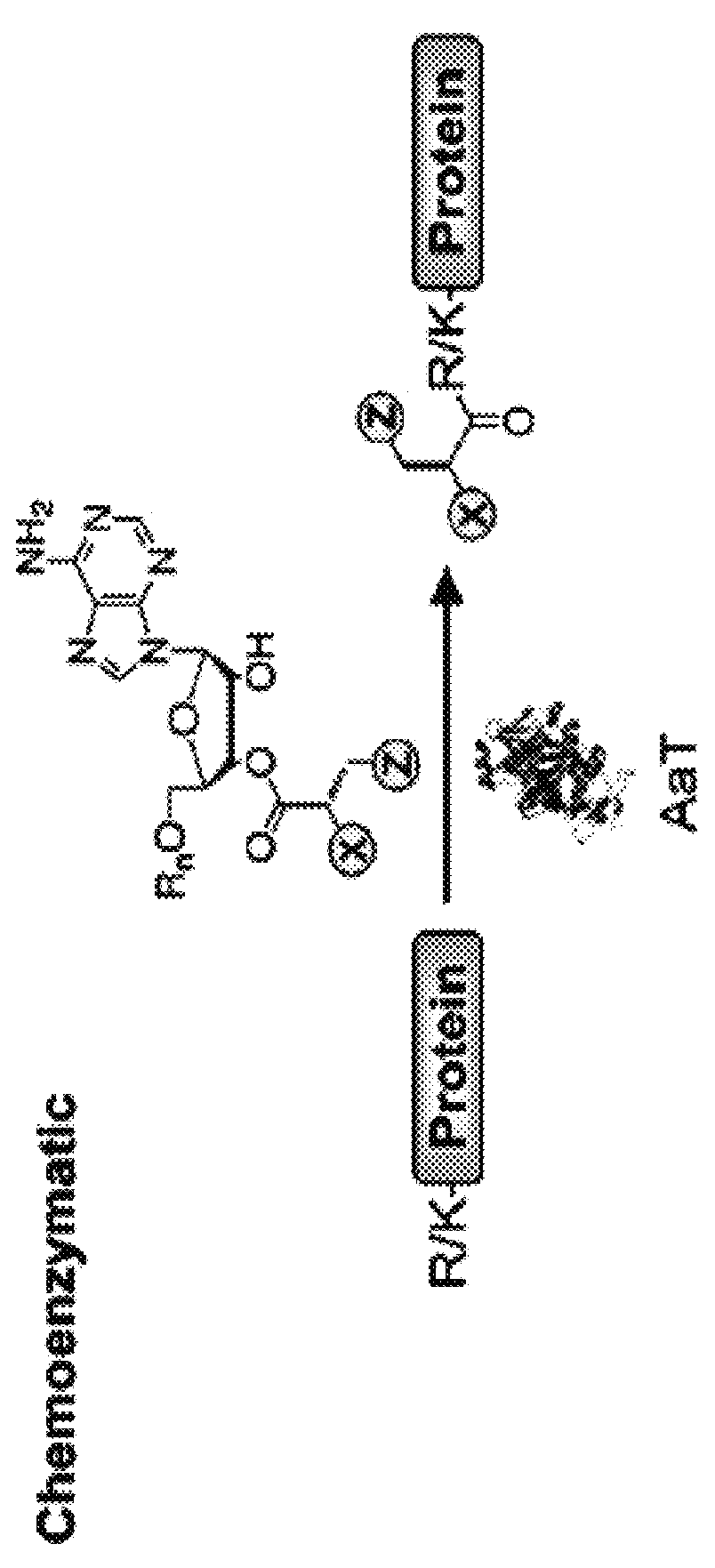
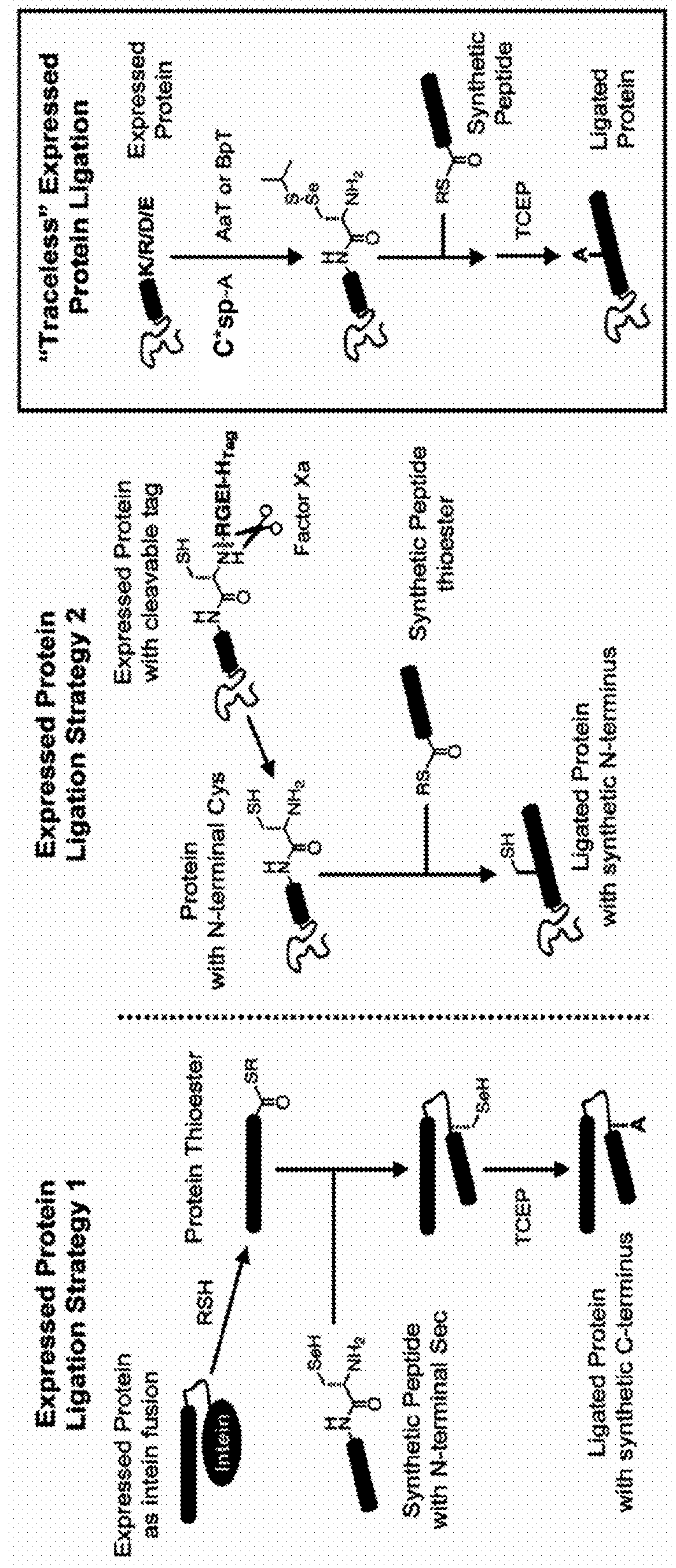
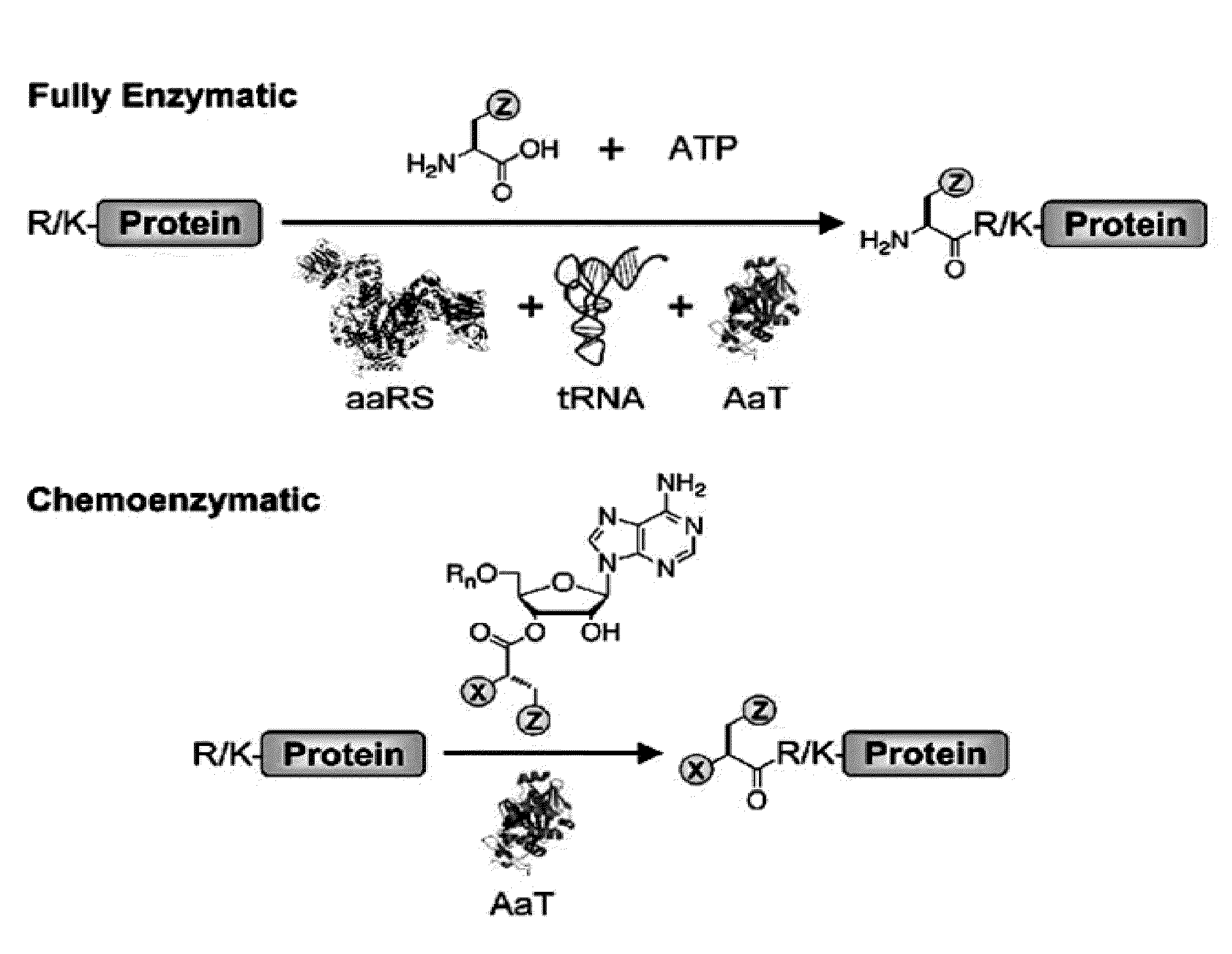
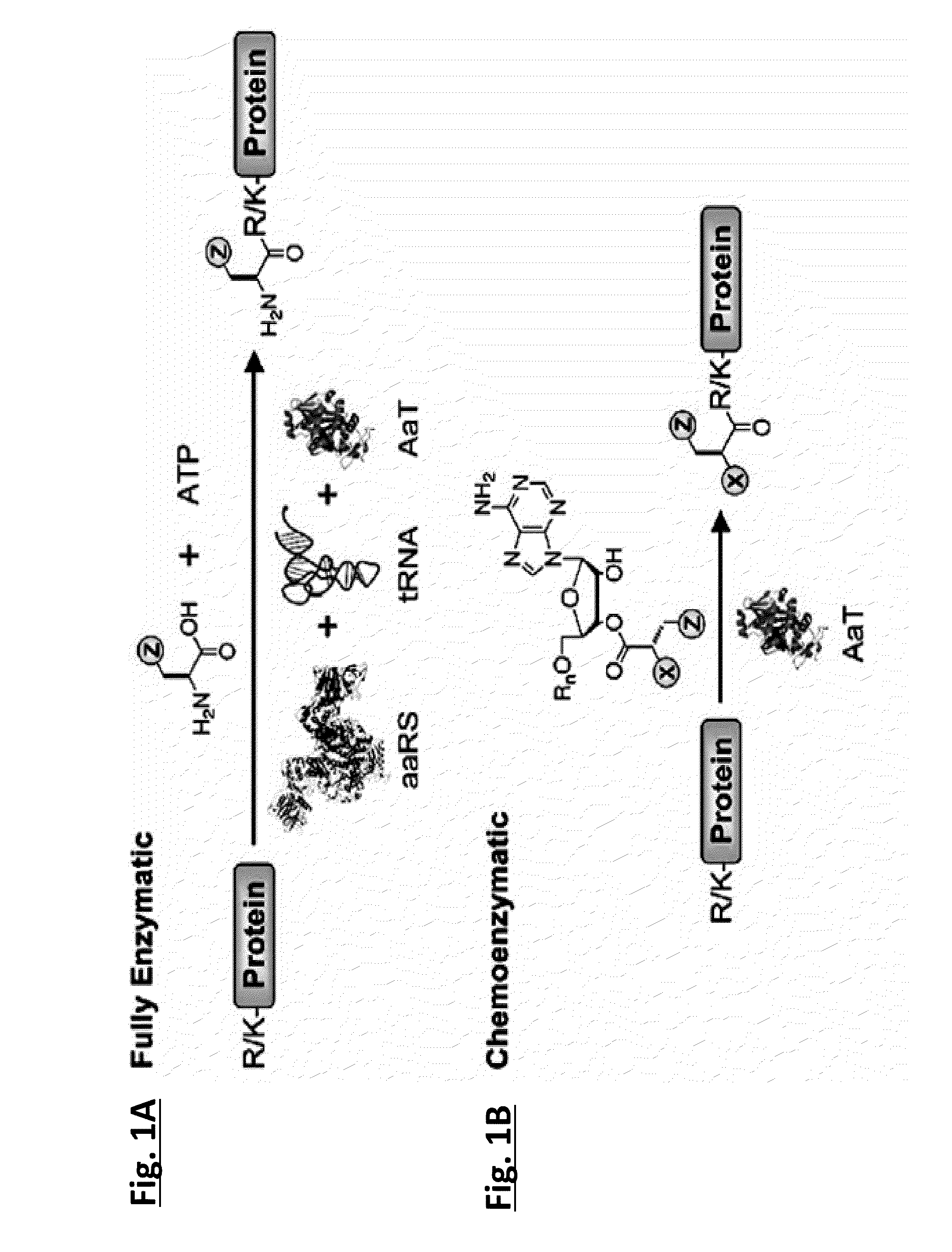
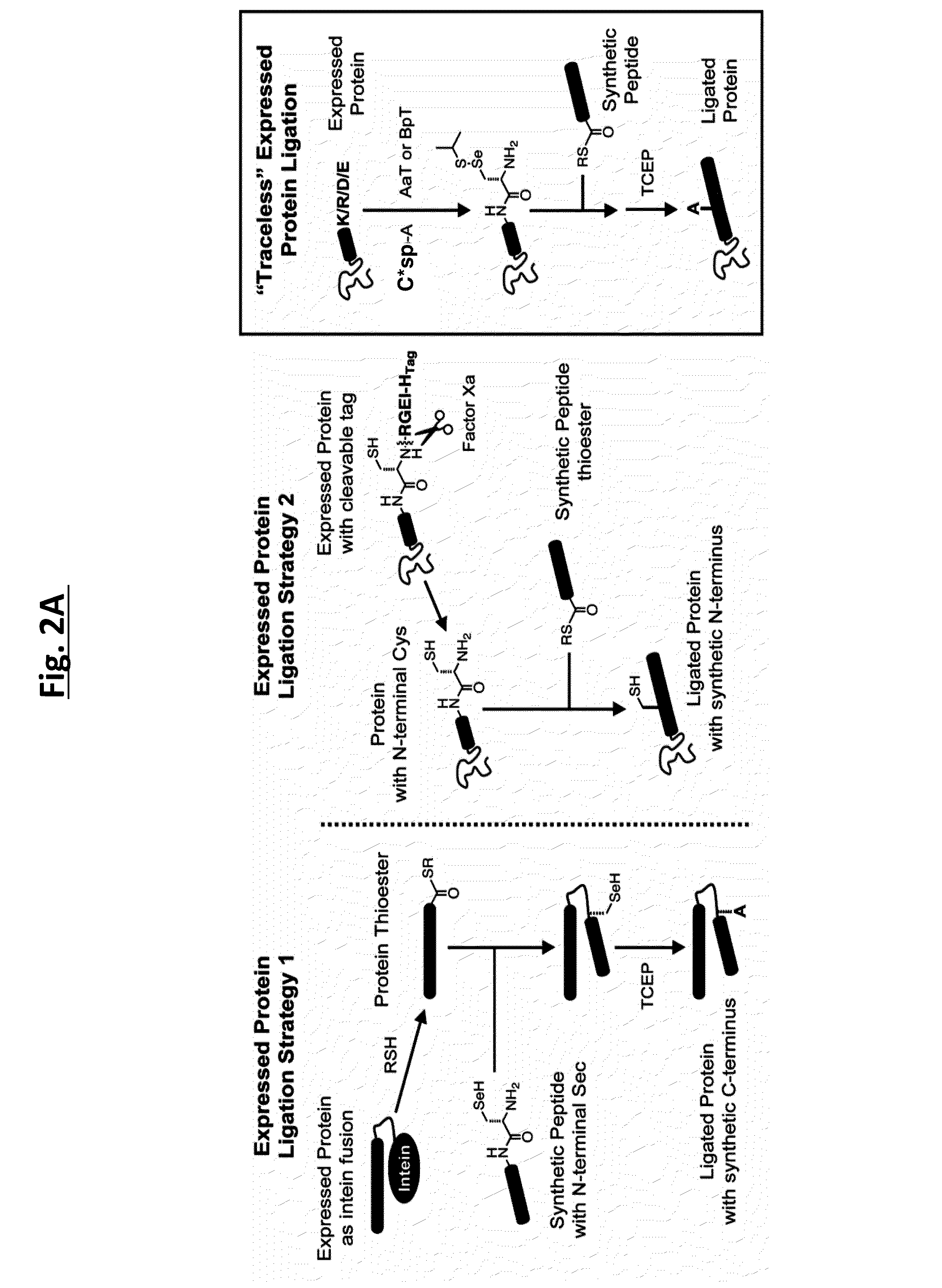
Methods of modifying N-termini of a peptide or protein using transferases
ActiveUS9376700B2Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsAminoacyl-tRNAADAMTS Proteins
The invention includes a selective method of modifying the N-terminus of a protein using an aminoacyl tRNA transferase. In certain embodiments, the method comprises contacting a solution of the protein or peptide with a transferase and a derivative of a molecule, whereby the N-terminus of the protein or peptide is derivatized with the molecule.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
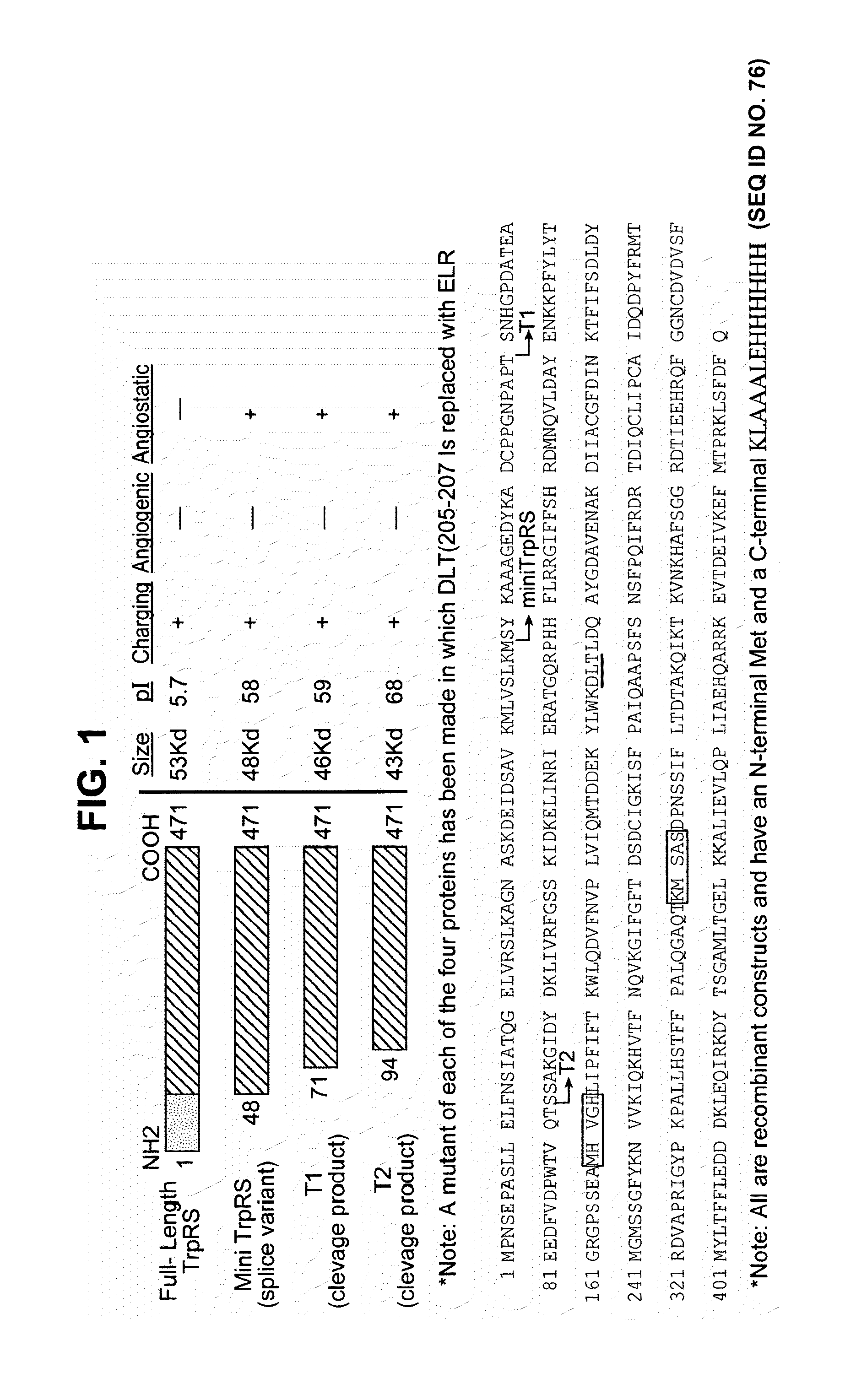
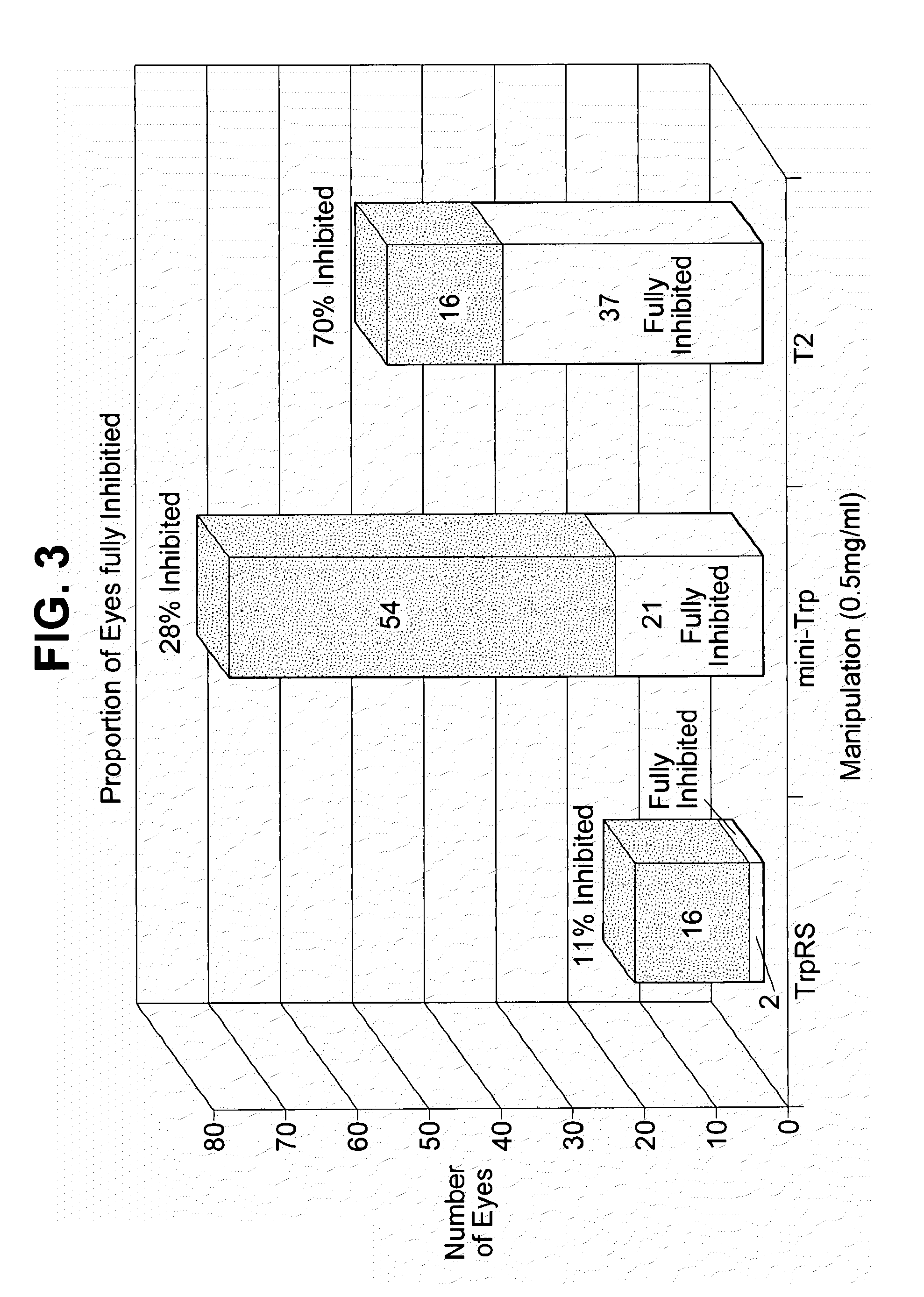
tRNA synthetase fragments
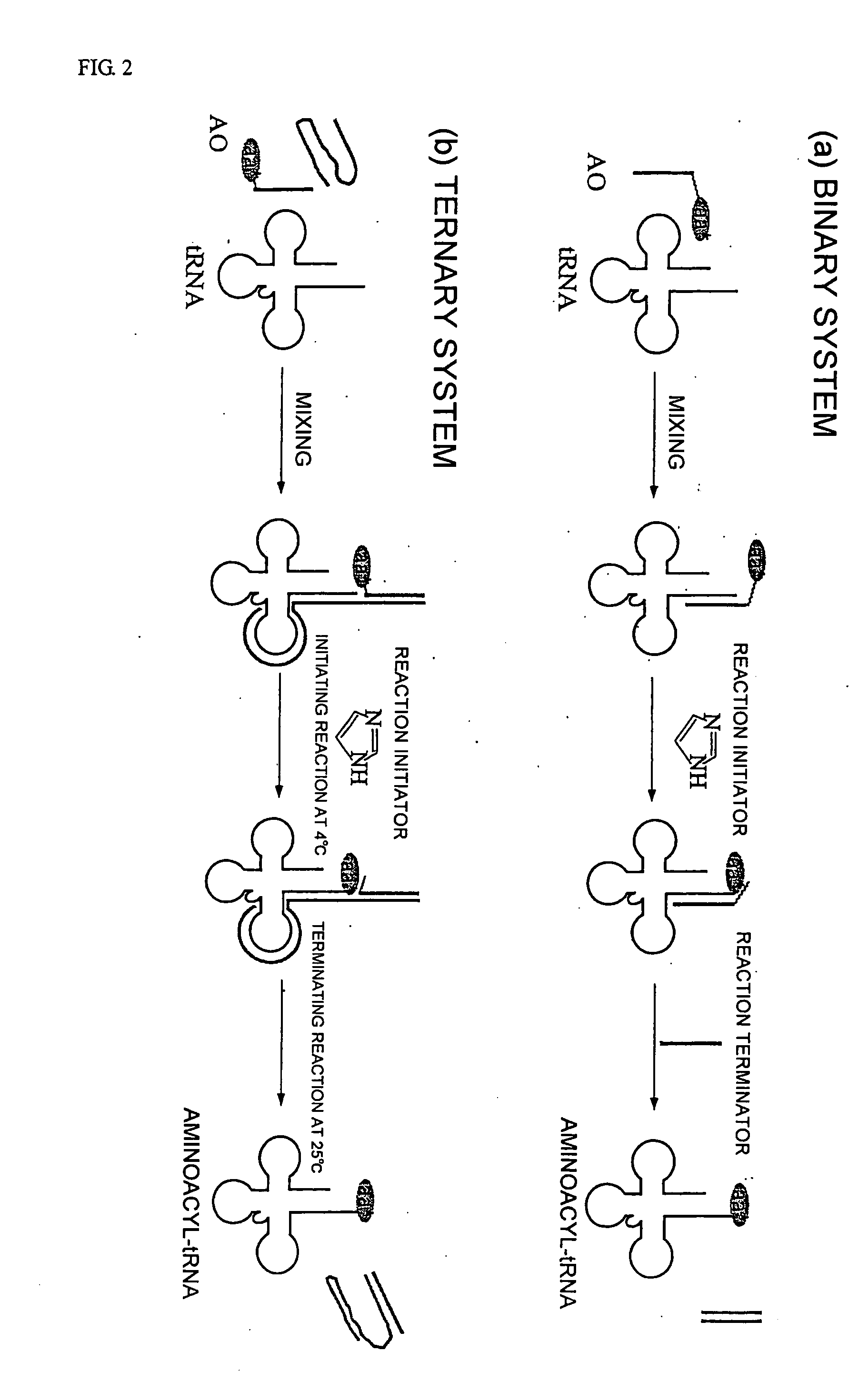
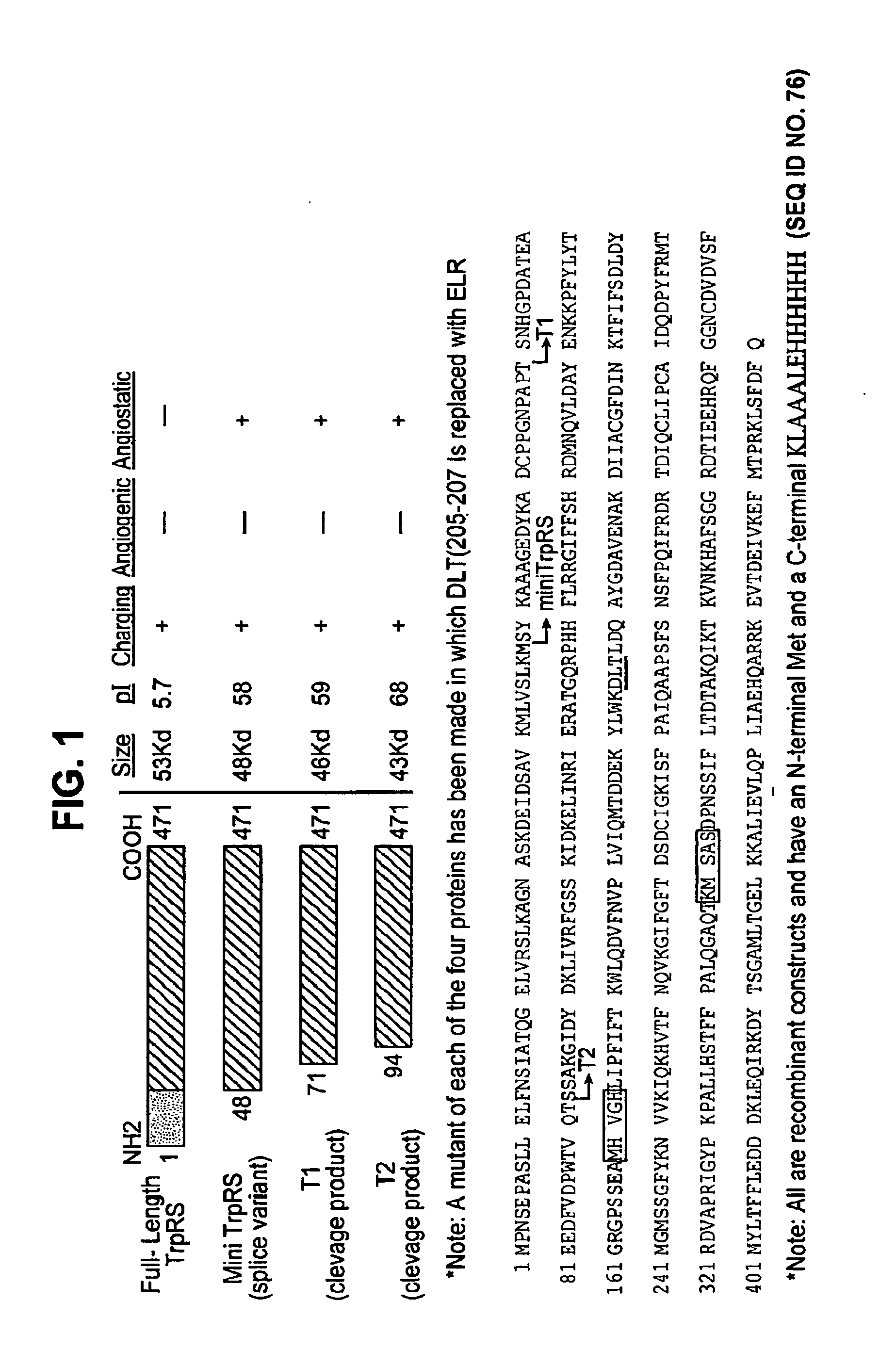
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating conditions associated with angiogenesis. In particular the present invention relates to multi-unit complexes of tRNA synthetase fragments and uses thereof; diverse multi-unit complexes including a