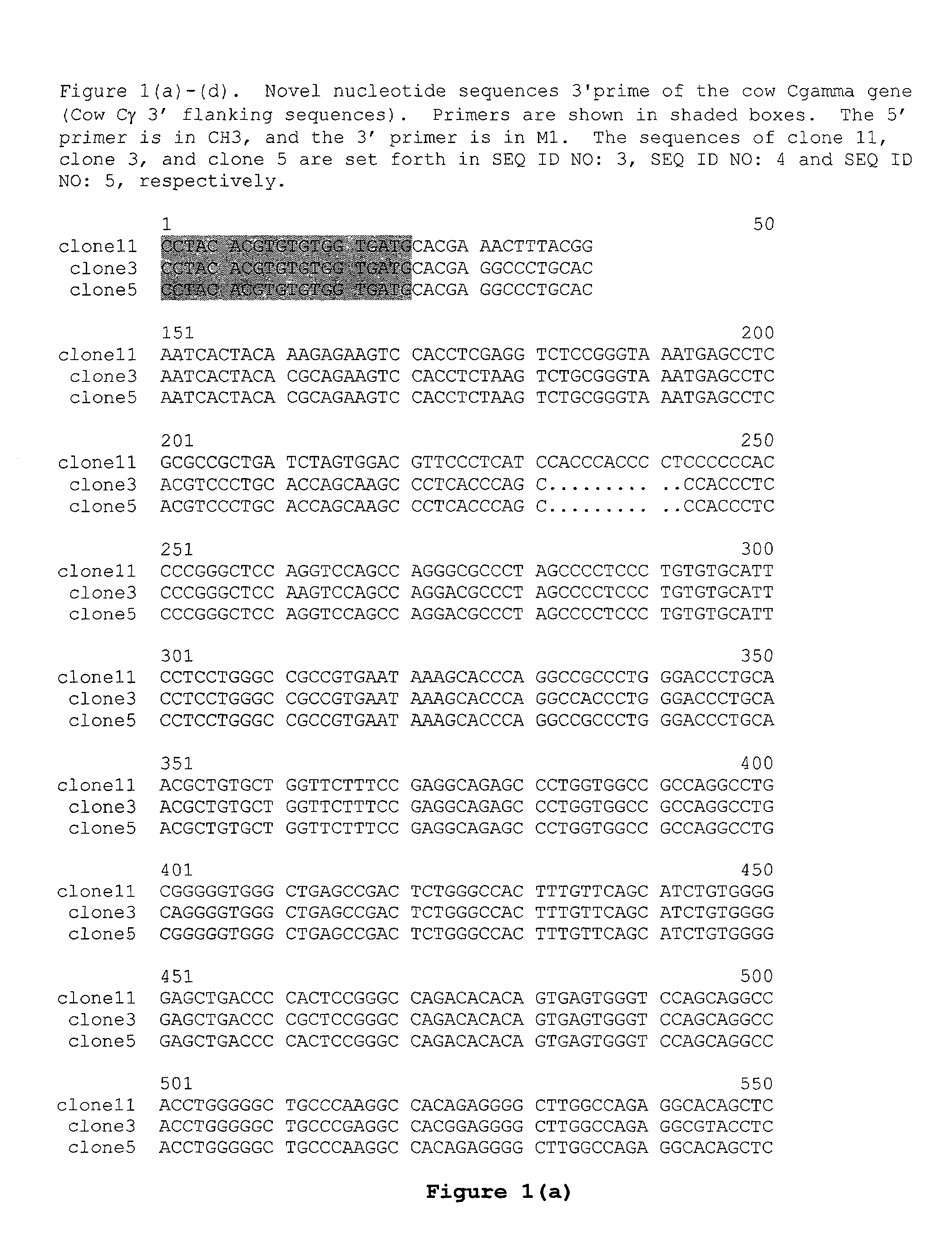
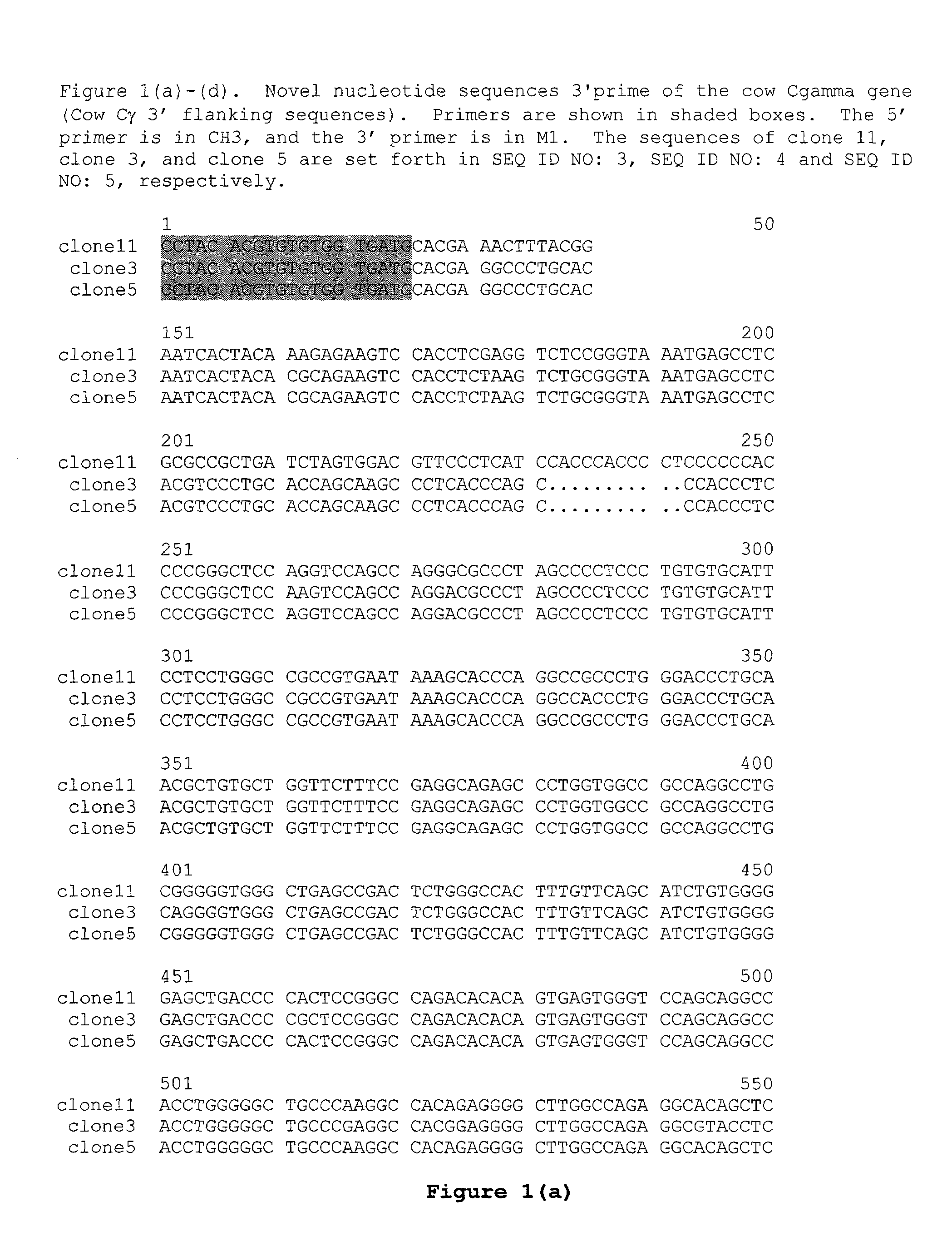
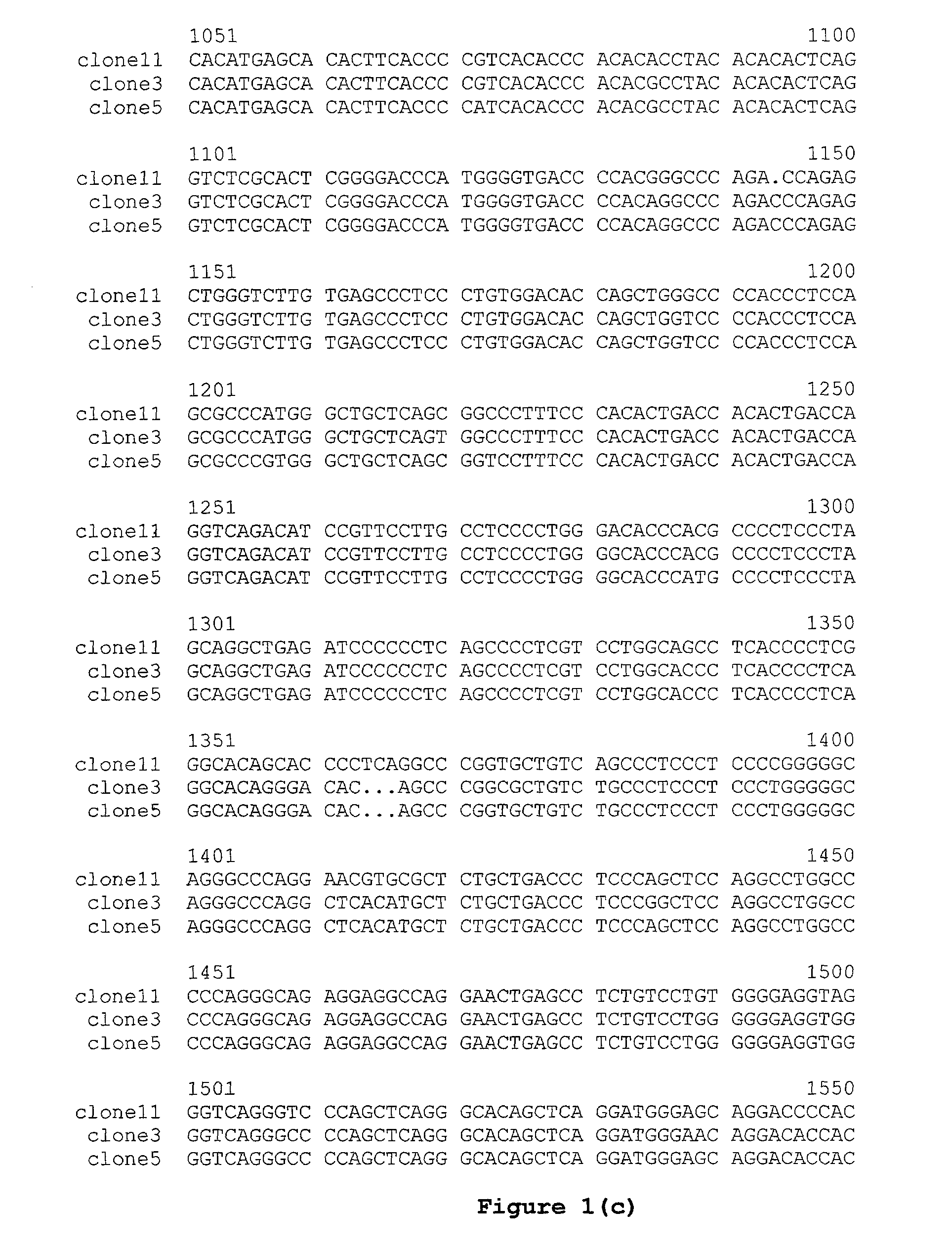
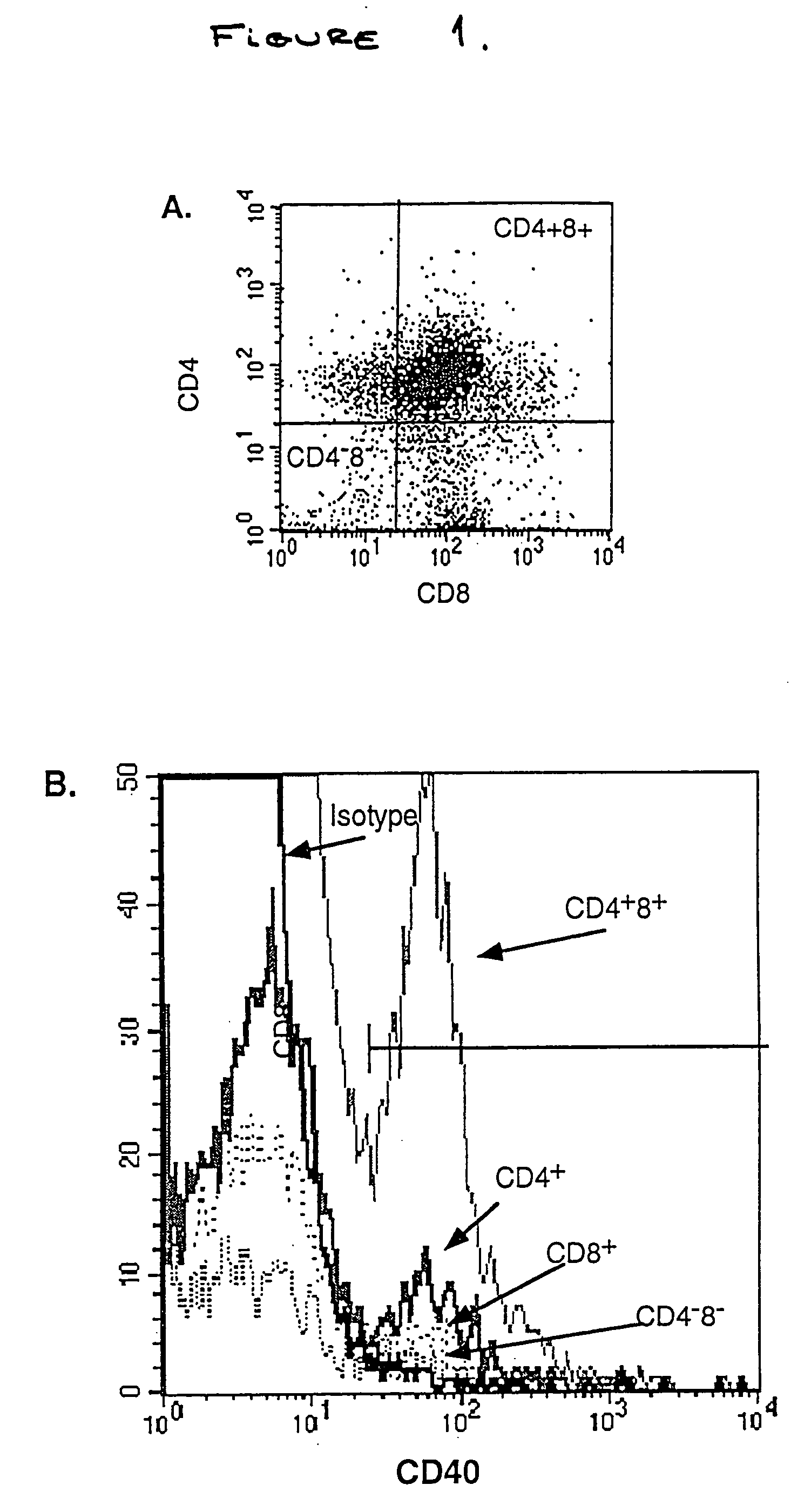
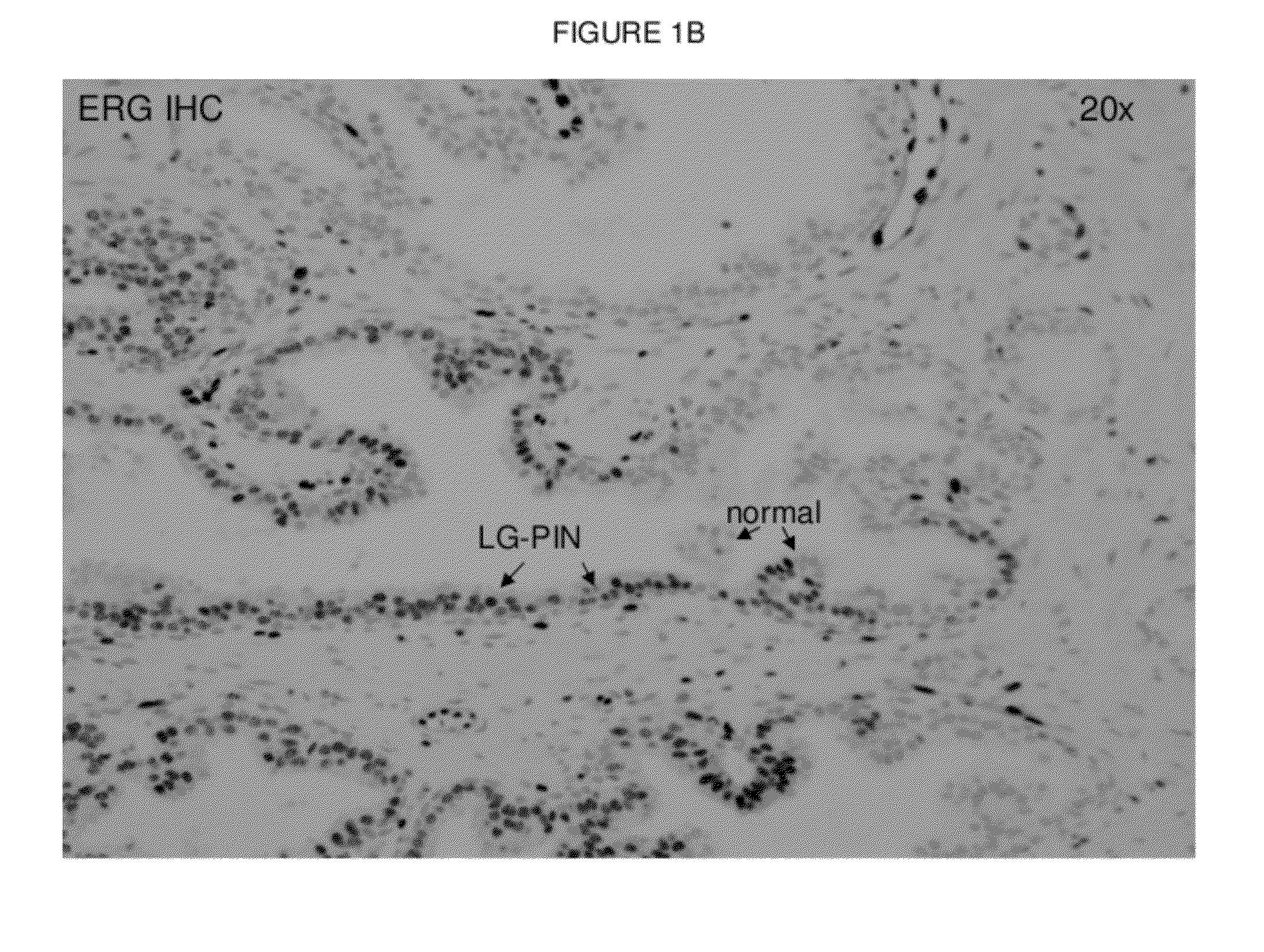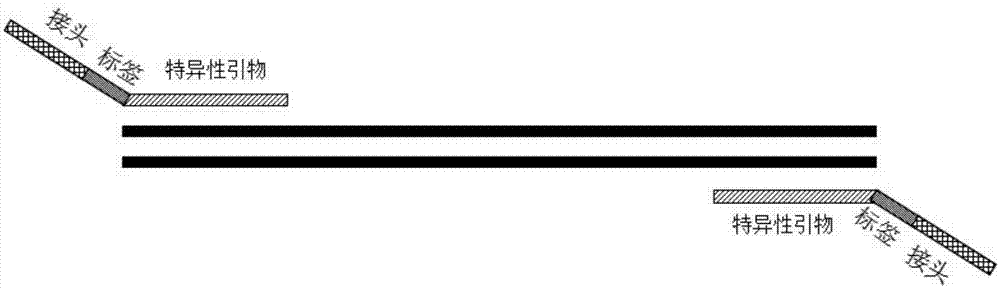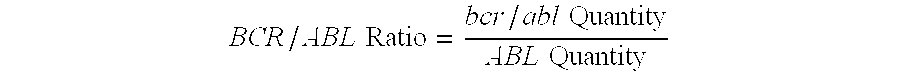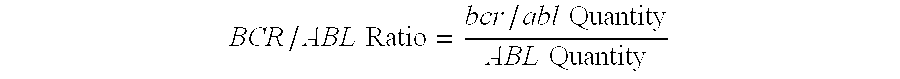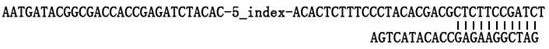Patents
Literature
69 results about "Gene rearrangement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Gene Rearrangements. Cancer is a collection of diseases caused by a wide range of molecular lesions (or mutations). One important class of mutation, called gene fusions, is a common cause of many cancers.
