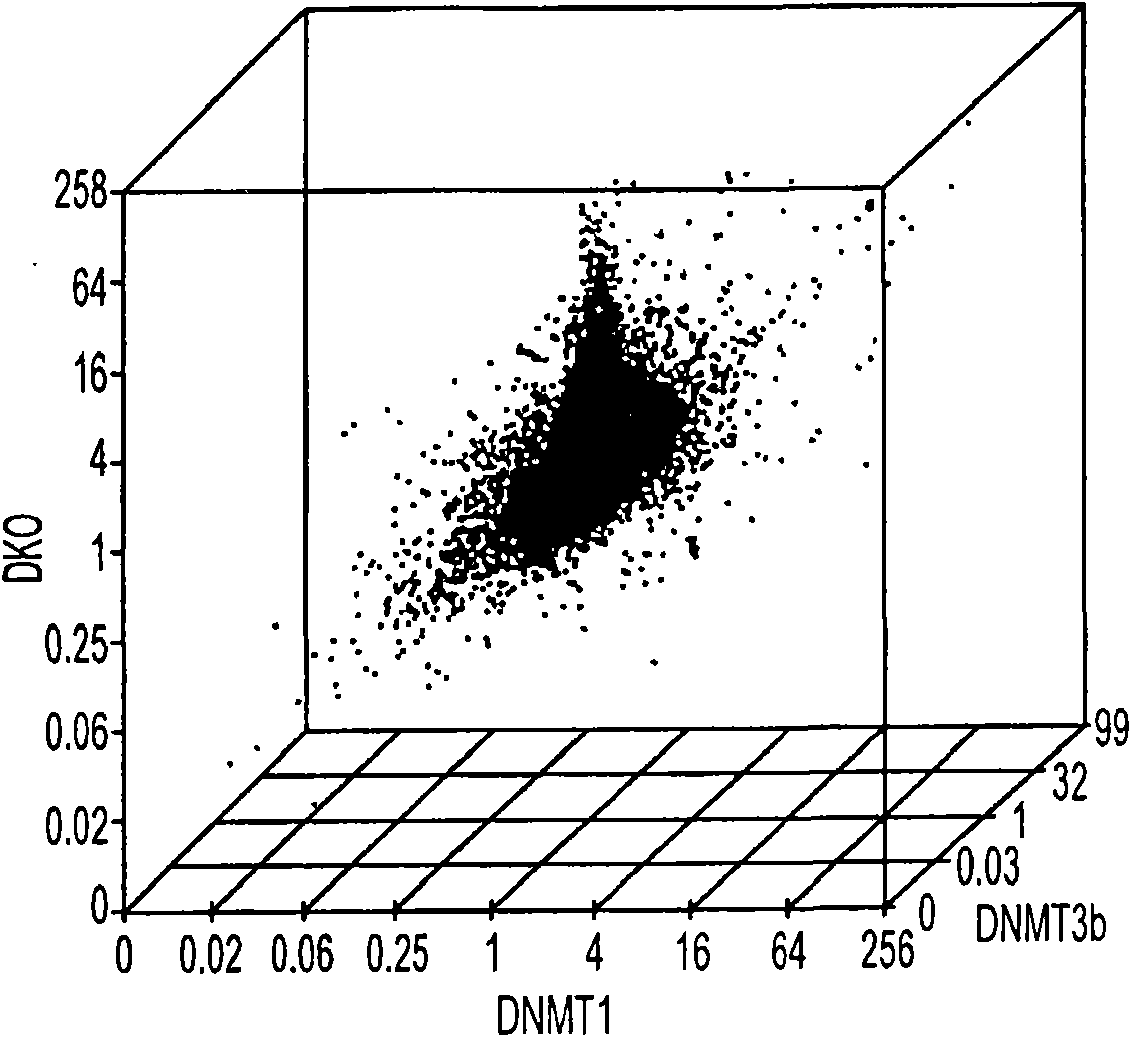
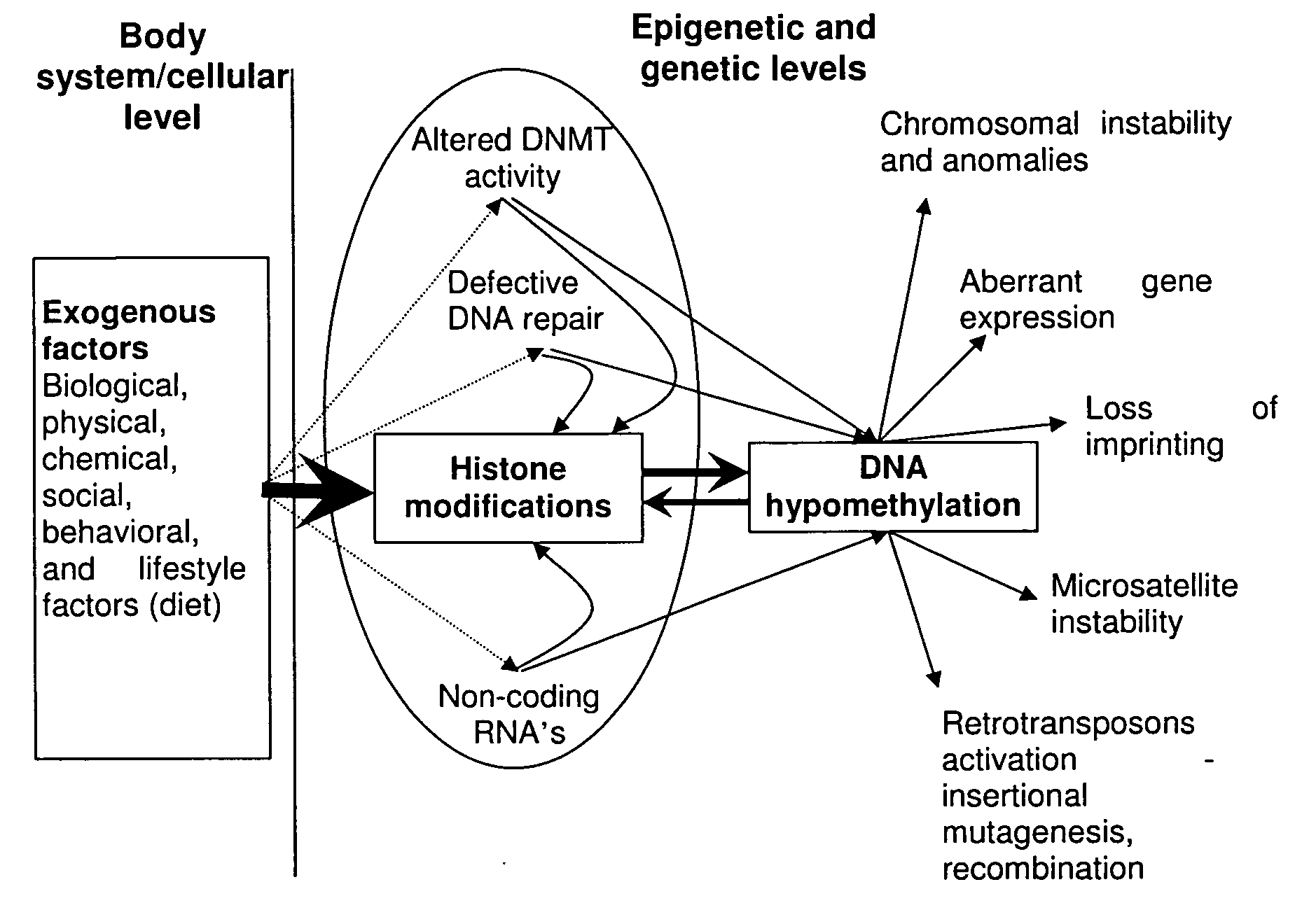
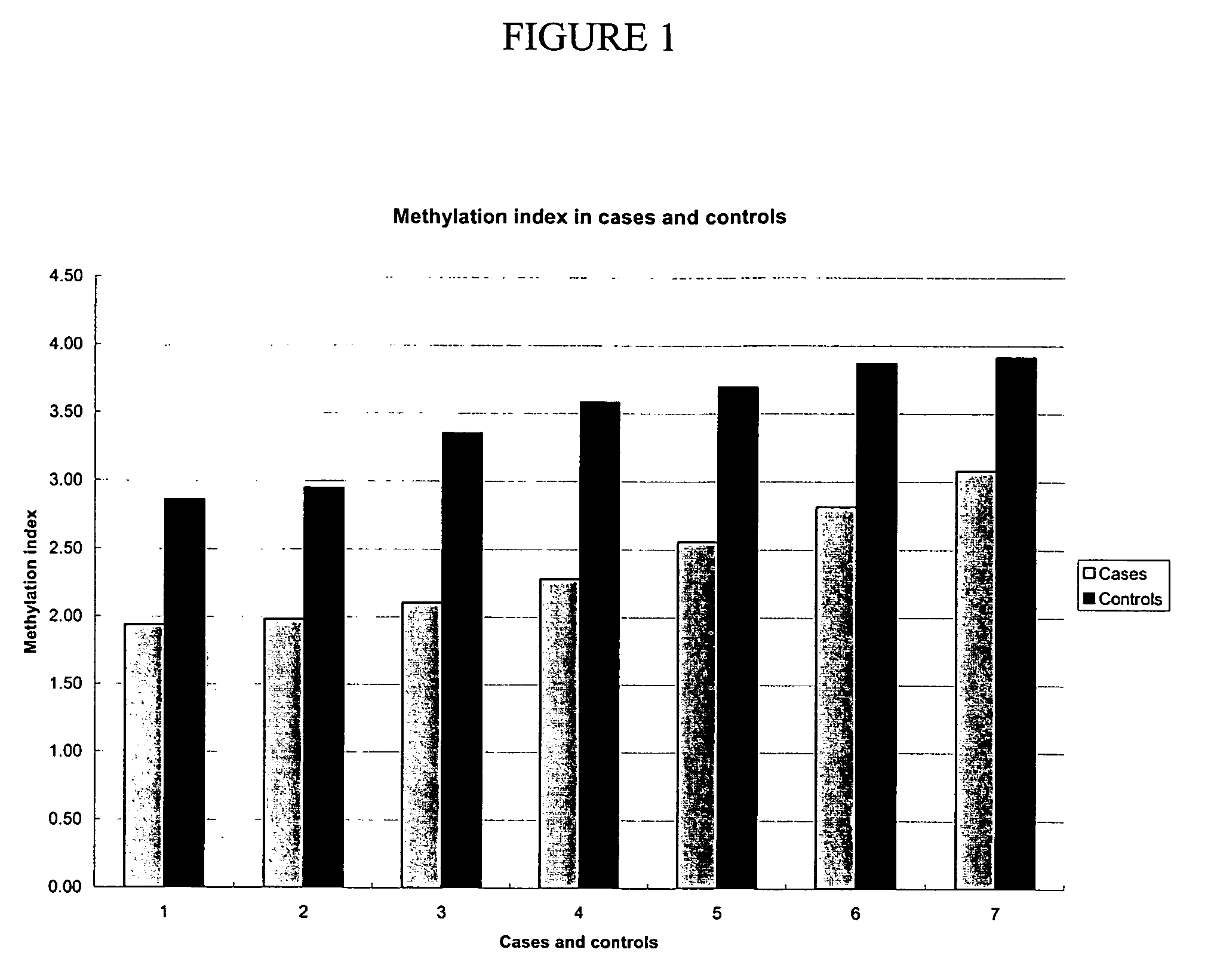
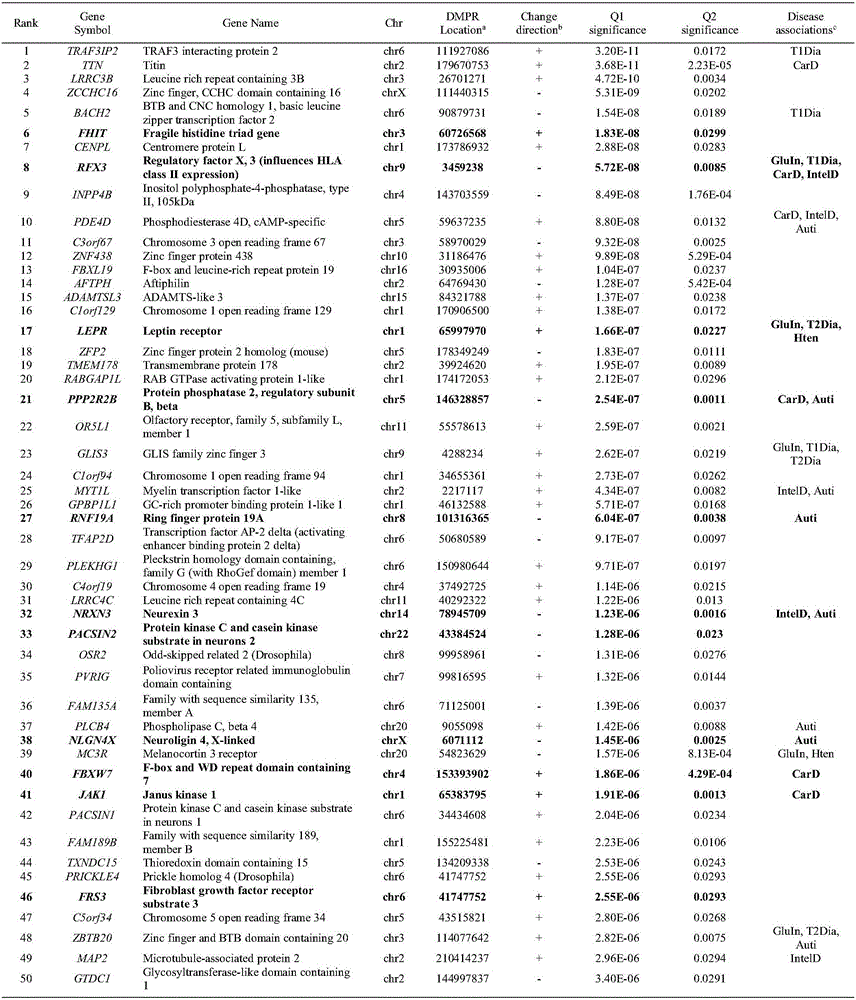
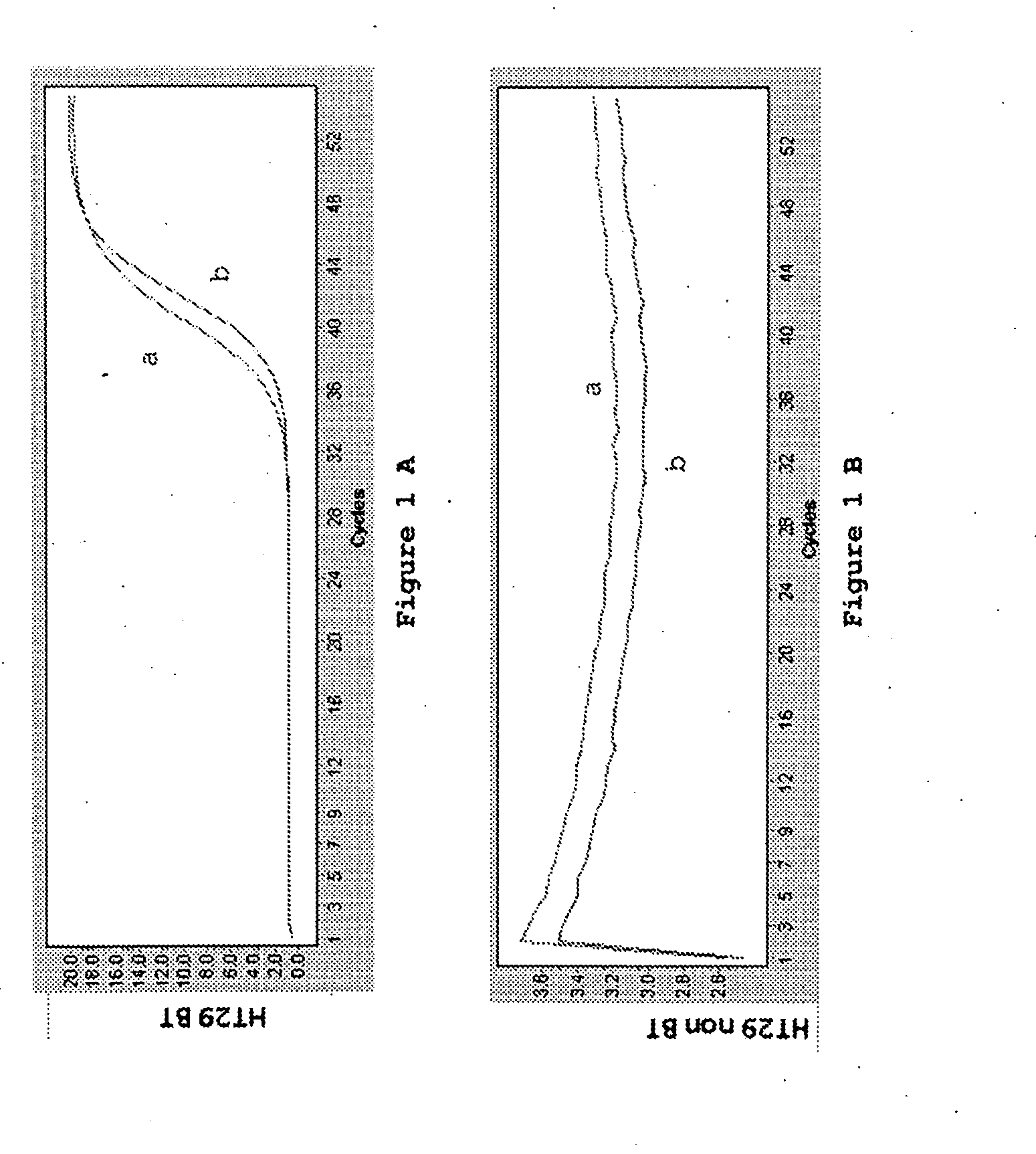
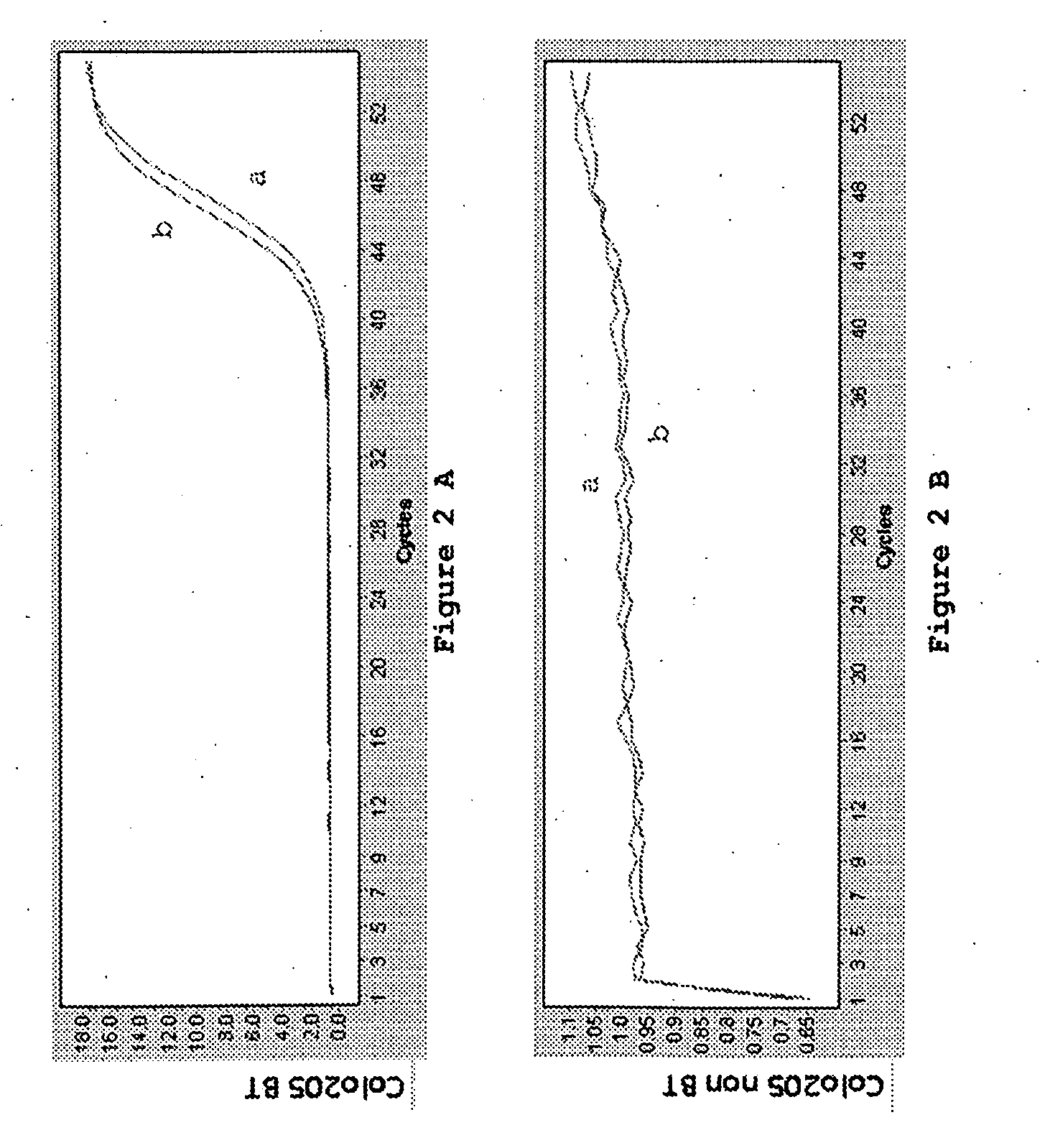
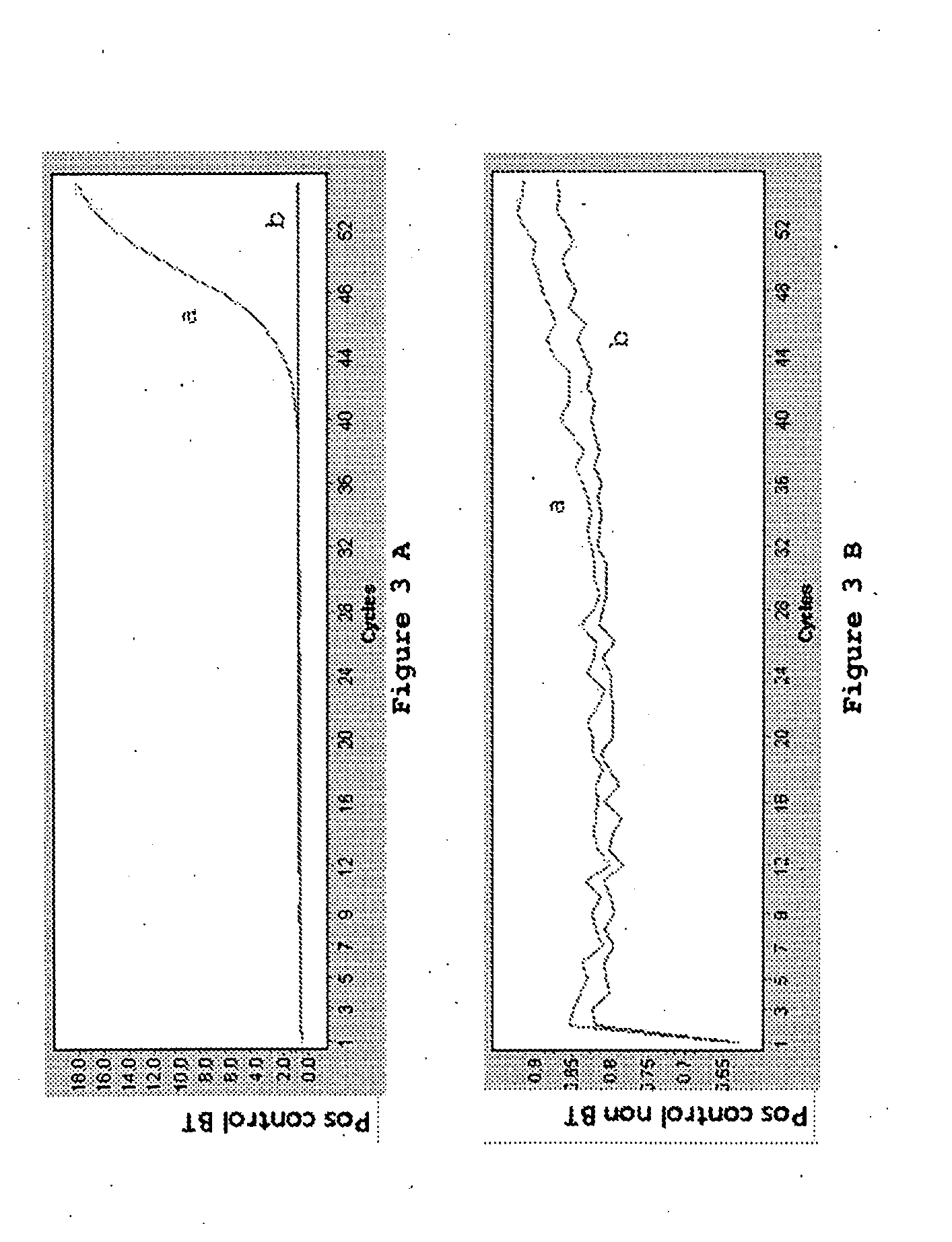
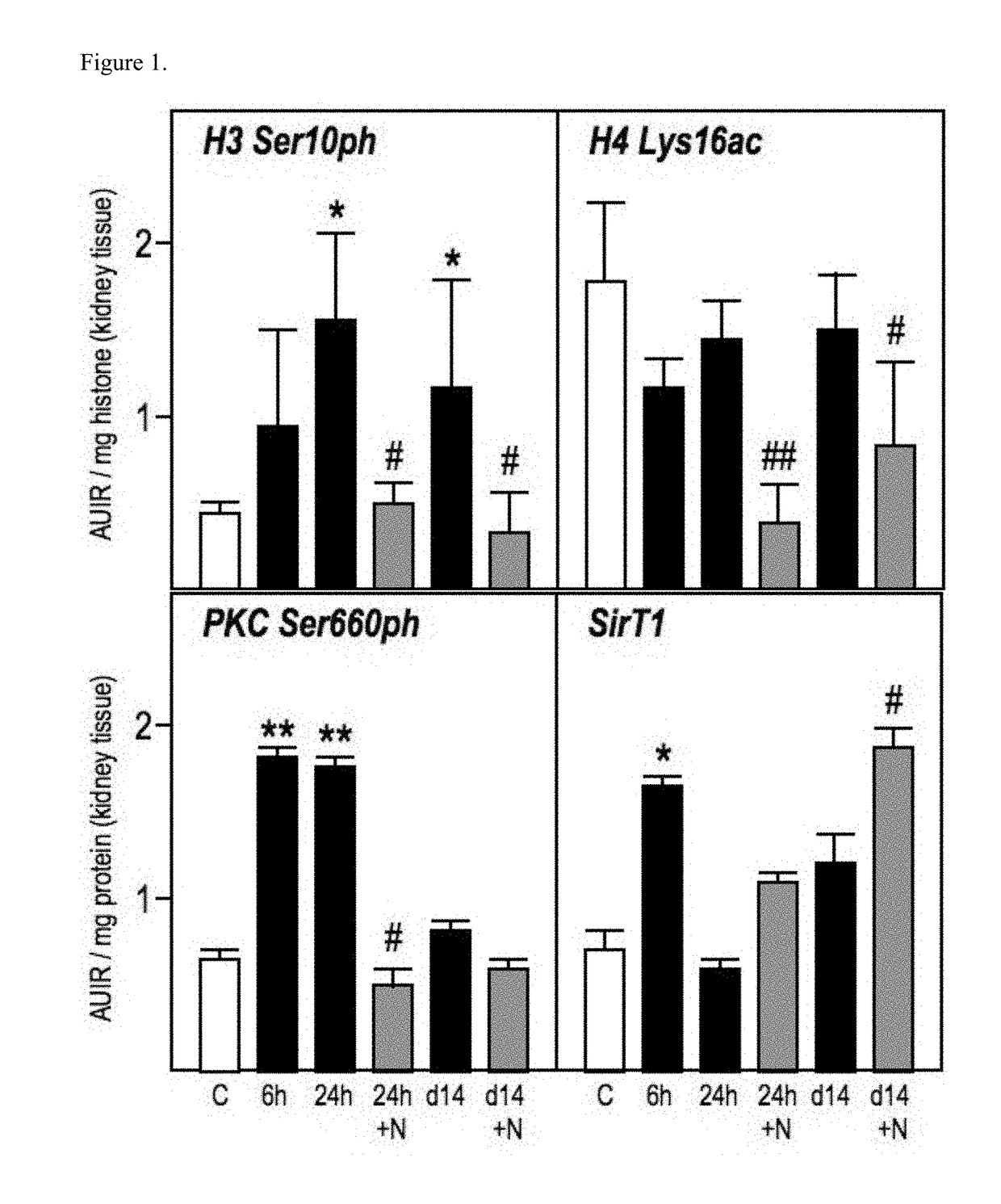
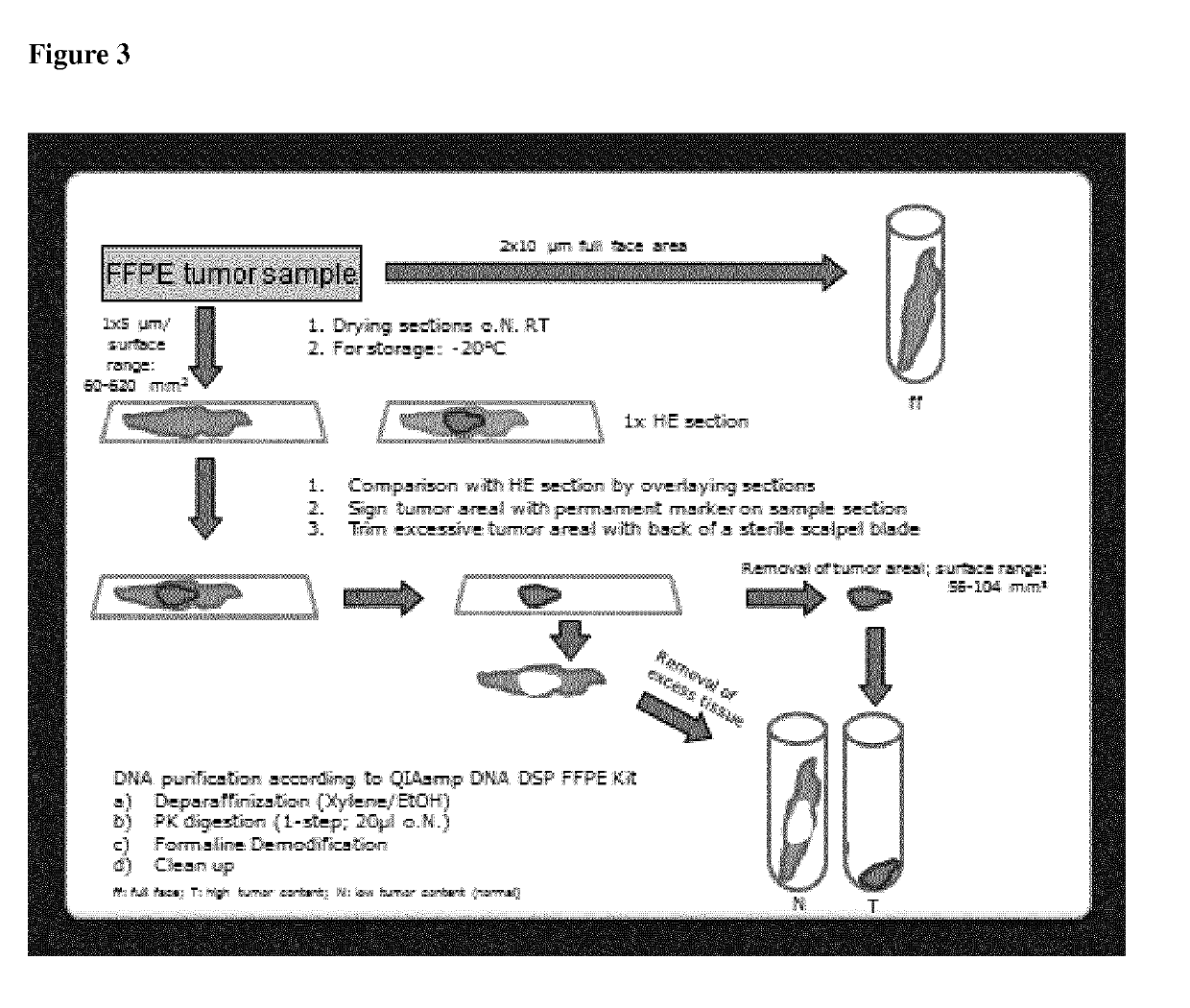
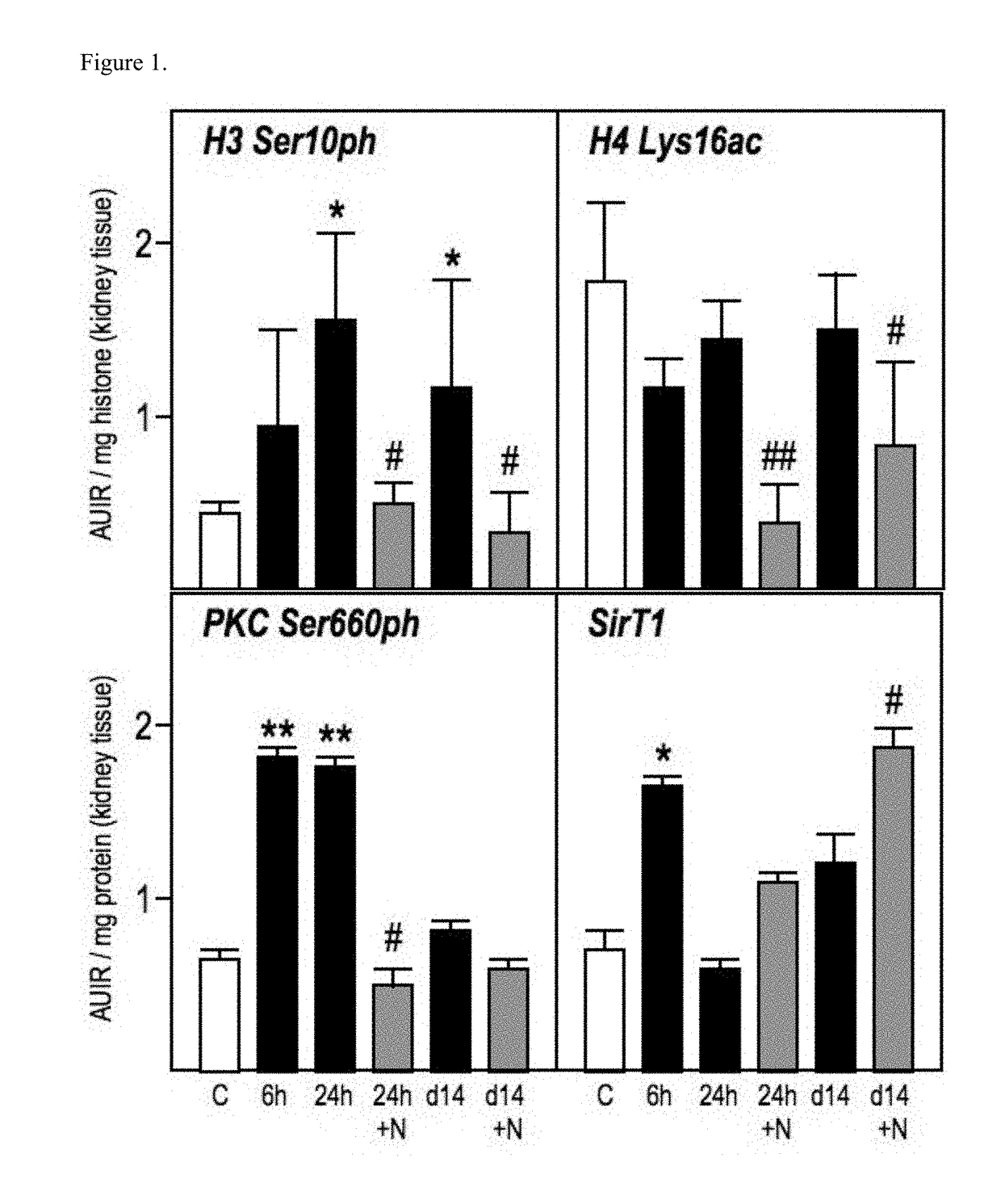
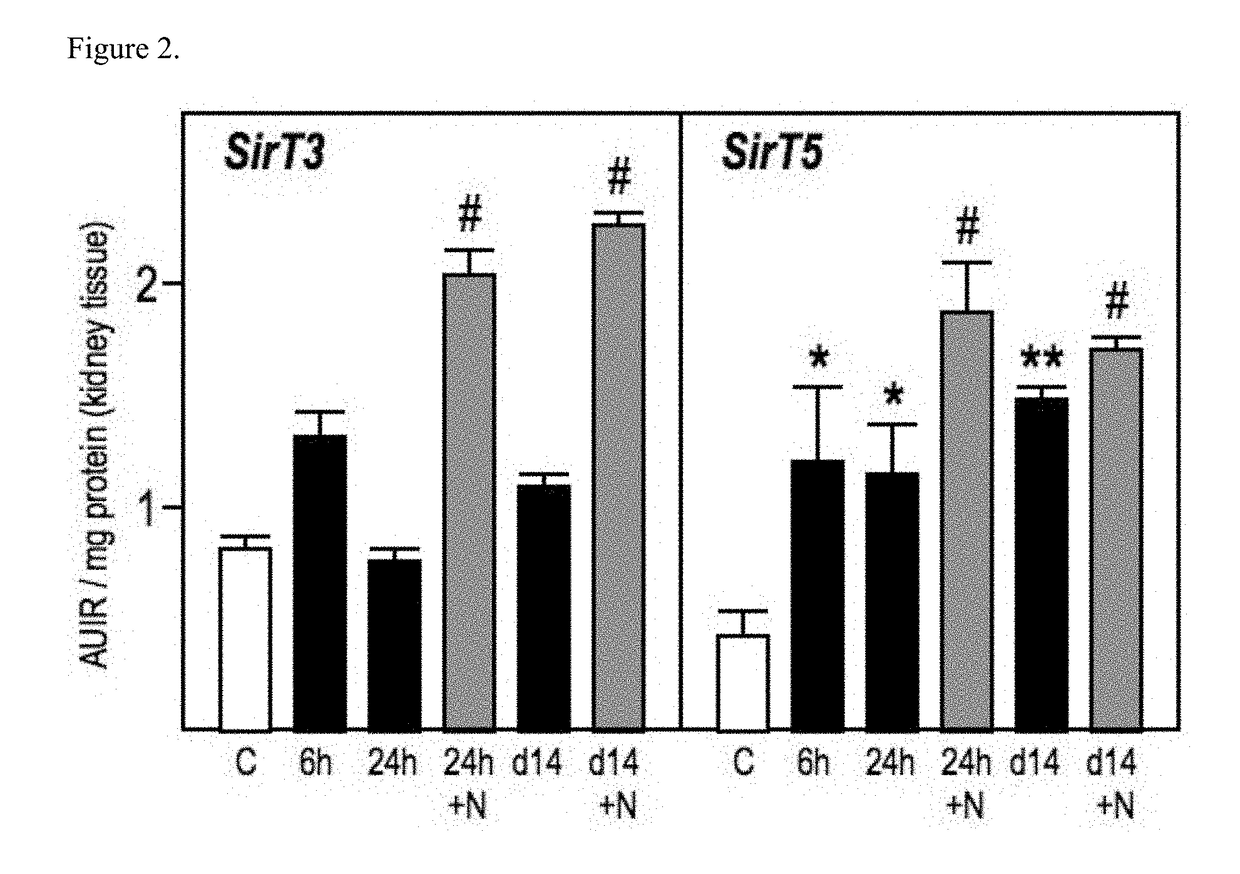
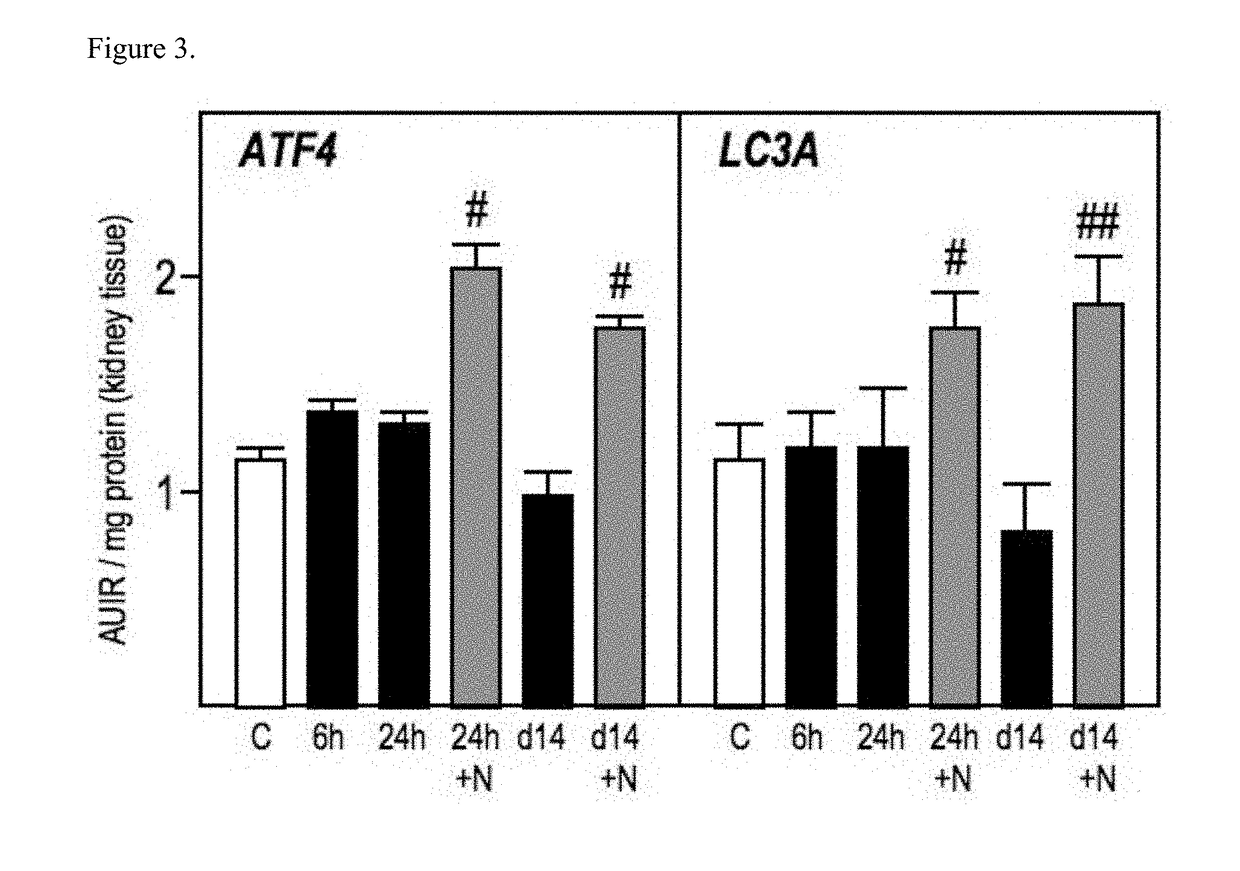
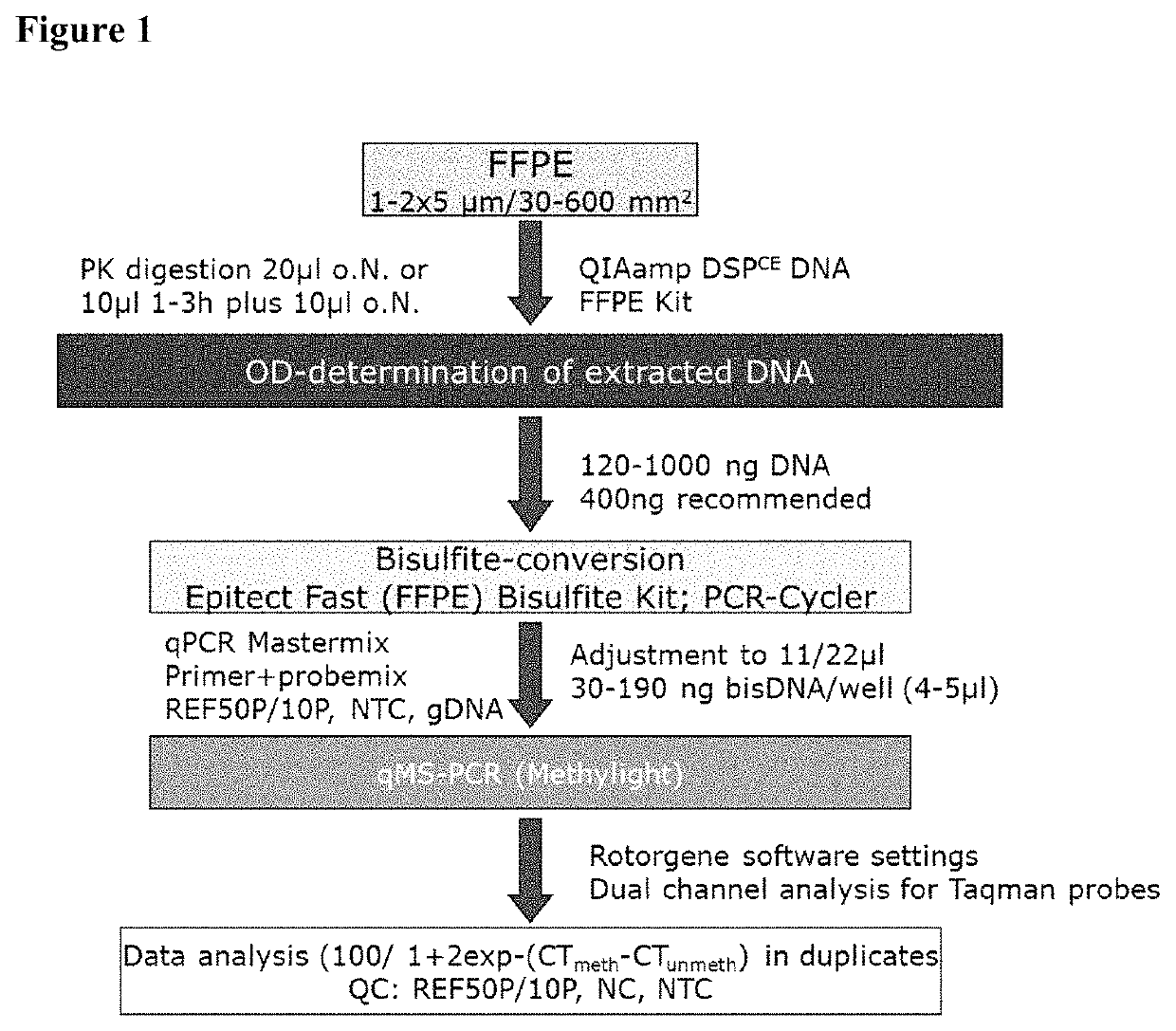
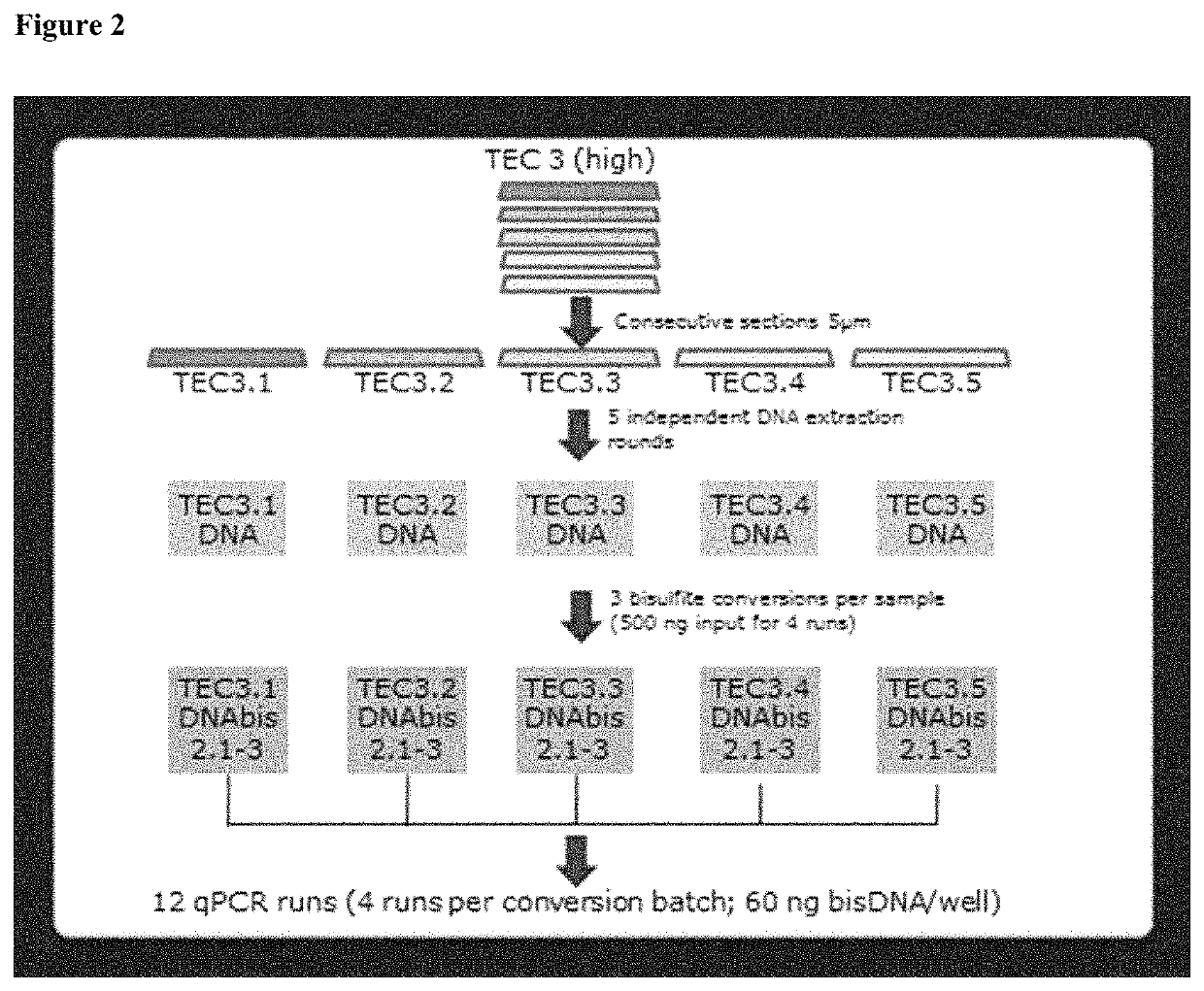
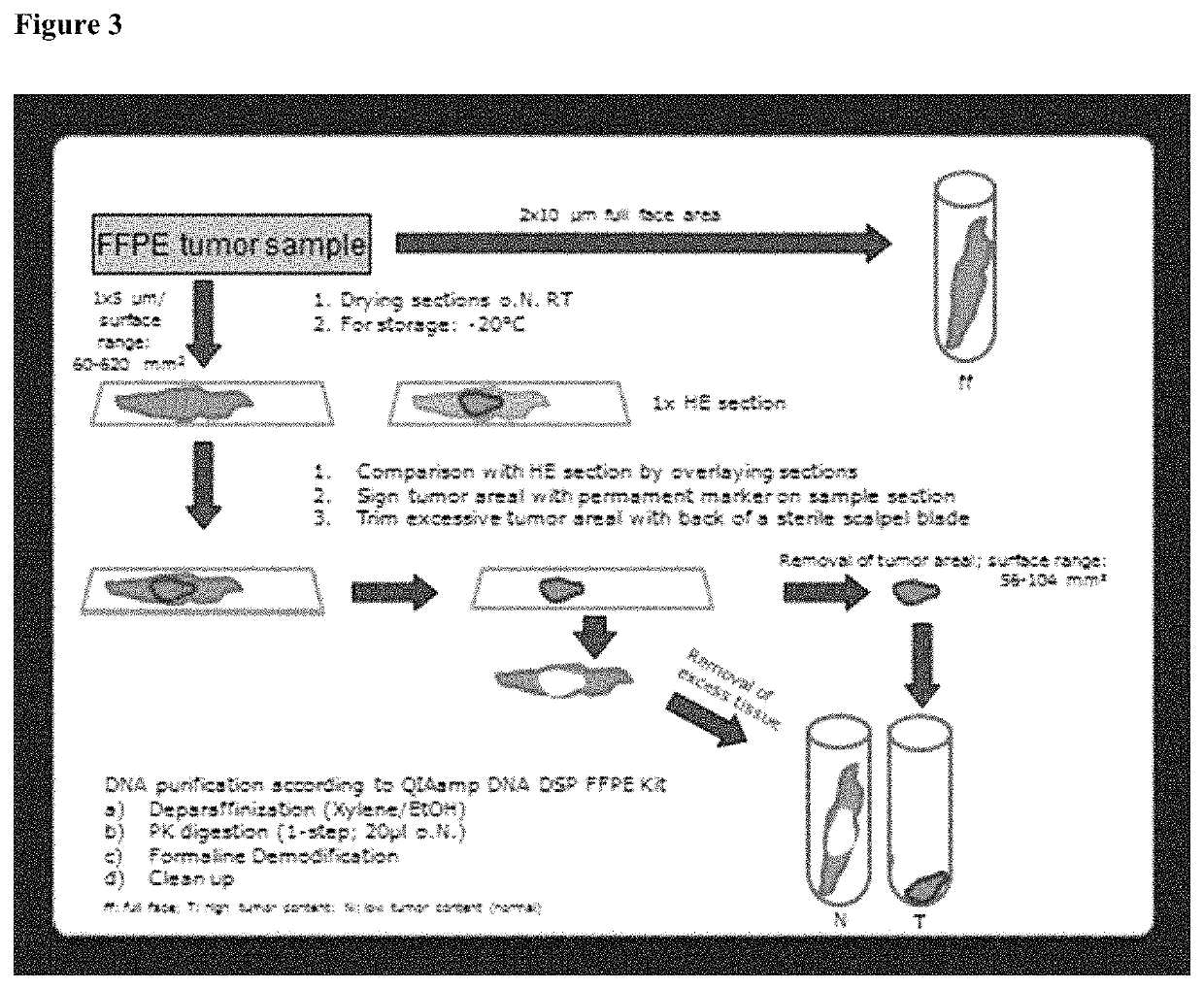
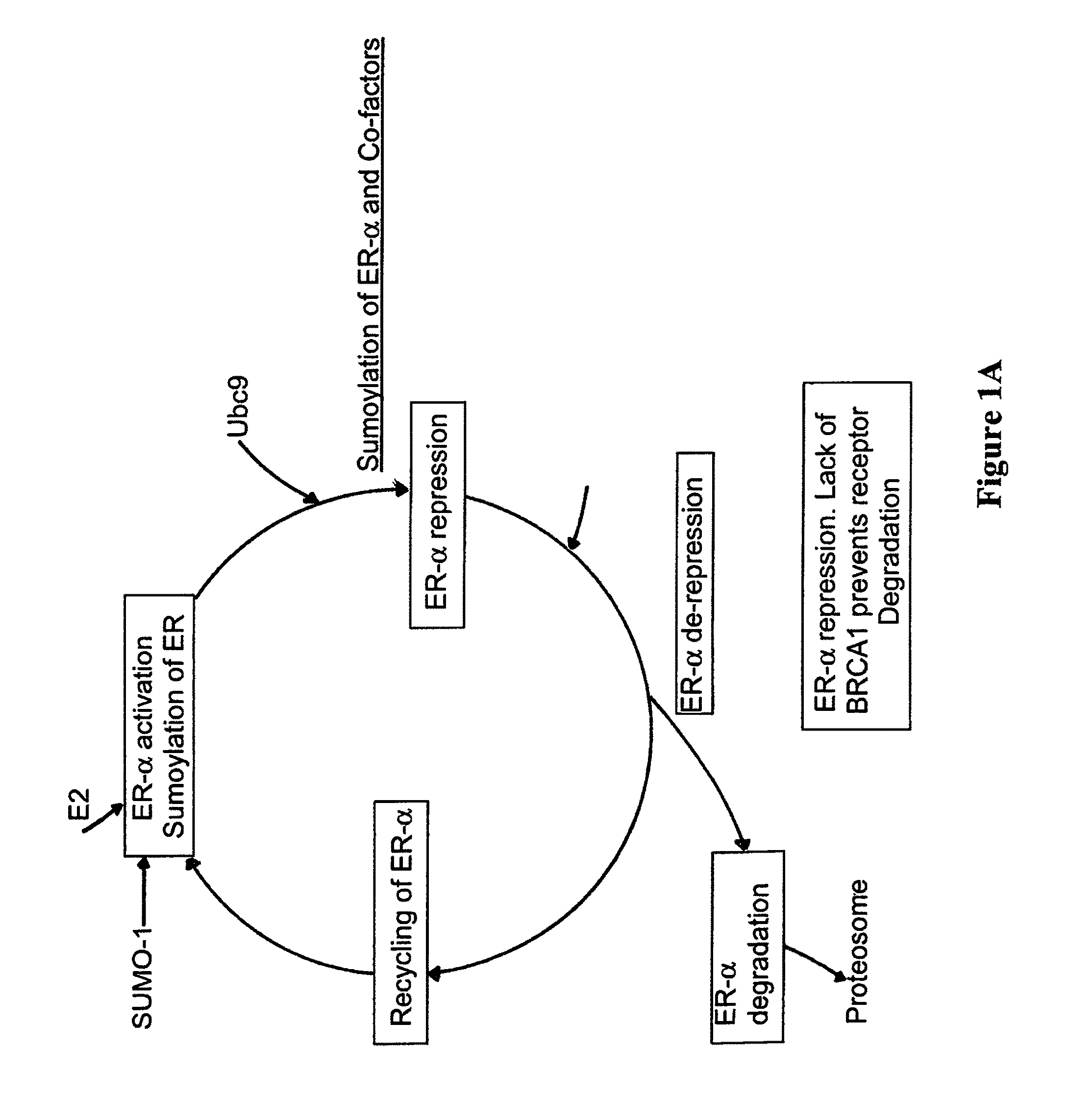
Patents
Literature
36 results about "Epigenetic Change" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Epigenetics literally means "above" or "on top of" genetics. It refers to external modifications to DNA that turn genes "on" or "off.". These modifications do not change the DNA sequence, but instead, they affect how cells "read" genes. Examples of epigenetics. Epigenetic changes alter the physical structure of DNA.
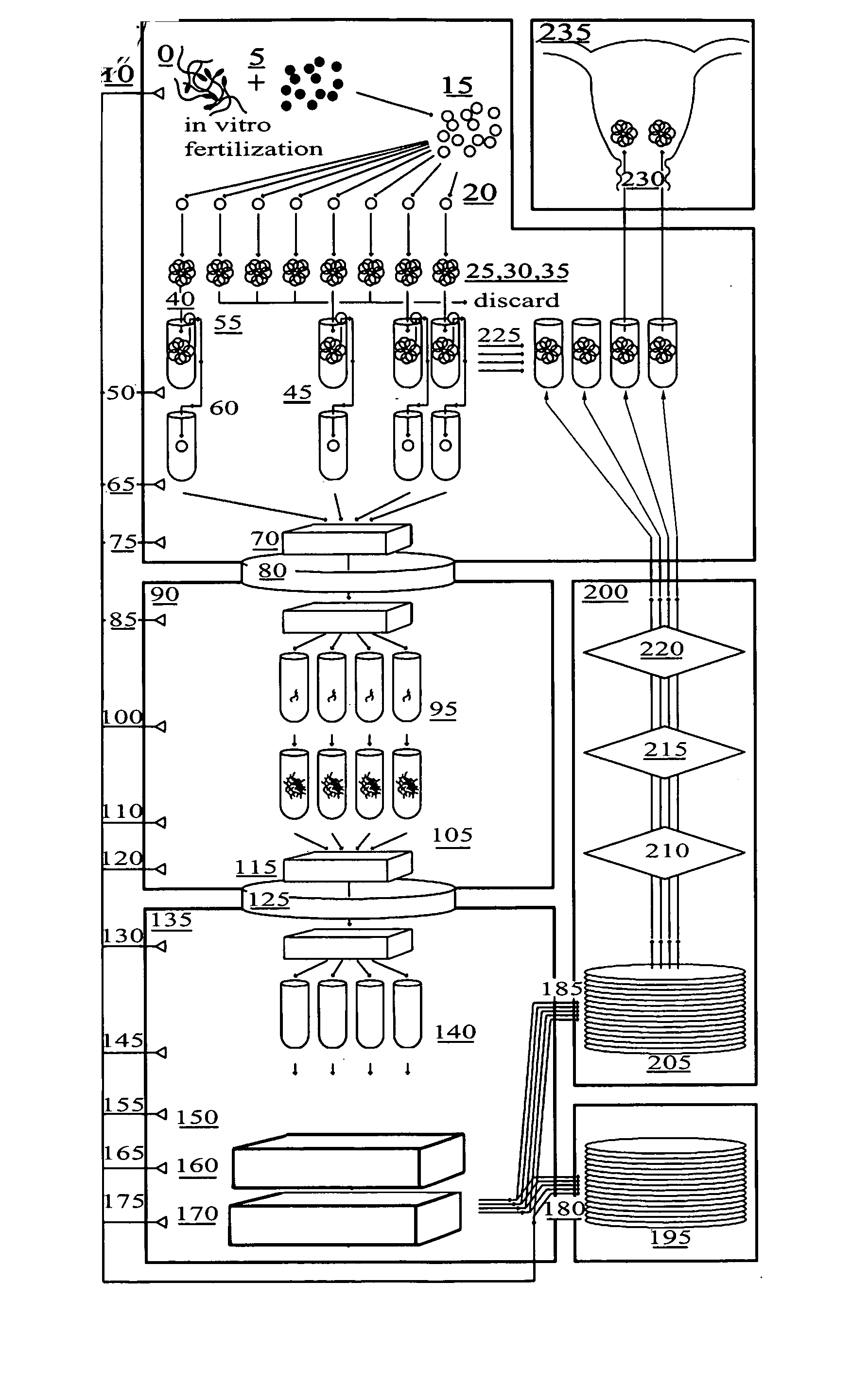
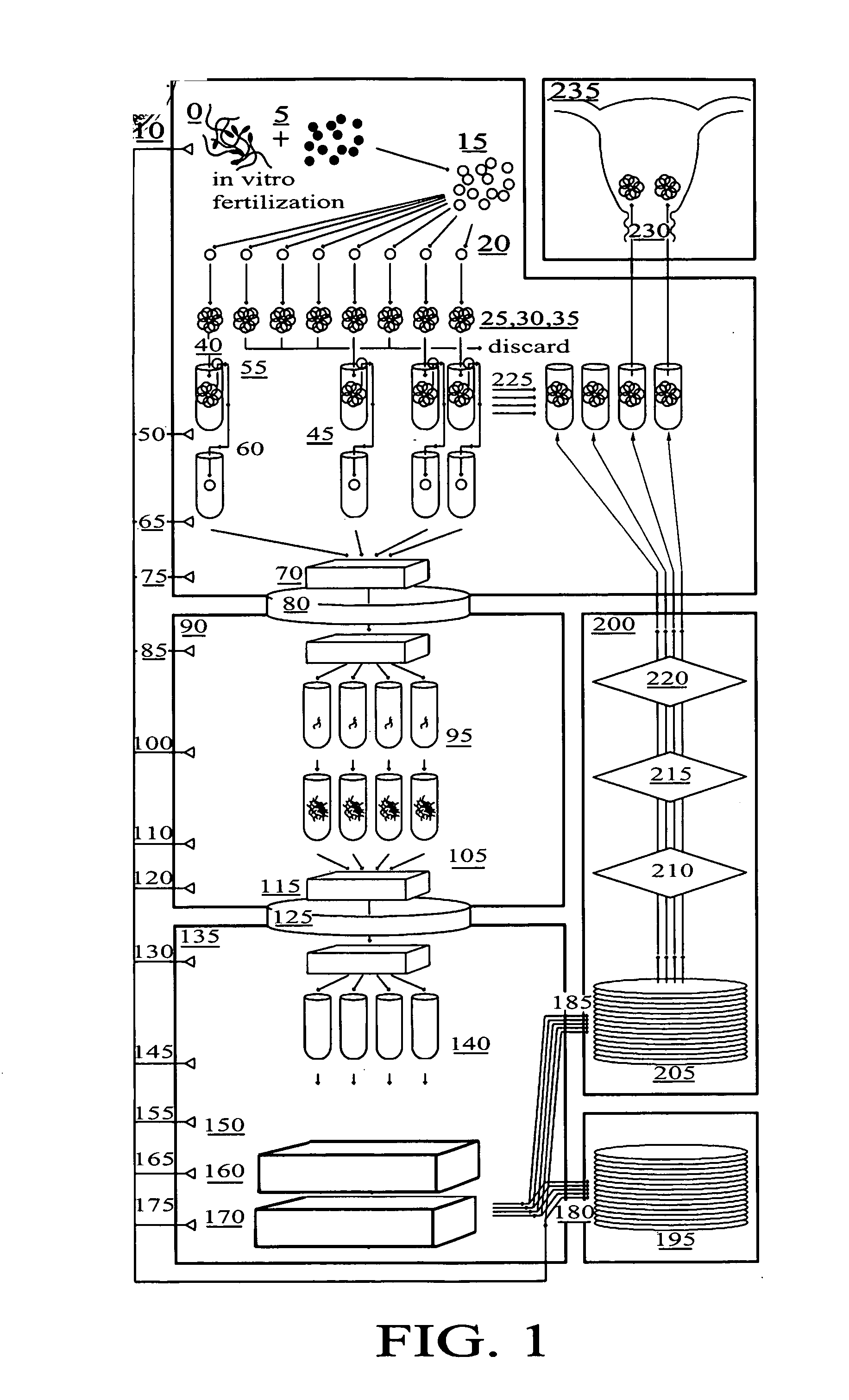
Method for genetic testing of human embryos for chromosome abnormalities, segregating genetic disorders with or without a known mutation and mitochondrial disorders following in vitro fertilization (IVF), embryo culture and embryo biopsy
InactiveUS20080085836A1Reduce significant riskImprove the level ofLibrary screeningLibrary member identificationLess invasiveContamination
We describe a method for interrogating the content and primary structure of DNA by microarray analyses and to provide comprehensive genetic screening and diagnostics prior to embryo transfer within an IVF setting. We will accomplish this by the following claims: 1) an optimized embryo grading