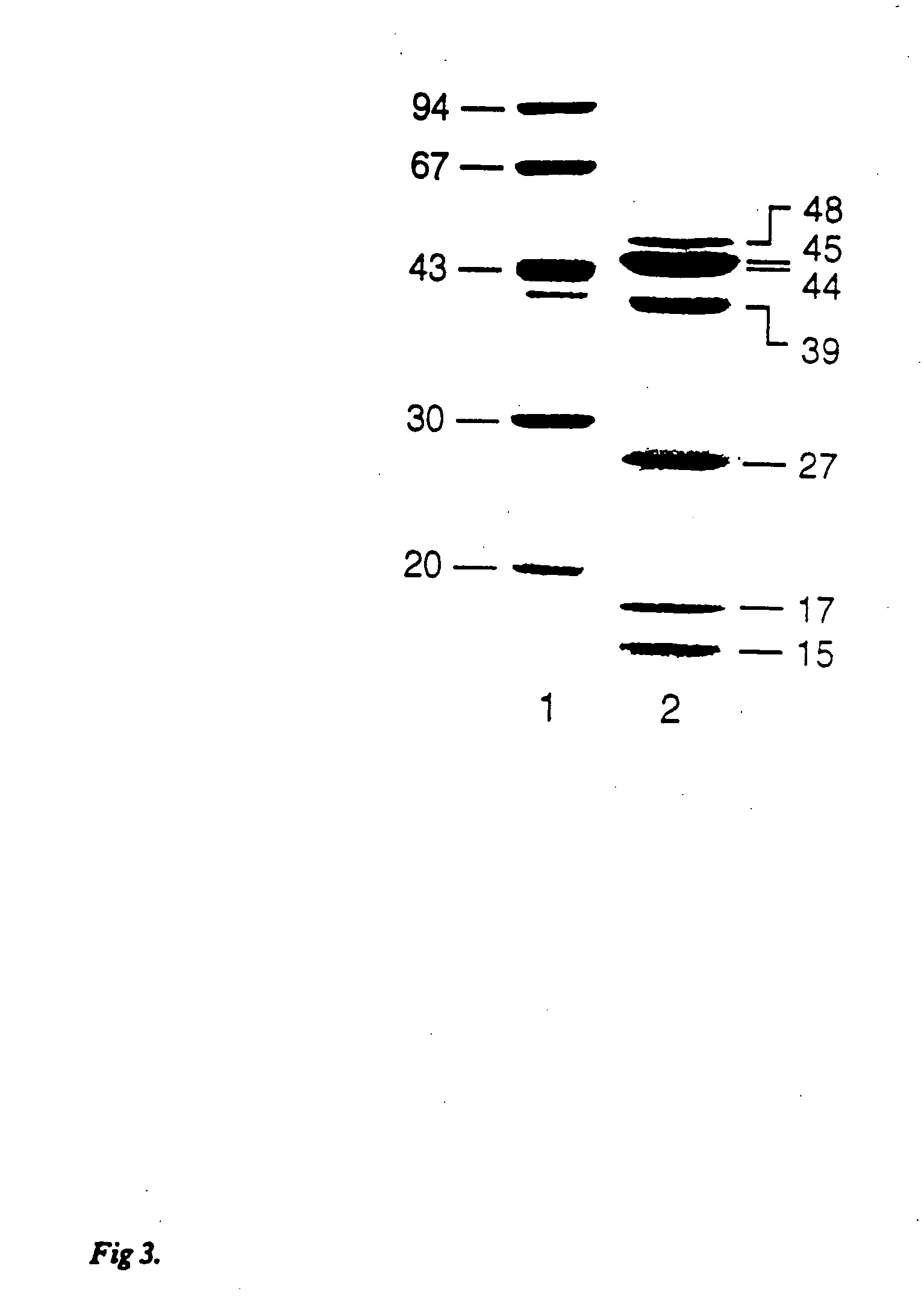
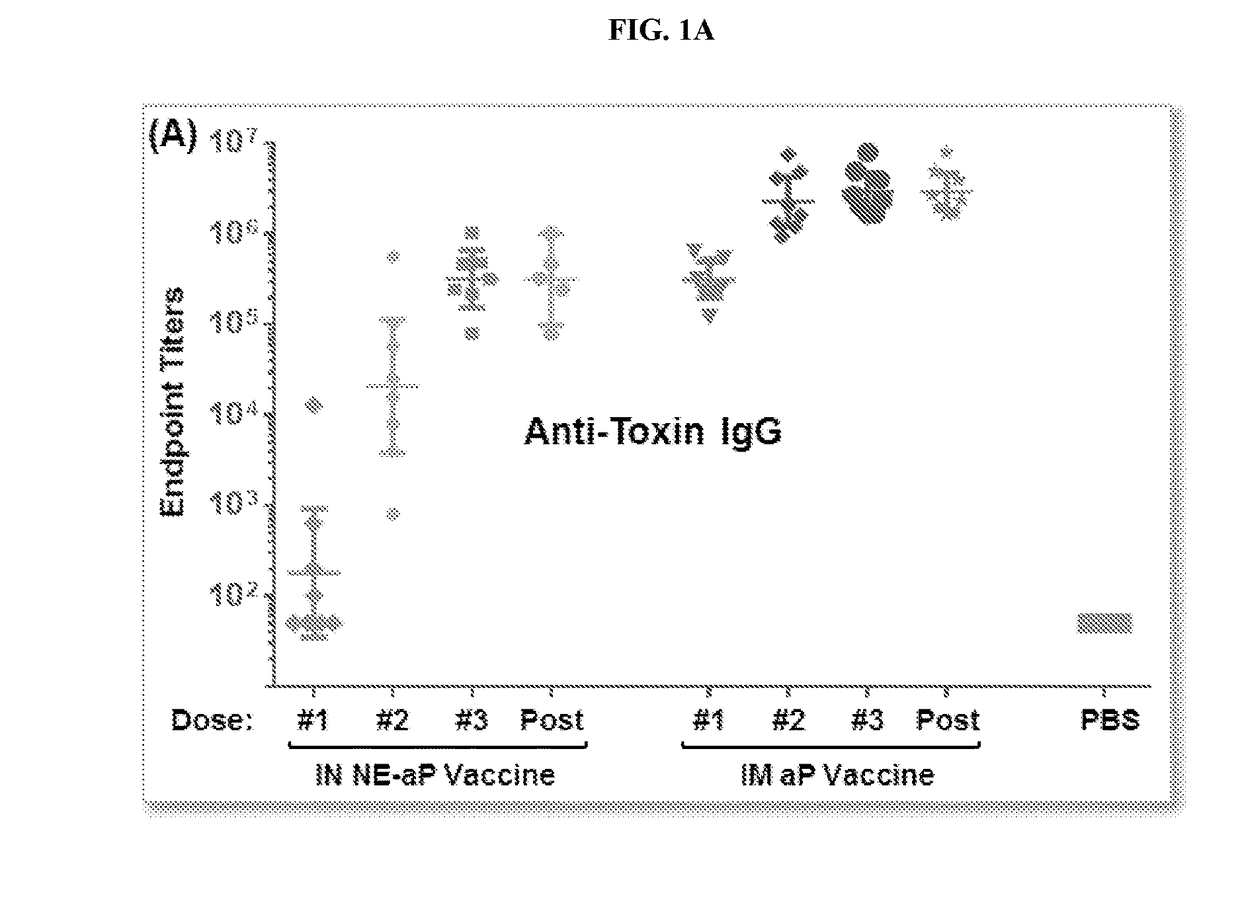
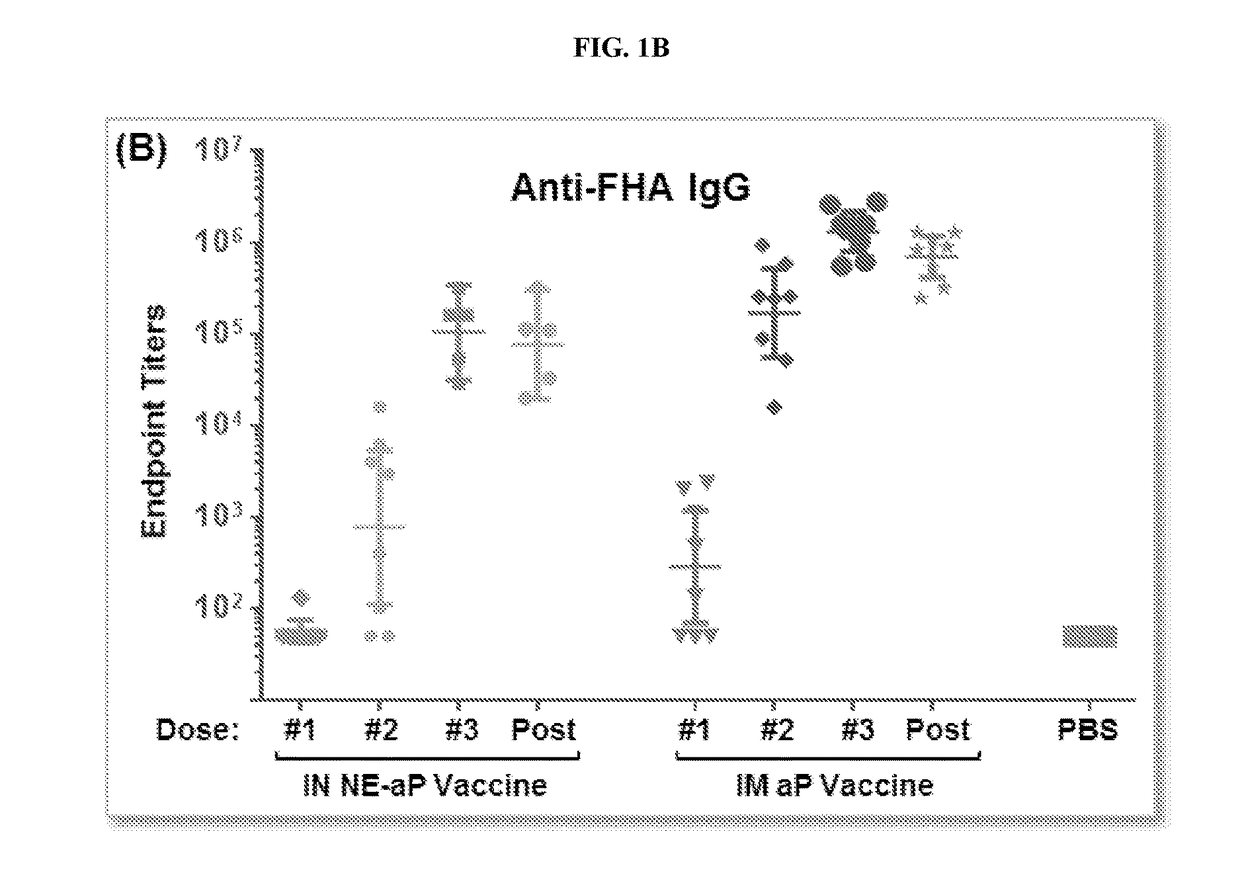
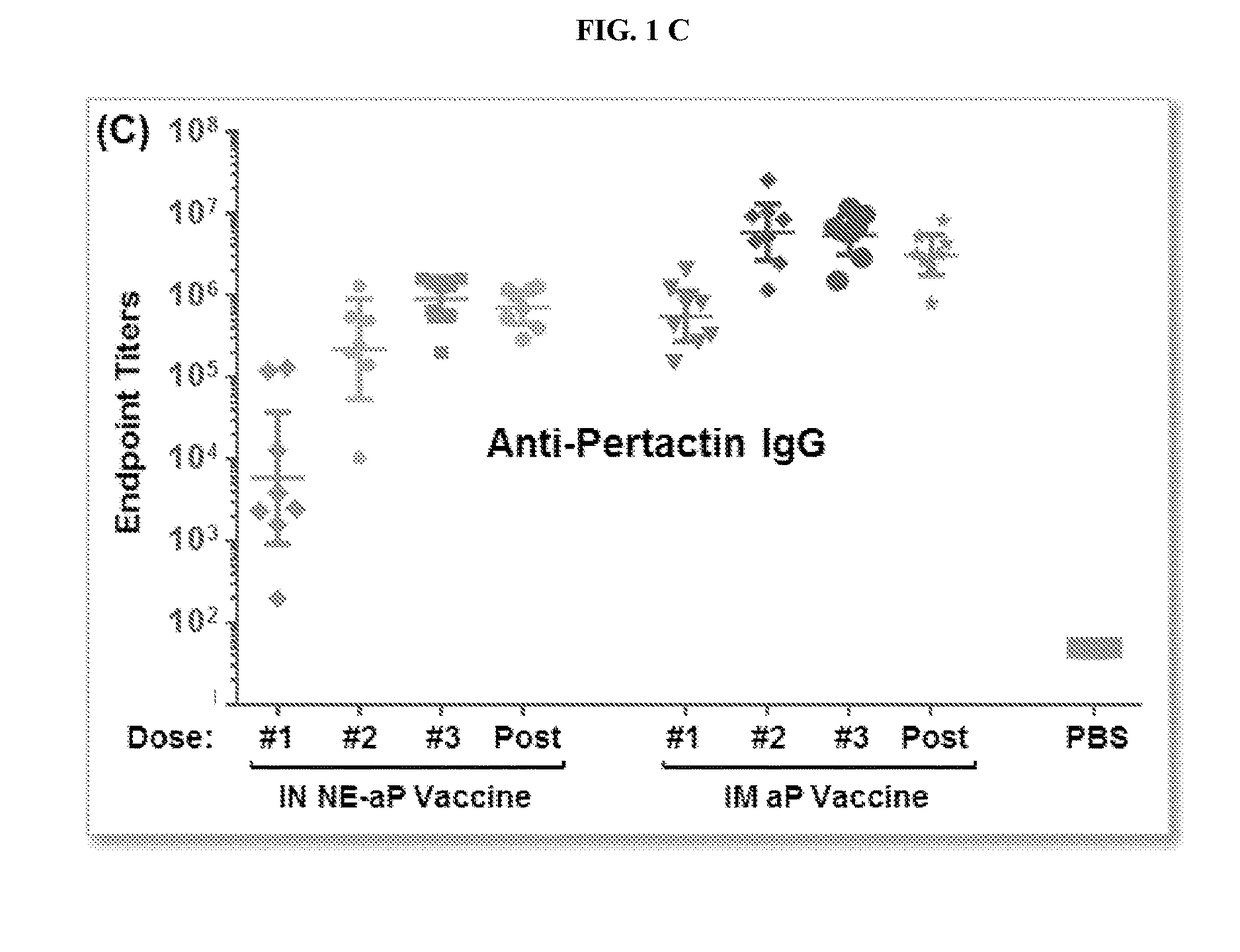
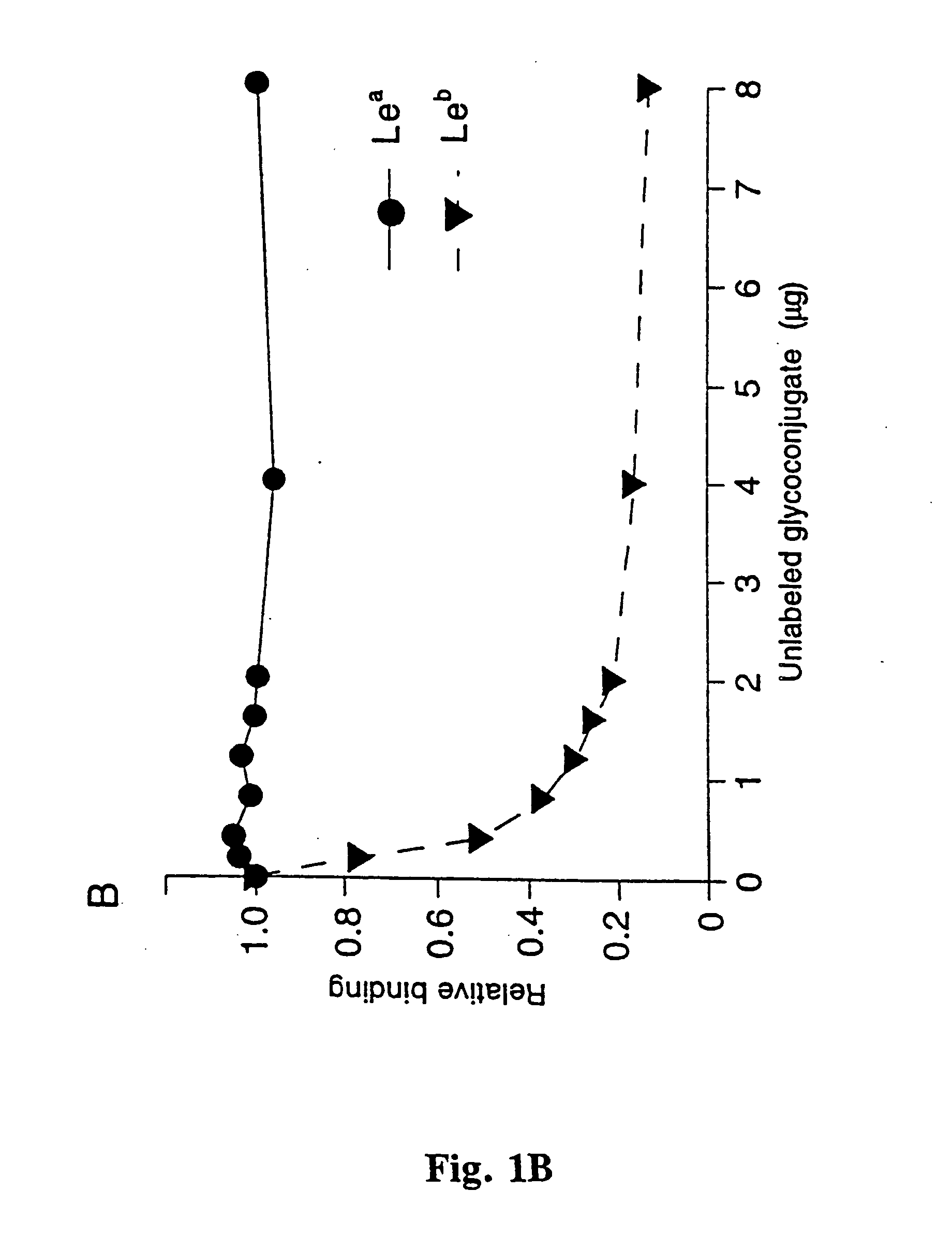
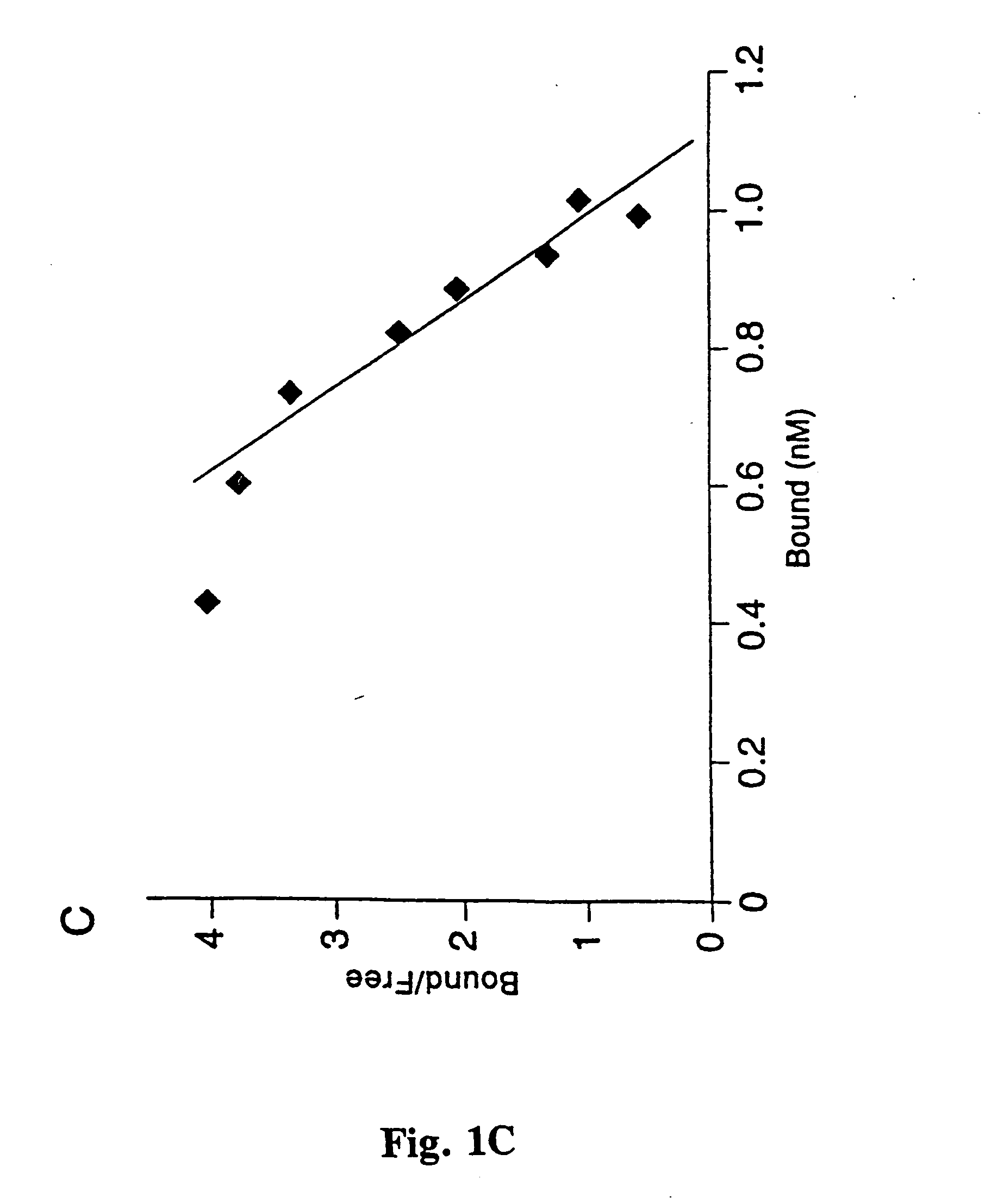
Patents
Literature
68 results about "Bacterial Adhesins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
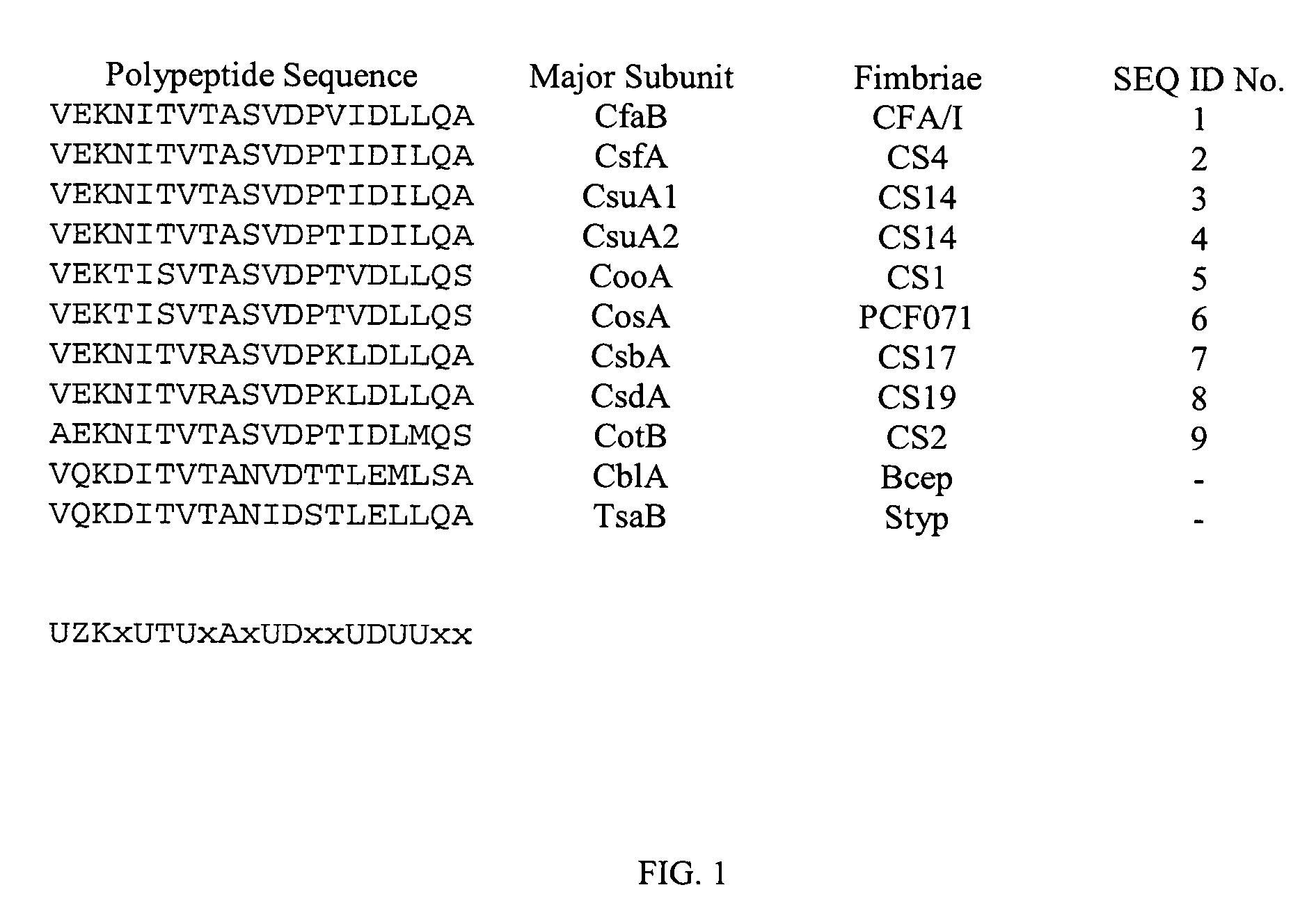
Bacterial adhesin. Adhesins are cell-surface components or appendages of bacteria that facilitate adhesion or adherence to other cells or to surfaces, usually the host they are infecting or living in. Adhesins are a type of virulence factor.
Adhesin as immunogen against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli
ActiveUS20060153878A1Inhibition of colonizationAvoid stickingAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliDiarrhea
The inventive subject matter relates to the methods for the induction of immunity and prevention of diarrhea resulting from Escherichia coli. The inventive subject matter also relates to the use Escherichia coli adhesins as immunogens and to the construction of conformationally stability and protease resistant Escherichia coli adhesin constructs useful for inducing immunity to Escherichia coli pathogenic bacteria. The methods provide for the induction of B-cell mediated immunity and for the induction of antibody capable of inhibiting the adherence and colonization of Escherichia coli including enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, to human cells.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Streptococcus pneumoniae 37-kDa surface adhesin a protein
The invention provides a nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein from Streptococcus pneumoniae. Also provided are isolated nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. The invention also provides purified polypeptides encoded by the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein from and the nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. Also provided are antibodies which selectively binds the polypeptides encoded by the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein and the nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. Also provided are vaccines comprising immunogenic polypeptides encoded by the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein and the nucleic acids comprising a unique fragment of at least 10 nucleotides of the 37-kDa protein. Further provided is a method of detecting the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a sample comprising the steps of contacting a sample suspected of containing Streptococcus pneumoniae with nucleic acid primers capable of hybridizing to a nucleic acid comprising a portion of the nucleic acid encoding the 37-kDa protein, amplifying the nucleic acid and detecting the presence of an amplification product, the presence of the amplification product indicating the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae in the sample. Further provided are methods of detecting the presence of Streptococcus pneumoniae in a sample using antibodies or antigens, methods of preventing and treating Streptococcus pneumoniae infection in a subject.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Oral delivery systems for microparticles