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS20030017534A1Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS7129084B2Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Molecular detection of chromosome aberrations
InactiveUS7034144B2High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementComparable sizeNucleic Acid Probes
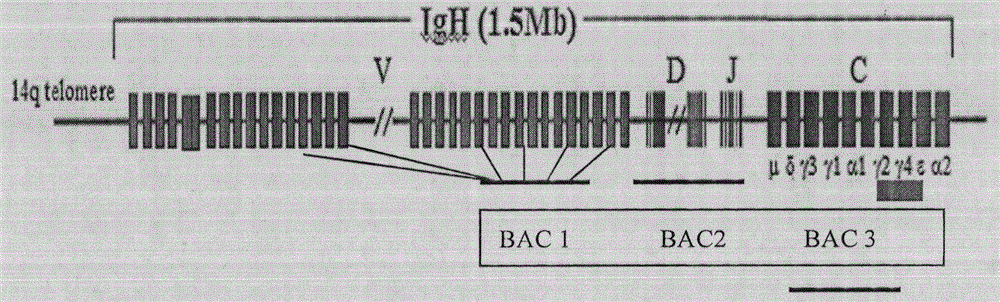
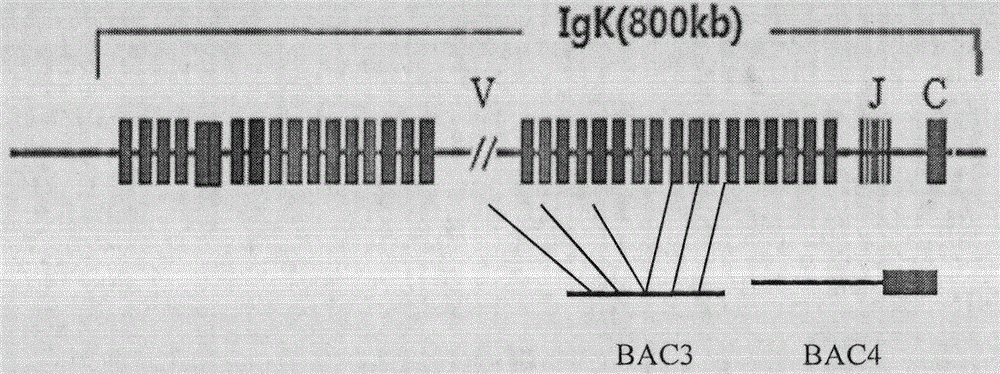
The invention relates to the field of cytogenetics and the application of genetic diagnostic techniques in pathology and hematology. Specifically, the invention relates to nucleic acid probes that can be used in hybridization techniques for the detection of chromosomal aberrations and other gene rearrangements such as immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements. The probes provided by the invention are a distinct and balanced set of probes of comparable size, each preferably being from 1 to 100 kb, or smaller, and flanking a potential breakpoint in a chromosome.
Owner:DAKOAS
Use of CD40 engagement to alter T cell receptor usage
InactiveUS20050048055A1Promote maturitySpecificity can be alteredSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsAntigenCell lineage
The invention relates to methods for altering and enhancing the immune response toward an antigen. More specifically, the present invention relates to methods of using CD40 engagement on T cells to induce T cell receptor gene rearrangement and enhance T cell affinity for a particular antigen. The invention also relates to methods for promoting developmental maturation of an immature cell of the T cell lineage.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF VERMONT +1
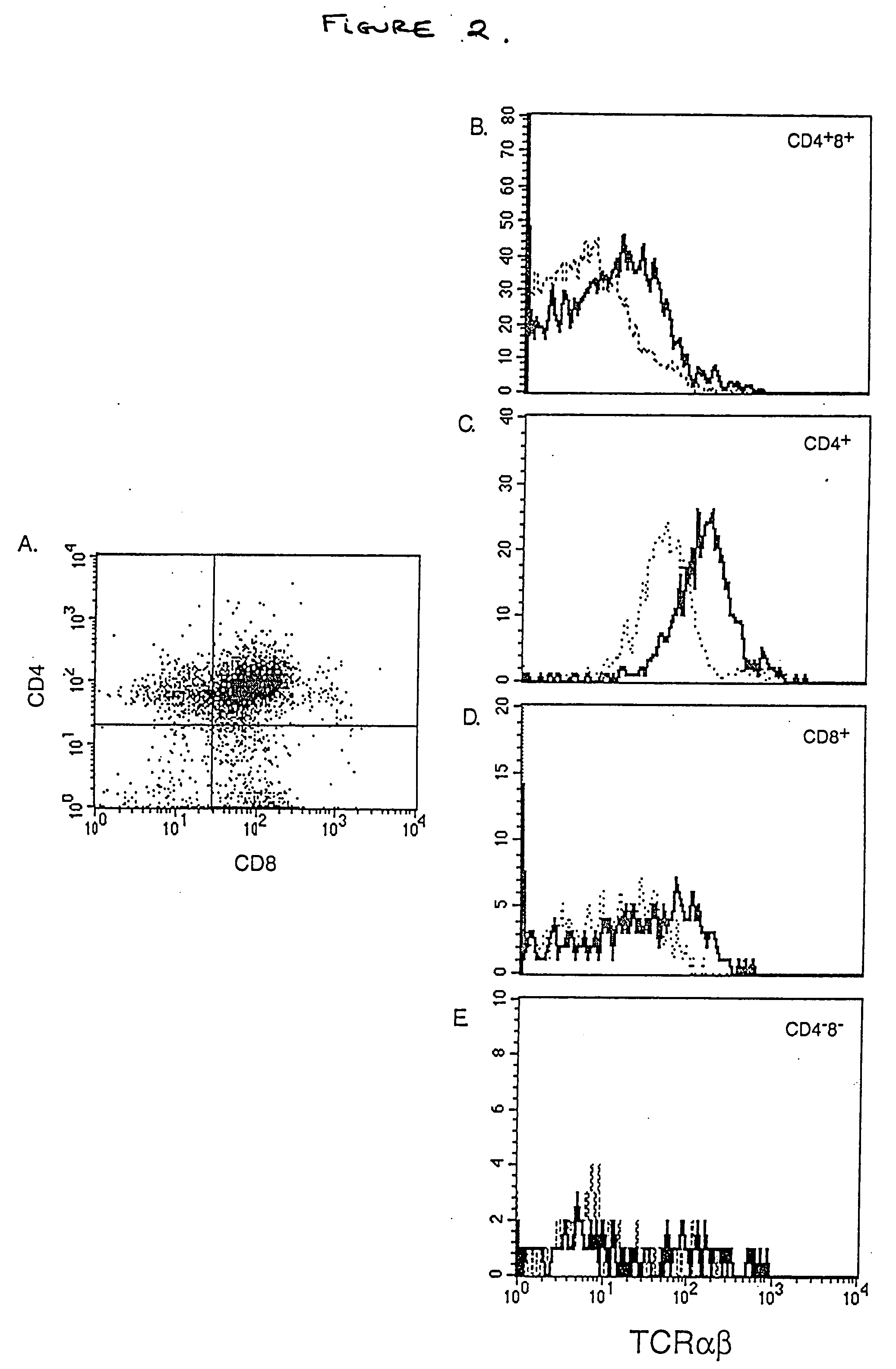
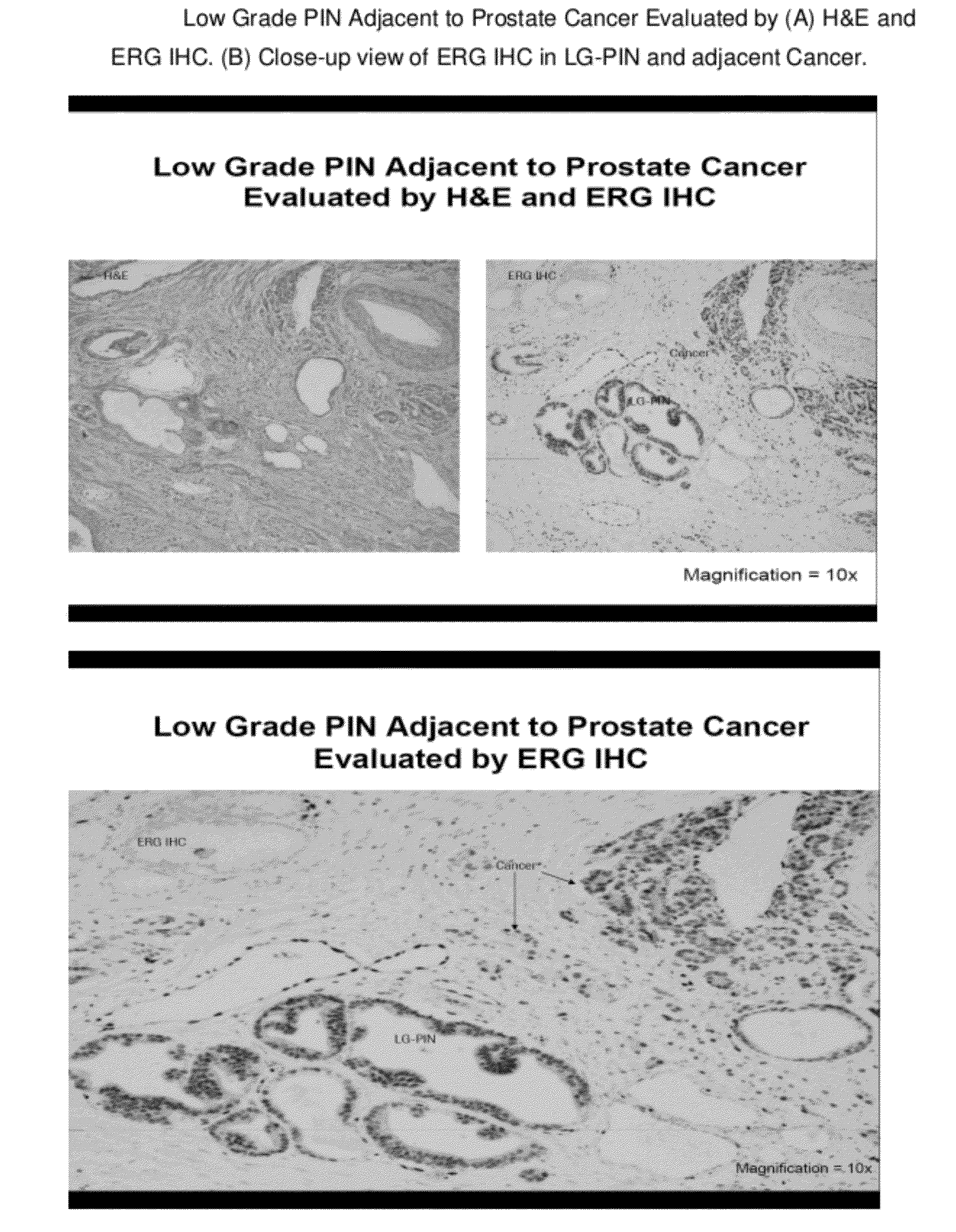
Presence of ERG Gene Rearrangements and Protein Over-expression in Low Grade PIN (LG-PIN) in Prostate Biopsies
InactiveUS20120220672A1Simple methodBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementWho gradeProtein insertion
Owner:VENTANA MEDICAL SYST INC
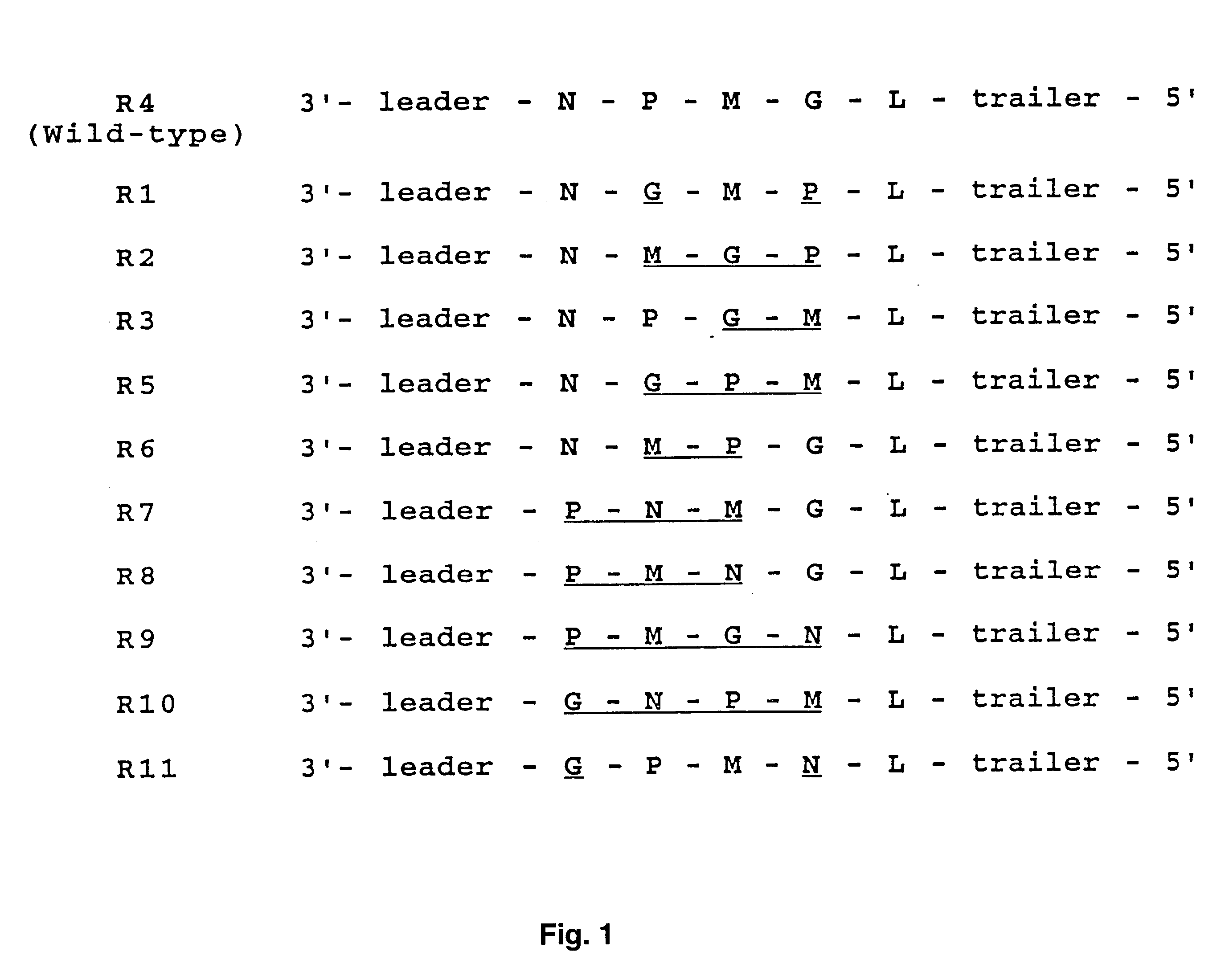
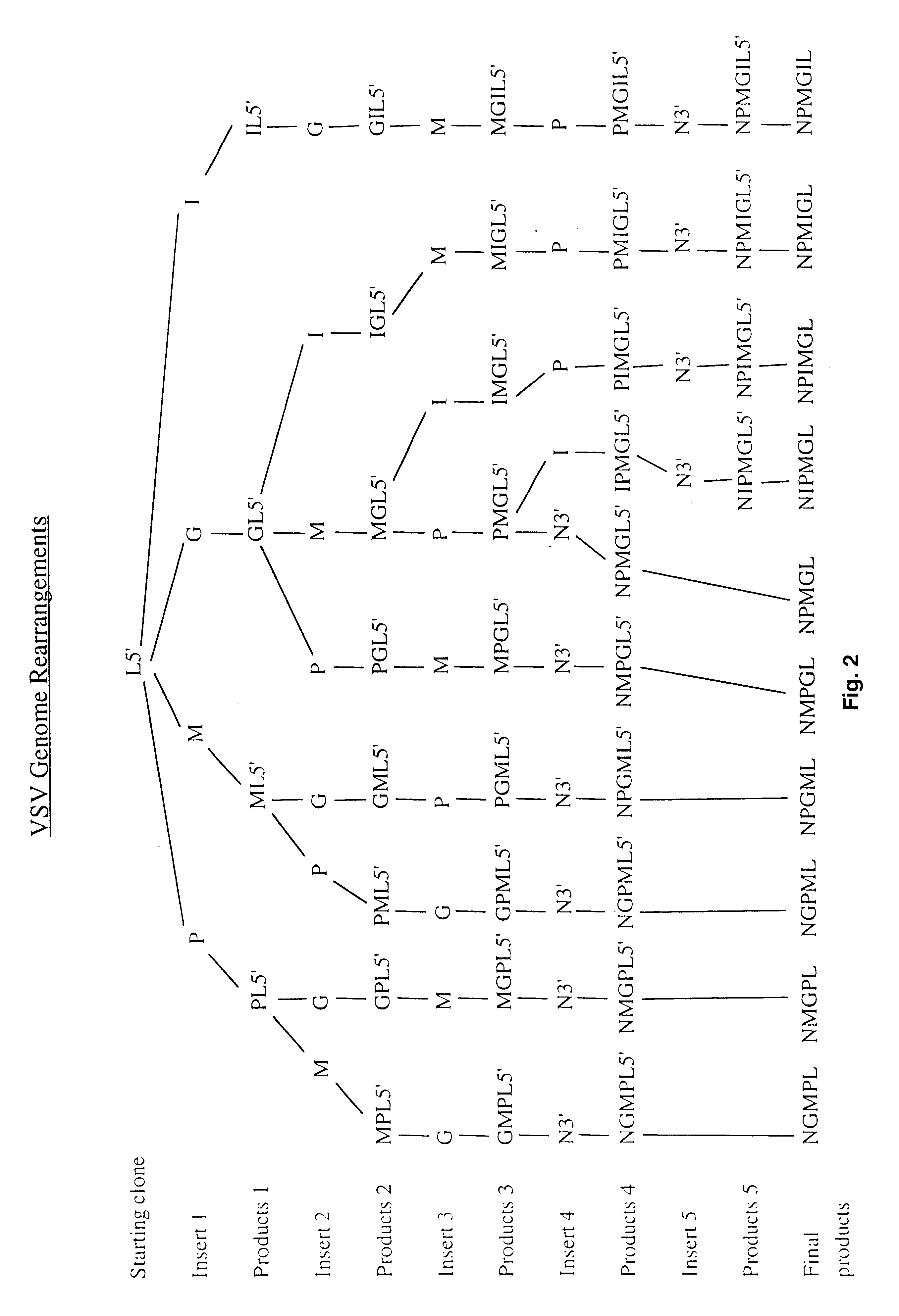
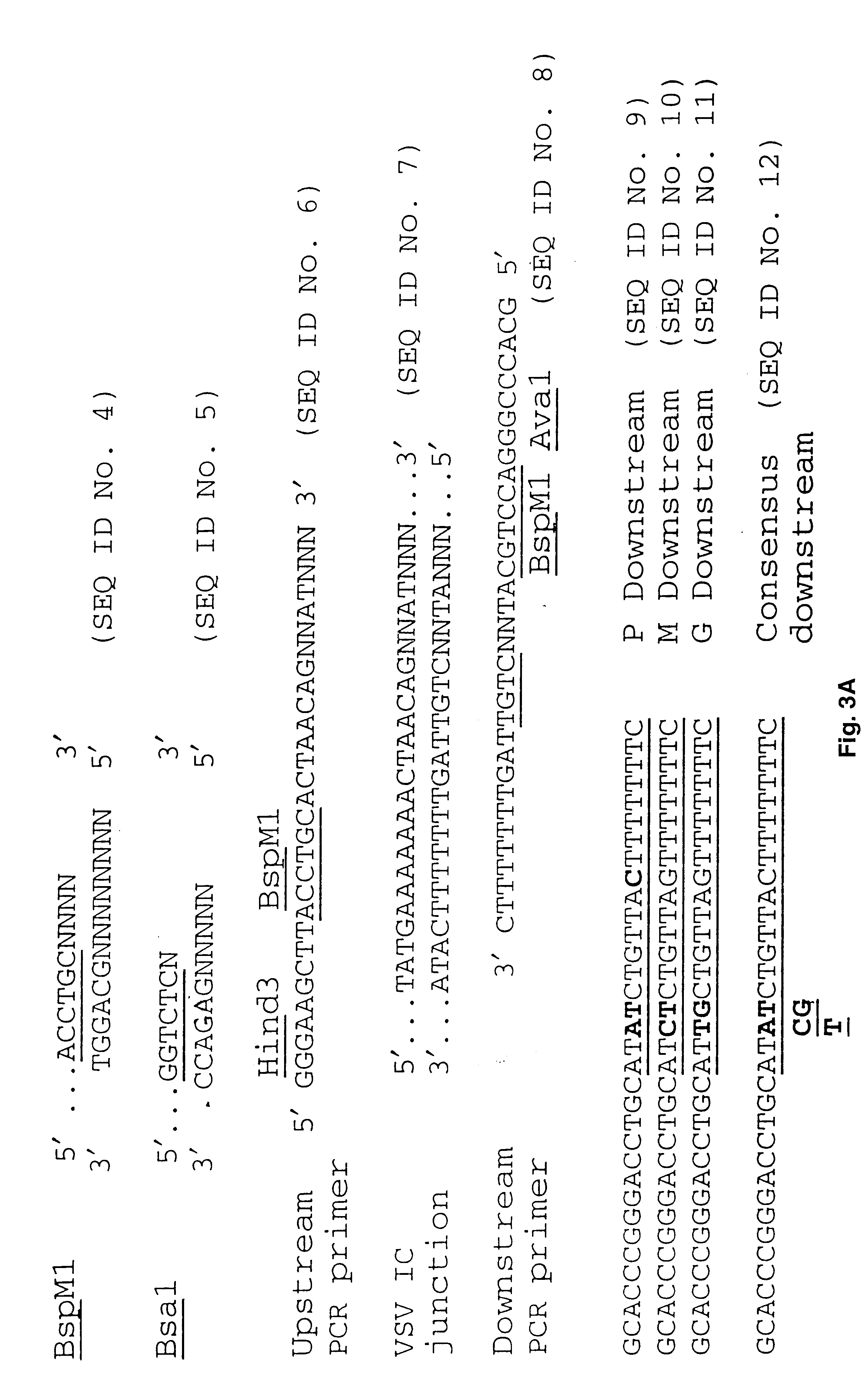
Manipulation of negative stranded RNA viruses by rearrangement of their genes and uses thereof
InactiveUS6596529B1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsOrder MononegaviralesRecombinant virus
The present invention provides a method of increasing expression of a promoter distal gene in a virus of the order Mononegavirales, and a recombinant virus constructed by such method. Also provided is a method of attenuating a virus of the order Mononegavirales, and of constructing an attenuated virus useful for a vaccine.
Owner:UAB RES FOUND
Preparation method of transgenic animal capable of expressing human antibody
ActiveCN103571872AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryGenomic DNAGene conversion
