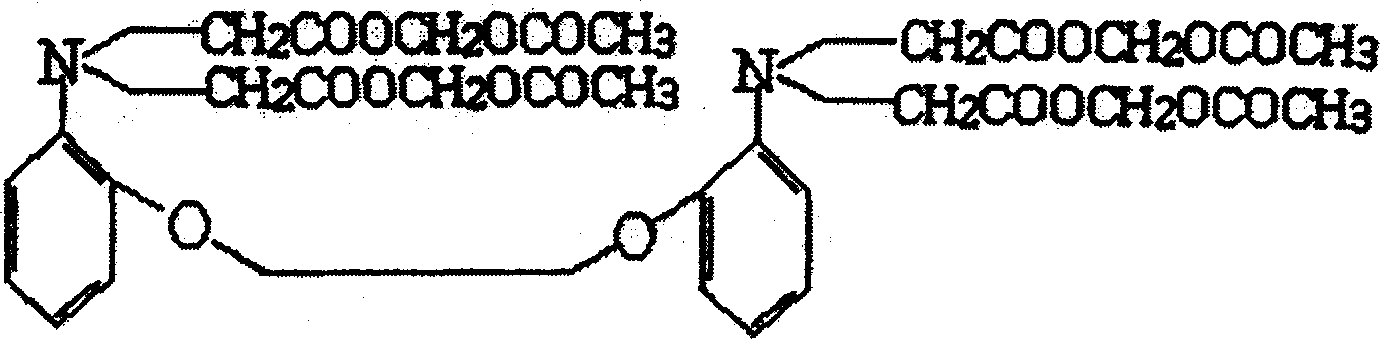
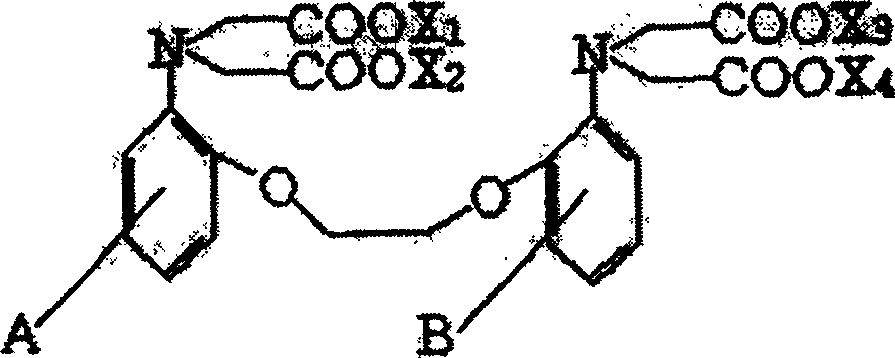
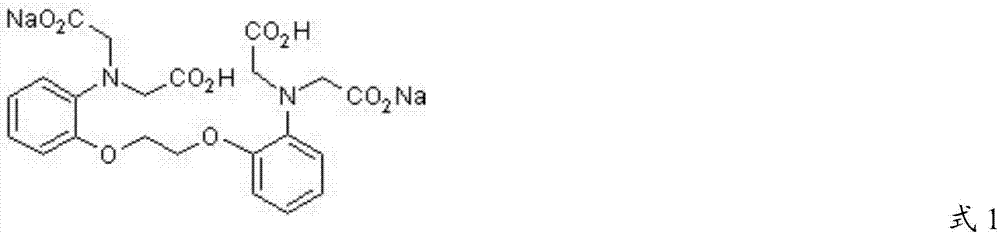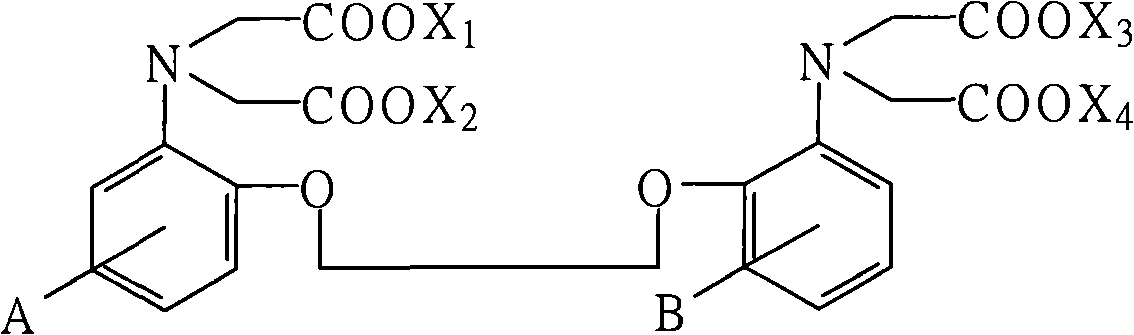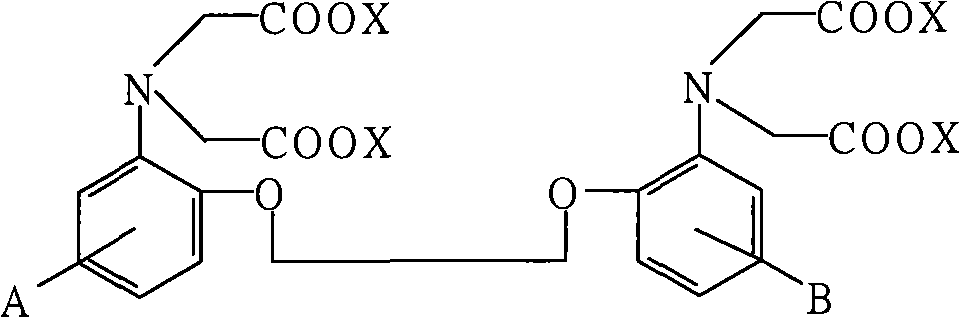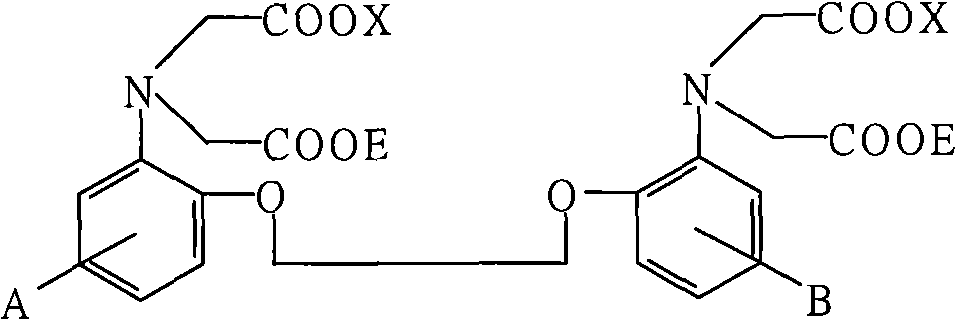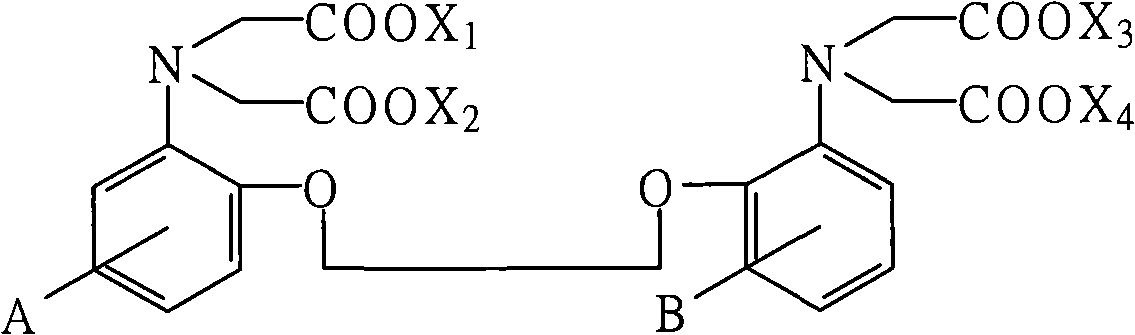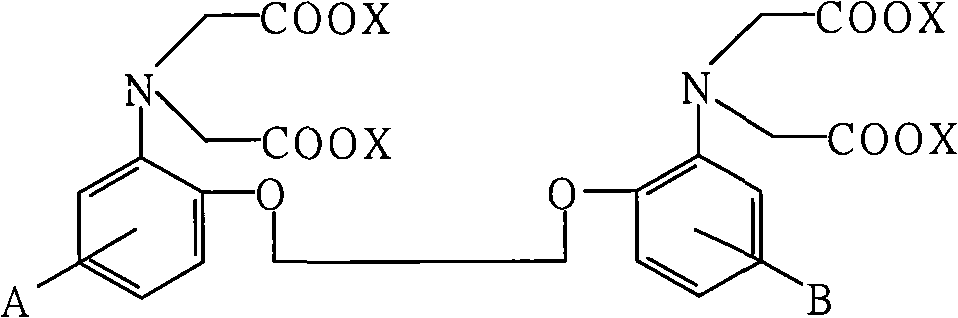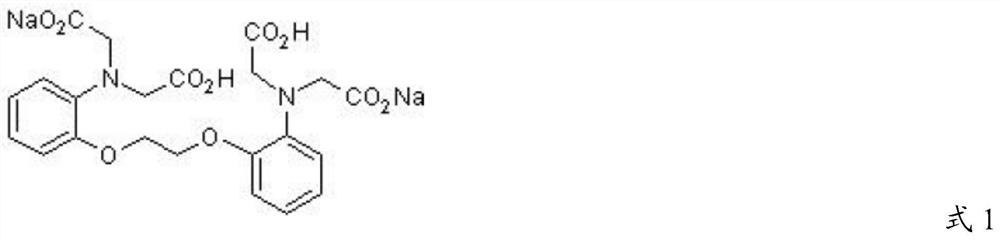Patents
Literature
33 results about "BAPTA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
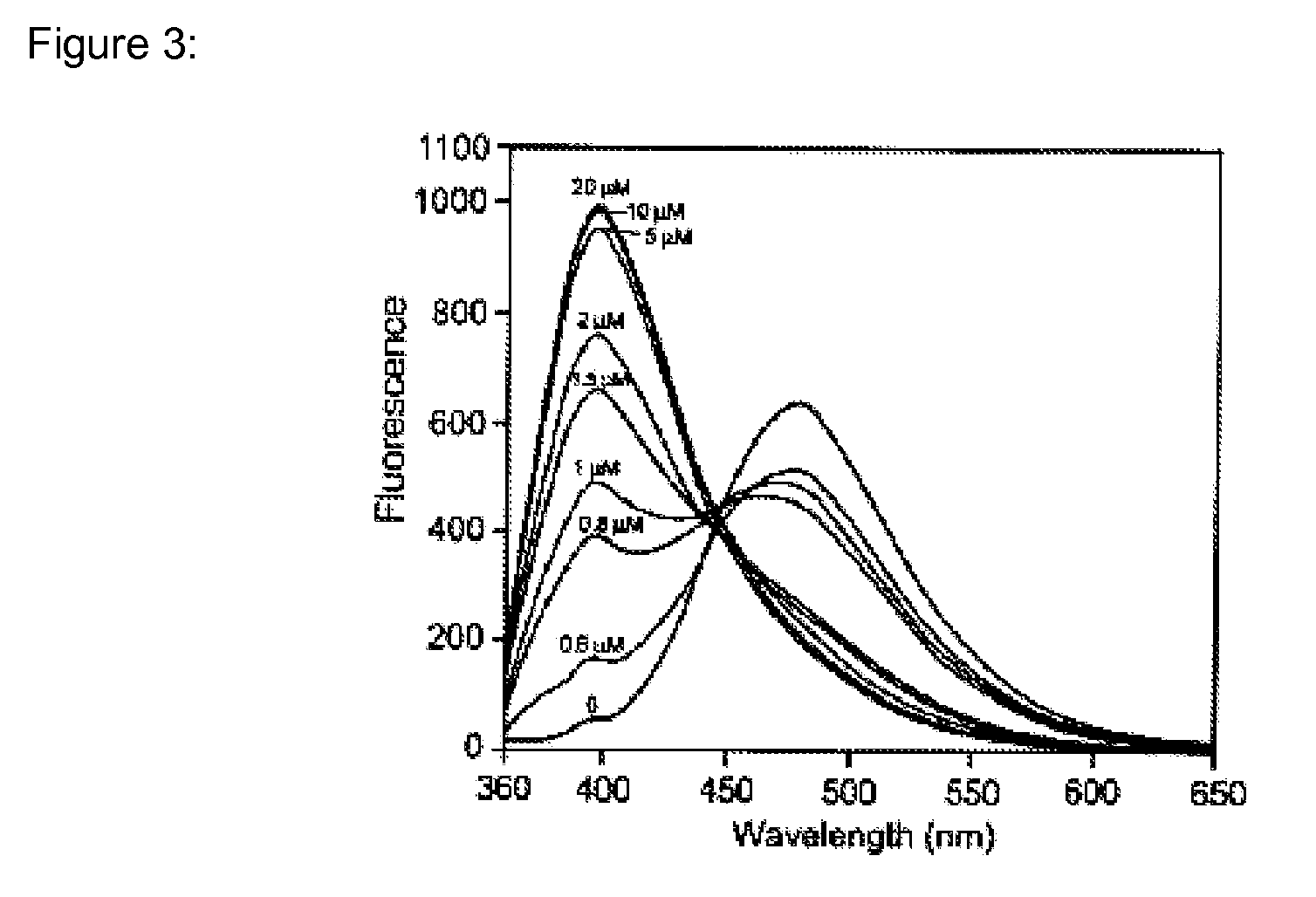
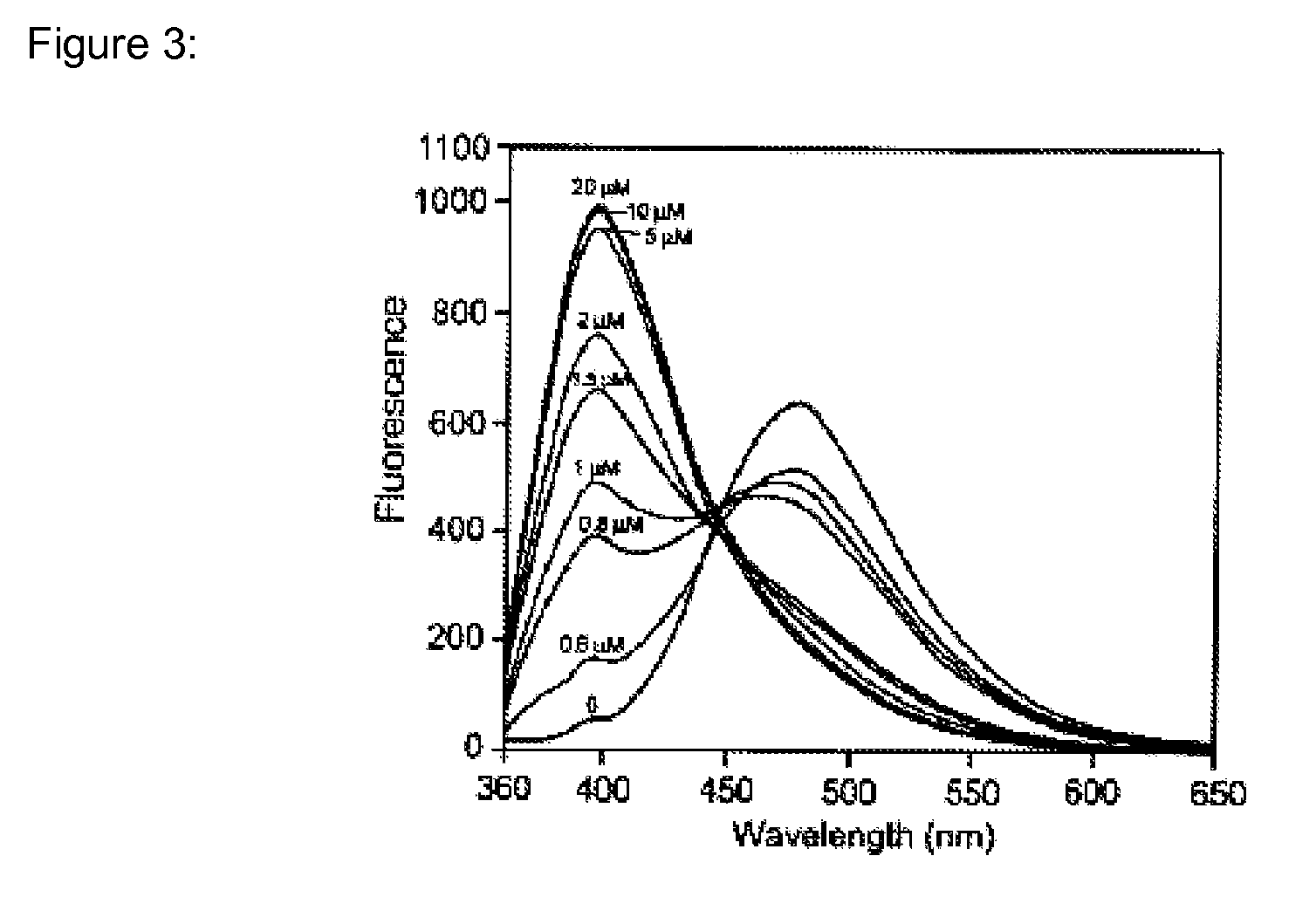
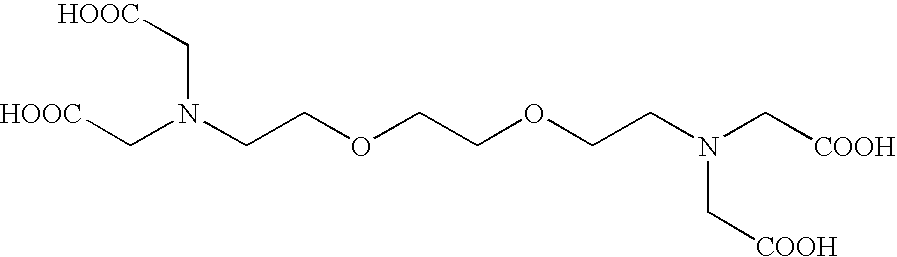
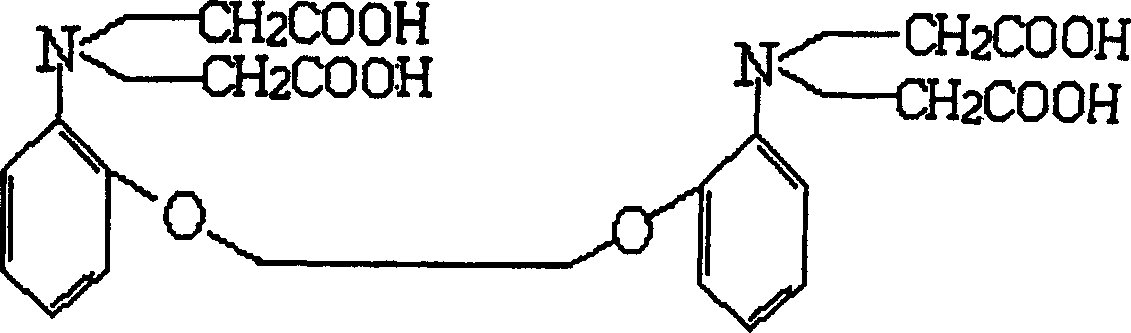
BAPTA (1,2-bis(o-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid) is a calcium-specific aminopolycarboxylic acid. The presence of four carboxylic acid functional groups makes possible the binding of two calcium ions. The extensive flexibility of the carboxylate ligands is critical to the coordination of calcium and other metal ions.