PCT No. PCT / AU92 / 00141 Sec. 371 Date Nov. 30, 1992 Sec. 102(e) Date Nov. 30, 1992 PCT Filed Apr. 2, 1992 PCT Pub. No. WO92 / 17167 PCT Pub. Date Oct. 15, 1992There are disclosed complexes and compositions for oral delivery of a substance or substances to the circulation or lymphatic drainage system of a host. The complexes of the invention comprise a microparticle coupled to at least one carrier, the carrier being capable of enabling the complex to be transported to the circulation or lymphatic drainage system via the mucosal epithelium of the host, and the microparticle entrapping or encapsulating, or being capable of entrapping or encapsulating, the substance(s). Examples of suitable carriers are mucosal binding proteins, bacterial adhesins, viral adhesins, toxin binding subunits, lectins, Vitamin B12 and analogues or derivatives of Vitamin B12 possessing binding activity to Castle's intrinsic factor.
Owner:ACCESS PHARMA
Immunogenic compositions for gram positive bacteria such as streptococcus agalactiae
InactiveUS20060165716A1InhibitionEasy to eliminateAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsBacteroidesVirulent characteristics
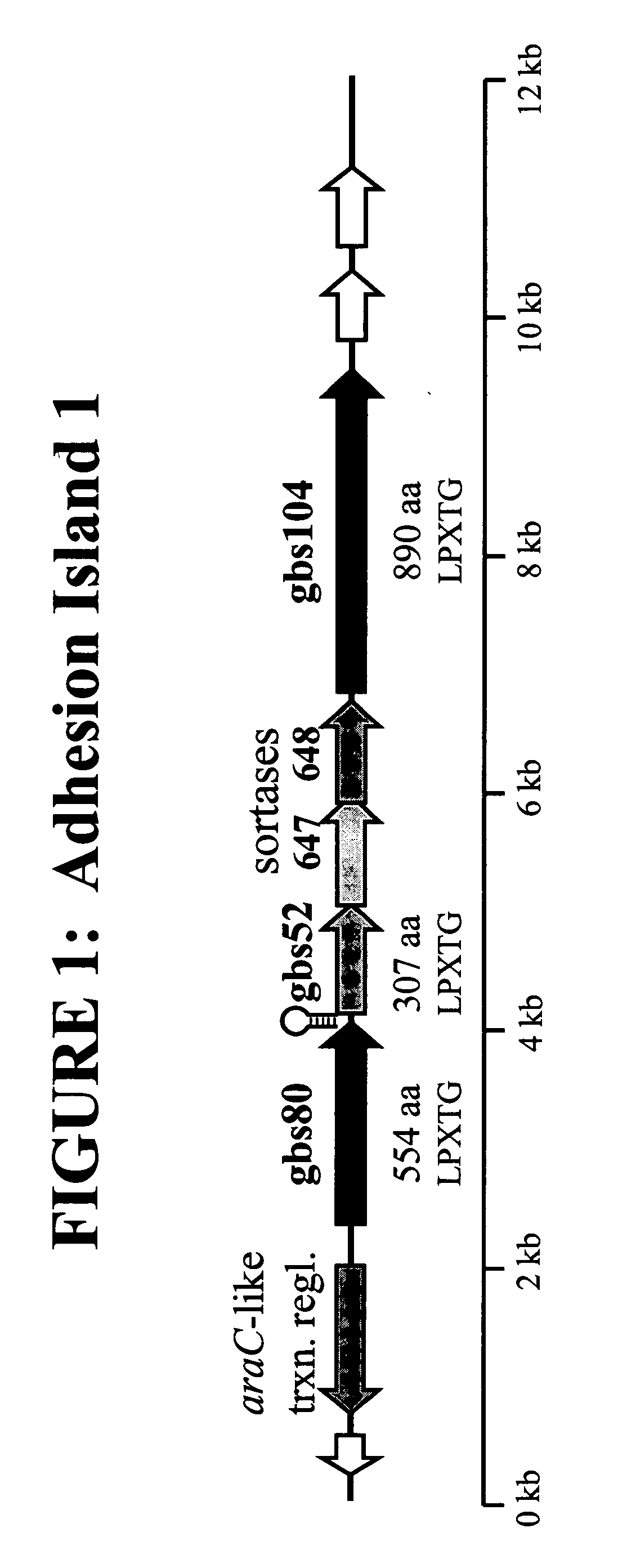
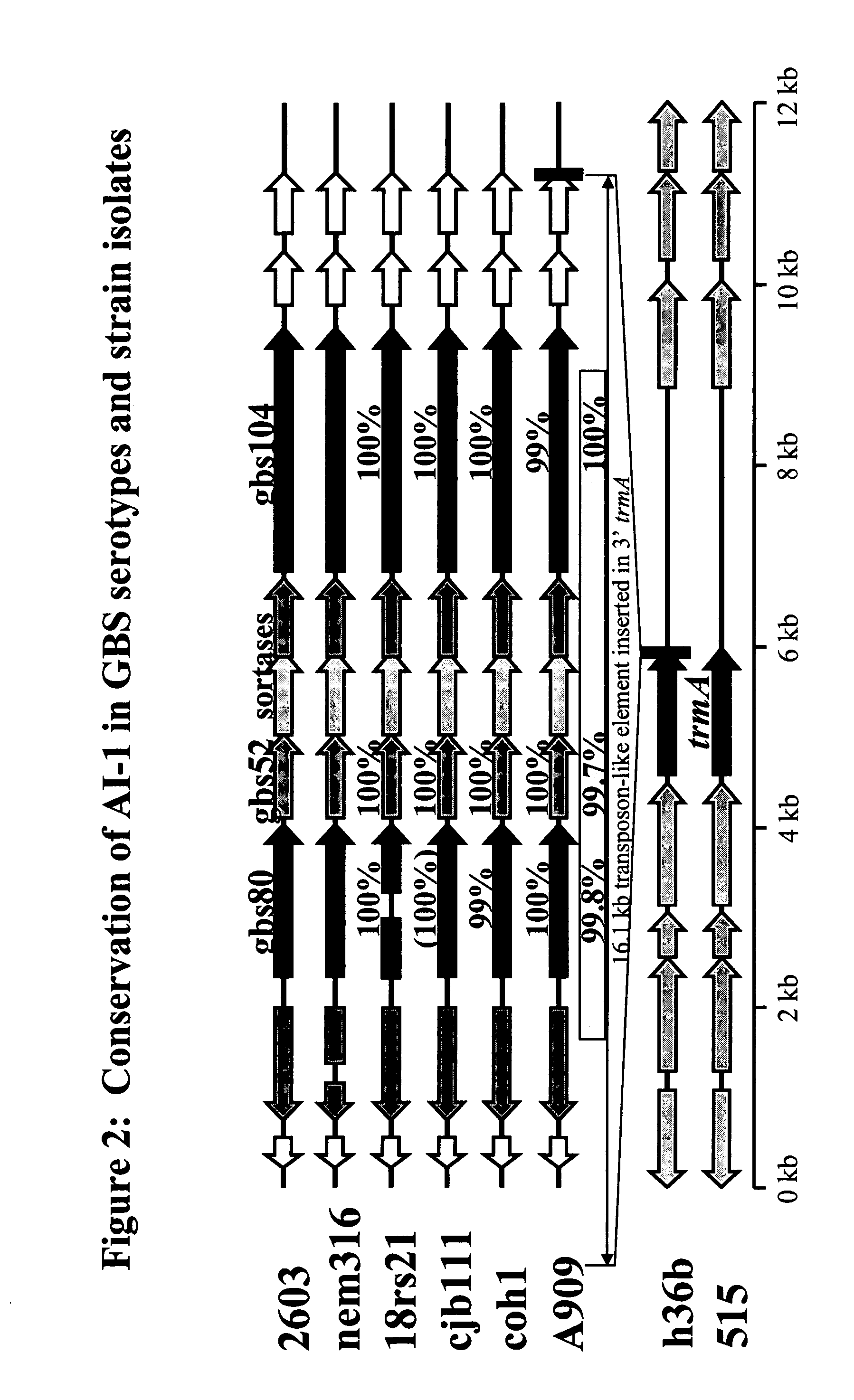
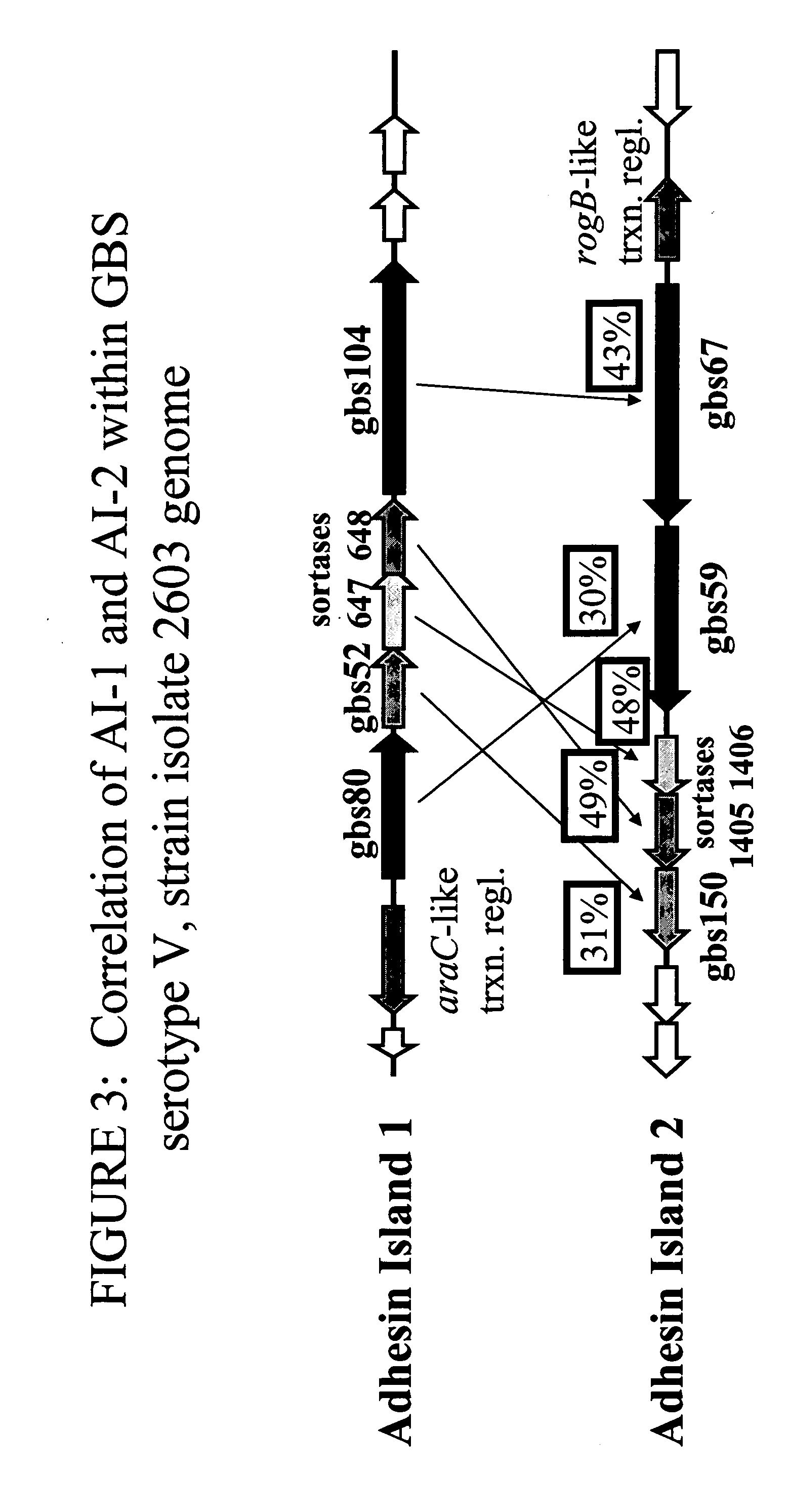
The invention relates to the identification of a new adhesin islands within the genomes of several Group A and Group B Streptococcus serotypes and isolates. The adhesin islands are thought to encode surface proteins which are important in the bacteria's virulence. Thus, the adhesin island proteins of the invention may be used in immunogenic compositions for prophylactic or therapeutic immunization against GAS or GBS infection. For example, the invention may include an immunogenic composition comprising one or more of the discovered adhesin island proteins.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Polysaccharide-staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein conjugates for immunization against nosocomial infections
ActiveUS20070141077A1Prevention and reduction of severityAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsCarrier proteinImmunogenicity
Immunogenic polysaccharide-protein conjugates having a polysaccharide antigen (or its oligosaccharide fragment representing one or more antigenic epitopes) derived from a nosocomial pathogen conjugated to a staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein are used in immunogenic compositions to elicit antibody responses to both the polysaccharide antigen and the staphylococcal surface adhesin carrier protein. Such immunogenic compositions are used to immunize against diseases caused by Staphylococcal aureus, Staphylococcal epidermidis or other nosocomial pathogens.
