Compositions and methods for treating hypophosphatasia
a technology of phosphatasia and compositions, applied in the field of compositions and methods for treating hypophosphatasia, can solve the problems of insufficient clinical improvement of plasma infusions of tnsalp, no definitive treatment is currently available, and defective bone mineralization, etc., to achieve the effect of increasing body weight and increasing life span
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation and Biochemical Characterization of Enzymes
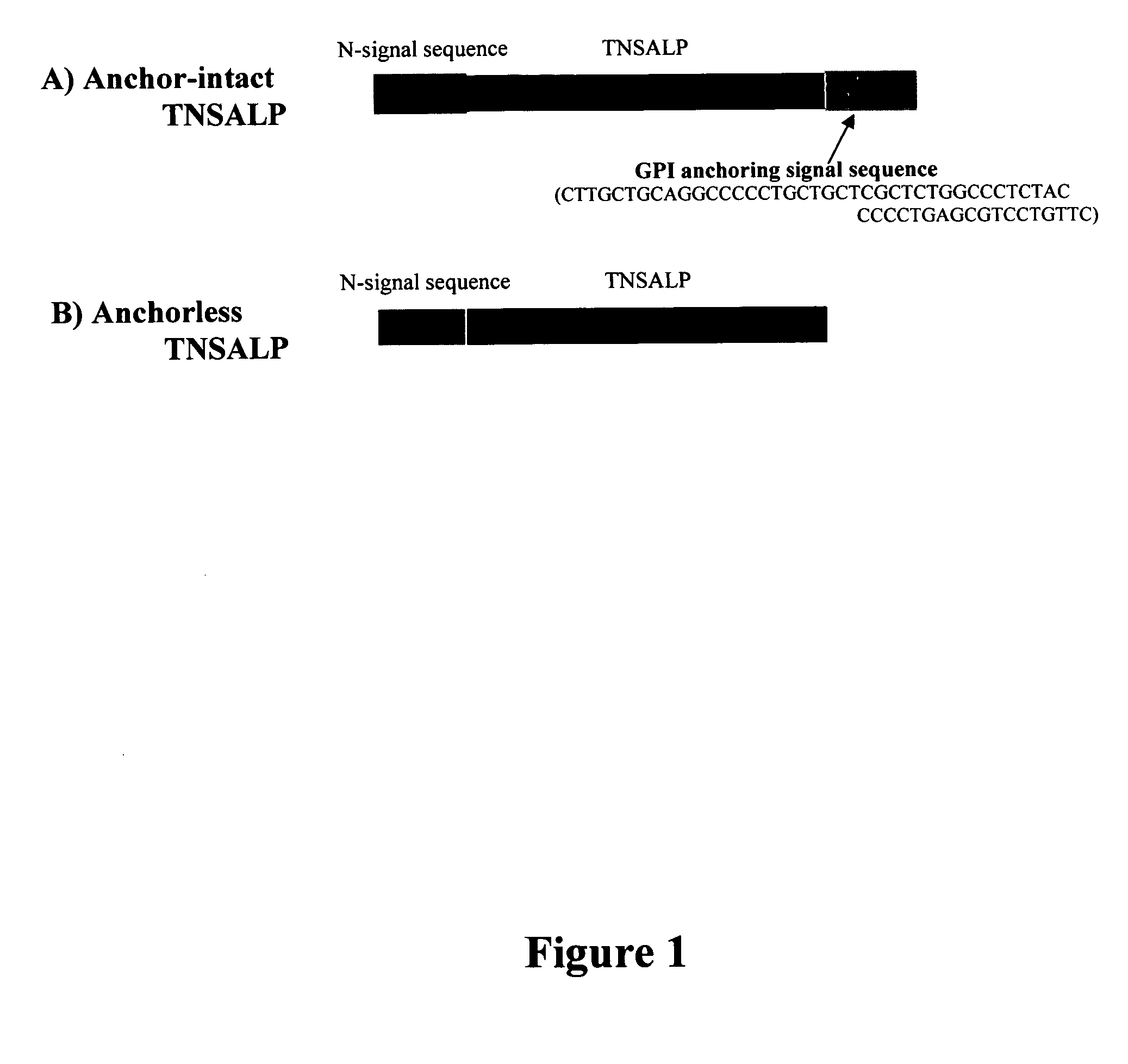
[0063] The GPI anchoring signal peptide 19 amino acid (SEQ:1 residues 506-524) sequence was removed from the C-terminal of the human TNSALP cDNA (SEQ:1) to release the enzyme in the media of CHO—K1 cells. (FIG. 1). The resultant anchorless rhTNSALP enzyme (>95%) was mainly secreted to culture medium in a transient expression study (data is not shown). Acidic oligopeptide-tagged enzymes (CD6-TNSALP and CD8-TNSALP), which also lack the GPI anchoring signal peptide, were secreted in to the culture medium as well. Constructs for the CD6- to CD8-TNSALP cDNA were made and transfected into CHO—K1 cells for transient expression. Cells stably expressed and secreted active TNSALP enzymes into the medium in linear fashion for 12 h. However expression of enzyme plateaued after 12 hours. The inventor's previous work with oligopeptide-tagged enzymes showed that increasing the number of Aspartic acid residues beyond eight caused a substantial...