The invention relates to a preparation method of a mouse capable of producing a human antibody. The preparation method of the mouse capable of producing the human antibody comprises the step of carrying out hybridization on a transgenic mouse carrying a fragment containing a human antibody heavy chain gene locus part and a mouse carrying a fragment which is inserted into mouse genomic DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) and contains an non-rearranged human antibody light chain gene locus part, wherein gene rearrangement and gene conversion can be carried out in the transgenic mouse by virtue of the human antibody heavy chain gene locus and the human antibody light chain gene locus, so as to produce various human immune globulins, and a mouse endogenous antibody heavy chain gene locus, a mouse endogenous antibody kappa light chain gene locus and a Lamda light chain gene locus are inactivated.
Owner:SHANDONG BIOANTY BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
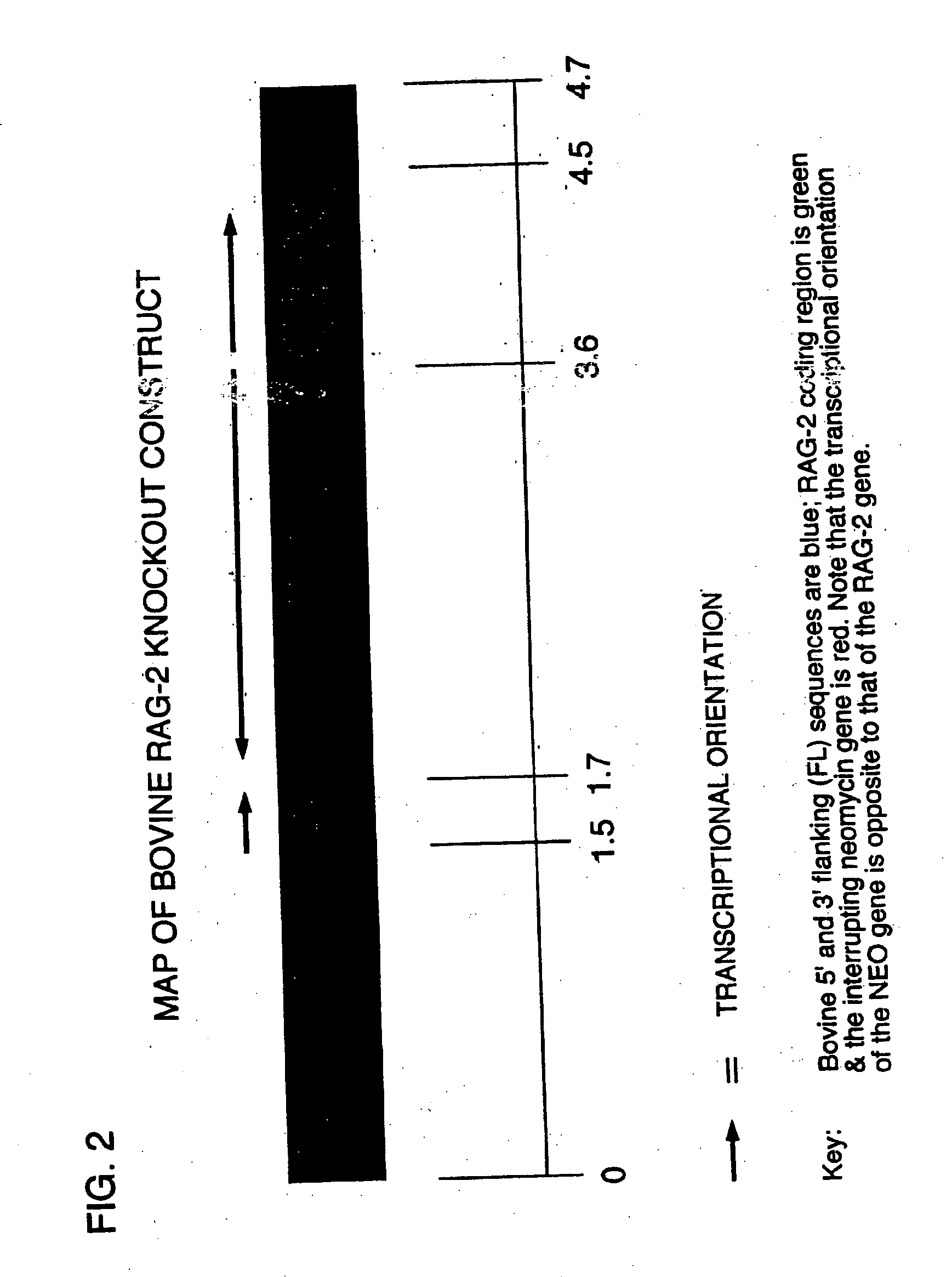
Production of ungulates, preferably bovines that produce human immunoglobulins
The present invention relates to a method of producing an ungulate having both copies of the IgM heavy chain (mu) rag-1 and / or rag-2 gene eliminated from its genome. Animals which have IgM, rag-1 and / or rag-2 eliminated from their genome are unable to conduct the gene rearrangements that are necessary to generate the antigen receptors of B or T lymphocytes, and therefore will not develop native B or T cells. Because they are unable to produce B and T lymphocytes, these IgM, rag-1 or rag-2 ungulates cannot reject human hematopoietic stem cell preparations, and B and T lymphocytes which develop therefrom. Therefore, the present invention also involves injecting into IgM, rag-1 and / or rag-2 deficient ungulates, in utero or shortly after birth, human B and T lymphocytes whose immune systems produce human immunoglobulin that can be processed for therapeutic uses in humans.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KIRIN CO LTD
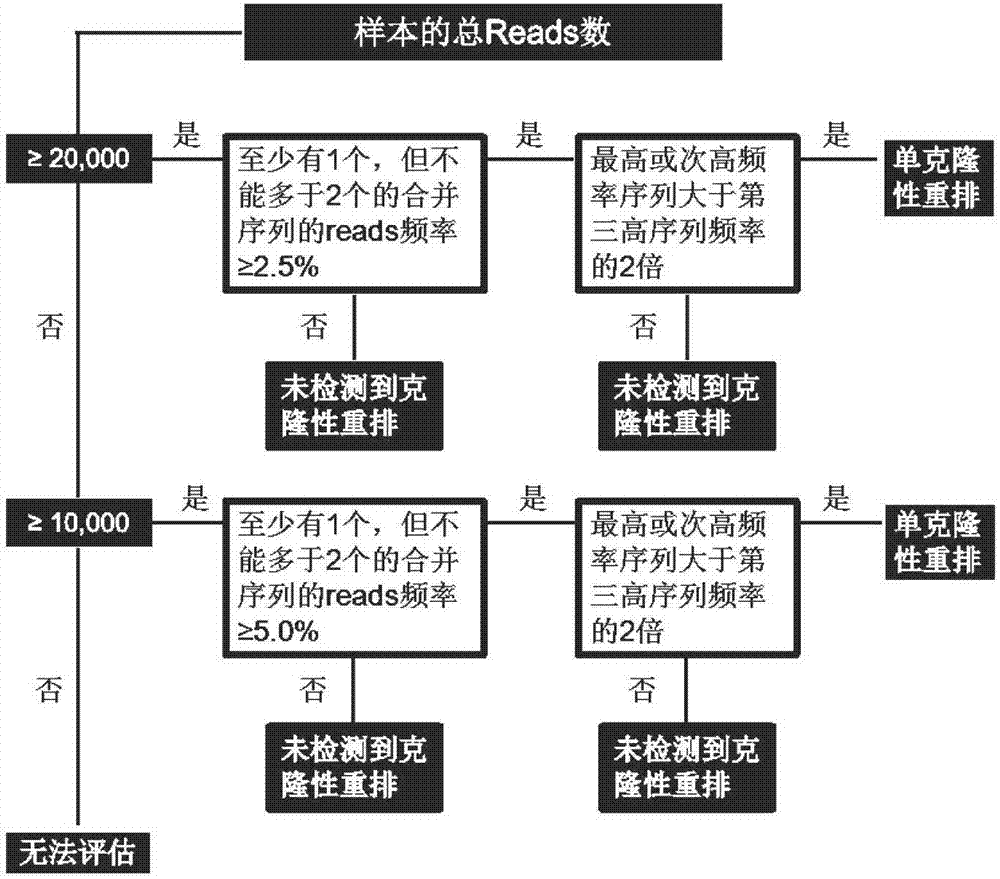
Method for detecting rearrangement clonality of correlative genes of lymphocyte
ActiveCN108004304AHigh detection throughputHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for detecting rearrangement clonality of correlative genes of lymphocyte and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the method, a high-throughput next-generation sequencing method is adopted for detecting rearrangement clonality of the correlative genes of lymphocyte tissue, and specifically, a multifunctional primer and a PCR reagent are utilizedto conduct multiplication on samples to be detected at first to obtain a multi-sample gene locus multiplication sublibrary, wherein both ends of the multiplication sublibrary are connected with DNA segments of different connectors, one side of the multiplication sublibrary is a sequencing connector which can contain a sample tag for distinguishing sequencing results of the different samples, and the other side of the multiplication sublibrary is a fixed connector used for connecting caught particles; then, high-throughput sequencing is conducted on the multiplication sublibrary, sequencing results are subjected to classified sorting according to a tag sequence, the samples and target genetic loci, and whether or not there is clonality rearrangement of target genes is analyzed. The method has the advantages that the detection throughput, the sensitivity and the specificity are high, the sensitivity can reach 0.01%, and the DNA concentration of the samples can be lowered to 0.1-1ng / microliter.
