Patents
Literature
53 results about "Transcript level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Promoter, promoter control elements, and combinations, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20060107346A1Improve featuresReduce the amount requiredBryophytesSugar derivativesTranscript levelNitrogen
The present invention is directed to nitrogen responsive promoter sequences and promoter control elements, polynucleotide constructs comprising the nitrogen responsive promoters and control elements and methods of identifying the nitrogen responsive promoters, control elements, or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present nitrogen responsive promoters or promoter control elements to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:CERES INC
Drought inducible promoters and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to drought responsive promoter sequences, polynucleotide constructs comprising the drought responsive promoters and methods of identifying the drought responsive promoters or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present drought responsive promoters to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:CERES INC
Root active promoters and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to root active promoter sequences, polynucleotide constructs comprising the root active promoters and methods of identifying the root active promoters, or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present root active promoters to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:CERES INC
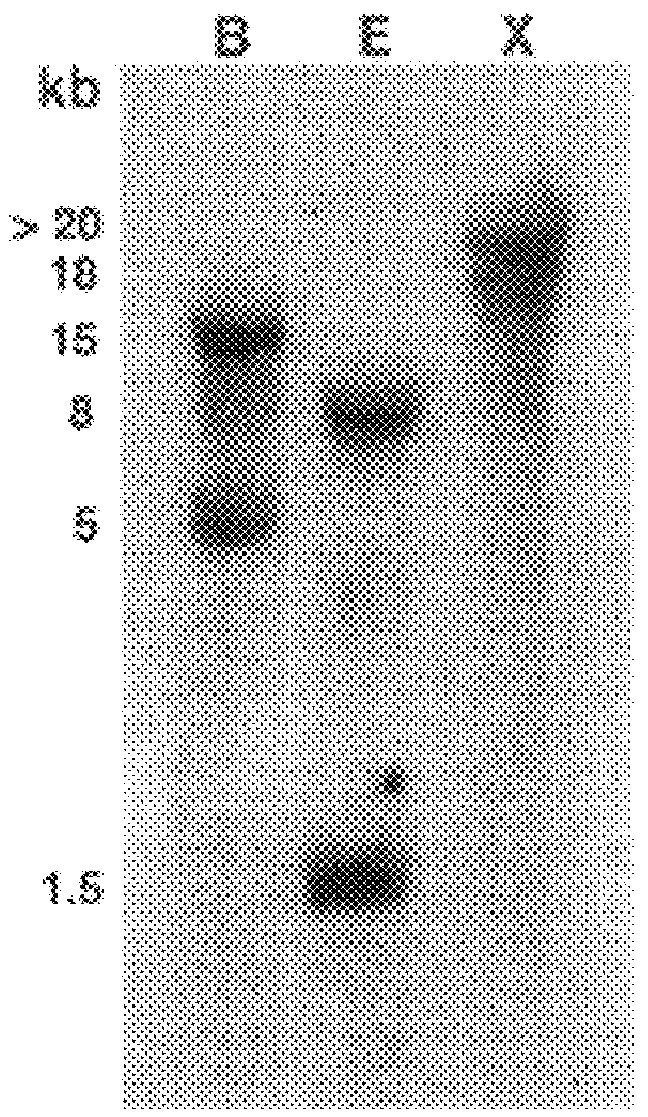
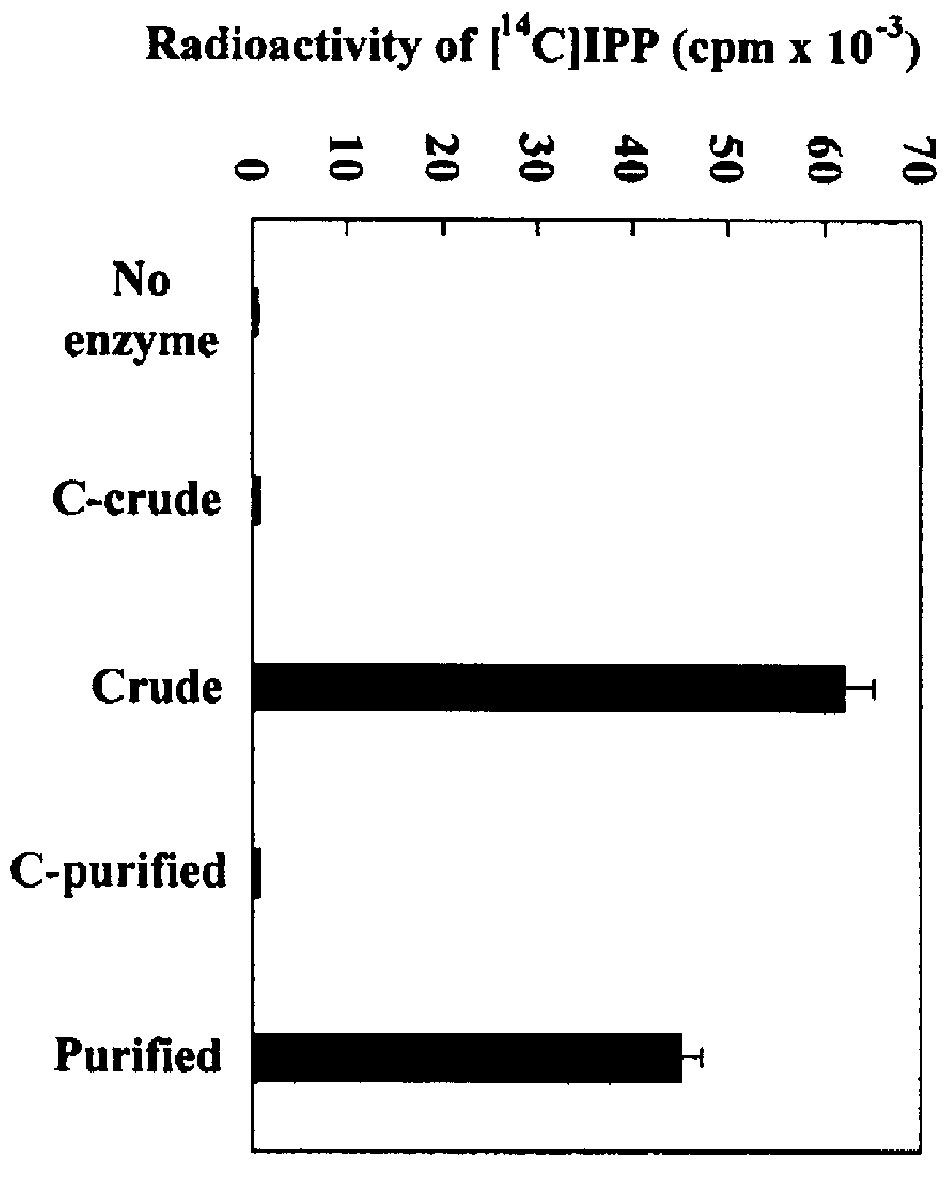
Isopentenyl diphosphate isomerase from Hevea brasiliensis and rubber producing method using the same
The present invention cloned a cDNA clone encoding isopentenyl diphosphate (hereafter "IPP") isomerase (EC 5.3.3.2) from a cDNA library of Hevea brasiliensis latex. The clone has a continuous open reading frame encoding a peptide of 234 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 26.7 kDa. The deduced protein is acidic with an isoelectric point of 4.7 and shows high sequence identity with other IPP isomerases. The recombinant protein expressed in Escherichia coli showed IPP isomerase activity. In vitro rubber biosynthesis assays using washed rubber particle (WRP) deprived of initiating allylic diphosphates were performed with the addition of IPP isomerase in the reaction mixture. Results revealed that the recombinant IPP isomerase is catalytically active in catalyzing the conversion of IPP to DMAPP, a key activation step of the basic five-carbon isoprene unit in rubber biosynthesis. Southern analysis indicated that the IPP isomerase is encoded by two genes in Hevea rubber tree. In Northern blot analysis, two different sizes of transcripts (1.2 and 0.6 kb) were detected from leaf tissues while only one hybridizing band (1.0 kb) was detected from latex. Analyses of RNA extracted from extruded latex and leaf tissues of the trees wounded with nails showed that wounding did not change the transcript level of IPP isomerase.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
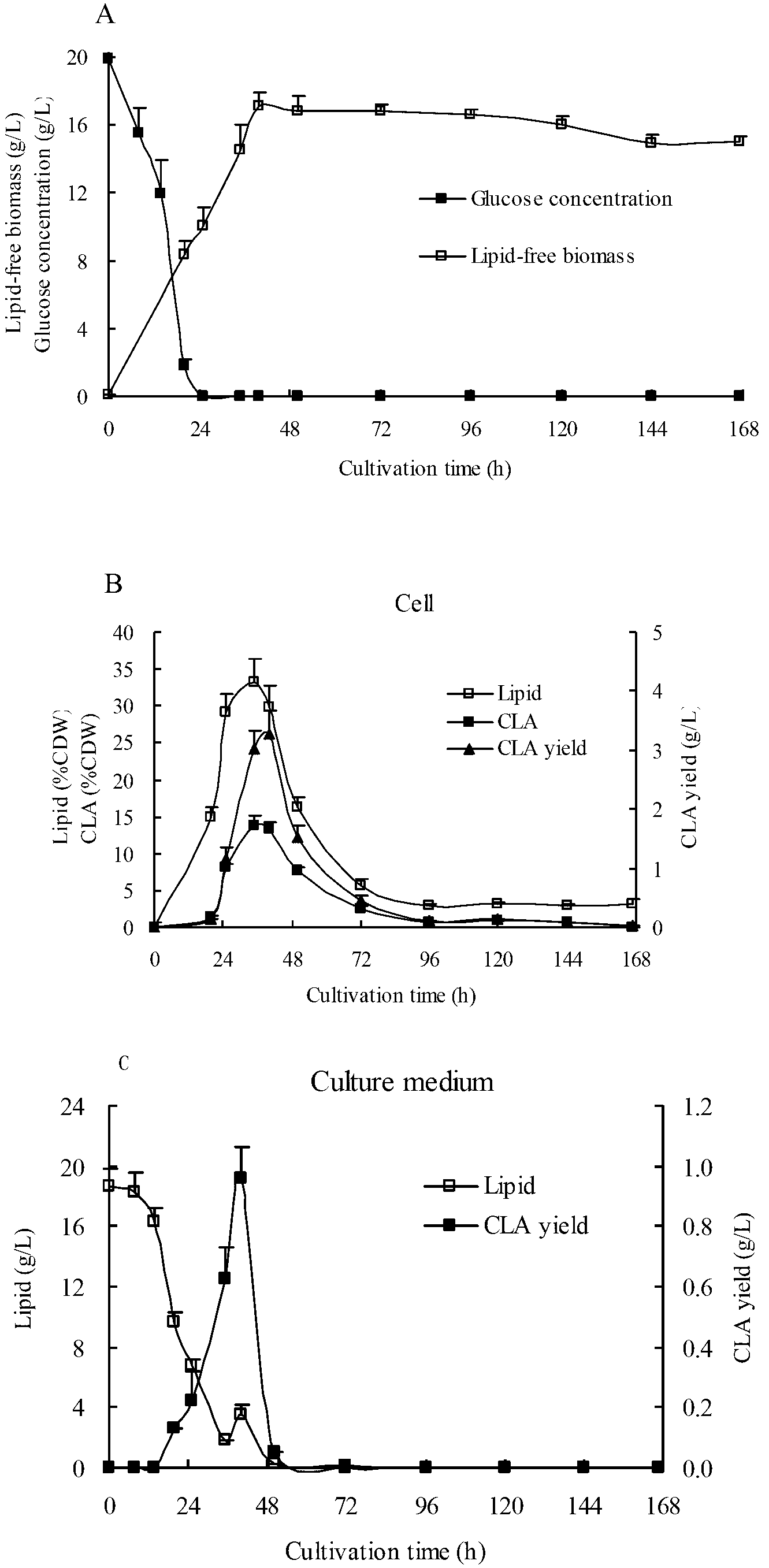
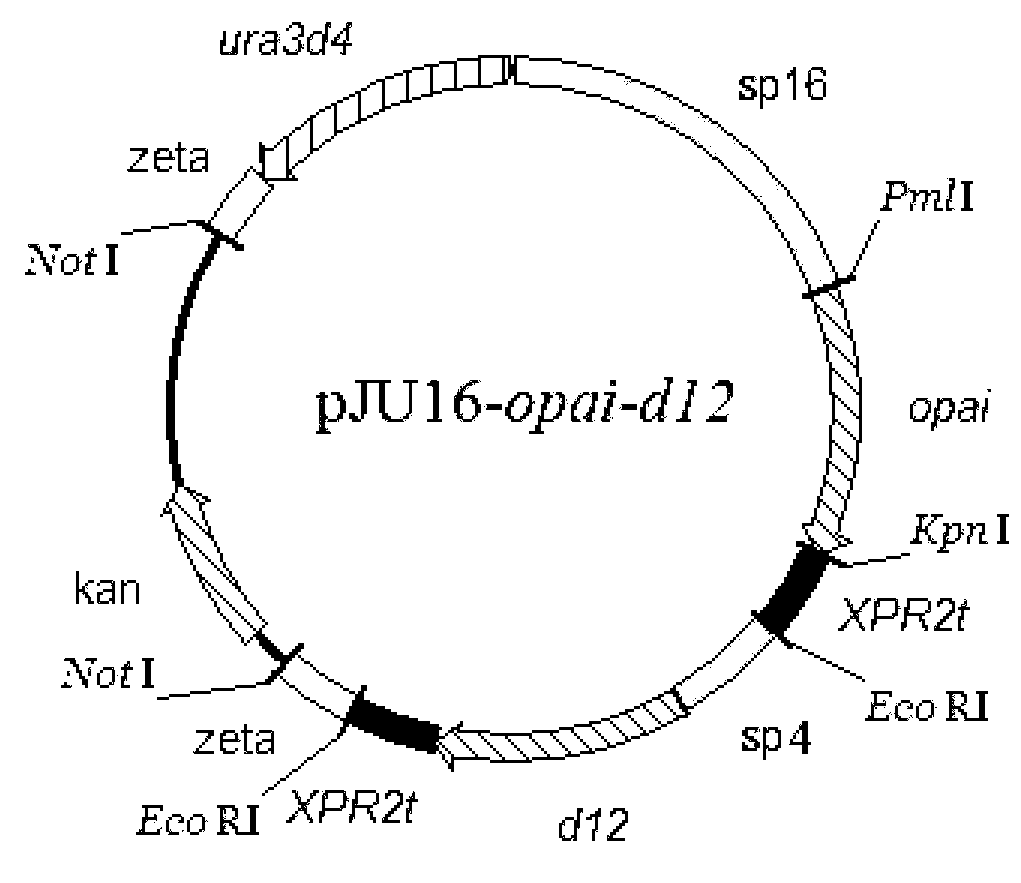
Method for optimizing conjugated linoleic acid synthesis by using Yarrowia lipolytica yeast recombinant strain based on genetic engineering strategy
According to the invention, delta-12 desaturase gene (FADS12, d12) from mortierella alpine ATCC32222 (M. alpina ATCC32222) is amplified, such that multi-copy expression plasmid with inserted opai / d12 co-expression gene and recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica yeast strain are prepared. According to the invention, the recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica yeast strain assists in increasing endogenous substrate linoleic acid (LA) amount and outer soybean oil increased substrate LA amount in fermentation medium, through expressing d12. In the strain, opai gene and d12 gene expression and transcript levels are increased with a multi-copy integration manner, such that conjugated linoleic acid t10 and c12-CLA specific isomer synthesis amount in recombinant Yarrowia lipolytica yeast strain can be further improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Improved strategies for transcript profiling using high throughput sequencing technologies
InactiveCN101365803AMicrobiological testing/measurementICT adaptationTranscript levelTranscript profiling
Described is a method for determining a nucleotide sequence within cDNA, the frequency of a nucleotide sequence in a cDNA sample, as well as a method for (unbiased) determination of relative transcript levels of genes without sequence information of these genes being required, said methods using complexity reduction and (high throughput) sequencing.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Strategies for trranscript profiling using high throughput sequencing technologies
InactiveUS20090247415A1Easy to useQuick sortingMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningTranscript levelNucleotide sequencing
Described is a method for determining a nucleotide sequence within cDNA, the frequency of a nucleotide sequence in a cDNA sample, as well as a method for (unbiased) determination of relative transcript levels of genes without sequence information of these genes being required, said methods using complexity reduction and (high throughput) sequencing.