Owner:WYETH HOLDINGS CORP
L-amino acid producing microorganism and a method for producing L-amino acid
InactiveUS20060160191A1Improve productivityImprove L-amino acid productivityBacteriaSugar derivativesBiotechnologyBacteroides
An L-amino acid producing bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family is described, wherein the bacterium has been modified so as to not produce type I fimbrial adhesin protein is cultured in a medium to produce and excrete said L-amino acid in the medium, and collecting said L-amino acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
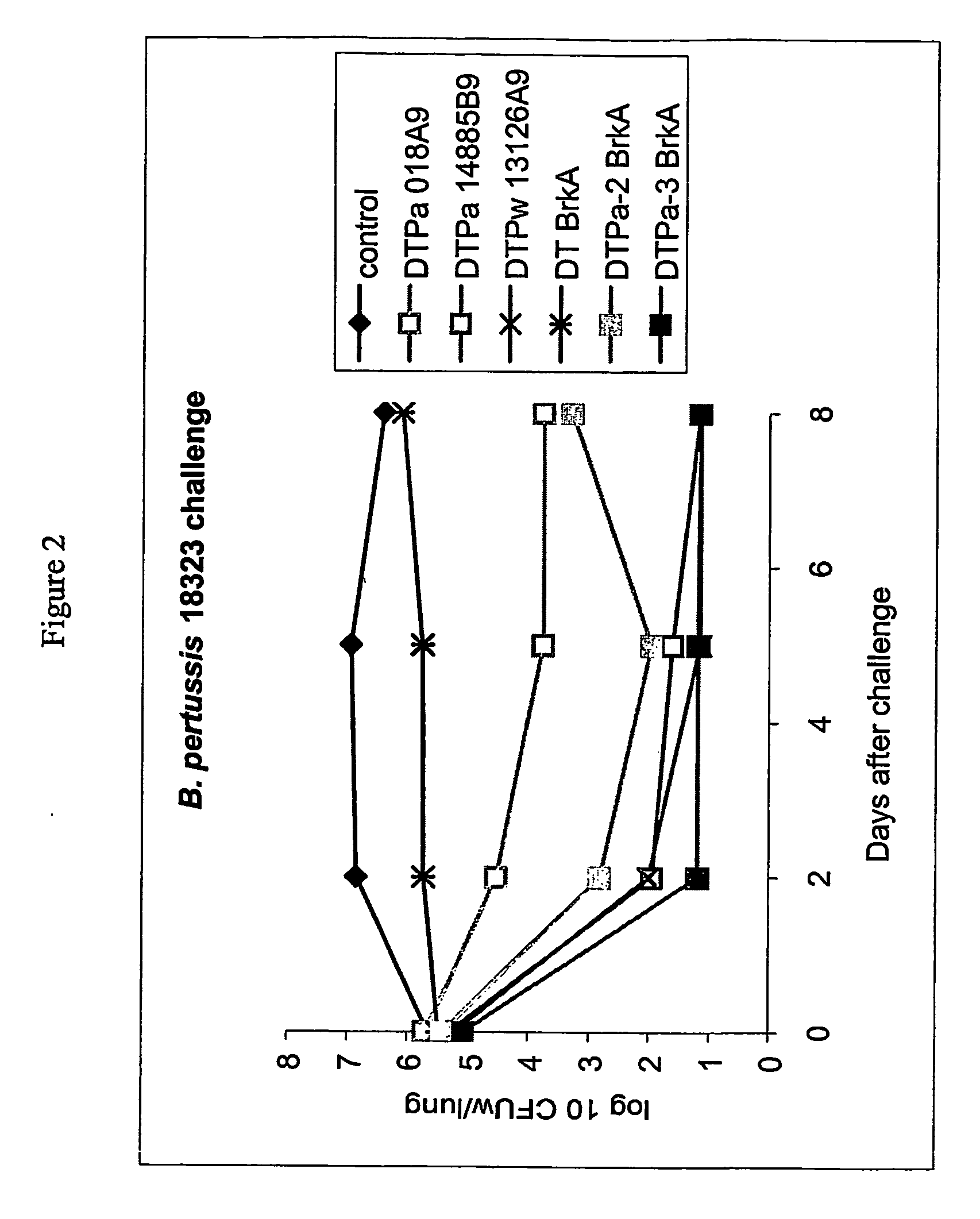
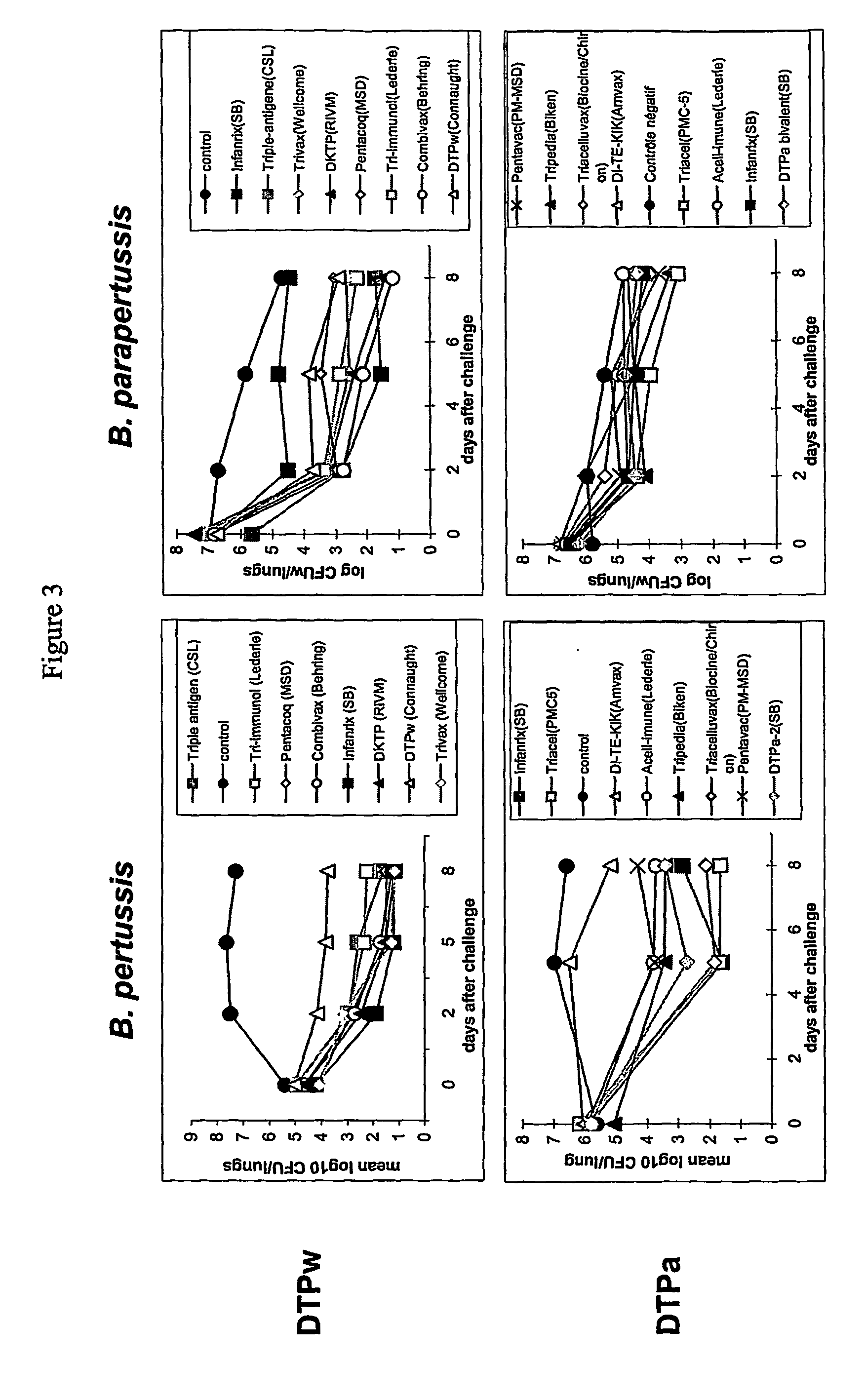
Pertussis antigens and use thereof in vaccination
ActiveUS20070116711A1Readily apparentBacterial antigen ingredientsSugar derivativesVaccinationBacterial Adhesins
The invention provides BASB232 polypeptides and polynucleotides encoding BASB232 polypeptides and methods for producing such polypeptides by recombinant techniques. Also provided are diagnostic, prophylactic and therapeutic uses. The invention further provides immunogenic compositions comprising a plurality of antigens selected from at least two different categories of antigen, having different functions within Bordetella. Examples of such categories of antigen are autotransporter proteins, iron acquisition proteins, lipoproteins, adhesins and toxins / invasins.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Capsular polysaccharide adhesin antigen, preparation, purification and use
A substantially pure capsular exopolysaccharide adhesin of coagulaso-negative staphylococcal strains, and a general method to prepare such adhesins, are described. Vaccines composed of such adhesins, and uses of such adhesins to produce polyclonal and mono-clonal antibodies against such adhesins, are also disclosed. The adhesins are useful in coating polymeric medical materials to prevent colonization by coagulase-negative staphylococcal strains, and as a probe in selecting desirable polymeric medical materials. Such adhesin antibodies are useful in vivo to prevent infection by noso-comial coagulase-negative staphylococcal strains, in assays for the detection of such bacteria, in assays for the estimation of such adhesins in complex mixtures, and as an affinity chromatography matrix.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Method of inhibiting Candida-related infections using donor selected or donor stimulated immunoglobulin compositions
InactiveUS20050287146A1Inhibit growthInhibit severityImmunoglobulins against bacteriaBiological material analysisYeastStaphylococcus
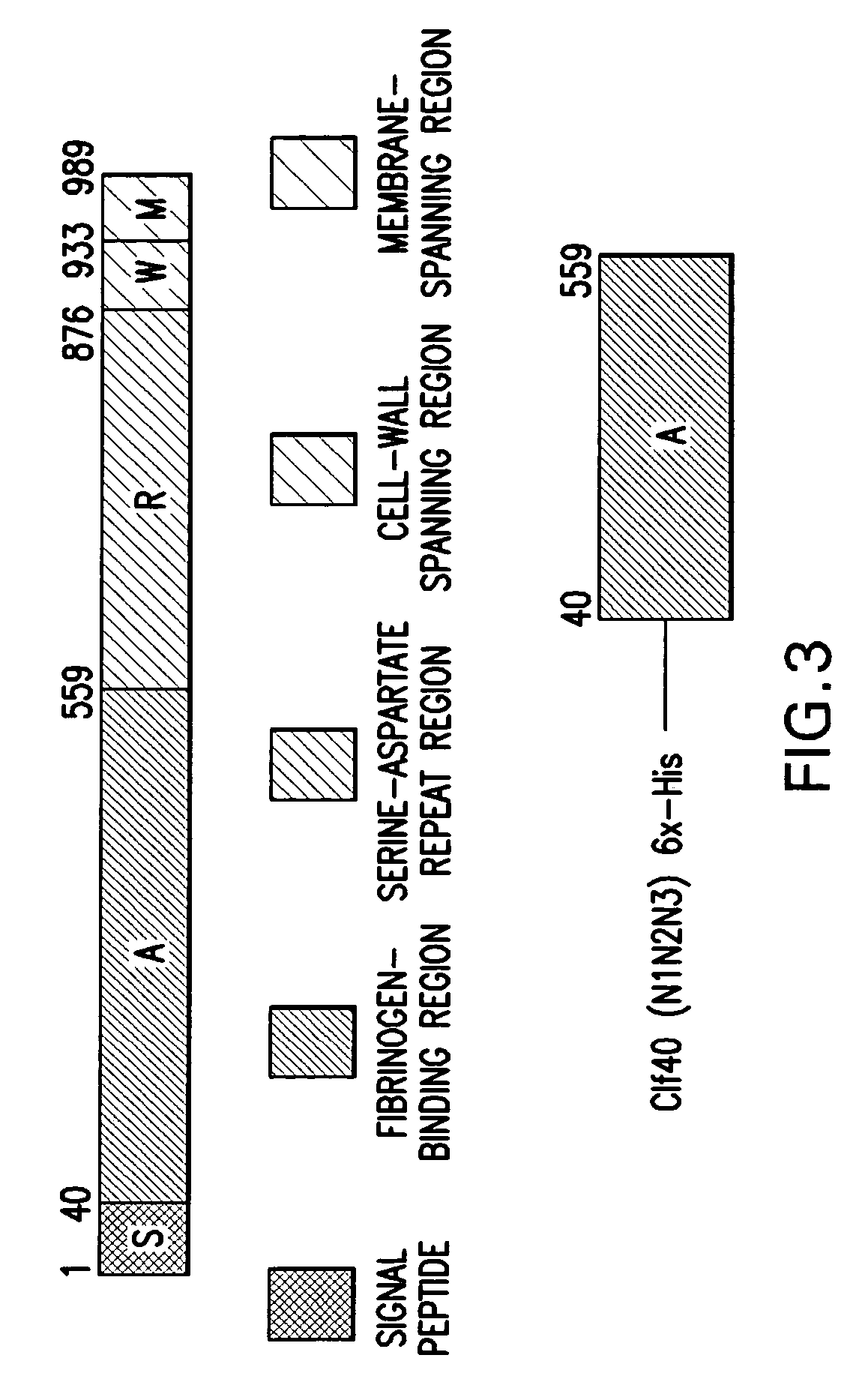
A method for treating or preventing infections from yeast of the Candida species is provided wherein an immunoglobulin composition containing high titers of antibodies to staphylococcal adhesins ClfA and SdrG is administered in an amount effective to inhibit the growth and progression of Candidial infections. The compositions and methods of the present invention are advantageous in that they can be used to treat both staphylococcal and Candidial infections at the same time, and they are particularly effective in treating or preventing late-onset sepsis in neonates.