Owner:北京旌准医疗科技有限公司
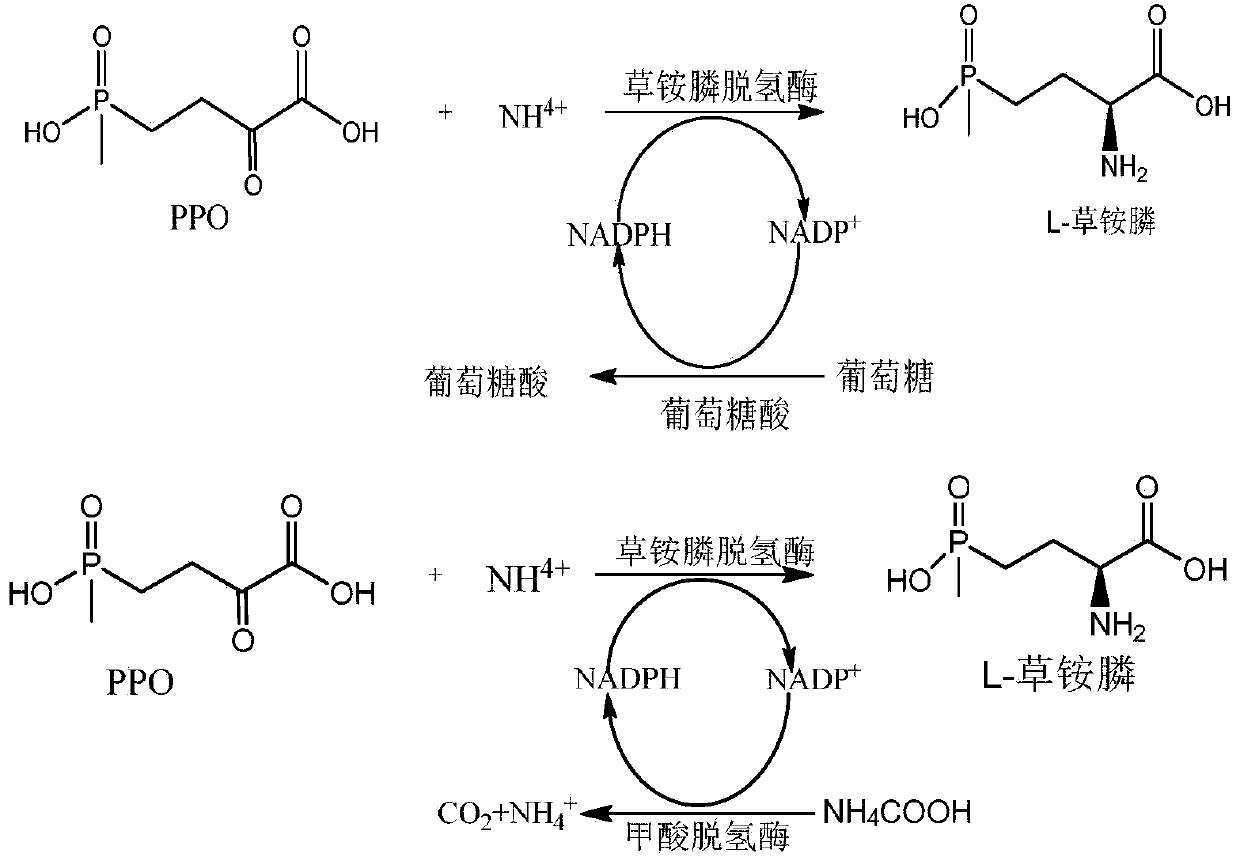
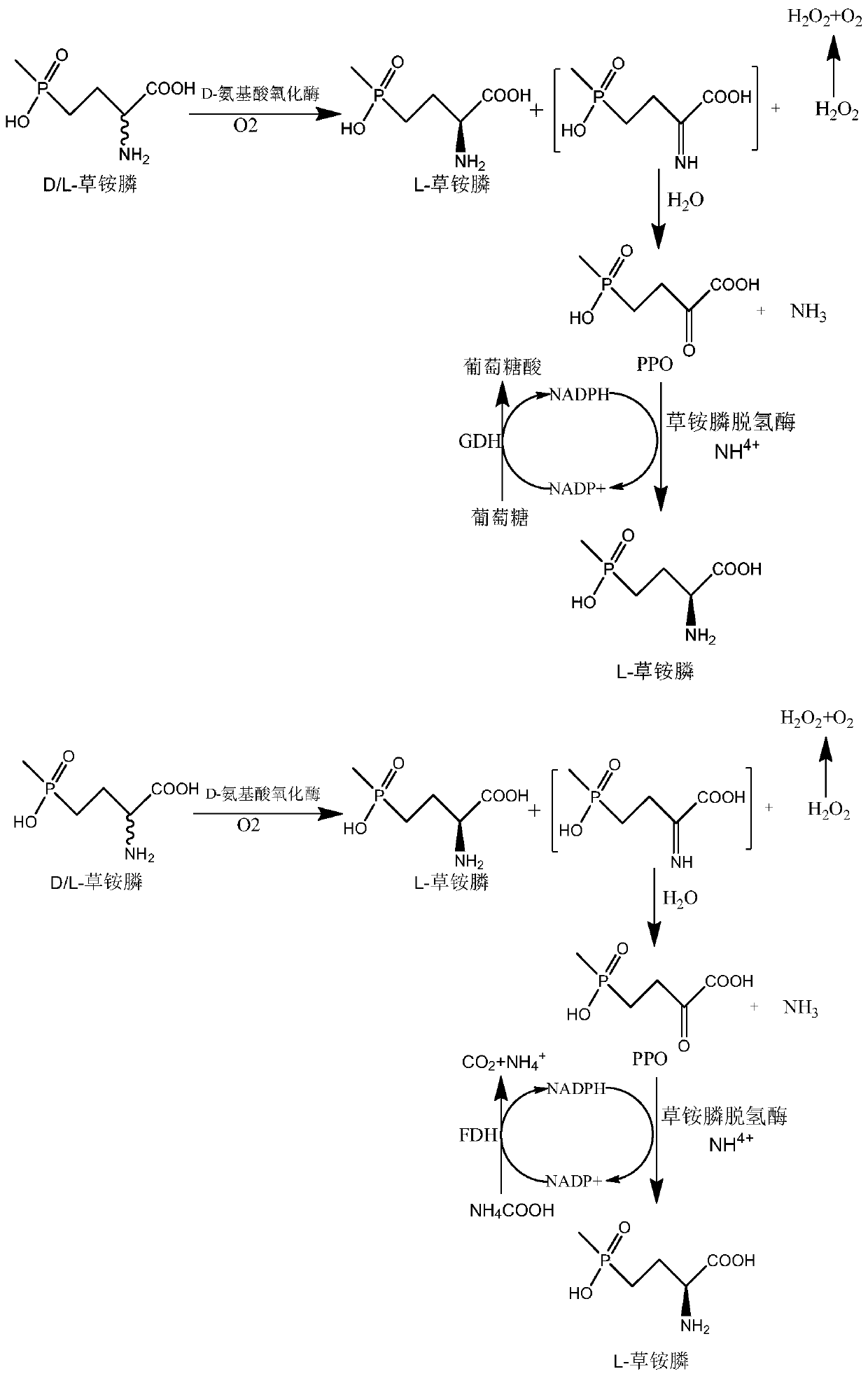
Recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase, genetically engineered bacterium and application of recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase in preparation of L-glufosinate-ammonium
InactiveCN110885803AIncrease enzyme activityImprove catalytic performanceBacteriaEnzymesEngineered geneticMutant
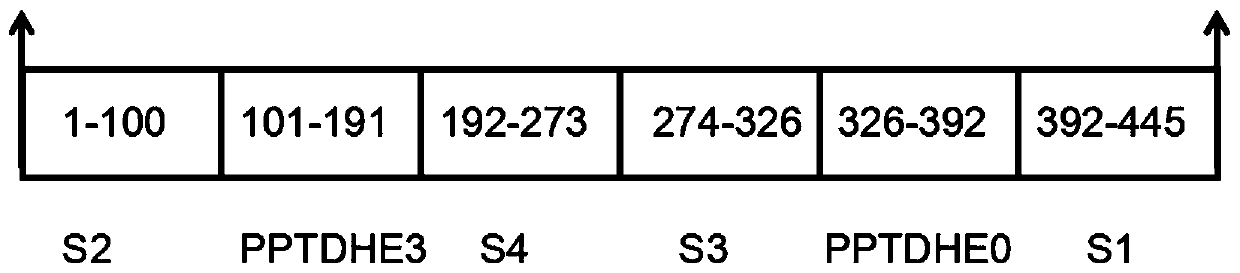
The invention discloses recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase, a genetically engineered bacterium and application of recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase in preparation of L-glufosinate-ammonium. The amino acid sequence of the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. According to the invention, a gene library of the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase is constructed through a staggered extension pcr gene rearrangement technology, and the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase with high enzyme activity, catalytic performanceand stereoselectivity is screened from the gene library; the activity of the recombinant glufosinate-ammonium dehydrogenase is respectively improved by 31% and 35% in comparison with the activity of aprevious mutant PPTDHE3-A164G and the activity of a previous mutant PPTDHE0-V375S; and finally, 108 g / L of 2-carbonyl-4-(hydroxymethyl phosphine oxide)-butyric acid is completely catalyzed to producethe L-glufosinate-ammonium, and only 20min is needed (transaminase generally needs 40h), wherein the ee value is larger than 99.5%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
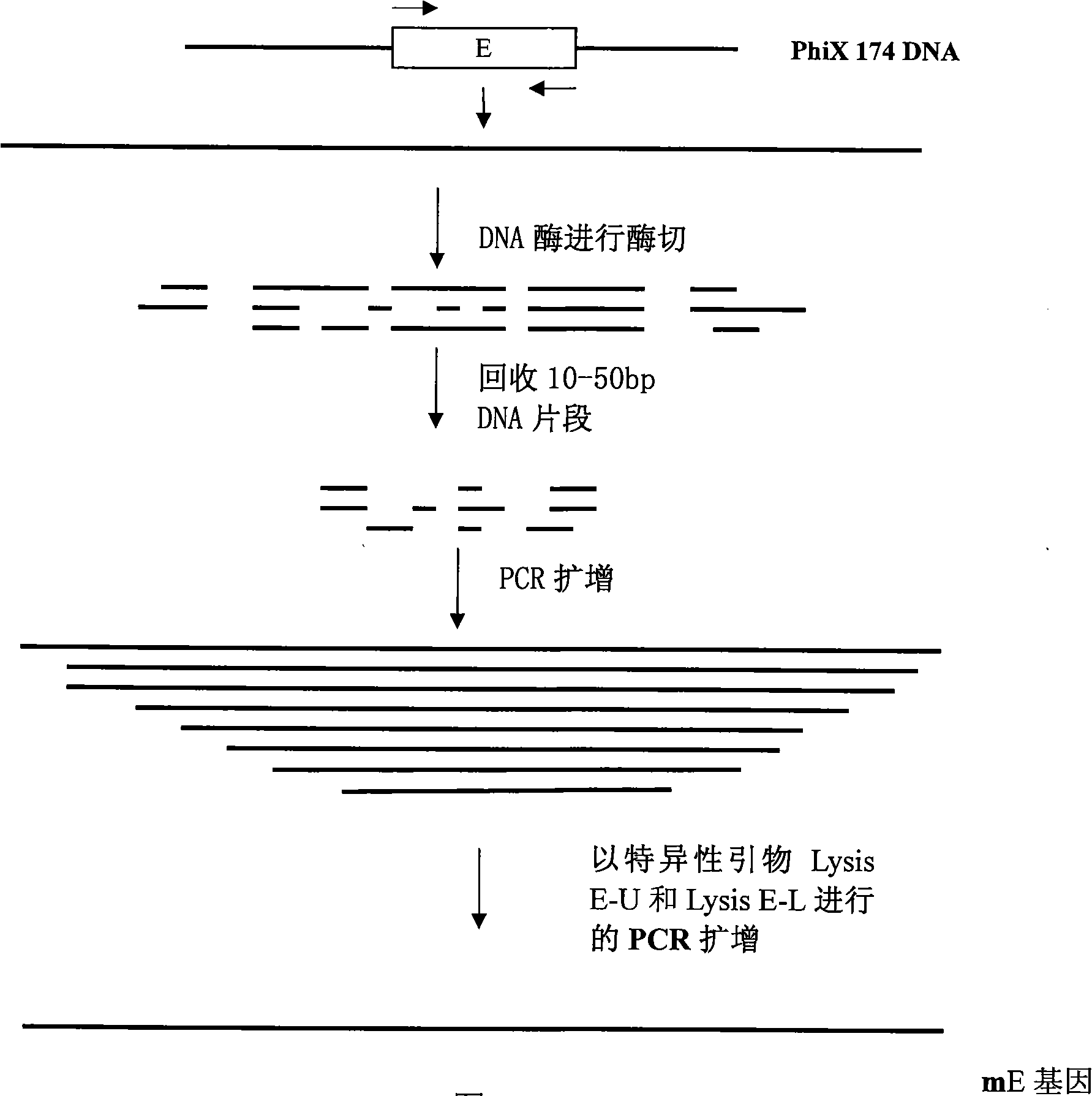
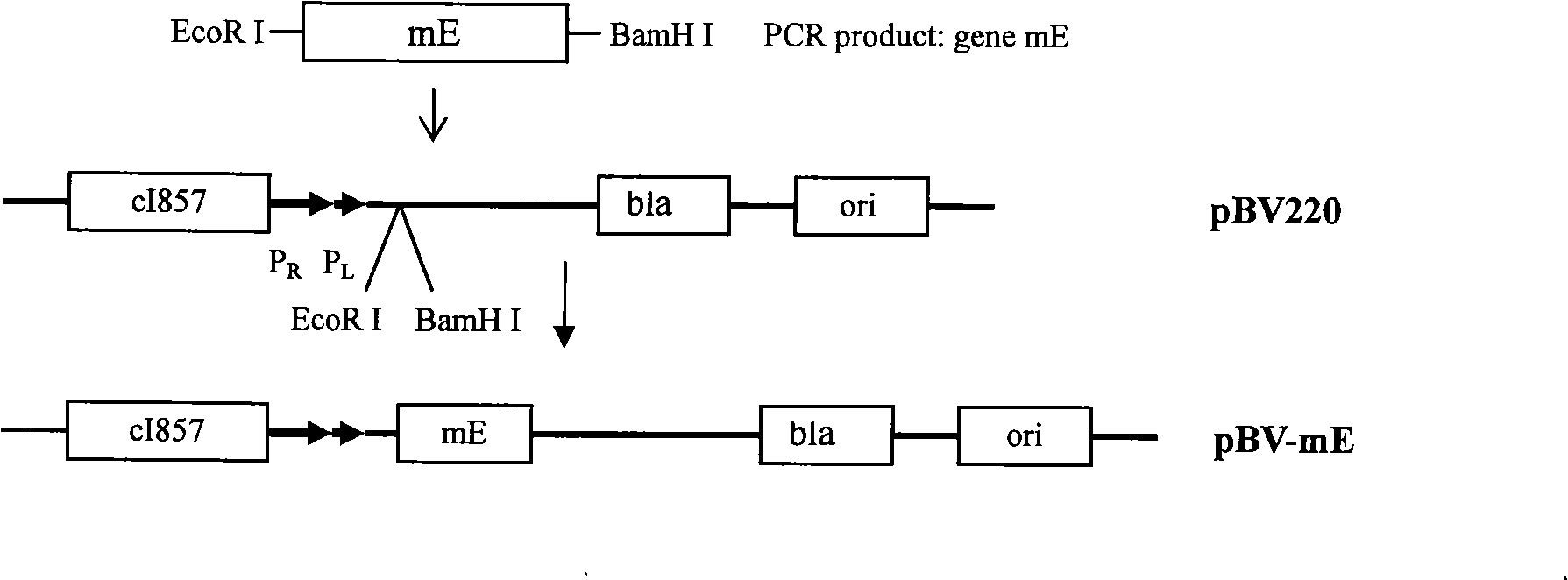
Rearranged bacterial virus E gene, perforating plasmid vector containing the same and use thereof
InactiveCN101302527AImprove drilling efficiencyImprove cracking efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacterial virusEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a PhiX174 bacterial virus mE gene obtained by gene rearrangement and a perforating plasmid vector containing the gene as well as a method for building the same. The invention further relates to an application of the perforating plasmid vector for making bacterial ghost, belonging to the gene engineering field. The PhiX174 bacterial virus E gene is rearranged by using the gene rearrangement technology so that a reading frame with E containing 276 nucleotides is mutated as a reading frame with mE (from ATG at the 76th site) containing 201 nucleotides by deleting A of an initial codon ATG at the first site. The made mE gene is maneuverably connected with pBV 220 vector to perforate the vector pBV-mE, and the vector pBV-mE can effectively improve perforation efficiency of the cell and lysis efficiency is up to 99.9613 percent. Compared with the prior perforating plasmid vector, the lysis efficiency of homophytic escherichia coli is more than three orders of magnitude.
