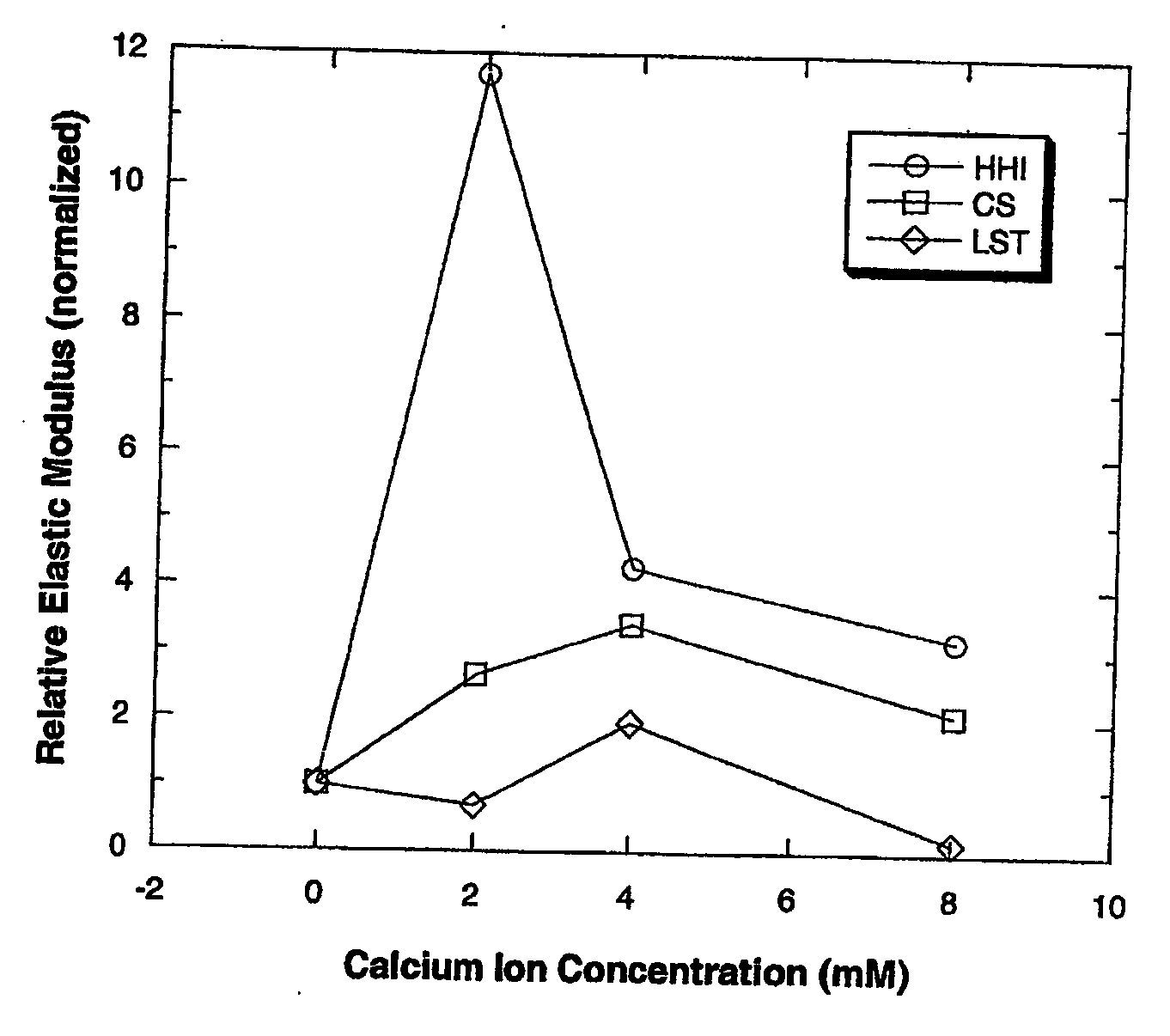
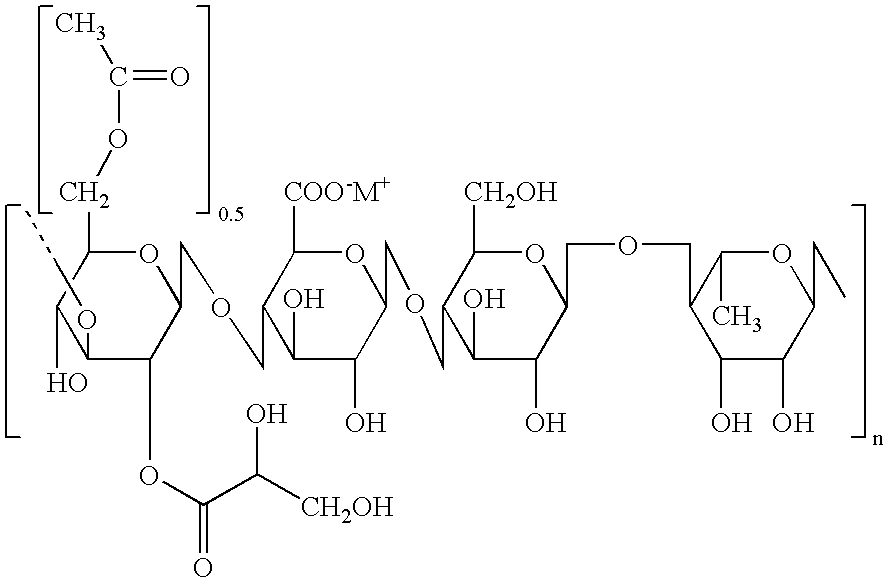
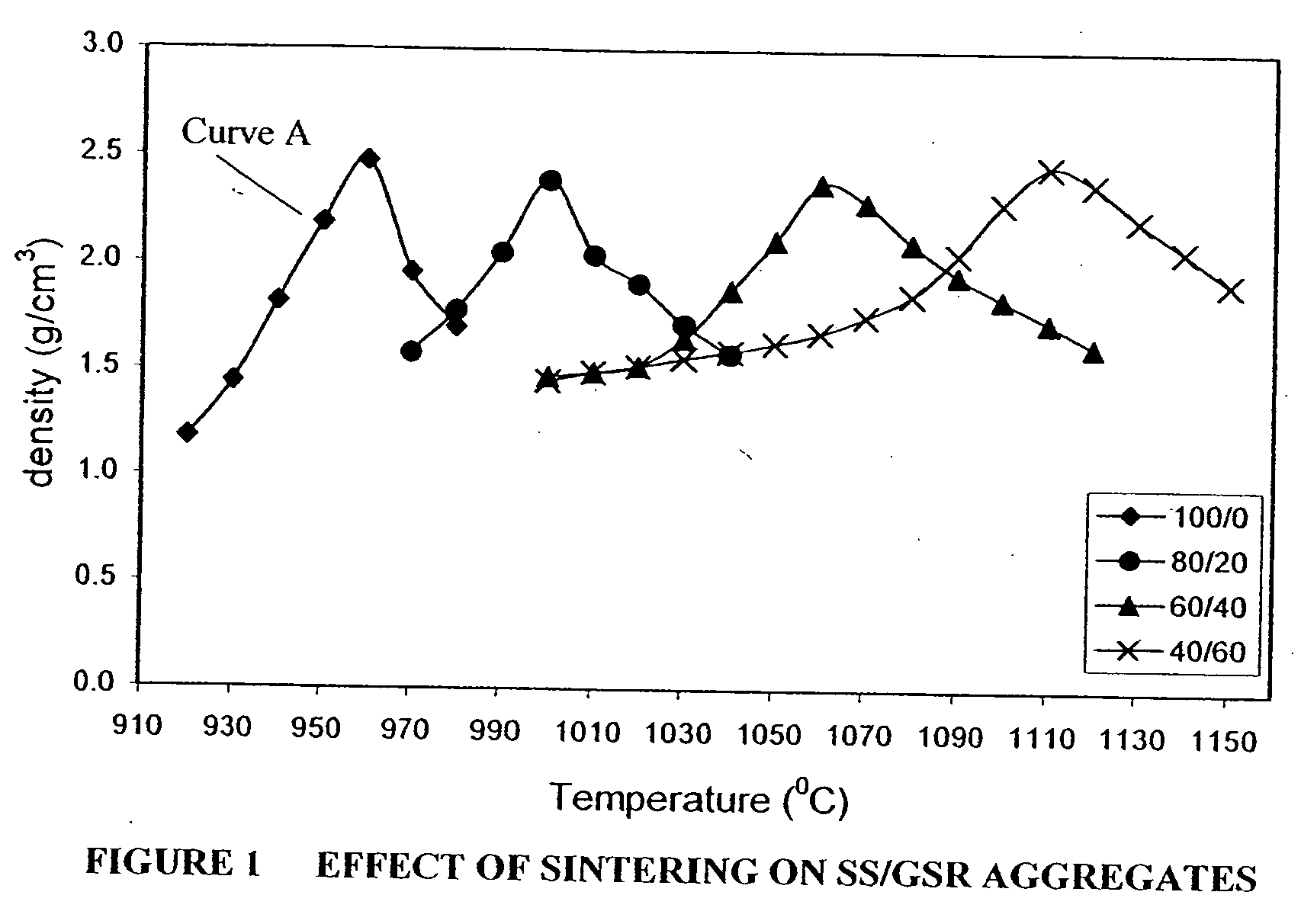
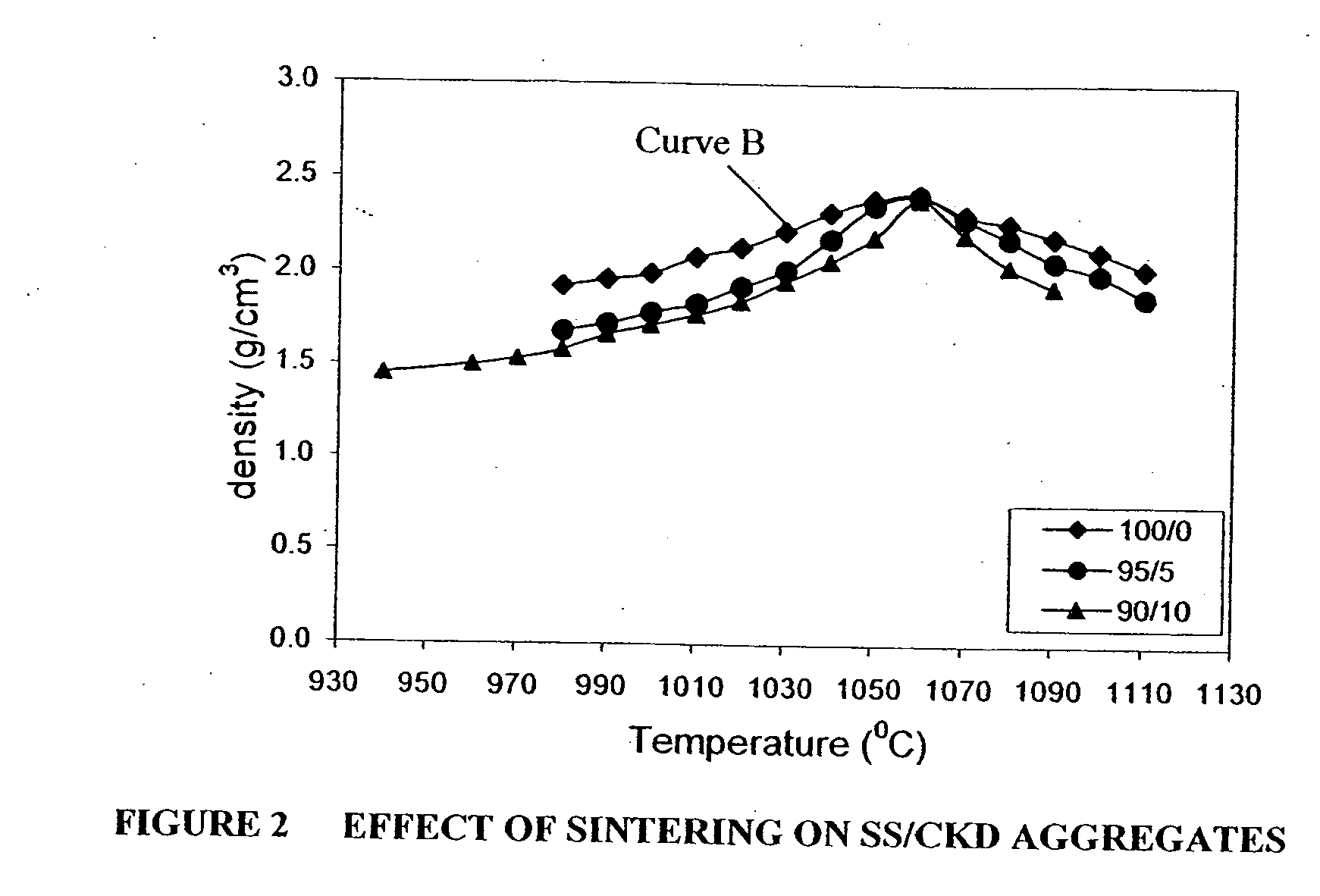
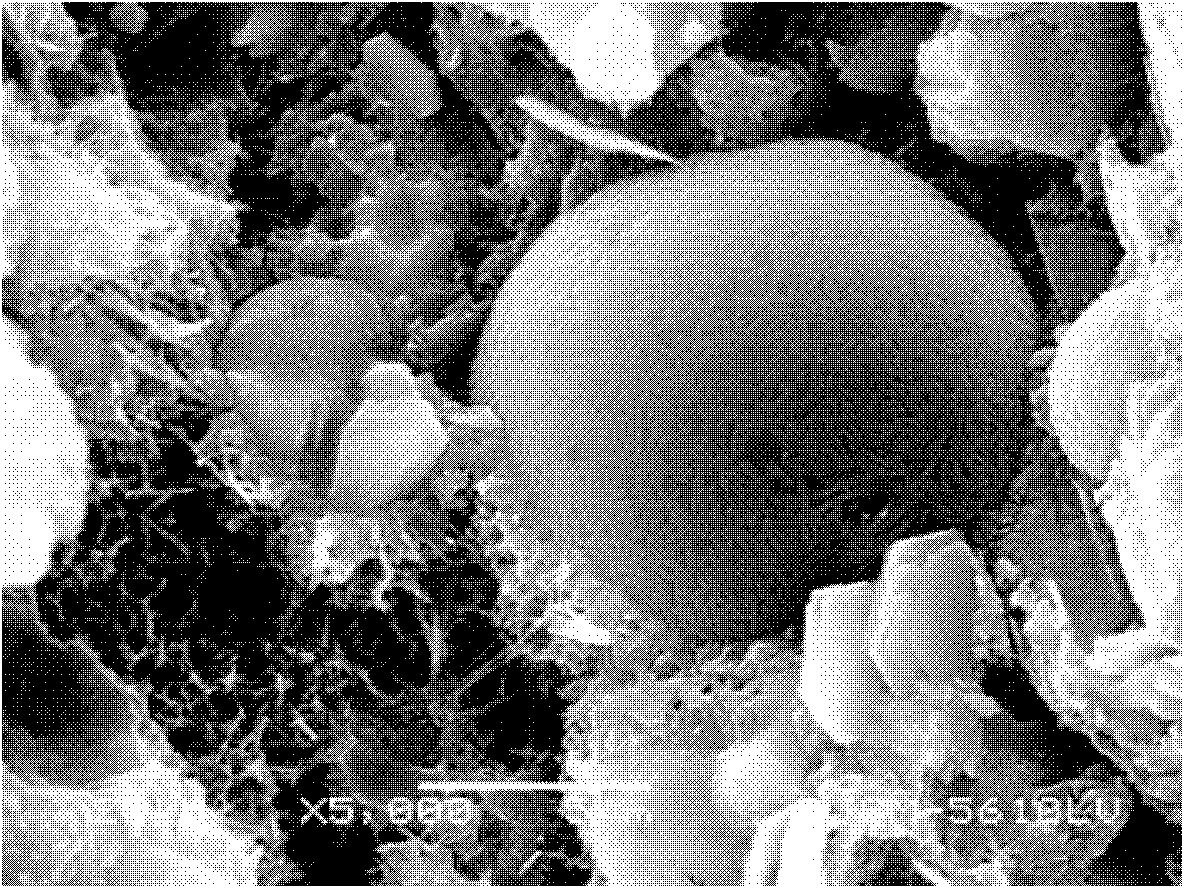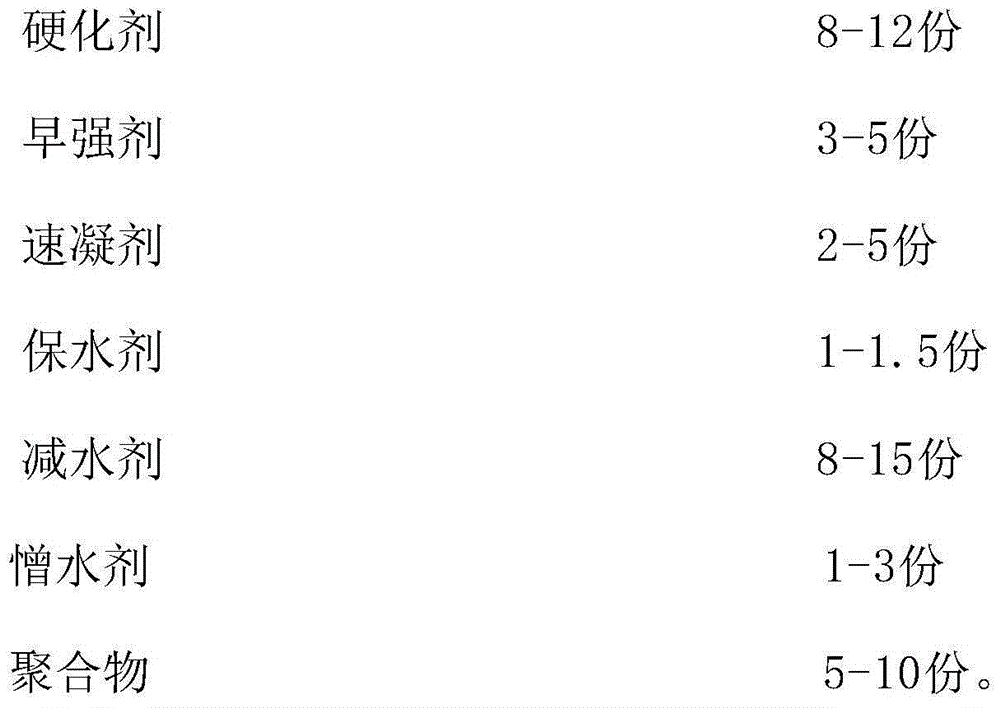Patents
Literature
312 results about "Low calcium" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Low total calcium (hypocalcemia) The most common cause of low total calcium is: Low blood protein levels, especially a low level of albumin, which can result from liver disease or malnutrition, both of which may result from alcoholism or other illnesses. Low albumin is also very common in people who are acutely ill.
