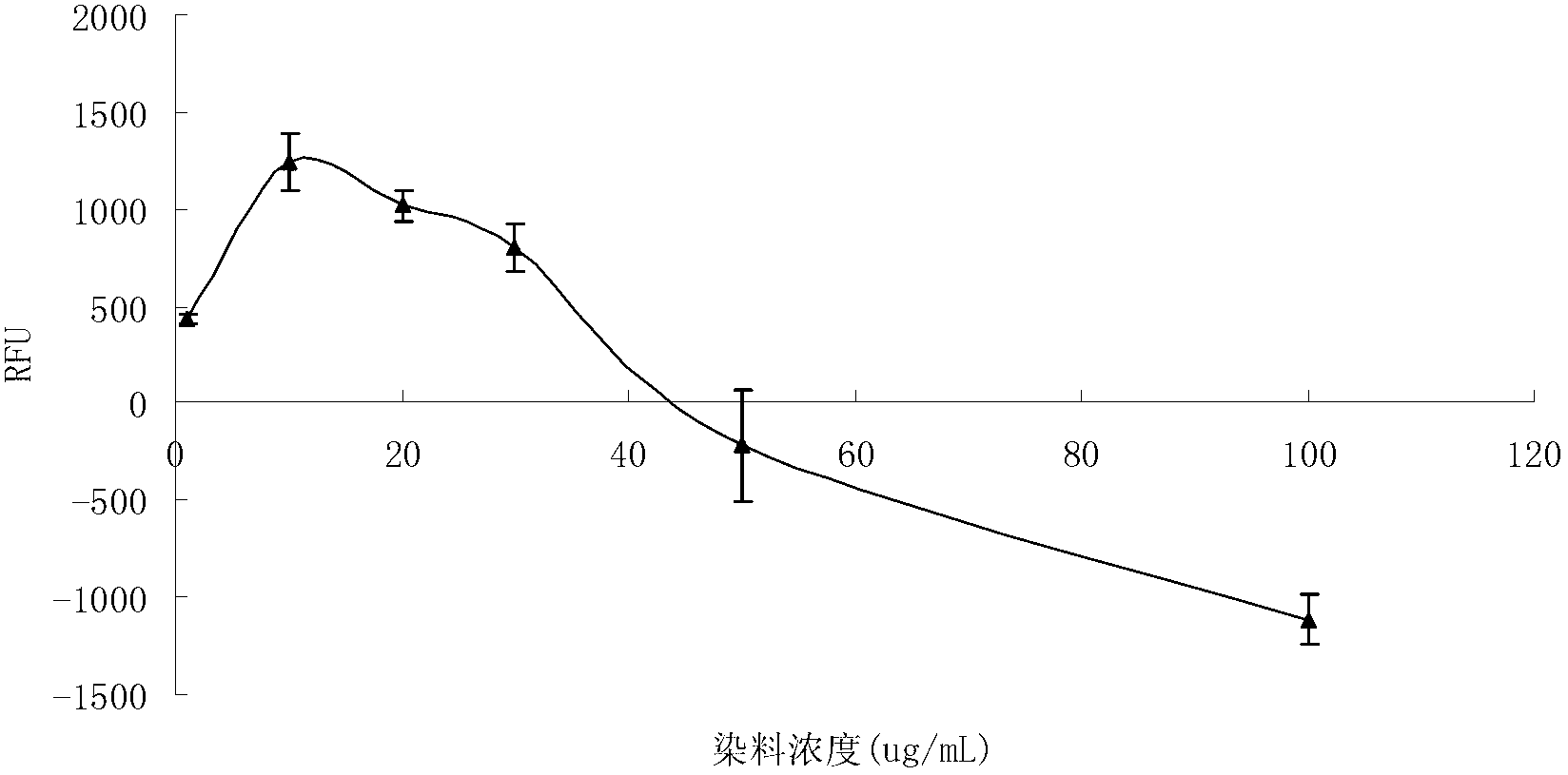
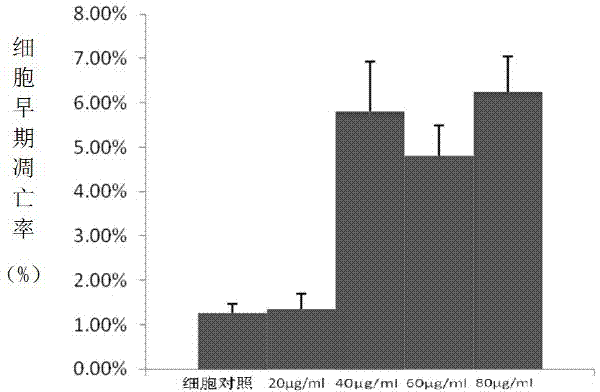
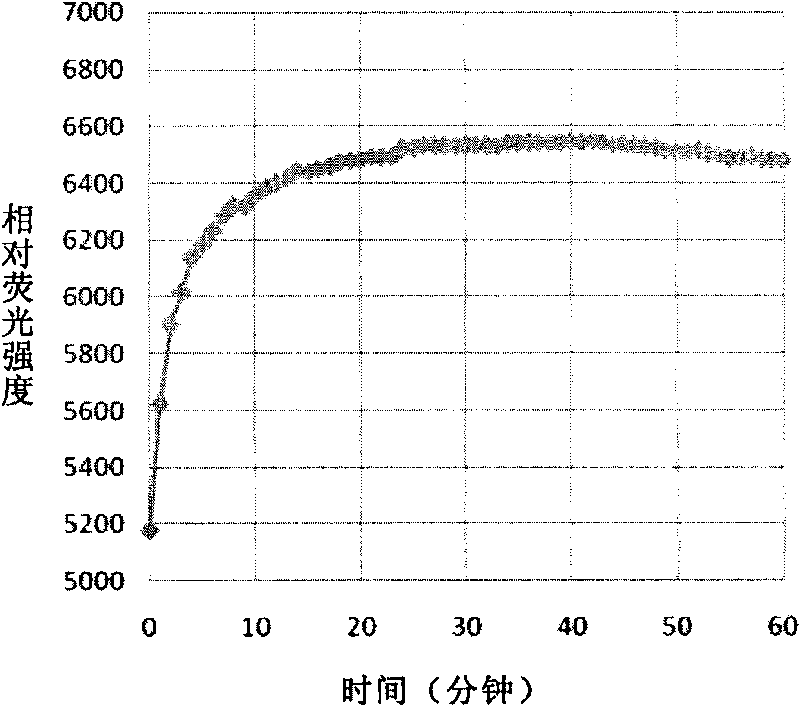
Patents
Literature
50 results about "Propidium iodide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
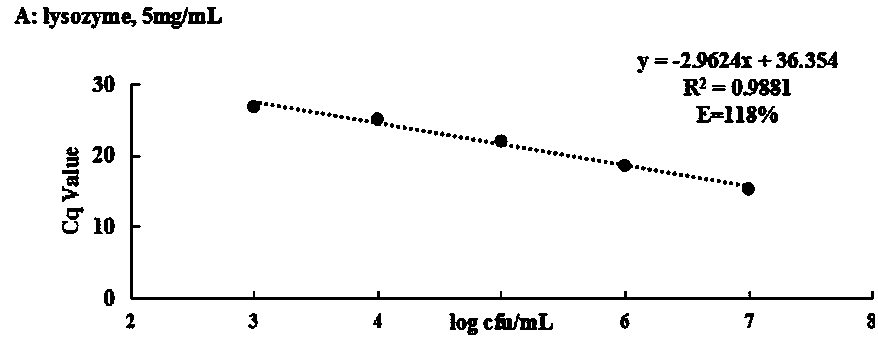
Propidium iodide (or PI) is a fluorescent intercalating agent that can be used to stain cells. PI binds to DNA by intercalating between the bases with little or no sequence preference. Propidium iodide is used as a DNA stain in flow cytometry to evaluate cell viability or DNA content in cell cycle analysis, or in microscopy to visualize the nucleus and other DNA-containing organelles. Propidium Iodide is not membrane-permeable, making it useful to differentiate necrotic, apoptotic and healthy cells based on membrane integrity. PI also binds to RNA, necessitating treatment with nucleases to distinguish between RNA and DNA staining.