Owner:HARBIN VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Lymphocyte gene rearrangement clonality assay kit and assay method thereof
InactiveCN102605070AWide coverageImproves and increases sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementLymphocyteLymphoid Neoplasm
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological reagents, and relates to the assay of gene rearrangement clonality related to lymphoid neoplasm diagnosis. The development of a full-primer coverage, low-cost and easy-to-operate lymphoid tissue gene rearrangement assay kit capable of being popularized in ordinary hospitals is urgently needed clinically. The invention discloses a lymphocyte gene rearrangement clonality assay kit, which is all-liquid reagent based on combined primers, and the invention also provides a related assay method and a hierarchical optimization scheme. When the kit is used for assaying the clonality of lymphocyte gene rearrangement, the assay accuracy can reach more than 99 percent, moreover, the steps of the assay method are simple, the total cost is low, and the invention is highly worth popularizing clinically.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
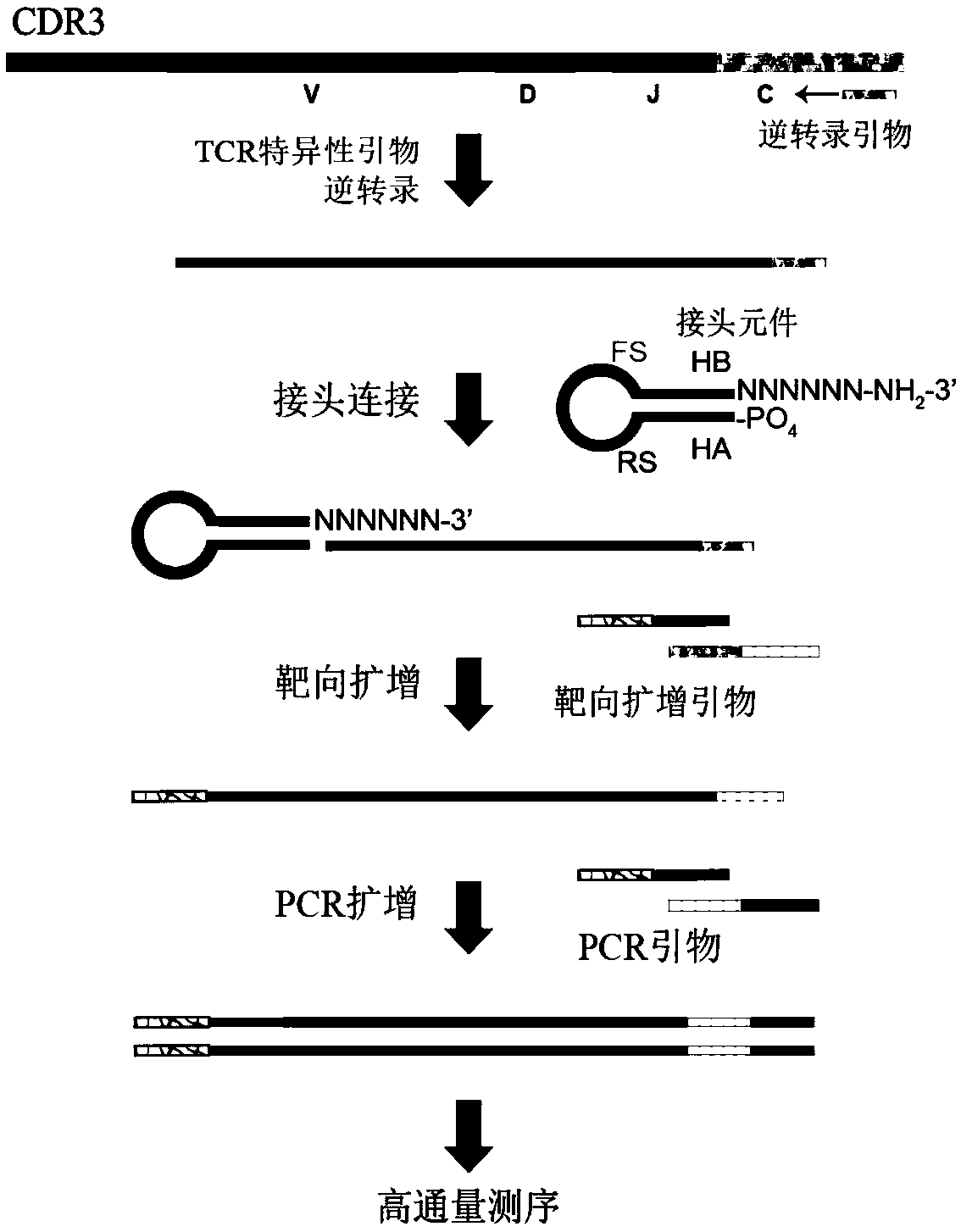
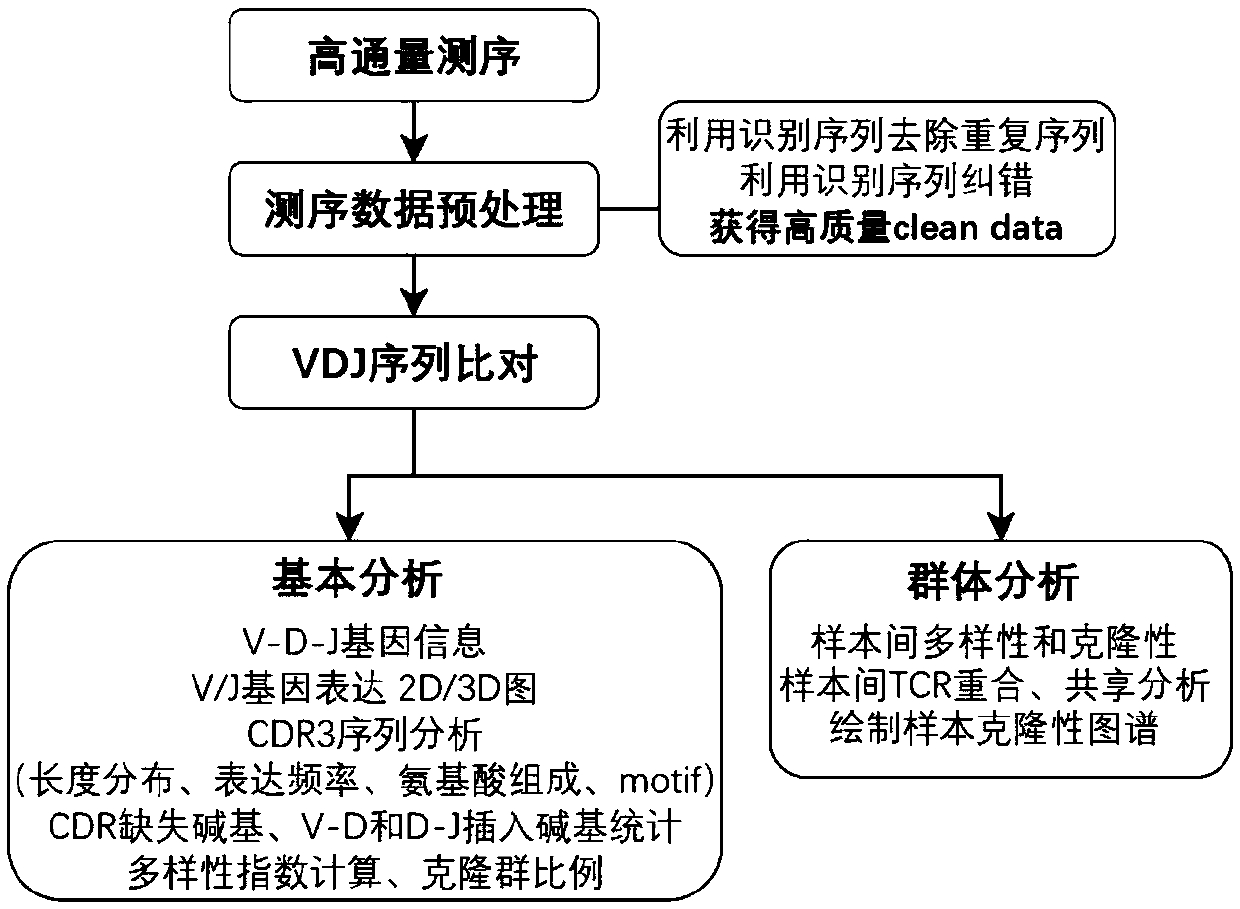
Specific recognition sequence based T cell receptor high-throughput sequencing library construction and sequencing data analysis method
PendingCN111363783AComprehensive and Accurate Diversity InformationLower preferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisA-DNAV region
The present invention discloses a specific recognition sequence based T cell receptor high-throughput sequencing library construction and sequencing data analysis method. According to the method, a specific reverse transcription primer is designed for an mRNA sequence of a C region of a TCR constant region, cDNA is obtained by reverse transcription, and the 3' end of the cDNA is connected with a library construction linker with a specific recognition sequence; then the linker with the specific recognition sequence is added by using a splint connection method, and a TCR gene rearrangement sequence is amplified under the action of DNA polymerase by utilizing a gene specific primer with a tag; and finally a DNA library is added with a sequencing linker by PCR amplification to prepare a high-throughput sequencing library, and the high-throughput sequencing library is used for sequencing. The TCR gene diversity is comprehensively analyzed by bioinformatics, and a rearrangement rule of TCR genes including J region, D region and V region genes can be accurately obtained. The method is high in library construction efficiency, few in library construction step, low in required RNA initial quantity and low in library construction cost.
Owner:武汉康测科技有限公司
A method for preparing transgenic animals capable of expressing human antibodies
ActiveCN103571872BVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryAntibody fragmentsGene conversion
The present invention relates to a method for preparing a mouse capable of producing human antibodies, the method comprising combining a transgenic mouse carrying a partial fragment of a heavy chain locus of a human antibody, and a human antibody carrying an unrearranged human antibody inserted into the genomic DNA of the mouse. Mouse crosses of partial fragments of antibody light chain loci that can undergo gene rearrangement and gene conversion in transgenic mice to produce various human immunoglobulins. Among them, the mouse endogenous antibody heavy chain locus, the mouse endogenous antibody κ light chain locus and the Lamda light chain locus were inactivated.
Owner:SHANDONG BIOANTY BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting gene rearrangement, device, storage medium and processor
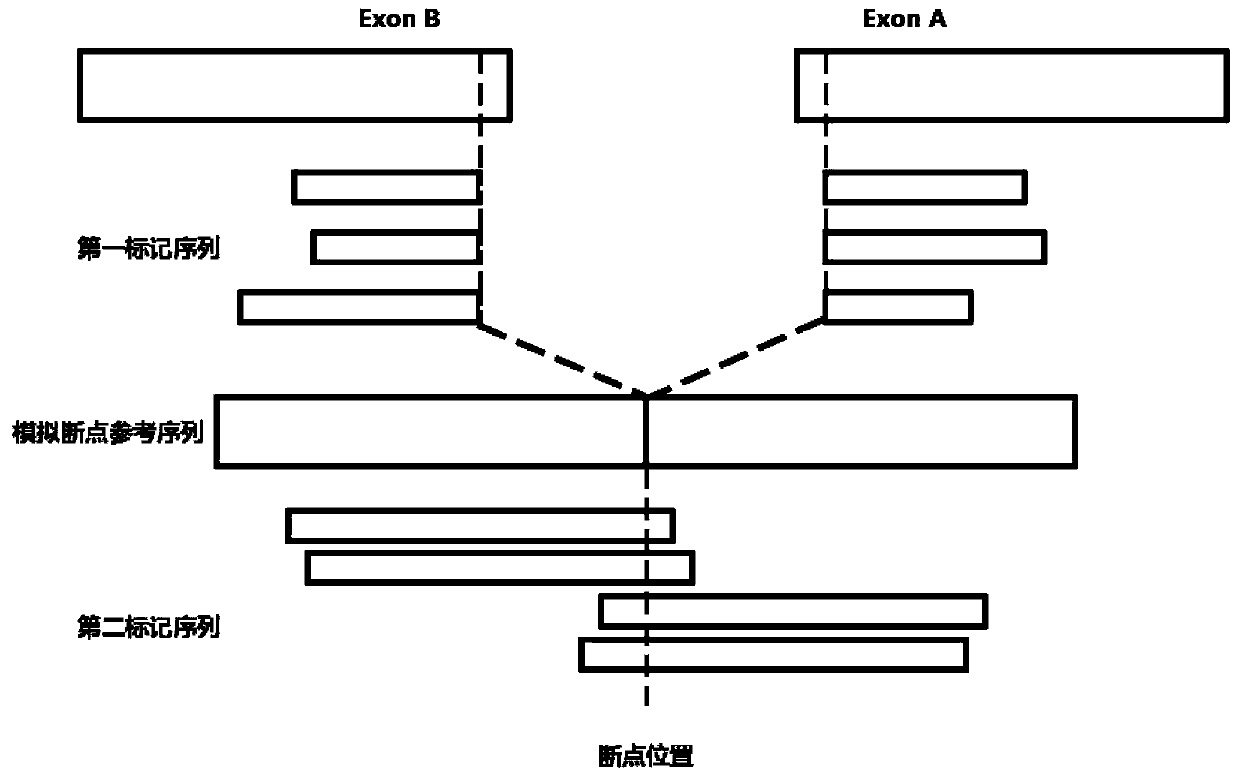
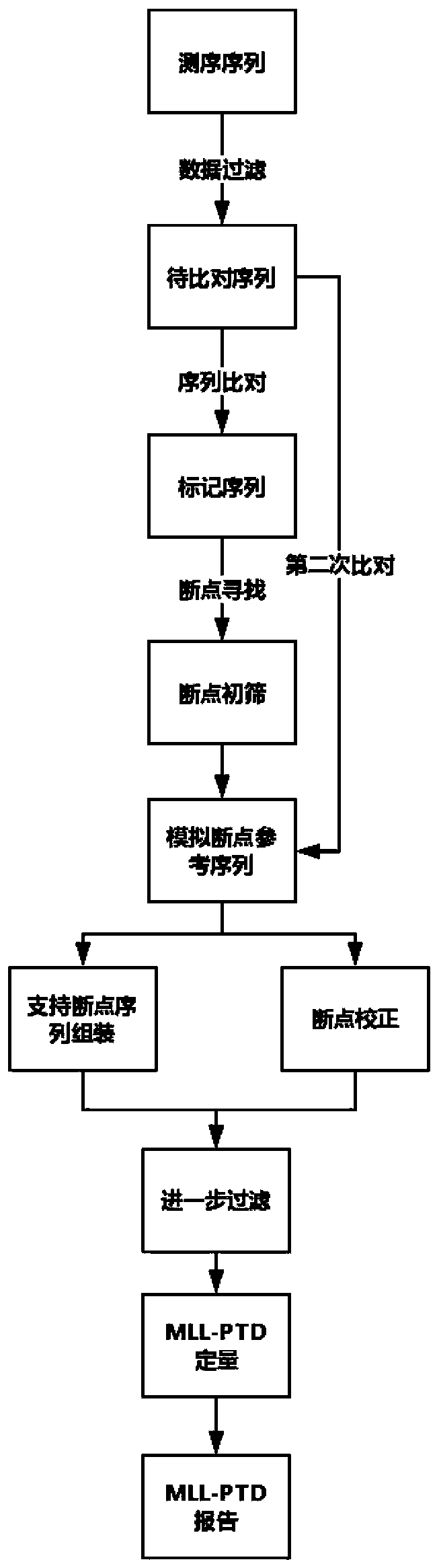
The invention provides a method for detecting gene rearrangement, a device, a storage medium and a processor. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a to-be-compared sequence of a to-be-tested sample; comparing the to-be-compared sequence with a reference genome, obtaining an abnormal comparison sequence, wherein the abnormal comparison sequence comprises the sequences with abnormal comparingpositions, the sequence with abnormal comparing directions, and the sequence incapable of comparing with the reference genome; determining the position of a candidate breakpoint according to the comparing position and the comparing direction of the abnormal comparison sequence in the reference genome; performing assembly by means of the sequence at the position which supports the candidate breakpoint in the to-be-compared sequence, and keeping the breakpoints same with the sequence information at the position of the candidate breakpoint in an assembling result as the breakpoints for gene rearrangement. The method, the device, the storage medium and the processor settle a problem of high difficulty in detecting the positions of the gene rearrangement in prior art.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
Hydrophobia-canine distemper-canine parvovirus genetic recombination virus strain, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN107988174AHigh expressionExpress influenceSsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsRabiesCanine parvovirus
The invention discloses a hydrophobia-canine distemper-canine parvovirus genetic recombination virus strain, a construction method and application thereof. Through a homologous recombination method, agene replacement method and a gene insertion method, a full-length genome of a virus is subjected to gene rearrangement, and a rearranged hydrophobia virus genome plasmid with a canine distemper G gene and a canine parvovirus VP2 gene is constructed and is named as a hydrophobia-canine distemper-canine parvovirus, which is pcDSRV9-NG-eGFP+CDV N-PM+VP2-L genome plasmid; the hydrophobia-canine distemper-canine parvovirus is rescued through a reverse genetic method, and is an rSRV9+CDV N+VP2 gene recombinant virus; a gene nucleotide sequence of a recombination hydrophobia virus is SEQ ID NO:1. The recombination gene virus provided by the invention can be applied to researching a trigeminy oral vaccine for hydrophobia, canine distemper and canine parvovirus of canine and other wild animals soas to prevent three infectious diseases.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI UNIV
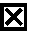
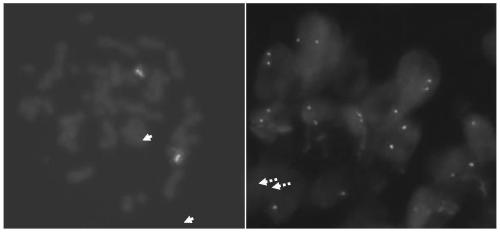
Assay for bcr/abl gene rearrangement
InactiveUS20050037373A1Uniform valueSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr methodProtein translocation
The present invention provides a simple high-throughput assay for detecting bcr / abl translocations. The method includes qualitative PCR methods for identifying the particular amplified translocation (e1a2 or b2a3 / b3a2) and real time PCR for quantifying an amount of bcr / abl transcript (e1a2, b2a3 and b3a2). Quantitative measurement of bcr / abl transcript in accordance with the methods of the invention is useful for monitoring response to therapy.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Assay for bcr/abl gene rearrangement
InactiveUS7700279B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPcr methodProtein translocation
The present invention provides a simple high-throughput assay for detecting bcr / abl translocations. The method includes qualitative PCR methods for identifying the particular amplified translocation (e1a2 or b2a3 / b3a2) and real time PCR for quantifying an amount of bcr / abl transcript (e1a2, b2a3 and b3a2). Quantitative measurement of bcr / abl transcript in accordance with the methods of the invention is useful for monitoring response to therapy.