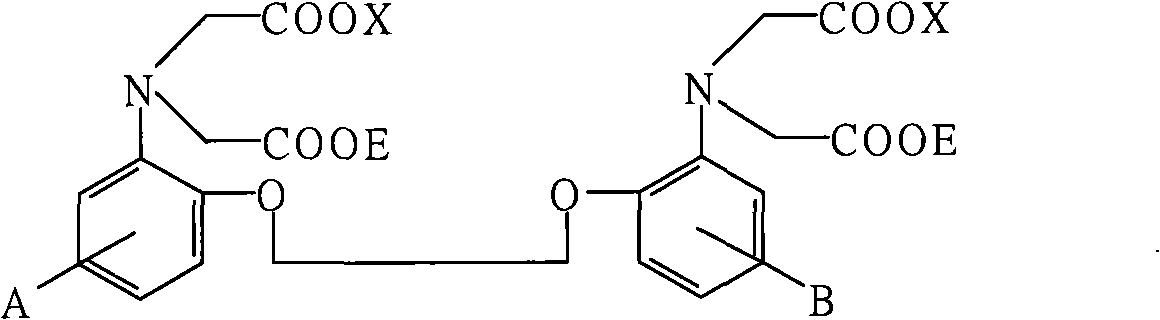
Zinc binding compounds and their method of use
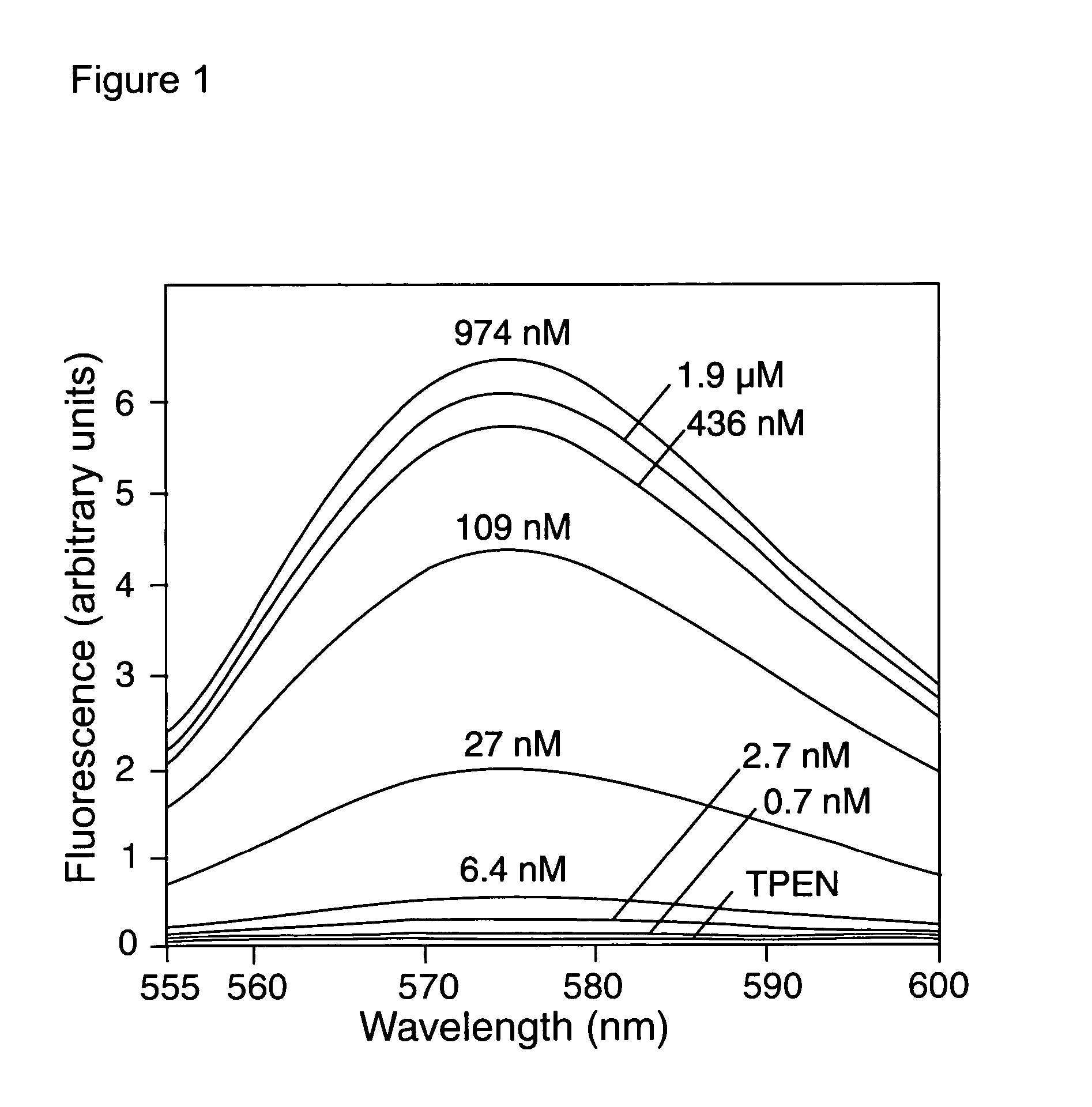
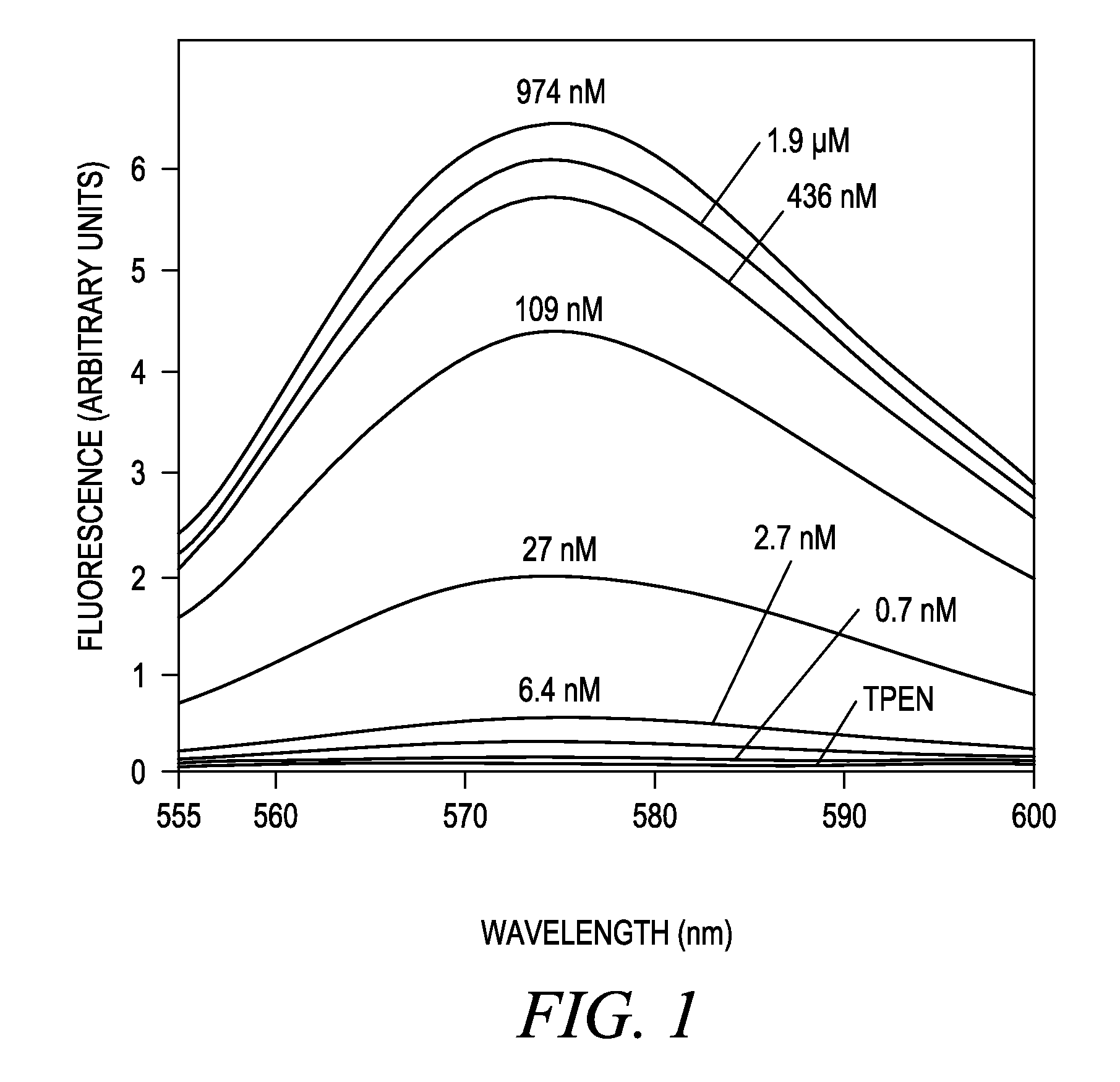
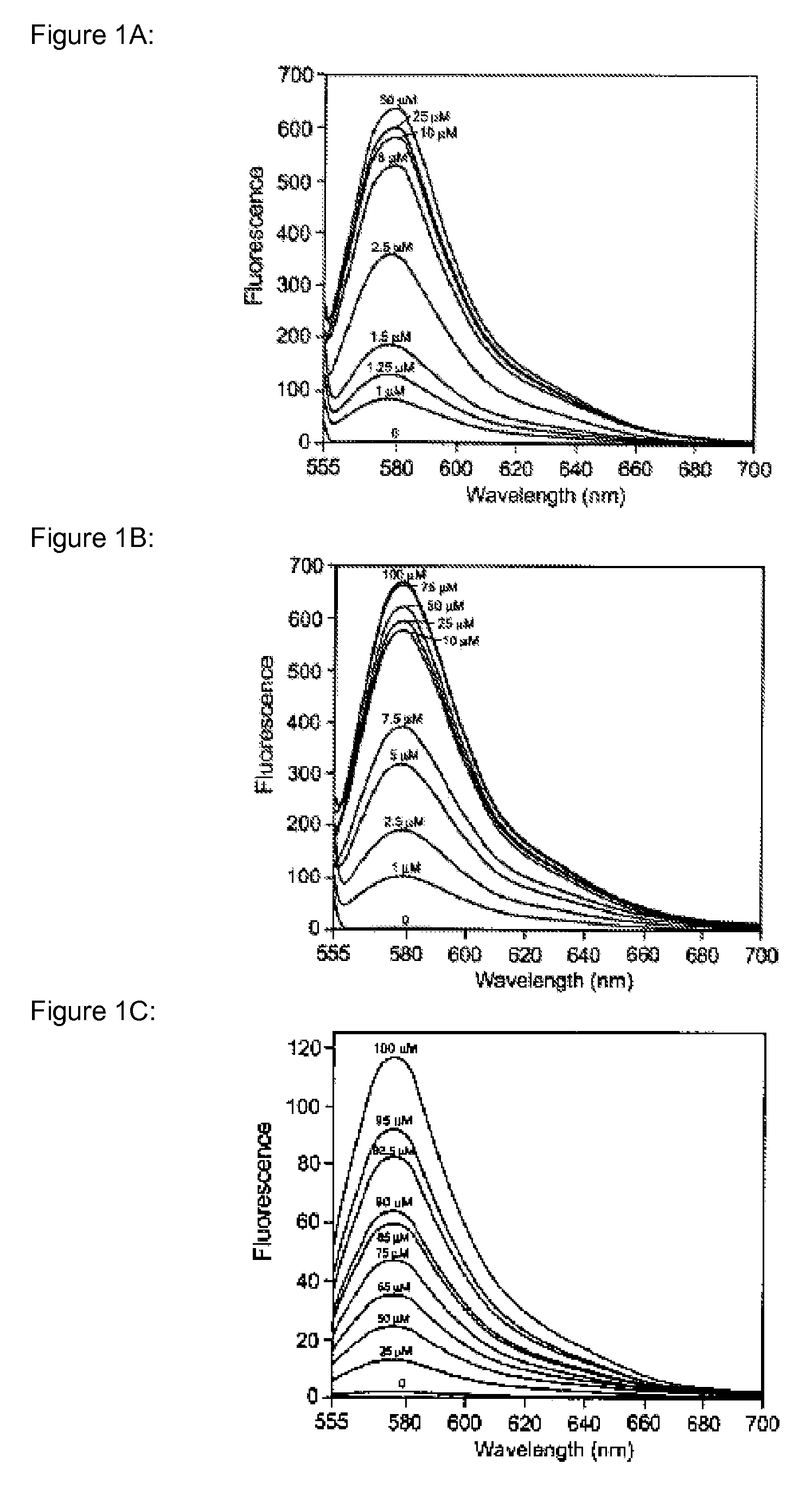
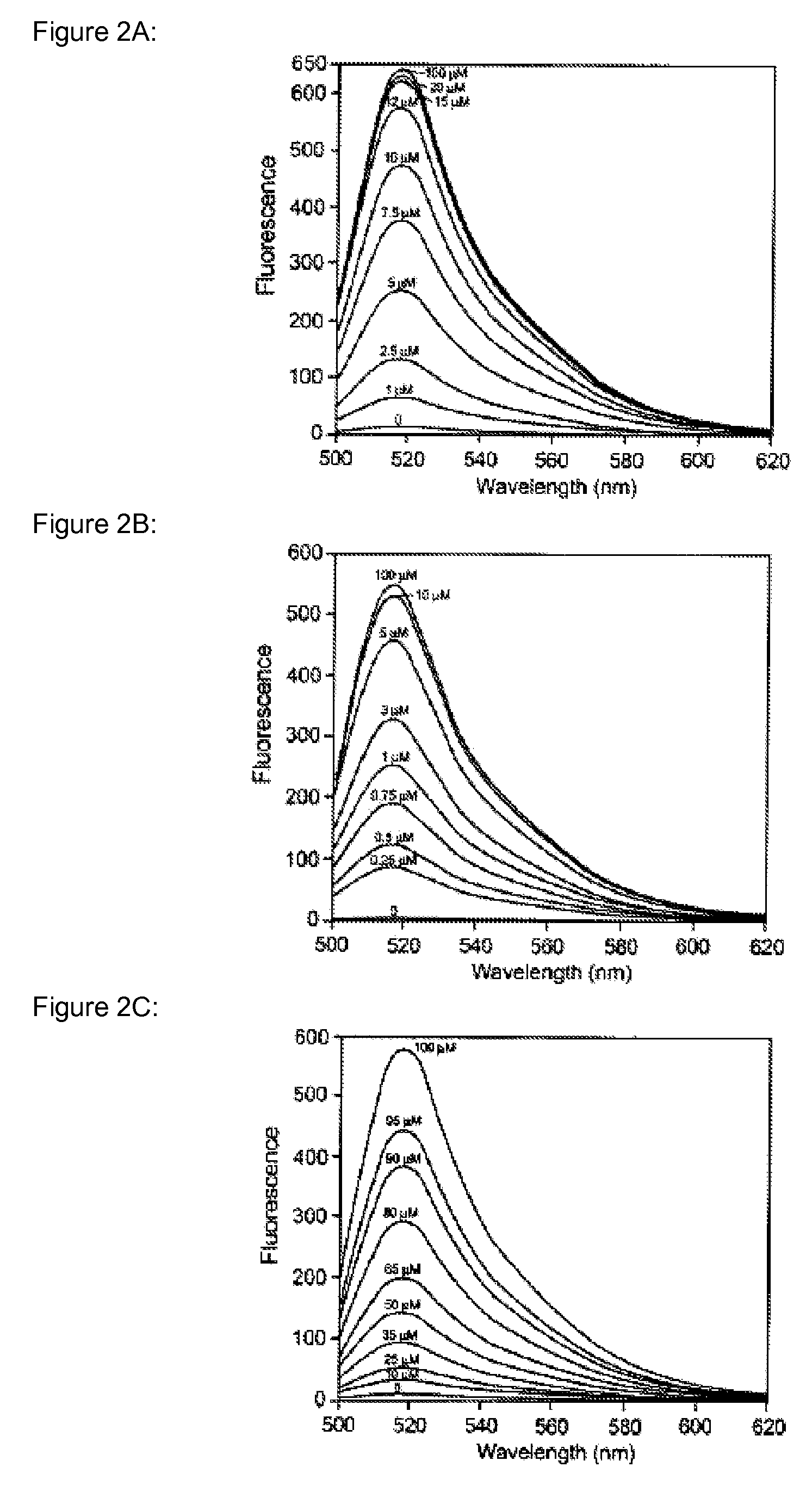
InactiveUS20050250214A1Efficient ConcentrationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistryMetal chelateZinc binding
The present invention provides a metal chelator and methods that facilitate binding, detecting, monitoring and quantitating of zinc ions in a sample. The metal chelating moiety of the zinc-binding compound is an analog of the well-known calcium chelator, BAPTA (1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′N′-tetraacetic acid), wherein the chelating moiety has been modified from a tetraacetic acid moiety to a tri- di- or monoacetic moiety. This change in acetic acid groups on the metal chelating moiety results in the selective bindings of zinc ions in the presence of calcium ions, both of which are present in biological fluids and intracellular cytosolic fluid and organelles.