Owner:KEYGENE NV
Application of PSMD4 protein in preparation of liver cancer prognostic evaluation kit
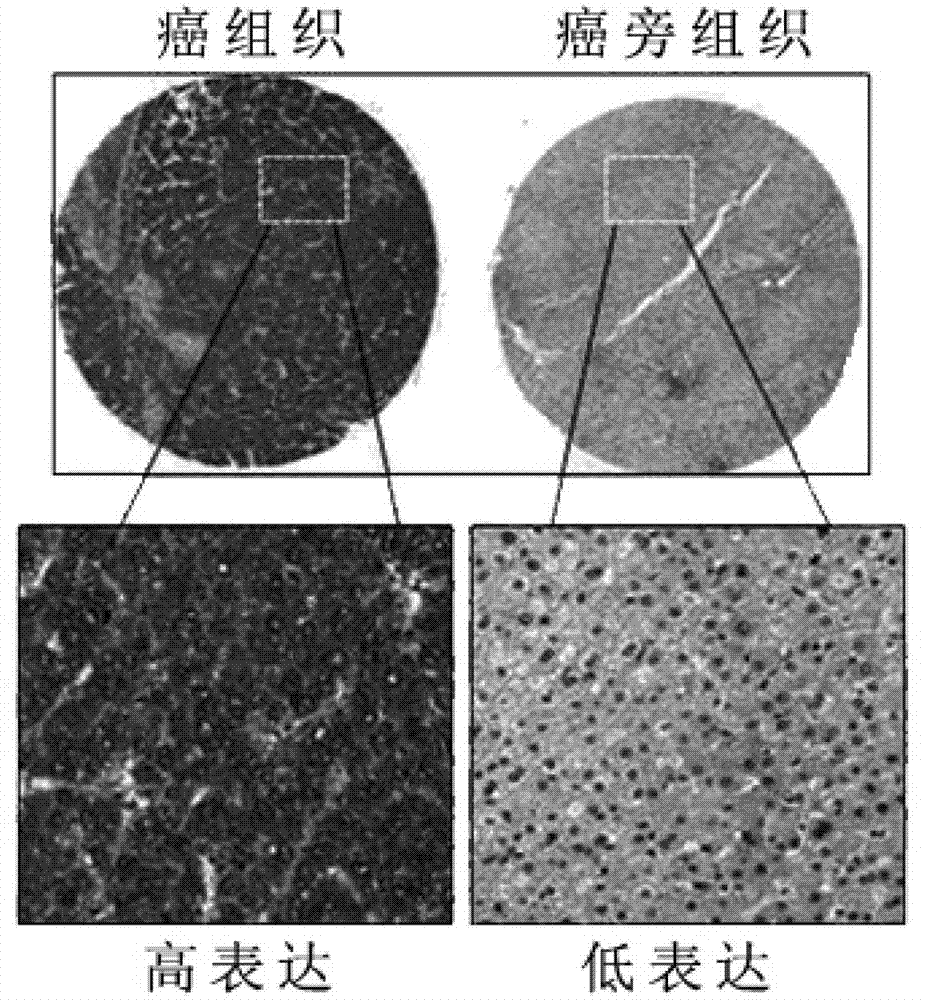
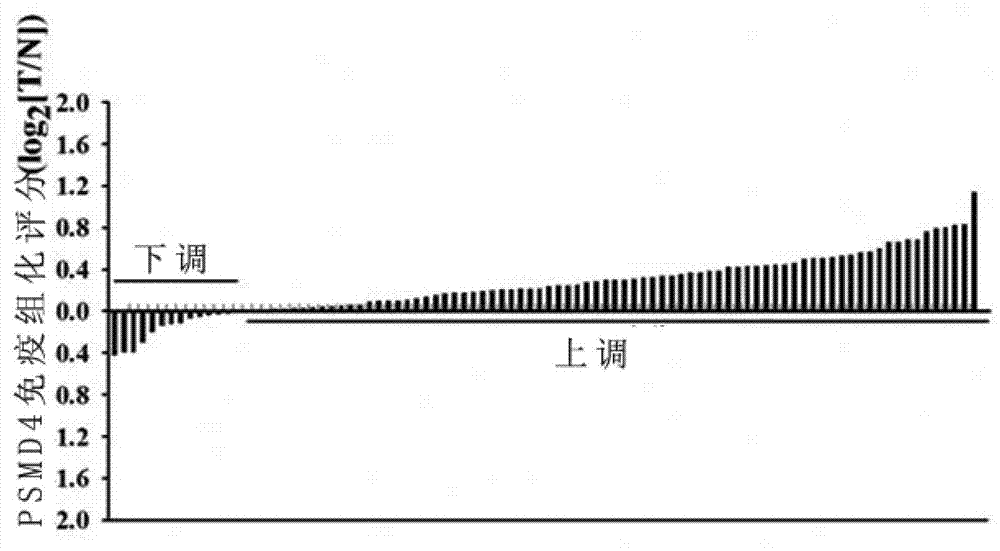
The invention belongs to the biotechnology field, relates to application of PSMD4 protein, and in particular relates to application of the PSMD4 protein in preparation of a liver cancer prognostic evaluation kit. The invention adopts an immunohistochemistry technology, a microscope photograph technology and computer image processing software to test the relative transcript level of PSMD4 protein of tumor tissues relative to the tumors and determine the correlation between the relative transcript level of PSMD4 protein and the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma patients after operation by a manner of combining the postoperative follow-up information. The PSMD4 protein can be used for preparing a protein molecular marker for judging prognosis of the liver cancer patients, and has important instruction significance to postoperative monitor and sequential therapy of the hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Quantification of microsphere suspension hybridization and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090136918A1Improve accuracyStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingDiseaseBiotin-streptavidin complex
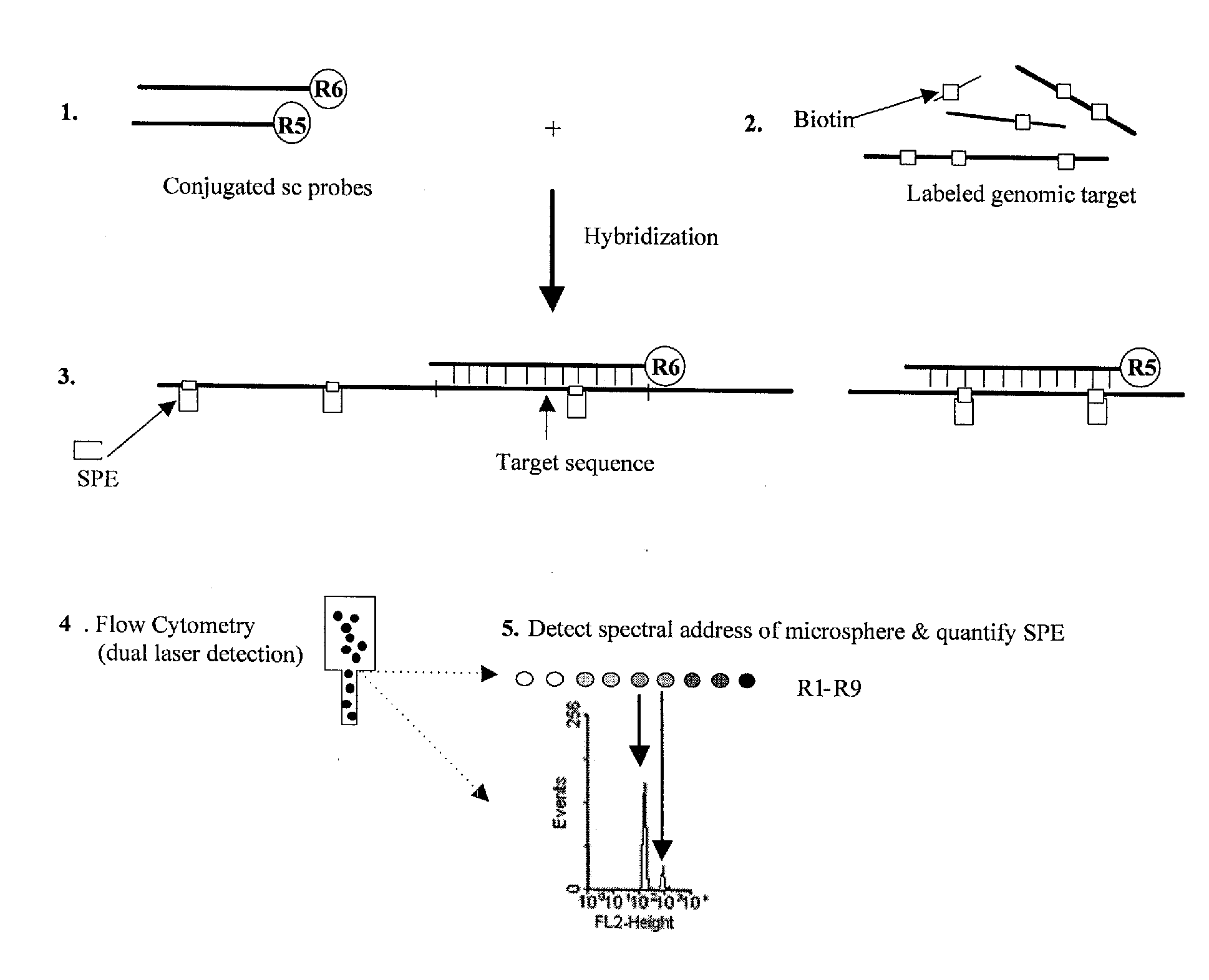
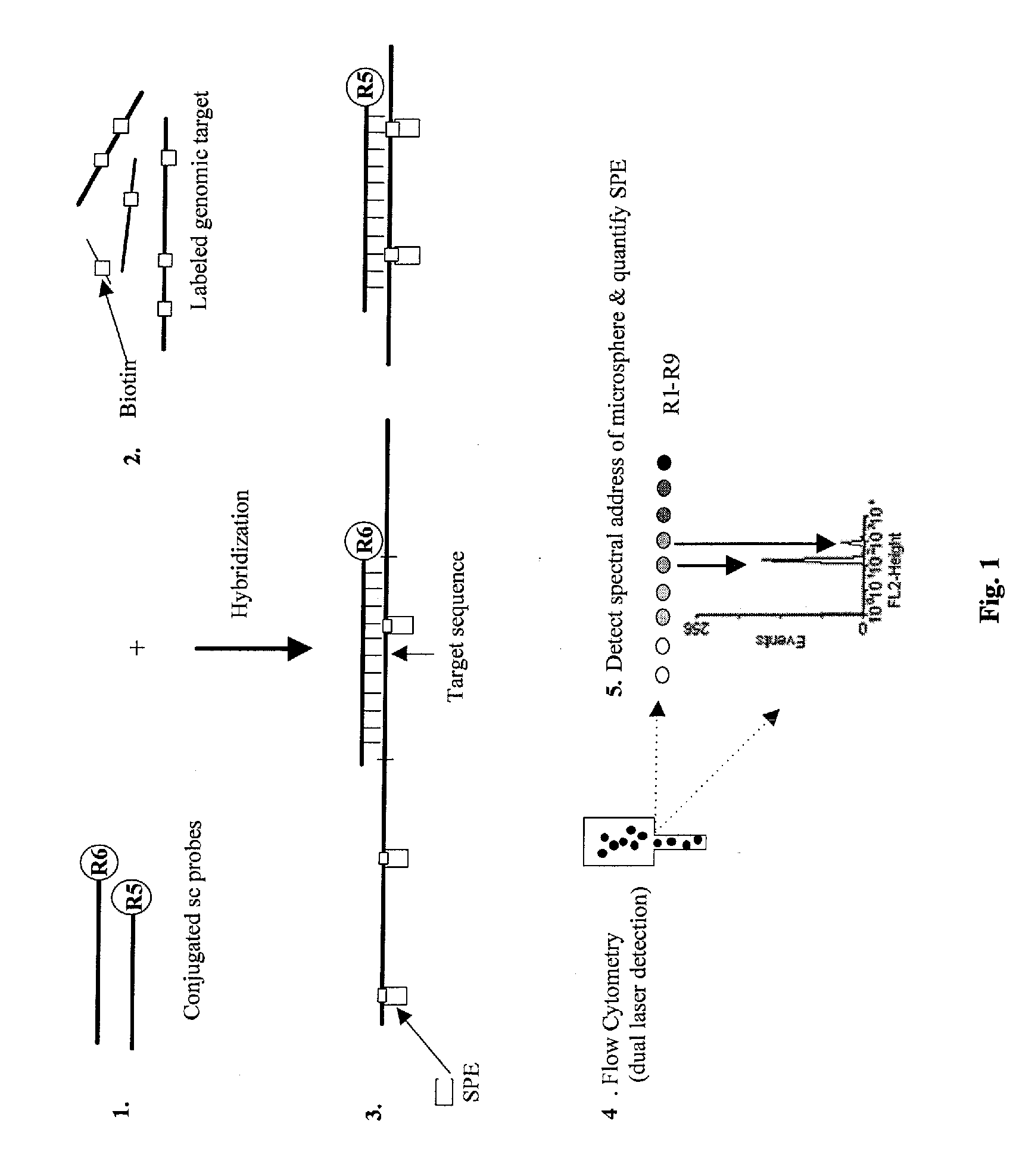
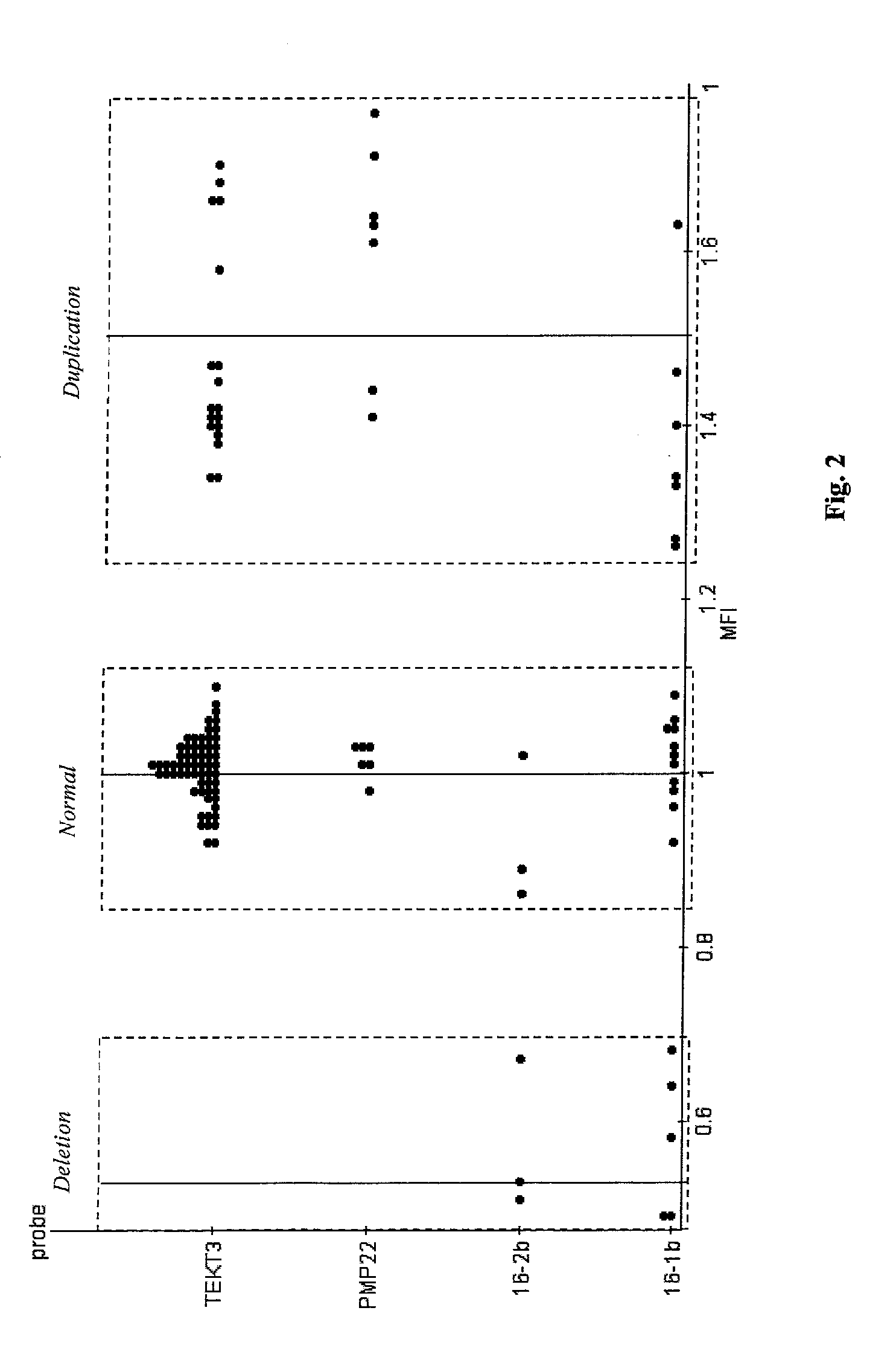
A novel suspension hybridization assay was used to determine nucleic acid copy number by flow cytometry. The assay was validated with low copy (lc) products ranging in length from 100 to 2304 bp conjugated to spectrally-distinct polystyrene microspheres. In the example provided herein, these conjugated microspheres were used as multiplex hybridization probes to detect homologous sequences in genomic DNA extracted from cytogenetic cell pellets and labeled with biotin-dUTP. Hybridization was detected with phycoerythrin-labeled streptavidin and analyzed by flow cytometry. Copy number differences were distinguishable by comparing the mean fluorescence intensities of test probes with a diploid reference probe in genomic DNA of patient samples and abnormal cell lines. The assay is capable of distinguishing a single allele and three alleles at a test locus from a biallelic reference sequence, regardless of chromosomal context. The assay is an improvement on previous methods which require prior amplification of locus-specific target DNA because, lc probes provide adequate specificity and sensitivity for accurate copy number determination of homologous targets. Because of its high sensitivity and accuracy, the assay is useful for determination of nucleic acid copy number for a variety of applications, including determination of genomic copy number in humans, animal models of disease and in solution, measurement of transcript levels, forensic DNA analysis, and quality control analysis in agriculture.