system, 2) a less invasive embryo biopsy with reduced cellular contamination, 3) an optimized DNA amplification protocol for single cells, 4) identify aneuploidy and structural chromosome abnormalities using microarrays, 5) identifying sub-telomeric chromosome rearrangements, 6) a modified DNA fingerprinting protocol, 7) determine imprinting and epigenetic changes in developing embryos, 8) performing genome-wide scans to clarify / diagnose multi-factorial genetic disease and to determine genotype / haplotype patterns that may predict future disease, 9) determining single gene disorders with or without a known DNA mutation, 10) determining mtDNA mutations and / or the combination of mtDNA and genomic (nuclear) DNA aberrations that cause genetic disease.
Owner:KEARNS WILLIAM G +1
Regulation of epigenetic control of gene expression
Methods are provided for the identification of compounds that selectively modulate epigenetic changes in gene expression. Compounds, compositions, kits or assays devices, and methods are provided for modulating the expression, endogenous levels or the function of small non-coding RNAs cognate to or transcribed by heterochromatic regions subject to epigenetic regulation (i.e., promoters, enhancers, centromeres, telomeres, origins of DNA replication, imprinted loci, or loci marked by dosage-compensation), and for modulating the formation or function of heterochromatin in cells, tissues or animals.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Early detection and prognosis of colon cancers
InactiveCN101688239ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenes mutationTumor specific