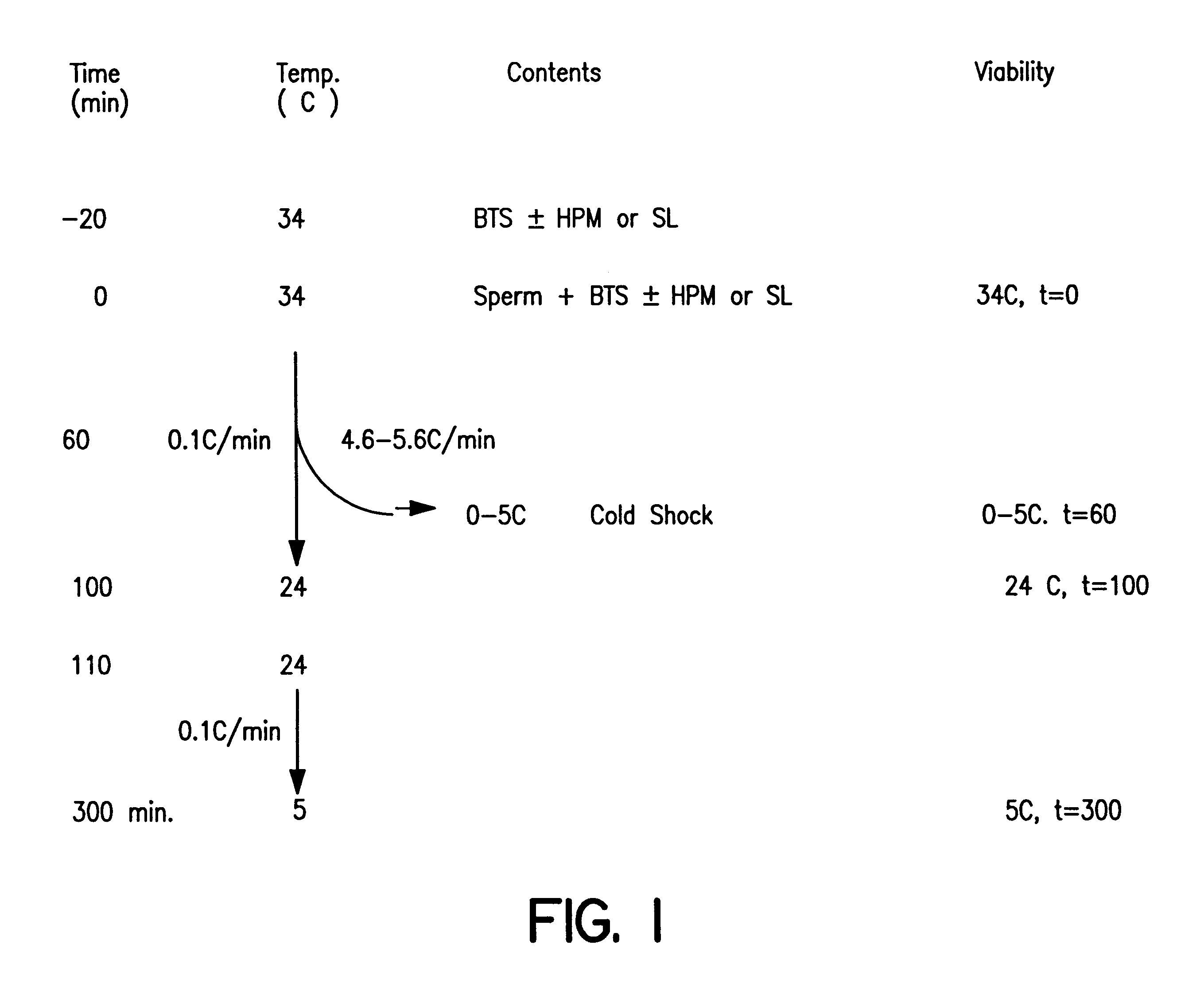
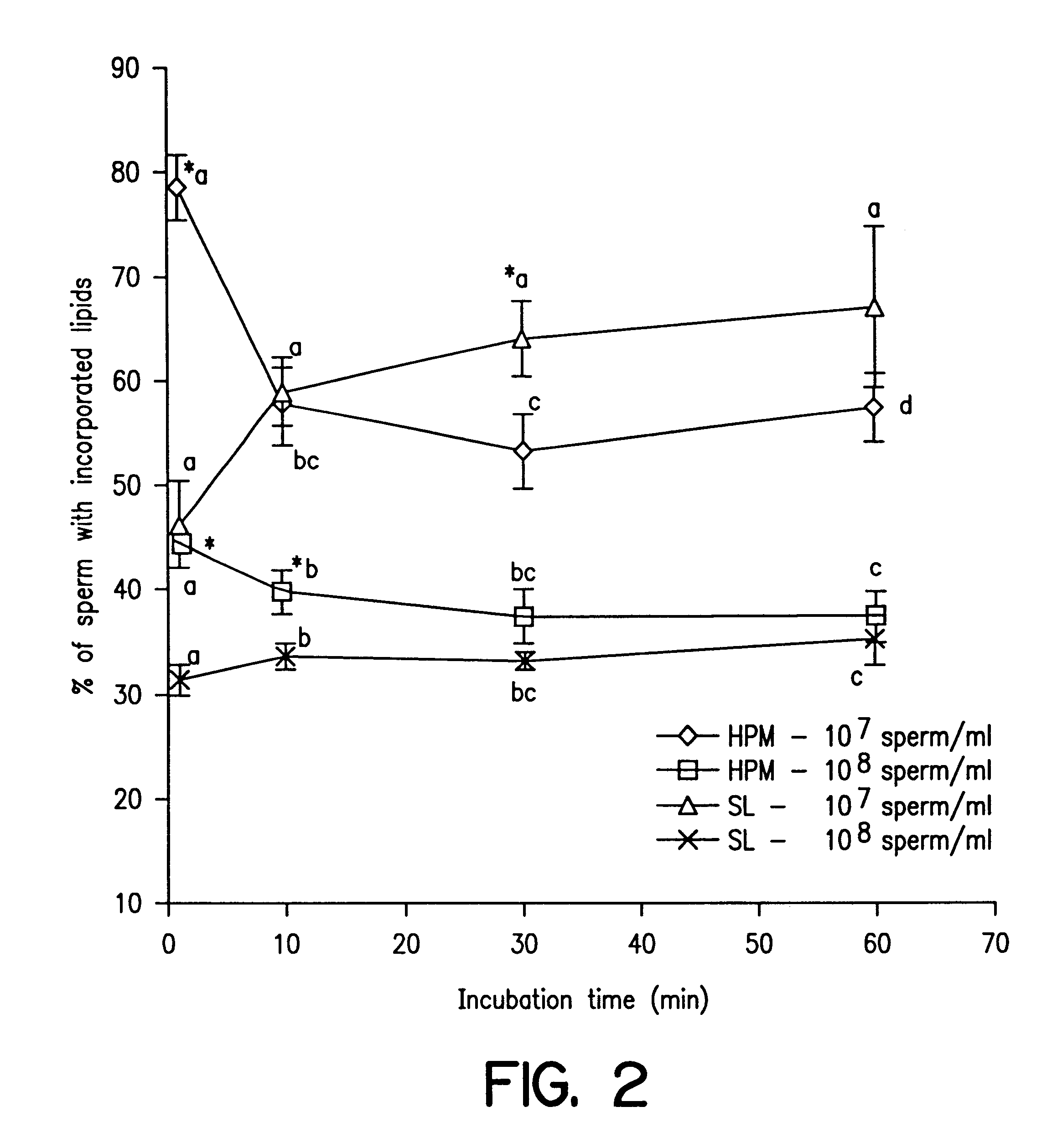
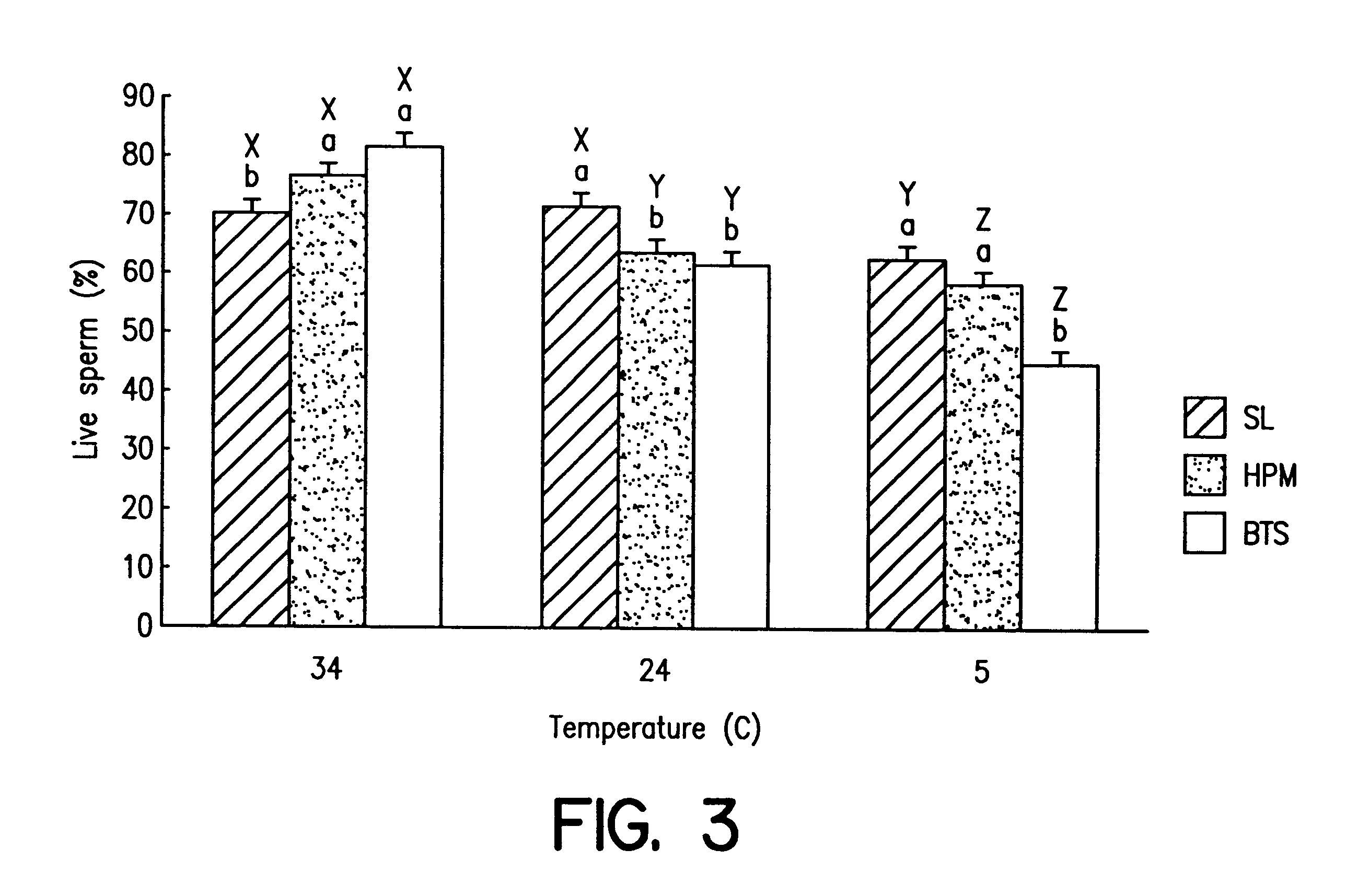
Reduction of sperm sensitivity to chilling
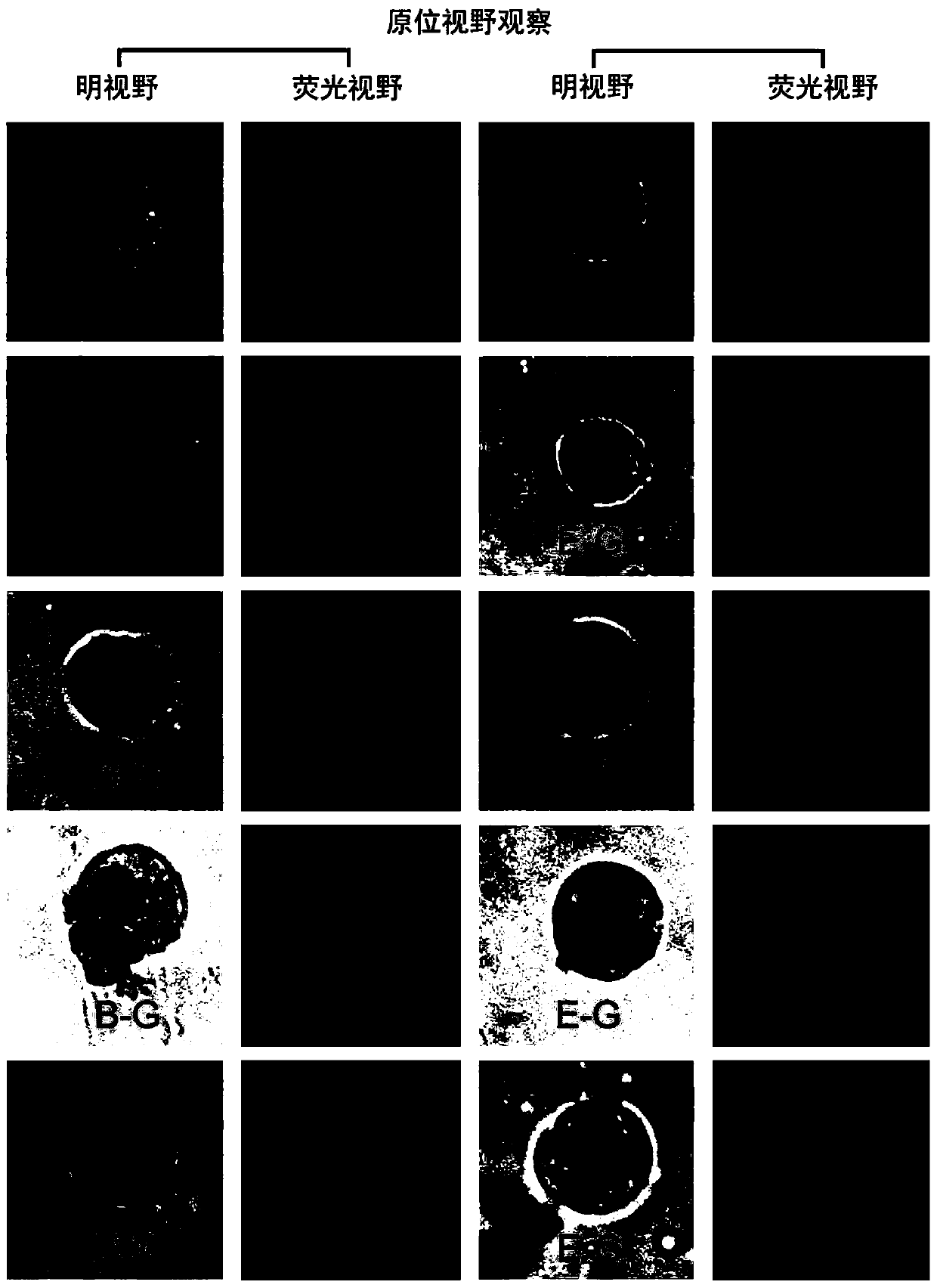
Cryopreserved boar spermatozoa is much less fertile than that of other species, which could be due to damage to sperm membrane lipids during the cryopreservation process. Incorporation of selected lipids improves the survival of boar spermatozoa following cryopreservation.Liposomes were made from lipids extracted from head plasma membrane (HPM) of boar spematozoa or from selected lipids (SL) which contained specific phospholipids. At a fixed lipid concentration, fusion efficiency with spermatozoa as measured by flow cytometry and R18 dequenching was affected by lipid type, sperm concentration and incubation time.SL and HPM improved sperm viability (SYBR-14 and propidium iodide) and motility during cooling to 5C., with SL±egg yolk better than or equal to HPM (P<0.05). Post-thaw, egg yolk showed a strong cryoprotective effect. Compared to HPM, SL-treated sperm had higher post-thaw viability, progressive motility and total motility in the extender including egg yolk and higher viability in the extender excluding egg yolk (P<0.05).
Owner:GUELPH UNIV OF
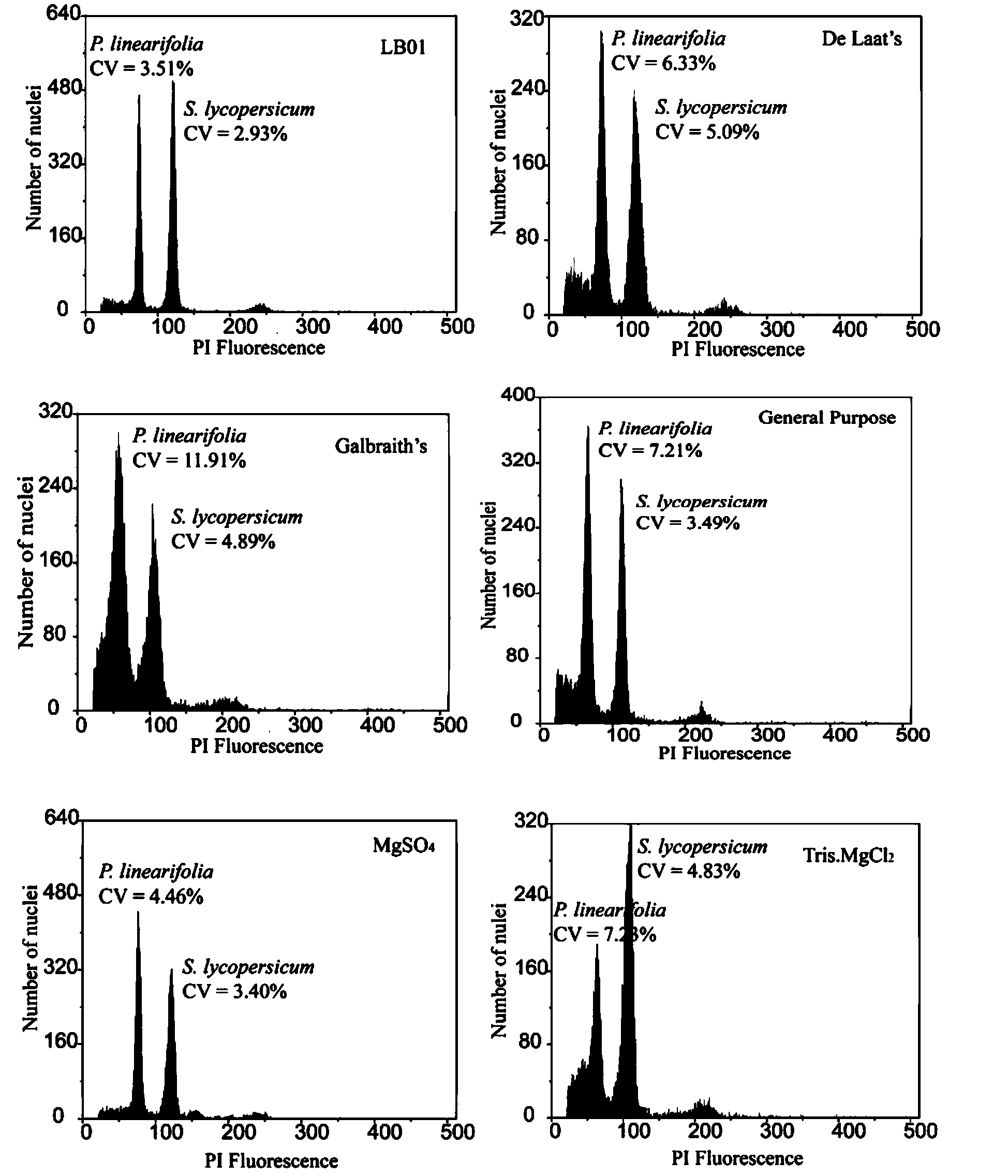
Method for measuring size of genome of gesneriaceae plant
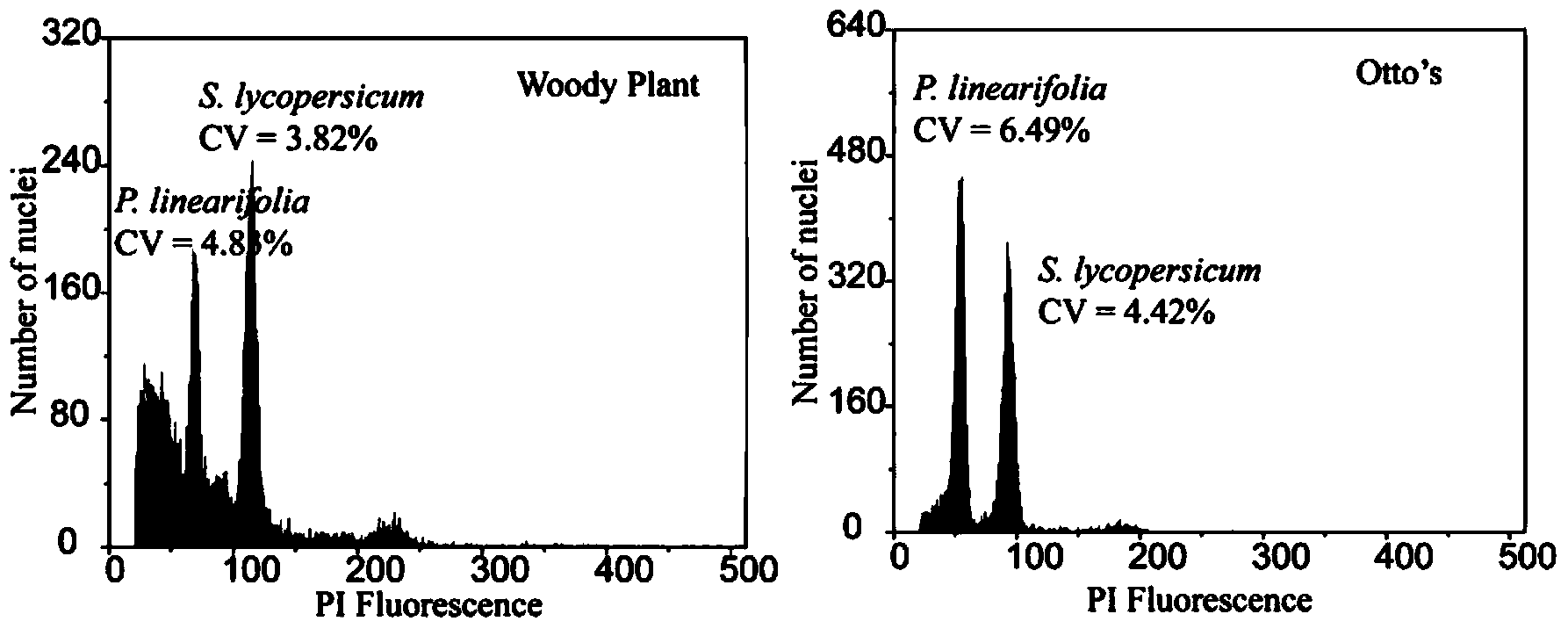
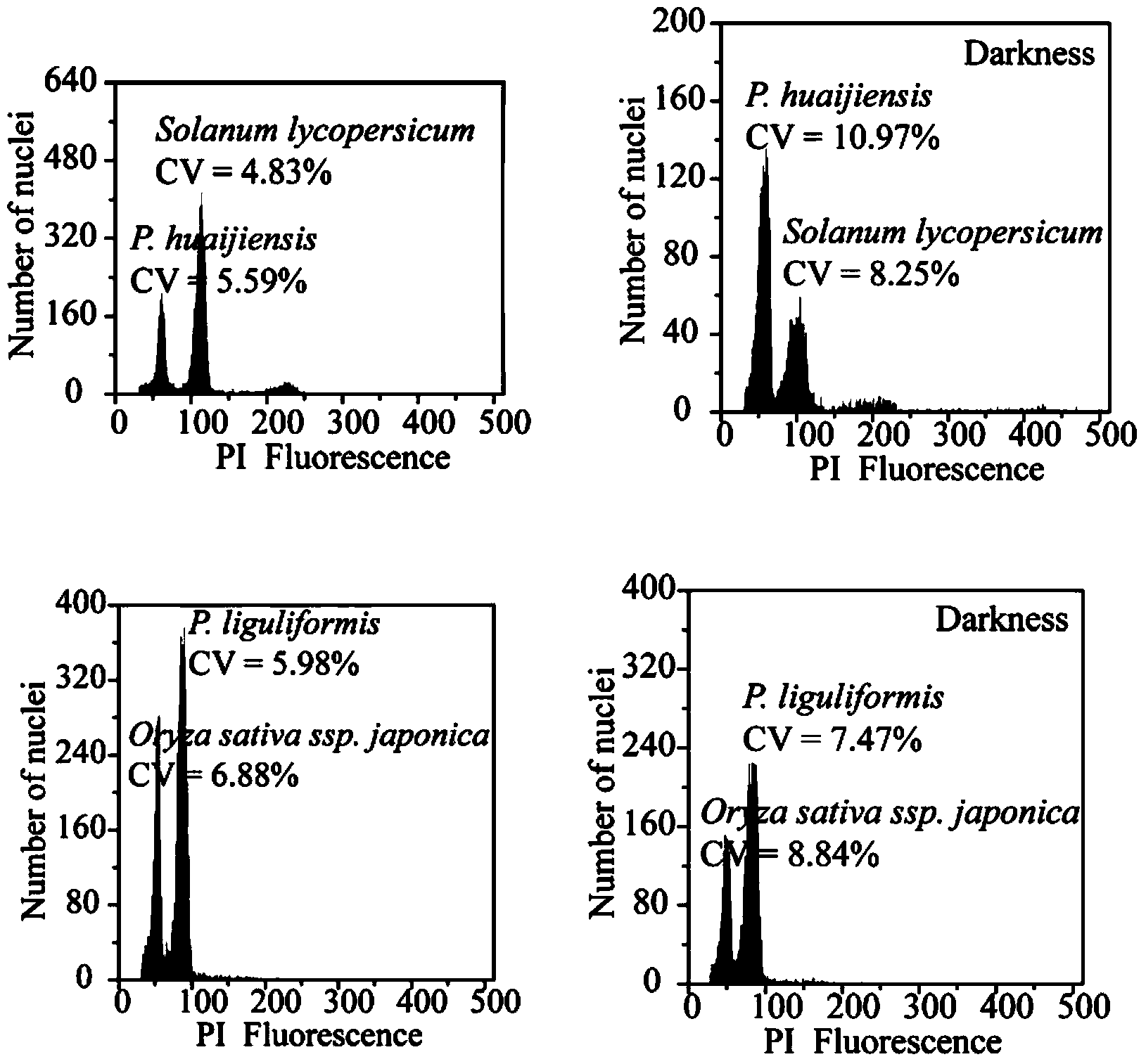
The invention discloses a method for measuring the size of the genome of a gesneriaceae plant. The method comprises the steps of taking fresh tender leaves of the gesneriaceae plant; with a tomato as a main internal reference and rice as a second internal reference, re-correcting the size of the genome of the rice by taking the size of the genome of the tomato as standard; according to the standard of adding 20 milligrams of tender leaves into 1ml of nuclear extraction buffering solution LB01, respectively adding the tender leaves of the target plant and the internal reference species into the nuclear extraction buffering solution LB01, chopping the tender leaves, performing filtration through a filtering net with the aperture of 50 microns to obtain a cell nucleus suspension, and putting the cell nucleus suspension on ice for later use; digesting RNA in the cell nucleus suspension through RNA digestive enzymes till the final concentration of the RNA digestive enzymes is 100 micrograms per ml, and then adding propidium iodide for fluorescence shading dyeing for 40 minutes; and measuring the size of the genome of the target plant through a flow cytometry. The method can measure the accurate sizes of the genomes of various gesneriaceae plants; the CV (Coefficient of Variation) is lower than 5 percent. The method is high in repetitiveness and easy to operate, and is suitable for gesneriaceae botanic research.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Fluorescent staining kit for rapid detection on biological cell viability, and application of same
ActiveCN103175768ALow toxicityEasy to useIndividual particle analysisFluorescence microscopeIndividual animal
