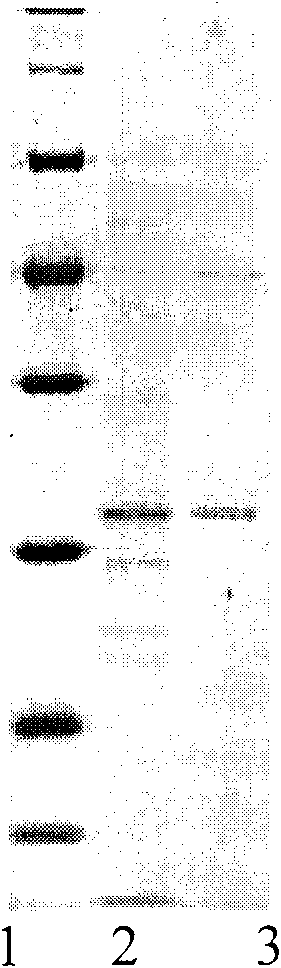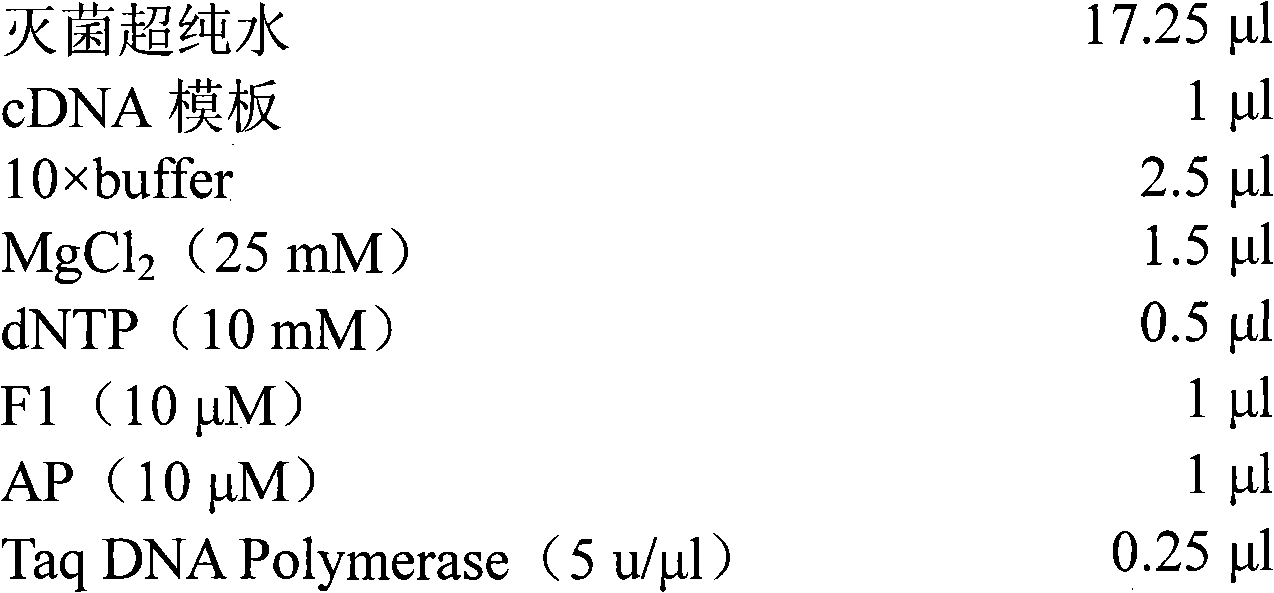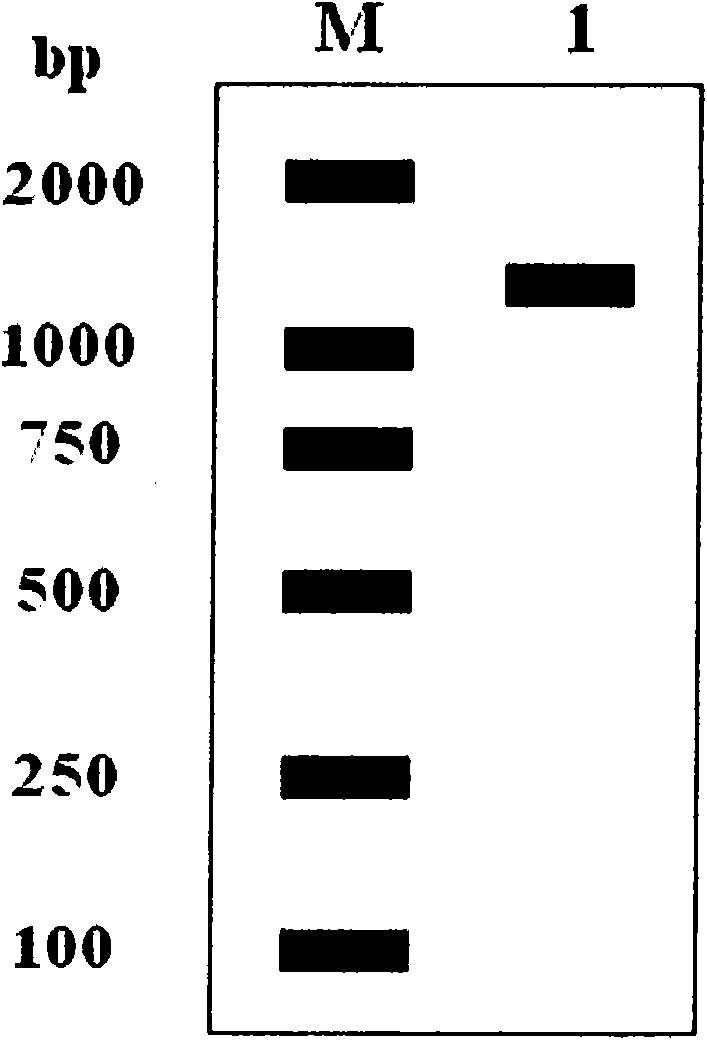Patents
Literature
72 results about "Rapid amplification of cDNA ends" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) is a technique used in molecular biology to obtain the full length sequence of an RNA transcript found within a cell. RACE results in the production of a cDNA copy of the RNA sequence of interest, produced through reverse transcription, followed by PCR amplification of the cDNA copies (see RT-PCR). The amplified cDNA copies are then sequenced and, if long enough, should map to a unique genomic region. RACE is commonly followed up by cloning before sequencing of what was originally individual RNA molecules. A more high-throughput alternative which is useful for identification of novel transcript structures, is to sequence the RACE-products by next generation sequencing technologies.
Method for generating pterostilbene by utilizing grape resveratrol-oxygen-methyl transferase to catalyze resveratrol
InactiveCN102120996AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationRapid amplification of cDNA endsBiotechnology
The invention discloses a method for generating pterostilbene by utilizing grape resveratrol-oxygen-methyltransferase to catalyze resveratrol, grape ROMT (resveratrol-oxygen-methyl transferase) genes are cloned by utilizing 5' and 3' RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) full-length gene cloning technology according to EST (expressed sequence tag) sequence of the ROMT genes of Chinese wild grapes in East China, and the full length of an open reading frame of the genes is 1074bp; and the cloned grape STS (steroid sulfatase) and ROMT genes can be simultaneously transferred into model plant tobacco, tobacco plant analysis is utilized for analyzing the biological synthesis path of generating the pterostilbene by utilizing the grape ROMT to catalyze the resveratrol, a grape ROMT gene sequence is obtained for orientation, and the ROMT genes can catalyze the resveratrol to generate the pterostilbene in the transgenic tobacco, thereby providing the sequence of the ROMT genes and the method for synthesizing the pterostilbene by utilizing plants and providing a basis for getting high-quality, disease-resistant and health care crops.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Lycium chinense miller lycopene beta-cyclase gene, recombinant vector containing gene, host cell and application
InactiveCN102321649AIncrease biosynthesisIncrease productionBacteriaFermentationHeterologousEscherichia coli
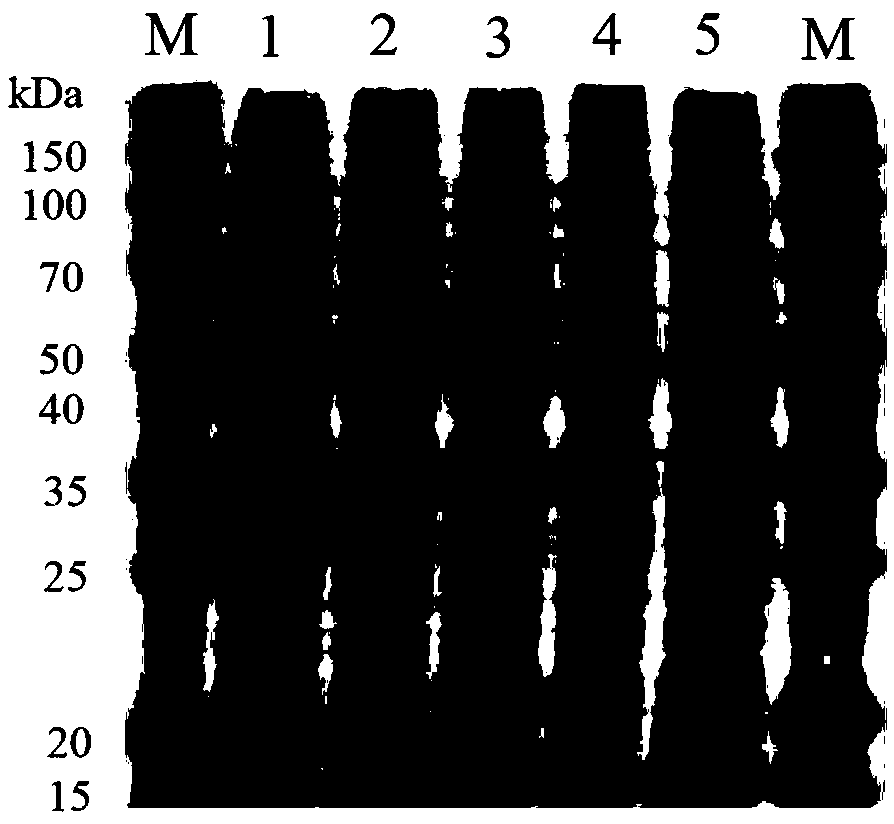
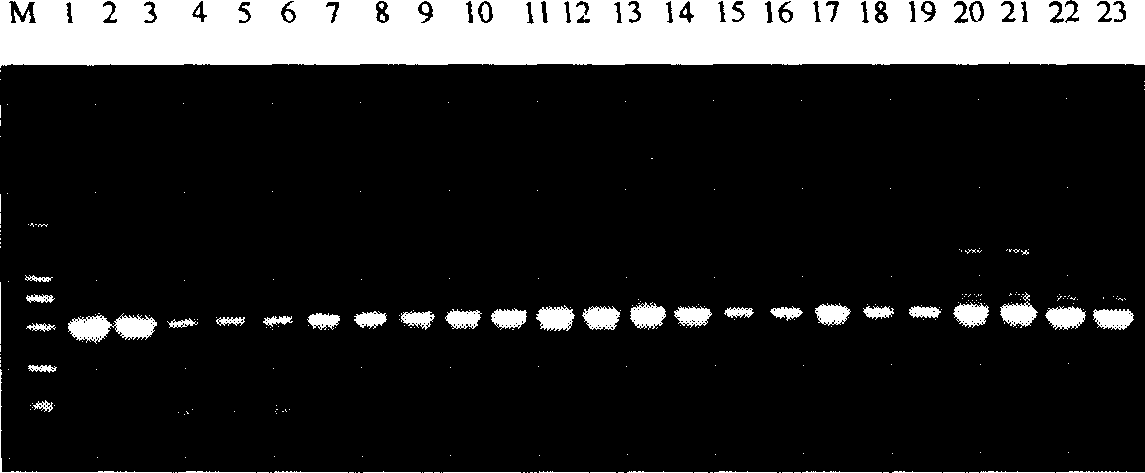
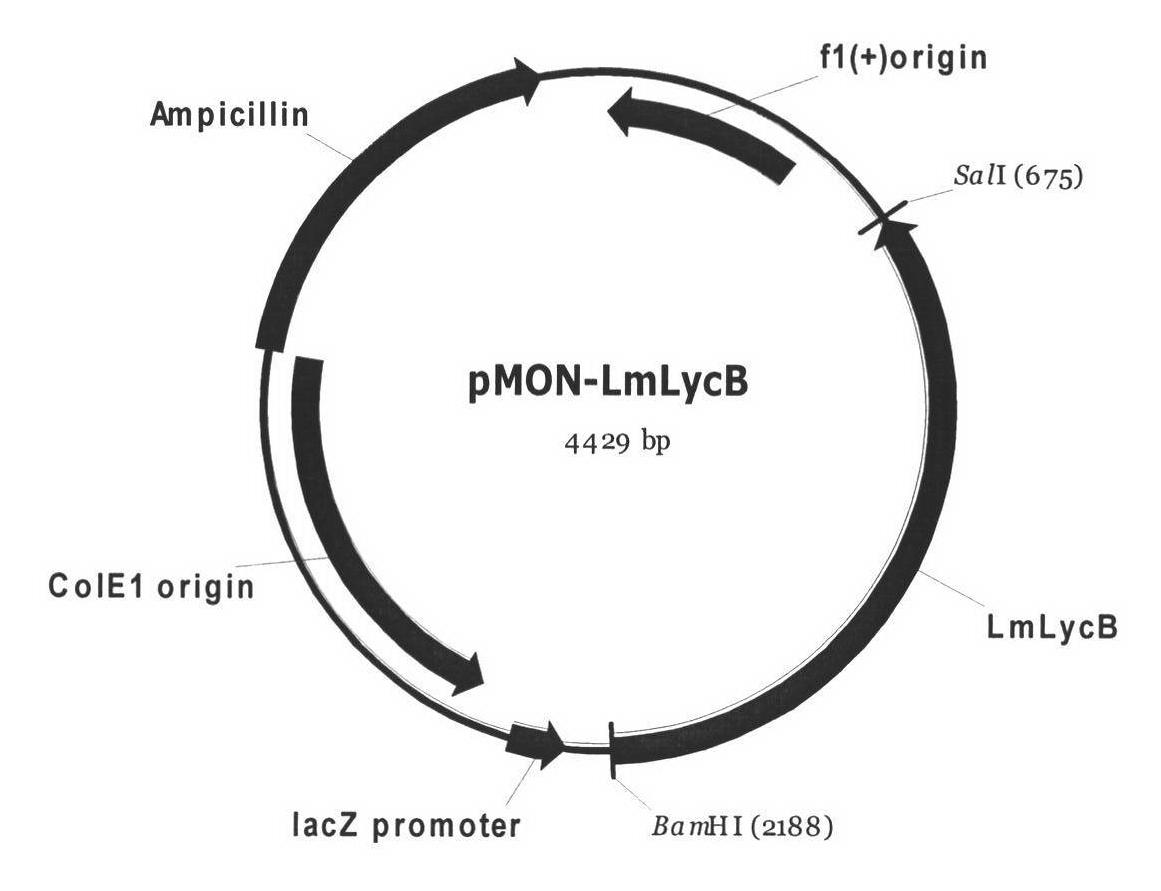
The invention discloses a lycium chinense miller lycopene beta-cyclase gene, a recombinant vector containing the gene, a host cell and application. Total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of fresh lycium chinense miller leaf is extracted, and lycopene beta-cyclase gene LmLycB is cloned by using 3' RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technology to obtain a complete gene sequence of 1,506bp. An Escherichia coli expression vector pMON-LmLycB is constructed; an escherichia coli heterogenous expression system is applied; the activity of cloned LmLycB gene-coded enzyme is identified; and two beta-lonone rings can be added at the tail end of lycopene by LmLycB to produce beta-carotene. A maize inbred line immature embryo genetic transformation system is optimized; a plant expression vector pCAMBIA2300-LmLycB-Bar containing a target gene is transformed into maize callus to finally obtain a transgenic positive plant; through HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) detection, the total carotinoid content of transgenic maize leaf is 165.70mug / g FW and is 12.76 percent greater than that of a wild maize; and beta-carotene content is 80.17mug / g FW and is 54.83 percent greater than that of the wild maize.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Cloning, expression and application of alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene
InactiveCN106191084AReduce manufacturing costIncreased substrate specificityFungiMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention discloses cloning, expression and application of an alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene. A coding gene is obtained from aspergillus tubingensis and is expressed in pichia pastoris GS115; specifically, total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of the aspergillus tubingensis is used as a template and cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of alpha-L-rhamnosidase is cloned through RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) and RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technologies; pPIC9k is used as an expression vector and is subjected to secreting expression in the pichia pastoris GS115. The alpha-L-rhamnosidase can be used for efficiently hydrolyzing naringin; when the naringin is used as a substrate, Km and Vmax values respectively are 1.27mu.mol / mL and 3445mu.M min<-1>; the thermal stability at 60 DEG C is good and the alpha-L-rhamnosidase gene has a good application prospect in food and biopharmaceutical industries.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
Cotton GbSTK gene, encoding protein thereof and application for resisting verticillium wilt of plants
InactiveCN101942426AHas anti-Verticillium wilt effectFungiBacteriaRapid amplification of cDNA endsThreonine
The invention relates to a cotton GbSTK gene and encoding protein thereof. Sea island cotton Pima90-53 is taken as a material, a cDNA-AFLP technology is used for screening to obtain differential fragments related to verticillium wilt resistance, and then, a reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and a RACE (rapid-amplification of cDNA ends) technology are used for amplifying to obtain a resistance gene of cotton verticillium wilt, namely a serine / threonine protein kinase (GbSTK) gene. The functional studies of the gene and the encoding protein thereof show that the GbSTK gene has certain effect on resisting verticillium wilt.
Owner:HEBEI AGRICULTURAL UNIV.
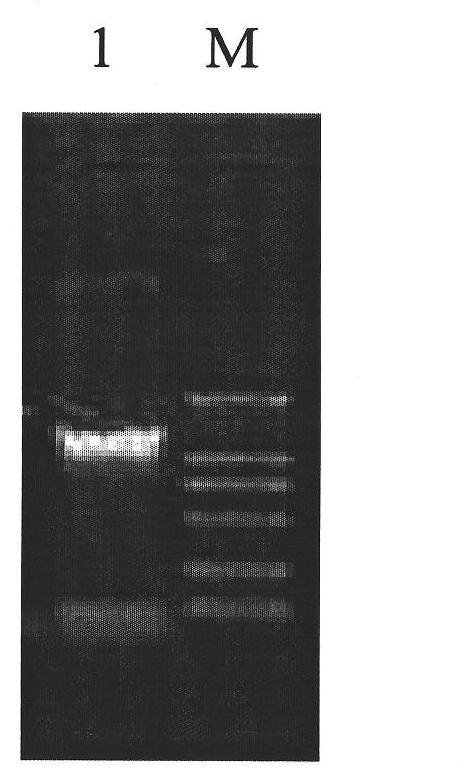
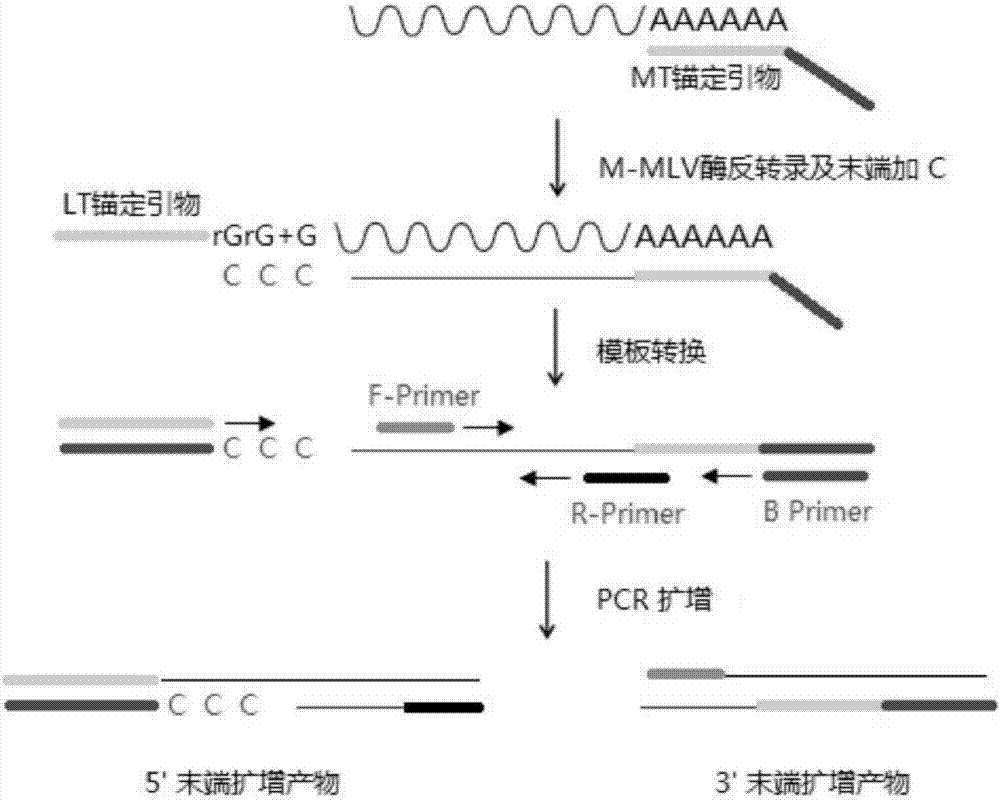
Anchor primer for efficient and rapid amplification of cDNA ends and amplification method
ActiveCN106868005ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationRapid amplification of cDNA endsNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses an anchor primer for efficient and rapid amplification of cDNA 5' and 3' ends. The two anchor primers can be specifically bound to a target nucleic acid sequence and trigger reverse transcription elongation reaction, thereby efficiently and rapidly amplifying cDNA 5' and 3' ends, and especially can be applied to rapid amplification of the 5' and 3' ends of cDNA in low abundance transcripts. In addition, the invention also provides a kit and an amplification method for efficient and rapid amplification of cDNA 5' and 3' ends.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV CANCER CENT
Clam ferroprotein gene as well as coding protein and application of in vitro recombinant expression product of same
InactiveCN102051363APeptide/protein ingredientsImmunological disordersRapid amplification of cDNA endsBiology
The invention relates to the technologies of clam ferroprotein gene cloning and in vitro recombinant expression in molecular biology. In the invention, the expression sequence tag (EST) technology and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) 3' and 5' are utilized to clone ferroprotein gene cDNA with the total length of 798bp from a clam larva, the cloned ferroprotein gene contains an open reading frame with the length of 513bp, 171 amino acids are coded, the length of a non-coding region 5' is 119bp, the length of a non-coding region 3' is 154bp, a tailing signal is contained, and the gene plays an important role in formation of a shell during development of the clam larva. In the invention, the in vitro prokaryotic recombinant expression technology is utilized to obtain recombinant clam ferroprotein; and the ferroprotein has antioxidant activity, can be used for regulating and controlling formation and growth of shells of shellfish larvae such as clams and the like, and can be applicable to development regulation and immunological enhancement in the shellfish larva production process.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
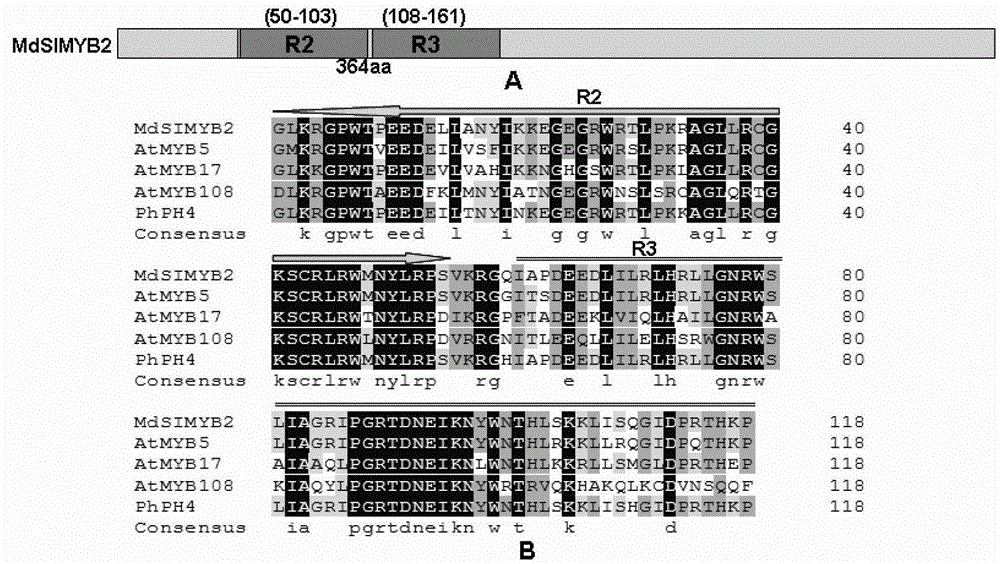
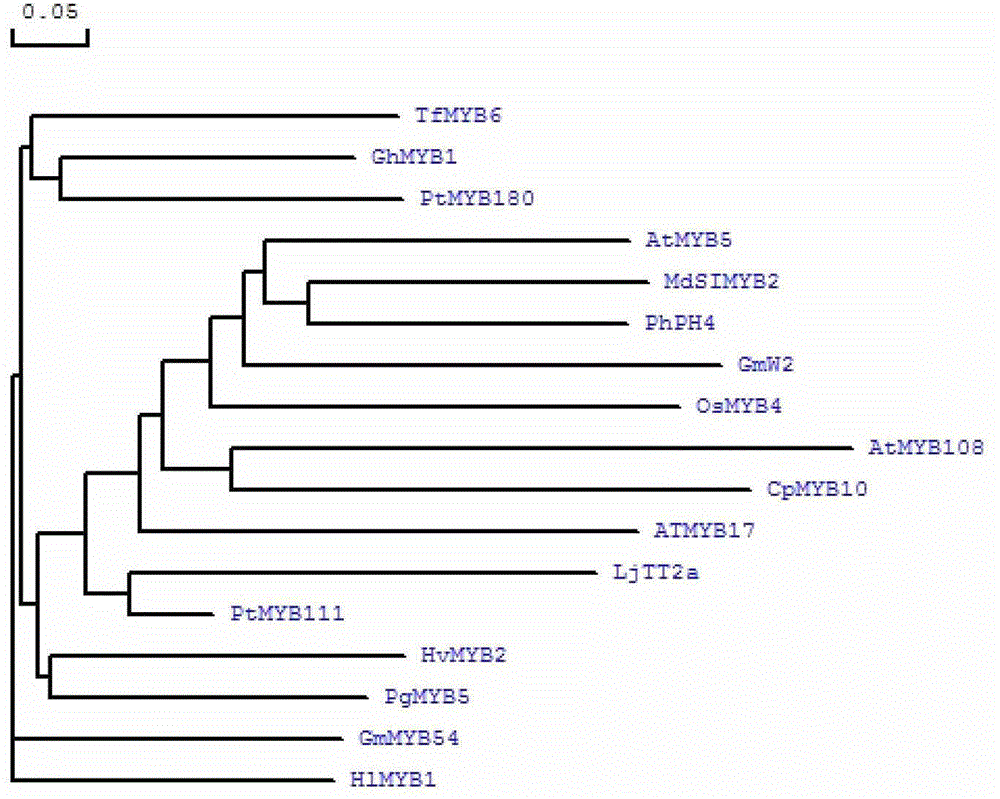
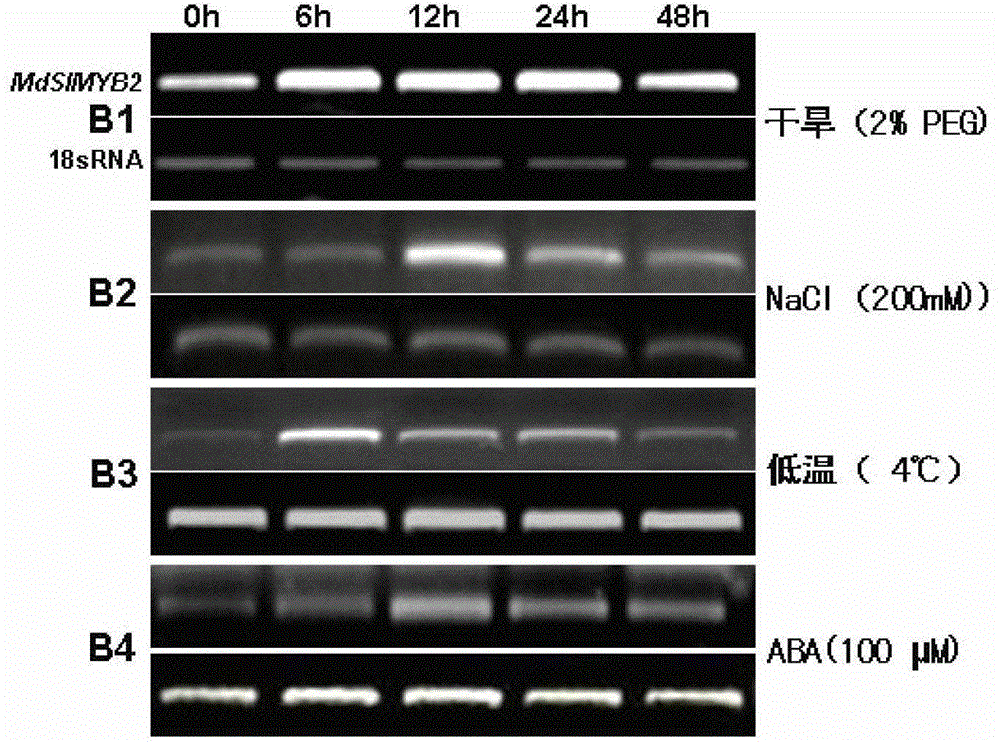
Cloning of apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2 and application of cloning of apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2