tRNA synthetase fragment; compositions and methods for modulating angiogenesis; polynucleotides encoding tRNA synthetase fragments and uses thereof; antibodies and epitopes specific to tRNA synthetase fragments; variants of tRNA synthetase fragments and uses thereof; methods for treating angiogenesis; methods for screening for anti-angiogenic agents; methods of modulating angiogenesis; kits for modulating angiogenesis; and business methods for modulating angiogenesis. Preferably the tRNA synthetase fragments are tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase fragments, and more preferably human tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase fragments.
Owner:ANGIOSYN
Glutamyl trna synthetase (GTS) fragments
InactiveCN102239253AAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsStreptococcus pneumoniaeAminoacyl-tRNA
The present invention relates to polypeptide fragments, including variants and analogs, of Streptococcus pneumonia (S. pneumoniae) glutamyl tRNA synthetase (GtS) protein and to vaccines comprising such polypeptide fragments. In particular, the present invention relates to the use of such vaccines for eliciting protective immunity to S. pneumoniae.
Owner:PROTEA VACCINE TECH
Method for maintaining foreign gene in cell stably
Disclosed is a method for preparing a protein or peptide encoded by a foreign gene by expressing the foreign gene, which comprises the steps of: inserting the foreign gene in such a manner that the foreign gene can be expressed, so as to prepare a recombinant vector carrying a gene encoding an aminoacyl tRNA synthetase in such a manner that the gene can be expressed; providing a mutant host cell or the like having the deletion of a chromosomal gene encoding the aminoacyl tRNA synthetase; transforming the mutant host cell with the recombinant vector to produce a transformant; and culturing the transformant to prepare a protein or peptide encoded by the foreign gene. It becomes possible to provide: a novel means for maintaining a recombinant DNA cloning vector in a host cell without the need of using any antibiotic or without any limitation in the composition of a culture medium; and a method for preparing a protein or peptide encoded by a foreign gene by utilizing the means.
Owner:JAPAN AGENCY FOR MARINE-EARTH SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for production of protein having non-natural type amino acid integrated therein
This invention provides a method for producing proteins into which non-natural amino acids have been incorporated at desired positions involving the use of either prokaryote-derived or eukaryote-type aaRS* and prokaryotic cells or eukaryote-type as host cells, the method comprising steps of: (a) introducing genes encoding prokaryote-derived aminoacyl tRNA synthetase mutants having enhanced specificity to non-natural amino acids similar to given natural amino acids (compared with specificity to the natural amino acids) and tRNA genes for non-natural amino acids capable of binding to the non-natural amino acids in the presence of the prokaryote-derived aminoacyl tRNA synthetase mutants into prokaryotic cells that express genes encoding eukaryote-type aminoacyl tRNA synthetase having specificity to the given natural amino acids and tRNA genes capable of binding to the natural amino acids in the presence of eukaryote-type aminoacyl tRNA synthetase; and (b) knocking out genes encoding aminoacyl tRNA synthetase having specificity to the natural amino acids, which are inherent in the prokaryotic cells, and inherent tRNA genes capable of binding to the natural amino acids in the presence of the inherent aminoacyl tRNA synthetase.
