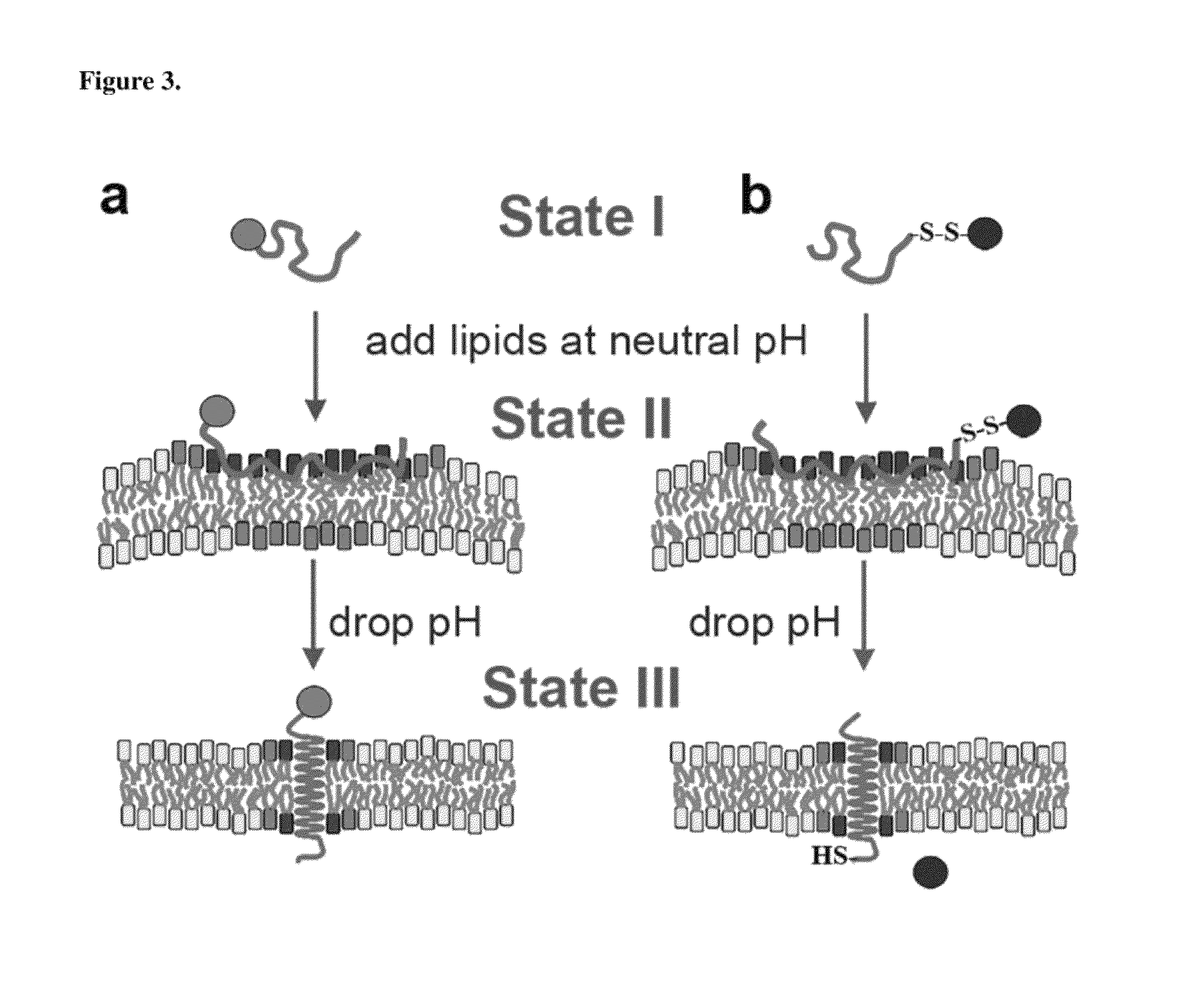Patents
Literature
198 results about "Membrane bound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Membrane-bound means that an organelle is surrounded by one or two membranes, each membrane being a bi-layer of lipids. Peroxisomes and vesicles (digestive, transport) are enclosed within a single membrane (bi-layer of lipids). Mitochondria, chloroplasts, and other plastids are surrounded by a double membrane -...
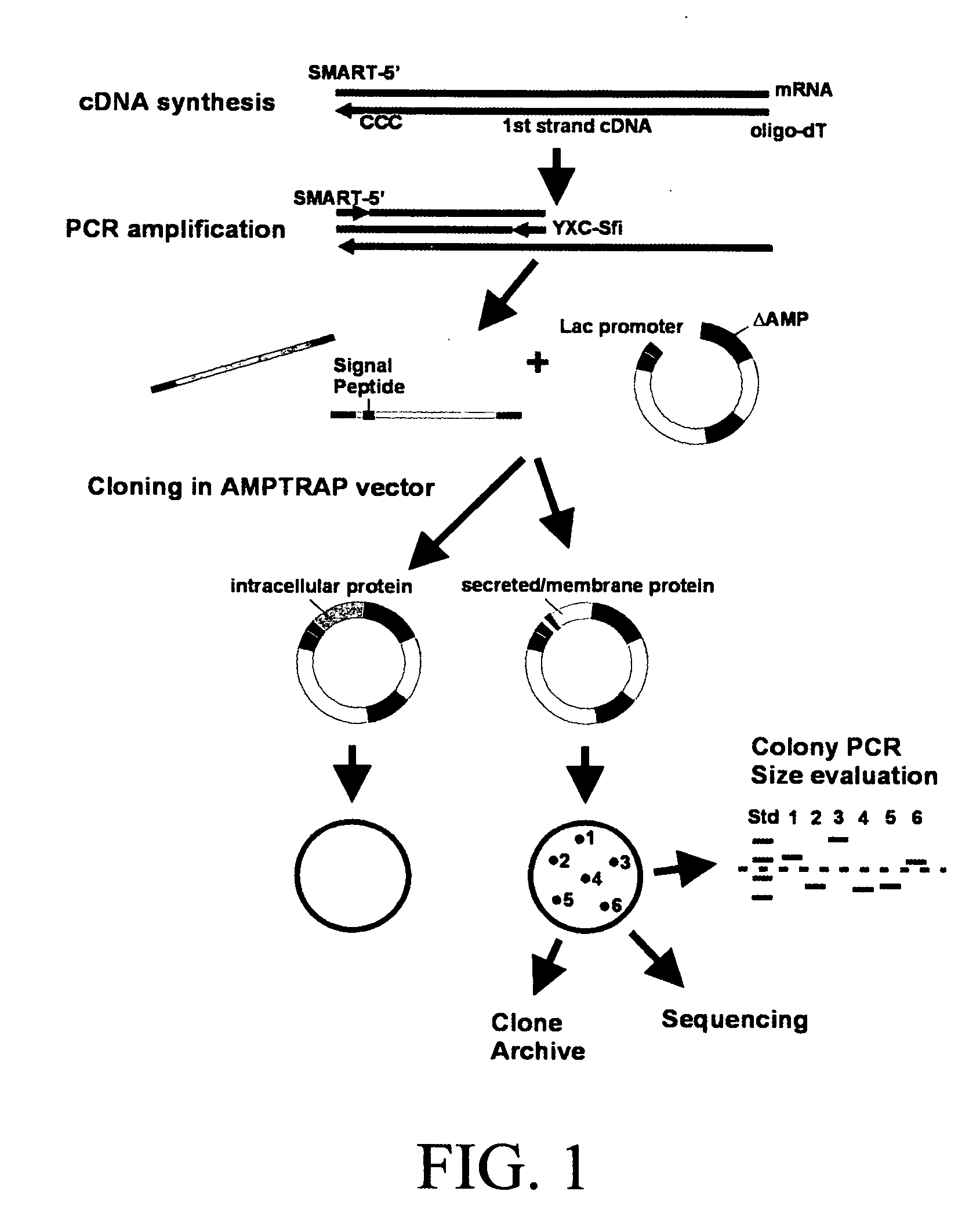
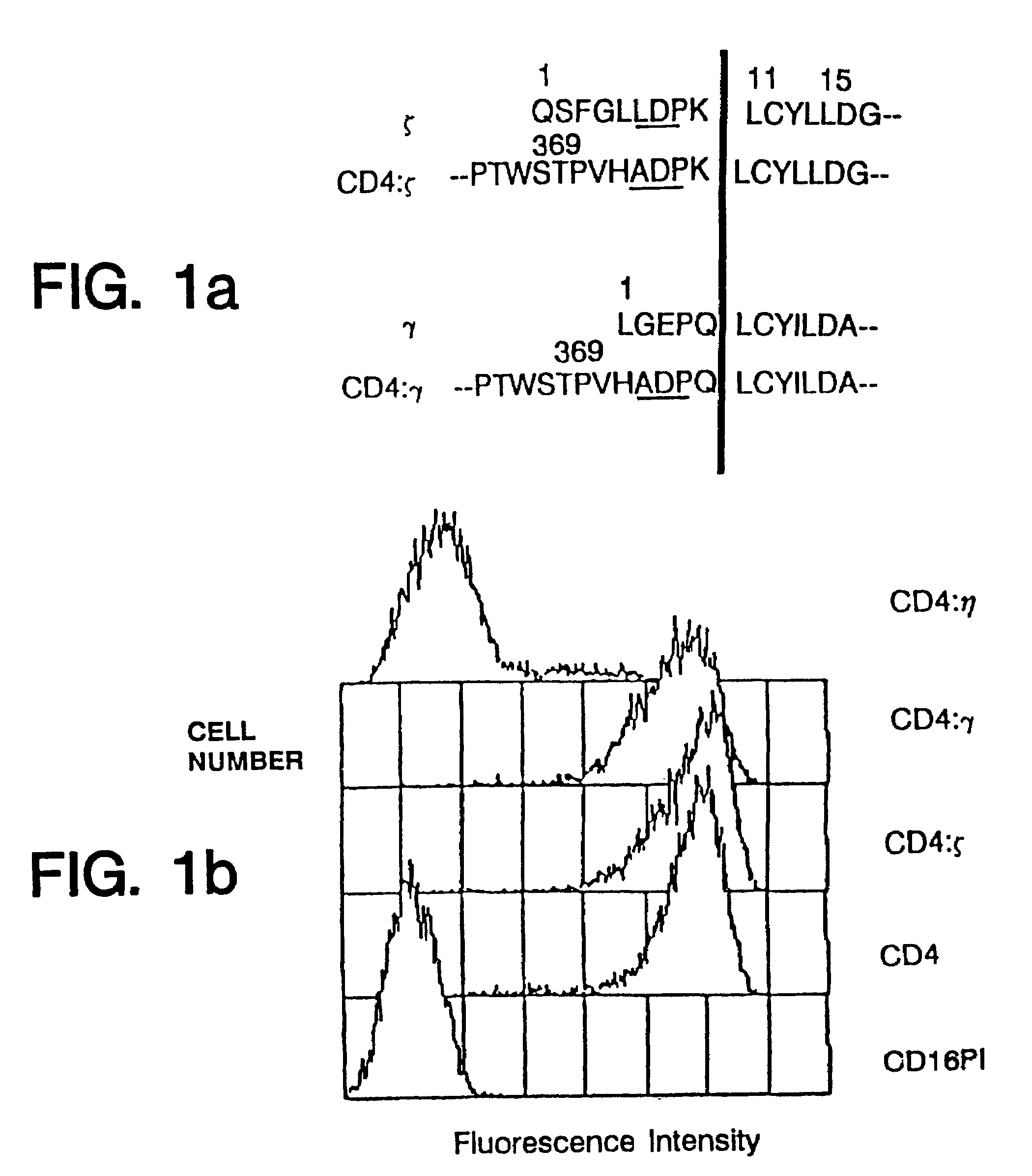
Targeted cytolysis of HIV-infected cells by chimeric CD4 receptor-bearing cells
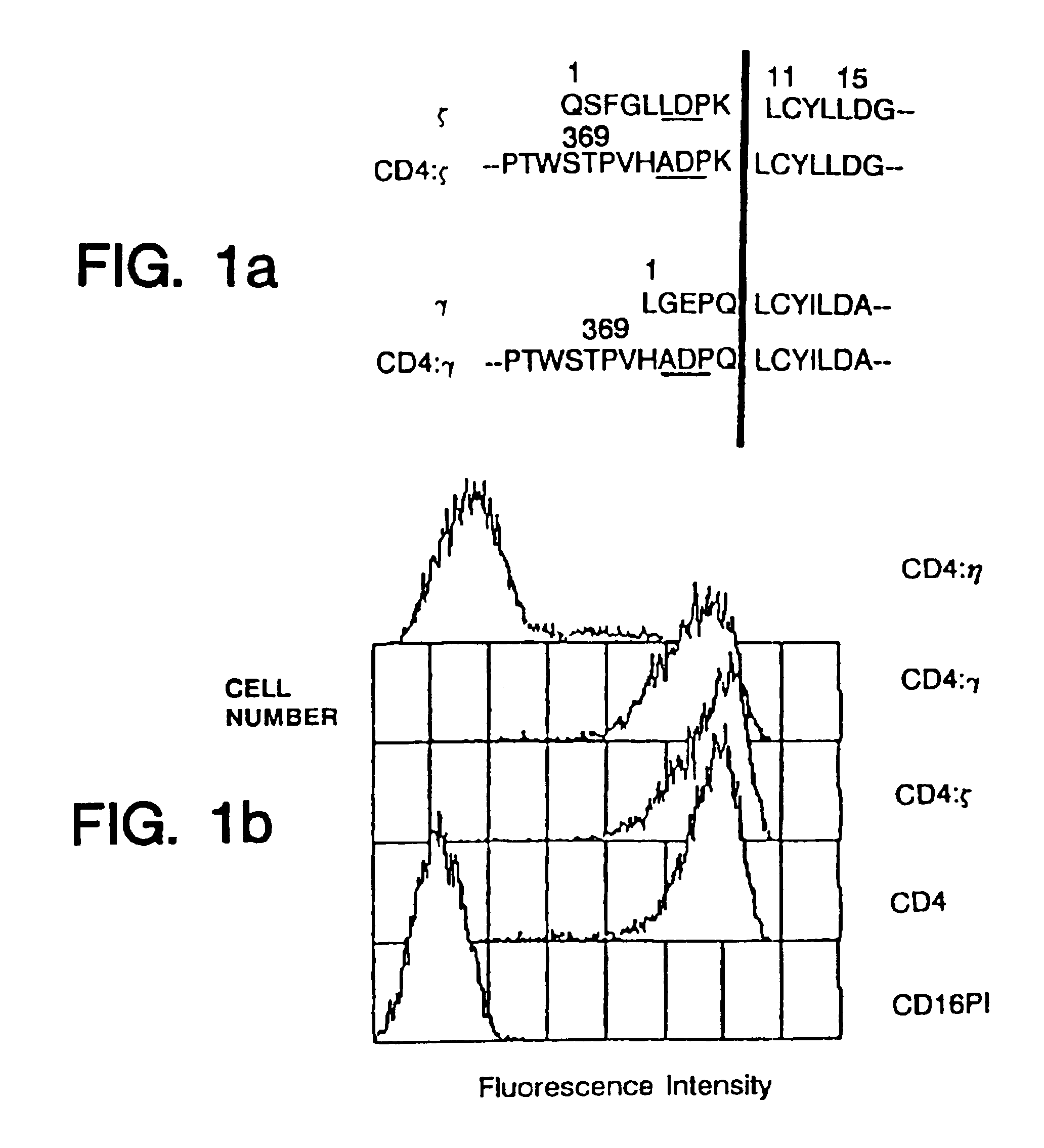
Disclosed is a method of directing a cellular immune response against an HIV-infected cell in a mammal involving administering to the mammal an effective amount of therapeutic cells which express a membrane-bound, proteinaceous chimeric receptor comprising (a) an extracellular portion which includes a fragment of CD4 which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the HIV-infected cell but which does not mediate HIV infection and (b) an intracellular portion which is capable of signalling the therapeutic cell to destroy the receptor-bound HIV-infected cell. Also disclosed is a second method of treating HIV in a mammal involving administering to the mammal an effective amount of therapeutic cells expressing a membrane-bound, proteinaceous chimeric receptor comprising an extracellular portion which includes a fragment of CD4 which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the HIV-infected cell but which does not mediate HIV infection. Also disclosed are cells which express the chimeric receptors and DNA and vectors encoding the chimeric receptors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Trans-capsular administration of high specificity cytokine inhibitors into orthopedic joints
ActiveUS20050025765A1Extended half-lifeEliminate side effectsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellOrthopedic department
The present invention relates to trans-capsularly administering into a diseased joint a high specificity antagonist selected from the group consisting of: i) an inhibitor of a pro-inflammatory interleukin; ii) an inhibitor of TNF-α synthesis; iii) an inhibitor of membrane-bound TNF-α; iv) an inhibitor of a natural receptor of TNF-α; v) an inhibitor of NO synthase, vi) an inhibitor of PLA2 enzyme; vii) an anti-proliferative agent; viii) an anti-oxidant; ix) an apoptosis inhibitor selected from the group consisting of EPO mimetic peptides, EPO mimetibodies, IGF-I, IGF-II, and caspase inhibitors, and x) an inhibitor of MMPs; and xi) an inhibitor of p38 kinase.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
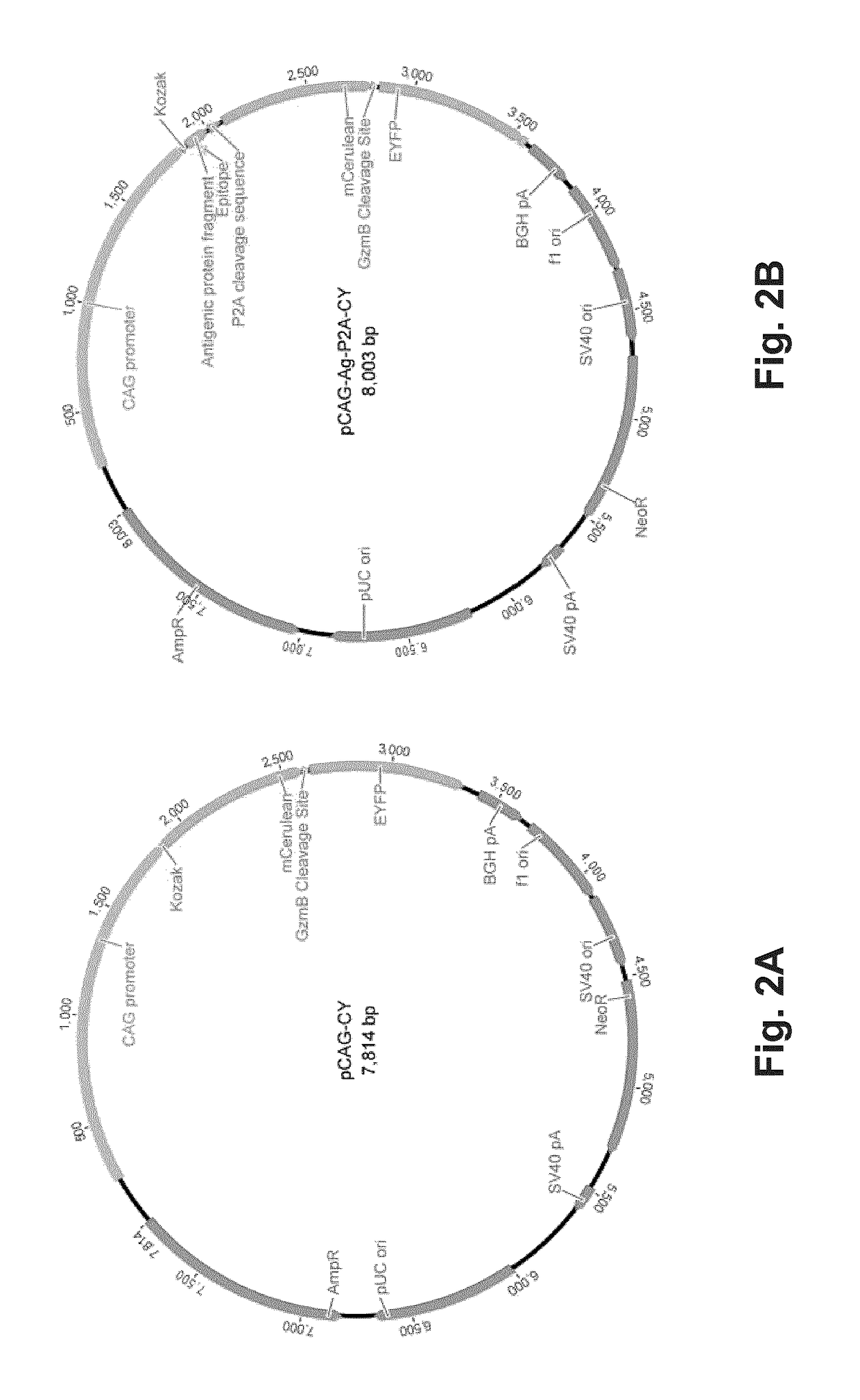
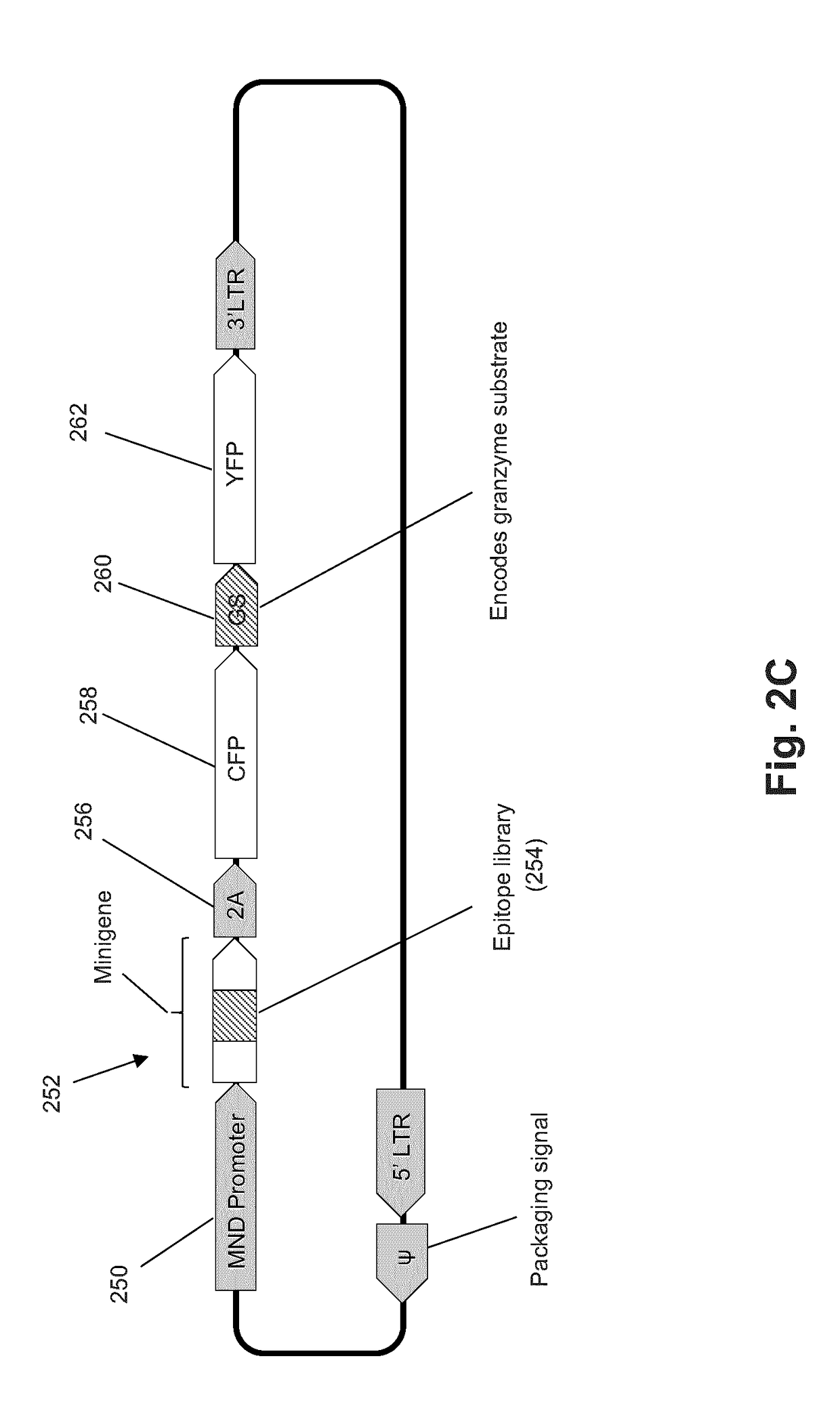
T-cell epitope identification
ActiveUS20180052176A1Efficient removalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNucleotideMembrane bound
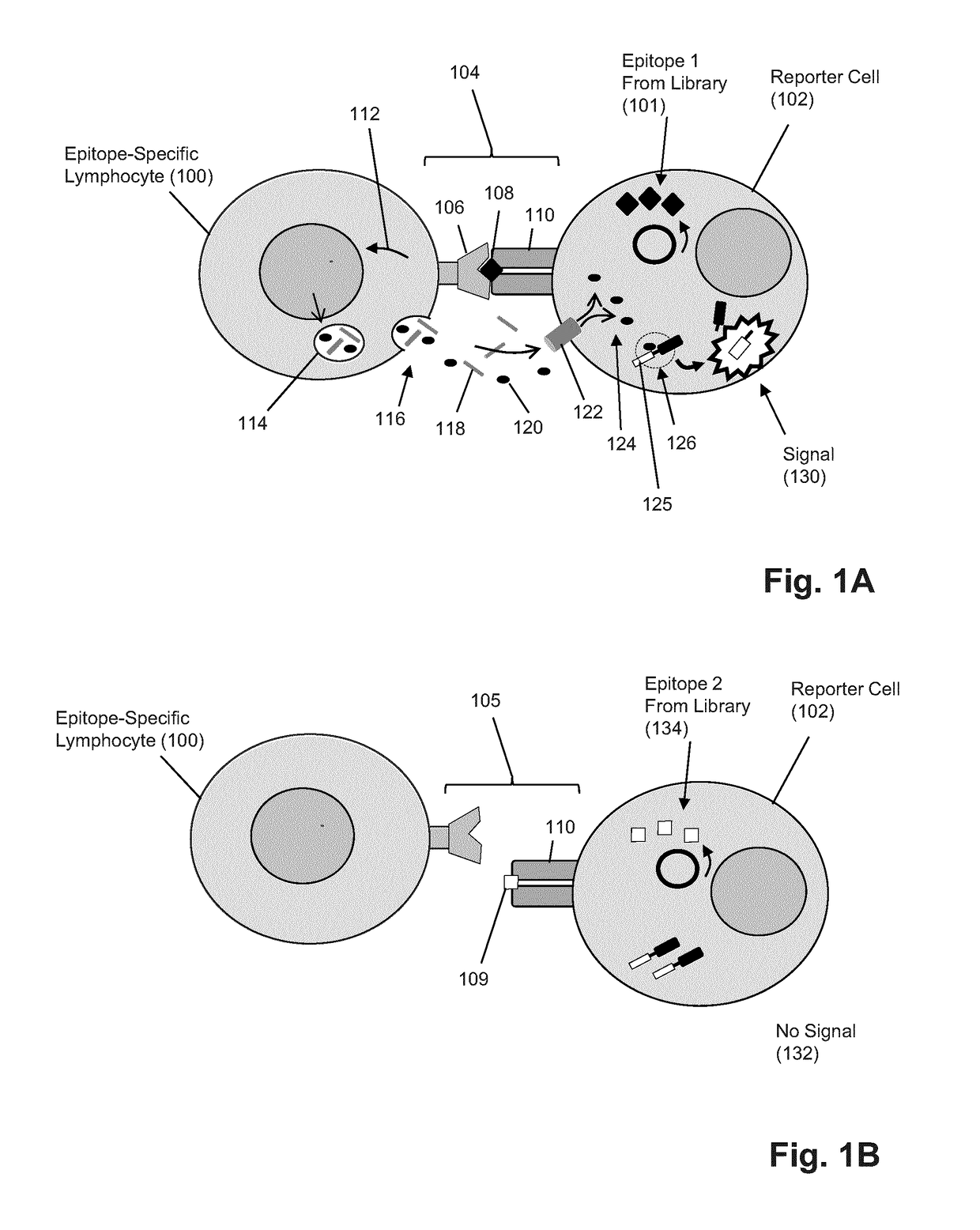
The present invention is a method for determining the identity of the epitopes recognized by T-cells. The method consists of expressing an encoded library of candidate epitope sequences in a recipient reporter cell capable of providing a detectable signal upon cytotoxic attack from a single cognate T-cell followed by contacting the reporter cells with T-cells of interest. The reporter cells with a single indicating cytotoxic attack from a T-cell are isolated and then analyzed by next-generation sequencing in order to identify the epitope sequences. Specifically disclosed is a method in which a library of candidate epitope-encoding nucleic acids are expressed in cells which feature a membrane-bound major histocompatibility complex (MHC) protein, said library produced by transfection of plasmids featuring both a nucleotide encoding the candidate epitope and a nucleotide encoding a FRET-based fluorescent protein cleaved by granzyme.
