Patents
Literature
207 results about "Metal Chelator" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
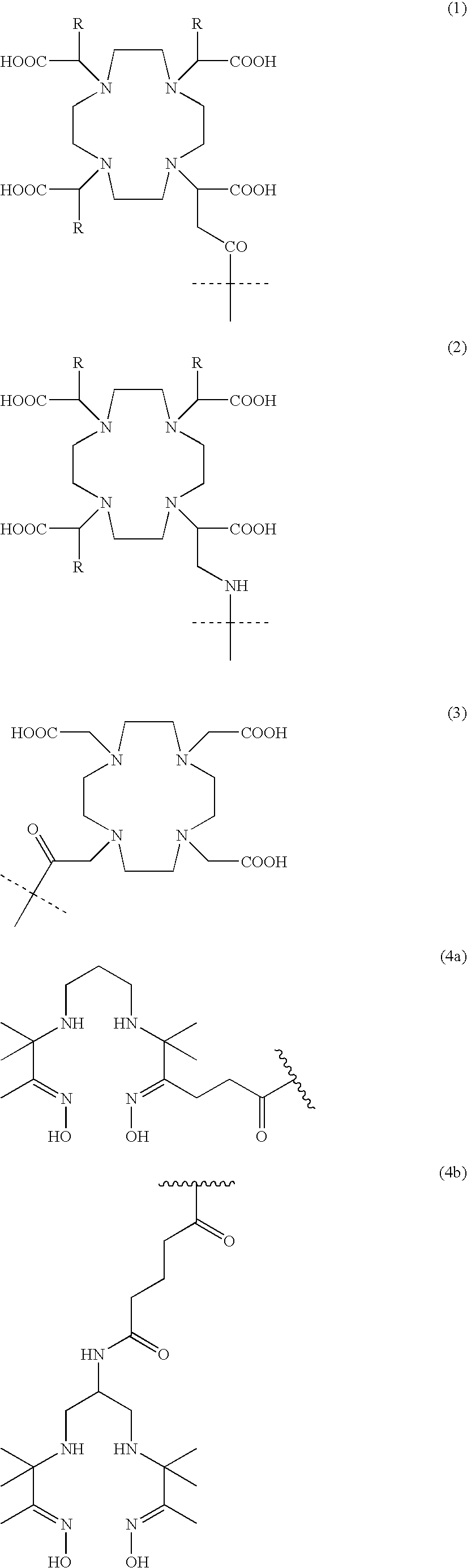
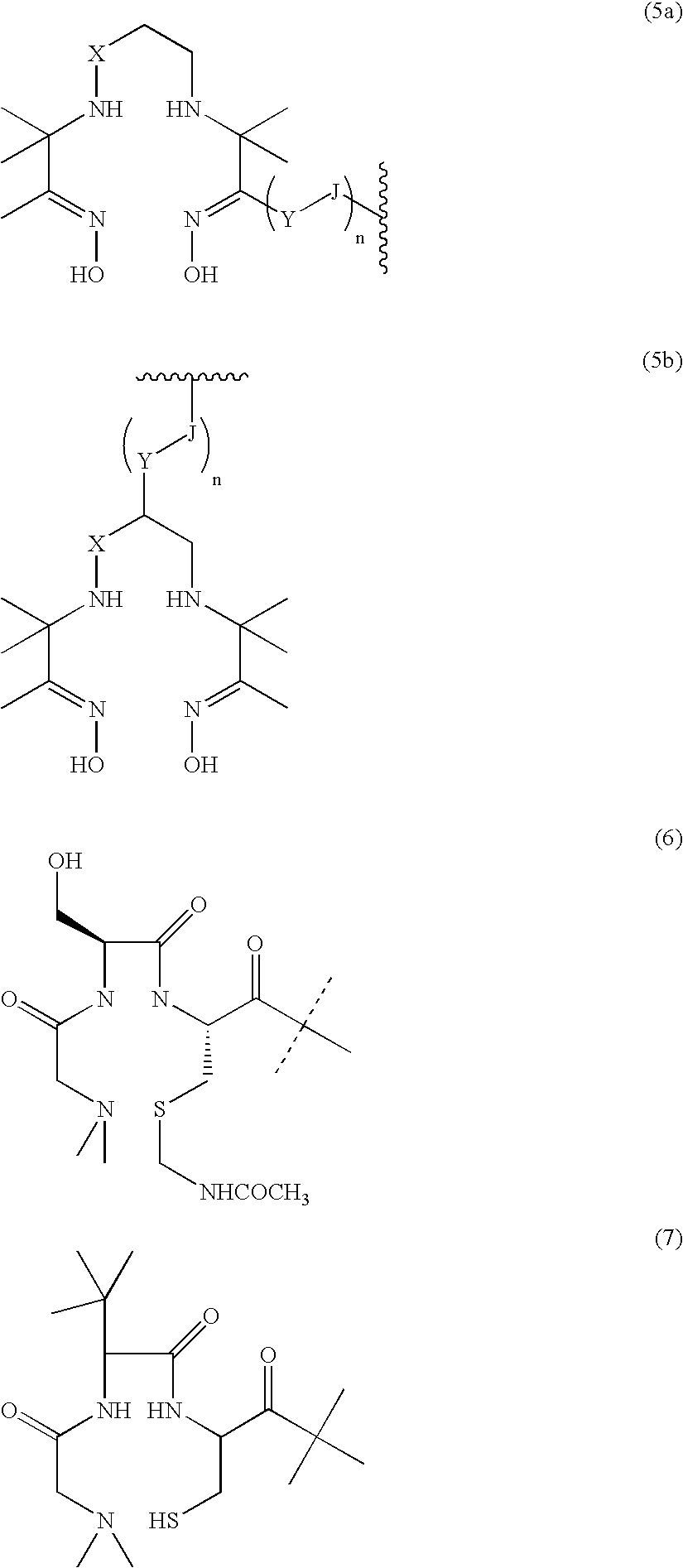
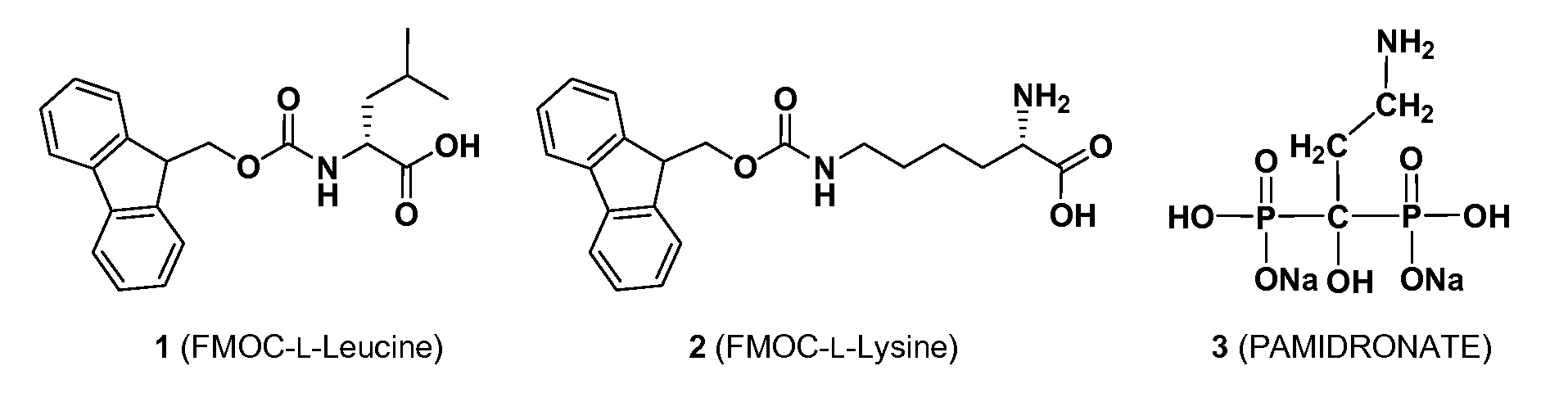
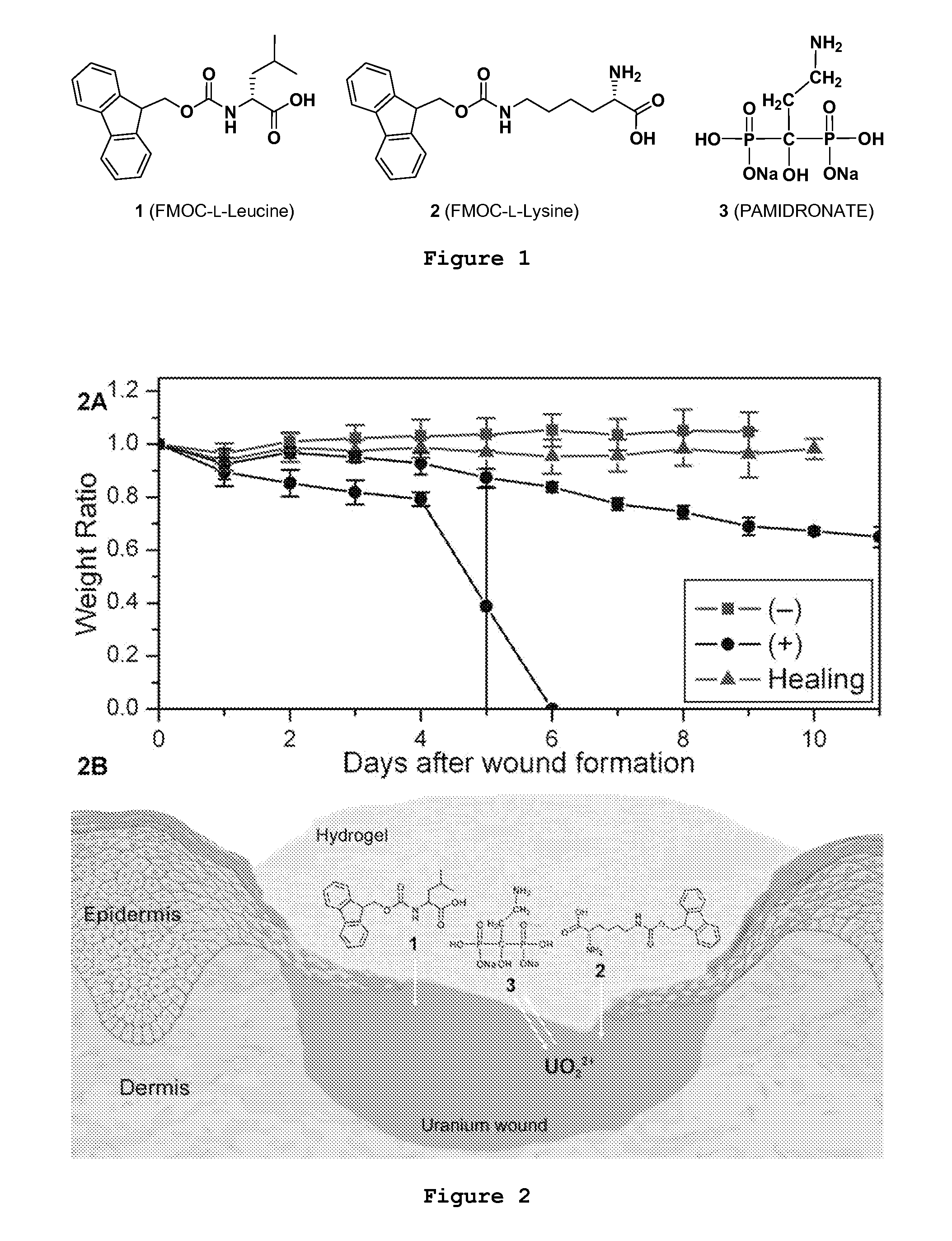
An inorganic or organic molecule which binds metal ions. Metal chelators are frequently polydentate, indicating that they form multiple bonds with the metal ion, resulting in more stable coordination complexes.
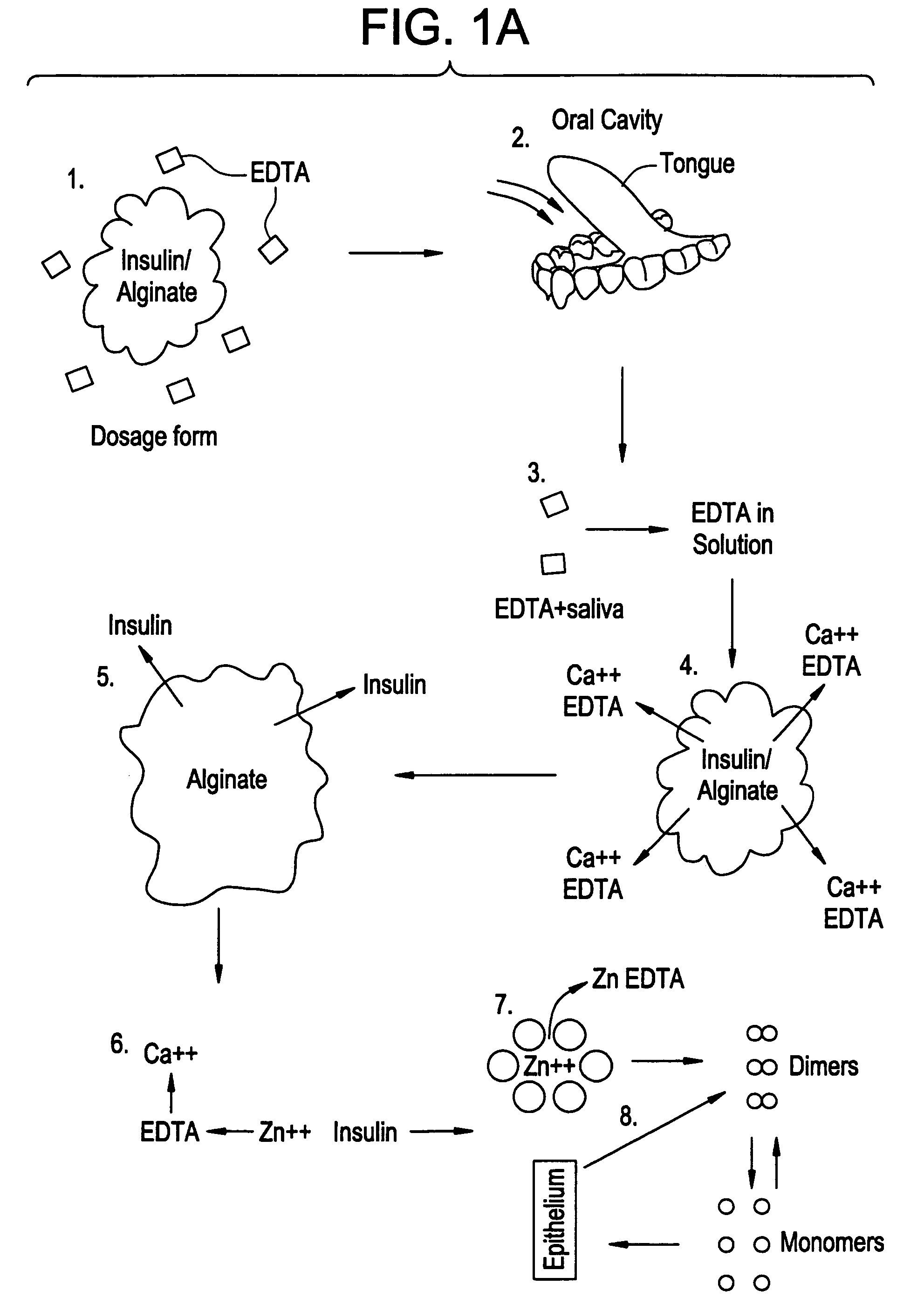
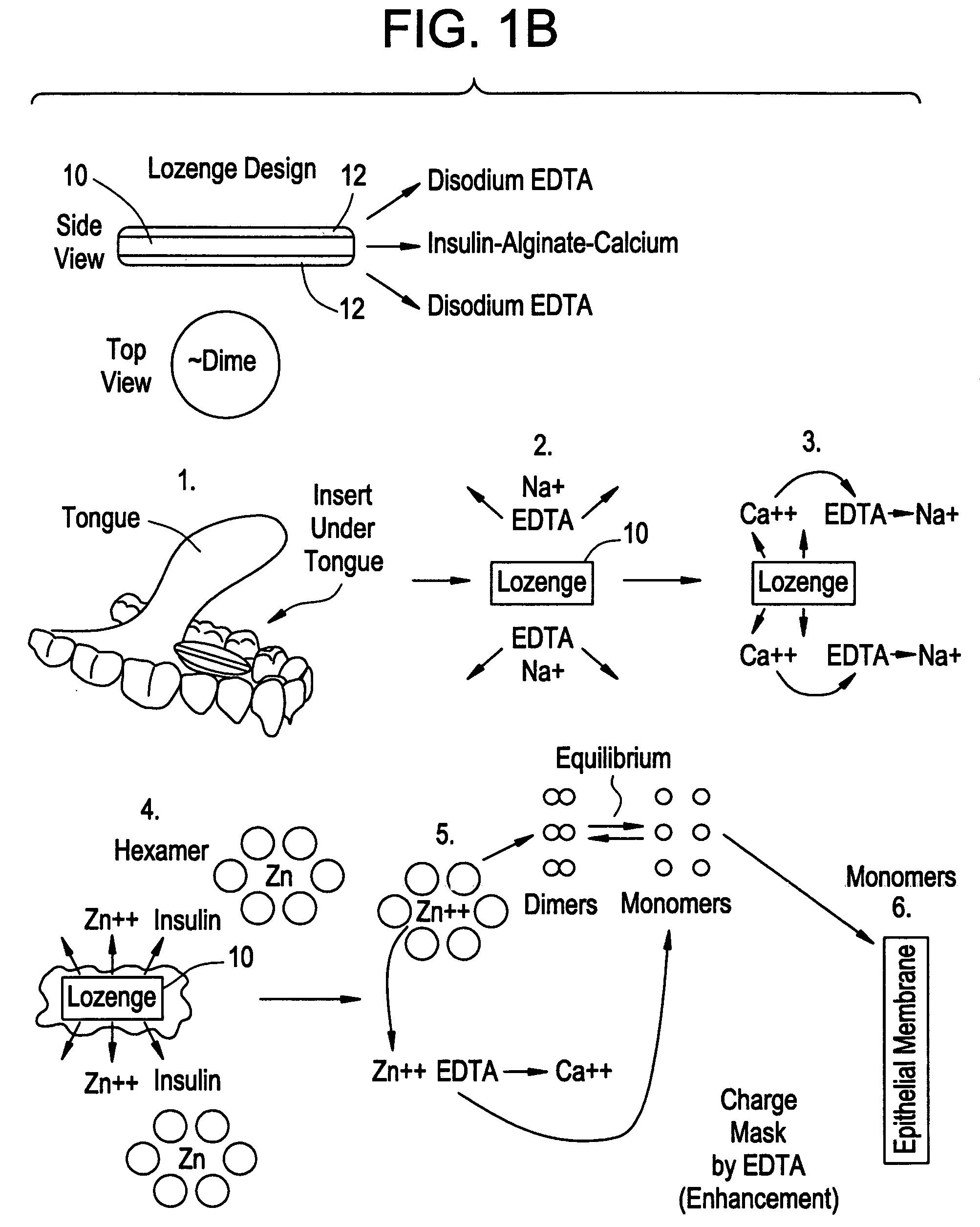
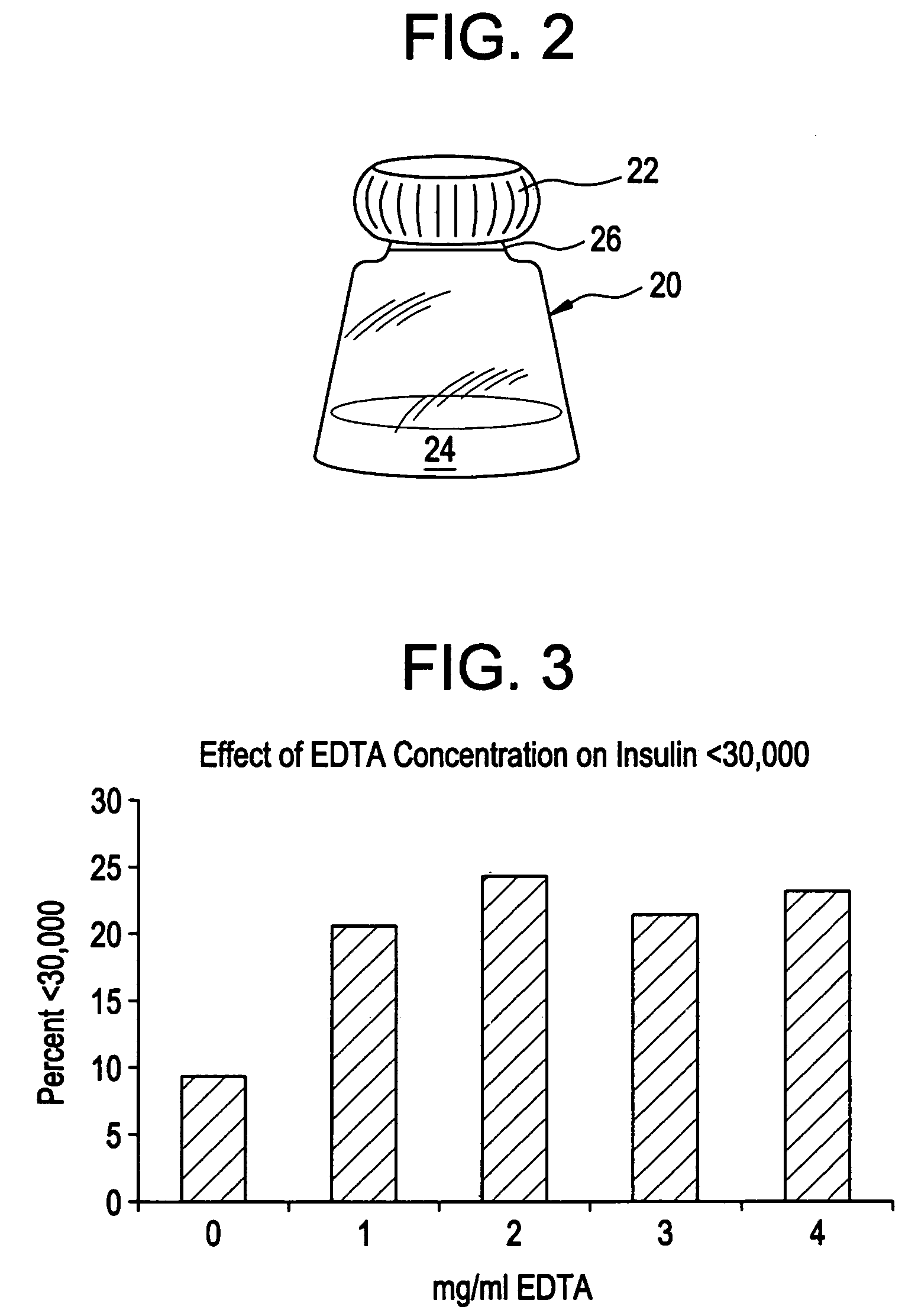
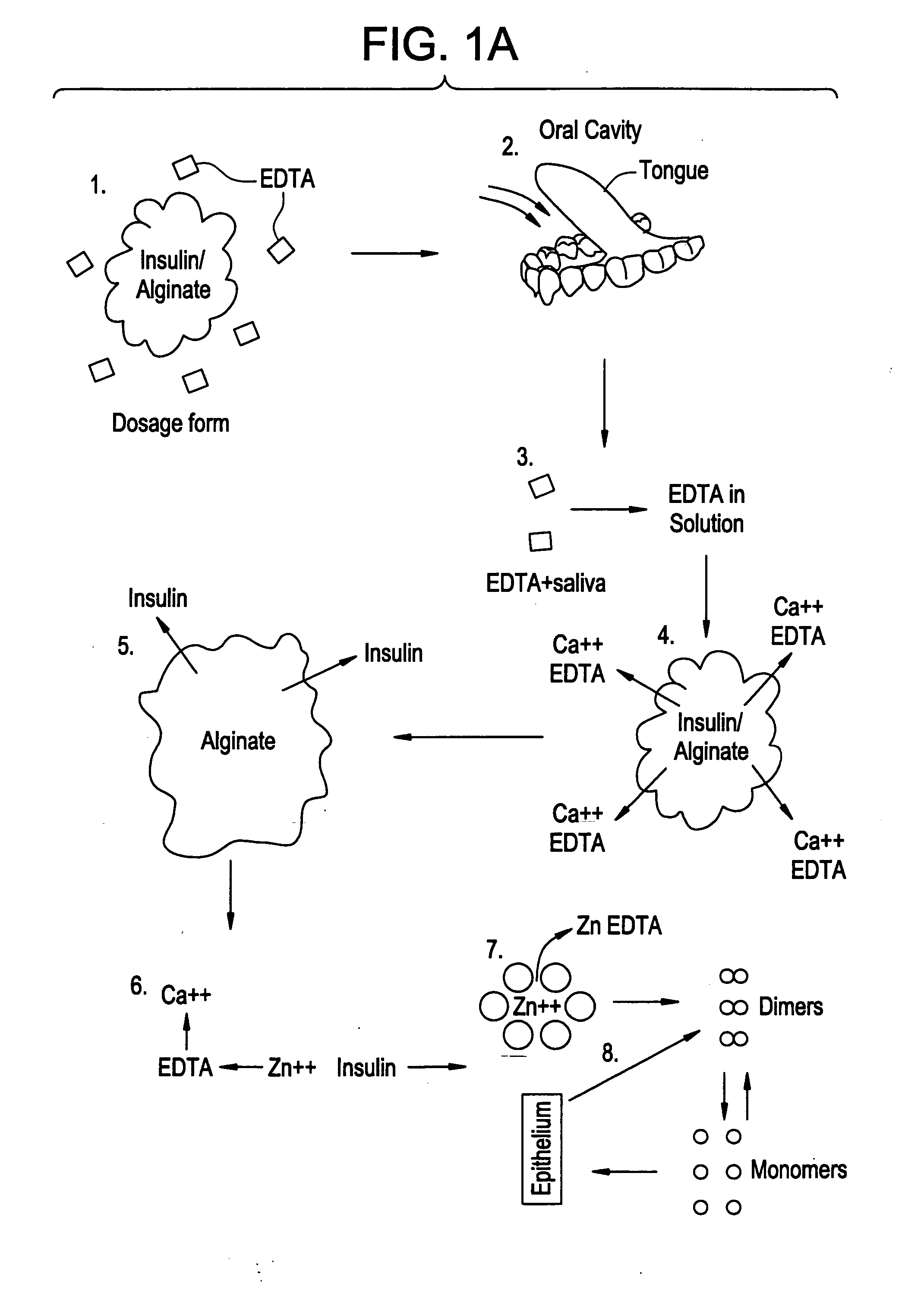
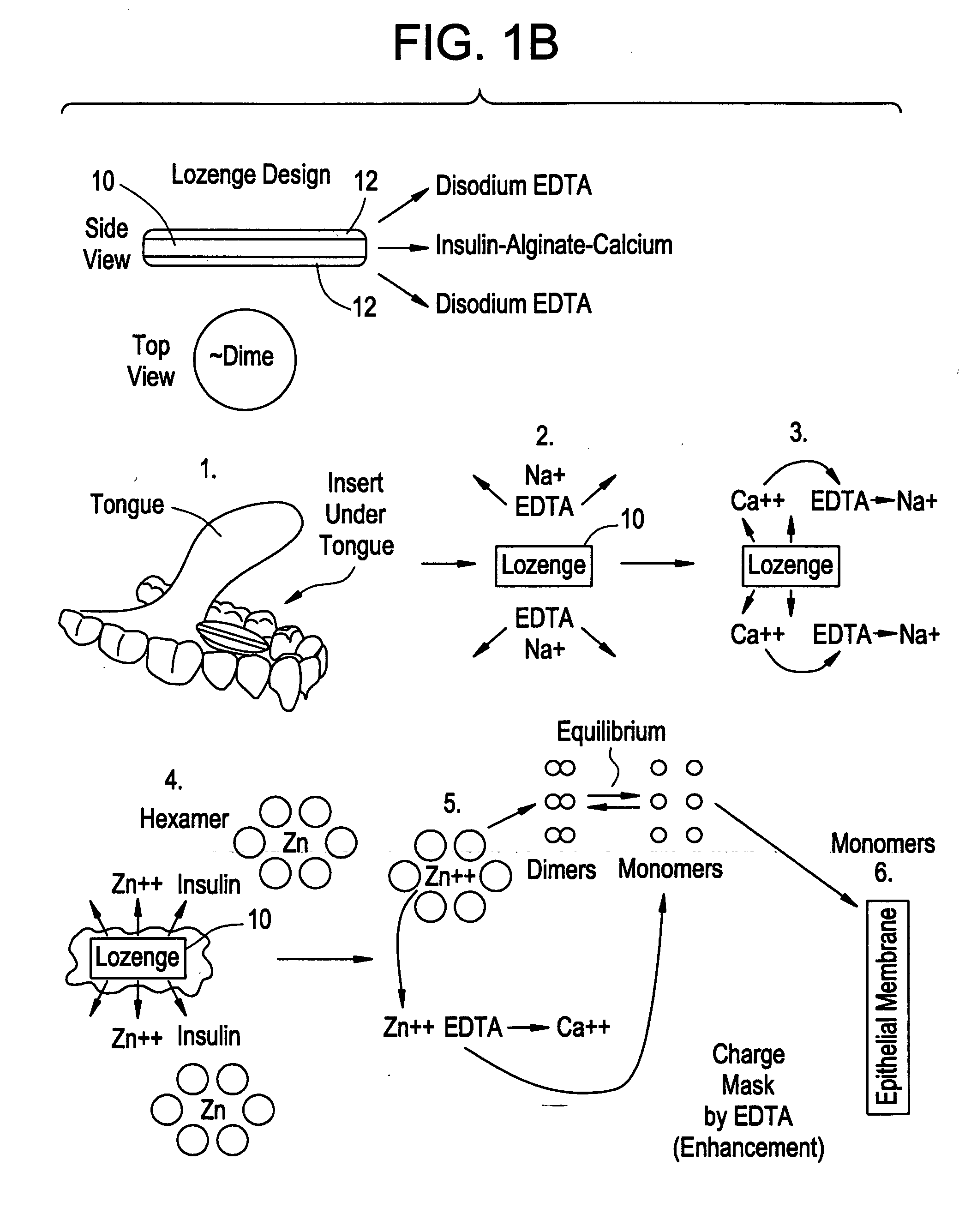
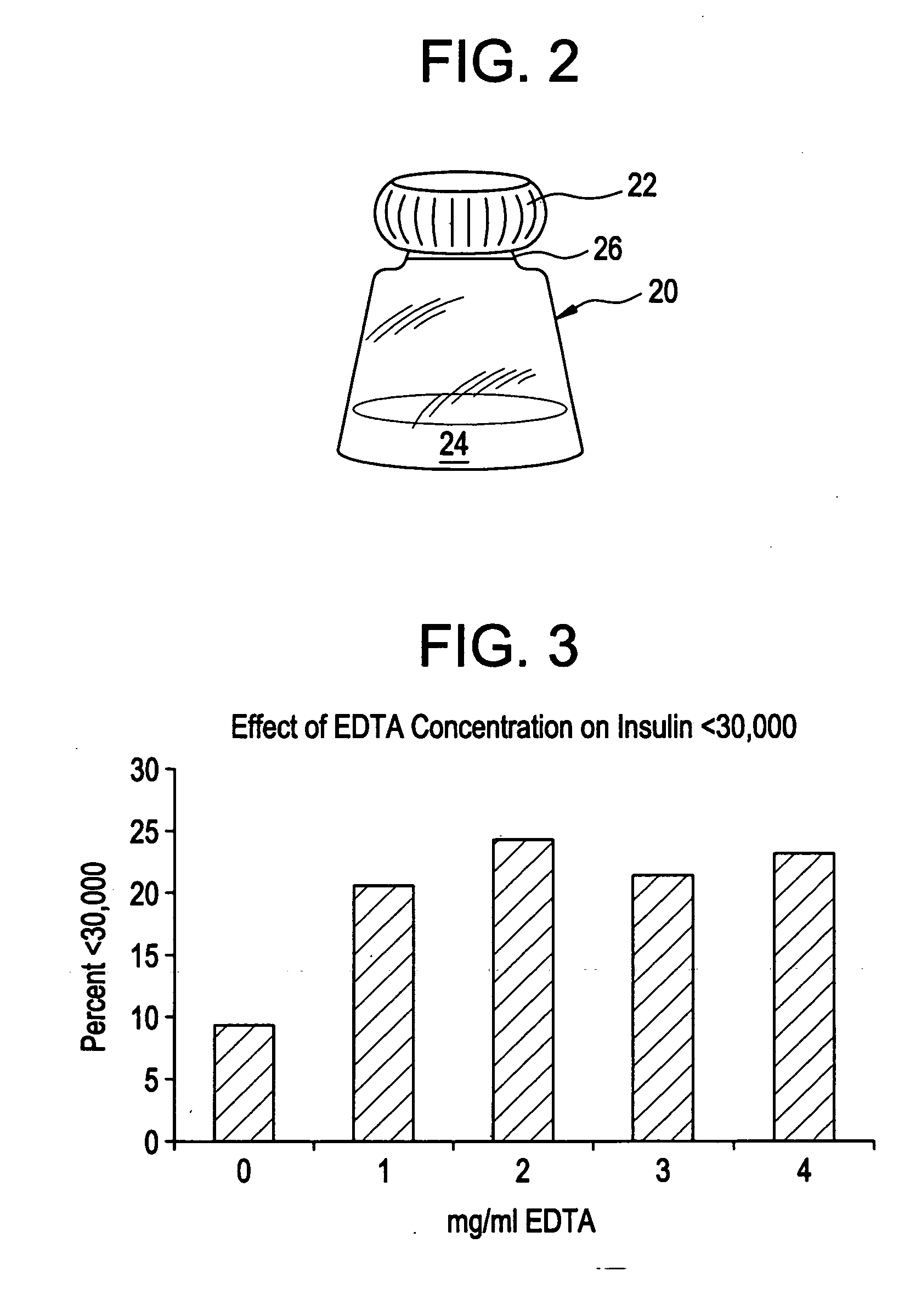
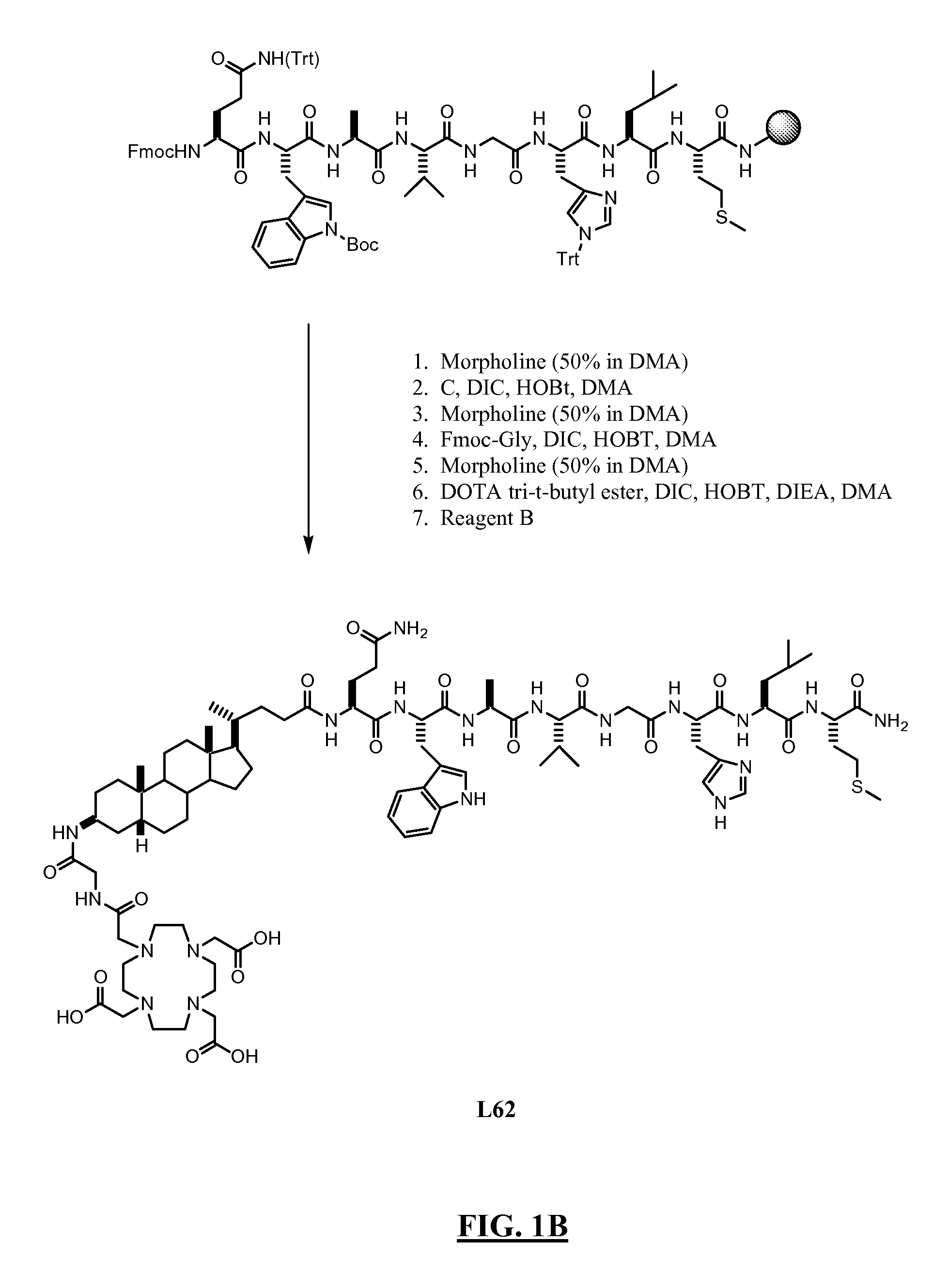
Rapid acting drug delivery compositions
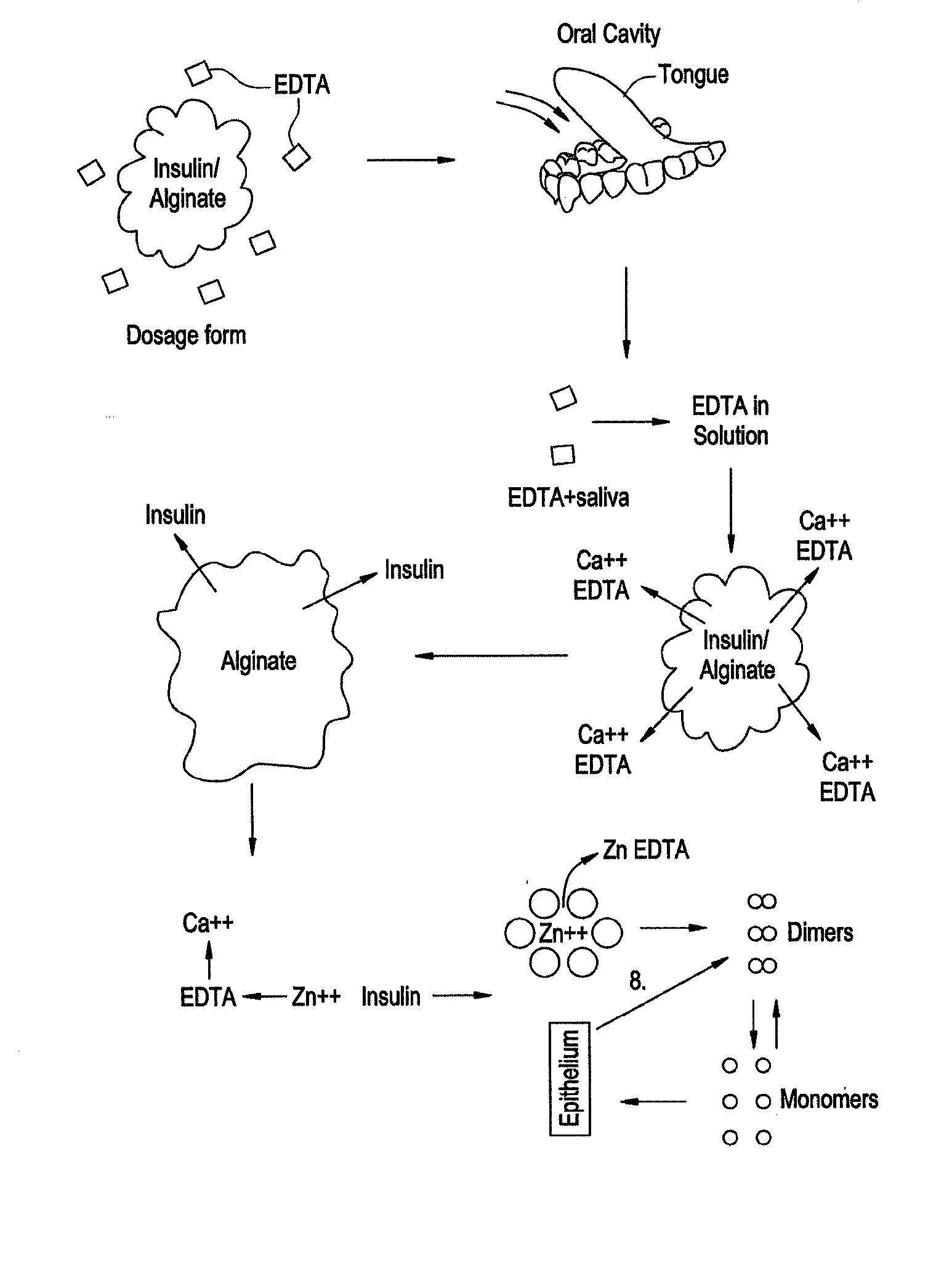
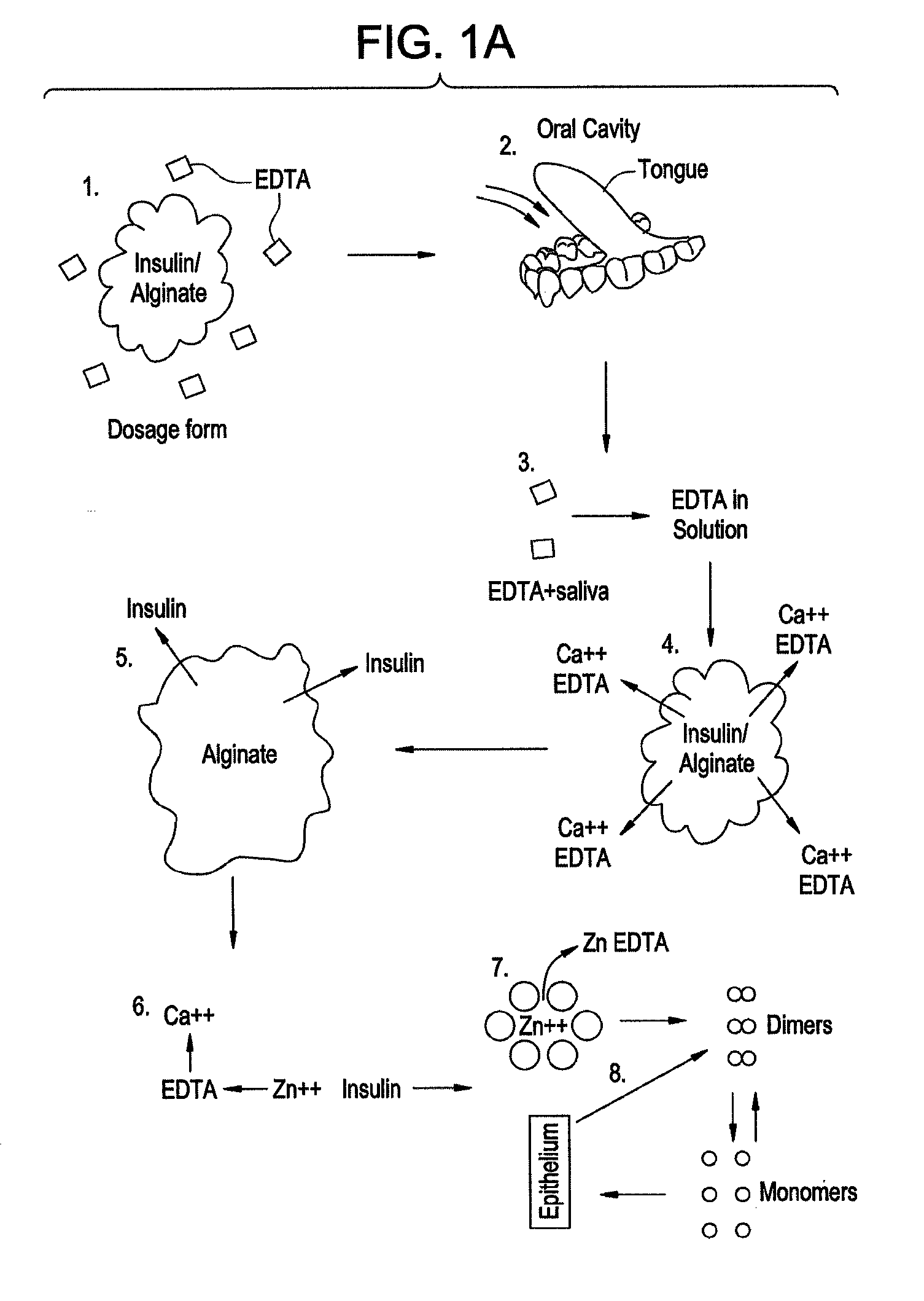
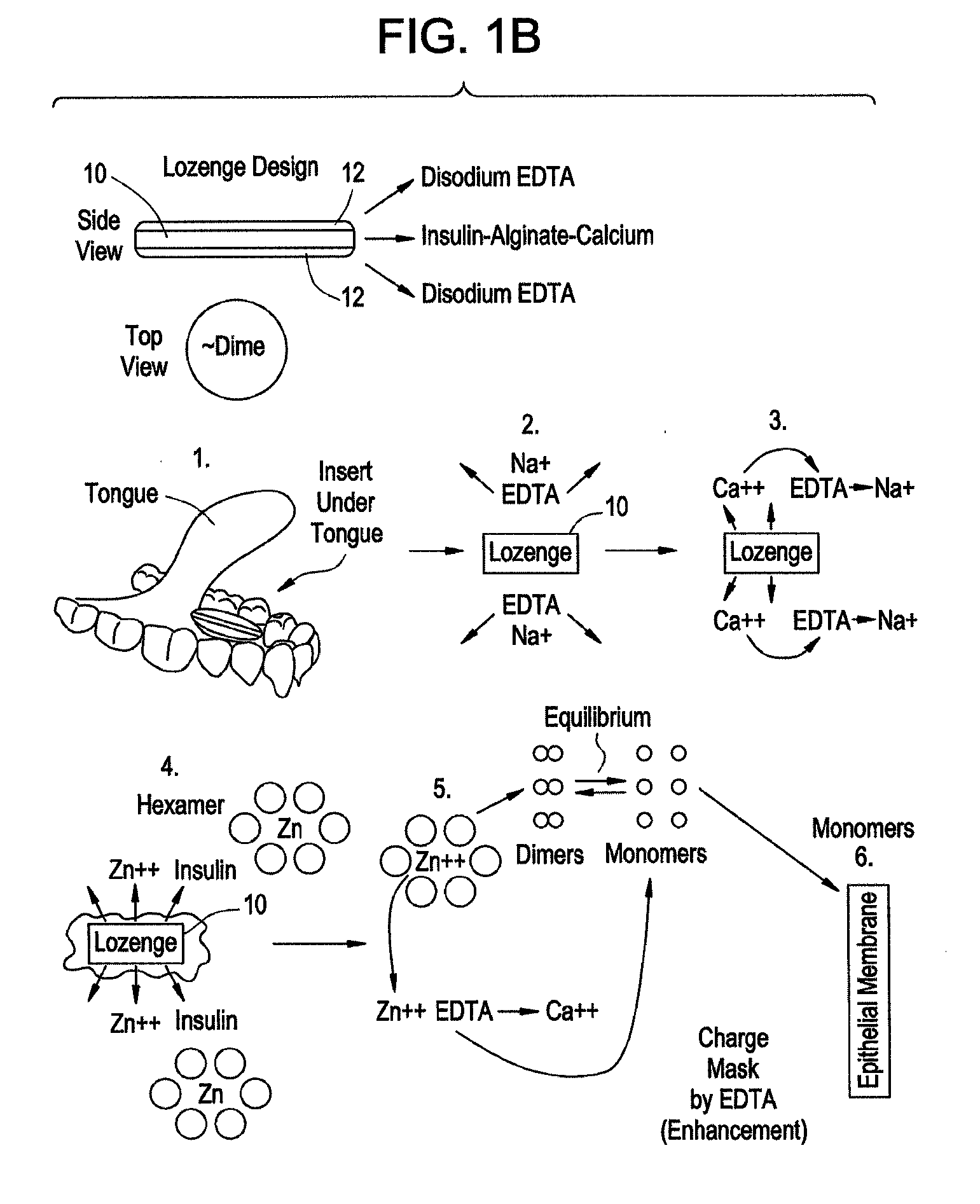
Drug formulations for systemic drug delivery with improved stability and rapid onset of action are described herein. The formulations may be administered via buccal administration, sublingual administration, pulmonary delivery, nasal administration, subcutaneous administration, rectal administration, vaginal administration, or ocular administration. In the preferred embodiments, the formulations are administered sublingually or via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain an active agent and one or more excipients, selected to increase the rate of dissolution. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is insulin, and the excipients include a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Following administration, these formulations are rapidly absorbed by the oral mucosa when administered sublingually and are rapidly absorbed into the blood stream when administered by subcutaneous injection. In one embodiment, the composition is in the form of a dry powder. In another embodiment, the composition is in the form of a film, wafer, lozenge, capsule, or tablet. In a third embodiment, a dry powdered insulin is mixed with a diluent containing a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, such as water or saline, a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Devices for storing and mixing these formulations are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Rapid acting drug delivery compositions
