Method for detecting gastric cancer by detecting VLDLR gene
A technology of tissue cells and detection methods, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve problems such as difficulty in finding target genes, difficulties, time-consuming and laborious identification of specific gene deletions, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
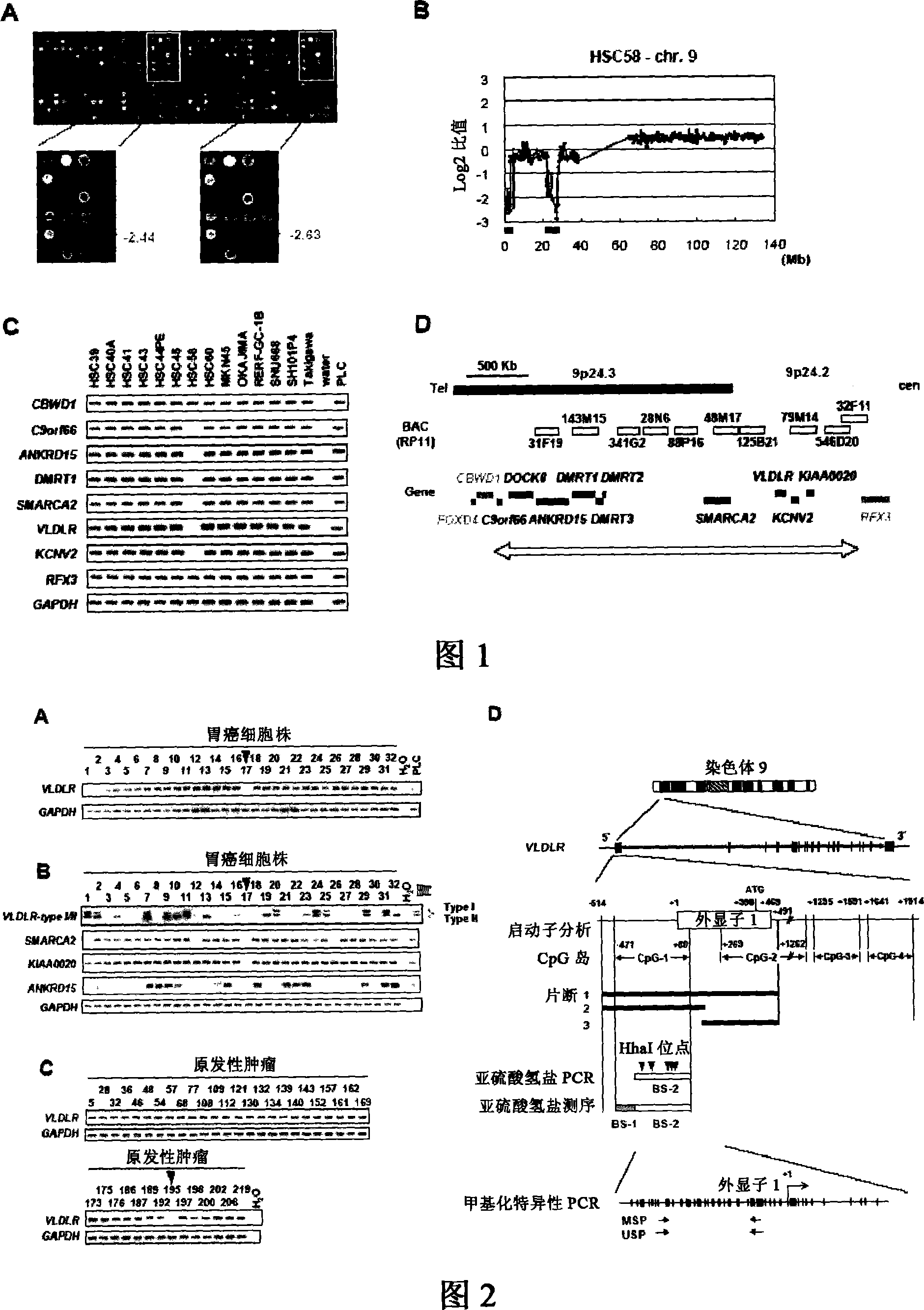
[0038] Dry spots can be prepared by dropping endless BAC DNA or the like on a substrate using a spotter, forming multiple spots, and then drying the spots. As the spotting device, an inkjet printer, a dot matrix printer, and a bubble jet (registered trademark) printer can be used, and an inkjet printer is preferably used. For example, GENESHOT (NGKINSULATORS Co., Ltd., Nagoya) etc. can be used.
[0039] In this way, a desired DNA-immobilization substrate can be prepared by immobilizing infinite BAC DNA or the like on a substrate, particularly preferably a solid substrate.