We have developed a transcriptome-wide approach to identify genes affected by promoter CpG island hypermethylation and transcriptional silencing in colorectal cancer (CRC). By screening cell lines andvalidating tumor specific hypermethylation in a panel of primary human CRC samples, we estimate that nearly 5% of all known genes may be promoter methylated in an individual tumor. When directly compared to gene mutations, we find a much larger number of genes hypermethylated in individual tumors, and much higher frequency of hypermethylation within individual genes harboring either genetic or epigenetic changes. Thus, to enumerate the full spectrum of alterations in the human cancer genome, and facilitate the most efficacious grouping of tumors to identify cancer biomarkers and tailor therapeutic approaches, both genetic and epigenetic screens should be undertaken. The genes we identified can be used inter alia diagnostically to detect cancer, pre-cancer, and likelihood of developing cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Epigenetic biomarkers for early detection, therapeutic effectiveness, and relapse monitoring of cancer
InactiveUS20100151468A1Strong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisEarly Cancer DetectionHistone H4
The present invention provides methods of detection, including early detection, for cancer or other diseases and normal physiologic processes mediated by global epigenetic changes, by using one or more of the following biomarkers: a global DNA methylation index, a global histone H4 acetylation index, and a global histone H4 trimethylation index. These methods are useful for, among other things, assessing the effectiveness of treatment, monitoring relapse, and clinical staging of cancer and other chronic as well as acute diseases. These methods are also useful for among other things monitoring the effectiveness of strategies and therapies used to modify lifestyle and contextual effects to prevent disease, foster wellness and enable health promotion.