ActiveUS20050214251A1Improve stabilityQuick effectPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsNasal cavityBuccal use
Drug formulations for systemic drug delivery with improved stability and rapid onset of action are described herein. The formulations may be administered via buccal administration, sublingual administration, pulmonary delivery, nasal administration, subcutaneous administration, rectal administration, vaginal administration, or ocular administration. In the preferred embodiments, the formulations are administered sublingually or via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain an active agent and one or more excipients, selected to increase the rate of dissolution. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is insulin, and the excipients include a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Following administration, these formulations are rapidly absorbed by the oral mucosa when administered sublingually and are rapidly absorbed into the blood stream when administered by subcutaneous injection. In one embodiment, the composition is in the form of a dry powder. In another embodiment, the composition is in the form of a film, wafer, lozenge, capsule, or tablet. In a third embodiment, a dry powdered insulin is mixed with a diluent containing a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, such as water or saline, a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Devices for storing and mixing these formulations are also described.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
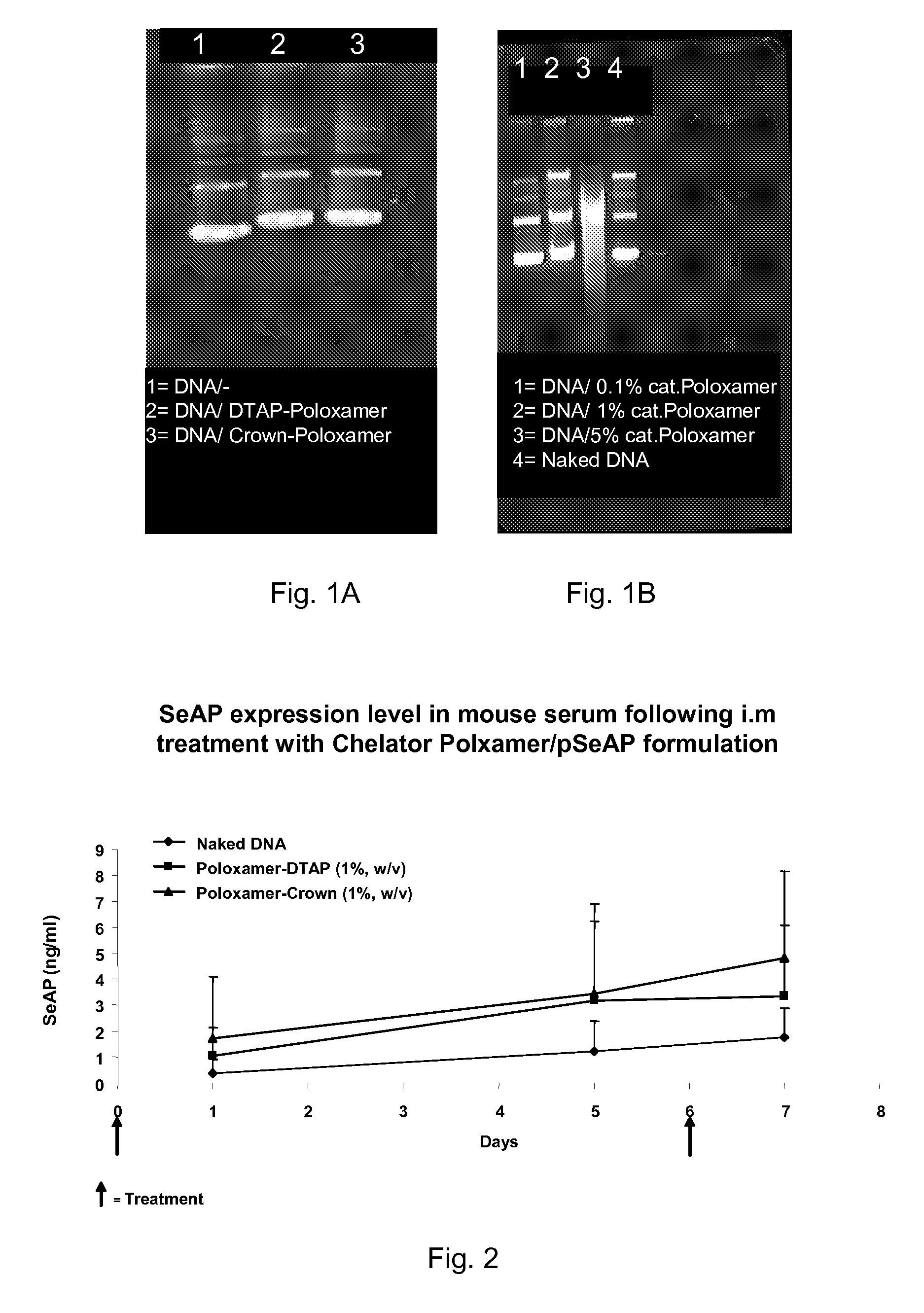
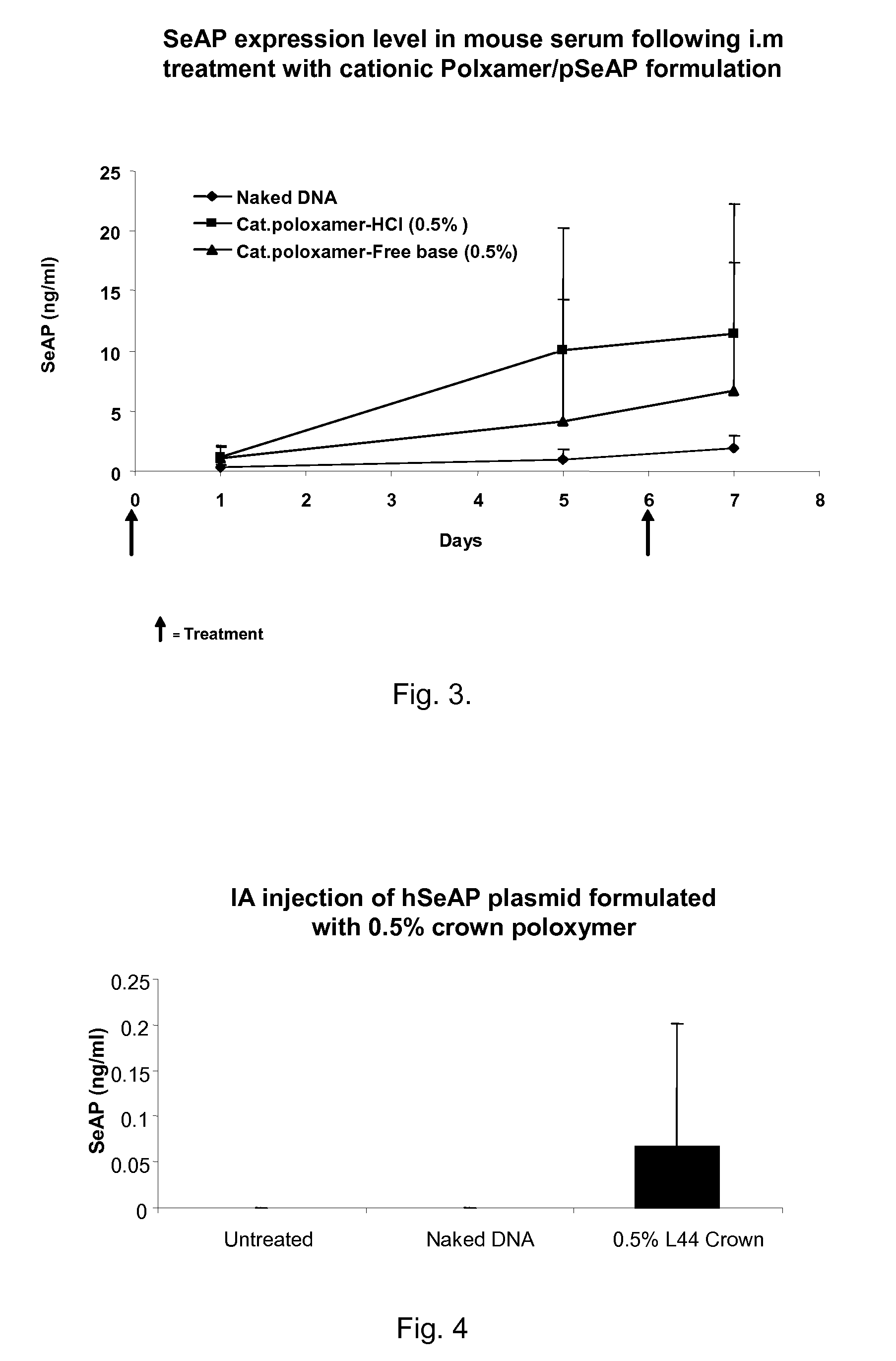
Modified Poloxamers for Gene Expression and Associated Methods
InactiveUS20100004313A1Inhibit expressionReduce deliveryGenetic material ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismGene deliverySolid tissue
Nucleotide delivery polymers, compositions, and associated methods for the enhancement of gene delivery and expression in solid tissues are provided. In one aspect, for example, a nucleotide delivery polymer may include a poloxamer backbone having a metal chelator covalently coupled to at least one terminal end of the poloxamer backbone. In another aspect, the nucleotide expression polymer has a metal chelator coupled to at least two terminal ends of the poloxamer backbone.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Use and production of citrate-stable neutral metalloproteases