Owner:RIKEN
Method for producing diverse libraries of encoded polymers
InactiveUS20060252051A1Increase the number ofGenerate lotSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAminoacyl-tRNACombinatorial chemistry
Described are aminoacyl tRNA analogues which comprise a tRNA, and an amino acid which acts as an acceptor and donor substrate for ribosome-directed translation, thus, incorporating unusual monomers into non-standard polymers by the action of ribosomes. Also described are methods for producing such tRNA analogues; non-standard polymers; libraries of encoded polymers; methods of screening the libraries; and target members and their uses. A key advantage of synthesizing non-standard polymer libraries of the present invention with aminoacyl tRNA analogues is that large libraries of high complexity can be easily made and functional library members (e.g. novel drugs) readily identified.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
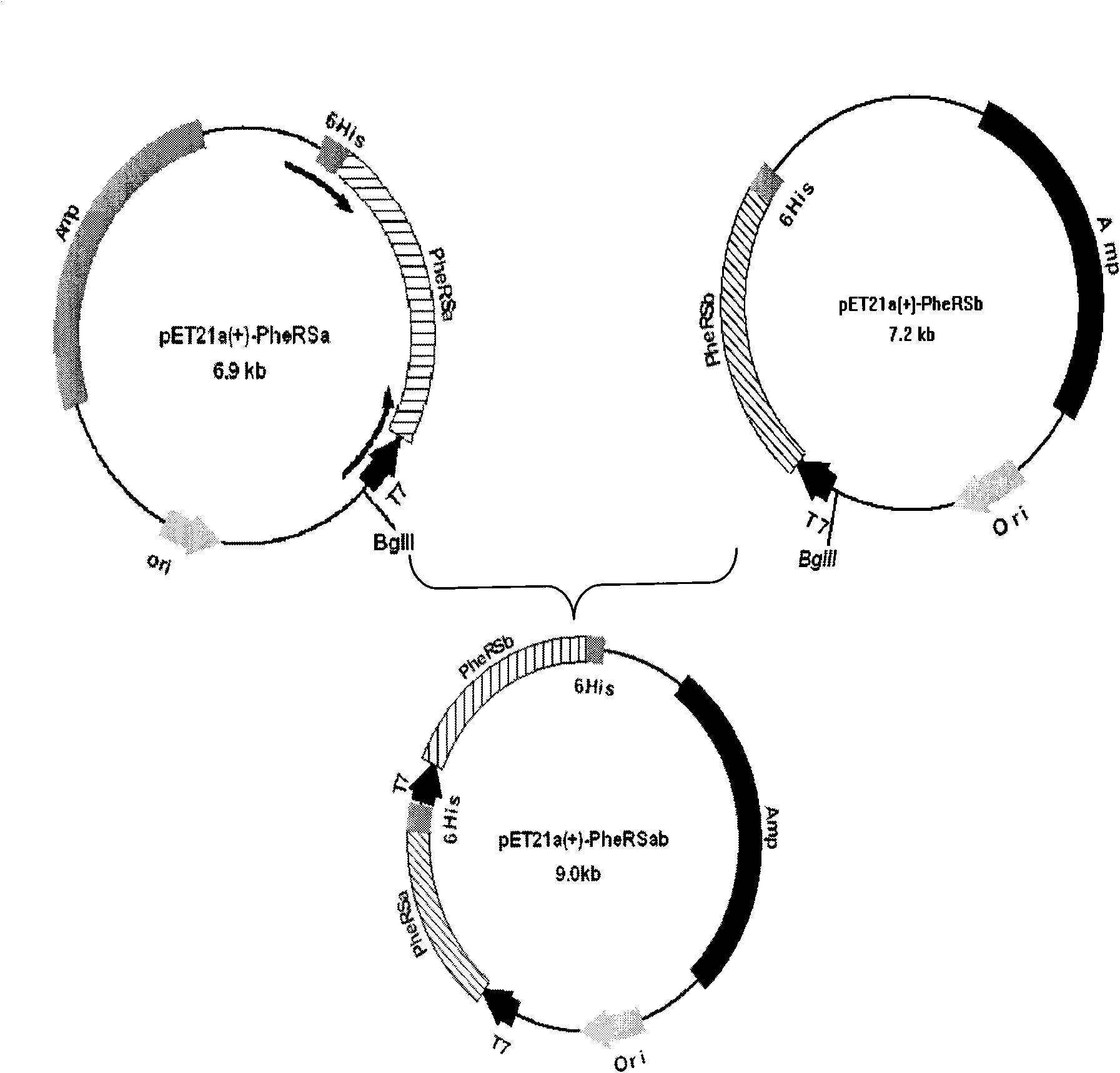
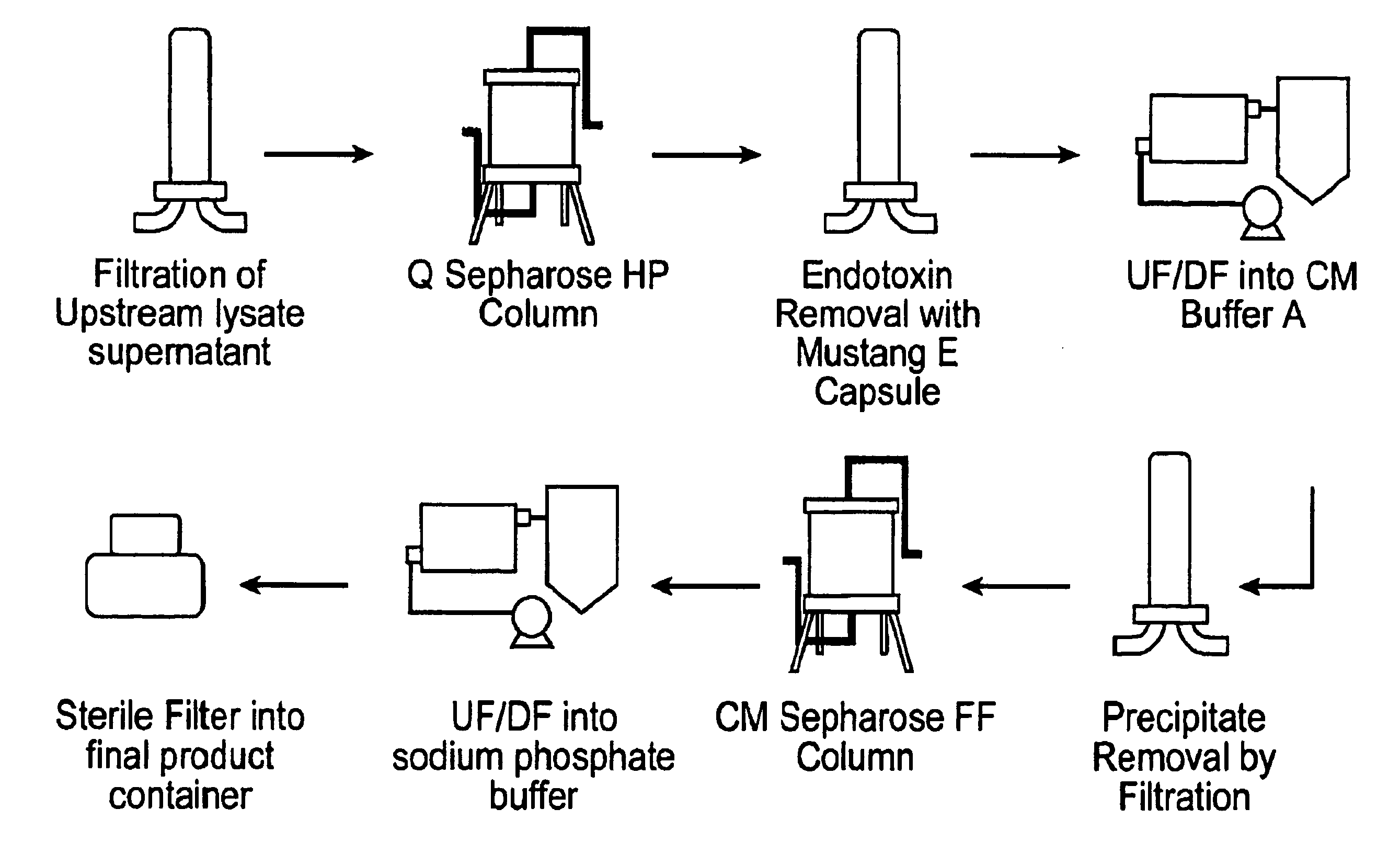
Trypanosoma brucei phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase preparation method
ActiveCN101633915ASimple stepsImprove the purification effectMicroorganism based processesEnzymesOperonAntiparasitic agent
The invention relates to a trypanosoma brucei phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase preparation method, belonging to the technical field of biology and the preparation method comprises the following specific steps: separately designing primers, amplifying the alpha subunit and beta subunit genes of trypanosoma brucei phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase; cloning the alpha subunit and beta subunit genes into prokaryotic expression vector pET21a(+), building pET21a(+)-PheRS alpha and pET21a(+)-PheRS beta expression vector; subcloning the operon of alpha subunit into pET21a(+)-PheRS beta, forming recombinant co-expression vector pET21a(+)-PheRS alpha beta; transforming the recombinant co-expression vector pET21a(+)-PheRS alpha beta into colibacillus BL21(DE3)RIPL, inducting expression with IPTG; collecting the supernate of the lysed bacteria solution, purifying proteins and obtaining the trypanosoma brucei phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase. The invention builds the recombinant plasmid of the trypanosoma brucei phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase (PheRS), and expresses and purifies trypanosoma brucei phenylalanyl-tRNA synthetase protein, thus laying a foundation for the screening of antiparasitic agent.
Owner:泰州新生源生物医药有限公司
One step n-terminal tagging of proteins
The invention includes a selective method of modifying the N-terminus of a protein using an aminoacyl tRNA transferase. In certain embodiments, the method comprises contacting a solution of the protein or peptide with a transferase and a derivative of a molecule, whereby the N-terminus of the protein or peptide is derivatized with the molecule.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for controlling cancer metastasis or cancer cell migration by modulating the cellular level of lysyl tRNA synthetase
ActiveUS9511085B2Promote migrationCancer metastasisOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCancer cell
The present invention relates to a novel function of lysyl tRNA synthetase (KRS) which enhances tumor cell migration and affects cancer metastasis via KRS's interaction with laminin receptor (67LR) by its translocation to membrane. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method for modulating cancer metastasis or migration, which comprises regulating intracellular levels of KRS; a composition for preventing or treating cancer; use of expression vector for inhibiting the expression of KRS; a method for preventing or treating cancer; use of an agent for inhibiting an activity of KRS; a method for screening an agent which modulates cancer metastasis or migration; and a method for screening an agent which inhibits the interaction of KRS with 67LR, by said novel function. Thus, KRS can modulate cancer metastasis or migration and furthermore, can modulate intracellular metabolism related to 67LR. The interaction between KRS and 67LR can be used effectively in treating, preventing and / or diagnosing of various diseases or disorders related to the interaction.
Owner:MEDICINAL BIOCONVERGENCE RES CENT
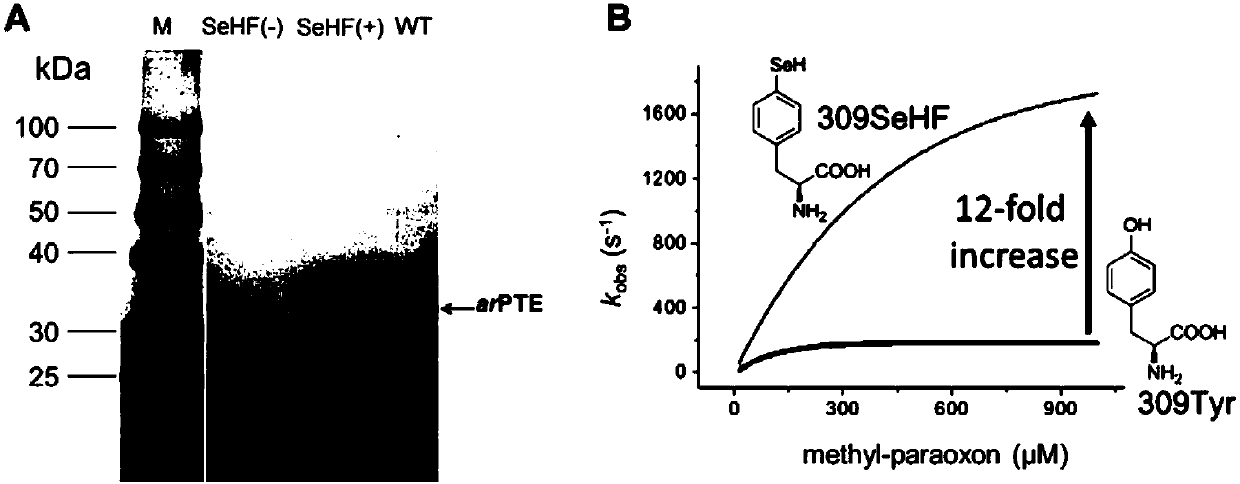
Selenotyrosine translation system and application thereof
ActiveCN110117580AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityHydrolasesLigasesSystems designProtein target
The invention relates to an aminoacyl-tRNA synthase mutant, which is an orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthase. The amino acid sequence contained in the mutant is selected from the amino acid sequence shown in SEQIDNO:4 or its conservative variants or homologues with the same enzyme activity. The invention further provides a selenotyrosine translation system, which comprises (i) selenotyrosine, (ii) the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, (iii) orthogonal tRNA and (iv) nucleic acid for encoding target protein, wherein the orthogonal aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase adopts the selenotyrosine for aminoacylation of the orthogonal tRNA preferentially, and the nucleic acid contains at least one selection codon for specifically recognizing the orthogonal tRNA. Moreover, the invention provides a method for modifying protease by utilizing the design of the selenotyrosine translation system and protease produced by encoding through the method.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Screening method for identifying new aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors
InactiveUS8183006B2Fast and cheap procedureStops growthMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisCell divisionAminoacyl-tRNA synthetases
The method comprising: a) obtaining a gene sequence codifying a naturally occurring aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase; b) engineering the gene codifying for said aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, resulting into an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase with a defective activity, with the proviso that the engineering does not affect the functionality of the catalytic site of the enzyme; c) cloning the gene resulting from step (b) in an expression vector; d) transforming isolated mammalian cells with the expression vector resulting from step (c); e) growing the recombinant cells resulting from step (d) in a nutrient medium under conditions which allow the expression of the engineered aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase, resulting the expression into cell death or a decrease in the rate of cell division; f) providing a substance to be tested to the medium resulting from step (e); and g) analyzing the resulting cell growth, wherein if there is an increase in cell growth, then the substance selectively inhibits the activity of the engineered aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and does not affect to its cellular ortholog, resulting in that said substance is a candidate to drug.