The invention relates to a fluorescent staining kit for rapid detection on biological cell viability, and application of the same. The kit comprises an anthocyanin dye and a propidium iodide dye. The detection comprises the following steps of: adding the anthocyanin dye and the propidium iodide in the kit are added in cell suspension, observing and counting the cells by a fluorescence microscope or detecting the cells by a microporous fluorescent plate reader under wavelength of emitted light, and reflecting the viability of the cells in biologic sample liquid according to the strength of fluorescence values of different colors. The kit can be used for rapidly observing or detecting the amount of living cells and the amount of dead cells of various cells in the sample in real time, is visual and handy, eliminates the inference of other substances and the defect of long culture cycle, and is not only suitable for animal cells, but also suitable for most gram negative bacteria and gram positive bacteria.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Method of detecting effect of oral tobacco products upon early apoptosis
InactiveCN104726532AEarly apoptotic effects are accurate and effectiveAccurate and efficient flow cytometric detection of early apoptotic effectsMicrobiological testing/measurementTest sampleSingle cell suspension
The invention discloses a method of detecting effect of oral tobacco products upon early apoptosis. The method includes: pretreating a sample, preparing single-cell suspension, calculating cell concentration of the single-cell suspension, inoculating cells, setting groups, setting dosage, adding a test sample, incubating the test sample, collecting cells, washing the cells, adding resuspended cells, mixing Annexin V-FITC and PI (propidium iodide) dye, allowing reaction, adding binding buffer, detecting the test sample after mixing, and performing detecting with a flow cytometer in one hour to obtain an early apoptosis influence rate. Through effective treatment of the sample, optimal setting of detection dosage and correct selection of target cells, the invention allows the effect of the oral tobacco products upon early apoptosis to be accurately and effectively detected.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Dyeing liquid as well as dyeing method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101225428ASignificant production and application valueMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceMicroscopic examColor changes
The invention relates to a dyeing liquor used to discriminate the protozoan cell activity, a method to discriminate the protozoan cell activity and the application of the method to discriminate activity of nosema bombycis, which is characterized in that: the dyeing liquor comprises the following components: three acridine oranges with the concentration of 0.05% to 0.3% and one propidium iodide with the concentration of 0.0067% to 0.026%; the acridine oranges and the propidium iodide are prepared by NaCl solution with the concentration of 0.38%; the method to discriminate the protozoan cell activity comprises adequate material choosing, dyeing liquor preparing, dyeing, microscopic examination and protozoan cell activity discriminating based on the color change of microscopic examination results. The dyeing liquor used to discriminate the protozoan cell activity has the advantages that: the spore activity of nosema bombycis can be discriminated quickly, sensitively, accurately and visually; the deficiency of the prior art is overcome.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for extracorporeally detecting survival rate of sperms