The present invention provides methods and compositions comprising at least one neutral metalloprotease enzyme that has improved stability in the presence of a metal chelator. In some embodiments, the neutral metalloprotease finds use in cleaning and other applications comprising citrate. In some particularly preferred embodiments, the present invention provides methods and compositions comprising variant neutral metalloprotease(s) engineered to resist citrate-induced autolysis.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
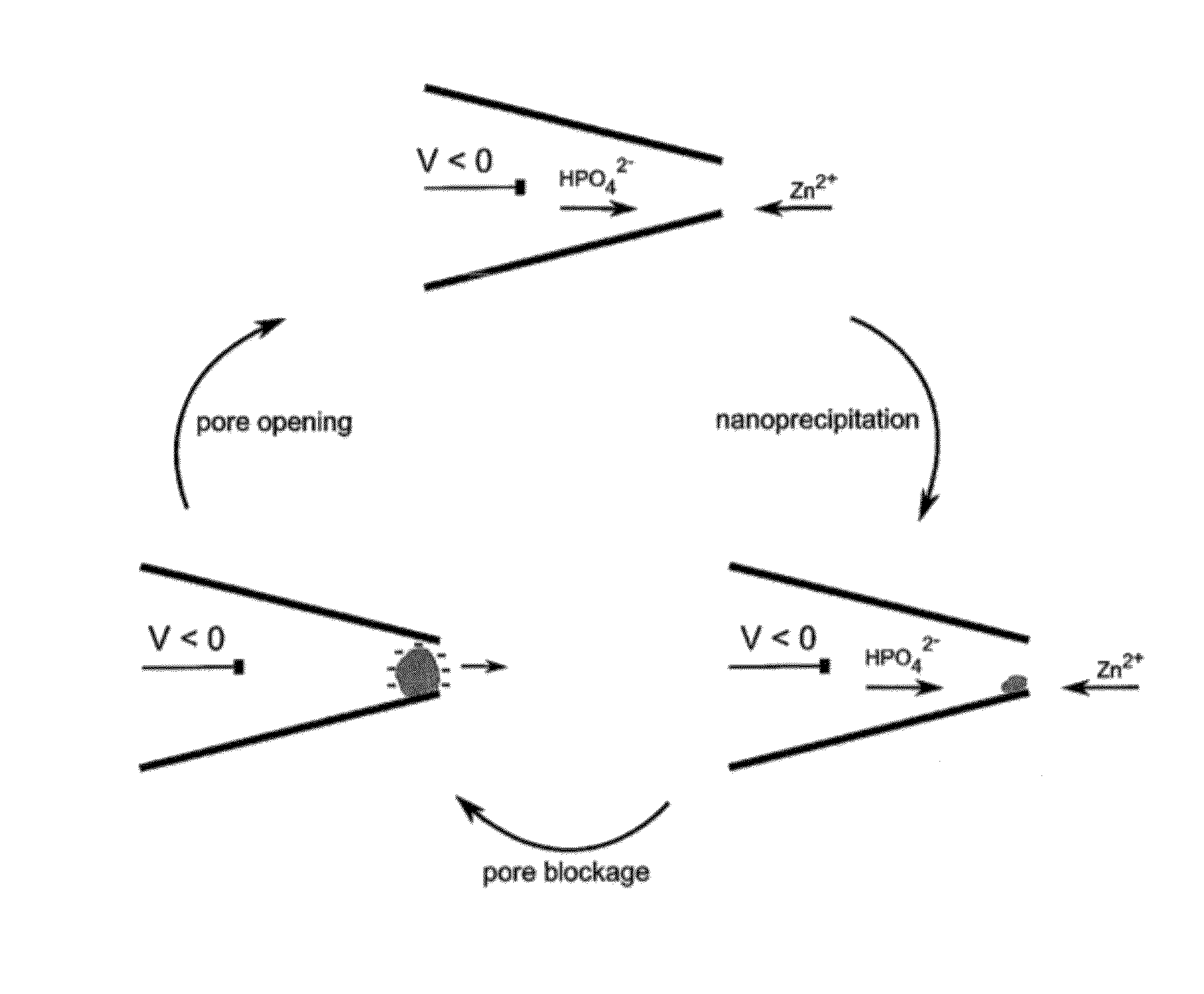
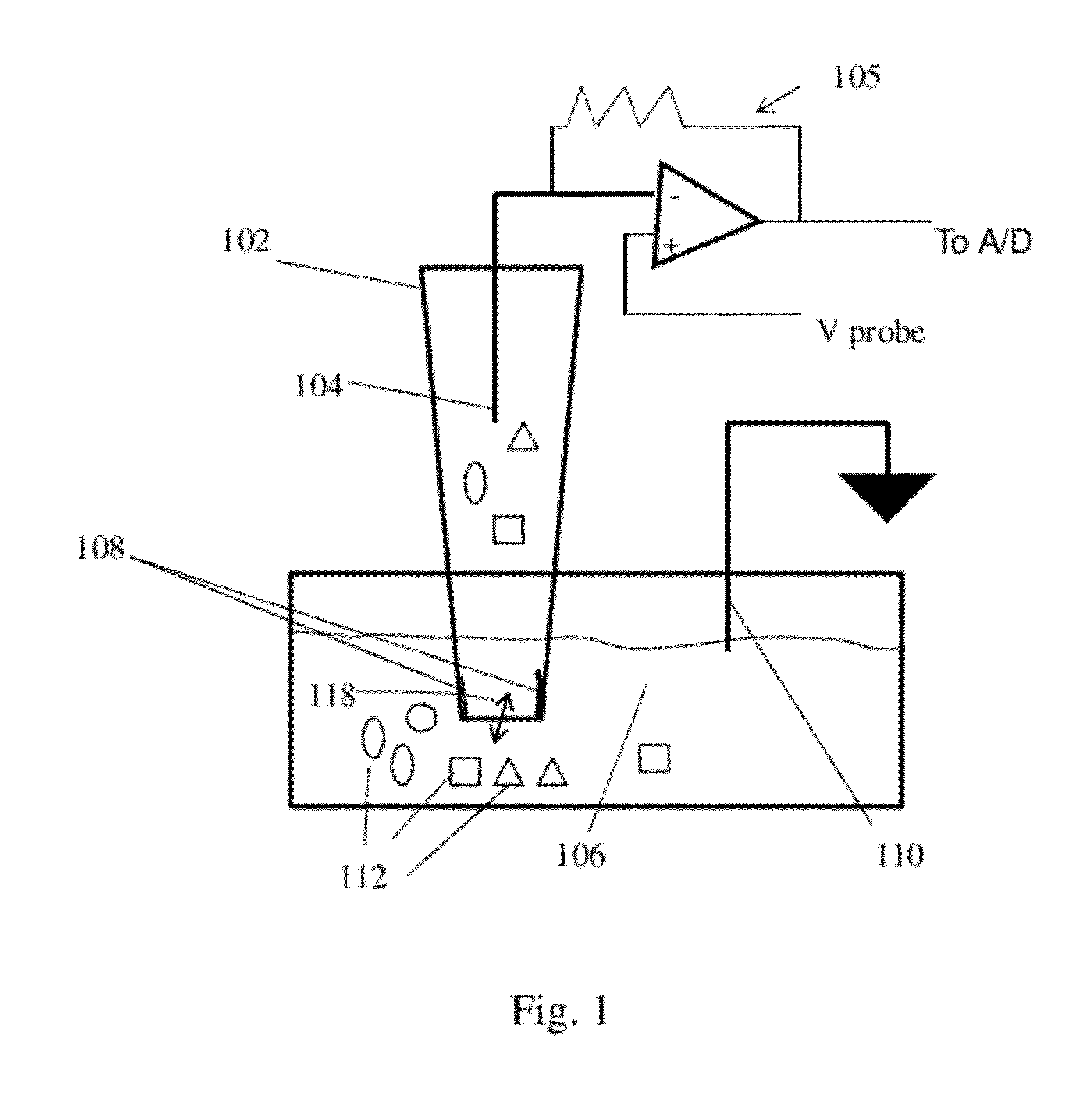
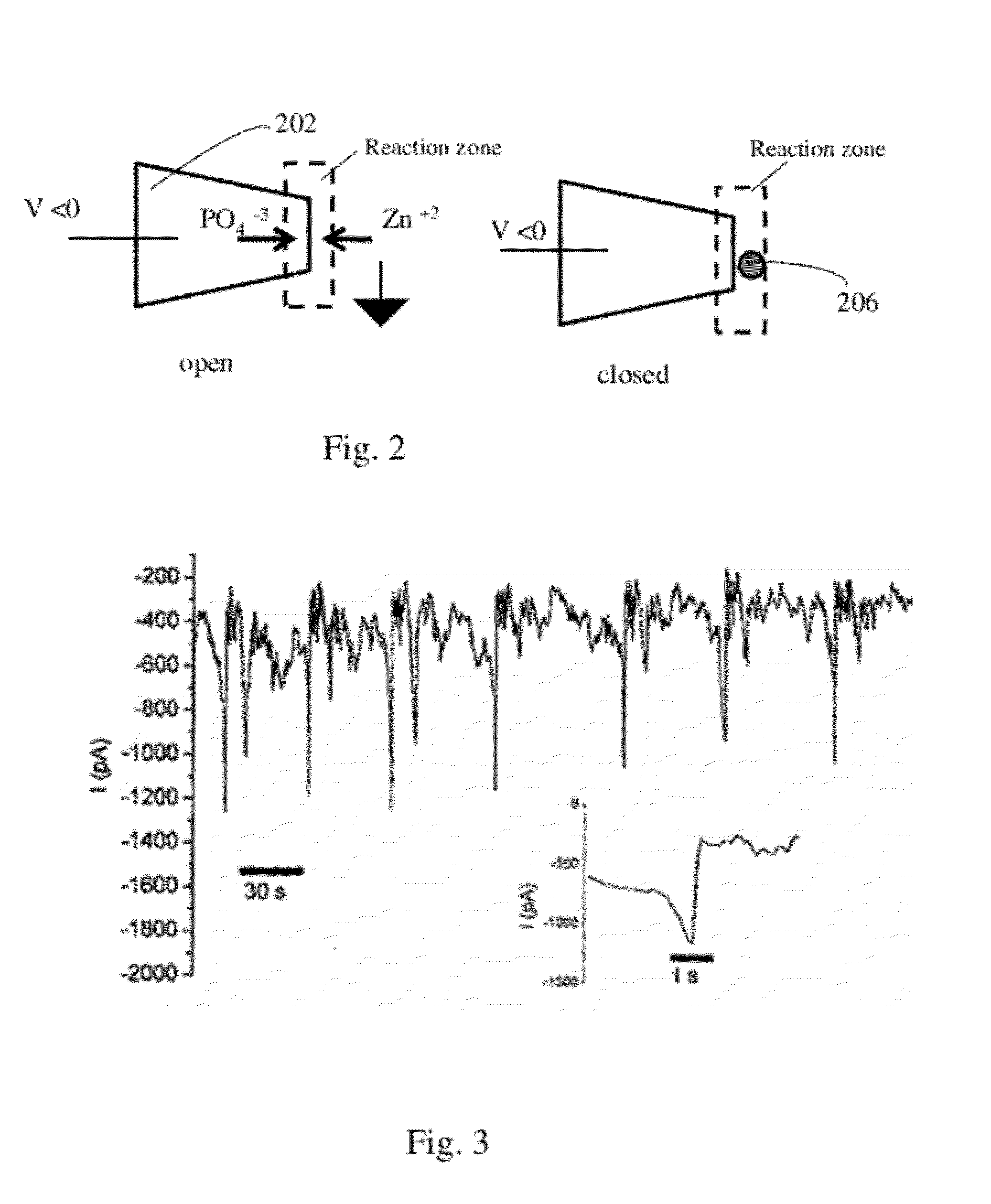
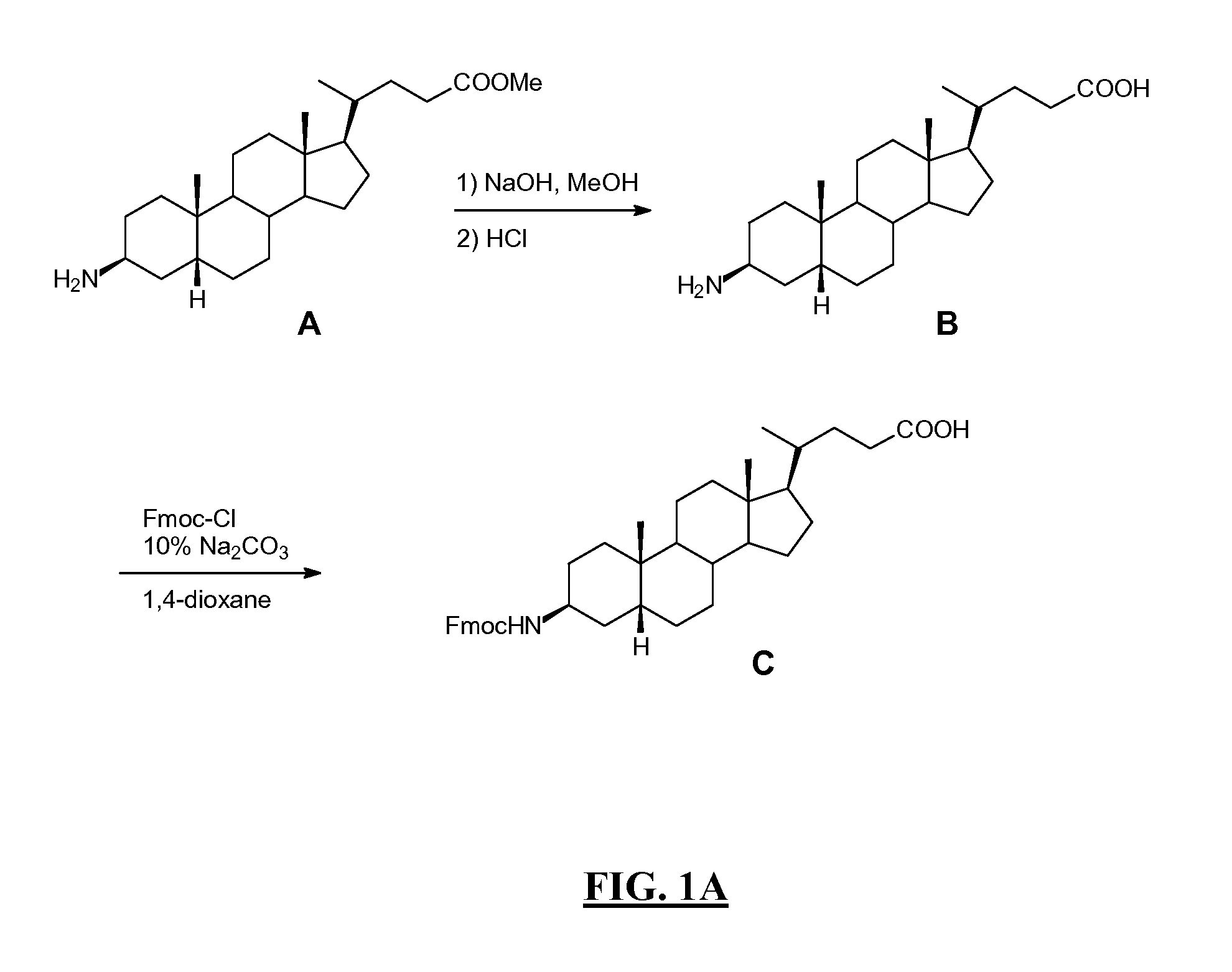
Nanopore Device for Reversible Ion and Molecule Sensing or Migration
Disclosed are methods and devices for detection of ion migration and binding, utilizing a nanopipette adapted for use in an electrochemical sensing circuit. The nanopipette may be functionalized on its interior bore with metal chelators for binding and sensing metal ions or other specific binding molecules such as boronic acid for binding and sensing glucose. Such a functionalized nanopipette is comprised in an electrical sensor that detects when the nanopipette selectively and reversibly binds ions or small molecules. Also disclosed is a nanoreactor, comprising a nanopipette, for controlling precipitation in aqueous solutions by voltage-directed ion migration, wherein ions may be directed out of the interior bore by a repulsing charge in the bore.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Gastrin Releasing Peptide Compounds
InactiveUS20080008649A1Improve targetingDecreasing aberrant vascular permeabilityRadioactive preparation carriersGastrin releasing peptideCholic acidTherapeutic Hormone
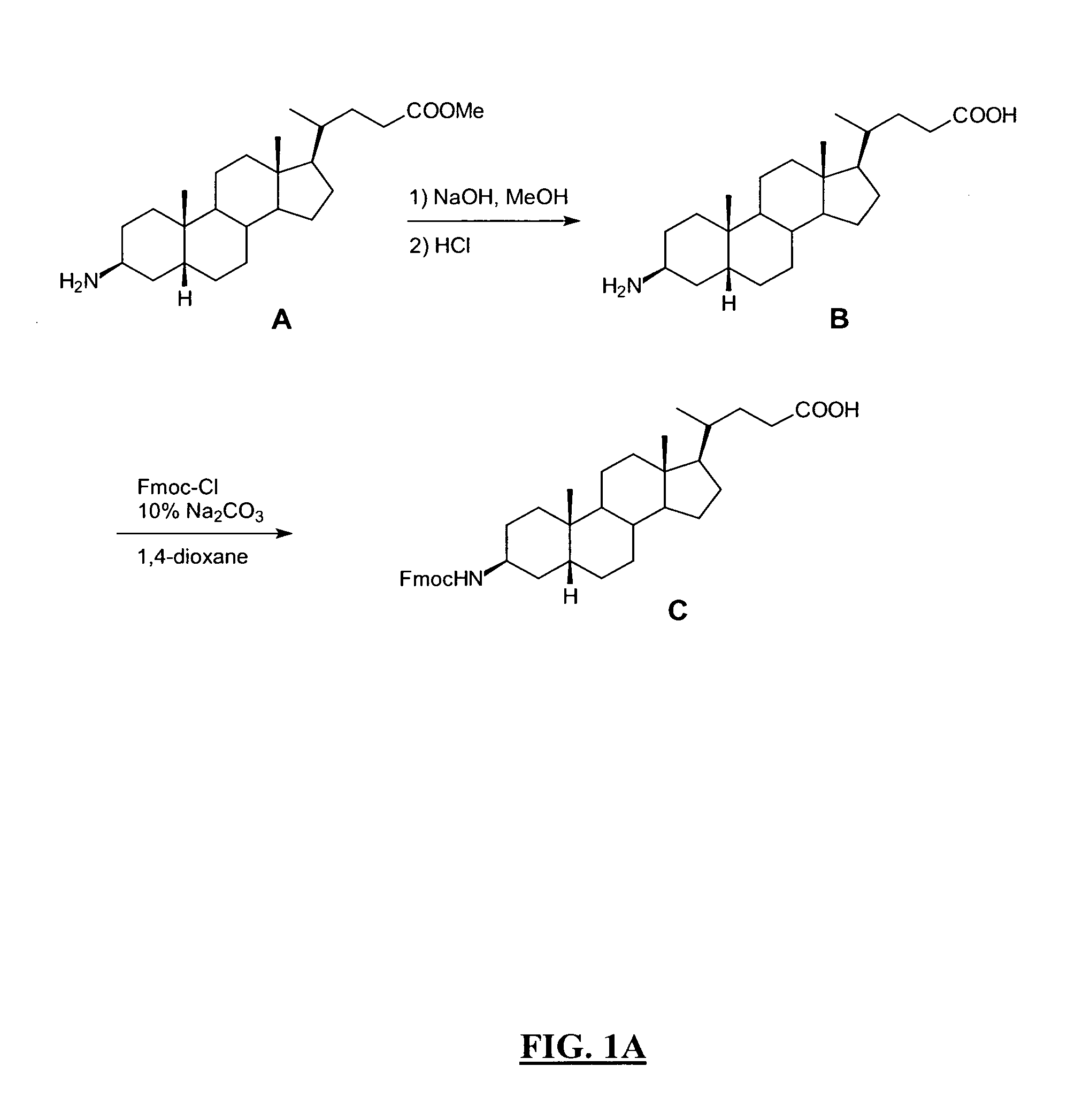
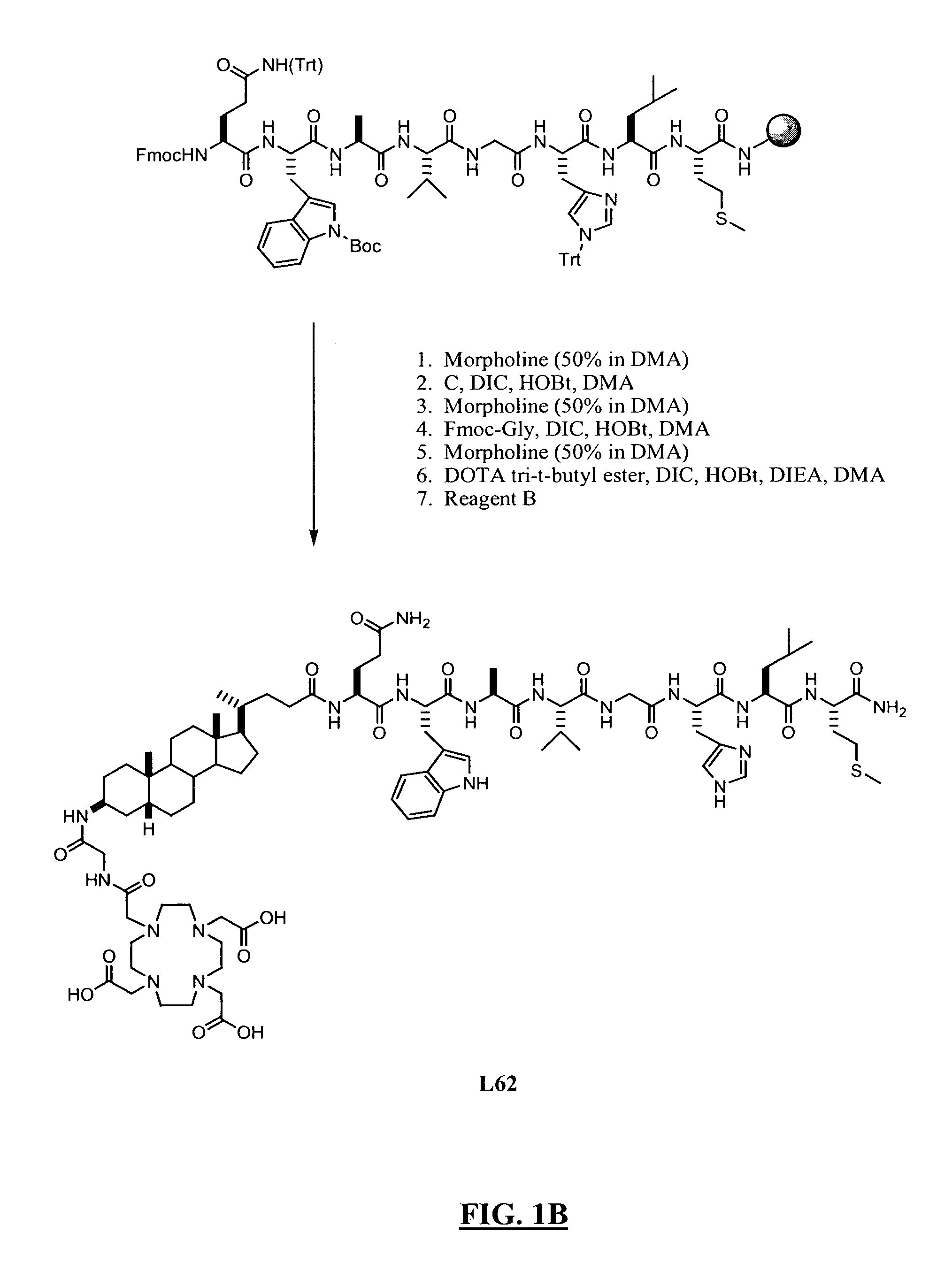
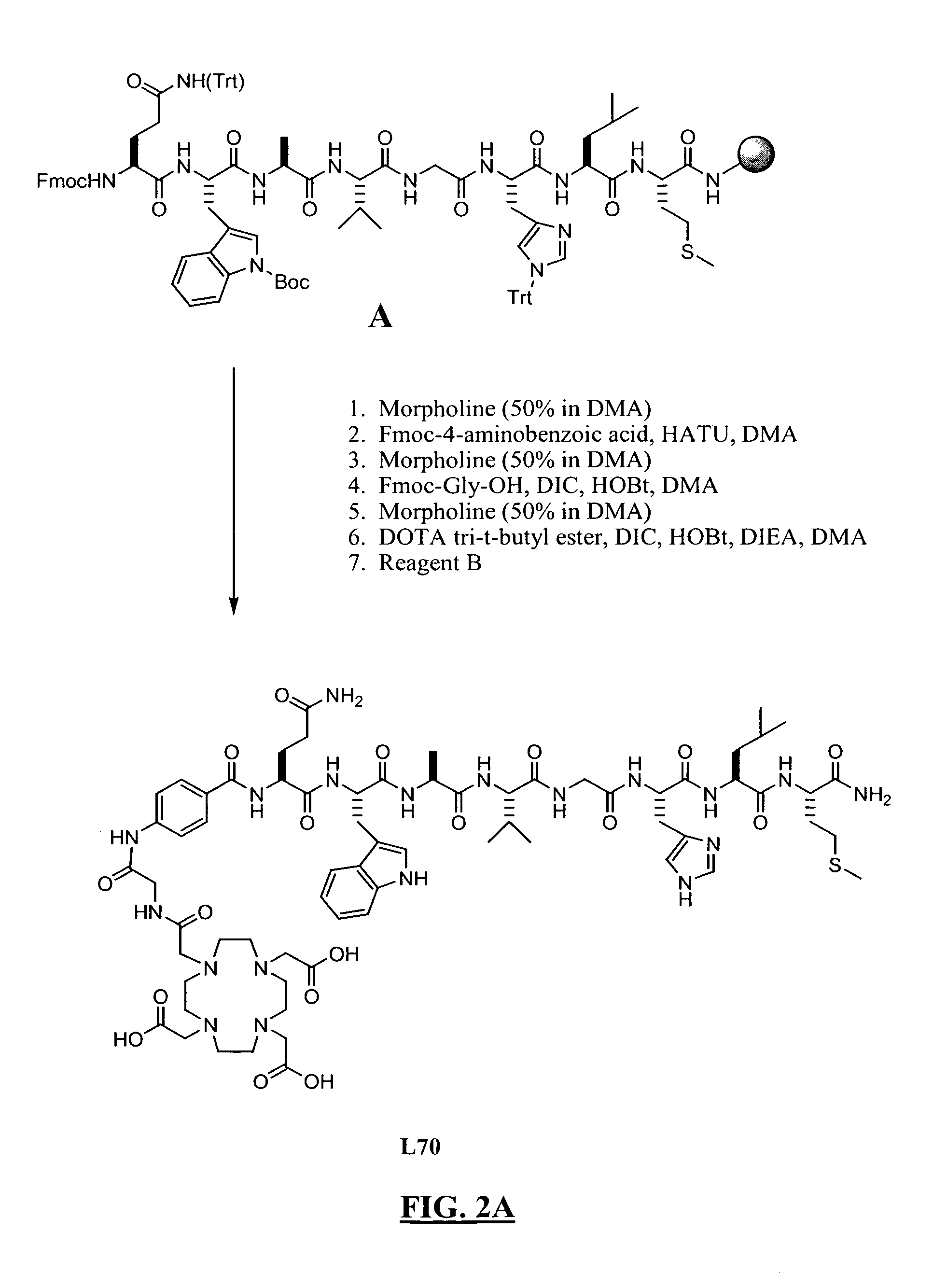
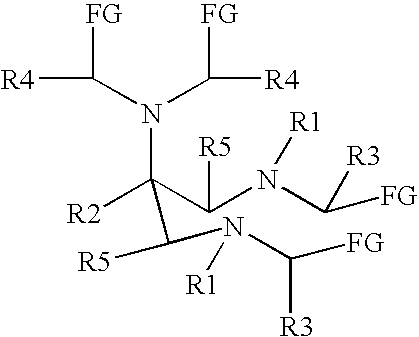