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
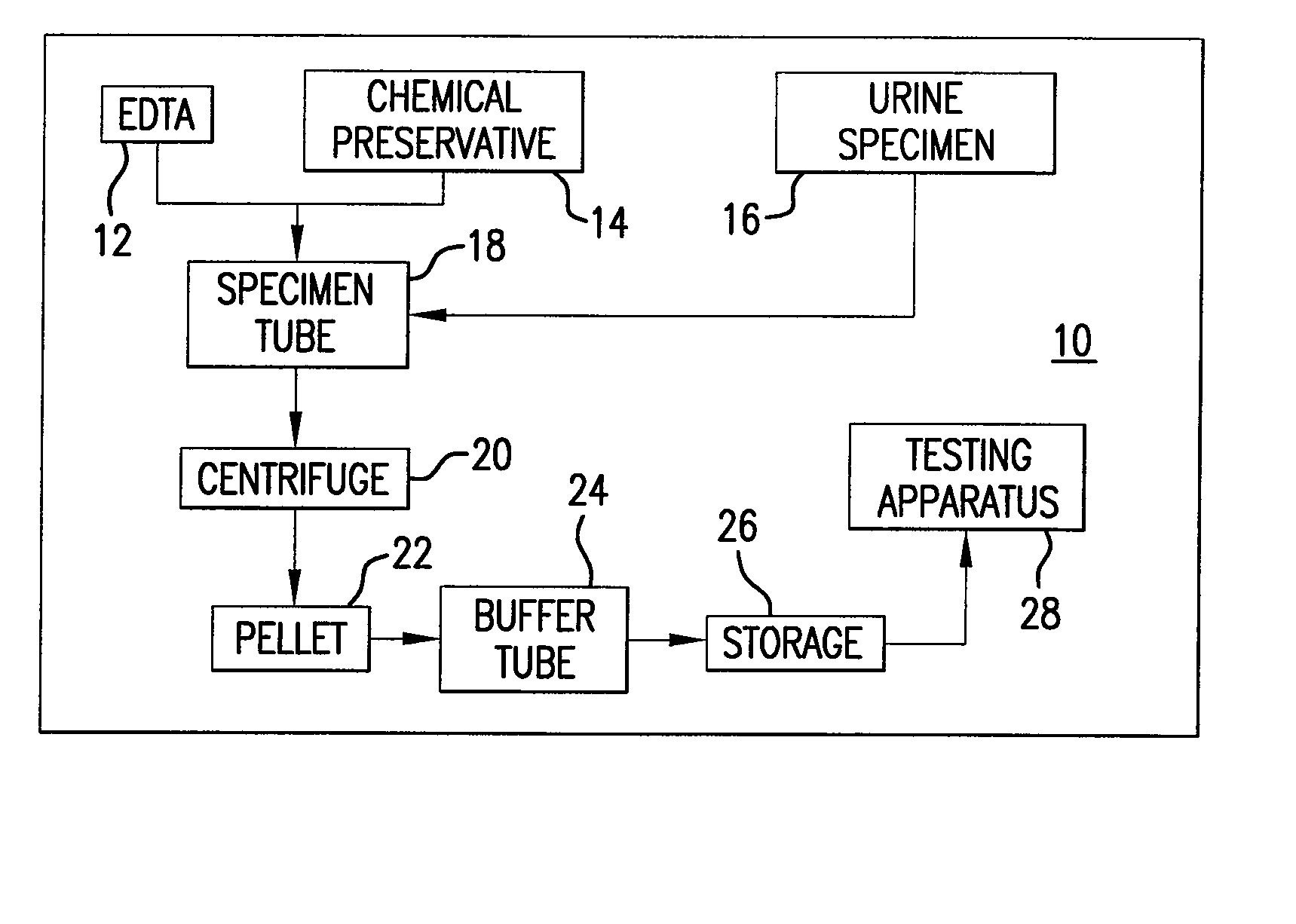
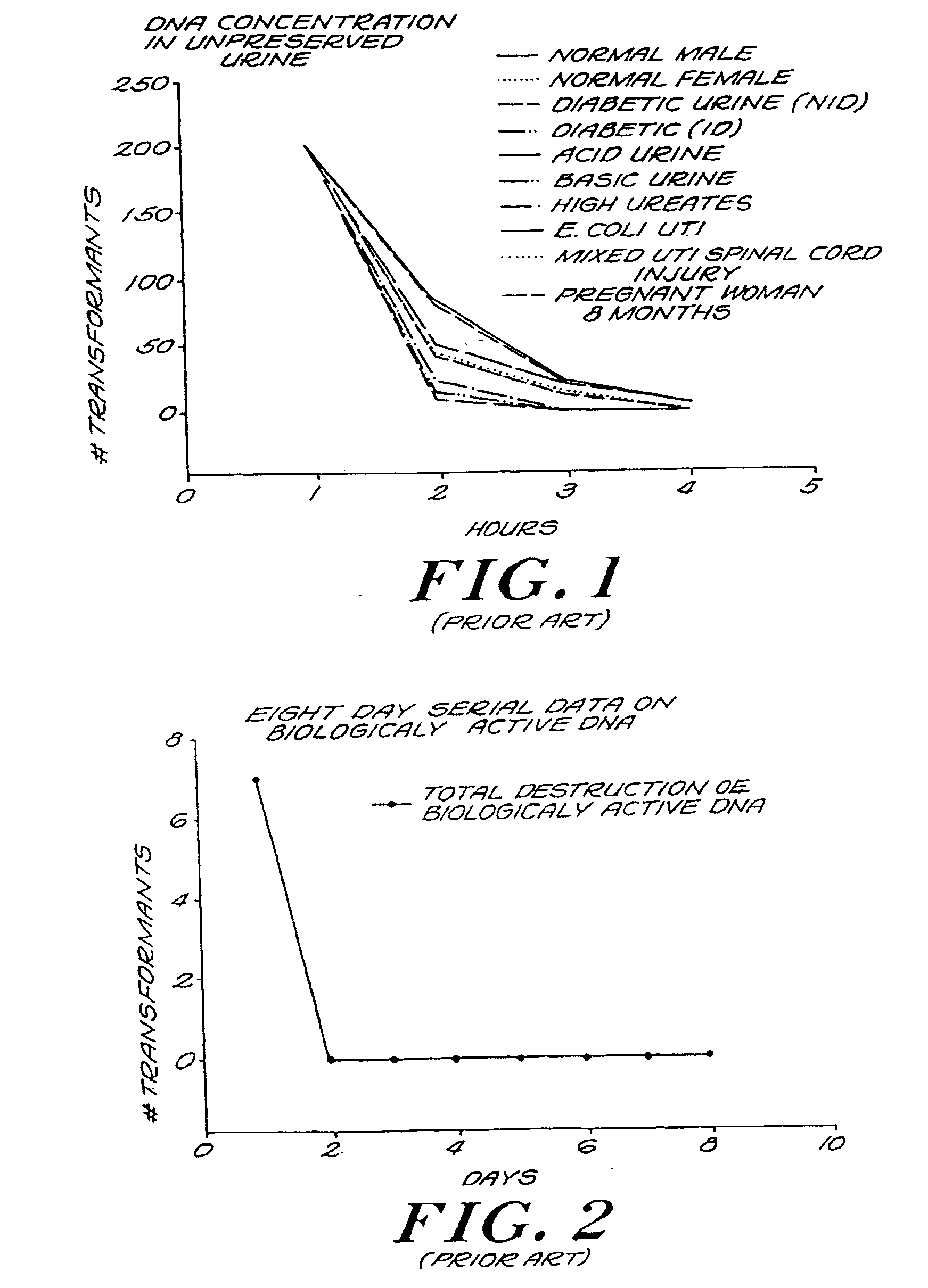
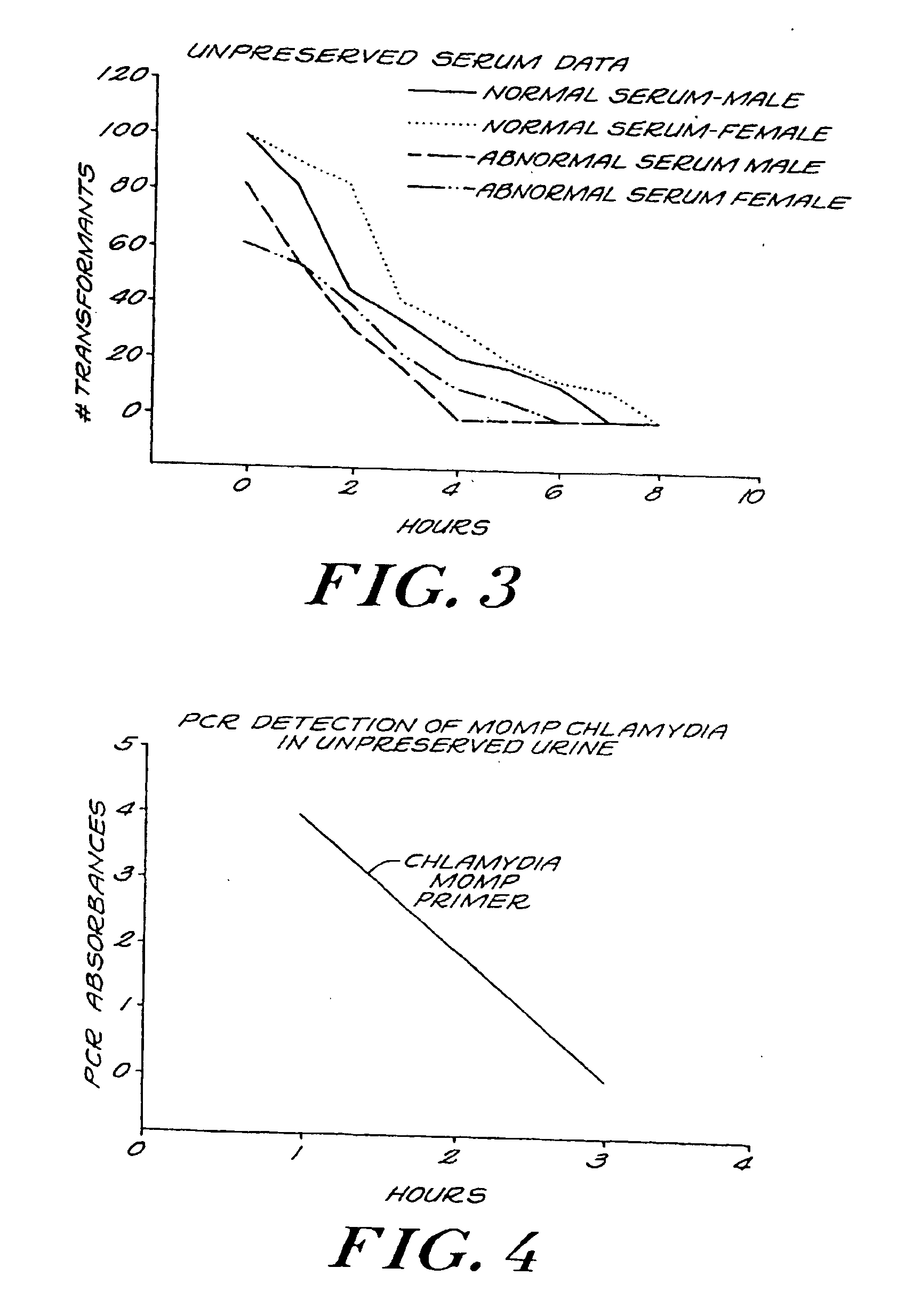
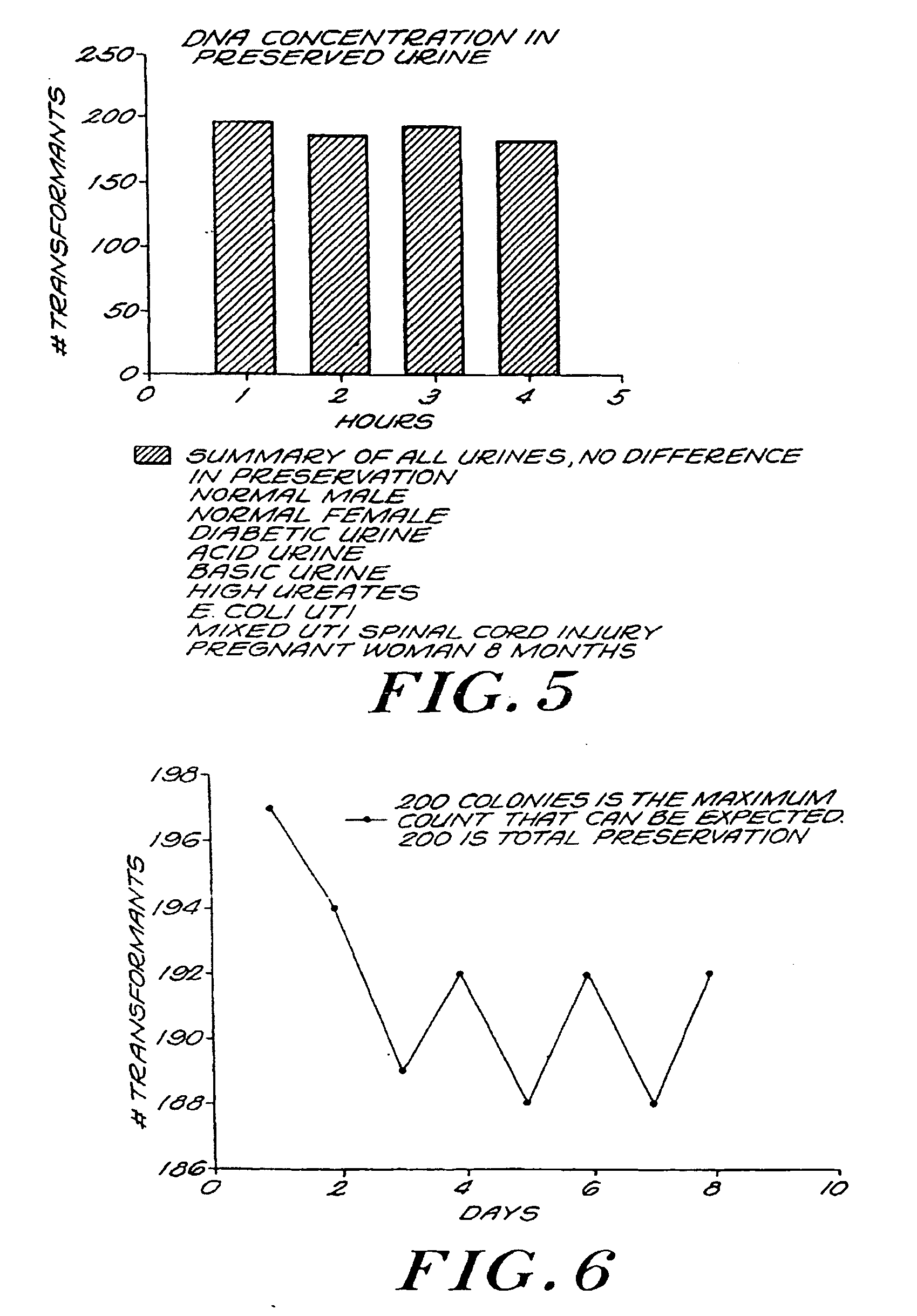
Urine Preservation System
An improved method of preserving a molecule in a bodily fluid comprises: (1) providing a preservative solution comprising: (a) an amount of a divalent metal chelator selected from the group consisting of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), (ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrilo))tetraacetic acid (EGTA), and 1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA) and salts thereof in the range of from about 0.001 M to about 2 M; and (b) an amount of at least one chelator enhancing component selected from the group consisting of lithium chloride, guanidinium chloride, guanidinium thiocyanate, sodium salicylate, sodium perchlorate, and sodium thiocyanate in the range of from about 0.1 M to about 10 M; and (2) adding the preservative solution to the bodily fluid, thus preserving the molecule. The molecule can be a protein or a small molecule, such as a steroid. The invention also encompasses preservative compositions suitable for preserving proteins or small molecules, and kits. Preservative compositions can further include at least one enzyme inactivating component selected from the group consisting of manganese chloride, sarkosyl, and sodium dodecyl sulfate in the range of up to about 5% molar concentration. Compositions and methods according to the present invention have many diagnostic and forensic uses, in addition to being suitable for preparing compositions usable by hunters for attracting animals.
Owner:SIERRA MOLECULAR CORP
Visible wavelength fluorescent calcium indicators that are (i) leakage resistant and (ii) operate near membranes
InactiveUS20050233467A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistryPropanoic acidFluorescence
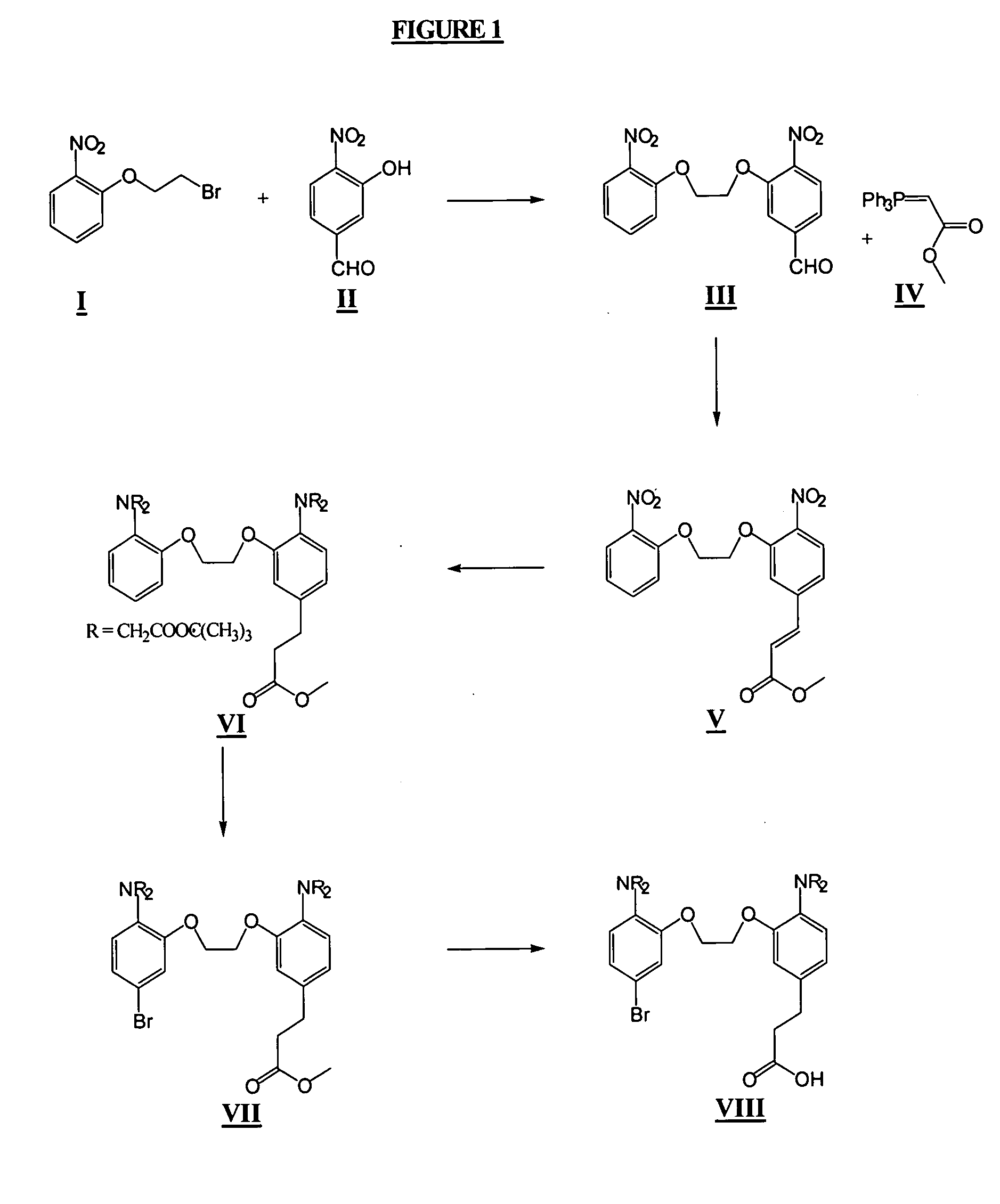
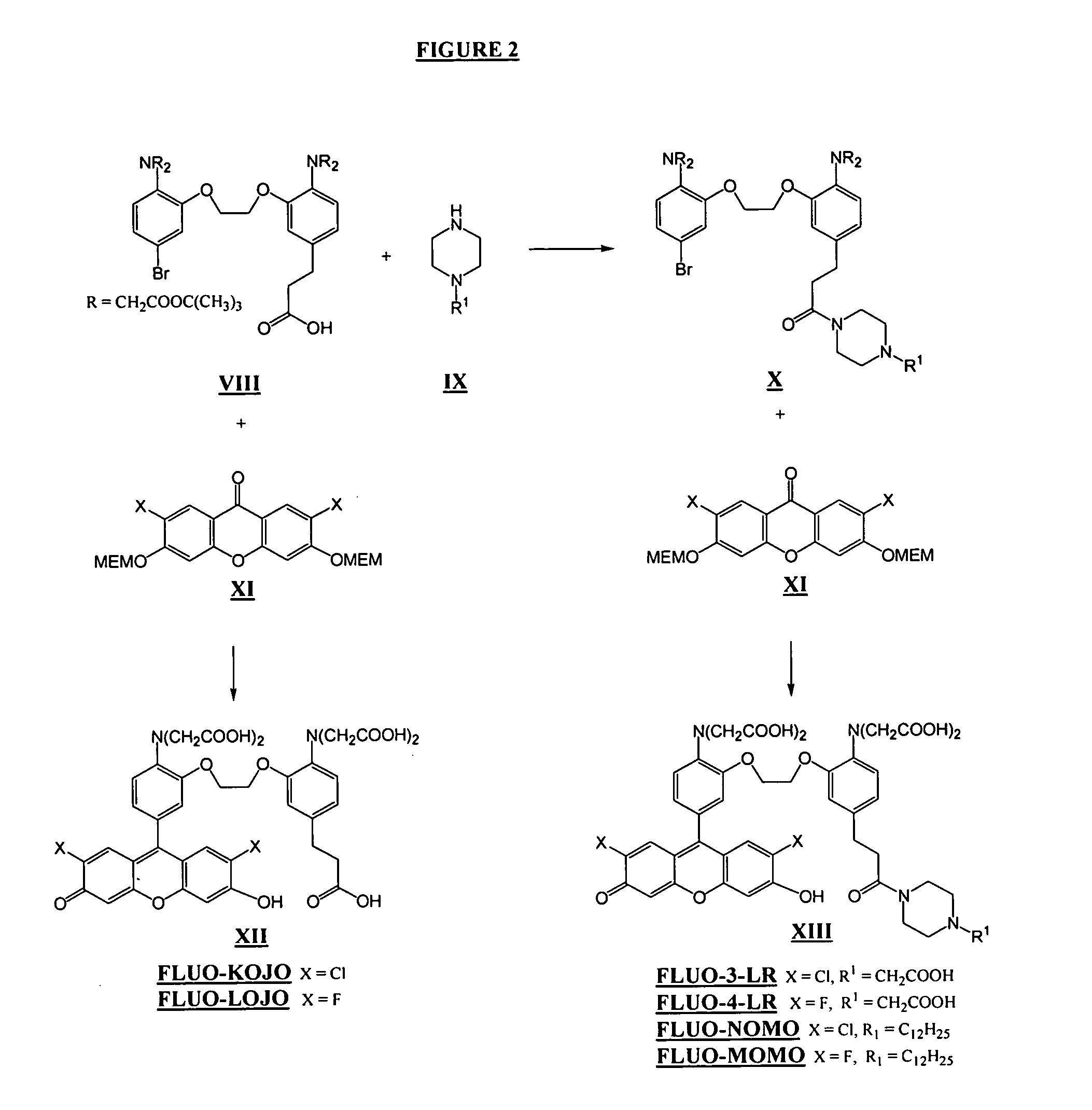
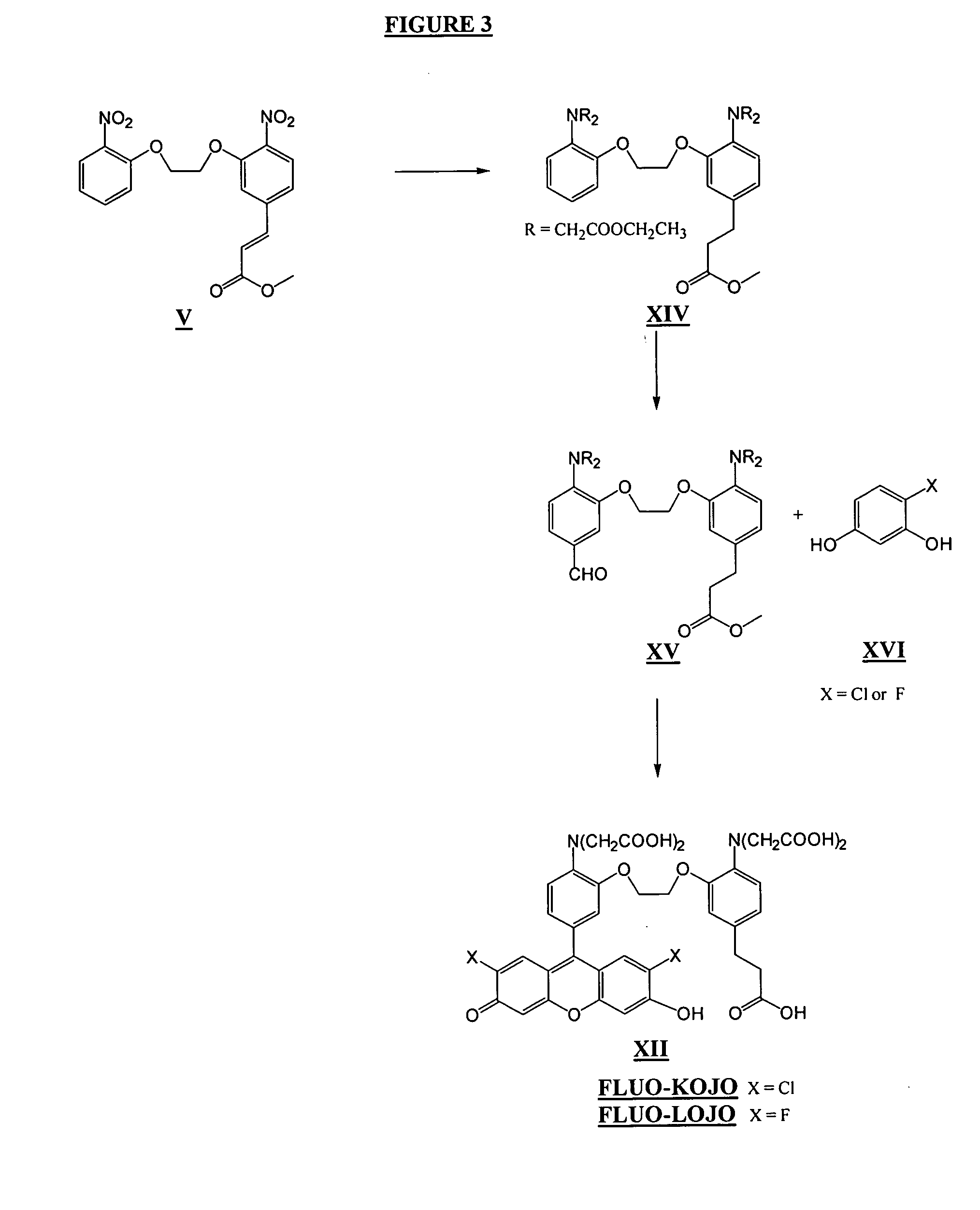
A new class of visible wavelength fluorescent calcium indicators with the BAPTA-like portion rendered zwitterionic by introduction of amine and carboxylic groups. “Fluo” compounds generally function with no extra ionized groups. The modified BAPTA moiety confers new properties while retaining ion selectivity and pH insensitivity. The dyes demonstrate reduced cell leakage and improved ability to study calcium near the cell membrane and preserve the fluorescent properties of “fluo” dyes. The modifications include (a) piperazinoacetic acid XIII for the leakage resistance (FLUO-LR), (b) dodecylpiperazine XIII for a near membrane indicator (FLUO-MOMO, FLUO-NOMO amphipathic “fluo” indicators which bind to cellular membranes and respond to calcium near the membrane), and (c) a propionic acid XII for general leakage resistance -FLUO-LOJO, FLUO-KOJO “fluo” indicators with an extra charge that enables them to resist leakage).