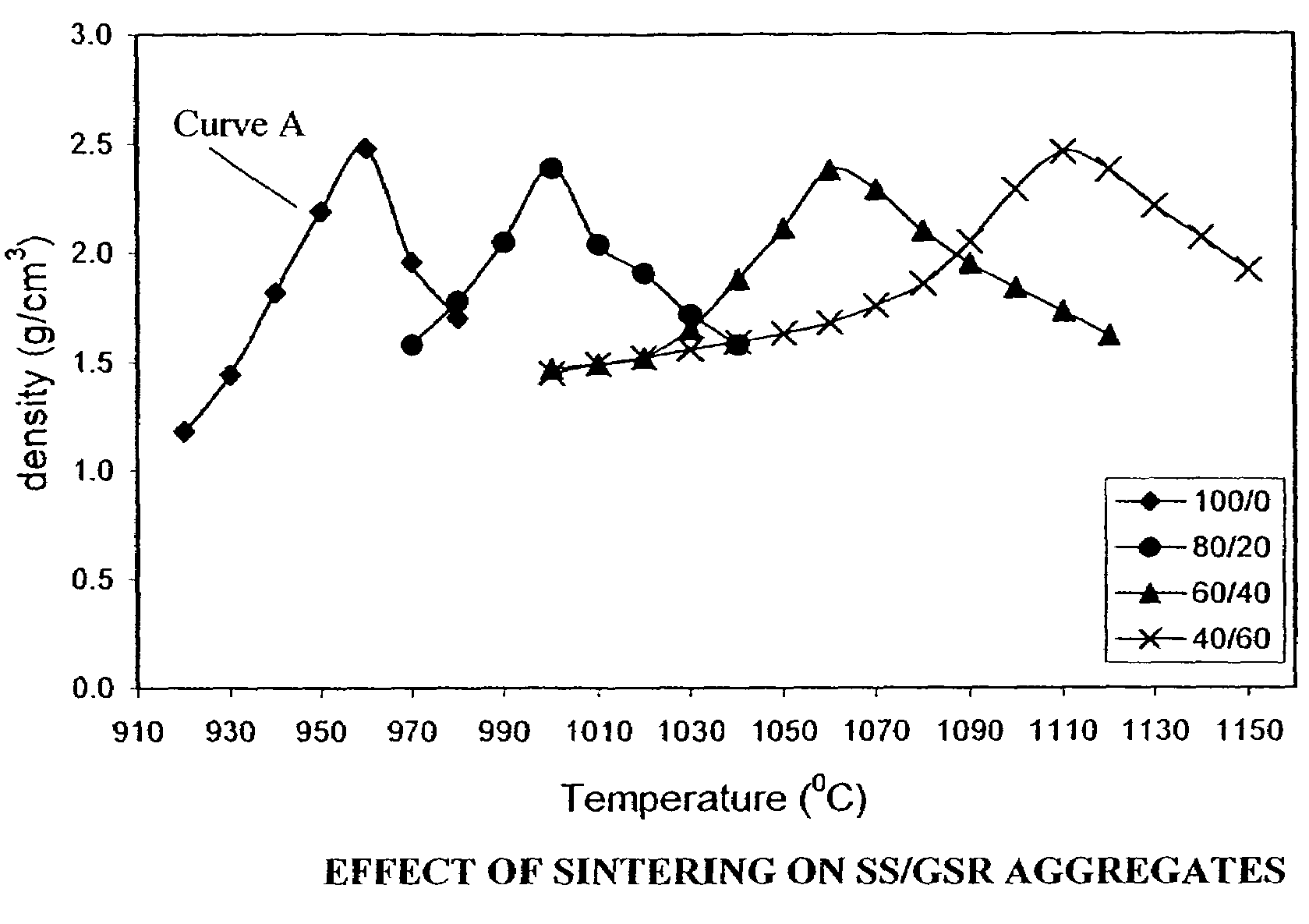
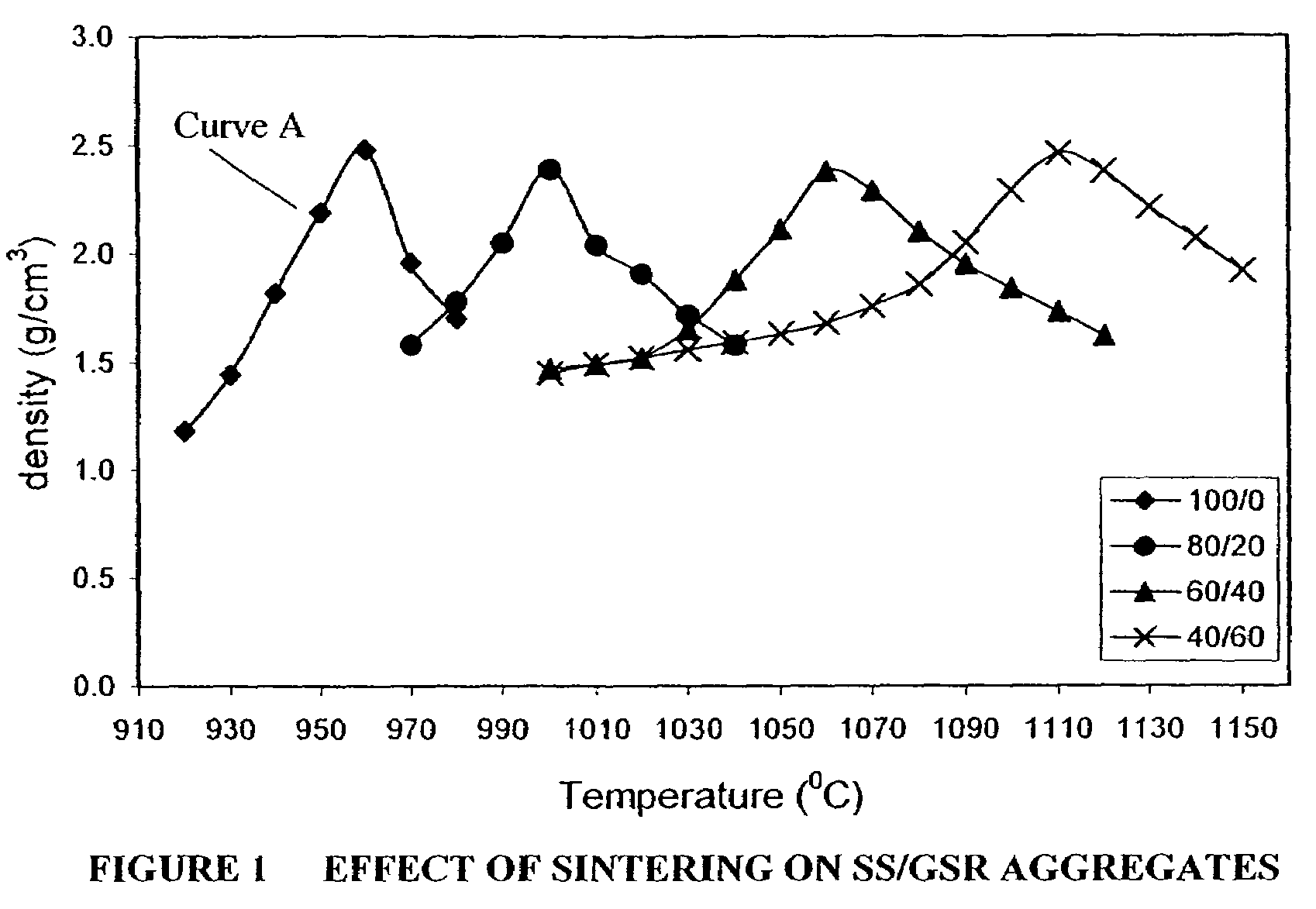
Synthetic aggregates comprising sewage sludge and other waste materials and methods for producing such aggregates
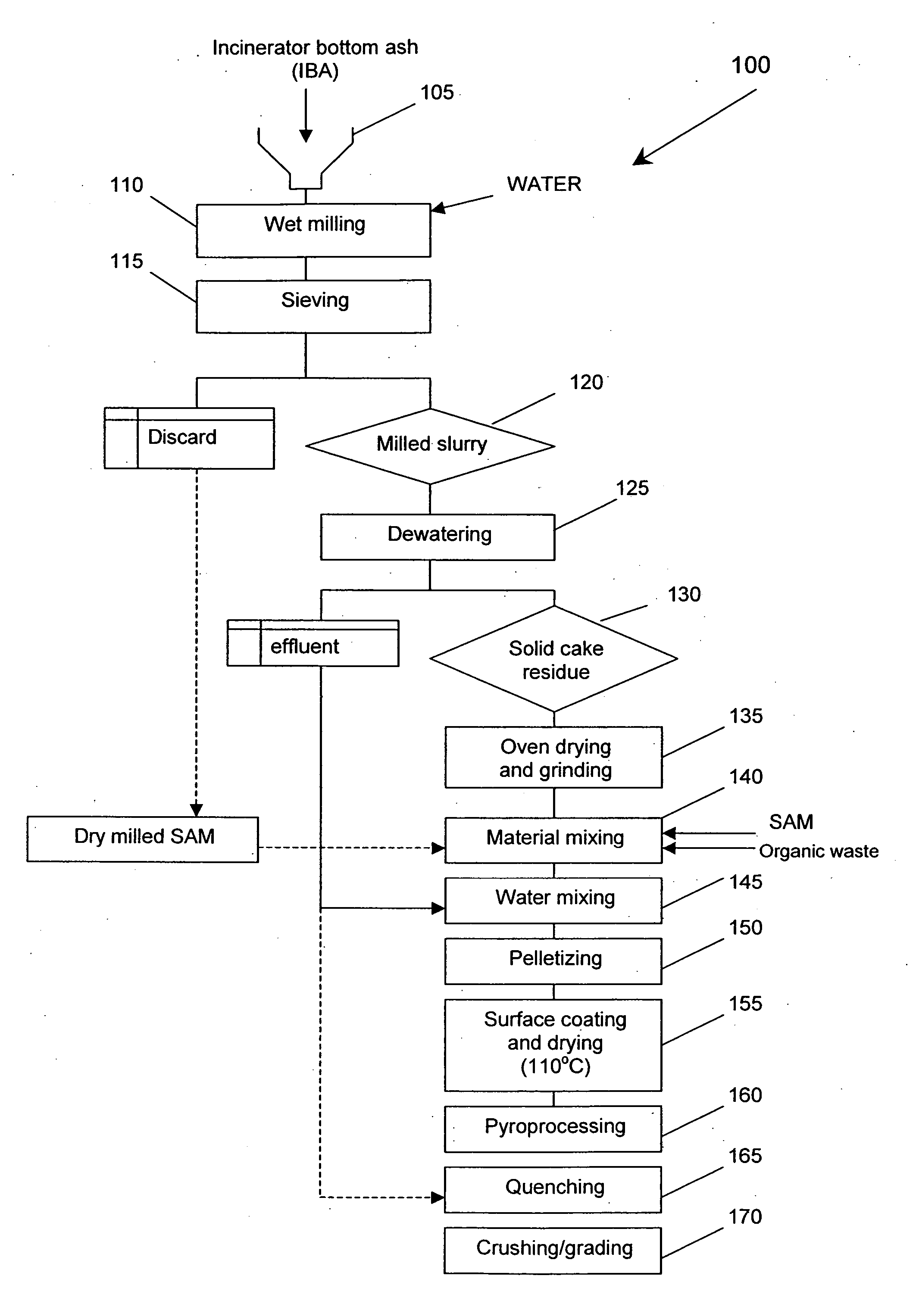
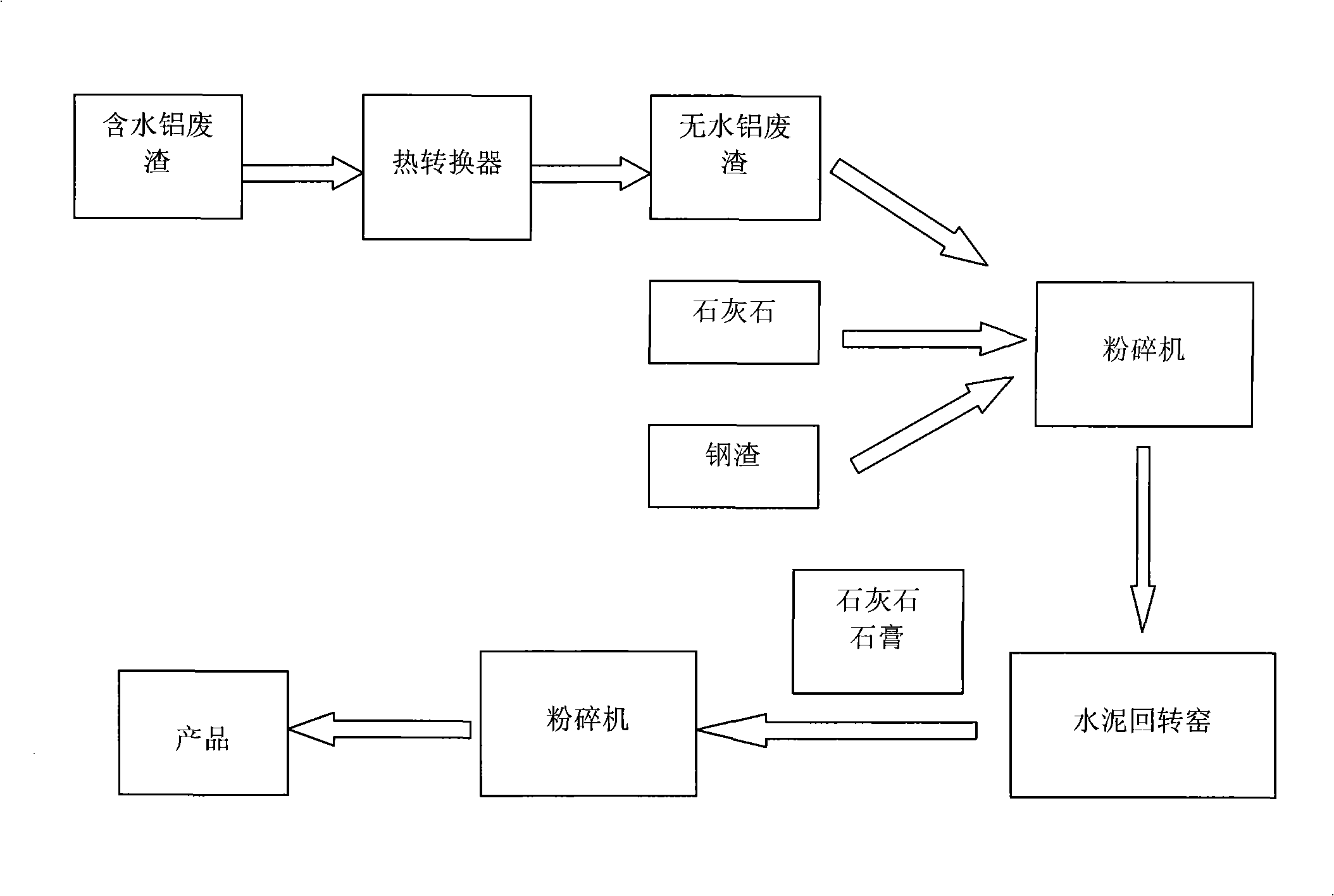
In one example of an embodiment of the invention, a method for producing an aggregate is disclosed comprising mixing sewage sludge from a waste water treatment facility with a non-coal combustion ash silicoaluminous waste material, agglomerating the mixture to form an agglomerate, and pyroprocessing the agglomerate to form an aggregate. The waste material may comprise municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash, incinerator fly ash, incinerator filter dusts, cement kiln dusts, waste glass, blast furnace slag, kiln dusts, and / or granite sawing residues, for example. The method may further comprise milling the waste material prior to mixing. Preferably, the milling is wet milling. Pyroprocessing of the agglomerate may take place in a rotary kiln. The resulting aggregate may be a lightweight or a normal weight, sintered or vitrified aggregate. Aggregates and methods for making aggregates of high and low calcium silicoaluminous materials are also disclosed.