New and improved compounds for use in diagnostic imaging or therapy having the formula M-N—O—P-G, wherein M is a metal chelator having the structure: wherein R1-R5 and FG are as defined herein (in the form complexed with a metal radionuclide or not), N—O—P is the linker containing at least one non-alpha amino acid with a cyclic group, at least one substituted bile acid or at least one non-alpha amino acid, and G is the GRP receptor targeting peptide. In the preferred embodiment, M is an Aazta metal chelator or a derivative thereof. Methods for imaging a patient and / or providing radiotherapy or phototherapy to a patient using the compounds of the invention are also provided. Methods and kits for preparing a diagnostic imaging agent from the compound is further provided. Methods and kits for preparing a radiotherapeutic agent are further provided. Novel methods of treating prostate tumors or of delaying the progression of prostate tumors are also provided, including, methods of treating bone or soft tissue metastases of prostate cancer, methods for treating hormone sensitive and hormone refractory prostate cancer, methods for delaying the progression of hormone sensitive prostate cancer, for facilitating combination therapy in patients with hormone sensitive prostate cancer and for decreasing aberrant vascular permeability in patients with hormone sensitive prostate cancer.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Rapid Acting Drug Delivery Compositions
Drug formulations for systemic drug delivery with improved stability and rapid onset of action are described herein. The formulations may be administered via buccal administration, sublingual administration, pulmonary delivery, nasal administration, subcutaneous administration, rectal administration, vaginal administration, or ocular administration. In the preferred embodiments, the formulations are administered sublingually or via subcutaneous injection. The formulations contain an active agent and one or more excipients, selected to increase the rate of dissolution. In the preferred embodiment, the drug is insulin, and the excipients include a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Following administration, these formulations are rapidly absorbed by the oral mucosa when administered sublingually and are rapidly absorbed into the blood stream when administered by subcutaneous injection. In one embodiment, the composition is in the form of a dry powder. In another embodiment, the composition is in the form of a film, wafer, lozenge, capsule, or tablet. In a third embodiment, a dry powdered insulin is mixed with a diluent containing a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, such as water or saline, a metal chelator such as EDTA and an acid such as citric acid. Devices for storing and mixing these formulations are also described.