Owner:INVITROGEN
Urine preservation system
An improved method of preserving a molecule in a bodily fluid comprises: (1) providing a preservative solution comprising: (a) an amount of a divalent metal chelator selected from the group consisting of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), (ethylenebis(oxyethylenenitrilo))tetraacetic acid (EGTA), and 1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA) and salts thereof in the range of from about 0.001 M to about 2 M; and (b) an amount of at least one chelator enhancing component selected from the group consisting of lithium chloride, guanidinium chloride, guanidinium thiocyanate, sodium salicylate, sodium perchlorate, and sodium thiocyanate in the range of from about 0.1 M to about 10 M; and (2) adding the preservative solution to the bodily fluid, thus preserving the molecule. The molecule can be a protein or a small molecule, such as a steroid. The invention also encompasses preservative compositions suitable for preserving proteins or small molecules, and kits. Preservative compositions can further include at least one enzyme inactivating component selected from the group consisting of manganese chloride, sarkosyl, and sodium dodecyl sulfate in the range of up to about 5% molar concentration. Compositions and methods according to the present invention have many diagnostic and forensic uses, in addition to being suitable for preparing compositions usable by hunters for attracting animals.
Owner:SIERRA MOLECULAR CORP
Heavy metal binding compounds and their method of use
ActiveUS20070161112A1Organic chemistryPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesHeavy metal bindingIon
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
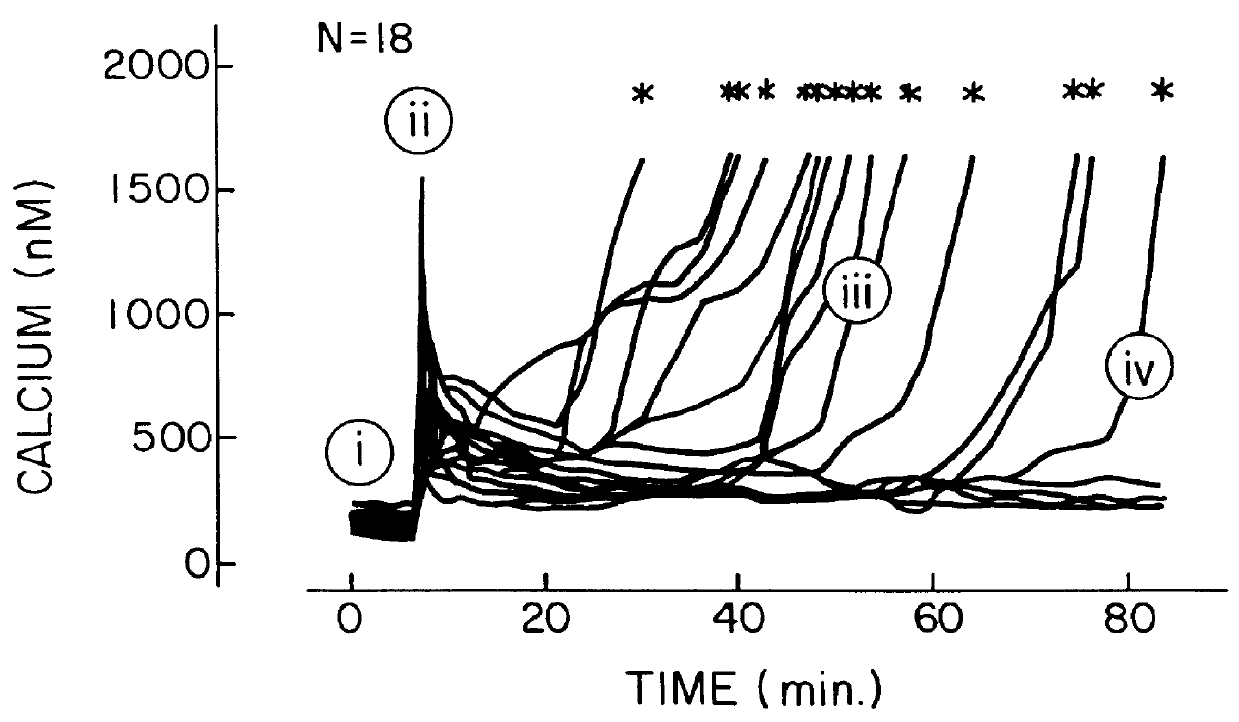
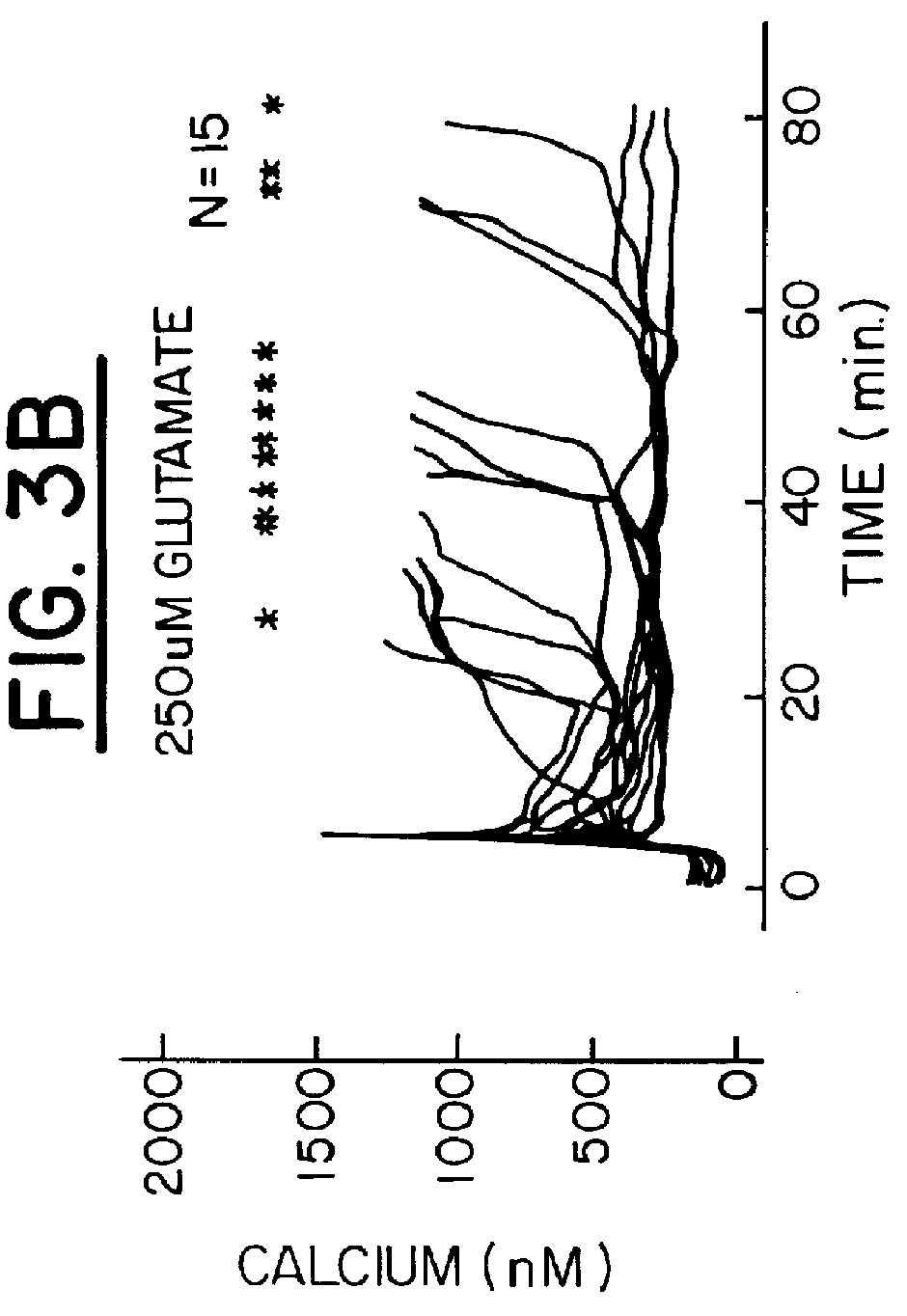
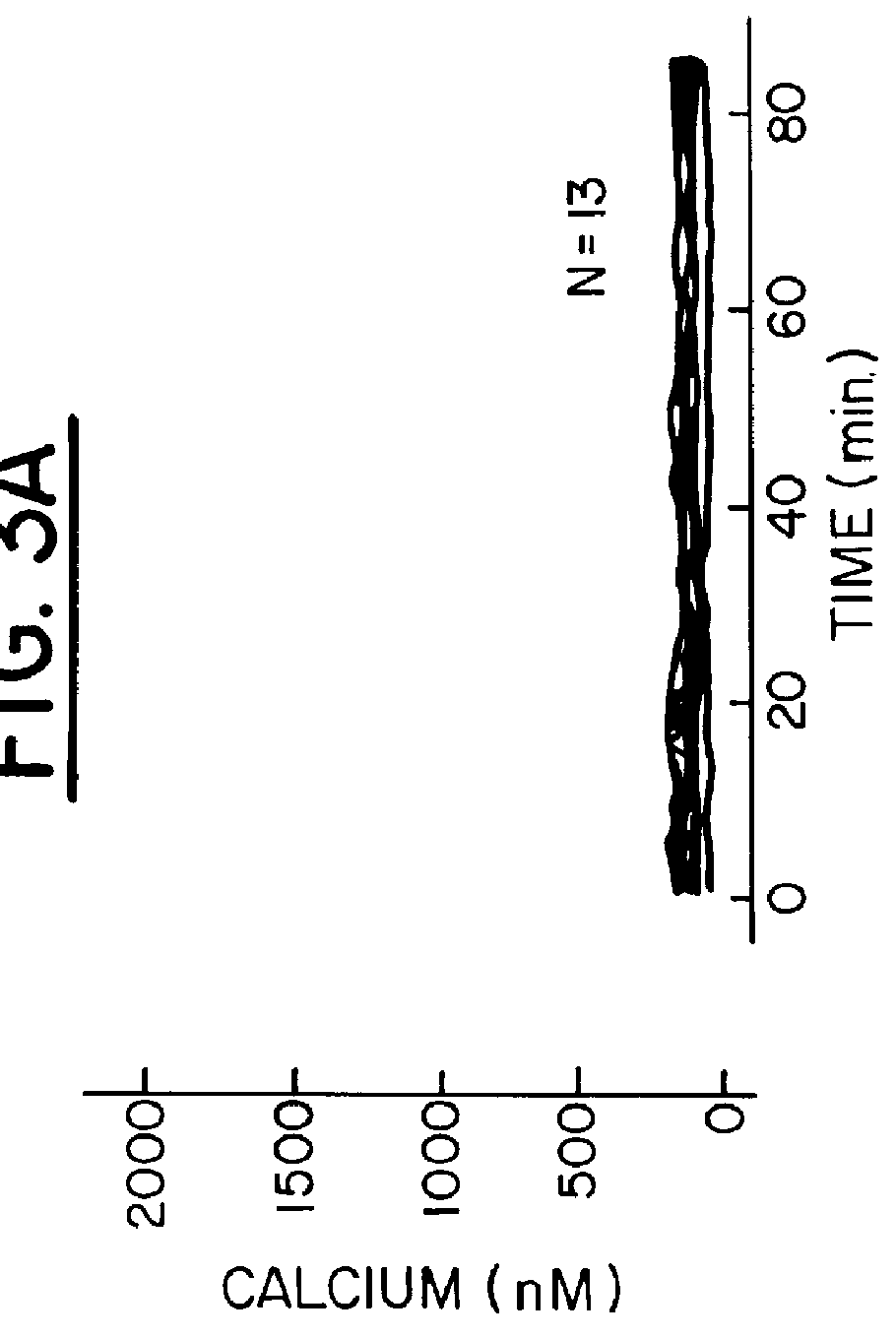
In vivo treatment of mammalian cells with a cell membrane permeant calcium buffer
A method of reducing the damaging effect of an injury to mammalian cells by treatment of the cell or mammalian tissue in vivo with a cell membrane permeant calcium buffer. The method comprises treating mammalian tissue with a damage reducing effective amount of the calcium buffer, preferably, a BAPTA derivative. The method may be used to control the concentration of Ca2+ ions in the vicinity of ion channel pores of the cells to prevent diffusion of toxic amounts of Ca2+ ions to subcellular sites located near the source of Ca2+ influx. The buffer treatment may be applied as a prophylactic or after the mammalian tissue has sustained injury.
Owner:TORONTO NEUROPROTECTION GROUP
Zinc binding compounds and their method of use
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Heavy metal binding compounds and their method of use
ActiveUS7521577B2Organic chemistryPyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesHeavy metal bindingIon
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
Non-aqueous ink-jet ink composition
ActiveUS7288144B2Good storage stabilityImprove performanceDuplicating/marking methodsInksNeutral carrierSolvent
A non-aqueous ink-jet ink composition contains at least a pigment, a solvent, and a dispersing agent. The non-aqueous ink-jet ink composition further contains a chelating agent, which is soluble in the solvent. The chelating agent may be a crown ether and / or a cryptand, which acts as a neutral carrier. Alternatively, the chelating agent may be at least one chelating agent acting as an ionic carrier, which is selected from the group consisting of GEDTA, BAPTA, and DTPA. The non-aqueous ink-jet ink composition has good storage stability and good jetting-out performance through suppression of occurrence of sediments due to a change with the passage of time.
Owner:RISO KAGAKU CORP
Application of medicament in magnesite flotation and calcium removal
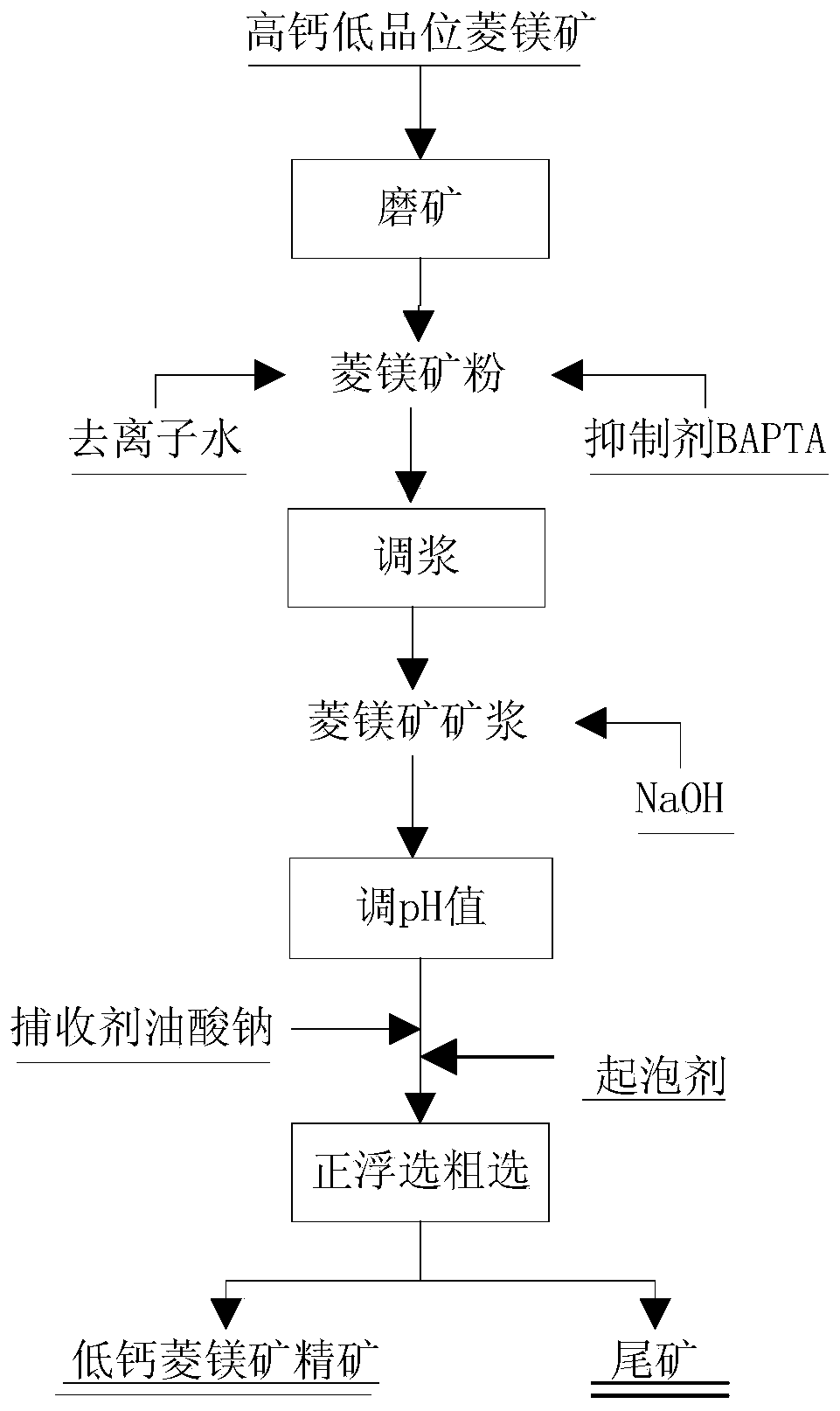
InactiveCN109847946AEnvironmentally friendlyShorten and simplify the flotation decalcification processFlotationSlurryDolomite
The invention discloses an application of a medicament in magnesite flotation and calcium removal, and belongs to the technical field of magnesite processing and purifying. An inhibitor BAPTA is applied to a magnesite flotation and calcium removal technology. The application method comprises following steps: grinding high calcium low-grade magnesite, carrying out ball milling to obtain magnesite powder; adding magnesite powder into flotation equipment, adding deionized water and an inhibitor namely a BAPTA dimethyl sulfoxide solution, evenly mixing, blending, adding NaOH into the magnesite slurry at a room temperature to adjust the pH to 10-12, adding a collecting agent (sodium oleate), evenly mixing, and carrying out direct floatation and rougher flotation to obtain low calcium magnesiteconcentrate. Due to the floatation difference of added inhibitor BAPTA on magnesite and impurity ore (dolomite) in magnesite, the calcium ores in magnesite can be removed, the magnesite quality is improved, and a novel medicament is provided for the flotation and calcium removal of high calcium low-grade magnesite.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Single\two-photon calcium ion fluorescent probe compound and preparation and application thereof
The invention provides a single\two-photon calcium ion fluorescent probe compound and preparation and application thereof. The calcium ion fluorescent probe compound has the structure of formula I. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: heating BAPTA-CH3-CHO and 4-methyl-N-methylpyridine iodate at a molar ratio of 1:(1.1-1.3) in the presence of ethanol solvent and piperidine catalyst to 78-83 DEG C for a reflux reaction; cooling to separate out precipitates; and filtering, washing, drying and recrystallizing to obtain a product. The fluorescent probe compound has good selectivity and sensitivity on calcium ions, and performs simple pretreatment of the detection sample; and moreover, the fluorescent probe compound has certain water solubility and excellent single\two-photon fluorescence, and can be widely used for detecting the calcium content in animals / plants, human cells, soil or water.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Application of BAPTA derivative in the preparing process of clinical medicine
InactiveCN1605333ALower levelAlleviate pathological changesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsDiseaseLiver necrosis
The present invention features that BAPTA derivative is applied in preparing medicine for treating acute great area cell death clinically. The medicine is prepared into particle preparation for the clinical salvage and treatment of acute great area cell death diseases, such as cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction, liver necrosis, ischemic kidney necrosis, necrotic pencreatitis, etc.