Owner:PRESTON RAFAEL GUERRERO
Early Detection and Prognosis of Colon Cancers
InactiveUS20080221056A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGenes mutationBiomarker (petroleum)
We have developed a transcriptome-wide approach to identify genes affected by promoter CpG island hypermethylation and transcriptional silencing in colorectal cancer (CRC). By screening cell lines and validating tumor specific hypermethylation in a panel of primary human CRC samples, we estimate that nearly 5% of all known genes may be promoter methylated in an individual tumor. When directly compared to gene mutations, we find a much larger number of genes hypermethylated in individual tumors, and much higher frequency of hypermethylation within individual genes harboring either genetic or epigenetic changes. Thus, to enumerate the full spectrum of alterations in the human cancer genome, and facilitate the most efficacious grouping of tumors to identify cancer biomarkers and tailor therapeutic approaches, both genetic and epigenetic screens should be undertaken. The genes we identified can be used inter alia diagnostically to detect cancer, pre-cancer, and likelihood of developing cancer.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Gene function association network-based method for discovering chronic disease mechanism and early warning intervention policy thereof
ActiveCN106126893AShow validityEpigenetic far-reachingHealth-index calculationProteomicsDisease riskCrowds
The present invention discloses a gene function association network-based method for discovering a chronic disease mechanism and an early warning intervention policy thereof. The method can be applied to the field of related research and application of biology, medicine and pharmacy. Epigenetic changes of the high-risk groups surveyed and discovered according to epidemiology before disease attack are detected, the epigenetic changes before the disease is associated with indicator gene changes of the disease through gene function network analysis, then a long-term molecular mechanism contributing to the disease risk is discovered, and risk early warning for the group, risky diagnosis for an individual, and indicators and methods for preventive intervention are provided. According to the method, a long-term steady biological path or biological function change may leave a mark on related gene epigenetic inheritance, and a chronic disease biological path or biological function level mechanism may be found through analysis of the synergistic effect of epigenetic differences.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Markers for Bladder Cancer Detection
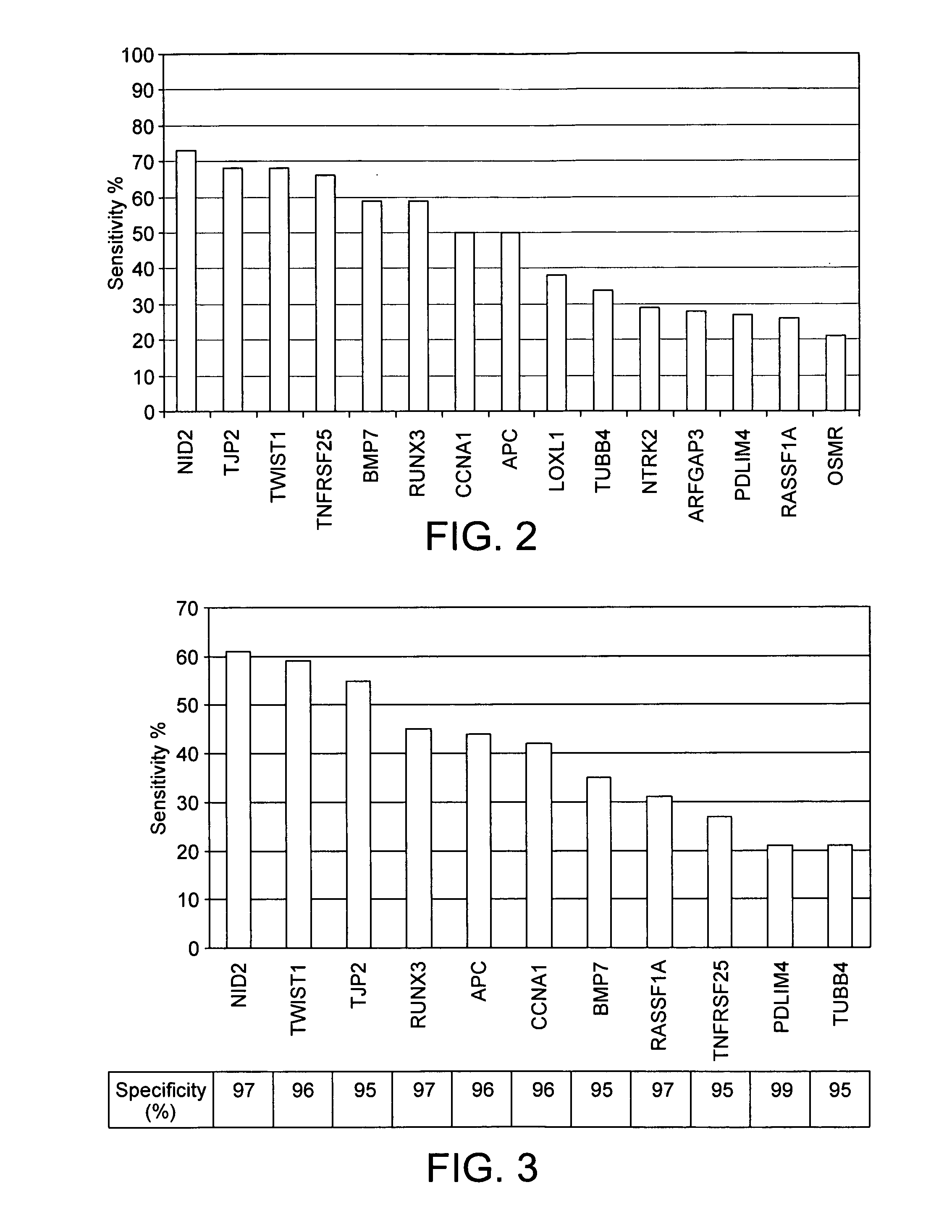
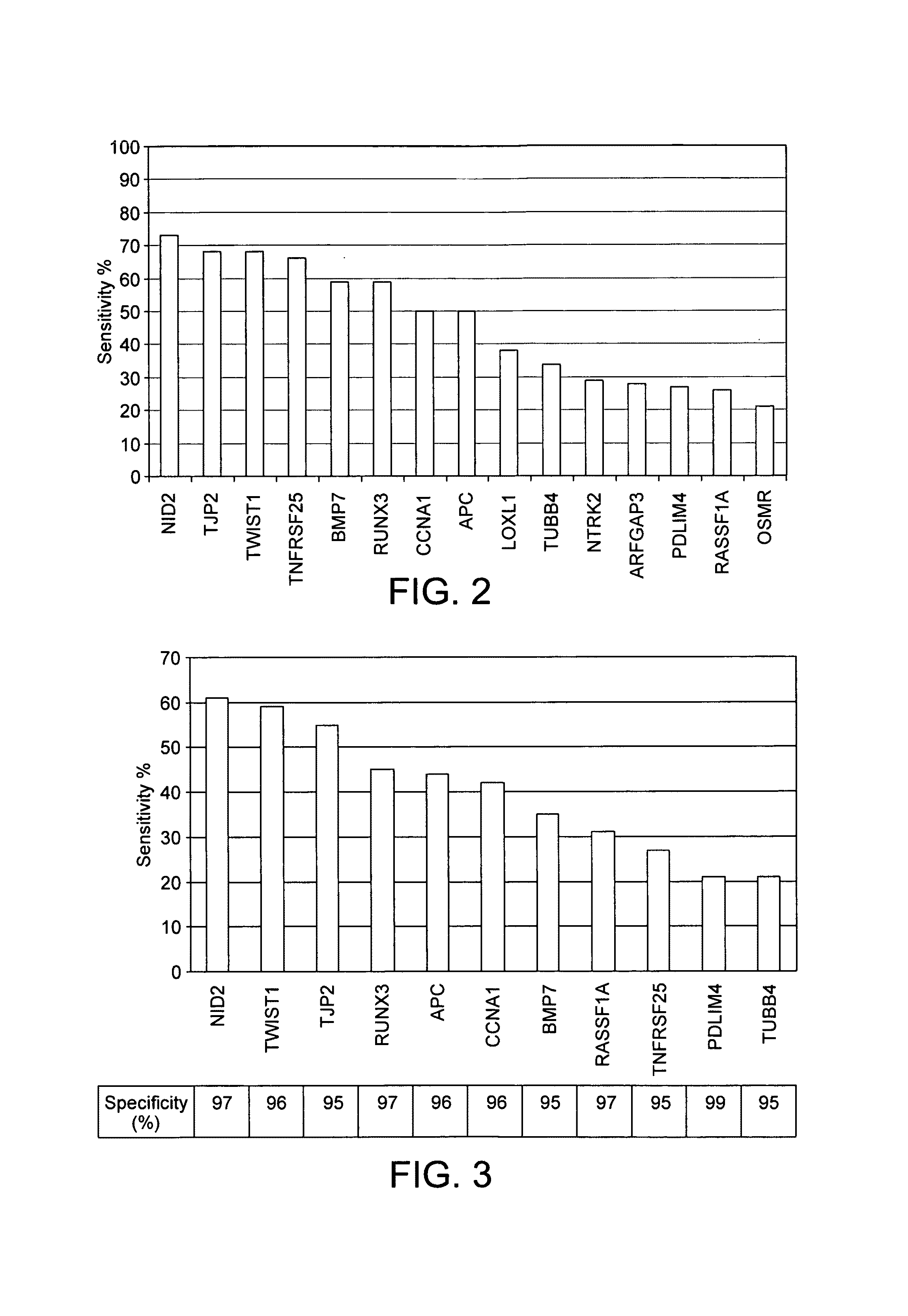
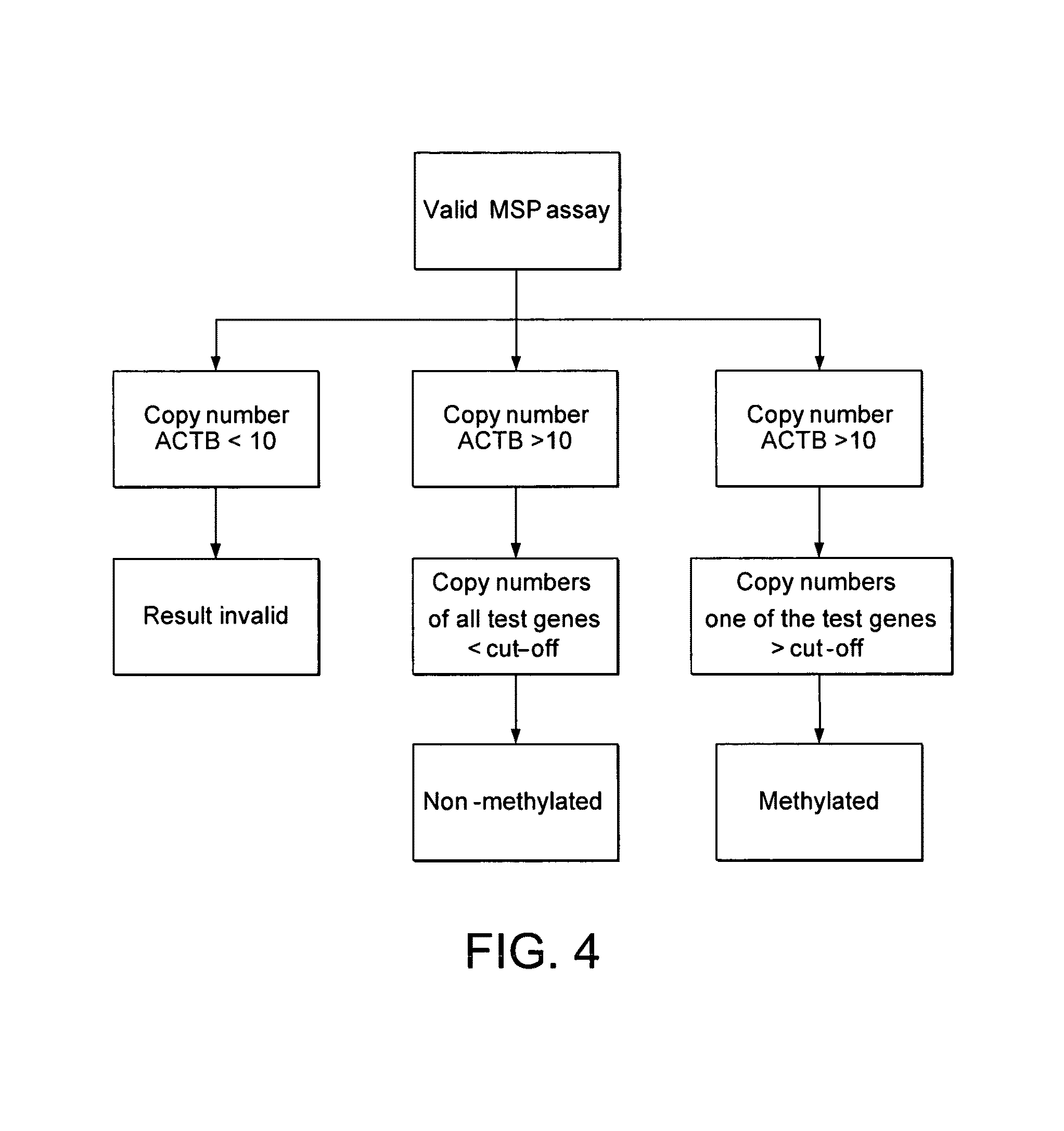
ActiveUS20100280134A1Reduce the possibilityAvoid the needBiocideSugar derivativesBladder cancerBacteriuria
A method of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprises detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from TWIST1, NID2, RUNX3, BMP7, CCNA1, PDLIM4, TNFRSF25, APC, RASSF1A, LOXL1, TUBB4, NTRK2, ARFGAP3, OSMR and TJP2. Detection of the epigenetic change is indicative of a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer. The gene may be TWIST1 or a panel of genes such as TWIST1, NID2 and RUNX3 may be screened. The epigenetic change may be methylation. A kit for detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprises at least one primer pair for determining the methylation status of each of NID2, TWIST1 and RUNX3. A kit for detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprises means for detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from TWIST1, NID2, RUNX3, BMP7, CCNA1, PDLIM4, TNFRSF25, APC, RASSF1A, LOXL1, TUBB4, NTRK2, ARFGAP3, OSMR and TJP2. The kit also contains means for processing a urine sample.
Owner:ONCOMETHYLOME SCI
Methylation detection
InactiveUS20090176655A1Reduce the possibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEpigenetic ProfileDifferential Methylation
A method of identifying nucleic acid molecules differentially methylated in a disease comprises steps of incubating fragmented DNA, from a disease cell, with a reagent which specifically binds to methylated DNA to thus concentrate methylated DNA fragments, incubating fragmented DNA, from a disease cell related to the disease cell utilised in step (a) in which DNA methyltransferase expression and / or activity has been inhibited, with a reagent which specifically binds to methylated DNA to thus concentrate methylated DNA fragments and comparing the methylated DNA fragments obtained in steps (a) and (b) to identify nucleic acid molecules differentially methylated in the disease. A method of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, colorectal cancer in a sample comprises detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from RASGRF2, SCNN1B, HOXD1, PLK2 and BHLHB9 wherein detection of the epigenetic change is indicative of a predisposition to, or the incidence of, colorectal cancer.
Owner:ONCOMETHLOME SCI
Methods of detecting long range chromosomal interactions
The present invention relates to a method of monitoring epigenetic changes comprising monitoring changes in conditional long range chromosomal interactions at at least one chromosomal locus where the spectrum of long range interaction is associated with a specific physiological condition, the method comprising the steps of:- (i) in vitro crosslinking of said long range chromosomal interactions present at the at least one chromosomal locus; (ii) isolating the cross linked DNA from said chromosomal locus; (iii) subjecting said cross linked DNA to restriction digestion with an enzyme that cuts at least once within the at least one chromosomal locus; (iv) ligating said cross linked cleaved DNA ends to form DNA loops; (v) identifying the presence of said DNA loops; wherein the presence of DNA loops indicates the presence of a specific long range chromosomal interaction.
