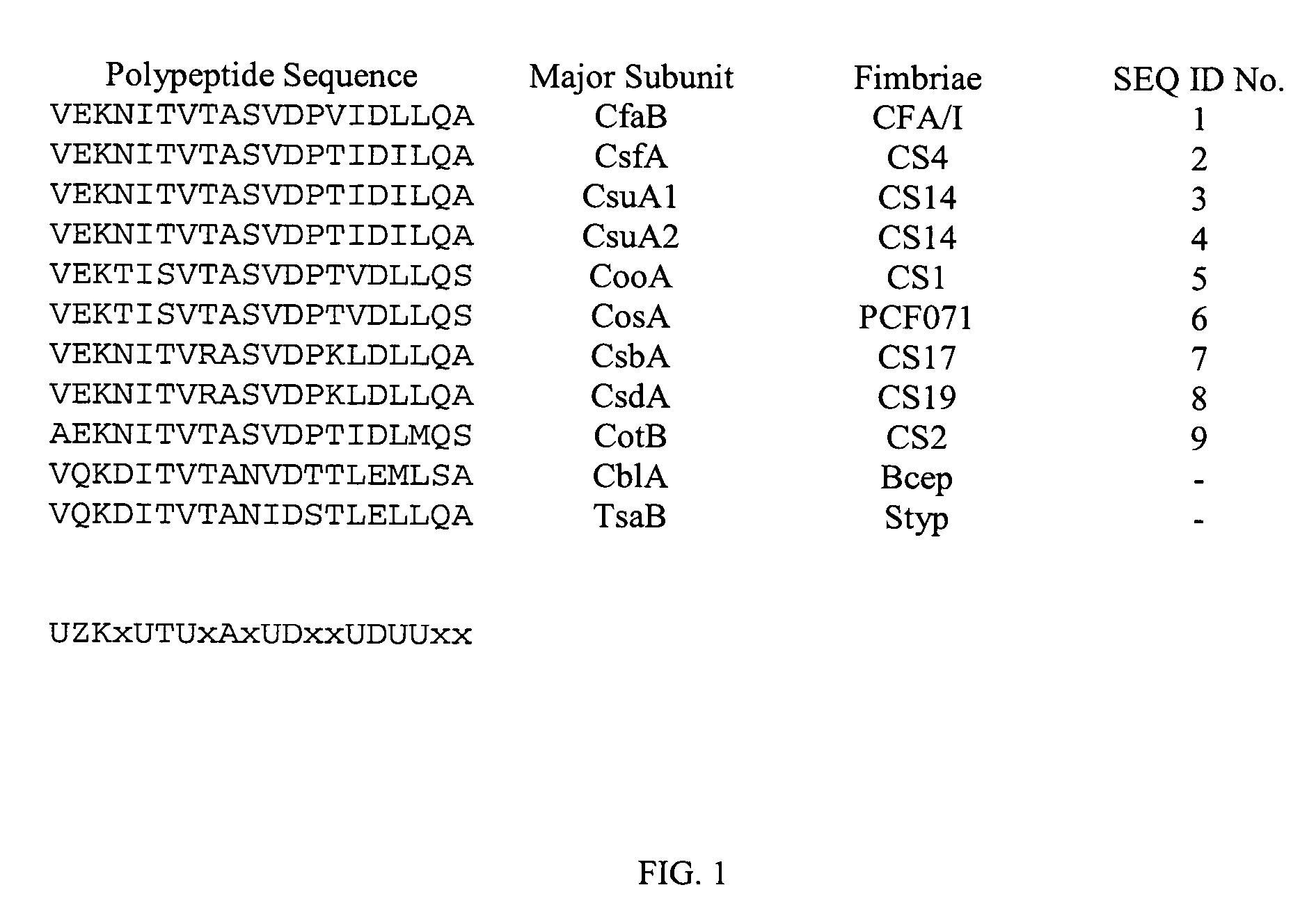
Anti-adhesin based passive immunoprophlactic
a technology of anti-adhesin and immunoprophlactic, which is applied in the direction of antibacterial agents, drug compositions, antibody medical ingredients, etc., can solve the problem of not currently licensed effective vaccines against
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Production of anti-CfaE Bovine Immunoglobulin
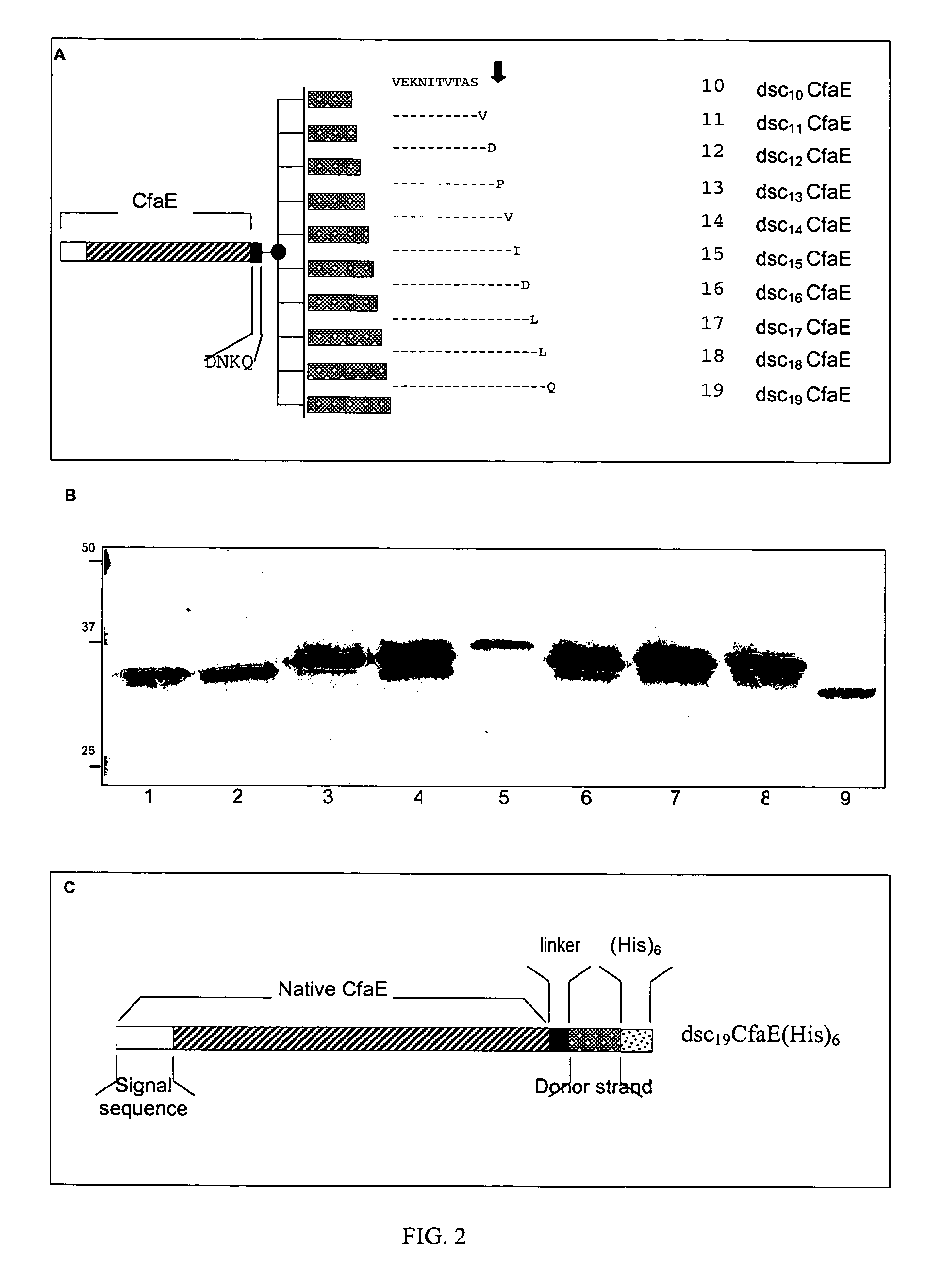
[0036] As mentioned above, the highly conserved nature of the amino-terminal β strand of CfaB and its homologs, together with other structure / function studies in type 1 fimbrial subunits, suggested this structure as a good candidate for the donor β strand that interlocks CFA / I subunits. In order to test this hypothesis with respect to the minoradhesive subunit, a plasmid was engineered to express a CfaE variant containing a C-terminal extension consisting of a flexible hairpin linker (DNKQ, SEQ ID No. 10) followed by an amino acid sequence of CfaB (FIG. 2). It was found that a CfaB donor strand length of at least 12 to as many as 19 amino acids was necessary to obtain a measurable recovery of CfaE. In studies using constructs containing a 12 to 19 amino acid donor strand, where mutations were introduced to break the β strand, it was demonstrated that the β strand is important to the observed stability achieved by the C-terminal amino aci...
example 2
Production of Anti-CfaD (CS17) Bovine Immunoglobulin
[0049] Use of other class 5 fimbrial adhesins are also contemplated as eliciting protective passive antibody production. As a further illustration, results of inhibition by antibody to CS17 (i.e., CsbD) is presented in FIG. 5. The antigen used to elicit antibody was a CsbD polypeptide (SEQ ID No. 22) expressing construct. The construct was engineered similar to that for CfaE, in Example 1, above but with a nucleotide sequence encoding CsbD (SEQ ID No. 19). The construct was designated dsc19CsbD[His]6. The donor strand consisted of 19 amino acids of CsbA (SEQ ID No. 7).
[0050] As can be seen in FIG. 5, like that for CfaE, antibody to CsbD was highly efficient at inhibiting MRHA. Also, like that observed for CfaE, anti-CsbD antibody also afforded cross-protection against CS4 and CS2.