Owner:BIODEL INC
Methods of inhibiting and treating bacterial biofilms by metal chelators
The invention presented herein provides methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment of bacterial infections. The methods are based on the discovery that depletion of bioavailable iron stimulates surface motility in bacteria thus inhibiting the ability of a bacterial population to develop into a biofilm.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Methods and compositions for preventing oxidative degradation of proteins
InactiveUS20050276823A1Improve the immunityExtend product shelf lifePharmaceutical delivery mechanismImmunoglobulinsScavengerProtein oxidation
Methods and compositions for preventing oxidative damage to proteins, particularly antibodies, are provided. The compositions include a combination of metal chelators, such as DTPA, EGTA, and / or DEF, and can further include one or more free radical scavengers, particularly scavengers of oxygen radicals. Methods for enhancing protein stability using the compositions of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:MEDAREX INC
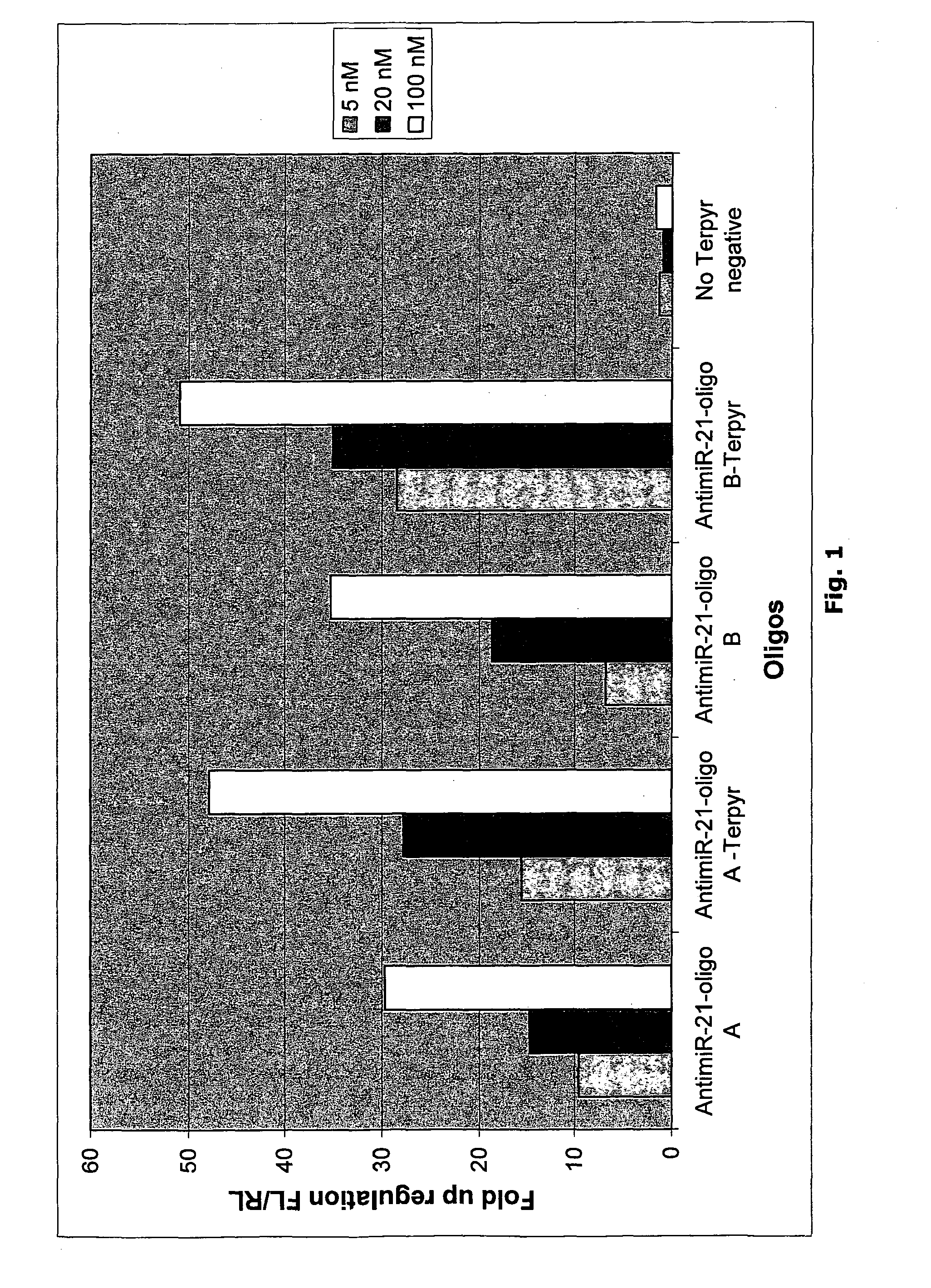
Mediated cellular delivery of lna oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20100035968A1Reduce deliveryOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesOligonucleotideChemistry
The present invention relates to novel modified oligomeric compounds and to methods of making and using such compounds. The invention further relates to methods of enhancing the cellular uptake of oligomeric compounds comprising conjugating a metal chelator to those.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
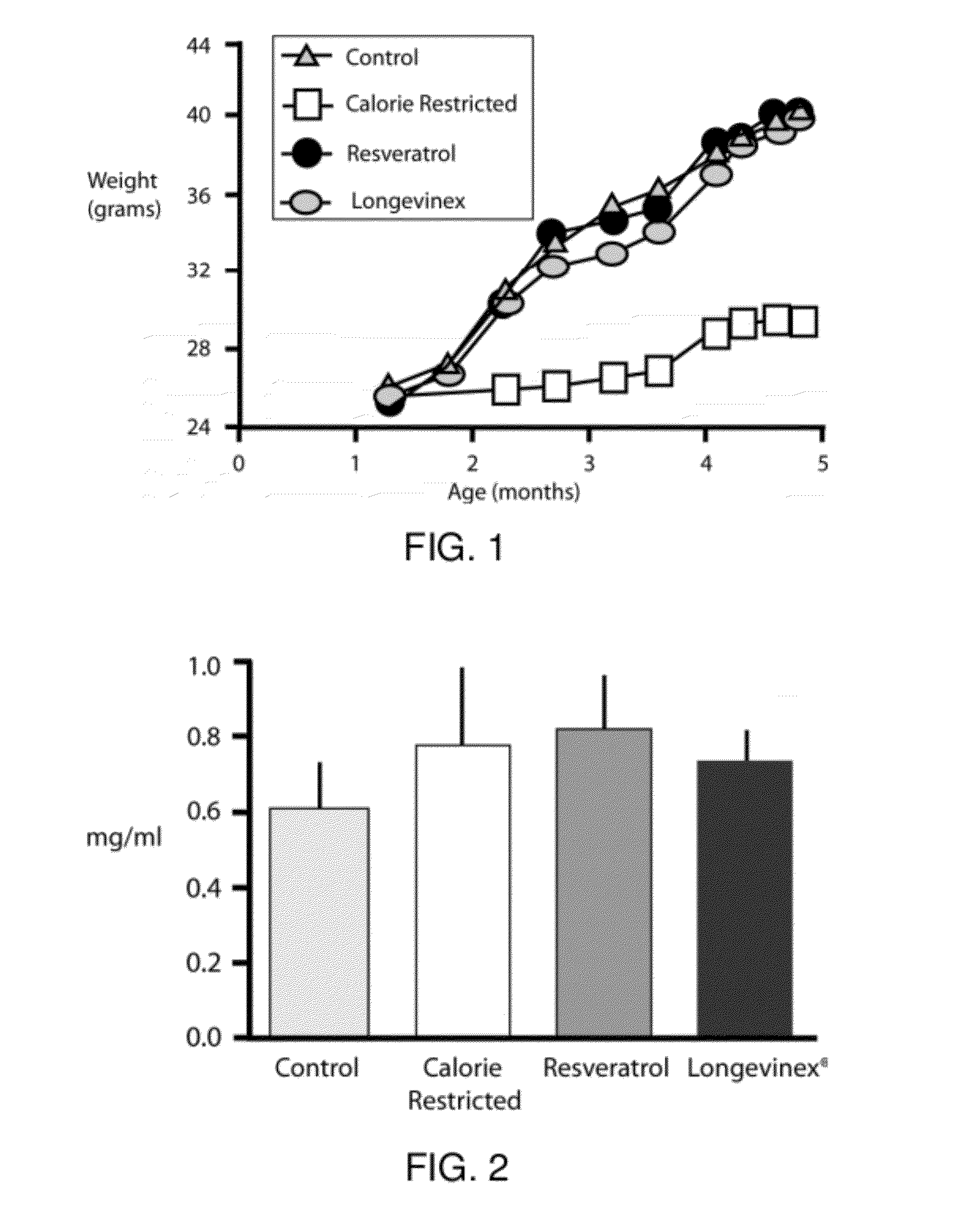
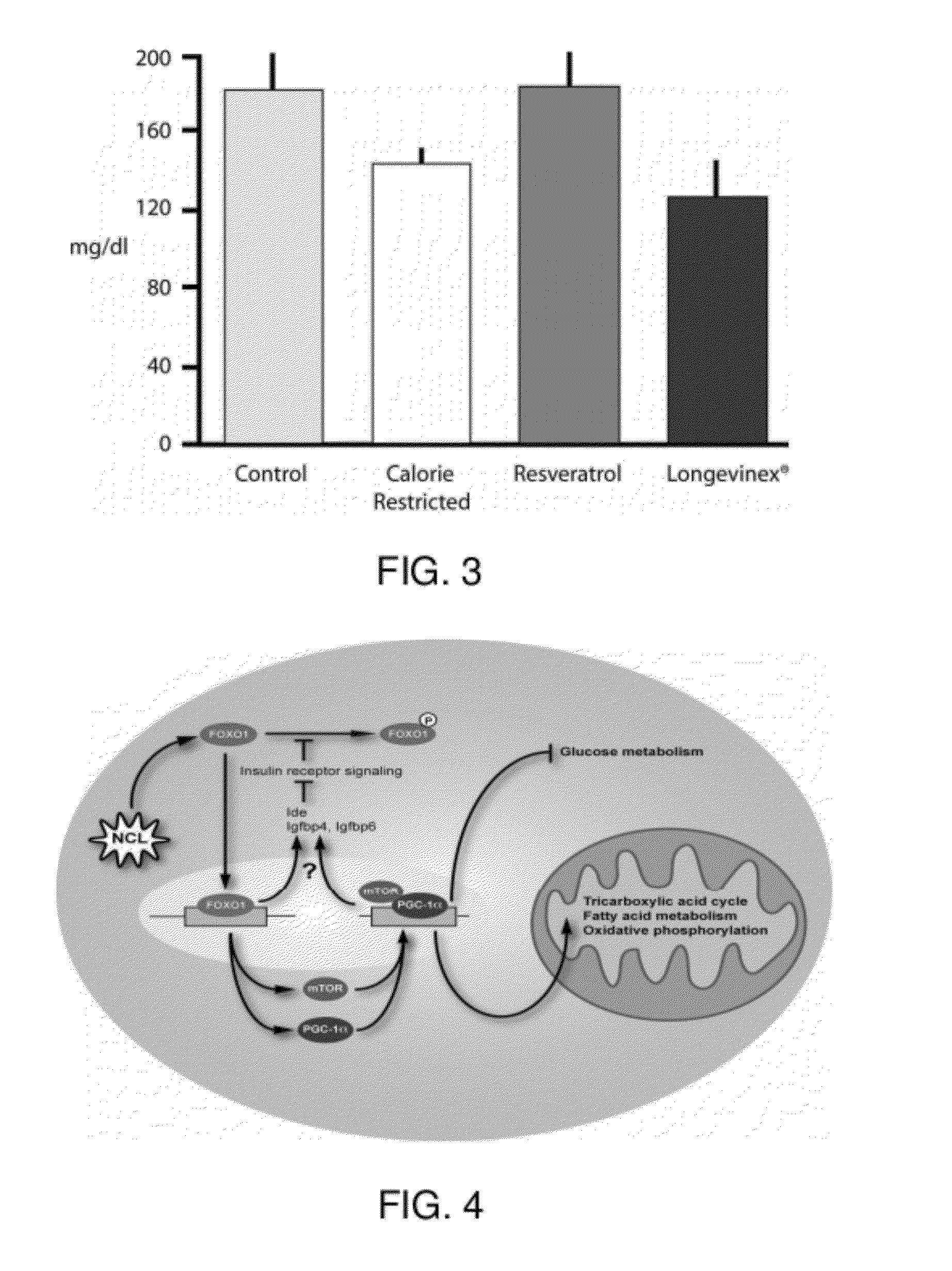
Resveratrol-Containing Compositions And Methods Of Use
A resveratrol-containing composition capable of providing a therapeutic benefit to a subject such as modulation of a biological activity, improving cell transplantation therapy, or improving macular degeneration or dystrophy treatments. The compositions comprise trans-resveratrol, a metal chelator, and one or more additional antioxidants such as phenolic antioxidants or vitamin D.