Owner:ALKEMY
Calcium stable high acyl gellan gum for enhanced colloidal stability in beverages
ActiveUS20050266138A1Improve colloidal stabilityGood particle suspensionSugar derivativesOther chemical processesGellan gumSphingomonas elodea
A low calcium sensitive (calcium stable) high acyl gellan gum is prepared for enhanced colloidal stability in beverages. The low calcium sensitive high acyl gellan gum has superior suspension performance for colloidal stability compared to other high acyl gellan gums. The low calcium sensitive high acyl gellan gum is prepared by adjusting the pH of a gellan fermentation broth (polymer solution) prior to pasteurization and reducing the pasteurization hold time compared to conventional pH levels and hold times.
Owner:CP KELCO U S INC
Synthetic aggregates comprising sewage sludge and other waste materials and methods for producing such aggregates
In one example of an embodiment of the invention, a method for producing an aggregate is disclosed comprising mixing sewage sludge from a waste water treatment facility with a non-coal combustion ash silicoaluminous waste material, agglomerating the mixture to form an agglomerate, and pyroprocessing the agglomerate to form an aggregate. The waste material may comprise municipal solid waste incinerator bottom ash, incinerator fly ash, incinerator filter dusts, cement kiln dusts, waste glass, blast furnace slag, kiln dusts, and / or granite sawing residues, for example. The method may further comprise milling the waste material prior to mixing. Preferably, the milling is wet milling. Pyroprocessing of the agglomerate may take place in a rotary kiln. The resulting aggregate may be a lightweight or a normal weight, sintered or vitrified aggregate. Aggregates and methods for making aggregates of high and low calcium silicoaluminous materials are also disclosed.
Owner:ALKEMY
Heart valve prosthesis
InactiveUS20080154358A1Large tensile stressesReduce tensile stressHeart valvesProsthesisCalcification
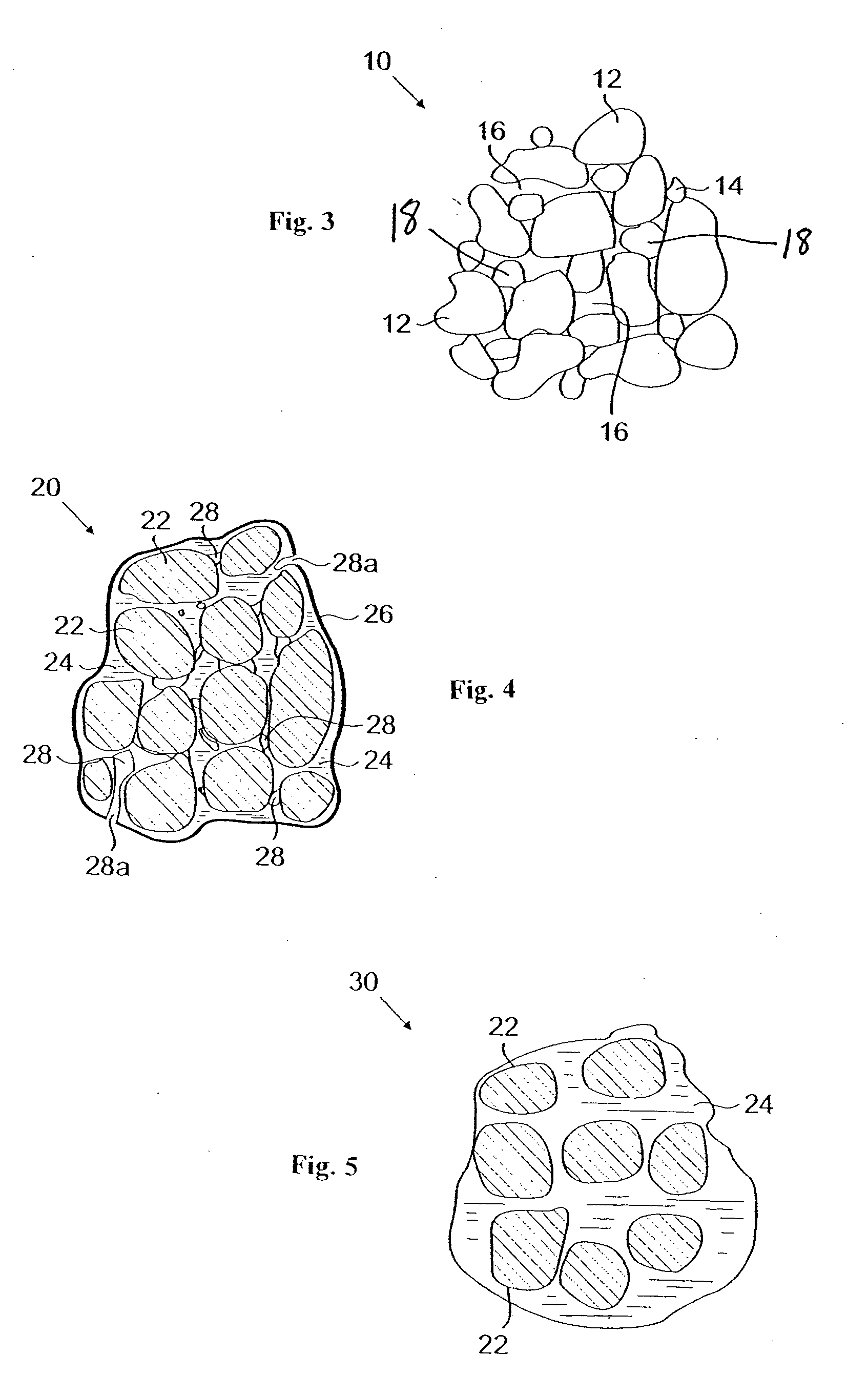
A heart valve prosthesis 4 for human implantation fabricated from bovine pericardial material which is harvested from a region of incipient low calcium content or other material, wherein pre-forming and fixing of the leaflets 5 of the valve to create a rapid change in direction of the surface modifies the stresses within the material leading to a reduction of the peak tensile stress magnitude and concomitant in-use calcification thereby to increase longevity of the valve,
Owner:TANSLEY GEOFFREY +1
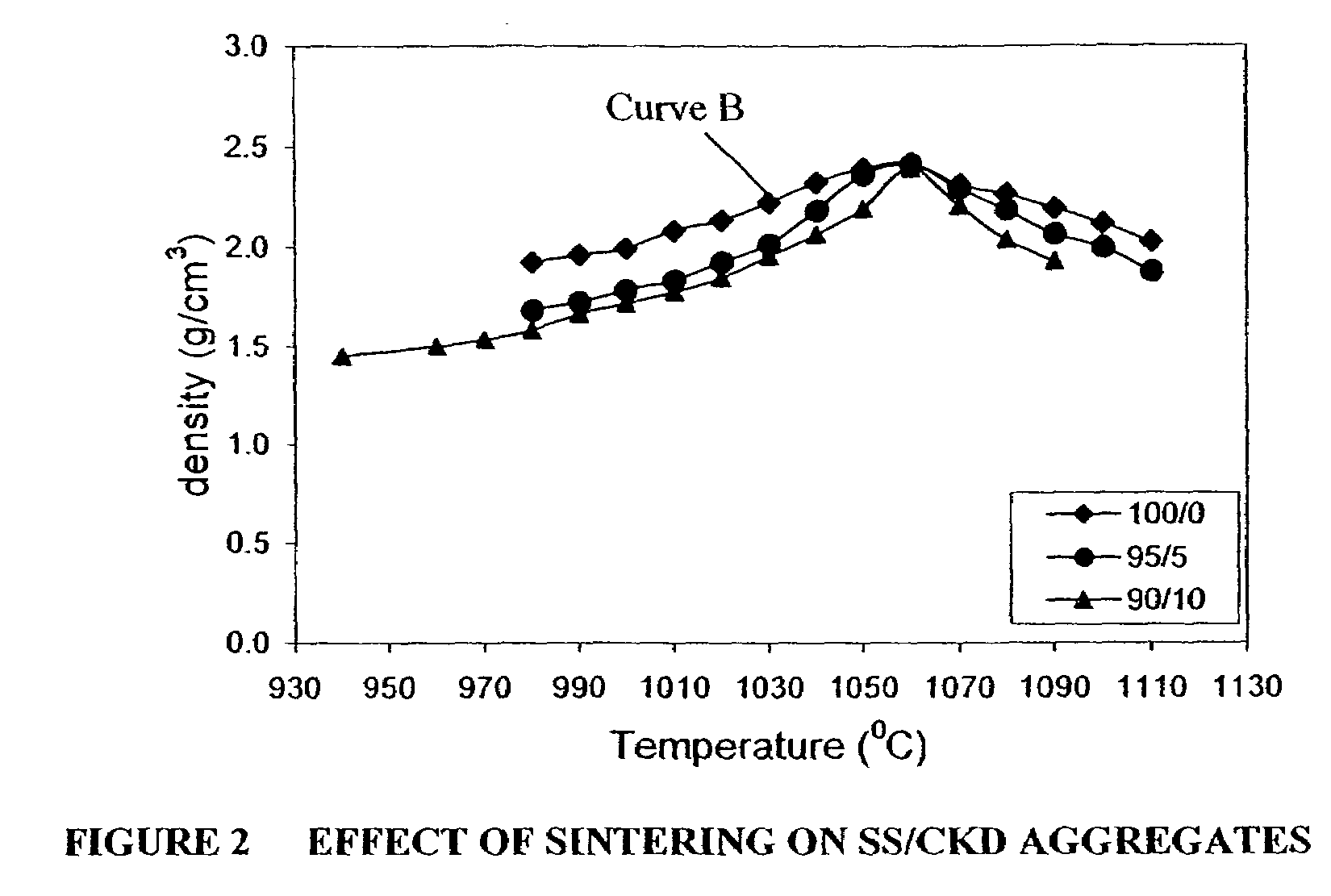
Pyroprocessed aggregates comprising IBA and low calcium silicoaluminous materials and methods for producing such aggregates
InactiveUS20060162619A1Big economySignificant environmental benefitsPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesBottom ashVitrification
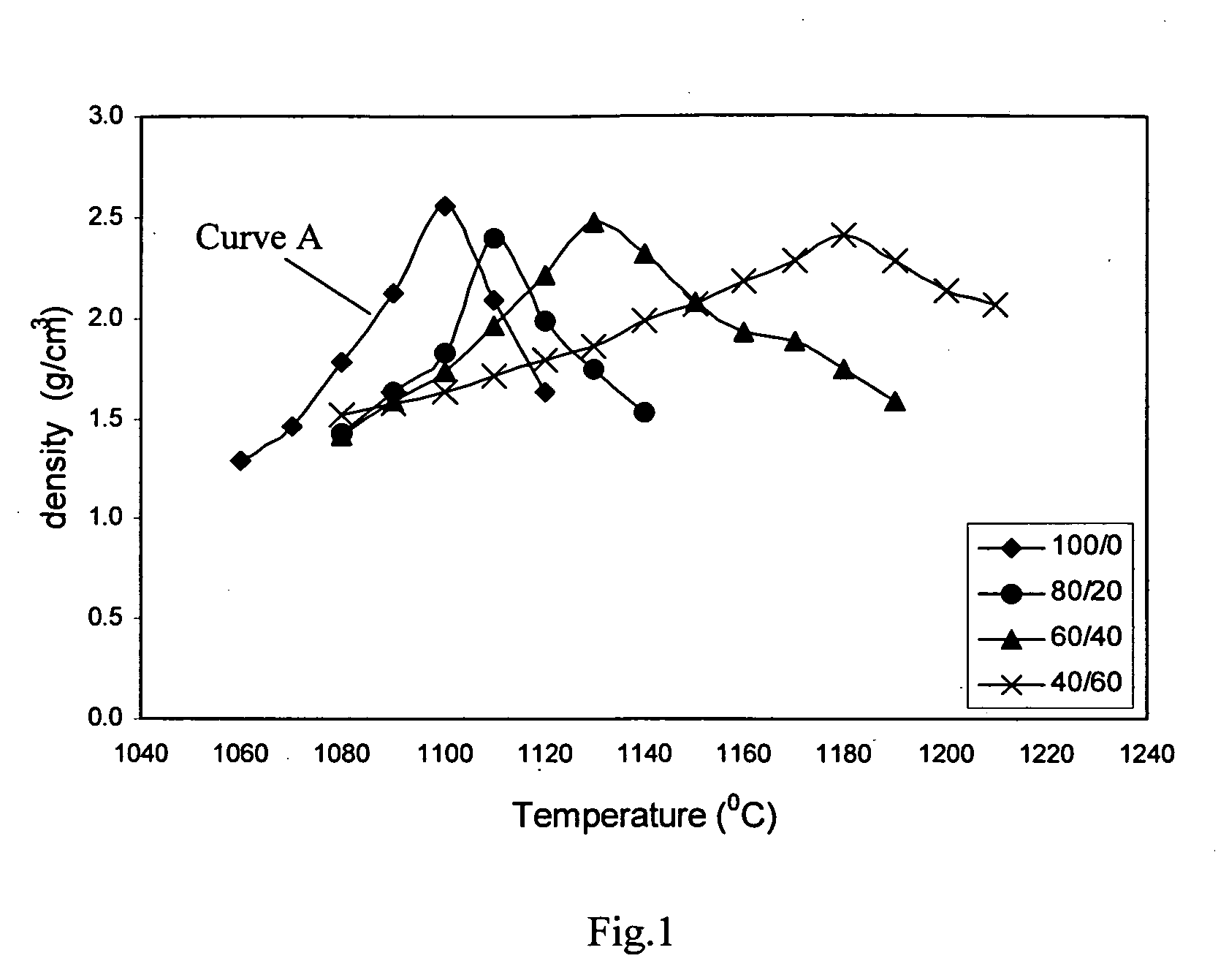
In accordance with an embodiment, a method for producing an aggregate is disclosed comprising mixing IBA and a second, silicoaluminous material having a calcium content less than the IBA. The method further comprises agglomerating the mixture, such as by pelletizing, and pyroprocessing the agglomerates, such as by sintering or vitrification, to form the aggregate. The second material may be a clay, such as bentonite or kaolin, a mining waste, such as granite sawing residues, waste glass, or furnace bottom ash, for example. The addition of the second material has been found to facilitate production of lightweight and normal weight aggregates. Preferably, the IBA or the mixture of IBA and the second material are wet milled prior to agglomeration. A lightweight sintered aggregate comprising IBA and the second material and an aggregate comprising IBA and the second material are also disclosed.
Owner:ALKEMY
Method for preparing manganese sulfate
ActiveCN101704554AOvercome the Difficulty of SeparationAvoid difficultiesManganese oxides/hydroxidesManganese sulfatesManganeseSulfide
The invention relates to a method for preparing manganese sulfate. The method comprises the following steps: quantitatively adding sulfide with reducibility into a manganese dioxide ore in a reaction molar ratio for sufficient reaction, determining a reaction end point, and separating and washing a solid-phase resultant; reacting the solid-phase resultant with 9 to 12mol / L H2SO4, controlling the reaction end point to the pH of between 3 and 5, controlling the concentration of MnSO4 in the reaction liquid in a range of between 300 and 400g / L, performing solid-liquid separation after the reaction is completed; acidizing the separated solution by H2SO4 until the pH value of the solution is between 2 and 3, adding hydrogen peroxide into the solution and heating the mixture, precisely filtering and removing the part of solid phase; and distilling, concentrating, crystallizing and dehydrating the filtrate to prepare the manganese sulfate. The method can prepare acid soluble manganous oxide and ensure that various heavy metals can generate insoluble sulfides so as to solve the problem of completely separating heavy metals and obtain the manganese sulfate with low calcium magnesium and low heavy metals.
Owner:贵州红星发展大龙锰业有限责任公司
Stabilisers useful in low fat spread production
ActiveUS20050170062A1Improve sensory propertiesReduce fatEdible oils/fats ingredientsMilk preparationEmulsionAdditive ingredient
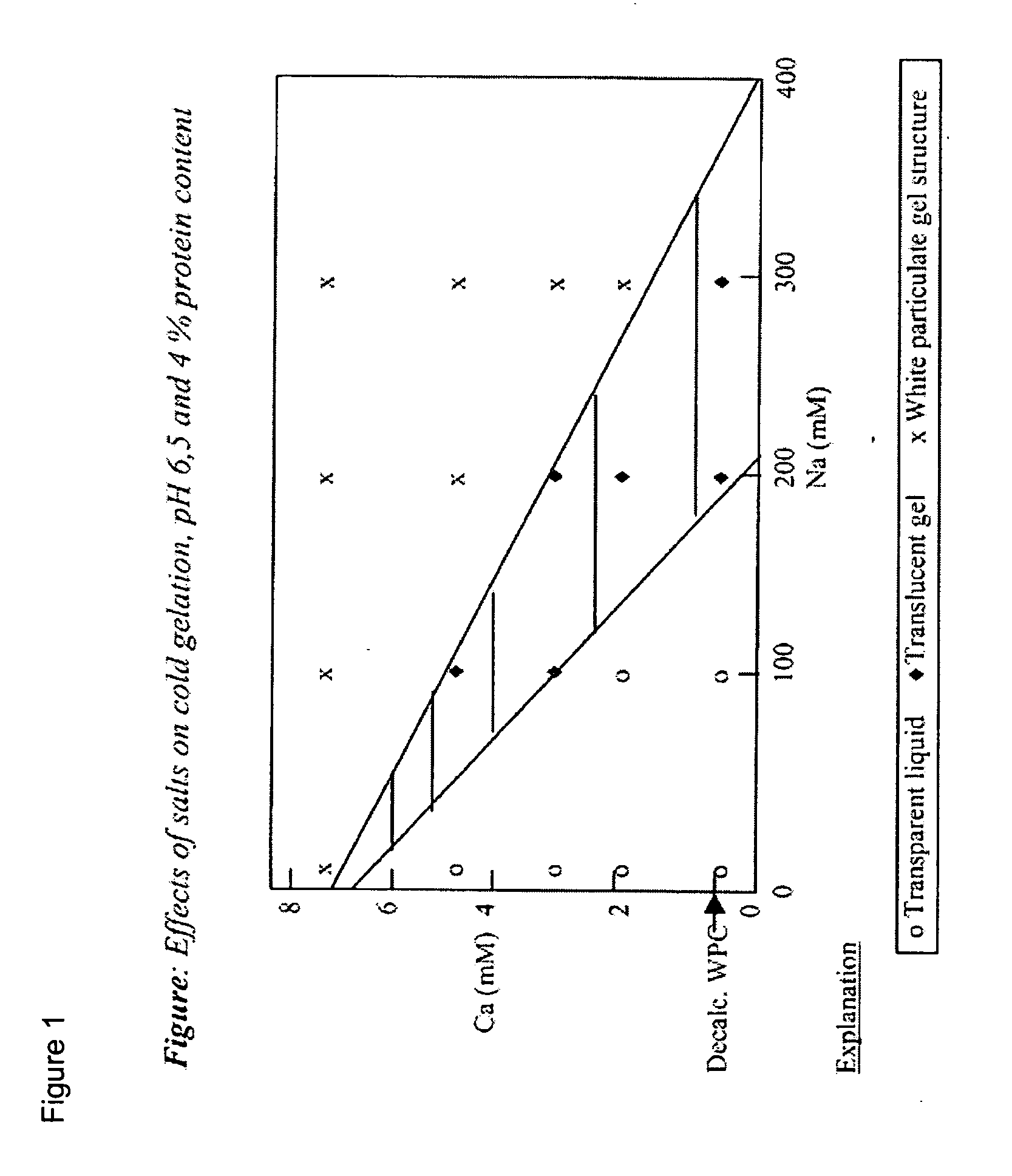
The present invention relates to methods for producing low fat spread emulsions stabilised with dairy proteins. The water phase is stabilised by heat denatured whey proteins at low calcium concentrations. After heat treatment pH of the water phase is adjusted to neutral or acid conditions. The present invention also relates to methods for producing a whey protein product that can be used as a stabilising food ingredient.