Owner:PROVINCIAL HEALTH SERVICES AUTHORITY
Fusogenic lipids and vesicles
InactiveUS20030082154A1Effective protectionReduce deliveryBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationCell membrane
Novel lipid compounds are provided that may be termed "pro-cationic" in that they are neutral or negatively charged until they are either brought into contact with cellular membranes or are internalized by cells. The lipids have a hydrophobic tail group and a hydrophilic head group, the head group incorporating both a positively and negatively charged region at physiological pH. The hydrophobic tail group is stably connected to the positive region of the head group which in turn is connected to the negative region by a disulfide bond that is susceptible to cleavage by membrane-bound and intracellular factors. Cleavage of the disulfide bond removes the negatively charged region from the head group resulting in a lipid that is cationic and therefor fusogenic with negatively charged cell membranes. Consequently, lipids of the invention are useful as components of liposomes that serve as vehicles for delivering pharmaceutical agents into cells with reduced toxicity.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
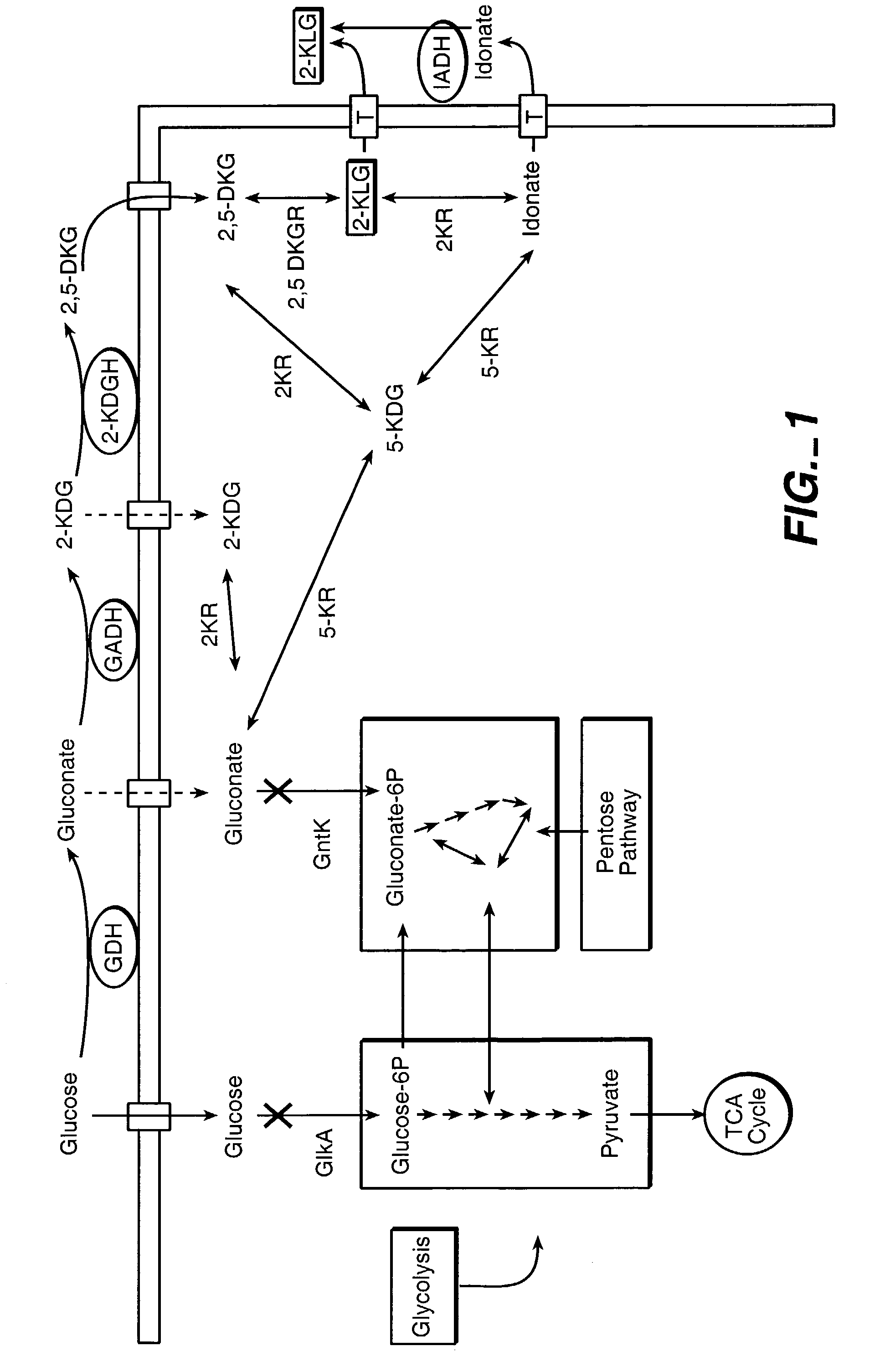
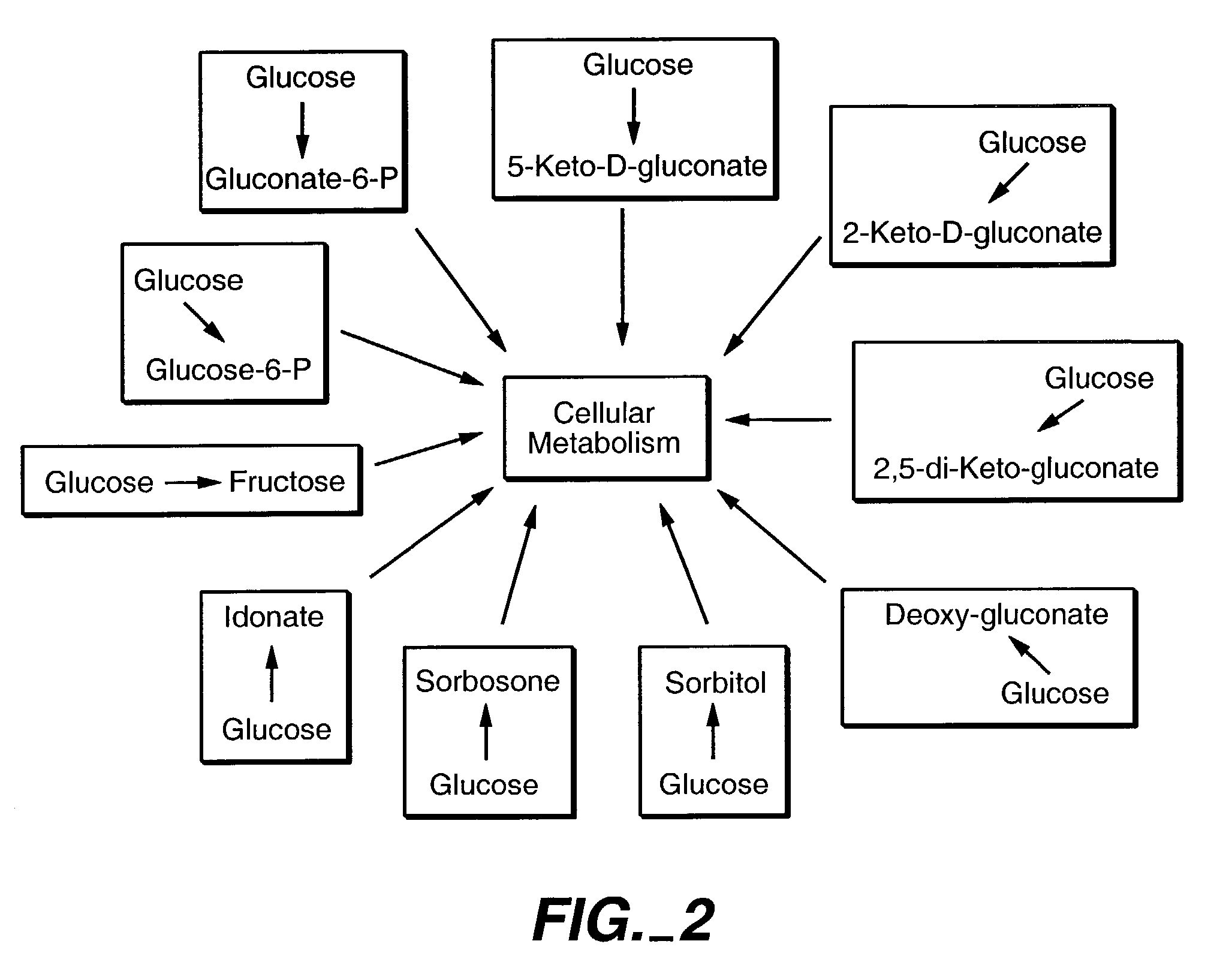
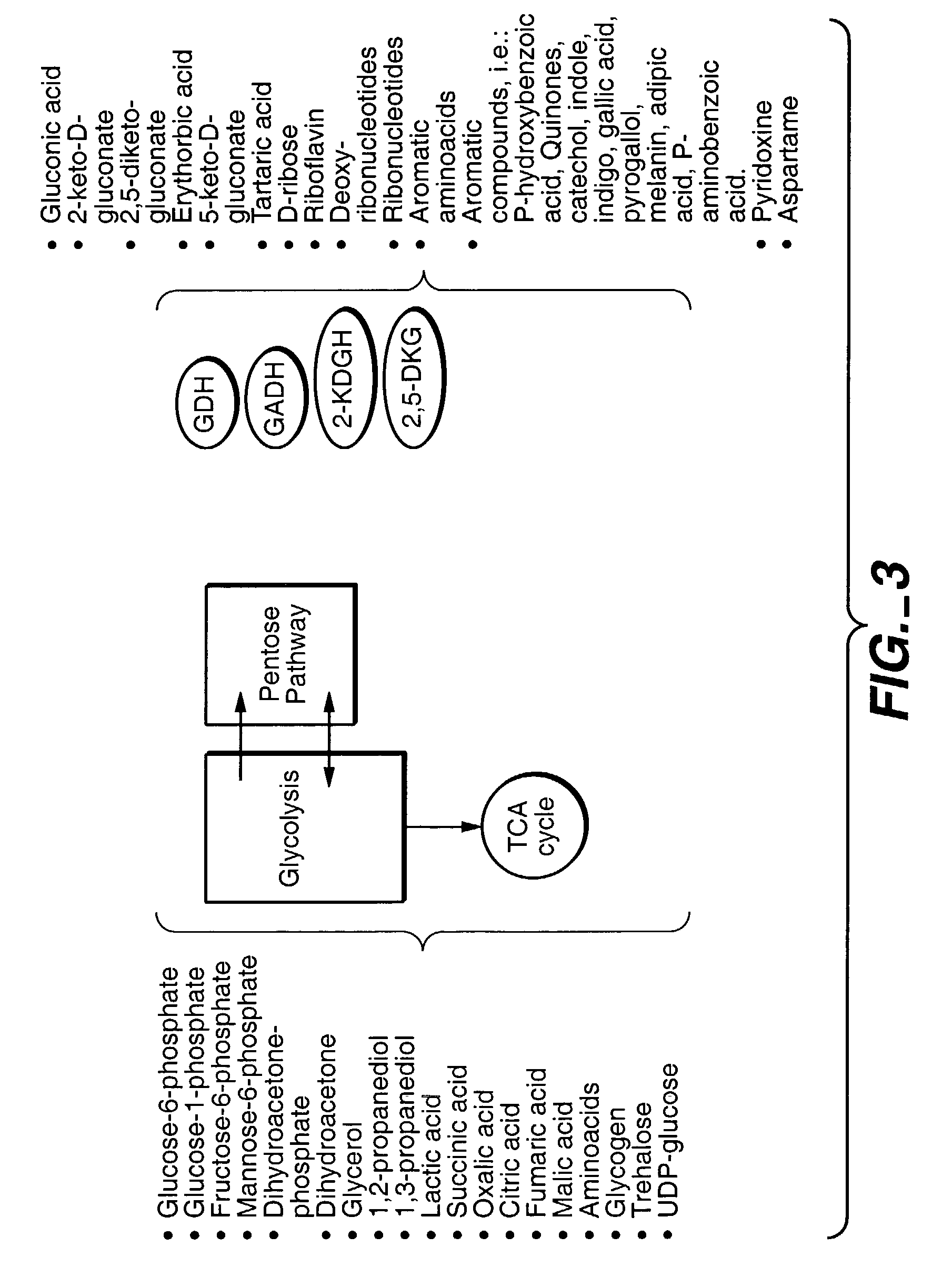
Method of uncoupling the catabolic pathway of glycolysis from the oxidative membrane bound pathway of glucose conversion
InactiveUS7241587B2Increase volumeMeet actual needsBacteriaSugar derivativesPhosphorylationGluconic acid
The invention provides methods for producing products comprising improved host cells genetically engineered to have uncoupled productive and catabolic pathways. In particular, the present invention provides host cells having a modification in nucleic acid encoding an endogenous enzymatic activity that phosphorylates D-glucose at its 6th carbon and / or a modification of nucleic acid encoding an enzymatic activity that phosphorylates D-gluconate at its 6th carbon. Such improved host cells are used for the production of products, such as, ascorbic acid intermediates. Methods for making and using the improved host cells are provided. Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for glucokinase and gluconokinase are provided.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
N-hdroxy-2-(alkyl, aryl, or heteroaryl, sulfanyl, sulfinyl or sulfonyl)-3-substituted alkyl, aryl or heteroarylamides as matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors
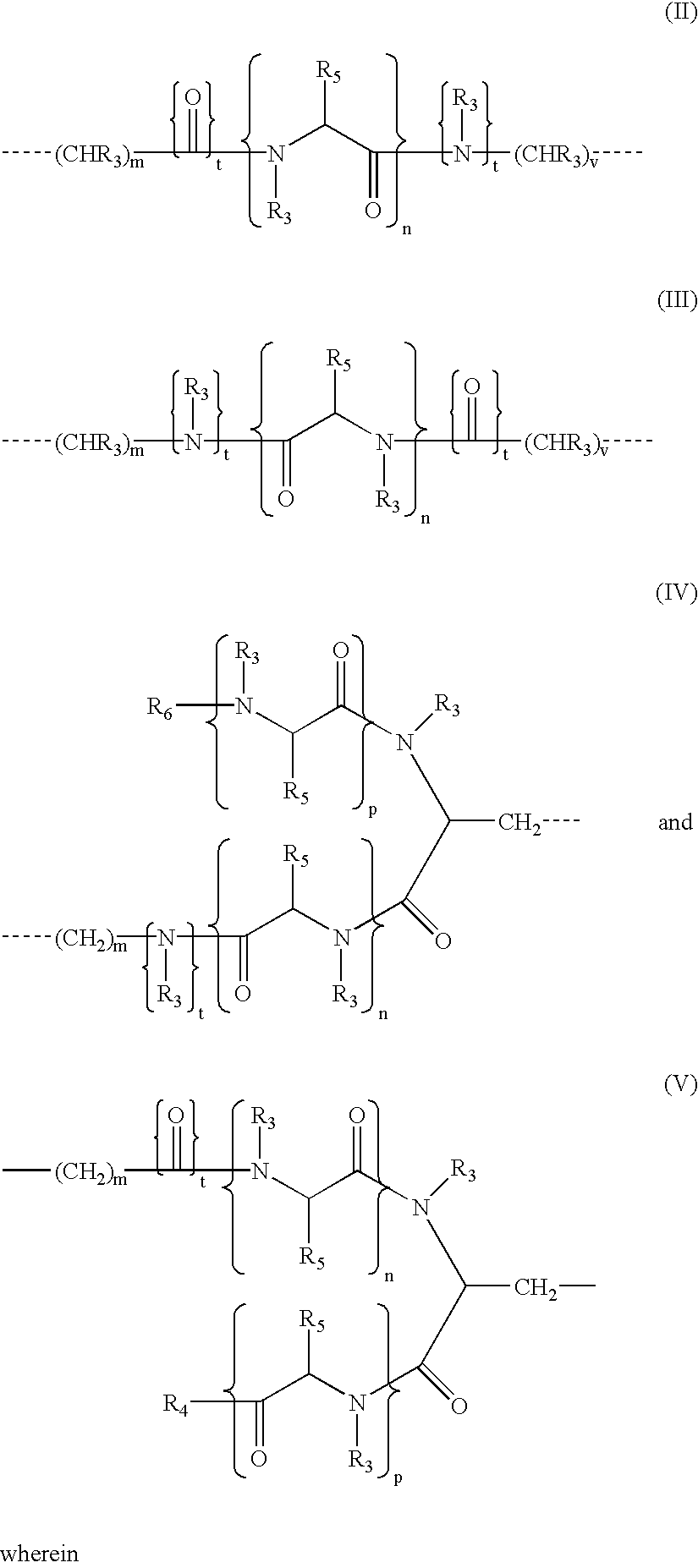
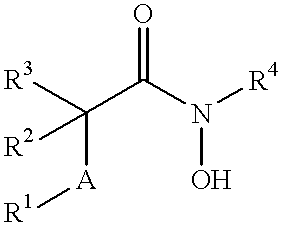
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a group of enzymes that have been implicated in the pathological destruction of connective tissue and basement membranes. These zinc containing endopeptidases consist of several subsets of enzymes including collagenases, stromelysins and gelatinases. TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE), a pro-inflammatory cytokine, catalyzes the formation of TNF-alpha from membrane bound TNF-alpha precursor protein. It is expected that small molecule inhibitors of MMPs and TACE therefore have the potential for treating a variety of disease states. The present invention provides low molecular weight, non-peptide inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and TNF-alpha converting enzyme (TACE) for the treatment of arthritis, tumor metastasis, tissue ulceration, abnormal wound healing, periodontal disease, bone disease, diabetes (insulin resistance) and HIV infection having the formulawherein R2 and R3 form a heterocyclic ring and A is S, S(O), or S(O)2, and R1 and R4 are defined herein.