ActiveCN102978218ARapid Breeding PathwayEnrich the theoretical system of anti-adversity genetic engineeringPlant peptidesFermentationRapid amplification of cDNA endsSalt resistance
The invention relates to cloning of an apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2 and an application of the cloning of the apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2. A homology-based cloning and rapid-amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) technology is utilized to obtain a novel apple stress-resistant related gene MdSIMYB2 from a gala apple, the nucleotide sequence of the MdSIMYB2 is shown in SEQ.ID.NO.1, and the protein amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ.ID.NO.2. The gene is transferred into a tomato, and the stress capabilities of drought resistance, salt resistance, cold resistance and the like of a transgenic tomato strain are improved; and through the overexpressing of the gene MdSIMYB2 in the apple, the expression level of the transgenetic apple can be improved, and moreover, the stress capabilities of drought resistance, salt resistance, cold resistance and the like of a transgenic apple strain are increased.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Cold-adapted marine yeast BoHai Sea-9145 low-temperature alkaline lipase gene, amino acid sequence and recombinant lipase
ActiveCN102363786AImprove featuresImprove temperature stabilityHydrolasesFermentationSequence signalRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention relates a gene for coding low-temperature alkaline lipase (LipY). The gene is obtained by cloning cold-adapted marine yeast (BoHai Sea-9145), which can secrete low-temperature alkaline lipase and is screened from sea mud of Bohai, by a method of combining degenerate primer polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE). The gene contains a 1206bp open reading frame (ORF), codes 401 amino acids and contains a signal peptide with 28 amino acids at the amino acid end. Each coded amino acid contains a conserved sequence (G-X-S-X-G) of the lipase and a potential N-glycosylation site. The lipase gene is cloned on an eukaryotic expression vector (pIc9K) and performs heterologous expression in Pichia pastoris (Gs115). High-activity recombinant lipase is obtained from supernate 96 hours after fermentation, wherein methanol serves as an inducer. An electrophoretic pure lipase sample is obtained by purifying the recombinant lipase by a nickel ion affinity column. The recombinant lipase has a series of advantages of high low-temperature catalytic activity, stable performance under the alkaline condition and the like, and has wide application prospect in the low-temperature catalytic fields of daily chemicals, textile, food processing and the like.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
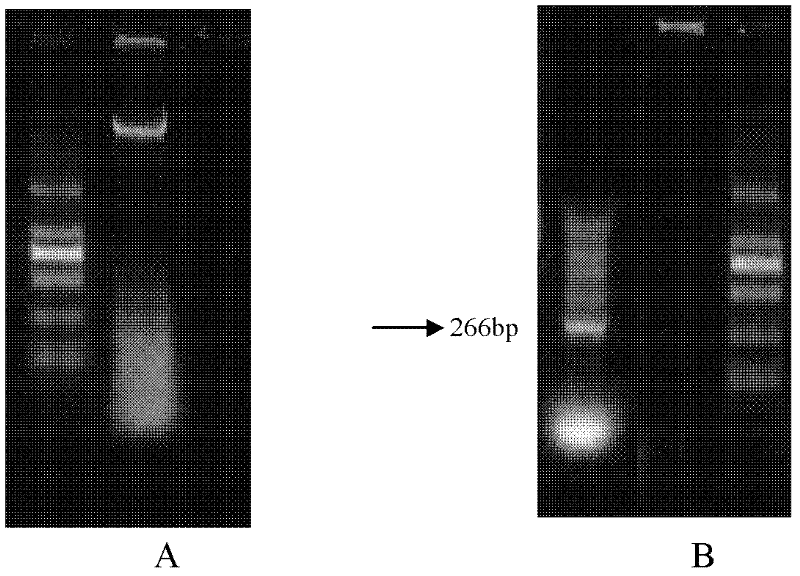
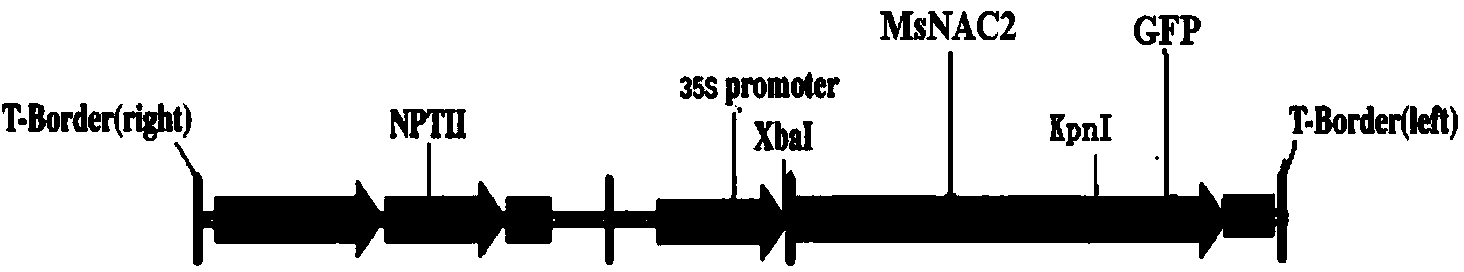
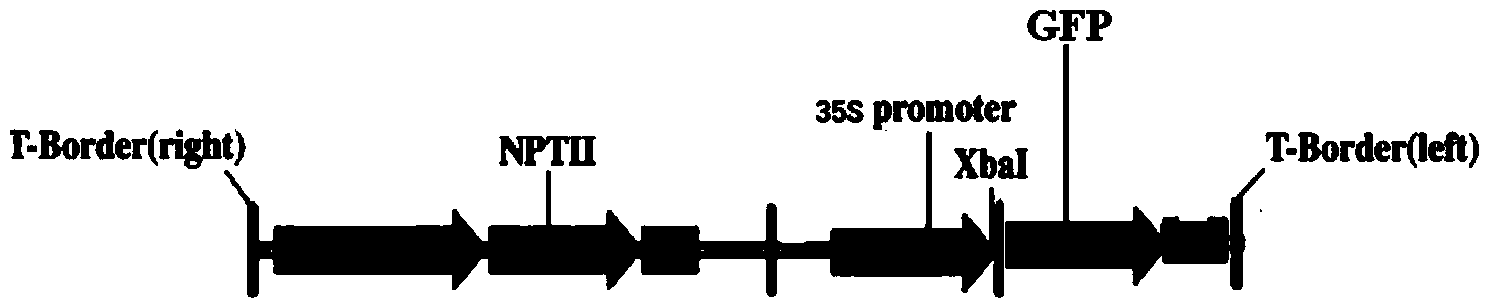
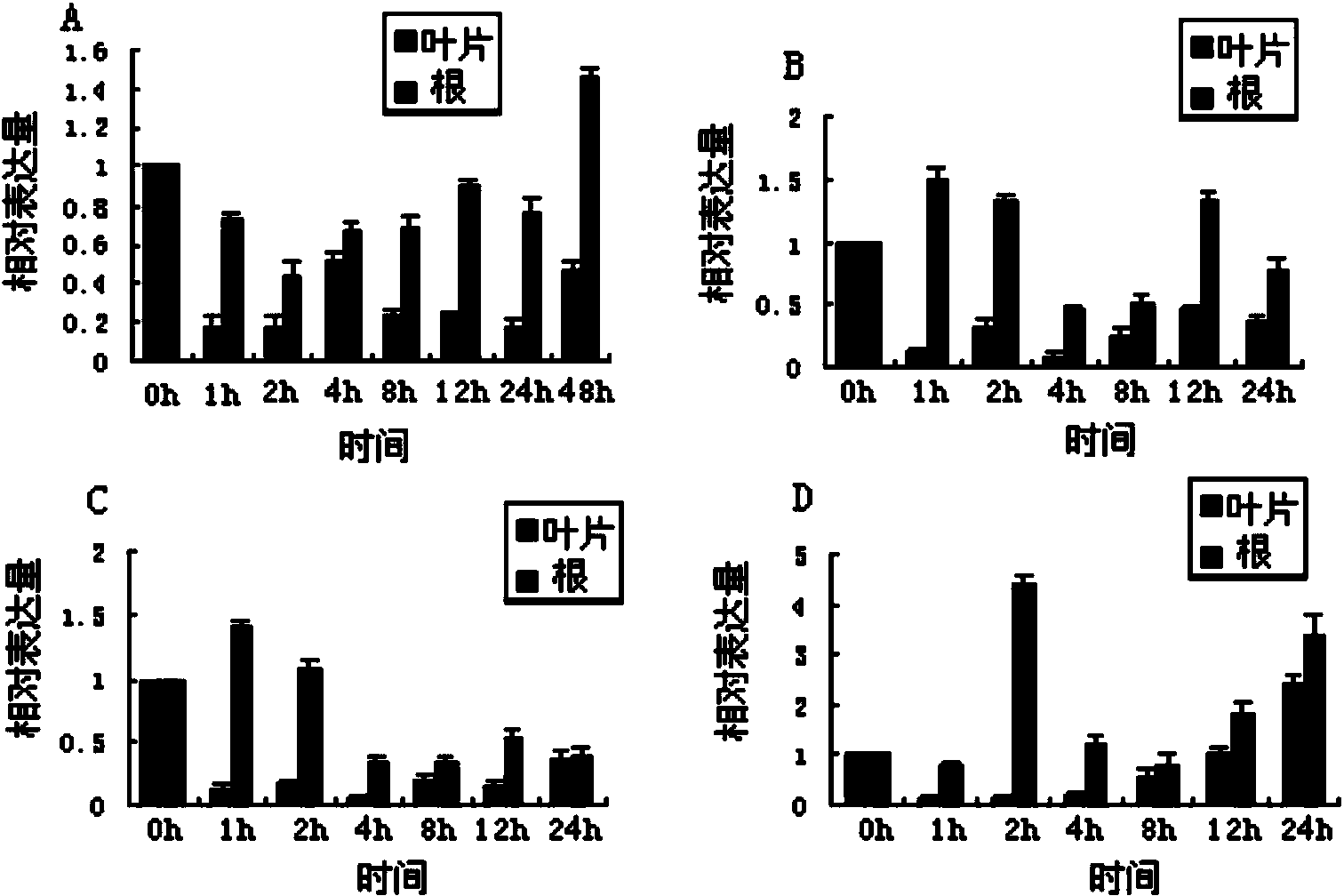
Alfalfa adversity stress responsive gene MsNAC2 and application thereof
InactiveCN103710357AImprove cold resistanceImprove drought resistanceFermentationPlant genotype modificationRapid amplification of cDNA endsNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to an alfalfa adversity stress responsive gene MsNAC2 and an application thereof. An NAC-family related gene is cloned from an alfalfa genome by applying RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) and an RACE (Rapid-Amplification of cDNA Ends) technology, and named as MsNAC2 with a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID No.11; and a fusion expression vector with an enhanced type green fluorescent protein (EGFP) gene is constructed. According to the invention, a fluorescent quantitative PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technology is applied to analyze an expression mode of the gene in the alfalfa as well as a relationship between the gene and adversity stress (cold damage, salt damage and drought), so that cold resistance, drought resistance and salt resistance of a transgenic tobacco plant can be found to be improved by over-expressing the gene in tobaccos; and the gene can be applied to genetic transformation of other monocotyledons and dicotyledons, so that stress resistance of the monocotyledons and dicotyledons is improved.