Owner:ARLA FOODS AMBA
High early strength and high corrosion resistant Portland cement and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN106082724AReduce tricalcium contentExtended service lifeClinker productionMass ratioPortland cement
Belonging to the field of cement production and also relating to the field of building materials, the invention provides a high early strength and high corrosion resistant Portland cement and a preparation method thereof. The high early strength and high corrosion resistant Portland cement is mainly applied to engineering projects in complex marine environments and the west harsh environments. The high early strength and high corrosion resistant Portland cement is characterized by containing, by weight percentage, 60%-90% of a high iron and low calcium cement clinker mineral component, 2%-10% of an auxiliary functional component, 5%-25% of an auxiliary cementitious component, and 3%-7% of industrial gypsum. The high iron and low calcium cement clinker mineral component is mainly prepared from high iron and low calcium Portland cement clinker and high iron and low calcium Q phase cement clinker in a mass ratio of 5-15:1. The cement not only has strong seawater erosion resistance and high early strength, but also has the characteristics of low shrinkage and low hydration heat.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Steel slag treating method
ActiveCN102559960AEliminate hazardsSafe useRecycling and recovery technologiesThermal energyCalcium silicate
The invention provides a steel slag treating method comprising the following steps of: directly mixing thermal-state revolving furnace steel slag with blast furnace slag in an arc furnace in proportion, adjusting the molten slag in the furnace into a proper temperature by virtue of the arcing of the arc furnace, and stirring the molten slag by virtue of arc disturbance, so that acidic oxide and basic oxide in the molten slag are sufficiently reacted with each other; reacting free calcium oxide and free magnesium oxide in the raw steel slag with silicon dioxide component and low-calcium calcium silicate in the blast furnace slag to generate safe calcium silicate and magnesium silicate, quenching the molten slag to form glass-state solid slag which is higher in hydration reactivity and free of short-term or long-term inflation harm, and further finely grinding the solid slag into slag powder which can be safely used for related building material as the blast furnace slag. According to the method, the damage caused by the free calcium oxide and free magnesium oxide in the steel slag can be removed, and a basis is provided for the whole use of the steel slag. The heat energy of the thermal-state molten slag can be sufficiently used, so that the energy source can be saved, the energy consumption can be reduced, the cost can be reduced, and the discharge of CO2 can be reduced, and the method is extremely high in social meaning and economic meaning.
Owner:北京联合荣大工程材料股份有限公司
Low-energy-consumption and low-emission cement and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102249576AImprove performanceWith the advantages of energy saving and emission reductionClinker productionCoesiteResource consumption
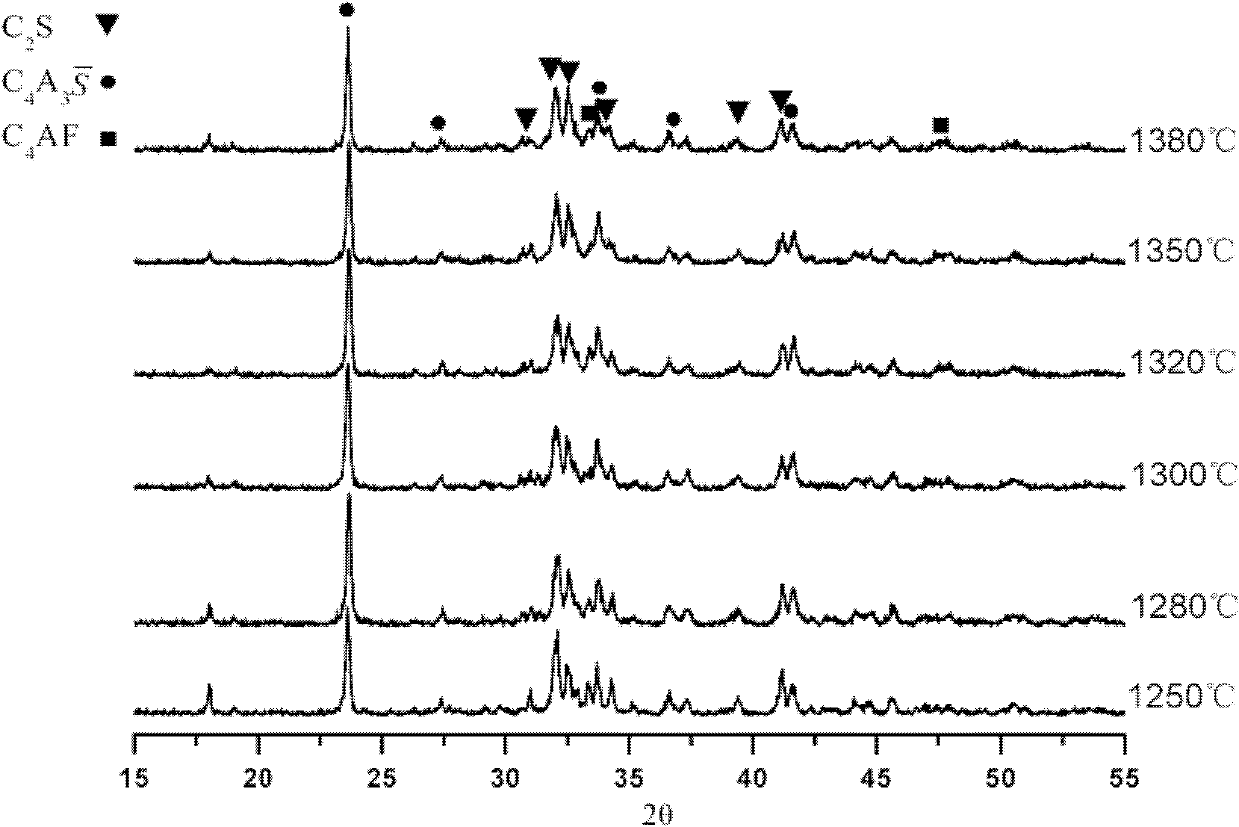
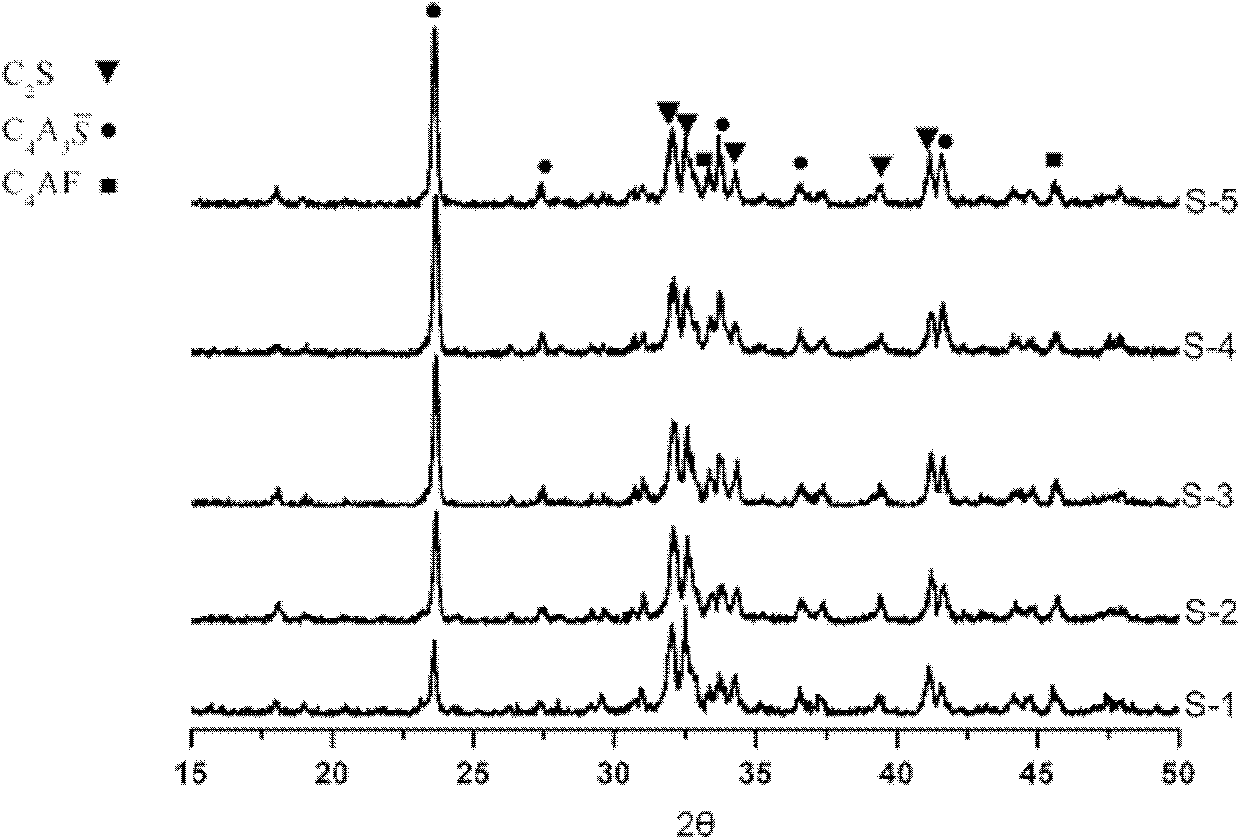
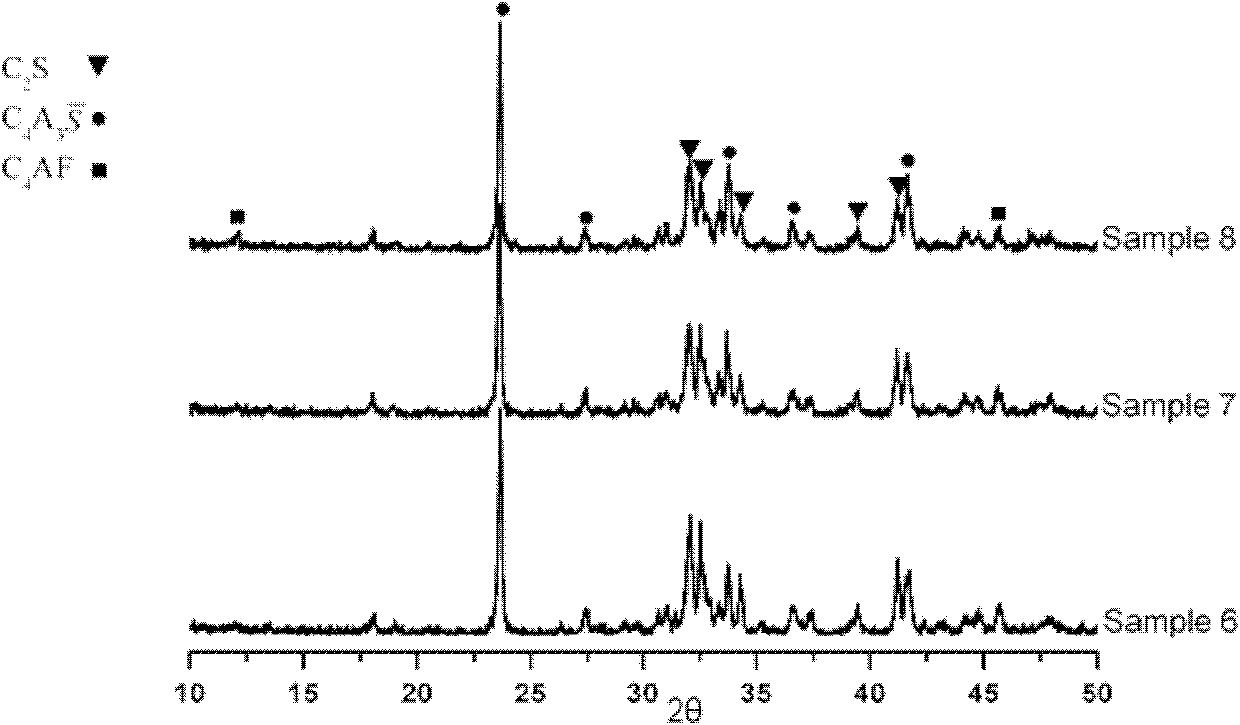
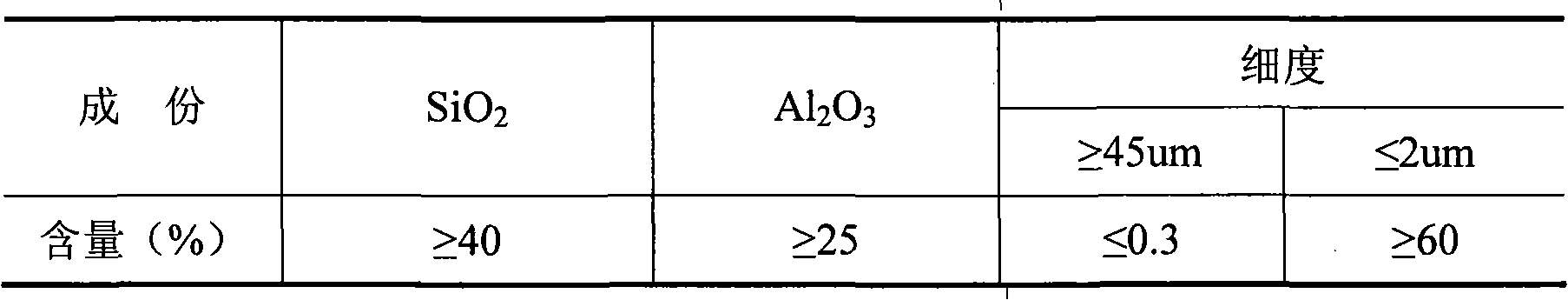
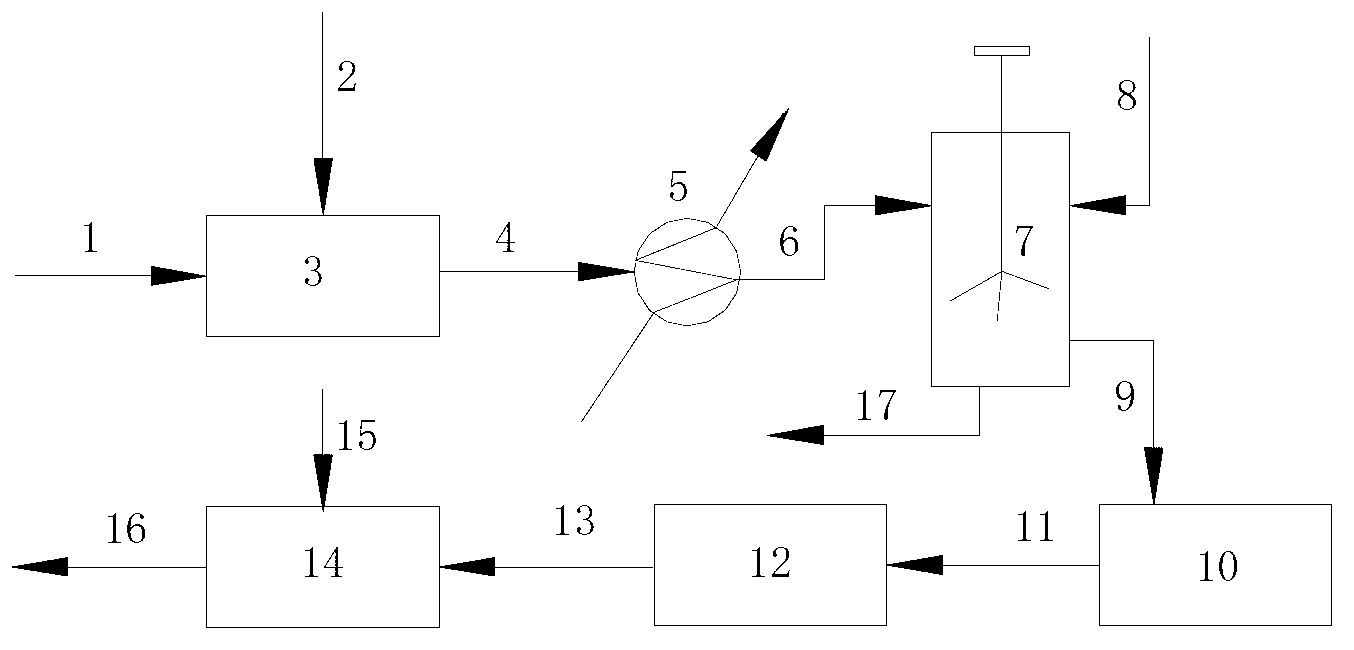
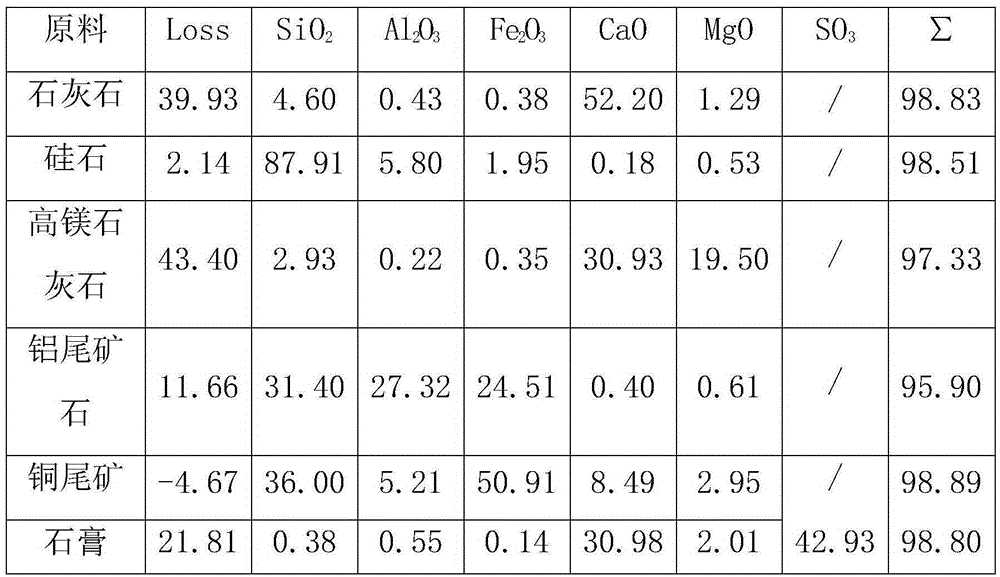
The invention discloses low-energy-consumption and low-emission cement and a preparation method and application thereof. Cement clinker mainly comprises the following minerals in parts by weight: 35-65 parts of C2S, 20-50 parts C4A3S and 5-15 parts of C4AF. A corresponding green stock consists of the following components in parts by weight: 30-60 parts of CaO, 25-35 parts of SiO, 5-35 parts of Al2O3, 1-6 parts of SO3 and 1-10 parts of Fe2O3. The cement clinker is a product which is prepared by calcining limestone, alumina and clay or sandstone and gypsum serving as raw materials at the temperature between 1,280 DEG C and 1,300 DEG C for 45-70 minutes by combining the advantages of low calcium content, low-temperature baking and high later strength of a belite mineral, low-temperature baking and high later strength of anhydrous calcium sulphoaluminate, and the like. The cement product has the advantages of excellent performance, low energy and resource consumption and low carbon dioxide emission, can play an important role in the field of construction, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Inorganic polymer material for sealing heavy metal castoff
InactiveCN101318788AImprove physicsImprove mechanical propertiesSolid waste managementCement productionSlagMetakaolin