Owner:RESVERATROL PARTNERS
Polymer-metal chelator conjugates and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090092664A1Stability of disulfide bondPrevent oxidationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPenicillamineGelatin product
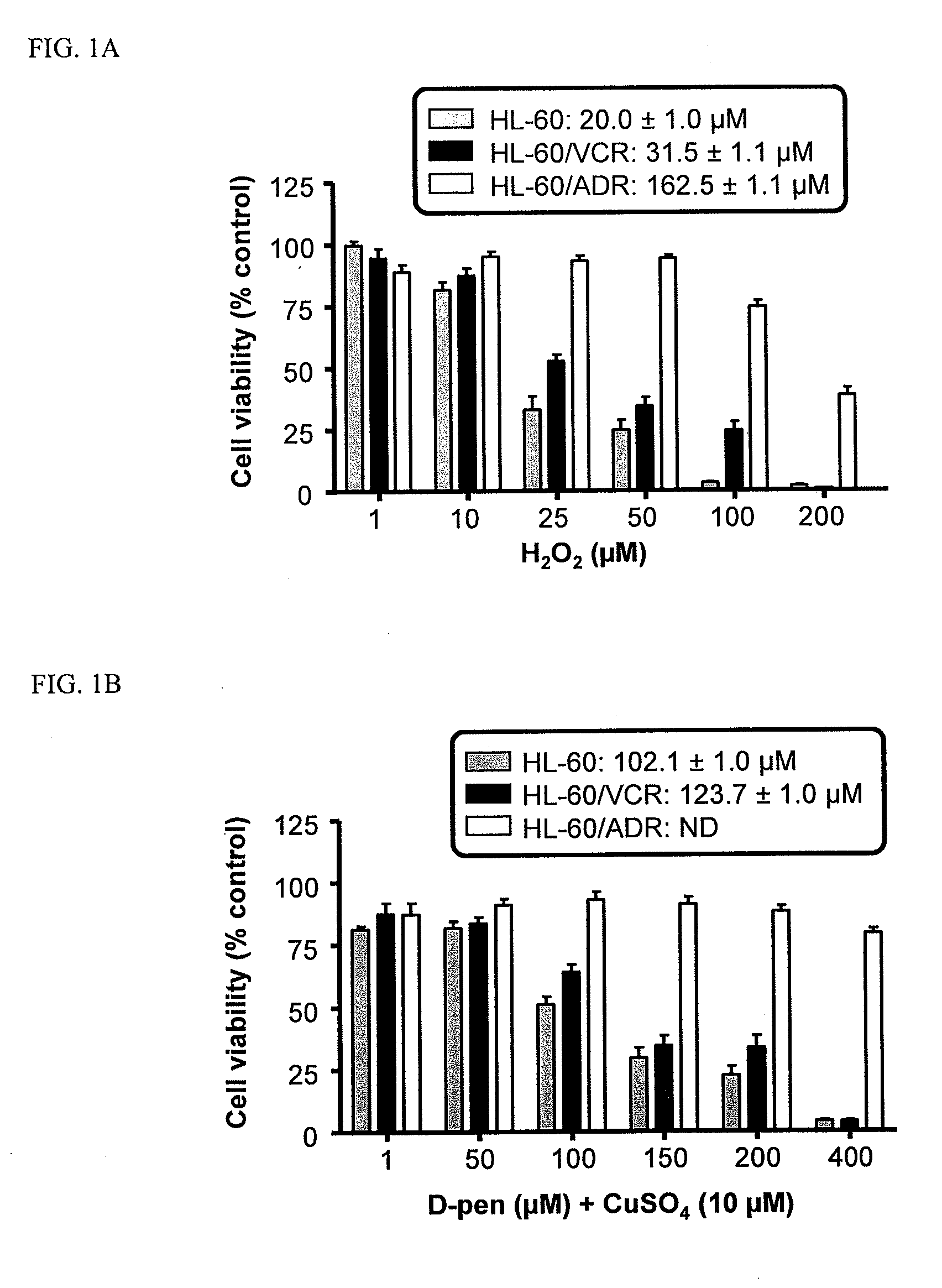
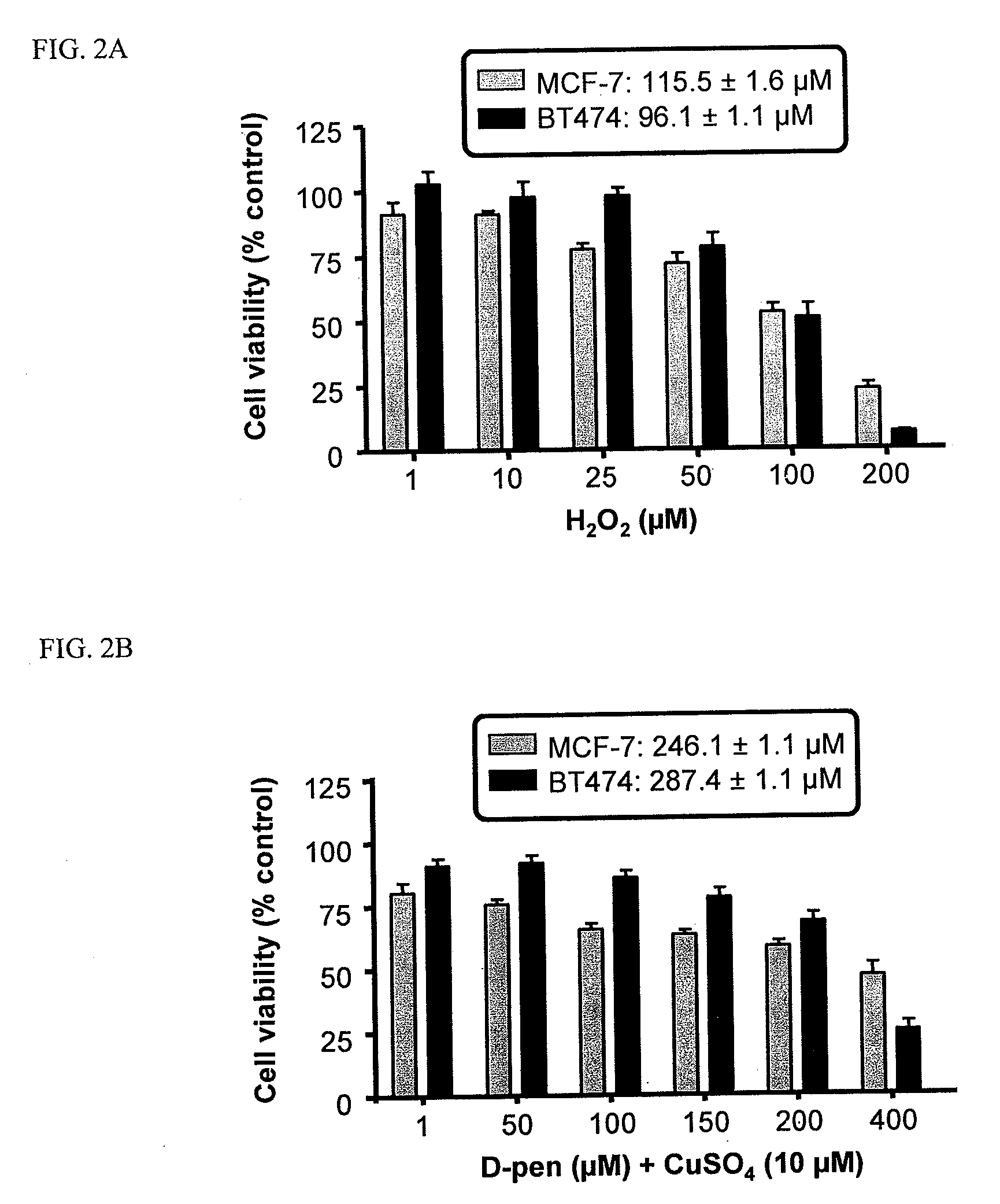
The present invention provides prodrugs comprising a polymer conjugated to a metal chelator via a disulfide bond. For example, D-penicillamine may be conjugated to a polymer (e.g., gelatin, chitosan, polyglutamic acid) via a linker, such as SPDP. Thus, the cellular delivery and pharmacokinetics of D-penicillamine can be substantially improved. Methods for the treatment of cancer using compositions of the present invention are also disclosed.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Polishing composition for noble metals
ActiveUS20060024967A1Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPhosphateOxidation state
The invention provides a polishing composition and a method of chemically-mechanically polishing a substrate comprising a noble metal, the polishing composition comprising (a) an oxidizing agent that oxidizes a noble metal, (b) an anion selected from the group consisting of sulfate, borate, nitrate, and phosphate, and (c) a liquid carrier. The invention further provides a polishing composition and a method of chemically-mechanically polishing a substrate comprising ruthenium, the polishing composition comprising (a) an oxidizing agent that oxidizes ruthenium above the +4 oxidation state, (b) a polishing additive selected from the group consisting of metal sequestering polymers, metal chelators, organic thiols, compounds that reduce ruthenium tetraoxide, lactones, and α-hydroxycarbonyl compounds.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
Gastrin releasing peptide compounds
InactiveUS7226577B2Peptide/protein ingredientsDigestive systemGastrin-releasing peptideImaging agent
New and improved compounds for use in radiodiagnostic imaging or radiotherapy having the formula M-N-O-P-G, wherein M is the metal chelator (in the form complexed with a metal radionuclide or not), N-O-P is the linker, and G is the GRP receptor targeting peptide. Methods for imaging a patient and / or providing radiotherapy to a patient using the compounds of the invention are also provided. A method for preparing a diagnostic imaging agent from the compound is further provided. A method for preparing a radiotherapeutic agent is further provided.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Gastrin releasing peptide compounds
InactiveUS20060018830A1Minimizing interference signalHigh quantum yieldBiocideCarbamic acid derivatives preparationGastrin-releasing peptideImaging agent
New and improved compounds for use in diagnostic imaging or therapy having the formula M-N-O-P-G, wherein M is a metal chelator having the structure: wherein R1-R5 and FG are as defined herein (in the form complexed with a metal radionuclide or not), N-O-P is the linker containing at least one non-alpha amino acid with a cyclic group, at least one substituted bile acid or at least one non-alpha amino acid, and G is the GRP receptor targeting peptide. In the preferred embodiment, M is an Aazta metal chelator or a derivative thereof. Methods for imaging a patient and / or providing radiotherapy or phototherapy to a patient using the compounds of the invention are also provided. Methods and kits for preparing a diagnostic imaging agent from the compound is further provided. Methods and kits for preparing a radiotherapeutic agent are further provided.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
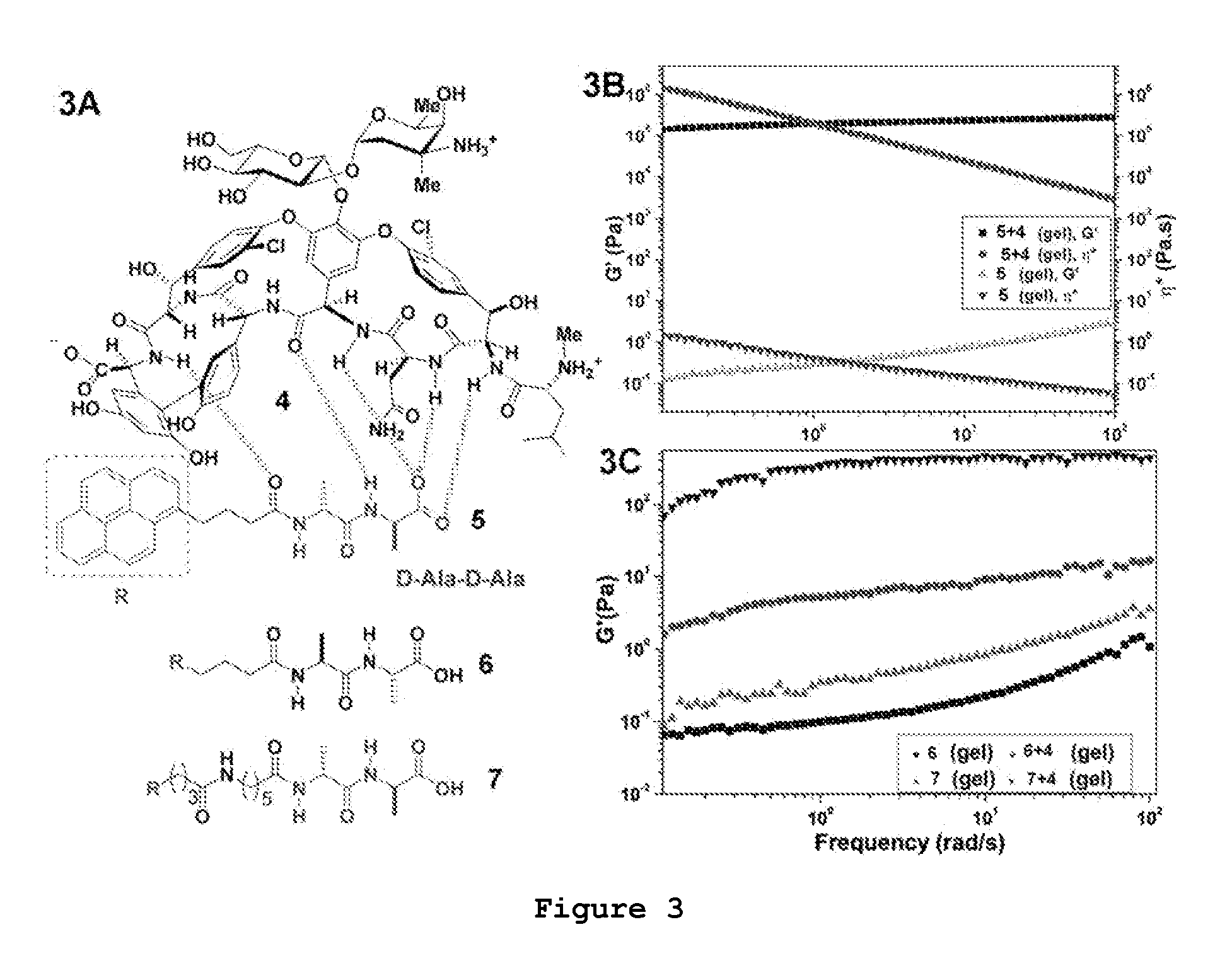
Multifunctional Supramolecular Hydrogels as Biomaterials
The present invention provides supramolecular hydrogels having a three-dimensional, self-assembling, elastic, network structure comprising non-polymeric, functional molecules and a liquid medium, whereby the functional molecules are noncovalently crosslinked. The functional molecules may be, for instance, anti-inflammatory molecules, antibiotics, metal chelators, anticancer agents, small peptides, surface-modified nanoparticles, or a combination thereof. Applications of the present invention include use of the supramolecular hydrogel, for instance, as a biomaterial for wound healing, tissue engineering, drug delivery, and drug / inhibitor screening.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Remediation of contaminates including low bioavailability hydrocarbons
InactiveUS7056061B2Solid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationChemical reactionHydrocotyle bowlesioides
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
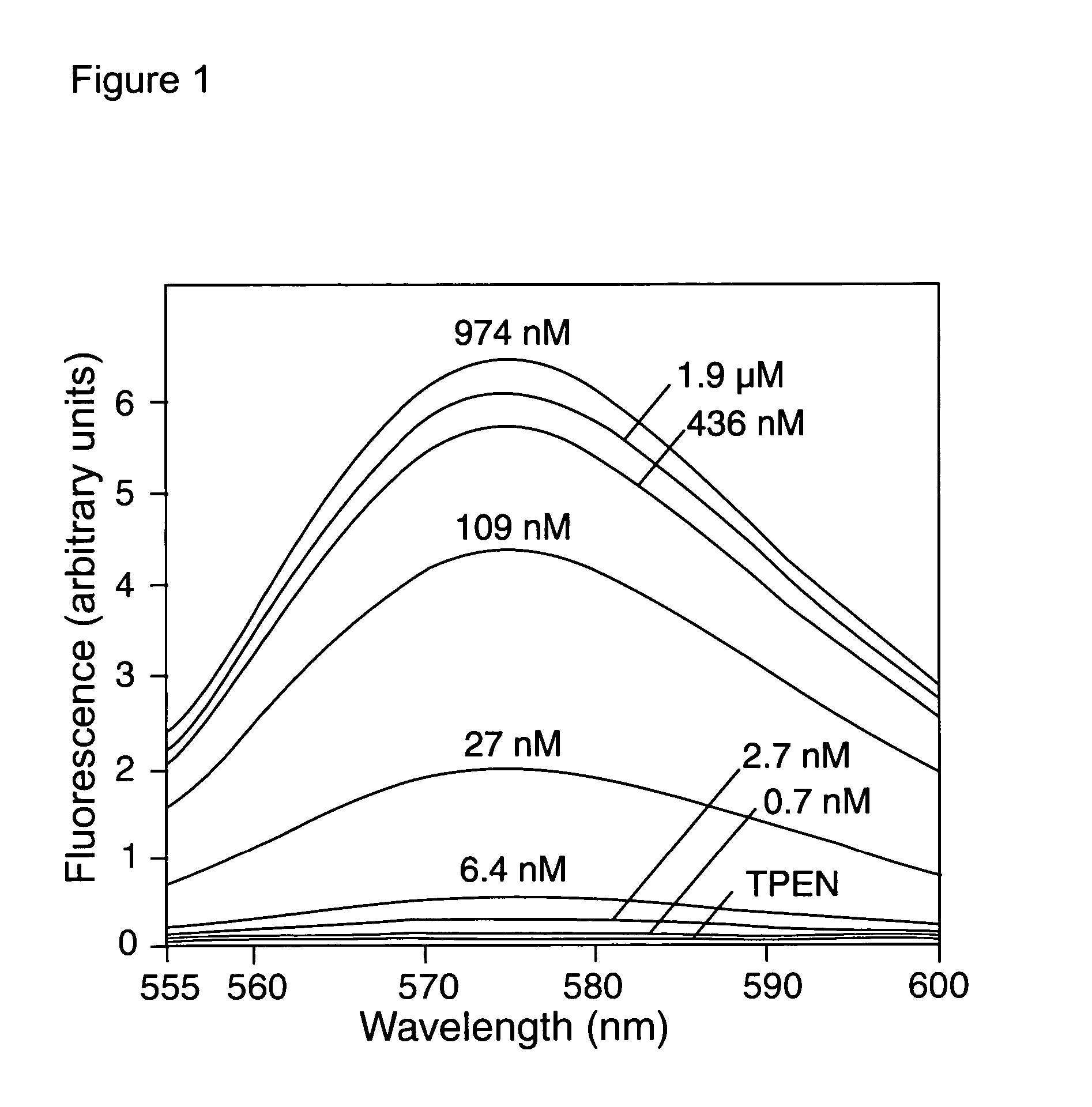
Zinc binding compounds and their method of use
InactiveUS20050250214A1Efficient ConcentrationAnalysis using chemical indicatorsOrganic chemistryMetal chelateZinc binding
The present invention provides a metal chelator and methods that facilitate binding, detecting, monitoring and quantitating of zinc ions in a sample. The metal chelating moiety of the zinc-binding compound is an analog of the well-known calcium chelator, BAPTA (1,2-bis(2-aminophenoxy)ethane-N,N,N′N′-tetraacetic acid), wherein the chelating moiety has been modified from a tetraacetic acid moiety to a tri- di- or monoacetic moiety. This change in acetic acid groups on the metal chelating moiety results in the selective bindings of zinc ions in the presence of calcium ions, both of which are present in biological fluids and intracellular cytosolic fluid and organelles.