Owner:CHILDRENS MERCY HOSPITAL
Root active promoters and uses thereof
InactiveUS20080235823A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyTranscript level
The present invention is directed to root active promoter sequences, polynucleotide constructs comprising the root active promoters and methods of identifying the root active promoters, or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present root active promoters to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:MEDRANO LEONARD +2
Extraction method of total protein from rumen epithelial tissue of milk cow
InactiveCN103570801AEfficient separationEasy to removePeptide preparation methodsFreeze-dryingTotal protein
The invention relates to an extraction method of protein from animal tissues, in particular to an extraction method of total protein from a rumen epithelial tissue of a milk cow. The method comprises the steps of putting a rumen epithelial tissue sample of the milk cow in a precooled mortar, adding liquid nitrogen, grinding into powder, adding an acetone solution of precooled trichloroacetic acid, oscillating, eddying, uniformly mixing for overnight aging, centrifugally collecting sediment, freeze-drying the tissue sediment, adding lysate, incubating and eddying at intervals, and centrifugally collecting supernate, namely the total protein of the rumen epithelial tissue of the milk cow. For the total protein of the rumen epithelial tissue of the milk cow, extracted by the method, a total protein mixture can be separated by a two-dimensional gel electrophoresis technology according to an isoelectric point and molecular weight of the protein, the relative abundance of the protein is acquired, the isoelectric point, the molecular weight and a relative transcript level of each protein can be clearly and visually shown in a gel atlas, and the method has the advantages of more obvious integrity and visualization in comparison with the prior arts such as a high efficiency liquid chromatography separation method, an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblotting.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY MEDICINE ANHUI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
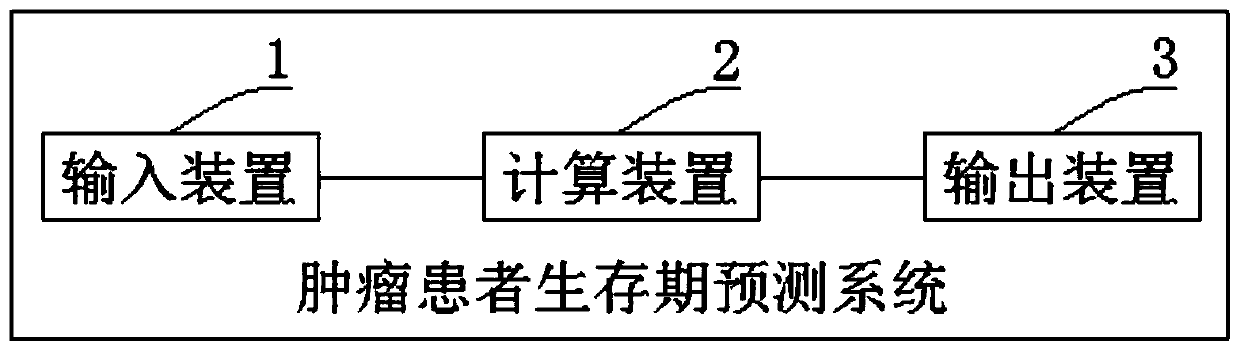
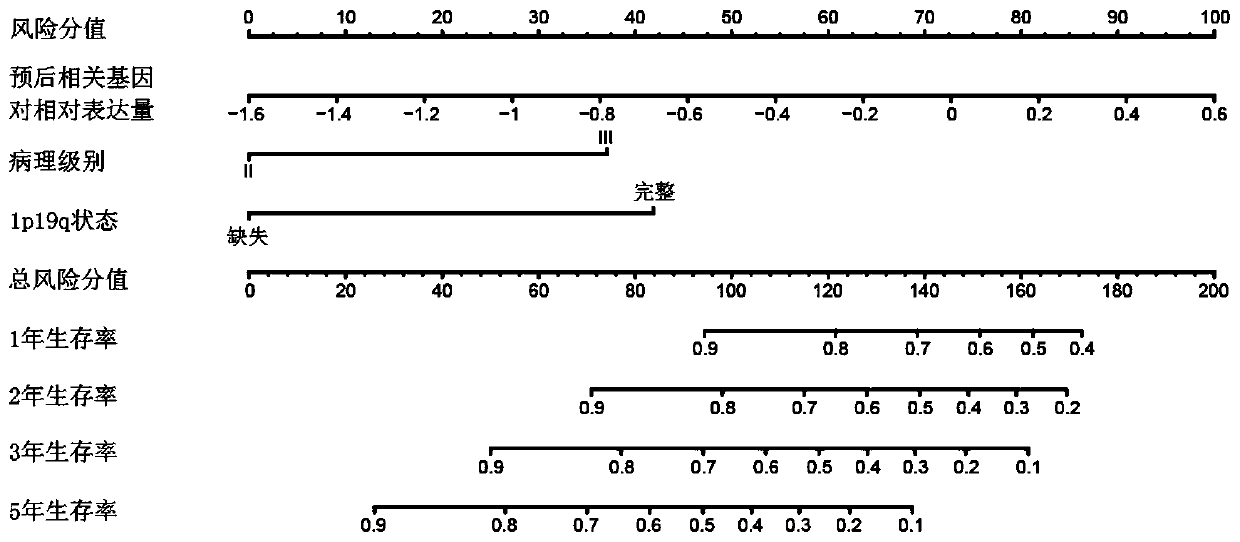
Tumor patient lifetime prediction system
ActiveCN110993104AEasy to getEasy accessMedical simulationHealth-index calculationTranscript levelAlgorithm
The invention relates to a tumor patient lifetime prediction system. The system comprises a calculation device, an input device used for inputting a risk score of the relative transcript level of a tumor prognosis related gene pair of a tumor patient individual, and an output device used for outputting a lifetime survival probability of a tumor patient; wherein the tumor prognosis related gene pair is a gene pair in which the relative size of the expression quantities of two genes in the gene pair is related to the lifetime of the tumor patient; the calculation device comprises a memory and aprocessor. A computer program is stored in the memory so as to realize a modeling algorithm and an algorithm of a discrimination function; and the modeling algorithm is a least partial squares algorithm. According to the tumor patient lifetime prediction system, variables which are easy to obtain clinically are synthesized, the prediction result of the tumor patient lifetime can be obtained rapidly and accurately, and the time and energy of a user are saved.
Owner:THE FIRST HOSPITAL OF CHINA MEDICIAL UNIV +1
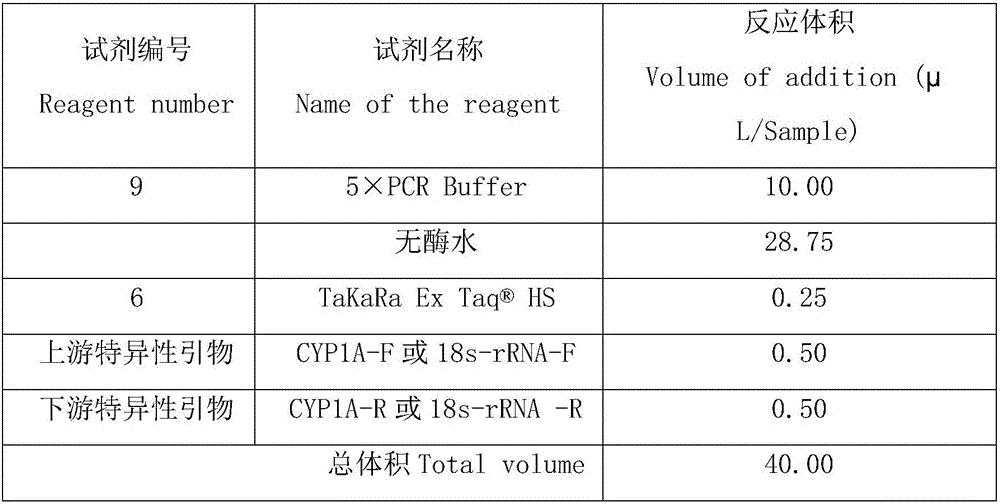
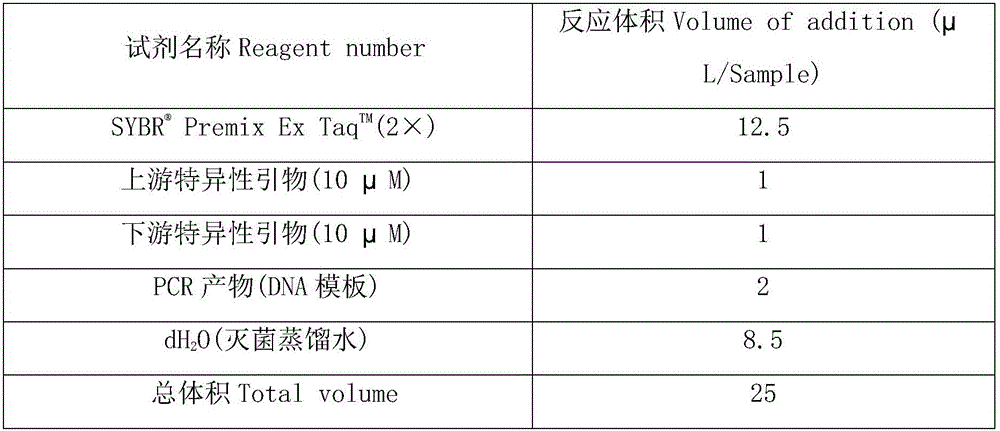
Method for monitoring phenanthrene pollution in water through gene CYP1A
InactiveCN106086202APrecise regulationPrecise prevention and controlMicrobiological testing/measurementEcological environmentTranscript level
The invention discloses a method for monitoring phenanthrene pollution in water through a gene P4501A (CYP1A). Fishes serve as biological samples for monitoring water pollution, and the gene CYP1A of the fishes serves as a sensitive biomarker for monitoring the phenanthrene pollution in water. The method has the advantages that the gene CYP1A serves as the sensitive biomarker for monitoring water pollution, the degree of water pollution is monitored by testing the relative transcript level of the gene CYP1A, and the method can sensitively reflect whether water is polluted or not and the degree of water pollution and even can sensitively detect the water pollution of a micro-pollution source; the perniciousness and the damage degree of phenanthrene pollution can be sensitively monitored from the biological angle, and an accurate, quick and scientific method is provided for water ecological environment monitoring, toxicology diagnosing, regulating, preventing and treating.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Root active promoters and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to root active promoter sequences, polynucleotide constructs comprising the root active promoters and methods of identifying the root active promoters, or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present root active promoters to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:CERES INC
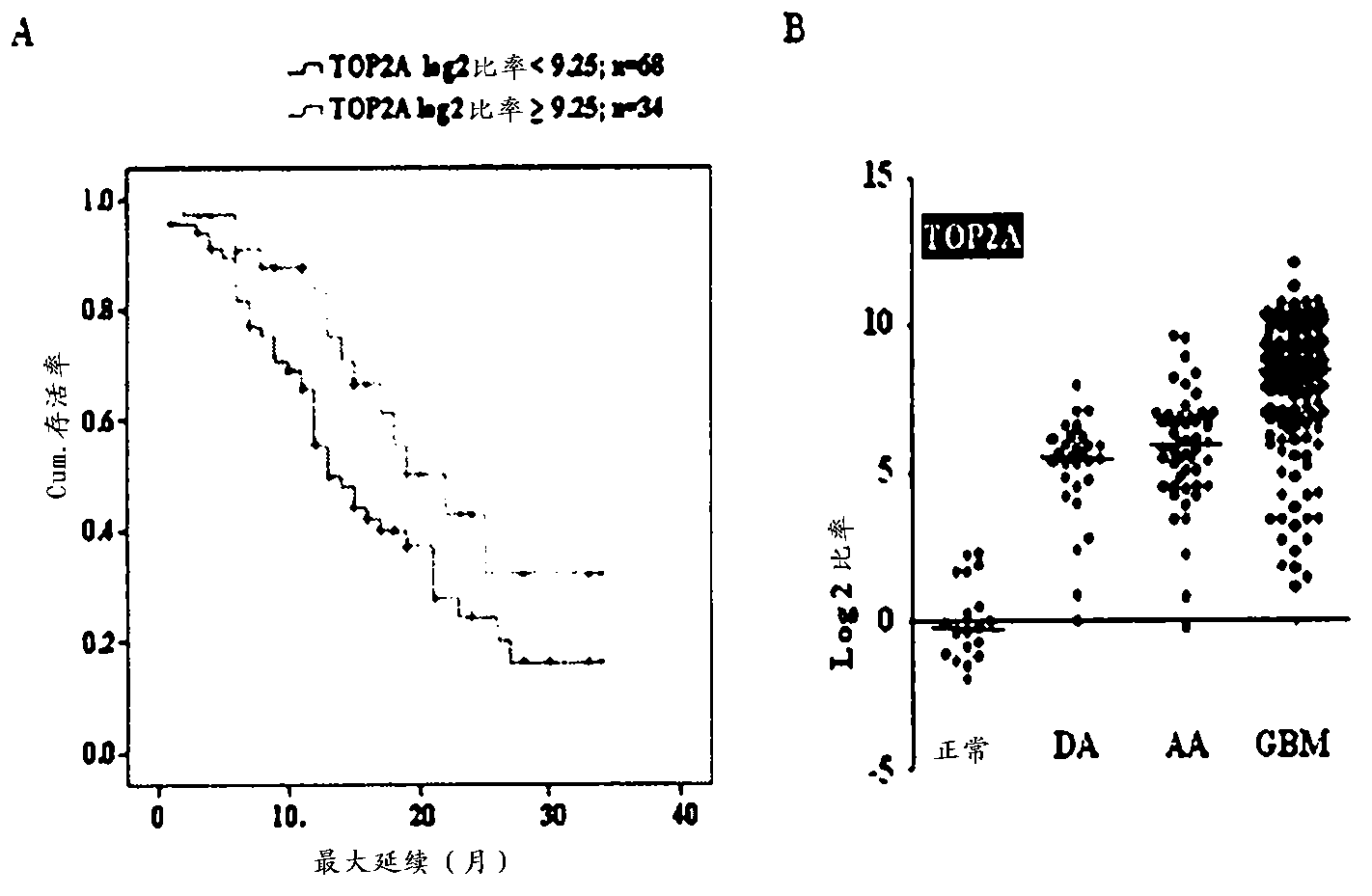
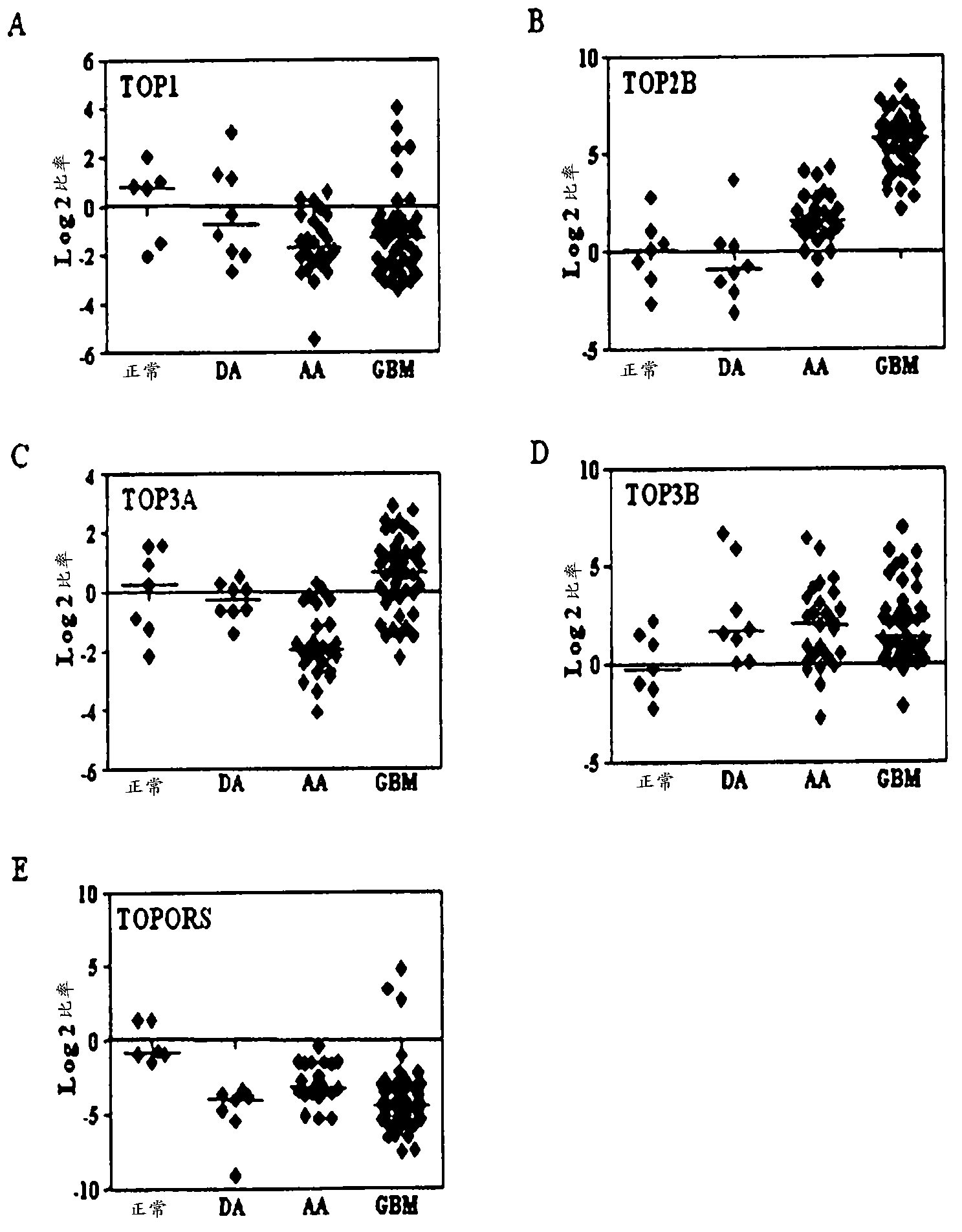
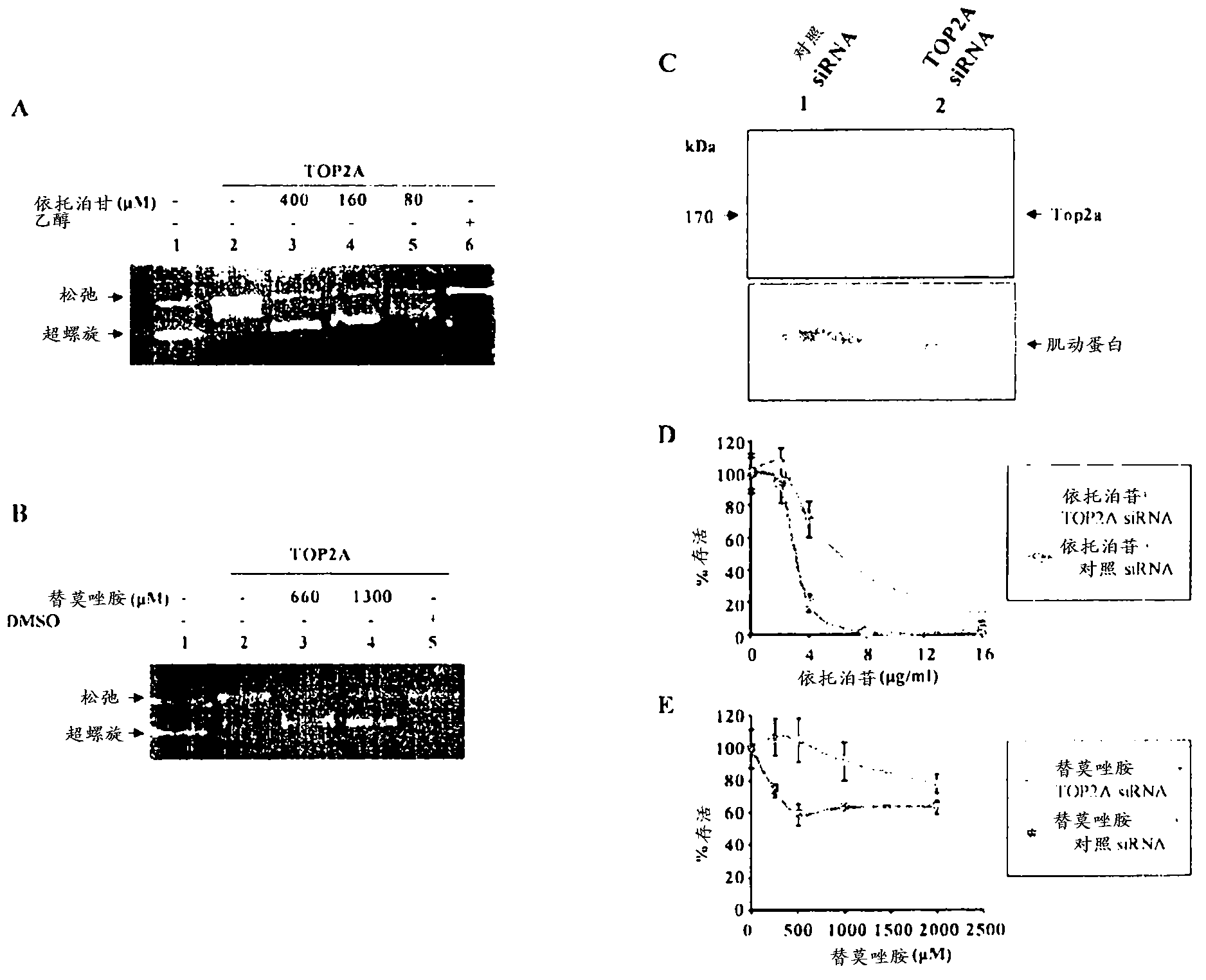
Top2a inhibition by temozolomide useful for predicting gbm patient's survival
ActiveCN103269710AOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPatient survivalTranscript level
The present invention provides a TOP2A inhibition by temozolomide useful for predicting glioblastoma patient's survival. Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most common, malignant primary adult brain tumor. The conventional treatments for GBM, include surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy which have only modestly improved patient survival. The patients with GBM expressing higher TOP2A transcript levels had better prognosis. More interestingly, the present invention reports that temozolomide is an inhibitor of TOP2A activity in vitro. The present invention further shows that siRNA knock down of TOP2A rendered a glioma cell line resistant to temozolomide chemotherapy.; Thus it is demonstrated for the first time that temozolomide is a TOP2A inhibitor and establishes that TOP2A transcript levels determines the chemosensitivity of glioblastoma to temozolomide therapy thus explaining the very high levels of TOP2A transcript being a good prognostic indicator in GBM patients receiving temozolomide chemotherapy.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Marker for identifying benign and malignant pulmonary nodules by using exosome protein and application of marker
The invention belongs to the technical field of cancer molecular diagnosis technique, in particular to a marker for identifying benign and malignant pulmonary nodules by using an exosome protein and an application of the marker. The marker comprises the following steps: S1, looking for differentially expressed proteins of exosomes in plasmas of patients suffering from benign and malignant pulmonary nodules; S2, screening the differential proteins; S3, verifying the differential diagnosis effect of FGB on the benign and malignant pulmonary nodules; and S4, analyzing the relative transcript level. The non-invasive liquid-state biopsy method is used to search out the molecular marker for identifying the benign and malignant pulmonary nodules, and the mass spectrometric detection and the subsequent bio-information analysis show that the molecular marker FGB provides a novel molecular target for the diagnosis of the pulmonary nodules and the observation of clinical effects.