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
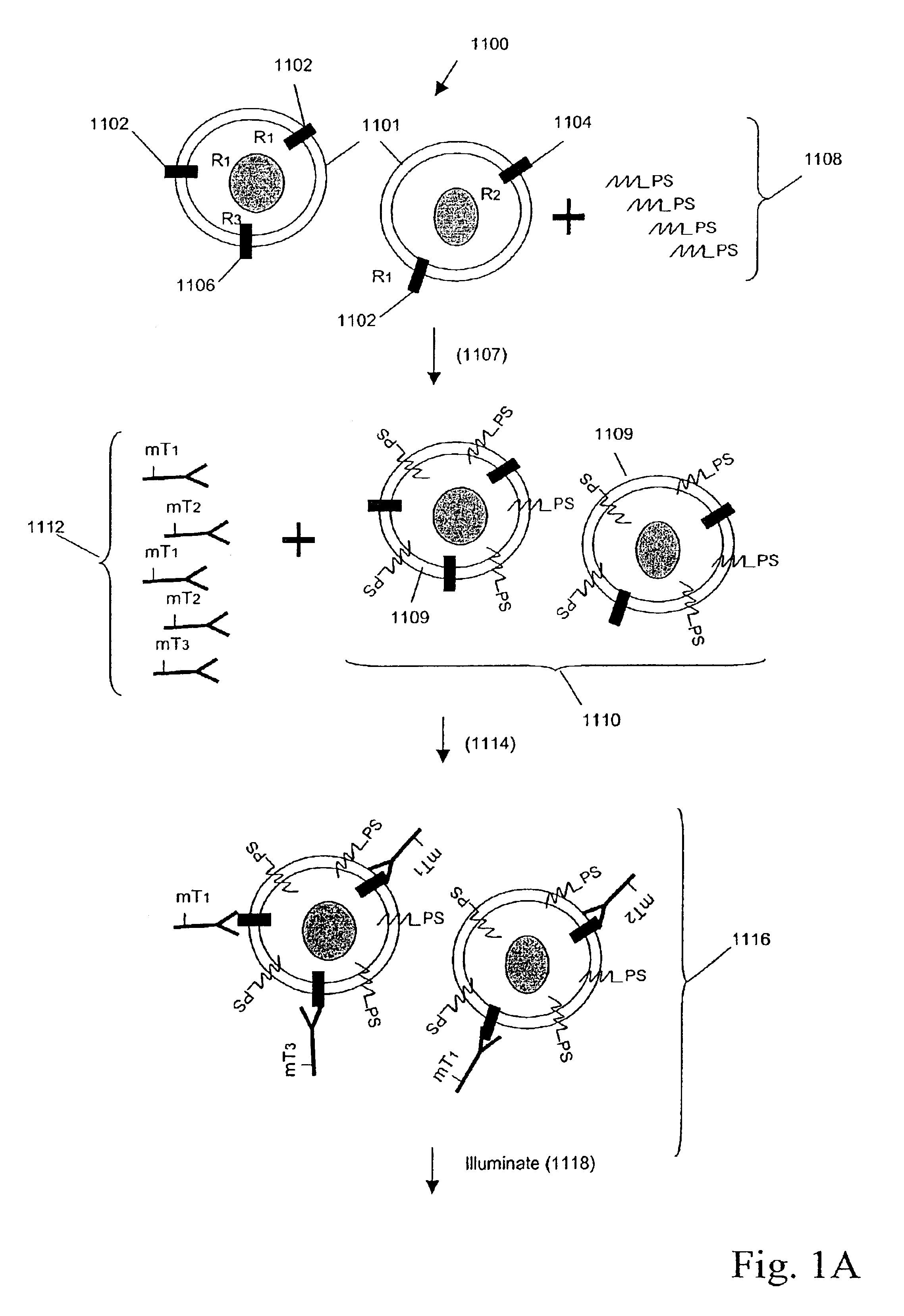
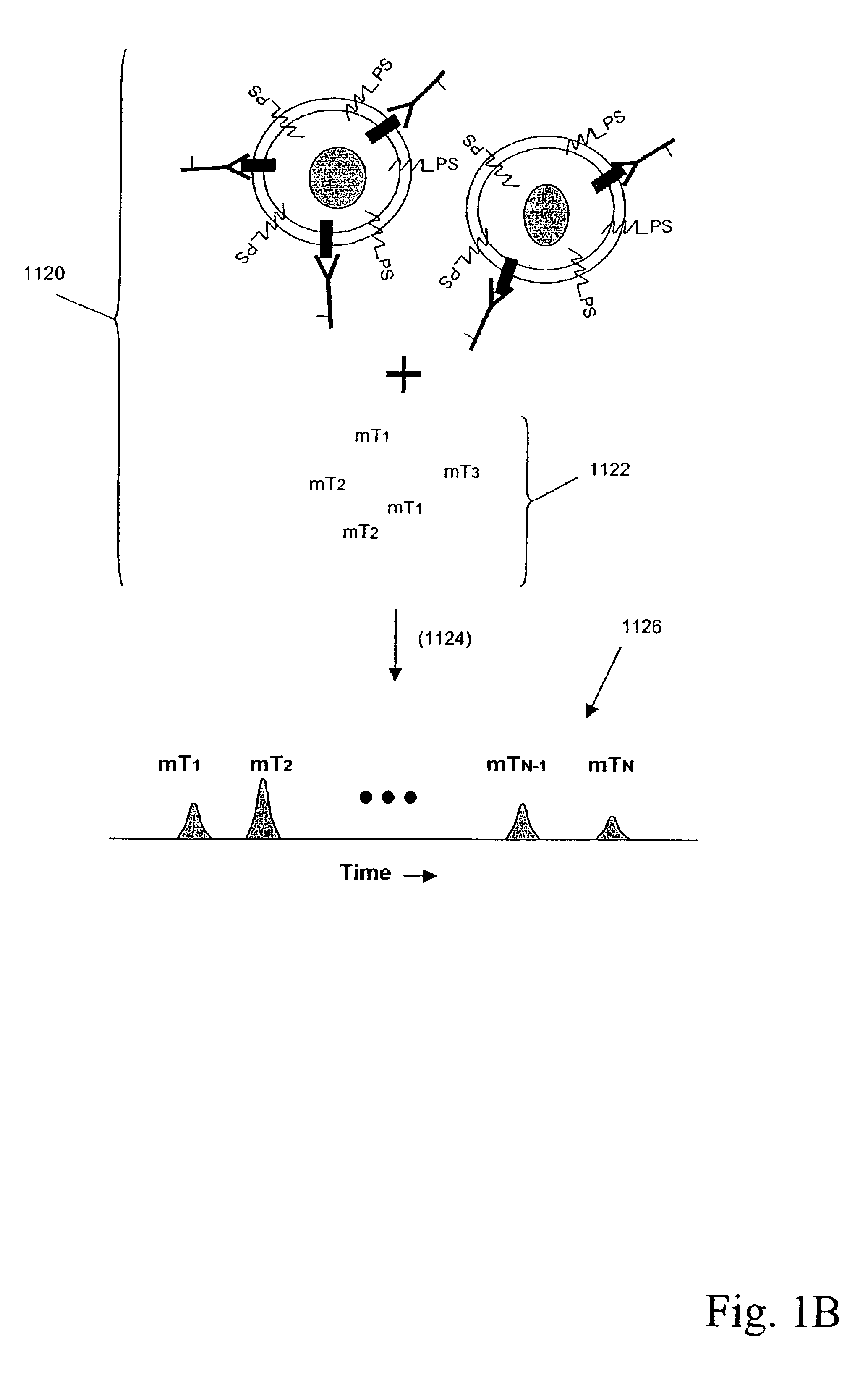
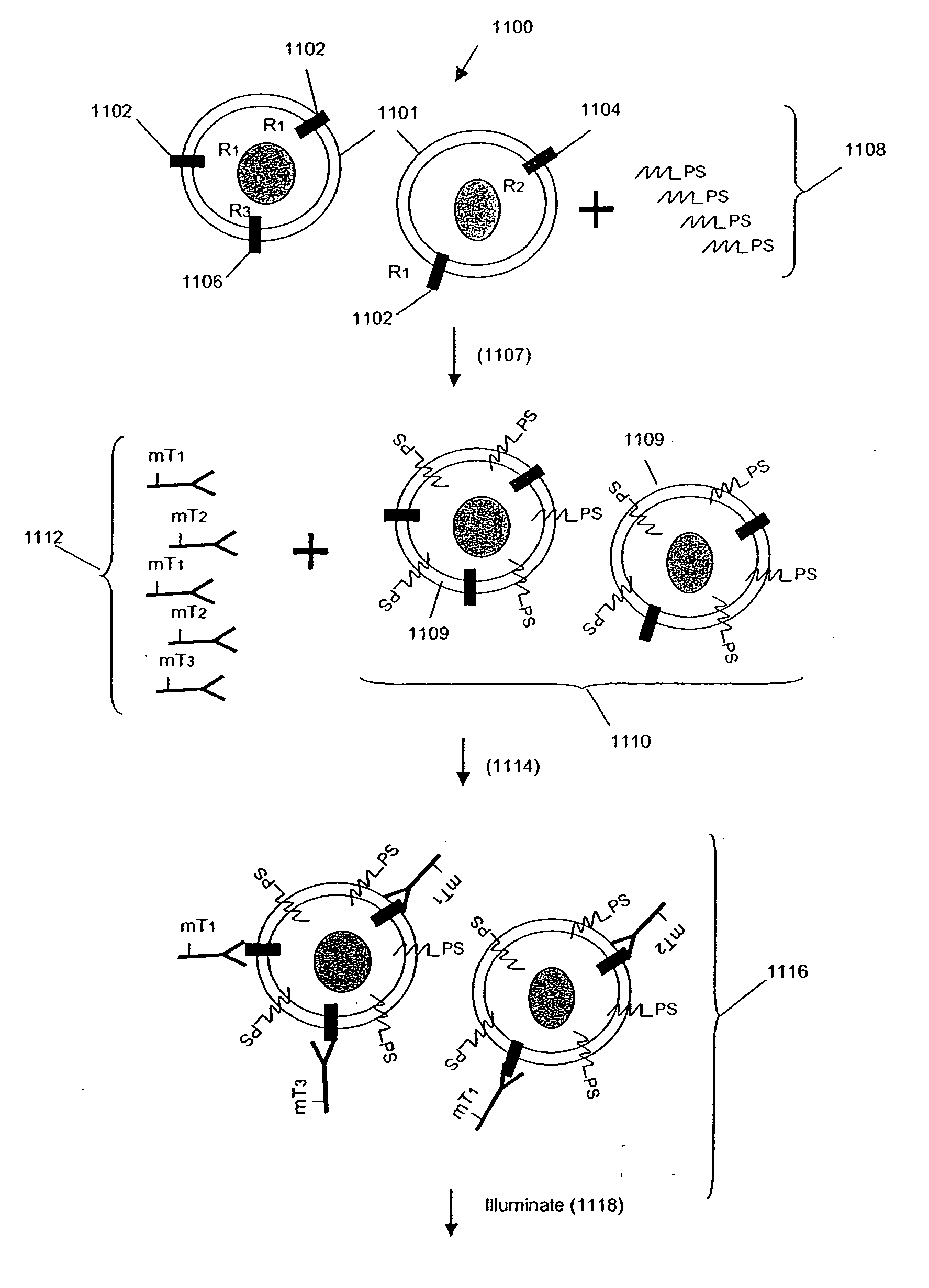
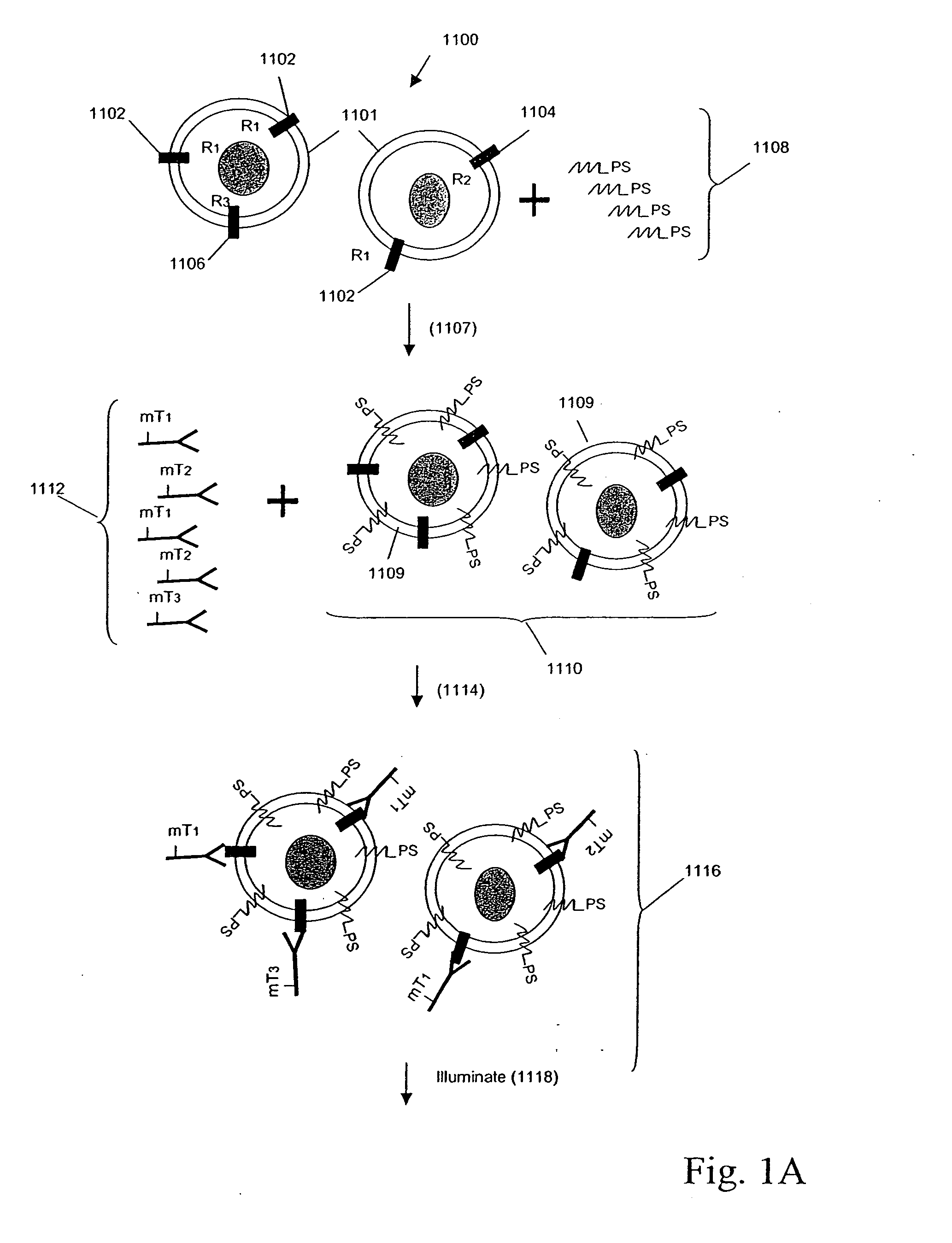
Multiplex analysis using membrane-bound sensitizers
InactiveUS6949347B2Low backgroundHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteBiological activation
Owner:ACLARA BIOSCIENCES INC +1
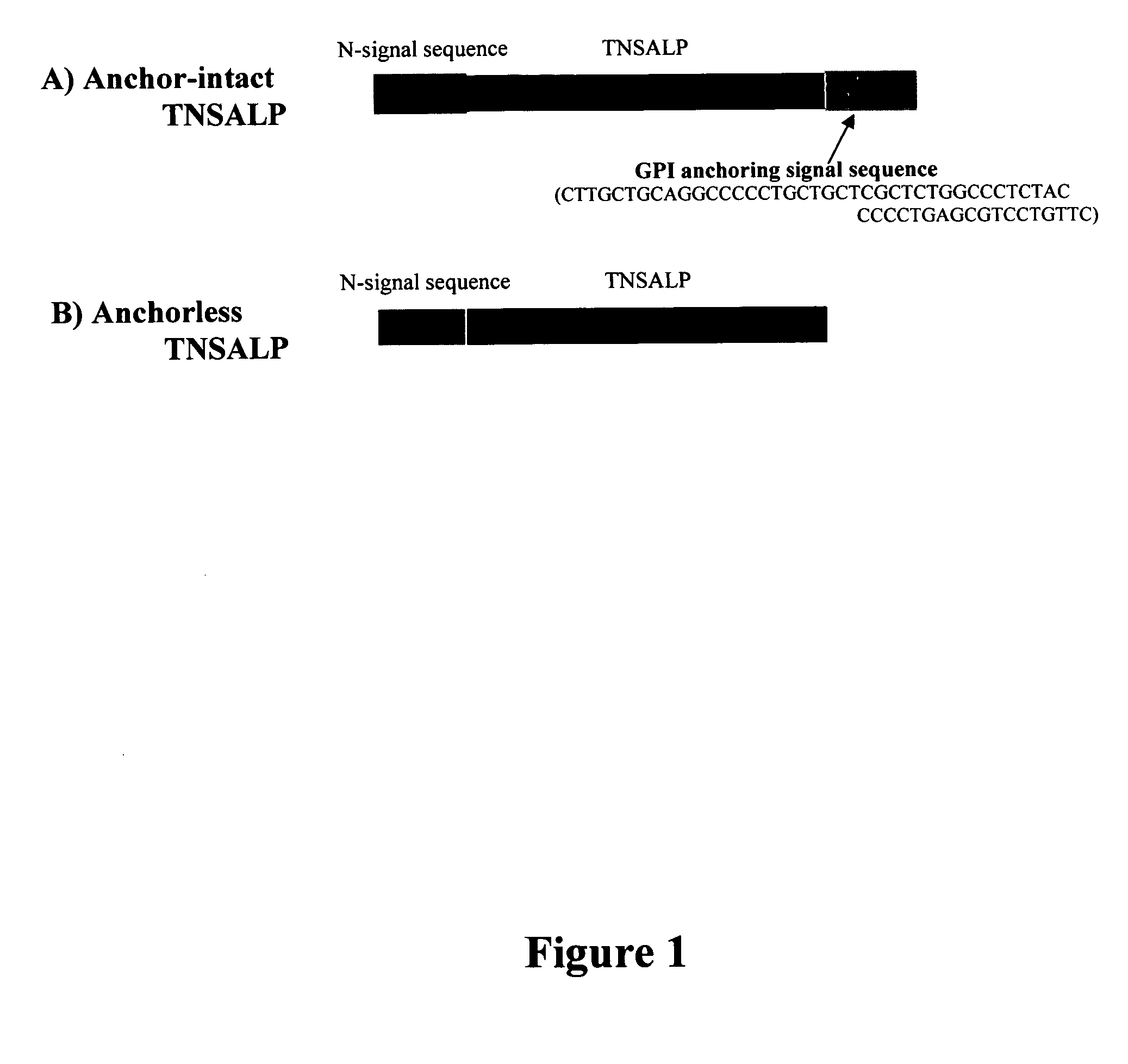
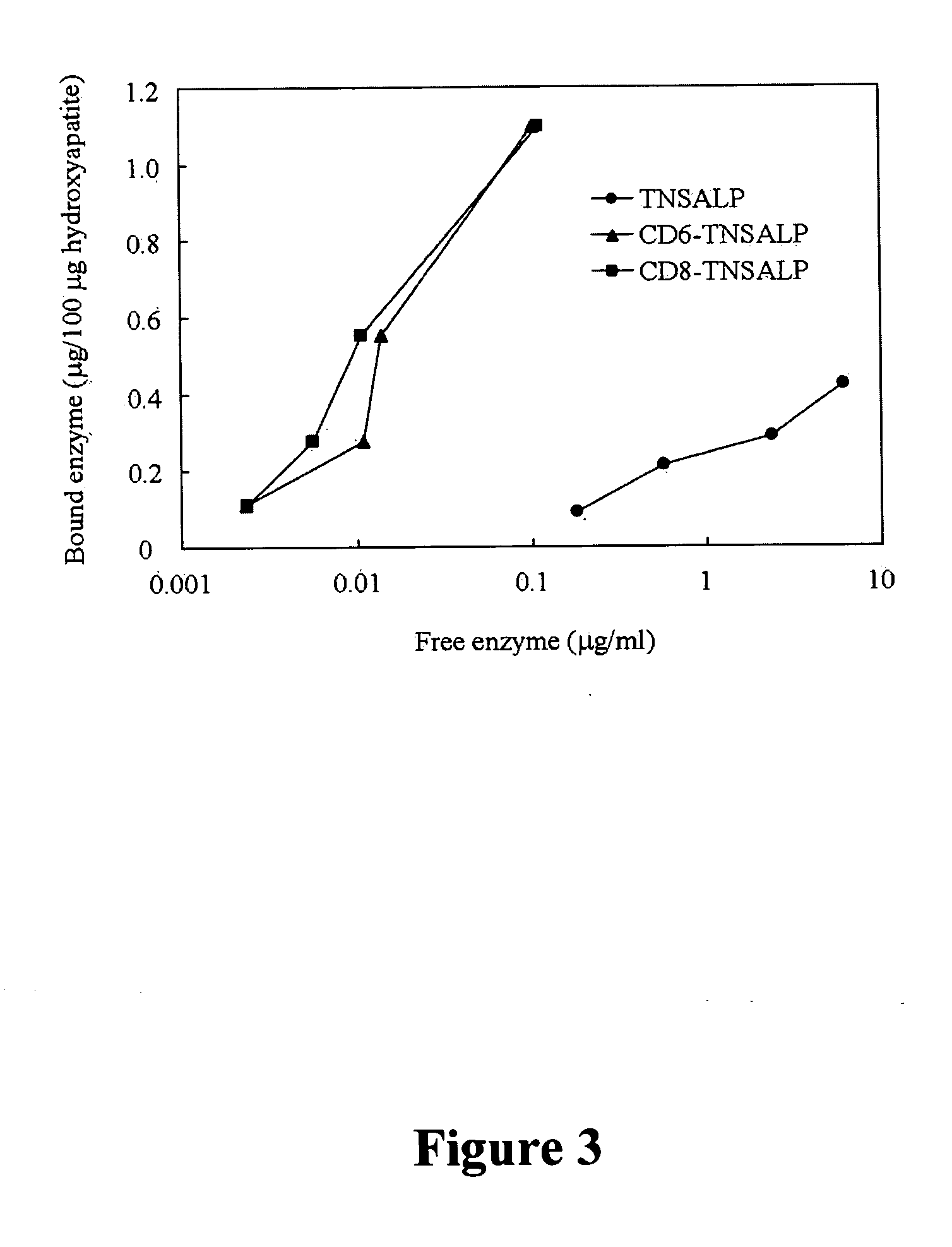
Compositions and methods for treating hypophosphatasia
InactiveUS20070081984A1Extend your lifeWeight increaseHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsBone tissueMembrane bound enzyme
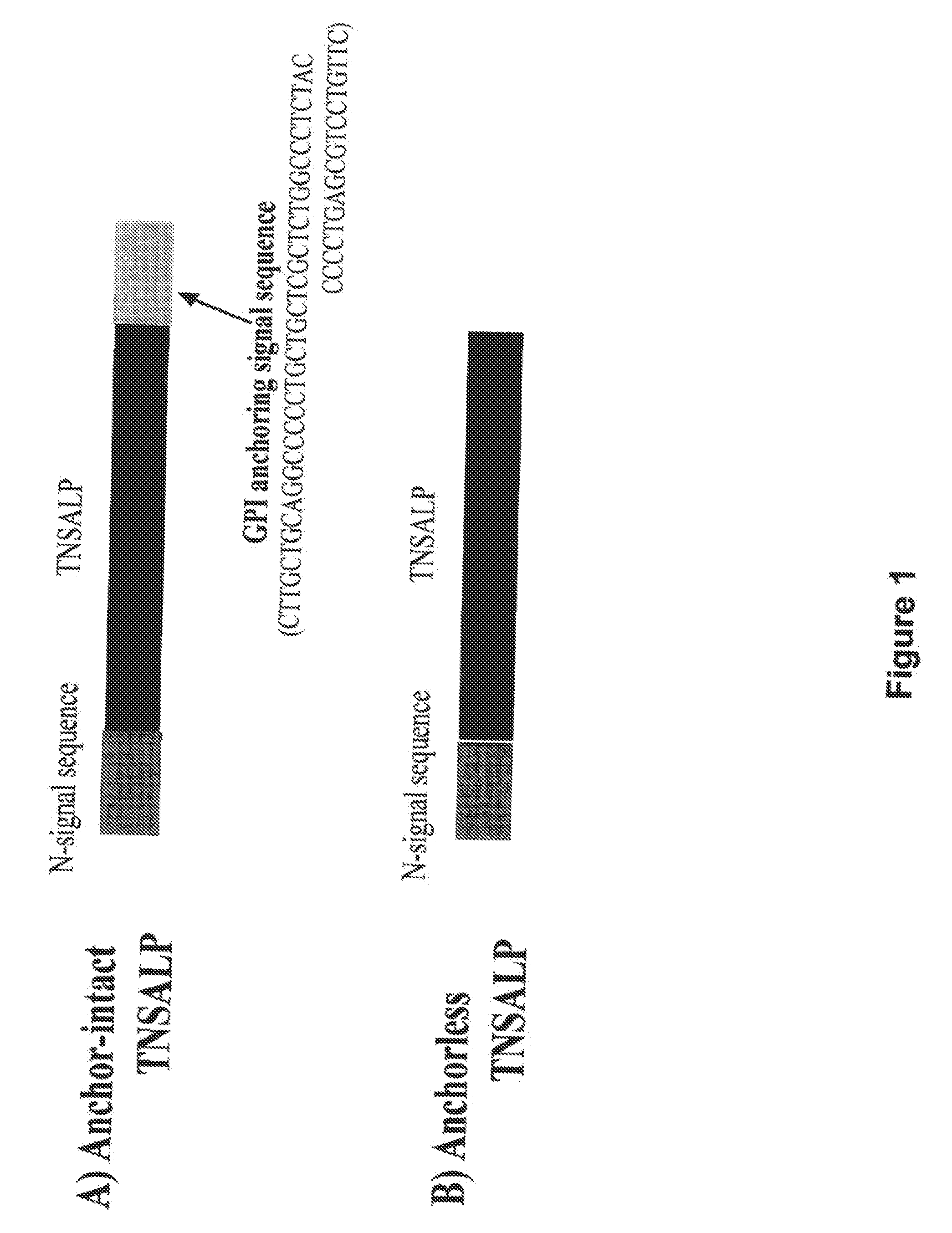
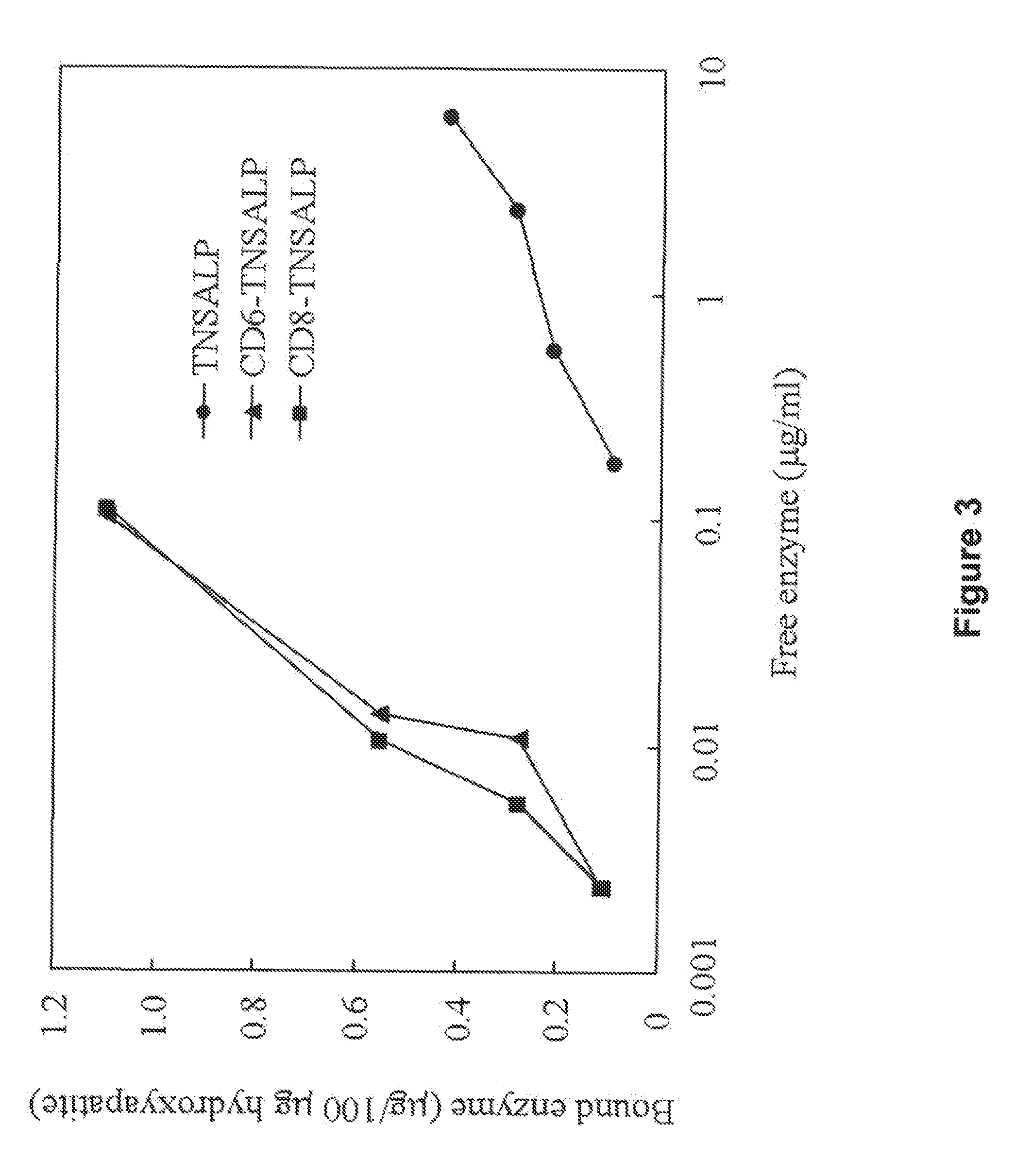
The present invention provides compositions and methods for use in enzyme replacement therapy. The inventors disclose a method of producing membrane bound enzymes in an active soluble form by eliminating the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) membrane anchor. In particular the inventors disclose a soluble active form of the membrane bound enzyme TNSALP which they produced by deleting the GPI anchor single peptide sequence. They have further shown that this composition is useful for treatment of hypophosphatasia. The inventors also disclose oligo acid amino acid variants thereof which specifically target bone tissue.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY +2
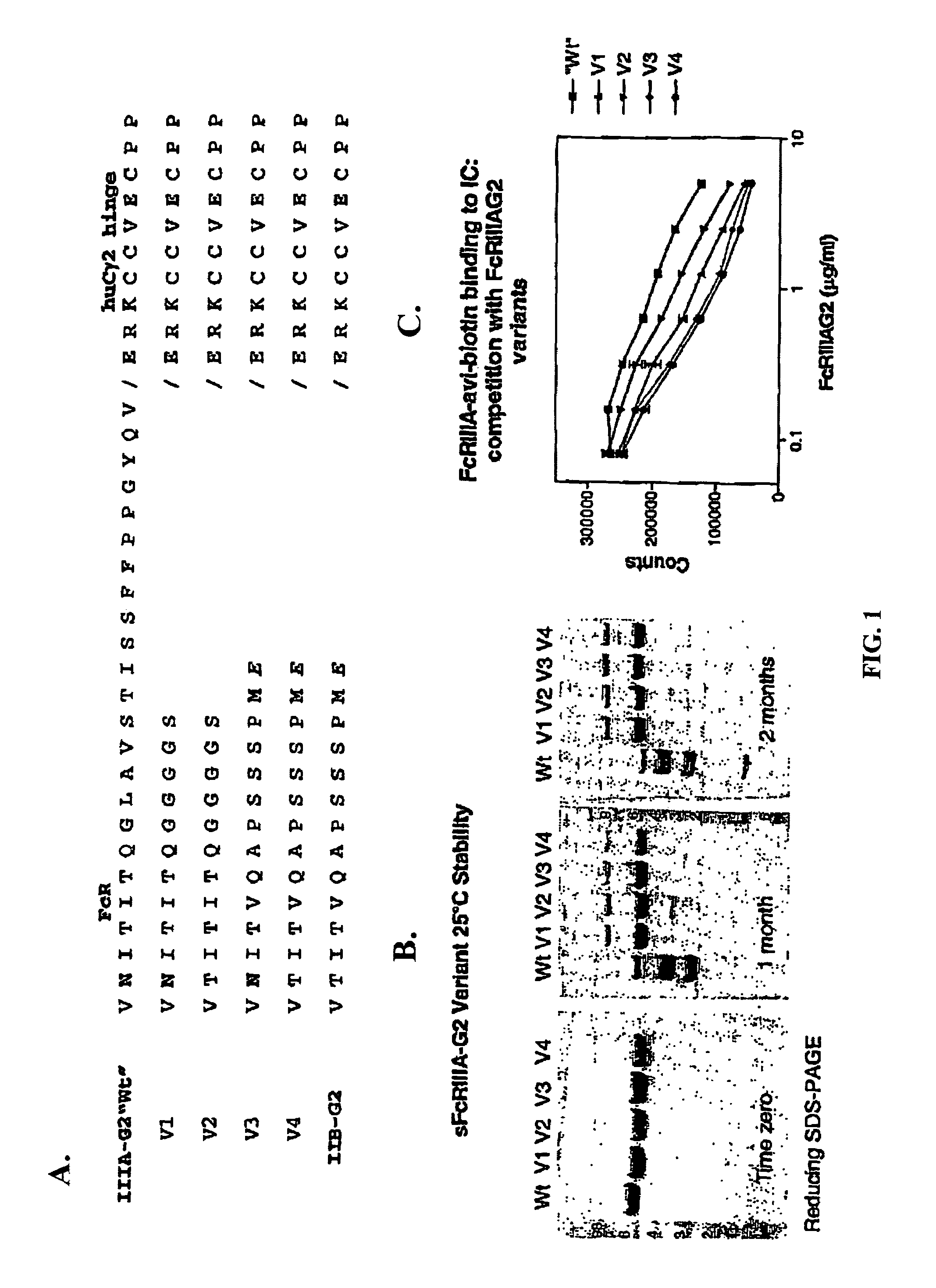
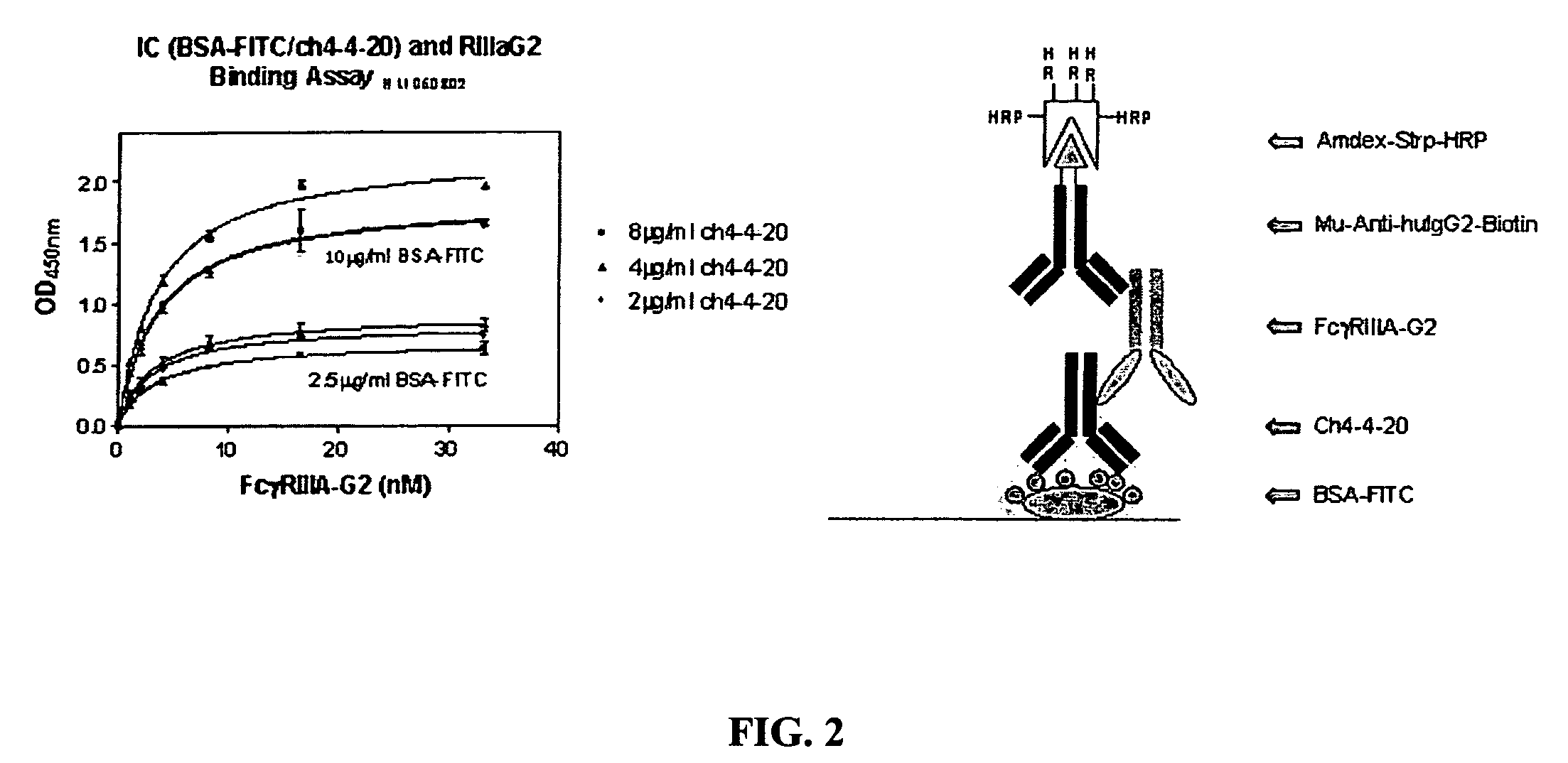
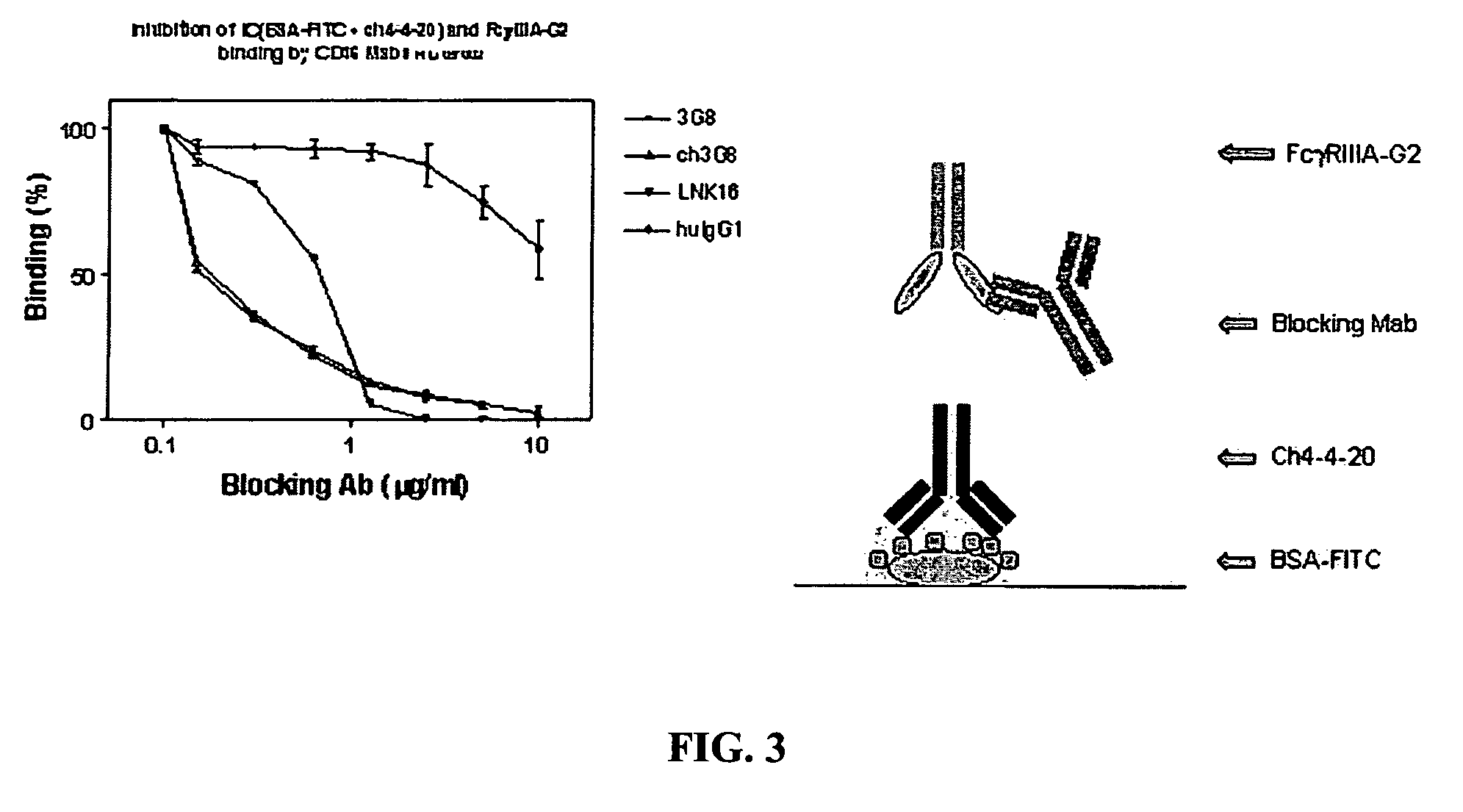
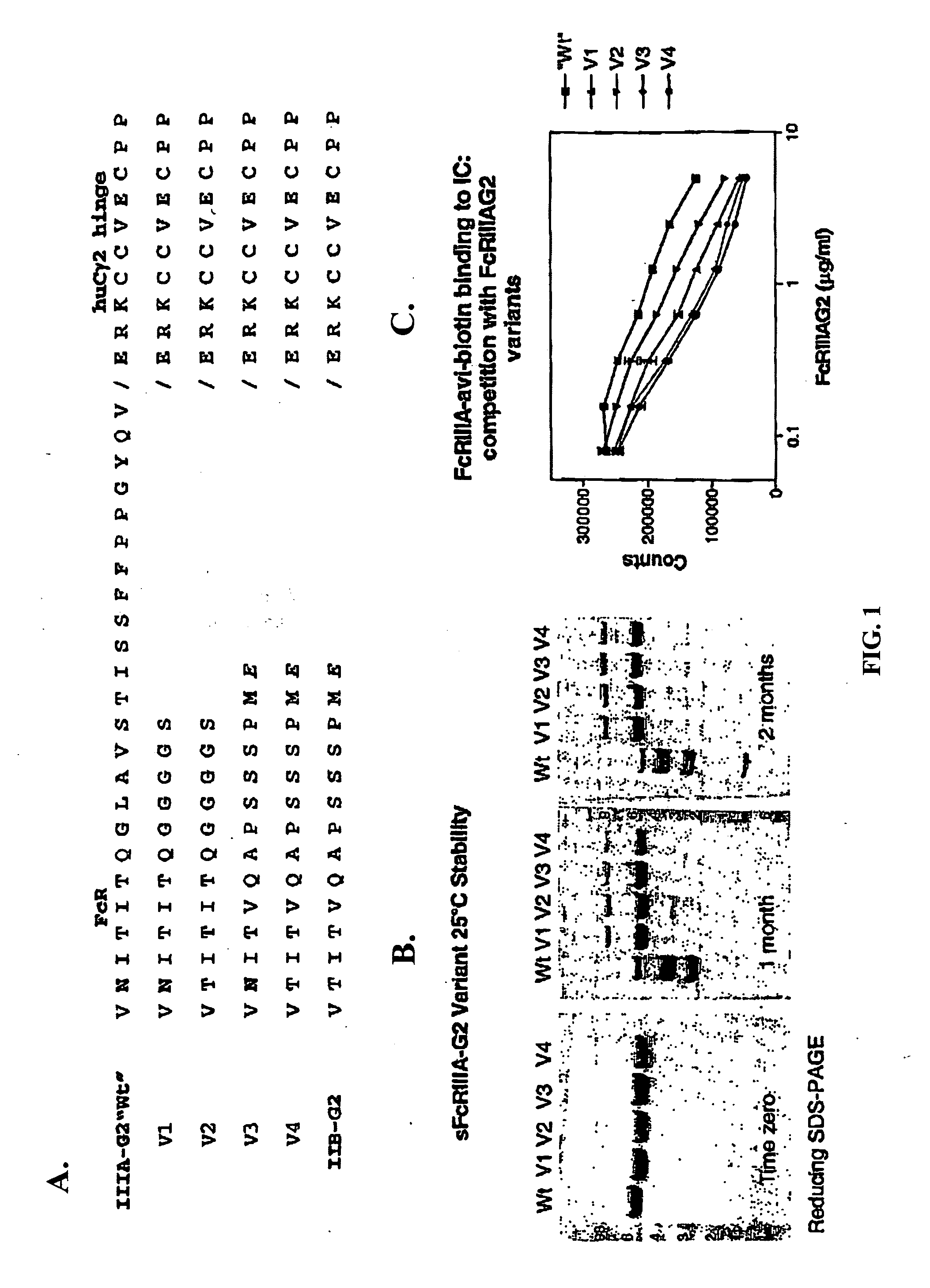
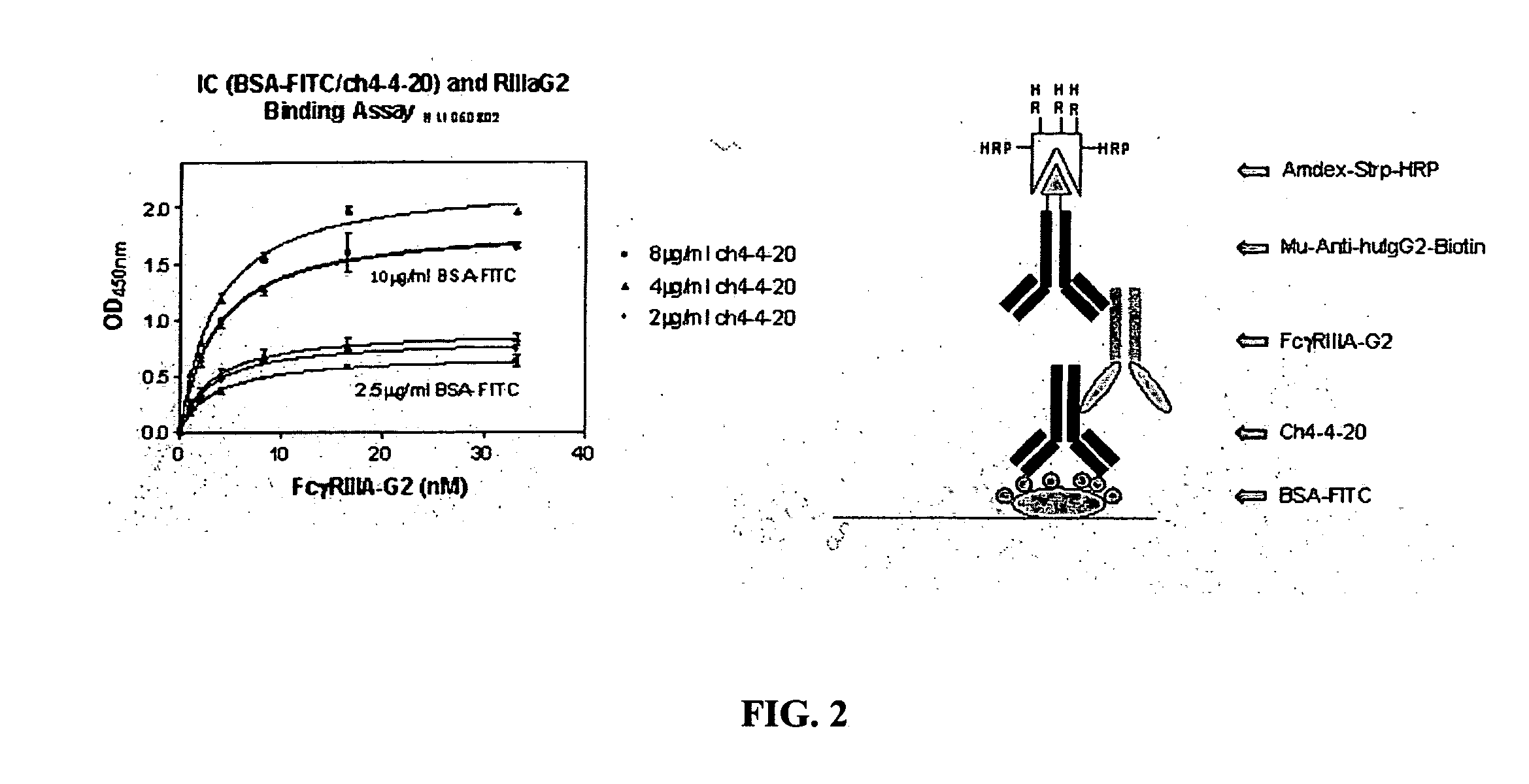
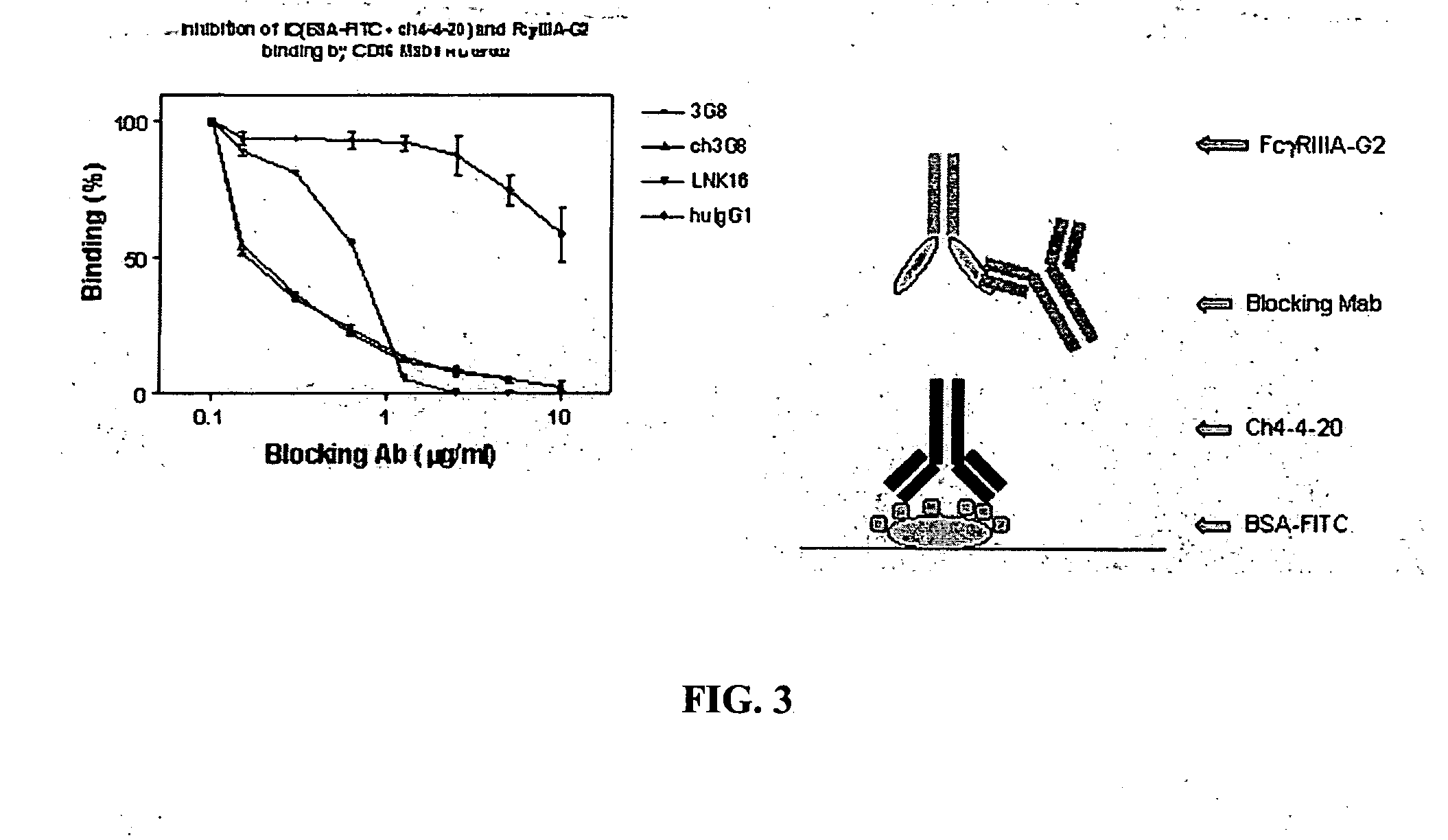
FcγRIIB fusion proteins and compositions thereof
ActiveUS7700100B2Preventing immune complexesTreatment and/or prevention of autoimmune diseasesNervous disorderImpression capsDiseaseIdiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
The present invention relates to molecules, preferably soluble (i.e., not membrane bound) polypeptides, most preferably soluble fusion polypeptides comprising the extracellular soluble regions of FcγRIIB, derivatives and analogs thereof, and nucleic acids encoding same. Molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment, management, or prevention of, or amelioration of one or more symptoms of, an autoimmune disease, especially for ameliorating serum platelet deficiency associated with immune thrombocytopenic purpura. The invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of standard, current or experimental therapies for an autoimmune disease by administering a molecule of the invention.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
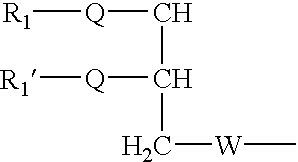
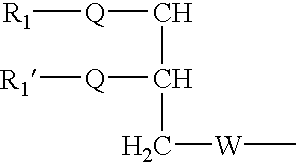