InactiveCN101762684AEfficient use ofAvoid the influence of subjective factorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingLuciferasesPropidium iodide
The invention discloses a method for extracorporeally detecting the survival rate of sperms, which is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps that: (a) a suspending liquid of the sperms is mixed with membrane-permeable nuclear dyes to produce a sample to be detected 1, and the membrane-permeable nuclear dyes are selected from Transgreen, SYTO or SYBR; (b) a luciferase reader is used to detect the sample to be detected 1 to obtain the first-time fluorescence intensity of the sample; (c) the sample to be detected 1 and propidium iodide PI are mixed to produce a sample to be detected 2; (d) the luciferase reader is used to detect the sample to be detected 2 to obtain the second-time fluorescence intensity of the sample; and (e) the bigger the obtained survival coefficient is, the higher the survival rate of sperms is.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PLANNED PARENTHOOD RES
Specific probe and method thereof for rapid and sensitive quantification of staphylococcus aureus
InactiveCN105506070AImprove work efficiencyReduce distractionsMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNucleic Acid ProbesStaphylococcus aureus
The invention relates to a specific probe and a method thereof for rapid and sensitive quantification of staphylococcus aureus. On the basis of the sequence of a 16s-rRNA conservation terminal of the staphylococcus aureus, a specific complementary nucleic acid probe is designed, the probe is named as SA-1 and 5' terminal is labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate FITC; and the sequence number of the SA-1 is shown as 5'-GCCGGTGGAGTAACCTTTTAGGAGC-3'. According to the invention, the specific complementary nucleic acid probe is designed on the basis of the sequence of the 16s-rRNA conservation terminal of the staphylococcus aureus and is named as SA-1, the 5' terminal is labeled with fluorescein isothiocyanate FITC, and the FIFC-labeled SA-1 can achieve specific combination with the processed staphylococcus aureus so as to excite fluorescent light from the staphylococcus aureus; and on the basis, propidium iodide PI is adopted for overall dyeing treatment on bacteria, sarcoid cells or intestinal contents, and fluorescence parameters are analyzed by virtue of a flow cytometry by taking a fluorescent microsphere with known concentration as internal reference, so that the purpose of quantifying bacteria is achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF POULTRY SCI
Preparation method of aligned film
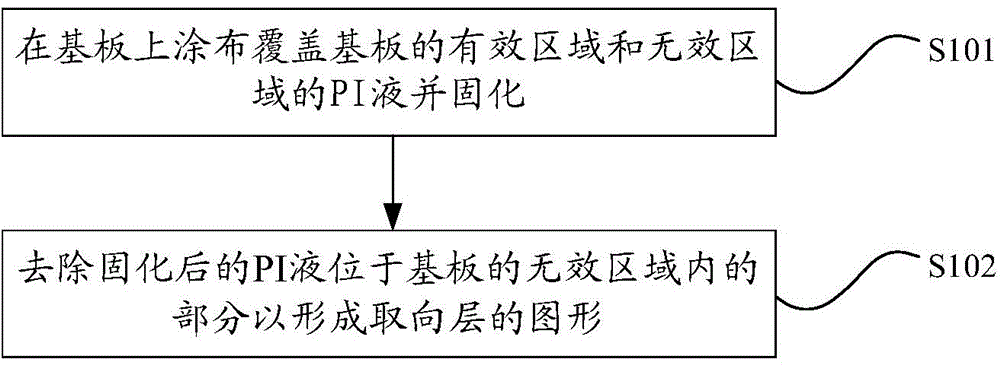
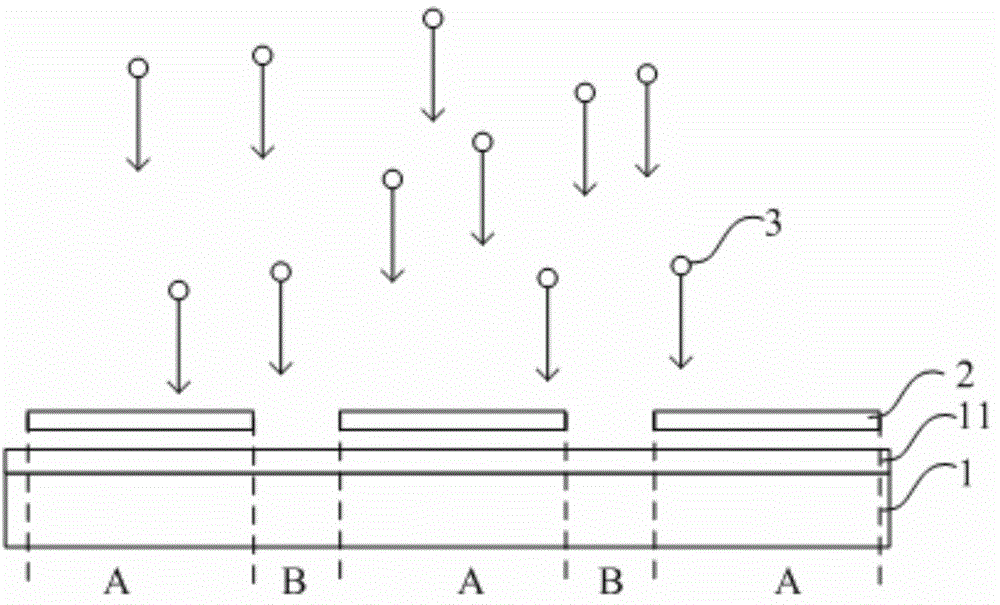
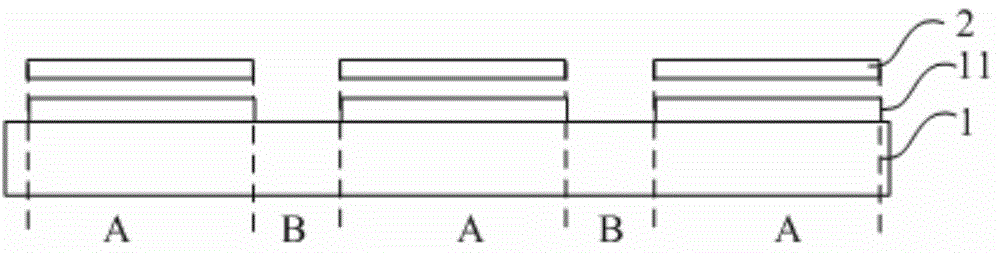
The invention relates to the technical field of displaying and discloses a preparation method of an aligned film. The preparation method includes: coating a substrate with PI (propidium iodide) liquid covering a valid area and an invalid area of the substrate, and solidifying the PI liquid; removing the part, located in the invalid area of the substrate, of the solidified PI liquid to form a pattern of the aligned layer. According to the preparation method, distinguishing the invalid area and the valid area of the substrate is not required when the PI liquid is applied to the substrate; the invalid area of the substrate is controlled in such a manner that the part, located in the invalid area of the substrate, of the solidified PI liquid to form the pattern of the aligned layer; at this moment, the PI liquid is solidified and has no fluidity, and accordingly, the invalid area of the substrate is convenient to control when the preparation method is used in preparing the aligned layer.