Owner:TEXAS A&M UNIVERSITY +1
Anti-adhesin based passive immunoprophlactic
The invention relates to an immunogenic composition and method of the immunogenic composition for the production and administration of a passive immunoprophylactic against enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. The immunoprophylactic is made collecting anti-adhesin in the colostrum or milk of vaccinated domesticated animals such as cows. The immunoprophylactic is administered either as a dietary supplement or in capsular or tablet form.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
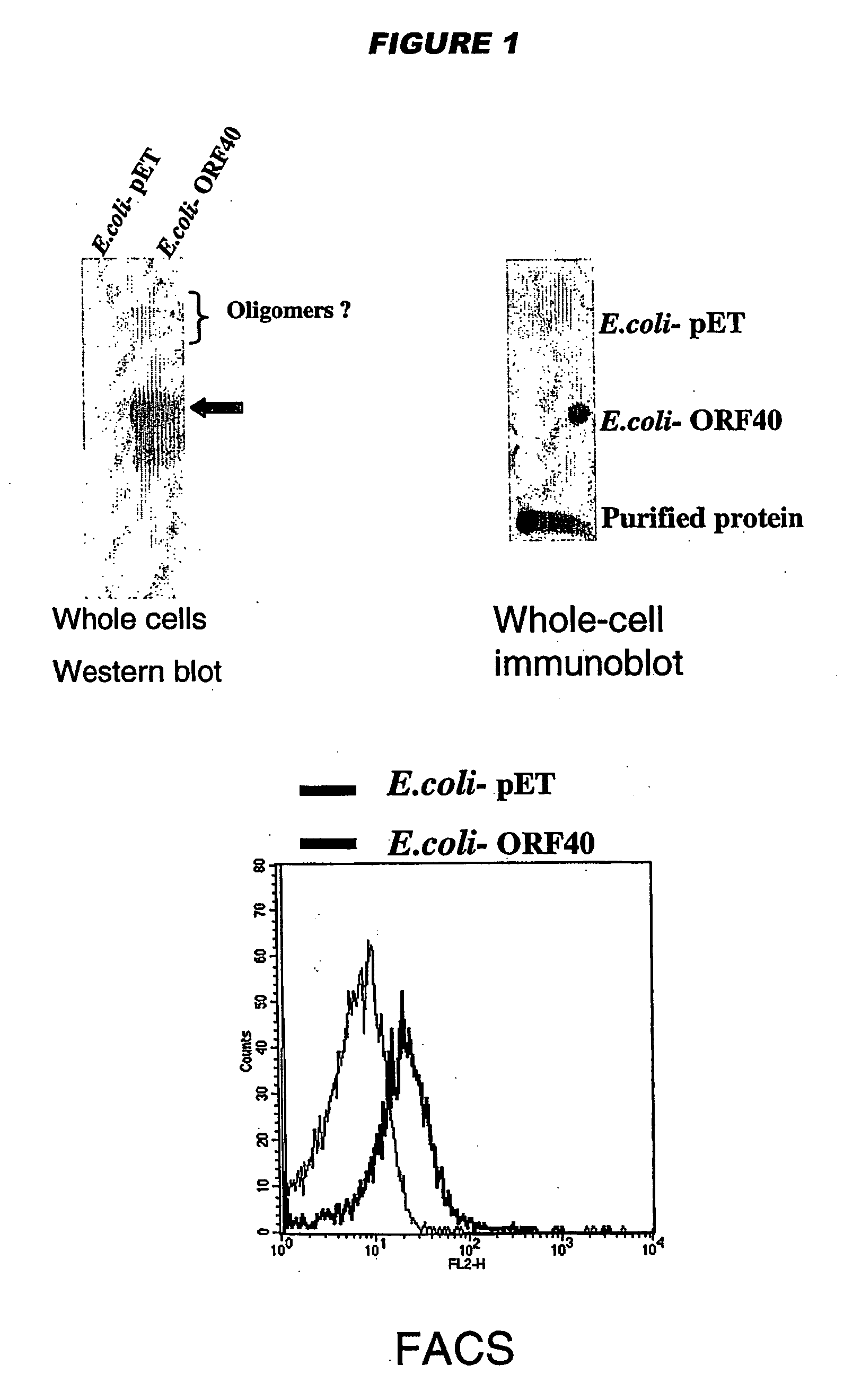
Meningococcus adhesins nada, app and orf 40
InactiveUS20050232936A1Inhibition of attachmentLower Level RequirementsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaEscherichia coliBacterial Adhesins
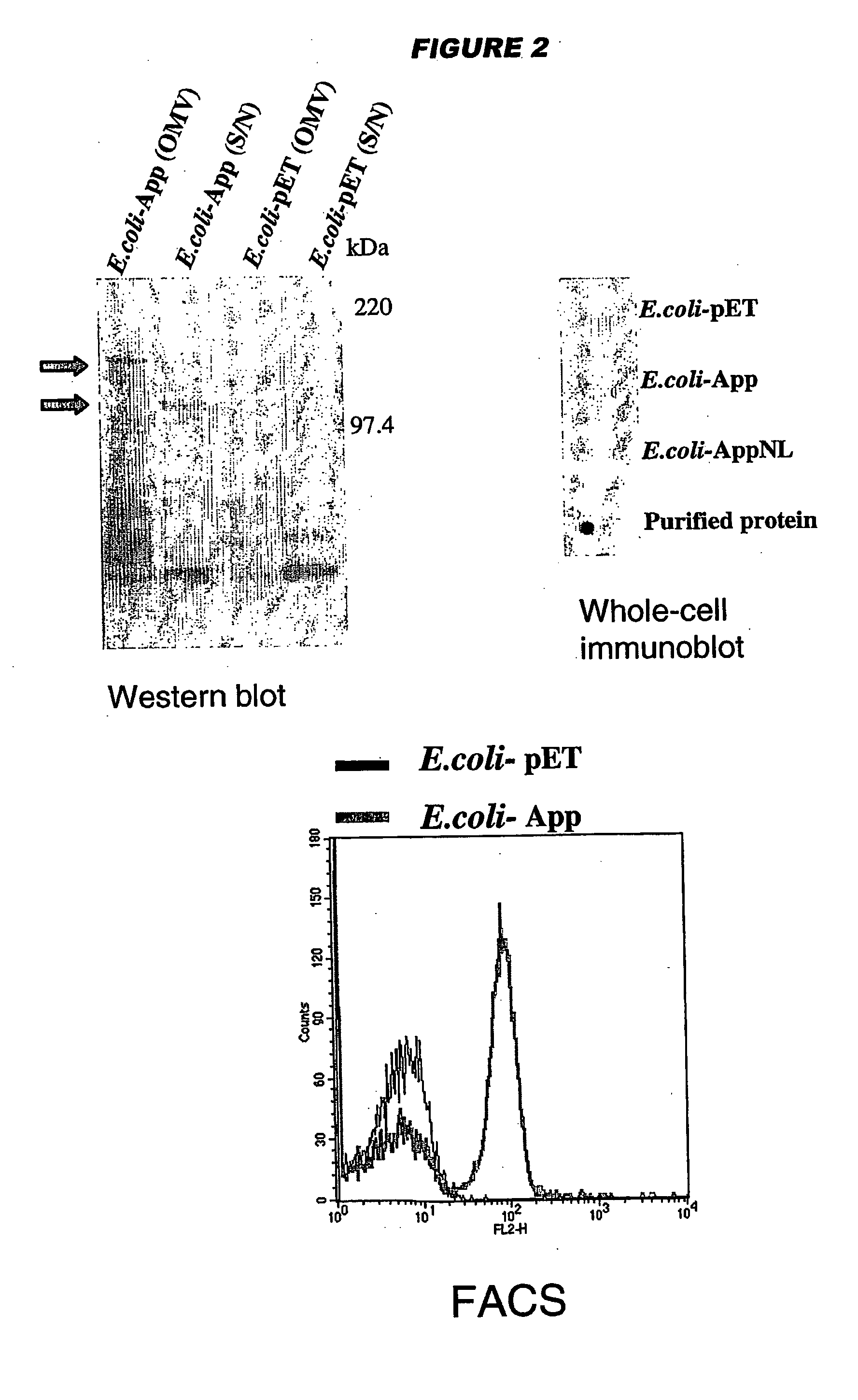
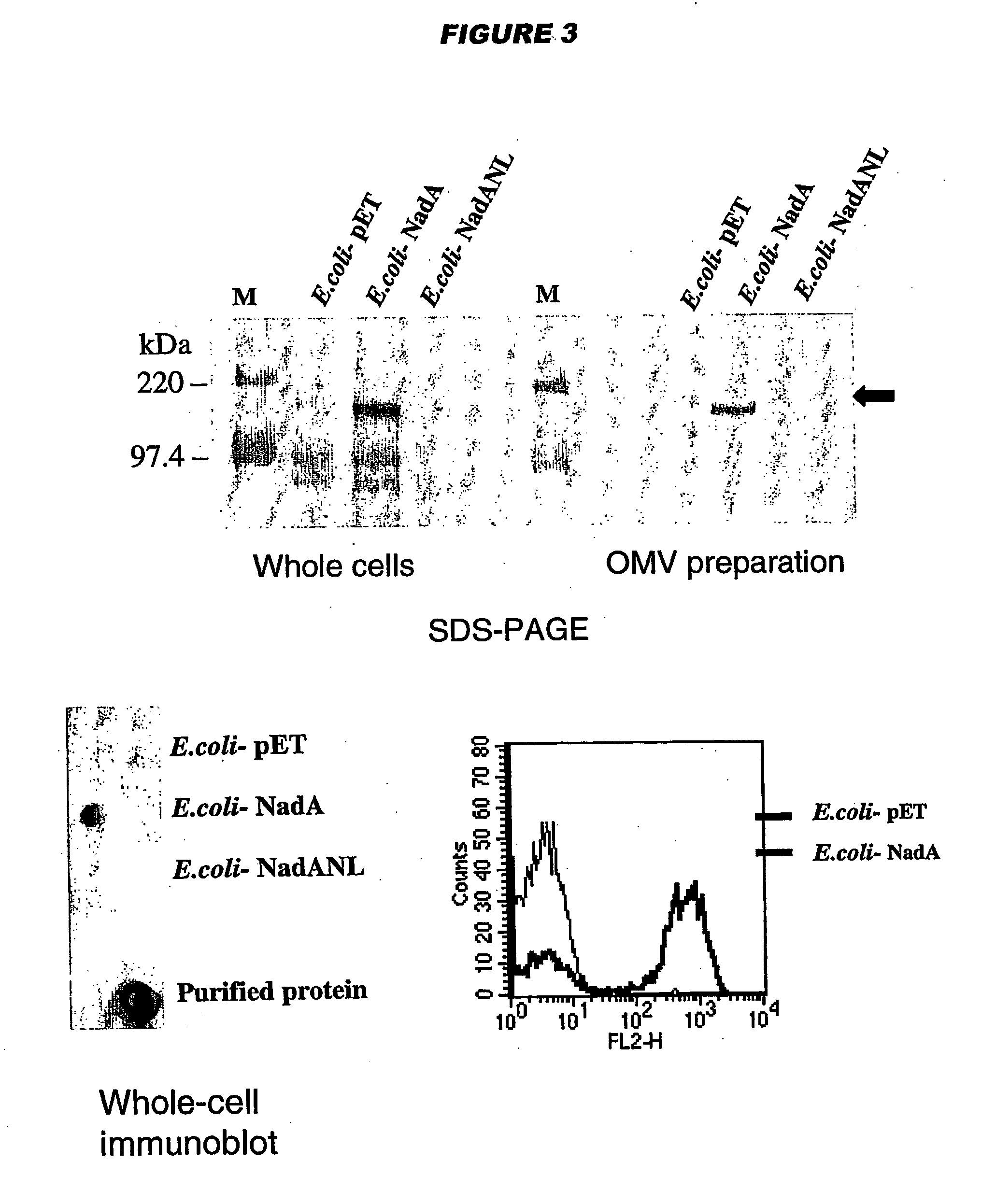
NadA, App and ORF40 function as adhesins in N. meningitidis. Adhesion can be modulated by targeting these three proteins. NadA allelic variants are disclosed. Autoproteolytic cleavage of App is disclosed, as is removal of the activity by mutagenesis. App is processed and secreted into culture medium when expressed in E. coli. Mature App proteins are disclosed. Knockout mutants are disclosed. Vesicles from non-Neisserial hosts with heterologous adhesin expression are disclosed.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Staphylococcus aureus exopolysaccharide and process
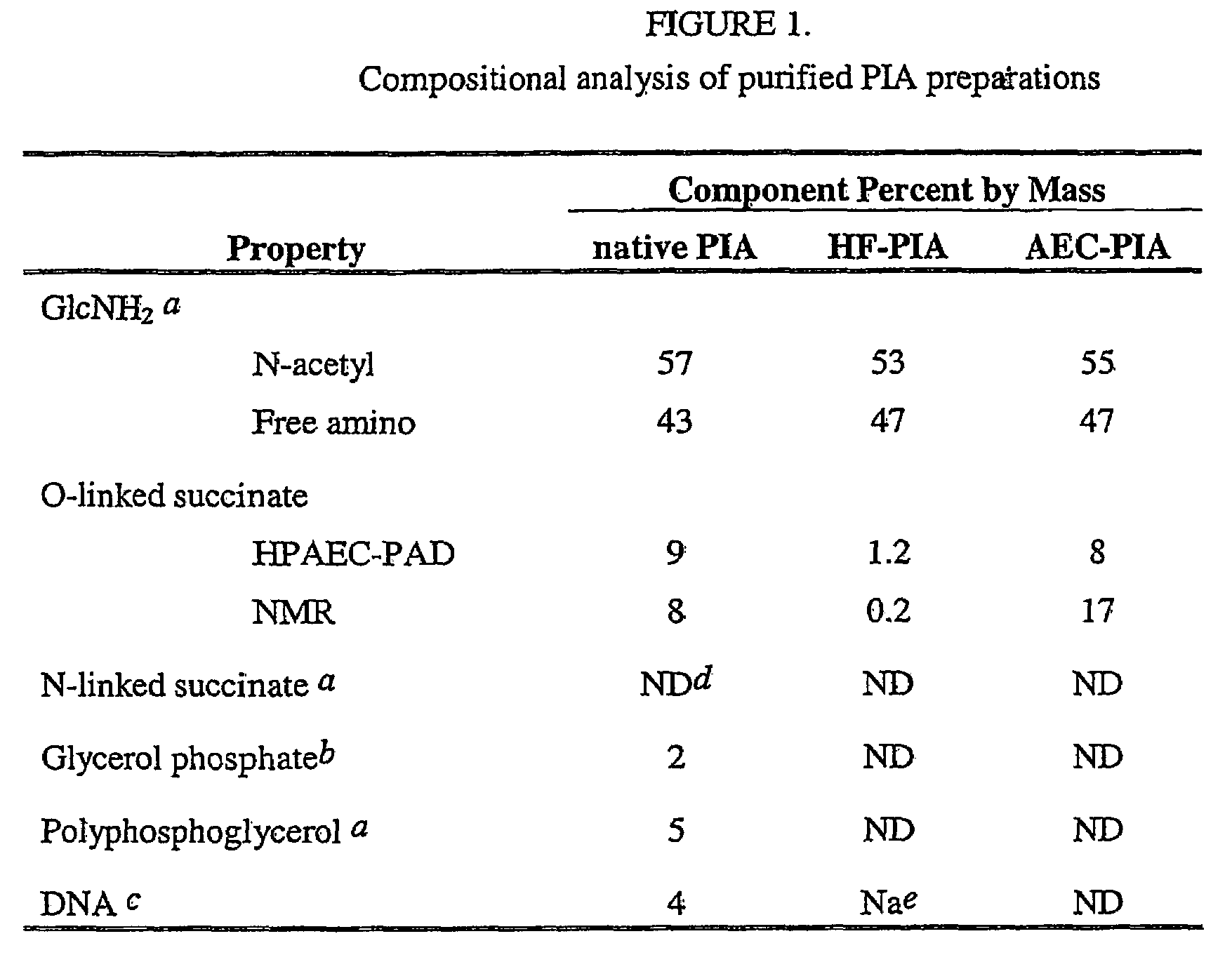
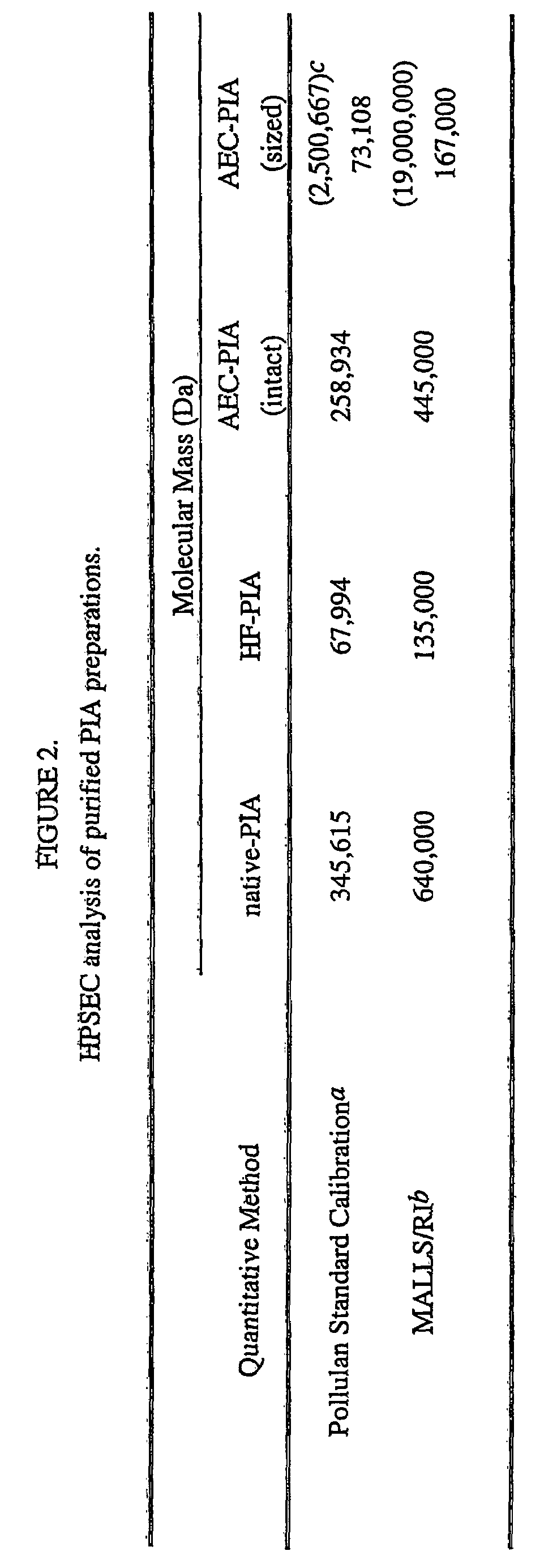
A high molecular weight polysaccharide intracellular adhesin (SAE) antigen having the general structure of poly-1,6,β-2-amidoglucopyranoside, which is variable substituted with N-acetyl and O-succinyl substituents is described. Also, a method is given for isolating this antigen from Staphylococcus aureus. The SAE can be used in a vaccine, either alone, conjugated to an immunogenic protein, and / or with an immunogenic adjuvant.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Diagnostics and treatments of periodontal disease
InactiveUS20110213129A1Mitigate prospectEfficient inductionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsPorphyromonas gingivalisArginine
This invention relates to the PrtR-PrtK cell surface protein of Porphyromonas gingivalis and in particular a multimeric cell association protein complex comprising the PrtR and PrtK proteins. Accordingly the invention provides a substantially purified antigenic complex for use in raising an antibody response directed against Porphyromonas gingivalis. The complex comprises at least one multimeric protein complex of arginine-specific and lysine-specific thiol endopeptidases each containing at least one adhesin domain, the complex having a molecular weight of greater than about 200 kDa. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions and associated agents based on said complex for the detection, prevention and treatment of Periodontal disease associated with P. gingivalis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
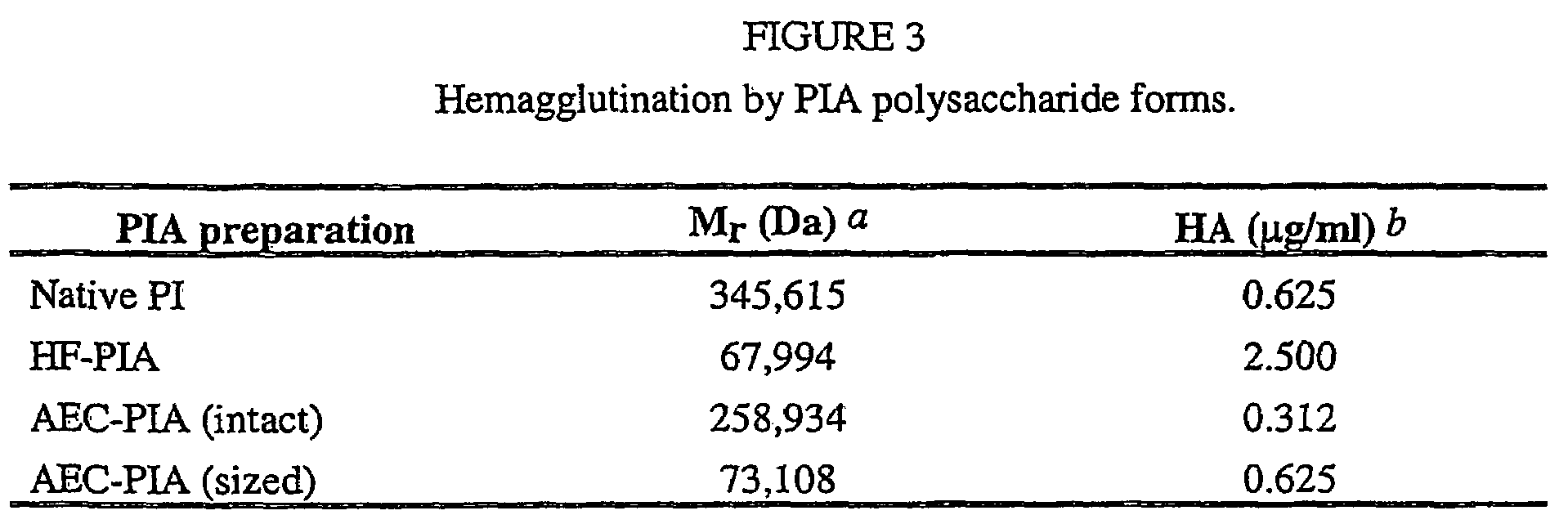