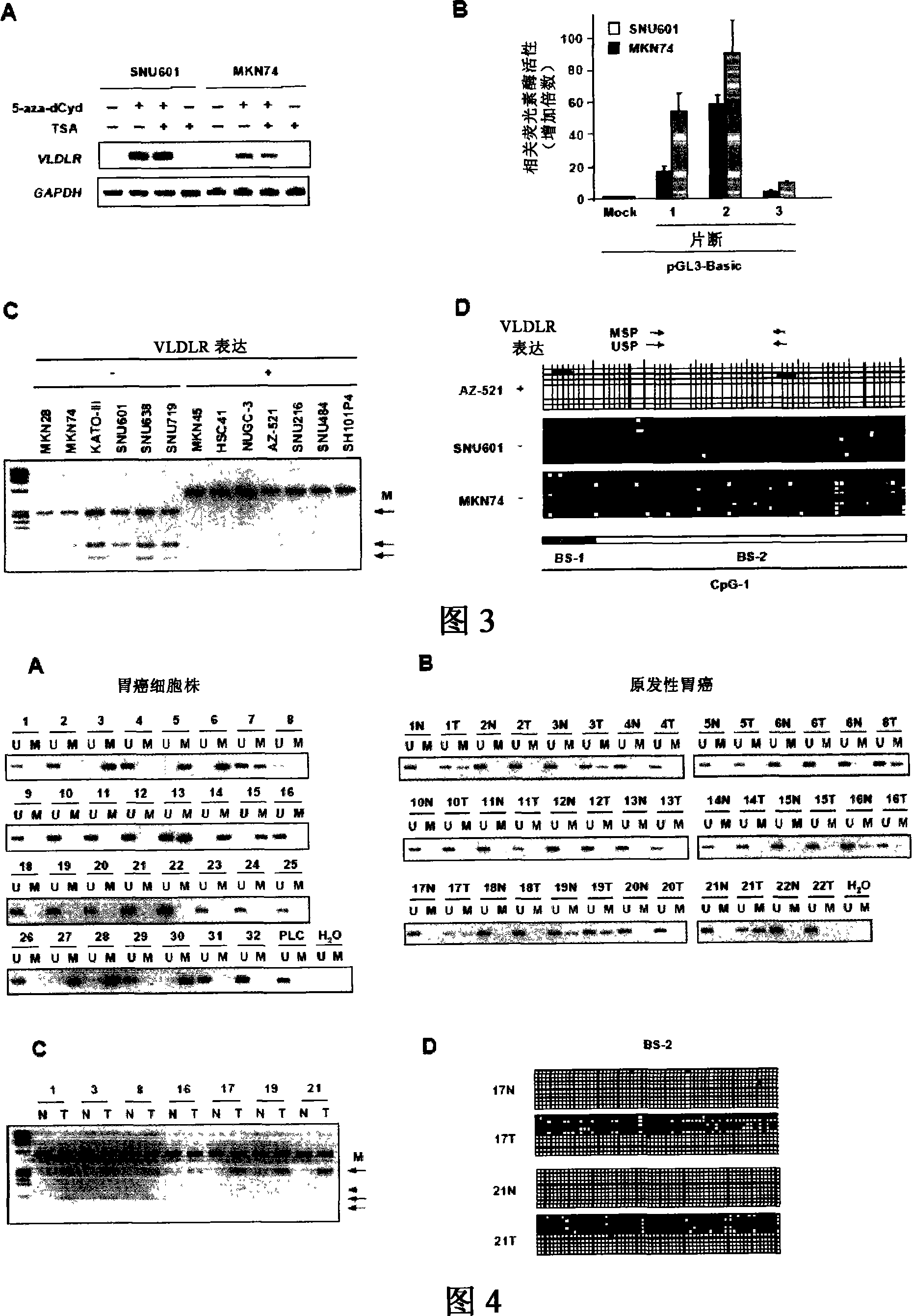
[0040] Further, as a method for directly detecting the deletion of the human VLDLR gene, the Northern blotting method can also be mentioned. The Southern blotting method is to separate and fix the genomic DNA obtained from the sample, and detect whether the gene exists in the sample by detecting its hybridization with the human VLDLR gene. In addition, both the base sequence and amino acid sequence of the...
Embodiment 1
[0056] From the genome database sites of National Cancer for Biotechnology and University of California Santa Crus Biotechnology and the BLAST search results of the selected DNA, genes or sequence tagged site markers (Sequence Tagged Site markers) that are extremely important for cancerization and cancer cell proliferation were selected. 800 BAC / PAC clones.
[0057] The BAC / PAC DNA was digested with DpnI, RsaI, and HaeIII, and ligated with adapter DNA (adaptor DNA). Next, 2 PCRs were performed using primers having linker sequences. One of the 5' ends of the two primers was aminated. This step is called "infinitization", and the resulting DNA is defined as "infinitization DNA". The infinite DNA was covalently printed on an oligomeric DNA microarray (Matsunami Glass Industry Co., Ltd., Osaka) twice using an inkjet spotter (GENESHOT, NGK Insulators, Nagoya).
Embodiment 2
[0059] In order to detect novel homozygous deletions in gastric cancer, CGH array analysis was performed using the CGH array of Example 1 using genomic DNA prepared from 32 types of gastric cancer cells.
[0060] In addition, as a control, genomic DNA from healthy males was used and labeled with Cy5. As DNA to be detected, genomic DNA prepared from the above gastric cancer cells was used and labeled with Cy3. Specifically, DpnI-digested genomic DNA (0.5 μg) in the presence of 0.2 mM dATP, 0.2 mM dTTP, 0.2 mM dGTP, 0.1 mM dCTP, and 0.4 mM Cy3-dCTP (gastric cancer cells) or 0.4 mM Cy5-dCTP (normal cells) Next, tagging is performed by nick translation. Cy3 and Cy5 labeled dCTPs were obtained from Amersham Biosciences (Tokyo). The two labeled genomic DNAs were added to ethanol in the presence of Cot-1 DNA (Invitrogen Co.), precipitated, and dissolved in 120 μl hybridization mixture (50% formamide, 10% dextran sulfate, 2×SSC ( 1×SSC: 150 mM sodium chloride / 15 mM sodium citrate))...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com