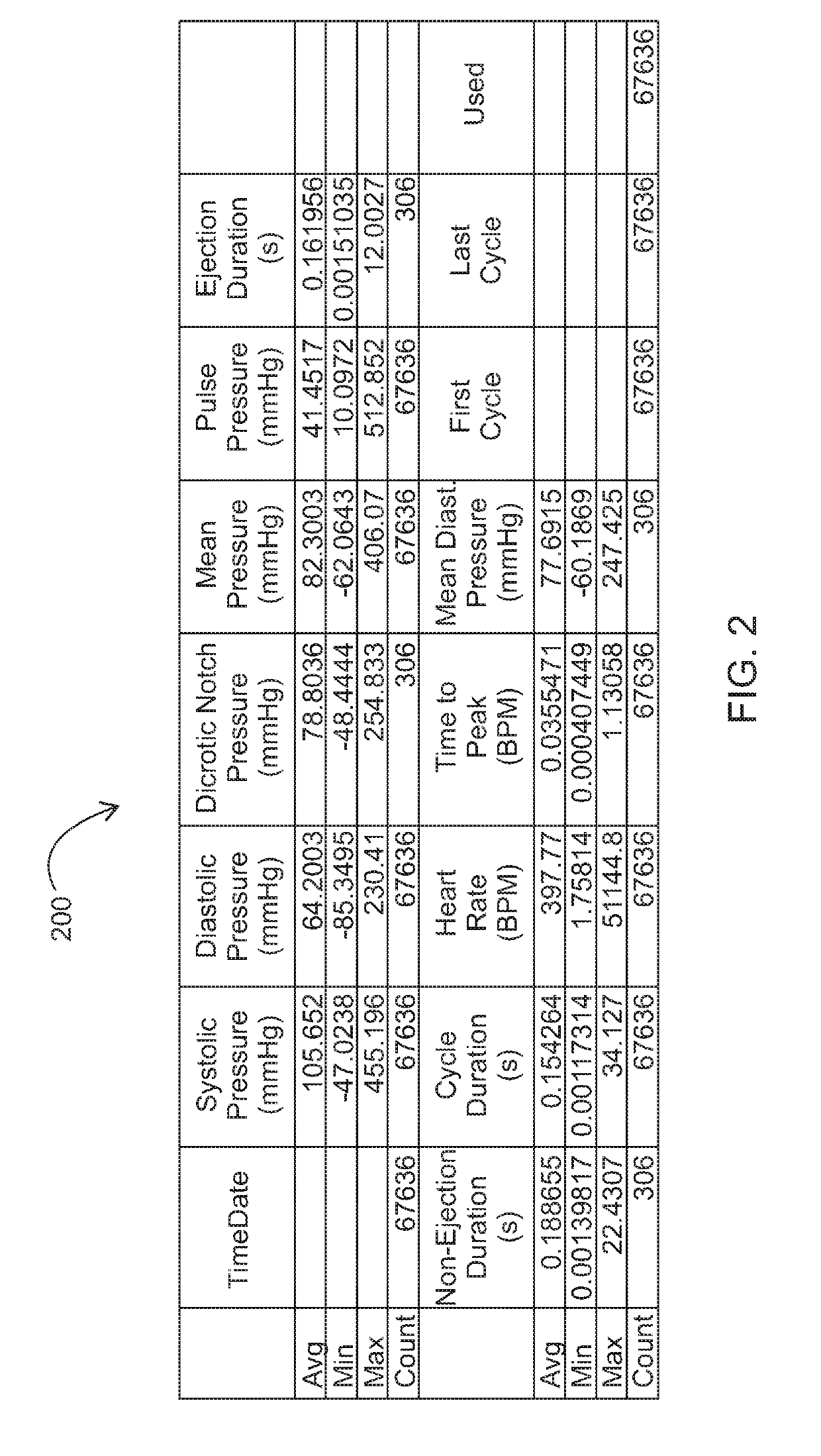
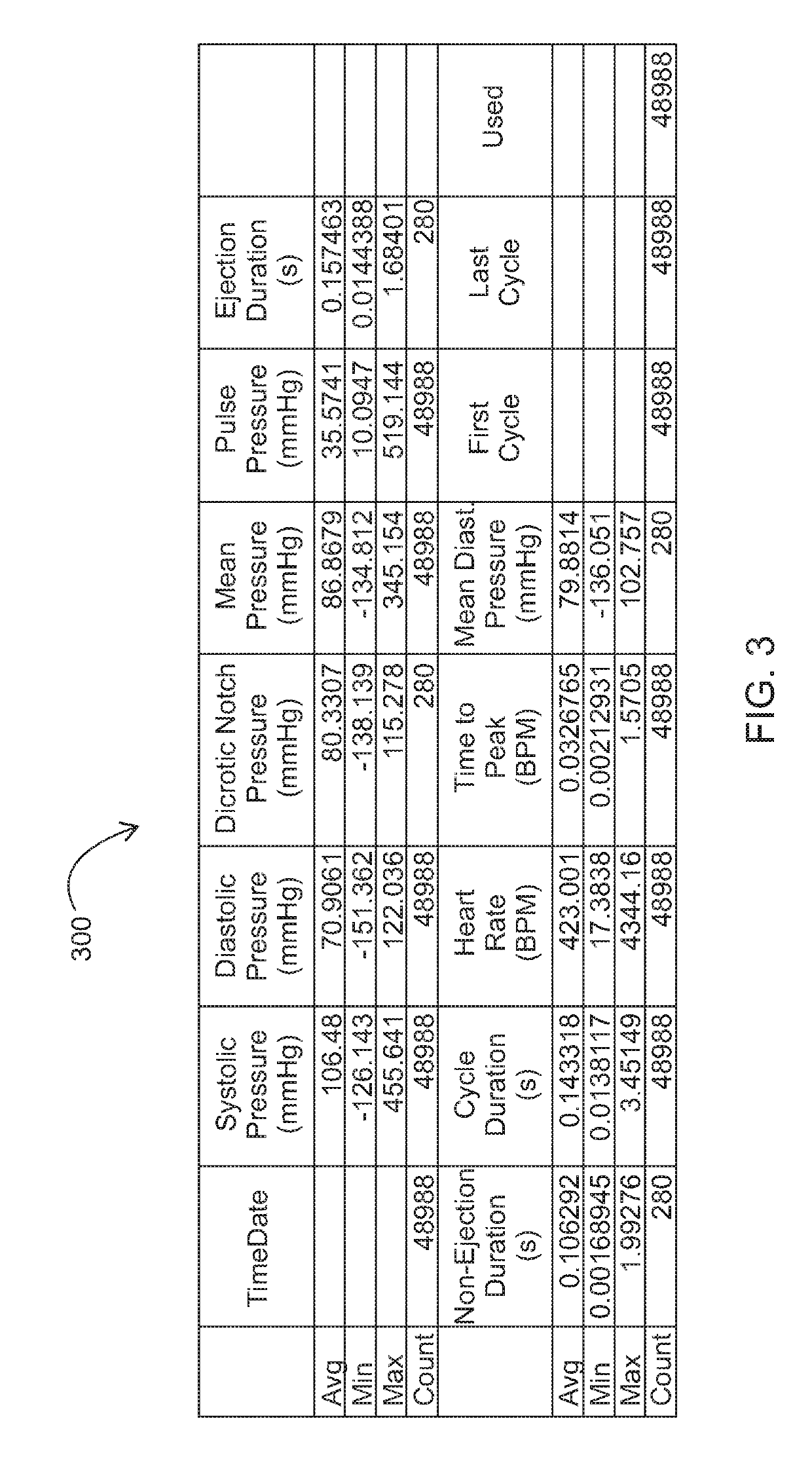
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Membrane bound protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Membrane-bound protein. A protein that is part of a cell membrane and acts as a receptor for substances transported in extracellular fluid or as an agent that mediates the transport of chemicals into or out of the cell.
Oral delivery systems for microparticles
PCT No. PCT / AU92 / 00141 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 30, 1992 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 30, 1992 PCT Filed Apr. 2, 1992 PCT Pub. No. WO92 / 17167 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 15, 1992There are disclosed complexes and compositions for oral delivery of a substance or substances to the circulation or lymphatic drainage system of a host. The complexes of the invention comprise a microparticle coupled to at least one carrier, the carrier being capable of enabling the complex to be transported to the circulation or lymphatic drainage system via the mucosal epithelium of the host, and the microparticle entrapping or encapsulating, or being capable of entrapping or encapsulating, the substance(s). Examples of suitable carriers are mucosal binding proteins, bacterial adhesins, viral adhesins, toxin binding subunits, lectins, Vitamin B12 and analogues or derivatives of Vitamin B12 possessing binding activity to Castle's intrinsic factor.
Owner:ACCESS PHARMA
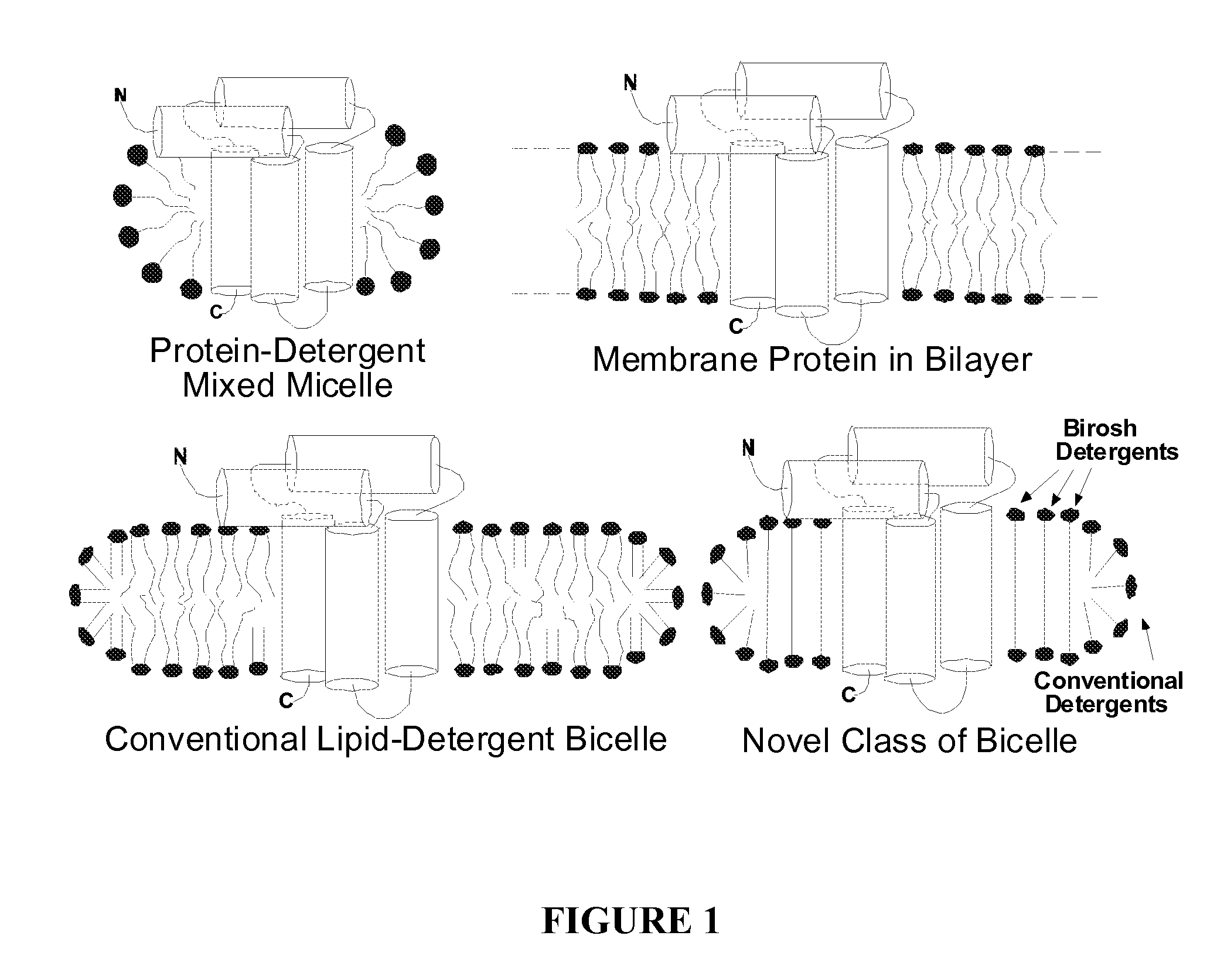
Amphiphilic agents for membrane protein solubilization
InactiveUS6172262B1Hydrolysed protein ingredientsAntibiotics chemistryMembrane bound proteinAmphiphilic Agents
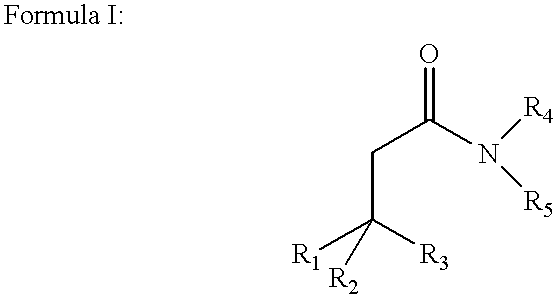
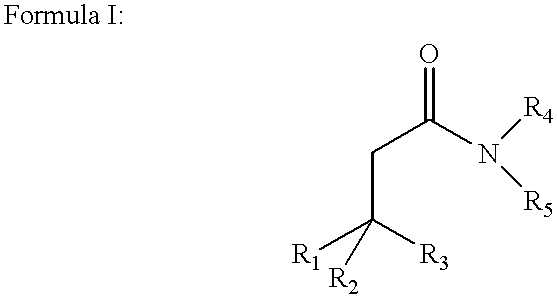
Disclosed are amphiphilic compounds comprising Formula I:wherein R1, R2, and R3 are C2-C12 straight or branched alkyl; unsubstituted phenyl, biphenyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkenyl; or phenyl, biphenyl, C3-C8 cycloalkyl, or C3-C8 cycloalkenyl substituted with one, two, or three C1-C6 straight or branched alkyl groups; or R1 and R2 combined are C3-C8 cycloalkyl, C3-C8 cycloalkenyl; or C3-C8 cycloalkyl or C3-C8 cycloalkenyl substituted with one, two, or three C1-C6 straight or branched alkyl groups; one of R4 or R5 is selected from the group consisting of C2-C6-straight or branched alkyl-(dimethyl-N-oxide), alkyl-(dimethylamine), alkyl-(trimethylammonium), alkyl-glucosyl, alkyl-maltosyl, glucosyl, maltosyl, and polyethylene(glycosyl); the other of R4 or R5 is selected from the group consisting of H, C2-C6 straight or branched alkyl or alkenyl, C2-C6-straight or branched alkyl-(dimethyl-N-oxide); alkyl-(dimethylamine), alkyl-(trimethylammonium), alkyl-glucosyl, alkyl-maltosyl, glucosyl, maltosyl, and polyethylene(glycosyl); and salts thereof. The compounds are detergents useful in the solubilization of membrane-bound proteins.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Processing for producing and crystallizing G-protein coupled receptors
InactiveUS20060188964A1High yieldGood luminous yieldCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesAntibodyMembrane bound protein
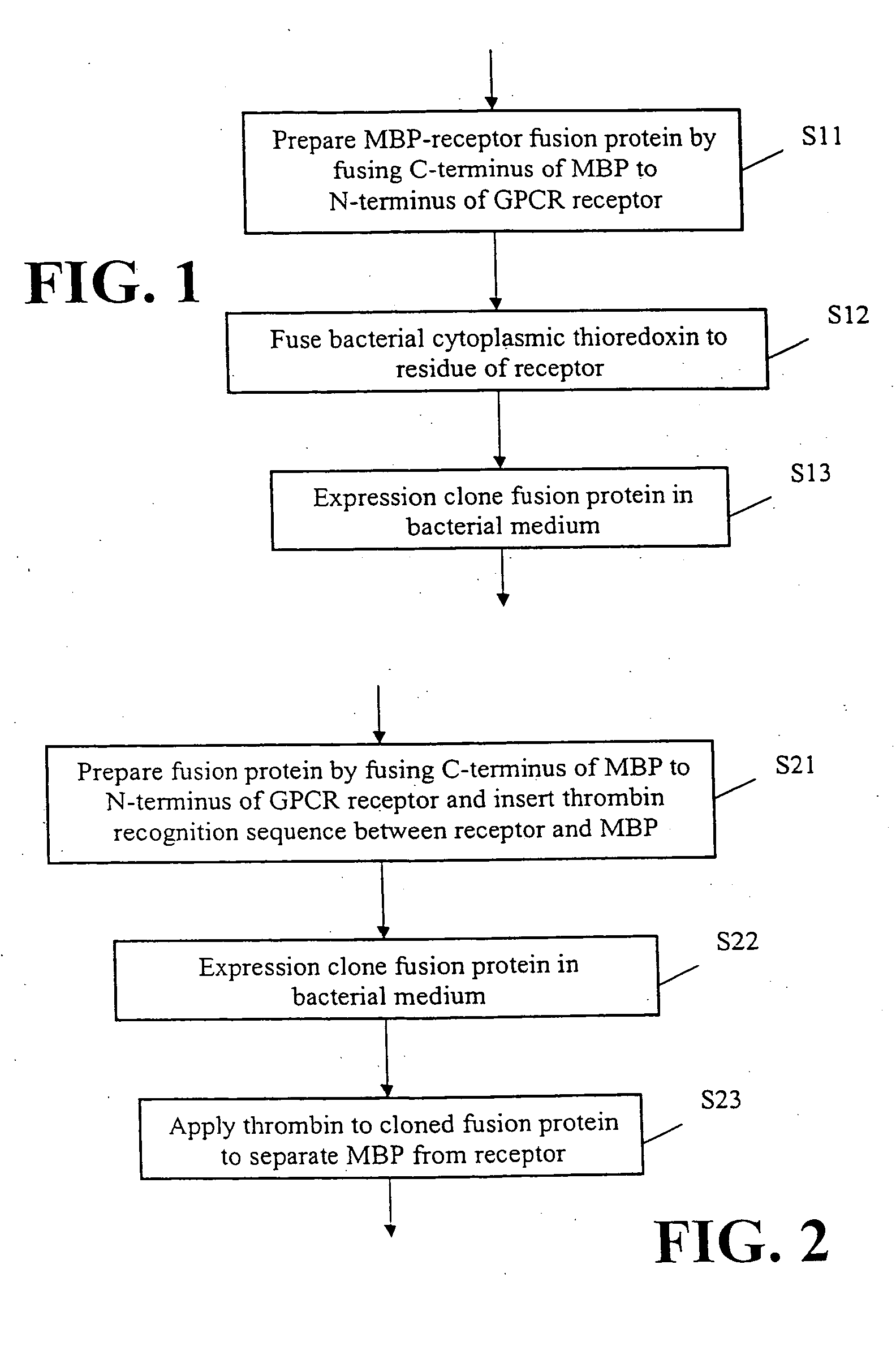
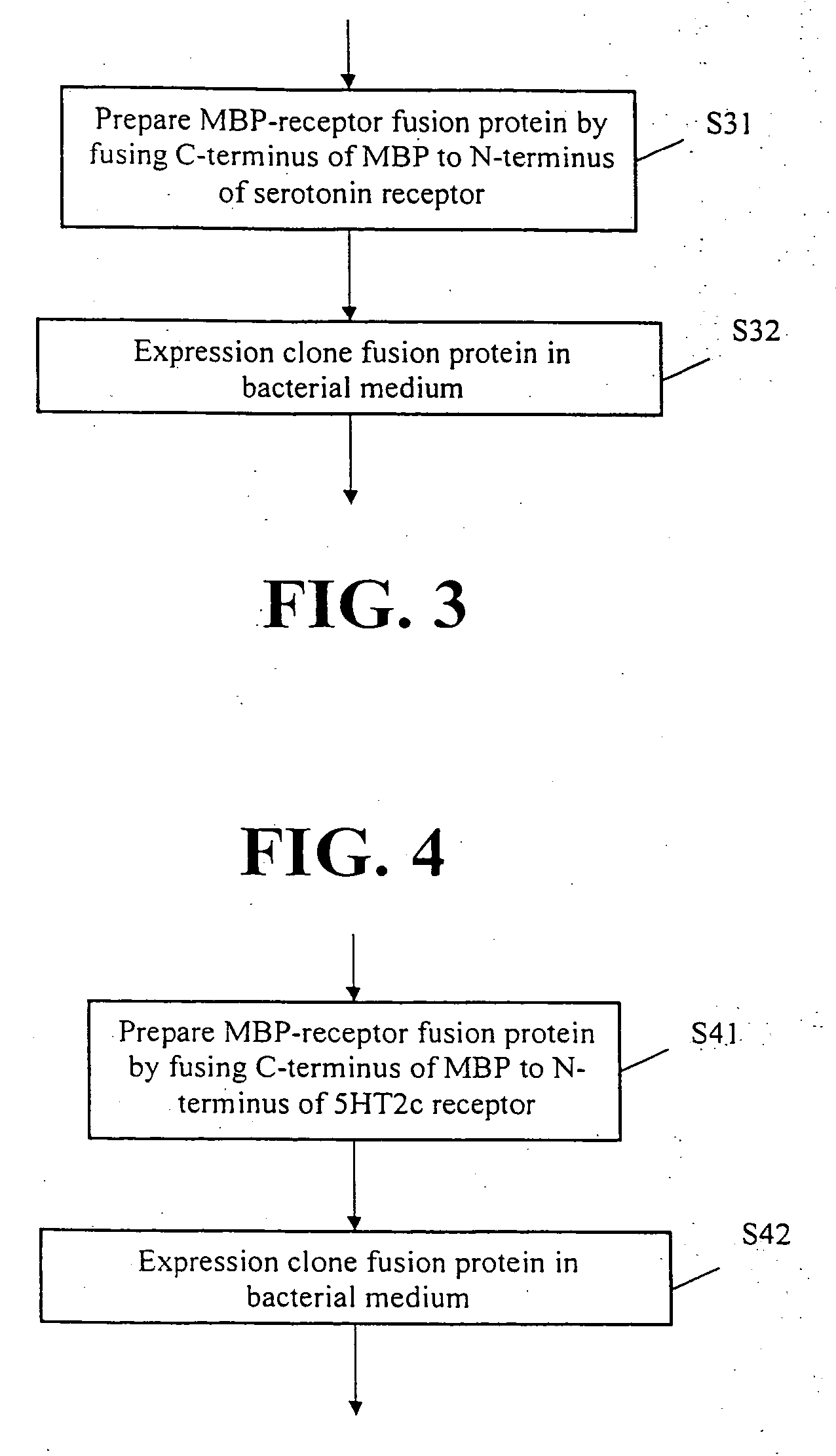
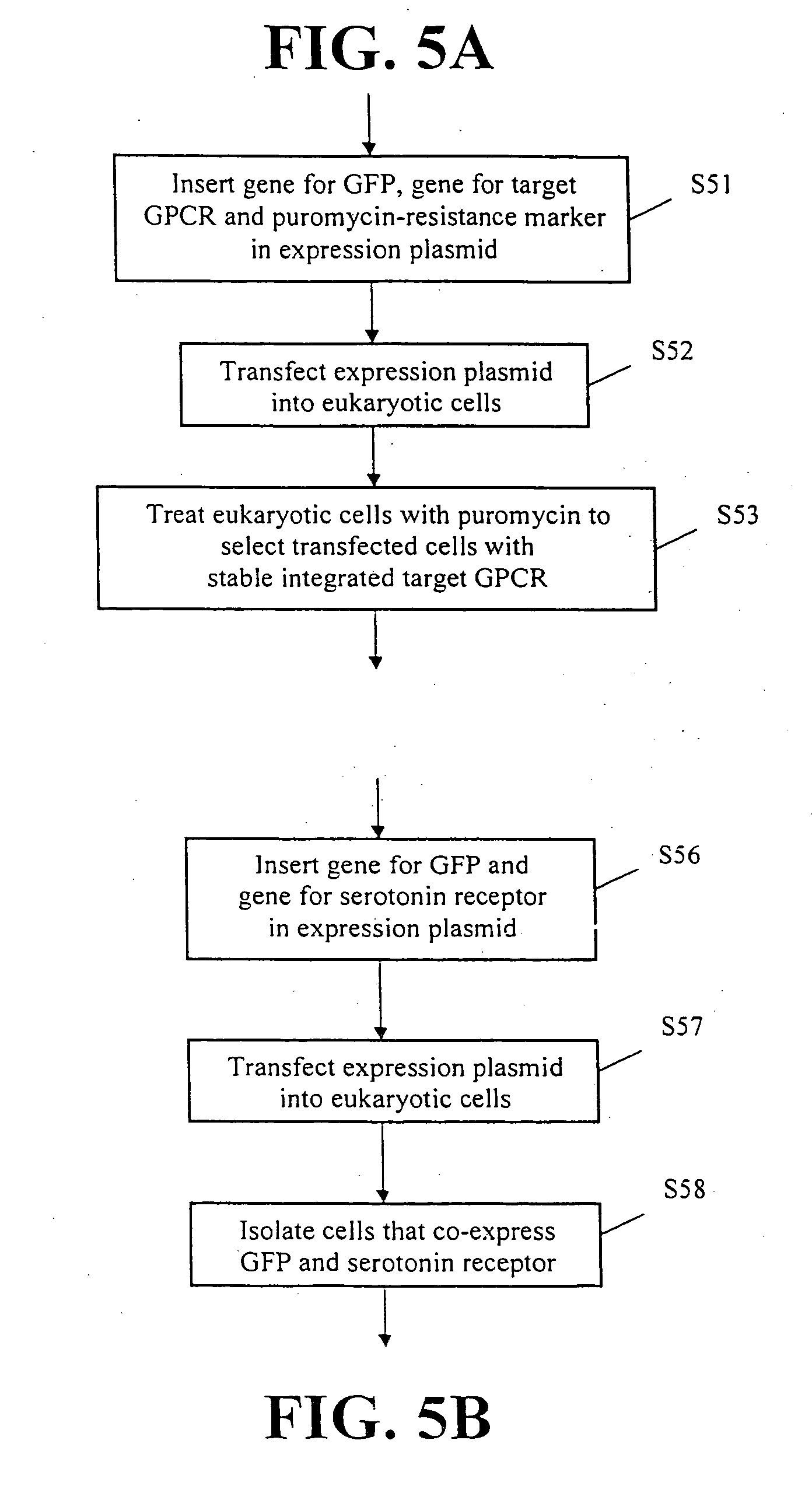
This invention provides methods for producing a membrane-bound protein in mammalian cells. This invention also provides nucleic acids for making novel fusion proteins (e.g., GPCR fusion proteins). This invention further provides related bacterial expression vectors; expression methods; fusion proteins; bacterial cells; GPCR vector screens; bacterial spheroplasts; methods for making anti-GPCR antibodies; and GPCR binding screens. This invention also provides a method for identifying a reagent in which a membrane protein is likely to crystallize. Finally, this invention provides methods for producing crystals of a protein which, in a cell, is a membrane-bound protein.