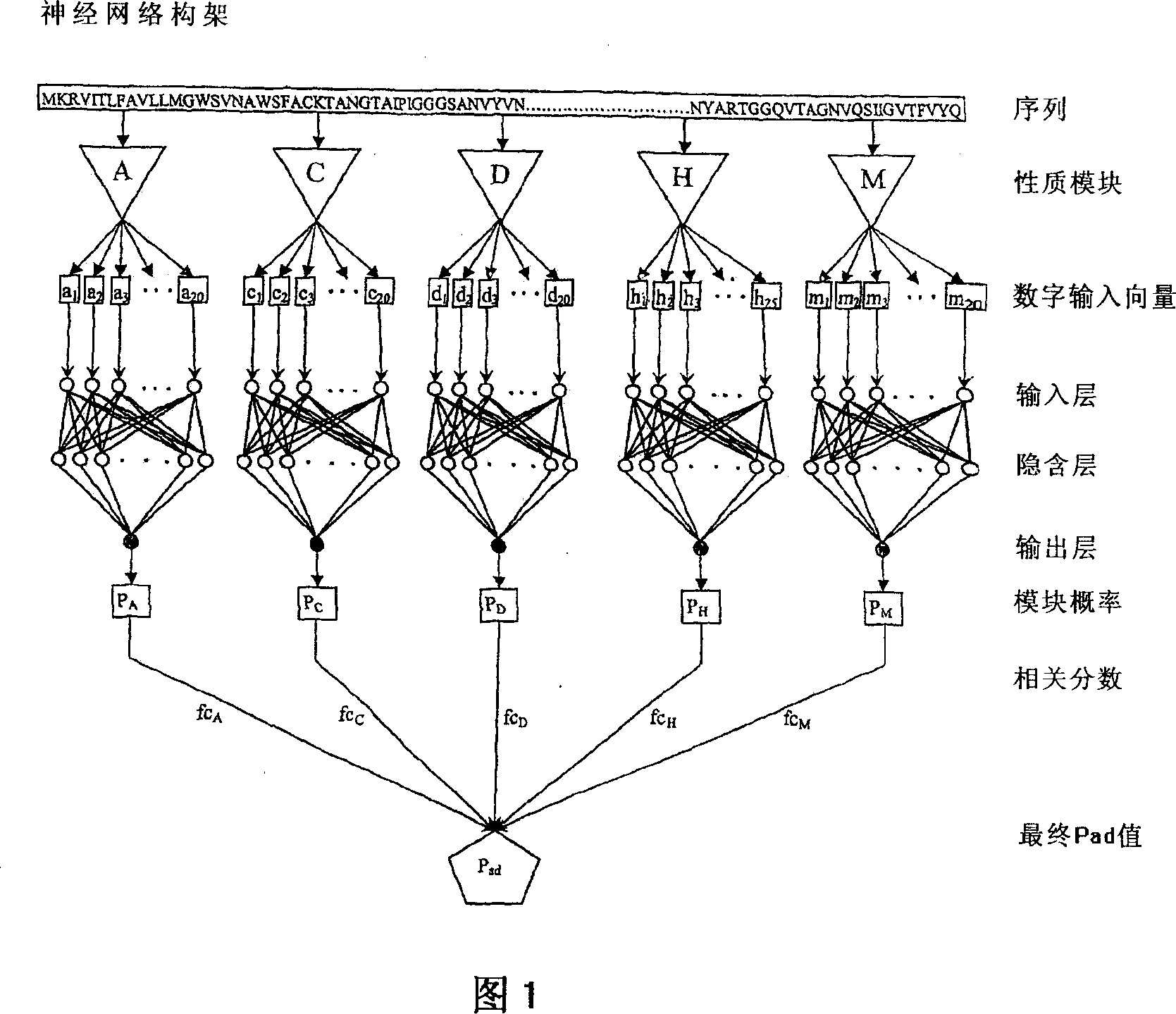
Computational method for identifying adhesin and adhesin-like proteins of therapeutic potential
InactiveCN101019123ABiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsDipeptideBacterial Adhesins
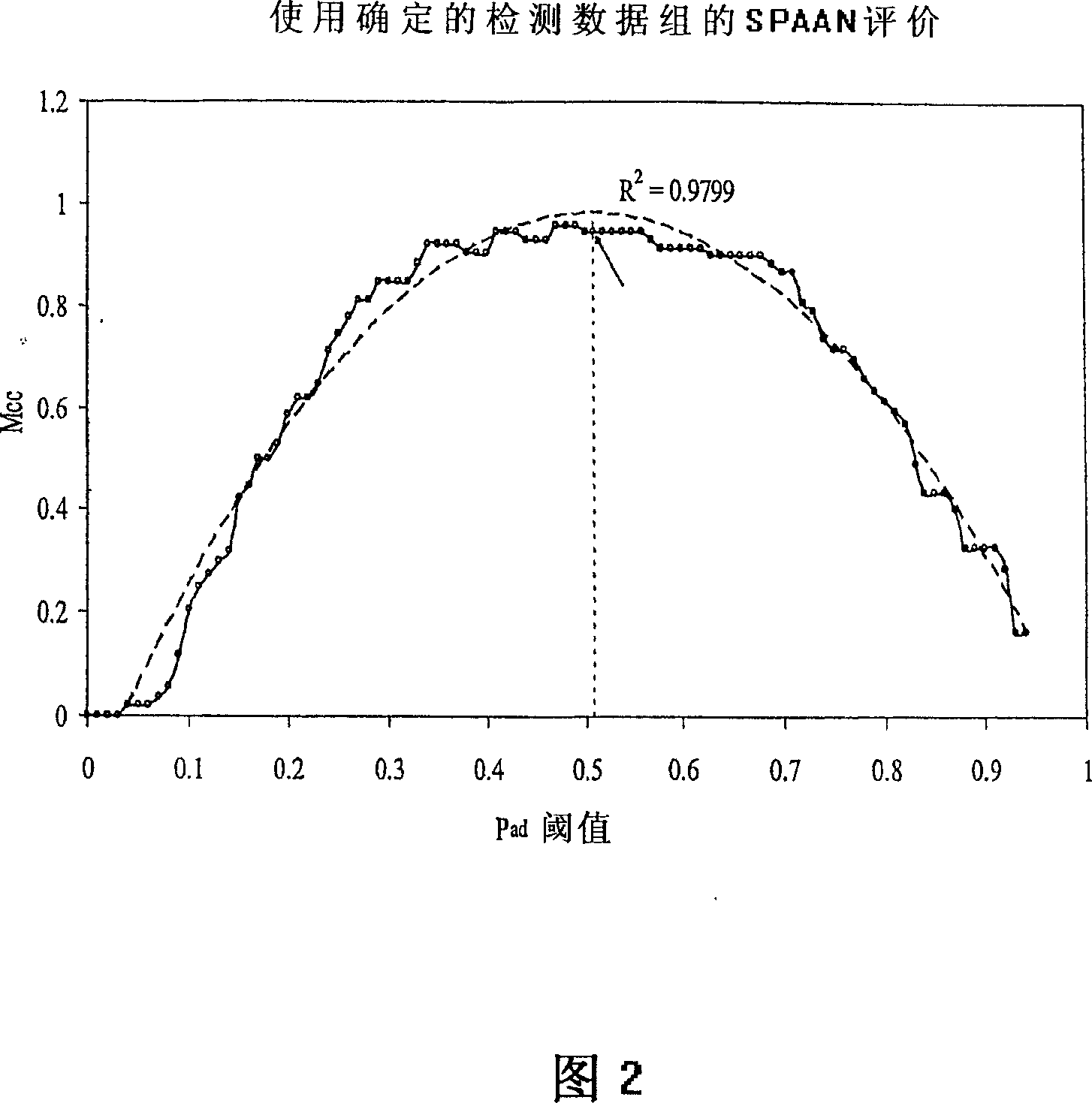
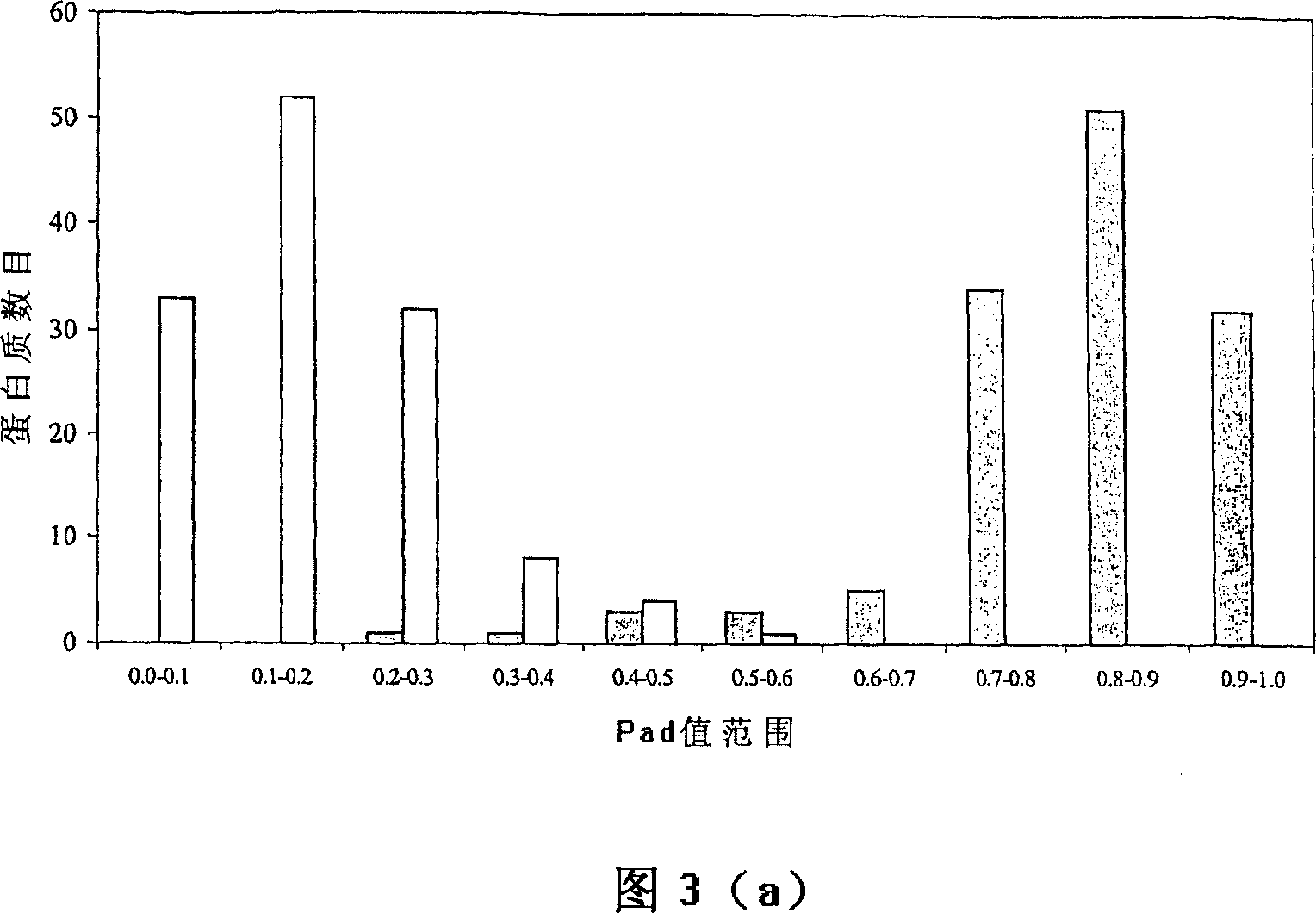
A computational method for identifying adhesin and adhesin-like proteins, said method comprising steps of computing the sequence-based attributes of a neural network software wherein the attributes are (i) amino acid frequencies, (ii) multiplet frequency, (iii) dipeptide frequencies, (iv) charge composition, and (v) hydrophobic composition, training the artificial neural Network (ANN) for each of the computed five attributes, and identifying the adhesin and adhesin-like proteins having probability of being an adhesin (Pad) as >= 0.51; a computer system for performing the method; and genes and proteins encoding adhesin and adhesin-like proteins.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Compositions and methods for removal or destruction of amyloid fibril or amyloid adhesin comprising aggregates
InactiveUS20130115257A1Reduce riskFacilitate communicationAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsHuntingtons choreaAmyloid beta
Methods and compositions for treating biofilms and diseases associated with amyloidosis such as Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease, and Type 2 diabetes, by destroying amyloid fibrils in a two-step treatment are disclosed. The first step consists of binding to the amyloid fibril an intercalating molecule with a negatively charged group such as Congo red. The second step consists of adding metal ions, such as silver, gold(I), copper(I), palladium or lead ions or metal colloids of silver or gold, which destabilize the amyloid-dye complex. This process results in a disintegration of the fibril into peptide monomers and small aggregates of monomers.
Owner:KATHOLIEKE UNIV LEUVEN
Adhesin-enterotoxin chimera based immunongenic composition against enterotoxigenic Escherichia Coli
The inventive subject matter relates to an immunogenic composition composed of a chimeric molecule including a conformationally stable adhesin from Escherichia coli fused to a bacterial toxin A subunit, such as cholera toxin A subunit or heat-labile Escherichia coli toxin A subunit. The invention also relates to the adhesin-toxin chimera noncovalently associated with a toxin B subunit of the same or different species as the A subunit. The invention also relates to a method of utilizing an adhesin / toxin fusion composition to elicit an immune response.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
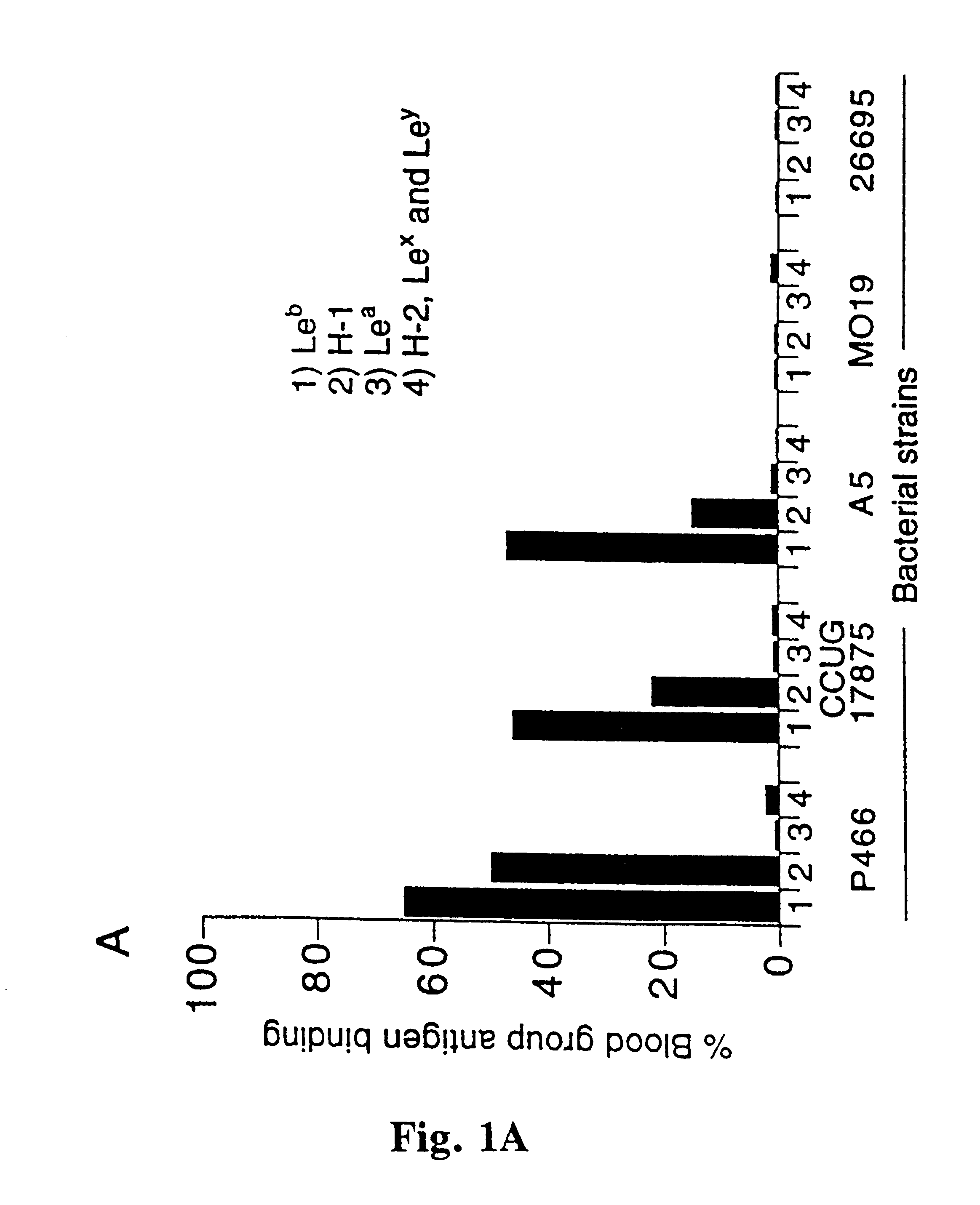
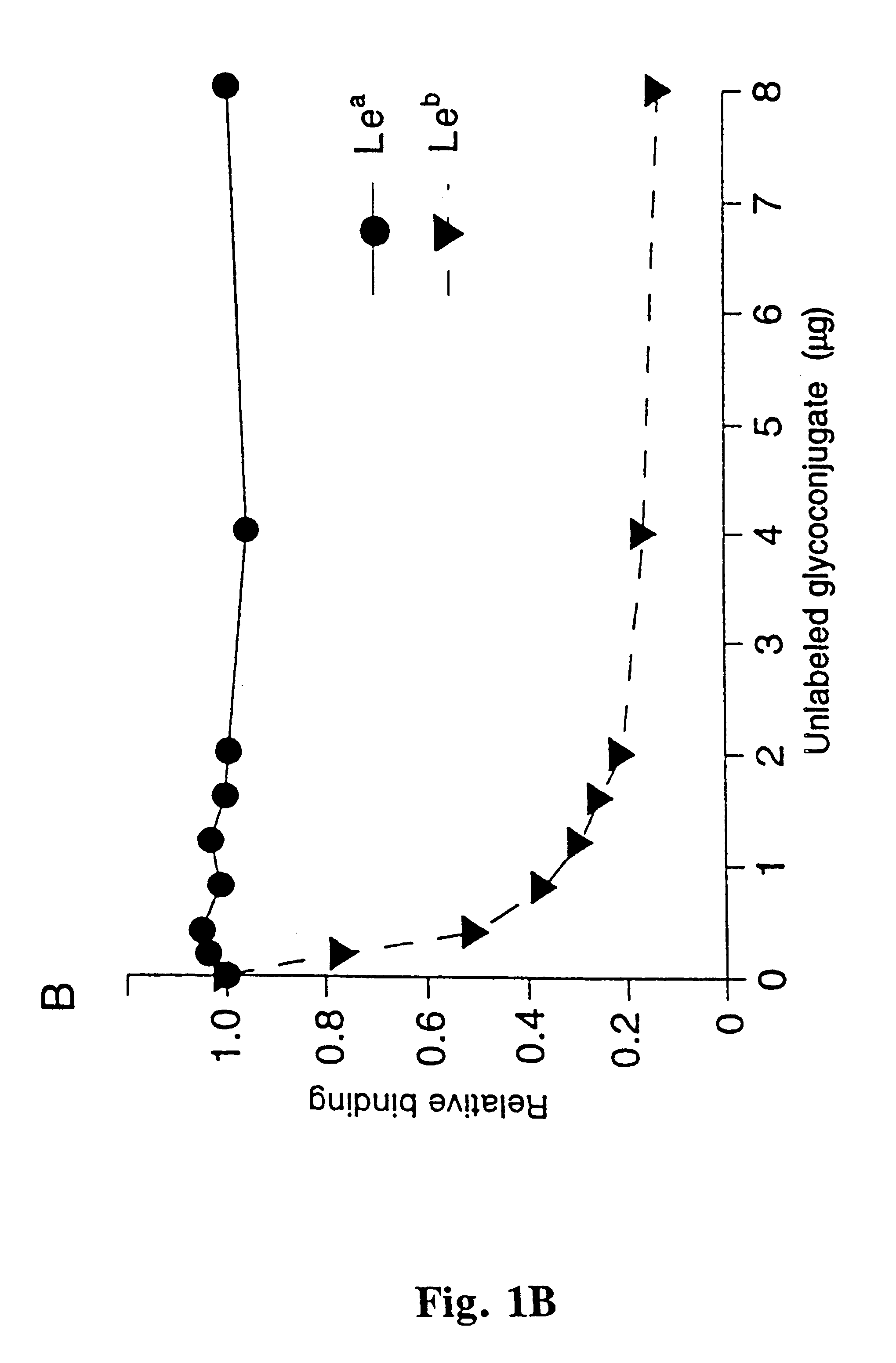
Helicobacter pylori adhesin binding group antigen
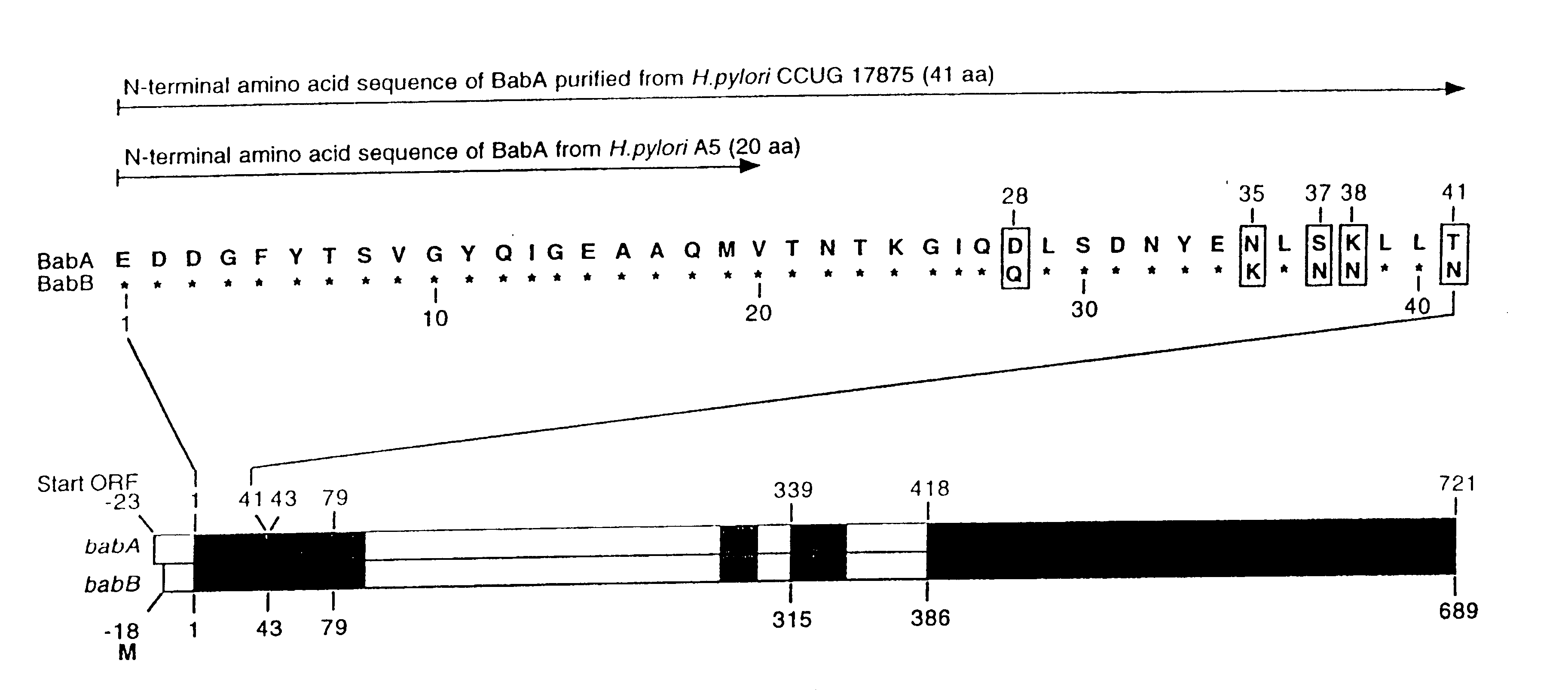
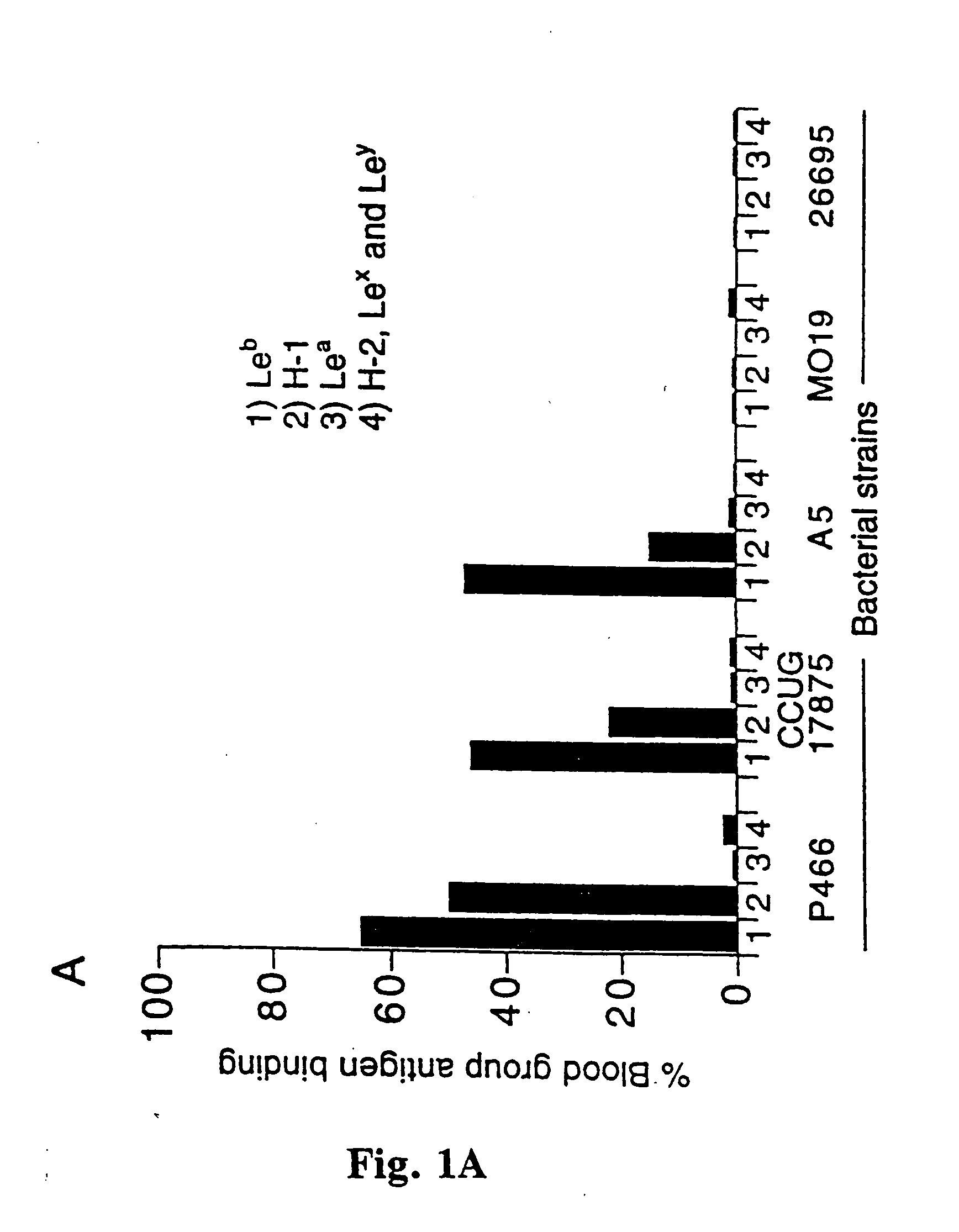