Owner:申玉华 +4
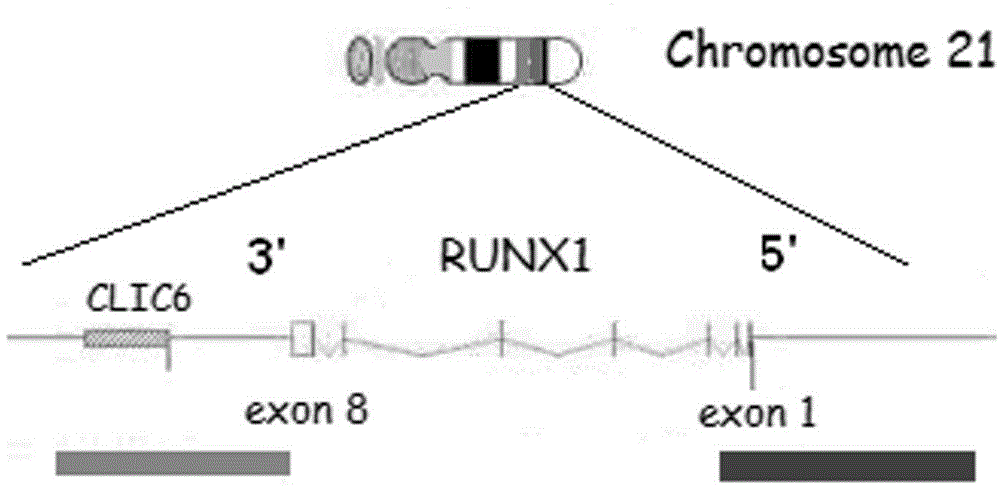
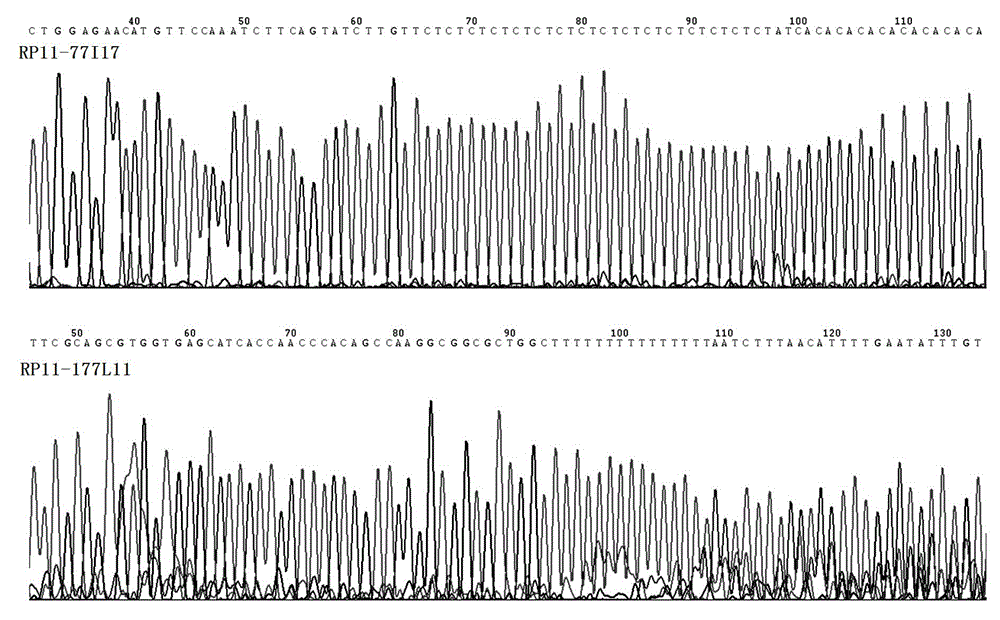
RUNX1 gene splitting and copy number increase detection kit and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103952485AAccurate identificationOvercoming the defects of detection meansMicrobiological testing/measurementRapid amplification of cDNA endsMicroscopic observation
The invention belongs to the technical field of RUNX1 gene splitting and copy number increase detection and provides a RUNX1 gene splitting and copy number increase detection kit and a preparation method thereof. A probe for detecting gene splitting is designed according to the characteristic of gene splitting. The preparation method is characterized by selecting RP11-177L11BAC and RP11-77I17BAC clones and respectively marking RP11-177L11BAC and RP11-77I17BAC with green and red to serve as probe sequences, carrying out FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) on the sequences and a cell to be detected after purifying, precipitating and dissolving the sequences, and carrying out fluorescent microscopic observation on cell signals, wherein normal somatic cells have two yellow signals; once genes are split, one red signal, one green signal and one yellow signal appear, and the corresponding quantity of yellow signals appear when the copy number increases. By adopting the kit and the preparation method, the method for accurately detecting gene splitting is created, the defects of the existing gene splitting detection means are overcome, the RUNX1 gene splitting and copy number increase incidents are rapidly and accurately detected and identified, and partner genes fused with an RUNX1 gene are determined in combination with subsequent RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) detection.
Owner:SHANXI MEDICAL UNIV
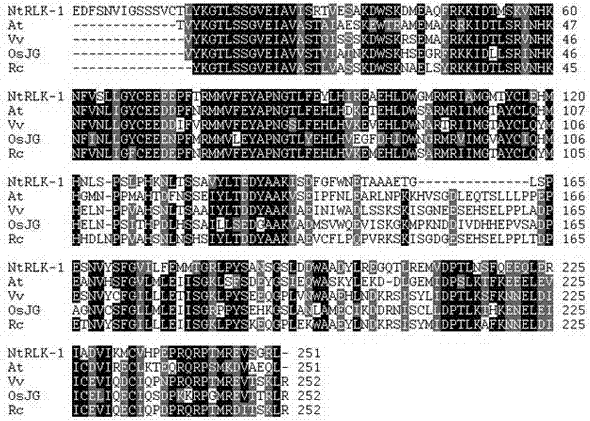
Application of NtRLK2 gene to resistance of tobacco to bacterial wilt
The invention relates to a sequence and functional application of an LRR (Leucine-Rich Repeat) acceptor protein kinase gene NtRLK2 related to the resistance of tobacco to bacterial wilt, and belongs to the technical field of molecular biology. According to the sequence and the functional application, through the analysis of a gene chip, a partial segment of one LRR acceptor protein kinase gene NtRLK2 of which the expression is up-regulated by 2 times when being induced by ralstonia solanacearum is obtained; a full-length cDNA (complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of the LRR acceptor protein kinase gene NtRLK2 is obtained through an RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA end) technique; the gene is cloned from a high-bacterial-wilt-resistance variety line 3 of the tobacco, is used for constructing over-expression and RNAi (Ribonucleic Acid interference) expression vectors, and is transferred into a bacterial wilt infected variety Cuibi 1# in the tobacco; indicated by inoculation identification, the RANi of the gene obviously enhances the disease resistance of a tobacco plant to the bacterial wilt; preliminarily predicted, the gene is possibly an interacting gene of an endogenous disease-resistant gene; the expression of the disease-resistant gene is inhibited. According to the application, a foundation is about to be laid for the bacterial-wilt disease-resistant genetic breeding of the tobacco.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Sequences of Saccharum officinarum sucrose phosphate synthase B (SofSPSB) gene and encoded protein thereof
The invention discloses sequences of a Saccharum officinarum sucrose phosphate synthase B (SofSPSB) gene and an encoded protein thereof. The sequences are obtained by the following steps: carrying out evolution analysis of full-length sequences of sucrose phosphate synthase genes of all plants, designing primers based on the conservative regions of the same family of sucrose phosphate synthase gene sequences, extracting total RNA from Saccharum officinarum tender leaves, carrying out reverse transcription, amplifying with a conventional PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method, and cloning into the full-length cDNA sequence of SofSPSB gene in combination with the RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) technique. The invention not only studies the transcription and expression mechanisms of sucrose phosphate synthase so as to lay a foundation for further discussion of a sucrose accumulation mechanism; and can obtain a purified protein with biological activity through an amino acid sequence so as to provide a basis of studying the biological function of sucrose phosphate synthase and improving the crop variety by using the SofSPS gene.
Owner:广西壮族自治区甘蔗研究所
Grass carp thymosin extrasin beta11 gene sequence
The invention discloses a grass carp thymosin extrasin beta11 gene sequence. A full expression sequence of a grass carp thymosin extrasin beta11 gene is obtained with a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method by designing primers with a thymosin extrasin beta11 EST sequence of a grass carp intestinal tract cDNA library preserved in the local laboratory used as a template, and combining with a RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technology. The invention provides important theoretical basis for researching the structural constitution of the grass carp thymosin extrasin beta11 gene, and probing into the function of the grass carp thymosin extrasin beta11 gene in the disease resistant mechanism of grass carps, the position of the grass carp thymosin extrasin beta11 gene in a functional area, and the difference with other species, and plays a pathbreaking role of exploration on establishing a bond between a grass carp genome project and a research on the grass carp disease resistant mechanism.