Owner:FUNDACIO PRIVADA PARC CIENTIFIC DE BARCELONA +2
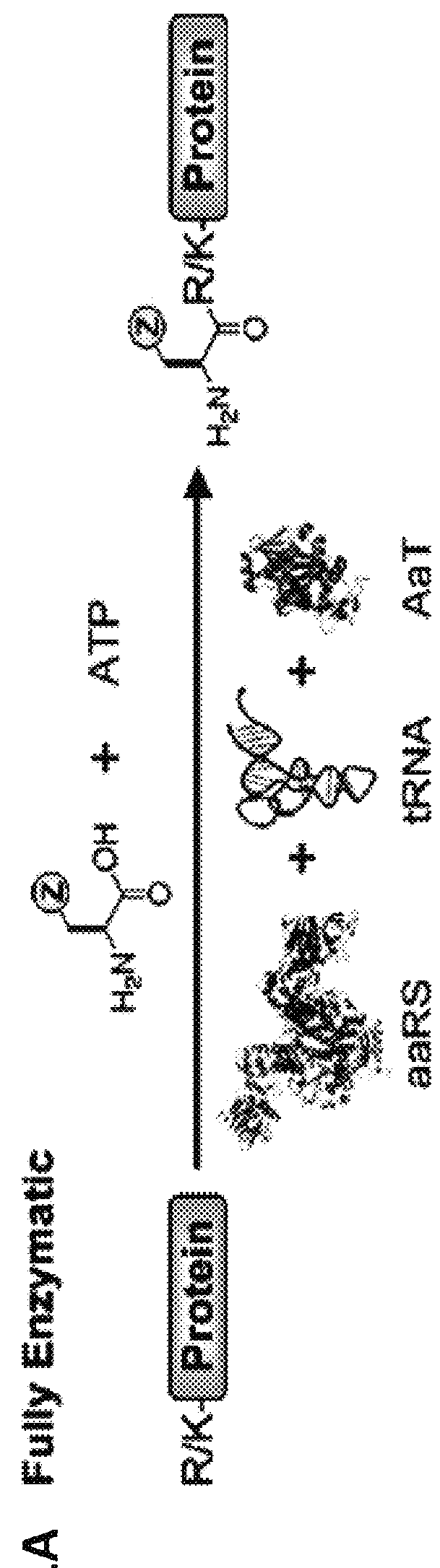
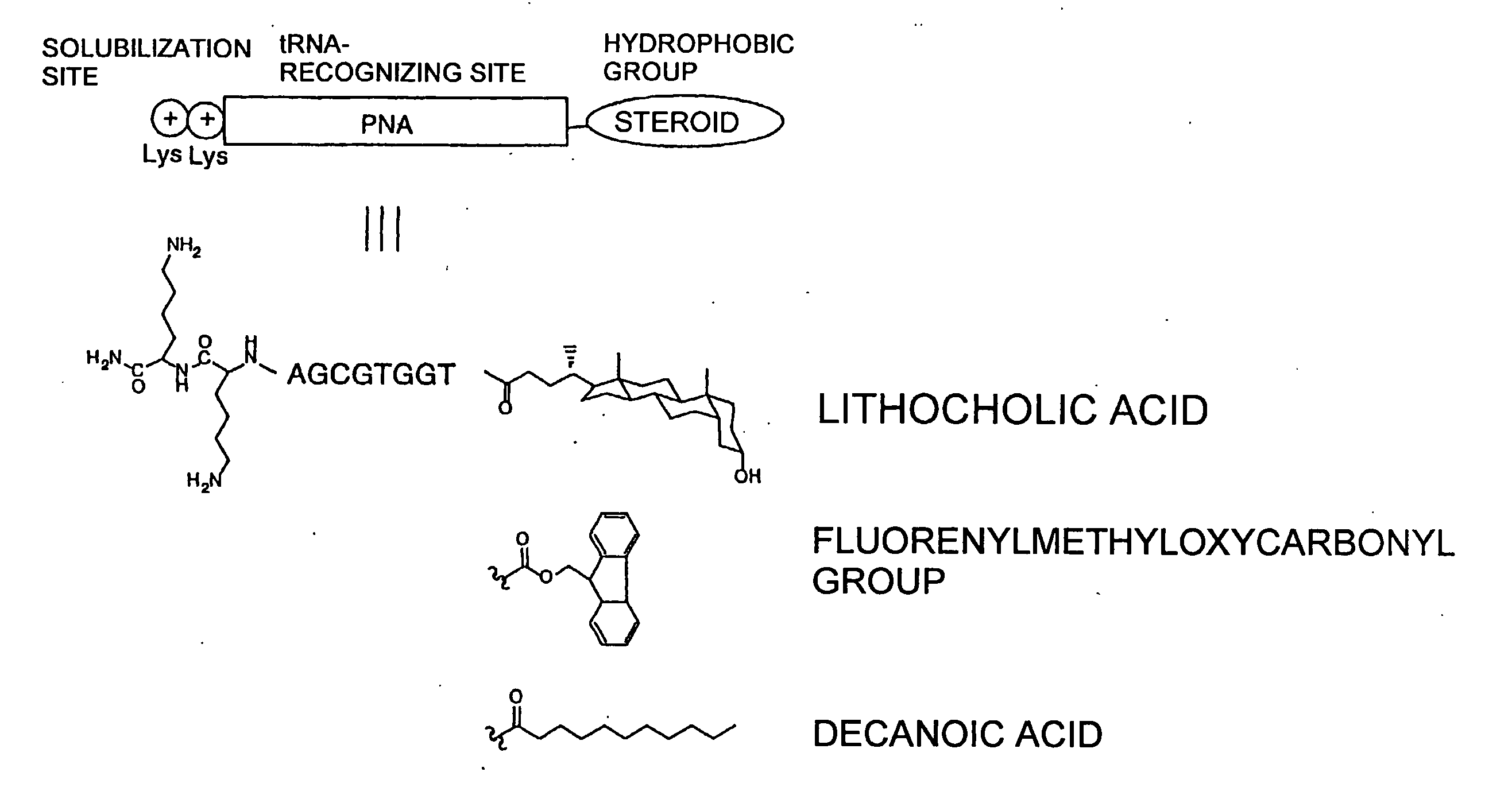
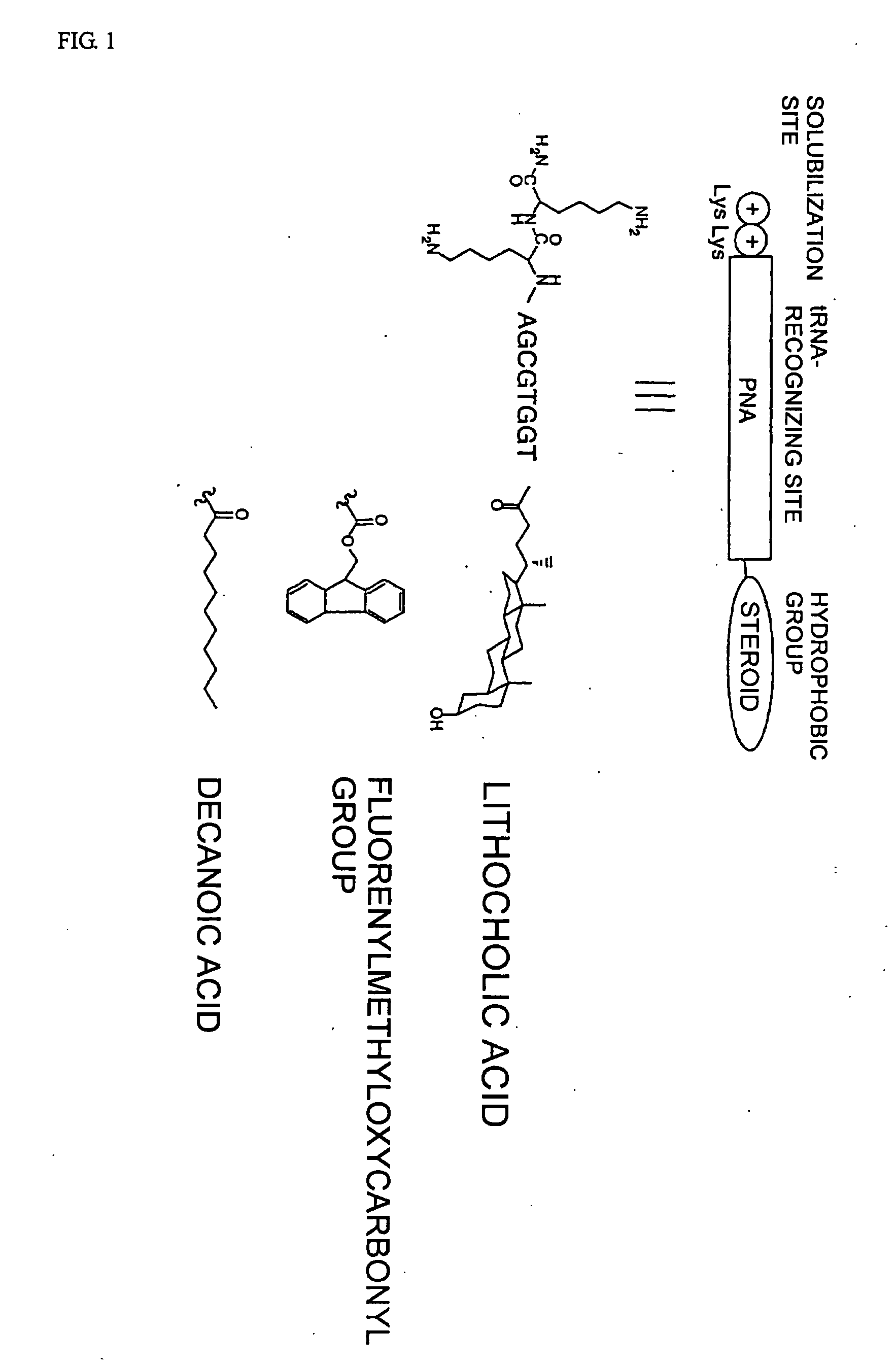
Method of aminoacylating trna
InactiveUS20060020111A1Efficient and highly practicalSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical synthesisAminoacyl-tRNA
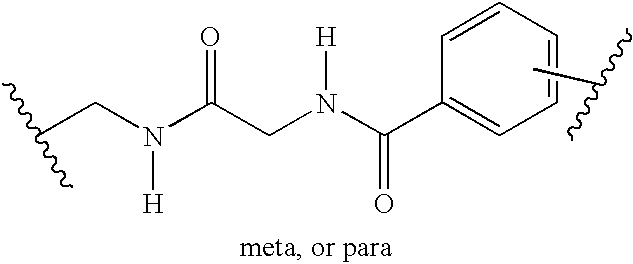
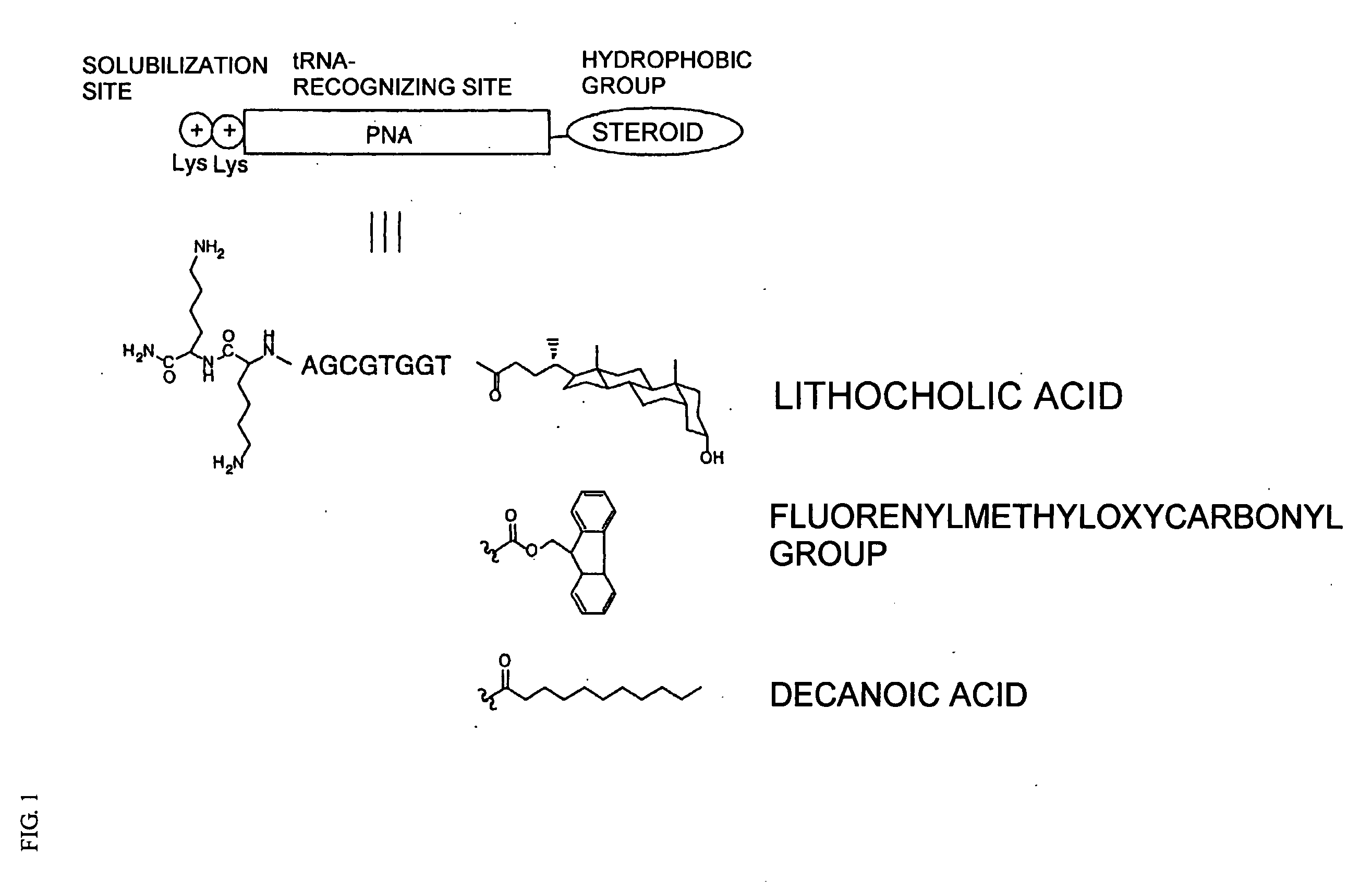
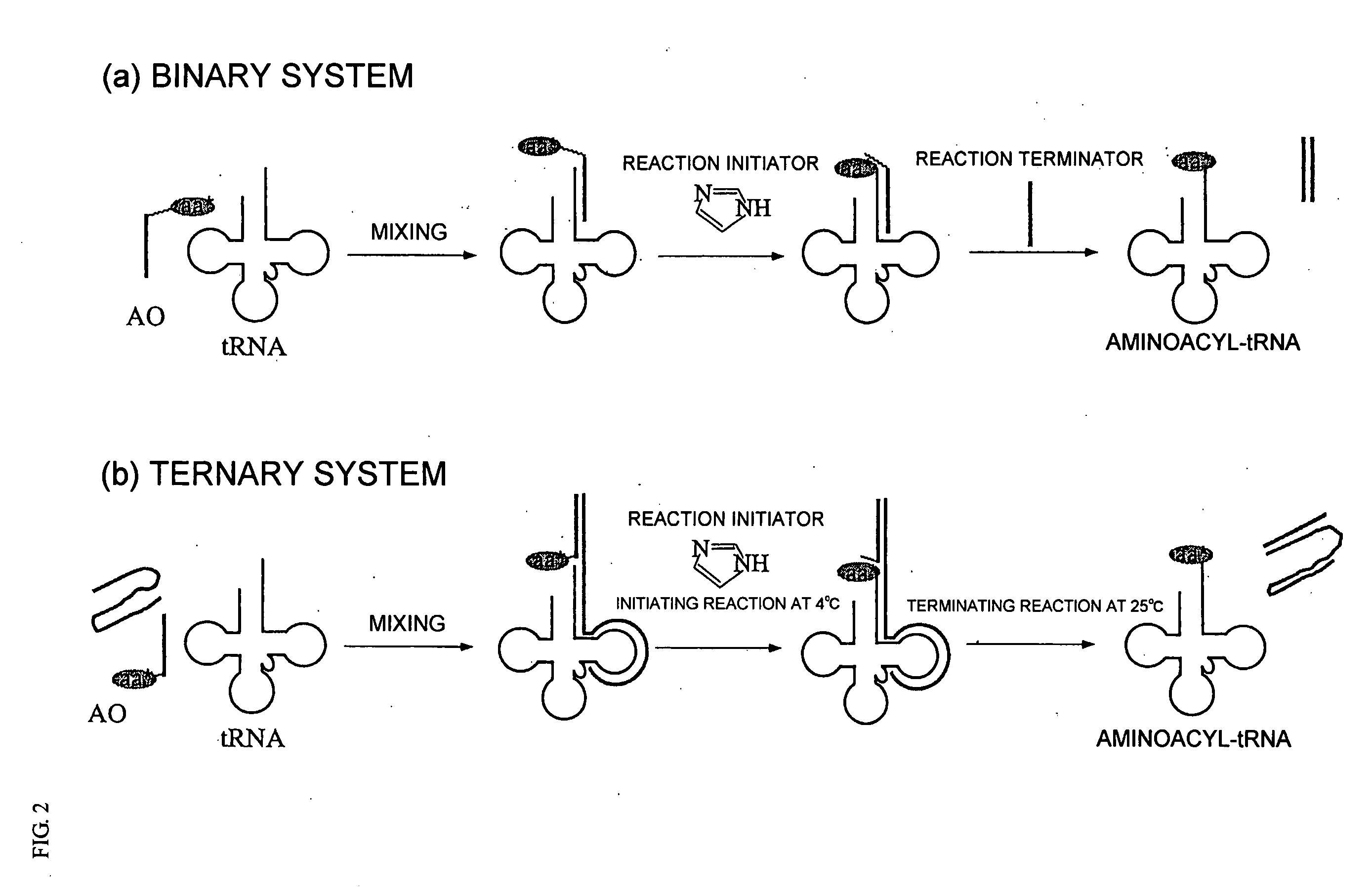
It is intended to provide a method of chemically synthesizing an aminoacyl tRNA which is completely different from the existing methods, namely, a highly efficient and practically usable method for synthesizing an aminoacyl tRNA whereby any nonnatural amino acid can be conveniently aminoacylated without a need for genetic engineering techniques and detected without resort to a radioactive isotope. The above-described aminoacylation method comprises enclosing a tRNA and an amino acid in the vicinity of the micelle-water interface and bringing them close to each other to thereby react the same, or providing between them a peptide nucleic acid specifically binding to the tRNA as an antisense molecule and bringing them close to each other to thereby react the same.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
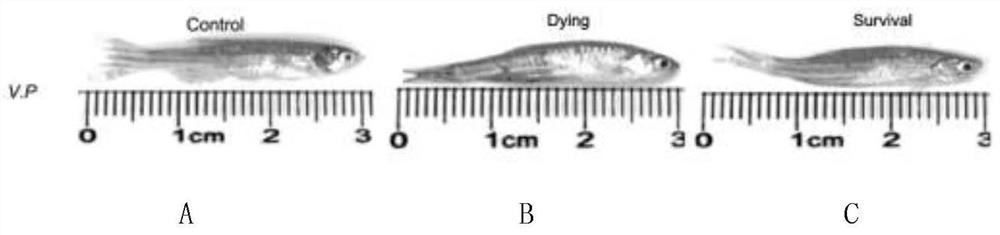
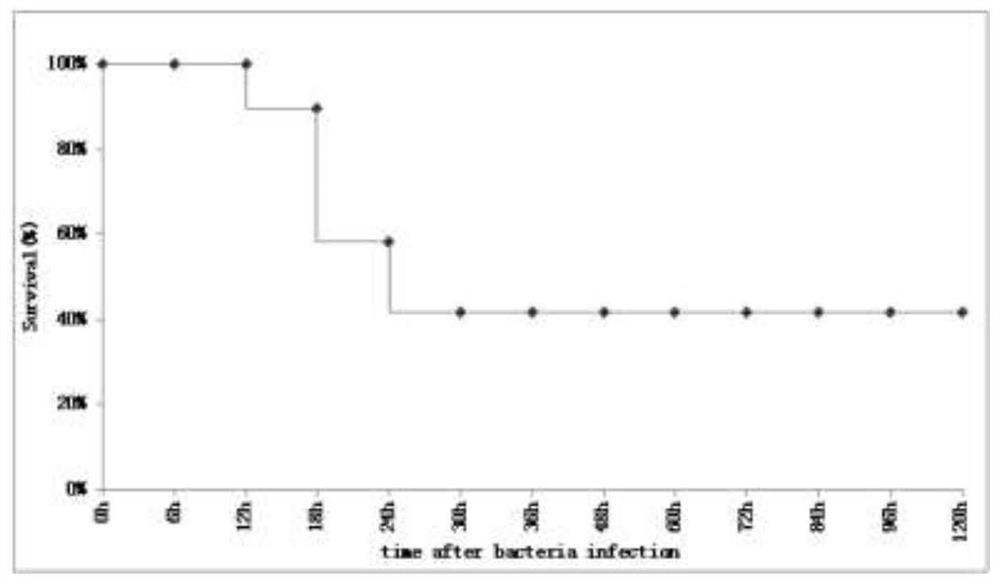
Body fluid small molecule metabolic marker of zebra fish infected bacteria and application of marker