The invention provides an inorganic polymeric material used to fixedly seal heavy metal wastes, which is an inorganic silicon-aluminum polymeric material used in the environmental protection field. The material comprises the following compositions in weight percentage: 9.9 to 35.1 percent of metakaolin, 3.94 to 27.6 percent of ore slag, 0.1 to 9.9 percent of active low calcium silicon-aluminum material, 9.6 to 10.6 percent of alkali excitant and 50.0 to 54.7 percent of sand. The material has the advantages of high doped quantity of the heavy metal wastes, high fixing seal efficiency, wide source of raw materials, convenient preparation and processing, high mechanical strength, excellent durability and low cost.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for selectively removing calcium ions from concentrated water byproduct of sea water desalination process and other high-calcium-magnesium-content concentrated brines
InactiveCN102936067AHigh removal rateQuick responseGeneral water supply conservationMultistage water/sewage treatmentLoss rateWater desalination
The invention relates to a method for selectively removing calcium ions from a concentrated water byproduct of a sea water desalination process and other high-calcium-magnesium-content concentrated brines, which comprises the following steps: regulating the pH value of the concentrated water to 7.0-8.5, and then heating to a certain temperature; introducing the concentrated water into a heat-insulating apparatus capable of realizing sealed stirring, adding a sodium sulfite or sodium carbonate solution having a certain concentration while stirring, reacting for 1-40 minutes while sufficiently stirring, standing for 5-10 minutes, and then filtering to remove calcium sulfite or calcium carbonate precipitate; and adding hydrochloric acid into the filtrate to regulate the pH value back to 6. According to the invention, the problems of low calcium removal rate, high magnesium loss rate, long stirring time and the like during the concentrated water treatment based on the traditional normal-temperature sodium carbonate precipitation method are overcome, the operation is convenient, the investment is low, and the operation cost is low; and the concentrated water liquid subjected to decalcification treatment can be further deeply concentrated through a membrane method or hot method, thereby improving the fresh water recovery rate and realizing the reutilization and zero discharge of the resources. The method provided by the invention is suitable for selectively removing calcium ions from sea water, sea water or brackish water subjected to other treatment processes such as reverse osmosis or multiple-effect evaporation and concentration, underground salt brines and concentrated water of industrial waste water subjected to reverse osmosis treatment.
Owner:天津凯铂能膜工程技术有限公司
Anti-erosion low calcium portland cement and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105347707AImprove corrosion resistanceErosion defensePortland cementUltimate tensile strength
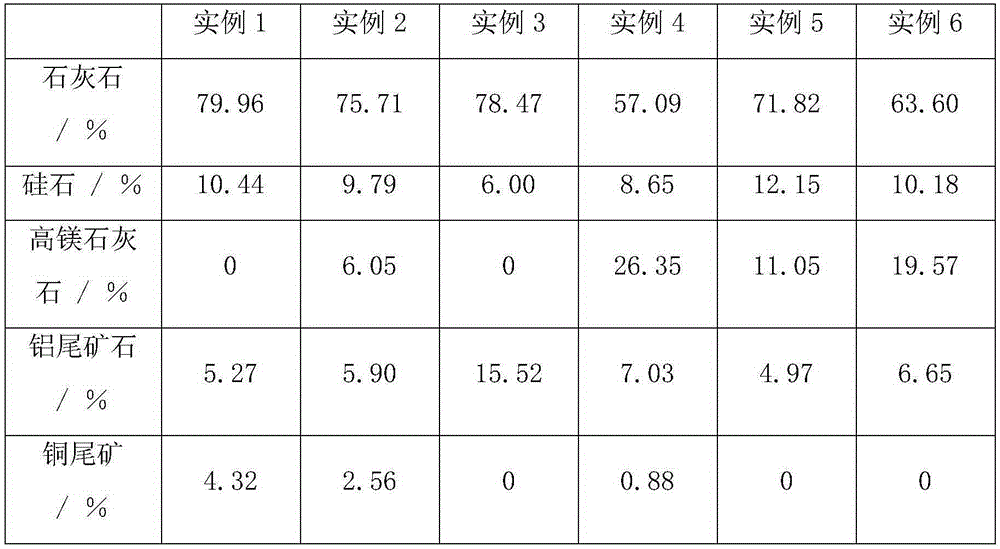
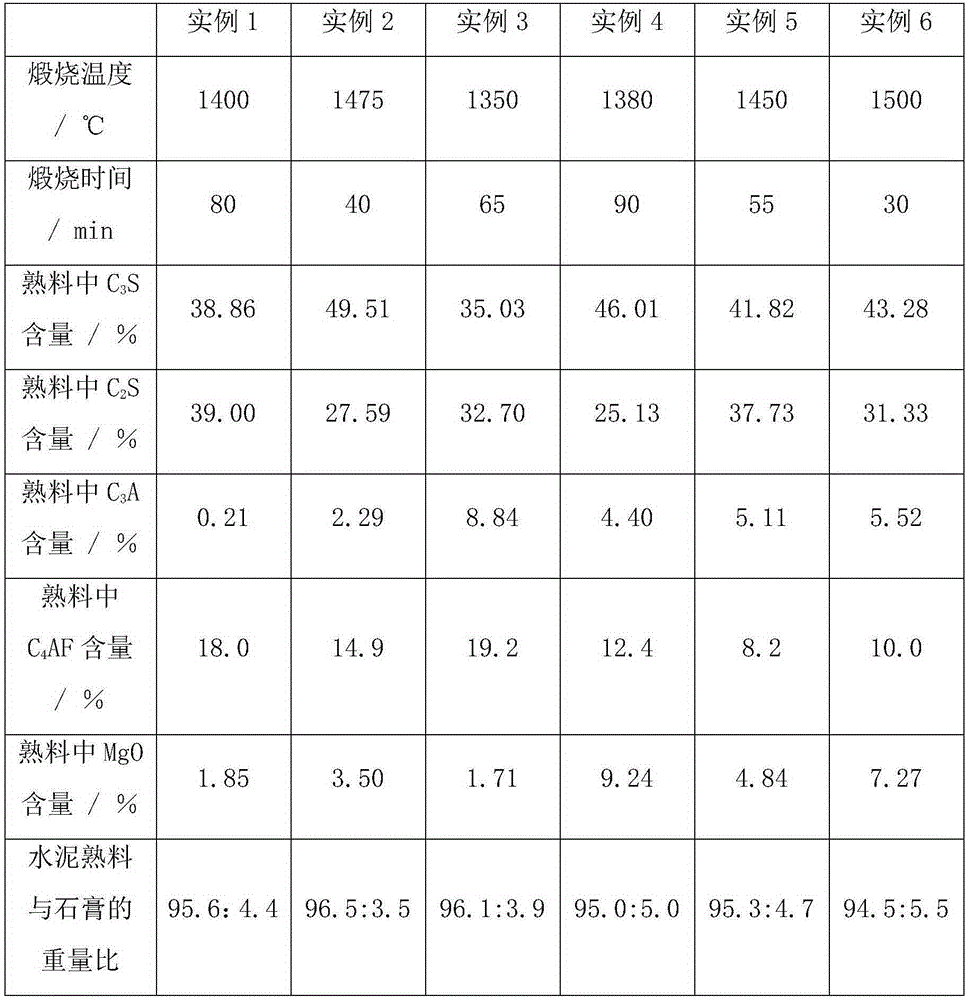
The invention discloses anti-erosion low calcium portland cement and a preparation method thereof. The anti-erosion low calcium portland cement comprises clinker and gypsum according to a weight ratio of 96.5: 3.5 to 94.5: 5.5. Minerals of the cement comprises, by weight, 35.03-49.51% of C3S, 25.13-39.00% of C2S, 0.21-8.84% of C3A, 8.2-19.2% of C4AF and 1.71-9.24% of MgO. The cement has good anti-erosion performances, can effectively prevent seawater erosion of concrete engineering, has small dry shrinkage and good anti-cracking ability, improves a service life of oceanographic engineering, and has high early strength. Compared with the existing low-heat portland cement, the anti-erosion low calcium portland cement is conducive to shortening of a concrete work form stripping period and processing progress.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Low calcium cementitious material and method of manufacturing low calcium cement
ActiveUS20120152152A1High economic valueSolid waste managementAlkali metal silicate coatingsMulliteRoom temperature
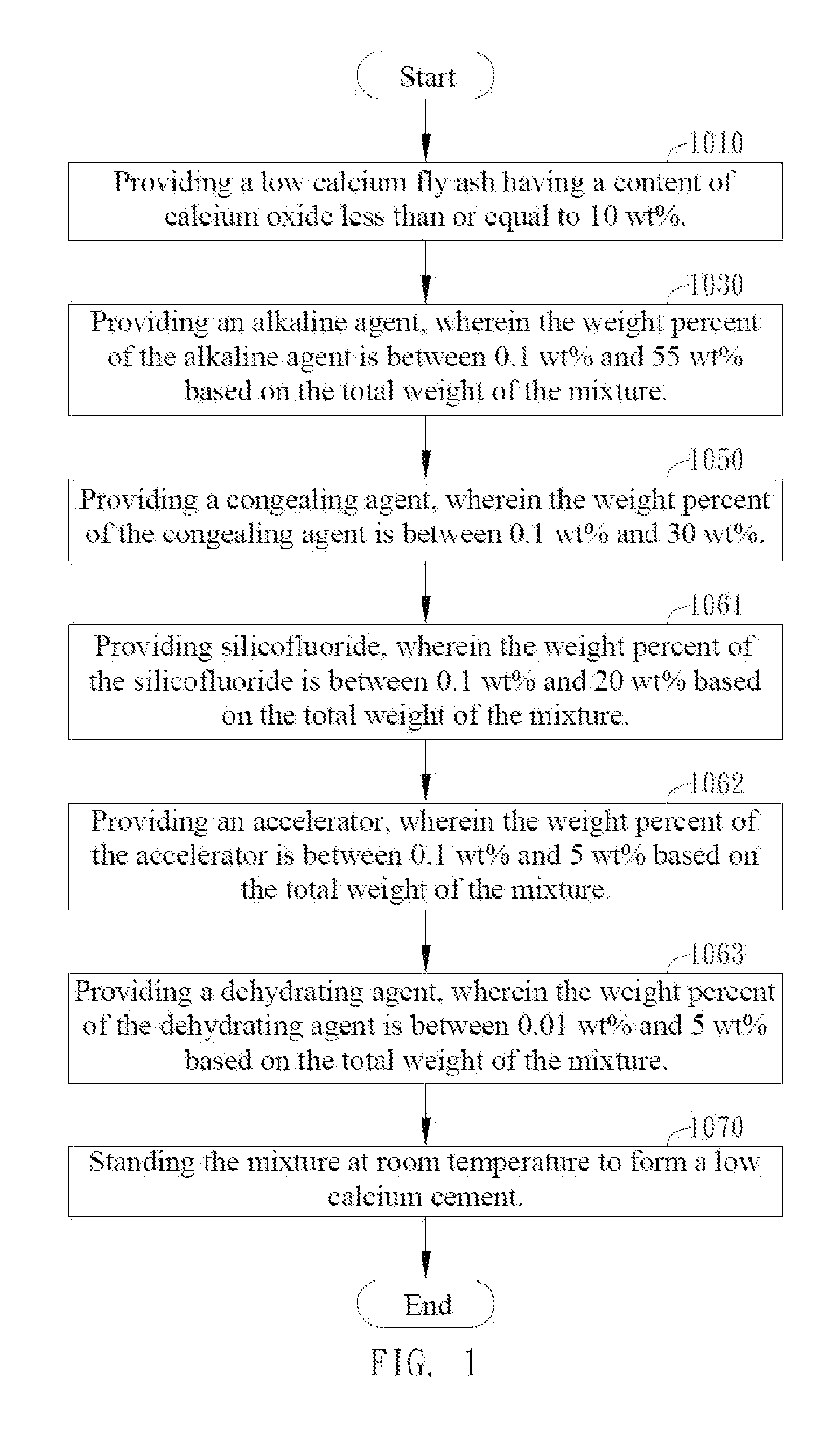
A low-calcium-cementitious material having a calcium oxide content less than or equal to 10 wt % which is processed at room temperature into a low calcium cement mainly composed of mullite and a method manufacturing of the low calcium cement are provided. The low-calcium-cementitious material includes low calcium fly ash, an alkaline agent, and a congealing agent, wherein the calcium oxide content of the low-calcium-cementitious material is less than or equal to 10 wt %. The low calcium fly ash has a calcium oxide content less than or equal to 10 wt %. The low calcium cement manufacturing method includes providing a low calcium fly ash having a calcium oxide content less than or equal to 10 wt %; providing an alkaline agent; providing a congealing agent; and mixing the low-calcium-content fly ash, the alkaline agent, and the congealing agent and standing the mixture at room temperature to form a low calcium cement.