Owner:TONGWEI
Siniperca chuatsi IFN-alpha 3 (interferon alpha-3) gene, recombinant protein, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108707195AIncreased transcript levelsHigh expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntiviralsRapid amplification of cDNA endsAnti virus
The invention discloses a siniperca chuatsi IFN-alpha 3 (interferon alpha-3) gene, recombinant protein, a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the siniperca chuatsi IFN-alpha 3 recombinant protein includes the steps of: cloning the full-length cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) sequence of the siniperca chuatsi IFN-alpha 3, as is shown in SEQ ID NO:1 by using rapid amplification RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA end) technology of cDNA ends; cloning the ORF (open reading frame) sequence of the cDNA sequence by using a primer with a restriction site; cloning the ORF sequence into a pMD19T vector and then conducting double enzyme digestion with EcoR I and Xho I to obtain a target fragment; performing double enzyme digestion of an pET32a(+) vector with EcoR I and Xho I, connecting the pET32a(+) vector going through the double enzyme digestion with the target segment to obtain a recombinant expression vector pET32a(+)-IFN-alpha 3 to be transferredto DH5 (competent cells) alpha competent cells, selecting positive clones, and extracting preservation plasmids; transferring the plasmids into an expression bacterium BL21 (electroporation) and adopting an IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactopyranoside) induced expression to obtain IFN-alpha 3 recombinant protein, as is shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The IFN-alpha 3 recombinant protein has the advantages of being capable of being used for immersion immunity to prevent viral diseases of the siniperca chuatsi, effectively activating the siniperca chuatsi into an anti-virus state, and reducing mortality.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Trichoderma viride alkali protease as well as eukaryotic expression method and application thereof
The invention discloses trichoderma viride alkali protease as well as an eukaryotic expression method and application thereof. The coding sequence of the trichoderma viride alkali protease is obtained through an RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) method, the length of an amino acid sequence is 410 amino acids, and the length of the coding sequence is 1233 nucleotides. The coding nucleotide sequence of the trichoderma viride alkali protease is constructed in an eukaryotic expression vector to perform eukaryotic expression, and trichoderma viride alkali protease capable of inhibiting growth of aflatoxin can be obtained. The trichoderma viride alkali protease has the function of inhibiting the growth of the aflatoxin.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Portunus trituberculatus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor PtALF-3 gene and encoding proteins and application thereof
InactiveCN102337272AHigh antibacterial activityAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCDNA libraryBiotechnology
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, in particular relates to a Portunus trituberculatus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor PtALF-3 gene and encoding proteins and application thereof. In the invention, a PtALF-3 gene cDNA is amplified from a Portunus trituberculatus by utilizing a cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library and an RACE (Rapid-amplification of cDNA Ends) technology and plays an important role in immune defense of the Portunus trituberculatus. A recombinant PtALF-3 protein has obvious antibacterial activity to Gram-negative Vibrio alginolyticus, P. Aeruginosa, Edwardsiella tarda, Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus, Micrococcus luteus and fungus Pichia pastoris, and the minimal inhibitory concentrations are respectively 0.58 mu M, 0.58 mu M, 9.26 mu M, 74.08 mu M, 18.52 mu M and 9.26 mu M. The invention lays a foundation for disease prevention and control, gene-assisted selection and development of feed additives of the Portunus trituberculatus.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cloning and functional expression method of gene AhAP2ER related to drought stress of peanuts
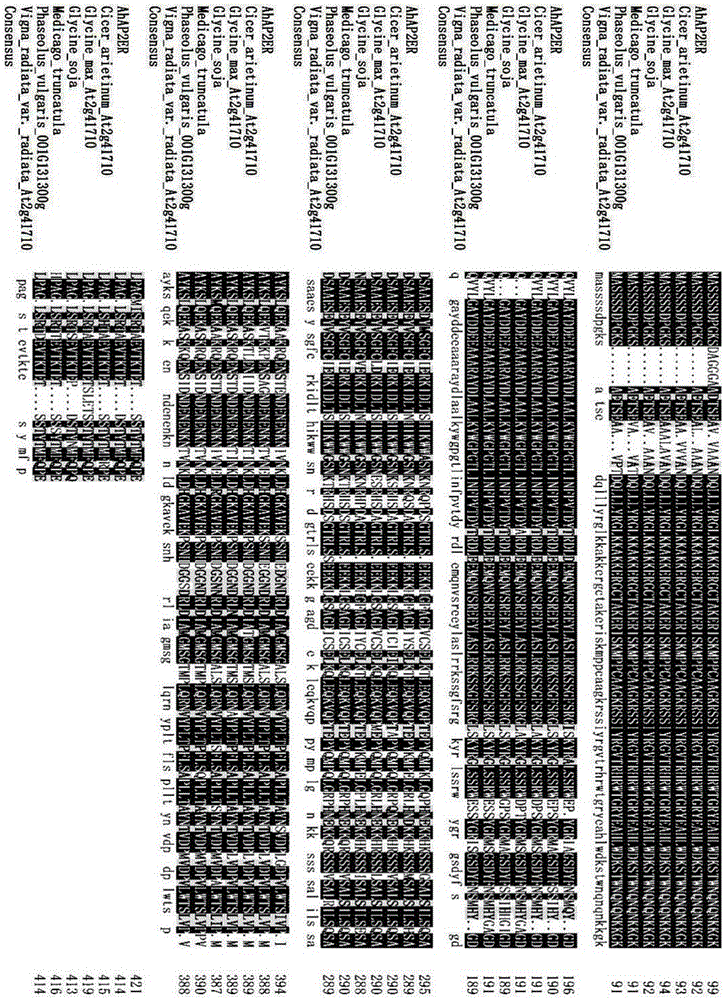
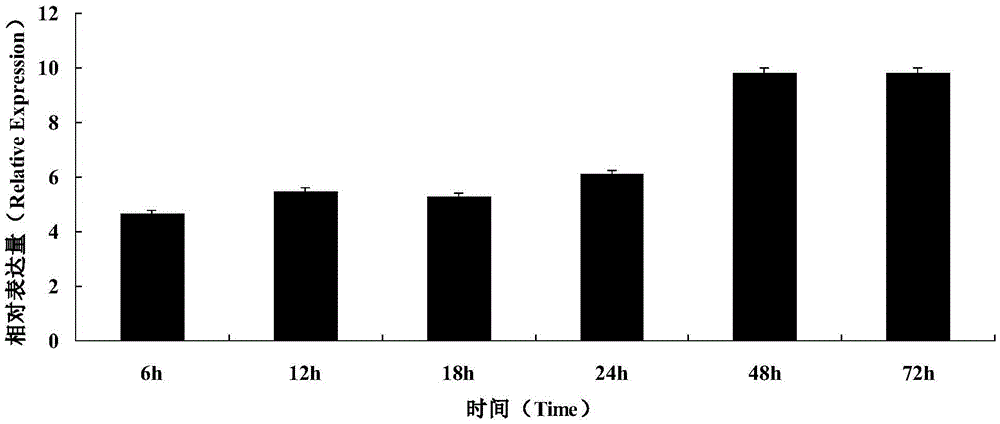
InactiveCN105462989AImprove drought resistanceIncreased transcript levelsMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesBiotechnologyRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention relates to the biotechnology field and in particular relates to a cloning and functional expression method of a gene AhAP2ER related to drought stress of peanuts. The gene AhAP2ER in drought stress response is synthesized through preparation and treatment of materials, extraction of RNA (ribonucleic acid), synthesis of cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) and RACE (rapid-amplification of cDNA ends) cloning technology. Expression of the gene AhAP2ER under the condition of drought stress is also analyzed by using fluorescent quantitative RT-PCR (reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction), thus finally drawing a conclusion that the gene AhAP2ER plays an important role in the adaptability of the peanuts to drought stress. The transgenic plants have obvious drought resistance characteristic compared with a control group by transferring the gene to the peanuts by transgenic means, indicating that the gene AhAP2ER can conduce to obviously improving the drought resistance of the peanuts.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Sugarcane flowering regulator protein ScFT-2 and encoding gene thereof
ActiveCN107365371APromote floweringShorten the breeding periodMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant peptidesRapid amplification of cDNA endsFluorescence