Owner:MANCIA FILIPPO +3
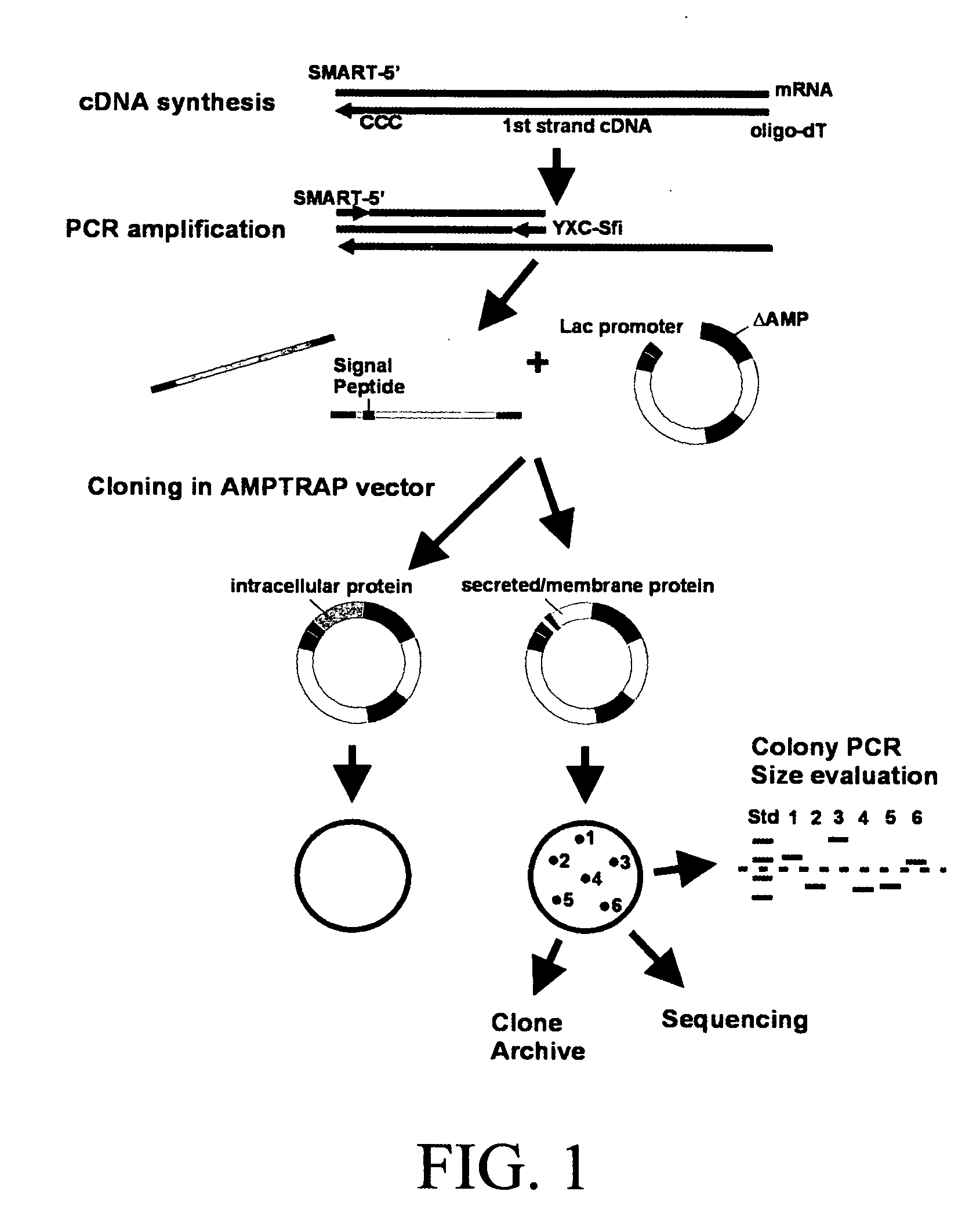
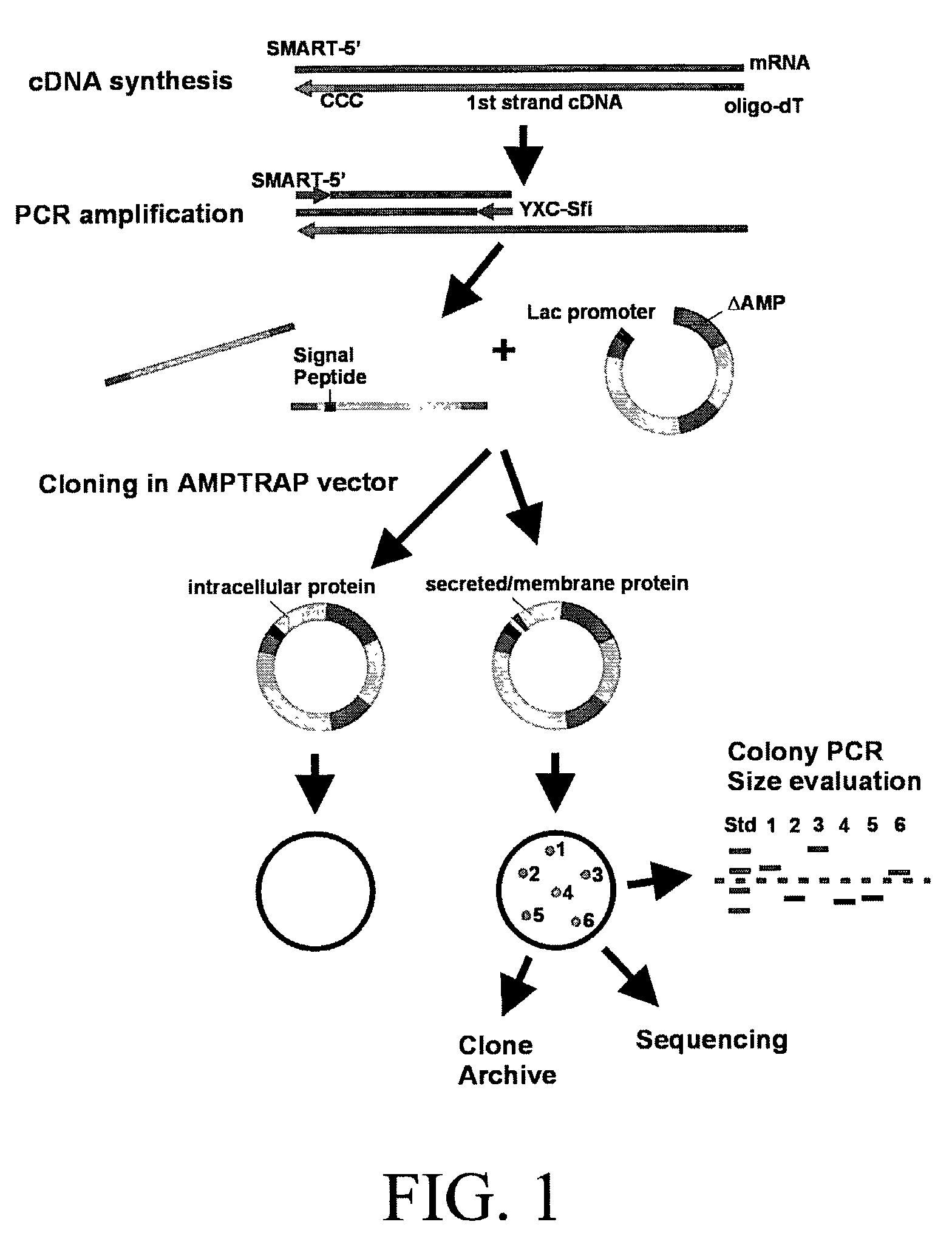
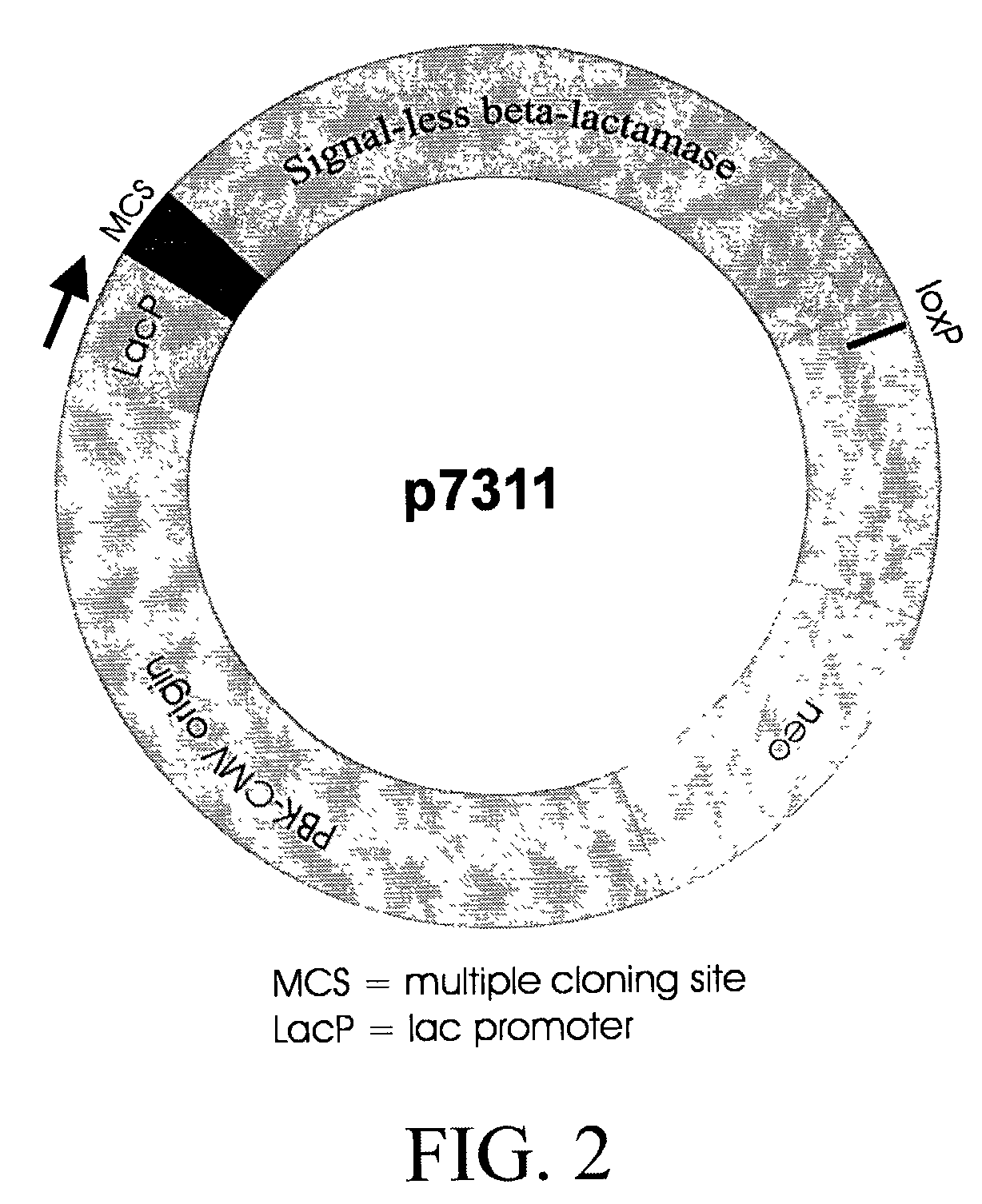
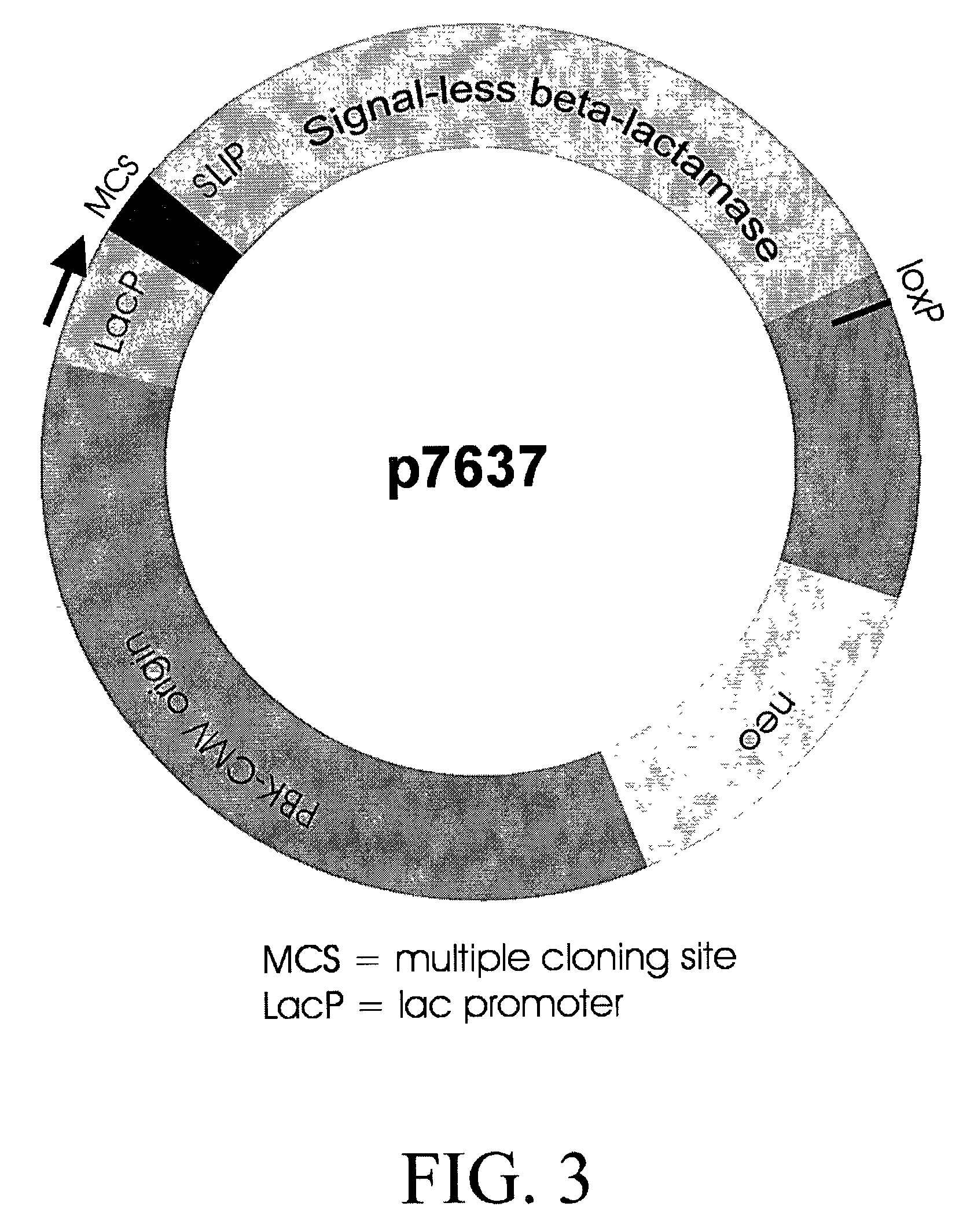
Method for identification of cDNAs encoding signal peptides
InactiveUS20020127557A1Fast wayBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening techniquesPresent method
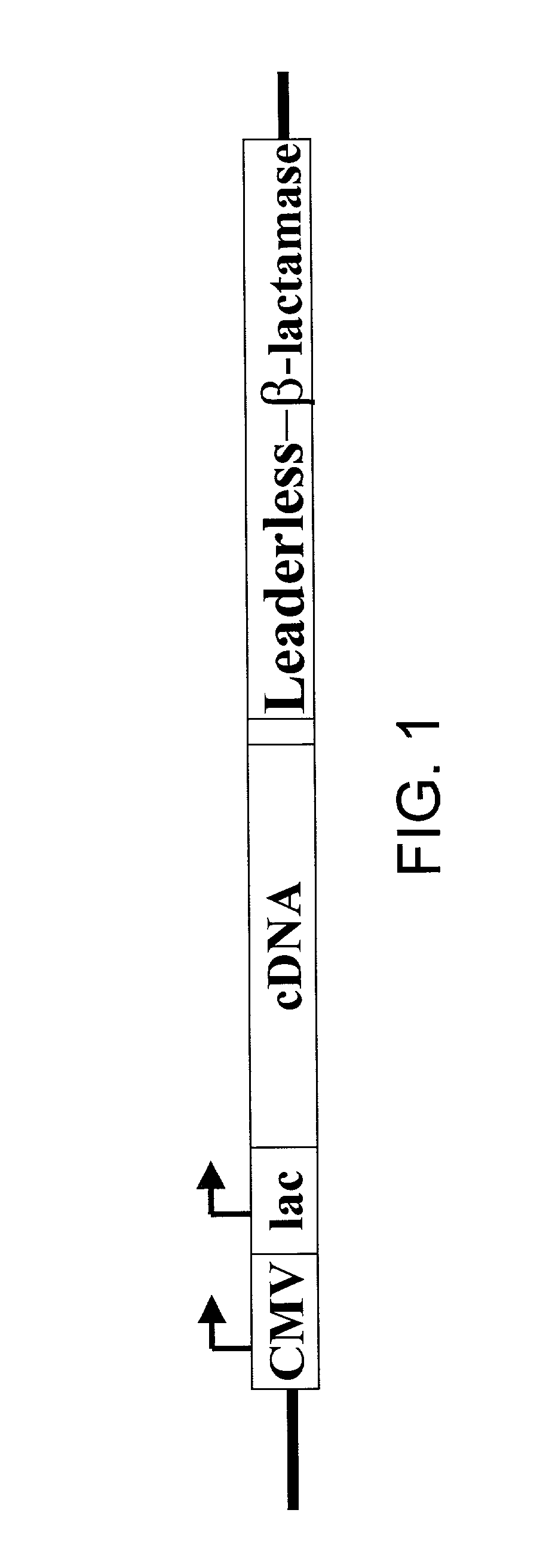
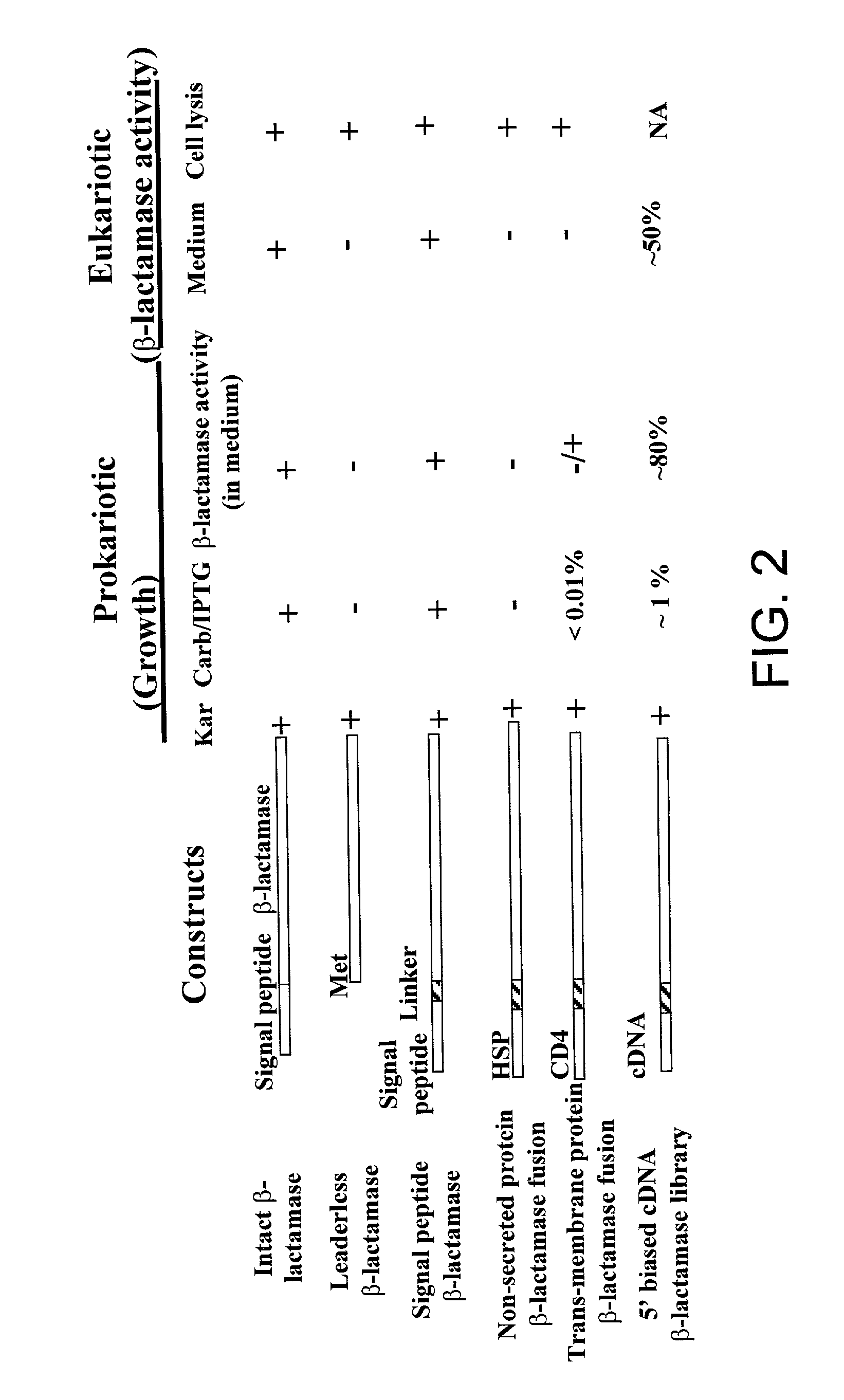
The present invention provides a method in which cDNAs that encode signal sequences for secreted or membrane-associated proteins are isolated using a fusion protein that directs secretion of a molecule that provides antibiotic resistance, e.g., .beta.-lactamase. The present method allows the isolation of signal peptide-associated proteins that may be difficult to isolate with other techniques. Moreover, the present method is amenable to throughput screening techniques and automation, and especially in validating the presence of the signal sequence via expression of the protein in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. This invention provides a powerful and approach to the large scale isolation of novel secreted proteins.
Owner:INCYTE CORP
Arrays of biological membranes and methods and use thereof
InactiveUS6977155B2Good biological affinityHigh affinityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCompound screeningG protein-coupled receptorBiological membrane
The present invention overcomes the problems and disadvantages associated with prior art arrays by providing an array comprising a plurality of biological membrane microspots associated with a surface of a substrate that can be produced, used and stored, not in an aqueous environment, but in an environment exposed to air under ambient or controlled humidities. Preferably, the biological membrane microspots comprise a membrane bound protein. Most preferably, the membrane bound protein is a G-protein coupled receptor, an ion channel or a receptor tyrosine kinase.