Owner:HENGXING PHARMA INST HEFEI
Synthesis method of calcium ion selective chelating agents
InactiveCN102617376ASimple processing methodOrganic compound preparationAmino-carboxyl compound preparationAcetic acidPurification methods
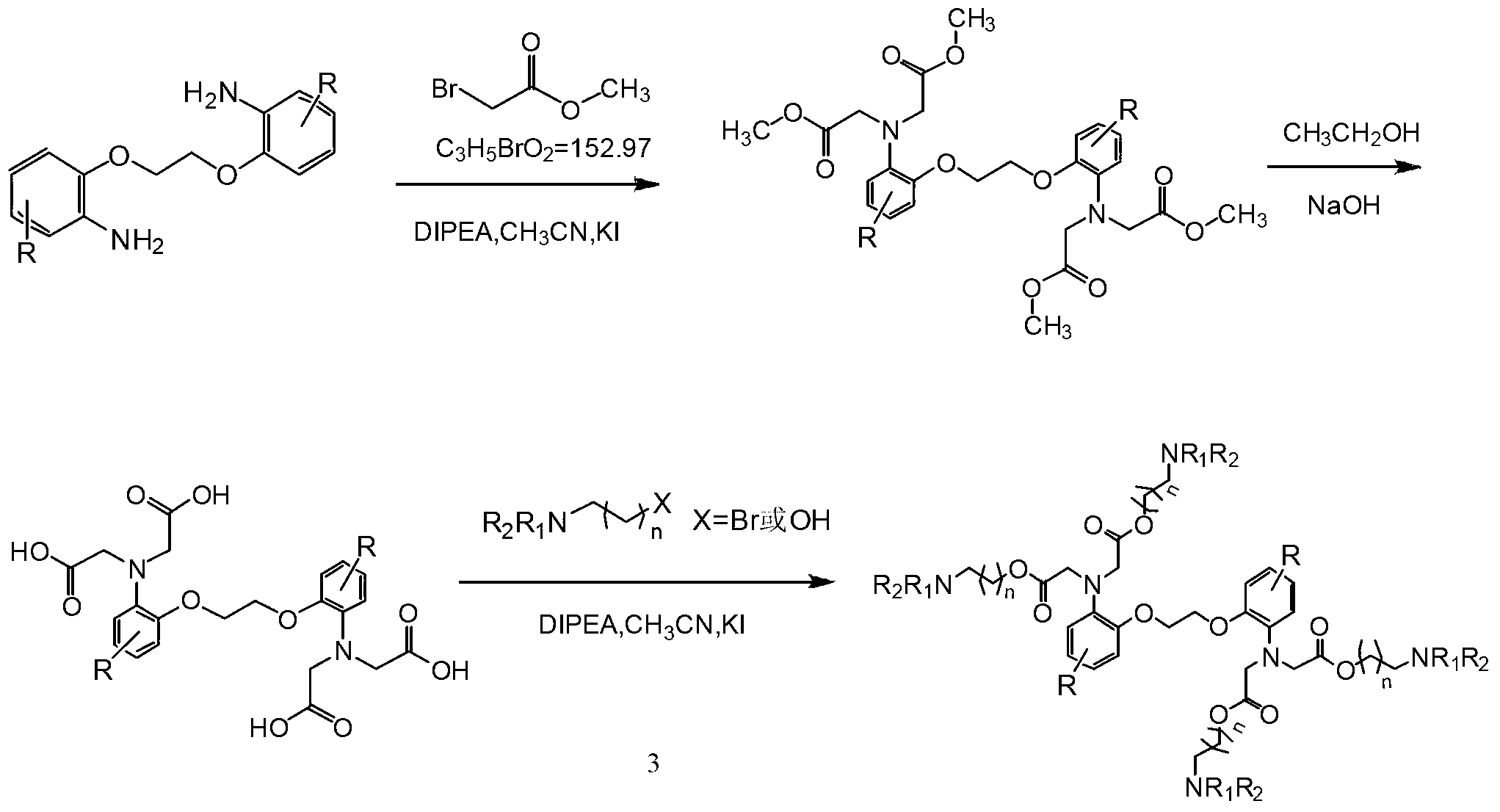
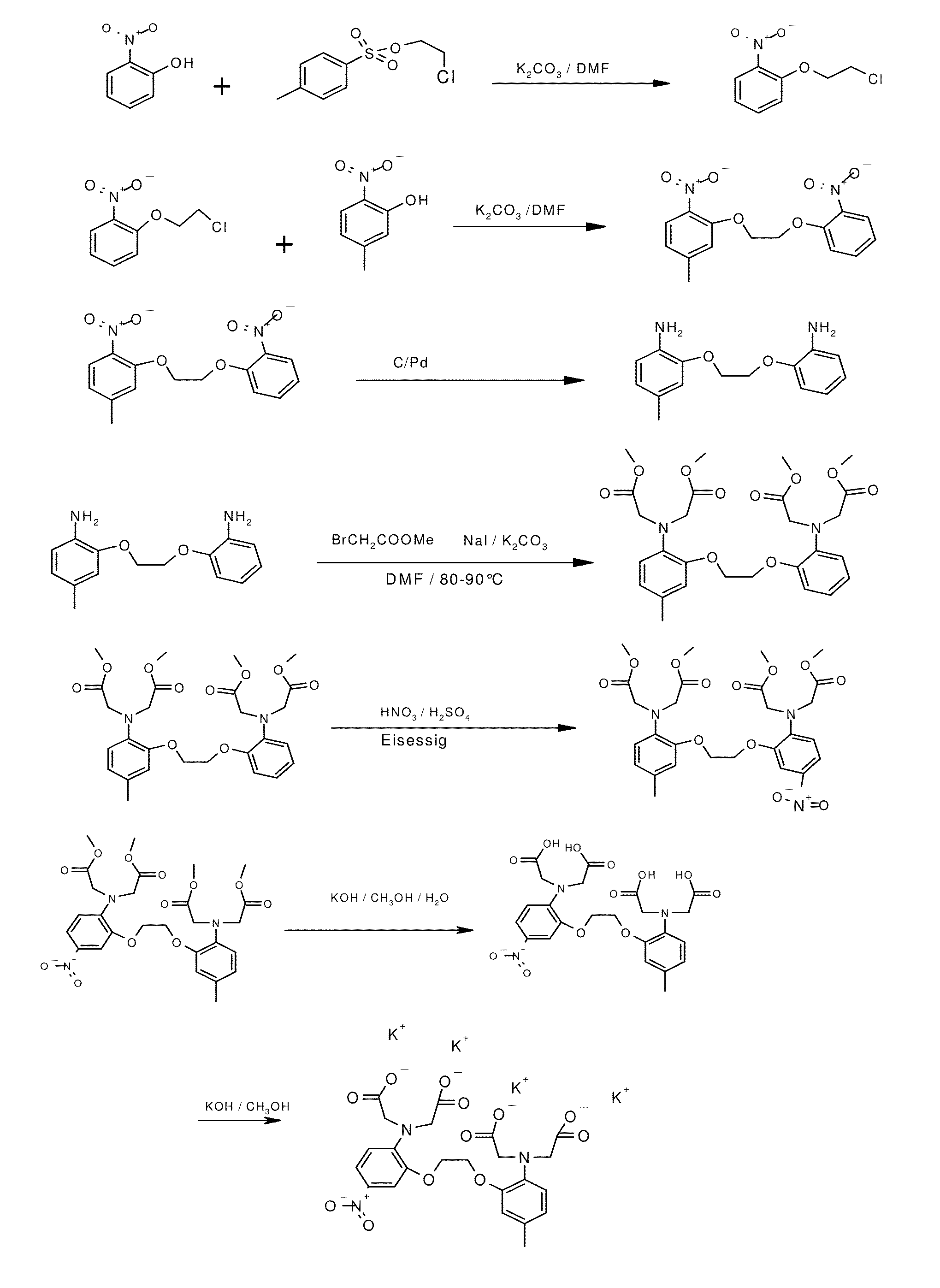
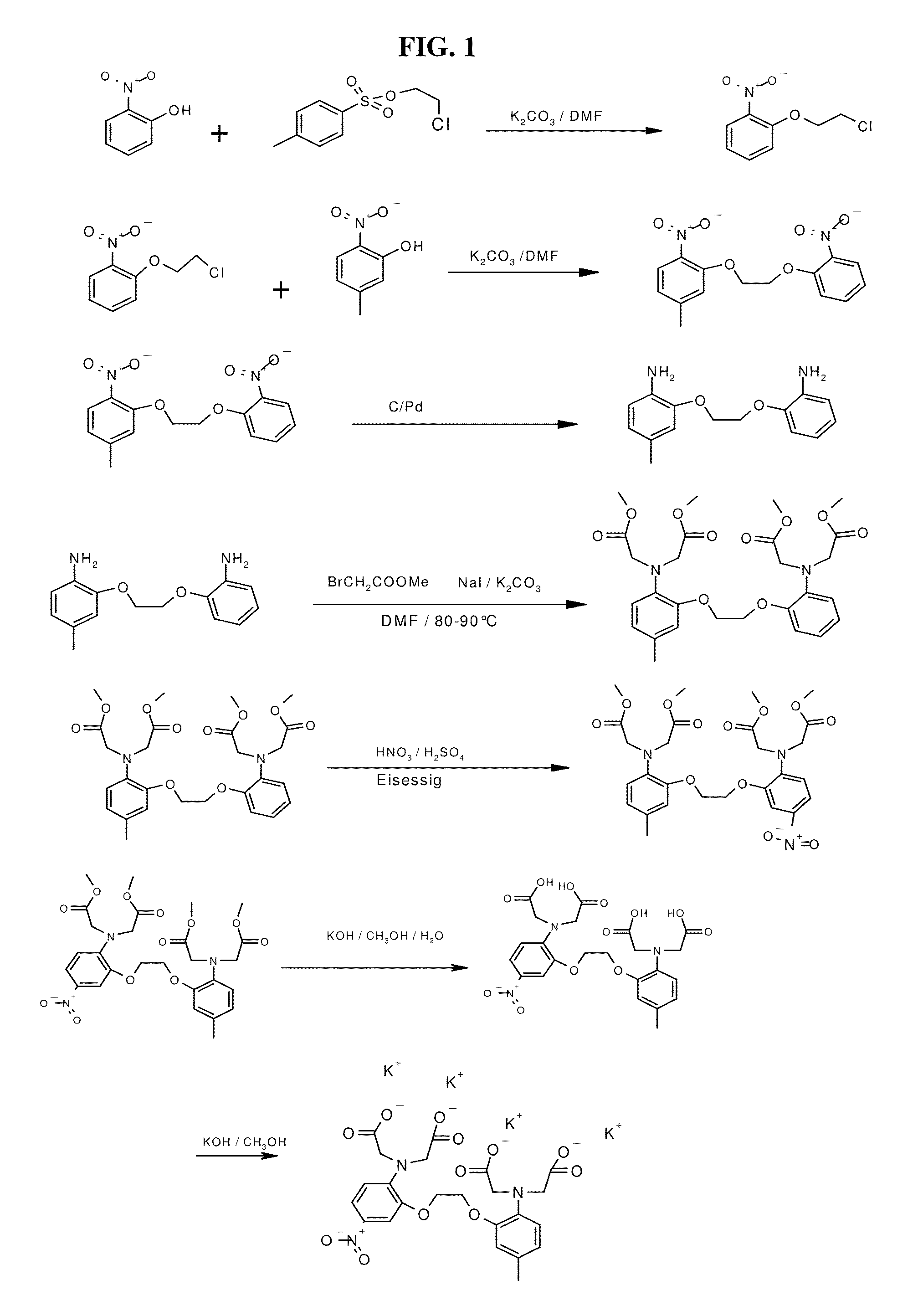
The invention provides a synthesis method of calcium ion selective chelating agents and relates to a synthesis method of biological medicaments. According to the synthesis method, 1, 2-bi(2-aminophenoxy) ethane is used as raw materials to take two steps of reaction: esterification reaction and acidification reaction, 2-bi(2-aminophenoxy) ethane-N, N, N', N'-quadrol(2a, BAPTA) is synthesized, and the structure of compounds 2a is shown by IR, 1HNMR. Through regulating the mixture ratio and the catalyst consumption, the mol ratio of 1, 2-bi(2-aminophenoxy) ethane to methyl bromoacetate to diisopropylethylamine is 1:5.2:5.2, the yield of the 2-bi(2-aminophenoxy) ethane-N, N, N', N'-quadrol methyl ester(1a, BAPTA methyl ester) is 86 percent, and the purity is 97.45 percent. A chemical purification method is adopted, the BAPTA purity can reach 99 percent, and the yield can reach 94 percent at the purity. The method has the advantages that the production cost is reduced, the process steps are optimized, and in addition, the quality and the yield are improved.
Owner:SHENYANG INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
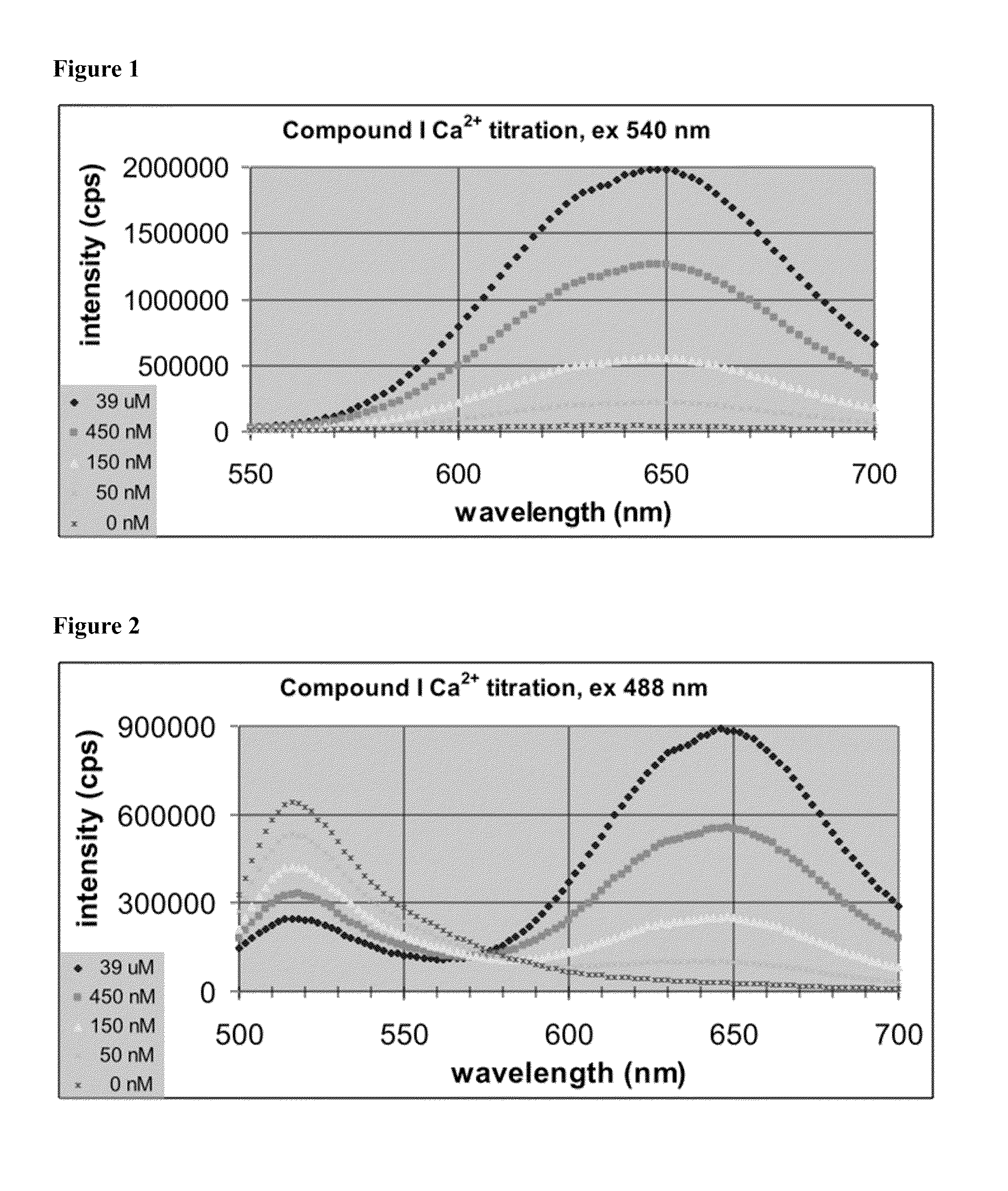
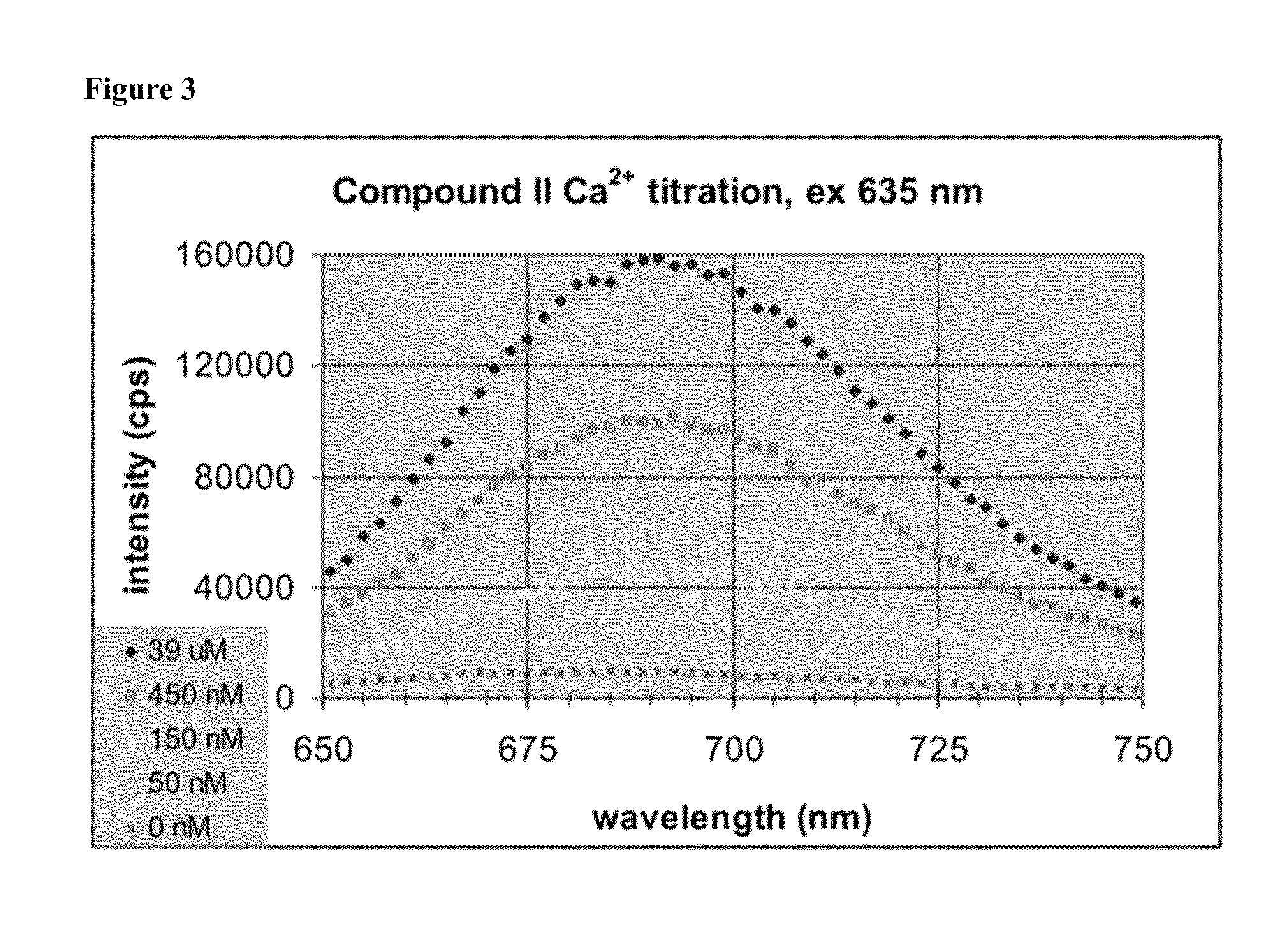
Fluorescent calcium indicators that are ratiometric and emit in the red spectrum
A new generation of fluorescent ion indicators for measuring cytosolic concentrations of calcium. These new indicators emit in the red portion of the visible spectrum and are ratiometric. The ratiometry consists of shifting in the emission upon binding calcium when exciting with an argon laser at 488 nm. These indicators also show marked increases in red fluorescence when excited with visible light at longer wavelengths. Like all calcium indicators, they comprise the usual chelating portion based on BAPTA (Bis Amino Phenyl Tetraacetic Acid) and a fluorophore portion, either a seminaphthofluorescein / seminaphthorhodamine or dinaphthofluorescein, which enable ratiometry. Unlike other naphthofluoresceins, the pKa has been adjusted on the naphtho moiety to make it suitable for biological calcium measurements. The invention relates to the structures of the indicators and to the method of synthesizing these indicators.