The invention discloses a body fluid micromolecular metabolic marker of zebra fish infected bacteria, and the marker is at least one of glutamine, lactic acid, serine and glycine, preferably glutamine. The bacteria are selected from vibrio parahaemolyticus. The invention also discloses an application of glutamine in improving the immunity of zebra fish responding to vibrio parahaemolyticus infection, an application of glutamine in preparing medicines or health care products for improving the immunity of zebra fish responding to vibrio parahaemolyticus infection, an application of glutamine inregulation and control of galactose metabolism of zebra fish, and an application of glutamine in regulation and control of a biosynthetic metabolic pathway of aminoacyl tRNA of zebra fish. It is foundthrough experiments that glutamine plays an important role in zebra fish responding to bacterial infection, plays an extremely important role in zebra fish innate immune response, and can be used forresearch of metabolome functions, detection and treatment of zebra fish infected bacteria and the like. The marker has high reference value for research of metabonomics related to zebra fish responseto bacterial infection immune response.
Owner:HEZE UNIV
Method of aminoacylating tRNA
InactiveUS20080096259A1Efficient and highly practicalSugar derivativesFermentationChemical synthesisAminoacyl-tRNA
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
tRNA synthetase fragments
The present invention relates to compositions and methods for treating conditions associated with angiogenesis. In particular the present invention relates to multi-unit complexes of tRNA synthetase fragments and uses thereof; diverse multi-unit complexes including a tRNA synthetase fragment; compositions and methods for modulating