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Activity detection method for fusarium virguliforme
InactiveCN102346107AGood repeatabilityPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpore germinationStaining
The present invention discloses an activity detection method for fusarium virguliforme. According to the method, a propidium iodide staining method is adopted, a laser scanning confocal microscopy is adopted to detect, and the dead spores and the living spores of the fusarium virguliforme can be rapidly, accurately and sensitively distinguished. The method provided by the present invention can replace the traditional spore germination method, and is applicable for the departments of port inspection and quarantine, agricultural production, plant protection and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Flow-cytometry-based kit for high-flux screening of ethanol-producing fungi and application thereof
InactiveCN104560725AEfficient screeningImprove Industrial Screening EfficiencyFungiBiotechnologyPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a flow-cytometry-based kit for high-flux screening of ethanol-producing fungi and application thereof. The kit comprises a box body, reagents, a cell culture plate, a centrifuge tube and a copper screen. The reagents are as follows: 1000 mL of reagent A composed of 6.15g of citric acid and 17.544g of sodium citrate, reagent B composed of 0.3mg of propidium iodide (PI) and 0.3mg of DCFH-DA, 50 mL of reagent C composed of 2g of glucose, 50 mL of reagent D composed of 10g of glucose, 50 mL of reagent E (pH value is 5.5) composed of 0.5g of yeast powder, 0.5g of tryptone, 0.05g of ammonium monoacid phosphate and 0.025g of magnesium sulfate, and 50 mL of reagent F (pH value is 5.5) composed of 0.05g of yeast powder, 0.05g of tryptone, 0.05g of ammonium monoacid phosphate and 0.025g of magnesium sulfate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Simultaneous dehydration and staining of tissue for deep imaging
A biopsy-sized tissue sample is stained for quick imaging. A significant amount of permeation enhancer is included in a mixed solution of permeant enhancer, fixative or dehydrant, and one or two fluorescent dyes to simultaneously dehydrate and dye the tissue sample. The permeation enhancer, e.g., 10% to 50% in the mixed solution, achieves an image of dyed tissue in the contacted tissue sample at a depth of at least 200 um within no more than 1.5 hours. One of the fluorescent dyes is a fluorescent nuclear dye such as DAPI, SYTOX green, acridine orange, propidium iodide, or a Hoechst dye. The other fluorescent dye is a fluorescent protein dye such as eosin or rhodamine B. The tissue sample is cleared with a clearing agent having a refractive index of at least 1.4[R2], e.g., using BABB. The mixed solution may further include Chloroform or other morphology preservative.