Owner:QUEST DIAGNOSTICS INVESTMENTS INC
Rapid detection kit and method of NTRK gene fusion
InactiveCN110144401ARapid hybridization testQuick layeringMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBac clonePolymerase L
The invention relates to a rapid detection method and kit of NTRK gene fusion and belongs to the field of molecular biological detection. According to the rapid detection kit of NTRK gene fusion, a probe is prepared through bought BAC cloning corresponding to the probe by use of phi29DNA polymerase labeling, a buffer solution component is determined by optimization, and the prepared kit can realize rapid hybridization within 2 h and accurate interpretation of NTRK gene rearrangement. The detection kit can better assist existing method for accurate layering, precise diagnosis and treatment of tumor through component optimization and detection of reagent commercialization and has better application prospects.
Owner:GUANGZHOU LBP MEDICINE SCI & TECH
Kit for combined detection of acute myeloid leukemia
The invention provides a kit for combined detection of acute myeloid leukemia. The kit comprises a special linker for DNA library construction, a specific composite primer for detecting gene rearrangement and gene whole exon mutation, and a composite primer for library amplification. The special linker is 8 dimers formed by a linker primer 1 and eight different i5-terminal primers respectively; the types of the gene rearrangement and the gene whole exon mutation are CBFB rearrangement, RUNX1 rearrangement, MLL rearrangement, RARA rearrangement, MECOM rearrangement and TP53 gene whole exon mutation; and the composite primer for library amplification has different i7 terminals. The kit provided by the invention can be used for detecting a plurality of common molecular genetic variations of acute myeloid leukemia at one time, and is simple to operate, short in time and high in detection efficiency.
Owner:苏州科贝生物技术有限公司
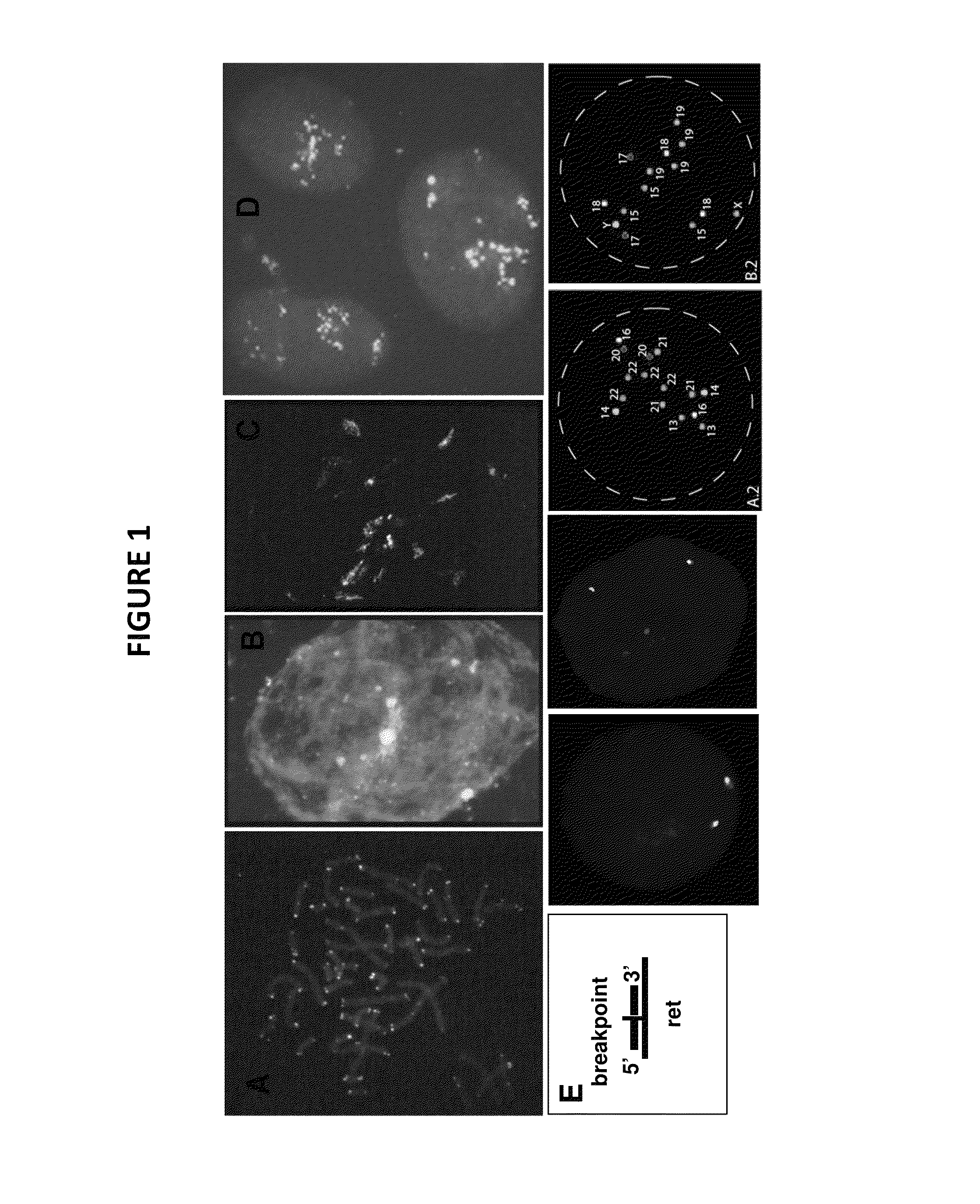
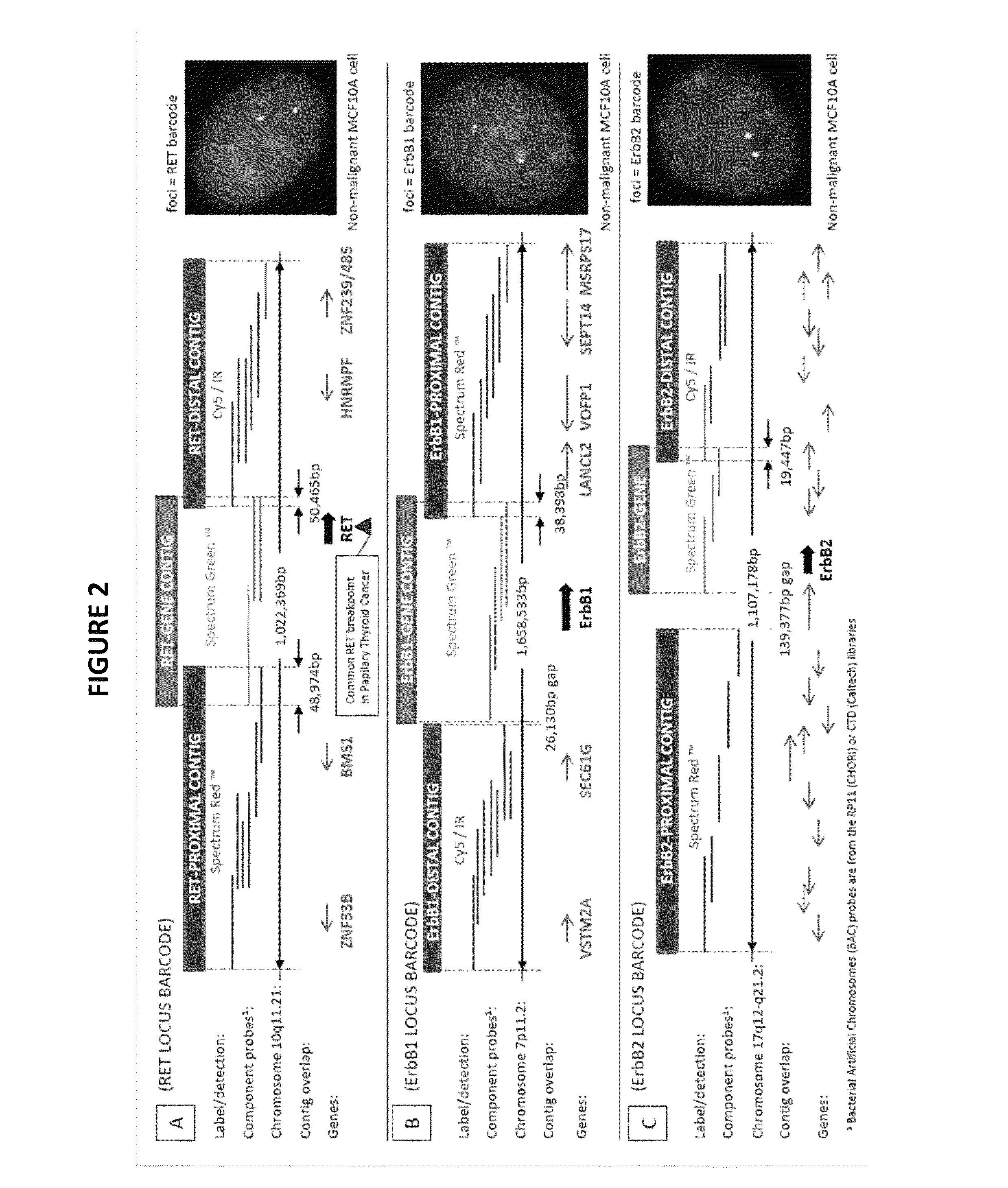
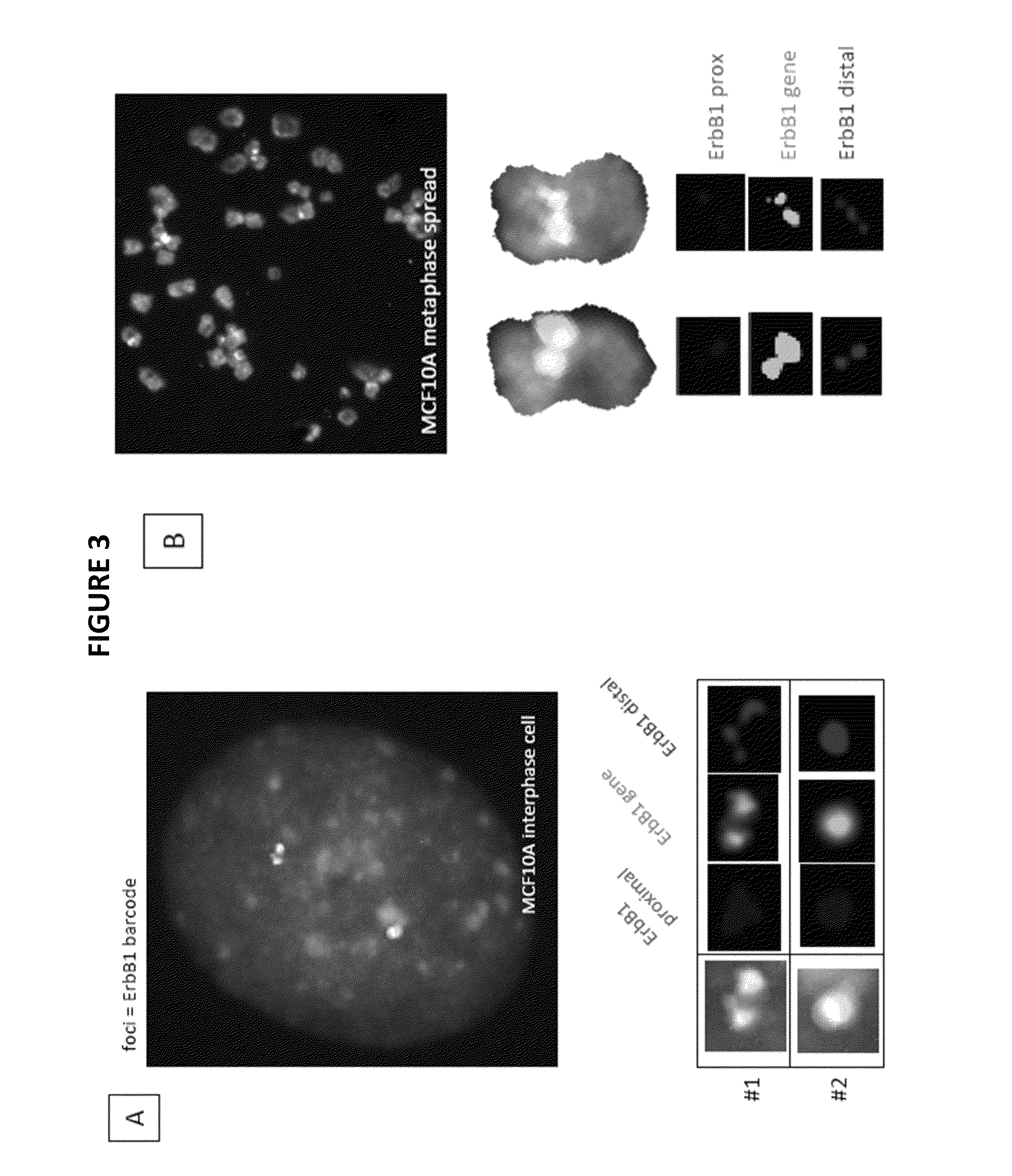
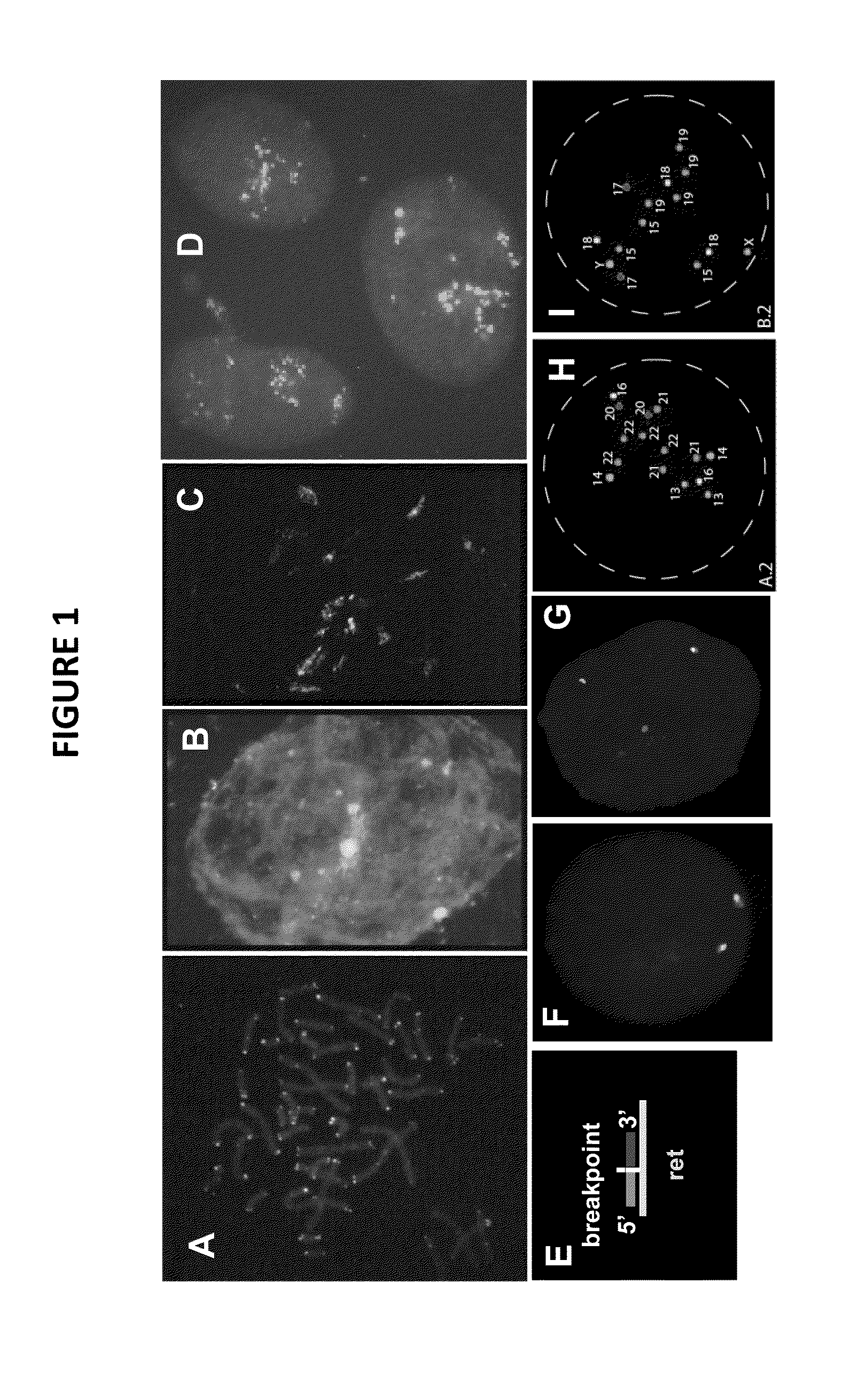
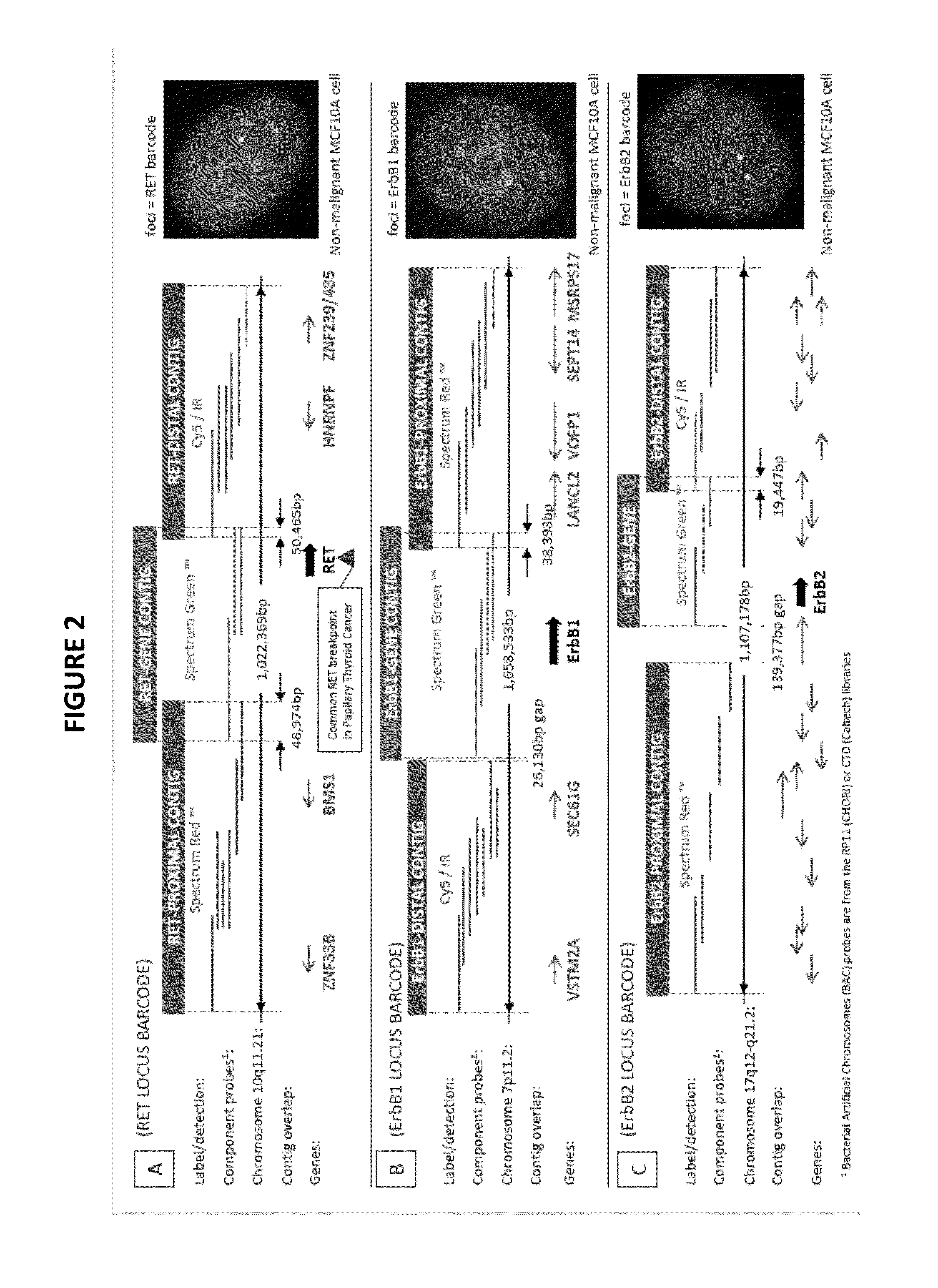
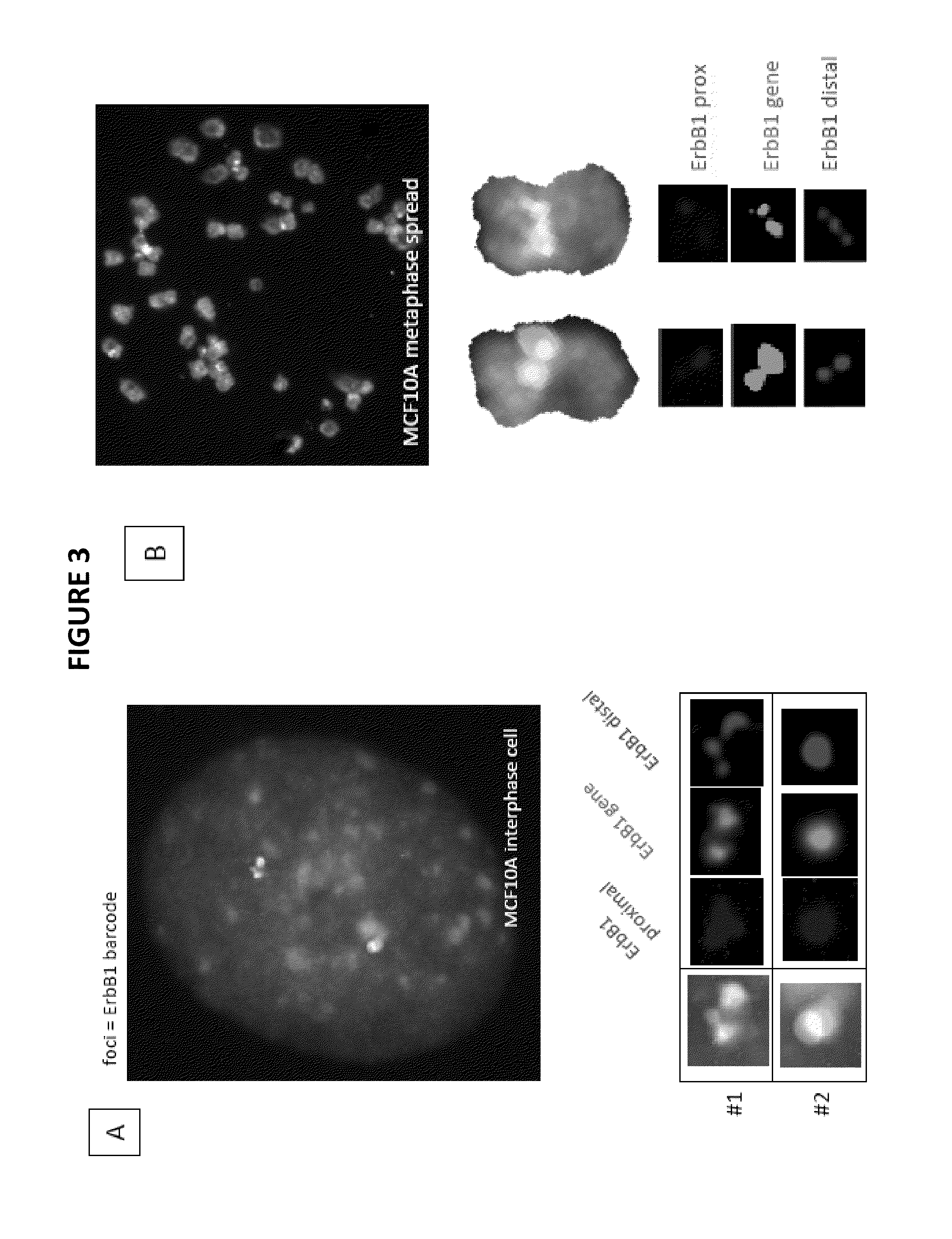
Genetic barcodes
ActiveUS9096902B2Easy to detectImprove applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseMulticolor fish
Herein are described multicolor FISH probe sets termed “genetic barcodes” targeting several cancer or disease-related loci to assess gene rearrangements and copy number changes in tumor cells. Two, three or more different fluorophores are used to detect the genetic barcode sections thus permitting unique labeling and multilocus analysis in individual cell nuclei. Gene specific barcodes can be generated and combined to provide both numerical and structural genetic information for these and other pertinent disease associated genes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Production of ungulates, preferably bovines that produce human immunoglobulins
InactiveUS7820878B2Eliminating expressionEnzymesGenetic engineeringLymphocyte antigen receptorIn utero
The present invention relates to a method of producing an ungulate having both copies of the IgM heavy chain (mu) rag-1 and / or rag-2 gene eliminated from its genome. Animals which have IgM, rag-1 and / or rag-2 eliminated from their genome are unable to conduct the gene rearrangements that are necessary to generate the antigen receptors of B- or T-lymphocytes, and therefore will not develop native B- or T-cells. Because they are unable to produce B- and T-lymphocytes, these IgM, rag-1, or rag-2 ungulates cannot reject human hematopoietic stem cell preparations, and B- and T-lymphocytes which develop therefrom. Therefore, the present invention also involves injecting into IgM, rag-1, and / or rag-2 deficient ungulates, in utero or shortly after birth, human B- and T-lymphocytes whose immune systems produce human immunoglobulin that can be processed for therapeutic uses in humans.