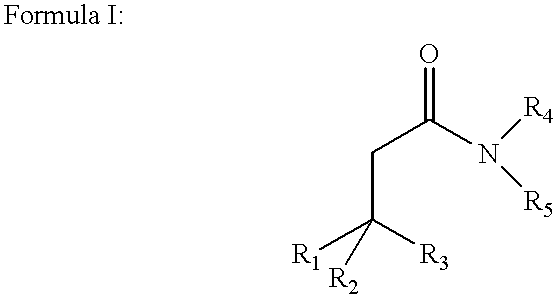
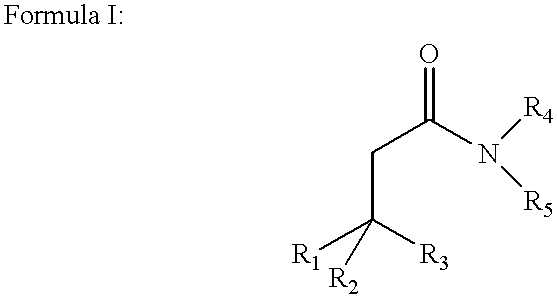
Amphiphilic agents for membrane protein solubilization
InactiveUS6172262B1Hydrolysed protein ingredientsAntibiotics chemistryMembrane bound proteinAmphiphilic Agents
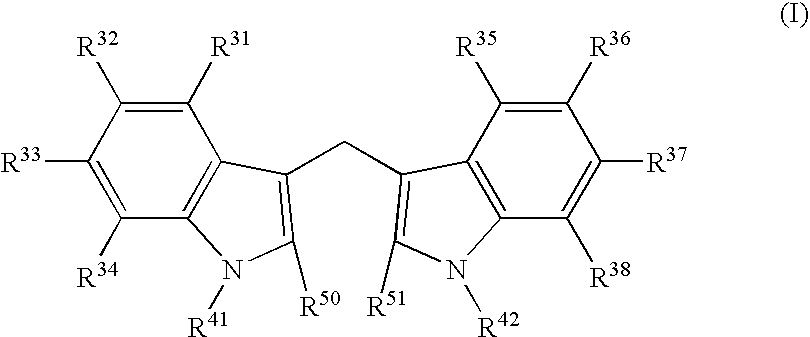
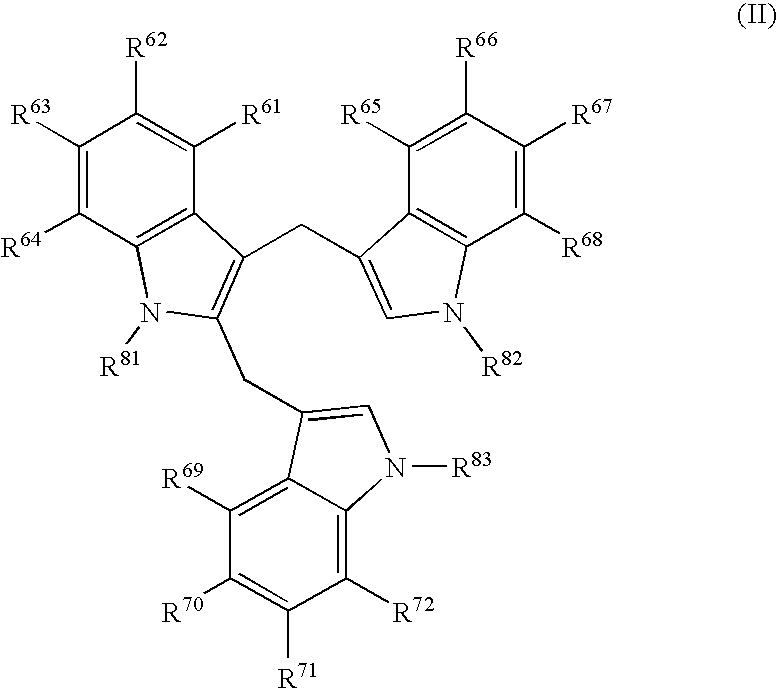
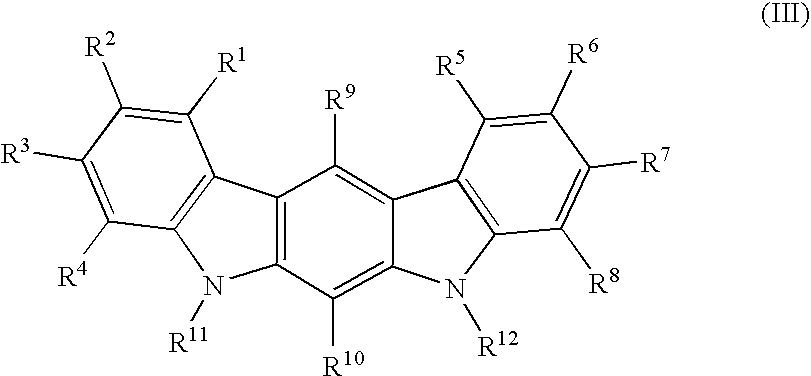
Disclosed are amphiphilic compounds comprising Formula I:wherein R1, R2, and R3 are C2-C12 straight or branched alkyl; unsubstituted phenyl, biphenyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkenyl; or phenyl, biphenyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkenyl substituted with one, two, or three C1-C6 straight or branched alkyl groups; or R1 and R2 combined are C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl; or C3-C8 cycloalkyl or C3-C8 cycloalkenyl substituted with one, two, or three C1-C6 straight or branched alkyl groups; one of R4 or R5 is selected from the group consisting of C2-C6-straight or branched alkyl-(dimethyl-N-oxide), alkyl-(dimethylamine), alkyl-(trimethylammonium), alkyl-glucosyl, alkyl-maltosyl, glucosyl, maltosyl, and polyethylene(glycosyl); the other of R4 or R5 is selected from the group consisting of H, C2-C6 straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl, C2-C6-straight or branched alkyl-(dimethyl-N-oxide); alkyl-(dimethylamine), alkyl-(trimethylammonium), alkyl-glucosyl, alkyl-maltosyl, glucosyl, maltosyl, and polyethylene(glycosyl); and salts thereof. The compounds are detergents useful in the solubilization of membrane-bound proteins.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
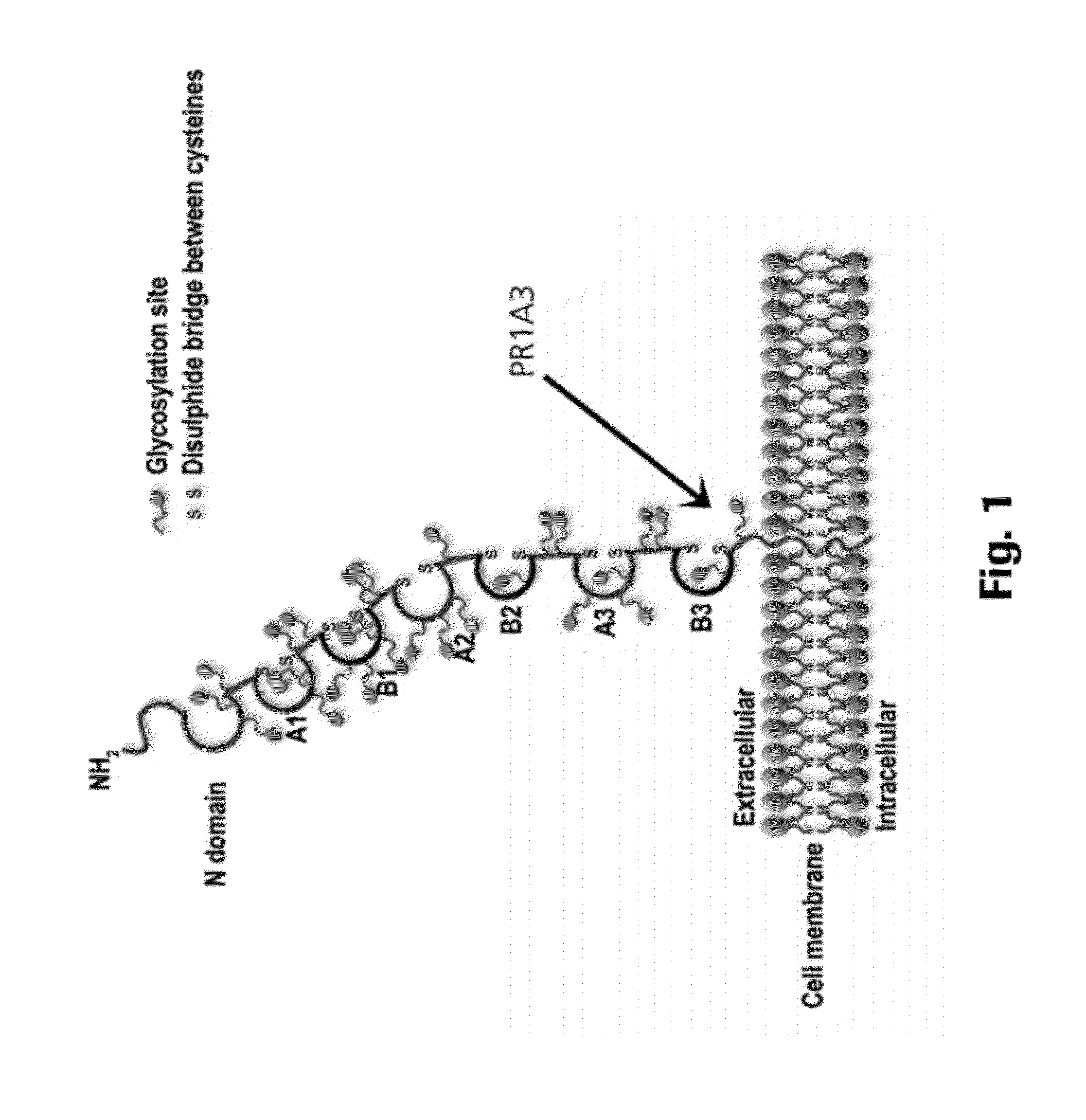
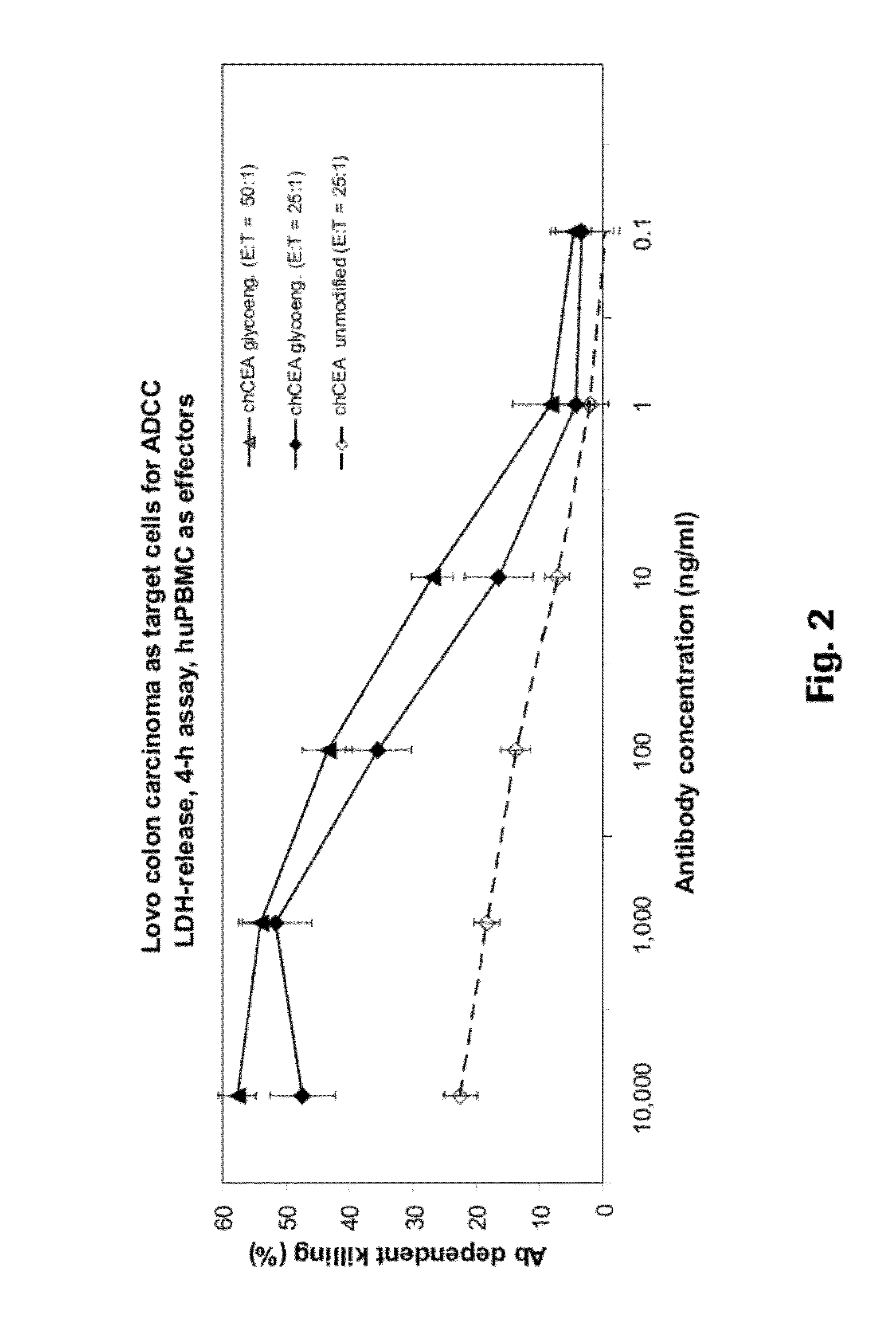
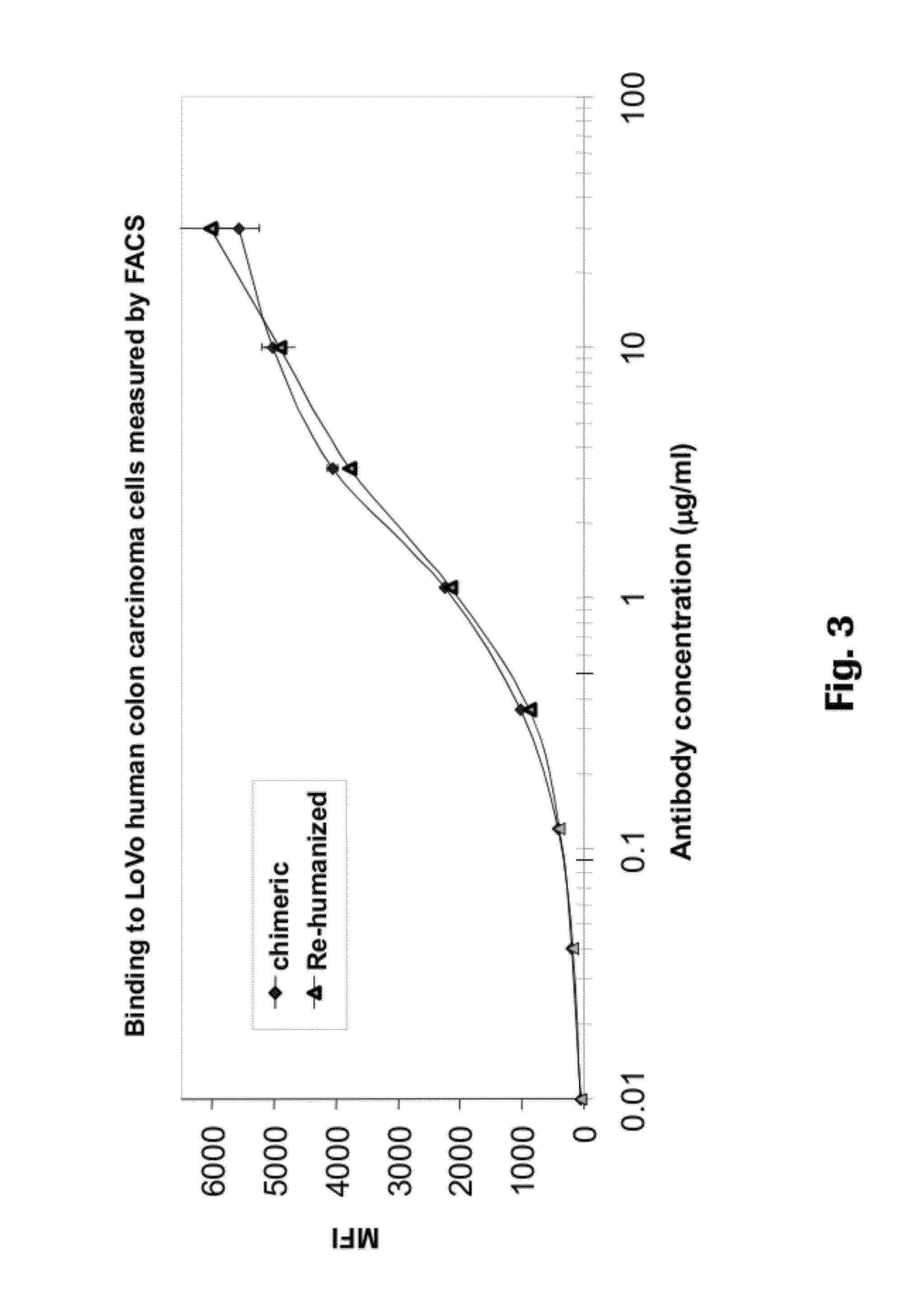
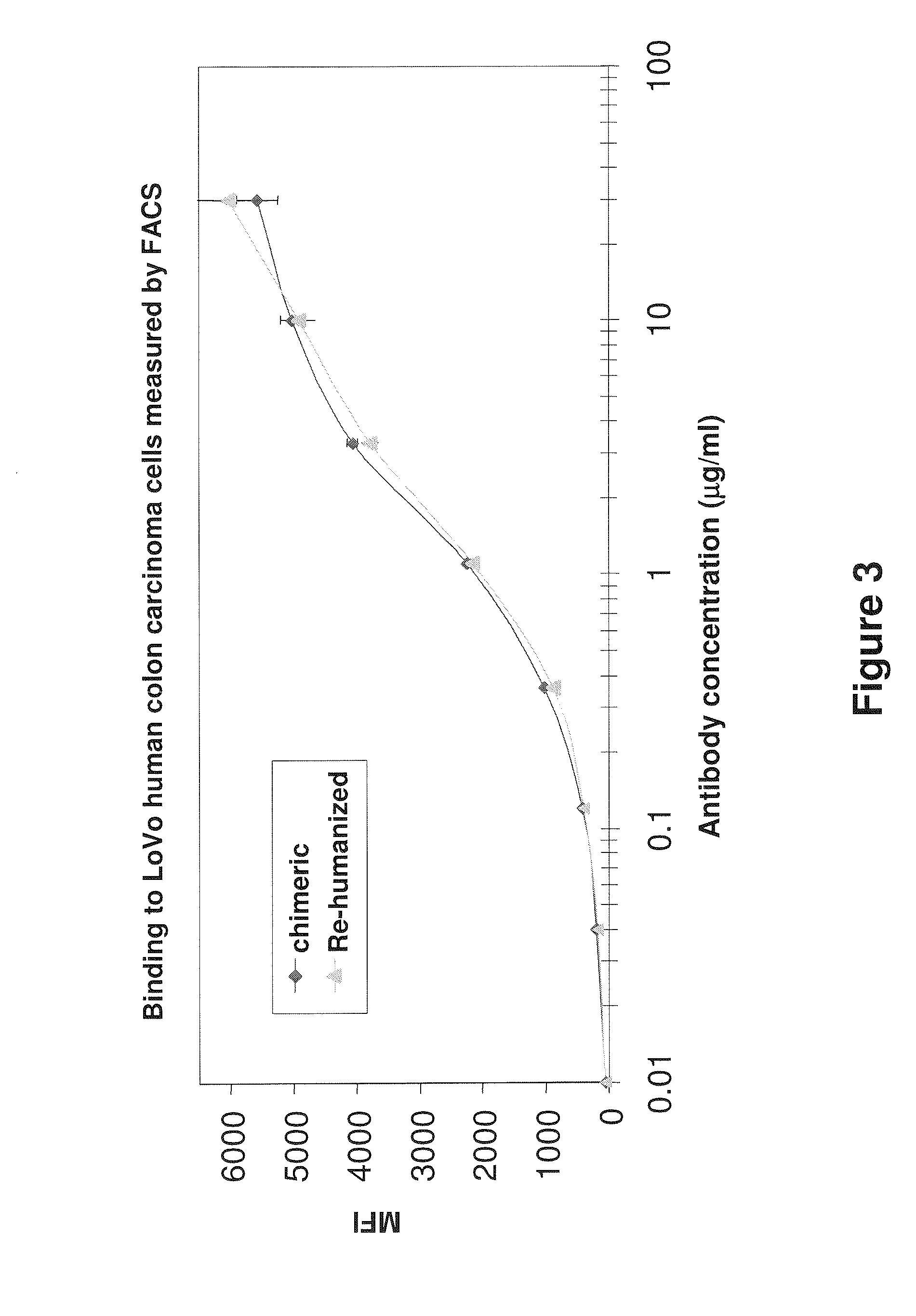
Anti-CEA antibodies
ActiveUS8642742B2Prolong survival timeMicroorganismsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigen bindingAnti-CEA Antibody
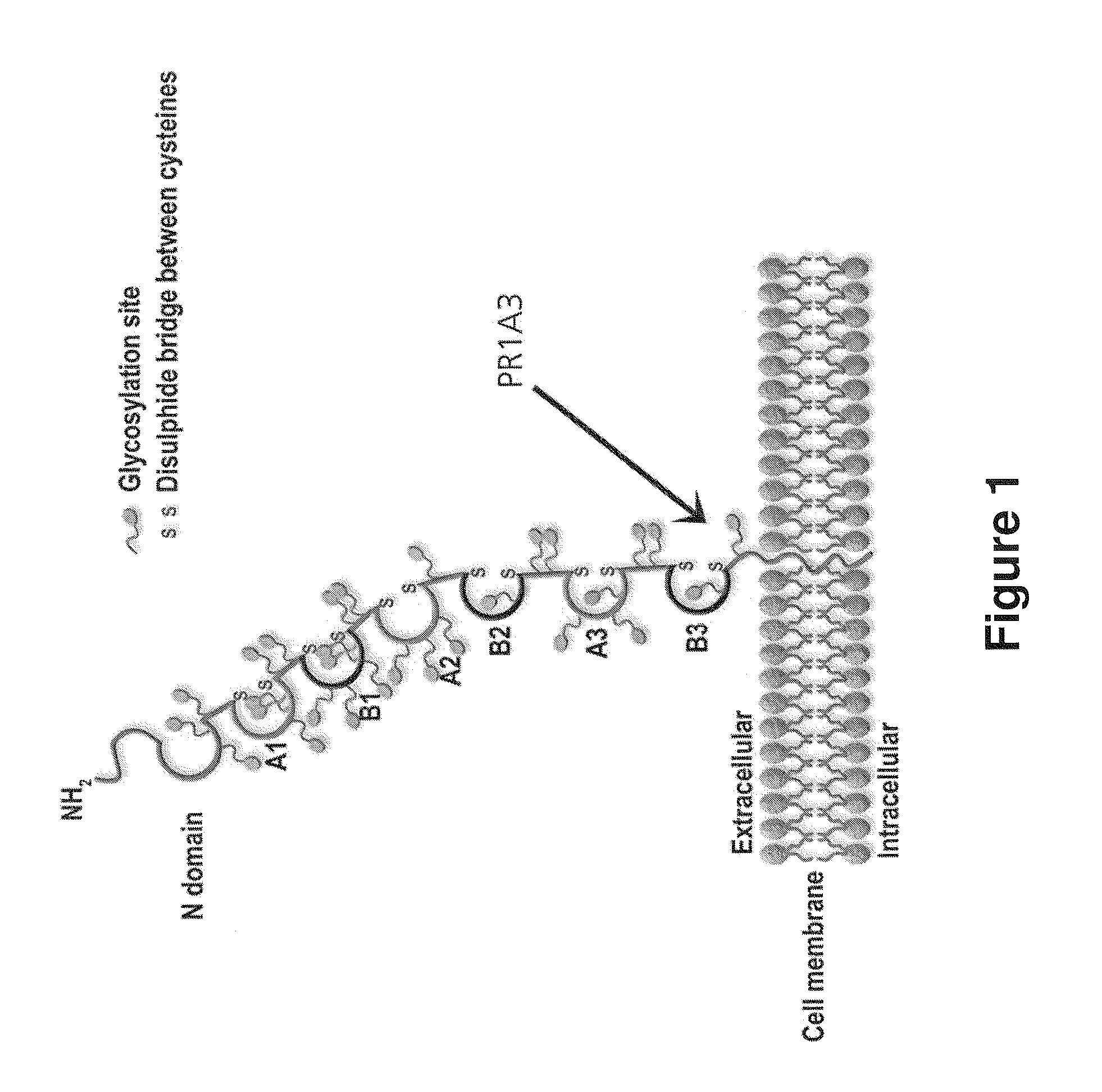
The present invention provides antigen binding molecules (ABMs) which bind membrane-bound CEA, including ABMs with improved therapeutic properties, and methods of using the same.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Soluble FcgammaR fusion protiens and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20040265321A1Loss in biological activityTreatment and/or prevention of autoimmune diseasesImpression capsNervous disorderDiseaseIdiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
The present invention relates to molecules, preferably soluble (i.e., not membrane bound) polypeptides, most preferably soluble fusion polypeptides comprising the extracellular soluble regions of an Fc³R, derivatives and analogs thereof, and nucleic acids encoding the same. Molecules of the invention are particularly useful for the treatment, management, or prevention of, or amelioration of one or more symptoms of an autoimmune disease, especially for ameliorating serum platelet deficiency associated with immune thrombocytopenic purpura. The invention provides methods and compositions for enhancing the therapeutic efficacy of standard, current or experimental therapies for an autoimmune disease by administering a molecule of the invention.