Owner:牛津生物动力公开有限公司
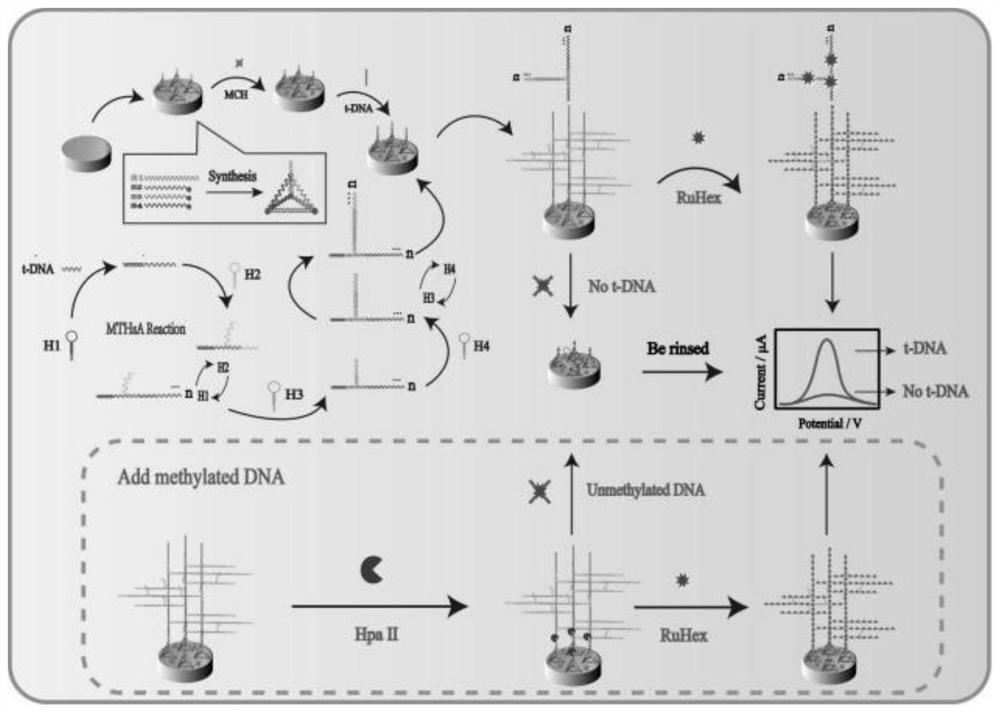
Construction of universal electrochemical biosensor ultra-sensitive detection target based on tetrahedral-tripod-assisted multi-hairpin cascade assembly
InactiveCN112649479AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical biosensorPhosphoric acid
Nucleic acid is an important genetic substance of a human body and plays an important role in storing, copying and transmitting genetic information, methylated DNA is one of main epigenetic modification modes, abnormal DNA sequences, base mutation and epigenetic changes often cause cancers, and in order to realize early target detection, the invention designs a tetrahedron-assisted multi-series hairpin cascade assembly detection target (DNA / RNA / methylated DNA and the like) universal electrochemical sensor, a plurality of hairpin cascade assemblies are incubated to trigger signal amplification reaction, electric signal detection is realized in a RuHex solution, and powerful electrostatic attraction acts on a DNA phosphoric acid skeleton to cause increase of DPV current response. The linear concentration range of target detection is 10 aM to 100 pM, and the lowest detection limit is 1.78 aM. By means of a specific enzyme digestion reaction, methylated DNA is incubated on an electrochemical platform to carry out related experiments, and the superiority of the platform is further proved.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
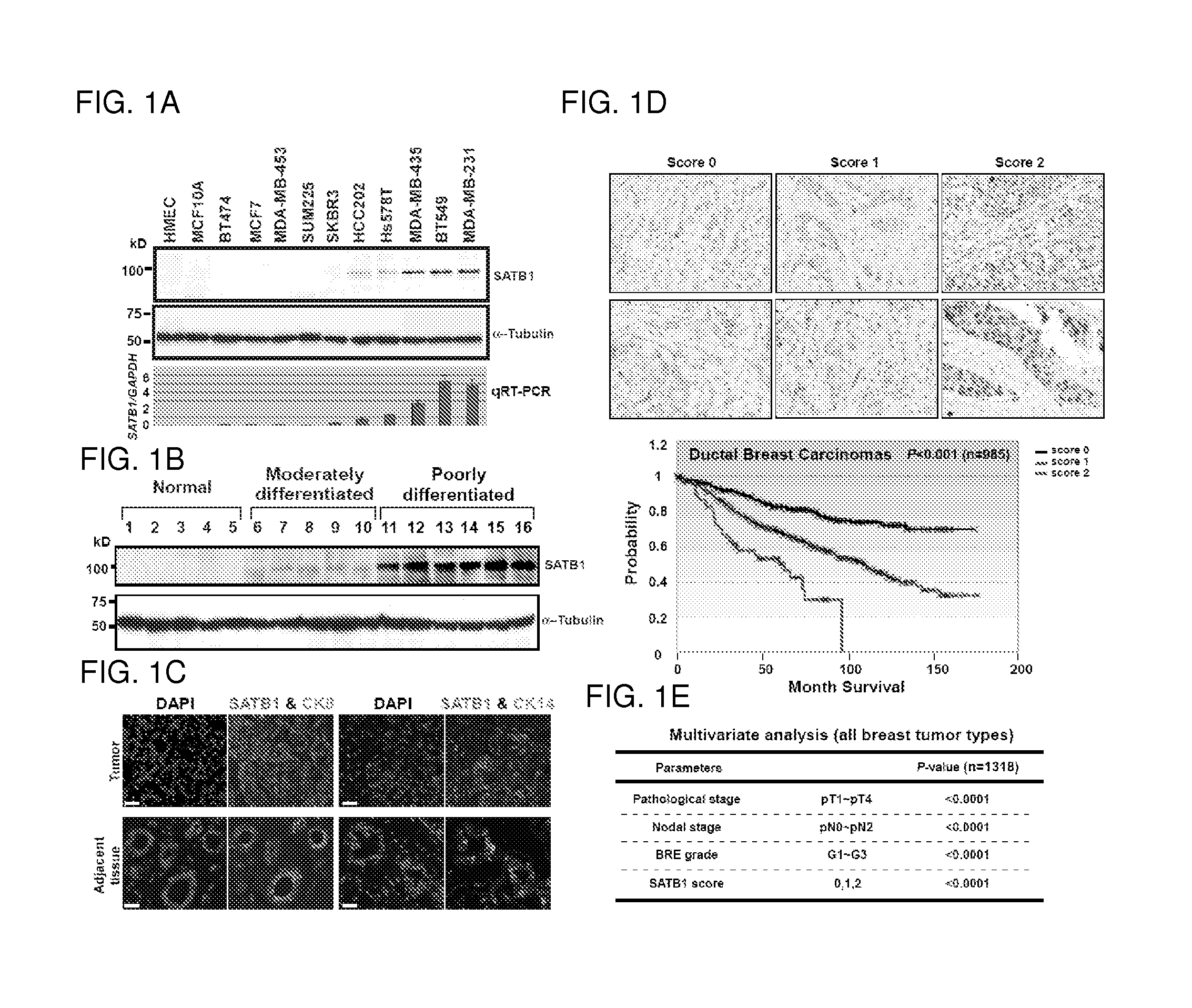
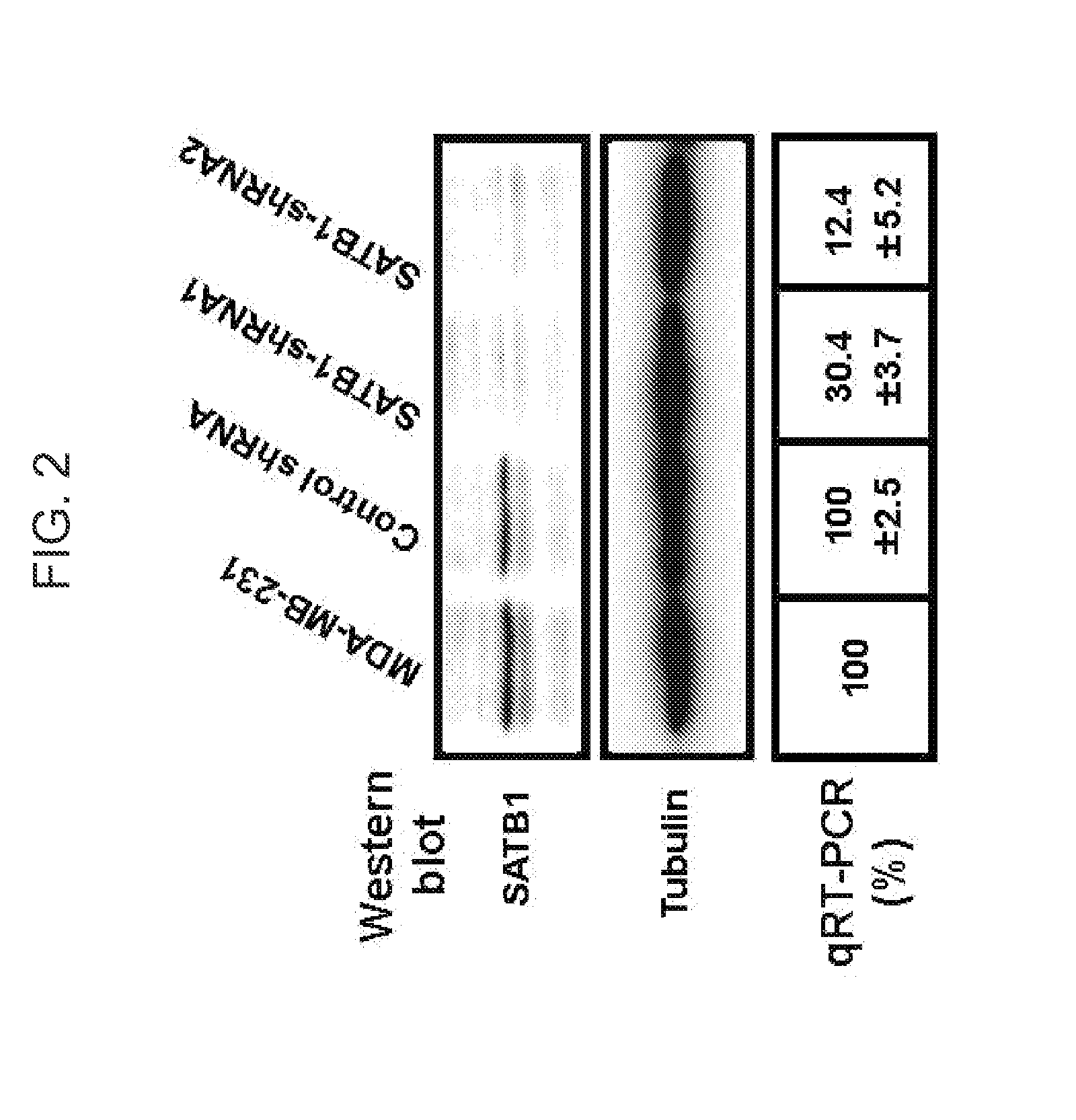
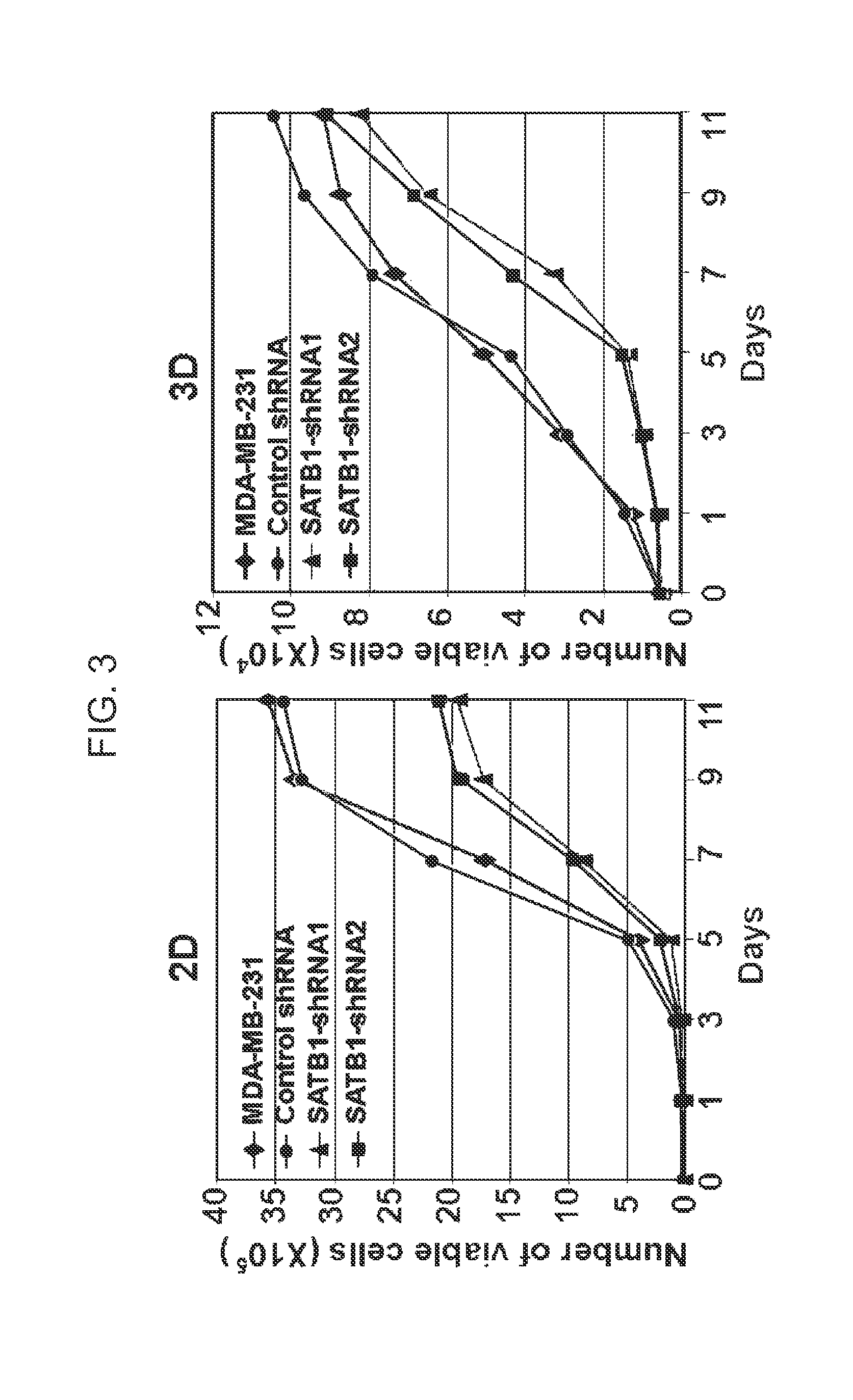
Satb1: a determinant of morphogenesis and tumor metastasis
InactiveUS20080280298A1Reliable diagnosisReliable prognosisOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCancer cellLymphatic Spread
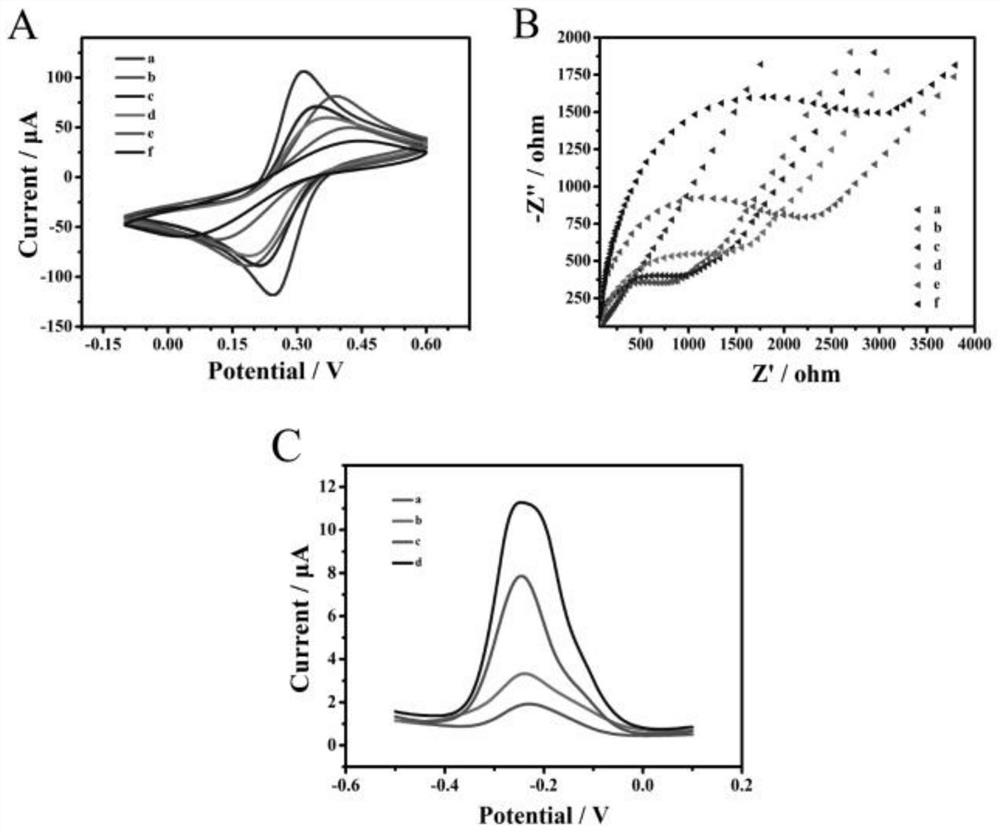
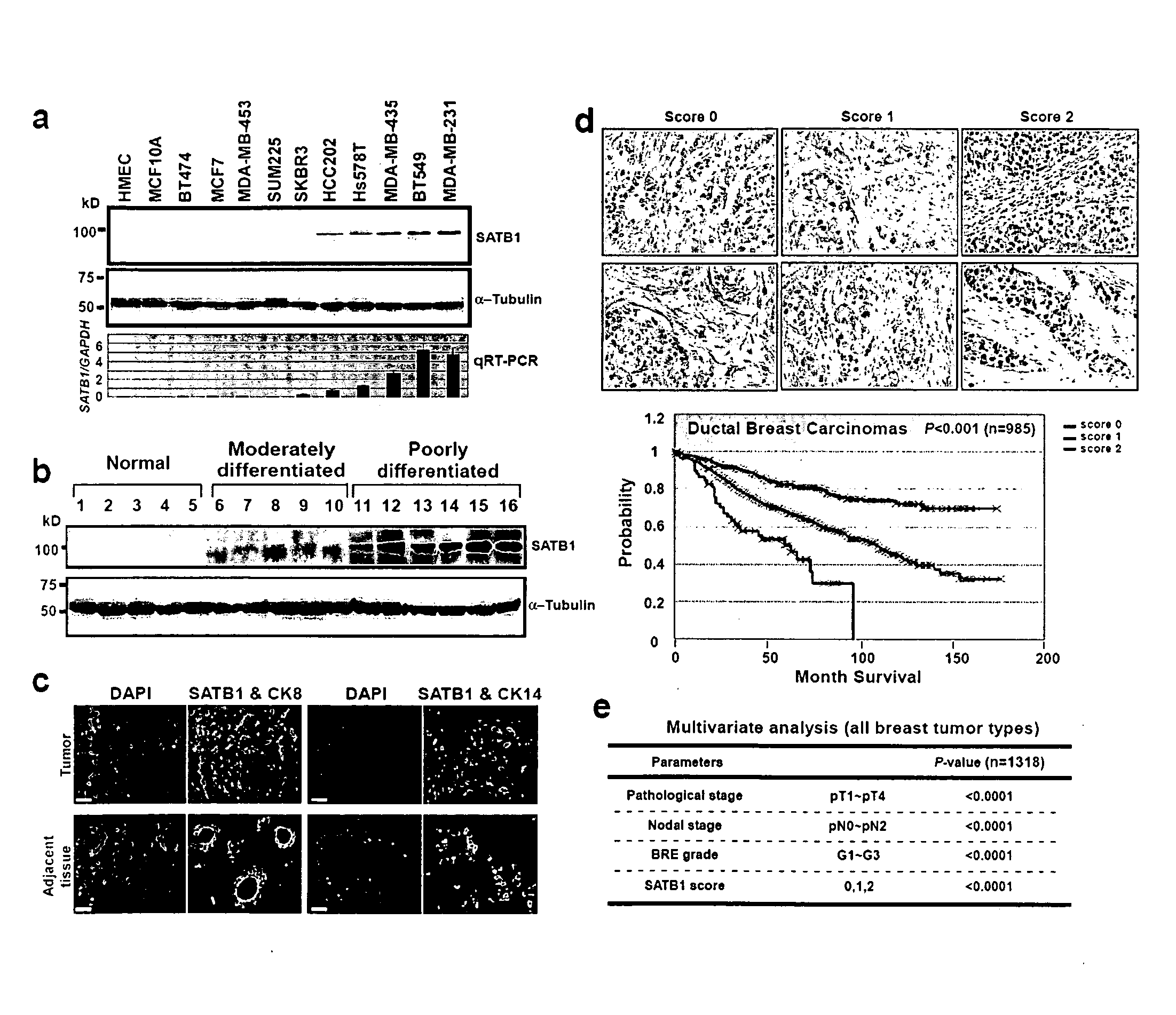
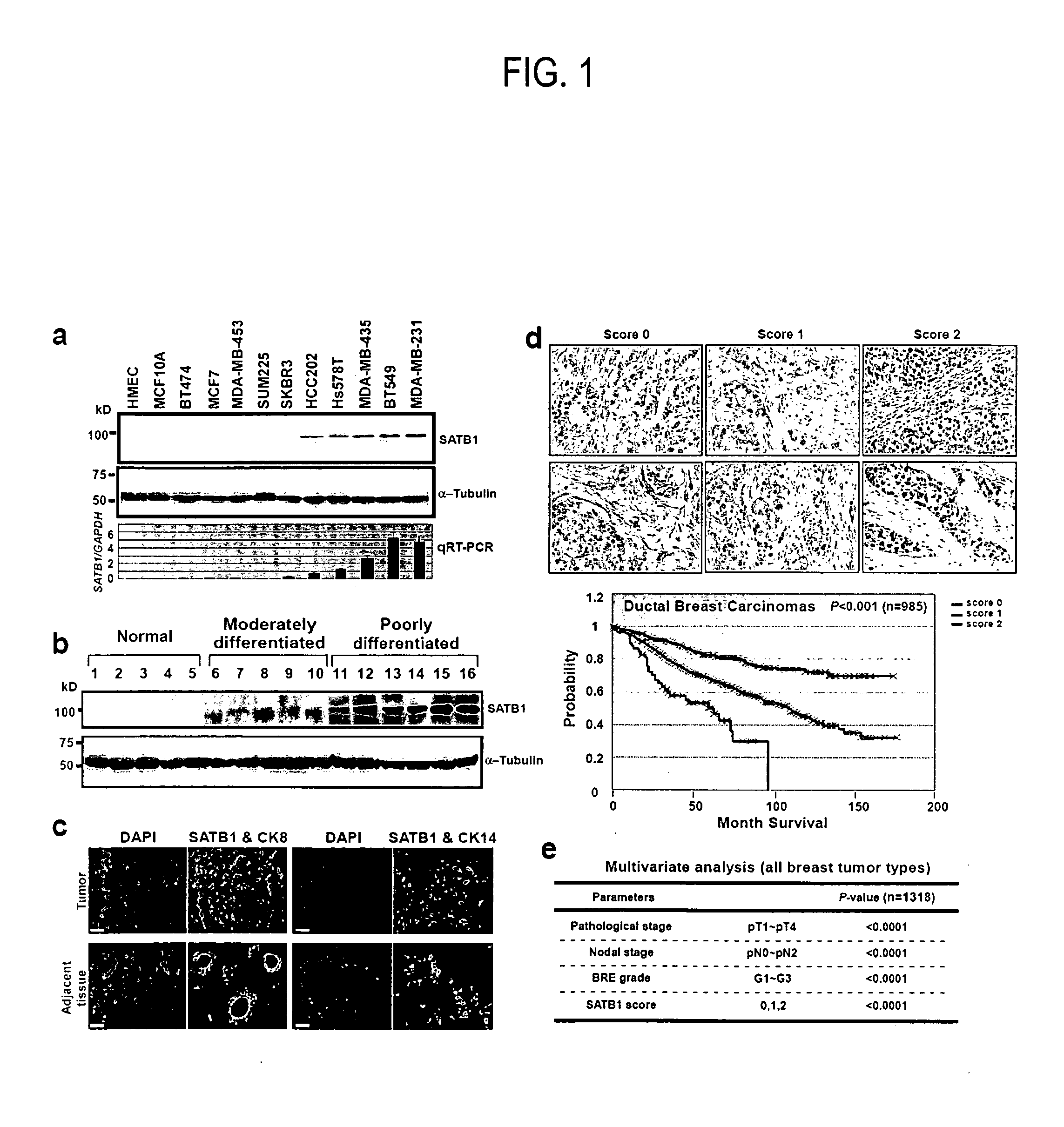
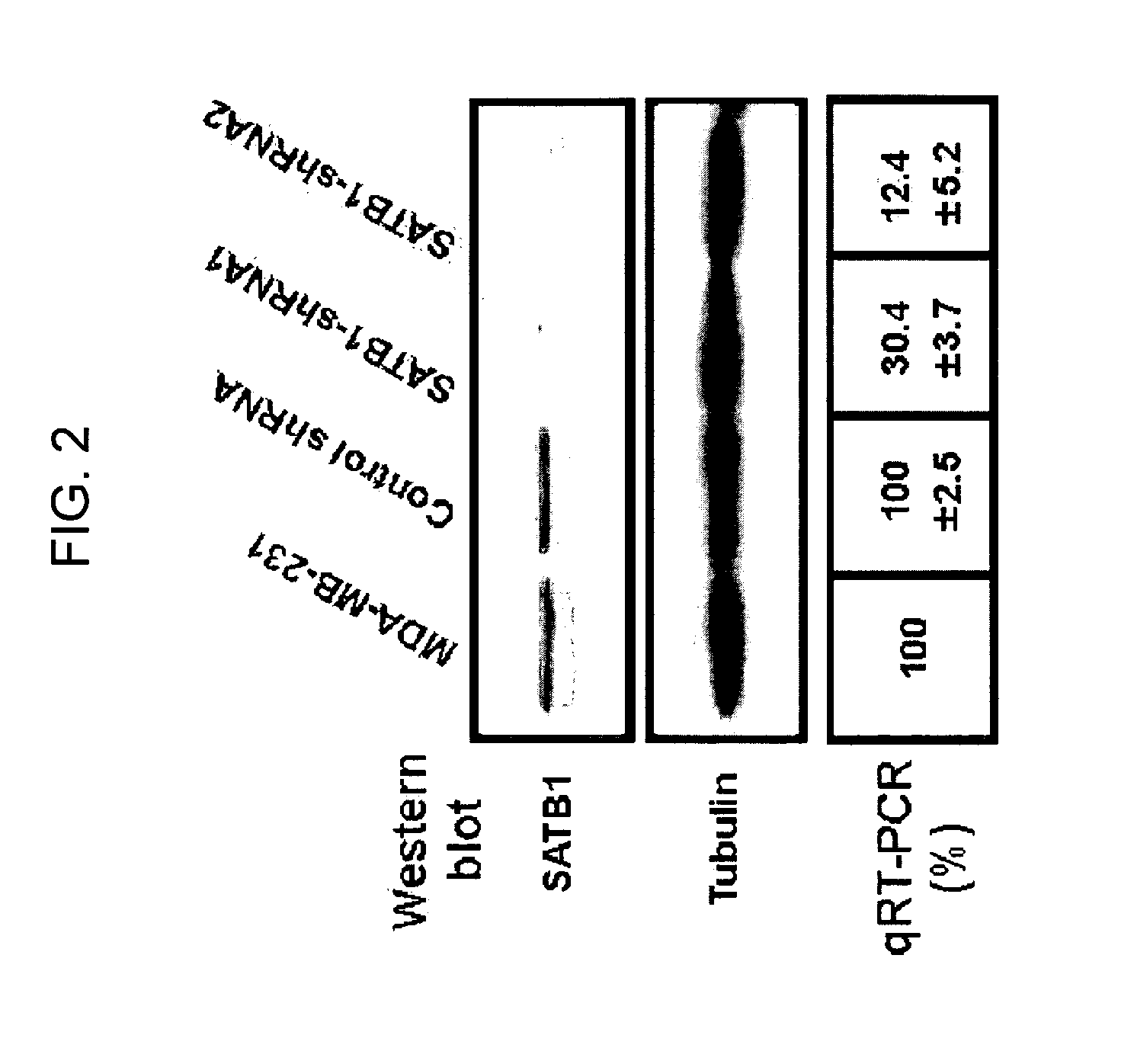
It is proposed that cancer cells express SATB1, and that SATB1 acts as a determinant for the acquisition of metastatic activity by controlling expression of a specific set of genes that promote metastatic activity. In order for cancer cells to gain the ability to metastasize, SATB1 re-organizes or re-packages genomic sequences in a specific manner to allow a switch in the pattern of gene expression. SATB1 expression was found restricted mainly to aggressive cancer cells where it may regulate the genetic and epigenetic changes that program the steps involved in the metastatic process. The present invention describes reagents and tools to detect the SATB1 protein for use in diagnosis and prognosis of aggressive cancers and therapeutics to inhibit SATB1 protein to deplete its expression in metastatic and aggressive cancers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Identification of genetic modifications
ActiveUS20190040457A1Minimize side effectsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSide effectNucleotide
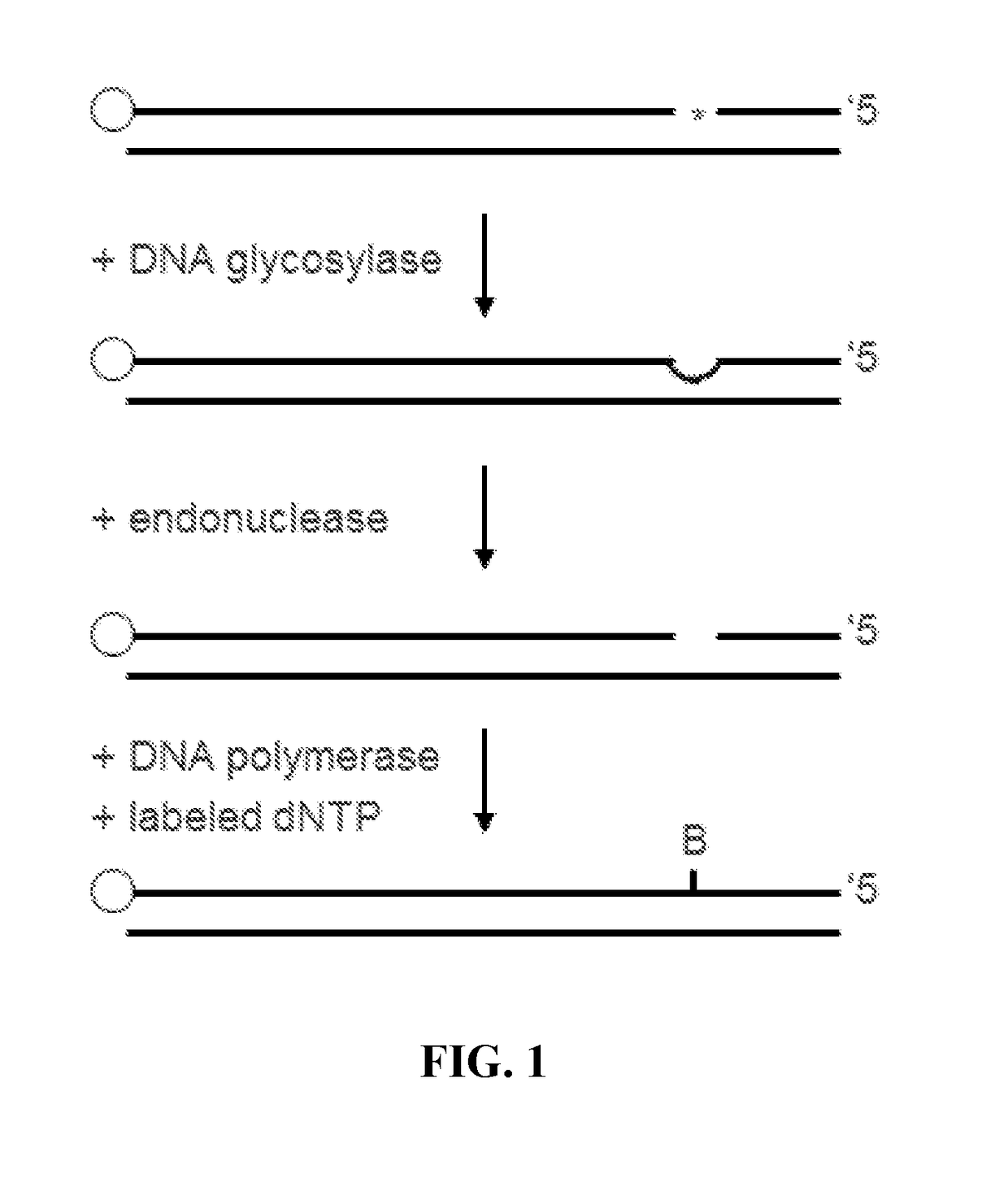
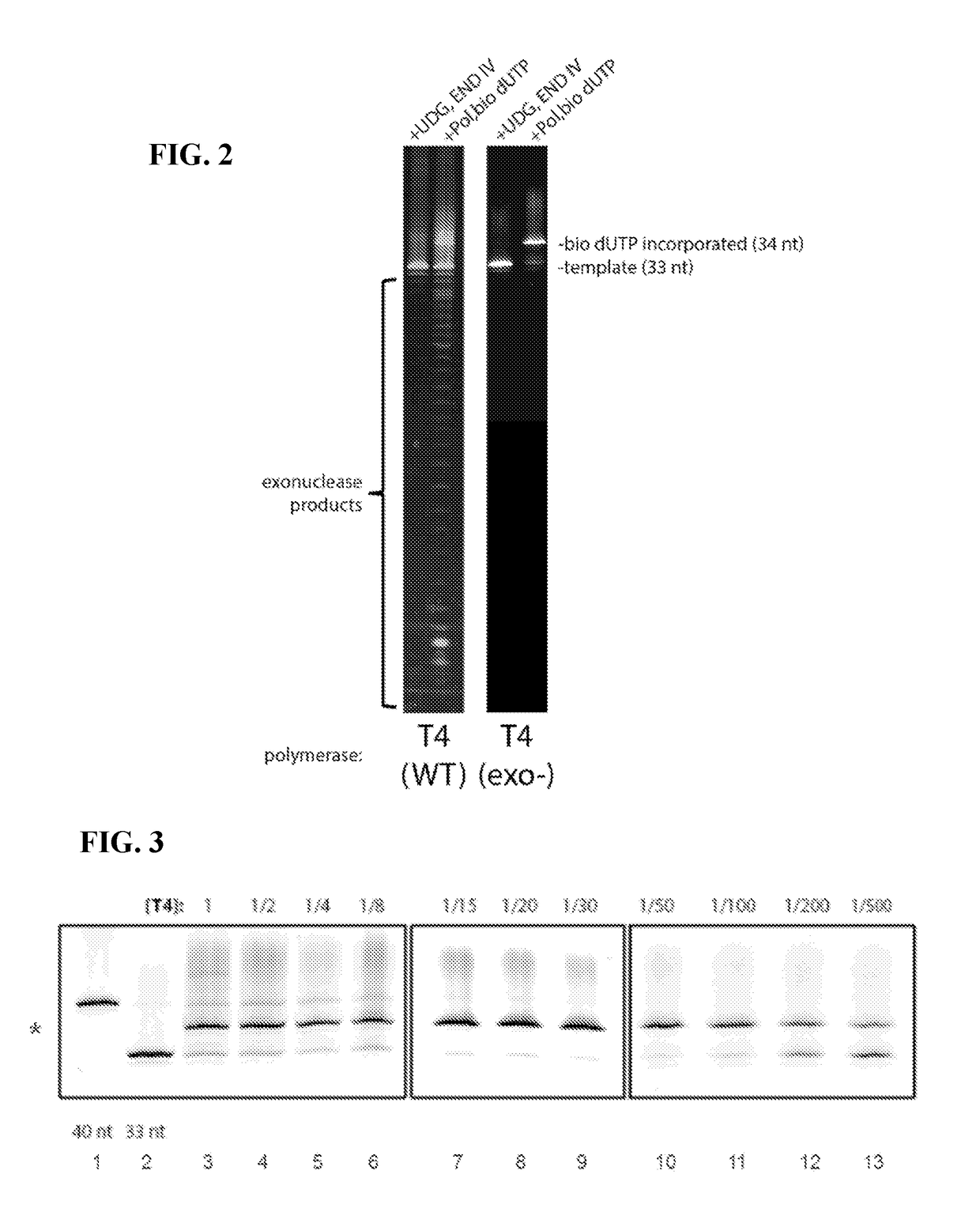
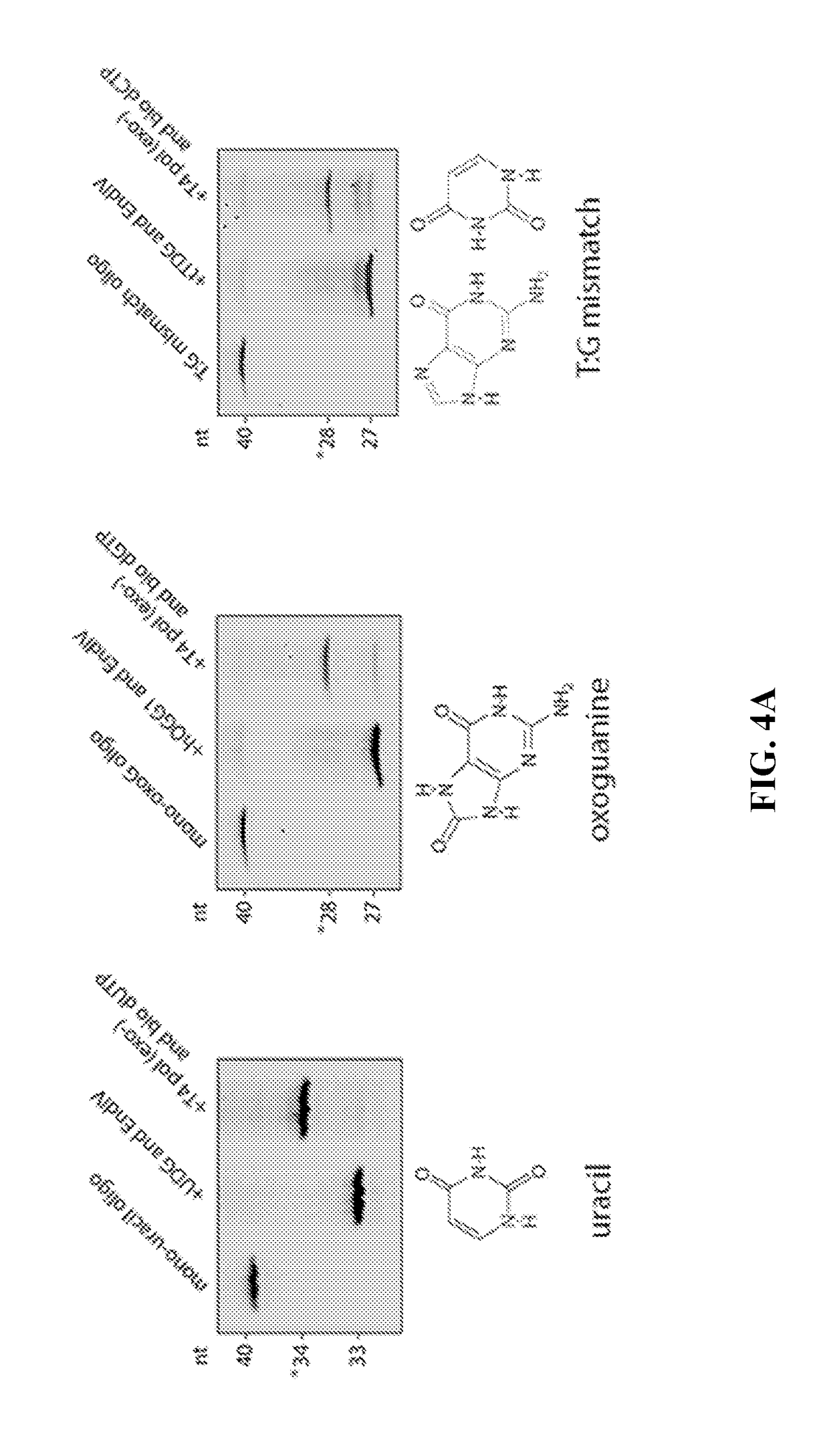
Described are methods of detecting modified nucleotide bases in a DNA sample using specific DNA glycosylases to excise target modified bases. DNA molecules are then labeled using a DNA polymerase lacking 3′→5′ exo-nuclease activity and strand displacement activity. The methods can be used to detect epigenetic changes and DNA damage. Provided are methods for diagnosing a disease or condition, determining risk of a disease or condition, identifying appropriate treatment, monitoring effectiveness of treatment, and monitoring side effects of treatment in subjects based on detection of modified bases. Also provided are methods for determining environmental exposure, or an environmental exposure time, of a biological sample containing DNA. Also provided are kits, systems, and devices for performing the described methods.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Methods for determining methylation of the TWIST1 gene for bladder cancer detection
ActiveUS9322065B2Reduce the possibilityAvoid the needMicrobiological testing/measurementAntineoplastic agentsBladder cancerTWIST1 gene
Disclosed are methods of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprising detecting an epigenetic change, such as methylation, in at least one gene selected from TWIST1, NID2, RUNX3, BMP7, CCNA1, PDLIM4, TNFRSF25, APC, RASSF1A, LOXL1, TUBB4, NTRK2, ARFGAP3, OSMR and TJP2, or a panel thereof. Also disclosed are kits for performing the disclosed methods, such as kits for detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprising at least one primer pair for determining the methylation status of each of NID2, TWIST1 and RUNX3. The kits may contain means for processing a urine sample.
Owner:ONCOMETHYLOME SCI
Methods of achieving high specificity of genome editing
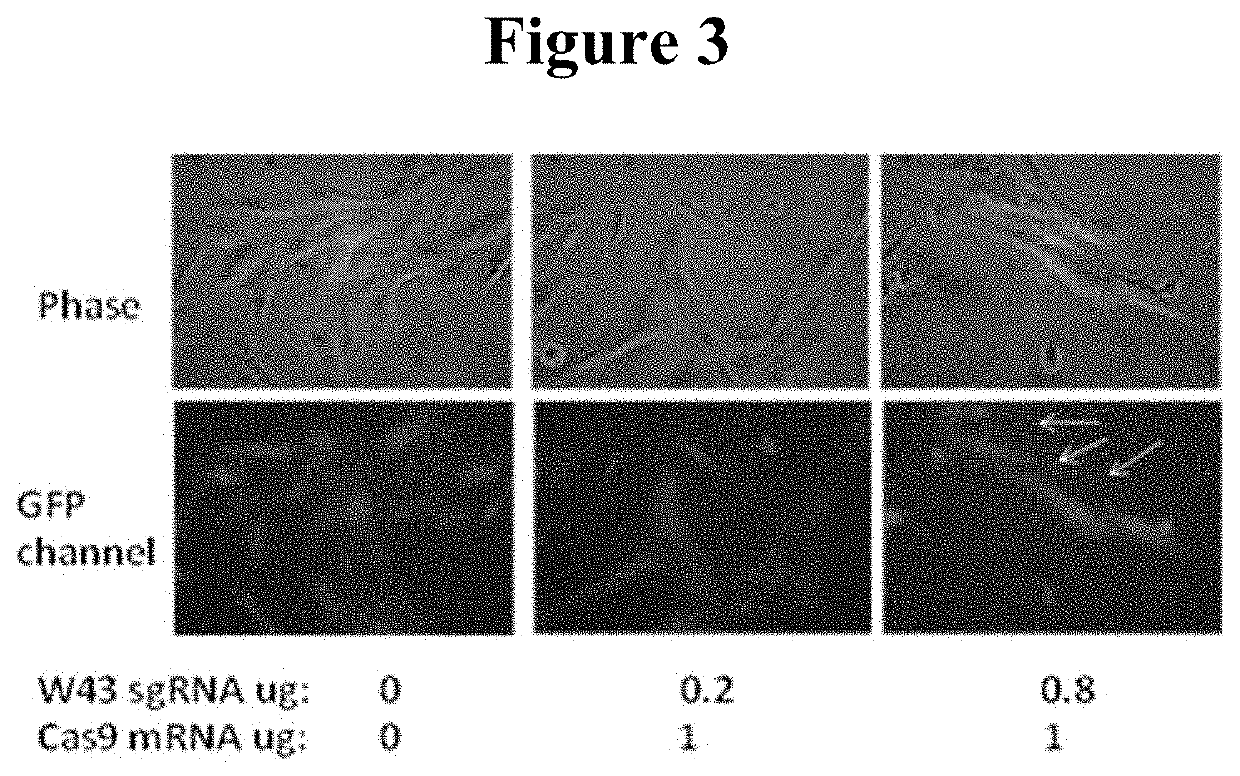
PendingUS20220195403A1Highly efficient DNA sequence alterationImprove efficiencyHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAEpigenetic ProfileSequence Alteration
A method is disclosed for highly efficient DNA sequence alterations. The method is useful for editing chromosomes, to engineer cellular markers through insertion of genes, or to create epigenetic changes by using cas9-enzyme fusions where the enzymes can be DNA epigenetic modifying enzymes or chromatin modifying enzymes, etc. The technology also differs from all previously known technologies in that the CRISPR / Cas system can function in ways that are “clean”, i.e. they have not been in contact with any virus, or are carried DNA molecules that can insert into the chromosome in unintended locations.
Owner:ALLELE BIOTECH & PHARMA
Identification of genes involved in angiogenesis, and development of an angiogenesis diagnostic chip to identify patients with impaired angiogenesis