The invention relates to sugarcane flowering regulator protein ScFT-2 and an encoding gene thereof, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. The sugarcane flowering regulator protein ScFT-2 is composed of an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID No. 1, and nucleotide sequences of the encoding gene and genome DAN are shown as in SEQ ID No. 2 and SEQ ID No. 3. Total RNA and genome DNA are extracted from mature leaves of the sugarcane variety Yue Tang 93-159, and full-length cDNA and genome DNA of the ScFT-2 are acquired via the PCR (polymerase chain reaction) method in conjunction with the RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) technique. The ScFT-2 gene herein acts on sugarcane stalk tips and young leaves, plays a part in sugarcane fluorescence regulation and ear formation and development, can promote sugarcane flowering, and has great practical value in studying the sugarcane flowering mechanism, promoting flowering of sugarcane parents, and researching and developing sugarcane fluorescence regulation techniques.
Owner:SUGARCANE RES INST OF YUNNAN ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Portunus trituberculatus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor PtALF-2 gene and encoding proteins and application thereof
InactiveCN102337271AHigh antibacterial activityNo obvious inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCDNA libraryRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, in particular relates to a Portunus trituberculatus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor PtALF-2 gene and encoding proteins and application thereof. In the invention, a PtALF-2 gene cDNA is amplified from a Portunus trituberculatus by utilizing a cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library and an RACE (Rapid-amplification of cDNA Ends) technology and plays an important role in immune defense of the Portunus trituberculatus. A recombinant PtALF-2 protein has obvious antibacterial activity to Gram-negative Vibrio alginolyticus, P. Aeruginosa, Edwardsiella tarda, Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus and Micrococcus luteus, and the minimal inhibitory concentrations are respectively 1.02 mu M, 2.04 mu M, 4.07 mu M, 16.30 mu M and 65.19 mu M; but the recombinant PtALF-2 protein has no obvious inhibitory action to fungus Pichia pastoris. The invention lays a foundation for disease prevention and control, gene-assisted selection and development of feed additives of the Portunus trituberculatus.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for extracting potato tuber total RNA (ribonucleic acid) by means of improved Trizol
InactiveCN103540585AIncrease acquisition rateAvoid smallDNA preparationRapid amplification of cDNA endsSodium acetate
The invention provides a method for extracting potato tuber total RNA (ribonucleic acid) by means of improved Trizol. The method is characterized by comprising the steps of adding phenol / chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) for performing primary extraction after extracting RNA by the regular Trizol (Invitrogen Company), then transferring liquid supernatant to a new tube, adding 0.7 time of isopropyl alcohol in comparison with the volume of the liquid supernatant and 0.2 time of 1mol / L sodium acetate in comparison with the total volume to precipitate RNA, respectively washing the obtained RNA once with 1mL of 3mol / L sodium acetate (pH=5.2) and 1mL of 75% alcohol, finally, drying, and dissolving with DEPC (diethylpyrocarbonate) water. Such method for extracting potato tuber total RNA by means of improved Trizol has high yield and high capacity; moreover, the obtained total RNA has excellent quality and high purity, and can meet the requirements of molecular biology researches, such as inverse transcription, Northern hybridization, gene in vitro translation, cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid) library construction and rapid amplification of cDNA ends.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Sugarcane sucrose transport protein SoERD6 (early responsive to dehydration) gene and encoding protein sequence thereof
InactiveCN102925461ABiologically activeIncrease varietyPlant peptidesGenetic engineeringRapid amplification of cDNA endsSaccharum
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Branchiostoma belcheri chitin-binding associated serine protease CASP gene for identifying chitin and application thereof
InactiveCN103509809AHas serine protease activityEnhance phagocytosisAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliRapid amplification of cDNA ends
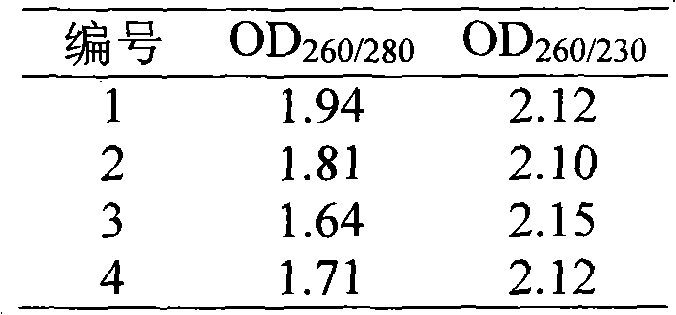
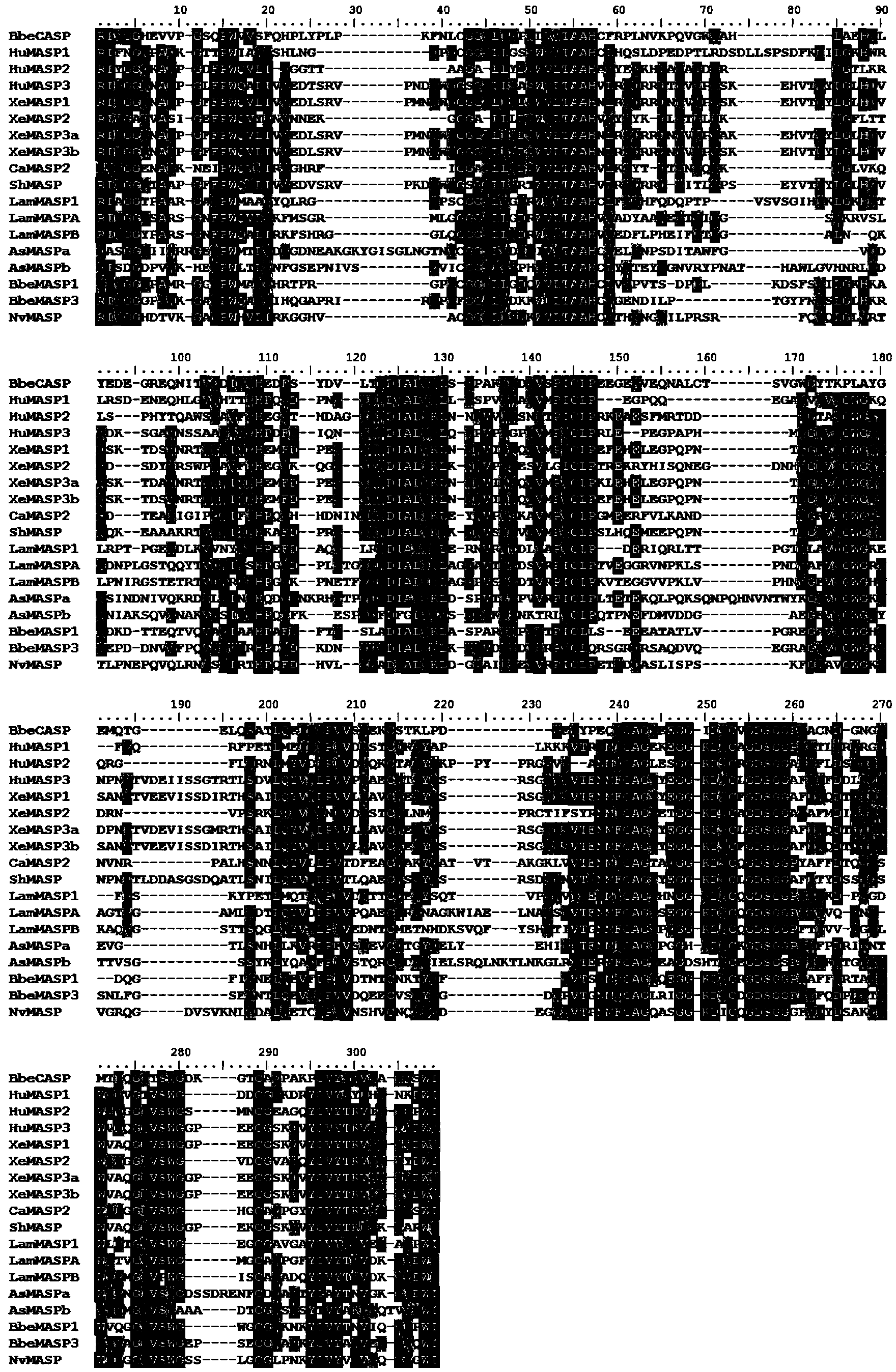
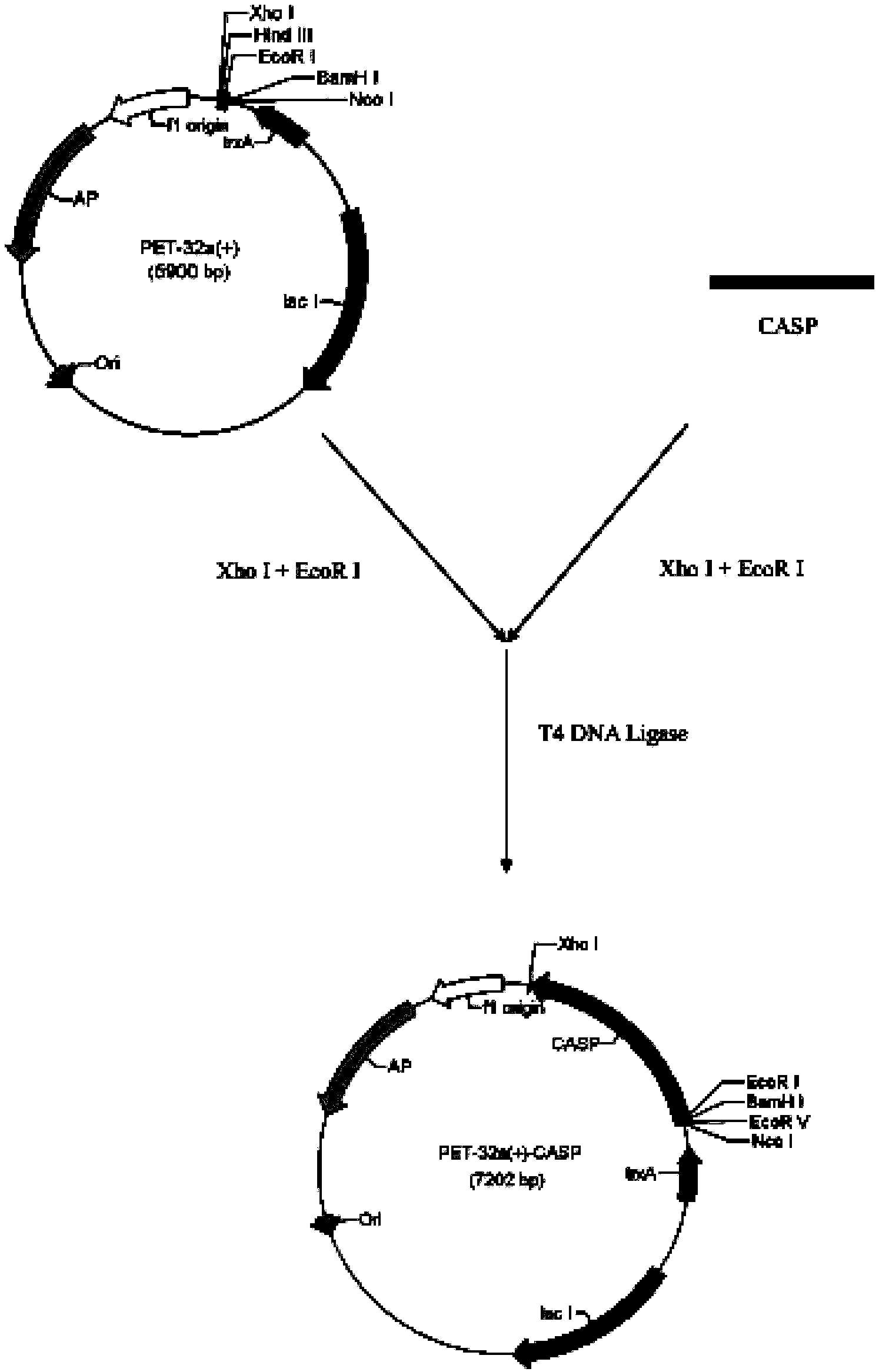
The invention relates to a branchiostoma belcheri chitin-binding associated serine protease CASP gene for identifying chitin, a protein coded by the gene and an expression method and application of the protein. The CASP gene is aN MASP (Mbl Associated Serine Protease) similar gene obtained by cloning from a total RNA (Ribose Nucleic Acid) of branchiostoma belcheri by a method of combining primer amplification and RACE (rapid-amplification of cDNA ends) amplification. The protein coded by the CASP gene is expressed in an intracellular soluble form in escherichia coli by a recombinant expression vector PET-32a(+)-CASP. The protein coded by the CASP gene takes an important effect of resisting to foreign pathogen and has the development value of becoming a high-efficiency natural antibacterial medicament.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Tea tree cytoplasm-type glutamine synthetase (GS) gene and encoding protein thereof
InactiveCN102311961ASimple designEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionRapid amplification of cDNA endsSequence analysis
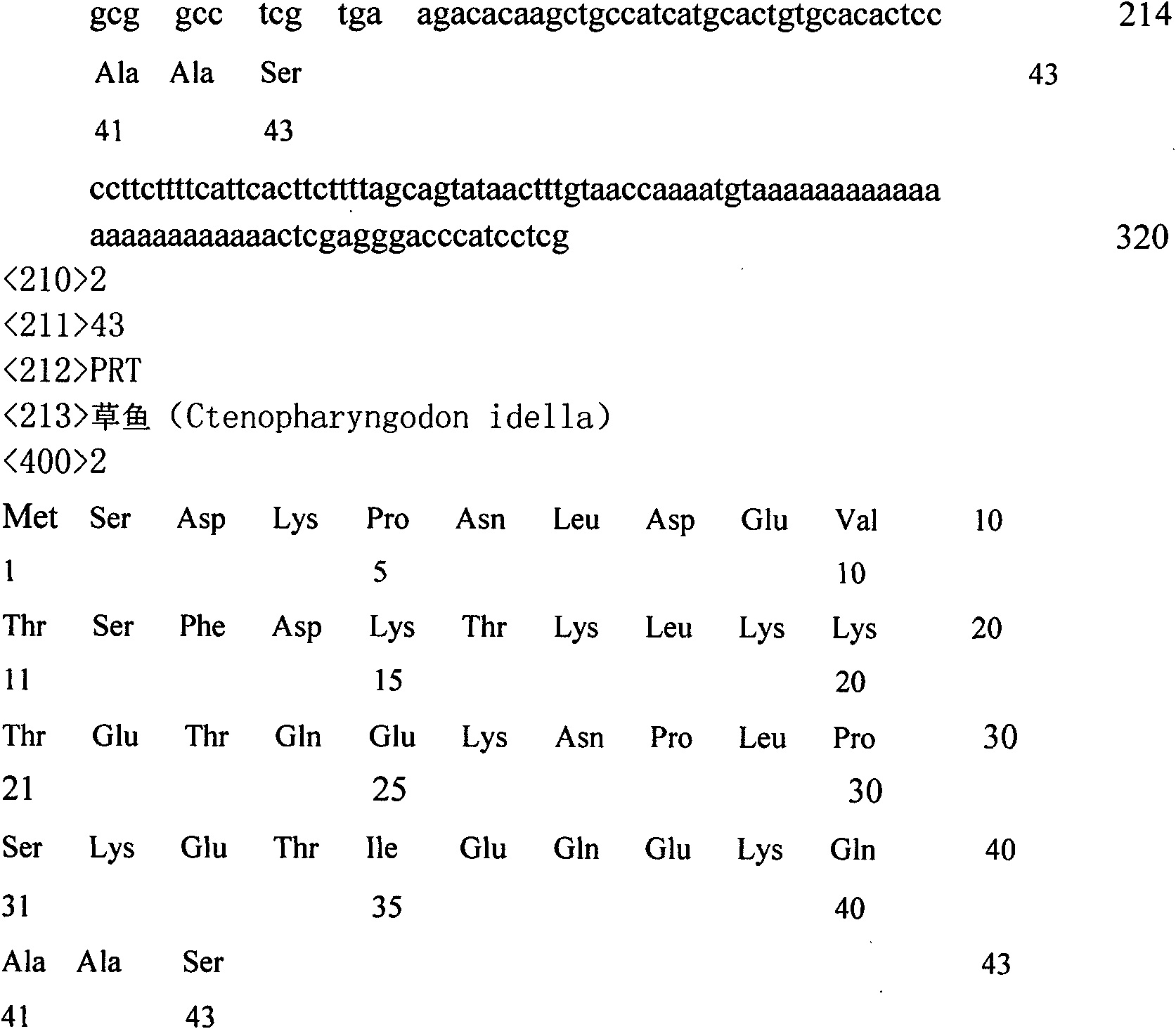
The invention relates to a tea tree cytoplasm-type glutamine synthetase (GS) gene and an encoding protein thereof. The tea tree cytoplasm-type GS gene is obtained by taking a tea tree (Dragon Well tea 43) total complementary deoxyribonucleic acid (cDNA) as a template through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification reaction. In the tea tree cytoplasm-type GS gene, part of homologous sequence published in national center of biotechnology information (NCBI) is utilized to design degenerate primer amplification to obtain an intermediate conserved sequence, and then, sequences of both ends are obtained through rapid amplification of cDNA Ends reaction; and the sequences of both ends are spliced through DNAman software to finally obtain the full-long sequence of tea tree cytoplasm glutamine synthetase, and the complete sequence analysis on the encoding zone of the gene is completed.