Owner:HUADONG HOSPITAL
Shade responsive promoter, promoter control elements, and combinations, and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050266559A1FermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscript level
The present invention is directed to promoter sequences and promoter control elements, polynucleotide constructs comprising the promoters and control elements, and methods of identifying the promoters, control elements, or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present promoters or promoter control elements to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:CERES INC
Drought inducible promoters and uses thereof
The present invention is directed to drought responsive promoter sequences, polynucleotide constructs comprising the drought responsive promoters and methods of identifying the drought responsive promoters or fragments thereof. The invention further relates to the use of the present drought responsive promoters to modulate transcript levels.
Owner:CERES INC
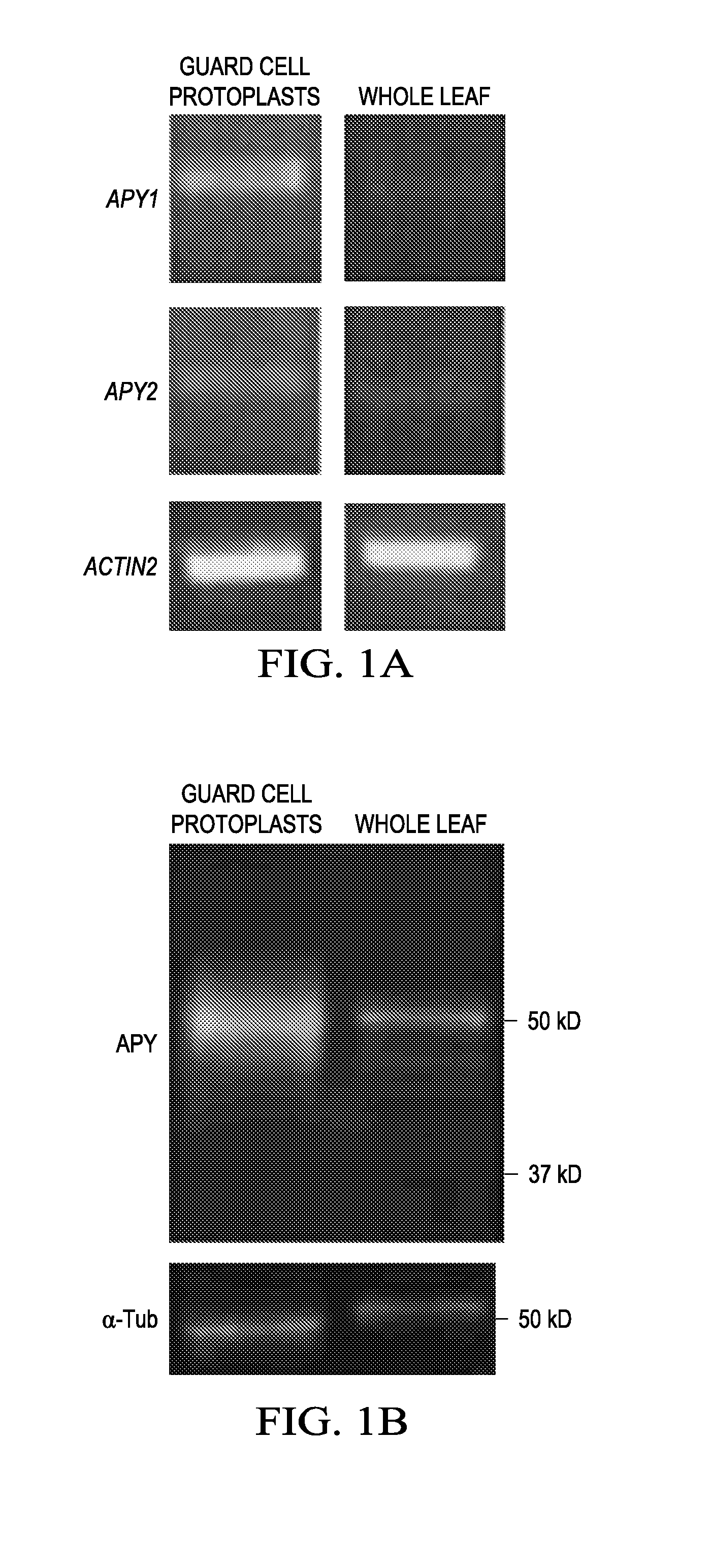
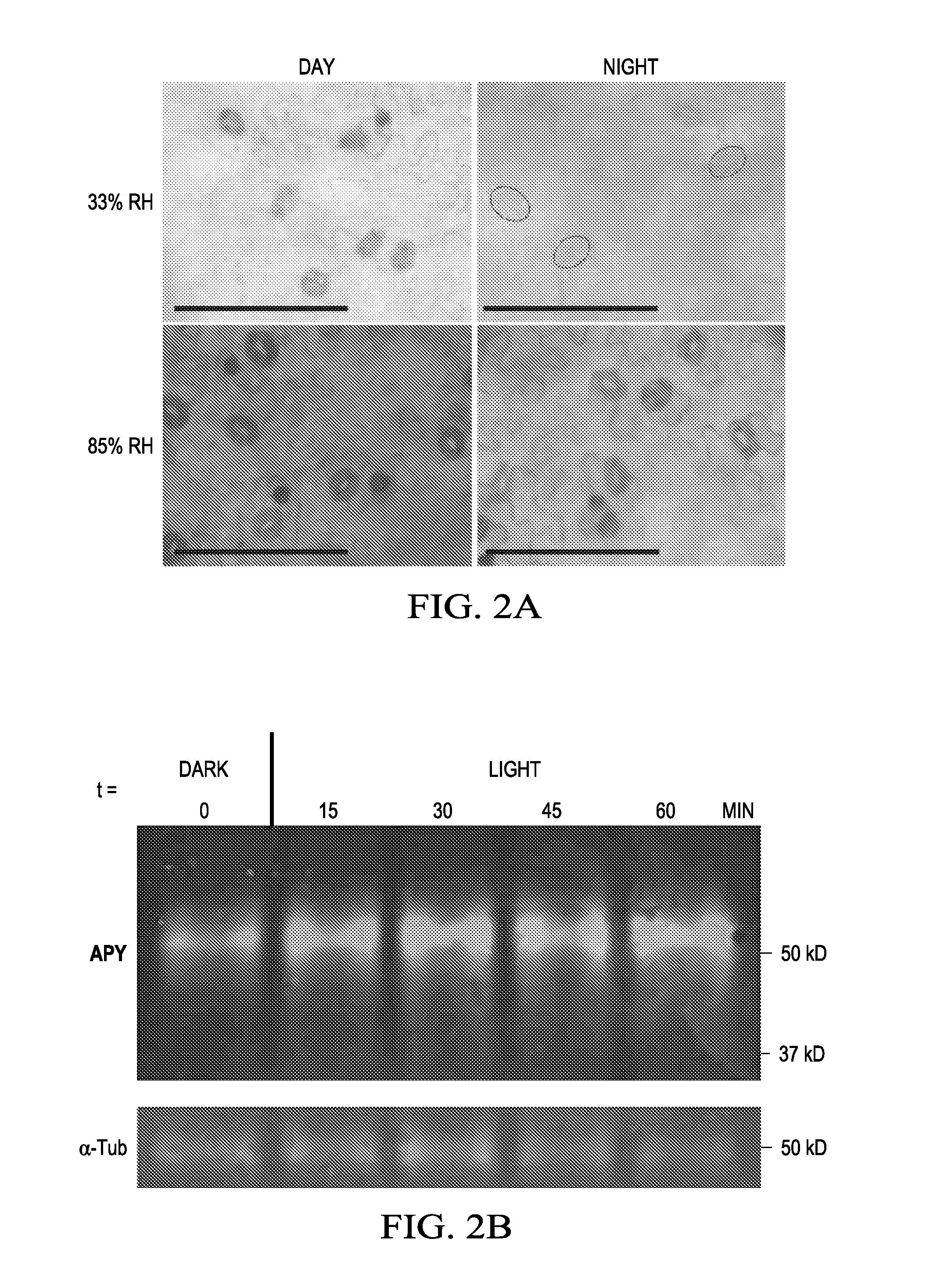
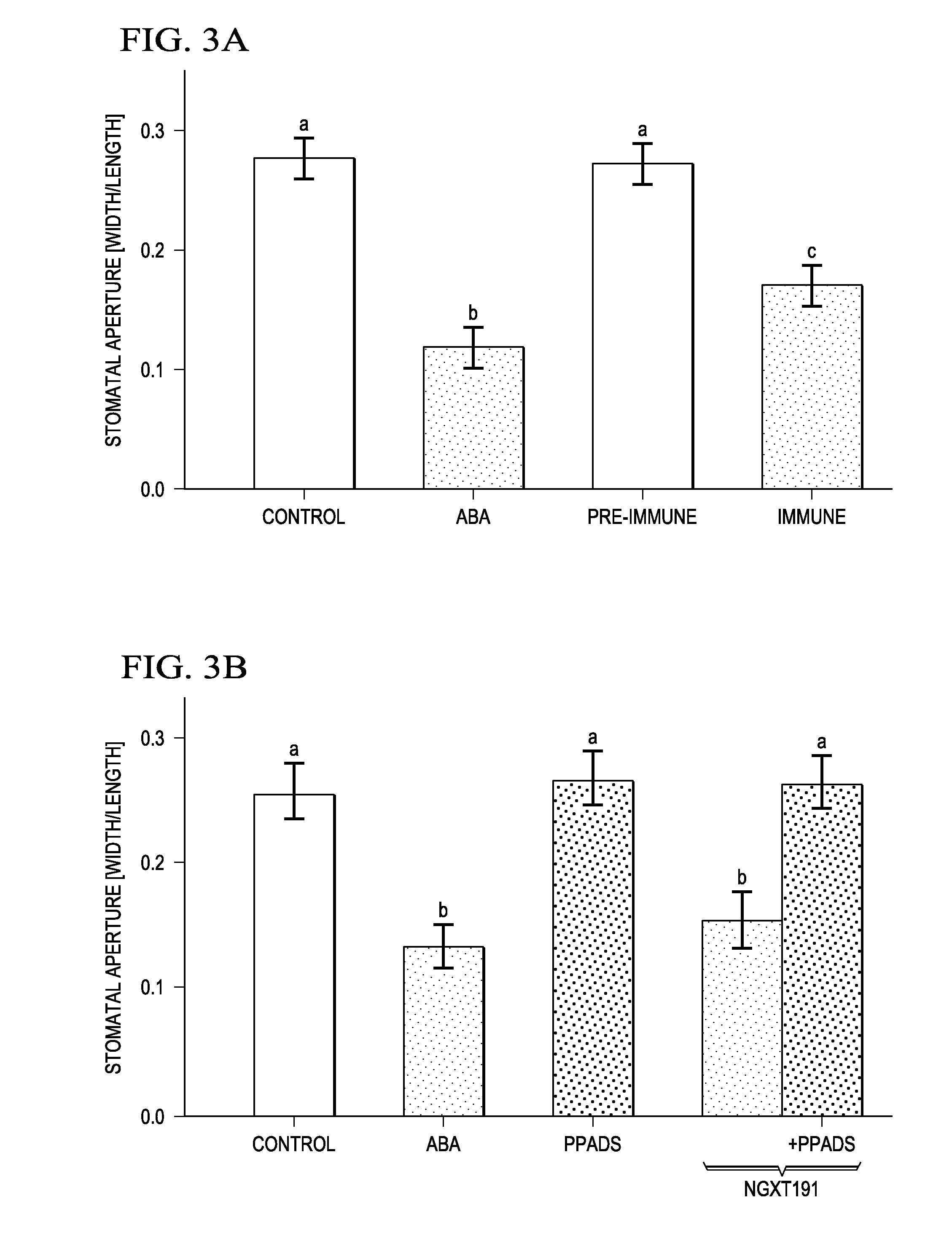
Regulation of Stomatal Apertures by Apyrases and Extracellular Nucleotides
The role of extracellular nucleotides and apyrase enzymes in the guard cells that border stomata in regulating stomatal aperture and the plant's resistance to drought and pathogens is disclosed herein. Expression of apyrases APY1 and APY2, in guard cell protoplasts is strongly correlated with cell growth, cell secretory activity and with conditions that favor stomatal opening. Both short-term inhibition of ectoapyrase activity and long-term suppression of APY1 and APY2 transcript levels significantly disrupt normal stomatal behavior in light. Furthermore, two punnoceptor inhibitors in mammals, pyridoxalphosphate-6-azo-phenyl-2′,4′-disulphonic acid (PPADS) and Reactive Blue 2, block ATPS- and ADPβS-induced opening and closing, and also partially block the ability of abscisic acid (ABA) to induce stomatal closure, and light-induced stomatal opening. Treatment of epidermal peels with ATPyS induces increased levels of nitric oxide and reactive oxygen species, and genetically suppressing the synthesis of these agents blocks the effects of nucleotides on stomatal aperture.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for high-throughput detection of gene mutation in single cells at full-length transcript level
InactiveCN109576357AMicrobiological testing/measurementComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidGene mutation
The invention discloses a method for high-throughput detection of gene mutation in single cells at a full-length transcript level and relates to the field of nucleic acid detection. The method comprises the following steps of: marking the single cells by utilizing a single cell analyzer and marking various mRNA (messenger Ribonucleic Acid) in the single cells; amplifying and utilizing a specific primer of a gene to be detected to amplify and enrich a full-length cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of the gene; constructing a three-generation sequencing library through a segmentobtained by amplification and sequencing a full-length cDNA library of the gene to be detected through a PacBio sequencer, so as to obtain sequence information of the gene to be detected at a singlecell level.
Owner:SHANGHAI OE BIOTECH CO LTD
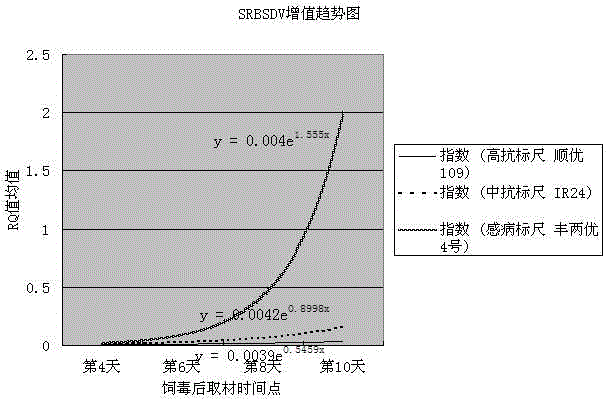
Method for rapidly evaluating rice SRBSDV variety resistance through detecting viral multiplication speed in coleoptile
The invention discloses a method for rapidly evaluating rice SRBSDV variety resistance through detecting a viral multiplication speed in coleoptile. The method comprises the following steps: (1) selecting an identifying scaleplate; (2) performing hypoxia induction on the rice to be tested and identifying the coleoptile of the scaleplate variety; (3) inoculating the toxic sogatella furcifera on the coleoptile and performing dark culture; (4) performing fluorogenic quantitative PCR to obtain a relative transcript level (RQ value) of an SRBSDV virus S9 and a reference gene in each rice variety period time; (5) drawing an SRBSDV proliferation index trend line; and (6) evaluating the resistance level and the resistance grade of the rice variety to be tested on the Southern rice black-streaked dwarf virus according to the SRBSDV proliferation index trend line formula. By detecting the viral multiplication speed in the coleoptiles and rapidly evaluating the resistance of the rice SRBSDV germplasm resistance, the resistance level and the resistance grade of the rice variety on the SRBSDV from the molecular level in the rice germination stage are determined, the identification period is short and the reliability is high, and the method has big breeding application value.