A novel blood group antigen binding (BAB) adhesin protein was isolated and purified, whereby said protein or fractions thereof bind specifically to Helicobacter pylori fucosylated blood group antibodies. Said adhesin has a molecular weight of about 73.5 kDa and the N-terminal sequence for the adhesin and the corresponding DNA show homologies between different strains of H. pylori. Said adhesin and / or DNA is useful for diagnose and therapy and / or profylax directed against H. pylori induced infections, e.g. gastritis and acid peptic disease.
Owner:BOREN THOMAS +4
Diagnostics and treatments of Periodontal disease
InactiveUS20070189982A1Mitigate prospectEfficient inductionCosmetic preparationsOrganic active ingredientsPorphyromonas gingivalisArginine
This invention relates to the PrtR-PrtK cell surface protein of Porphyromonas gingivalis and in particular a multimeric cell association protein complex comprising the PrtR and PrtK proteins. Accordingly the invention provides a substantially purified antigenic complex for use in raising an antibody response directed against Porphyromonas gingivalis. The complex comprises at least one multimeric protein complex of arginine-specific and lysine-specific thiol endopeptidases each containing at least one adhesin domain, the complex having a molecular weight of greater than about 200 kDa. The invention also relates to pharmaceutical compositions and associated agents based on said complex for the detection, prevention and treatment of Periodontal disease associated with P. gingivalis.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MELBOURNE
Immunogenic compositions for use in vaccination against bordetella
InactiveUS20180071380A1Efficient combinationAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsVaccinationVirulent characteristics
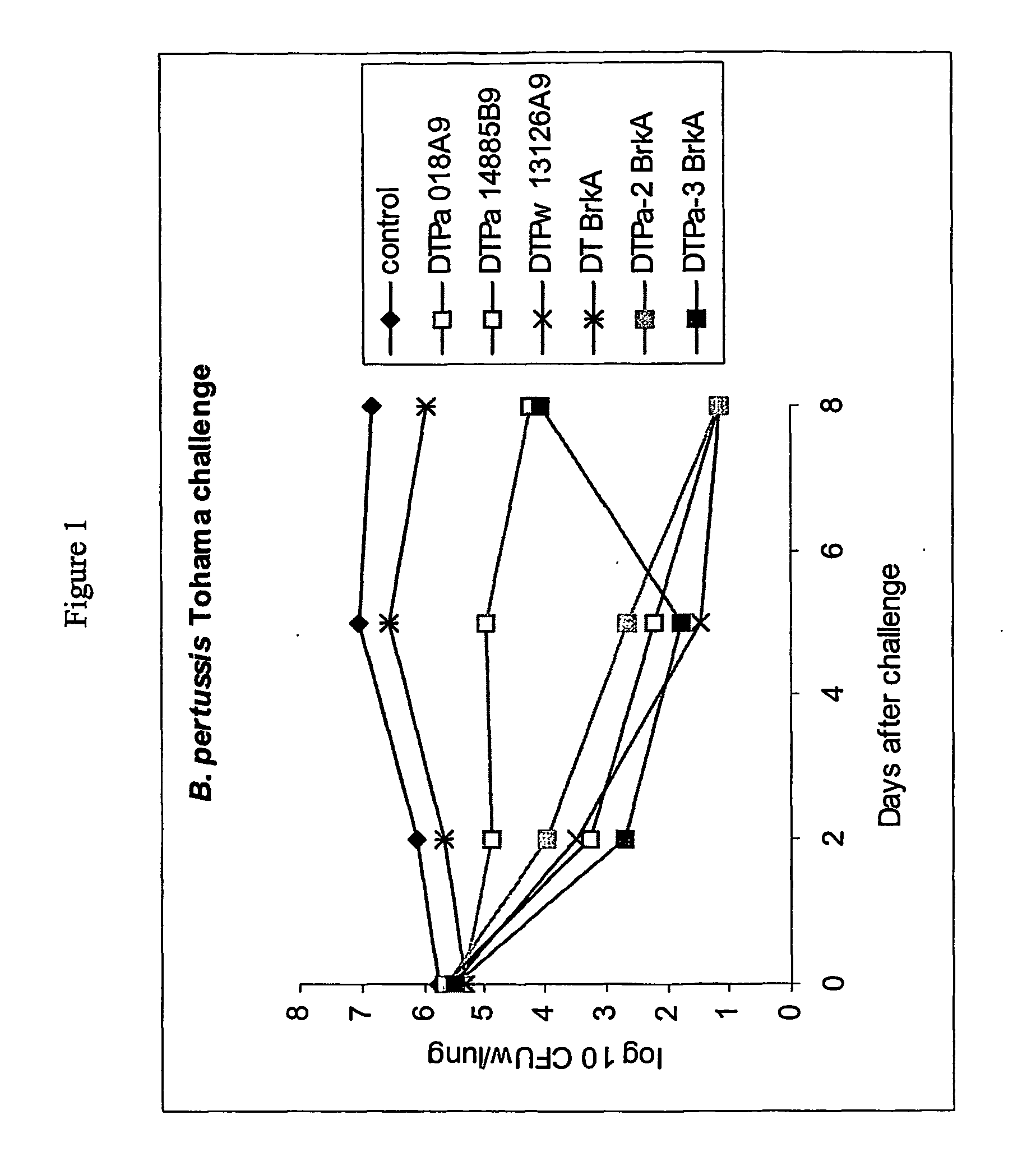
The present application relates to immunogenic compositions comprising a mixture of Bordetella (e.g., B. pertussis) antigens and an oil in water nanoemulsion. In particular, the invention provides immunogenic compositions comprising nanoemulsion and a combination of Bordetella (e.g., B. pertussis) antigens that have different functions, for example, combinations including B. pertussis adherence factors (adhesins), B. pertussis toxins or B. pertussis virulence factors. Vaccines, methods of treatment, uses of and processes to make a pertussis or whooping cough vaccine are also described. Compositions and methods of the present invention find use in, among other things, clinical (e.g. therapeutic and preventative medicine (e.g., vaccination)) and research applications.
Owner:NANOBIO CORP +1
Novel mannose-specific adhesins and their use
InactiveUS20090214476A1Maximizing numberMinimize the numberAntibacterial agentsBiocideBacteroidesBacterial Adhesins
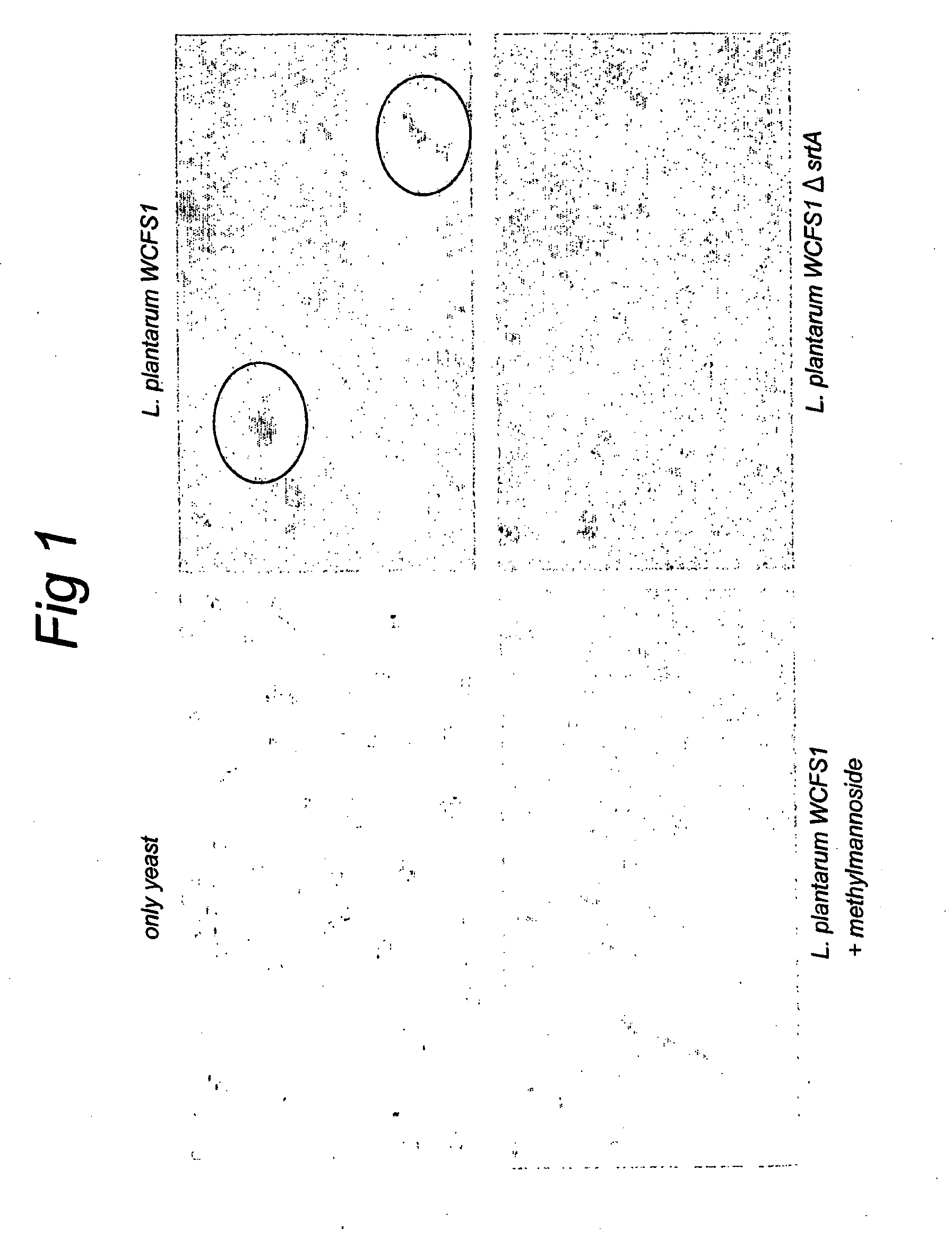
The present invention relates to novel mannose-specific adhesins, and variants thereof, as well as nucleic acid sequences encoding these. The invention also relates to host cells expressing nucleic acids encoding the mannose-specific adhesins or variants thereof, as well as to pharmaceutical or nutraceutical compositions comprising the mannose-specific adhesins and / or host cells expressing the adhesins, and their use in treating or preventing bacterial infection. Further, screening methods suitable for identifying bacteria strains with probiotic properties are provided.