Owner:MACROGENICS INC
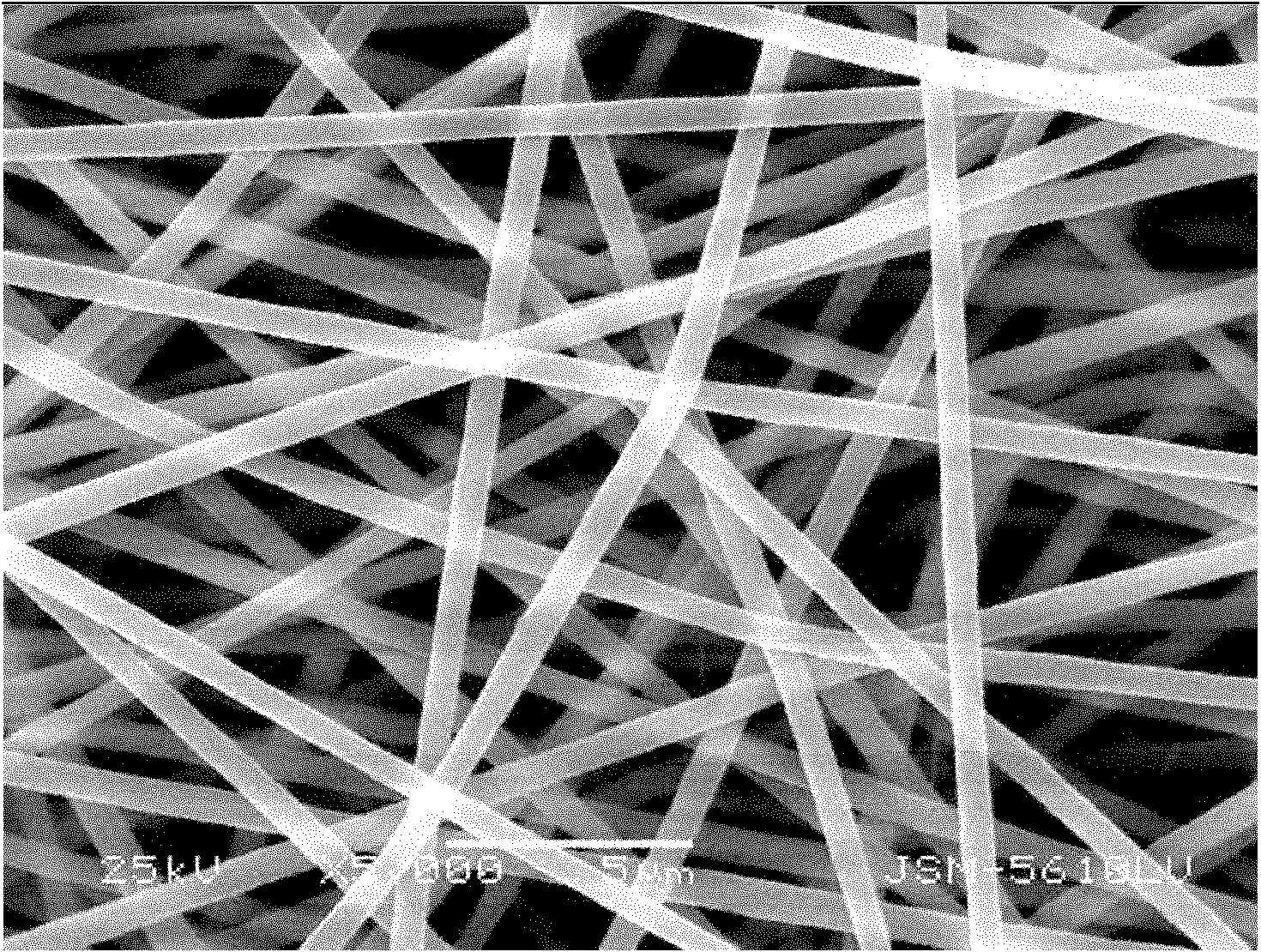
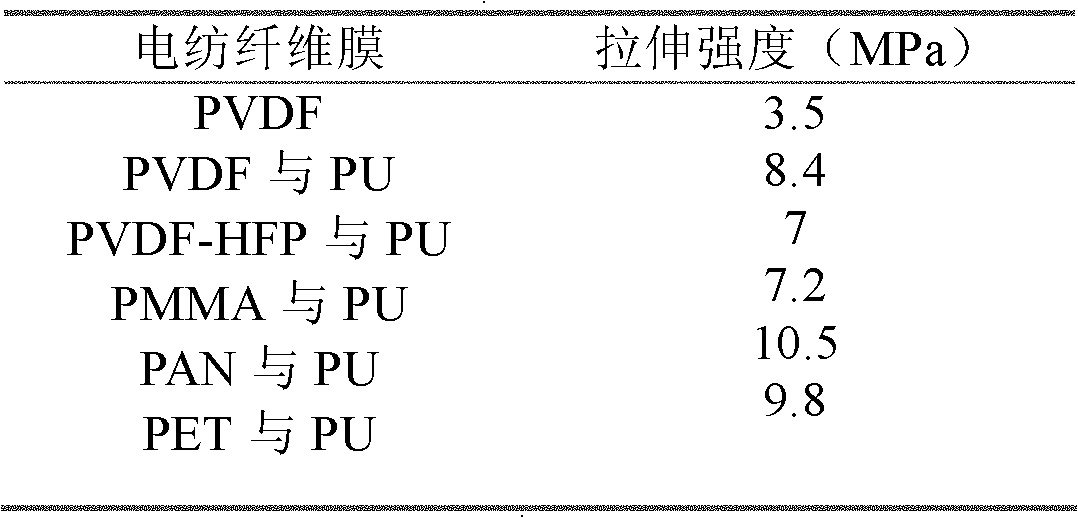
Enhanced bi-component nanofiber porous membrane and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102140734AHigh porosityImprove wettabilityFilament/thread formingCell component detailsPolymer scienceVoid ratio
The invention relates to an enhanced bi-component nanofiber porous membrane and a preparation method thereof. The porous membrane is a lithium ion battery membrane with two components of polymer resin and polyurethane. The membrane is in a semi-interpenetrating network structure which has a void ratio of 60-80%, and the mechanical property is 2-3 times higher than a single-component porous membrane of polymer resin. The preparation method comprises the steps of: dissolving a polymer resin and polyurethane prepolymer bi-component composition in a solvent, and preparing a nonwoven membrane through an electrospinning technology; and putting the nonwoven membrane at room temperature to make -NCO in the polyurethane prepolymer react with the -OH bond of water in the air to produce polyurethanethrough crosslinking and autopolymerization. In the invention, the nanofiber in the nonwoven membrane binds to form the polymer resin and polyurethane bi-component compound membrane, and the mechanical strength of the fibrous membrane is improved greatly. The method is easy, and the prepared nonwoven membrane maintains the advantages of high void ratio, and good thermal stability of polymer resinof the membrane prepared by using the electrospinning technology, and the membrane has good ion permeability and electrolyte affinity.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
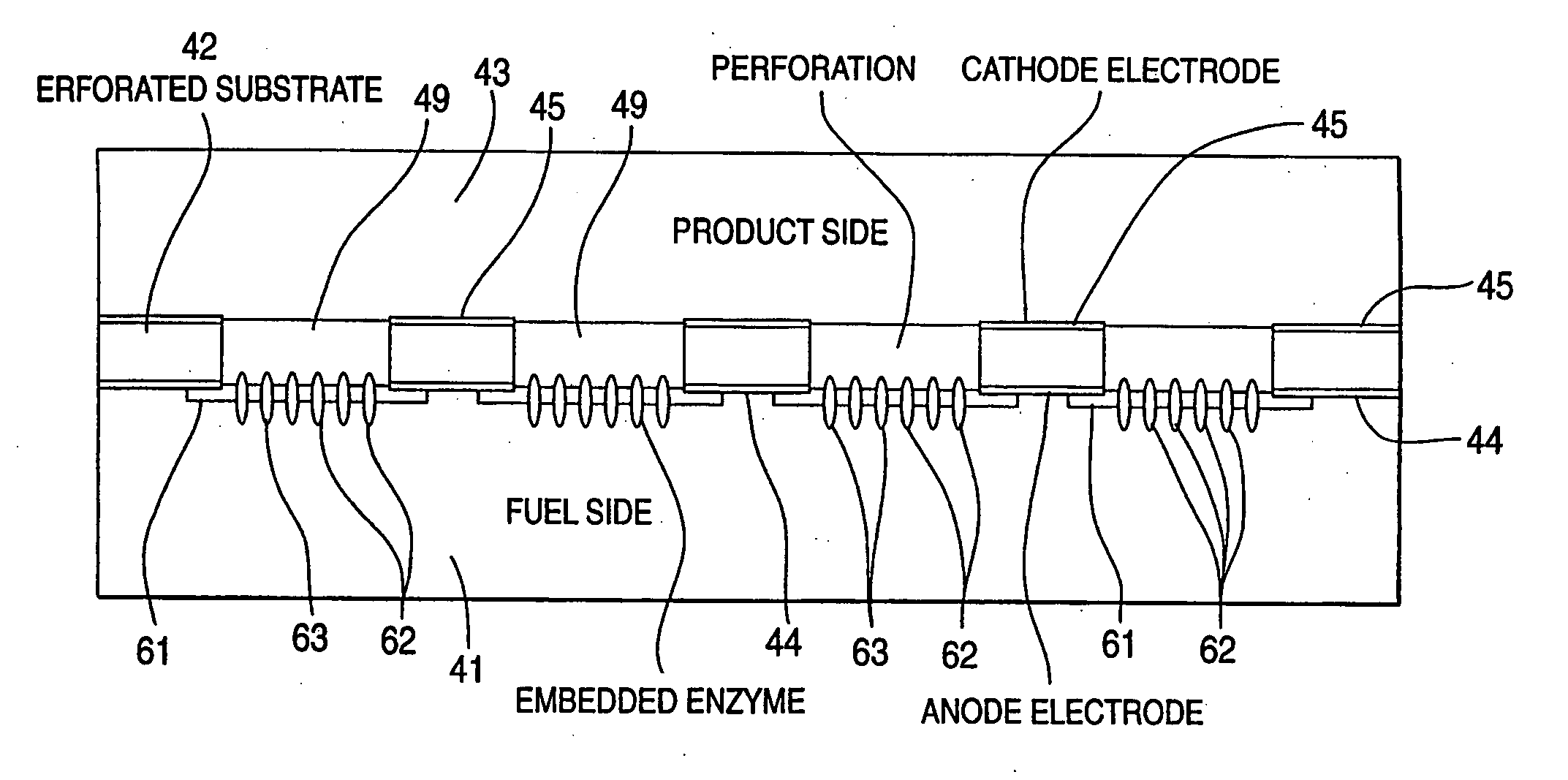
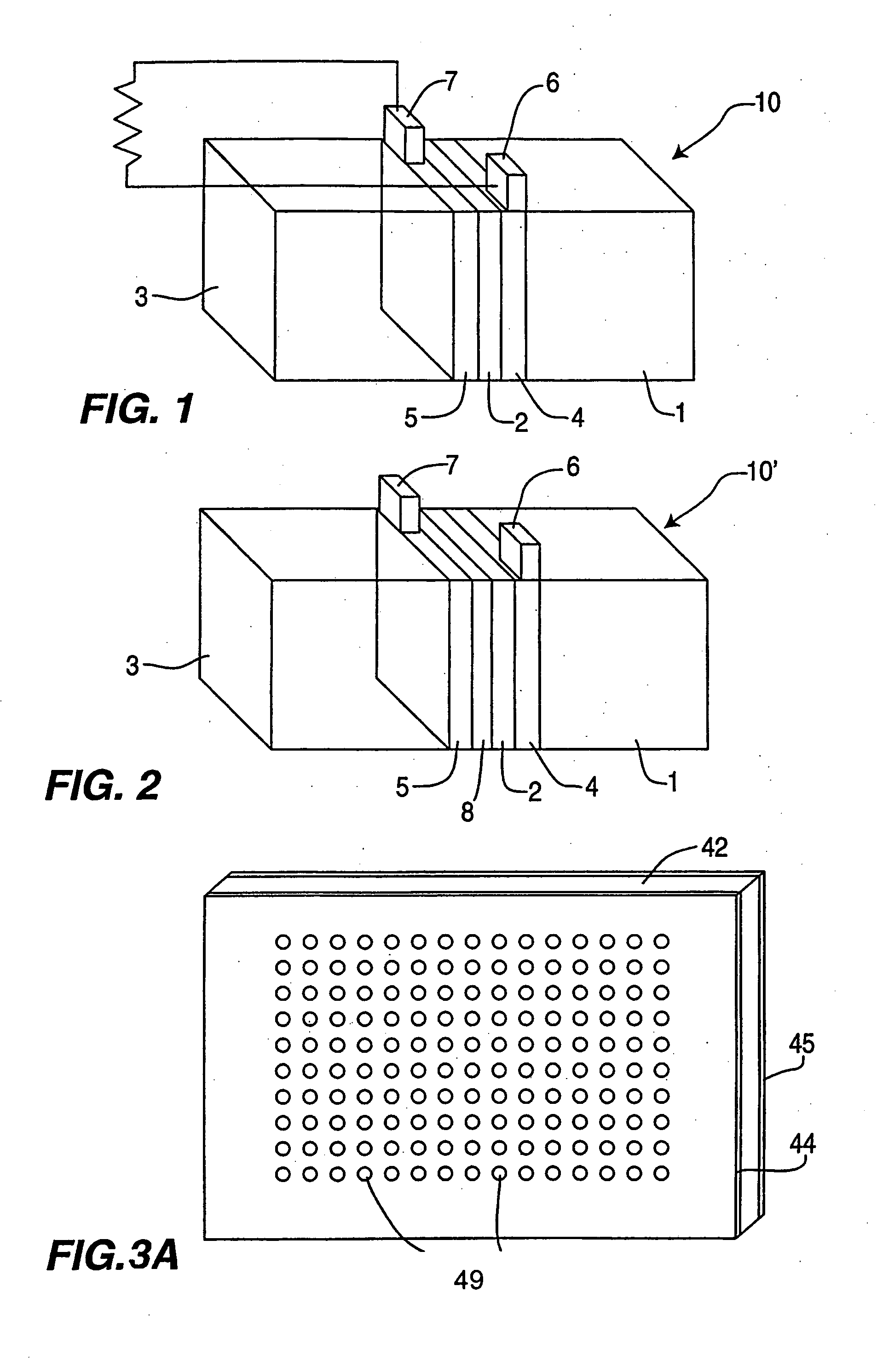
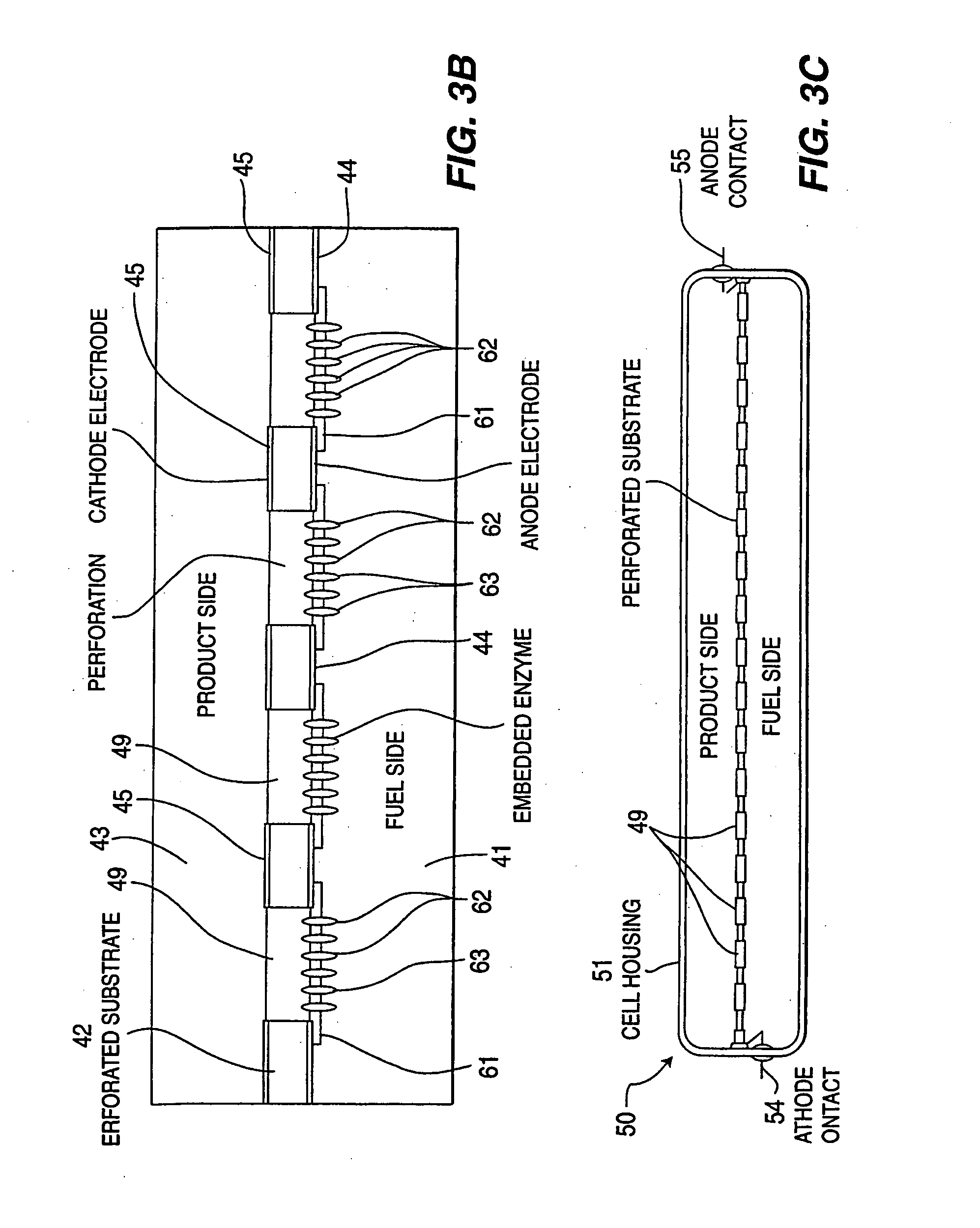
Enzymatic fuel cell with membrane bound redox enzyme
InactiveUS20050266290A1Efficiently conveyedLow viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesRedox enzymesFuel cells
Still further provided is a fuel cell with an anode compartment and a cathode compartment comprising: in the anode compartment, an anode electrode and, integrated into biocompatible membrane tethered to the anode electrode, a redox enzyme that can receive electrons from an electron carrier; in the cathode compartment, a cathode electrode which, when a conductive pathway to the first electrode is formed, is effective to convey the electrons to an electron acceptor composition in the cathode compartment; and a barrier separating the anode compartment from the cathode compartment but effective to convey protons from the anode compartment to the cathode compartment.
Owner:POWERZYME
Synthetic Lipid Rafts and Methods of Use
Compositions and methods for delivering cargo to cells are provided. One aspect provides a synthetic vesicle containing caveolin 1 or a fragment thereof in an amount effective to form lipid rafts in the vesicle. The synthetic vesicles can be used to deliver polynucleotides, proteins, therapeutic agents, or a combination thereof to specific membrane-bound compartments of a cell. In certain aspects, the synthetic vesicles can deliver cargo to cellular organelles such as mitochondria.