example 2
Characteristics of Poly-Aspartic Acid—Tagged Anchorless rhTNSALP
Affinity for Hydroxyapatite
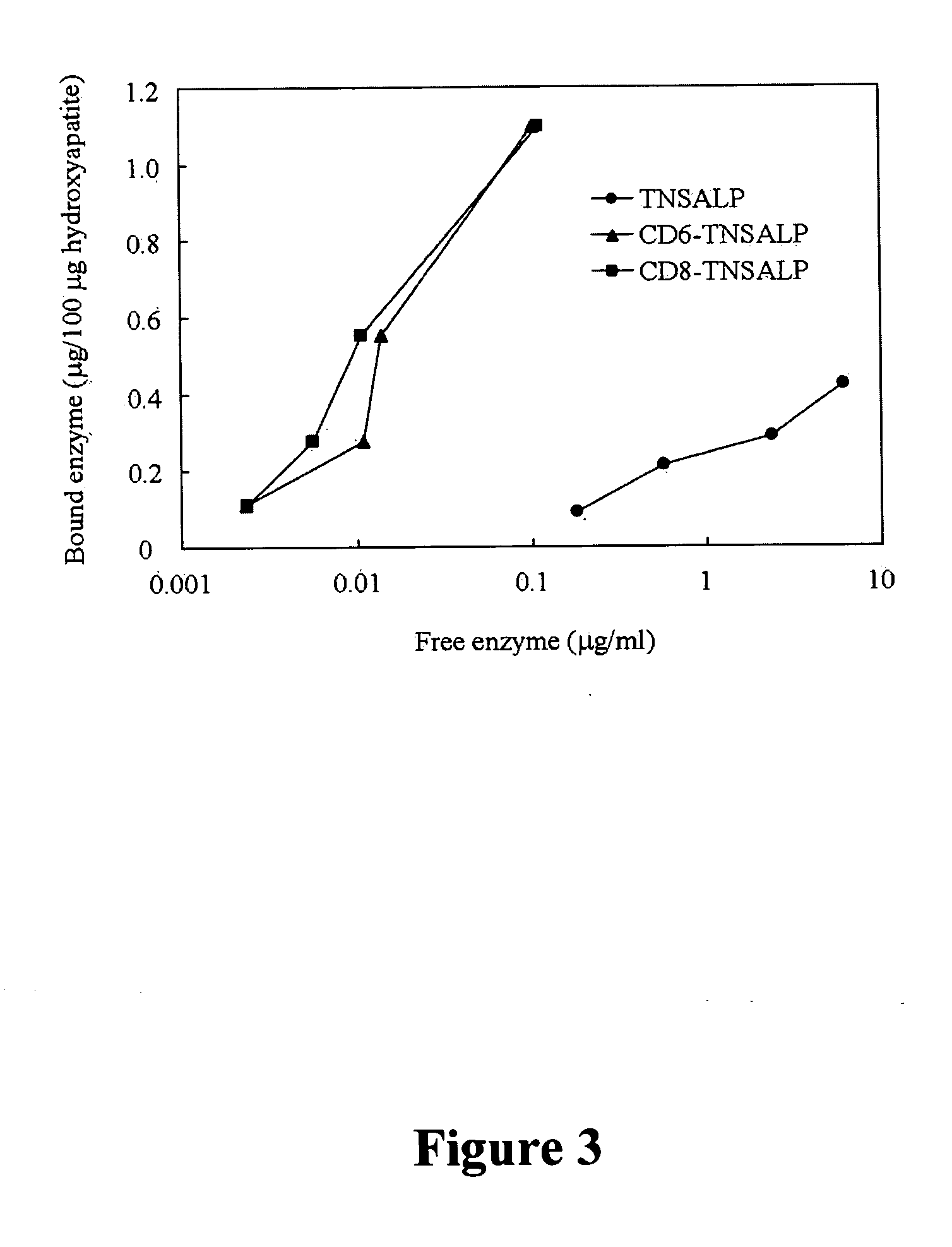
[0067] A remarkable difference between the tagged and untagged enzymes was observed in their affinity to hydroxyapatite. Affinity to hydroxyapatite for the tagged enzymes was 10-fold higher than that for the untagged enzyme and the binding to hydroxyapatite was seen even at low concentration of the tagged enzyme (FIG. 3). The binding parameters, Kb and Bmax, are shown in Table 4. The values of Kb and Bmax of the tagged enzymes were 10- and 3-fold, respectively, higher than those of the untagged enzyme. Although no significant difference was observed between CD6- and CD8-TNSALP.
TABLE 4Binding parameters of three enzymes to hydroxyapatite. Each valuerepresents the mean ± S.D. of 3 experiments. Kb binding constantand Bmax maximum binding rates were determined form double-reciprocal plots.KbBmax (ug / 100 ug(ug−1 ml)hydroxyapatite)rhTNSALP 1.7 ± 1.00.5 ± 0.2CD6-TNSALP36.7 ± 7.91.6 ± 0.3CD8-TNSA...
example 3
Effect of Anchorless rhTNSALP on Mineralization in the Presence of PPi in Primary Bone Marrow Cell Culture
[0072] In human bone marrow cells derived from a hypophosphatasia patient, mineralization never occurred in the absence of TNSALP even when β-glycerophosphate was added. The addition of one of the enzyme resulted in marked recovery of mineralization (FIG. 9). In contrast, mineralization was observed when Pi was used in the medium instead of β-glycerophosphate even in the absence of any enzyme. The presence of any of the enzymes did not provide any additive effect for the mineralization. These findings indicate that the anchorless rhTNSALP enzyme played a biological role in the mineralization process by providing free Pi released during the hydrolysis of β-glycerophosphate. We added PPi, an inhibitor of mineralization, to see whether the anchorless rhTNSALP enzyme hydrolyze PPi to restore the mineralization. PPi itself completely inhibited the mineralization even in the presence...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| molecular mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com