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
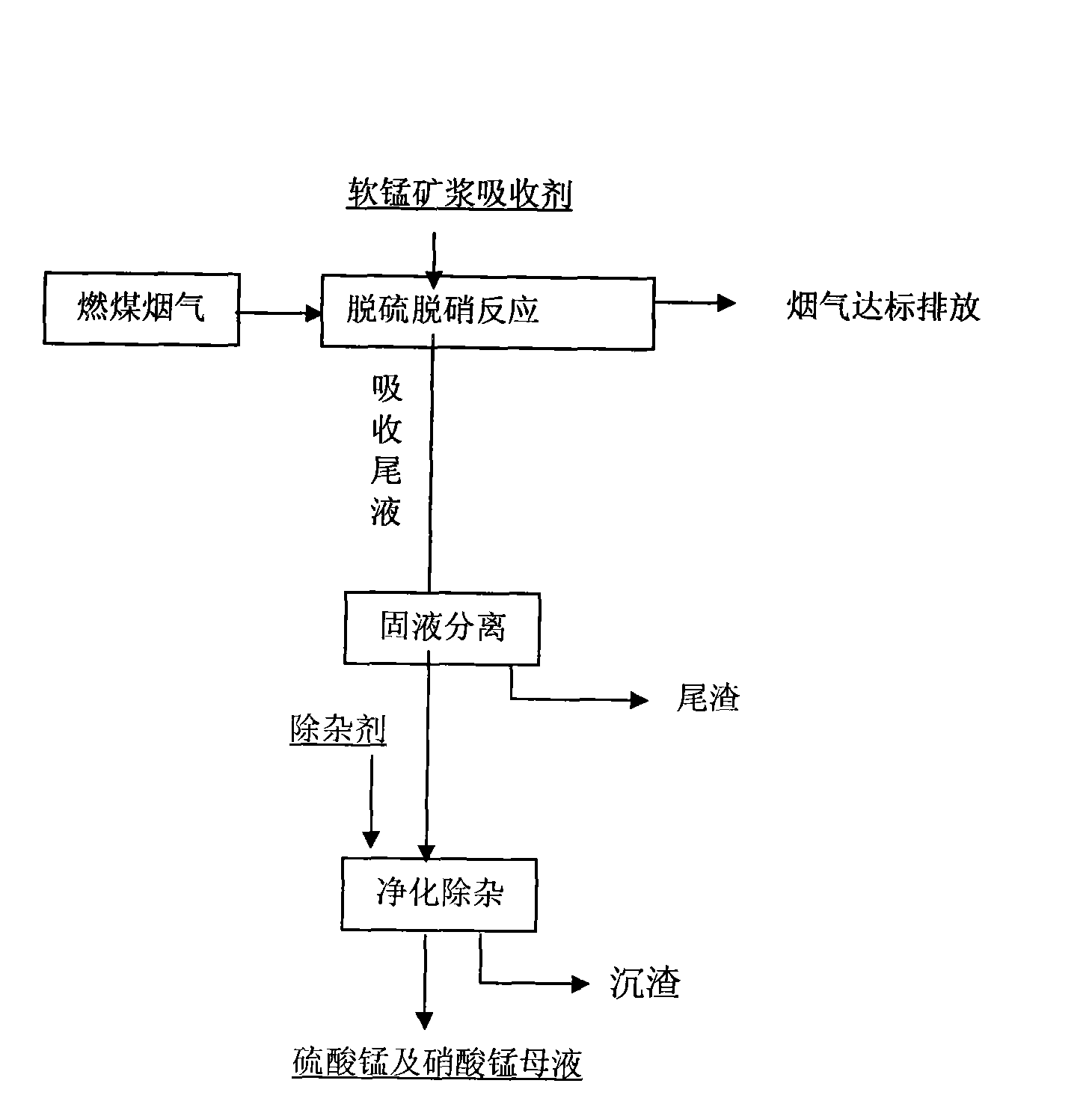
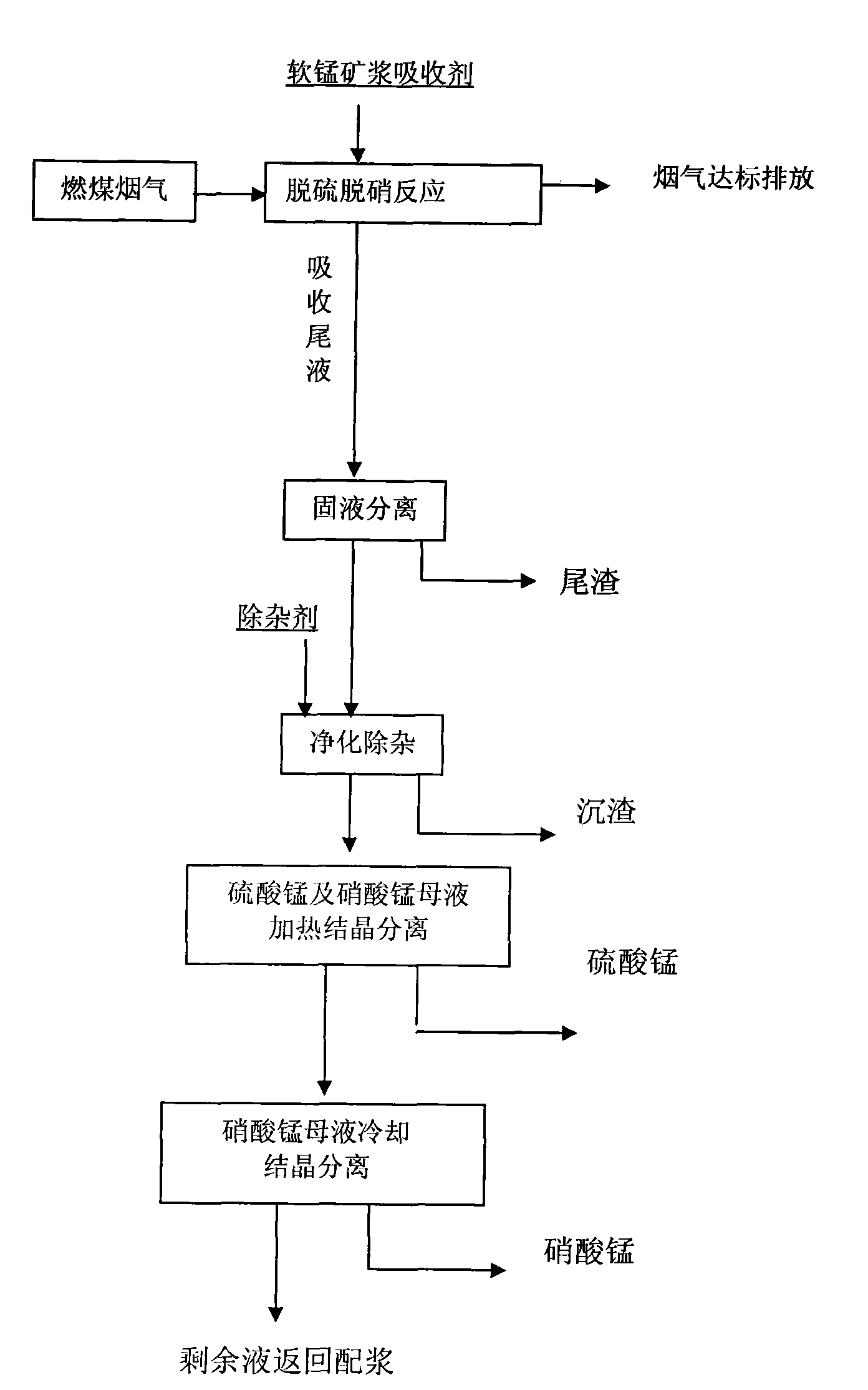
Synchronous desulphrization and denitration method of flue gas pyrolusite pulp for reclamation
ActiveCN101574617ARich reservesLow priceDispersed particle separationProcess efficiency improvementSolubilityPyrolusite
The invention discloses a synchronous desulphrization and denitration method of flue gas pyrolusite pulp for reclamation. The method mainly comprises the following steps: pyrolusite, water and metal-chelator are prepared into pulp which is taken as an absorbing agent; sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides in the flue gas are synchronously absorbed and removed by the absorbing agent; the flue gas is discharged when the purification reaches a standard; the primary product of the mixed mother solution of manganese sulfate and manganese nitrate is obtained after absorbing tail solution is purified; and by utilizing the different solubility of manganese sulfate and manganese nitrate at same temperature, the mixed mother solution is heated firstly to cause the manganese sulfate therein to be crystallized and separated, next, the left mother solution is cooled to cause the manganese nitrate therein to be crystallized and separated, and the left solution is returned to preparation pulp for recycling. No waster water is discharged in the whole process, thereby achieving the purposes of controlling waste by waste, recycling sulfur resources and improving the comprehensive utilization value of pyrolusite. The method is characterized by high desulphrization and denitration efficiency and manganese utilization rate, little secondary pollution, obvious economic benefit and the like.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Heavy metal pollutant immobilized reagent composition and immobilization treatment method
InactiveCN102921142AReduce usageReduce active (migratable) heavy metal contentContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersPhosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of soil environment treatment, and particularly relates to a heavy metal immobilization chemical reagent composition and a treatment method of heavy metal in immobilization polluted soil. The immobilized reagent composition comprises phosphate chemical compound of 5-70%, metal sulfide of 1-60%, metal oxide of 5-80%, strong alkali and weak acid salt of 5-65%, metal stabilizers of 0.1-15% and metal chelator of 0.1-10%. The invention further provides a method of restoring heavy metal polluted soil in an immobilization mode by immobilized reagents. The immobilized reagents can enable various heavy metal pollutants in the polluted soil to be immobilized, the content of activated state (transportable) heavy metal in soil is lowered, and restoration and treatment to the heavy metal polluted soil are achieved. The heavy metal pollutant immobilized reagent composition and the immobilization treatment method have the advantages of being good in immobilization effect, simple and easy in operating process, low in cost, and free of secondary pollution and the like.
Owner:LAIWO SAGACITY GREEN TECH BEIJING CO LTD
Methods of inhibiting and treating bacterial biofilms by metal chelators
The invention presented herein provides methods and compositions for the prevention and treatment of bacterial infections. The methods are based on the discovery that depletion of bioavailable iron stimulates surface motility in bacteria thus inhibiting the ability of a bacterial population to develop into a biofilm.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
Stabilized albuterol compositions and method of preparation thereof
InactiveUS20040109826A1Extended shelf lifeBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSalbutamolBuffering agent
Stabilized albuterol compositions are provided. The compositions are aqueous inhalation compositions containing albuterol; a buffer, such as citric acid; and a metal chelator, such as EDTA.
Owner:DEY
Preparation method of transition metal doped carbon fluorescent quantum dots
The invention relates to a preparation method of transition metal doped carbon fluorescent quantum dots. According to the method, a metal chelator and transition metal salt are dissolved in an organicphase and water which are incompatible with each other, then, a heating reaction is conducted, concentration and purification are performed after the reaction, and transition metal doped carbon fluorescent quantum dots with different solubility are prepared. The method is convenient to operate, doping of carbon fluorescent quantum dots with metal ions can be realized without harsh reaction conditions or large instruments. The obtained carbon dots have multiple different characteristics according to different types of doping metal ions and different solvents. The prepared carbon dots have great application value in preparation of bio-labeling sensing and medical imaging, photoelectric and light-emitting devices and the like due to these characteristics.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for hydrophobic-association cationic polyacrylamide
The invention relates to a preparation method for hydrophobic-association cationic polyacrylamide. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, adding distilled water, acrylyl oxyehtyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride monomer and acrylamide monomer to a reaction device, uniformly stirring the mateirals until the materials are completely dissolved into a monomer aqueous solution; secondly, adding proper solubilizer, metal-chelator and initator to the monomer aqueous solution, uniformly stirring the materials and regulating the pH value of the mixture; ventilating high-pure nitrogen gas to the reaction device for removing the air in the reaction device; thirdly, sealing the reaction device and then putting the sealed reaction device to a ultraviolet-light reaction device for carrying out a polymerization reaction to prepare hydrophobic-association cationic polyacrylamide colloid; and finally, purifying, washing and refining the colloid, and drying the treated colloid in a vacuum drying box and grinding the dried colloid to obtain the finished product. The preparation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the two monomers can be directly polymerized by an aqueous solution without adding surfactant, so that the process is simple, and the polymerization reaction time is short; moreover, the reaction process is free of temperature control, the energy consumption is reduced, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU HENGFENG FINE CHEM CO LTD
Gastrin releasing peptide compounds
InactiveUS7611692B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPeptide/protein ingredientsGastrin-releasing peptideImaging agent
New and improved compounds for use in diagnostic imaging or therapy having the formula M—N—O—P—G, wherein M is an optical label or a metal chelator (in the form complexed with a metal radionuclide or not), N—O—P is the linker, and G is the GRP receptor targeting peptide. Methods for imaging a patient and / or providing radiotherapy or phototherapy to a patient using the compounds of the invention are also provided. Methods and kits for preparing a diagnostic imaging agent from the compound is further provided. Methods and kits for preparing a radiotherapeutic agent are further provided.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
Vitamin C sustained-release pellets and method for preparing same
ActiveCN102908319AHigh drug loadingLarge particle sizeOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderSustained release pelletsVitamin C
A vitamin C sustained-release pellet applied to the vitamin C sustained-release preparation field and a method for preparing the same are disclosed. The vitamin C sustained-release pellet is composed of a vitamin C sustained-release pill and a sustained-release coating, wherein the vitamin C sustained-release pill is composed of a mother nucleus and a lamination layer, or composed of a vitamin C and vitamin C pill accessory, or composed of vitamin C; the sustained-release coating is composed of a sustained-release coating material and a sustained-release coating accessory, or composed of the sustained-release coating material; the vitamin C sustained-release pill accessory is one or two selected from a filler and a binder; the sustained-release coating accessory is one or two selected from a plasticizer and an antisticking agent; the weight percentage content of the vitamin C in the mother nucleus is the same as that in the lamination layer; and the filler is one or several selected from microcrystalline cellulose, powdered sugar, starch, dextrin and lactose. The vitamin C sustained-release pellet disclosed by the invention is simple in prescription, free of metal-chelator or antioxidant, great in unit volume drug loading capacity, good in stability and capable of keeping sustained release for a long time; and the preparation method of the vitamin C sustained-release pellet is short in operation time and low in cost.