Owner:ANHUI NORMAL UNIV
Black spot disease resisting candidate gene sequence of dowing grape as one of China vitis wild species and use
InactiveCN1683536AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationWild speciesRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The present invention relates to conventional grape crossbreeding, molecular marker assisted breeding, and gene location and mapping method and technology. By means of resistant geneanalogus (RGAs), the present invention obtains 26 black spot disease resisting candidate gene DNA segments of Chinese V. quinquangularis Read and these segments are cloned and sequenced and have size of 492-550 bp. Black spot disease resisting marker assisted breeding is performed based on these sequences as the probes for detecting black spot disease resisting gene. Black spot disease resisting gene is located and mapped based on the distribution of these segments in the hybrid progeny of Chinese V. quinquangularis Read and European V. Or, specific primer is designed, and the technology of rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) is adopted in cloning the black spot disease resisting gene of Chinese V. quinquangularis Read, so as to improve grape variety in gene engineering technology.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Portunus trituberculatus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor PtALF-1 gene, protein encoded by gene and application of protein
InactiveCN102329801AHigh antibacterial activityNo obvious inhibitory effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCDNA libraryDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and in particular relates to a Portunus trituberculatus anti-lipopolysaccharide factor PtALF-1 gene, a protein encoded by the gene and an application of the protein. A cDNA (complementary Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) library and a RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technology are utilized for amplification to obtain PtALF-1 gene cDNA from the Portunus trituberculatus. The gene performs an important action on the immunologic defense aspect of the Portunus trituberculatus. The recombinant PtALF-1 protein has obvious Gram-negative bacterium and gram-positive bacterium bacteriostatic activity, has the minimum inhibitory concentration on Vibrio alginolyticus, pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus and the Micrococcus luteus of respectively 2.33mu M, 18.64mu M, 18.64mu M and 18.64mu M, and does not have obvious inhibition action on fungus Pichia pastoris. The invention lays the foundation on prevention and control of diseases and insect pests, gene-assisted breeding and development of feed additive of Portunus trituberculatus.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of in-vitro expression of gekko japonicus Hoxc10 (homebox gene c10) protein and preparation of polyclonal antibody
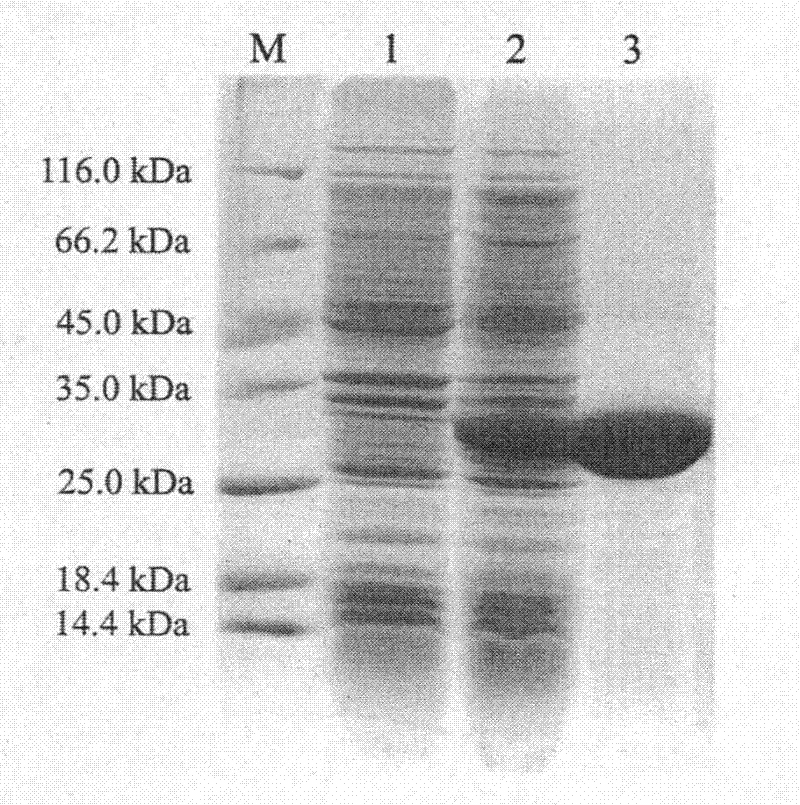
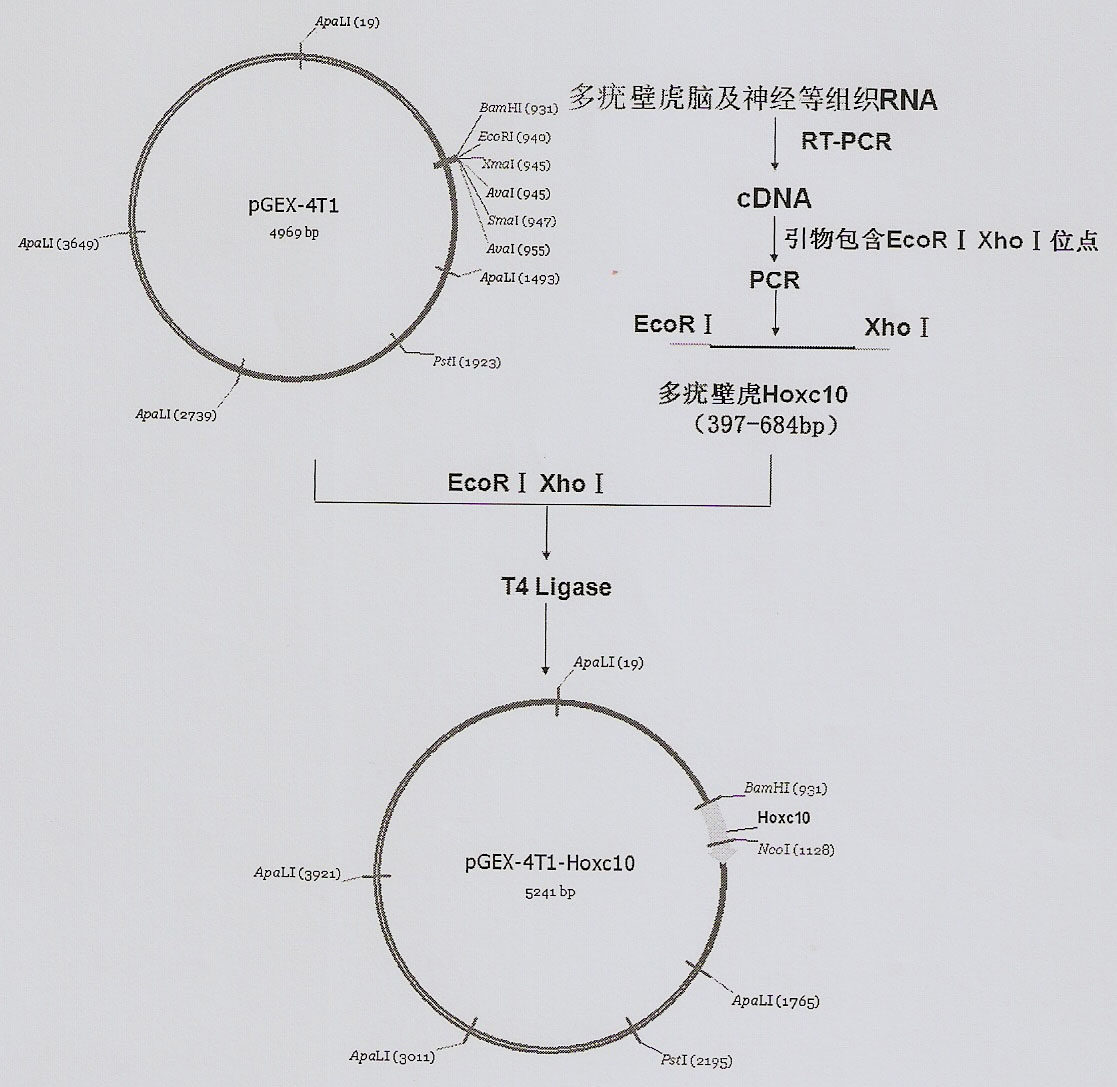
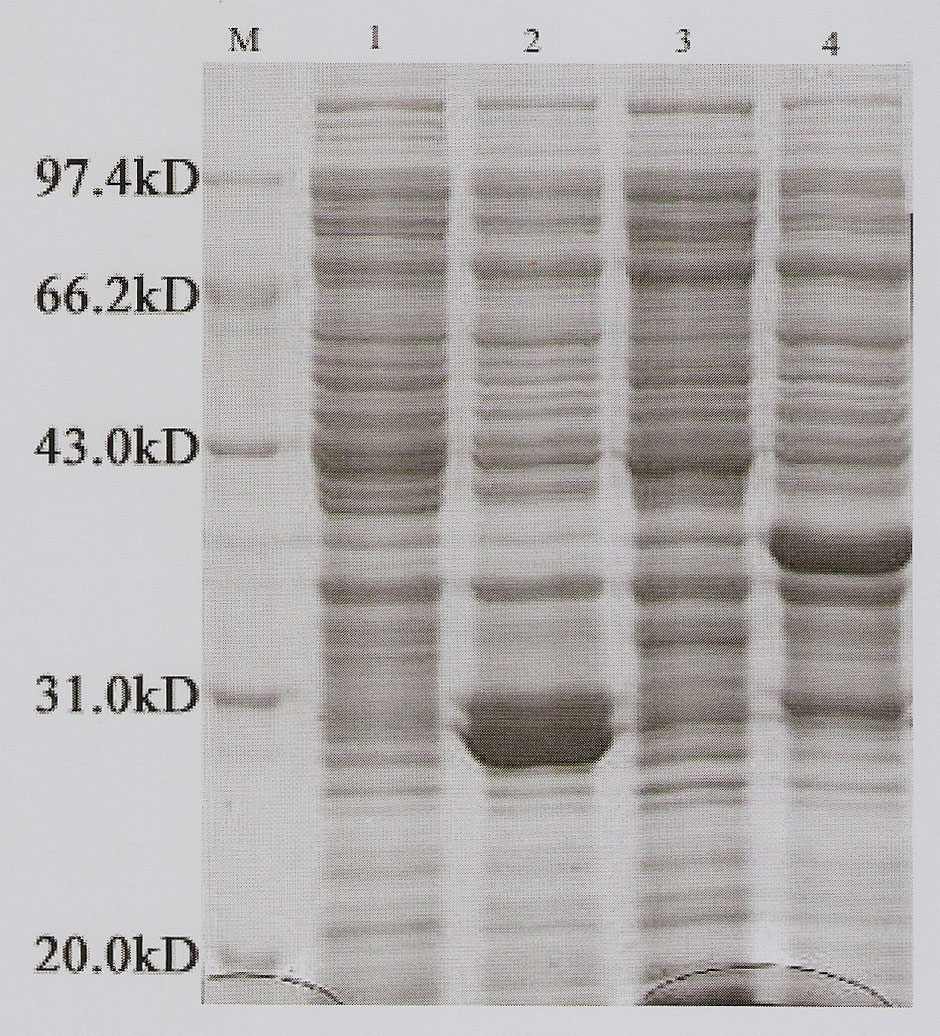
InactiveCN102206647AHigh antisera titerEasy accessSerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansRapid amplification of cDNA endsFusion Protein Expression
The invention discloses a method of the in-vitro expression of a gekko japonicus Hoxc10 (homebox gene c10) protein and the preparation of a polyclonal antibody, comprising the following steps of: obtaining an EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) sequence of gekko japonicus Hoxc10; obtaining an overall length sequence of the gekko japonicus Hoxc10 through an RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) method; predicting an antigenic epitope of the gekko japonicus Hoxc10 protein on line by adopting DNASTAR software and SWISS-PLOT; constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the gekko japonicus Hoxc10 by selecting superior epitope peptides; inducing the expression of fusion proteins in vitro; purifying the fusion proteins; preparing the polyclonal antibody, and the like. In the invention, an in-vitro gekko japonicus Hoxc10 expression system constructed on the basis of pGEX-4T1 can efficiently express a target protein in BL21 and further purify the target protein; and a large quantity of GST-Hoxc10 fusion proteins can be conveniently obtained; in addition, a rabbit gekko japonicus Hoxc10 antiserum prepared by immunizing a New Zealand rabbit through the GST-Hoxc10 fusion proteins has high titer and good specificity.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
3'RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) method for acquiring complete 3' end sequence as 3' end having repetitive sequence
InactiveCN106636074ASolve the problem that the complete end sequence cannot be obtainedMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationRapid amplification of cDNA endsRepetitive Sequences
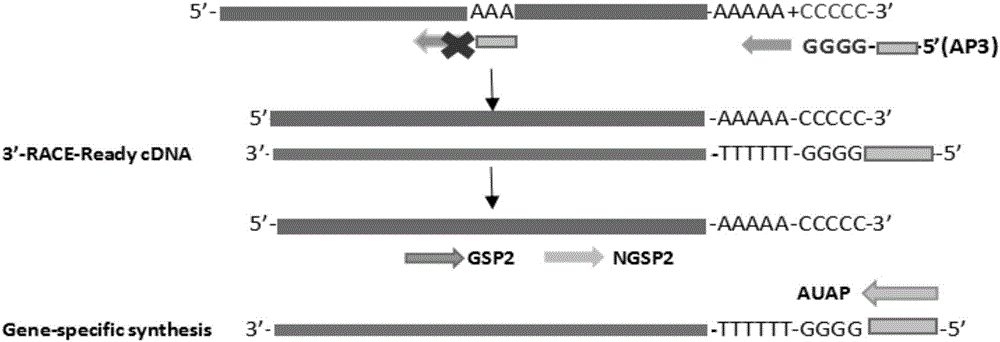
The invention discloses a 3'RACE (rapid amplification of cDNA ends) method for acquiring a complete 3' end sequence as a 3' end having a repetitive sequence. The method comprises the following steps: 1) tailing mRNA with terminal transferase, so that a connector sequence is added: tailing the mRNA with dCTP or dGTP, so that a single-base repetitive sequence of 16-22bp is added; 2) synthesizing first chain cDNA: conducting reverse transcription on the tailed mRNA by taking an anchor primer having oligodG or oligodC as a connector sequence; and 3) conducting 3'RACE amplification: with the cDNA having the connector sequence as a template, an internal specific primer GSP2 of the template which is designed in accordance with a RACE primer design principle as well as a corresponding nested primer NGSP2 thereof as forward primers of the amplification, and a complementary sequence (AUAP) of the connector sequence as a reverse amplification primer, conducting 3'RACE on the cDNA sequence having the connector. With the application of the 3'RACE method provided by the invention, the problem that a complete end sequence cannot be acquired in 3'RACE due to a special structure (having the A repetitive sequence) of the sequence can be solved.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Method for promoting gene cloning efficiency
InactiveCN102660538AQuick searchIncrease success rateDNA preparationRapid amplification of cDNA endsAgarose electrophoresis
The invention discloses a method for promoting gene cloning efficiency, and relates to a gene cloning method. The method comprises the following steps of: designing one pair of specific primers at an intermediate fragment of an object gene; carrying out specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on templates of different sources in an RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) process; subjecting an amplification product to the electrophoretic analysis of 1.5% agarose, detecting whether a positive band of the product exists or not and the brightness of the positive band, so as to determine the level of the copy number of the object gene in an RACE to-be-amplified template, and determining the efficiency of each enzymatic reaction step in the RACE process to obtain the most proper template used for 5' RACE amplification, so that the purpose of improving the amplification mission success rate of a target gene is achieved. By using the method, the most proper template for the RACE amplification and a condition are efficiently selected by quickly and sensitively detecting the effective copy numbers of the object genes in the templates of the different sources.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Leukocyte chemoattractant gene sequence 2 of grass carp
The invention discloses leukocyte chemoattractant genes 2 of a grass carp. By using an EST (Expressed Sequence Tag) sequence of the leukocyte chemoattractant genes 2 in a grass carp intestinal tract cDNA (complementary DNA) library saved in a laboratory as a template design primer and combining with an RACE (Rapid-Amplification of cDNA Ends) technique, the full expression sequence of the leukocyte chemoattractant genes 2 in grass carp intestinal tract cells is obtained by amplification and cloning in a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. The invention provides important theoretical basis for the research on the structural composition of the leukocyte chemoattractant genes 2 of the grass carp, the discussion on the action and the functional zone position of the leukocyte chemoattractant genes 2 in the disease resistance of the grass carp and the difference from other species. The invention has a pioneering action on a method for exploring and establishing a link between grass carp genome planning and functional feed industrialization.