Owner:APPLIKATE TECH INC
Method used for detecting ostrea plicatula eosinophilic and basophilic granulocyte phagocytic ability
InactiveCN103994963AEasy to operateAccurate operationPreparing sample for investigationIndividual particle analysisBasophilEosinophilic cell
The invention relates to a method used for detecting ostrea plicatula eosinophilic and basophilic granulocyte phagocytic ability, and the method comprises (1) ostrea plicatula blood cell suspension preparation; (2) fluorescent microsphere phagocytosis; (3) staining with neutral red; (4) lining dying with propidium iodide; and (5) microscopy. The method has the advantages of being simple in operation, rapid and accurate, strong in specificity, high in repeatability, and the like.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
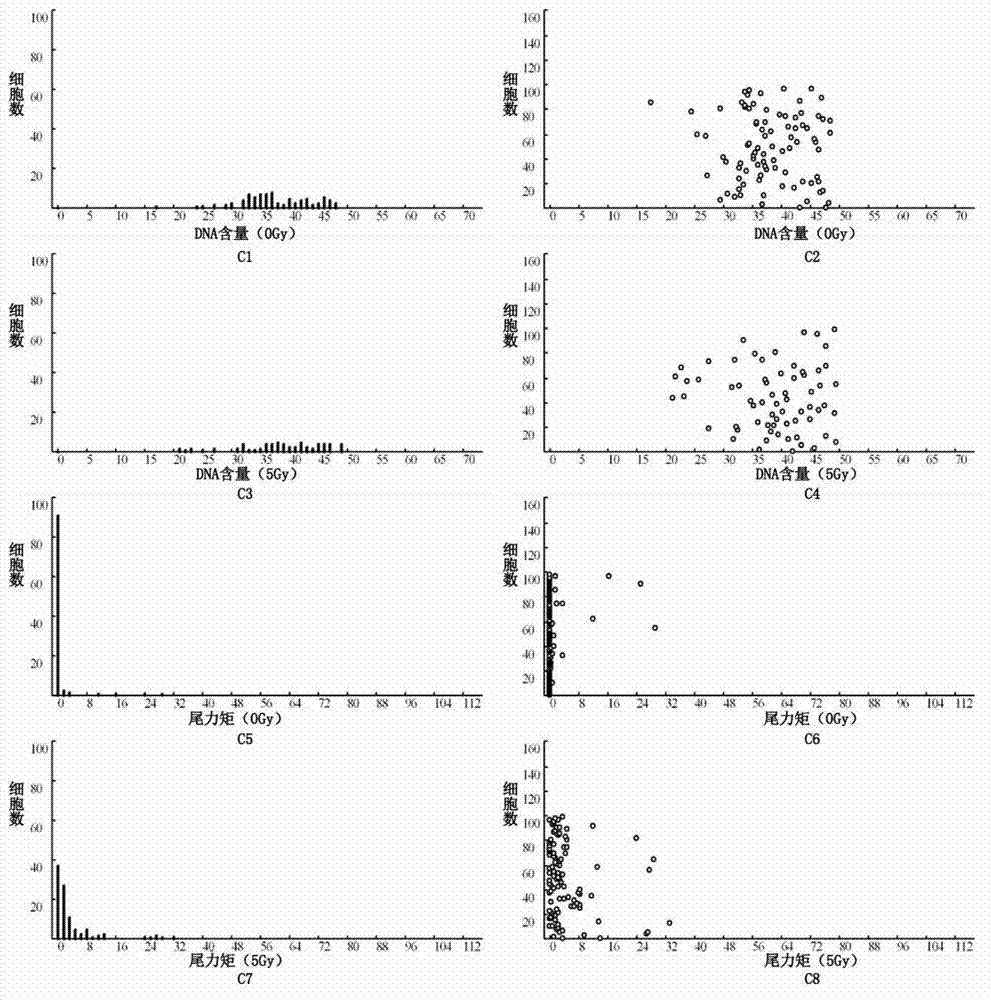
Detection method for radiosensitivity of solid tumor cell
InactiveCN103091341AIncreased radiosensitivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSingle cell suspensionX-ray
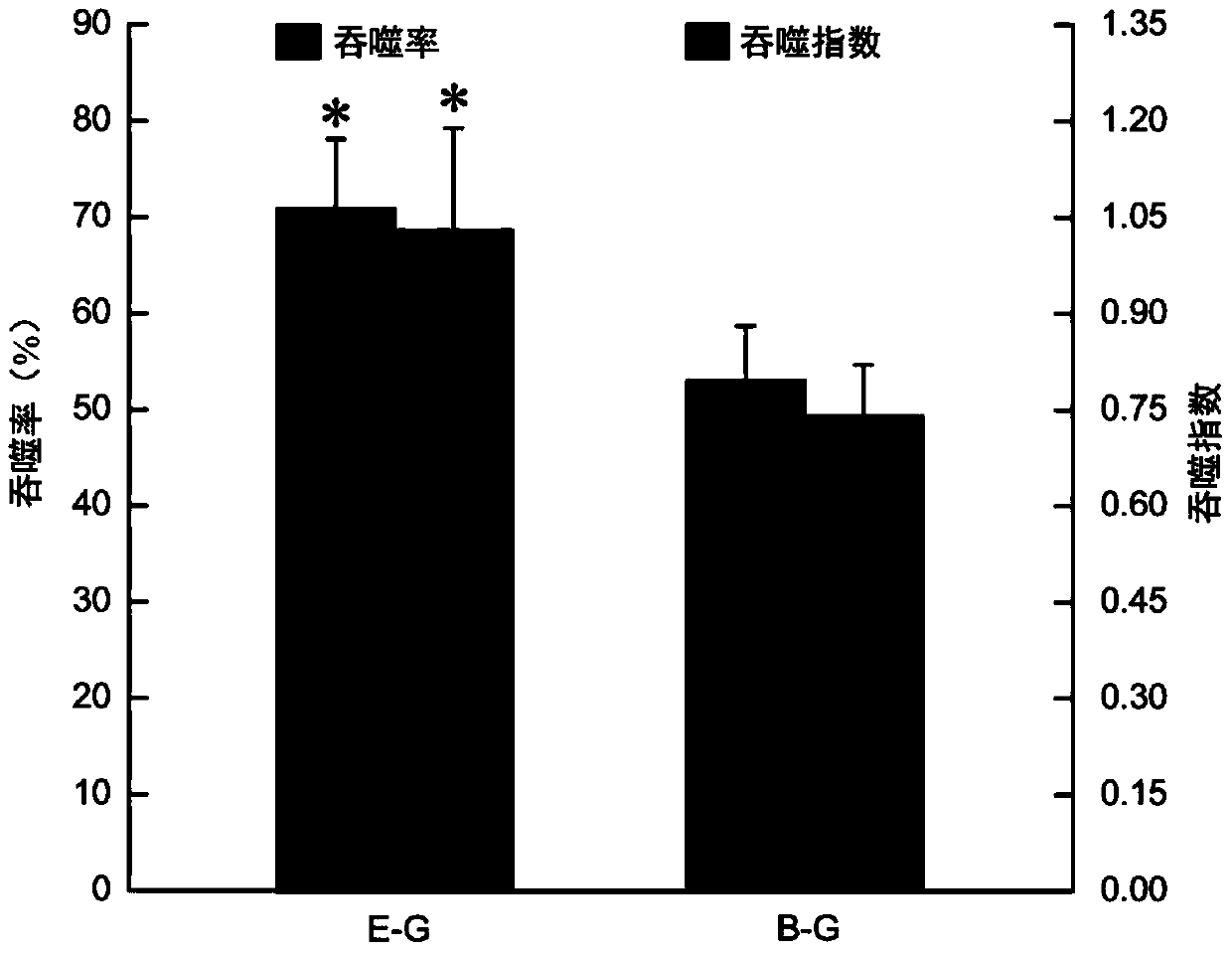
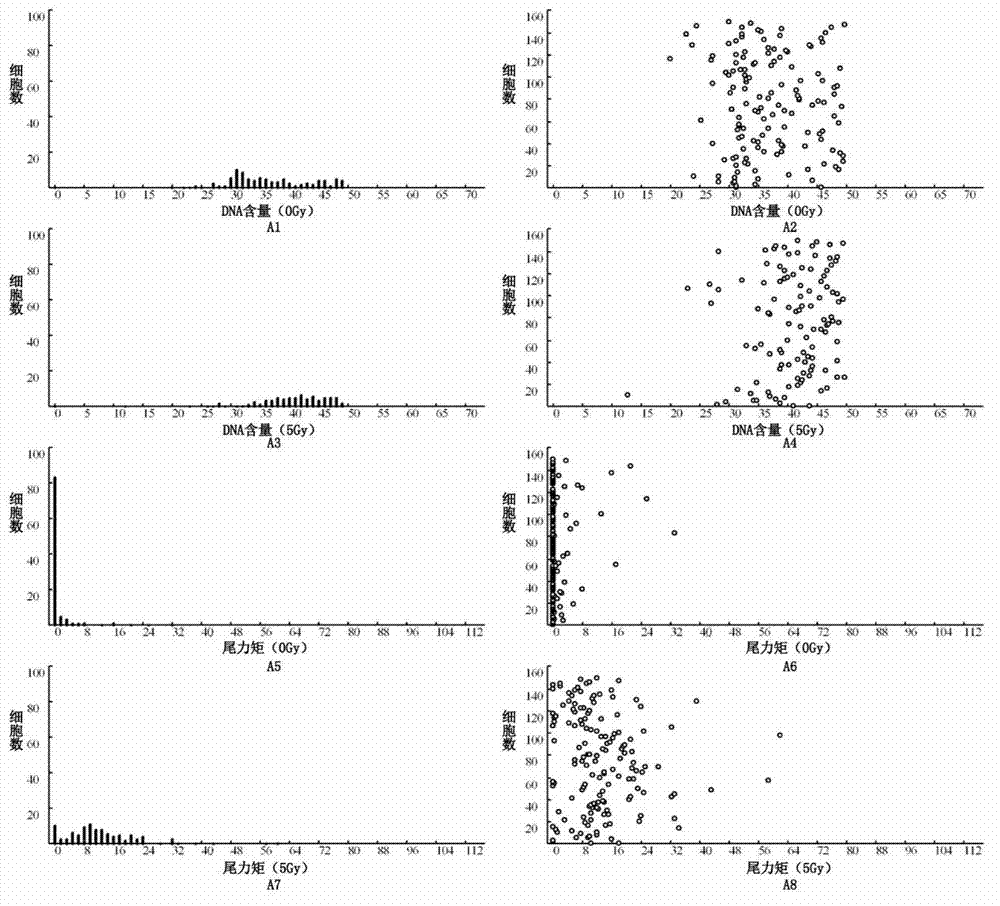
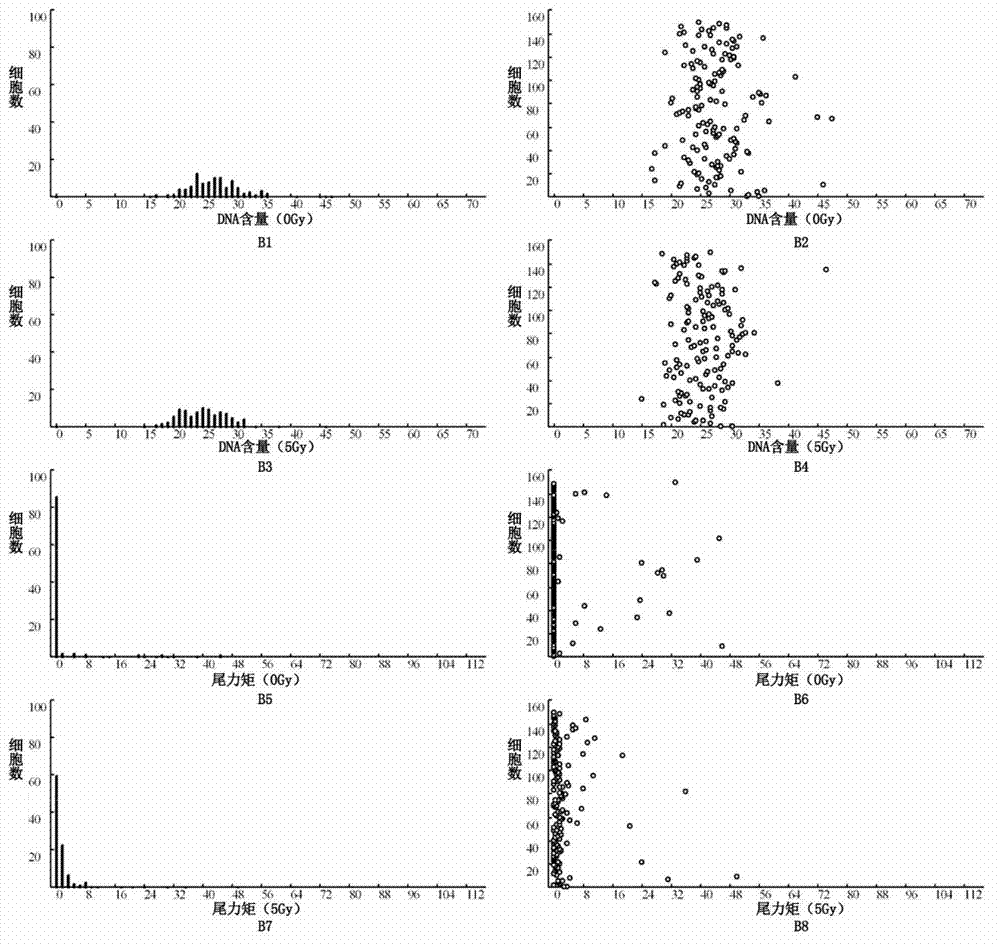
The invention relates to a detection method for radiosensitivity of a solid tumor cell. The detection method comprises the steps of taking detected tumor sample tissues, and preparing the detected tumor sample tissues into single-cell suspensions; taking lymphoma cells subjected to in vitro suspension cultivation as outer contrasts; respectively dividing detected tumor samples and the single-cell suspensions of the lymphoma cells taken as the outer contrasts into an illumination group and a blank control group, and carrying out single-pass illumination on the single-cell suspensions in the illumination group by adopting an X ray in a dosage of 5 Gy, wherein the single-cell suspensions in the blank control group are not subjected to radioactive ray illumination; carrying out cell disruption and rinsing on each group of the single-cell suspensions; carrying out electrophoresis on each group of the cells after disruption; carrying out PI (Propidium Iodide) dyeing on each group of the cells after electrophoresis; under a fluorescence microscope, respectively carrying out tumor / normal cell classification image capturing on the cells in the illumination group and the blank control group of the detected tumor samples, and carrying out image capturing on outer contrast cells; and carrying out data processing on images of the tumor cells, the normal cells and the outer contrast cells in the cells of the detected tumor samples, thus judging the radiosensitivity of the cells of the detected tumor samples.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Optical alignment detection unit and optical alignment method and device
The application discloses an optical alignment detection unit and an optical alignment method and device, wherein the optical alignment detection unit comprises a substrate; the substrate is providedwith an optical alignment indicative layer that is provided with an optical alignment PI (propidium iodide) liquid layer. The optical alignment detection unit and the optical alignment method and device have the advantages that the optical alignment indicative layer is provided, PI liquid generates macromolecular chains containing aniline groups after being exposed to ultraviolet, an indicator inthe optical alignment indicative layer is used for monitoring the amount of aniline groups, the aniline groups react with the indicator to generate a colored pigment after the aniline groups exist, and particularly, the optical alignment detection unit changes the color finally; color changes of glass coated with the indicator are judged at last to judge optical alignment process and uniformity; irradiating brightness and time of an ultraviolet lamp are controlled according to the color changes, so that uniform optical alignment is achieved and it is avoided that overexposure causes adverse effect on optical properties of products.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Immunofluorescence microscopy observation method for marine bivalve meiosis device