Owner:FRIESLAND BRANDS BV
Recombinant strain for expression of enterotoxin colibacillus adhesin gene and its application in vitelline antibody fodder
InactiveCN101113428AReduce diarrhea rateImprove feed conversionBacteriaAnimal feeding stuffBacterial AdhesinsRecombinant escherichia coli
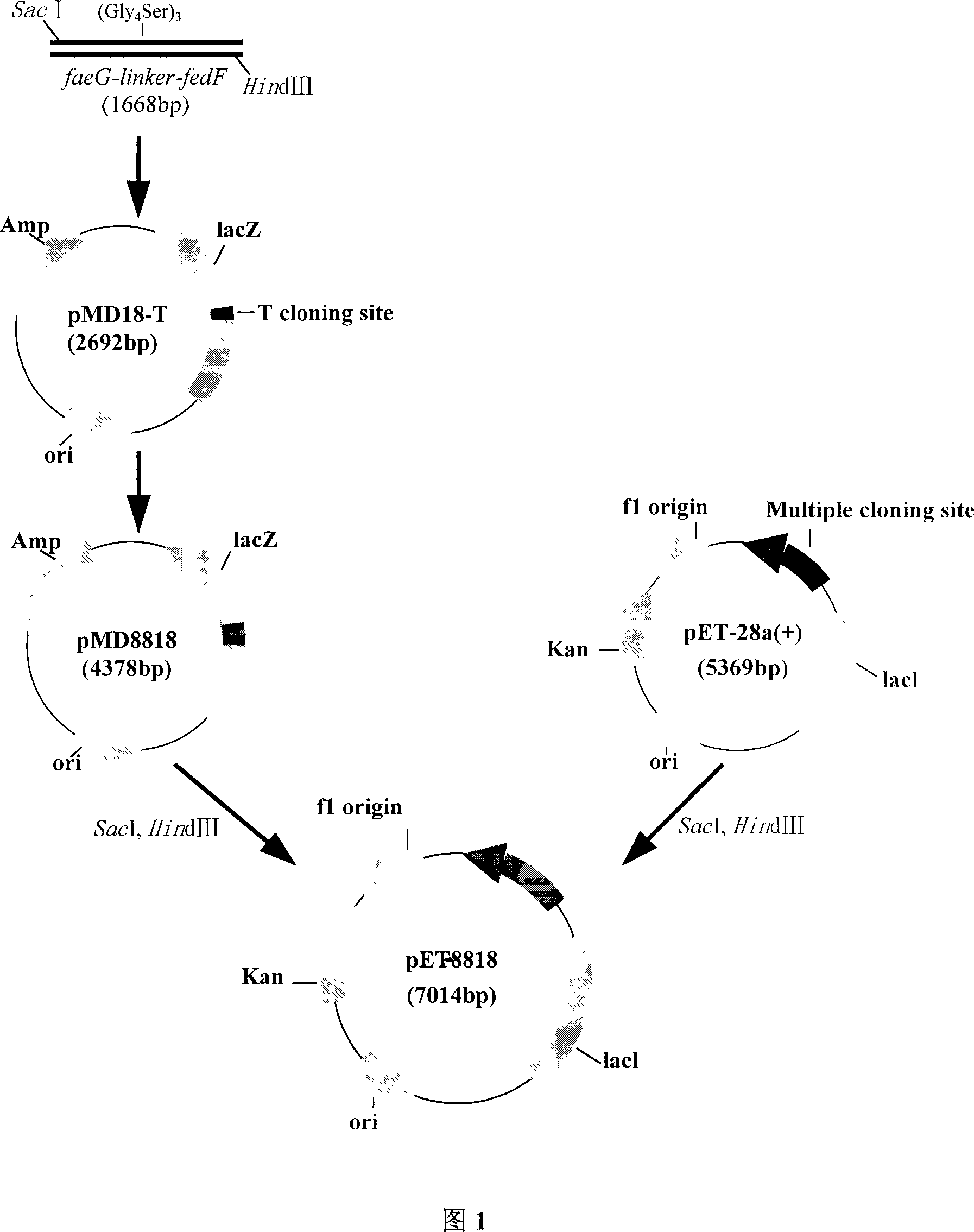
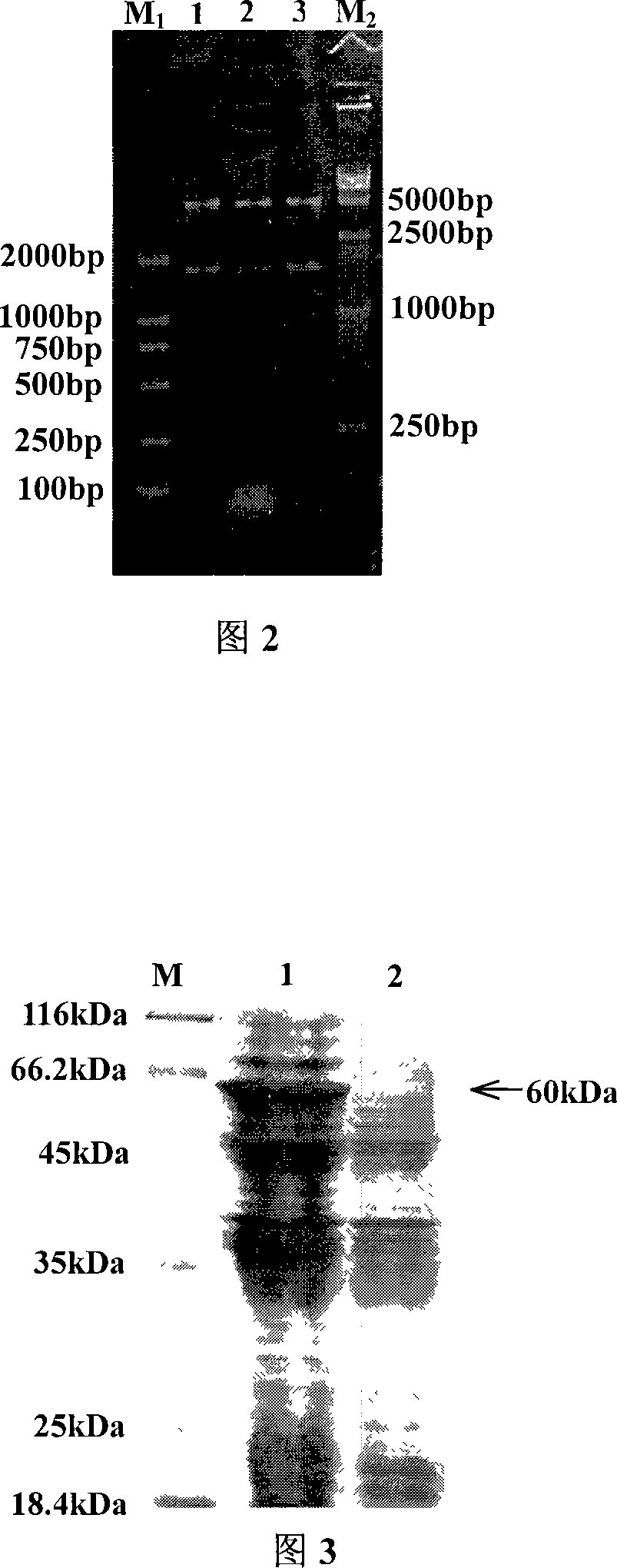
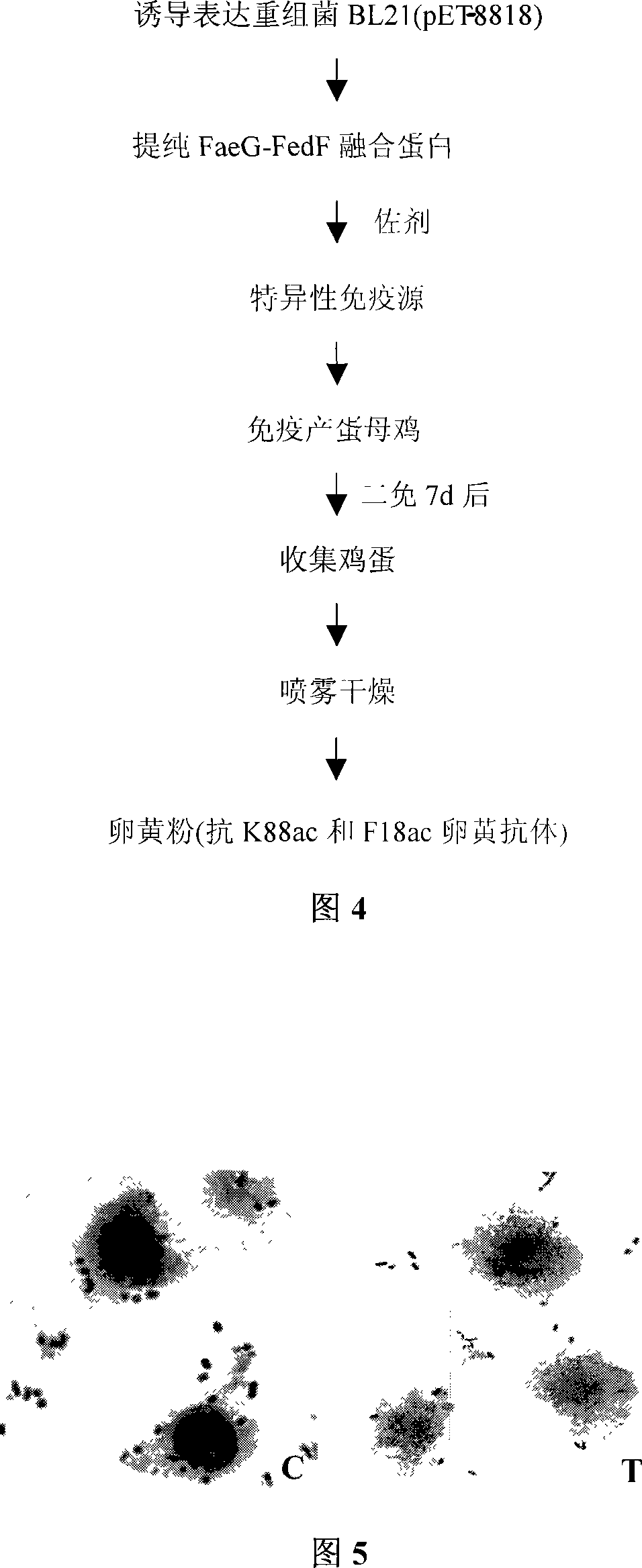
The invention pertains to the scientific technical field of animal nutrition and feed, meanwhile, relates to application of animal molecular biologic technology. Particularly, the invention relates to an expression for constructing escherichia coli K88 of enterotoxin of chitterlings and recomposed escherichia coli of F18 adhesion gene faeG and fedF and application thereof in preparation of egg-yolk antibody feed. The escherichia coli expressed the recomposed plasmids of escherichia coli K88ac of the enterotoxin and the adhesion genes faeG, F18ac and fedF is constructed by constructing fusion gene of faeG and fedF by using connecting peptid, and inserting the fusion gene into a prokaryotic expression carrier pET28a. The recomposed escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) / pET-8818 of the invention are preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) with a preservation number of CCTCC NO: M207090. The invention also discloses application of the recomposed escherichia coli with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M207090 in the preparation of the egg-yolk antibody feed.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
L-amino acid producing microorganism which has been modified to inactive the fimH gene, and a method for producing I-amino acid
InactiveUS7547531B2Improve productivityProducing an L-amino acidSugar derivativesBacteriaMicroorganismBiotechnology
An L-amino acid producing bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family is described, wherein the bacterium has been modified so as to not produce type I fimbrial adhesin protein is cultured in a medium to produce and excrete said L-amino acid in the medium, and collecting said L-amino acid from the medium.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
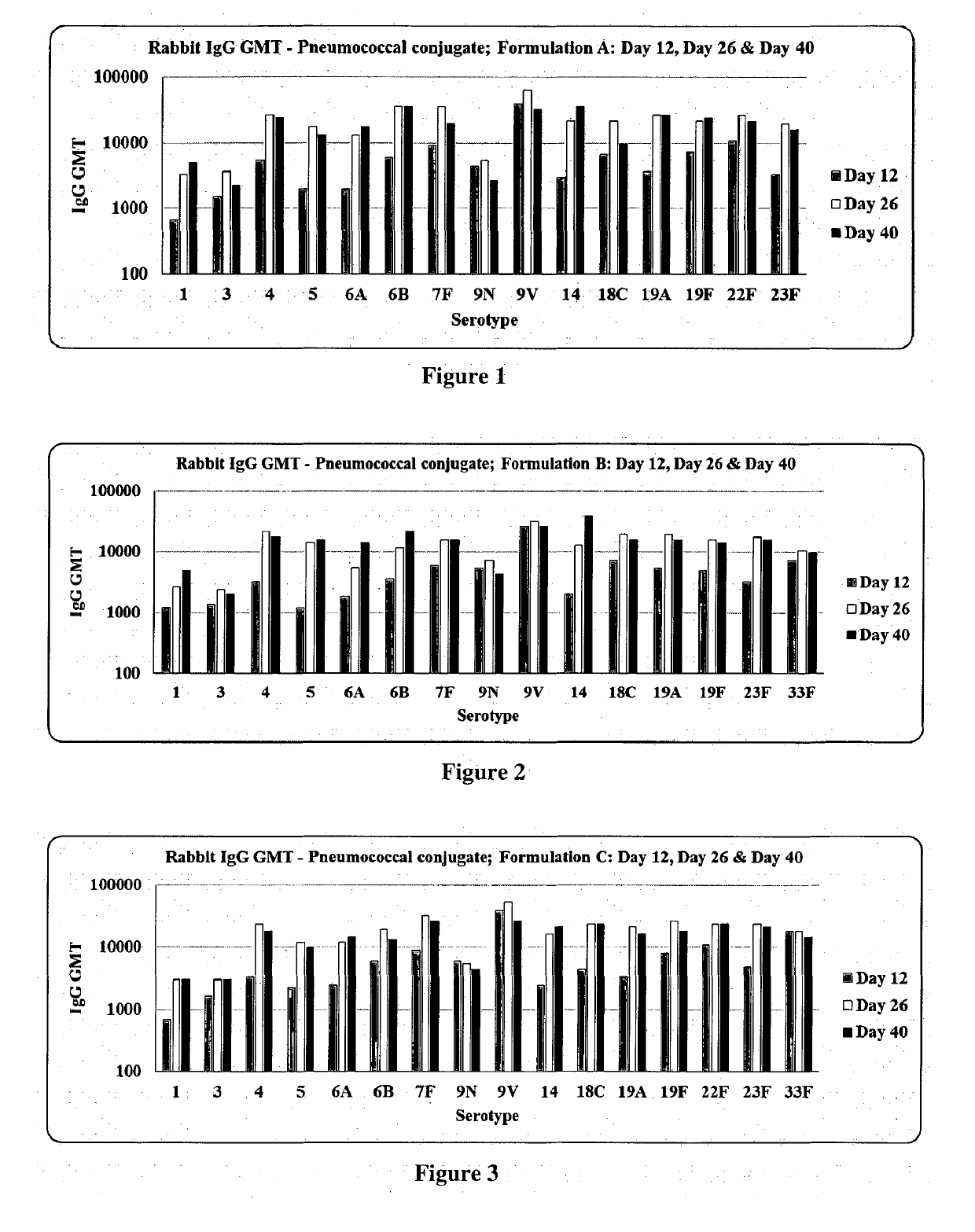
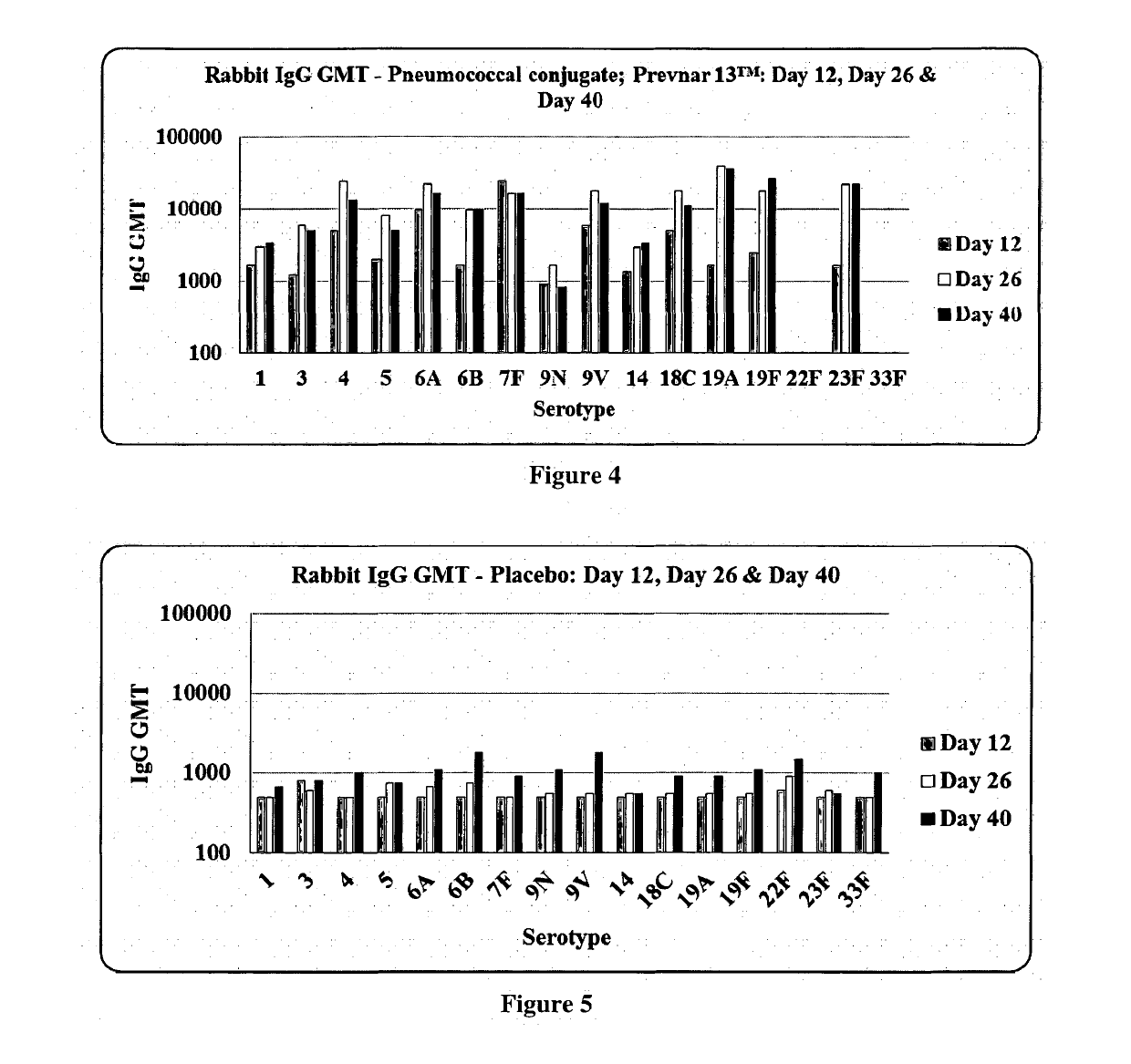
Multivalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine
The present invention relates to a multivalent Pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) composition comprising: 1) at least 12 capsular polysaccharides selected from serotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6B, 7F, 9N, 9V, 15B, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F, 22F, 23F and 33F of S. pneumoniae activated with CDAP and conjugated to carrier protein selected from CRM197, pneumococcal surface protein A (PspA), pneumococcal adhesin protein (PsaA) or combination thereof and 2) a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, wherein the composition does not contain capsular polysaccharide from serotype 6A.