Owner:SAB LLC
Method For Introducing Exogenous Mitochondria Into A Mammalian Cell
InactiveUS20170159017A1The process is simple and effectiveStable expressionGenetically modified cellsOther foreign material introduction processesDiseaseSite-directed mutagenesis
The present disclosure provides a method for producing a cell with exogenous mitochondria by obtaining synthetic mitochondria via introduction of exogenous mitochondrial DNA into mitochondria or empty mitochondrial shells, and incorporating the same into mammalian cells via endocytosis. As such, effective functionality of exogenous mitochondria in cells is realized. The synthetic mitochondrial DNA genes introduced according to the present disclosure can be stably expressed and effectively passaged. The method for introducing exogenous mitochondrial DNA into mammalian cells as disclosed herein may be used as a whole new mitochondrial molecular cloning means to perform site-directed mutagenesis, gene insertion, gene knockout, gene rearrangement, and the like in mitochondria. Therefore, any molecular cloning modification can be performed on a mammalian mitochondrial DNA, which is of great importance to therapeutic schemes of diseases derived from mitochondrial DNA mutations.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
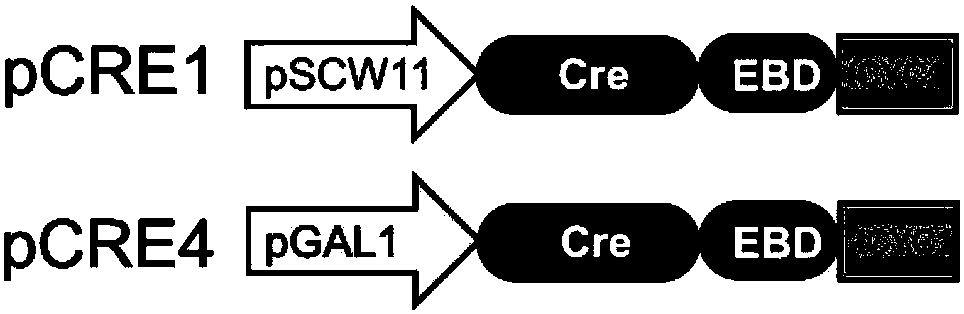
Gene element for accurately controlling gene rearrangement and recombinant plasmid and application thereof
ActiveCN108342408AAvoid the problem of leaky expressionsFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementYeastGenetic element
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and particularly discloses a genetic element for accurately controlling gene rearrangement and recombinant plasmid and application thereof. The gene element is formed by sequentially splicing a pGAL1 promoter, a Cre-EBD fusion protein gene and a terminator. According to the the gene element, the pGAL1 promoter, the Cre-EBD fusion protein gene and the terminator are combined to form a 'switch' of the SCRaMbLE-based gene rearrangement, and the gene element can control the expression of Cre, accurately control the opening and closing of the gene rearrangement, and avoid a leakage expression problem. The gene element can be applied to the subsequent construction of the recombinant plasmid and recombinant yeast strains and screening of dominant phenotypic yeast strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
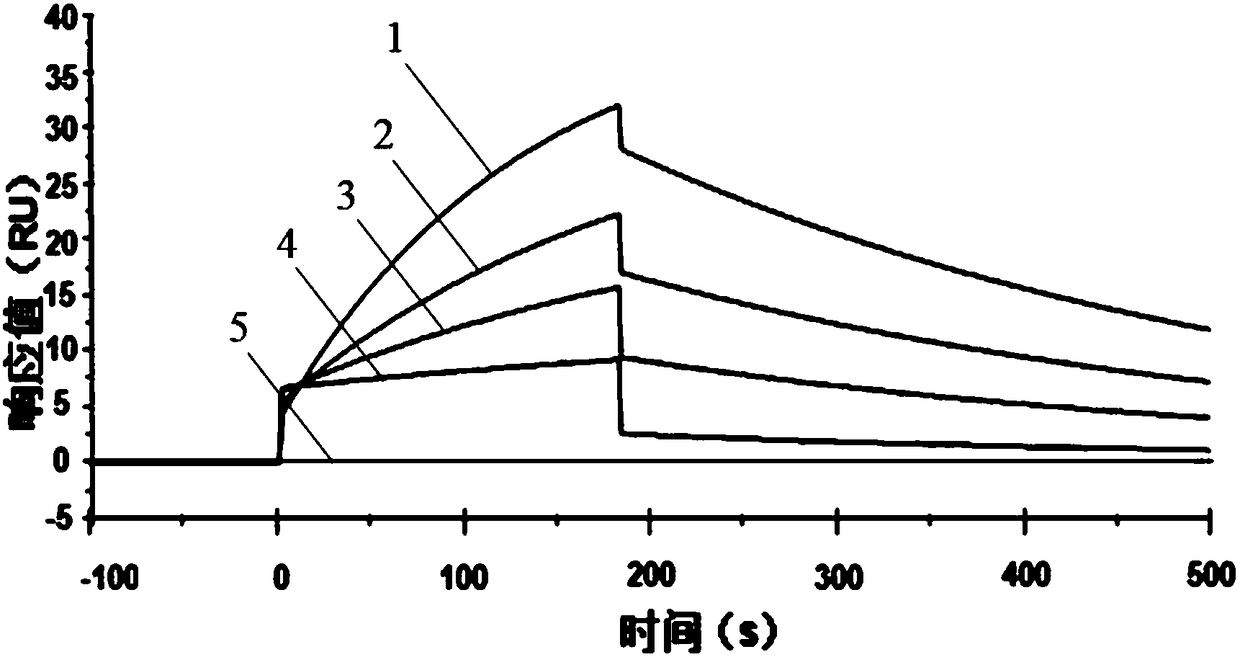
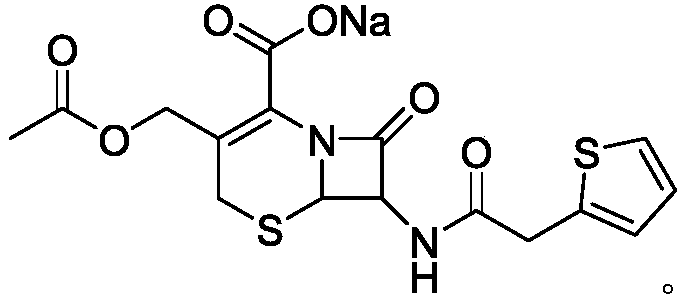
Applications of cefalotin sodium in anti-leukemia drugs
The invention provides applications of cefalotin sodium in preparation of drugs used for preventing or treating leukemia, and especially applications of cefalotin sodium in preparation of drugs used for preventing or treating mixed-lineage leukemia (MLL). According to an application method, histone lysine methyltransferases DOT1L participating in gene rearrangement of mixed-lineage leukemia is taken as a target protein, SPR technology is adopted, and cefalotin sodium with inhibition effect on the target protein is selected as an inhibitor; cefalotin sodium is combined with the target protein so as to inhibit the activity of the target protein, prevent participation of DOT1L in MLL gene rearrangement process, and prevent and treat leukemia. The invention also provides a drug used for preventing or treating leukemia.