InactiveCN101639441AEasy to operateOperation time savingBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceCytochemistryFluorescence
The invention relates to cytochemistry and cellular immunology, which are particularly used for observing a marine bivalve meiosis device through immunofluorescence microscopy. A sample can be observed after pre-treatment of fixing and the like, dyeing and flaking. The sample is fixed by phosphate buffered saline (PBS) of paraformaldehyde at a mass percentage concentration of 2 to 6 percent; then,permeabilization treatment and sealing treatment are performed sequentially; immunofluorescence dyeing is performed on sample spindle bodies, and fluorescence dyeing is performed on chromosomes withthe phosphate buffered saline containing propidium iodide of which the concentration is 5 to 20 mg of per liter; and the sample is flaked after dyeing for observation through fluorescence microscopy.The cytological immunofluorescence observation method is suitable for observing the spindle bodies and the chromosomes of the marine bivalve meiosis device synchronously, has the advantages of simpleand direct operation, high definition and high study efficiency, and is a qualitative, positioning and quantitative cytological immunofluorescence observation method which inosculates forms and functions.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for testing toxicity of high algae-laden aquatic organisms
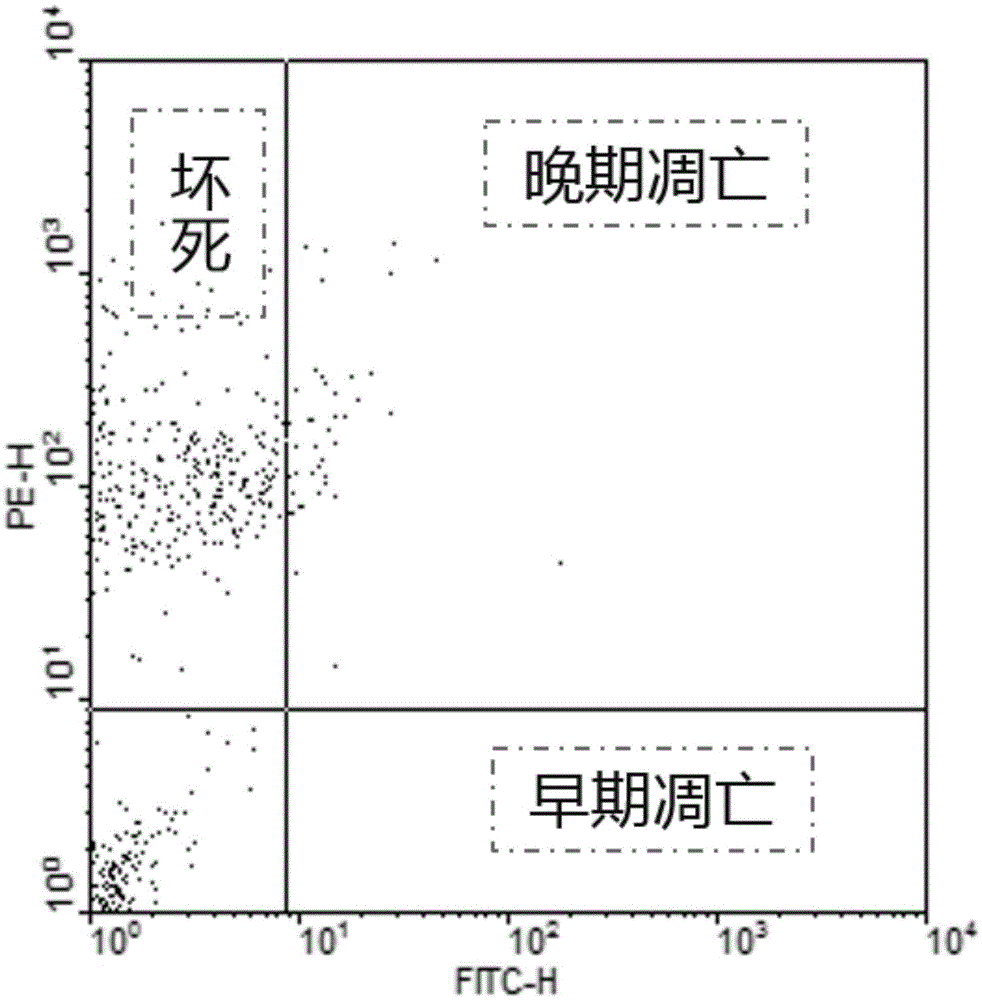
InactiveCN105483202AFacile apoptosis rateSimple death ratePollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTesting toxicityPhosphate
The invention discloses a method for testing the toxicity of high algae-laden aquatic organisms. The method comprises the steps that saccharomyces cerevisiae is cultured in a solid medium containing 5% of YPD and 1.5% of agar firstly, after clone is grown out, a YPD fluid medium of 5% is inoculated with monoclone, and overnight shake cultivation is conducted based on 180-250 rpm and 25-58 DEG C; phosphate buffer is added to a culture solution with the OD value of 1.5-1.8 to obtain a blank sample A, a high algae-laden water sample is added to the culture solution with the OD value of 1.5-1.8 to obtain a detection sample B, and the two samples are placed on a mixer for oscillation lasting 2 h; cell washing is conducted on the sample A and the sample B twice by means of PBS, and cell suspension with the concentration of 1*105-1*106 cel ls / mL is prepared; the sample A and the sample B are both added to Annexin V-FITC of 5 mug / mL to be evenly mixed, and then propidium iodide of 5 mug / mL is added to be evenly mixed; reaction is conducted at the room temperature away from light for 5-15 min; flow cytometry detection is conducted within 1 h; the proportion of dead cells, the proportion of living cells and the proportion of apoptotic cells are detected by means of flow cytometry; the apoptosis rate and the death rate of the sample B are compared with those of the blank sample A, so that water toxicity is judged. Early warning technical support is provided for high algae-laden water pollution, so that high water supply quality is guaranteed.