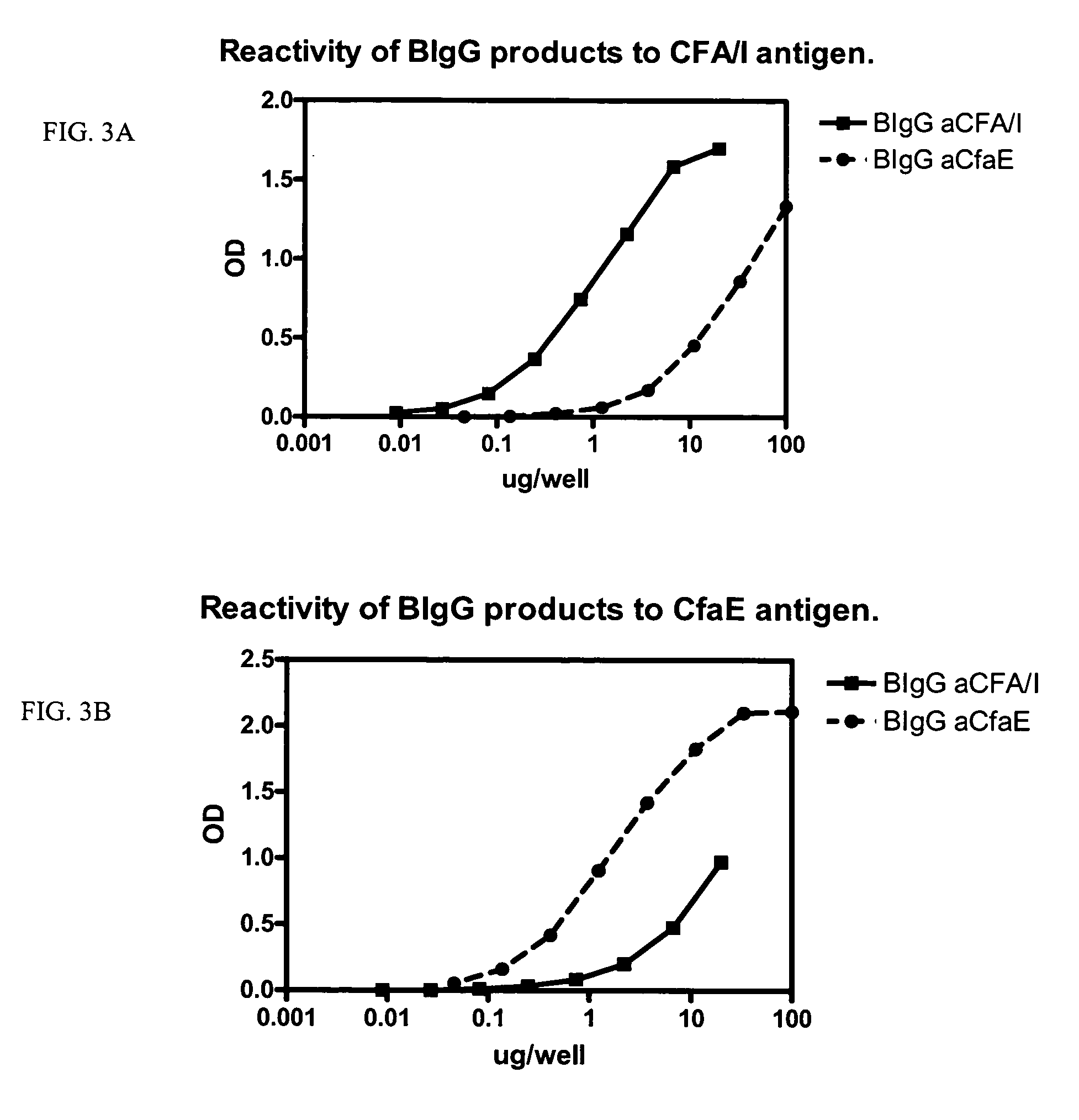
[0051] The functional activity of BIgG to CS17 and CsbD was also evaluated, as in FIG. 4. These results are illustrated in FIG. 6. Like that observed f...
example 3
Specific Regions of ETEC Fimbrial Adhesin are Important for Immunoreactivity and Stability
[0052] Crystollgraphic analysis of the dscCfaE reveals that fimbrial adhesin is composed of two domains, an adhesin domain, formed by the amino-terminal segment of the adhesin molecule and a C-terminal pilin domain. The two domains are separated by a three amino acid linker. In an attempt to understand those regions of fimbrial adhesin, amino acid substitutions where made and the ensuing immunoreactivity analyzed. It was found that replacement of arginine 67 or arginine 181 with alanine, on CfaE abolishes the in vitro adherence phenotype of the molecule. These amino acids positions are located on exposed regions of the molecule with residue Arg 181 located on the distal portion of the amino-terminus of the domain. Therefore, this region of CfaE and the comparable region of the other fimbrial adhesins, is important for efficacious immune induction. Table 3 summarizes the positions in the eight ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pharmaceutical composition | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| heat-labile | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com