The invention is directed to methods for angiotyping individual patients to predict the likelihood of whether a given individual will develop good vs. poor collaterals naturally. Accordingly, this can involve obtaining and providing a list of genes involved in collateral development. In particular, angiotyping individual patients can be used to predict the likelihood of whether a given individual will develop good vs. poor collaterals in response to specific angiogenesis therapy. From an array of genes that have been determined through experimental studies as being differentially expressed in tissues in which collaterals are developing in response to arterial occlusion, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs), or other epigenetic changes, such as DNA methylation patterns, can be identified. SNPs and DNA methylation patterns are detected using microchips or similar technology assaying for all, or most, of the genes determined to play a role in collateral development. In addition, abnormally low or abnormally high differential expression of any combination of the candidate genes can be detected in such tissue as peripheral blood cells. The presence of a predisposition to develop poor vs. good collaterals is indicated by the presence of SNPs, and / or alterations in DNA methylation patterns, and / or difference in expression levels involving one or more of the genes.
Owner:MEDSTAR RES INST
Satb1: a determinant of morphogenesis and tumor metastatis
InactiveUS20150323536A1Reliable diagnosisReliable prognosisOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsCancer cellMorphogenesis
It is proposed that cancer cells express SATB1, and that SATB1 acts as a determinant for the acquisition of metastatic activity by controlling expression of a specific set of genes that promote metastatic activity. In order for cancer cells to gain the ability to metastasize, SATB1 re-organizes or re-packages genomic sequences in a specific manner to allow a switch in the pattern of gene expression. SATB1 expression was found restricted mainly to aggressive cancer cells where it may regulate the genetic and epigenetic changes that program the steps involved in the metastatic process. The present invention describes reagents and tools to detect the SATB1 protein for use in diagnosis and prognosis of aggressive cancers and therapeutics to inhibit SATB1 protein to deplete its expression in metastatic and aggressive cancers.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Epigenetic markers for detection of autism spectrum disorders
InactiveUS20140349977A1Increased and decreased level of methylationBiocideTetracycline active ingredientsMedicineAutism spectrum disorder
Methods for determining if a patient has, or is at risk of having, and autism spectrum disorder by detecting epigenetic changes in the genome of the patient. For example, a method can comprise determining the methylation status of one or more genes in a blood sample.
Owner:ZYMO RES CORP
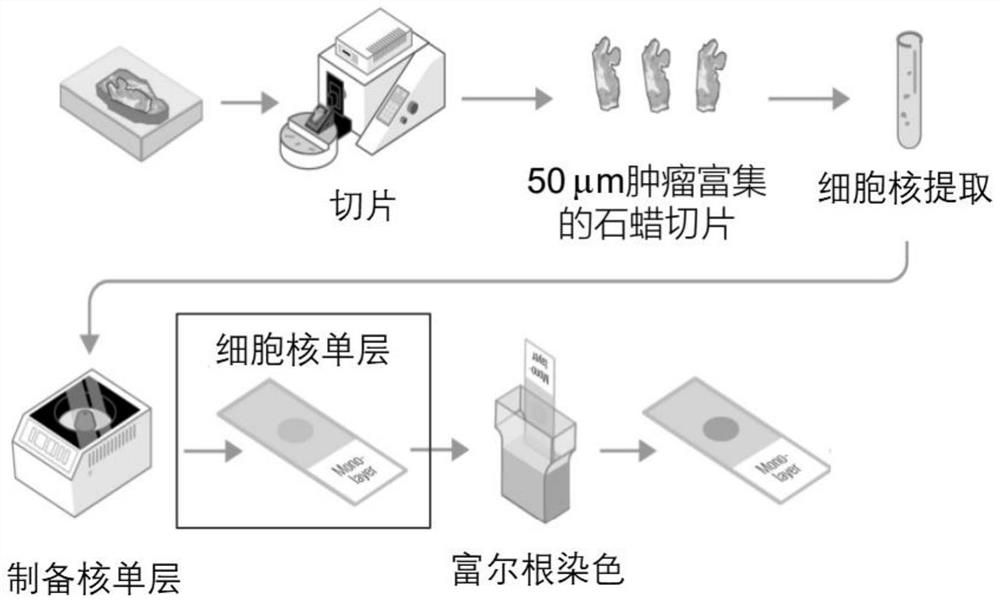
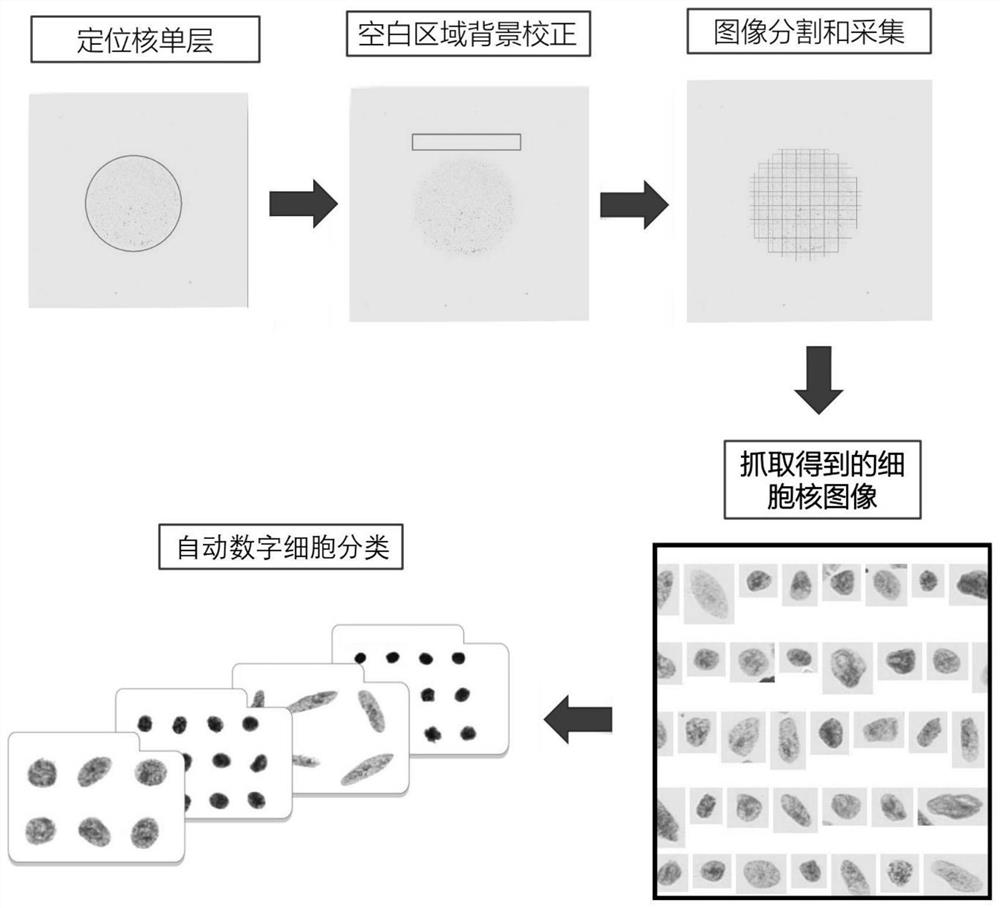
Paraffin-embedded tissue sample processing method and kit for tumor prognosis evaluation
PendingCN114076707AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by optical meansStainingBiology
The invention discloses a paraffin-embedded tissue sample processing method and a kit for tumor prognosis evaluation. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a cell nucleus monolayer from a paraffin-embedded tumor tissue sample, dyeing the cell nucleus by using a dyeing reagent, and collecting an image by using a digital pathological scanning analysis system. The content of cell DNA in the abnormal tissue is detected through image analysis of the gray scale and the IOD value of the cell nucleus, and the DNA ploidy is reflected; through image analysis of cell nucleus textures, chromatin structures are quantified, and the structures comprehensively reflect gene changes and epigenetics changes. According to the method, the combined quantitative analysis of two prognosis risk factors is realized on the paraffin-embedded tissue sample through one-time sampling and one-time processing flow by utilizing a digital pathological scanning analysis system, and the analysis result can be used for prognosis evaluation of a patient, so that the efficiency and the accuracy of evaluation work are greatly improved, and reasonable medication is guided.
Owner:MY BIOMED TECH (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
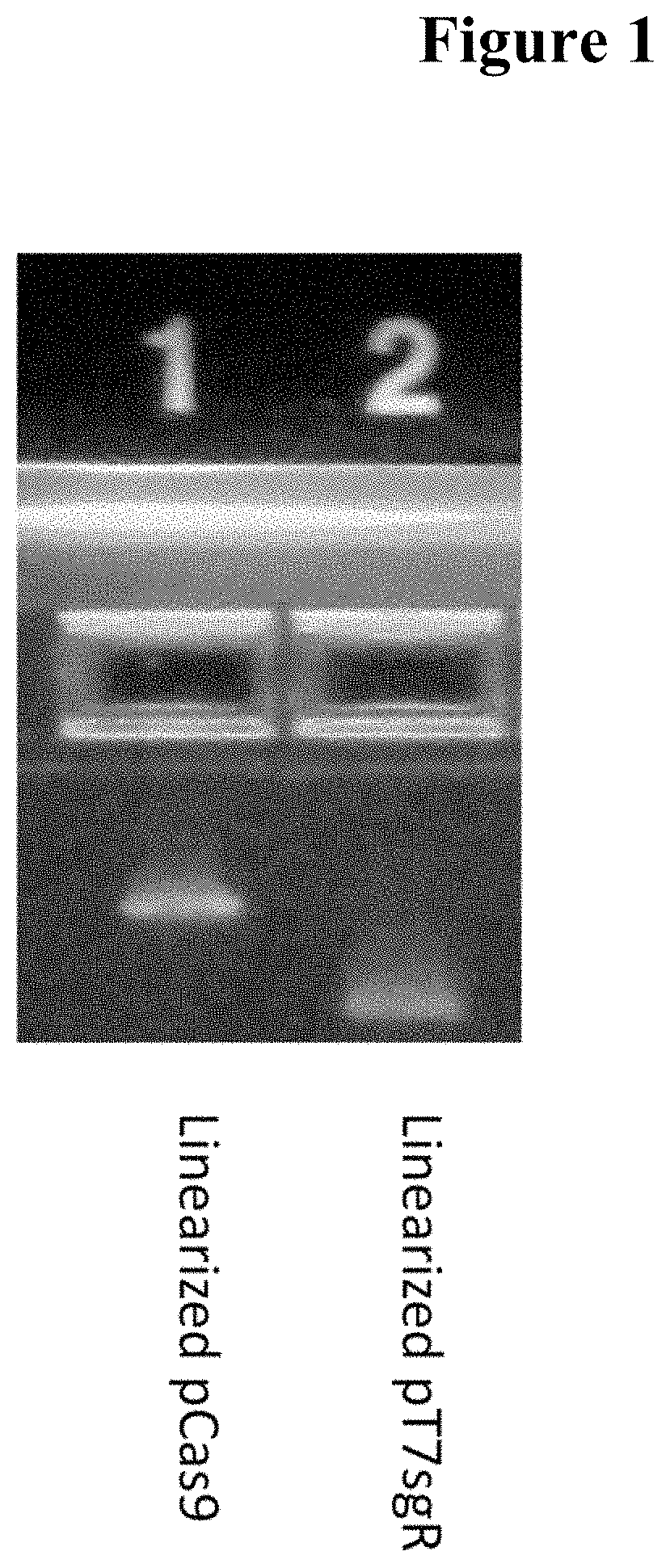
Methods of Detecting Mutations and Epigenetic Changes
ActiveUS20140322714A1Rapid assessmentEliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementEpigenetic ProfileBioinformatics
Disclosed are methods for assessing the methylation and mutation status of nucleic acid in a sample. The methods provide for methylation-dependent modification of the nucleic acid in a sample, and subsequently nucleic acid amplification processes to distinguish between mutated and non-mutated target sequence.
Owner:MDXHEALTH
Modulation of epigenetic stress response
ActiveUS20180185442A9Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyEpigenetic Change
Owner:MASCARENHAS DESMOND D
Methods for assessing the treatment response of tnbc patients to neo-adjuvant chemotherapy by analysing cpg methylation
Owner:THERAWIS DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
Modulation of epigenetic stress response
ActiveUS20180078608A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyEpigenetic Change
The present invention is related to methods and compositions useful in the detection and treatment of epigenetic changes during traumatic, autoimmune and other disease processes. The methods described herein comprise identifying and using certain agents to modulate pathophysiological processes in animal and human subjects. The methods of the invention may be used for therapeutic or diagnostic purposes.