Owner:CORNING INC
Vector system for selection of genes encoding secreted proteins and membrane-bound proteins
InactiveUS20070111283A1Rapid and robust selectionImprove efficiencyBacteriaSugar derivativesVector systemENCODE
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
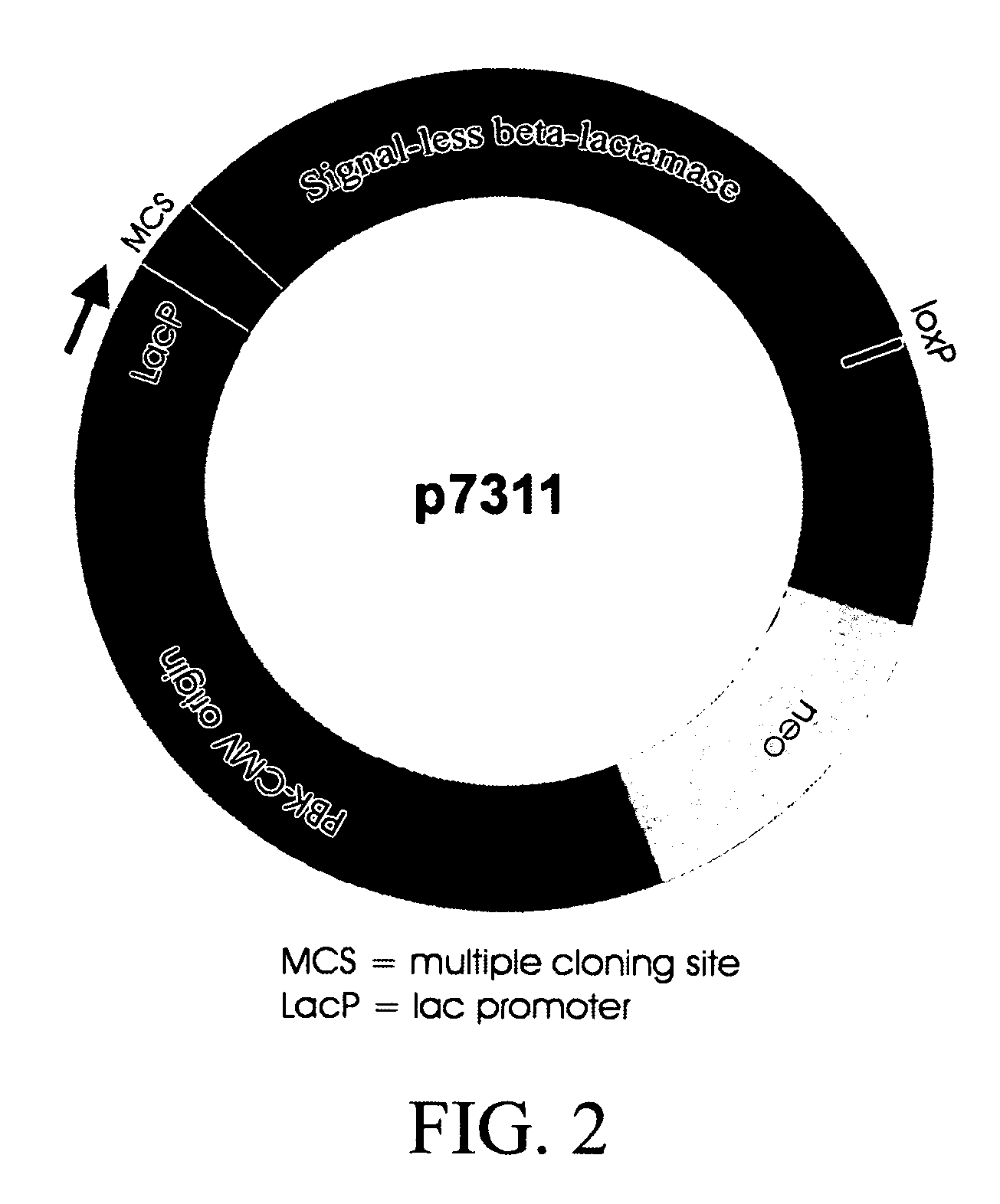
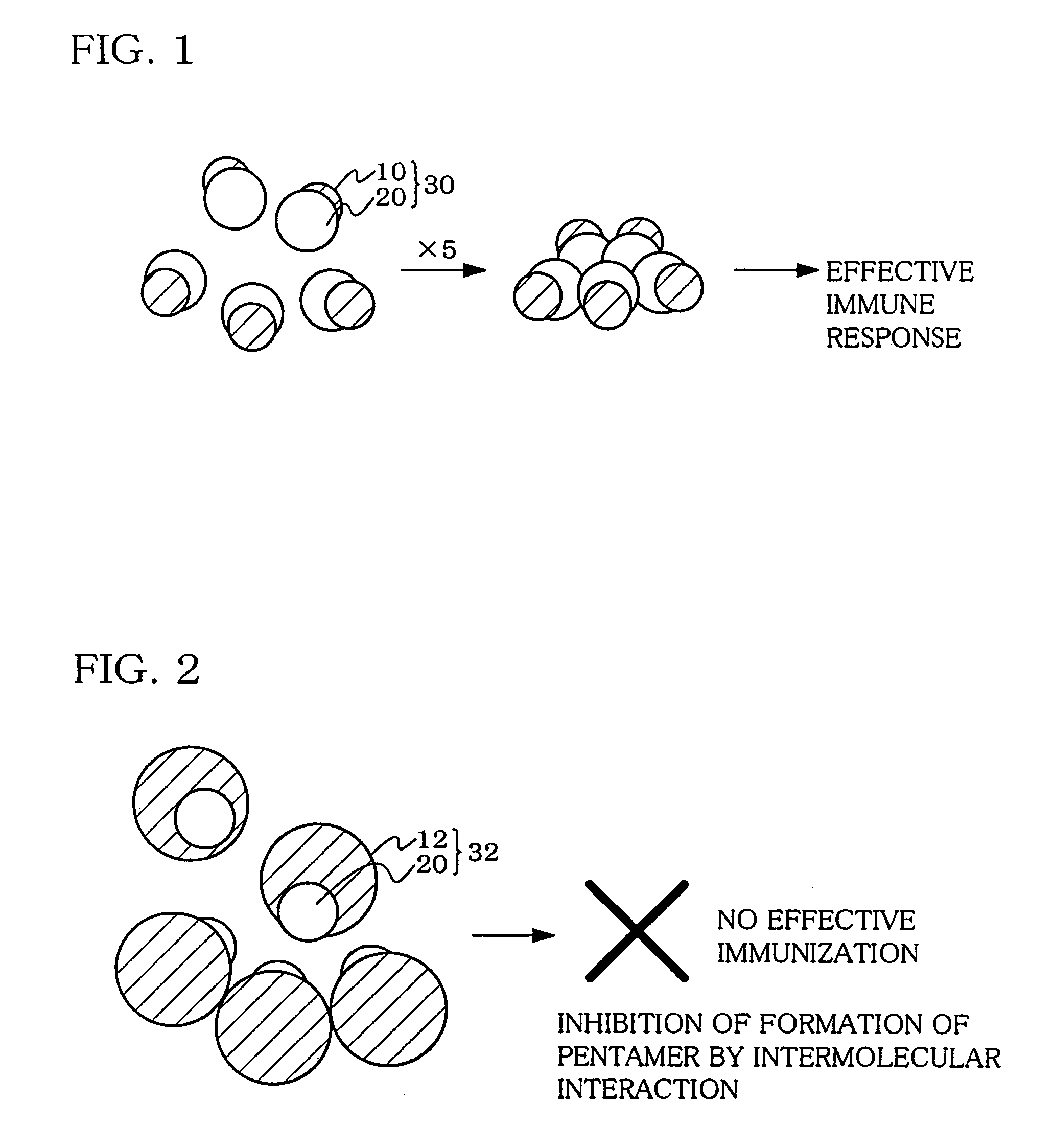
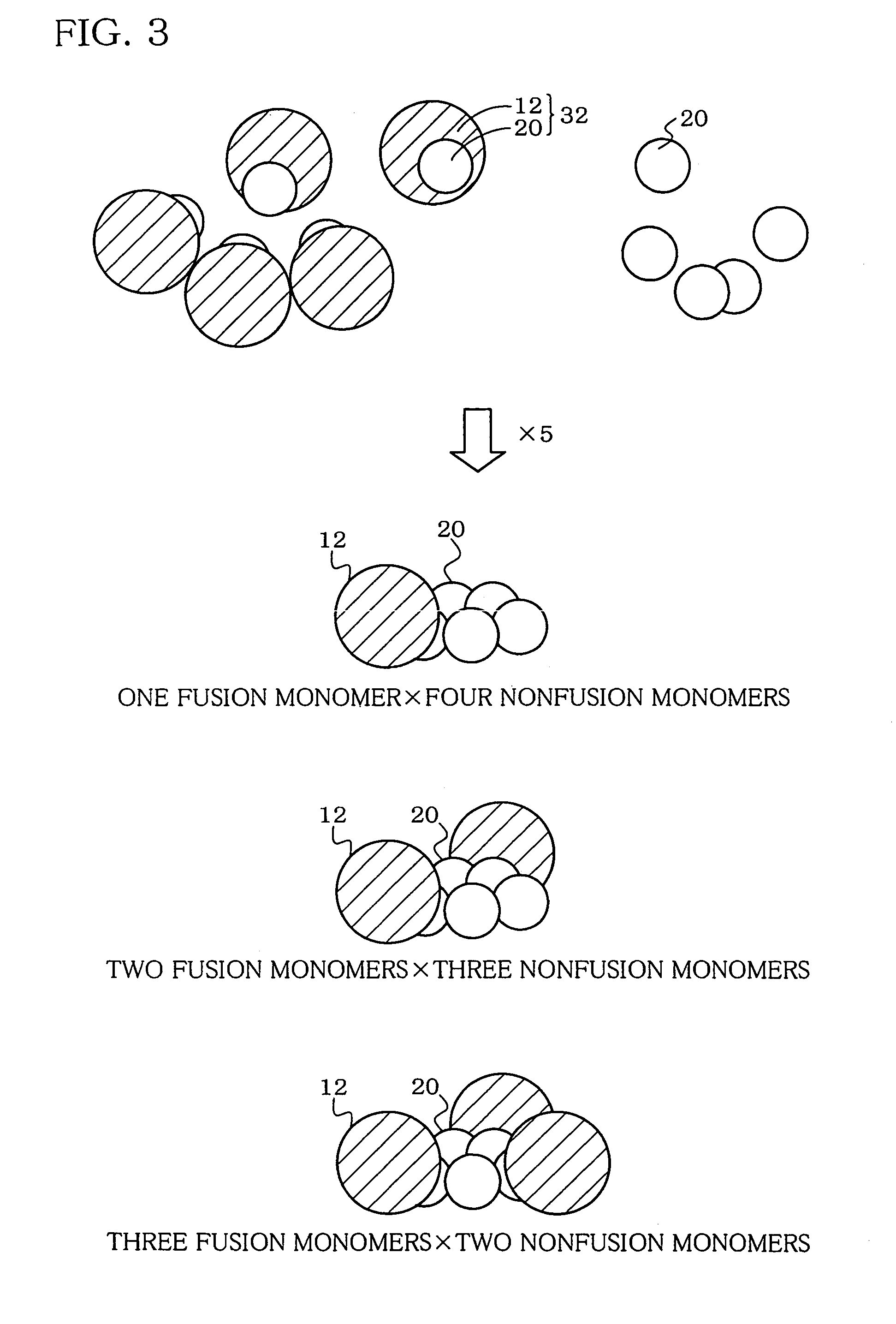
Hetero type pentamer recombinant vaccine
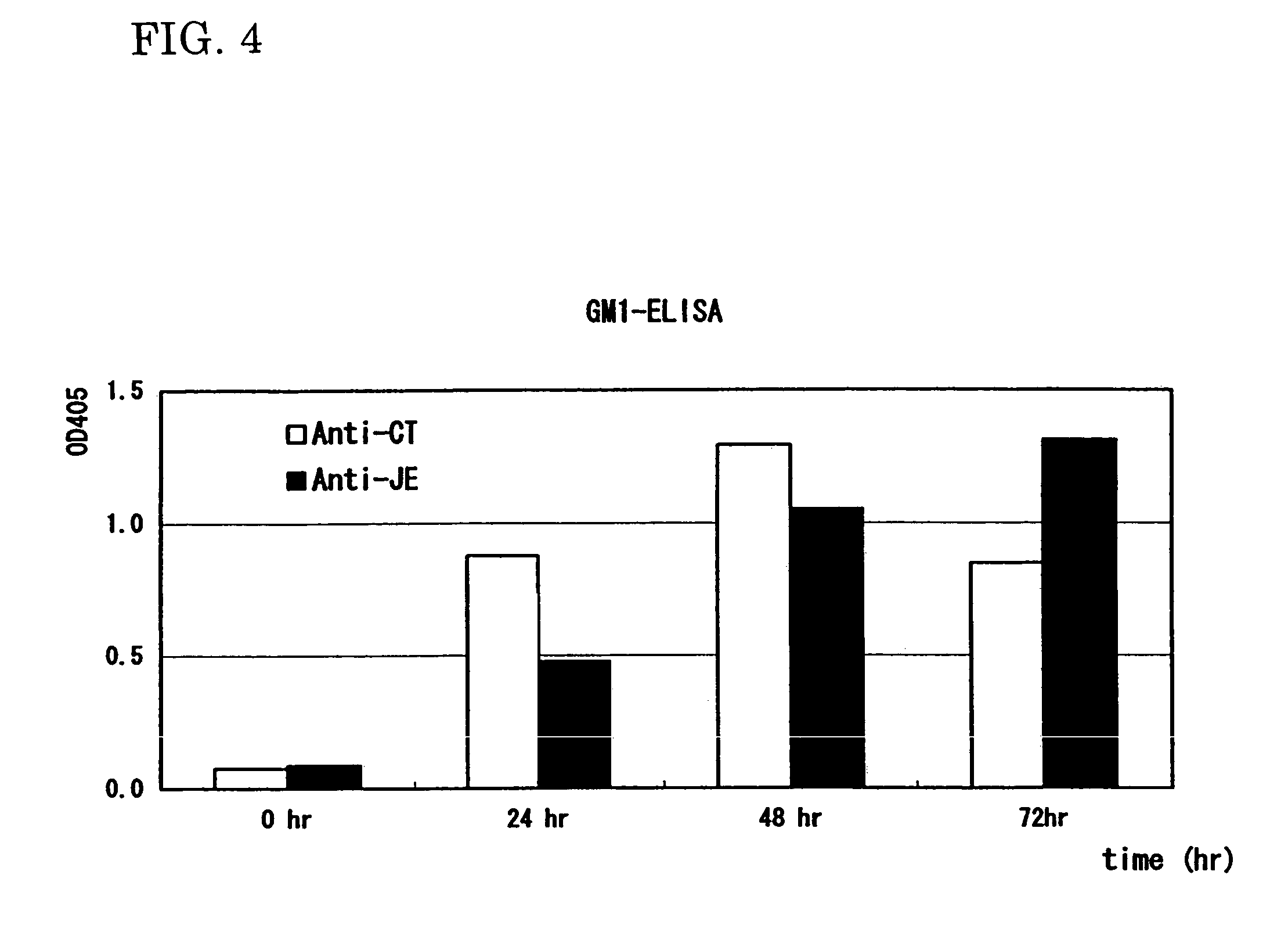
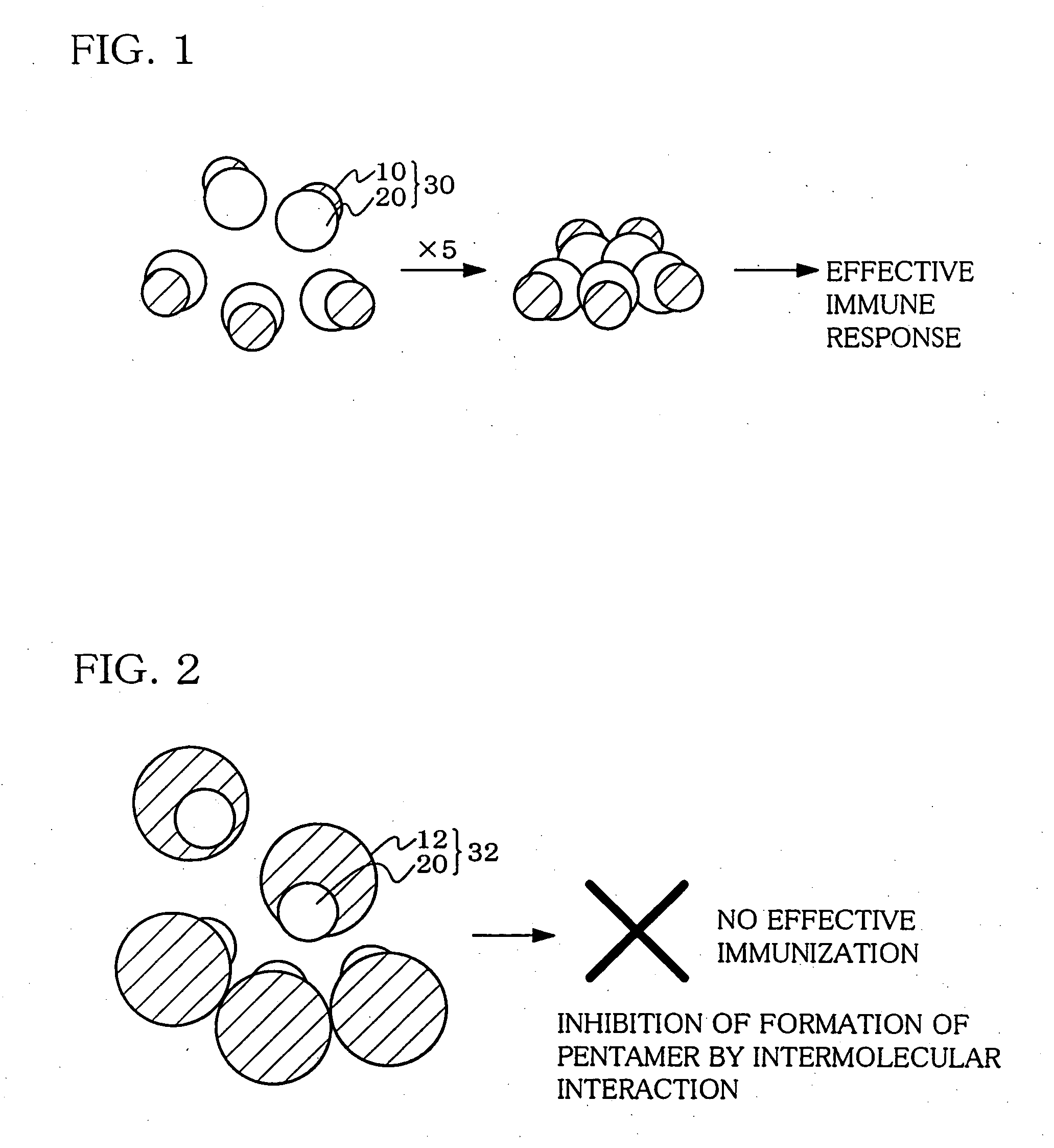
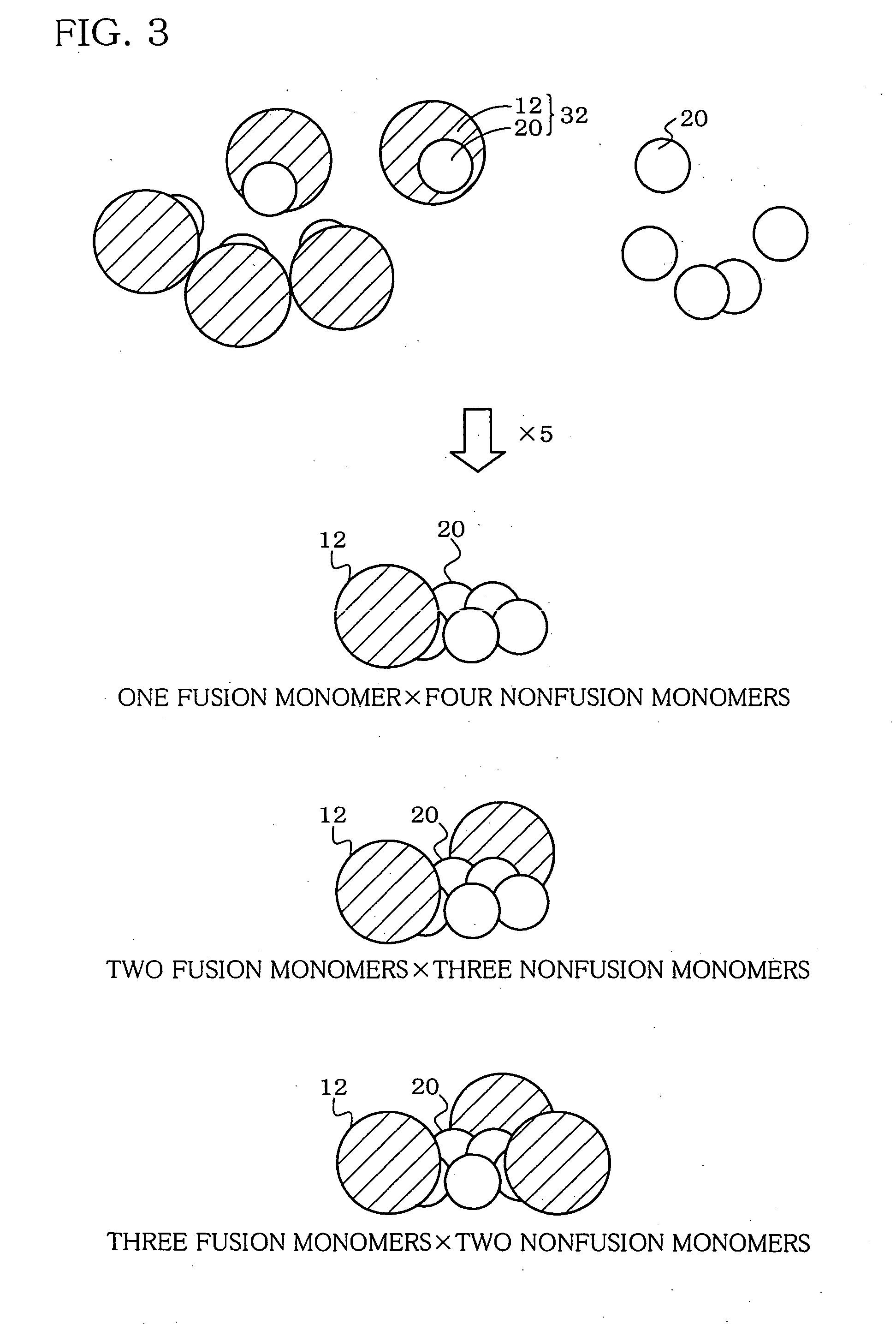
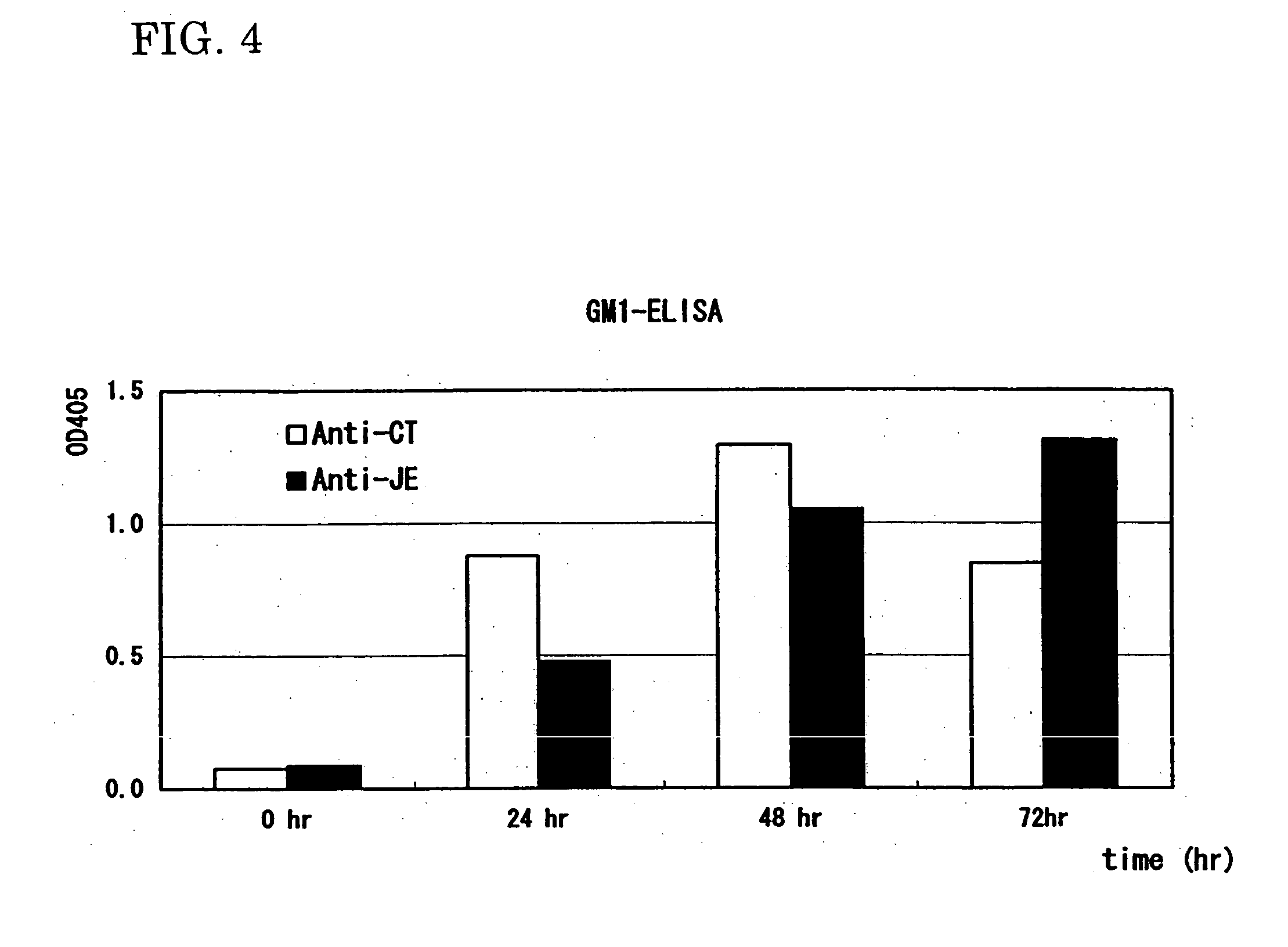
A heteropentamer composed of a fusion monomer (32) comprising a fusion protein of an antigenic amino acid sequence and an amino acid sequence of a monomer of a mucous membrane-binding protein and a nonfusion monomer (20) of an amino acid sequence of a monomer of a mucous membrane-binding protein. A homopentamer composed of a fusion monomer including a fusion protein of an antigen derived from an envelope protein of Japanese encephalitis virus and an amino acid sequence of a monomer of a mucous membrane-binding protein. These heteropentamer and the homopentamer can be used as a vaccine.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL BIOLOGICAL SCI INST +1
Multi-target chimeric antigen receptor
InactiveCN108250301AEliminate dependenciesReduced activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyTransmembrane domainChimeric antigen receptor
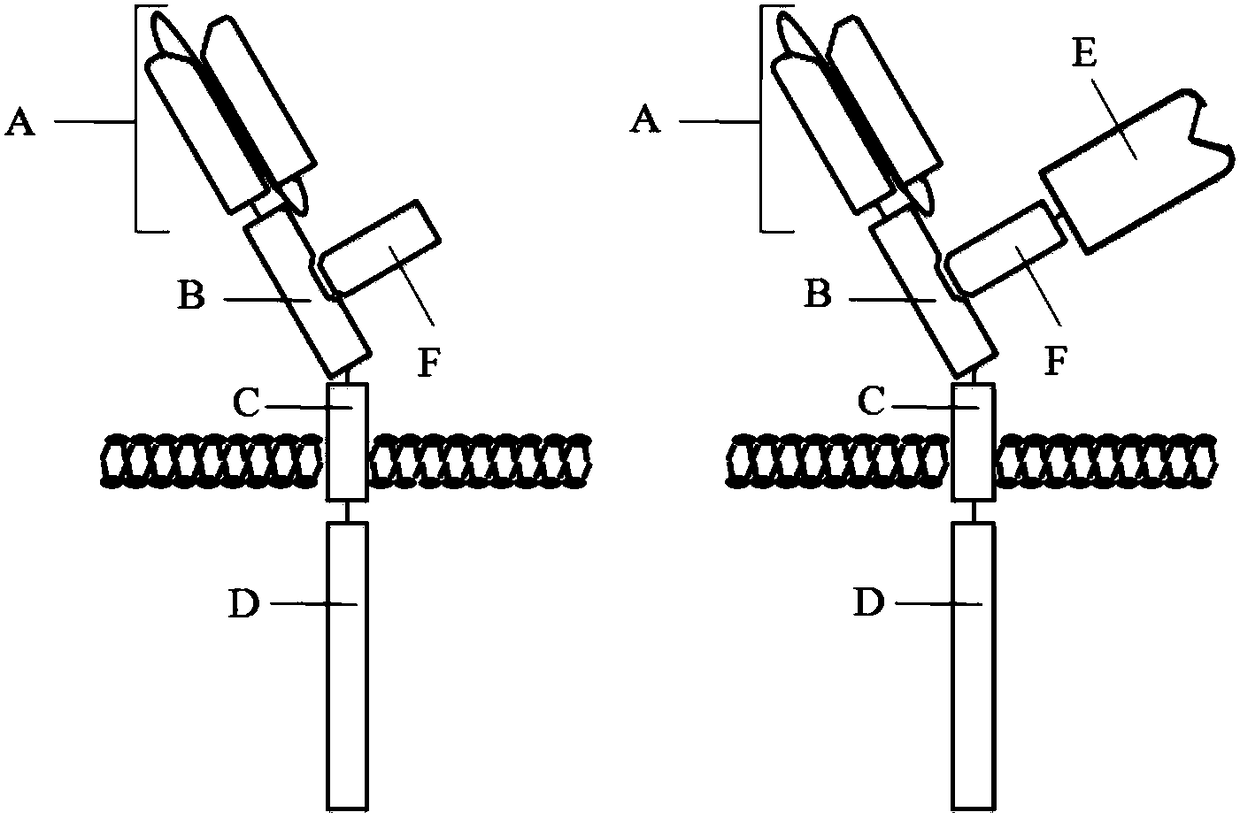
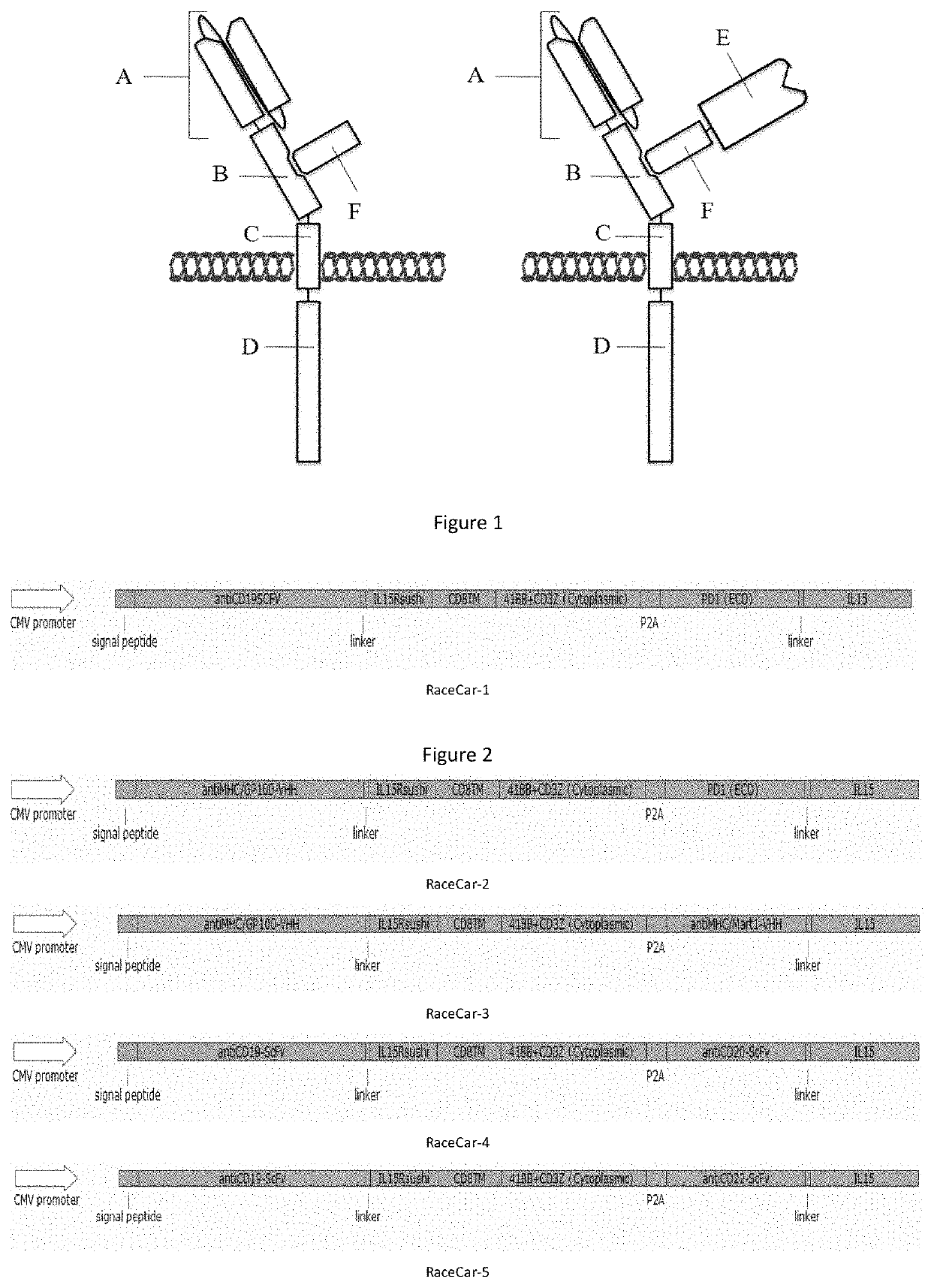
The invention discloses a multi-target chimeric antigen receptor. The multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention consists of a main peptide chain and an assistant peptide chain.The main peptide chain includes an antigen binding domain A, an assistant peptide chain connection domain B, a transmembrane domain C and an intracellular signal conduction domain D. The assistant peptide chain includes a main peptide chain connection domain F. The antigen binding domain A is a polypeptide with antigen-bonding function. The assistant peptide chain connection domain B and the mainpeptide chain connection domain F are mutually combined. The transmembrane domain C is the transmembrane domain of arbitrary membrane binding protein or the transmembrane domain of transmembrane protein. The intracellular signal conduction domain D includes a primary signal conduction region. The multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention can mediate specific cell killing bycombining two antigen binding domains with different antigens. Also a cytokine and cytokine receptor compound are introduced into the multi-target chimeric antigen receptor provided by the invention and can play the role of cytokines.
