Method for selectively removing calcium ions from concentrated water byproduct of sea water desalination process and other high-calcium-magnesium-content concentrated brines
A concentrated brine, selective technology, applied in concentrated water decalcification, high calcium and magnesium concentrated brine in the field of selective removal of calcium ions, can solve the problem of unsuitable for selective decalcification treatment, low calcium removal rate, high operating cost, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of reducing operating cost, low operating cost and long stirring time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
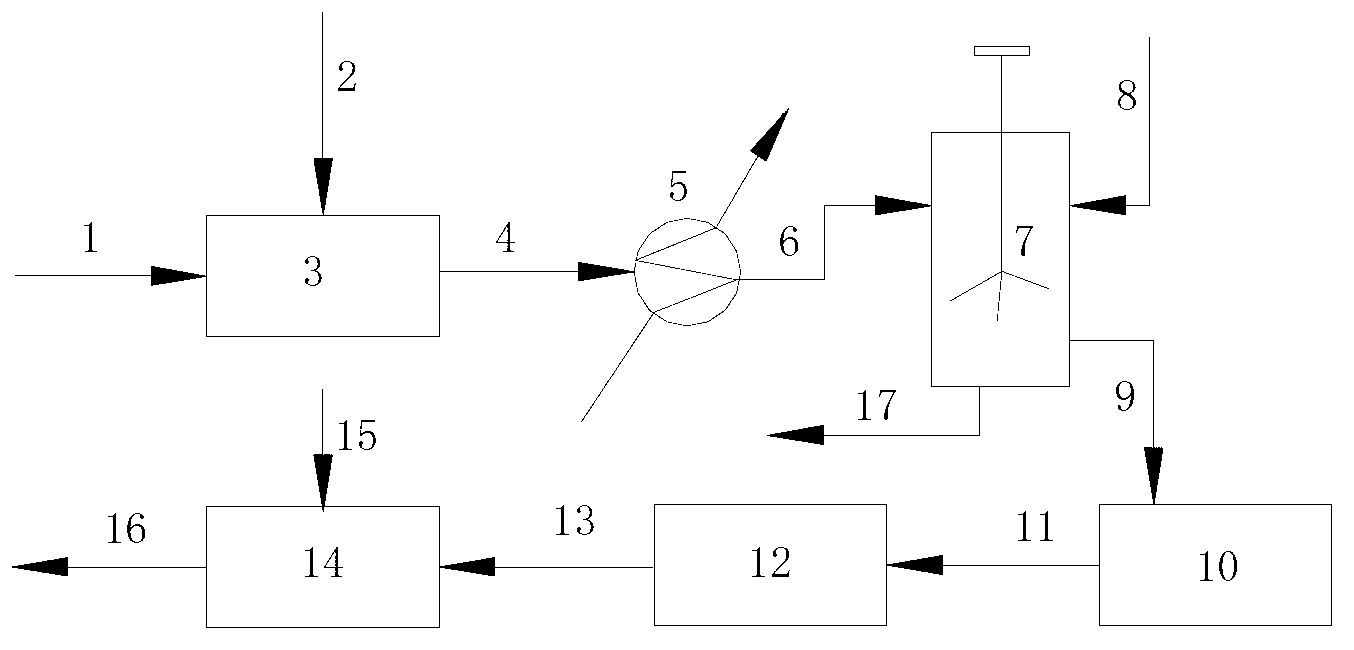
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] Concentrated water by-product of a multi-stage flash seawater desalination plant, 5.4°Bé, pH=8.2, [Ca 2+ ]=650mg / L, [Mg 2+ ]=2000mg / L, heated to 85°C in a closed container with stirring, and then added the theoretical equivalent (n Ca2+ :n Na2SO3 =1:1.2) 20% (wt) of Na 2 SO 3 Solution, stirred for 40min, filtered after standing for 5min, according to [Ca 2+ ] to calculate Ca 2+ The removal rate is 90.5%, Mg 2+ The loss rate is 0.45%;
Embodiment comparative example 2
[0044] Concentrated water quality is the same as in Example 1, 20% (wt) Na is used at 25°C 2 SO 3 Solution processing, other operating conditions are with embodiment 1, after processing Ca 2+ The removal rate is 72.5%.
[0045] In addition, add concentrated hydrochloric acid to the filtrate obtained in Example 1 to adjust the pH to 6.2, then use an evaporator to evaporate and concentrate, and no precipitation occurs when the concentration is 25 ° Bé; or the concentrated water after decalcification is aerated for 30 minutes, and then use an evaporator Concentrated by evaporation, no precipitation occurs when the concentration is 25°Bé.
Embodiment 2
[0047] Concentrated water by-product of reverse osmosis seawater desalination in a factory, 6°Bé, pH=7.0, [Ca 2+ ]=871mg / L, [Mg 2+ ]=2680mg / L, heated to 85°C in a closed container with stirring, and then added the theoretical equivalent (n Ca2+ :n Na2SO3 =1:1.2) 20% (wt) of Na 2 SO 3 solution, stirred for 40min, filtered after standing for 5min, measured Ca 2+ The removal rate is 92.5%, Mg 2+ The loss rate is 0.40%.
[0048] The comparative example of embodiment 2:
[0049] Concentrated water quality and operating conditions are the same as in Example 2, and the precipitant is changed to 20% (wt) Na 2 CO 3 solution, after treatment Ca 2+ The removal rate is 81.5%, Mg 2+ The loss rate was 12.5%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com