Owner:MINTA AKWASI +1
Method for delaying autolyzing of body wall of stichopus japonicus
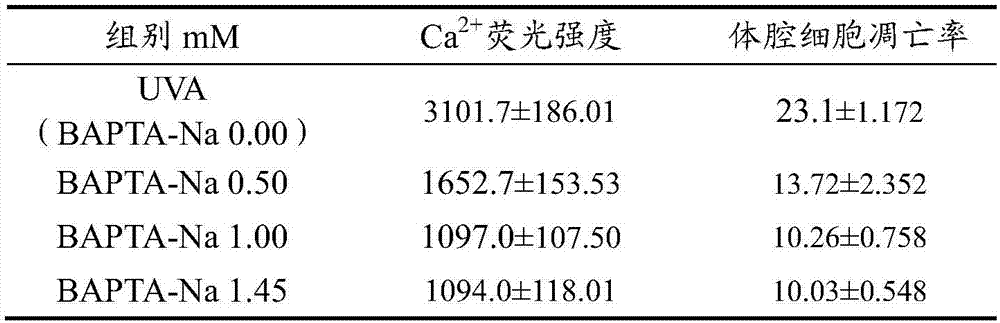
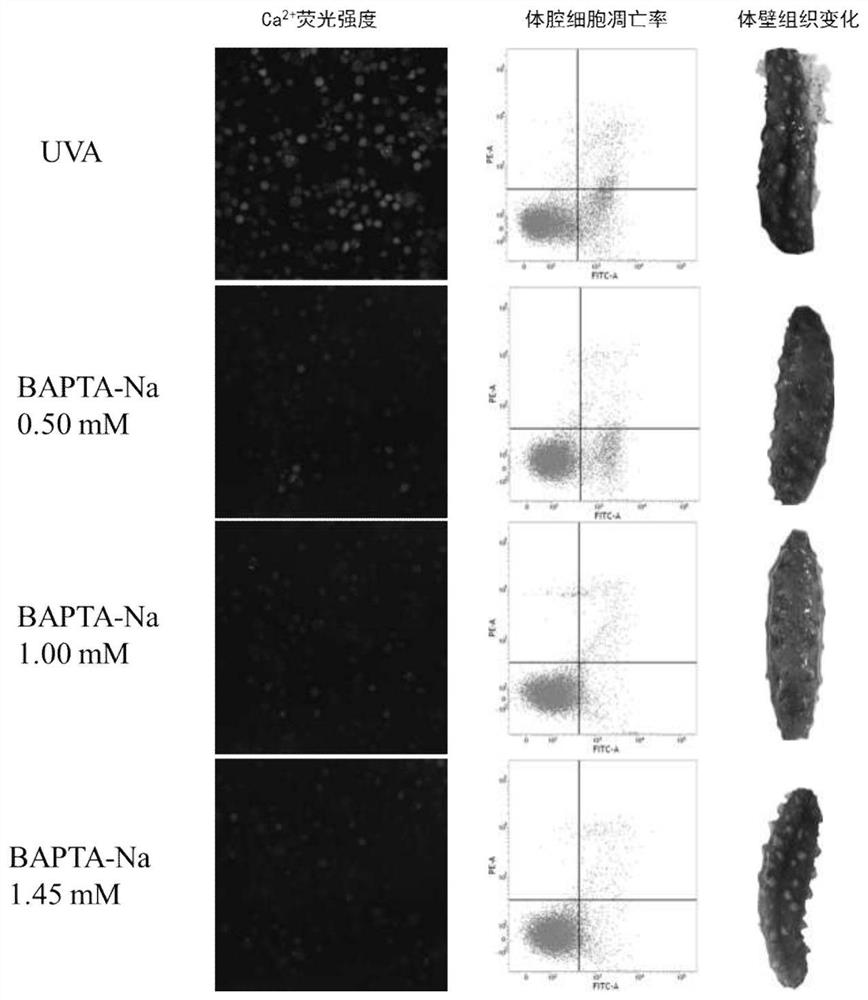
ActiveCN107873587ATo achieve the purpose of keeping fresh and aliveInhibit apoptosisPisciculture and aquariaStichopusCoelom
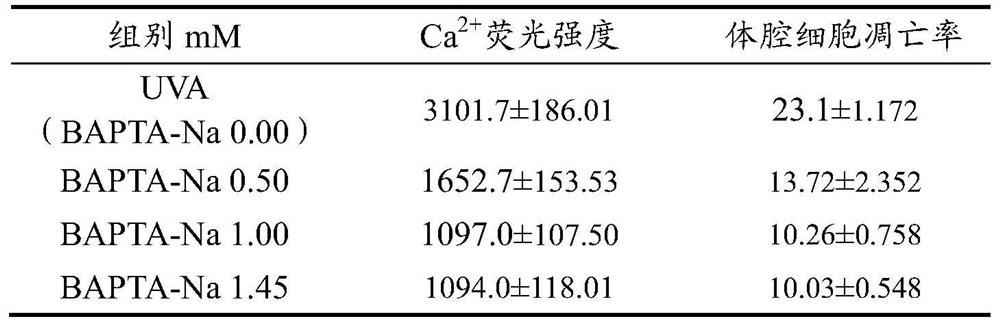
In order to keep the precious marine products alive, the coelom cell apoptosis rate of the stichopus japonicus can be regulated and controlled when the stichopus japonicus is stimulated by the outside, and then autolyzing of the body wall of the stichopus japonicus can be delayed. The invention provides a method for delaying autolyzing of body wall of stichopus japonicas. A calcium ion chelating agent BAPTA-Na is injected into the coelom of the stichopus japonicus; the calcium ion chelating agent BAPTA-Na. The calcium ion chelating agent BAPTA-Na is injected into the coelom of the stichopus japonicus in different doses in a median lethal concentration range, and with the increase of the dosage, the coelom cell apoptosis of the stichopus japonicas is obviously inhibited, autolyzing of the body wall is delayed, and the purpose of preserving and keeping the stichopus japonicus is achieved. The BAPTA-Na is directly injected into the coelom of the living stichopus japonicus and can directlyact with calcium ions in a coelom cell, and the living experiment verifies that the new application of BAPTA-Na has persuasion.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
BAPTA and application of derivant thereof in preparing analgesic drugs
The invention discloses a BAPTA and an application of a derivant thereof, in particular to an application of the derivant in preparing analgesic drugs. Clinical indications include headache, prosopalgia, dysmenorrheal, postoperative pain, cancer pain, viscera pain, postherpetic neuralgia, phantom limb pain, HIV, pathologic pain related to multiple sclerosis, morphine class medicine tolerance or addiction patient pain and serious chronic intractable pain or usual clinical pain diseases.
Owner:HENGXING PHARMA INST HEFEI
Lipophilic diesters of chelating agent for inhibition of enzyme activity
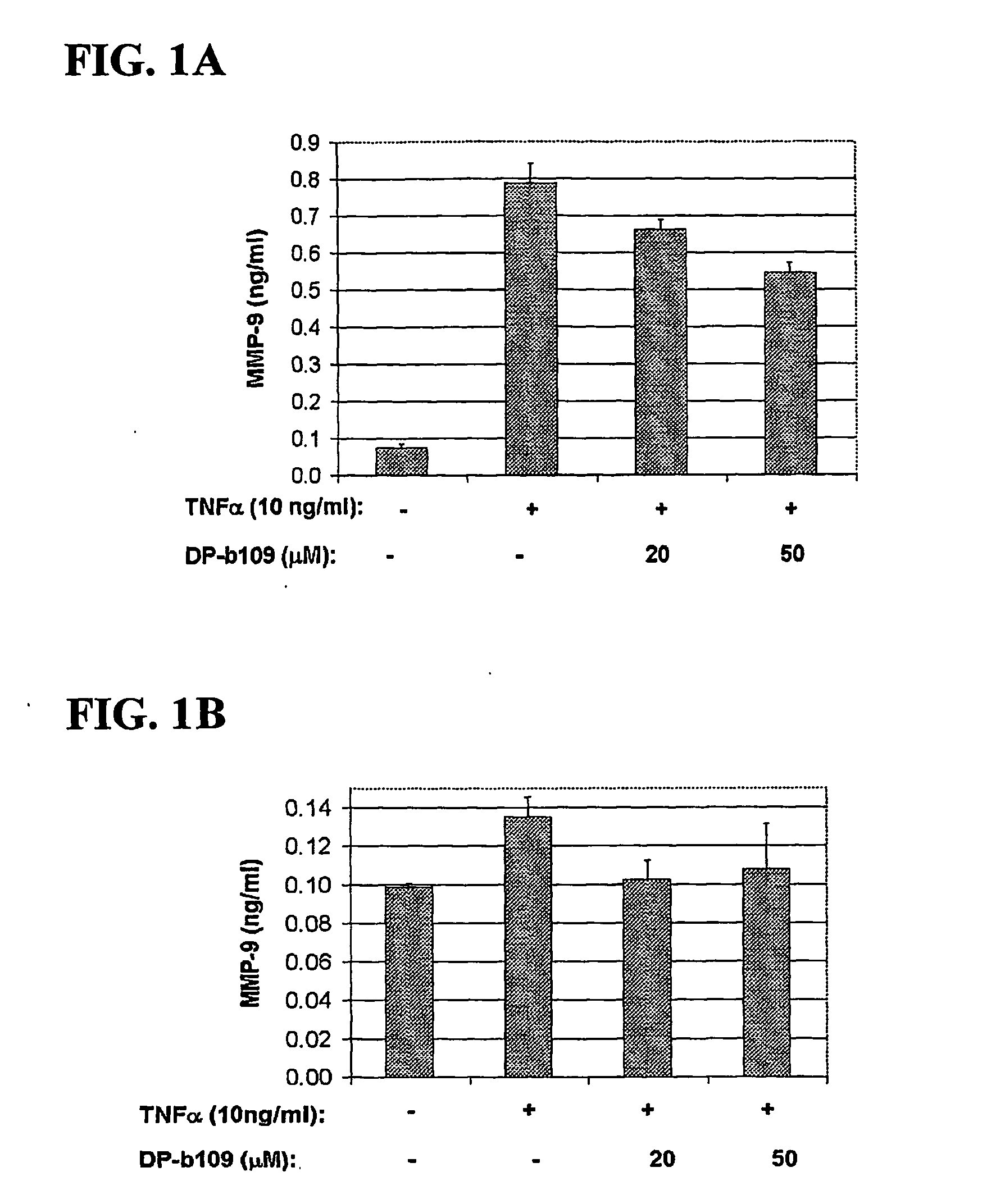
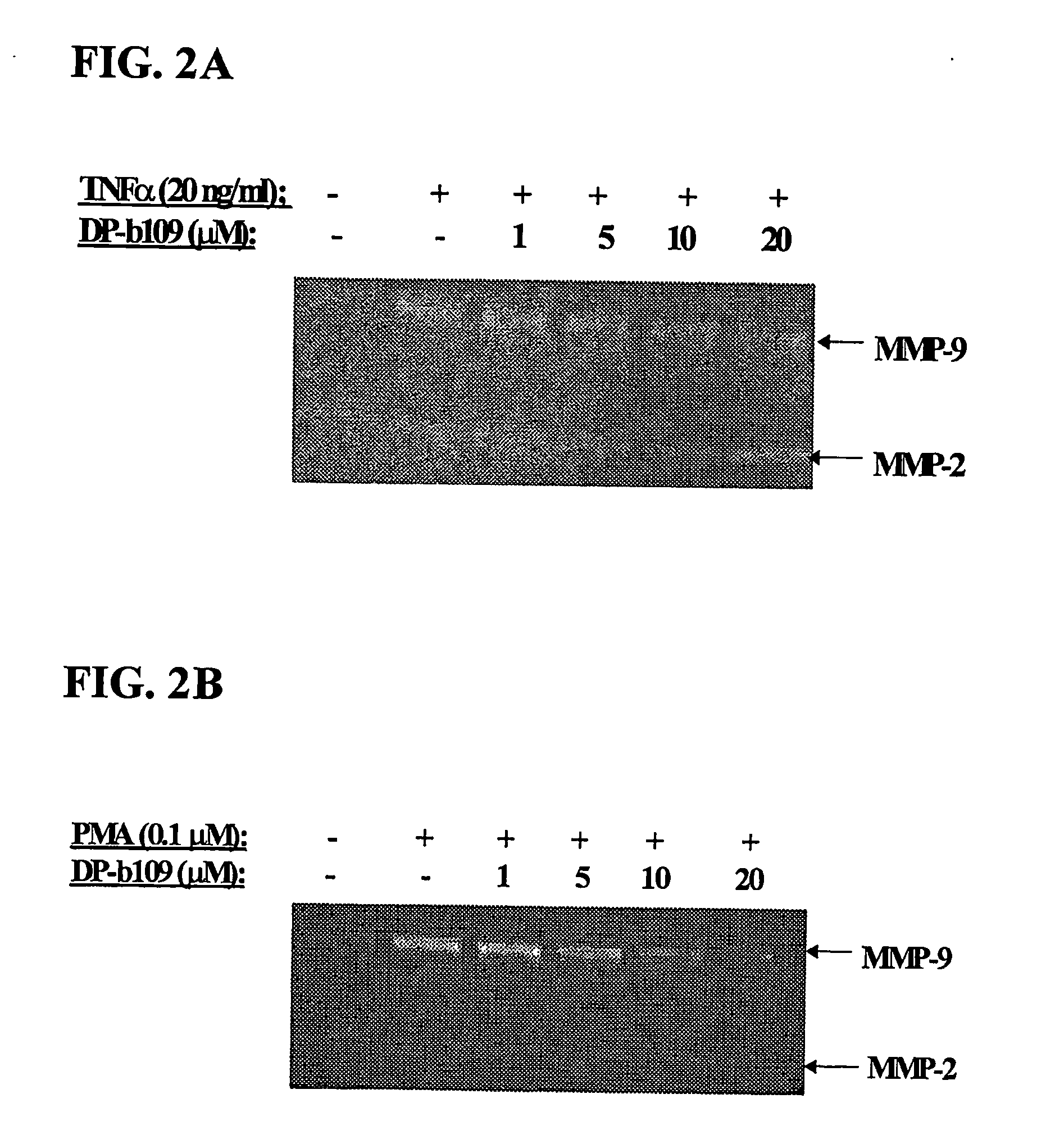
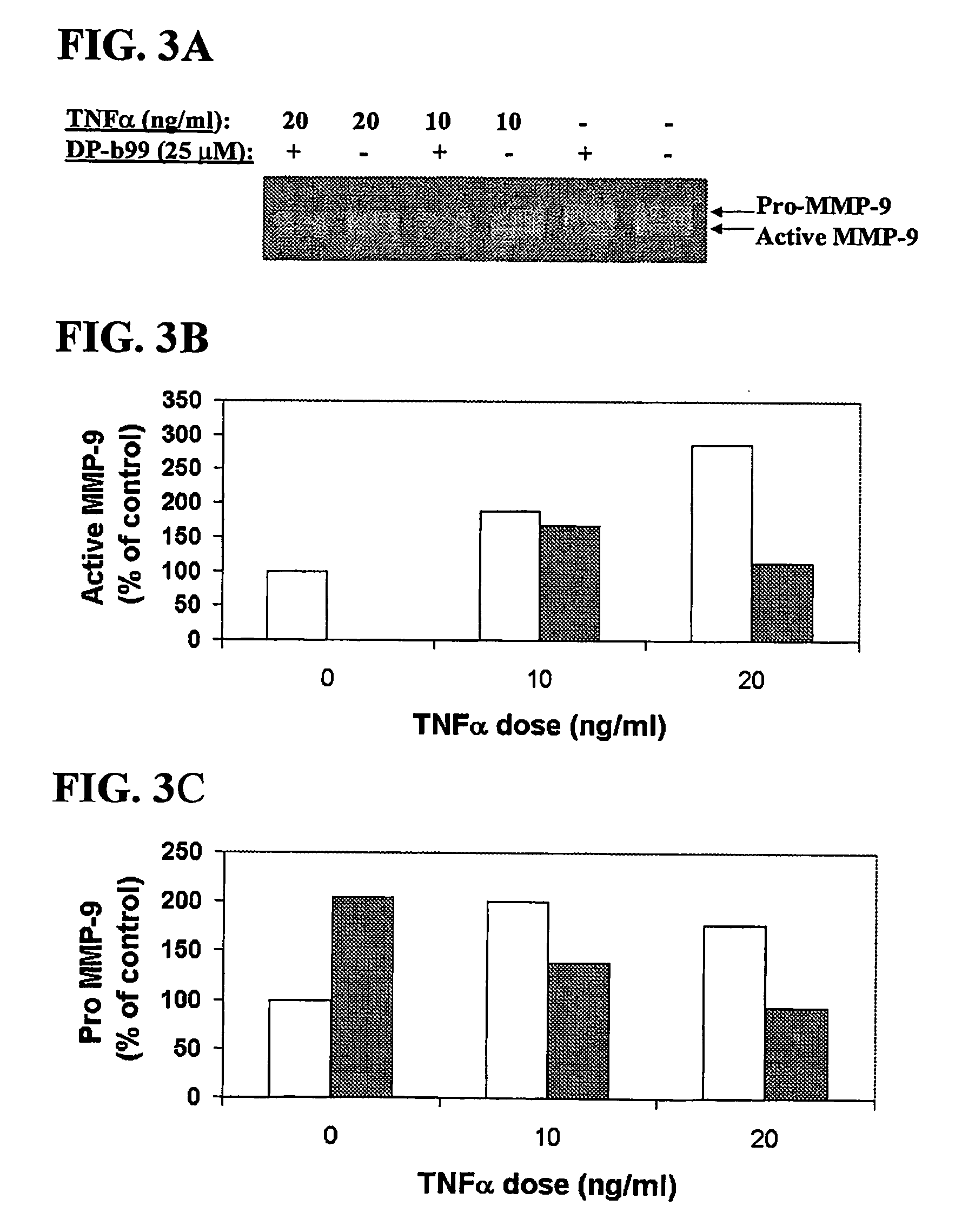
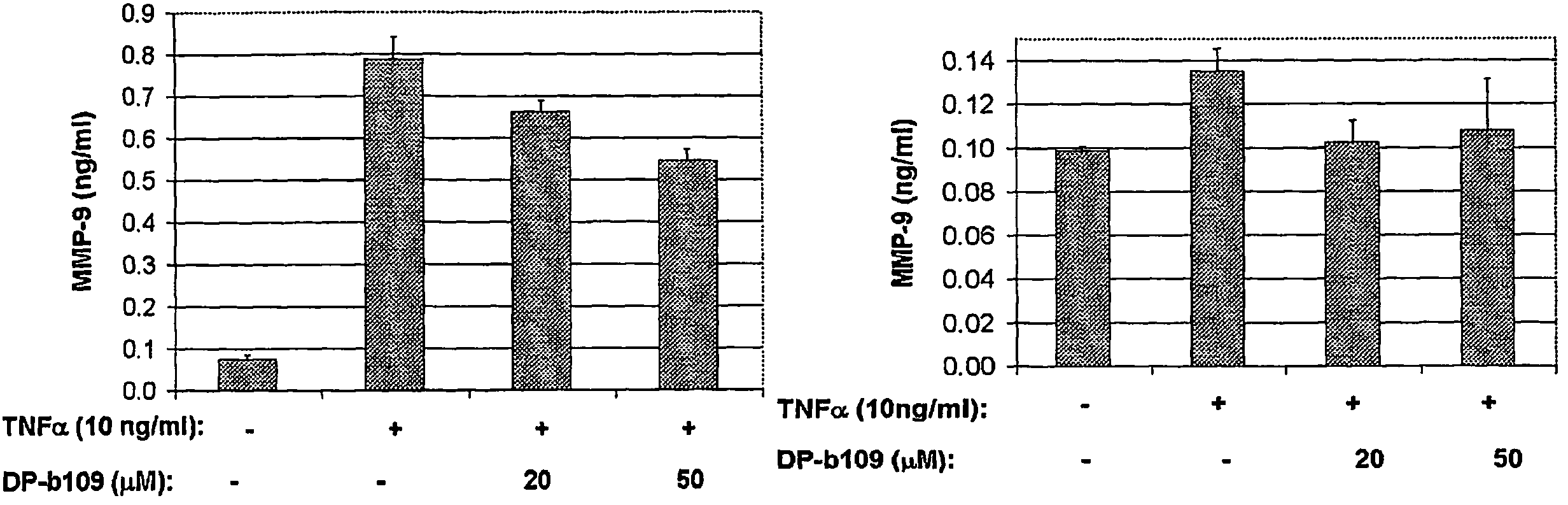
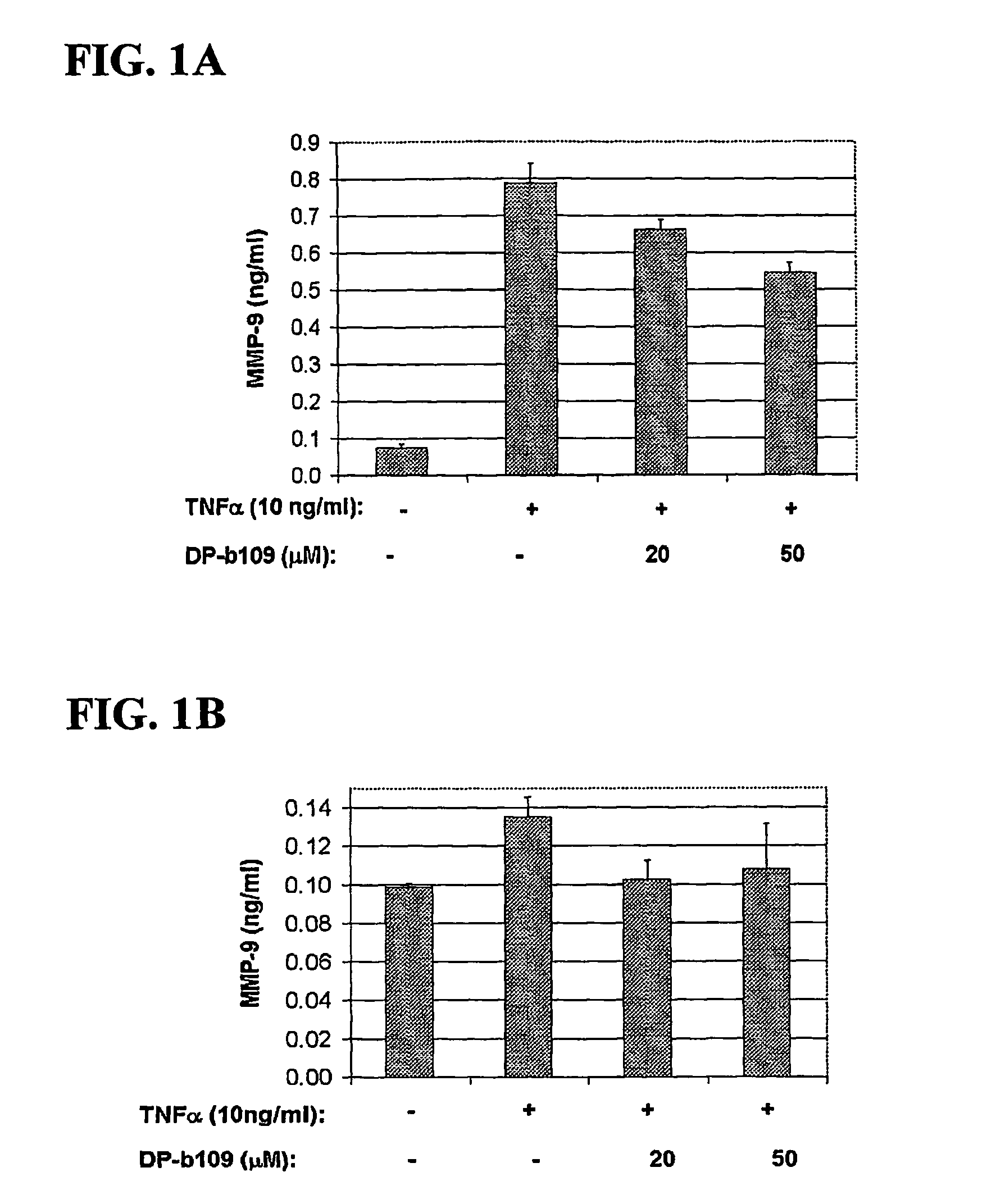
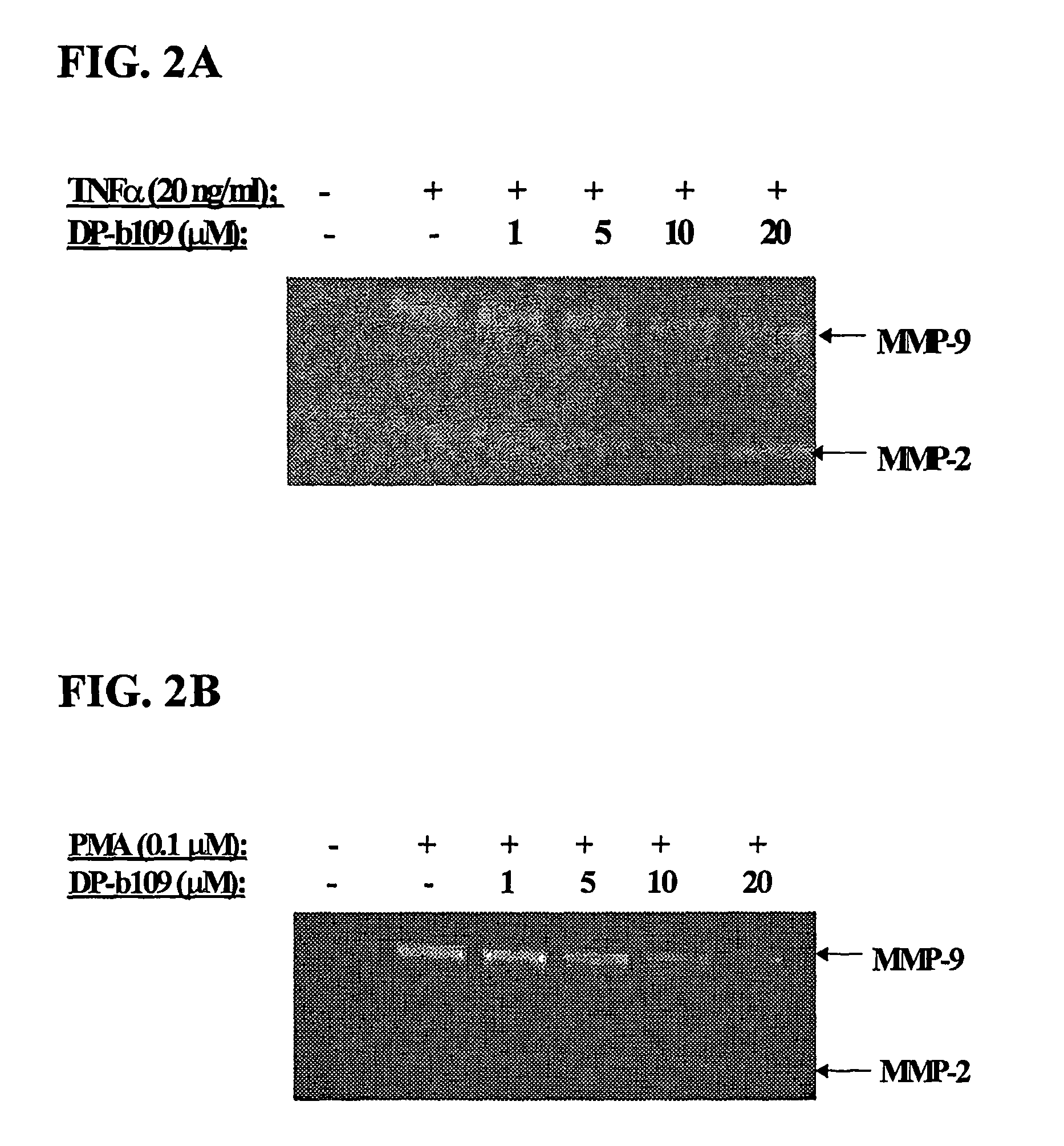
The present invention relates to the use of lipophilic diesters of the chelating agent 1,2-bis(2 aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA) for inhibition of proteolytic activities of certain metalloproteinases and of calpain. The invention further relates to methods for preventing, treating or managing MMP-related and calpain-related diseases or disorders in mammals comprising administering to a mammal in need thereof, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of said lipophilic diesters of the chelating agent BAPTA.
Owner:D PHARMA LTD
BAPTA and application of derivant thereof in rescuing and treatment medicine of hepatic failure
The invention discloses a BAPTA and an application of derivant thereof, in particular an application in rescuing and treatment medicines of hepatic failure.