Owner:RUENTEX MATERIALS CO LTD
High-calcium fly ash concrete
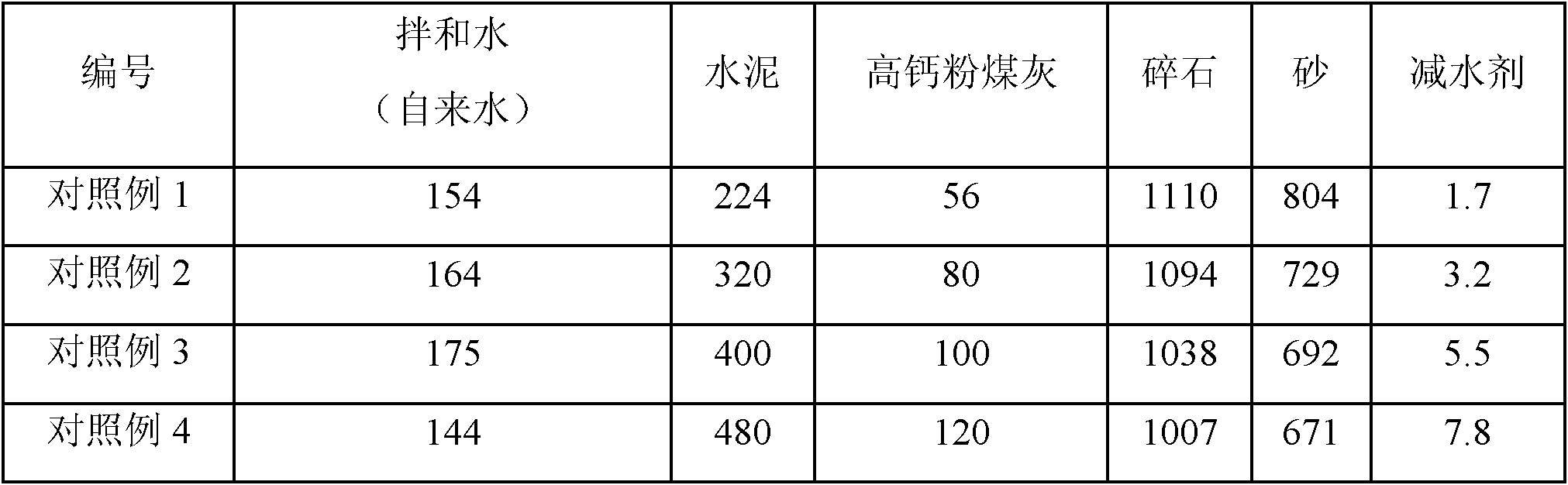
The invention belongs to the technical field of building materials, particularly relating to high-calcium fly ash concrete. The high-calcium fly ash concrete comprises the following raw materials by weight in per cubic meter of concrete: 144-175 kg of mixing water, 224-480 kg of cement, 35-135 kg of high-calcium fly ash, 1007-1120 kg of gravels, 671-804 kg of sand, 1.7-9 kg of water reducing agents, 0-110 kg of low-calcium fly ash and 0-110 kg of slag powder, wherein the mixing water is temporary hardwater, and the concentration of HCO3<-> in the mixing water is greater than 300 mg / L. The concrete has the characteristics of easy production and high operability, the high-calcium fly ash resource can be fully utilized, and the poor stability is eliminated.
Owner:CHINA STATE CONSTR READY MIXED CONCRETE CO LTD
Clinker-free baking-free fly ash polymer cement
InactiveCN101182164ARedundant label reductionEfficient use ofSolid waste managementSlagMaterials science
A burn-free fly ash ground polymer cement is characterized in that the cement contains the following components with the weight percentage of 65-86 percent of low-calcium fly ash, 4-20 percent of calcium containing compound, 10-18 percent of alkali excitant and 0-5 percent of admixture. And the calcium containing compound is one or a mixture of more than two of phosphorous slag, kiln dust or lime; the alkali excitant is the composite of NaOH or KOH with rapidly dissolved powdery sodium silicate, liquid silica sol and industrial water glass; the admixture is early strength agent and / or water reducing agent.
Owner:严云 +1
Method for circularly purifying manganese sulfate and manganese carbonate
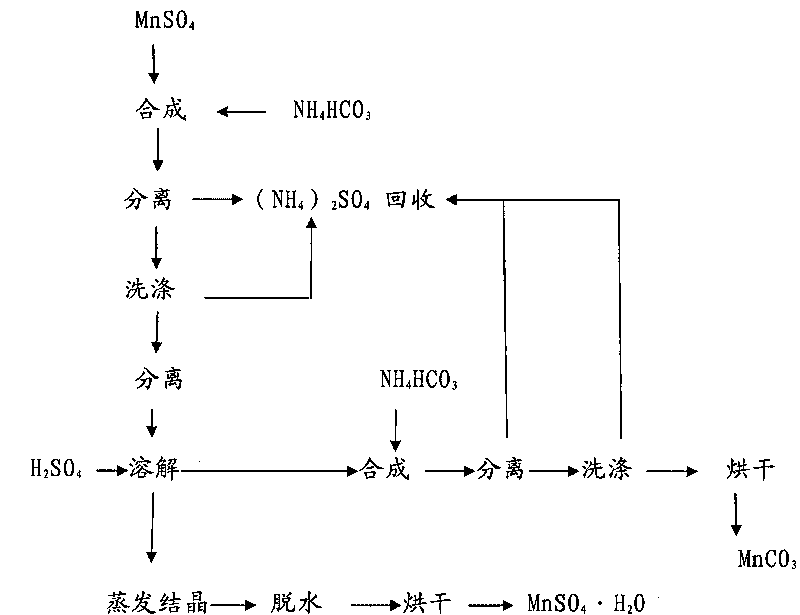
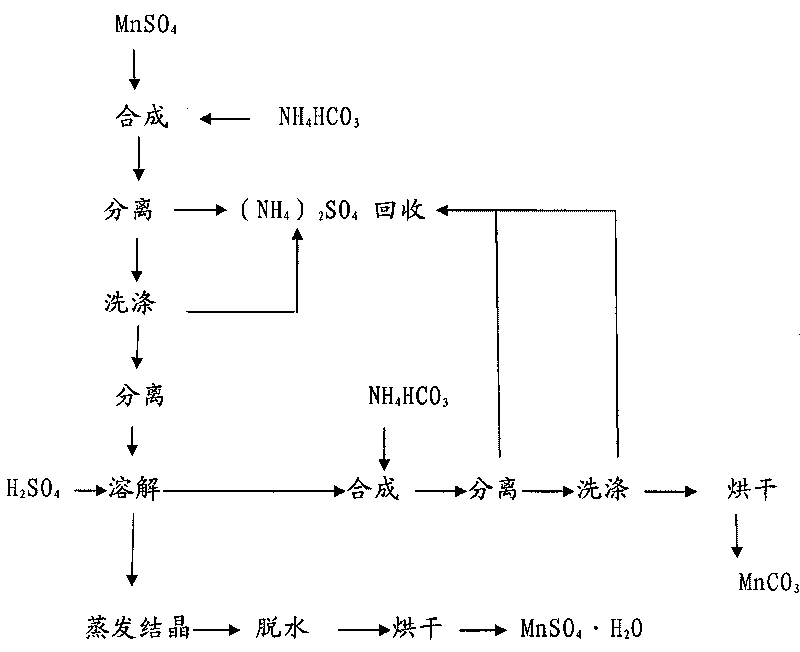
The invention relates to a method for circularly purifying manganese sulfate and manganese carbonate. The method comprises the following steps: A, stirring manganese sulfate solution at the temperature of between 40 and 80 DEG C, and adding ammonium bicarbonate into the solution for synthesis, controlling the synthesis end point to be an equimolar reaction, separating solid, and washing the solid with hot water to prepare manganese carbonate; B, adding the prepared manganese carbonate into 6 to 12mol / L H2SO4 for reaction, controlling the pH value of the reaction solution to be between 1 and 2, and heating and boiling the solution; C, adding the manganese carbonate prepared in the step A into the reaction solution in the step B, and adjusting the pH value of the solution back to be 4 to 5; and D, performing solid-liquid separation on the reaction solution, distilling and crystallizing the prepared filtrate, and drying the crystal to prepare the manganese sulfate. The circularly purifying method can prepare high-purity manganese sulfate and manganese carbonate with low calcium magnesium and low potassium and sodium.
Owner:GUIZHOU REDSTAR DEVING +1
Cement plate composite modifier
The invention discloses a cement plate composite modifier, and belongs to the field of composite modifier production. The composite modifier is composed of a hardening agent, an early strength agent, an accelerator, a water-retaining agent, a water reducer, a water repellent, and polymer. Compared with the prior art, the provided composite modifier can solve the problems that the demoulding strength of cement plate is low, the setting time is long, the cement plate secretes water, and the cement plate is brittle; moreover, the modifier can avoid or reduce the risk that the steel bars are corroded by chlorine ions and sulfate ions; at the same time, the activity of low-calcium fly ash is effective excited, a scheme is provided for the large mixing amount utilization of low-calcium fly ash, and the product cost is reduced.
Owner:ZHUO DA NEW MATERIAL TECH GRP
Aquatic collagen peptide food used for adjuvant therapy of osteoporosis and arthritis
The invention relates to the field of medical food and discloses an aquatic collagen peptide food used for adjuvant therapy of osteoporosis and arthritis. Every 100g of the food contains multiple nutritional ingredients as follows: 9-11g of cod skin collagen protein peptide powder, 4-6g of squid skin collagen protein peptide powder, 2-3g of whey protein powder, 2-3g of soybean protein powder, 9-11g of MCT fat, 2-3g of soybean oil, 58-62g of carbohydrate and other vitamins and microelements. The aquatic collagen peptide food takes cod skin collagen protein peptide powder, squid skin collagen protein peptide powder and whey protein powder as main raw materials and has relatively high digestive absorptivity, and collagen protein peptide can promote bone formation and reinforce a bone collagen structure at low calcium level, so that bone strength is improved; bone metabolism can be improved, and ossification can be enhanced; and bone diseases such as the osteoporosis, hyperostosis and swelling and pain of bone joints can be prevented.
Owner:ZHEJIANG MARINE DEV RES INST
PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) fiber reinforced superhigh-toughness polymer-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a PVA (polyvinyl alcohol) fiber reinforced superhigh-toughness polymer-based composite material. The PVA fiber reinforced superhigh-toughness polymer-based composite material is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 542 parts of low-calcium fly ash, 136 parts of high-calcium fly ash, 0 to 20 parts of metakaolin, 183 to 203 parts of quartz sand, 160 parts of water, 38 parts of sodium hydroxide, 14 to 17 parts of PVA fiber, and 173 parts of sodium silicate. The invention also provides a preparation method of the superhigh-toughness polymer-based composite material. The superhigh-toughness polymer-based composite material has the advantages that cement is replaced with a large amount of industrial waste slag fly ash, industrial wastes are changed into valuables, the environment is effectively protected, the consumption of energy source is decreased, and the emission of carbon dioxide is reduced; the toughness of the polymer-based composite material is reinforced by the PVA, the defect of poor ductility of the traditional polymer-based composite material is overcome, and the polymer-based composite material is conveniently popularized and applied in the engineering field of China.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
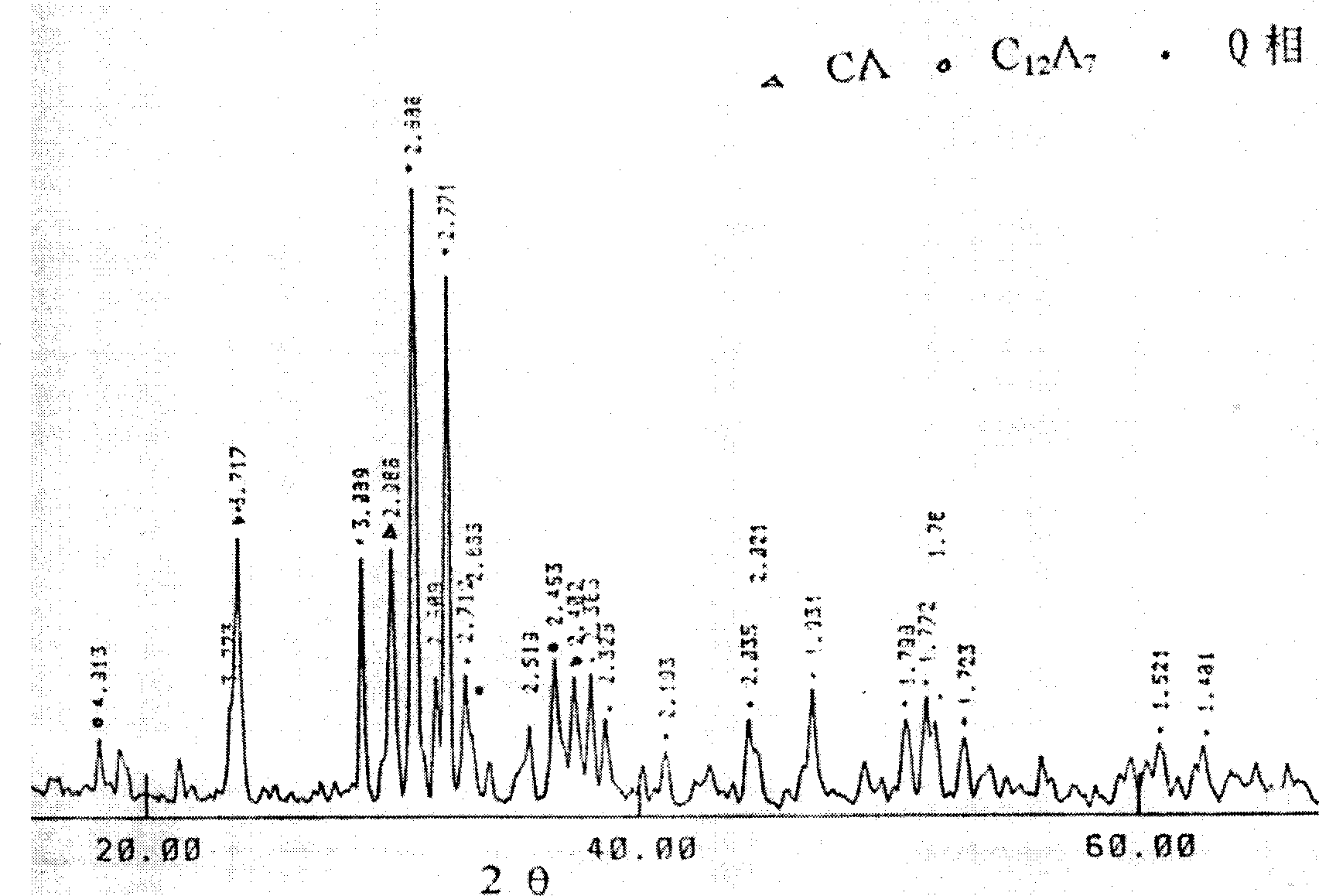
Aluminate cement material of containing mineral in Q phase
The invention provides an aluminate cement material containing. Q phase mineral that weight percenge is 40-80. The invention cement material has advantages of excellent functin of early strength and quick hardening, low firing temp., chalk containing magnesium-silicon and low-grade bauxite can be used as raw material to produce the cement material with high aluminium and low calcium.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Pyroprocessed aggregates comprising IBA and low calcium silicoaluminous materials and methods for producing such aggregates
InactiveUS7780781B2Low melting pointPyroprocessing behavior unpredictablePigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesBottom ashVitrification
In accordance with an embodiment, a method for producing an aggregate is disclosed comprising mixing IBA and a second, silicoaluminous material having a calcium content less than the IBA. The method further comprises agglomerating the mixture, such as by pelletizing, and pyroprocessing the agglomerates, such as by sintering or vitrification, to form the aggregate. The second material may be a clay, such as bentonite or kaolin, a mining waste, such as granite sawing residues, waste glass, or furnace bottom ash, for example. The addition of the second material has been found to facilitate production of lightweight and normal weight aggregates. Preferably, the IBA or the mixture of IBA and the second material are wet milled prior to agglomeration. A lightweight sintered aggregate comprising IBA and the second material and an aggregate comprising IBA and the second material are also disclosed.