Owner:TIMMUNE BIOTECH INC
Arrays of biological membranes and methods and use thereof
InactiveUS20050260685A1Good biological affinityHigh affinityMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsG protein-coupled receptorThreonine
The present invention overcomes the problems and disadvantages associated with prior art arrays by providing an array comprising a plurality of biological membrane microspots associated with a surface of a substrate that can be produced, used and stored, not in an aqueous environment, but in an environment exposed to air under ambient or controlled humidities. Preferably, the biological membrane microspots comprise a membrane bound protein. Most preferably, the membrane bound protein is a G-protein coupled receptor, an ion channel, a receptor serine / threonine kinase or a receptor tyrosine kinase.
Owner:FANG YE +4
Nucleic acid molecules encoding annexins from plants
InactiveUS20050089872A1Improvement of resistance to environmental damageResist damageImmunoglobulinsFermentationAbscisic acidAnnexin
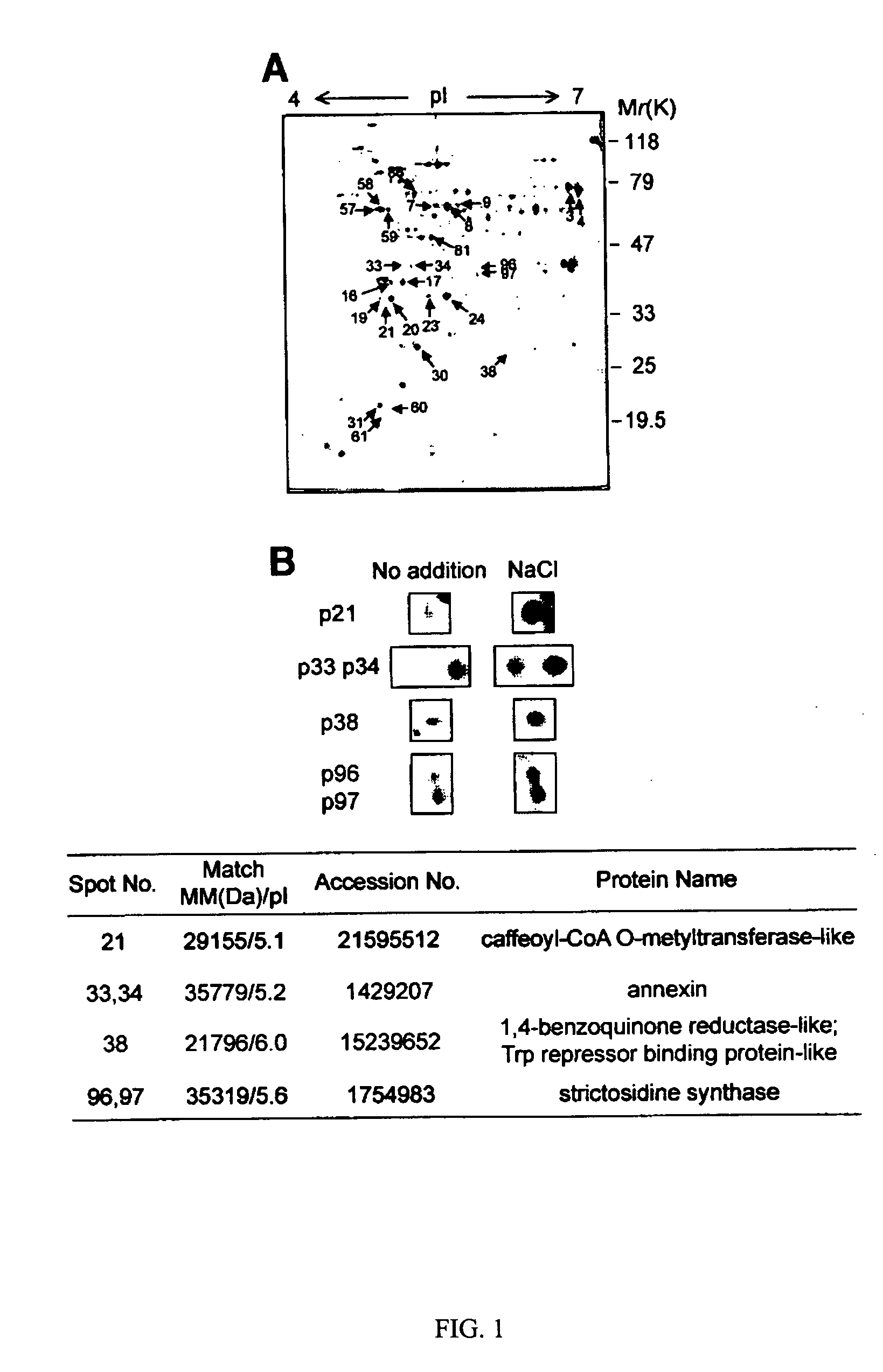
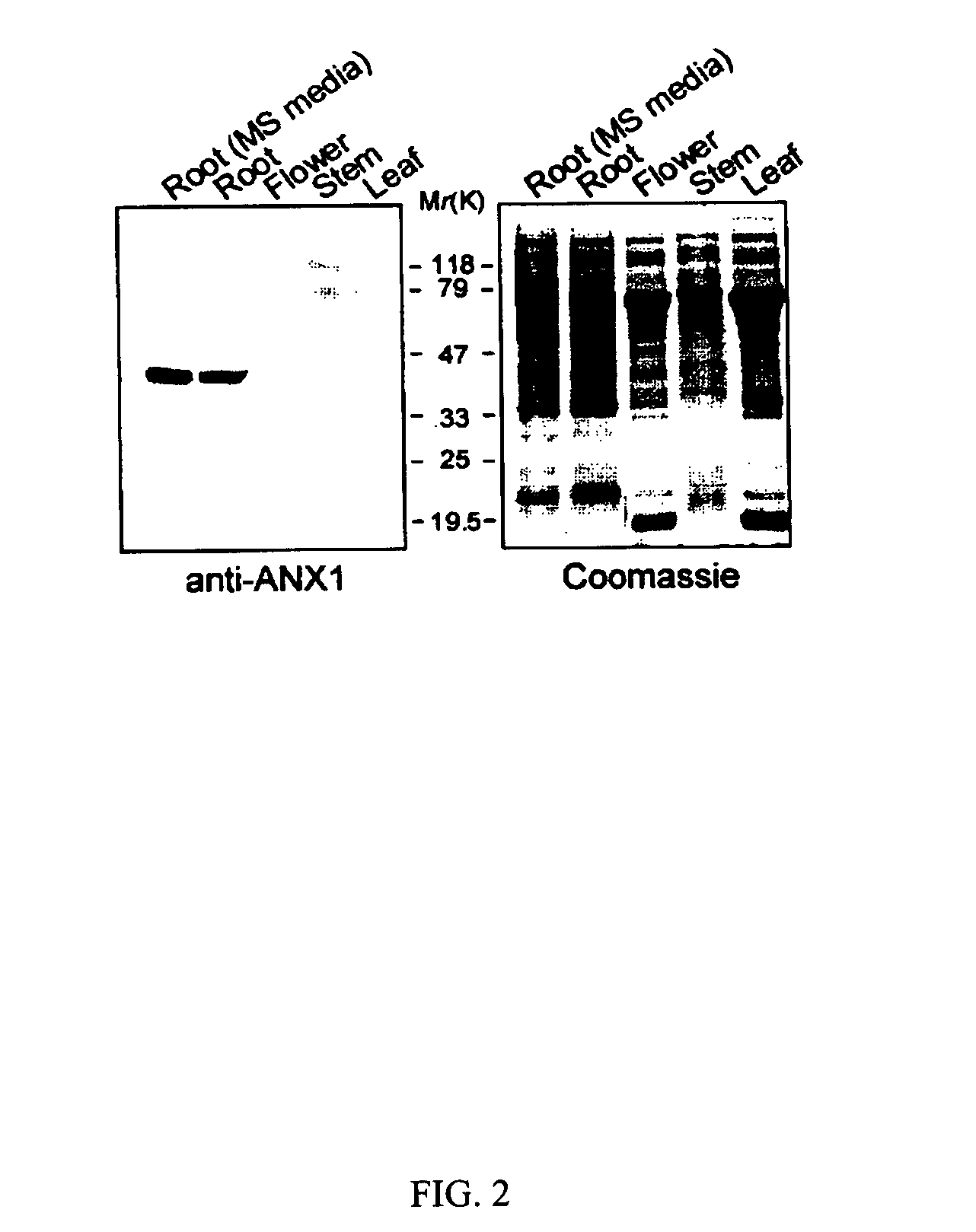
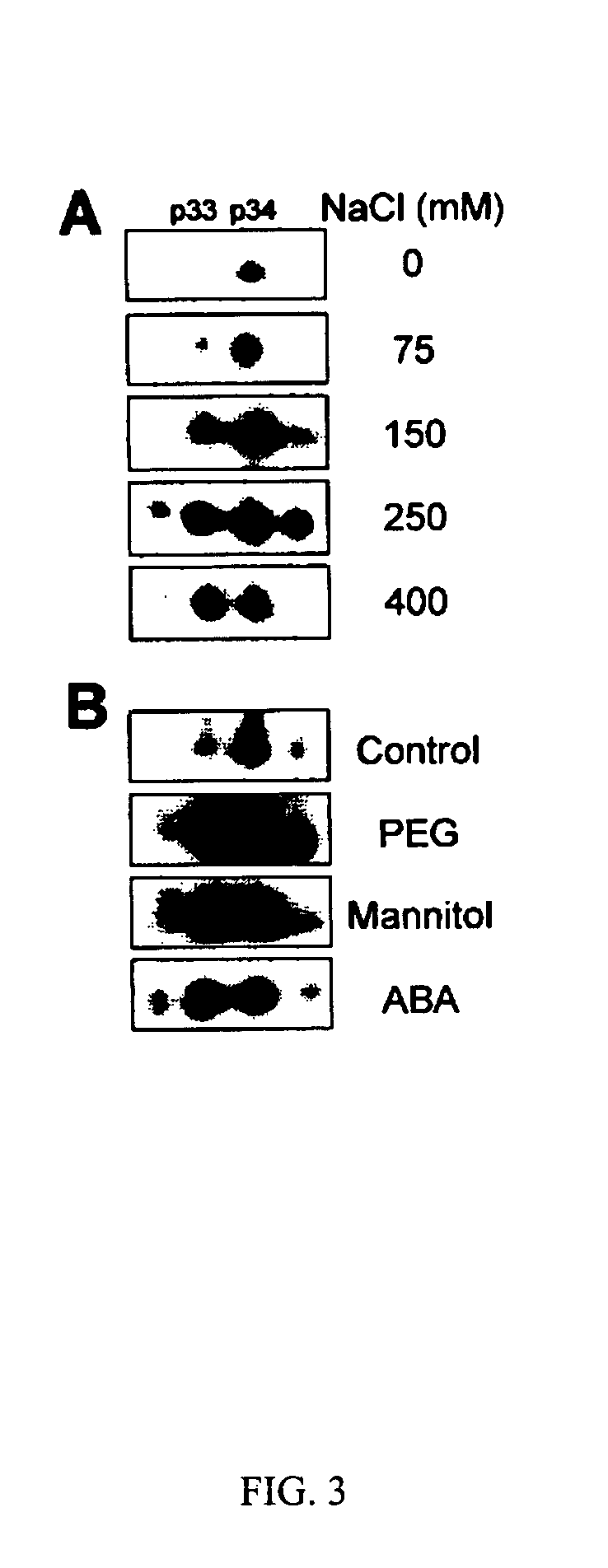
The present invention provides nucleic acid molecules encoding annexin 1 (ANX1) and annexin 4 (ANX4) that belong to a multigene family of calcium-dependent membrane binding proteins. ANX1 and ANX4 are inducible by abscisic acid (ABA), salt and other various stress treatments. The anx1 and anx4 mutant plants are characterized by their hypersensitivity to salt and ABA during seed germination and early seedling growth. The invention can be utilized to generate transgenic plants that are tolerant to environmental stress.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
System for high throughput GPCR functional assay
InactiveUS20080207466A1High speedImprove throughputLibrary screeningLibraries apparatusPorous substrateFunctional assay
A functional assay detection system for membrane bound proteins. The system comprises a biological array including a porous substrate having a plurality of membranes adhered thereto and a first side and a second side, a fluorescent labeling reagent configured to couple to the membrane bound proteins, a pulsed light assembly configured to excite the fluorescent labeling reagent, and a time-delayed imaging device configured to capture emitted fluorescence of the fluorescent labeling reagent. The pulsed light assembly is configured to excite the fluorescent labeling reagent from at least one of the first side and the second side of the porous substrate, and the fluorescent labeling reagent comprises a fluorophore that has an emission lifetime that is in the range of microseconds.