Owner:HENGXING PHARMA INST HEFEI
Zinc binding compounds and their method of use
The present invention provides a metal chelator and methods that facilitate binding, detecting, monitoring and quantitating of zinc ions in a sample. The metal chelating moiety of the zinc-binding compound is an analog of the well-known calcium chelator, BAPTA (1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid), wherein the chelating moiety has been modified from a tetraacetic acid moiety to a tri- di- or monoacetic moiety. This change in acetic acid groups on the metal chelating moiety results in the selective bindings of zinc ions in the presence of calcium ions, both of which are present in biological fluids and intracellular cytosolic fluid and organelles.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Novel BAPTA derivative, preparation method thereof and medicinal use thereof
InactiveCN103288664AEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsOrganic compound preparationMedicinal chemistryDrug
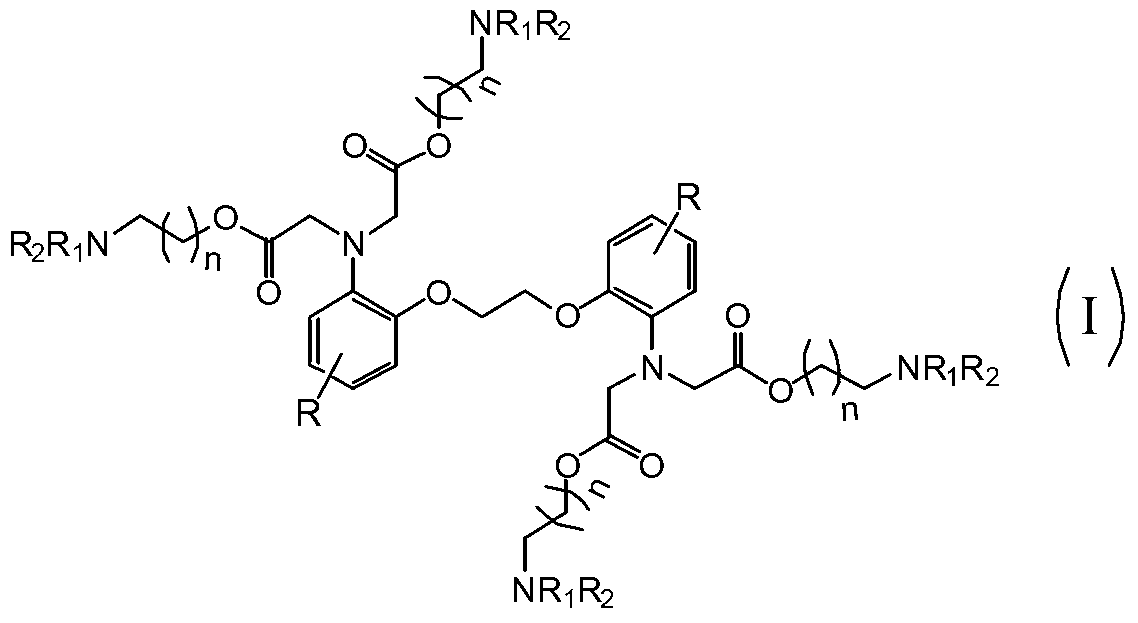
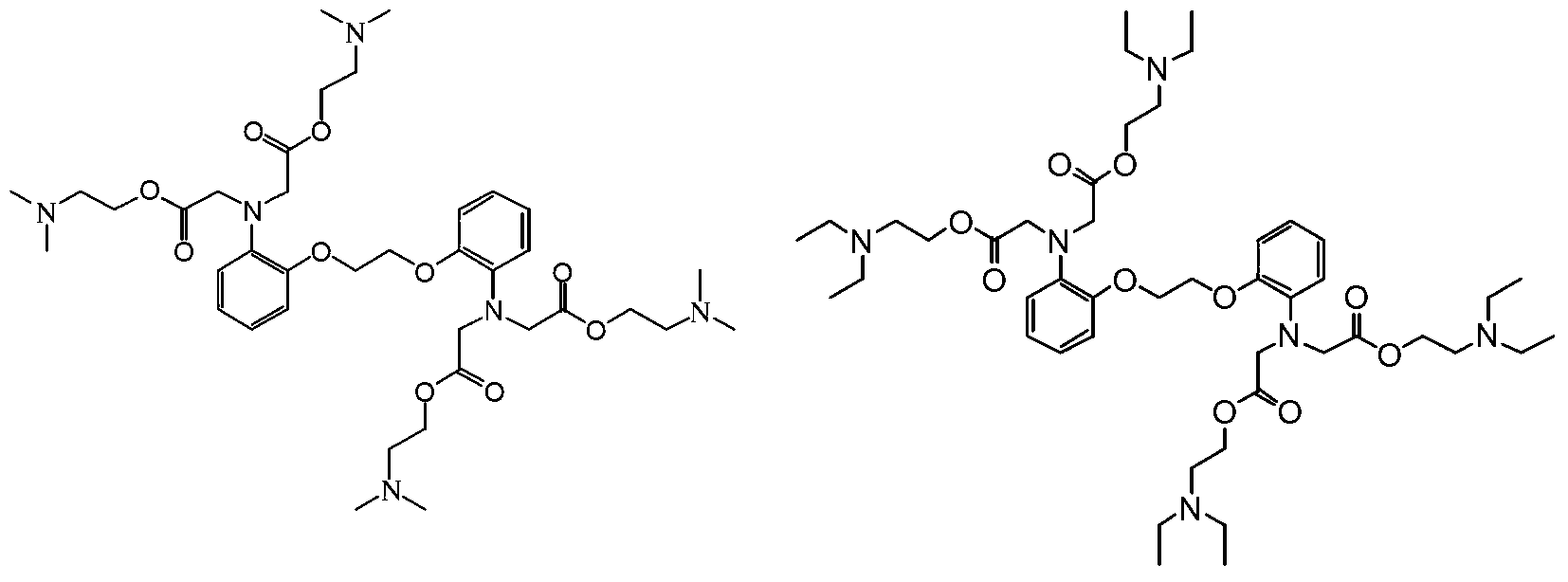
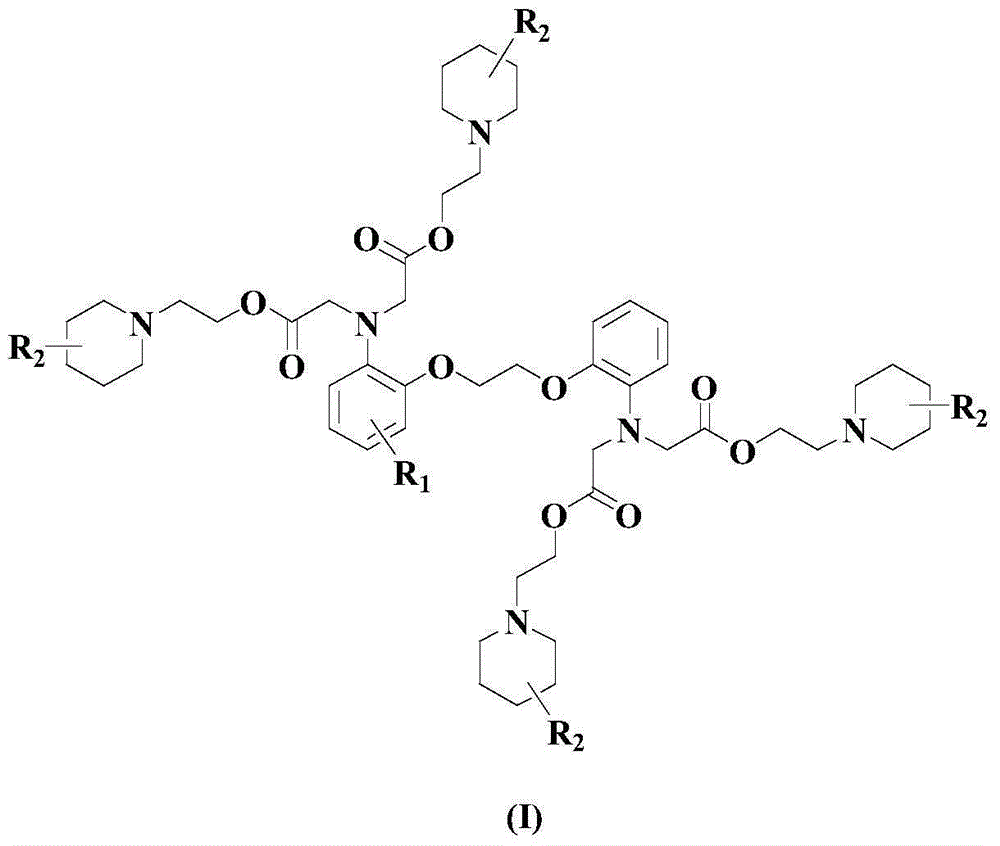
The invention relates to the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and particularly relates to an improved BAPTA derivative general formula (I), a preparation method of the improved BAPTA derivative, a medicinal preparation containing the improved BAPTA derivative, and medicinal use of the improved BAPTA derivative, wherein R, R1, R2 and n are defined as in the description. The invention further provides a preparation method of the derivative compounds and applications in medicine.
Owner:HENGXING PHARMA INST HEFEI
Zinc binding compounds and their method of use
ActiveUS20110159517A1Efficient ConcentrationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesAcetic acidChemical compound
The present invention provides a metal chelator and methods that facilitate binding, detecting, monitoring and quantitating of zinc ions in a sample. The metal chelating moiety of the zinc-binding compound is an analog of the well-known calcium chelator, BAPTA (1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid), wherein the chelating moiety has been modified from a tetraacetic acid moiety to a tri- di- or monoacetic moiety. This change in acetic acid groups on the metal chelating moiety results in the selective bindings of zinc ions in the presence of calcium ions, both of which are present in biological fluids and intracellular cytosolic fluid and organelles.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Lipophilic diesters of chelating agent for inhibition of enzyme activity
The present invention relates to the use of lipophilic diesters of the chelating agent 1,2-bis(2 aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (BAPTA) for inhibition of proteolytic activities of certain metalloproteinases and of calpain. The invention further relates to methods for preventing, treating or managing MMP-related and calpain-related diseases or disorders in mammals comprising administering to a mammal in need thereof, a pharmaceutical composition comprising a therapeutically effective amount of said lipophilic diesters of the chelating agent BAPTA.