Owner:BIOLOGICAL E LTD
Constructing genetic engineering Vaccine of adhesin of confluent Helicobacter pylor and preparation method
InactiveCN1563388ANumber of consistent peaksGood attentionPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsEscherichia coliAdjuvant
This invention discloses the construction of a fused poloric spirillum adhesion gene engineered bacterial vaccine characterizing that the adhesion HpaA is used to construct an adjuvant fused engineered vaccine of poloric spirillum adhesion and colibacillus heat-labile enterotoxin B sub unit or cholear toxin B sub unit intramolecular to get large quantity of necessary vaccine proteins by high density fermentation, occlusion body extraction, renaturation and purification to be proprared to peroral, injection and spray agents.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Multi-component vaccine to protect against disease caused by Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis
InactiveUS6391313B1Enhanced primary anti-H91A Hin4 responseLower immune responseAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsDiseaseHaemophilus
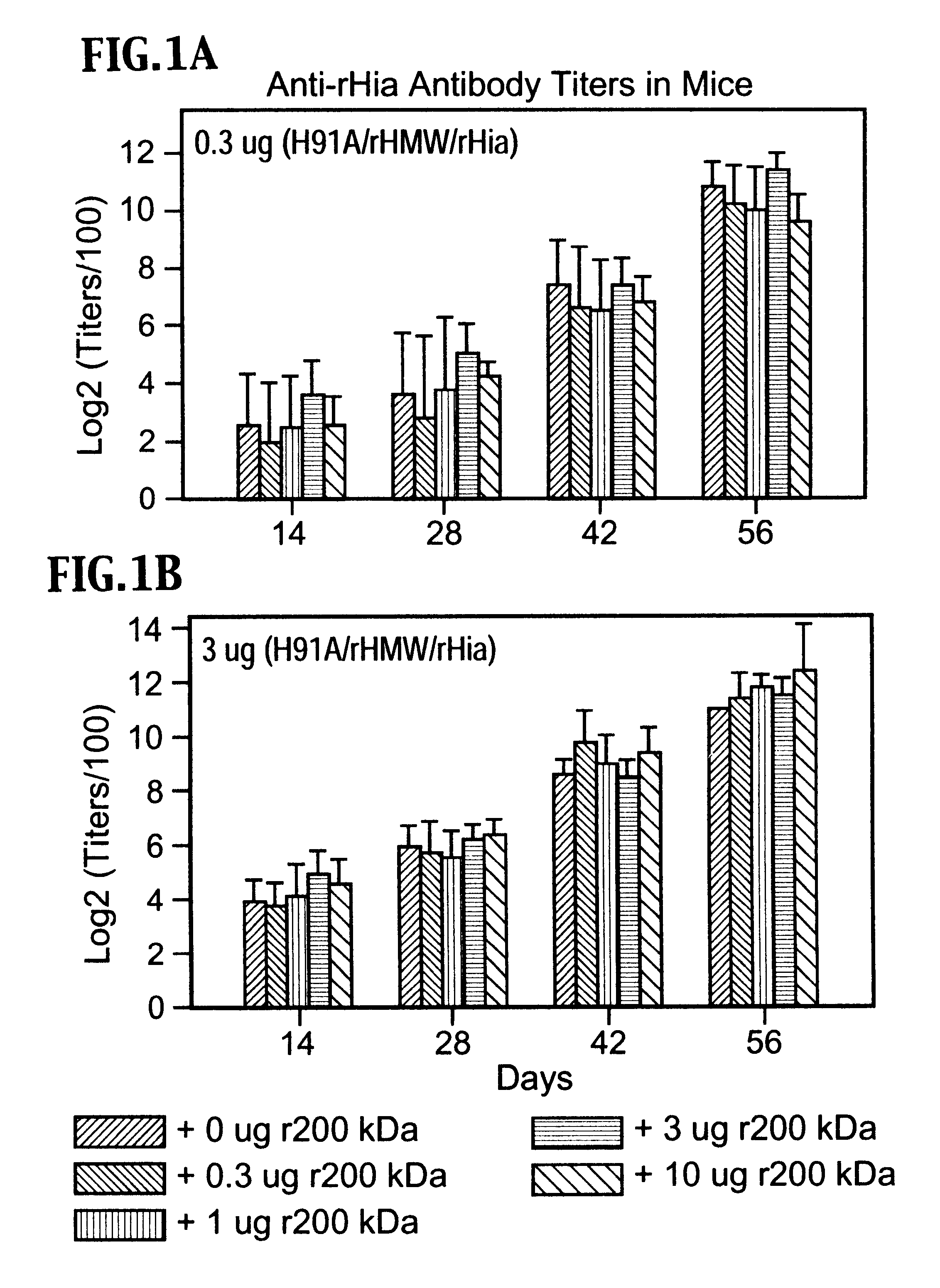
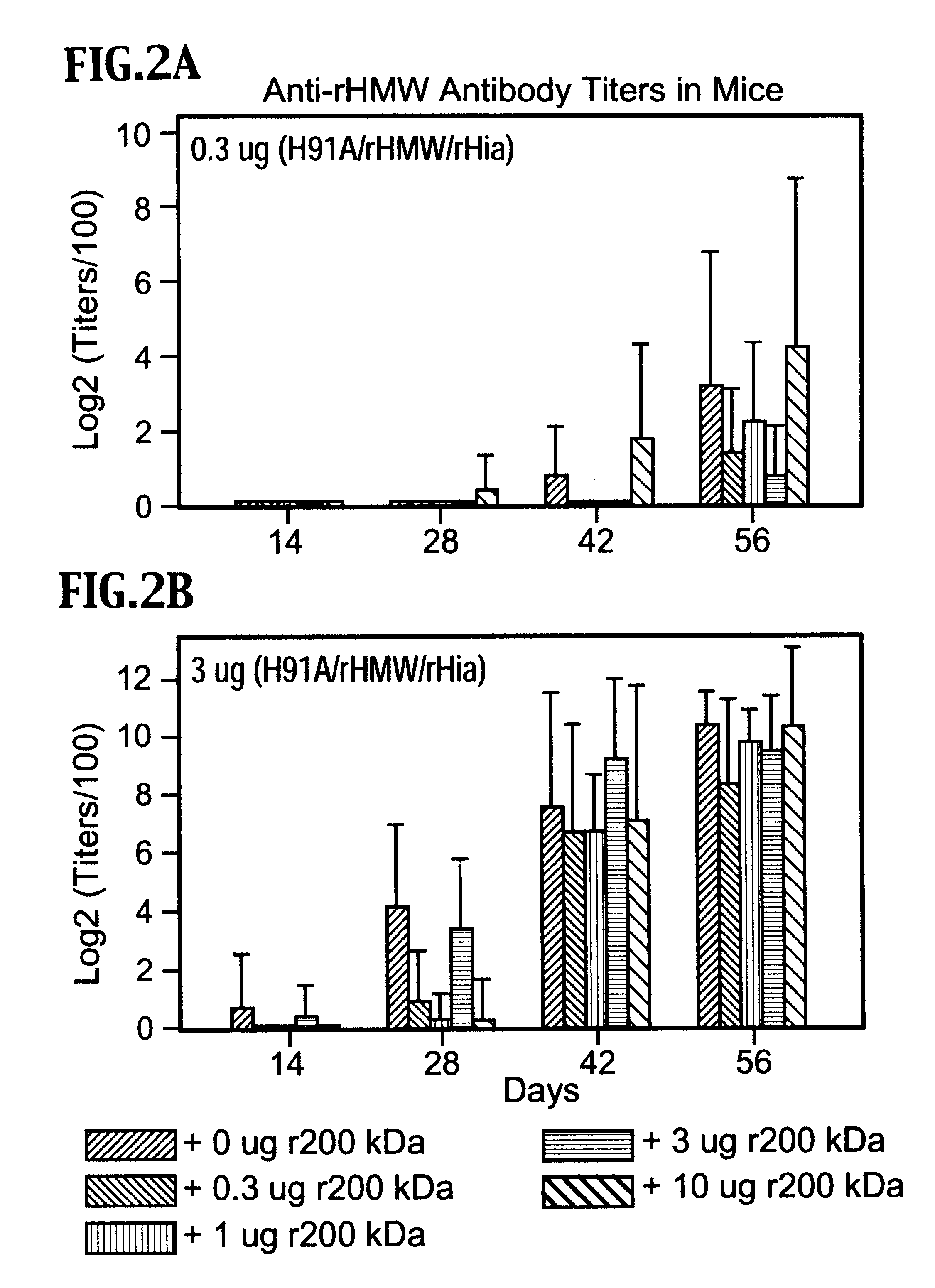
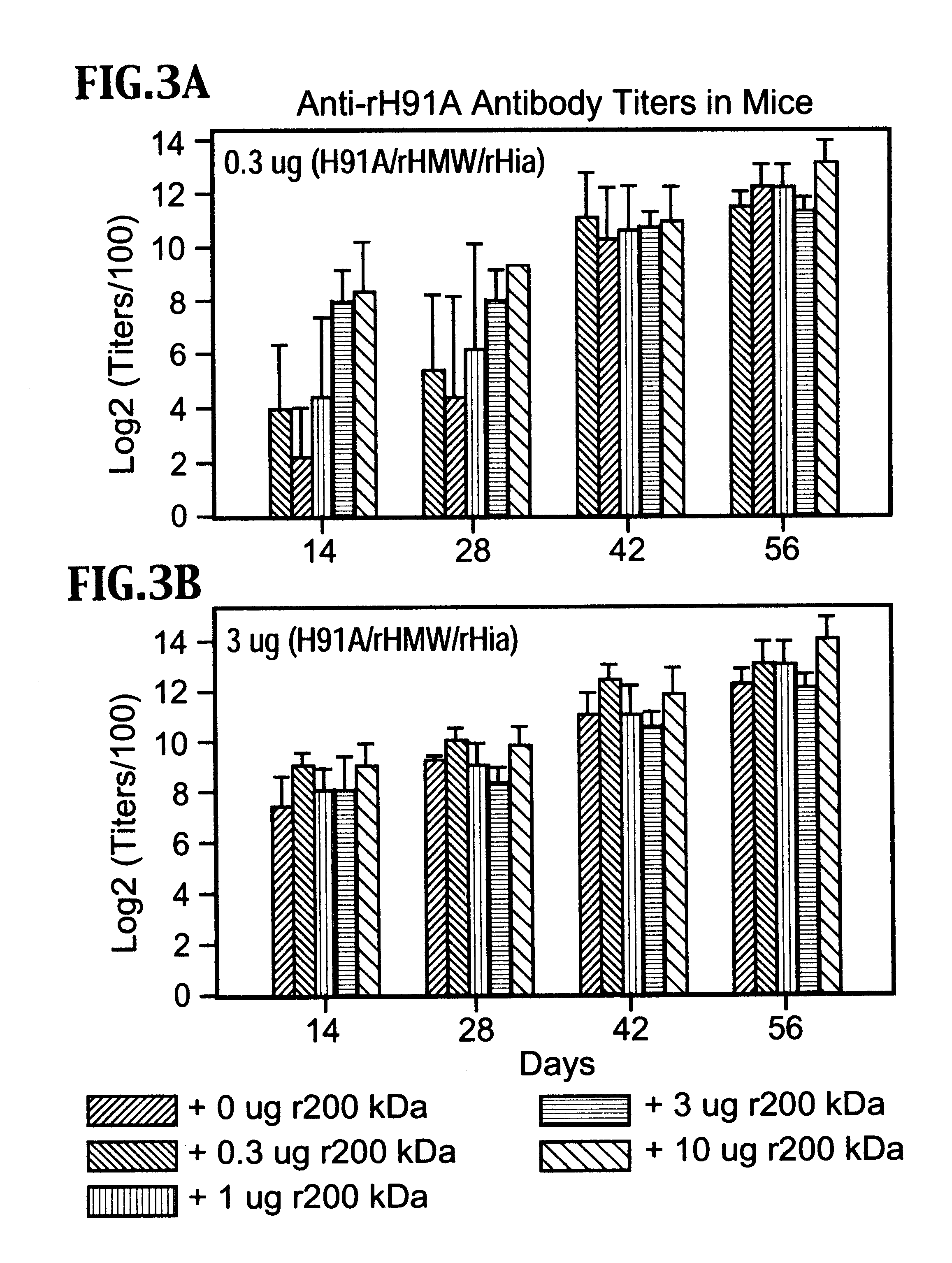
A multi-valent immunogenic composition confers protection on an immunized host against infection caused by both Haemophilus influenzae and Moraxella catarrhalis. Such composition comprises at least four antigens comprising at least one antigen from Haemophilus influenzae, and at least one antigen from Moraxella catarrhalis. Three of the antigens are adhesins. High molecular weight (HMW) proteins and Haemophilus influenzae adhesin (Hia) proteins of non-typeable Haemophilus and a 200 kDa outer membrane protein of Moraxella catarrhalis comprise the adhesin components while the other antigen is a non-proteolytic analog of Hin47 protein. Each component does not impair the immunogenicity of the others. The multi-valent immunogenic composition may be combined with DTP component vaccines, which may also include non-virulent poliovirus and PRP-T, to provide a component vaccine without impairment of the immunogenic properties of the other antigens.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
Carrier capable of showing and expressing helicobacter pylori protein on surface of lactococcus lactis, and preparation method and application of carrier
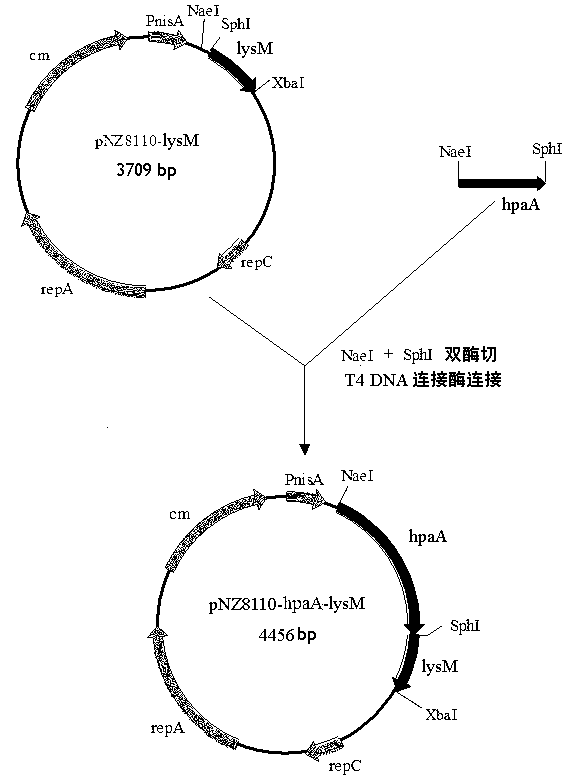
InactiveCN102796757AAchieve the purpose of displaying the vaccine antigen HpaAAvoid infectionAntibacterial agentsMilk preparationEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
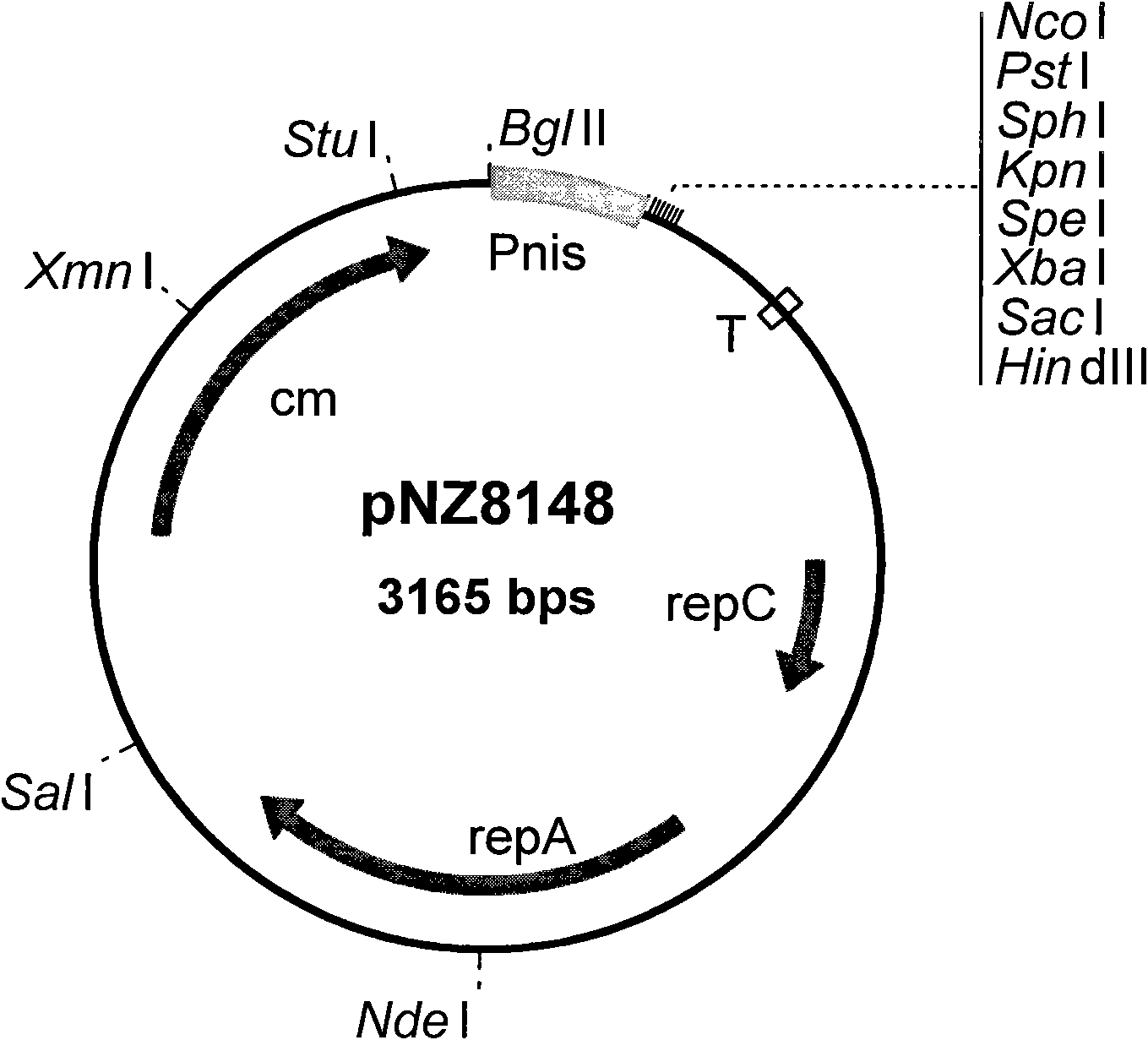
The invention relates to a carrier capable of showing and expressing helicobacter pylori protein on the surface of lactococcus lactis, and a construction method and application of the carrier. The construction method of the carrier comprises the following steps of: amplifying helicobacter pylori adhesin A (hpaA) gene by taking helicobacter pylori genomic deoxyribose nucleic acid (DNA) as a template by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) method; performing enzyme digestion on the obtained hpaA gene and an expression carrier pNZ8110-lysM and connecting, wherein a connection product is used for transforming escherichia coli; screening and identifying positive transformation bacteria, and extracting recombinant plasmid pNZ8110-hpaA-lysM from the positive transformation bacteria; transferring the recombinant plasmid into a lactococcus lactis NZ3900 strain by an electroporation method, and screening and identifying to obtain a recombinant strain L.1actis NZ3900 / pNZ8110-hpaA-lysM; and culturing the recombinant strain, and introducing the expression of the hpaA gene by using an inductive agent Nisin. Western blots analysis shows that the protein of the cell wall of the recombinant strain contains the expressed HpaA protein which has immunocompetence. The expression carrier and the recombinant strain containing the carrier can be applied to preparation of helicobacter pylori resistance vaccine and a diagnostic reagent or food processing.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Construction method and application of faeG expressing gene engineering probiotic
InactiveCN102031262AEasy to manufactureImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaWestern blotDiarrhea
The invention discloses a construction method and application of a faeG expressing gene engineering probiotic. The method comprises the following steps of: according to the gene sequence and the expression vector plasmid characteristic of a disclosed F4 escherichia coli pilus adhesin faeG, designing a primer which contains a specific endonuclease site; performing polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification by taking deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of an enterotoxigenic escherichia coli plasmid as a template to obtain a faeG gene-containing segment, linking the segment with an expression vector plasmid pNZ8148 to obtain a recombinant plasmid pNZ8148-faeG, transferring the recombinant plasmid into lactobacillus or a galactococcus cell by using an electrotransformation method to obtain gene engineering probiotic which expresses enterotoxigenic escherichia coli pilus adhesin faeG, expressing under the induction of nisin and analyzing and proving a target gene by SDS-PAGE and Western blot so as to express correctly. A recombinant strain can be used for preventing colibacillus diarrhea of suckling pigs and weanling pigs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method and device for trichomonas detection
InactiveUS7291477B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsBacteriuriaBacterial Adhesins
A method and kit for detecting Trichomonas vaginalis infection in a human subject are disclosed. In the method, a body-fluid sample such as a vaginal swab sample or urine is obtained from the subject and contacted with an antibody specific against a Trichomonas adhesin peptide, forming an antibody-adhesin peptide complex if the subject is infected with Trichomonas. The presence or absence of the complex establishes, with a reliability of at least 80%, in the case of a vaginal swab sample, and with a reliability of at least 40% in the case of a urine sample, the presence or absence, respectively, of Trichomonas infection in the subject. A preferred test kit employs a dry-strip, sandwich assay, format.
Owner:XENOTOPE DIAGNOSTICS INC +1
Helicobacter pylori adhesin binding group antigen
A novel Helicobacter pylori blood group antigen binding (BAB) adhesin protein was isolated and purified, whereby said protein or fractions thereof bind specifically to fucosylated blood group antigens. The protein sequence of said adhesin is disclosed in this application. Simultaneously the DNA sequences for two genes, babA and babB, producing highly similar proteins, are disclosed. Said adhesin and / or DNA is useful for diagnose and therapy and / or prophylaxis directed against H. pylori induced infections, e.g. gastritis and acid peptic disease, i.e. active vaccination. A new immunoglobulin composition, which exhibits specific activity to a Lewisantigen binding Helicobacter pylori adhesin, or preferably, monoclonal and / or polyclonal antibodies to said adhesin offer a new and more efficient method of treatment and / or prevention of gastrointestinal diseases, caused by Helicobacter pylori or other Helicobacter species, i.e. passive vaccination.
Owner:BOREN THOMAS +4
Acellular pertussis combined vaccine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104707134AClear ingredientsLittle side effectsAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsHemagglutininSide effect
The invention discloses an acellular pertussis combined vaccine and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of production and preparation of vaccines. The acellular pertussis combined vaccine is prepared from the following raw material components: 5-40Mu g of pertussis toxin, 5-40Mu g of filamentous hemagglutinin, 2-10Mu g of pertussis adhesin, 10-25lf of diphtheria toxoid, 4-10lf of tetanus toxoid, 1.0-2.0mg / ml of aluminium hydroxide and 7.5-9.5g / L of sodium chloride. The preparation method of the acellular pertussis combined vaccine comprises the following steps: preparing monovalent vaccine original fluids, mixing and diluting. The acellular pertussis combined vaccine is clear and definite in ingredients, quality control can be easily realized, the side effect is small, and the safety is high; and the preparation method of the acellular pertussis combined vaccine is simple to operate, convenient in preparation and low in cost, so that the acellular pertussis combined vaccine is applicable to industrial mass production.
Owner:CHENGDU OLYMVAX BIOPHARM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com