Owner:CORNING INC
Method of screening for agents that regulate the shedding of membrane bound proteins and methods of use
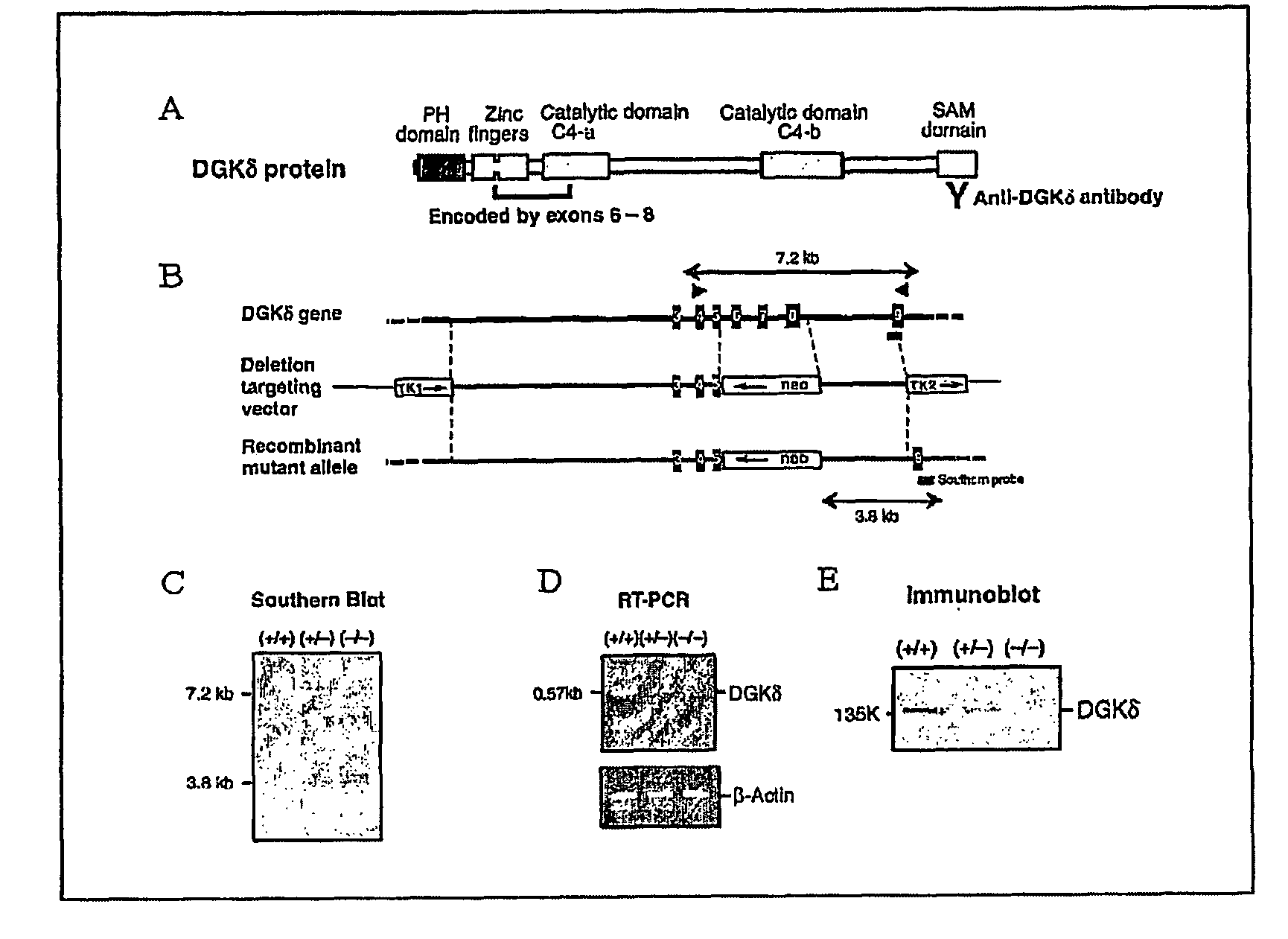
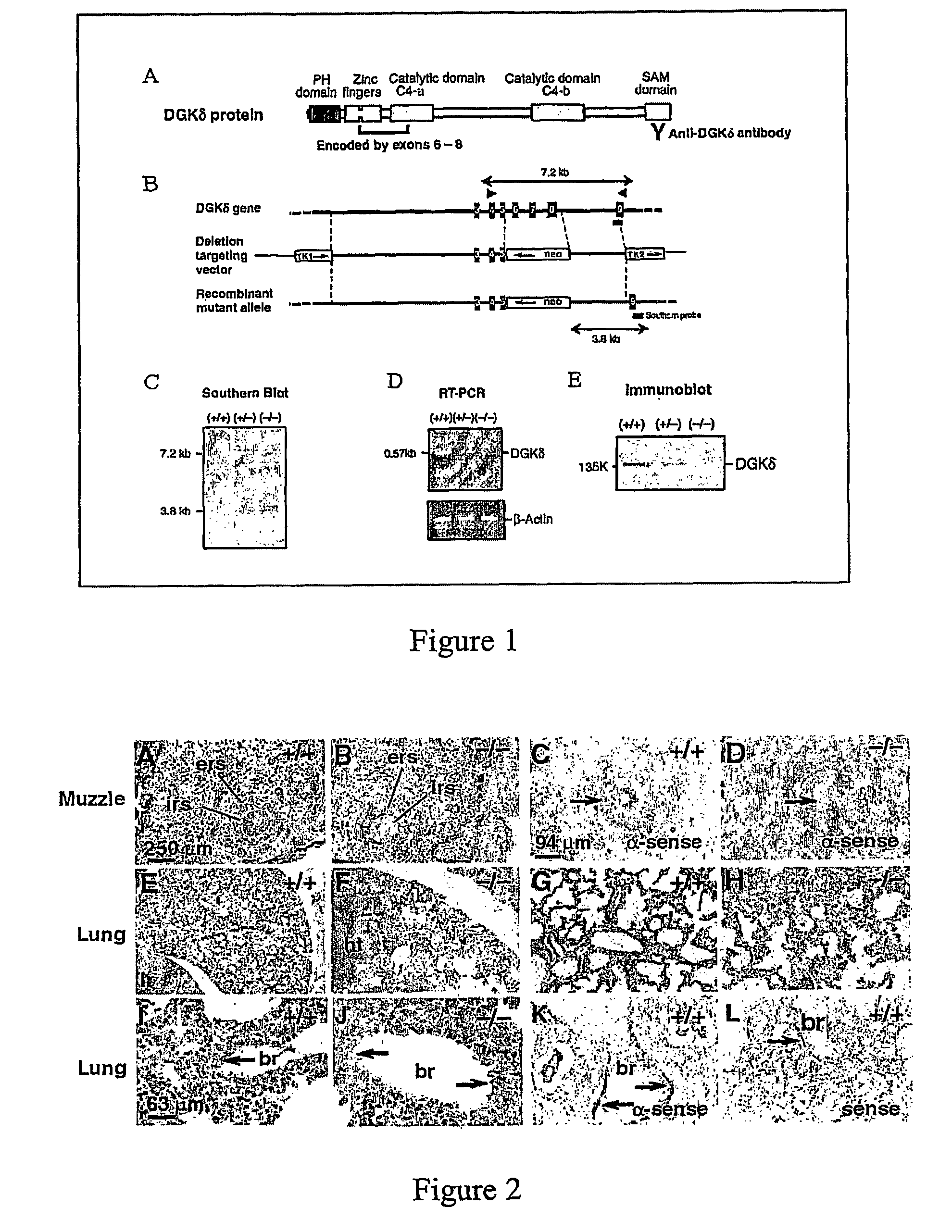
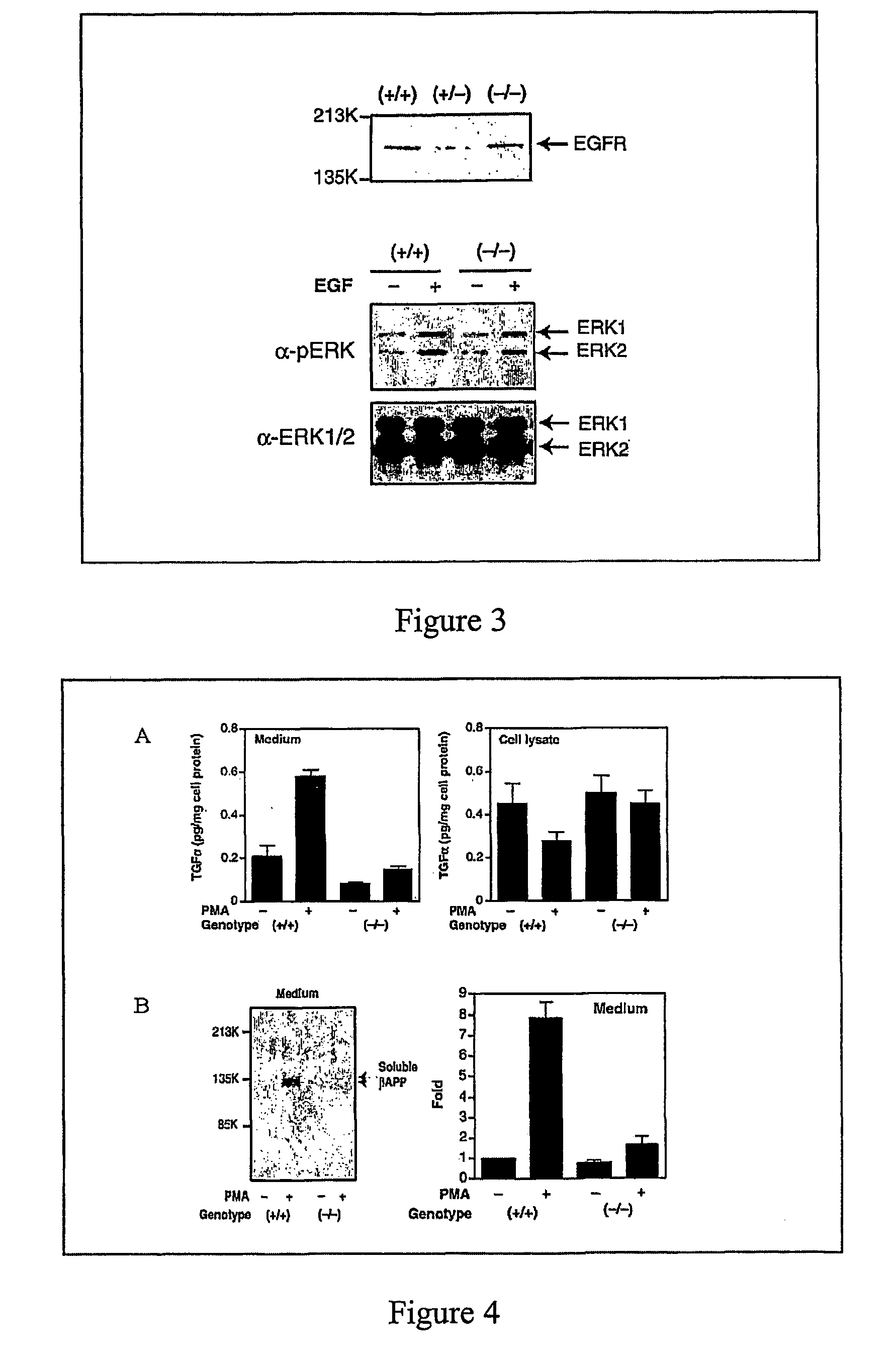
The present invention provides a method of screening for agents which may regulate or inhibit the activities of TACE and TGF-α. These agents may act by enhancing or inhibiting the activity of DGK-δ. An activity of DGK-δ is the enzymatic conversion of DAG to PA. The method includes contacting a cell or organism with a test agent determining the activity of DGK-δ within the cell. An agent with reduces or increases the activity of DGK may be used to regulate or inhibit the activity of TACE and TGF-α. Such agents can be used to treat diseases such as cancer where cell growth and division and inflamation are important factors.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Arrays of biological membranes and methods and use thereof
InactiveUS7678539B2High affinityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyReceptor Serine/Threonine KinaseG protein-coupled receptor
The present invention overcomes the problems and disadvantages associated with prior art arrays by providing an array comprising a plurality of biological membrane microspots associated with a surface of a substrate that can be produced, used and stored, not in an aqueous environment, but in an environment exposed to air under ambient or controlled humidities. Preferably, the biological membrane microspots comprise a membrane bound protein. Most preferably, the membrane bound protein is a G-protein coupled receptor, an ion channel, a receptor serine / threonine kinase or a receptor tyrosine kinase.
Owner:CORNING INC
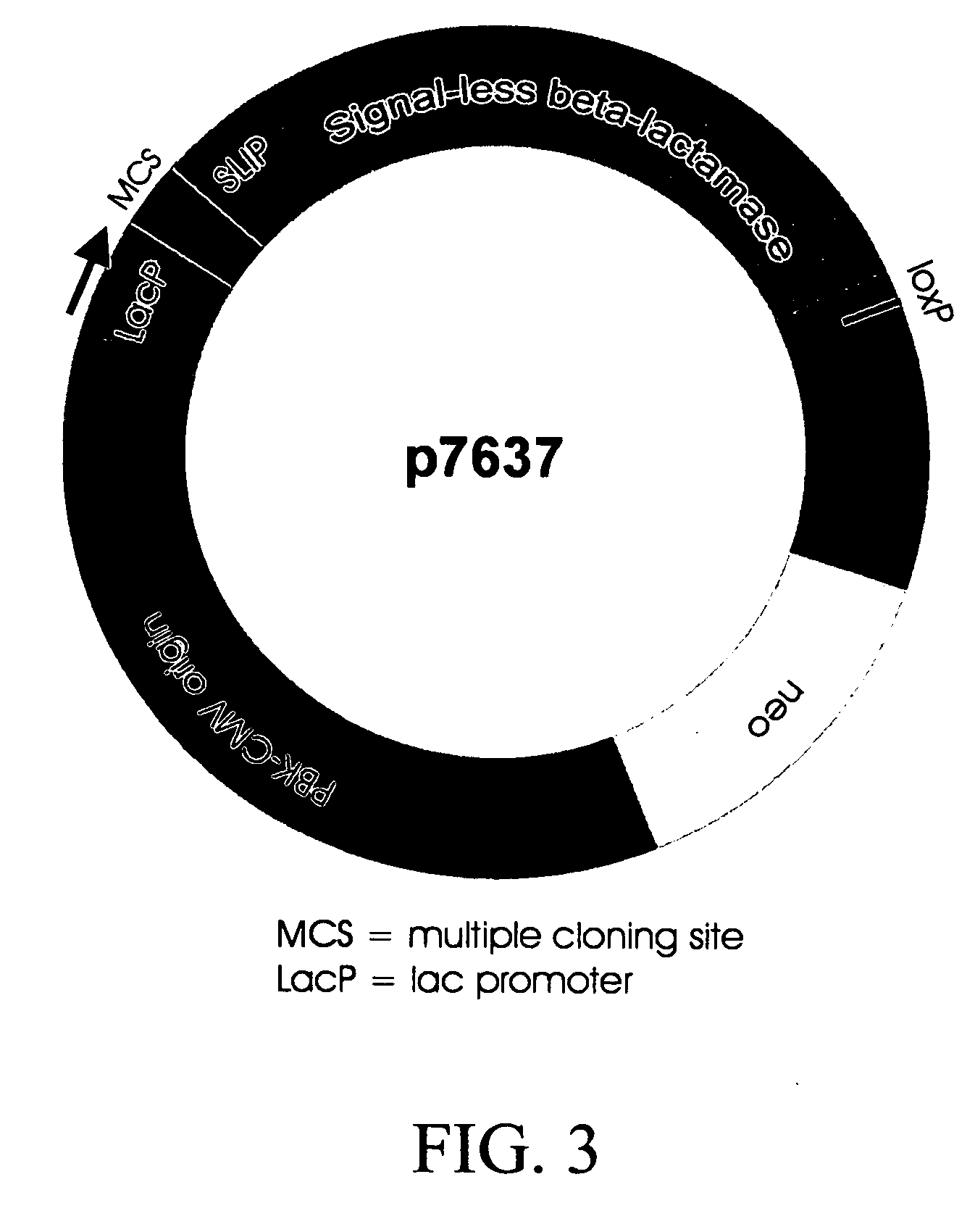
Hetero type pentamer recombinant vaccine
A heteropentamer composed of a fusion monomer (32) comprising a fusion protein of an antigenic amino acid sequence and an amino acid sequence of a monomer of a mucous membrane-binding protein and a nonfusion monomer (20) of an amino acid sequence of a monomer of a mucous membrane-binding protein. A homopentamer composed of a fusion monomer including a fusion protein of an antigen derived from an envelope protein of Japanese encephalitis virus and an amino acid sequence of a monomer of a mucous membrane-binding protein. These heteropentamer and the homopentamer can be used as a vaccine.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL BIOLOGICAL SCI INST +1
Target evaluation using biological membrane arrays
InactiveUS20050079507A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProtein targetCell membrane
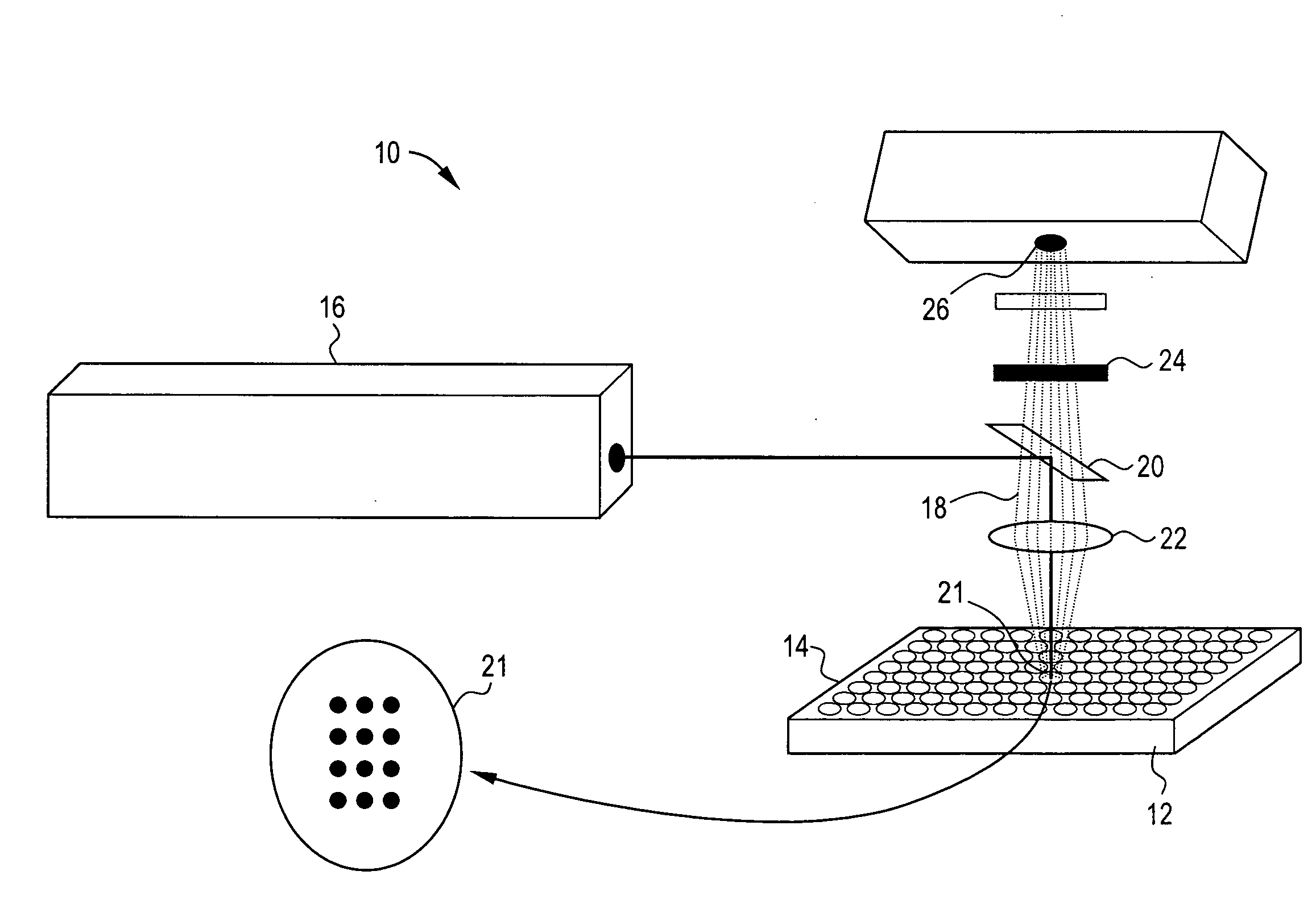
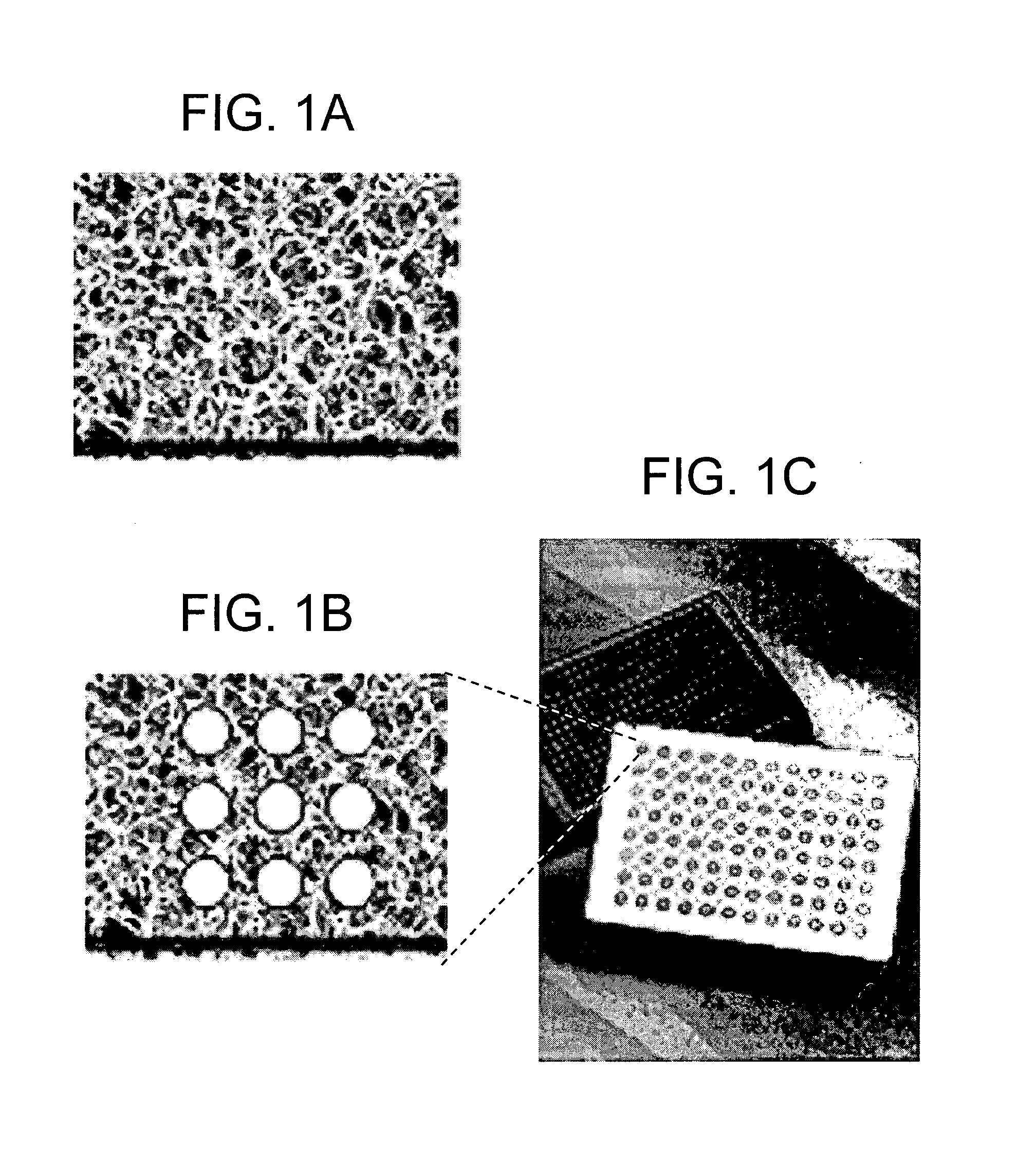
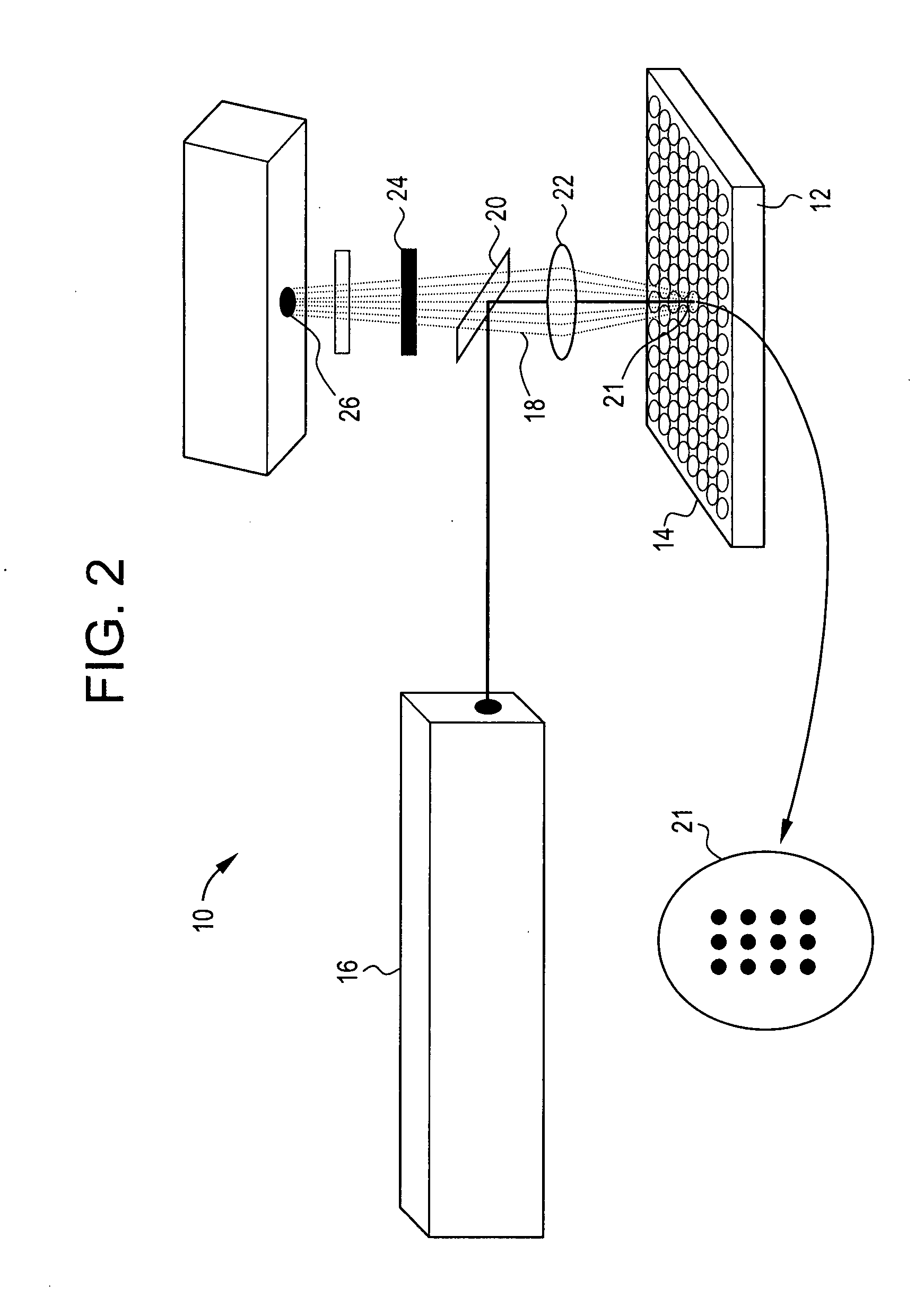
Novel uses of biological membrane microarrays and a new product platform or assembly are described. The invention involves cell membranes from different tissues or cells or organelles to fabricate tissue-specific cell membrane microarrays. The invention provides methods for identifying the relative distribution and / or abnormal expression levels of different membrane bound proteins, including G protein coupled receptors, in specific tissues or cells. In addition, the invention provides methods for screening target proteins that interact with membrane receptors.
Owner:CORNING INC
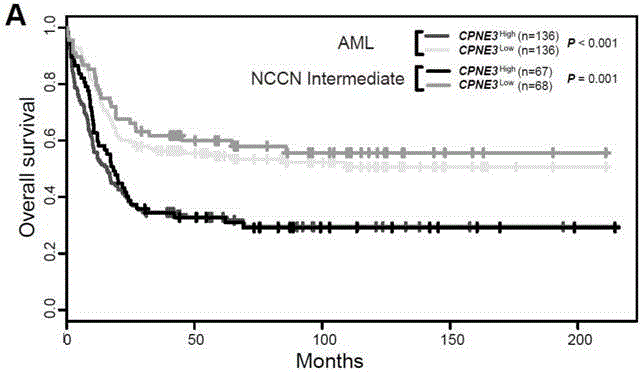
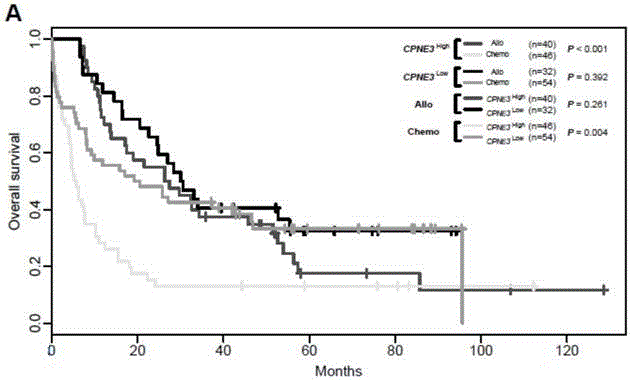
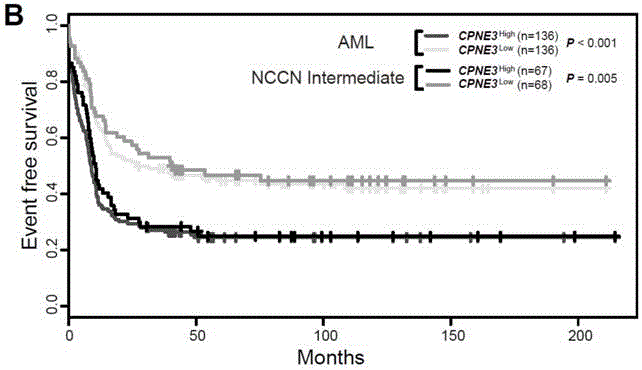
Kit for adult AML (acute myeloid leukemia) risk stratification and clinical prognosis evaluation and application of CPNE3
ActiveCN106244675ANucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementMyeloid leukemiaClinical prognosis
The invention provides a kit for adult AML (acute myeloid leukemia) risk stratification and clinical prognosis evaluation and an application of CPNE3, namely a gene chip and the kit for conducting risk stratification or clinical prognosis evaluation on patients with adult AML, wherein primer pairs of calcium-dependent membrane combined proteins copine III genes are used, and the sequences of one of the primer pairs are shown as agactcccacgaaactcagg (SEQ ID NO:2) and ctgtgcgctcaacctcatac (SEQ ID NO:3) or complementary sequences thereof, and the primer pairs are used for detecting the expression level of calcium-dependent membrane combined proteins in adult AML cells or tissues.