Owner:D PHARMA LTD
Subcellular area targeting, long-wavelength and dual-wavelength ratio method Ca<2+> fluorescent probe and synthesis method thereof
InactiveCN101620225ASuitable affinityAchieve markupBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceSynthesis methods
The invention relates to design and synthesis of subcellular area targeting, long-wavelength and dual-wavelength ratio method Ca<2+> fluorescent probe. In the synthesis of the probes, 1, 2-di(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N, N, N', N'-tetraacetic acid tetraethyl ester is taken as the initial material to first synthesize Ca<2+> receptor (5, 5'-dicarboxo-BAPTA) with two formyl active groups as the key intermediate of the Ca<2+> fluorescent probes. Then, the key intermediate is condensed with the substrate containing active methyl in agreeable organic solvent to obtain a series of Ca<2+> fluorescent probes excited by visible light, fluorescence excitation and emission peak as well as position all change before and after the probes combine with Ca<2+>, and Ca<2+> can be measured by dual-wavelength ratio method. The probes can carry out targeting marking on the specified subcellular area after entering cells. With the probes adopted, the real-time dynamic measurement of Ca<2+> content in the cells and space-time distribution condition can be realized in the subcellular level, thereby, an efficient means for cell calcium signal transduction research is provided.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
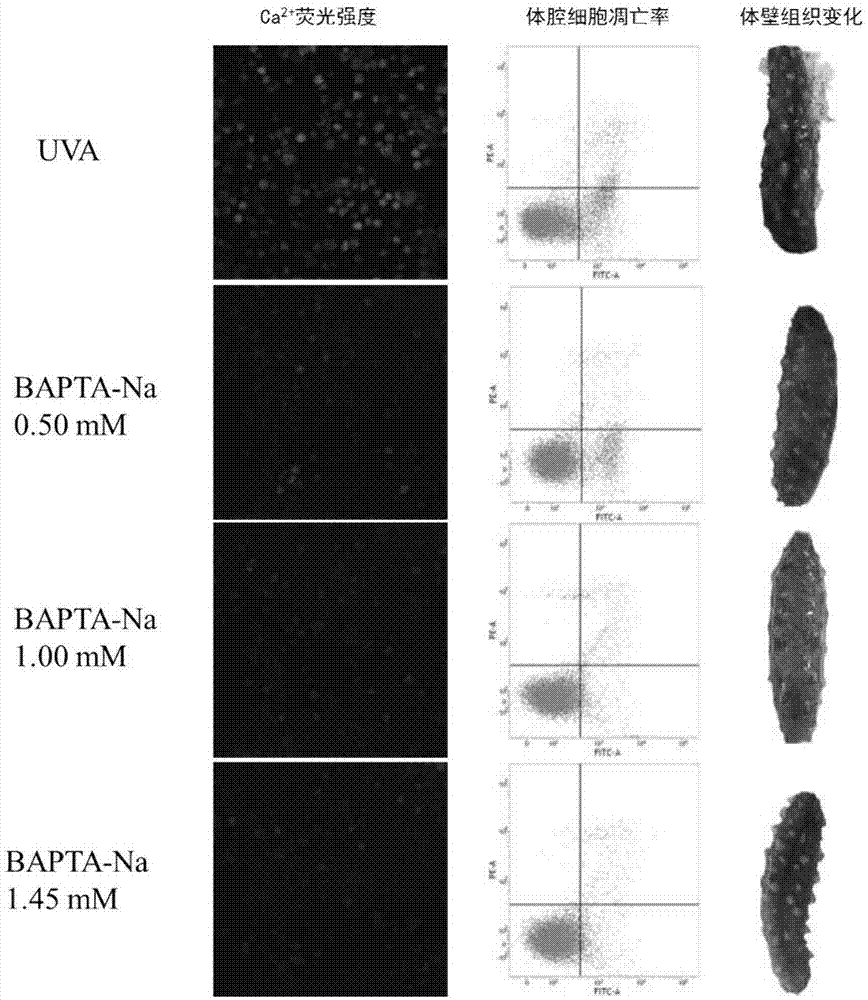
A kind of method for delaying autolysis of sea cucumber body wall
ActiveCN107873587BMonitor changesTo achieve the purpose of keeping fresh and alivePisciculture and aquariaApoptosisIn vivo experiment
In order to keep sea treasures fresh and alive, regulate the apoptosis rate of body coelom cells of sea cucumbers when they are stimulated by the outside world, and delay the autolysis of sea cucumber body walls, the present invention provides a method for delaying body wall autolysis of sea cucumbers, Inject the calcium ion chelating agent BAPTA-Na into the body cavity of the sea cucumber; the calcium ion chelating agent BAPTA-Na. The calcium ion chelating agent BAPTA-Na adopted in the present invention is poured into the body cavity of sea cucumbers in different doses within the semi-lethal concentration range. Dissolve, in order to achieve the purpose of keeping fresh and alive sea cucumber. BAPTA-Na is directly infused into the body cavity of fresh sea cucumber, which directly interacts with calcium ions in coelomocytes, and the in vivo experiment verifies that the new application of BAPTA-Na is convincing.
Owner:DALIAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
A culture medium for promoting immature oocyte maturation in vitro and its application
ActiveCN107460161BImprove the ability of in vitro culture and developmentIncrease available quantityCulture processGerm cellsMaturation oocyteAnimal science
The invention relates to an immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium and application thereof. The immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium is screened out through research on effects of different additives on immature oocytes and prepared by adding 20-100 mu M of BAPTA-AM in normal oocyte in vitro maturation culture solution. The immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium is safe and free to side and toxic effects, enables meiosis of the immature oocytes, particularly those in level 3 cumulus-oocyte complexes, improves the in vitro development of the oocytes, promotes maturation, improves the cleavage rate and the blastula development rate after the mature oocytes are parthenogenetically-activated and further improves embryo quality. Application of the immature oocyte in vitro maturation promoting culture medium provides favorable support for the technology of in vitro propagation of animal embryos.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Novel calcium-ion selective chelating agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105001180AImprove biological activityHigh yieldOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryOxygen deprivationIschemia
The invention provides a novel calcium-ion selective chelating agent as shown in the formula (I) and a preparation method and application thereof. The compound has excellent capacity of ischemia and oxygen deprivation resistance, meanwhile has excellent transcellular capacity serving as a transport substrate of OATP1B1 transport proteins and has very important meaning and potential value in research of BAPTA derivates.
Owner:ANHUI HEALSTAR PHARM CO LTD
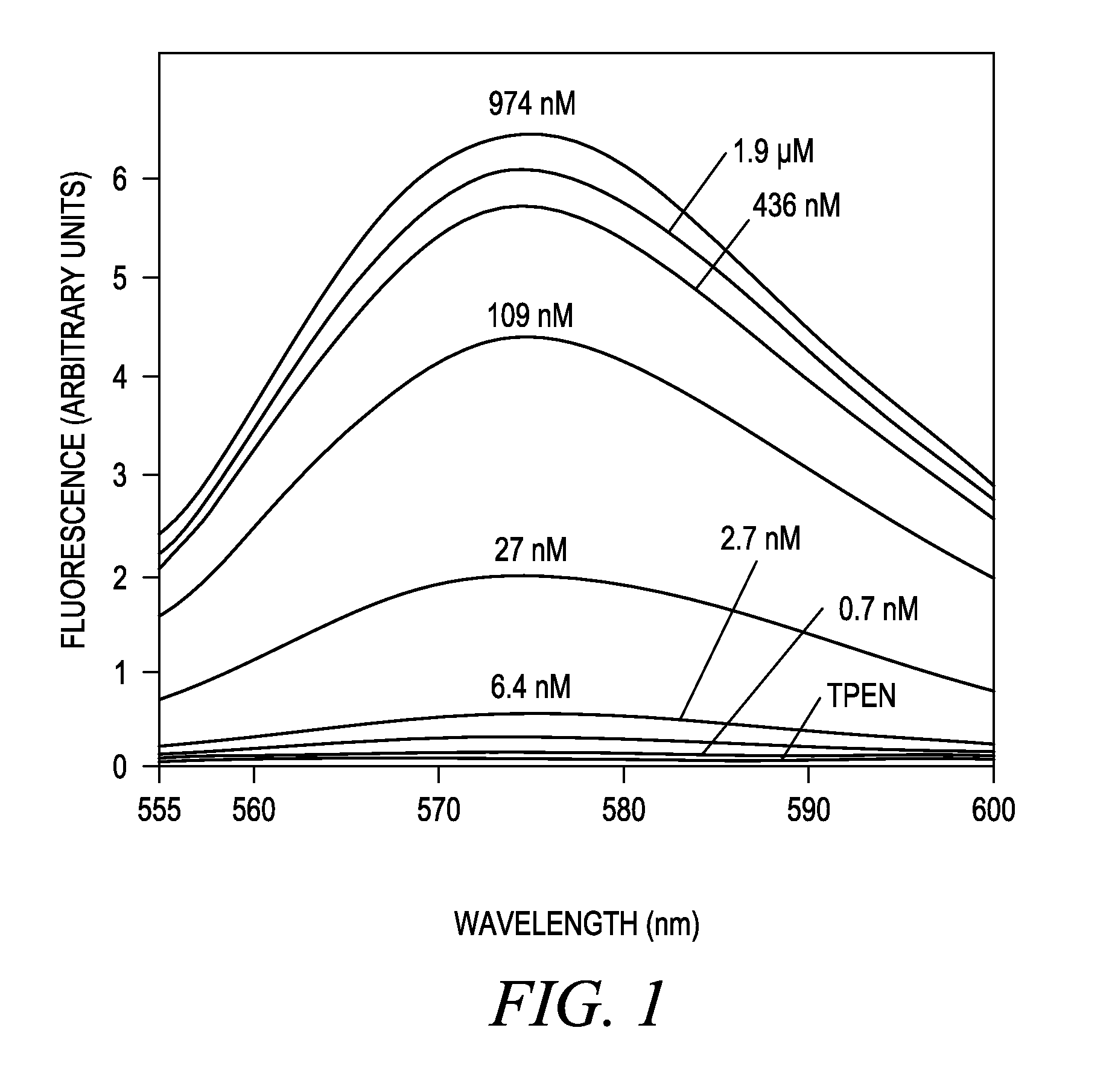
Methods for measurement of calcium ions
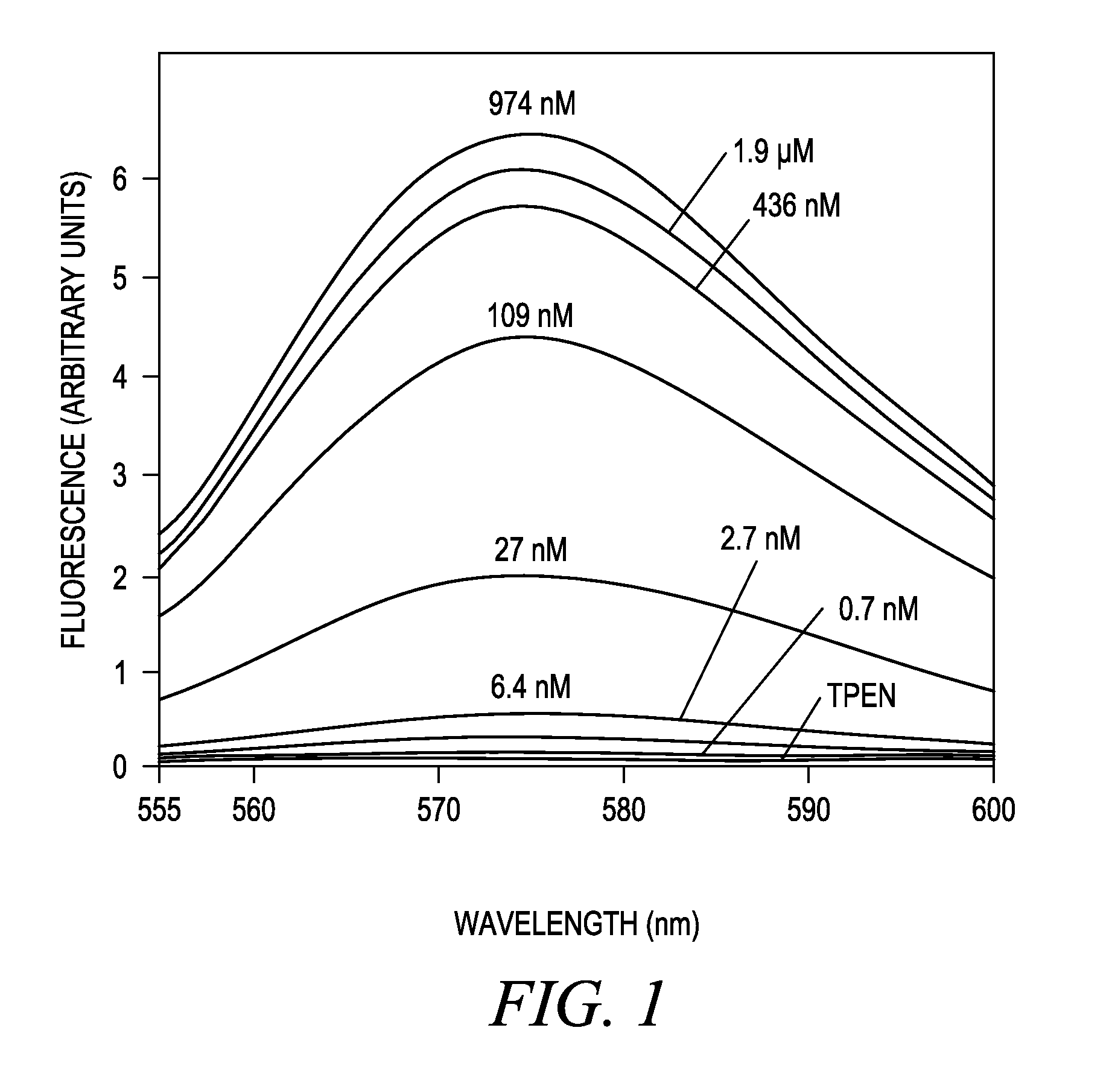
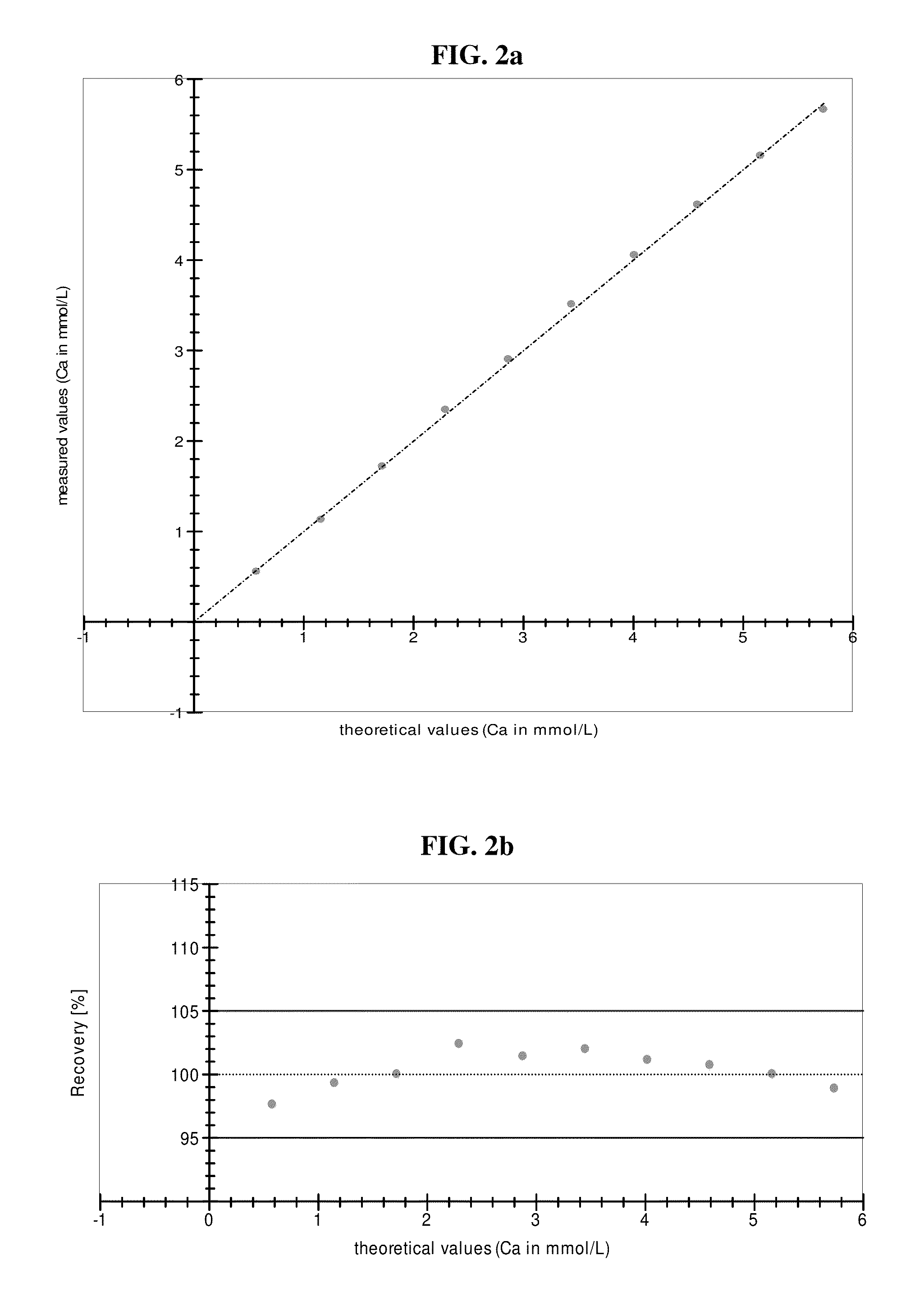
ActiveUS8962338B2Rapid determinationHigh sample throughputOrganic chemistryAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionBlood plasmaCalcium EDTA
Reagents and methods for determination of calcium within a sample. Specific embodiments include a reagent for determination of calcium comprising a mono-nitro substituted BAPTA-type chelator (BAPTA=1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid). Methods for accurate determination of calcium in a sample, such as a blood, whole blood, plasma or serum or any other aqueous liquid sample including cerebrospinal fluid, lymph, salivary juice or urine. Embodiments are also useful for clinical diagnoses.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Nontoxic environmental-protection building decorative material
The invention discloses a nontoxic environmental-protection building decorative material which is composed of the following ingredients, by weight, 2-3 parts of maleic anhydride, 5-10 parts of a film-forming additive, 1-3 parts of microlite, 3-4 parts of a phosphite antioxidant, 10 parts of a carboxylic styrene butadiene emulsion, 2-5 parts of open-cell expanded perlite, 4-8 parts of zinc oxide, 1-3 parts of silicon oxide, 8-11 parts of polypropylene, 5-10 parts of BAPTA, 10-14 parts of natural latex, 10-20 parts of a fire retardant, 3-6 parts of an anti-aging agent, 1-3 parts of glycerol triglycerate and 5-20 parts of a cosolvent. The invention has the following beneficial effect: microlite powder, an organic filler and the like are used as main raw materials, and the prepared building decorative material contains no chemical toxic or harmful substances, is environmentally-friendly and is simple to operate and convenient to construct.
Owner:黄艳
Single\two-photon calcium ion fluorescent probe compound and preparation and application thereof
The invention provides a single\two-photon calcium ion fluorescent probe compound and preparation and application thereof. The calcium ion fluorescent probe compound has the structure of formula I. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: heating BAPTA-CH3-CHO and 4-methyl-N-methylpyridine iodate at a molar ratio of 1:(1.1-1.3) in the presence of ethanol solvent and piperidine catalyst to 78-83 DEG C for a reflux reaction; cooling to separate out precipitates; and filtering, washing, drying and recrystallizing to obtain a product. The fluorescent probe compound has good selectivity and sensitivity on calcium ions, and performs simple pretreatment of the detection sample; and moreover, the fluorescent probe compound has certain water solubility and excellent single\two-photon fluorescence, and can be widely used for detecting the calcium content in animals / plants, human cells, soil or water.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Application of BAPTA derivative in the preparing process of clinical medicine
InactiveCN1273125CLower levelAlleviate pathological changesPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsDiseaseLiver necrosis
The present invention features that BAPTA derivative is applied in preparing medicine for treating acute great area cell death clinically. The medicine is prepared into particle preparation for the clinical salvage and treatment of acute great area cell death diseases, such as cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction, liver necrosis, ischemic kidney necrosis, necrotic pencreatitis, etc.
Owner:HENGXING PHARMA INST HEFEI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com