Owner:创世纪复交生物科技发展有限公司
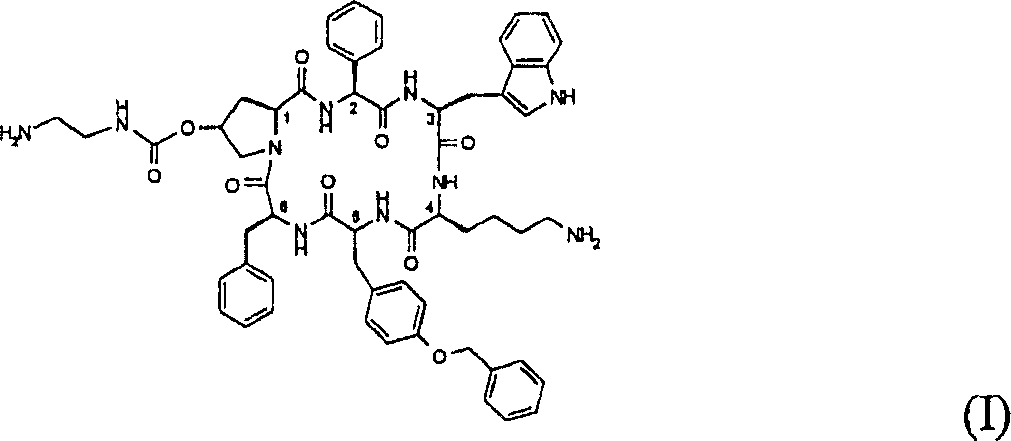
Biomarkers for the efficacy of somatostatin analogue treatment
InactiveCN1905895APeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementSomatotropic hormonePituitary gland
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
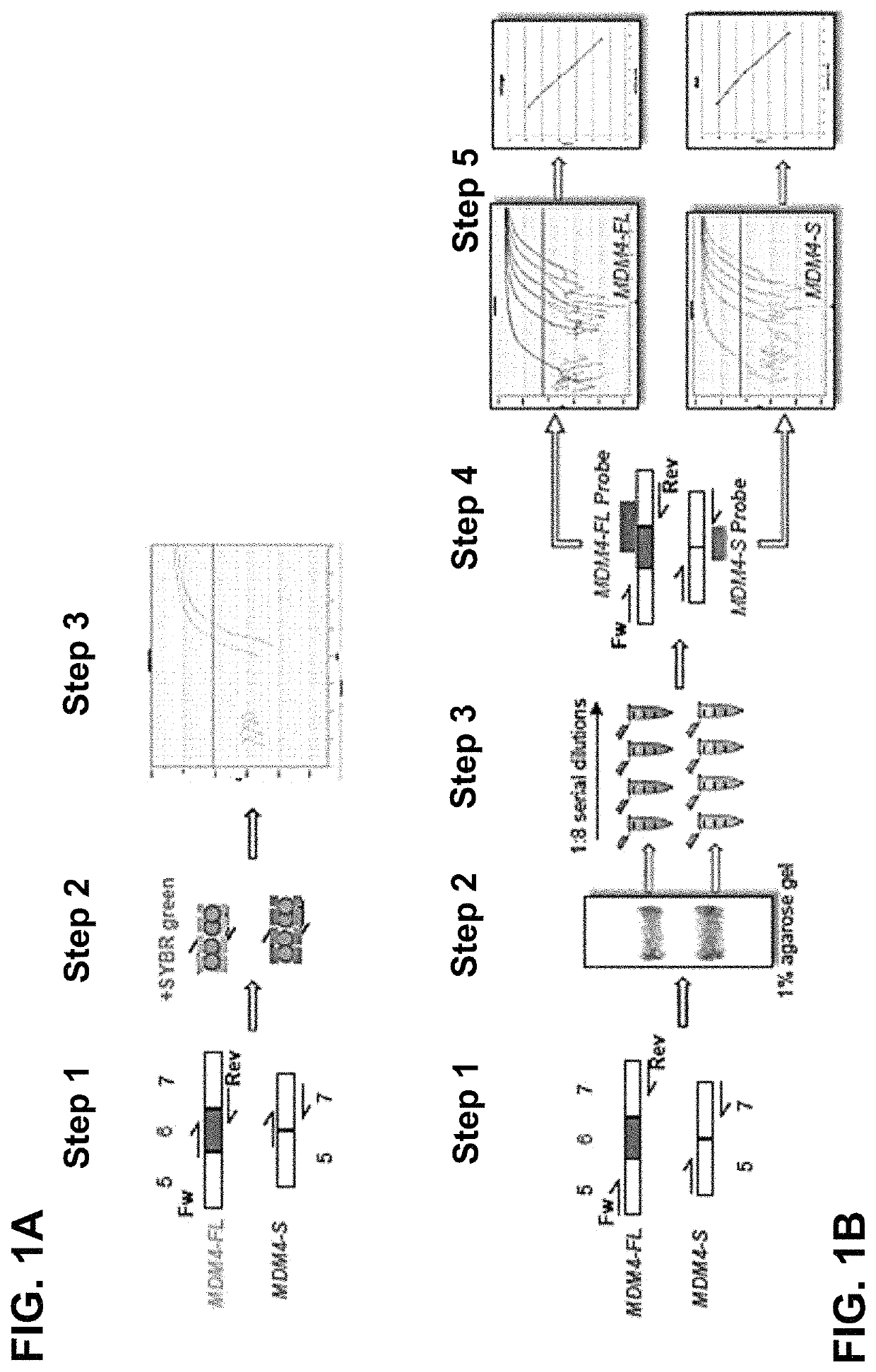
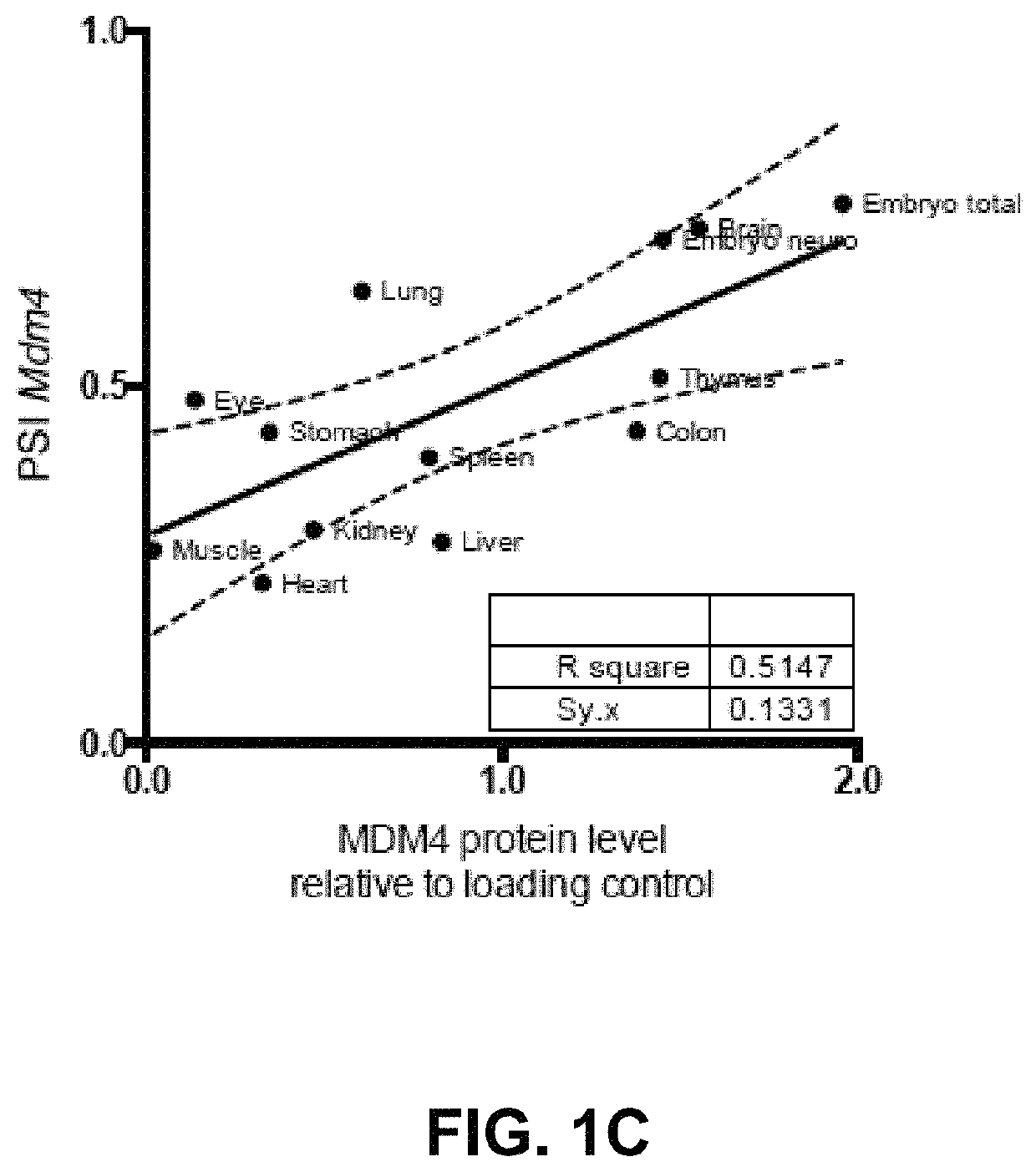
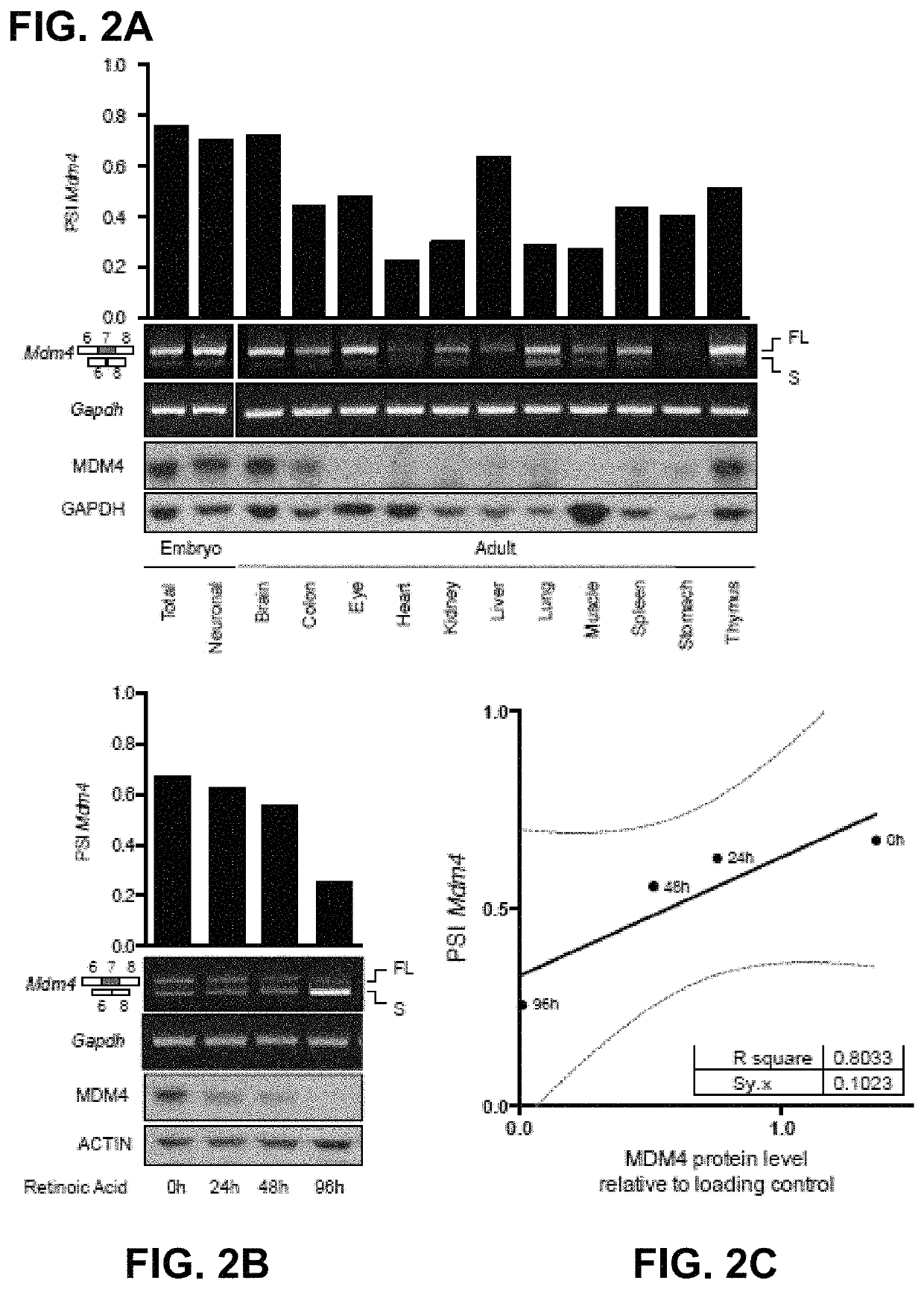
Direct and selective inhibition of MDM4 for treatment of cancer
ActiveUS10767182B2Easy to achieve pharmacologicallyFaster to introduce into the clinicOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationBlastomaMelanoma
The present application relates to the field of cancer, particularly that of cancers with high MDM4 protein levels (such as melanoma, breast, colon or lung cancers, glioblastoma, retinoblastoma, etc.). It is shown herein that direct and selective inhibition of MDM4, e.g., by antisense RNA, leads to growth inhibition of cancer cells and sensitization to chemo or targeted therapies. Also provided are simple ways of determining which patients are most amenable for such treatment by comparing specific transcript levels.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES +2
Methods of diagnosing cancer
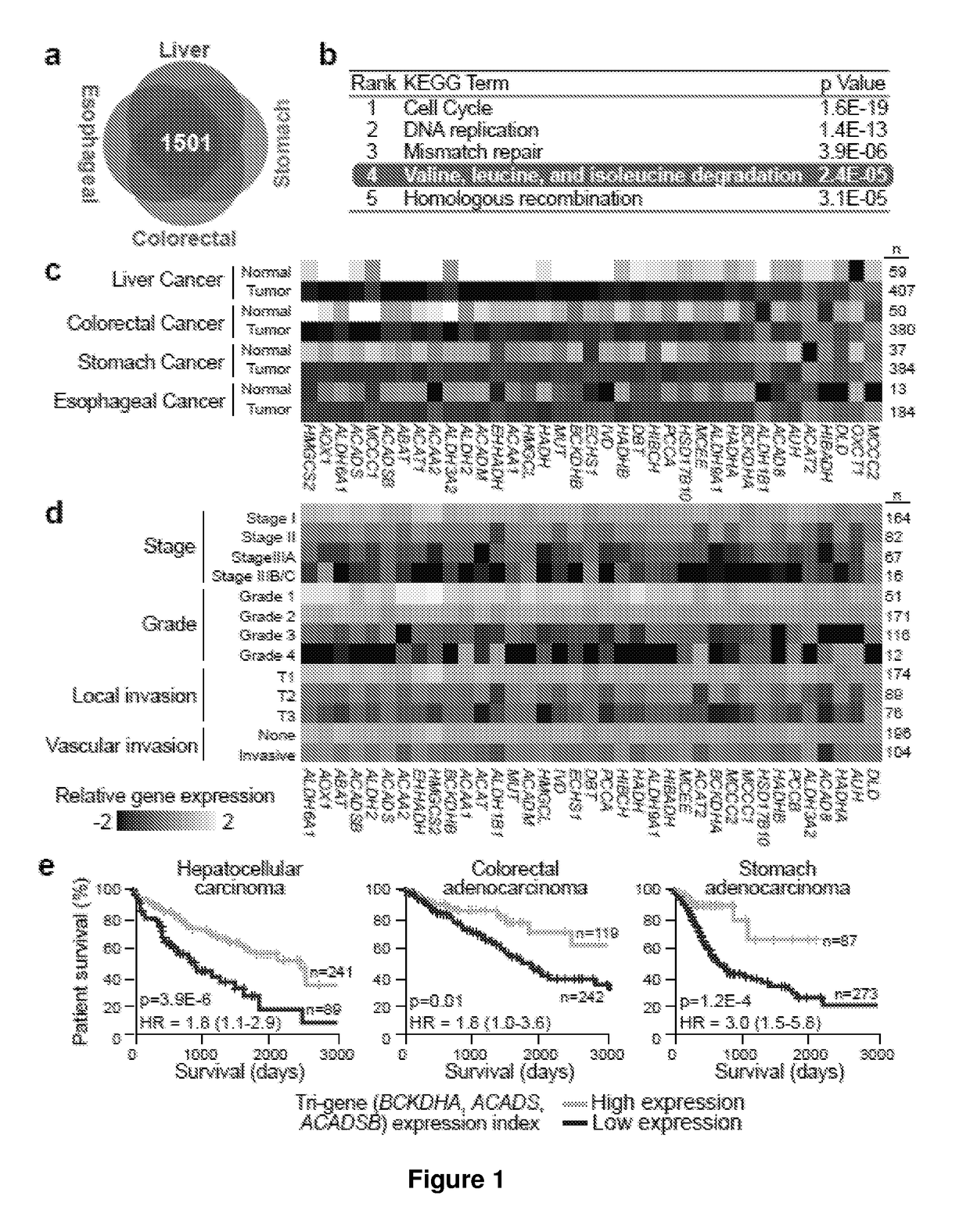
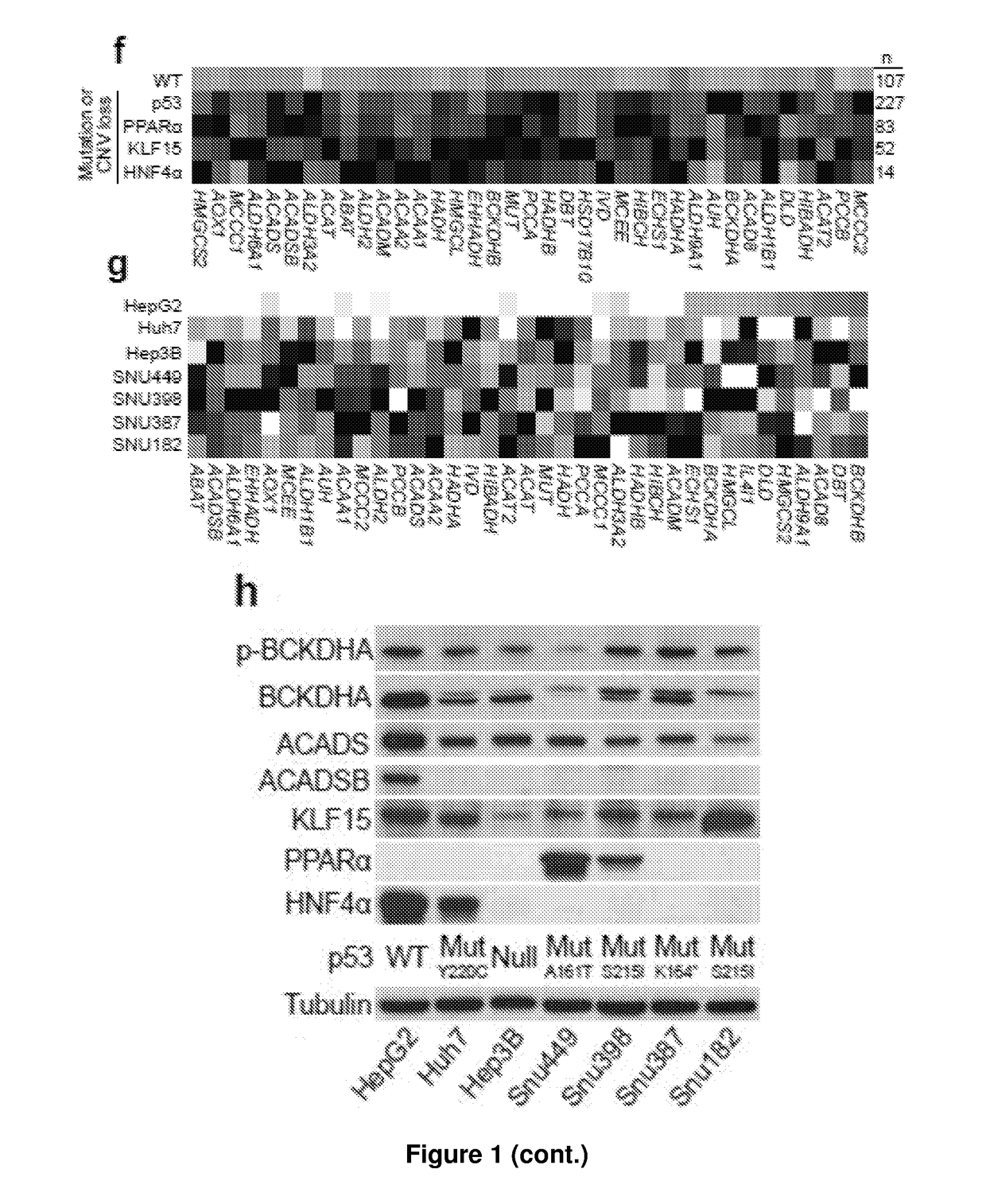
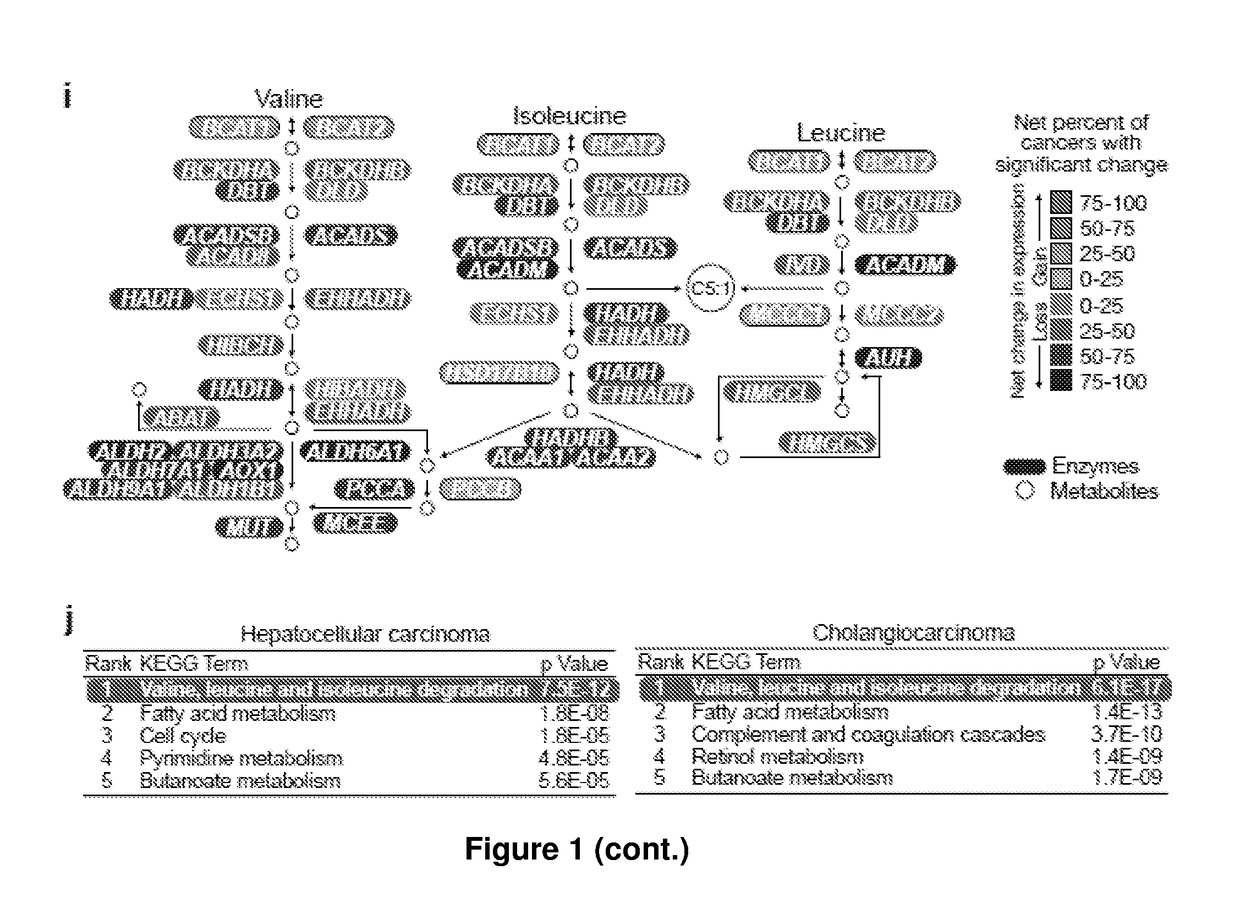
Disclosed are two methods of treating or preventing a proliferative disease as characterized and / or diagnosed by at least one selected from an accumulation of branched-chain amino acid(s) (BCAA), suppression of activity or transcripts level of BCAA catabolic enzyme(s) and a decrease in acylcarnitine level (C5:1), one comprising the administration of a BCAA catabolism enhancer and / or branched chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC) kinase inhibitor and the other comprising administration of a meal replacement with low BCAA levels. In three separate embodiments, methods of diagnosis or prognosis are disclosed, each comprising the measurement of the levels of a different marker, i.e. BCAA, BCAA catabolic enzymes or acylcarnitine (C5:1). In preferred embodiments, the proliferative disease is cancer. Also disclosed is a kit or microarray chip useful for methods thereof.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for screening fine progeny strain polyploidy plant of Chinese gooseberry Hort 16A
InactiveCN106191267ASignificant progressSignificantly substantialMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesSolubility
The invention discloses a method for screening a fine progeny strain polyploidy plant of Chinese gooseberry Hort 16A, and relates to the screening of a fine strain polyploidy of the plant. The method comprises the following steps: extracting total RNA of a leaf of a tissue culture seedling, reversely transcribing RNA into cDNA, selecting 1 to 2 differential genes having an up-regulation trend in transcriptomes of diploid and polyploidy plants, taking a housekeeping gene Elongation factor EC as a reference gene, fluorescently quantifying a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), drawing an amplification curve and a solubility curve for the differential genes, selecting the differential genes, calculating a relative transcript level, and taking the tissue culture seedling, whose differential genes are more than twice those of the diploid, as the tissue culture seedling of the polyploidy. The theory and the method for screening the polyploidy variant plant are innovated, and the efficient feasible method is provided for screening the polyploidy plant of the Chinese gooseberry.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
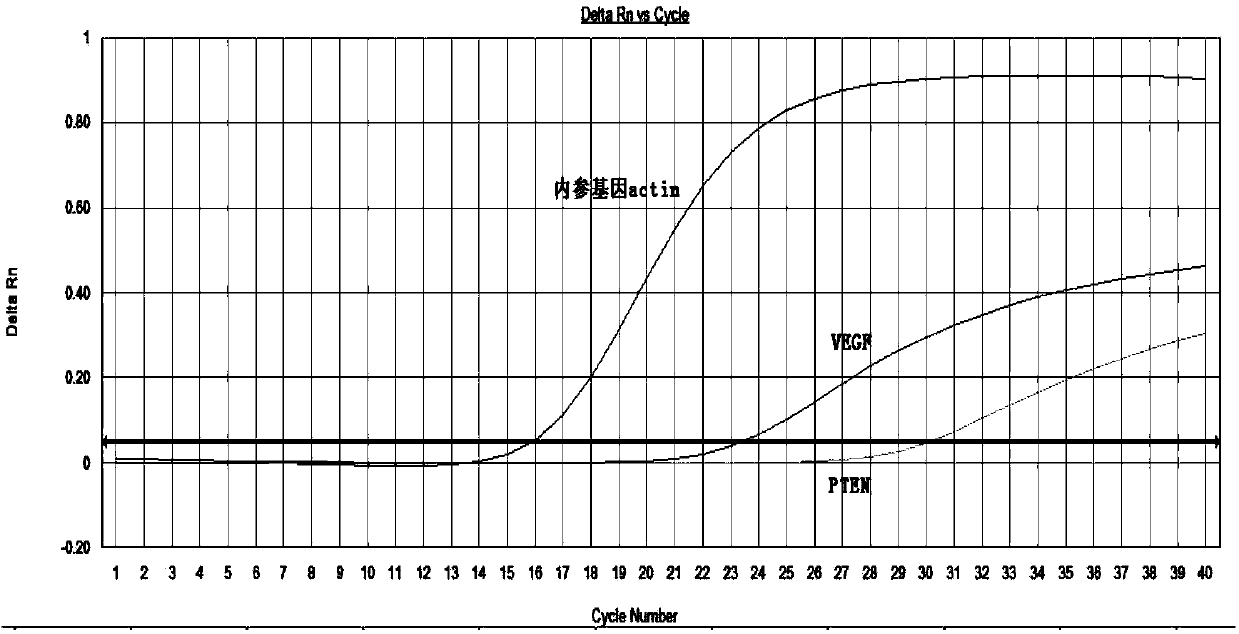
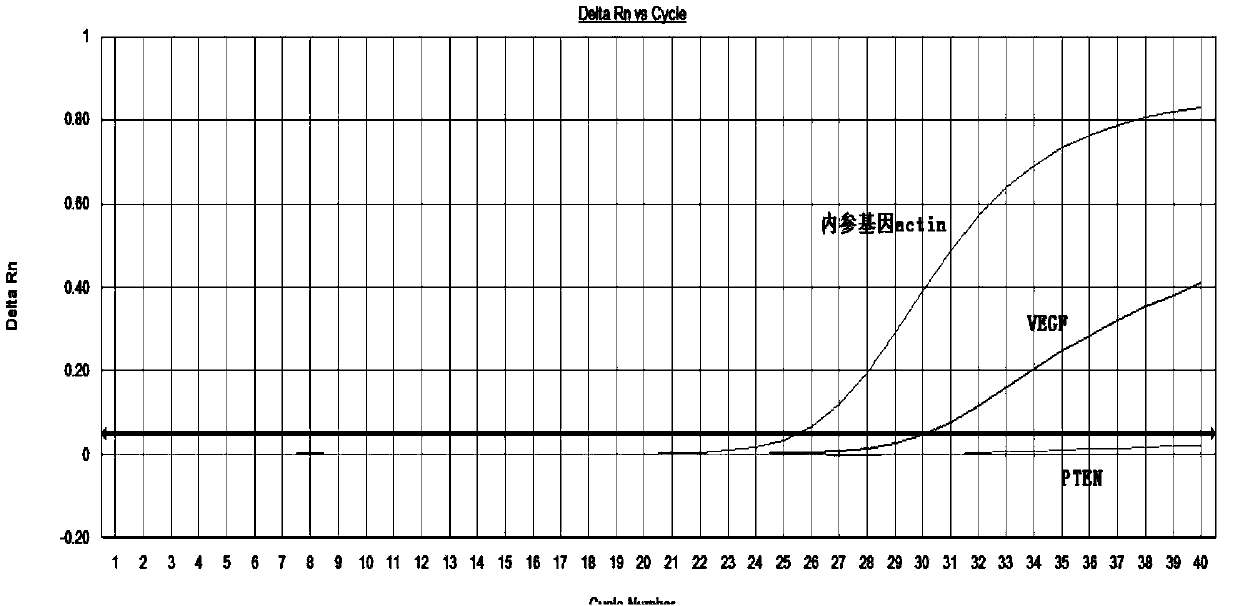
Oligonucleotide and method for joint detection of relative transcript levels of genes PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten) and VEGF (vascular endothelial cell growth factor)
InactiveCN103740820AAchieve accurate quantificationSolve the problem of false positivesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerReference genes
The invention provides oligonucleotide and a method for joint detection of relative transcript levels of genes PTEN (phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten) and VEGF (vascular endothelial cell growth factor) based on fluorogenic quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction), mainly relating to a forward primer PTEN-F, a reverse primer PTEN-R and a probe PTEN-Probe for detecting the gene PTEN; an forward primer VEGF-F, a reverse primer VEGF-R and a probe VEGF-Probe for detecting the gene VEGF; and a forward primer Actin-F, a reverse primer Actin-R and a probe Actin-Probe for detecting a reference gene actin. The relative transcript levels of the detected genes PTEN and VEGF are respectively compared with reference values of the relative transcript levels of the genes PTEN and VEGF of a healthy person, and the comparison result can be used for auxiliary diagnosis of various kinds of cancers.