Owner:石金龙
Methods for the identification of agents for the treatment of seizures, neurological diseases, endocrinopathies and hormonal diseases
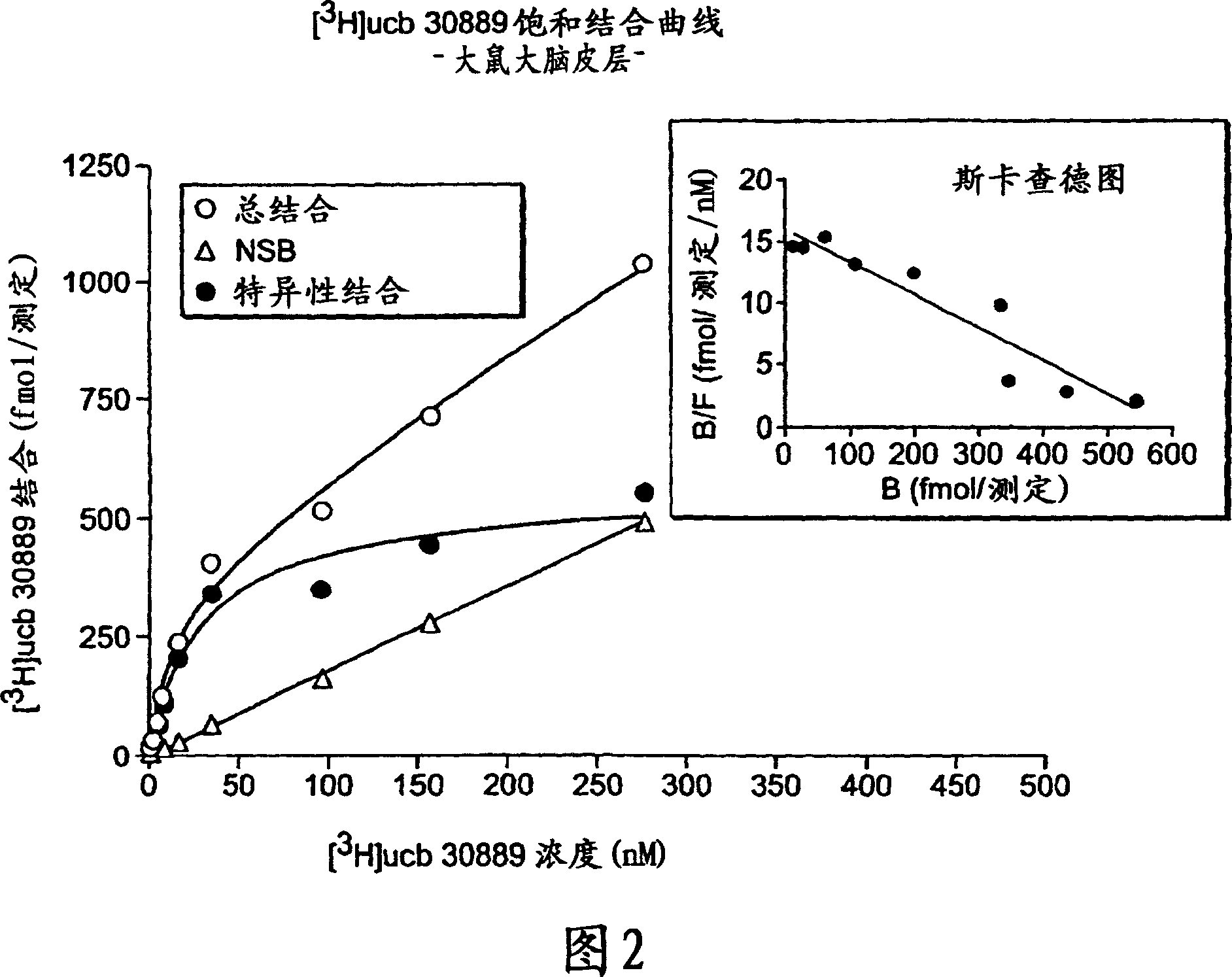
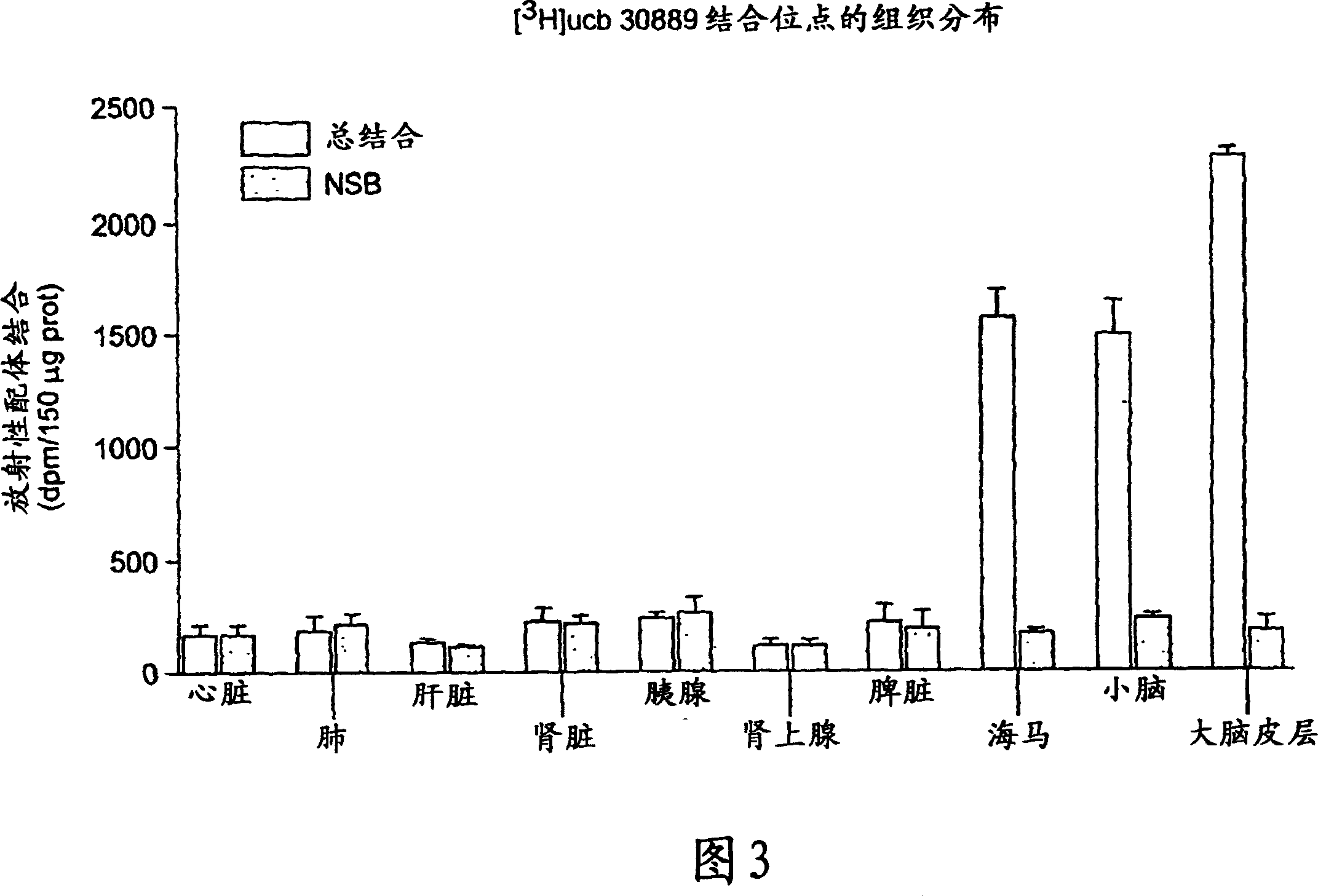
The present invention is drawn to methods of characterization of the properties and functions of SV2 proteins. The invention further includes methods of identifying compounds or agents which modulate the activity of SV2 proteins. Included in these methods is the identification of compounds or agents which modulate the binding of levetiracetam to SV2 proteins, including SV2A. Additionally, the present invention provides biotinylated ligands as a tool to screen chemical libraries and characterize the SV2 proteins. Further, the present invention provides a method of solubilizing and purifying functionally active membrane associated proteins, such as SV2.
Owner:UCB SA
Method for effective search for target molecule
InactiveUS20090042318A1Efficient executionIncrease volumeMaterial analysisCombinatorial chemistryImproved method
The present invention provides a solid phase carrier capable of adsorbing a highly hydrophobic target molecule, for example, a membrane associated protein, and a solid phase carrier optimized not only for a highly hydrophobic target molecule, but also for an optionally chosen target molecule. More specifically, the present invention provides a solid phase carrier having a ligand and a capping agent immobilized thereon, with the hydrophobic property of the surface thereof adjusted to enable the binding of the target molecule to the ligand, or to increase the amount of target molecule bound to the ligand; various methods using the solid phase carrier (for example, method of concentrating, isolating, or purifying a target molecule, a method of selectively adsorbing a particular target molecule to the solid phase carrier, or a method of analyzing the interaction between ligand and target molecule therefor); a production method for the solid phase carrier; and an improvement method for a solid phase carrier having a ligand and a capping agent immobilized thereon and the like.
Owner:REVERSE PROTEOMICS RES INST
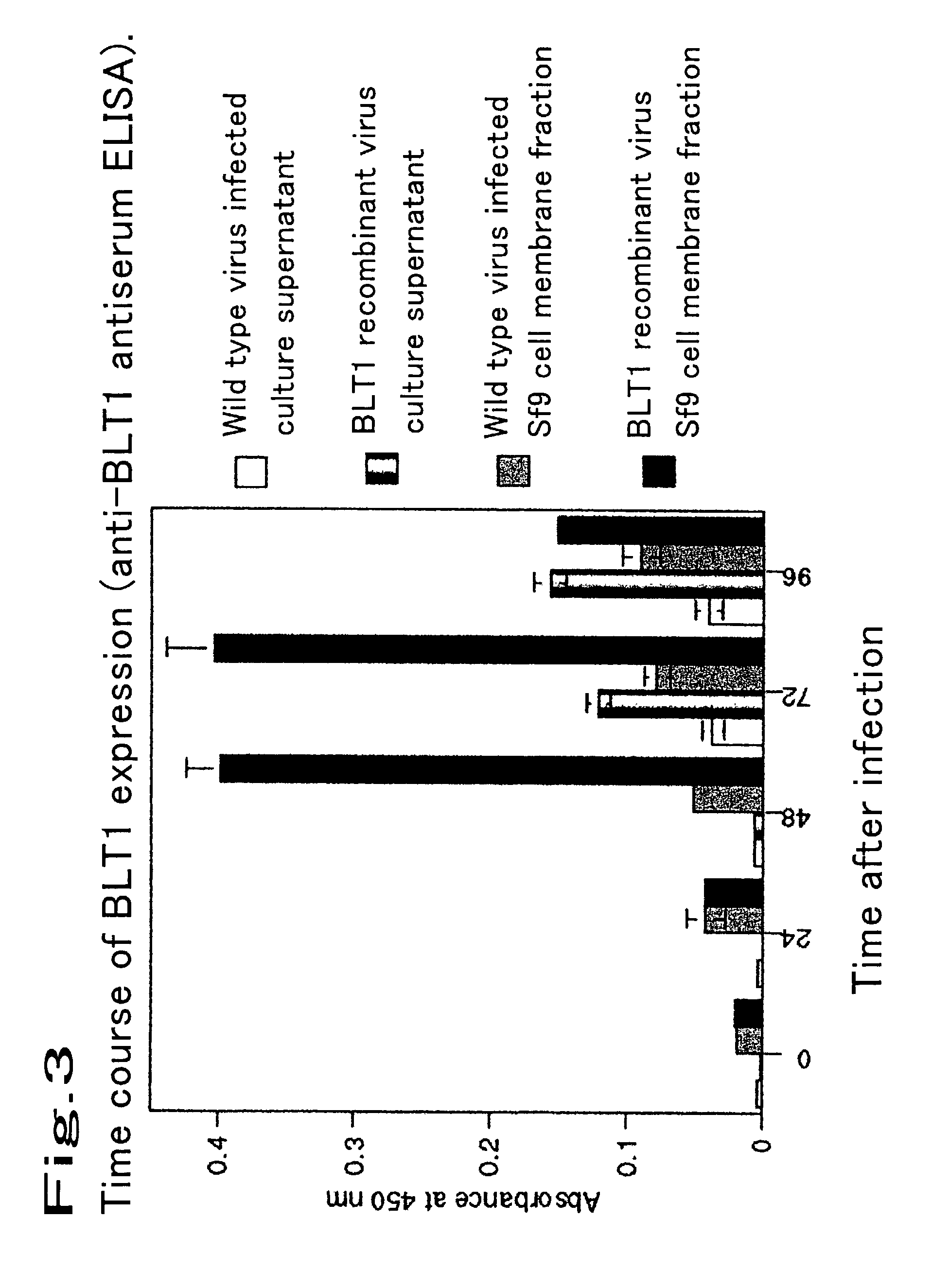
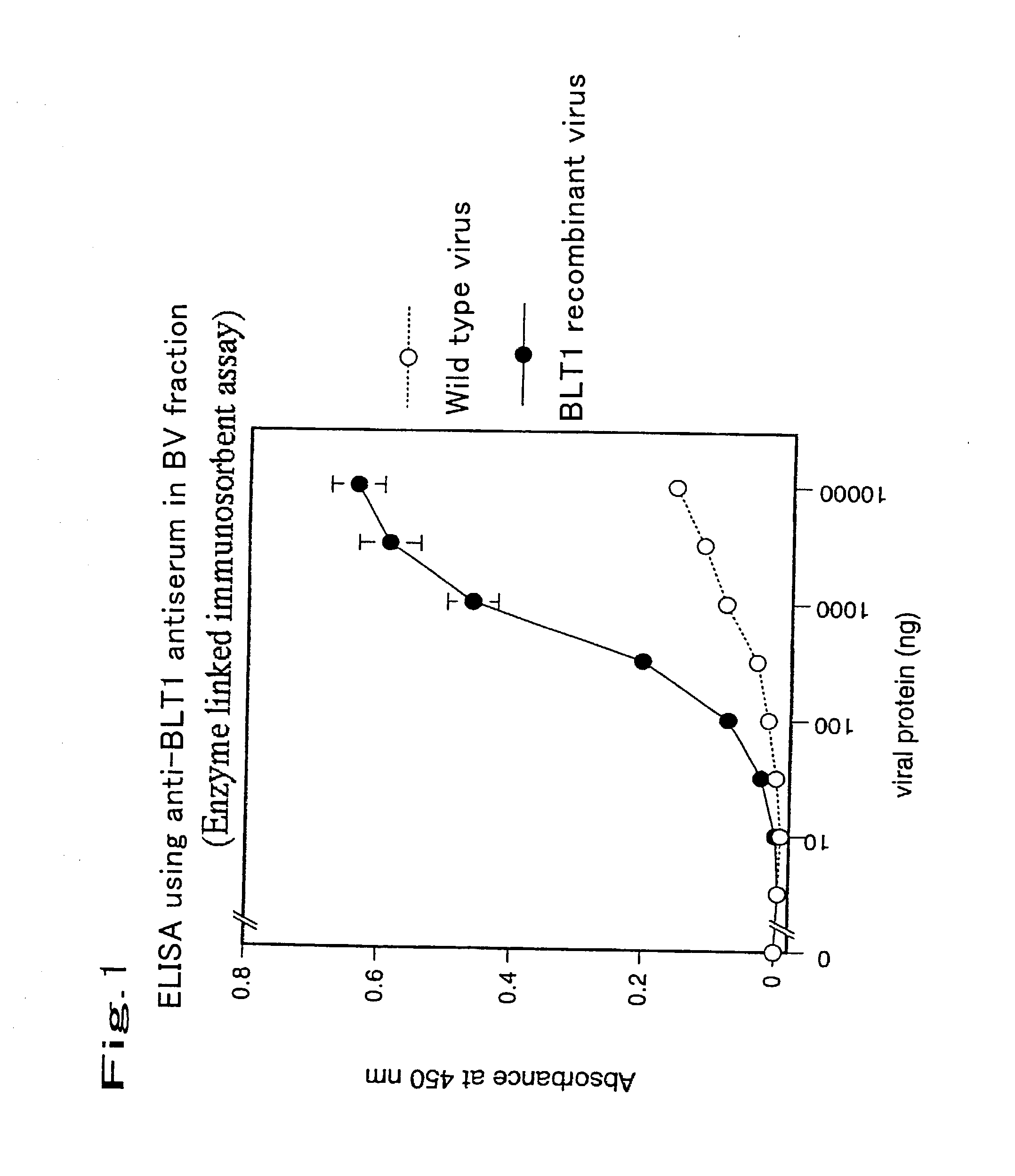
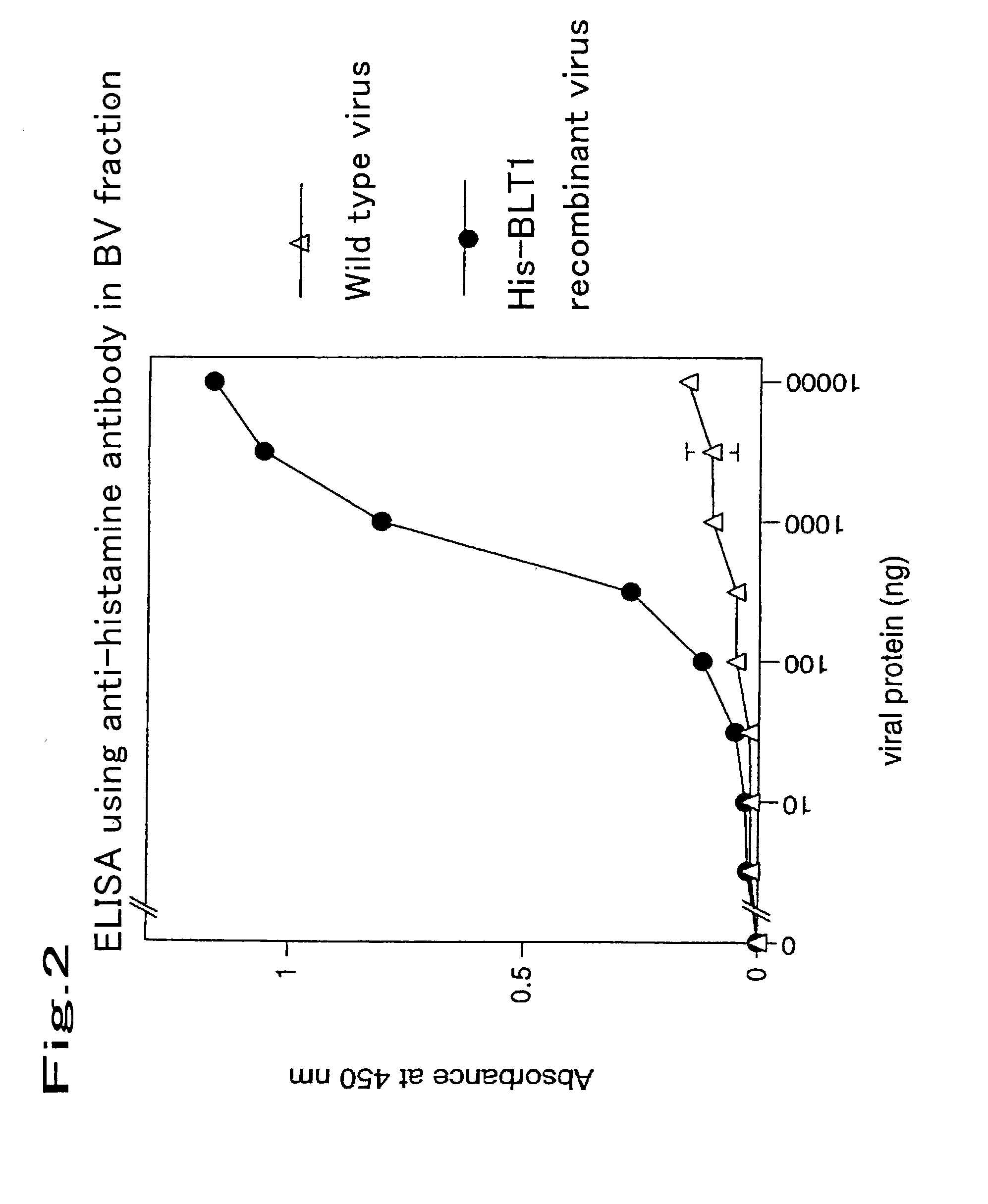
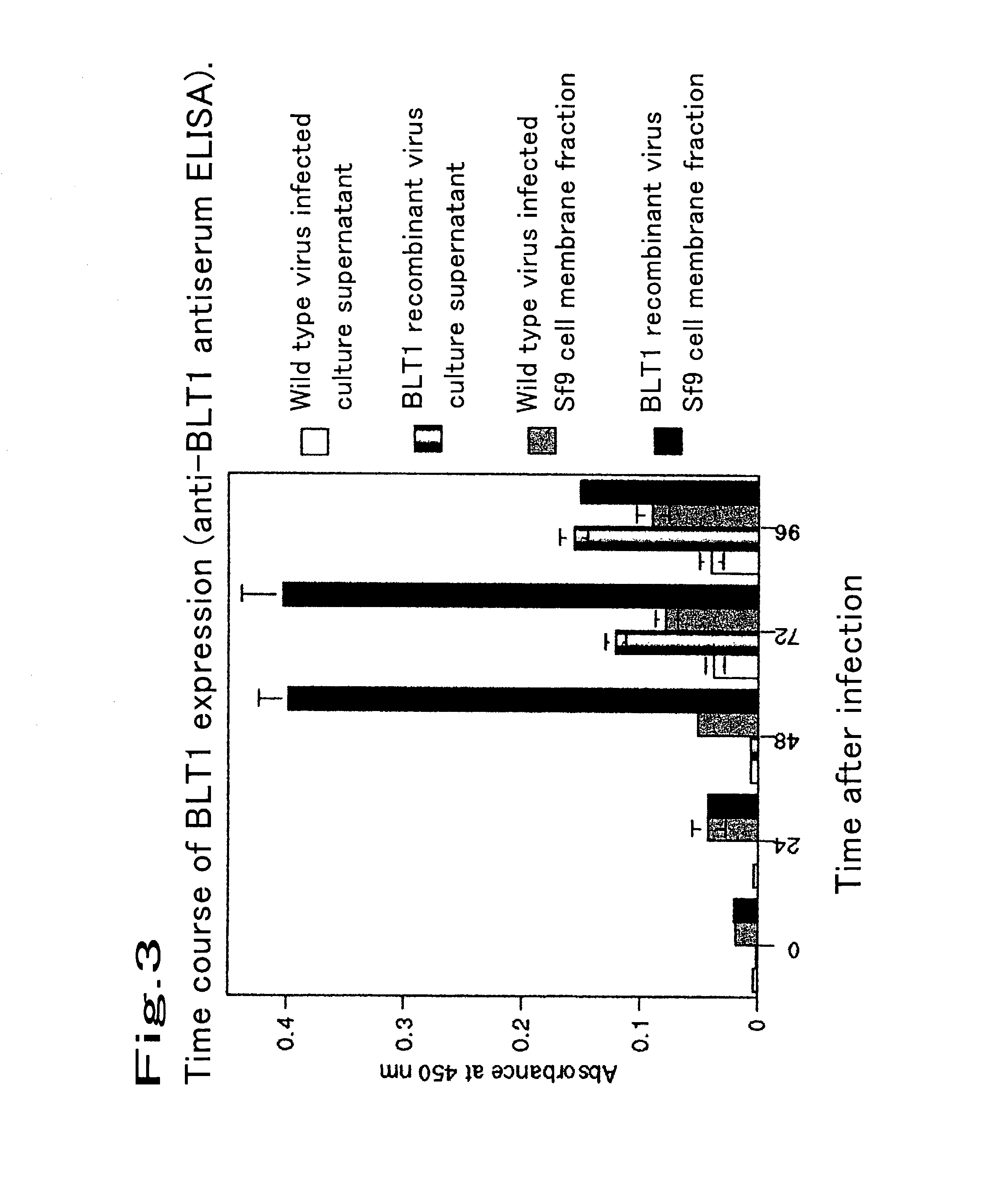
Method for expressing a functional membrane-bound receptor protein using budded baculovirus
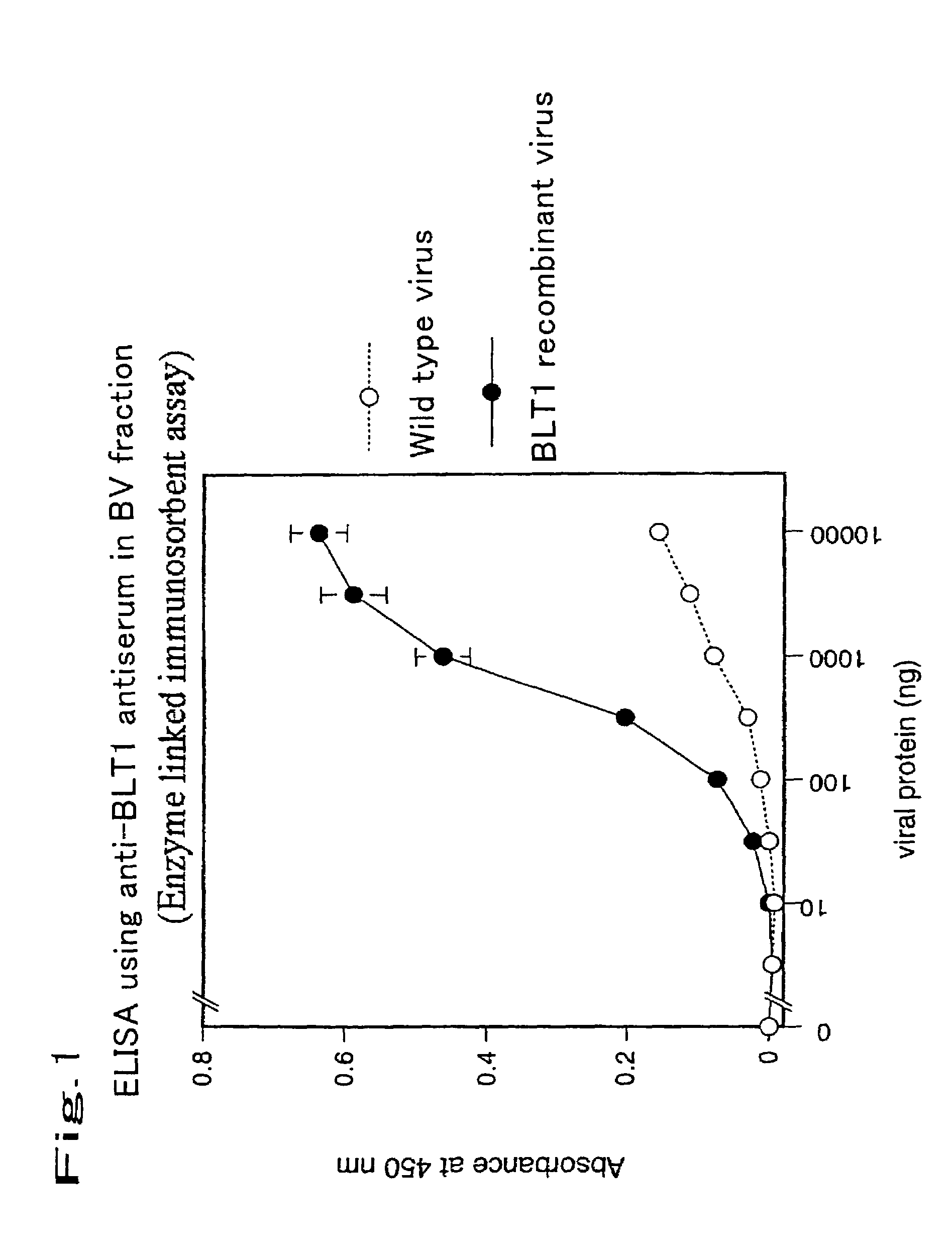
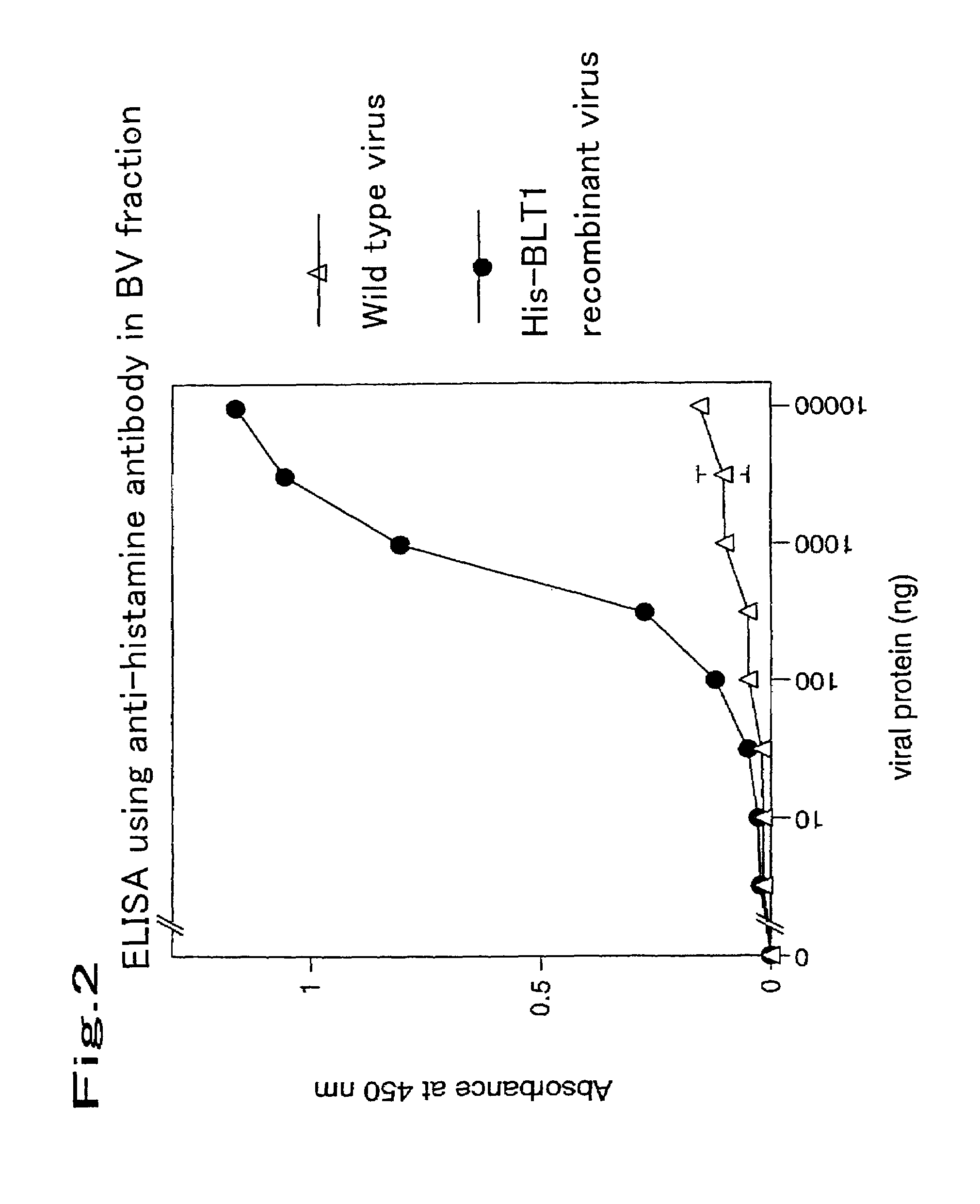
The object of the present invention is to develop a technique for expressing a functional membrane-bound protein by using baculovirus and insect cell expression system. The present invention provides a method for expressing a functional membrane-bound receptor protein which comprises steps of culturing a host infected with at least one type of recombinant baculovirus which contains a gene encoding an interacting protein and a gene encoding a membrane-bound receptor protein which interacts with said interacting protein to perform its function, and co-expressing said interacting protein and said membrane-bound receptor protein in a budded baculovirus released from said host.