Owner:ALKEMY
Autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement, and making method of prefabricated products thereof
ActiveCN105347706ALower firing temperatureReduce production processHigh concentrationShrinkage cracking
The invention relates to an autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement, and a making method of a prefabricated product thereof. The autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement is made from limestone, sandstone and iron ore, the CaO content of the prepared autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement is 40-60%, and the main mineral phase of the autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement is CS, C3S2, gamma-C2S and a liquid phase. The activity of the cement is excited by using high-concentration CO2 gas in a short period (8h) to make the prefabricated products of the autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement, and the prefabricated products can be a sheet, a building block, a brick and a tile, and can also be solid or hollow or porous high-strength prefabricated products. The problems of long curing period, high energy consumption and shrinkage cracking of ordinary Portland cement prefabricated products are solved in the invention; and additionally, the autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement has the advantages of low energy consumption in the baking process, small CO2 discharge amount, high early strength, and slow increase of the later strength, and the product of the autogenously-pulverizable low calcium cement has the advantages of excellent physical and mechanical performances, good durability, fire and corrosion resistance, good decorativeness and processability, environmental protection, energy saving and emission reduction, and very good social, economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
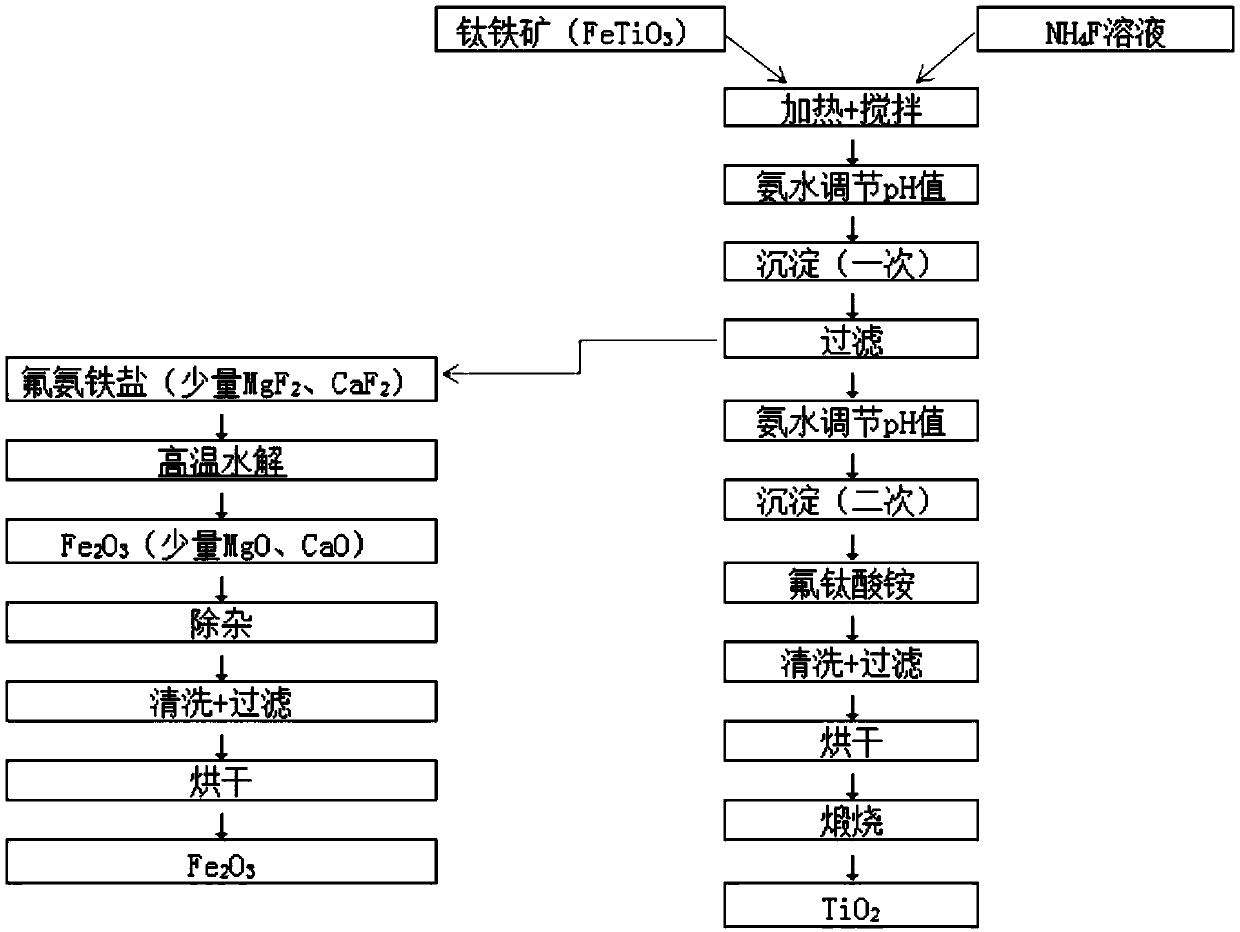
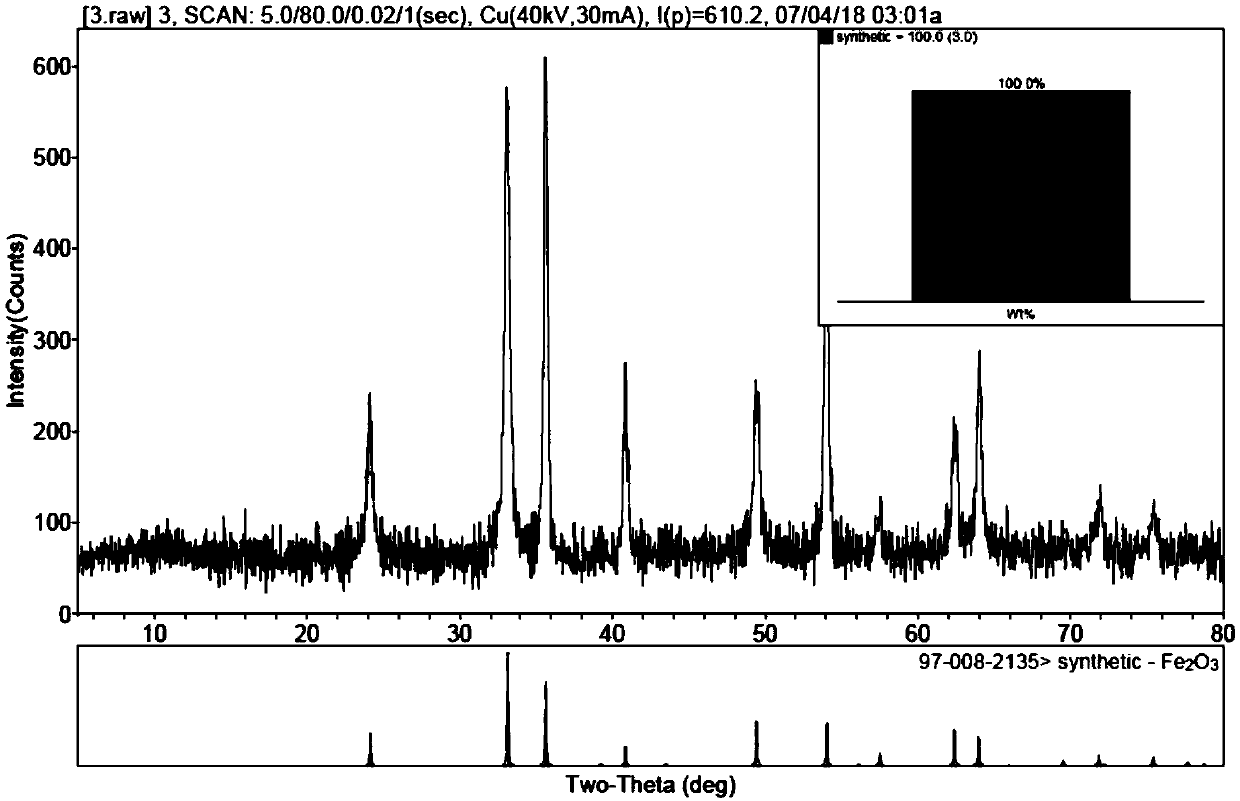
Method for preparing titanium dioxide and iron oxide by using fluoride purifying titanium-iron material
InactiveCN109626420ALow calcium and magnesium impuritiesEasy to separateMaterial nanotechnologyFerric oxidesIron(II) oxideAmmonium compounds
The invention provides a method for preparing titanium dioxide and iron oxide by using a fluoride purifying titanium-iron material. The method comprises the steps of mixing and heating a titanium-ironmaterial and a fluorine ammonium compound solution to obtain a mixture, wherein the fluorine ammonium compound is an ammonium fluoride or ammonium hydrogen fluoride; regulating the primary pH of themixture to obtain a first precipitate; separating the first precipitate and then regulating the secondary pH of the residual material to obtain a second precipitate; hydrolyzing the first precipitateat high temperature to obtain Fe2O3; roasting the second precipitate to obtain TiO2. By adopting the method, titanium and iron elements in the titanium-iron material can be thoroughly separated, and high-quality TiO2 and Fe2O3 pigment products are respectively obtained. The method is especially suitable for purifying and purifying treatment of high-calcium-magnesium titanium iron resources in a Panxi area (components and their analogs), materials with low calcium and magnesium impurity contents are obtained, namely titanium-rich materials, and titanium dioxide or titanium metal is produced fora subsequent sulfuric acid method and a chlorination method.
Owner:HUNAN KUNTAI METALLURGICAL ENG TECHCO LTD
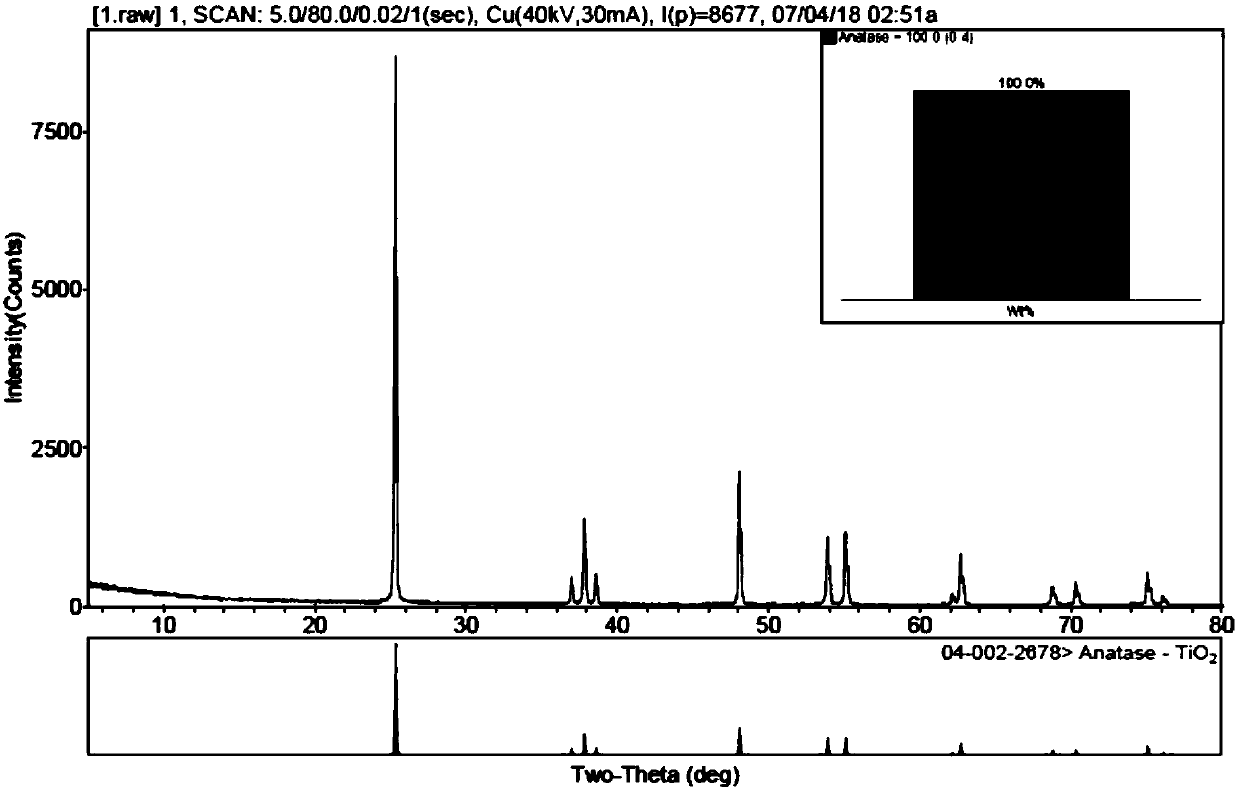
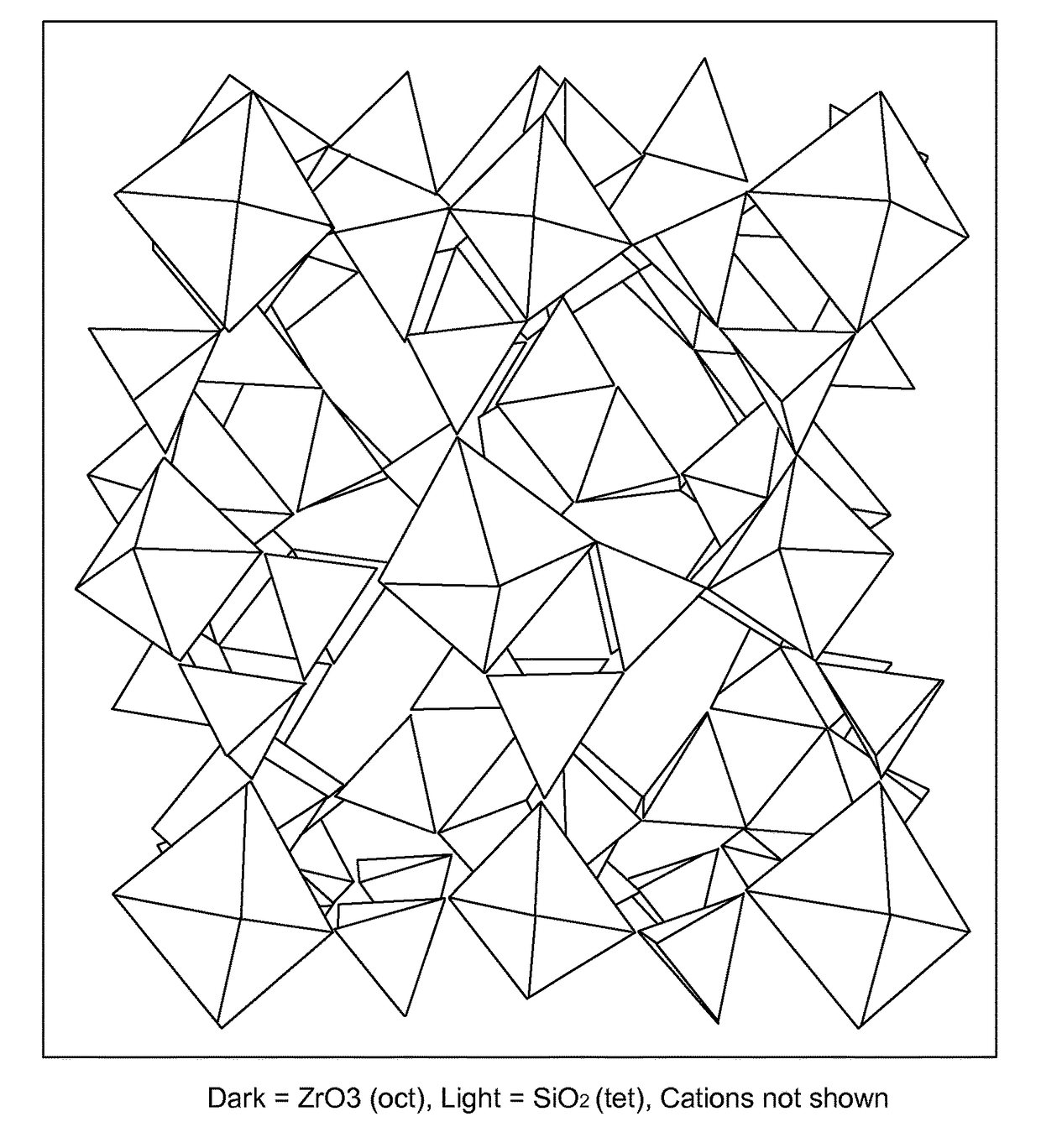
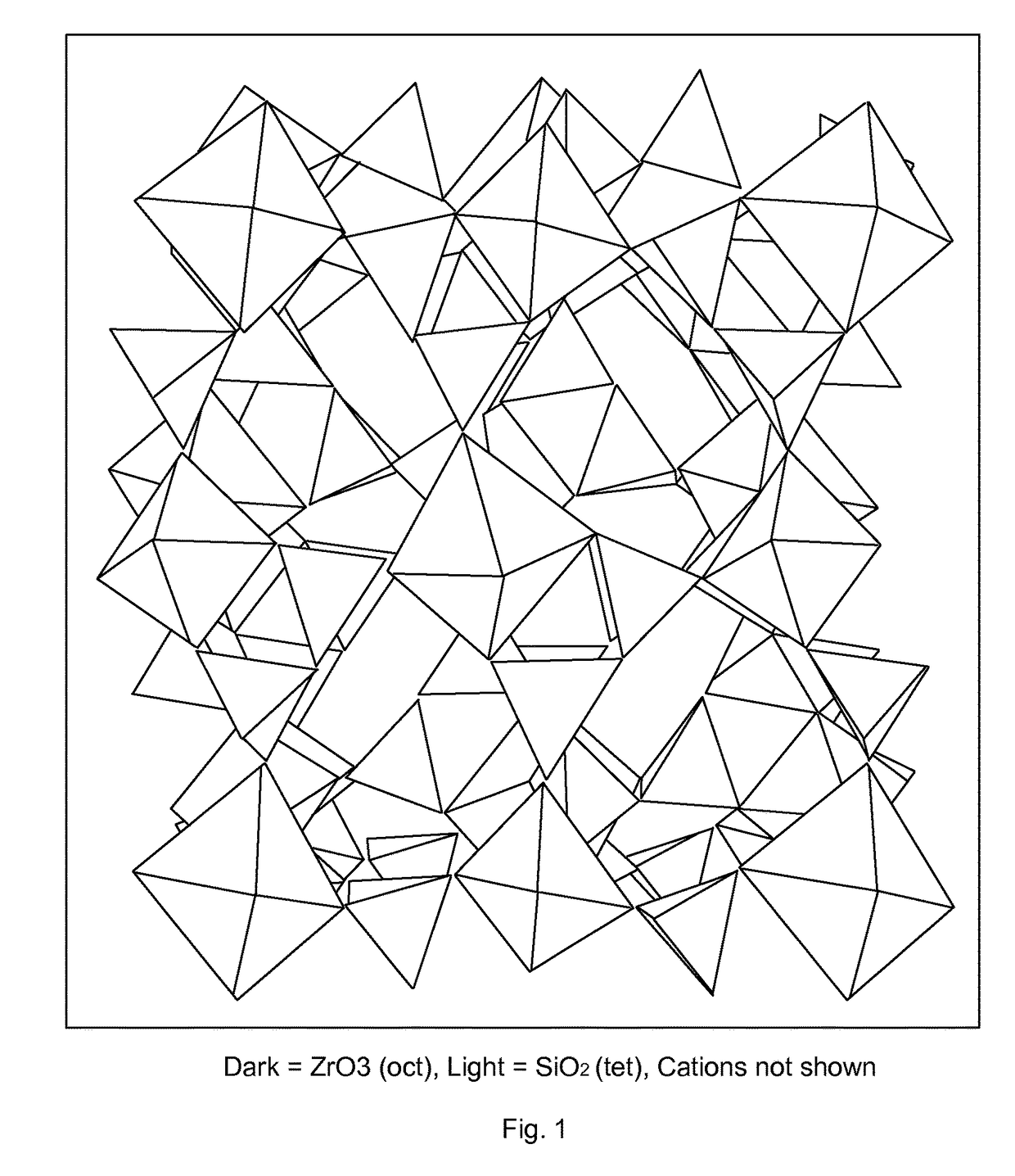
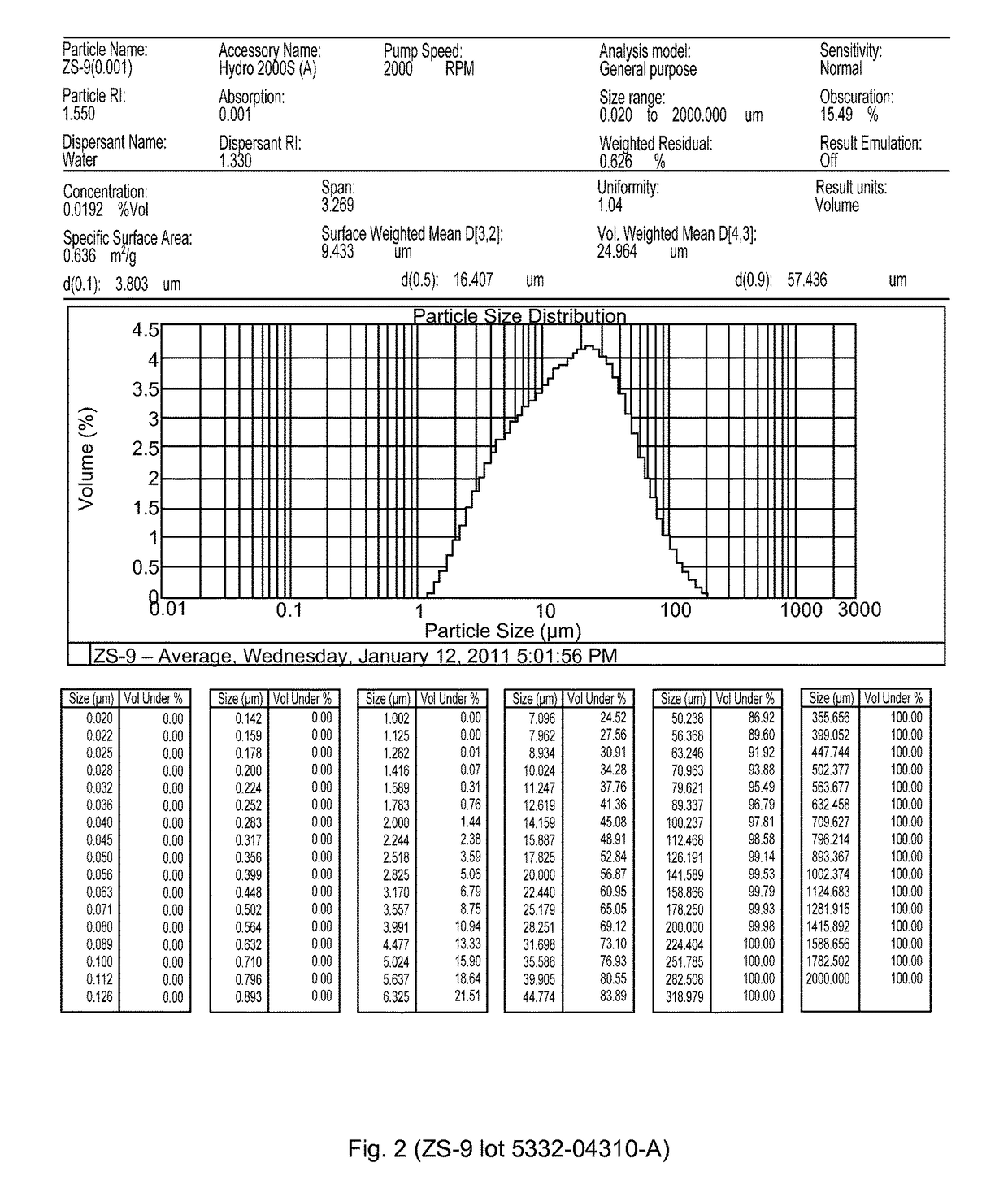
Microporous zirconium silicate for the treatment of hyperkalemia in hypercalcemic patients and improved calcium-containing compositions for the treatment of hyperkalemia
ActiveUS9707255B2High in calciumIncrease switching capacityHeavy metal active ingredientsSilicon organic compoundsPotassium ionsIncreased calcium
The present invention relates to novel calcium-containing microporous zirconium silicate compositions that are formulated to remove toxins, e.g. potassium ions, from the gastrointestinal tract at an elevated rate without removing calcium from the patient's body. Also disclosed are methods of using calcium-free or low calcium microporous zirconium silicate compositions for the treatment of hyperkalemia in patients also suffering from hypercalcemia.