Owner:TIANJIN INT JOINT ACADEMY OF BIOTECH & MEDICINE
Genetic Barcodes
ActiveUS20130316342A1Easy to detectInexpensive and accurateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementMulticolor fishBarcode
Herein are described multicolor FISH probe sets termed “genetic barcodes” targeting several cancer or disease-related loci to assess gene rearrangements and copy number changes in tumor cells. Two, three or more different fluorophores are used to detect the genetic barcode sections thus permitting unique labeling and multilocus analysis in individual cell nuclei. Gene specific barcodes can be generated and combined to provide both numerical and structural genetic information for these and other pertinent disease associated genes.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
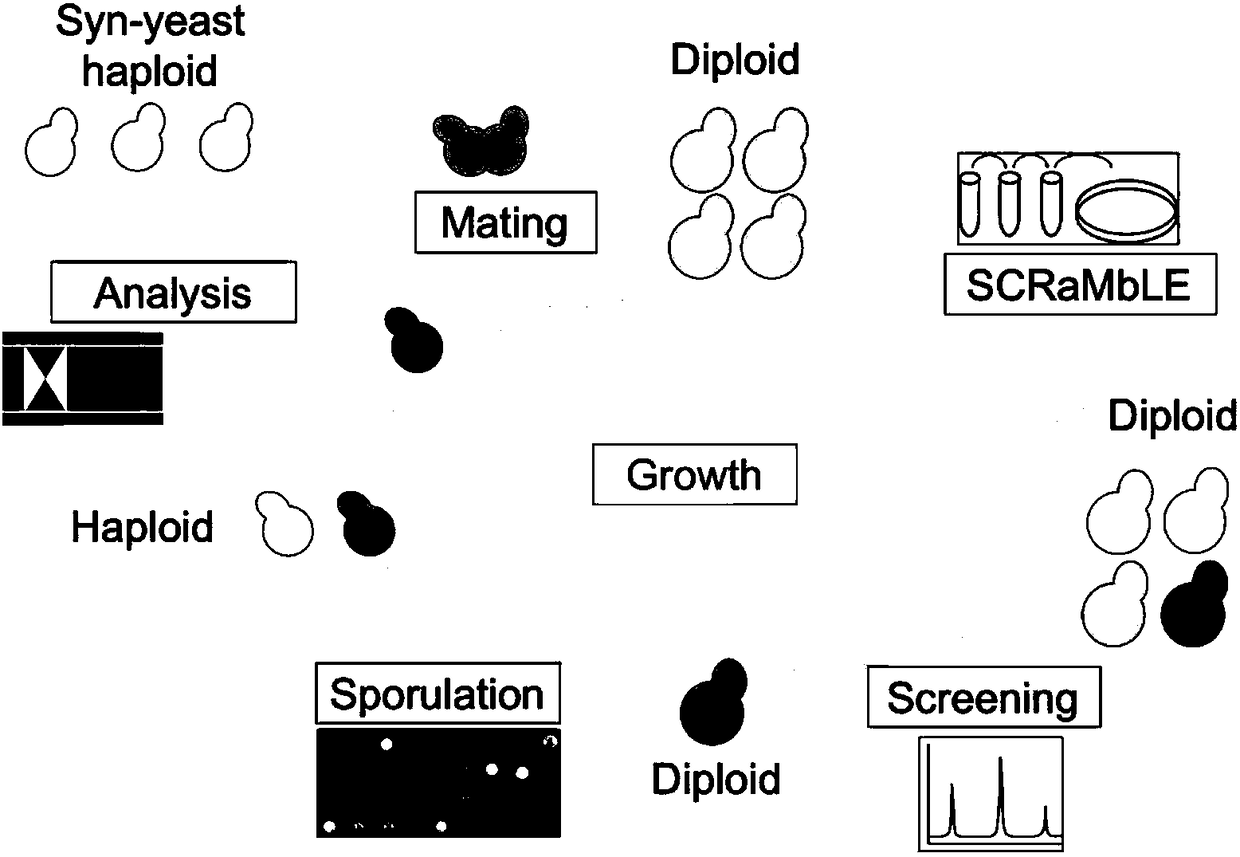
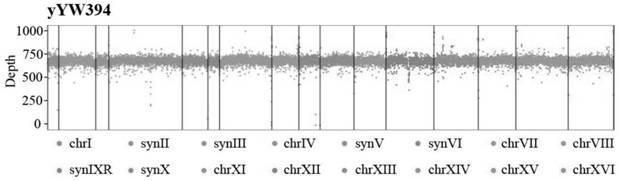
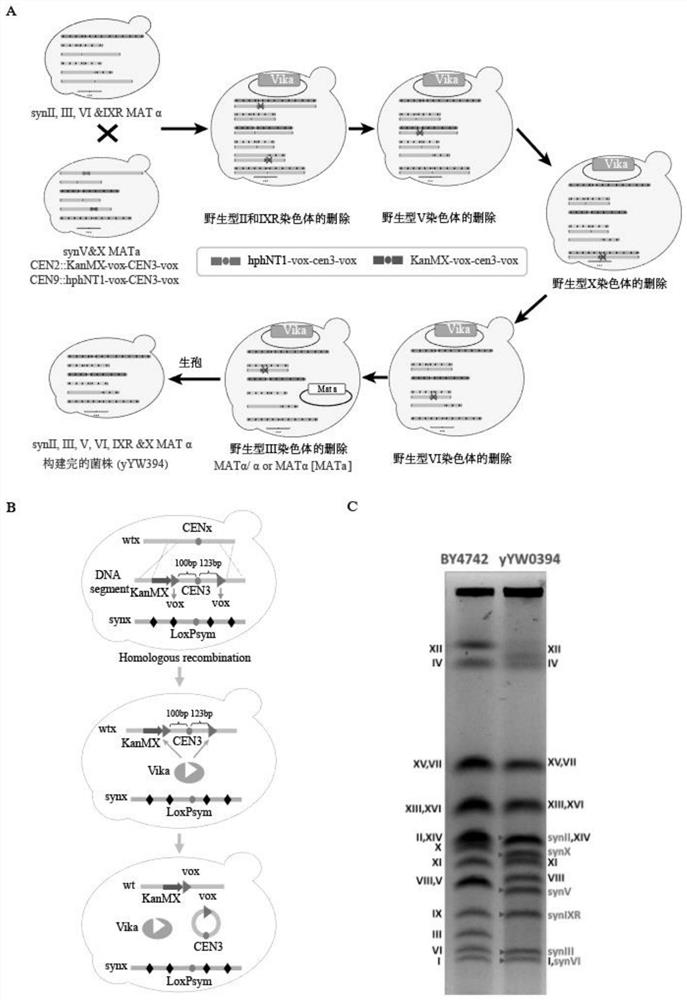
Yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and construction method thereof
ActiveCN113046255AAchieve knockoutAchieve integrationFungiStable introduction of DNABiotechnologyYeast chromosome
The invention relates to the technical field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and a construction method thereof. According to the yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and the construction method thereof, a complete yeast chromosome is cut off by using a Vika / vox technology, so that homologous recombination is generated by chromosome centromeres, the whole chromosome is knocked out, six synthetic chromosomes are integrated, and a large-scale rearrangement event is generated. Compared with existing achievements, the yeast for large-scale gene rearrangement and the construction method thereof have the following beneficial effects that cutting of the yeast chromosome is achieved simply, efficiently and quickly; cross exchange of sister dyeing monomers is avoided, and haploid yeast integrated by the six synthetic chromosomes is obtained; and very large-scale genome rearrangement is generated simply, efficiently and quickly.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
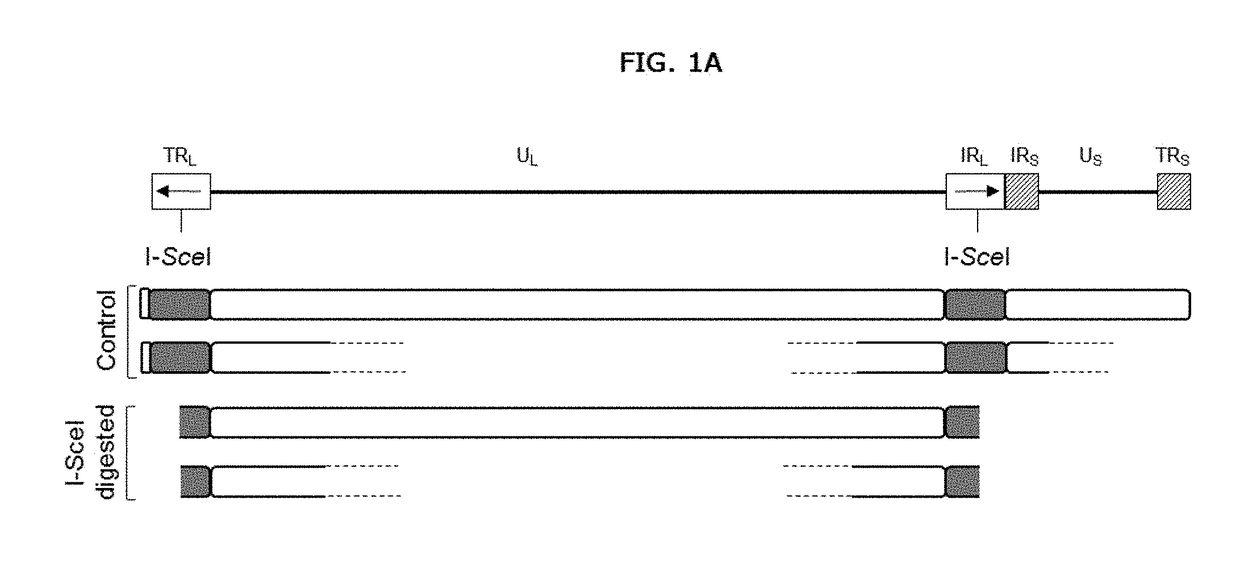
Method for the monitoring of modified nucleases induced-gene editing events by molecular combing
InactiveUS20180135080A1Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNACombingNuclease
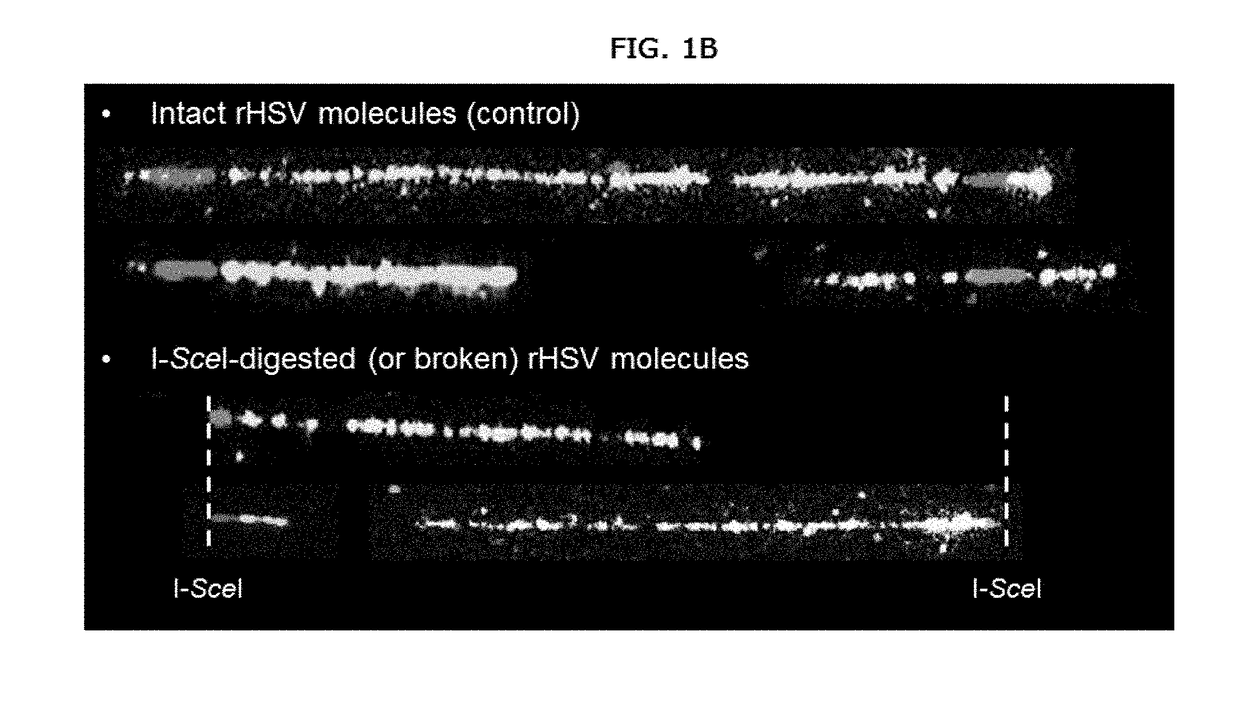
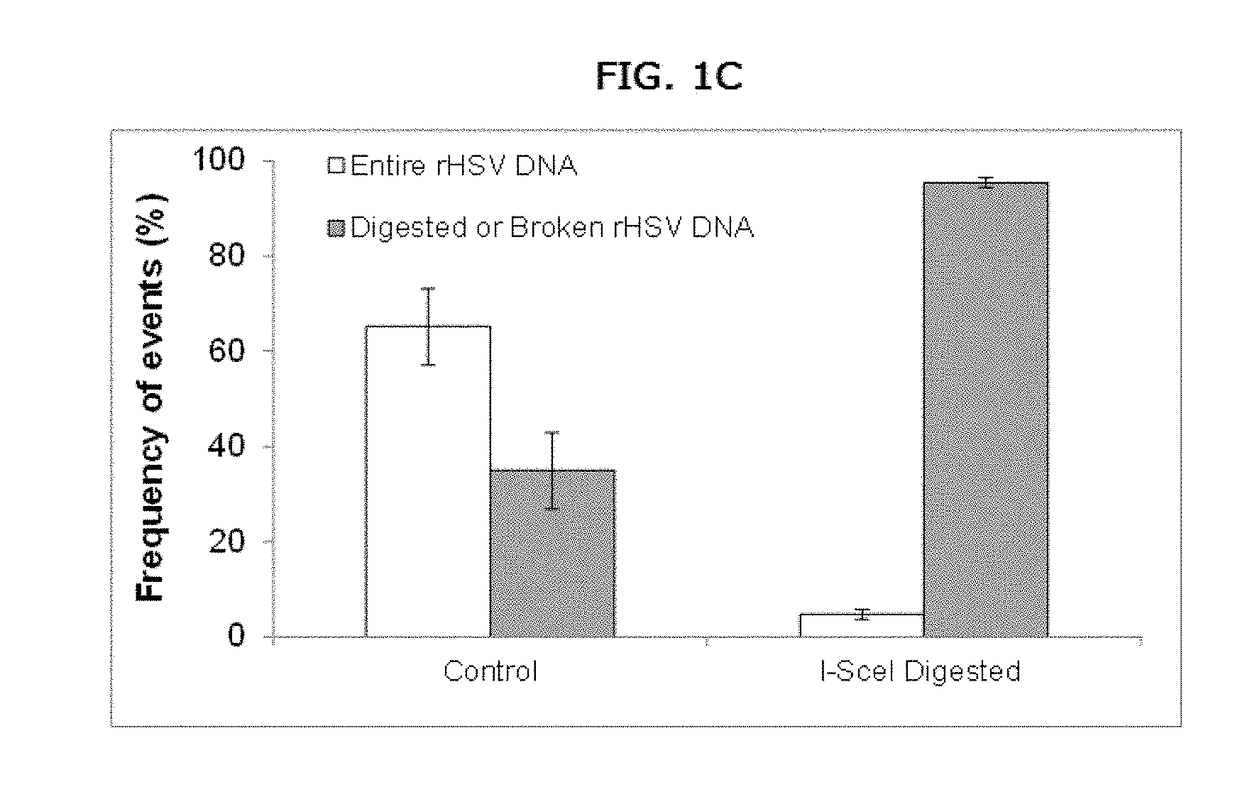
Methods for detecting and characterizing large genomic rearrangements induced by modified nucleases at high resolution and for quantifying the frequency of the large genomic or gene rearrangements induced by modified nucleases using Molecular Combing.
Owner:GENOMIC VISION
Molecular detection of chromosome aberrations
InactiveUS20060014199A1High sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementComparable sizeNucleic Acid Probes
The invention relates to the field of cytogenetics and the application of genetic diagnostic techniques in pathology and hematology. Specifically, the invention relates to nucleic acid probes that can be used in hybridization techniques for the detection of chromosomal aberrations and other gene rearrangements such as immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor gene rearrangements. The probes provided by the invention are a distinct and balanced set of probes of comparable size, each preferably being from 1 to 100 kb, or smaller, and flanking a potential breakpoint in a chromosome.
Owner:DAKOAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com