Owner:MASCARENHAS DESMOND D
Methods for assessing the treatment response of TNBC patients to neo-adjuvant chemotherapy by analysing CpG methylation
The present invention relates to methods for predicting the efficacy of anthracycline-based neo-adjuvant chemotherapy in triple-negative breast cancer. This is achieved by determining epigenetic changes within the PITX2 gene. Detection of the methylation state of Cp G sites in a genomic sequence of PITX2 allows an estimate of the response or failure of an individual breast cancer patient to neo-adjuvant therapy.
Owner:THERAWIS DIAGNOSTICS GMBH
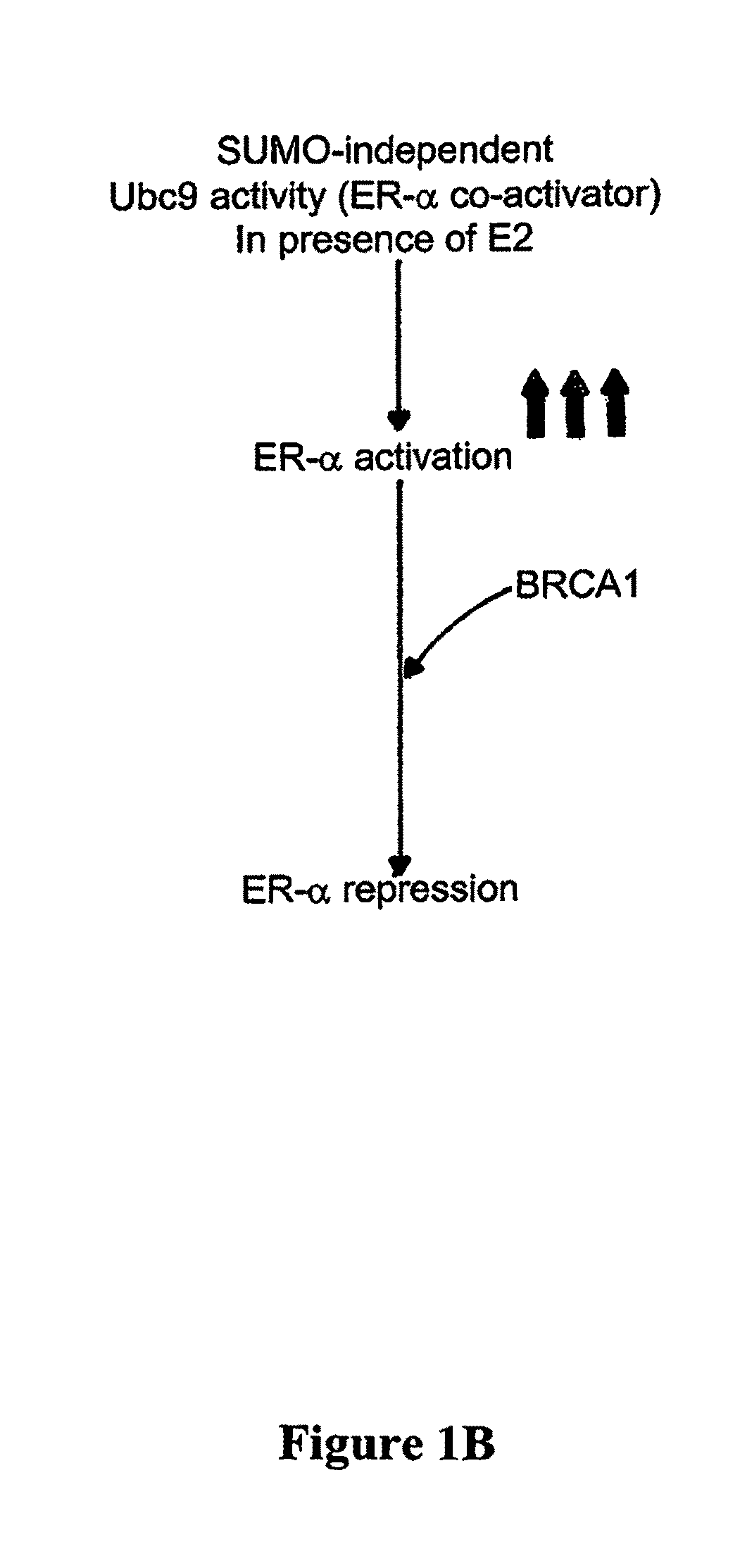
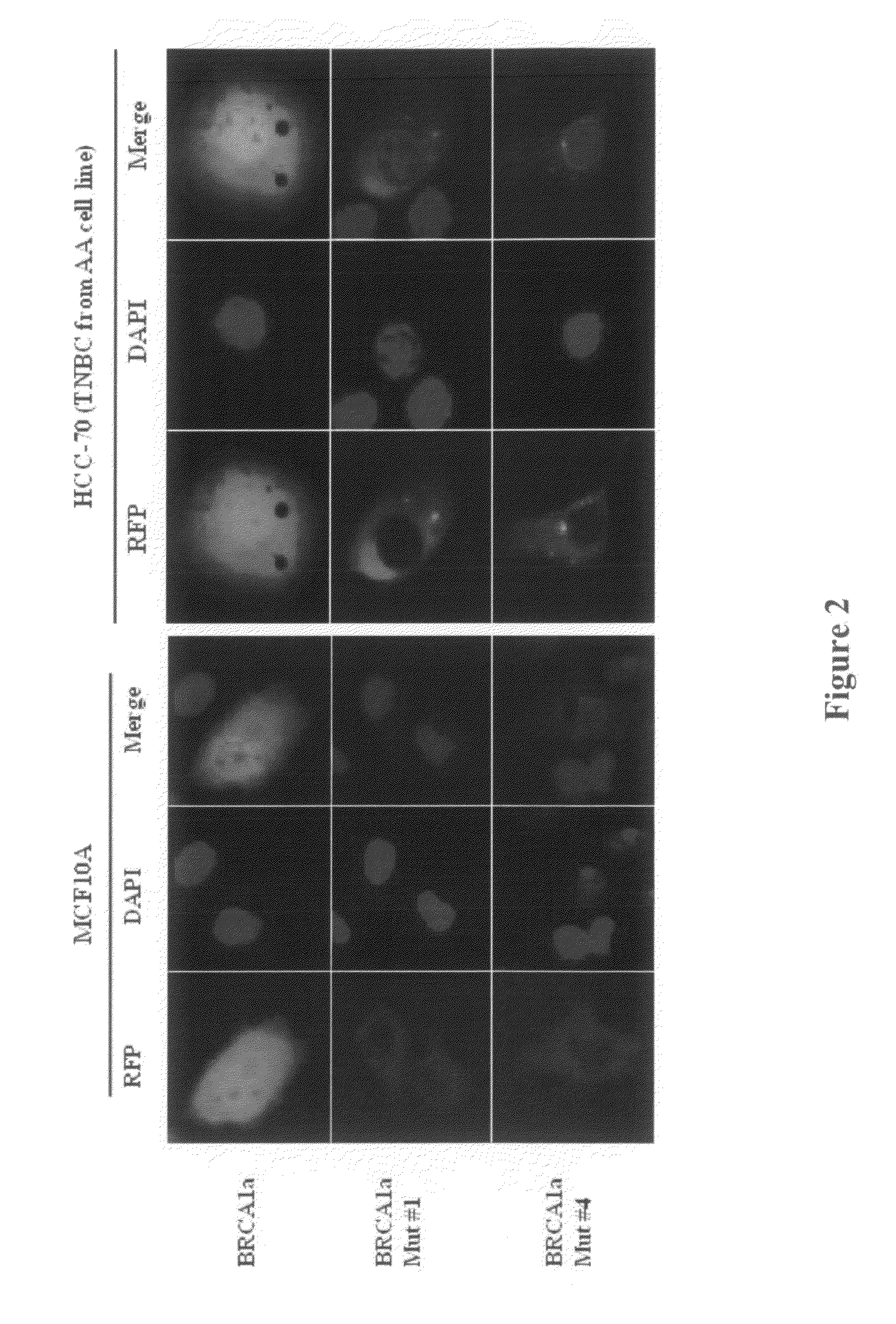
BRCA1 function-based cellular assays
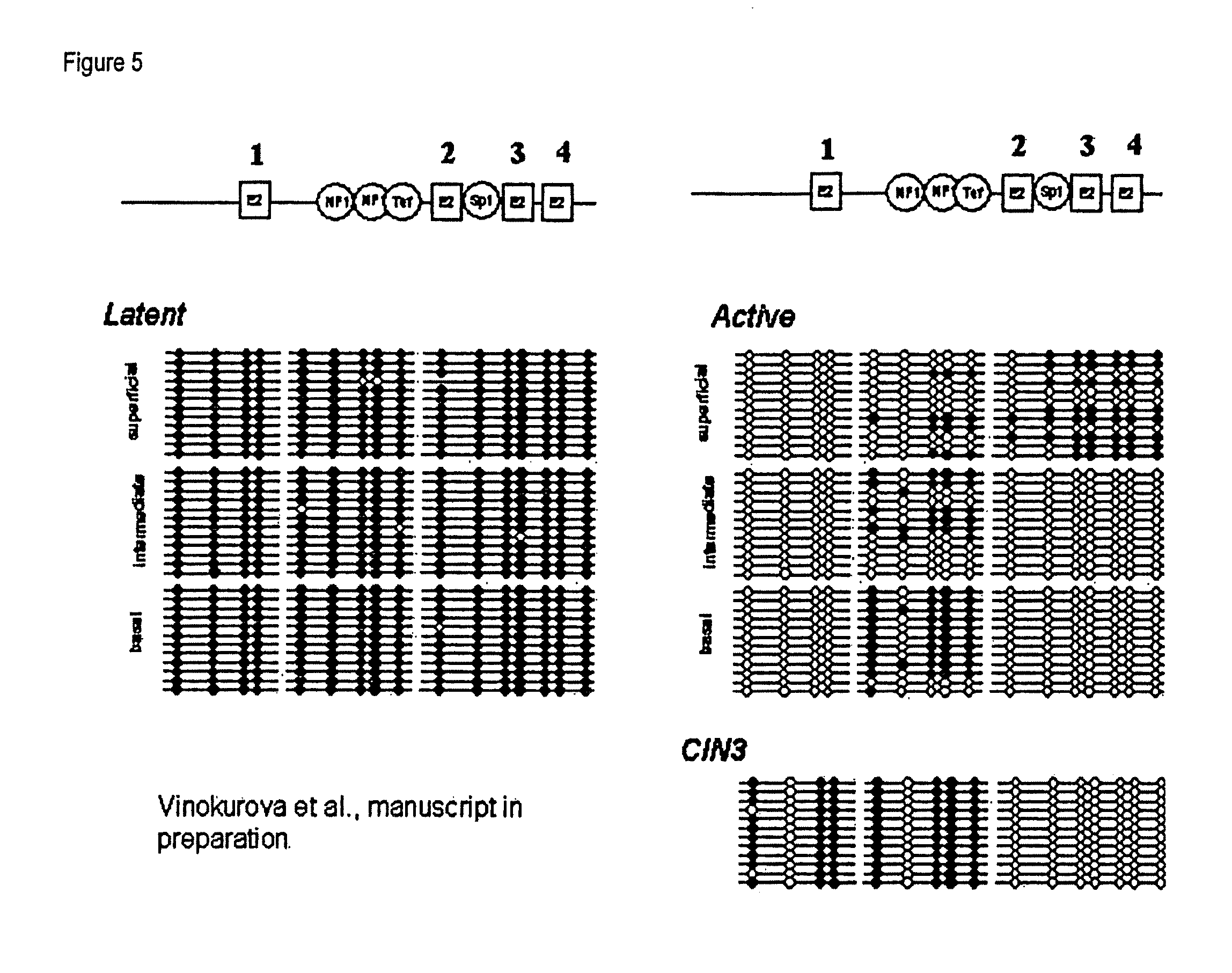
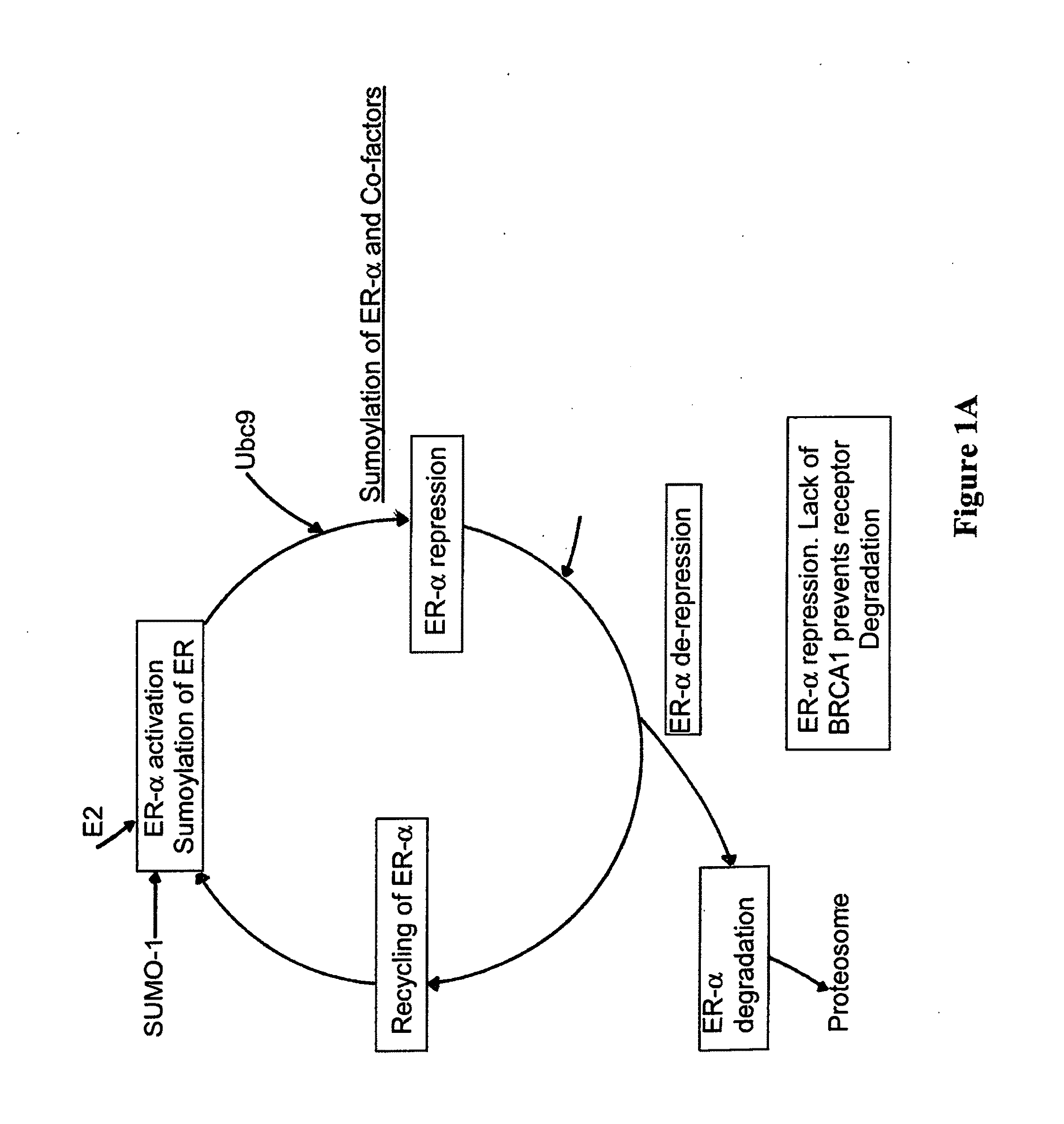
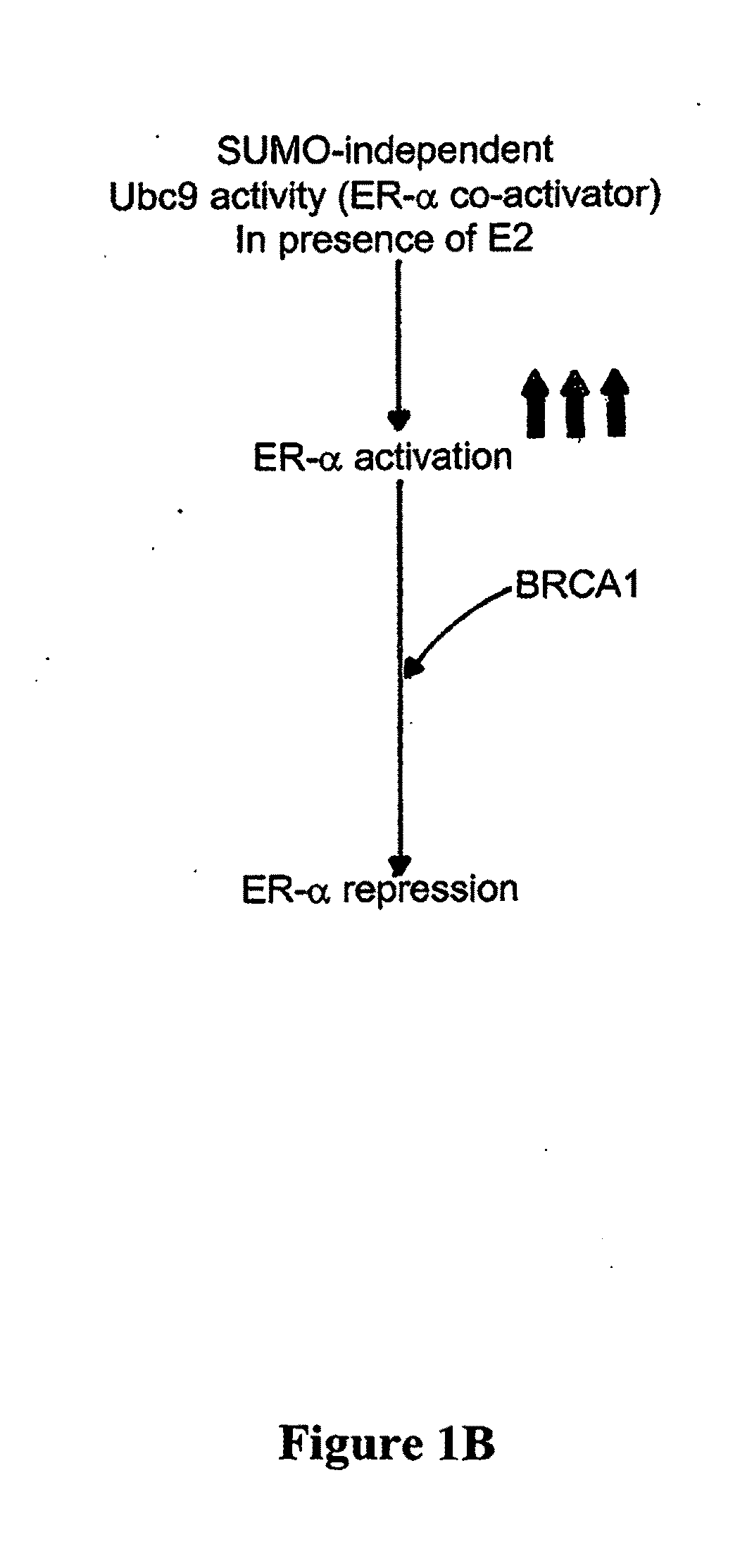
ActiveUS8372580B2Promote degradationArresting its developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisBrca1 proteinAssay
Assays using binding studies involving function of BRCA1a protein have use for diagnosis and for evaluation of possible tumorogenicity of agents, particularly estrogenic agents. The assays do not rely on use of a probe for only specific sequences, but on effects of known and unknown or not previously studied sequences (consequence of genetic changes) or posttranslational modification of BRCA1 proteins (as a consequence of epigenetic changes) as seen in hereditary and sporadic cancers.