angiogenesis; polynucleotides encoding tRNA synthetase fragments and uses thereof; antibodies and epitopes specific to tRNA synthetase fragments; variants of tRNA synthetase fragments and uses thereof; methods for treating angiogenesis; methods for screening for anti-angiogenic agents; methods of modulating angiogenesis; kits for modulating angiogenesis; and business methods for modulating angiogenesis. Preferably the tRNA synthetase fragments are tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase fragments, and more preferably human tryptophanyl tRNA synthetase fragments.
Owner:GLIDDEN PAUL
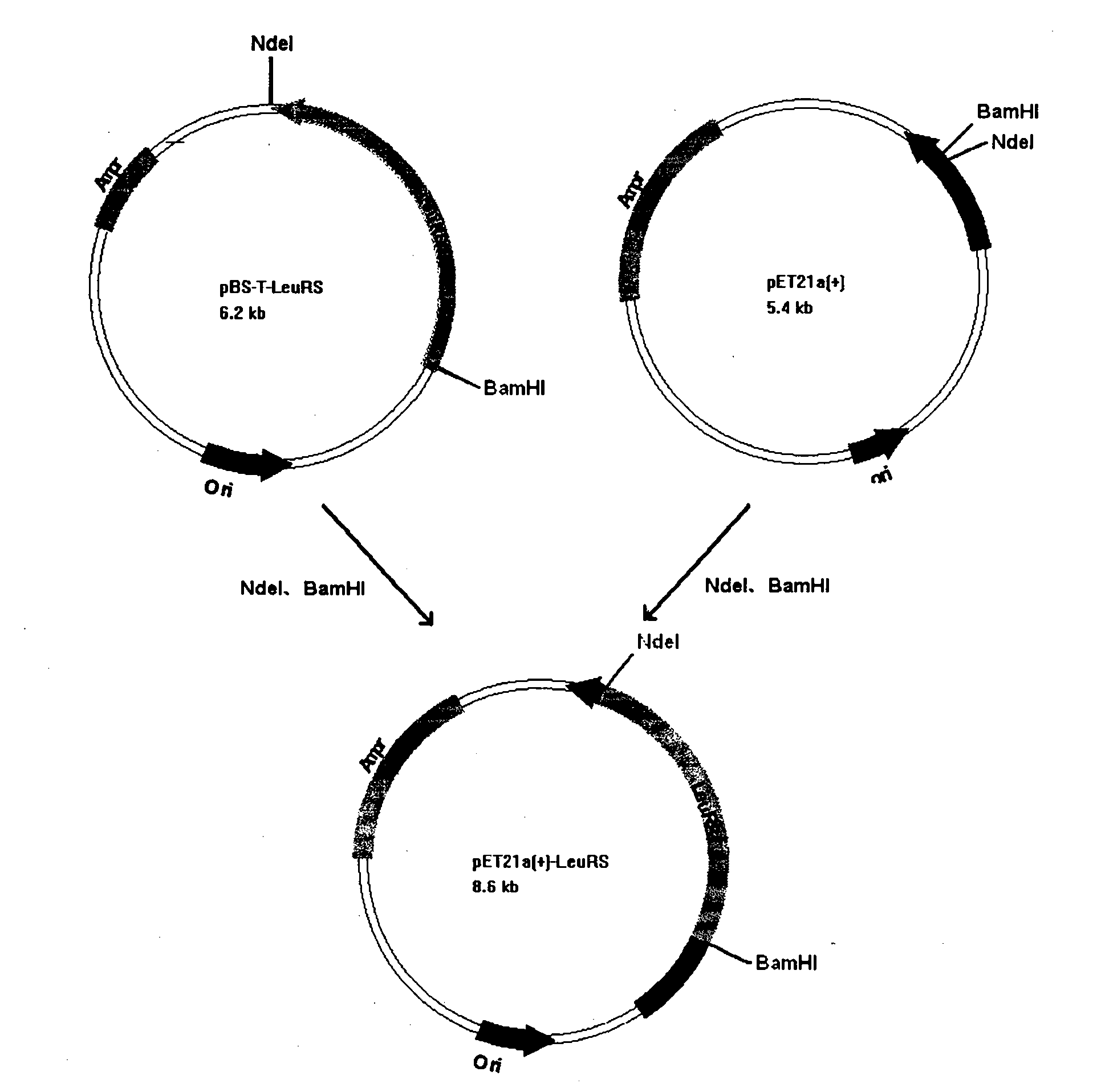
Method for preparing trypanosoma brucei leucyl tRNA synthetase activated protein
The invention relates to a method for preparing trypanosoma brucei leucyl tRNA synthetase activated protein in the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps of: designing a specific primer and amplifying a trypanosoma brucei genome; recovering cut glue to obtain a trypanosoma brucei leucyl tRNA synthetase gene; connecting the gene obtained in the last step into a cloning vector to construct a gene cloning plasmid; subcloning the cloning plasmid into an expression vector, identifying, and converting into escherichia coli; cultivating the converted escherichia coli monoclone and inducing; and purifying expressed fusion protein to obtain the trypanosoma brucei leucyl tRNA synthetase activated protein. The leucyl tRNA synthetase activated protein can be used as a target for drug screening and is widely applied to the field of drug screening.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com