Owner:TONGWEI
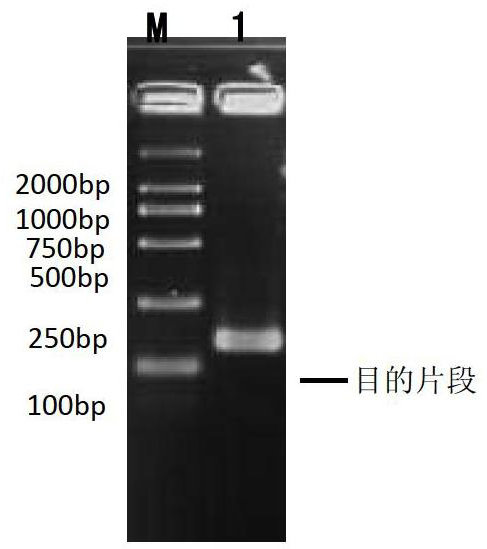
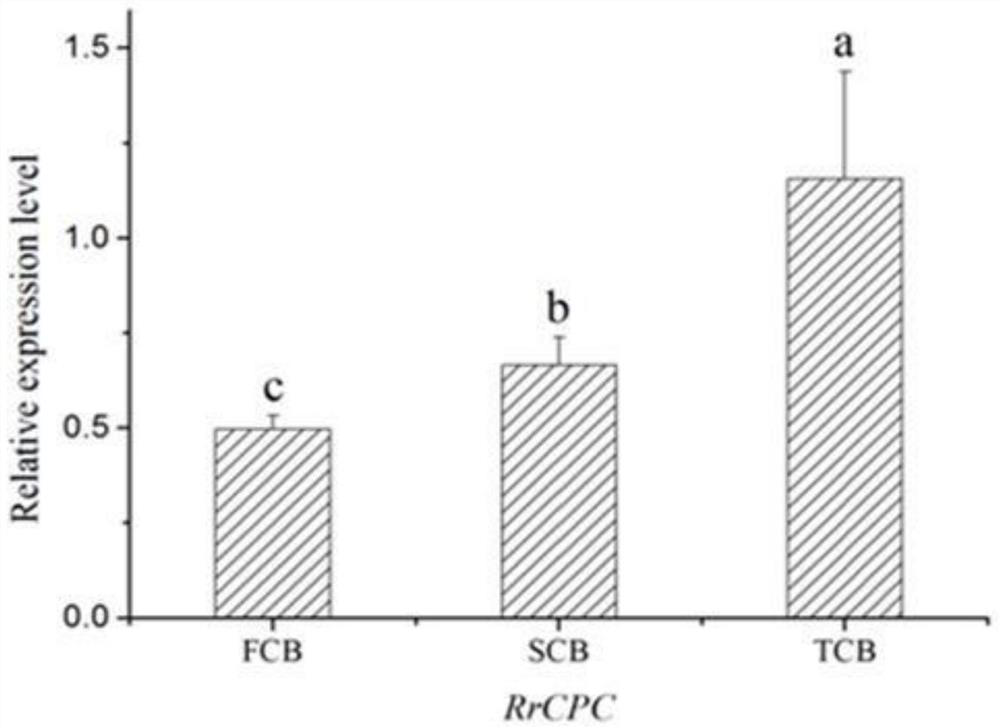
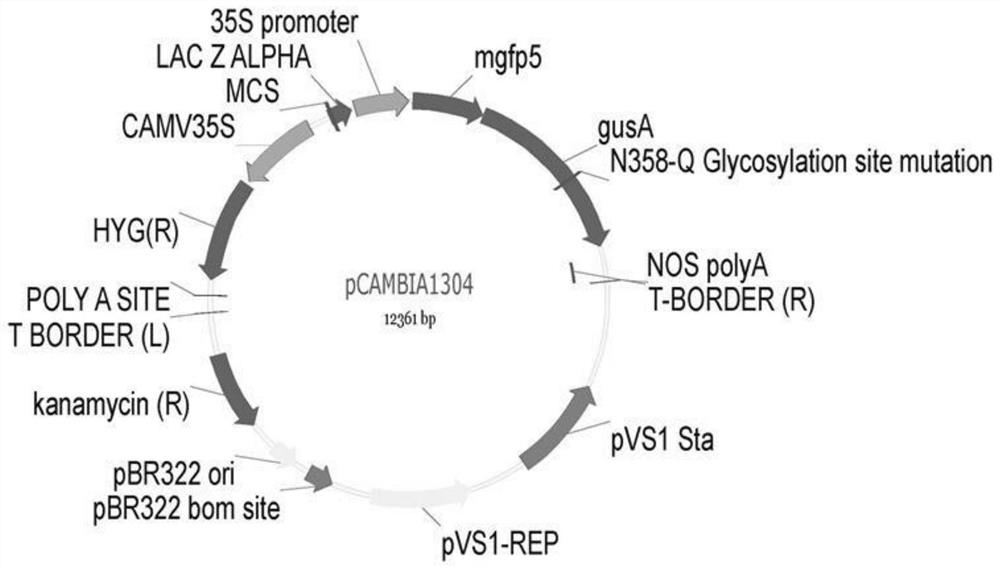
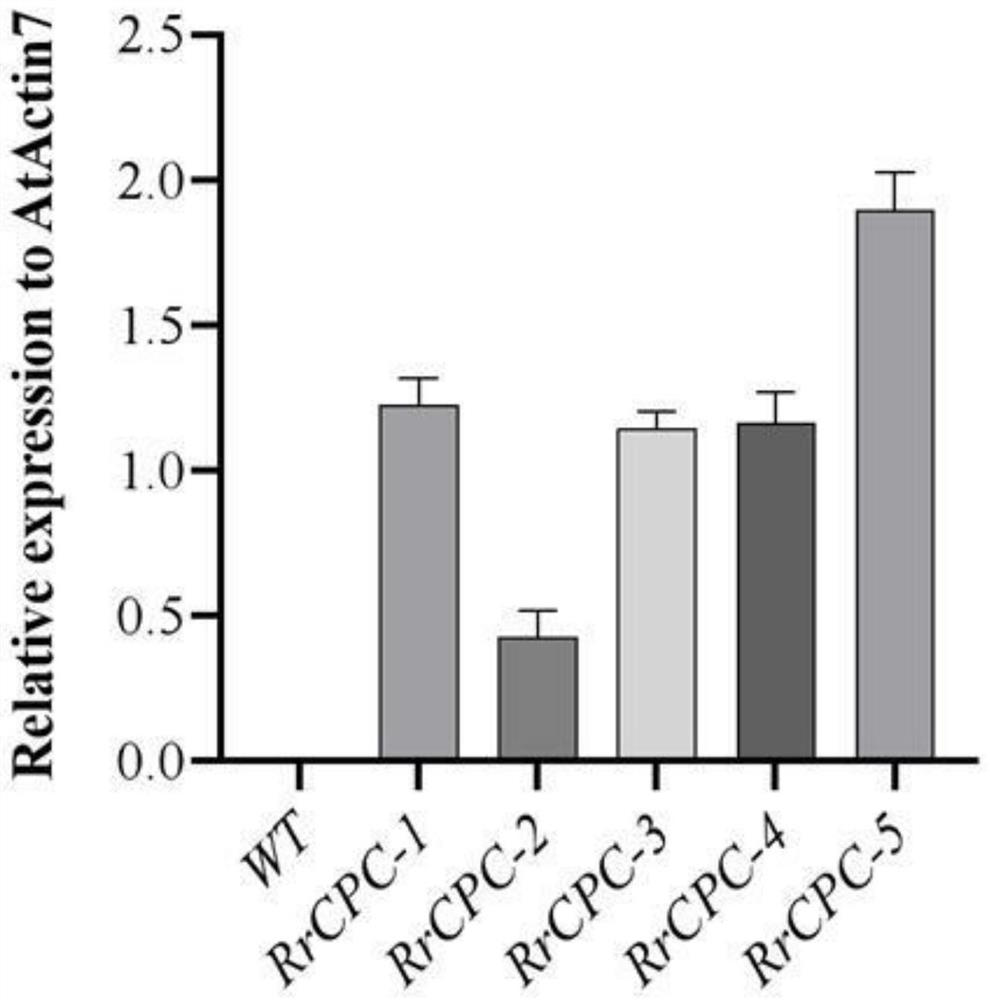
Rose skin thorn regulation gene RrCPC and application thereof
ActiveCN114438097AImprove management efficiencyPlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyRapid amplification of cDNA ends
The invention relates to a rose skin thorn regulation and control gene RrCPC and application thereof, and the RrCPC gene is cloned by taking purple-branch rose as a material through RACE (Rapid Amplification of cDNA Ends) technology. The expression mode of the RrCPC gene on different levels of lateral branches of roses is detected through a real-time fluorescent quantitative detection technology, meanwhile, arabidopsis thaliana is transformed by constructing an overexpression vector, it is proved that the RrCPC gene is a negative regulatory factor for epidermal hair generation, and the RrCPC gene has important application value for cultivating few-thorn or thorn-free rose new germplasm and improving rose management efficiency. The invention provides a rose skin thorn regulation gene RrCPC and application thereof in few-thorn and thorn-free roses, and the rose skin thorn regulation gene RrCPC has important application value in the field of thorn-free rose breeding.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com