Owner:合肥艾迪康医学检验实验室有限公司
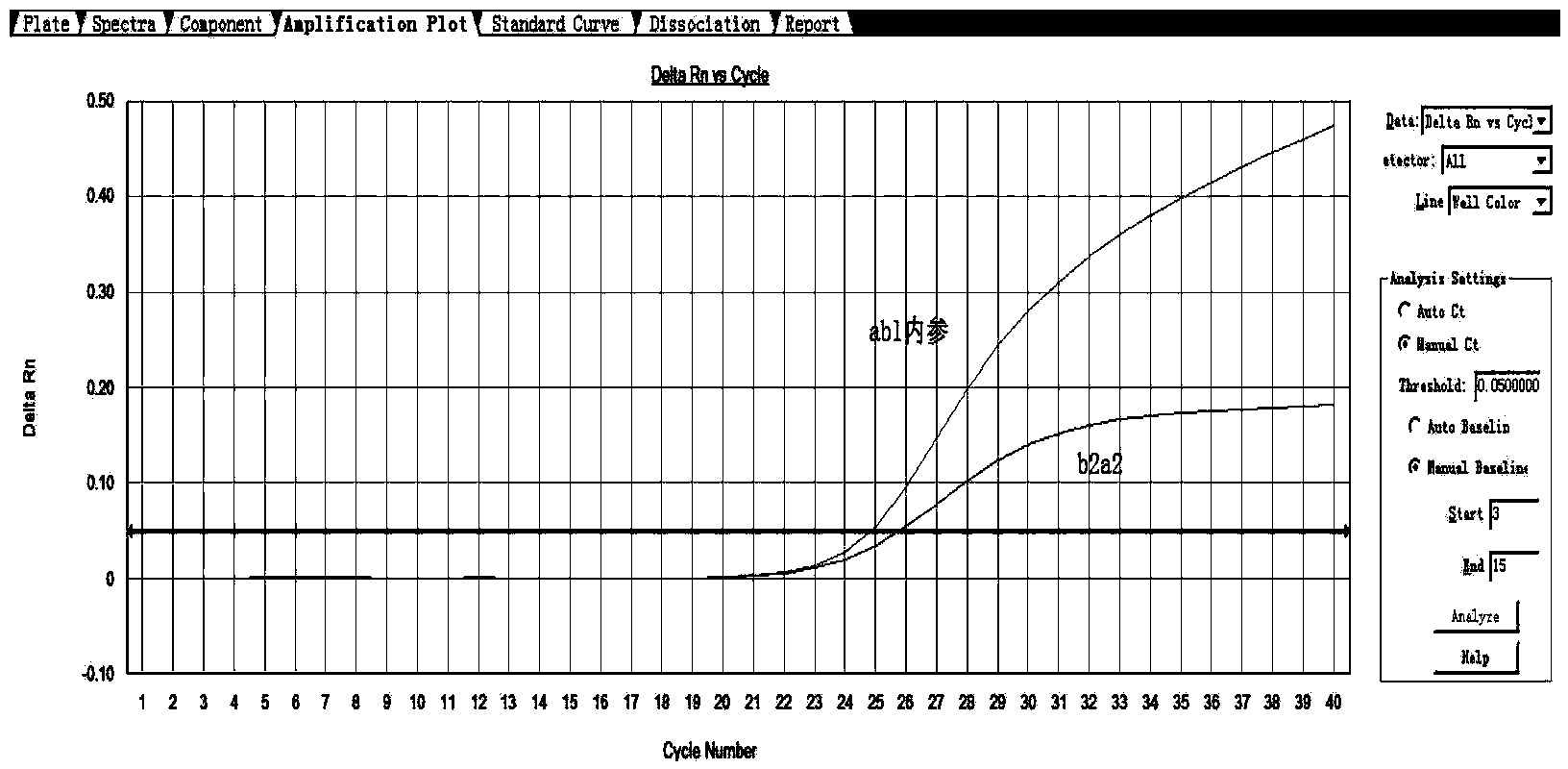
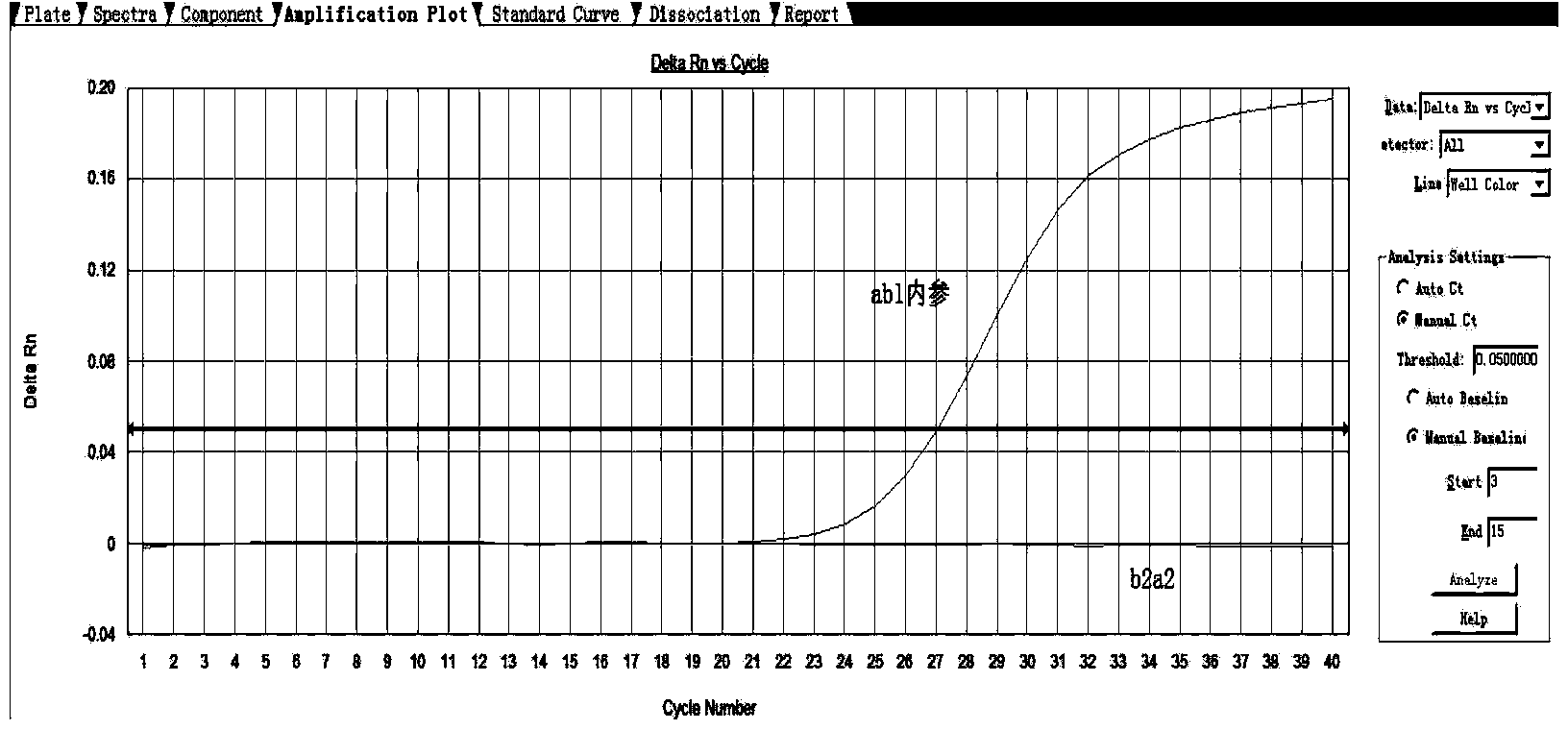
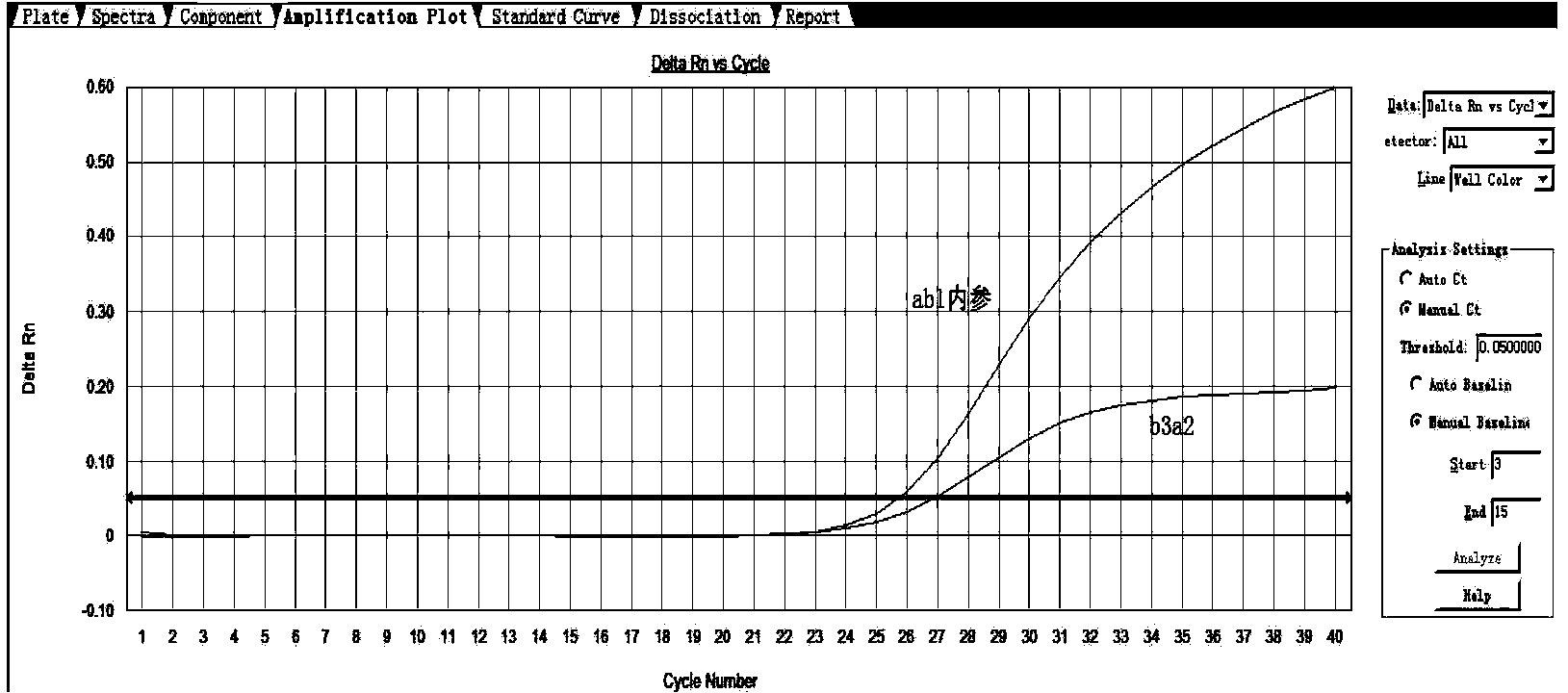
Primer and method for detecting leukemia BCR/ABL b3a2 and b2a2 fusion gene relative transcript level
ActiveCN103667457AImprove detection accuracyHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationReference genesTranscript level
The invention discloses a primer for detecting leukemia BCR / ABL fusion gene relative transcript level. The primer comprises (1) upstream and downstream primers b3a2-F, b2a2-F and b3a2 / b2a2-R and a b3a2 / b2a2-probe for detecting target genes, and (2) primers abl-F and abl-R and an abl-probe for detecting reference genes. The invention further discloses a method for detecting the leukemia BCR / ABL fusion gene relative transcript level, the detection accuracy is high, the operation is simple, the detection cost can be reduced, and the detection time is saved.
Owner:WUHAN ADICON CLINICAL LAB
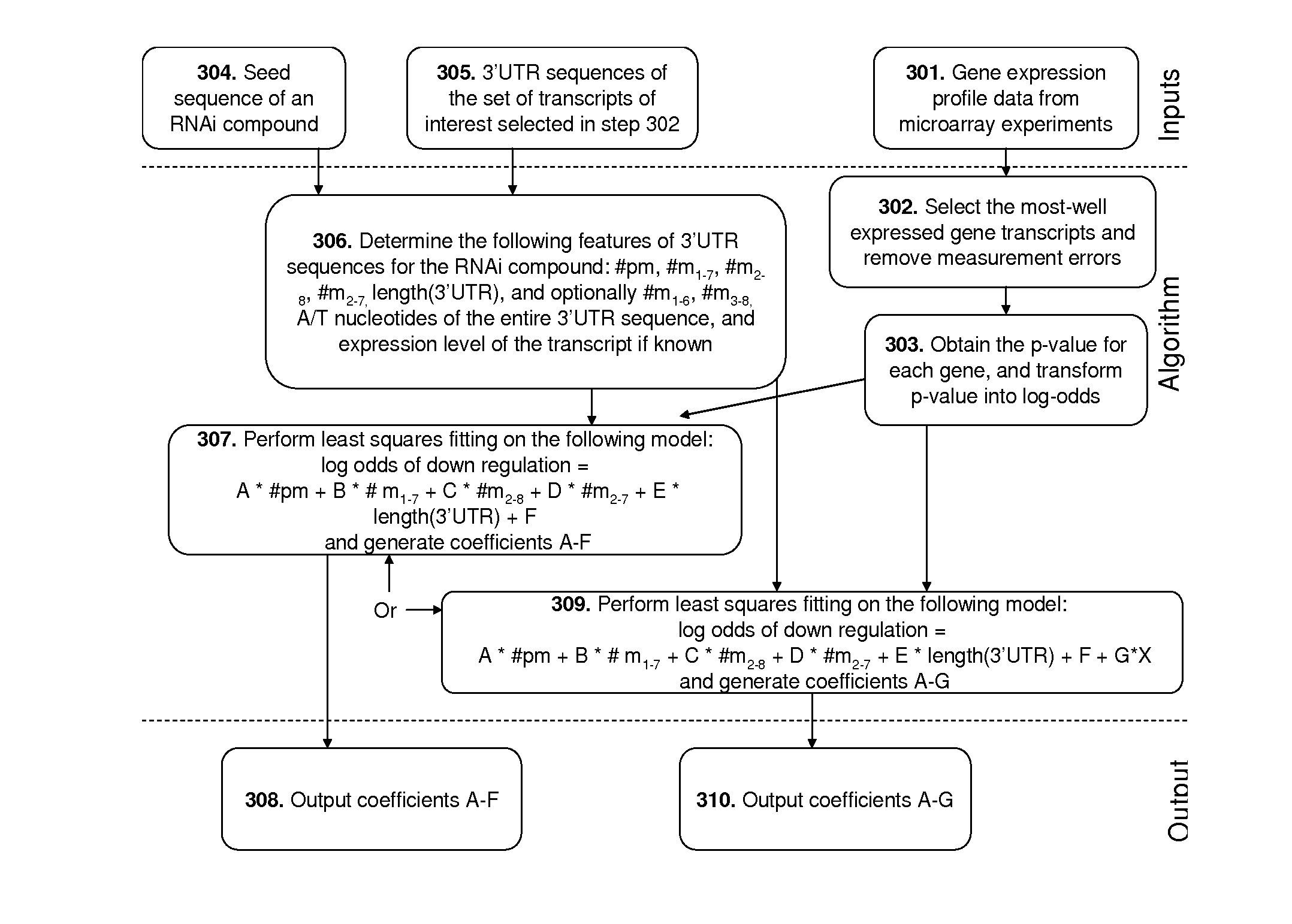
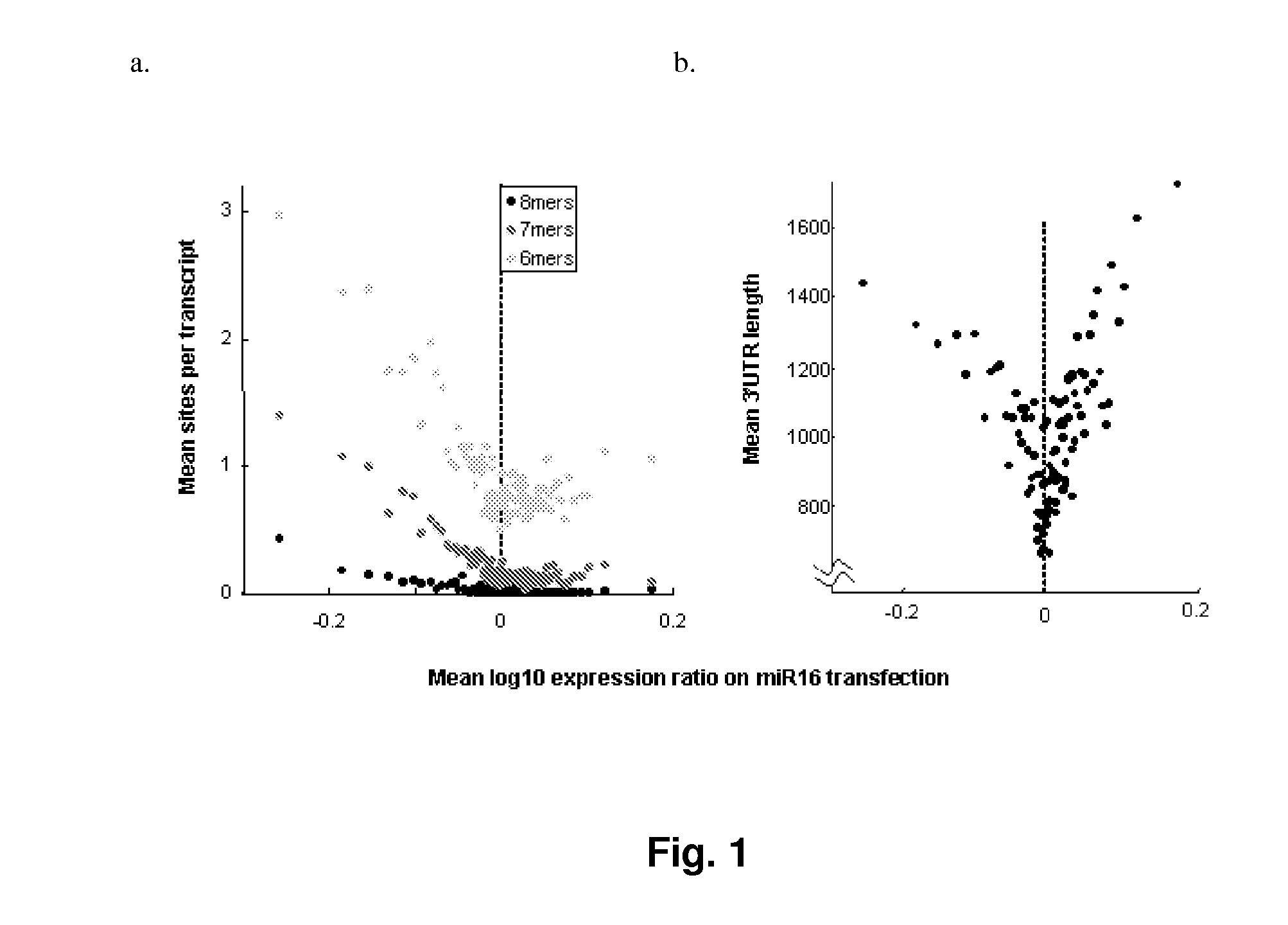
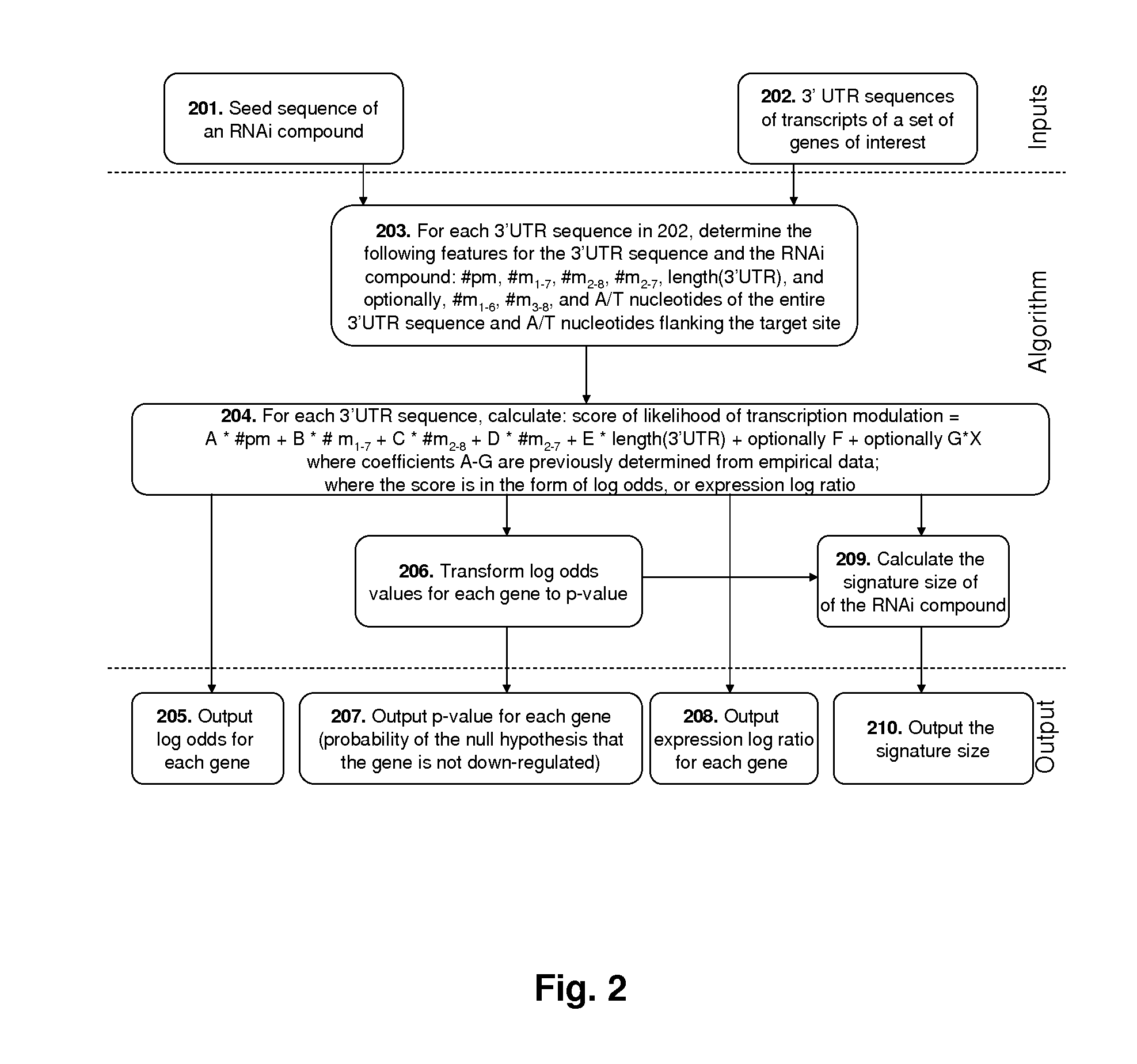
Methods of Predicting The Probability of Modulation of Transcript Levels By RNAI Compounds
InactiveUS20140088937A1Reduce silencingImprove RISC loadingComputation using non-denominational number representationProteomicsTranscript levelGenetics
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for production of transgenic cotton plants
ActiveUS20160340687A1Increase productionClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesDevelopmental stageFiber
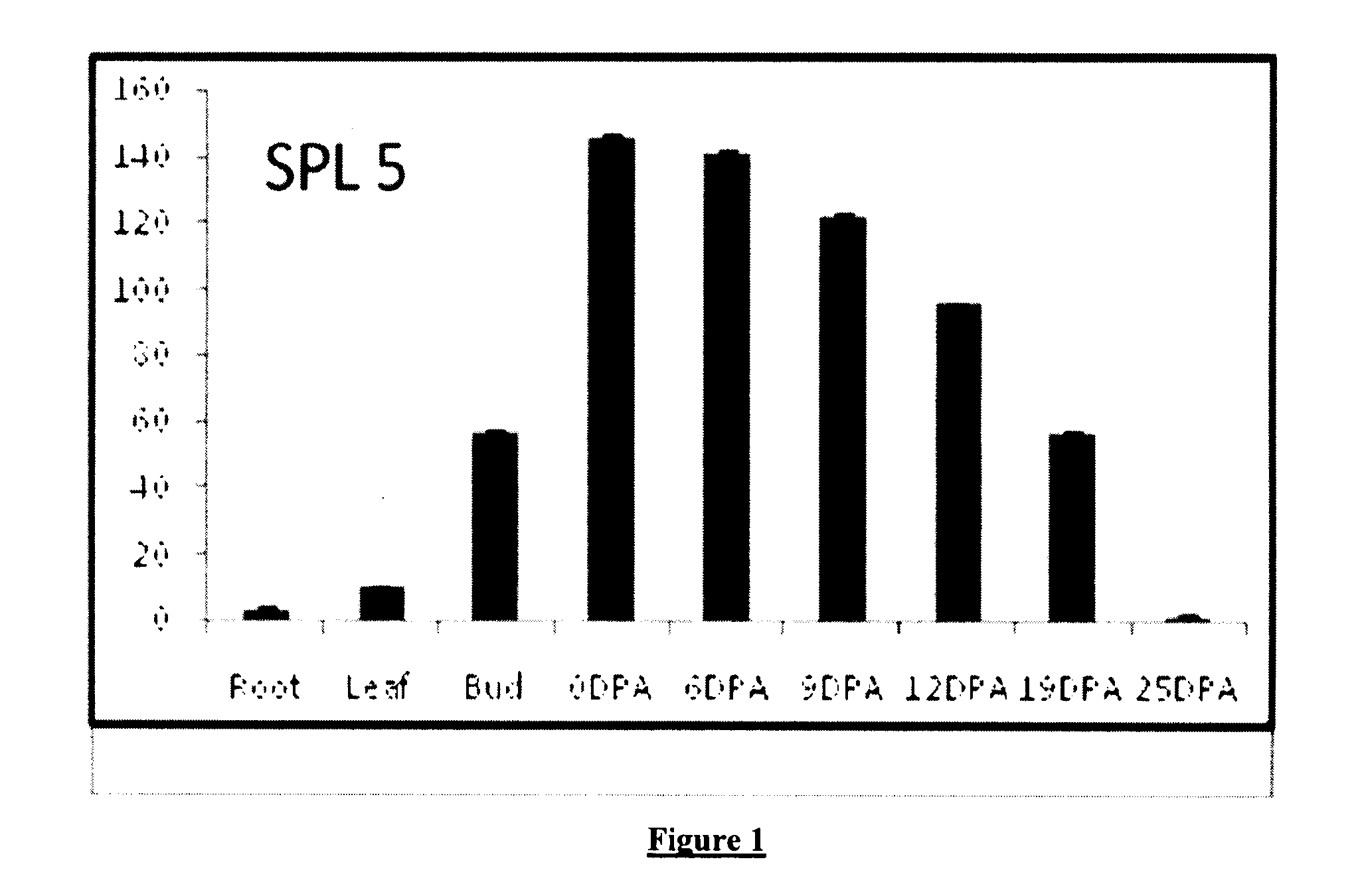