Owner:TOUDAITLO LTD
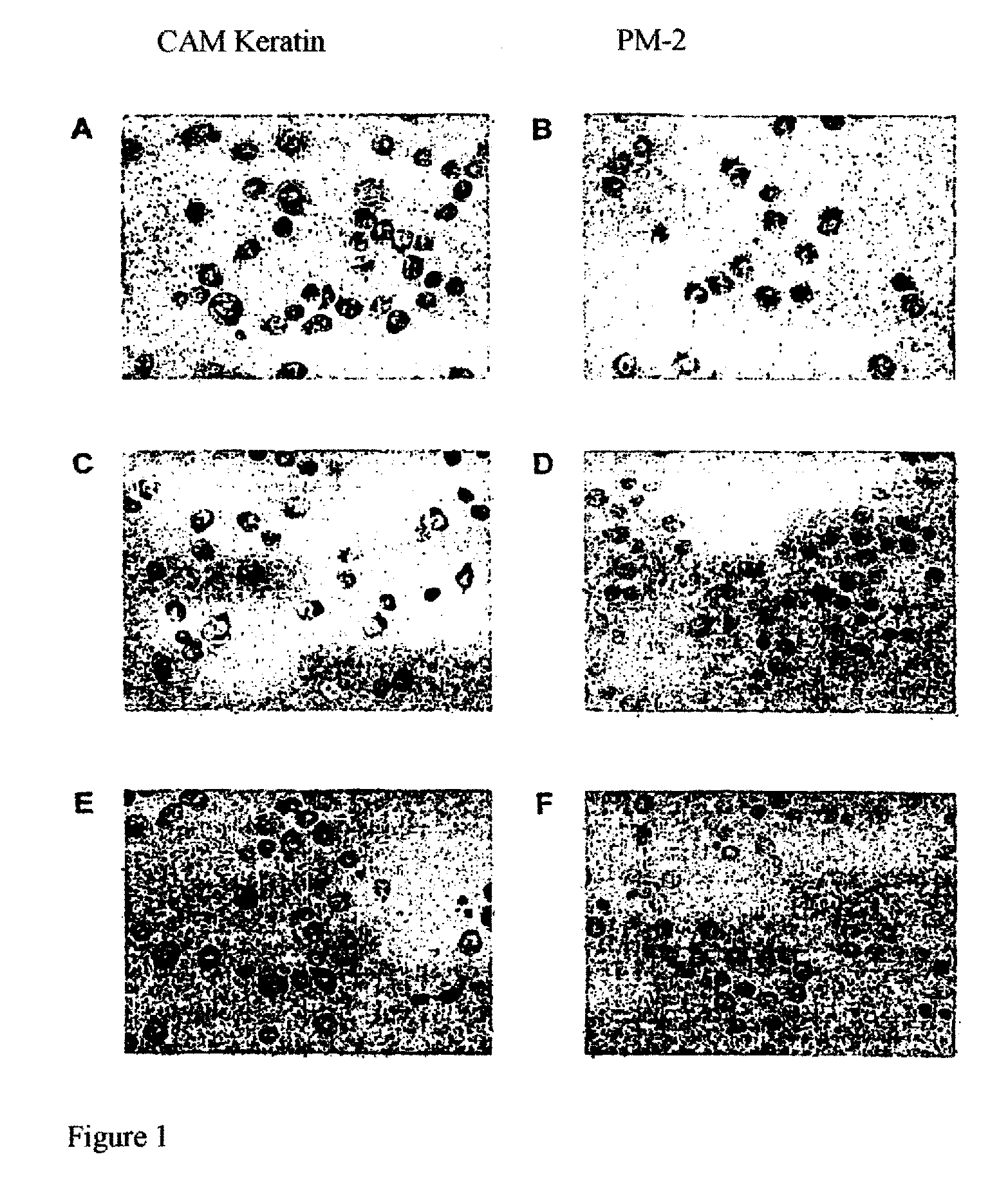
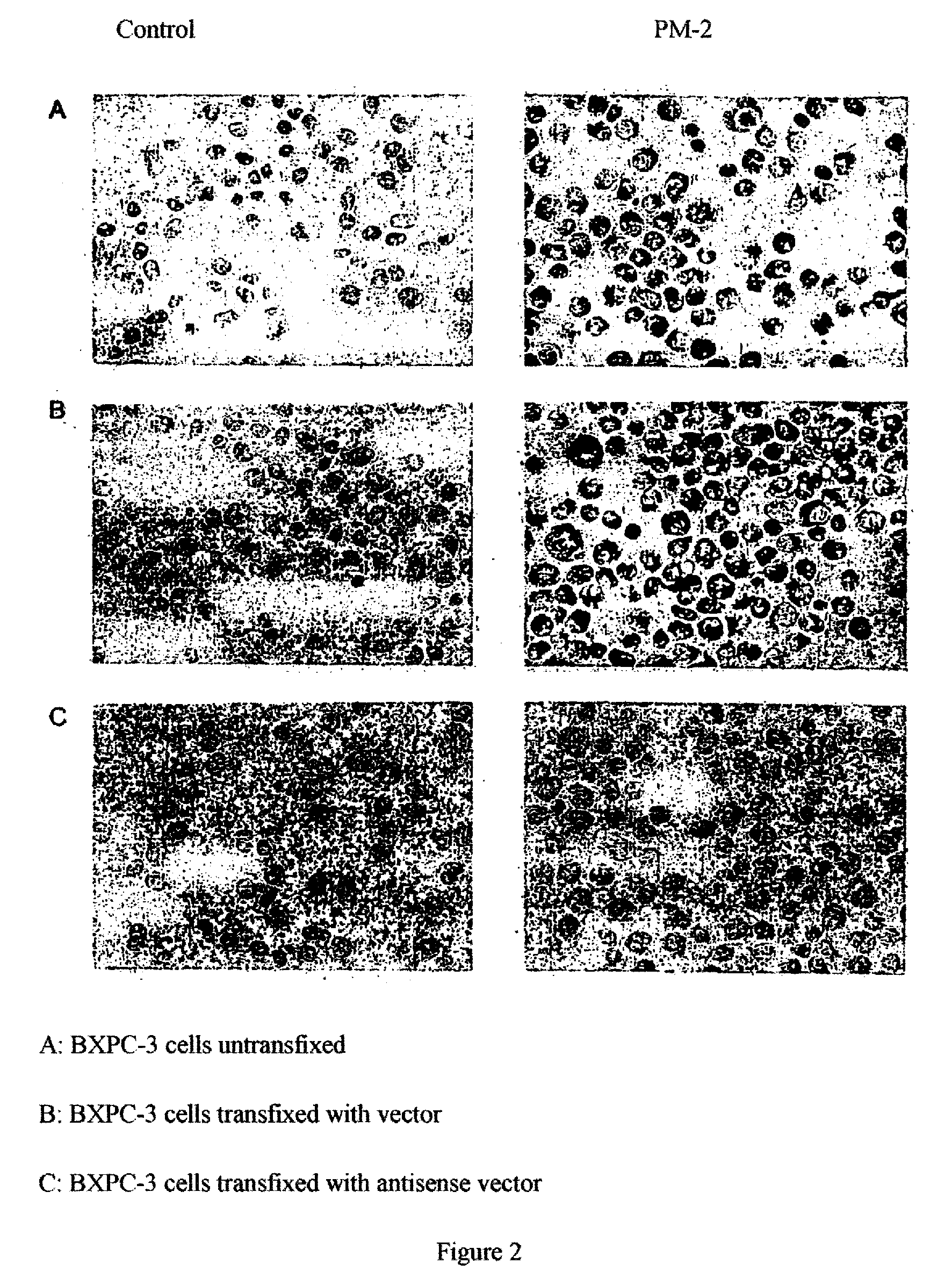
Antigen of the Pm-2 Antibody and Use Thereof
InactiveUS20080281083A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsDepsipeptidesAntigenMembrane bound protein
A polypeptide, which is expressed on the cell surface as a membrane-bound protein, is glycolyzed at one or more points (i.e., membrane glycoprotein) and has an amino acid sequence that corresponds partially or completely to that of the integrin binding protein p80 (accession #AJ131720) or REV1 (accession #AF206019.) The membrane glycoprotein, is expressed by neoplastic cells and not by non-neoplastic cells as an antigen, specifically binds the human monoclonal antibody PM-2 (DSM number: DSM ACC2600) and is, in addition, N-glycosidically and O-glucosidically linked. A related method is provided for the isolation or production of the antigen and for the use of the latter for producing a medicament for immunization. The isolated antigen can also be used to identify medicaments with an apoptotic cell-proliferation inhibiting action. The membrane glycoprotein can also be used as a tumor marker.
Owner:PATRYS
Vector system for selection of genes encoding secreted proteins and membrane-bound proteins
InactiveUS7112434B2Improve efficiencyRapid and robust selectionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementVector systemENCODE
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
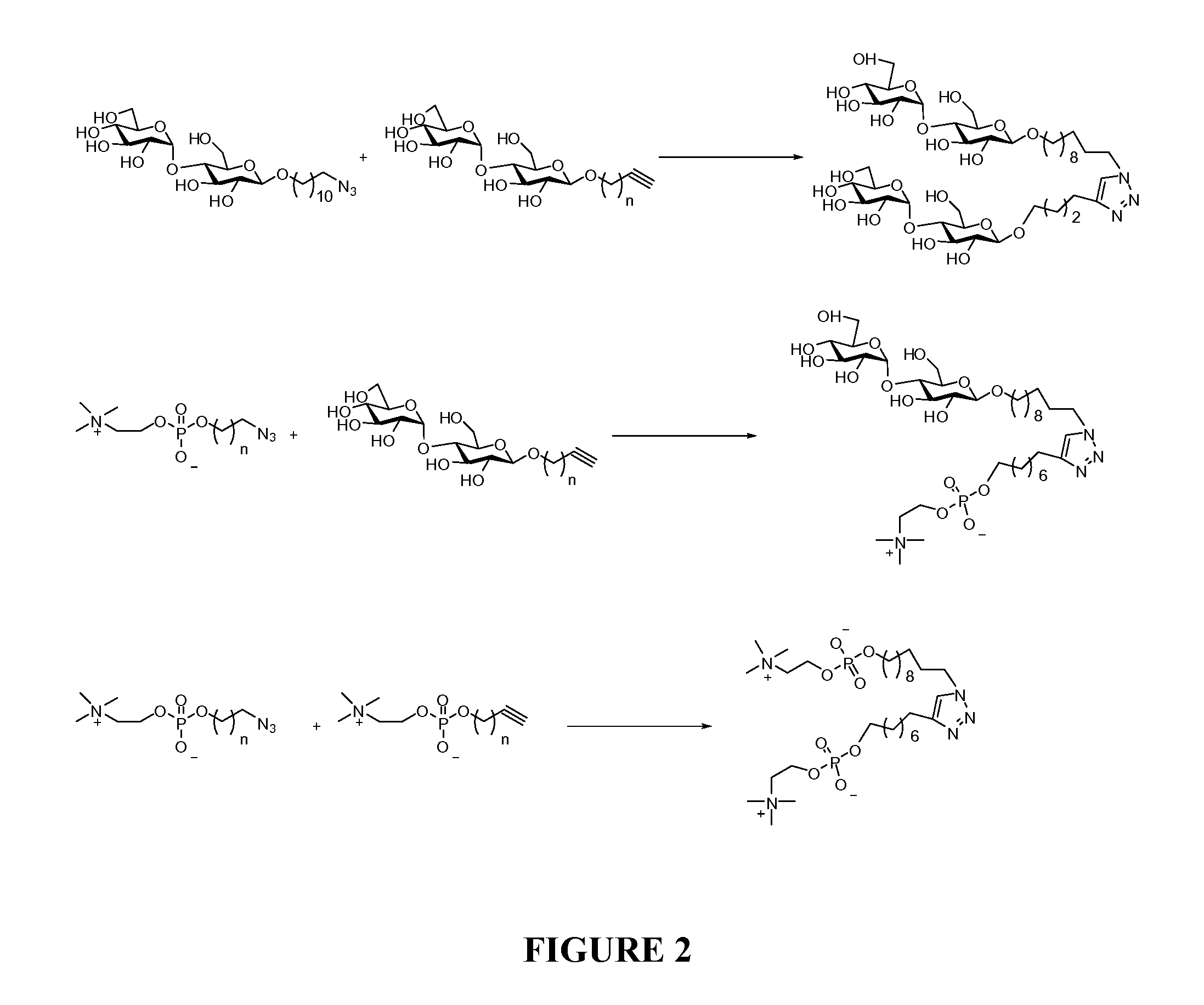
Maltoside and Phosphocholine Derivatives, Uses thereof and Methods of Preparing Artificial Lipid Structures Thereof
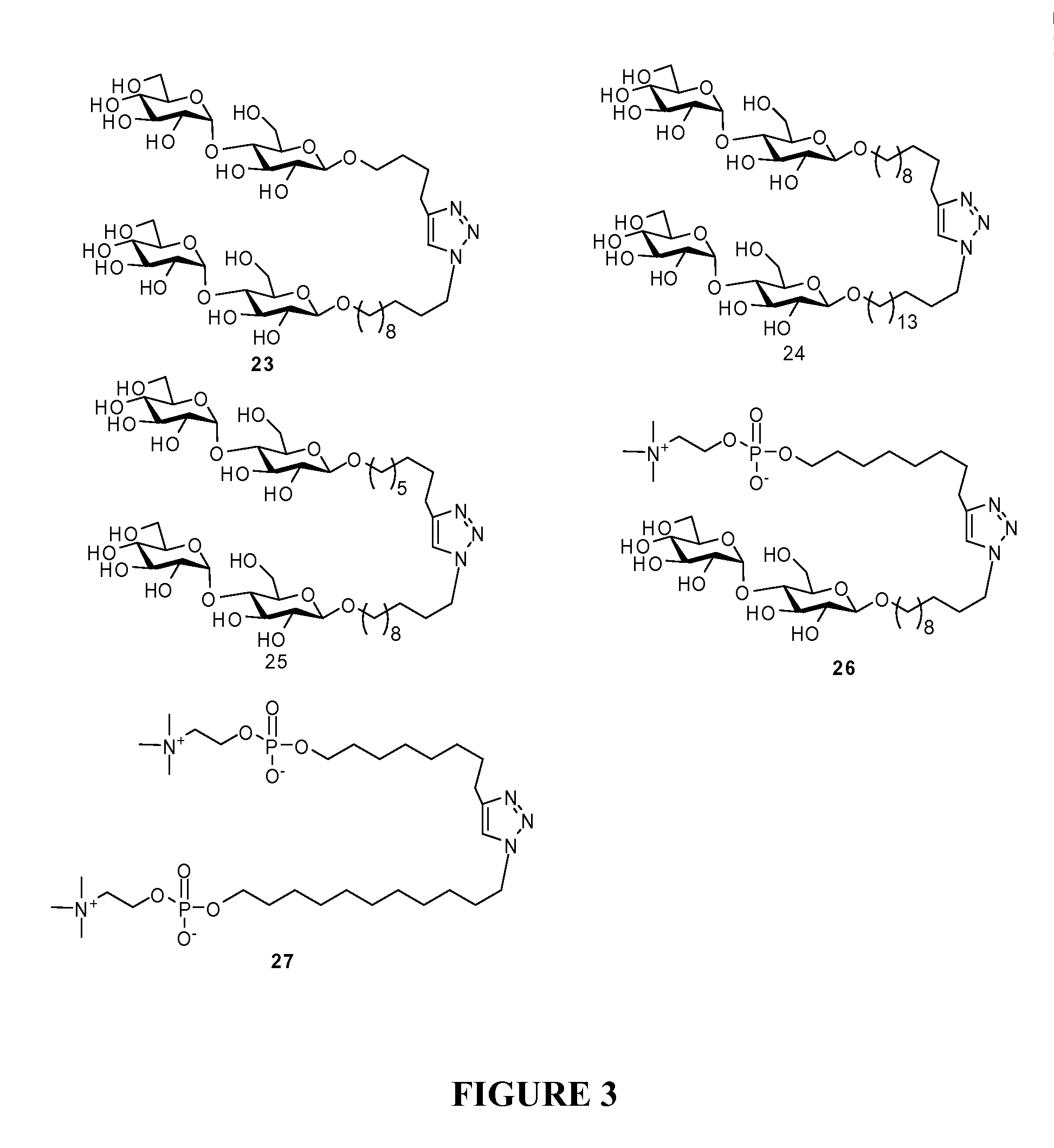
Disclosed are saccharide and phosphocholine derivatives. The derivatives include azide and alkyne derivatives which form one end of a variable length carbon chain. The opposite end of the variable length carbon chain is covalently linked to the saccharide or phosphocholine. The saccharide may be, for instance, a maltoside. The alkyne and azide derivatives of the saccharides and phosphocholine may be reacted together to form amphiphilic molecules useful in cellular membrane studies and applications. By adjusting the length of the carbon chain, the biochemical and biophysical properties of the resultant 1,4-disubstituted 1,2,3-triazole compounds may be custom tailored for the intended application. Resultant molecules may form micelles, bicelle, lipid bilayers and other like structures useful in the isolation and purification of membrane bound or membrane associated proteins and biochemical components. The saccharides and phosphocholine molecules may be alternatively substituted as desired to provide additional flexibility in designing the desired end product.
Owner:ANATRACE PROD
Method for expressing a functional membrane-bound receptor protein using budded baculovirus
InactiveUS20070287146A1Promotes and inhibits interactionCompound screeningVirusesBaculovirus expressionMembrane-bound receptors
The object of the present invention is to develop a technique for expressing a functional membrane-bound protein by using baculovirus and insect cell expression system. The present invention provides a method for expressing a functional membrane-bound receptor protein which comprises steps of culturing a host infected with at least one type of recombinant baculovirus which contains a gene encoding an interacting protein and a gene encoding a membrane-bound receptor protein which interacts with said interacting protein to perform its function, and co-expressing said interacting protein and said membrane-bound receptor protein in a budded baculovirus released from said host.