Owner:ZS PHARMA
Method for extracting vanadium from high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag
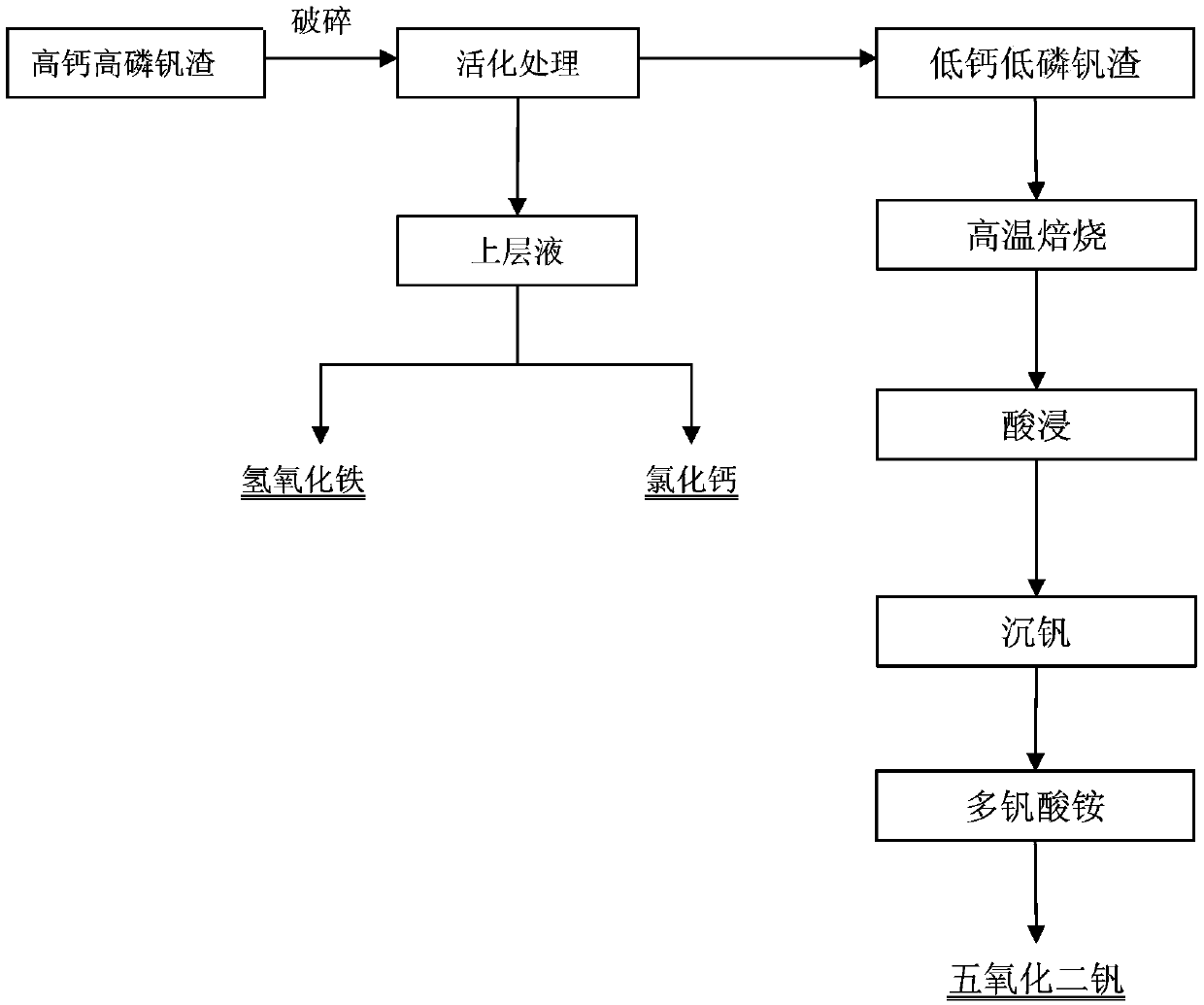
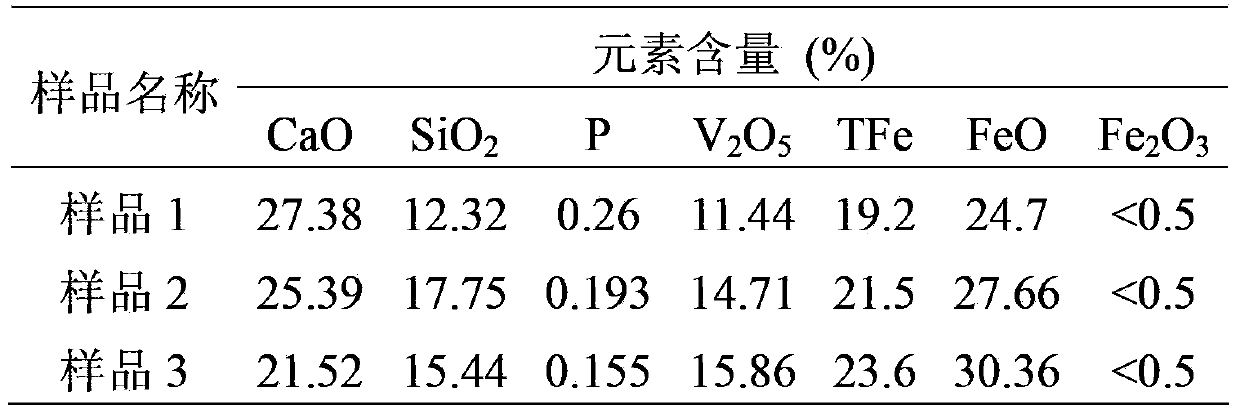
The invention provides a method for extracting vanadium from high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag. The method comprises the following steps of: crushing the high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag, and adding concentrated hydrochloric acid into the crushed high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag to carry out activating treatment, wherein the CaO / V2O5 content in the high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag is higher than 1, and the phosphorus content in the high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag is higher than 0.15wt%; filtering and separating to obtain a supernatant and low-calcium and low-phosphorus vanadium slag; regulating the pH value of the supernatant to 2.5-10, filtering to obtain ferric hydroxide, evaporating and concentrating the filtered solution, and then, cooling and crystallizing to obtain calcium chloride; roasting the low-calcium and low-phosphorus vanadium slag within the temperature range of 800-1500 DEG C to obtain clinker, and then, carrying out acid leaching to obtain a vanadium liquid; regulating the pH value of the vanadium liquid to 1-5, and then, adding soluble ammonium salt to enable vanadium to be settled to obtain ammonium vanadate; and calcining and decomposing the ammonium vanadate to obtain vanadium pentoxide. The method has the advantages that the vanadium element in the high-calcium and high-phosphorus vanadium slag can be effectively utilized, and two byproducts including the ferric hydroxide and the calcium chloride can be obtained.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for preparing manganese carbonate
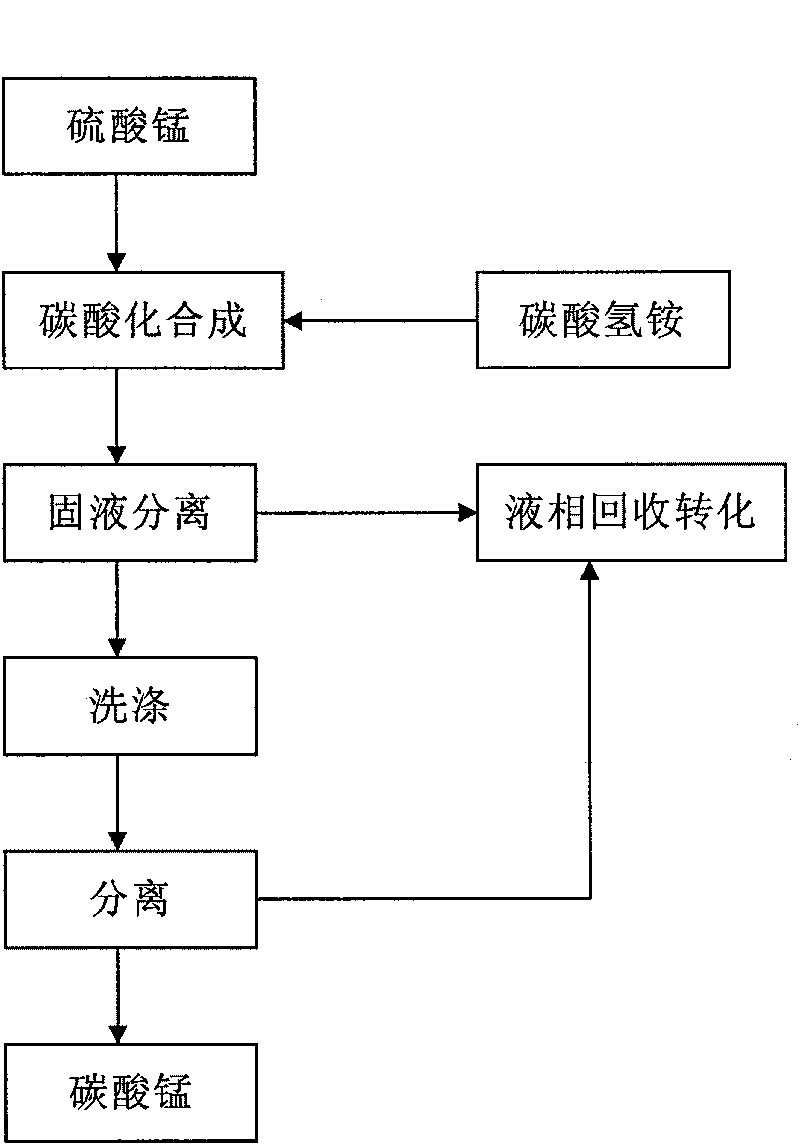
The invention relates to a method for preparing manganese carbonate, which comprises the steps of: adding MnSo4 into H2SO4, and adjusting the pH value to be between 2 and 4; adding ammonium hydrogen carbonate into the mixture for synthesis under the stirring at the temperature of between 30 and 80 DEG C, and controlling a synthesis end point to ensure an equimolar reaction to obtain a synthetic fluid; and performing solid-liquid separation on the synthetic fluid, using hot water at the temperature of between 80 and 100 DEG C to wash a solid phase, and then drying the solid phase to obtain the manganese carbonate. The method can prepare manganese carbonate with low calcium and low manganese, and can obtain the manganese carbonate with different particle size distributions.
Owner:GUIZHOU REDSTAR DEVING
Low-calcium silicate cement produced by using waste slag of aluminum and method of producing the same
InactiveCN101492262AReduce energy consumptionHigh mechanical strengthClinker productionCalcium silicateSlag
The invention discloses a low-calcium silicate cement produced by using aluminum waste slag and a preparation method thereof. The low-calcium silicate cement comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 65 to 85 percent of limestone, 6 to 10 percent of the aluminum waste slag, and 9 to 25 percent of steel slag or iron slag. The method for preparing the low-calcium silicate cement comprises the following steps: (1) drying and treating the aluminum waste slag so as to dehydrate the aluminum waste slag; (2) adding the dehydrated aluminum waste slag, the limestone and the steel slag into a crusher according to the proportion, and crushing the materials; (3) adding the crushed materials into a cement rotary kiln, and heating and calcining the materials; and (4) adding a ball milling assistant into the sintered clinker, and ball-milling and packaging the mixture to obtain the low-calcium silicate cement. Compared with the prior cement, the low-calcium silicate cement produced by using the industrial wastes as the aluminum waste slag has higher mechanical strength, simultaneously has the characteristics of simple process, low sintering temperature and energy consumption of a unit product, and high rate of finished products, and is suitable for industrial popularization because the prior equipment is directly used.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method and application of astragalus polysaccharide-calcium complex
InactiveCN102351958AGood water solubilityImprove absorption rateOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSolubilityFiltration
The invention relates to a preparation method and application of an astragalus polysaccharide-calcium complex, and can solve the problems of poor water solubility, low calcium supplement absorptivity and influence on eating effects. The method comprises the steps of: adding astragalus medicinal material into water for extraction, and conducting filtration so as to obtain an astragalus polysaccharide solution; adding a CaCl2 ion solution drop by drop into the astragalus polysaccharide solution under stirring till saturation, and simultaneously adding a NaOH ion solution for complex reaction till the pH value of the solution in the range of 9-11, standing and stirring the solution for 0.5-2h, thus obtaining a astragalus polysaccharide-calcium complex solution, then carrying out dialysis with a dialysis bag or condensation and filtration, then adding ethanol of 95% in mass concentration till the ethanol content up to 80-85%, standing the solution for 8-24h, carrying out filtration or centrifugation so as to obtain a sediment, which is then dried and crushed into particles, i.e. the astragalus polysaccharide-calcium complex. The complex of the invention has good water solubility and high absorptivity, thus being a major innovation in traditional Chinese medicine.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF CHINESE MEDICINE
Process for treating pectin containing plant material
InactiveUS20060099302A1Animal feeding stuffFruits/vegetable preservation using acidsPectin esteraseLow calcium
Owner:CP KELCO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com