The present invention provides a method for producing transgenic Cotton plants. In one method transformed plants, that overexpress the transgene shows a phenotype that includes increased boll number, size and lint percentage in compare to the wild type plants; whereas in the second method transformed plants that reduced the transgene level produced plants with decreased number of cotton boll, size and lint percentage in compare to wild type and overexpression line both. q-RT PCR analysis showed that transgene transcript level was higher at fiber initiation stage (0 DPA) after that its level decreases throughout all developmental stages.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Bacterial Metastructure and Methods of Use
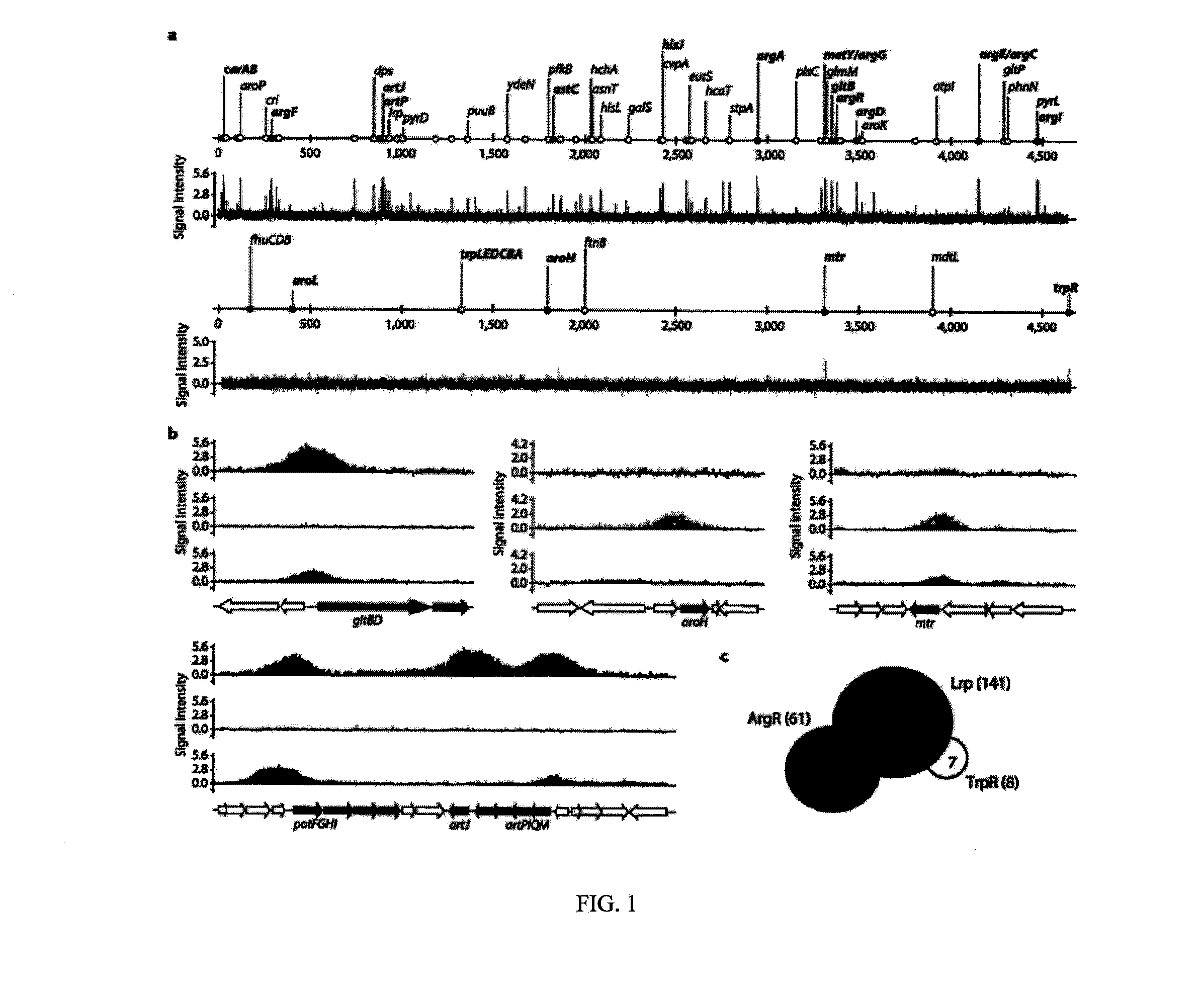
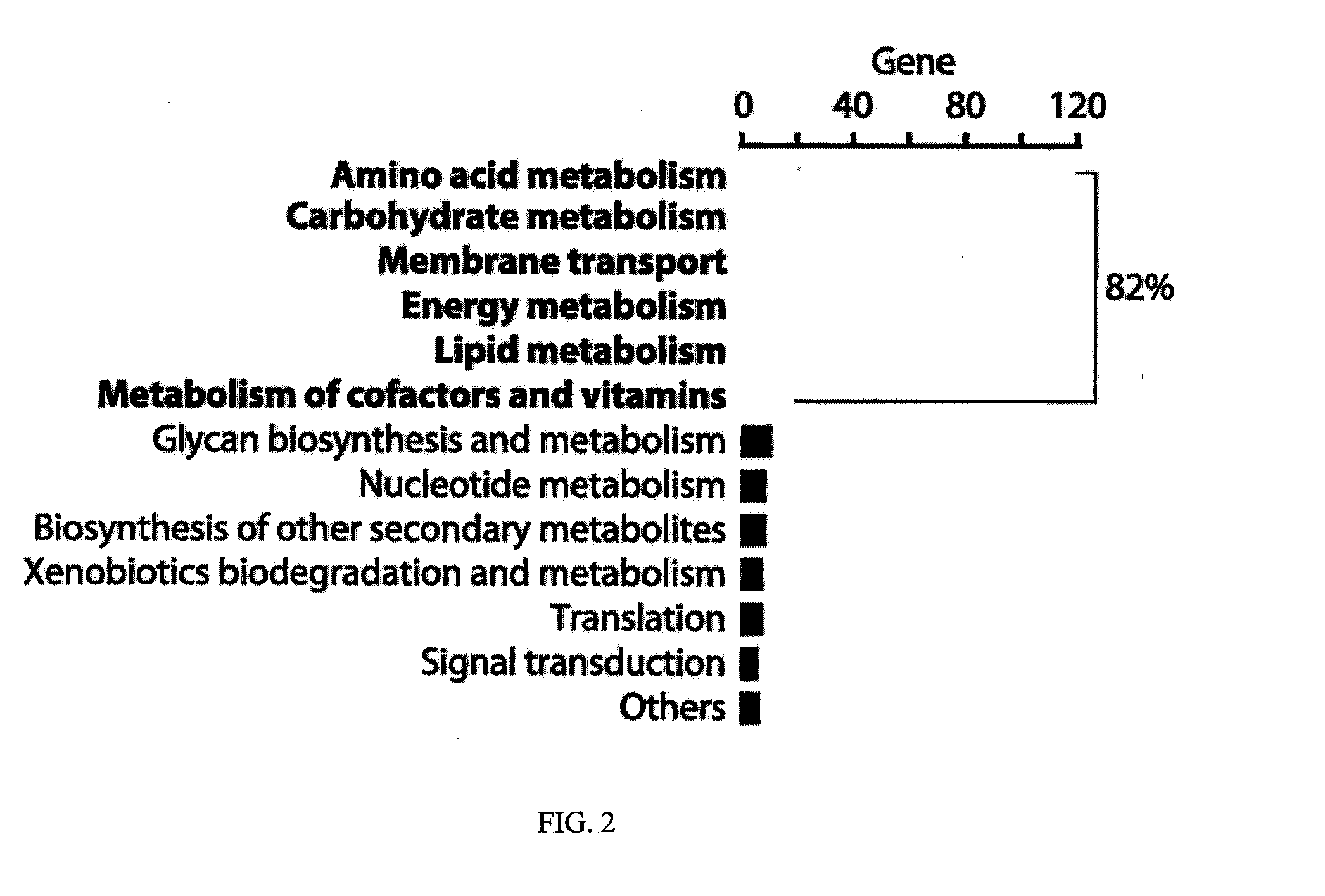
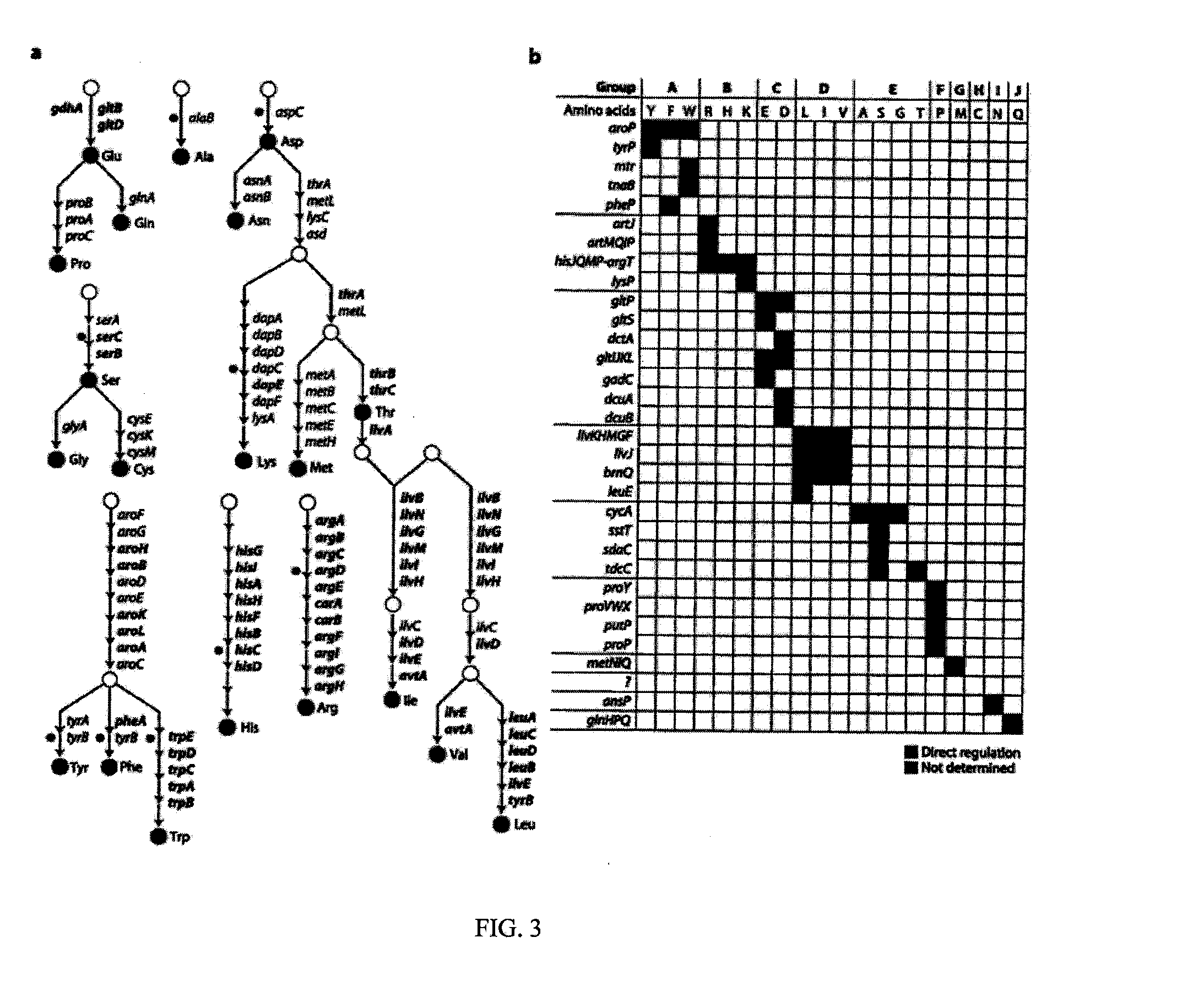
Although metabolic networks have been reconstructed on a genome-scale, the corresponding reconstruction and integration of governing transcriptional regulatory networks has not been fully achieved. Here such an integrated network was constructed for amino acid metabolism in Escherichia coli. Analysis of ChlP-chip and gene expression data for the transcription factors ArgR, Lrp, and TrpR showed that 19 / 20 amino acid biosynthetic pathways are either directly or indirectly controlled by these regulators. Classifying the regulated genes into three functional categories of transport, biosynthesis, and metabolism leads to elucidation of regulatory motifs constituting the integrated network's basic building blocks. The regulatory logic of these motifs was determined based on the relationships between transcription factor binding and changes in transcript levels in response to exogenous amino acids. Remarkably, the resulting logic shows how amino acids are differentiated as signaling and nutrient molecules. This reveals the overarching regulatory principles of the amino acid stimulon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com