Owner:GENCIA
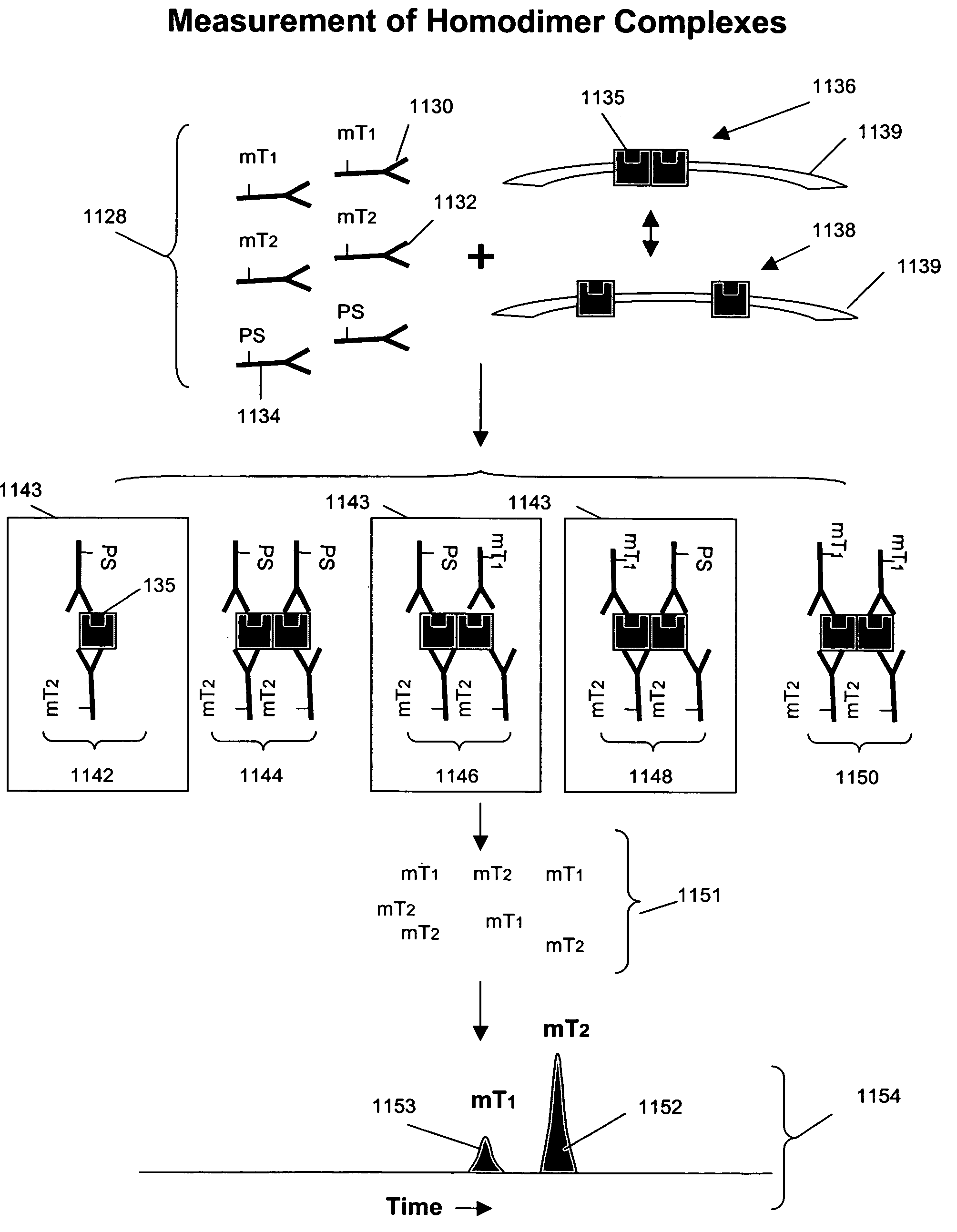
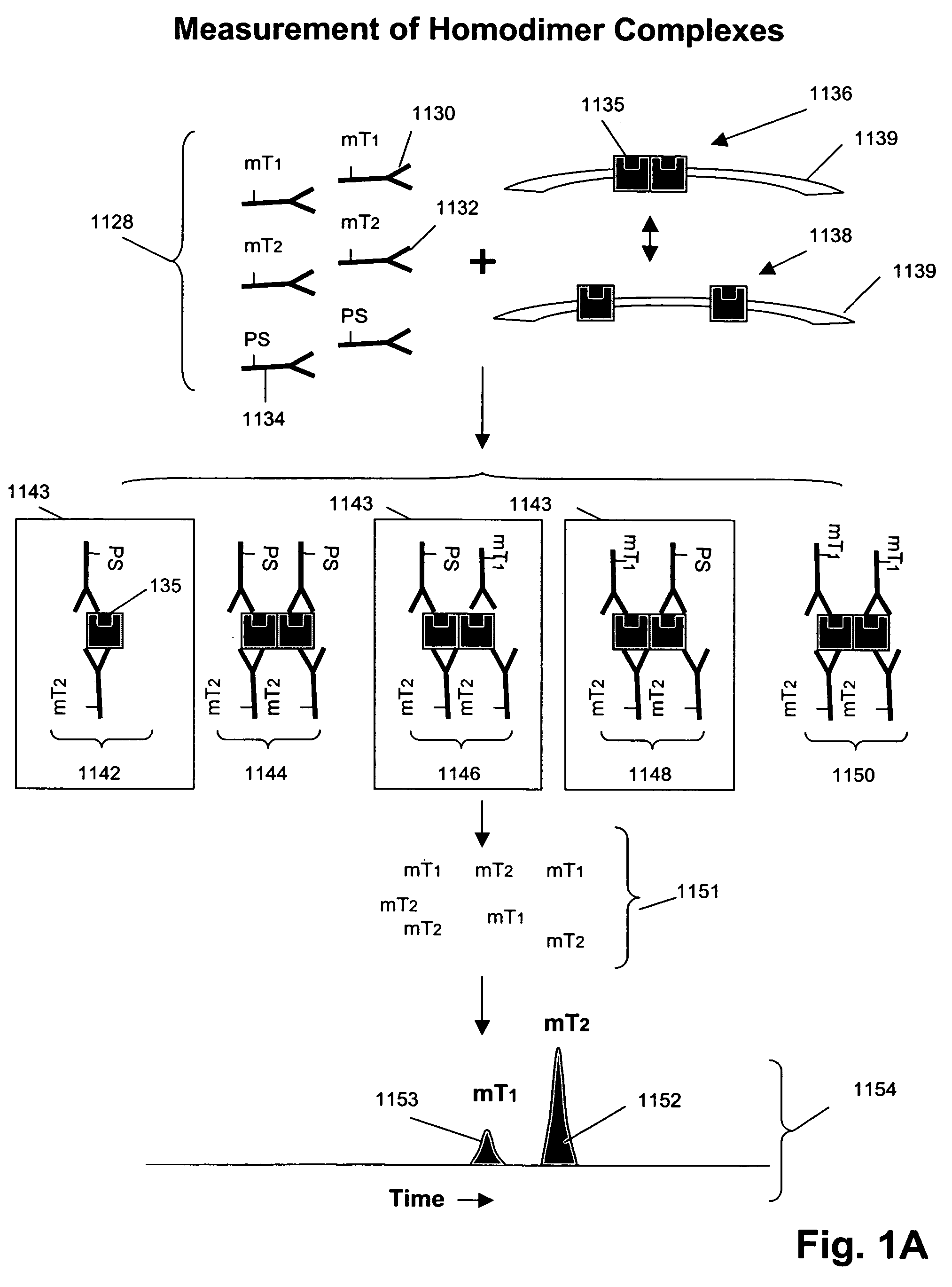
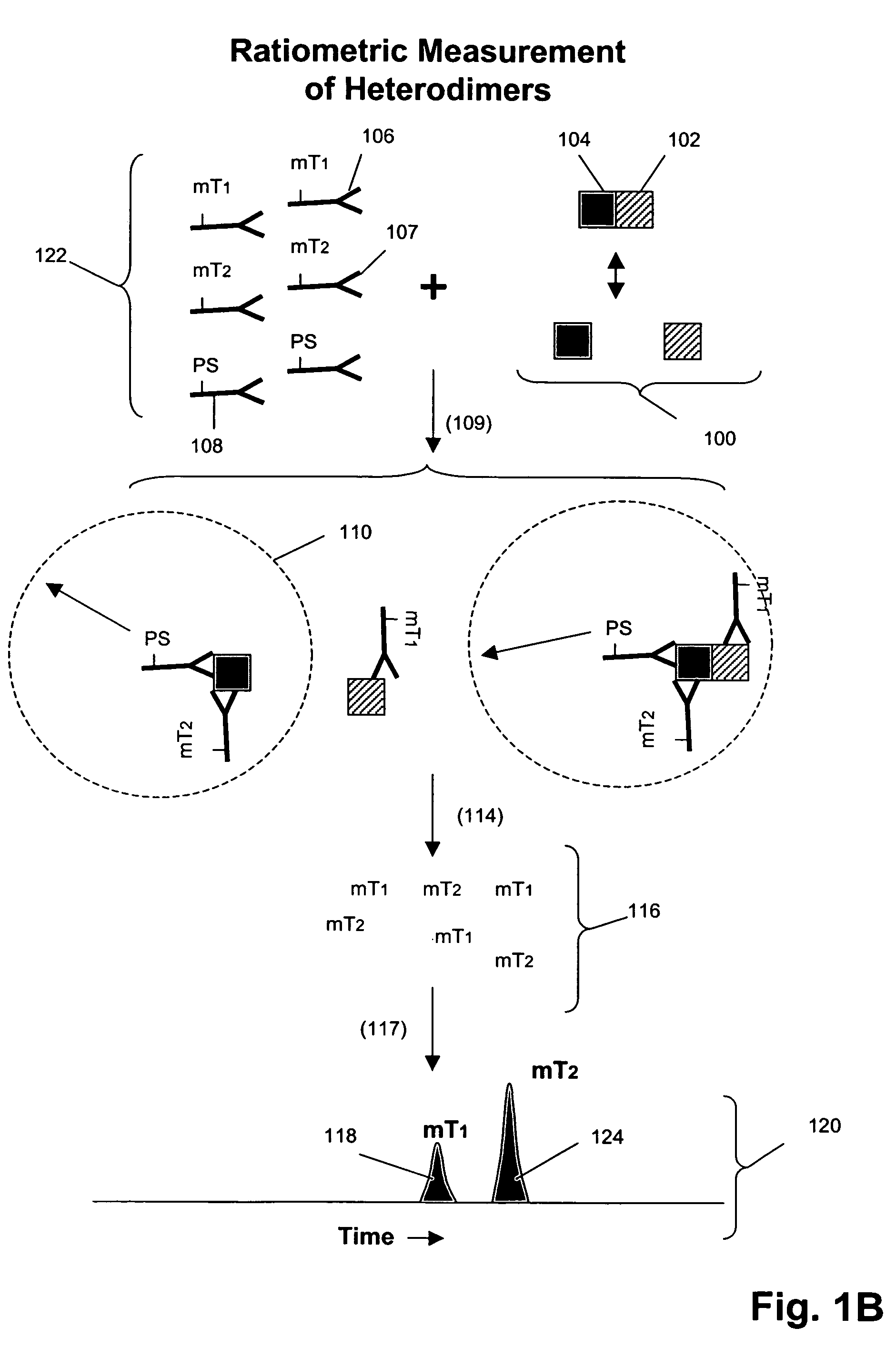
Measuring receptor homodimerization
InactiveUS7402398B2Low backgroundHigh sensitivityComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementEpitopeAnalyte
The invention provides methods and kits for detecting and / or measuring receptor homodimers on a cell surface membrane. In one aspect, the methods employ pairs of probes comprising binding compounds and a cleaving probe, such that at least one binding compound binds specifically to the same epitope of a membrane-bound analyte as the cleaving probe. The binding compound includes one or more molecular tags attached through a cleavable linkage, and the cleaving probe includes a cleavage-inducing moiety that can cleave the linkage when within a defined proximity thereto. Binding of the two probes to a homodimer of a cell surface molecules results in release of molecular tags from the binding compounds, providing a measure of formation of the homodimeric complex.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
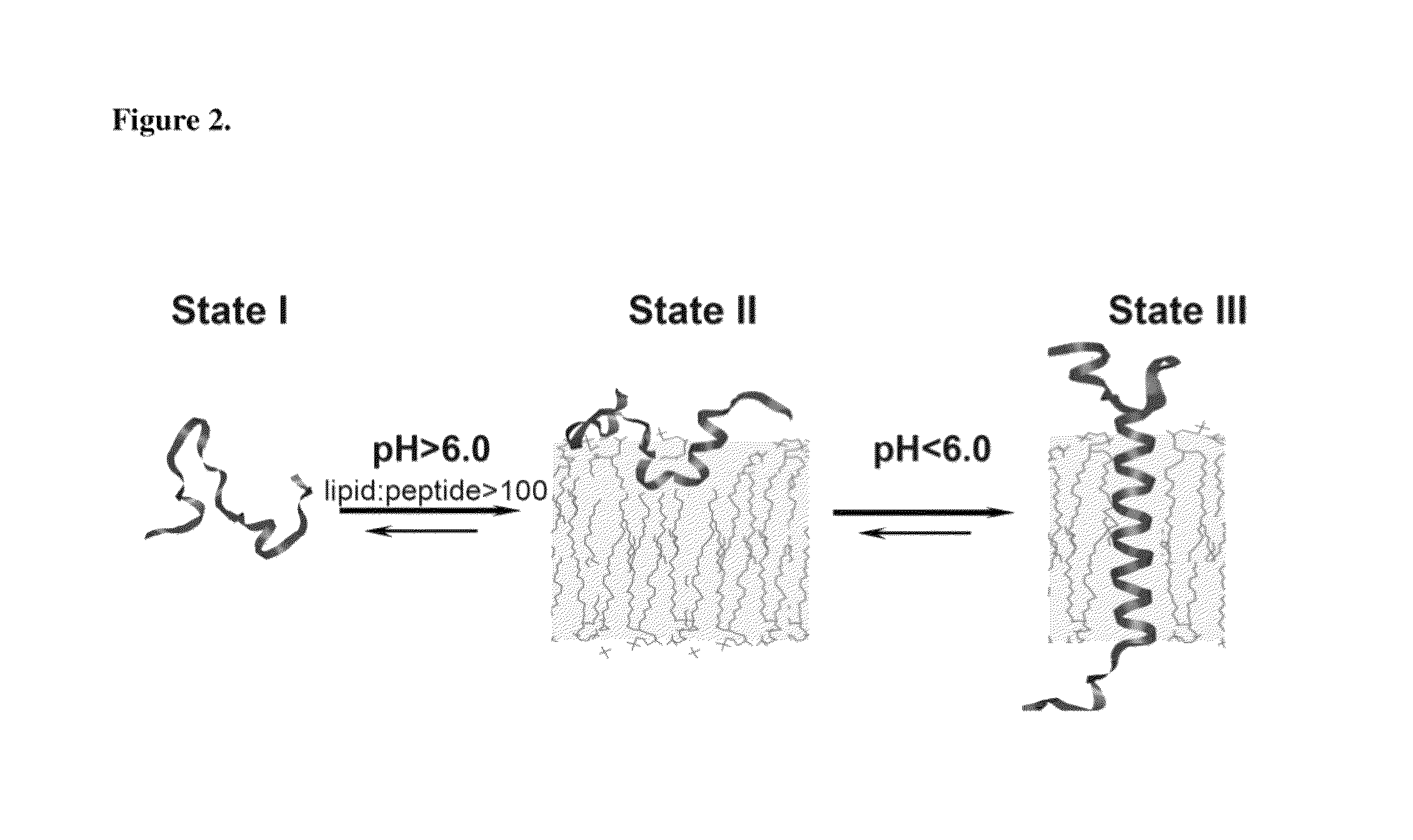
Environmentally sensitive compositions and methods of use in the treatment and diagnosis of tumors
ActiveUS9289508B2Easy to insertAffect performanceInorganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSolubilityMembrane bound
An environmentally sensitive membrane binding polypeptide, pH (low)-sensitive membrane peptide (pHLIP) has improved insertion kinetics balanced with solubility to selectively target acidic tissues.
Owner:YALE UNIV +2
Rapid and non-invasive method to evaluate immunization status of a patient
InactiveUS6927068B2Rapid and reliable and non-invasive and safe testingRapidly evaluate immunization status of a patientBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSpecific iggAnthrax protective antigen
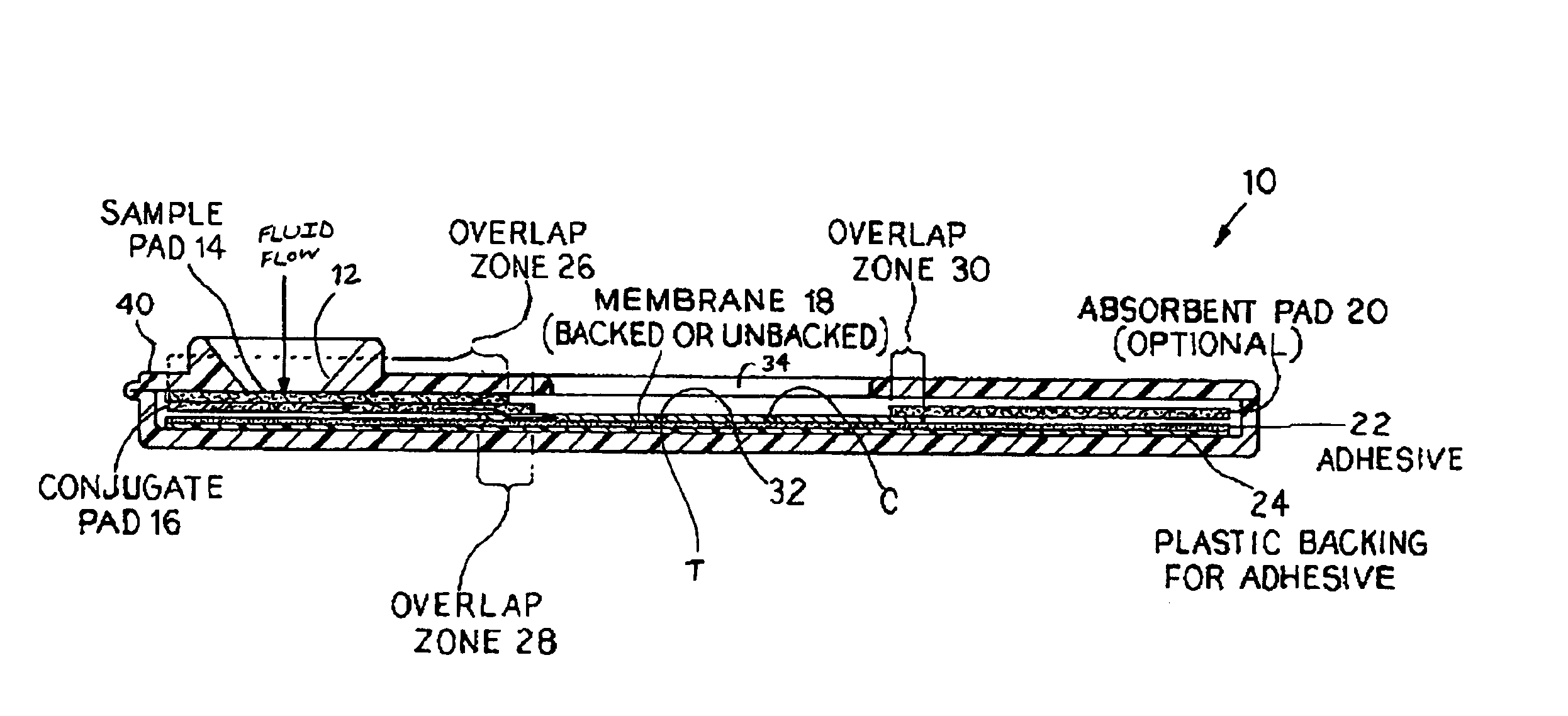
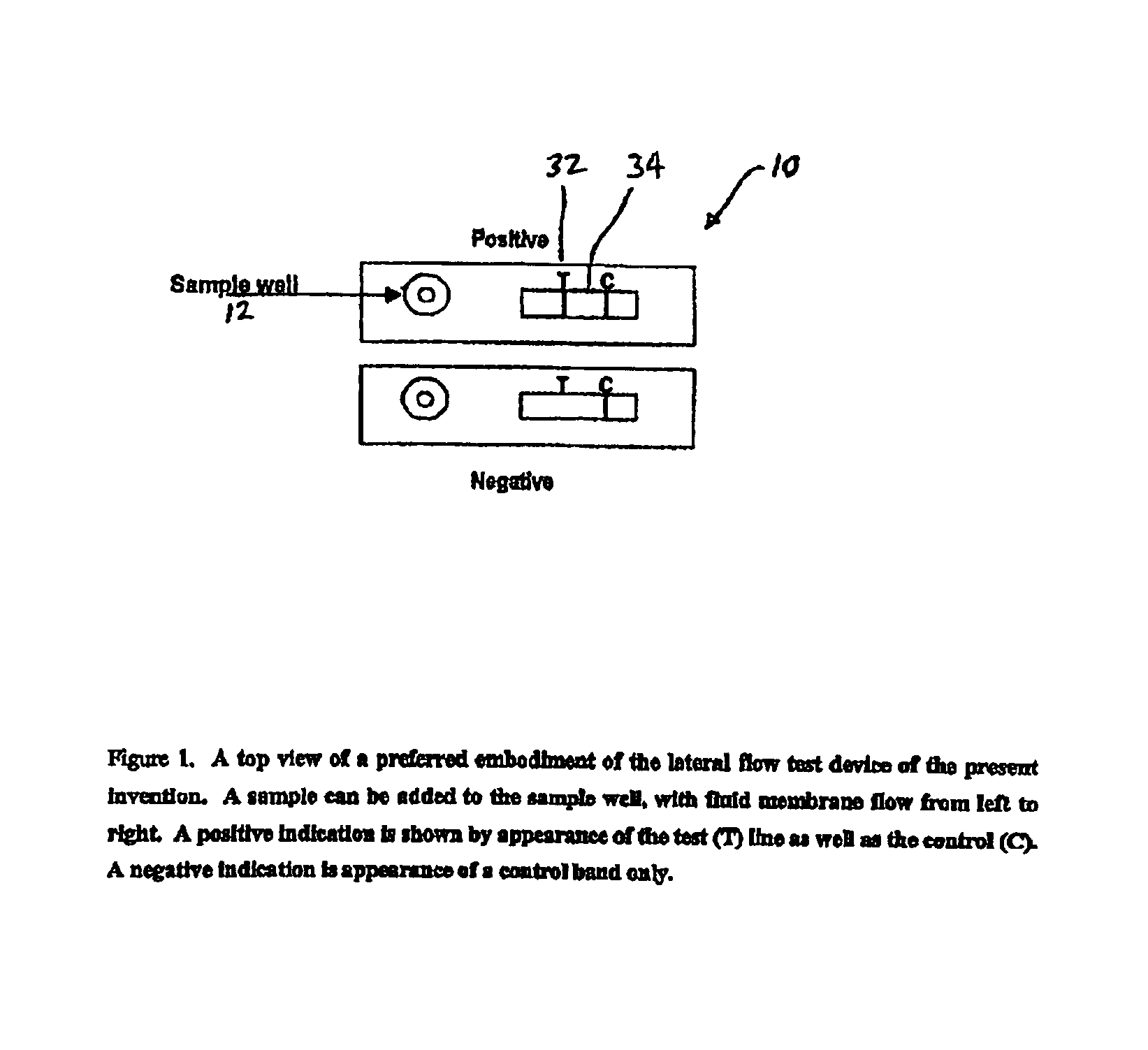
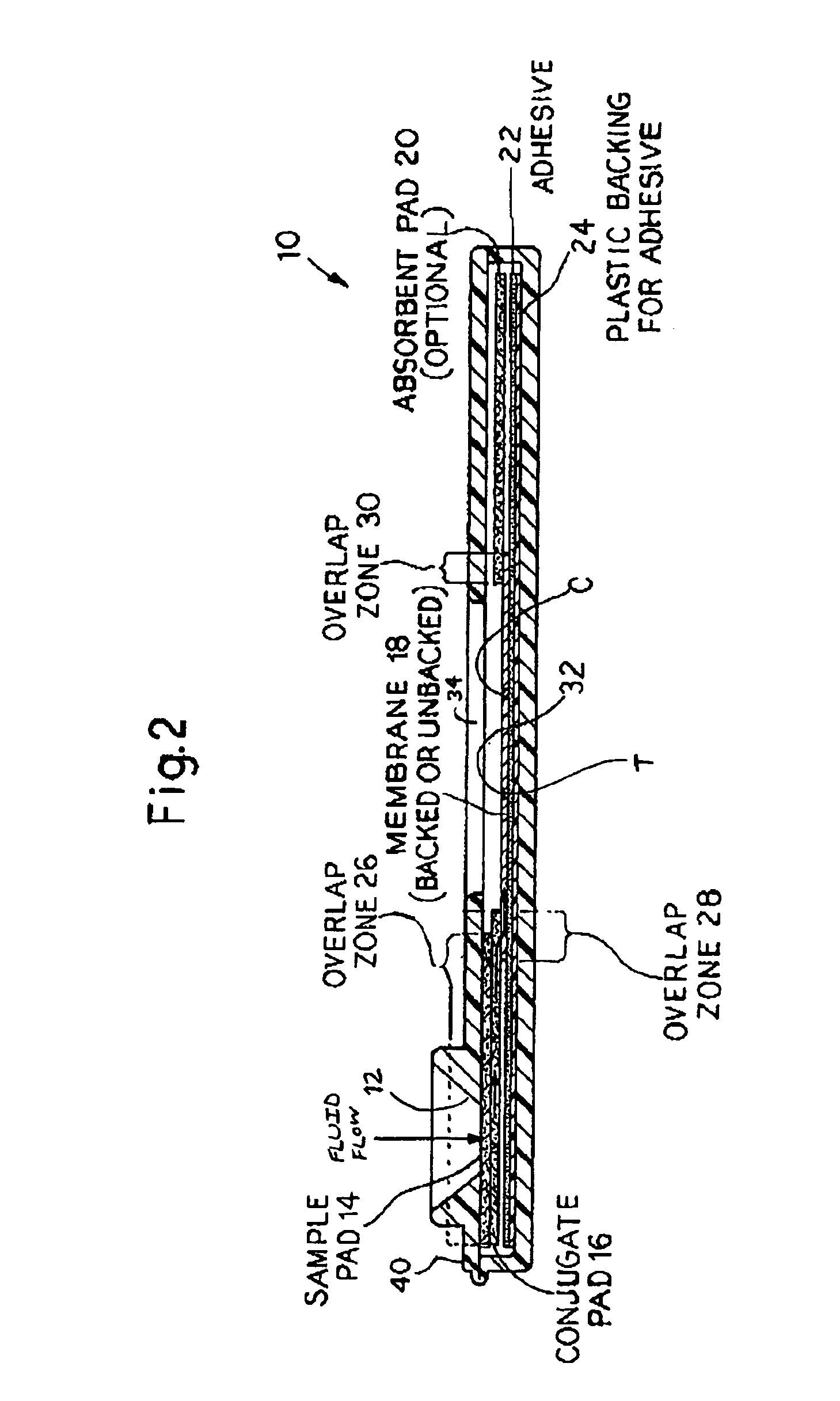
An assay method and kit for detecting the presence of a predesignated, target IgG antibody in a sample selected from one or more patient bodily fluids. The method comprises the following steps: (a) contacting the sample of one or more patient bodily fluids with a membrane-bound recombinant protective antigen to bind to the target IgG antibody in the sample; (b) previously, simultaneously or subsequently to step (a), binding the protective antigen (PA) with a conjugated label producing a detectable signal; and (c) detecting the signal whereby the presence of the target IgG antibody is determined in the sample by the intensity of the signal. The method can further comprise the step of evaluating immunization status of the patient from whom the sample came by comparing the signal or lack thereof with immunizations previously received by the patient. In a preferred embodiment, the recombinant protective antigen (PA) specifically binds to anthrax protective antigen-specific IgG antibodies. Preferably, the immunoassay of the present invention comprises a lateral-flow assay comprising a membrane, a conjugated label pad, and a recombinant protective antigen (PA) bound to the membrane.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Compositions and methods for treating hypophosphatasia
ActiveUS20090238814A1Extend your lifeWeight increaseHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsMembrane bound enzymeBone tissue
The present invention provides compositions and methods for use in enzyme replacement therapy. The inventors disclose a method of producing membrane bound enzymes in an active soluble form by eliminating the glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) membrane anchor. In particular the inventors disclose a soluble active form of the membrane bound enzyme TNSALP which they produced by deleting the GPI anchor single peptide sequence. They have further shown that this composition is useful for treatment of hypophosphatasia. The inventors also disclose oligo acid amino acid variants thereof which specifically target bone tissue.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY +2
Antibodies to carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), methods of making same, and uses thereof
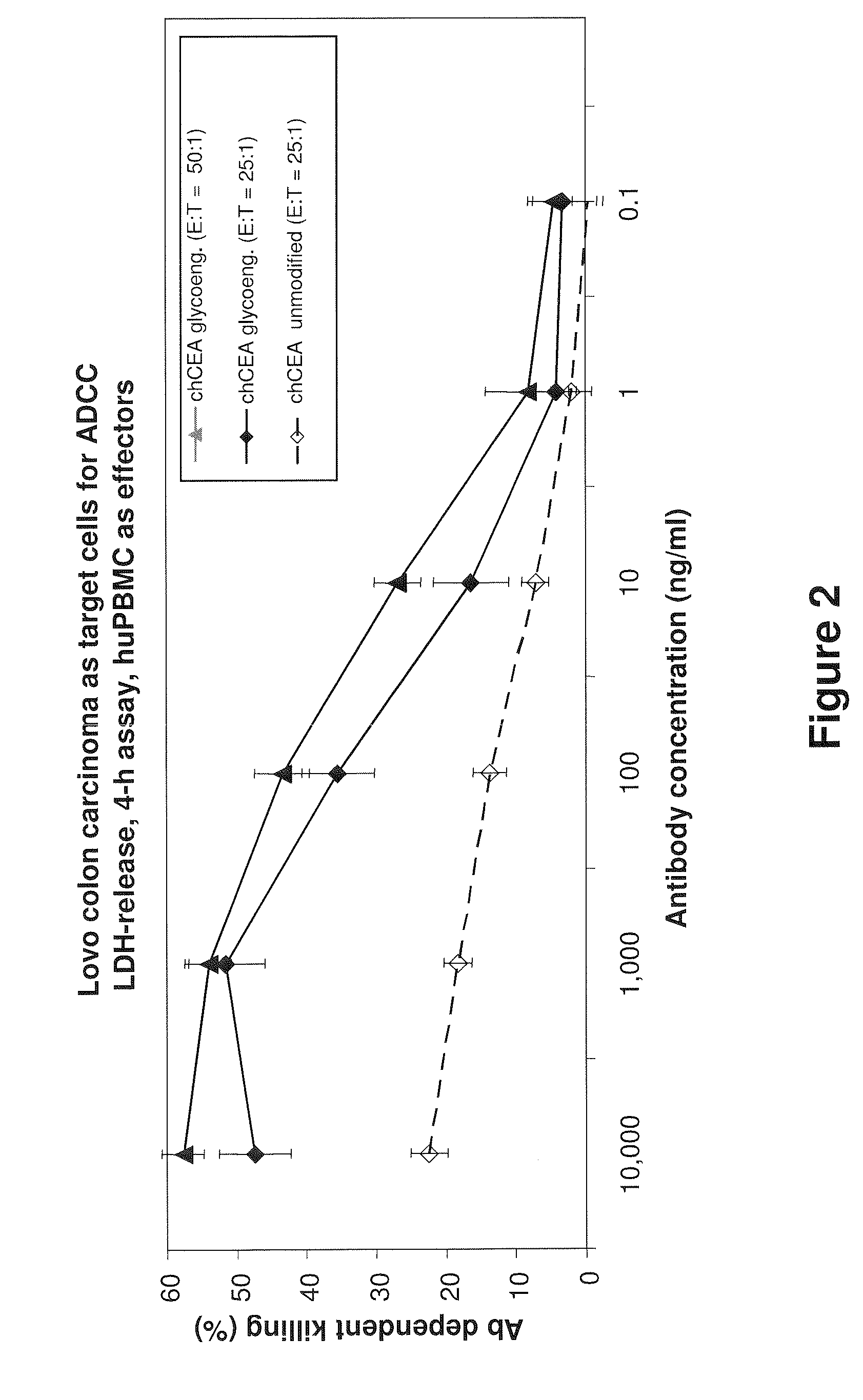
The present invention relates to antigen binding molecules (ABMs). In particular embodiments, the present invention relates to recombinant monoclonal antibodies, including chimeric, primatized or humanized antibodies or variants thereof specific for cell surface or membrane bound human CEA. In addition, the present invention relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding such ABMs, and vectors and host cells comprising such nucleic acid molecules. The invention further relates to methods for producing the ABMs of the invention, and to methods of using these ABMs in treatment of disease. In addition, the present invention relates to ABMs with modified glycosylation having improved therapeutic properties, including antibodies with increased Fc receptor binding and increased effector function.