Owner:SHENYANG NO 1 PHARMA FACTORY DONGBEI PHARMA GRP
Fluorogenic protein kinase substrates
The present invention relates to kinase sensors comprising a metal chelator and a fluorophore, where the chelator comprises a quinoline group and where the fluorophore is conjugated to the chelator. The invention also relates to methods of using these kinase sensors as well as kits comprising the kinase sensors.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Dry preparation method of transition metal doped carbon fluorescent quantum dot
The invention relates to a dry preparation method of transition metal doped carbon fluorescent quantum dots. According to the method, a metal chelator and transition metal salt are subjected to a thermal reaction in the absence of a solvent, and the transition metal doped carbon fluorescent quantum dots are prepared with extraction, centrifugation and dialysis methods after the reaction. The method is convenient to operate, doping of carbon fluorescent quantum dots with metal ions can be realized without harsh reaction conditions or large instruments, and the obtained carbon dots have good water solubility and wider fluorescence emission ranges. The obtained carbon dots have multiple different characteristics according to different types of doping metal ions and different solvents. The prepared carbon dots have great application value in preparation of bio-labeling sensing and medical imaging, photoelectric and light-emitting devices and the like due to these characteristics.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
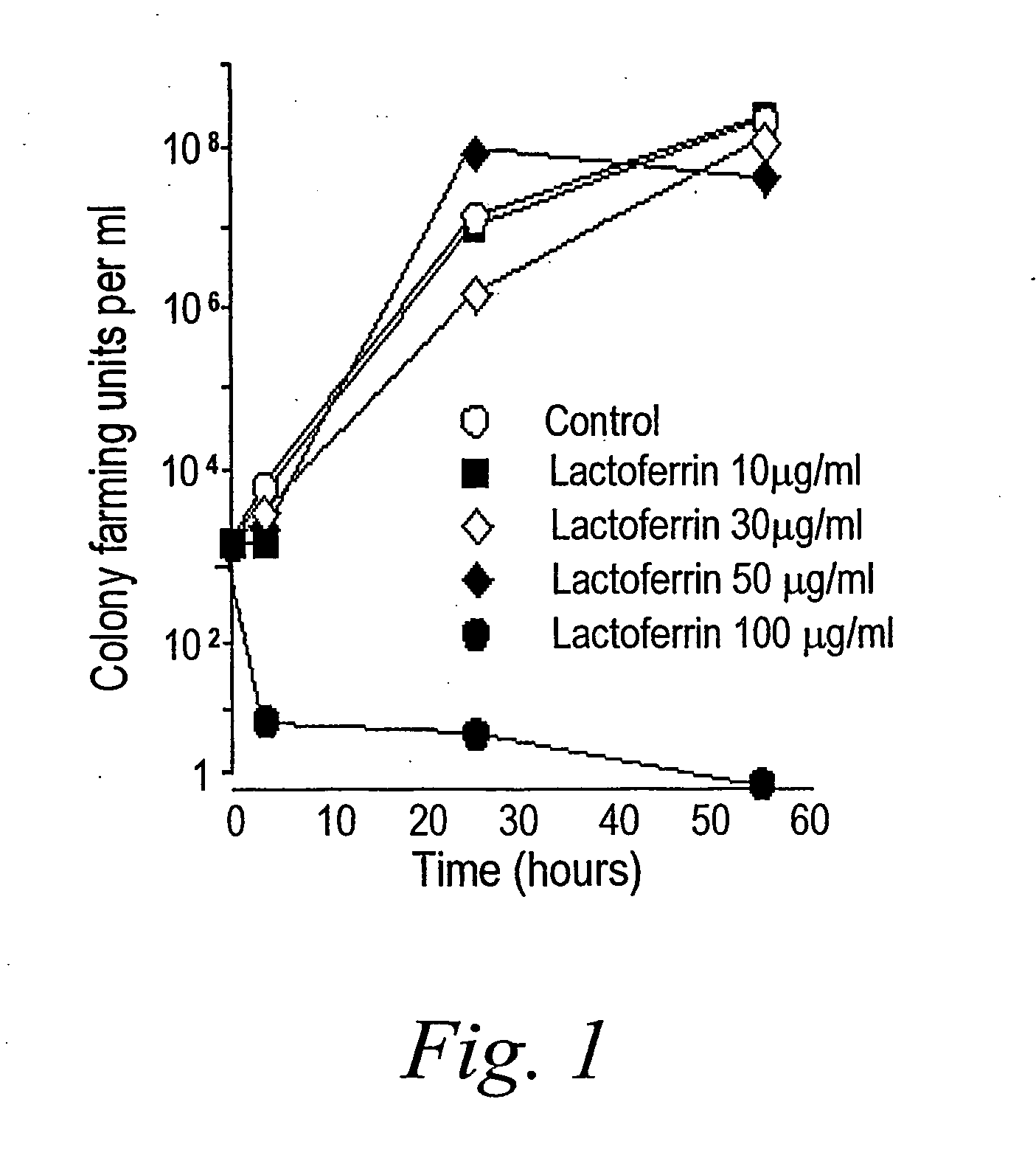
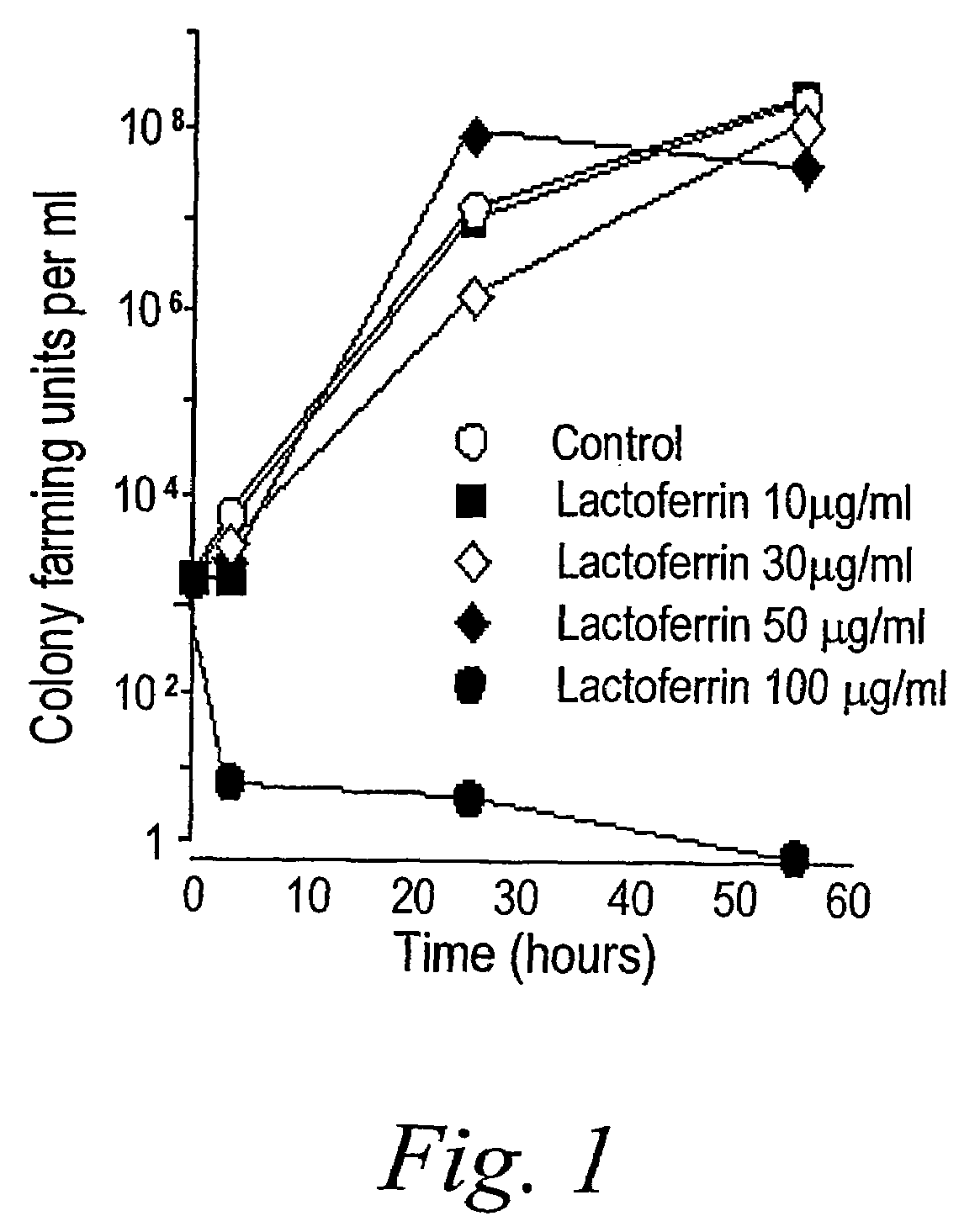
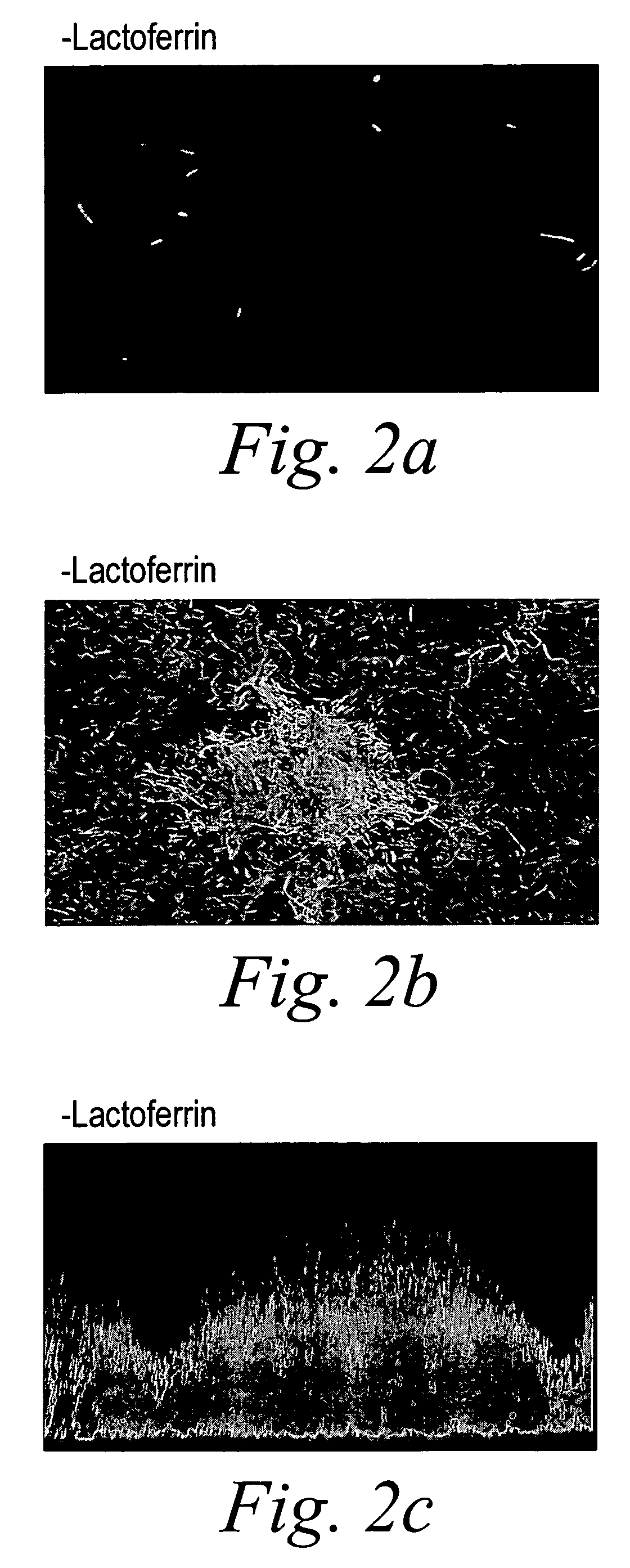
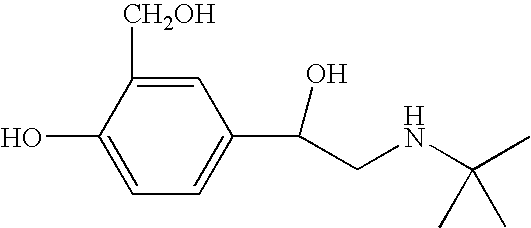
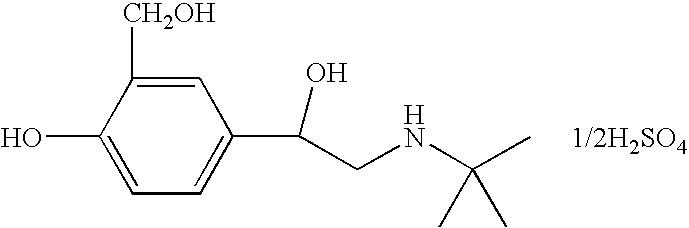
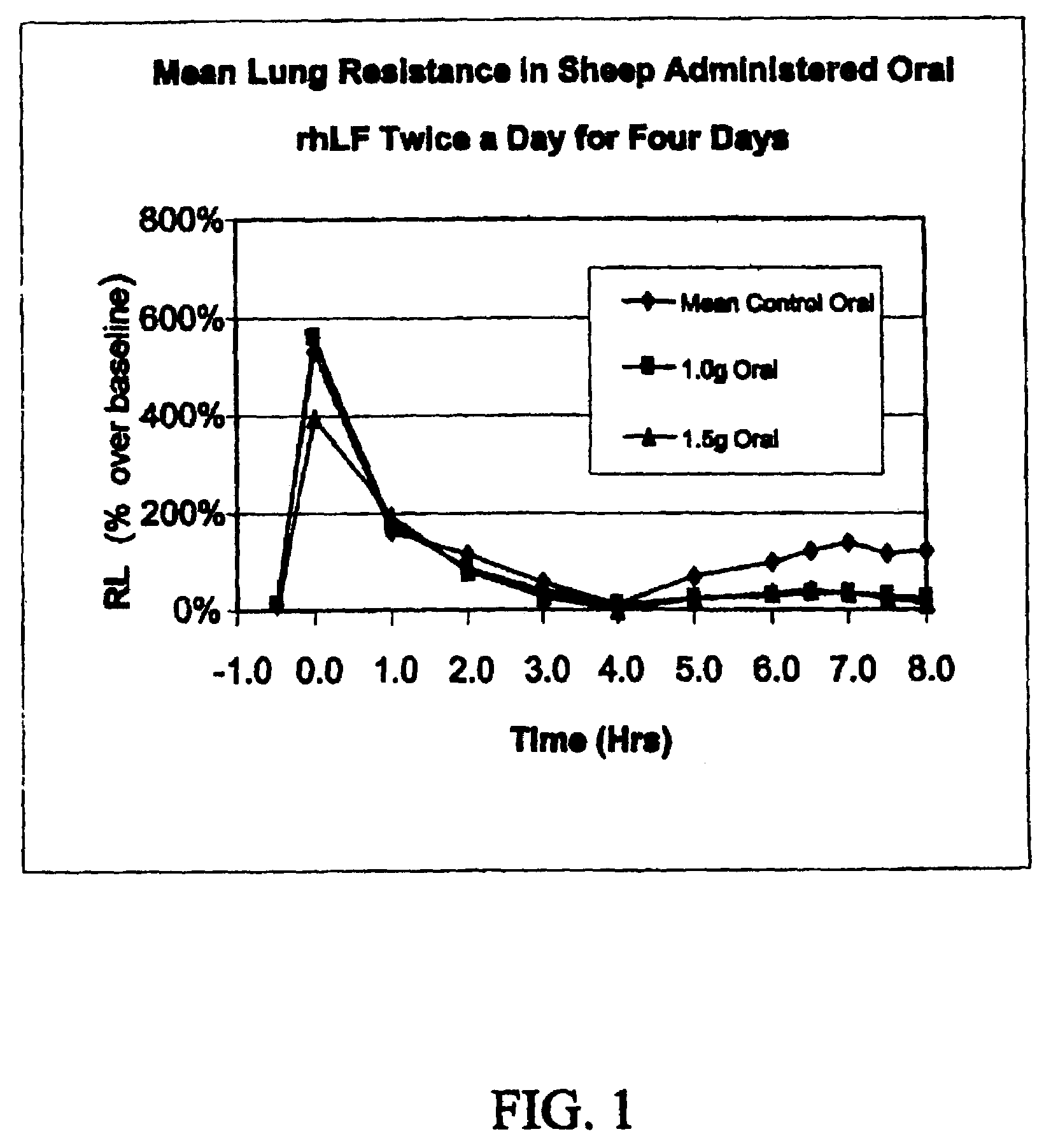
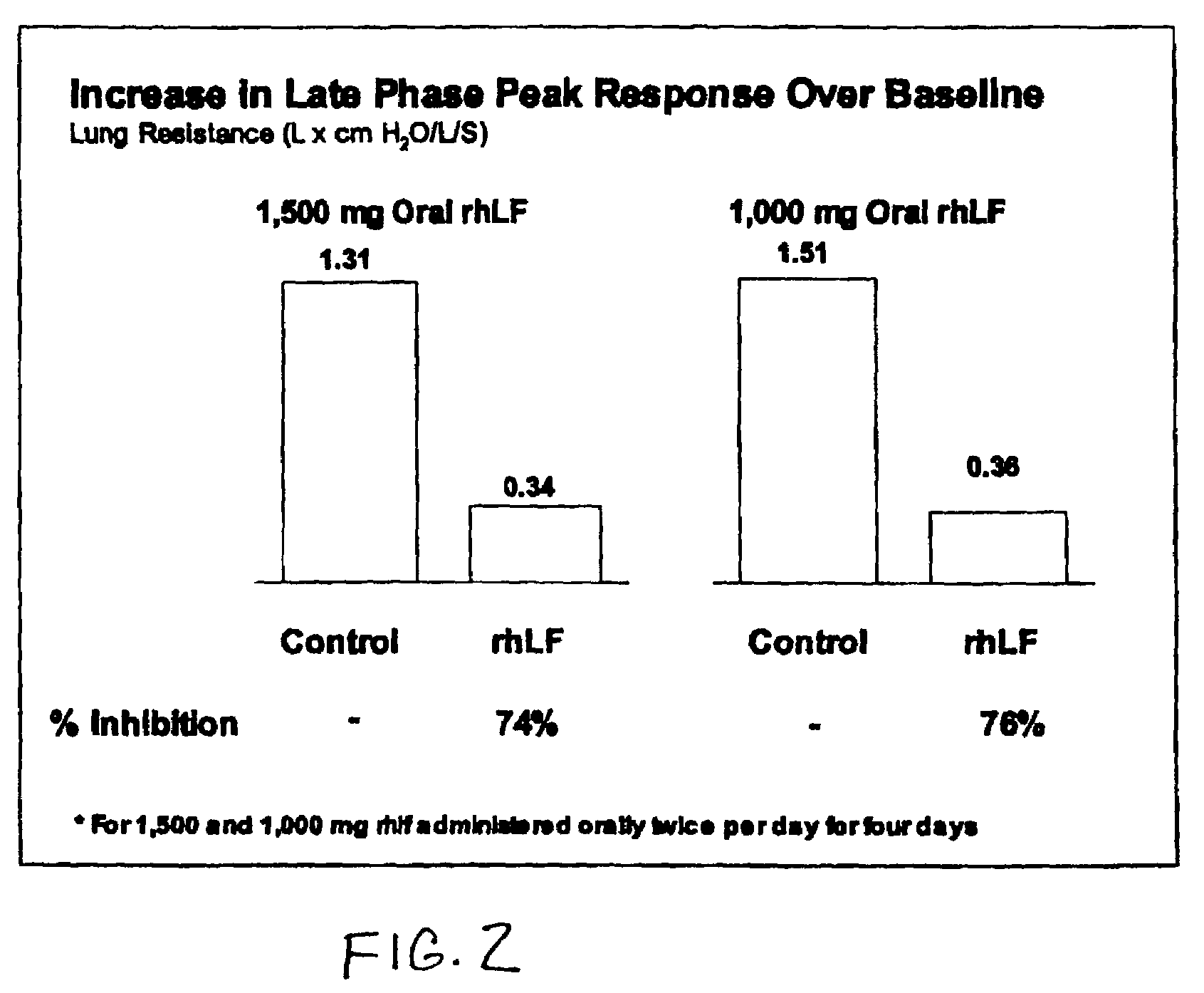
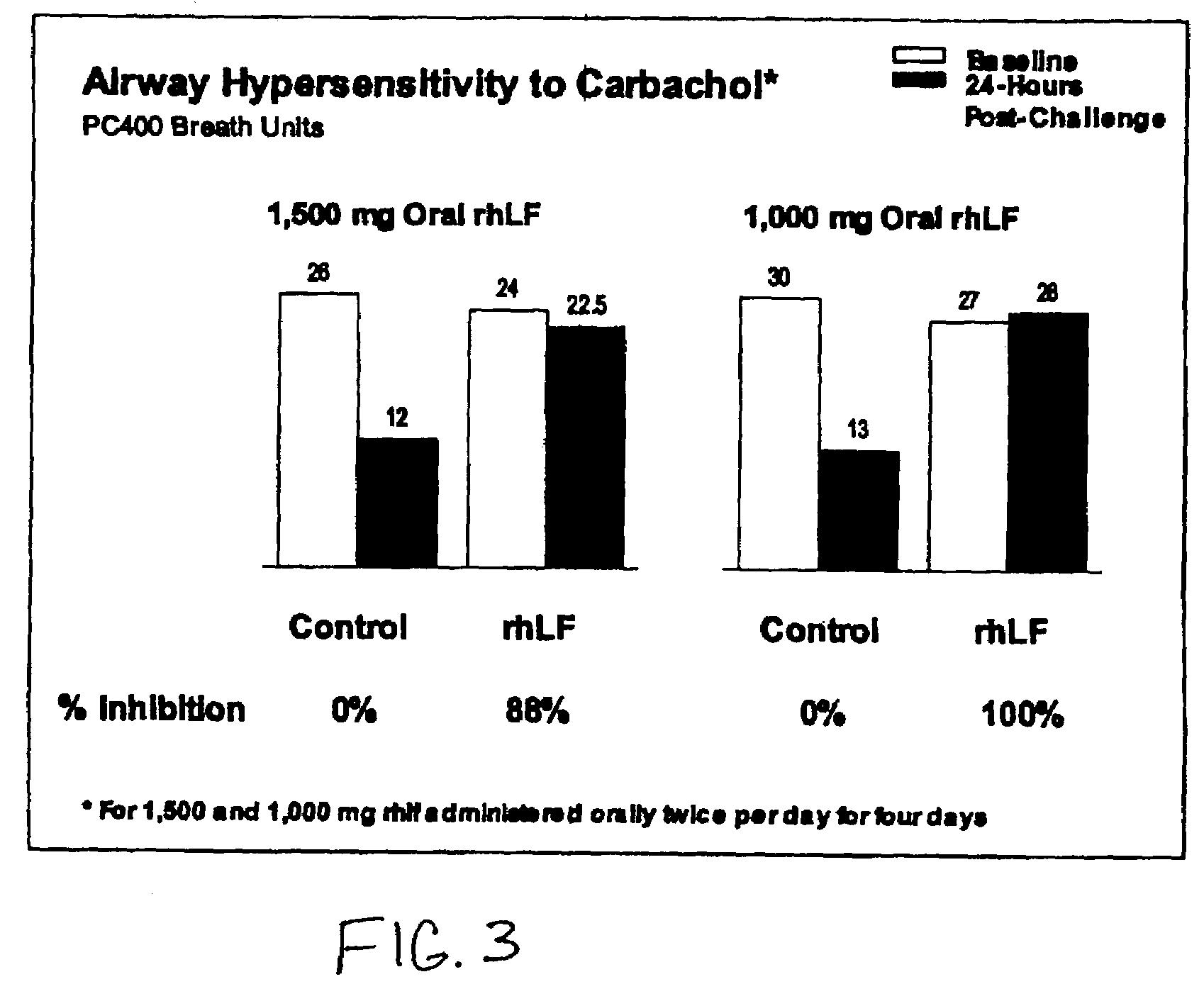
Oral lactoferrin in the treatment of respiratory disorders
InactiveUS7238661B2Increase productionEnhance immune responseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDiseaseNon allergic
The present invention relates to methods of treating an allergic or non-allergic respiratory disorder by administering orally a composition of lactoferrin alone or in combination with metal chelators to treat respiratory disorders.
Owner:AGENNIX
Nanometer-sized up-converting phosphor fluoride particles and process of preparation
Nanometer-scaled up-converting fluoride phosphor particles and processes of making them are disclosed. In the process, an aqueous solution consisting of soluble salts of rare-earth metal ions at a molar ratio of (yttrium, lanthanum or gadolinium): ytterbium:(erbium, holmium, terbium or thulium)=(70-90):(0-29):(0.001-15) is mixed a rare-earth metal chelator and a soluble fluoride salt to form precipitates, which are then annealed at an elevated temperature to produce nanometer-scaled up-converting fluoride phosphor particles. The particle size is between 35 nm and 200 nm, and can be controlled by the amount of the metal chelator added to the solution. The nanometer-sized particle is applicable to many biological assays.
Owner:CAPITAL BIOCHIP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com