Owner:RAO VEENA
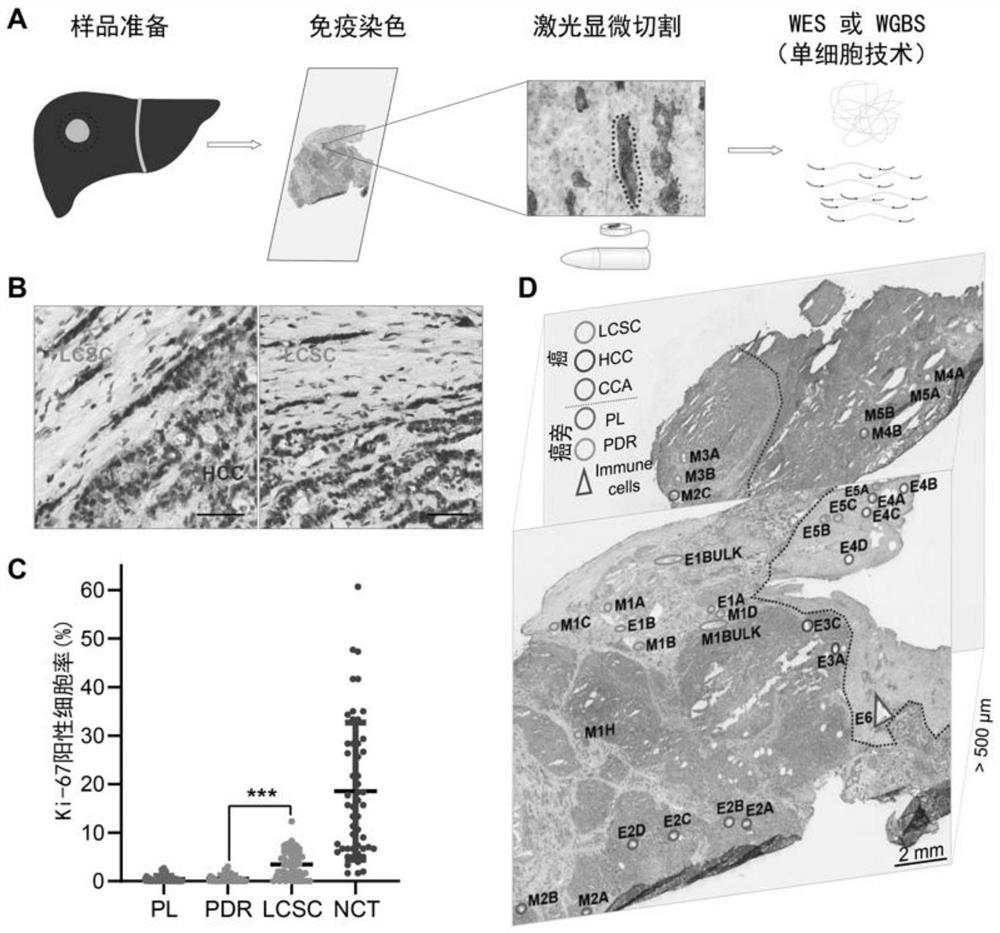
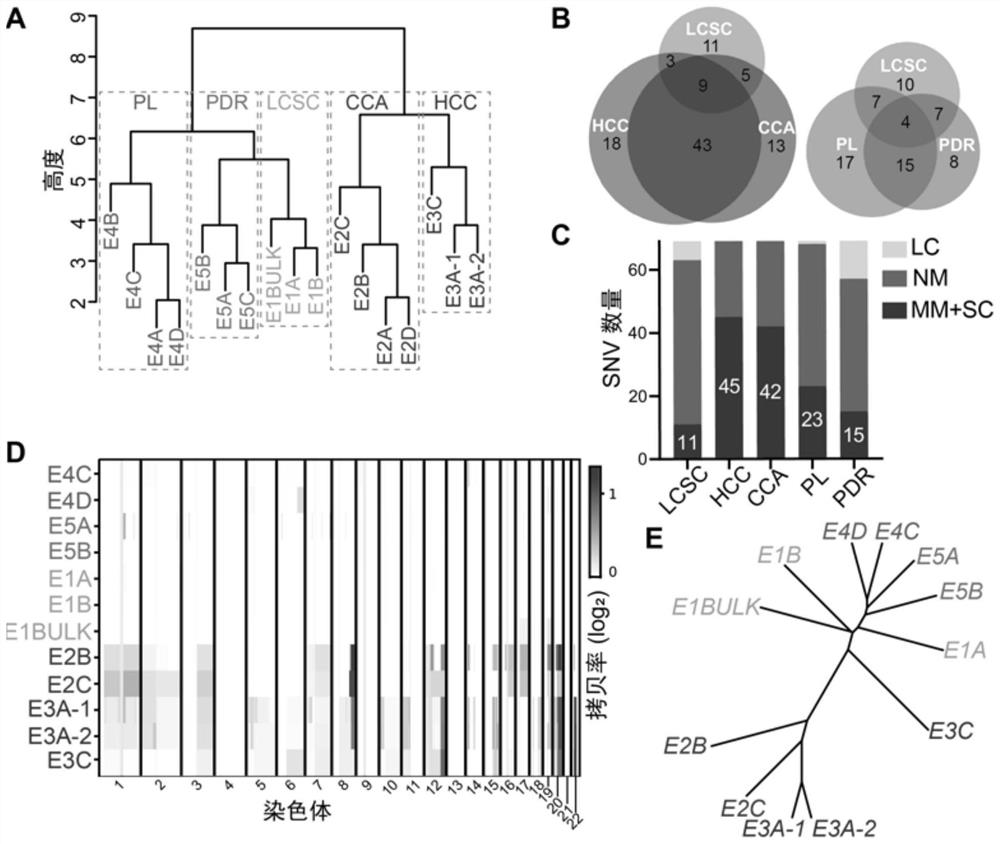
Method for detecting genetic and epigenetic changes in tumor stem cells
PendingCN113025712AEffective human cancer treatmentGood treatment effectMicrobiological testing/measurementEpigenetic ProfileTherapeutic effect
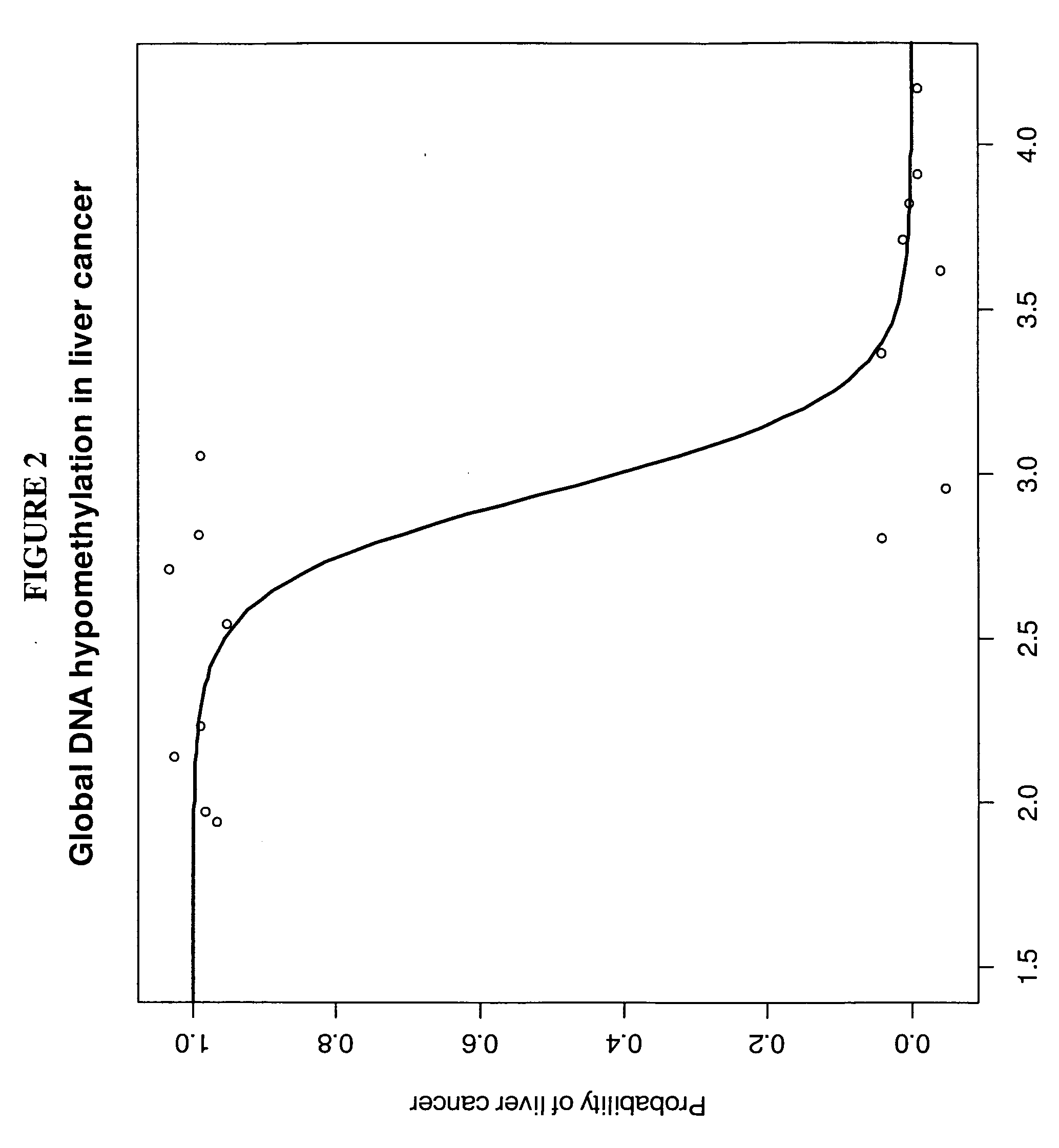
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a method for detecting genetic and epigenetic changes in tumor stem cells and clinical application. It is found that compared with para-carcinoma tissue, although wide genetic and epigenetic changes exist in liver cancer tissue, only a small amount of key genetic and epigenetic changes exist in liver cancer stem cells in the liver cancer tissue. For treatment of key genetic and epigenetic changes occurring in the tumor stem cells, the treatment effect on cancers may be better. The invention provides a new target discovery method for treatment of liver cancer.
Owner:THE NAVAL MEDICAL UNIV OF PLA
Novel Markers for Bladder Cancer Detection
ActiveUS20120027870A1Raise the possibilityReduce the possibilityBiocideInorganic active ingredientsBladder cancerGATA4
A method of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprises detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from FOXE1 and GATA4. Detection of the epigenetic change is indicative of a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer. The sample comprises nucleic acid molecules from bladder cells. The methods may be used to select treatments and patients for treatment. Related kits include primers allowing the methylation status of the genes to be determined.
Owner:MDXHEALTH
Methylation of the GATA4 gene in urine samples as a marker for bladder cancer detection
ActiveUS9388471B2Loss of gene functionRaise the possibilityBiocideSugar derivativesBladder cancerGATA4
A method of detecting a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer in a sample comprises detecting an epigenetic change in at least one gene selected from FOXE1 and GATA4. Detection of the epigenetic change is indicative of a predisposition to, or the incidence of, bladder cancer. The sample comprises nucleic acid molecules from bladder cells. The methods may be used to select treatments and patients for treatment. Related kits include primers allowing the methylation status of the genes to be determined.
Owner:MDXHEALTH
Methods of detecting mutations in BRAF and epigenetic changes
ActiveUS9605312B2Rapid methylationRapid mutationMicrobiological testing/measurementEpigenetic ProfileEpigenetic Change
Disclosed are methods for assessing the methylation and mutation status of nucleic acid in a sample. The methods provide for methylation-dependent modification of the nucleic acid in a sample, and subsequently nucleic acid amplification processes to distinguish between mutated and non-mutated target sequence.
Owner:MDXHEALTH
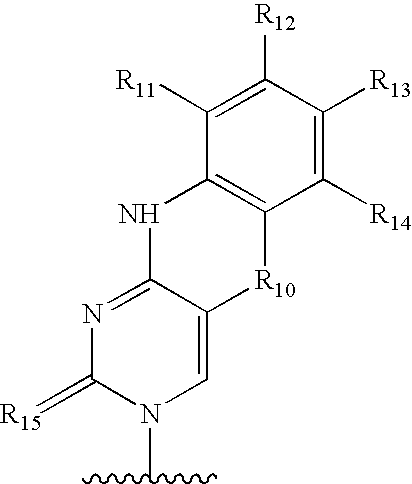
Compounds and methods associated with differential methylation of human papilloma virus genomes in epithelial cells
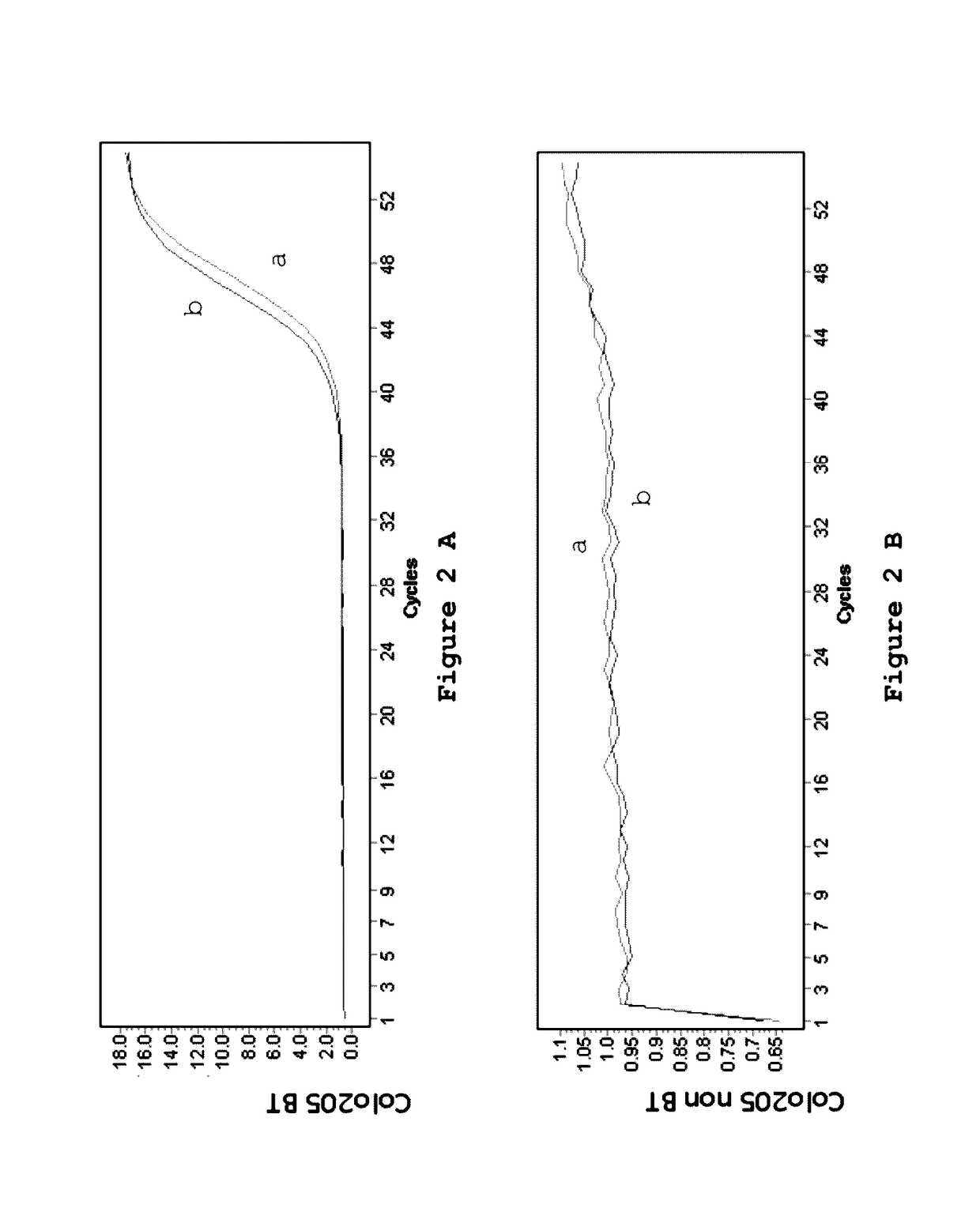
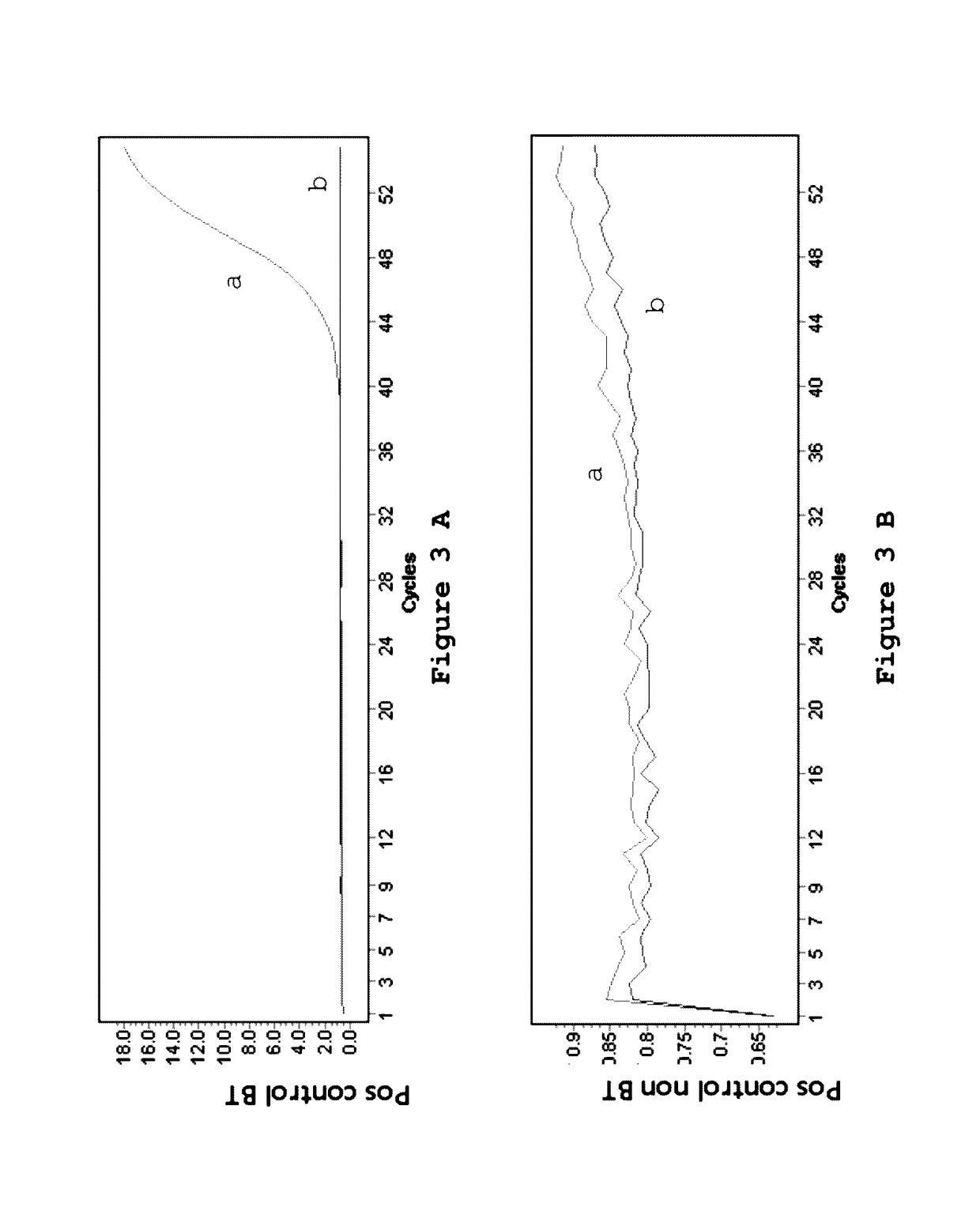
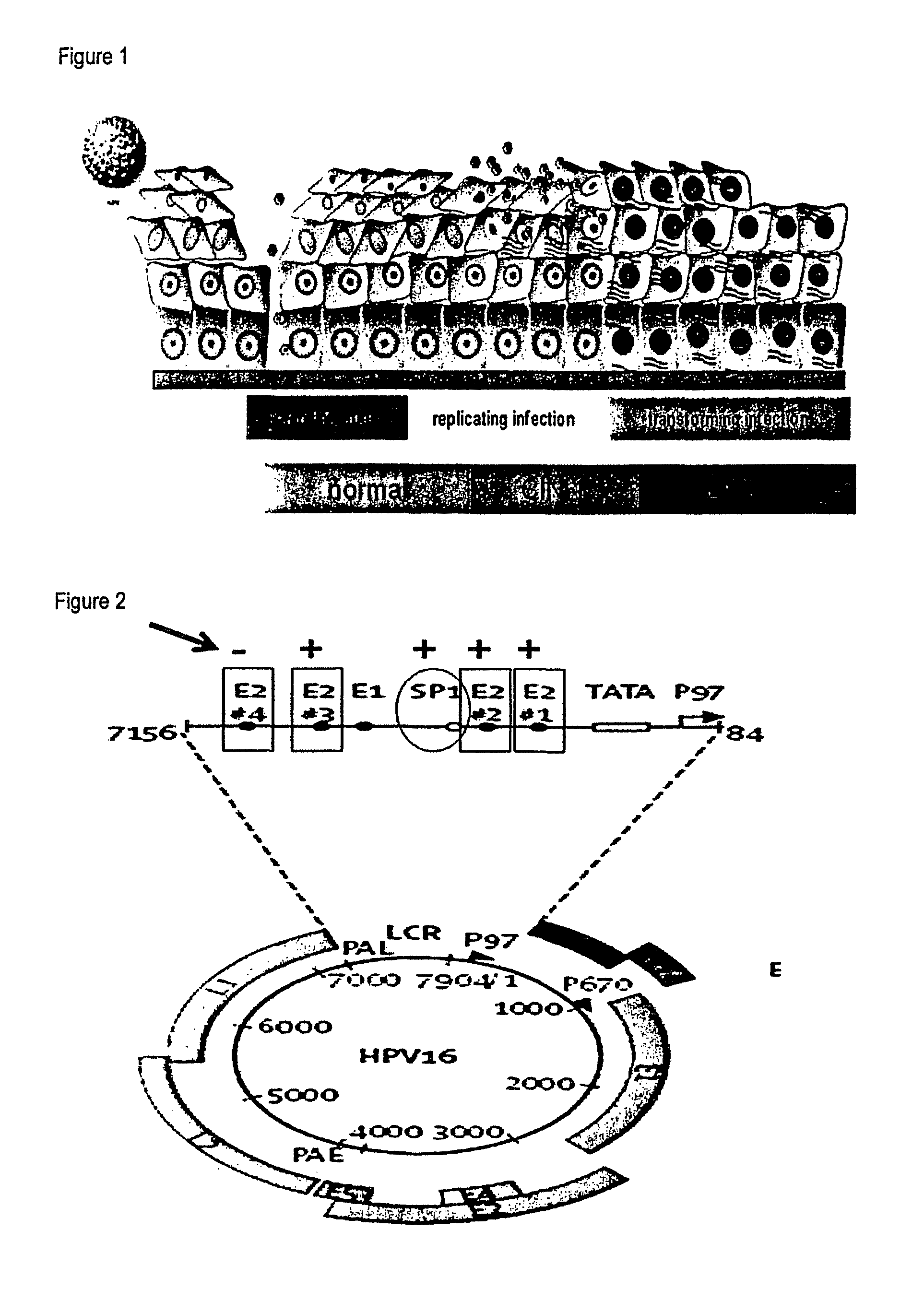
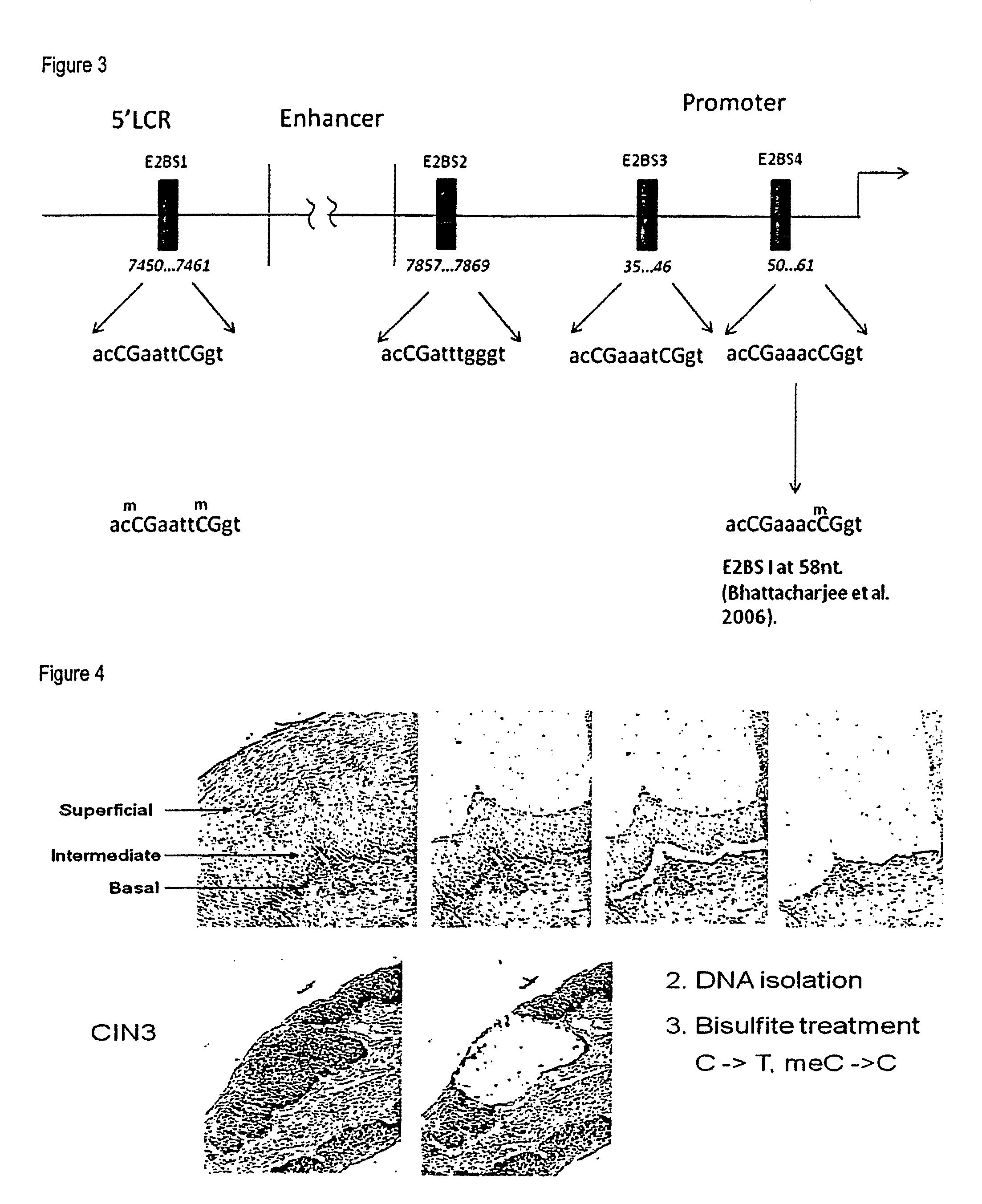
The invention relates to compounds and methods useful in detection and therapy of HPV-associated diseases. The invention is based on the elucidation of a mechanism by which replication of HPVs occurs in naturally infected tissues and cells. Moreover it is based on the identification of distinct epigenetic changes of the viral genome in infected cells that allows promotion of the affected cells to precancerous and cancerous cells. The invention therefore provides methods of diagnosing neoplasias and their precursor lesions as well as methods of preventing the development of malignancies or inhibiting tumor growth.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF HEIDELBERG
BRCA1 function-based cellular assays
ActiveUS20110027814A1Stop tumor developmentPromote degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingBrca1 proteinGenetic Change
Assays using binding studies involving function of BRCA1a protein have use for diagnosis and for evaluation of possible tumorogenicity of agents, particularly estrogenic agents. The assays do not rely on use of a probe for only specific sequences, but on effects of known and unknown or not previously studied sequences (consequence of genetic changes) or posttranslational modification of BRCA1 proteins (as a consequence of epigenetic changes) as seen in hereditary and sporadic cancers.
Owner:RAO VEENA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com