Owner:ROCHE GLYCART AG
Organic compounds
InactiveUS20100330572A1Lack of activityAnimal cellsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsNucleotideChemical compound
The present invention relates to a novel selection system for use in a eukaryotic cell culture process and for expression of a recombinant product of interest. The selection system is based on the introduction of an exogenous functional membrane-bound folate receptor gene together with the polynucleotide or gene encoding the product of interest into a eukaryotic cell and can be widely utilized with eukaryotic cells for which cellular viability is dependent upon folic acid uptake.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Use of diindolylmethane-related indoles and growth factor receptor inhibitors for the treatment of human cytomegalovirus-associated disease
The present invention includes compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of conditions associated with Human Cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection. HCMV-associated conditions include infections (active and latent), benign cell-proliferative conditions, pre-cancerous cell-proliferative conditions, and cancerous conditions. In particular, the present invention describes new therapeutic and preventative uses for 3,3′-diindolylmethane (DIM), or a DIM-related indole, in combination with an inhibitor of a membrane bound Growth Factor Receptor (GFR), to treat conditions associated with exposure to HCMV. In certain embodiments, the compositions of the invention can be used in combination with radiation therapy.
Owner:BIORESPONSE
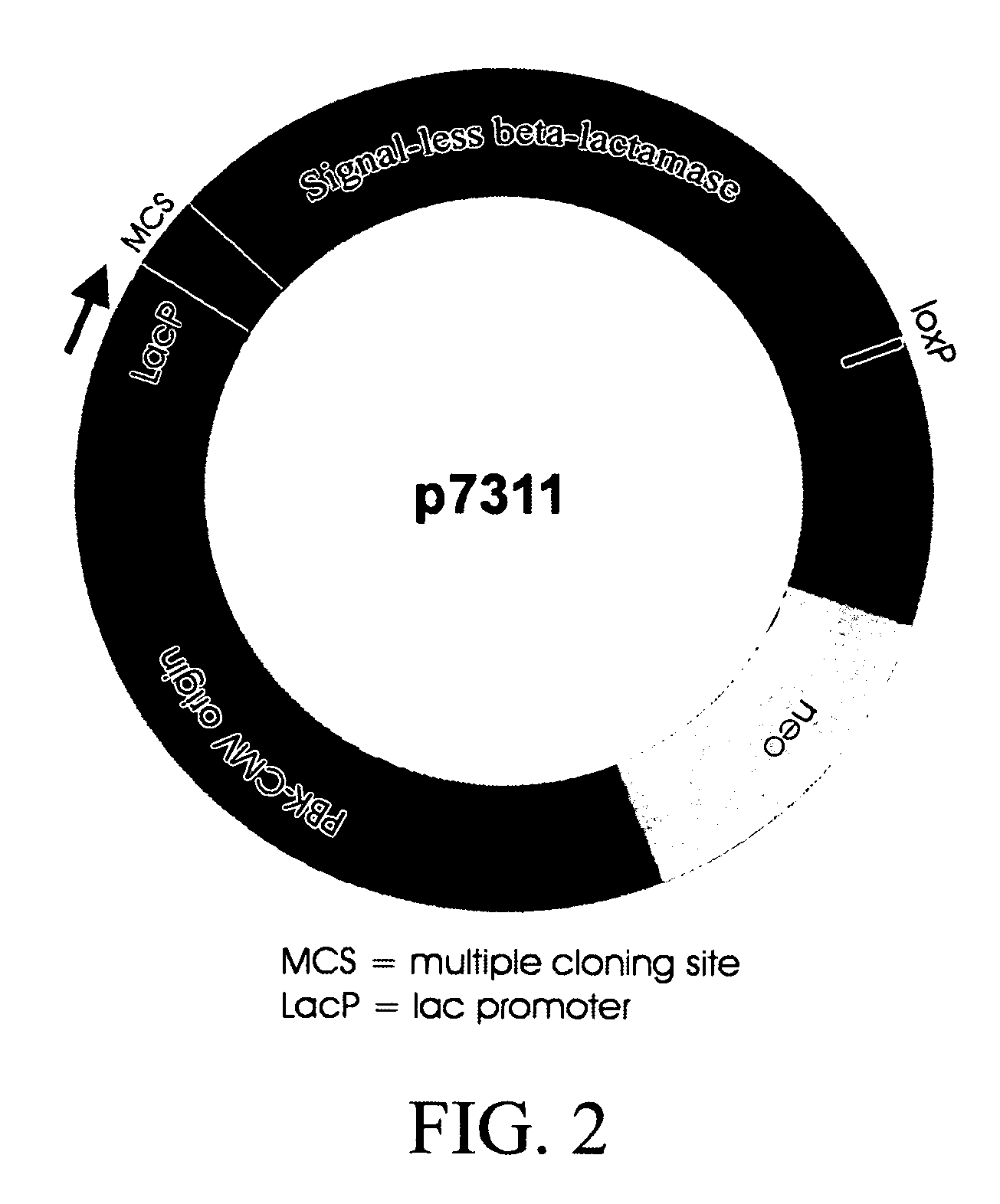
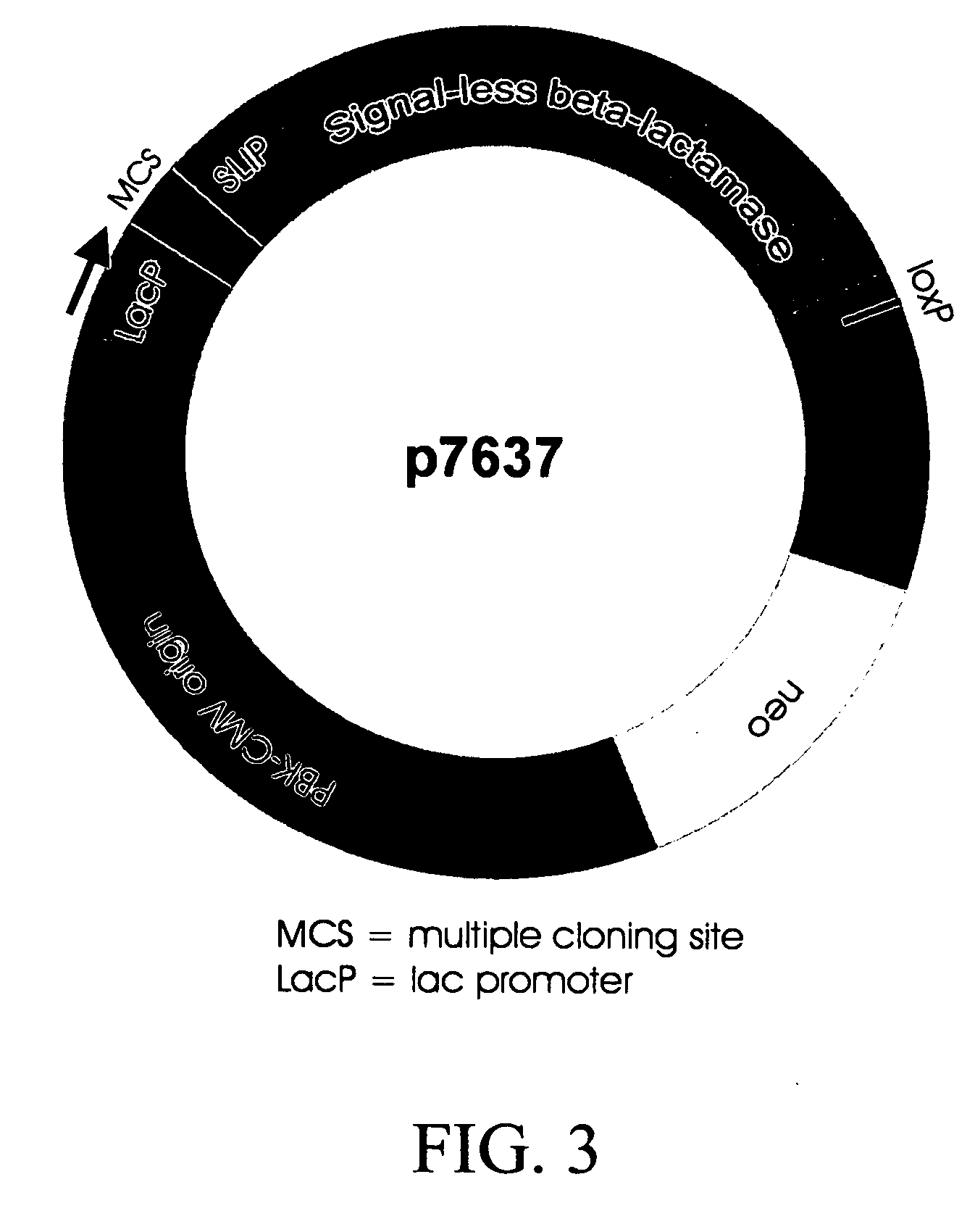
Vector system for selection of genes encoding secreted proteins and membrane-bound proteins
InactiveUS20070111283A1Rapid and robust selectionImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesVector systemENCODE
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Targeted cytolysis of HIV-infected cells by chimeric CD4 receptor-bearing cells
InactiveUS7094599B2Promote absorptionProlong lifeVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsMammalEphA Receptors
Disclosed is a method of directing a cellular immune response against an HIV-infected cell in a mammal involving administering to the mammal an effective amount of therapeutic cells which express a membrane-bound, proteinaceous chimeric receptor comprising (a) an extracellular portion which includes a fragment of CD4 which is capable of specifically recognizing and binding the HIV-infected cell but which does not mediate HIV infection and (b) an intracellular portion which is capable of signalling the therapeutic cell to destroy the receptor-bound HIV-infected cell. Also disclosed are cells which express the chimeric receptors and DNA and vectors encoding the chimeric receptors.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
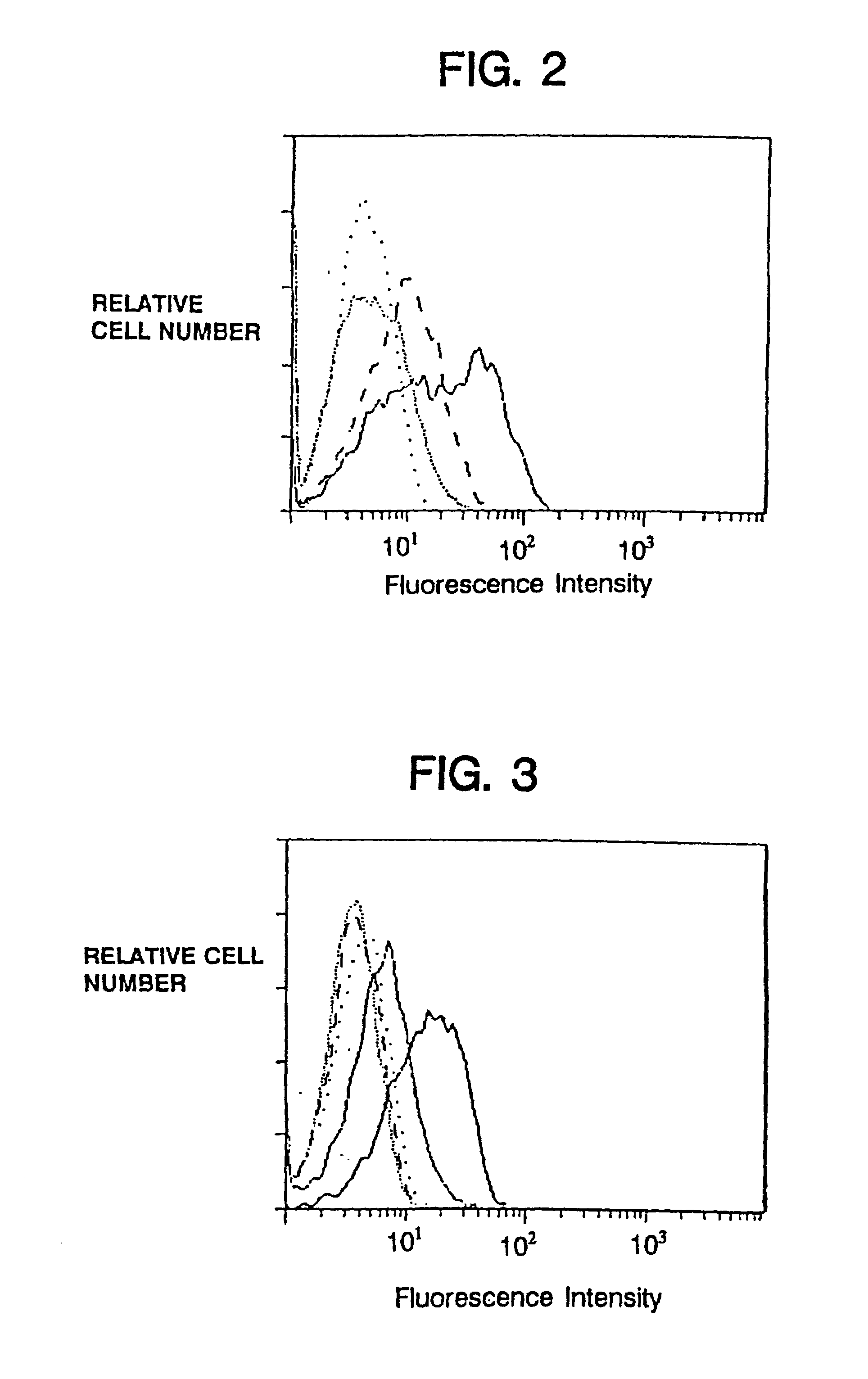
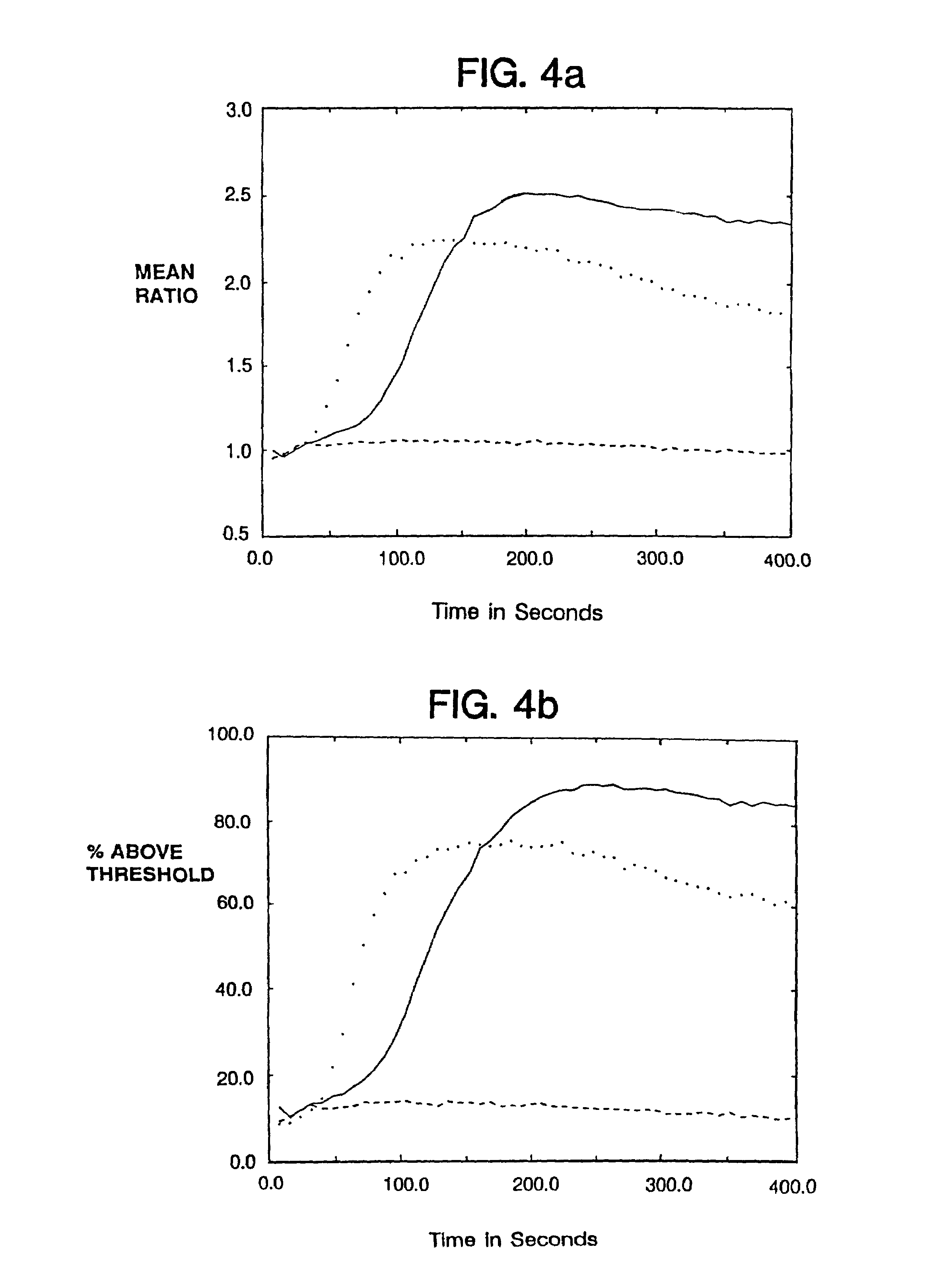
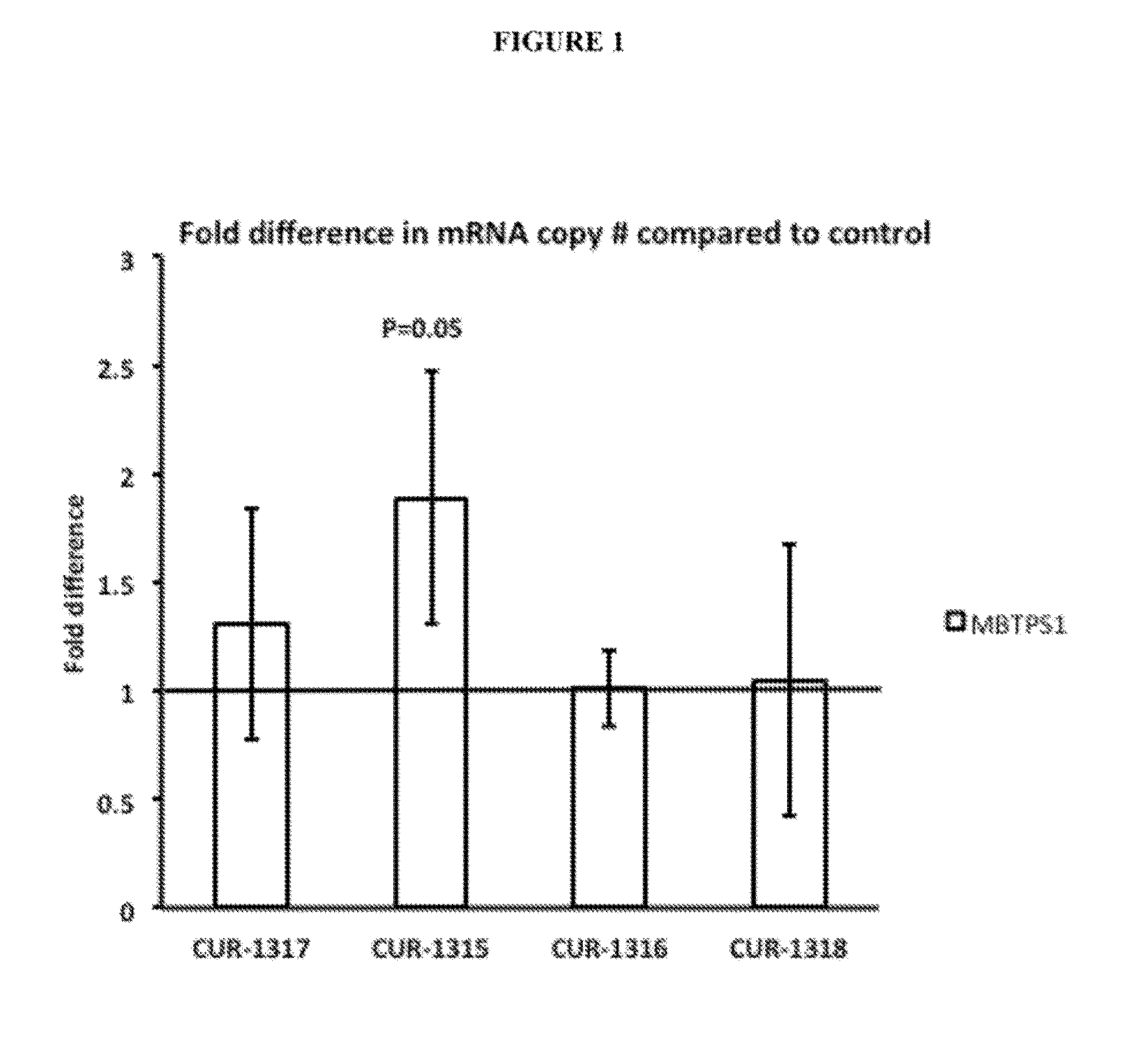
Treatment of membrane bound transcription factor peptidase, site 1 (mbtps1) related diseases by inhibition of natural antisense transcript to mbtps1
ActiveUS20130116300A1Modulate its functionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseasePolynucleotide
The present invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that modulate the expression of and / or function of Membrane Bound Transcription Factor Peptidase, site 1 (MBTPS1), in particular, by targeting natural antisense polynucleotides of Membrane Bound Transcription Factor Peptidase, site 1 (MBTP-S1). The invention also relates to the identification of these antisense oligonucleotides and their use in treating diseases and disorders associated with the expression of MBTPS1.