Owner:TOUDAITLO LTD
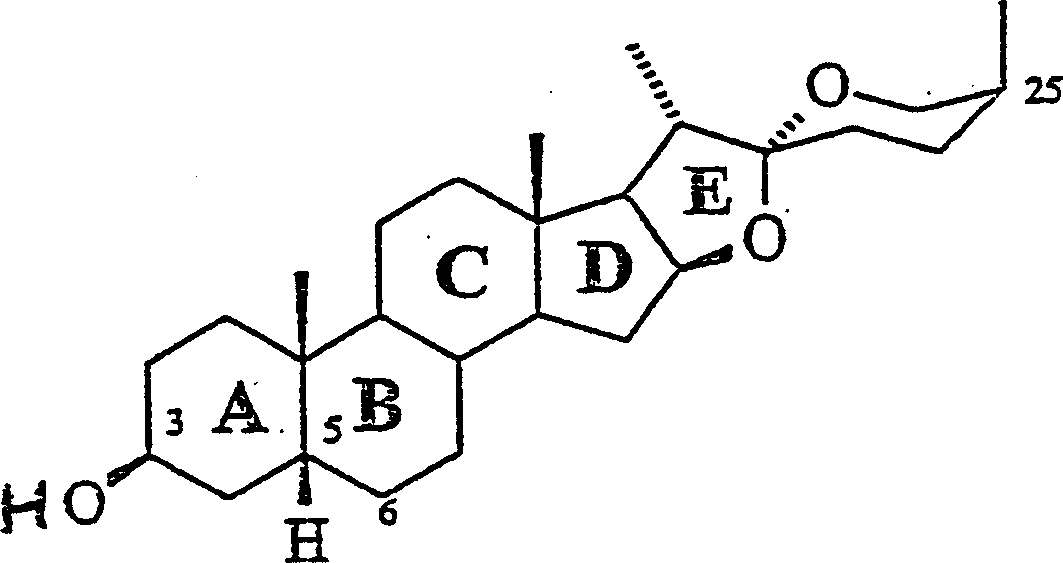
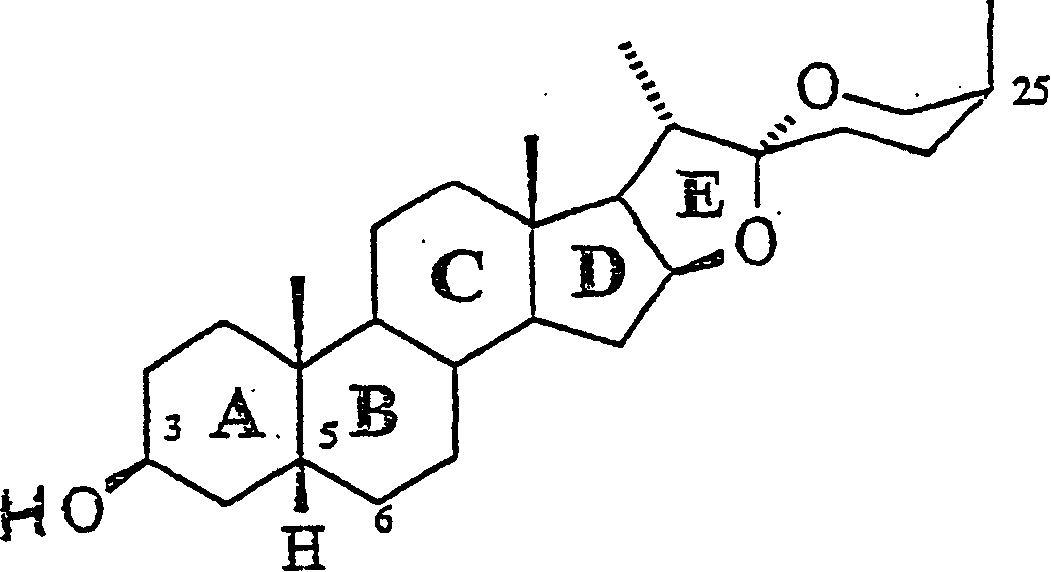
Steroidal sapogenins and their derivatives for treating alzheimer's disease
The invention discloses one or more applications of non-steroidal estrogen of saponins or saponin elements for preparing combinations treating the Parkinson's disease, except to the saponin elements and saponins which can effectively impact a retractile force of myocardium, the material can directly or non-directly adjust functions of the cytoplasm, the nucleolus, the membrane-binding protein or acceptors. When the protein or accepters are activated by the agonist that combines them, or the activity is promoted by making the antagonist deactivation, it can increase and / or normalize the organizations, organs, cell types or amount and / or turnover of the membrane receptor combination in the cellular organ.
Owner:PHYTOPHARM LTD
Multi-target chimeric antigen receptor
PendingUS20220064595A1Low immunogenicityReduce the steric hindrancePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifImmunoglobulin superfamilyAntigen receptorAntigen binding
Disclosed in the present invention is a multi-target chimeric antigen receptor. Provided in the present invention is a multi-target chimeric antigen receptor consisting of a main peptide chain and an auxiliary peptide chain; the main peptide chain comprises an antigen binding domain A, an auxiliary peptide chain connecting domain B, a transmembrane domain C and an intracellular signaling domain D; the auxiliary peptide chain comprises a main peptide chain connecting domain F; the antigen binding domain A is a polypeptide having an antigen-binding function; the auxiliary chain connecting domain B and the main peptide connecting domain F are combined with each other; the transmembrane domain C is a transmembrane domain of any membrane-binding protein or a transmembrane protein; and the intracellular signaling domain D comprises a primary signaling region. The multi-target chimeric antigen receptor of the present invention can bind to different antigens through the two antigen binding domains thereof, and mediates specific cell killing; and a cytokine and cytokine receptor complex playing the role of a cytokine are introduced into the multi-target chimeric antigen receptor of the present invention.
Owner:SHENZHEN BEIKE BIOTECH
Method for producing peptide ACE inhibitors
ActiveUS11324810B2Lower blood pressurePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPROTEIN S HEERLENVirus inhibitors
Owner:ST MARIE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HLDG LLC
Method for producing peptide ace inhibitors
ActiveUS20190262436A1Lower blood pressurePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesBlood plasmaMembrane bound protein
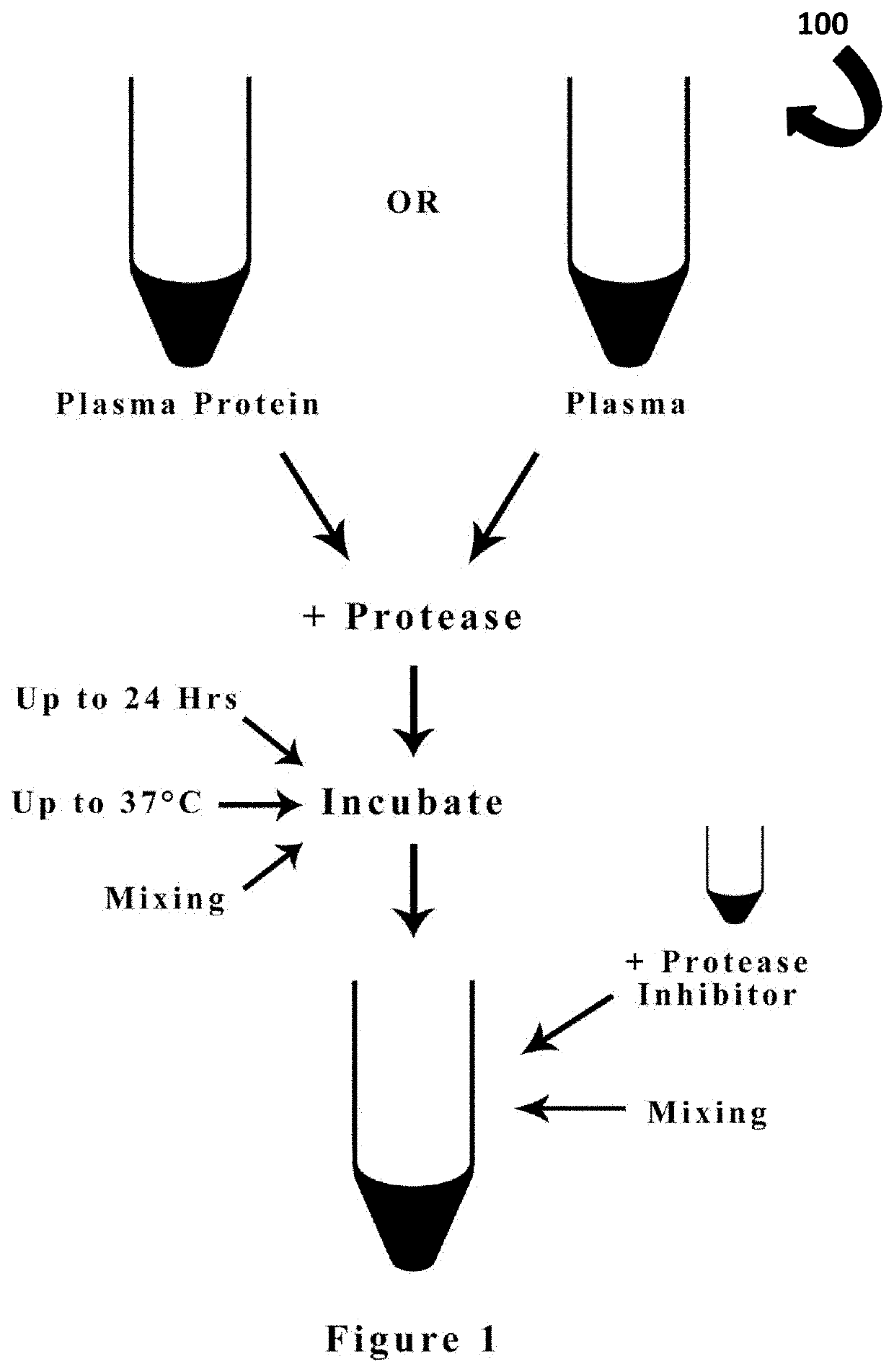
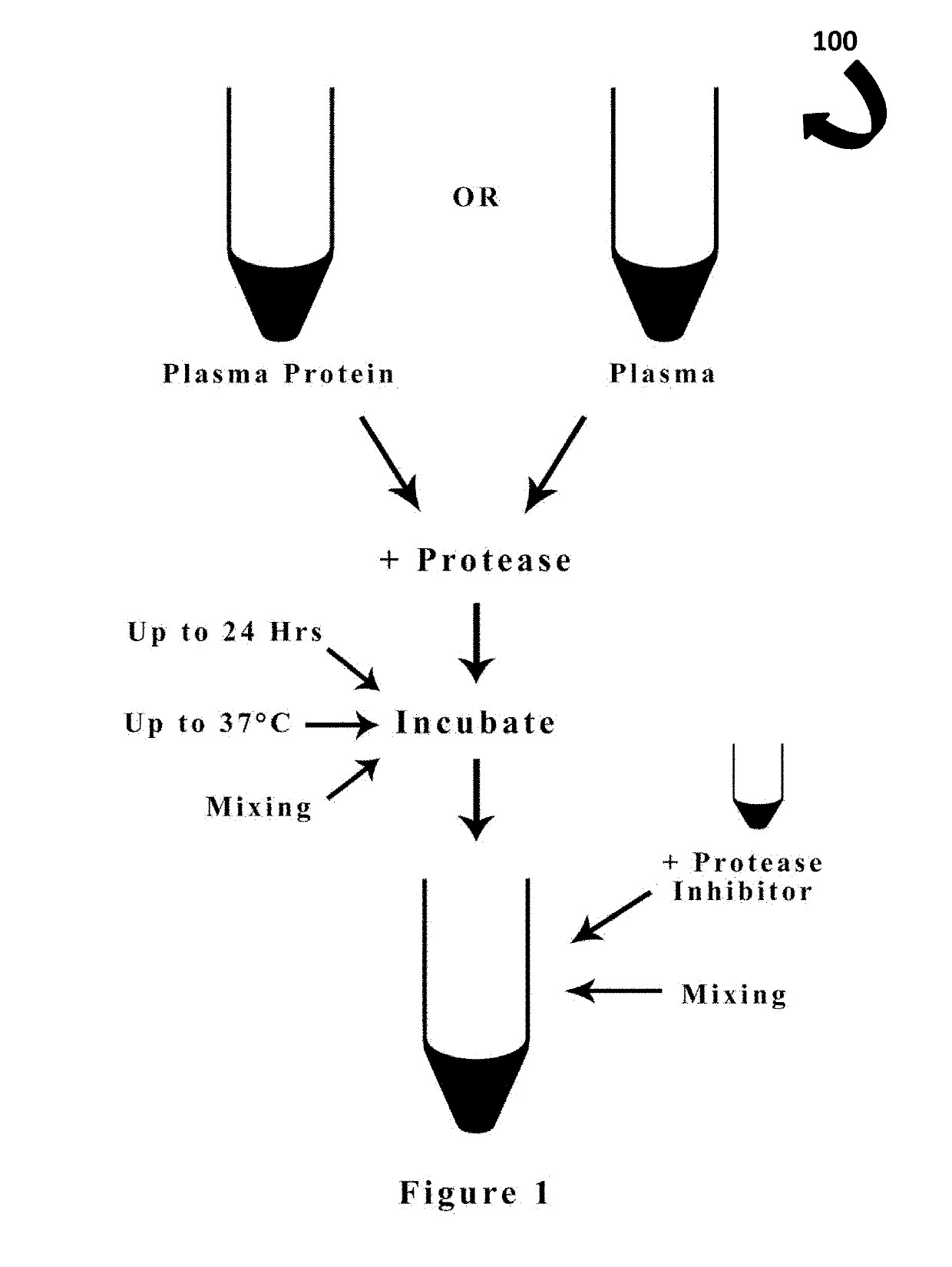
A method for producing ACE Inhibitor peptides from a protein source or plasma is disclosed. The method utilizes proteolysis by intestinal, blood-circulating, or membrane-bound proteases. The initial synthesis step could require obtaining a protein source either from a human or animal. A protease is added to either a given plasma protein or plasma and incubated. Following incubation, the protease activity must be quenched using a protease inhibitor to inactivate the protease. After incubation with protease inhibitor, the solution will contain a mixture of bioactive ACE inhibitory peptides and inert peptides. This mixture may be purified to select for the ACE inhibitory peptides through centrifugation. The mixture may also be sterilized to remove any microbial contaminants. The ACE inhibitory peptides can be mixed with protein powders, incorporated into baked good and put into other food products to provide food products with the added benefit of lowering blood pressure.
Owner:ST MARIE INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HLDG LLC
System for high throughput GPCR functional assay
InactiveUS7998414B2High speedImprove throughputLibrary screeningAnalysis by electrical excitationPorous substrateTime delays
Owner:CORNING INC
Application of steroidal sapogenins and their derivatives in medicine preparation
The invention discloses one or more applications of non-steroidal estrogen of saponins or saponin elements for preparing combinations treating the Parkinson's disease, except to the saponin elements and saponins which can effectively impact a retractile force of myocardium, the material can directly or non-directly adjust functions of the cytoplasm, the nucleolus, the membrane-binding protein or acceptors. When the protein or accepters are activated by the agonist that combines them, or the activity is promoted by making the antagonist deactivation, it can increase and / or normalize the organizations, organs, cell types or amount and / or turnover of the membrane receptor combination in the cellular organ.
Owner:PHYTOPHARM LTD
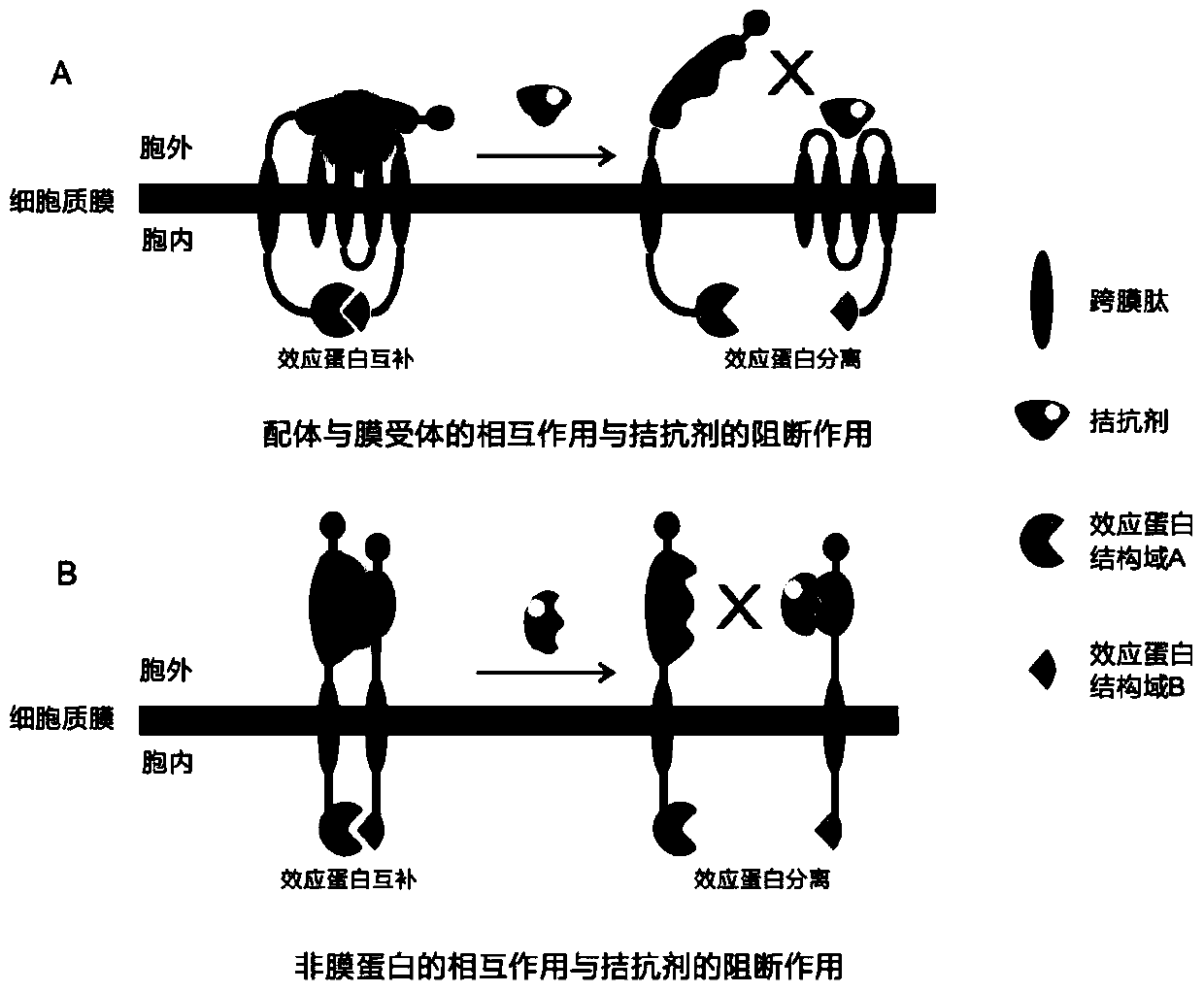
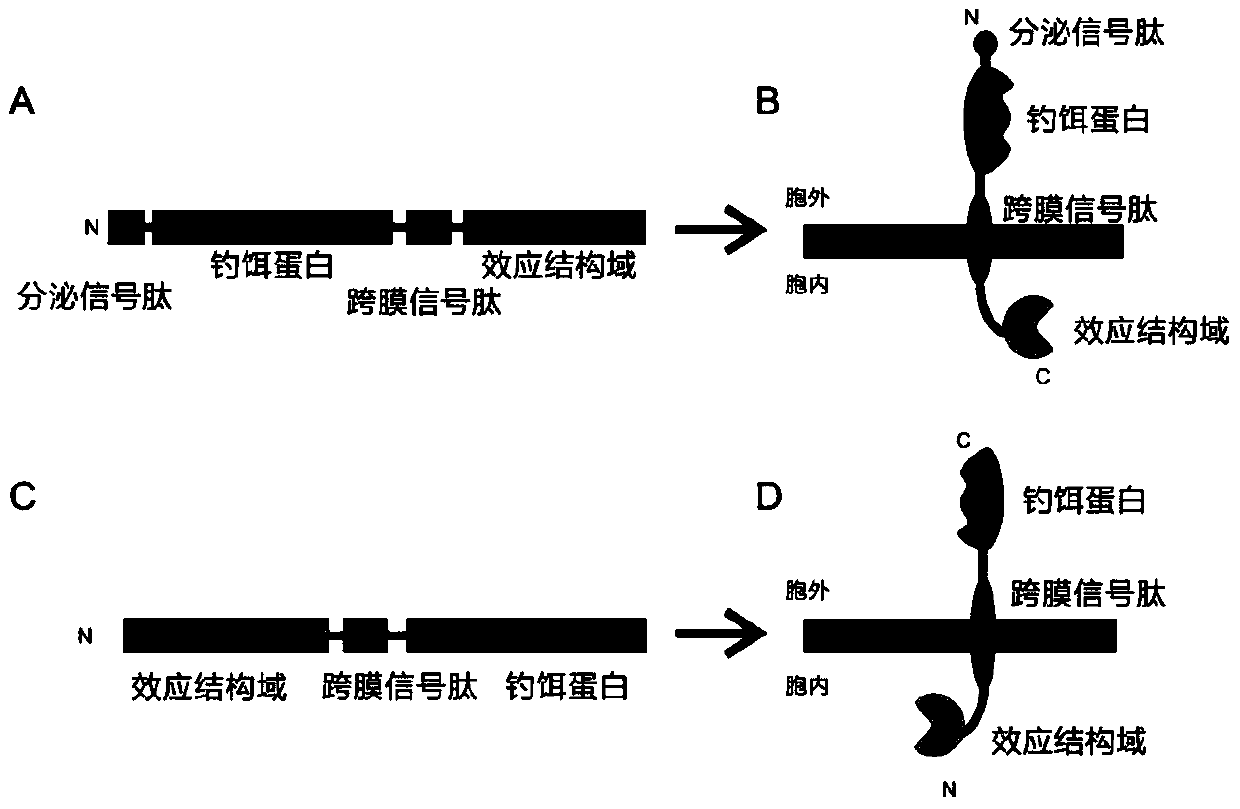
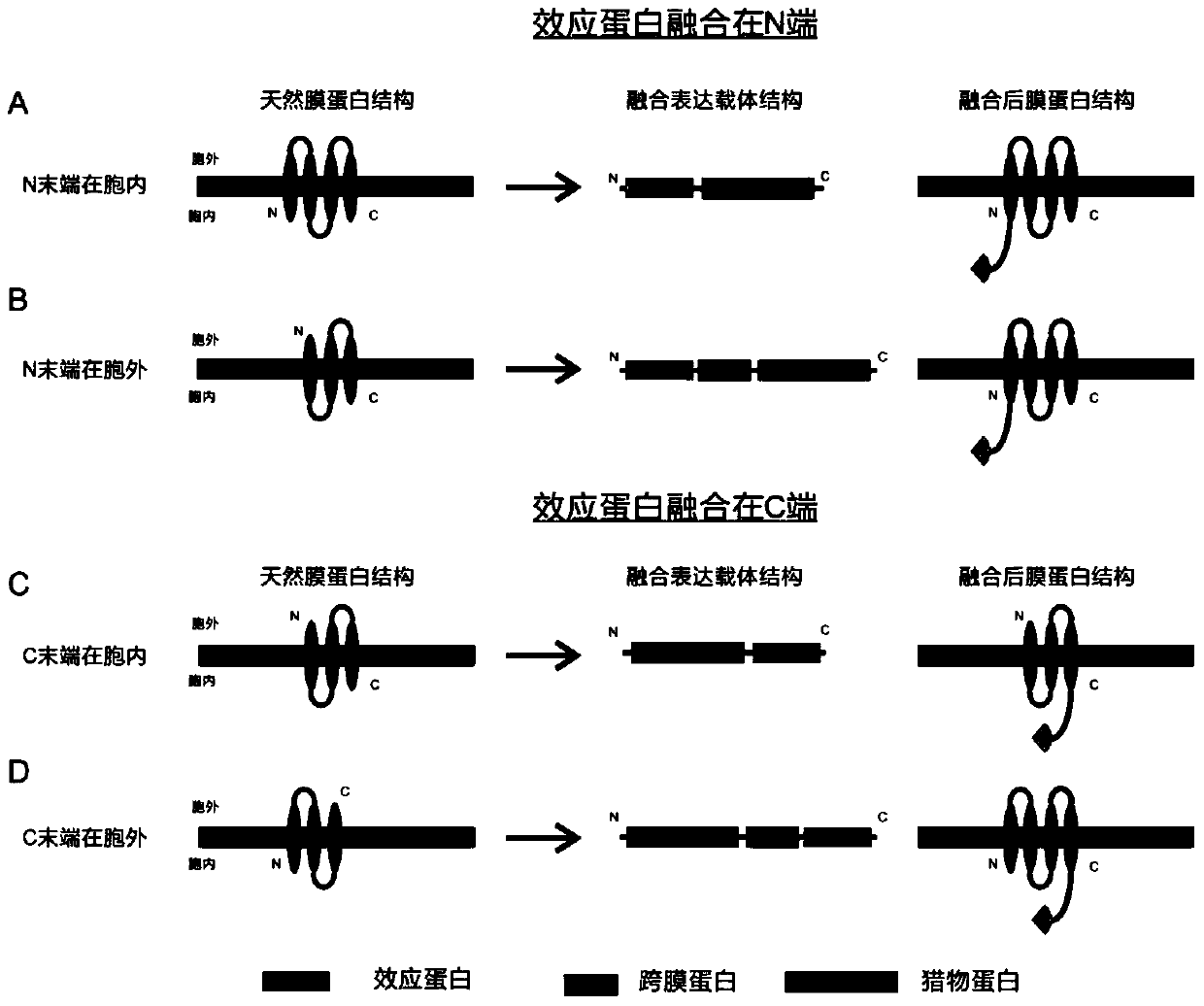
A High-Throughput Screening Method for Prey Antagonists Based on Membrane-Bound Proteins and Fluorescence Complementation
ActiveCN105986001BAvoid loss of activityImprove reliabilityFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementExtracellularIntracellular
The invention provides a high-flux prey antagonist screening method based on membrane binding protein and fluorescence complementation, relates to the field of gene engineering, and concretely discloses a novel method for screening a receptor antagonist and application thereof. According to the method, a ligand existing outside a cell and a receptor are expressed to the cytomembrane through a signal peptide fusion expression strategy; a ligand structural domain generating mutual action with the receptor is enabled to be remained at the outer side of the cytomembrane; the ligand is coupled with intracellular effect proteins through transmembrane peptide; the ligand and the receptor take mutual effects at the outer side of the cytomembrane, or the effect proteins coupled in the cells are antagonized; and the effect is converted into a macroscopical biological effect, so that the method is provided for the screening of the secretion type ligand and receptor antagonists.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com