Method for separation and identification of kenaf root knot nematode
A root-knot nematode and identification method technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve problems such as harming kenaf, affecting the yield and quality of kenaf, and achieving the effects of strong accuracy, simple operation and high purity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
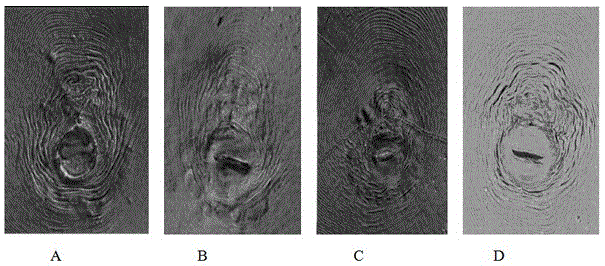
[0017] (1) Morphological identification: select typical root-knot nematode diseased plants of kenaf, and use the five-point sampling method to collect about 500g of the host root system and the surrounding 5-20cm deep plow layer soil. Under greenhouse conditions, the diseased roots and diseased soil were inoculated on potted tomatoes cultivated in sterilized soil for 45 days in advance for purification and cultivation; under a stereomicroscope, female worms and egg masses were picked out from the inoculated tomato roots with a dissecting needle, and the Eggs were placed in a petri dish filled with distilled water and hatched for 4-5 days to obtain J2. The male worms in the soil were separated by the Berman funnel method; like figure 1 Shown: A, B, C, D are the perineal patterns of M. incognita, M. elegans, M. javanica and M. peanut respectively;
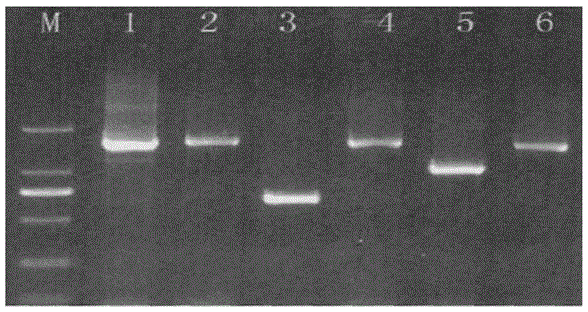
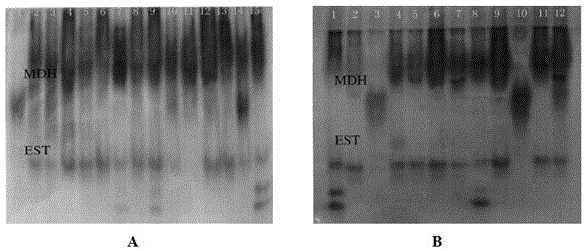
[0018] (2) Analysis and identification of isoenzymes: Using conventional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis technology, the purifi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com