Owner:CURNA INC
Simple membrane assay method and kit
ActiveUS20070202611A1Highly reliable simple test methodReduce generationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteBiology
The present invention is to provide a simple membrane assay method for detecting or quantitating an analyte in a specimen sample using an assay device equipped with a membrane bound with a capture-substance to capture the analyte, comprising the steps of filtering a specimen sample using a filter, dropping the filtrate onto said membrane and detecting the presence of the analyte in said specimen sample, as well as a simple membrane assay kit for detecting the presence of an analyte in a specimen sample, comprising (1) a filter tube, and (2) an assay device equipped with a membrane bound with a capture-substance to capture the analyte. The method or the kit can decrease the occurrence of false positivity and can provide a highly accurate detection of the analyte such as pathogen and antibody in a specimen collected in a medical scene or by an individual.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
Multiplex analysis using membrane-bound sensitizers
InactiveUS20060024846A1Low backgroundHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteBiological activation
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
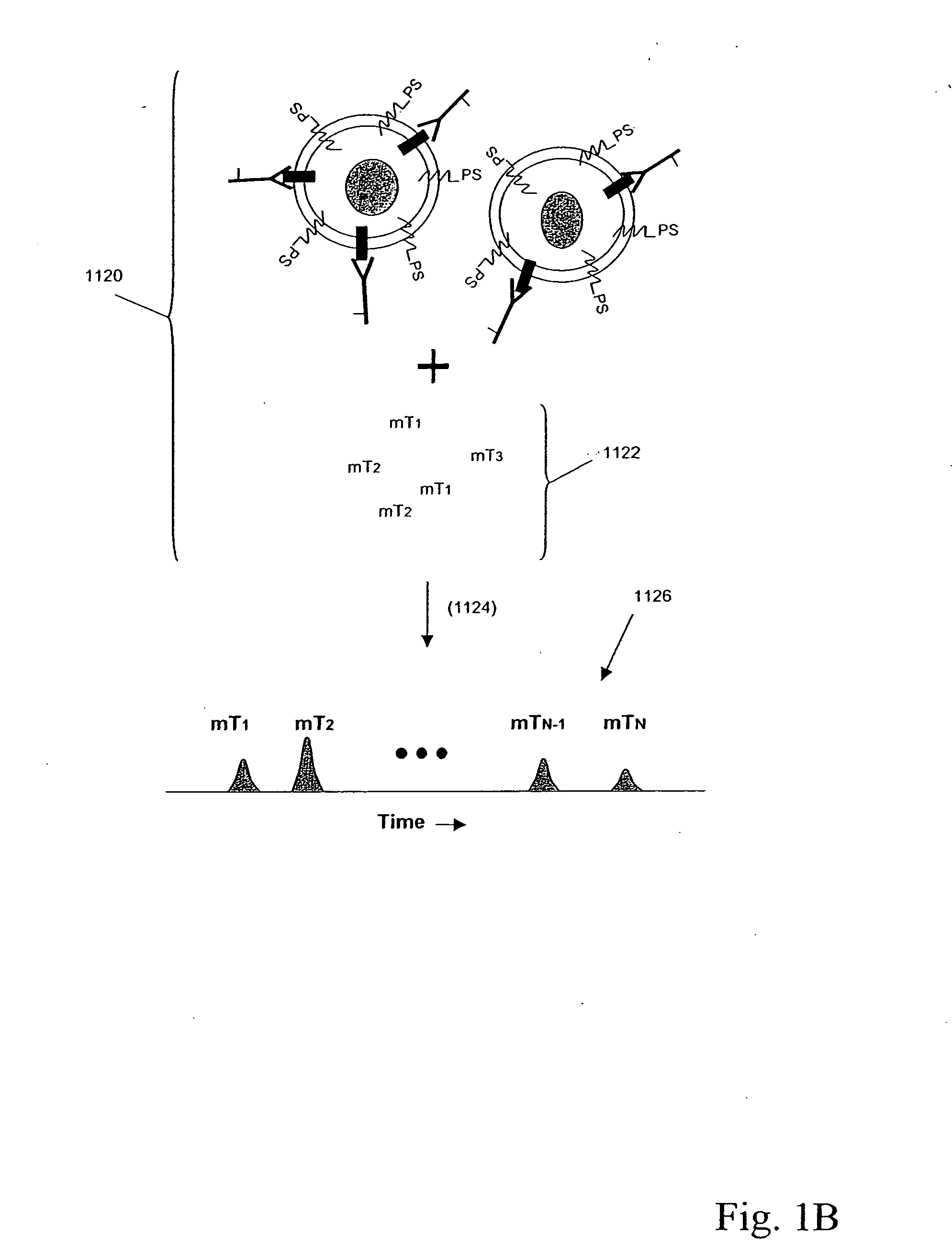
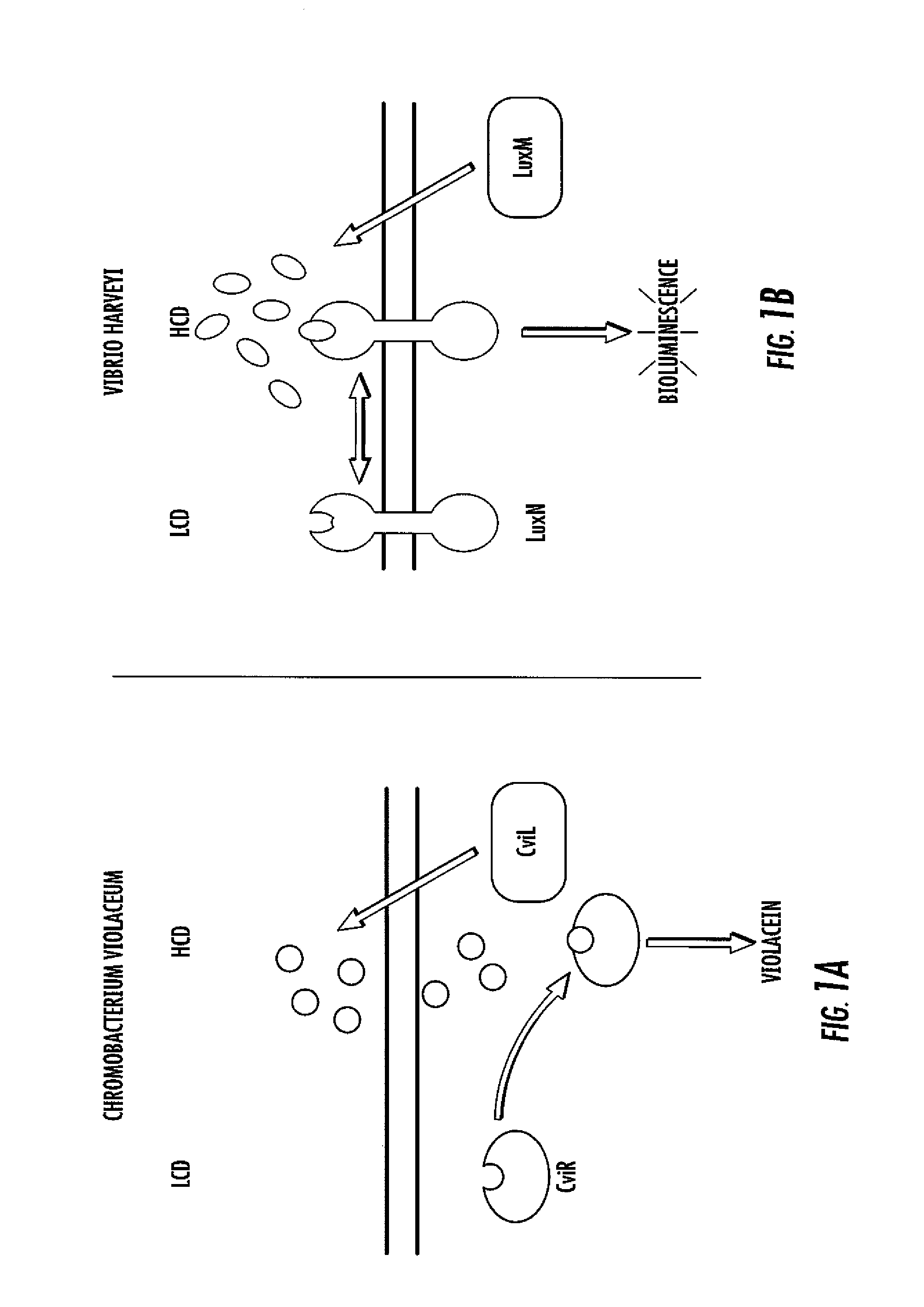
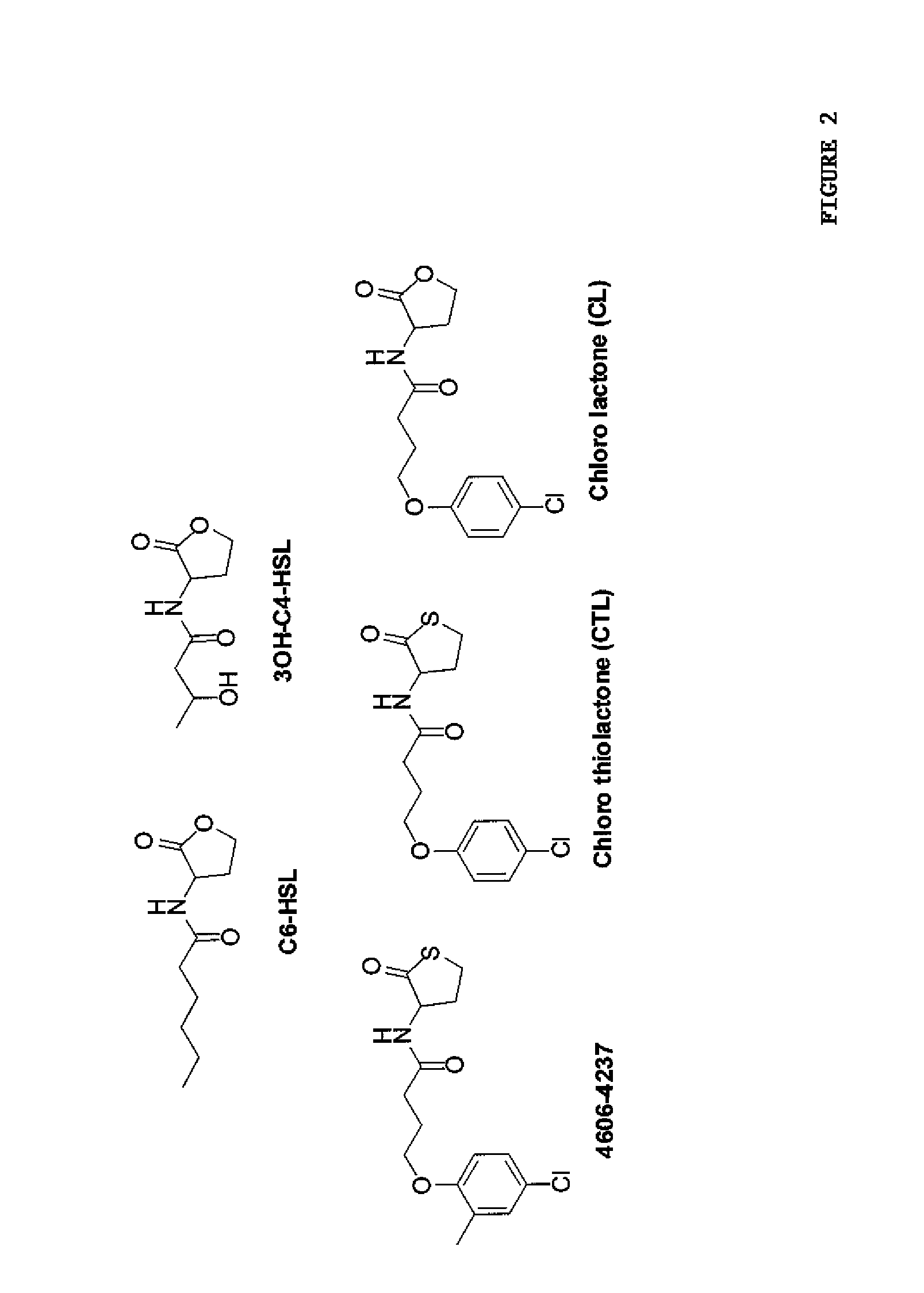
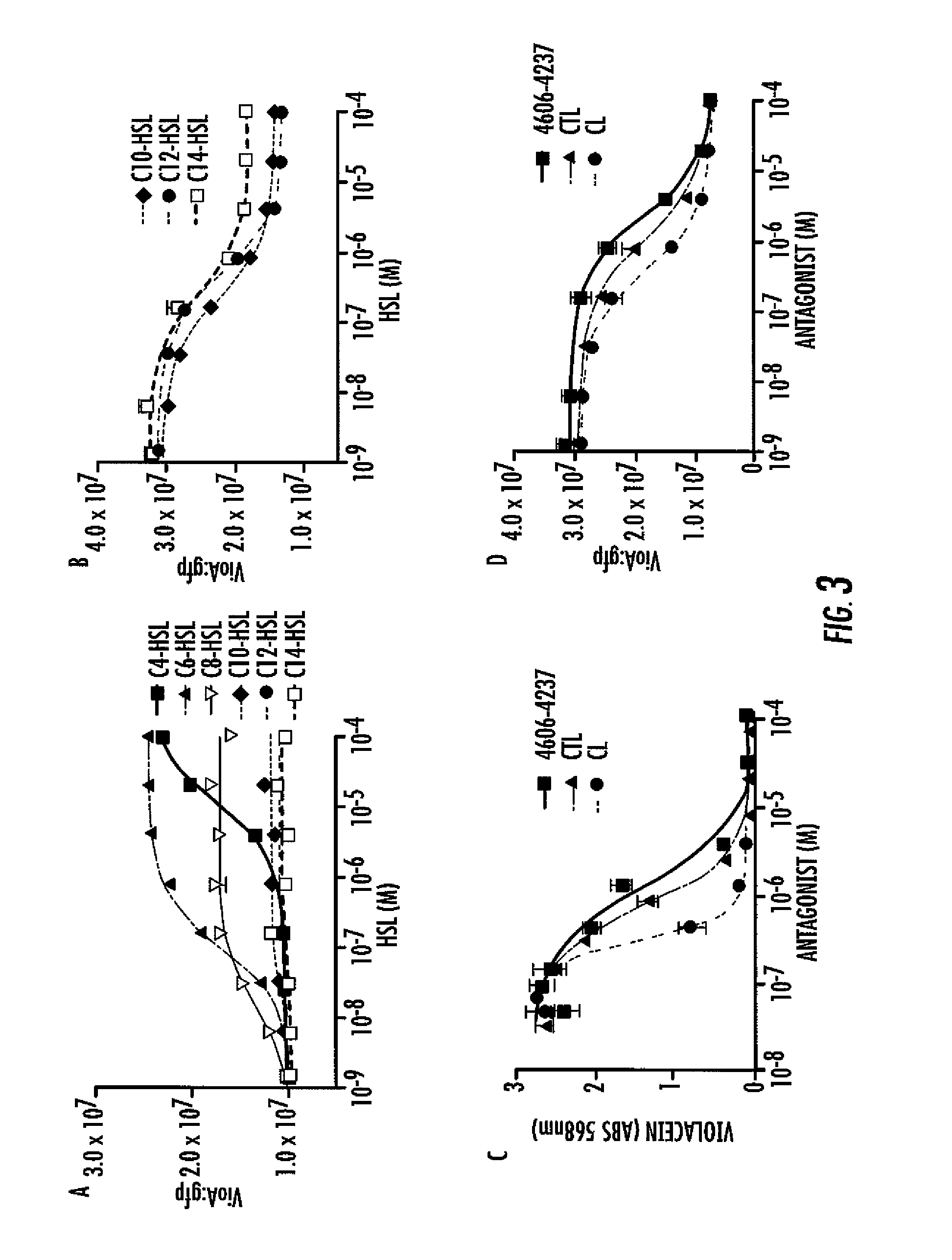
Small molecule antagonists of bacterial quorum-sensing receptors
A novel small molecule antagonizes two types of acyl homoserine lactone receptors: membrane-bound and cytoplasmic. A focused library of analogs and derivatives of the original antagonist was synthesized. Analog and derivative molecules harbor a range of activities. The novel small molecule and most potent antagonist protects the eukaryote Caenorhabditis elegans from quorum-sensing-mediated killing by the bacterial pathogen Chromobacterium violaceum. The saving of C. elegans demonstrates the use of these molecules as small molecule antimicrobials.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
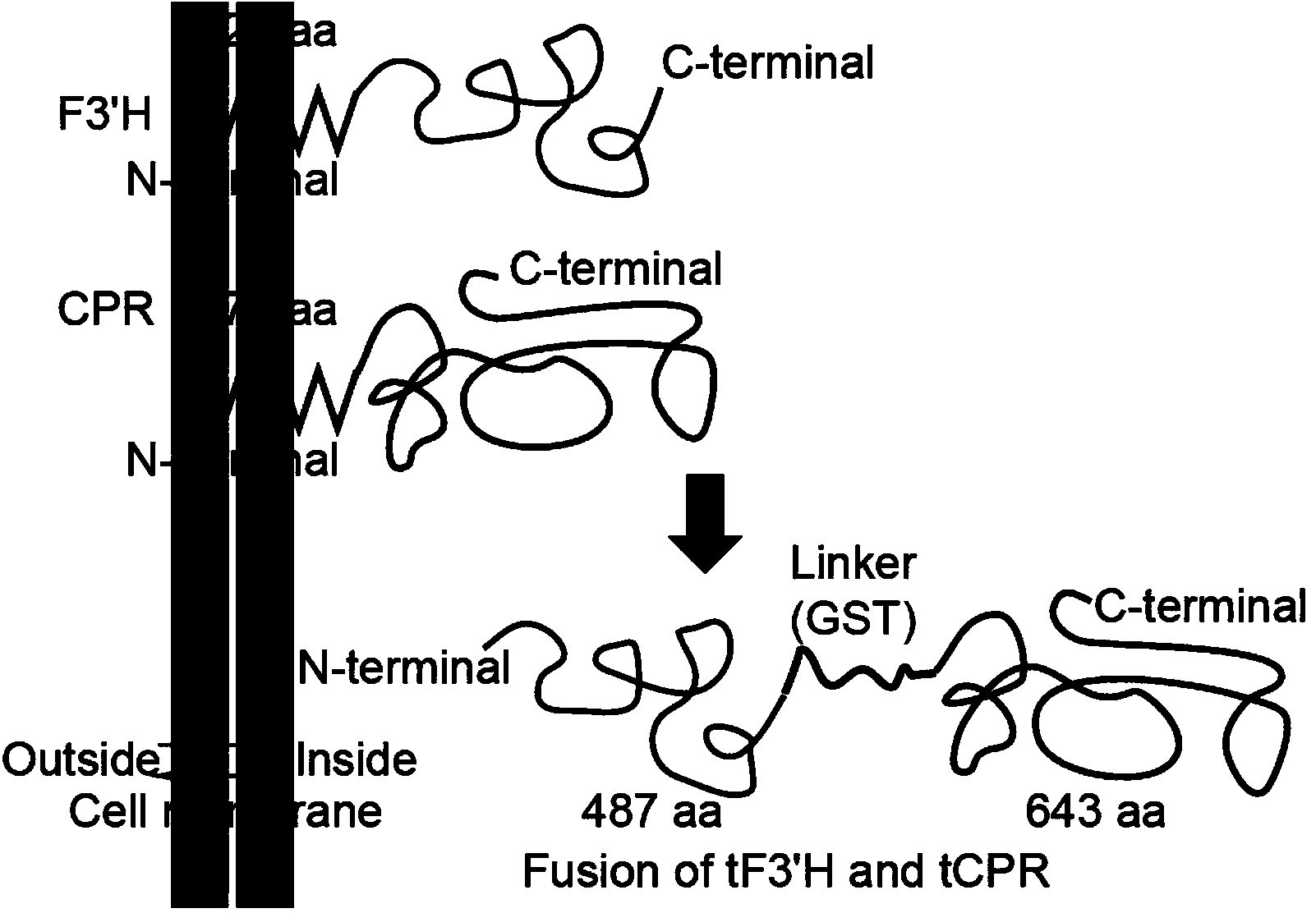
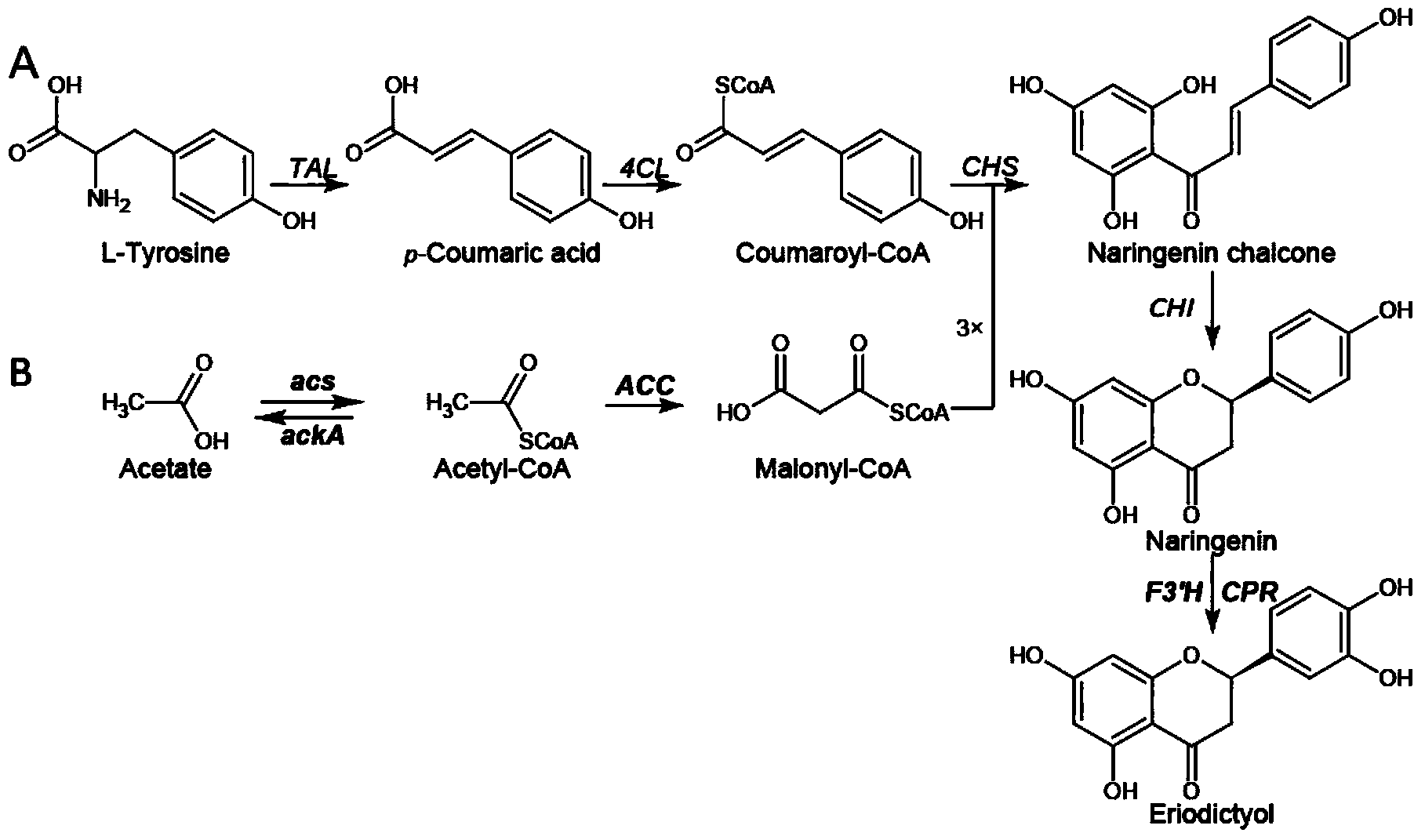
Method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering
ActiveCN103865864AReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
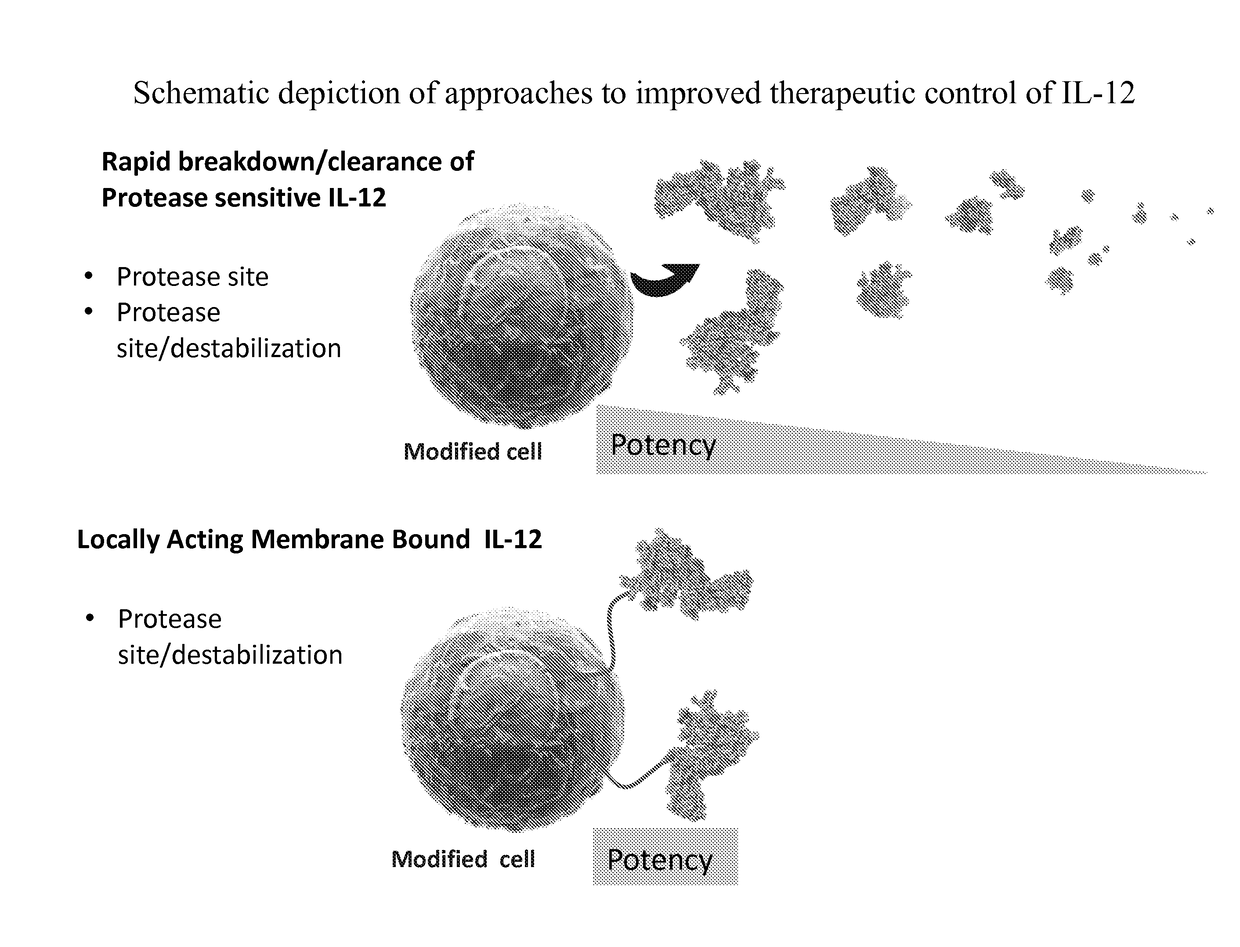
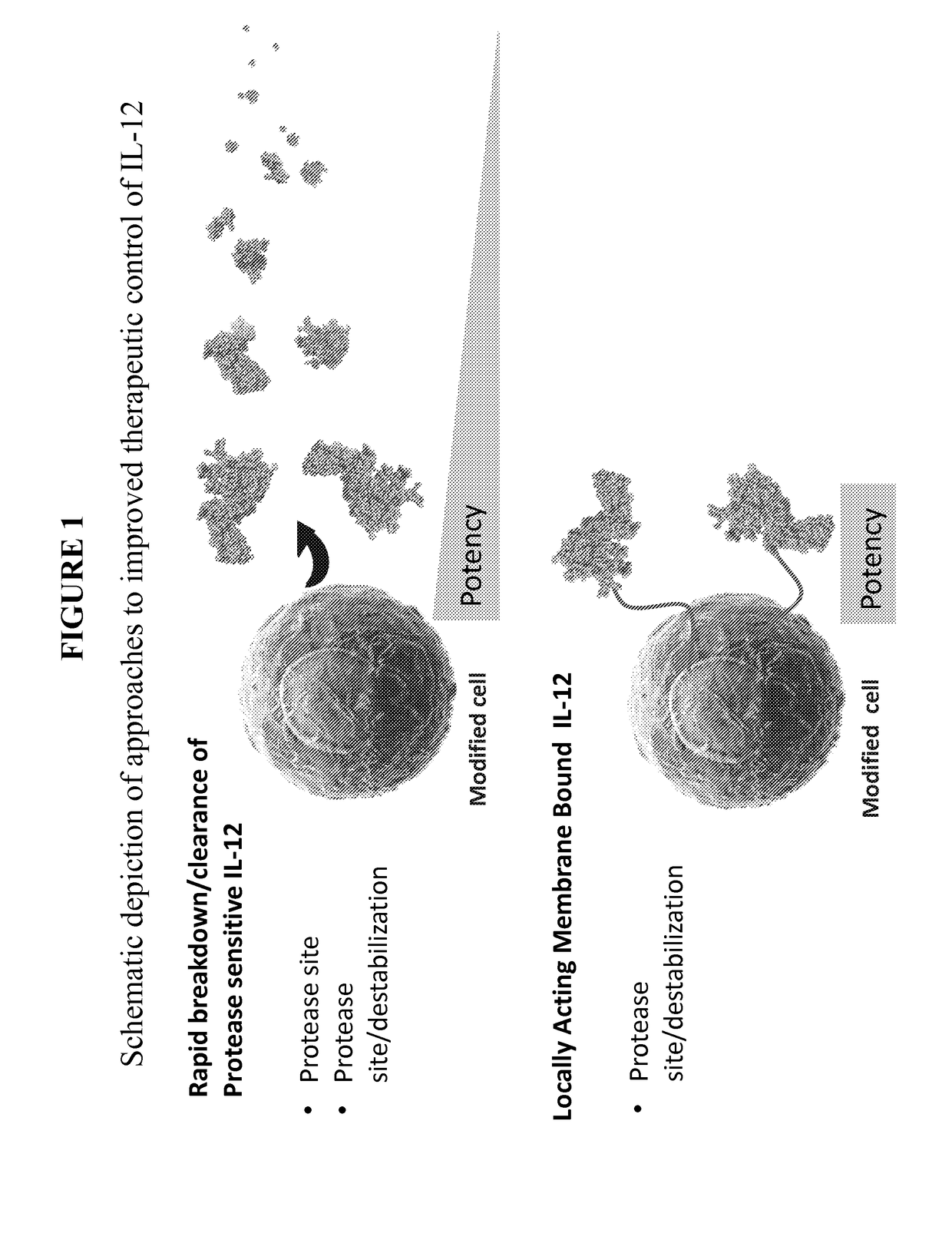
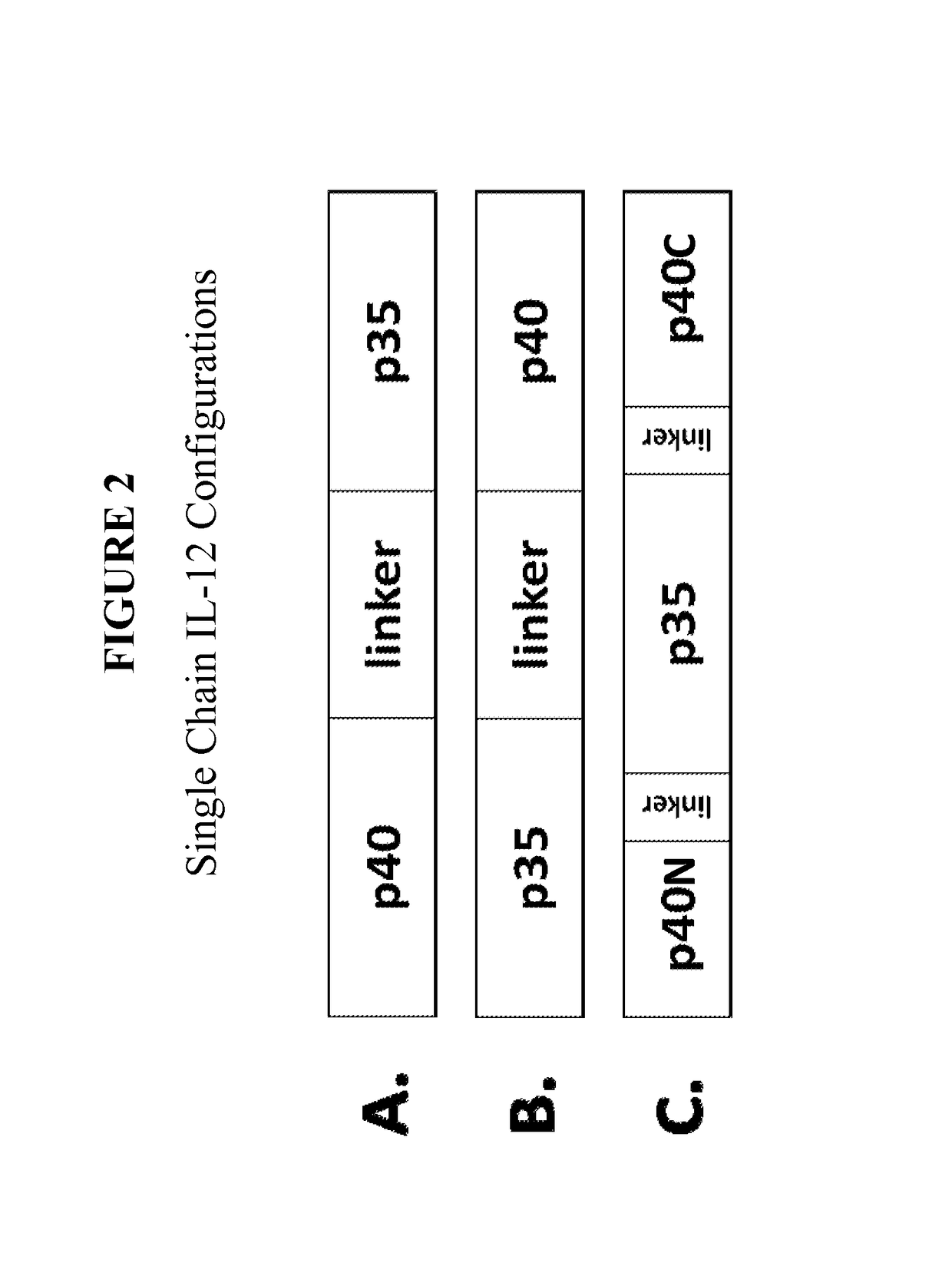
Improved therapeutic control of heterodimeric and single chain forms of interleukin-12
InactiveUS20170291934A1Shortened in vivo half-lifeEnhanced localization of biological effectPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological testingWhite blood cellHalf-life
The present invention relates to modified forms of IL-12. These modified forms of IL-12 may be engineered to have a shortened in vivo half-life compared and / or enhanced localization of biological effects compared to that of corresponding non-modified form of IL-12. Short half-life and membrane bound forms of IL-12 may provide greater therapeutic control for in vivo therapeutic delivery, in particular when used in combination with ligand inducible delivery of IL-12. Modified forms of IL-12 engineered to have shortened in vivo half-life and / or enhanced localization of biological effects include heterodimeric p35 / p40, single chain and membrane bound forms of IL-12 wherein a naturally occurring IL-12 amino acid sequence is genetically modified to enhance susceptibility of the IL-12 molecule to in vivo proteolytic degradation.
Owner:PRECIGEN INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com