Owner:上海艾耐基科技股份有限公司 +1
Chromosome localization method of scallop (Chlamys farreri)
InactiveCN101323881AThe hybridization signal is clear and stableImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFluorescenceBiotin
The invention relates to a high-efficiency chromosomal mapping method for chlamys farreri genes. First, the preparation of chlamys farreri chromosome is carried out on a glass slide by the method of air-drying; then online primer design and primer synthesis are carried out according to the sequence of the gene to be mapped; the chromosomal mapping of rRNA gene is carried out; the glass slide supporting the chromosome is treated by utilizing a ligase; then formamide denaturalization treatment is carried out to the chromosome; LAMP reaction mixture is added and LAMP reaction in situ is carried out; after the reaction is finished, the glass slide is cleaned and added with a biotin antibody marked by fluorescence for incubation; finally, a propidium iodide anti-fading solution is used for redyeing the chromosome; a stable and clear hybridization signal is used for determining the position of a target gene on the chromosome. The method of the invention causes chlamys farreri gene to fast obtain a plurality of amplification products; the hybridization signal is clear and stable, thus promoting the correctness and specificity of chromosomal mapping. As for the mapping of a single-copy or low-copy gene, the method also has very great application potential.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
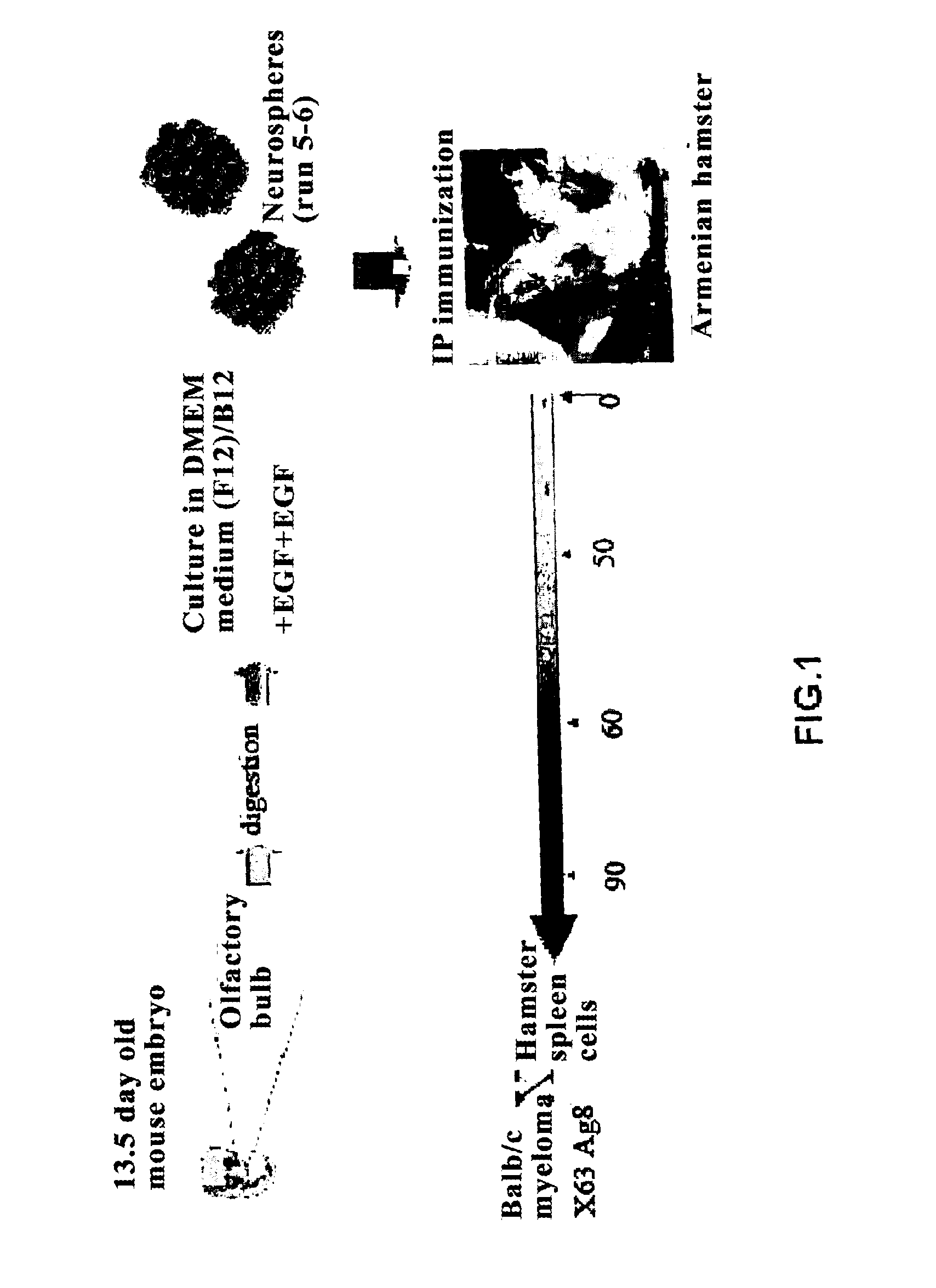
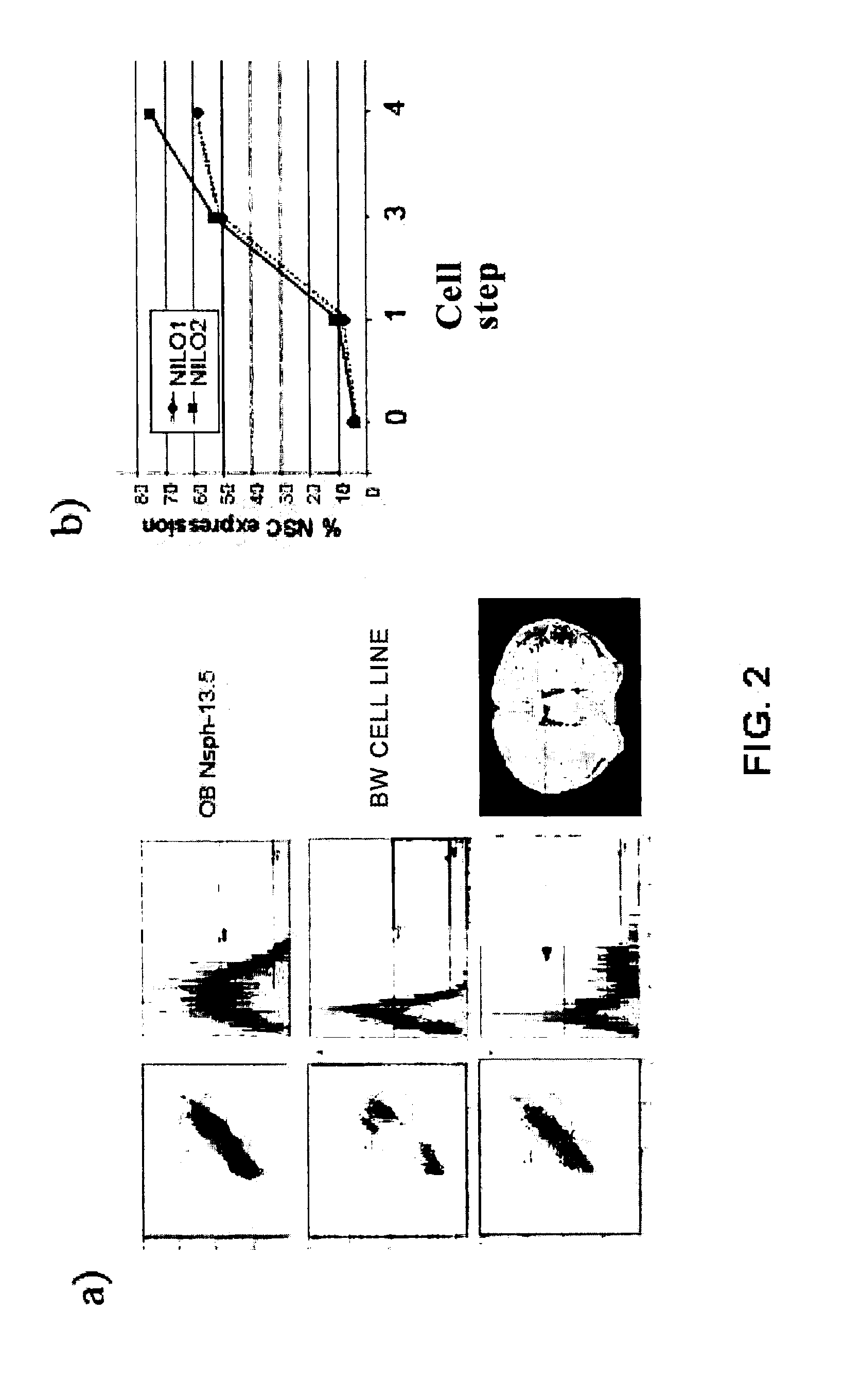
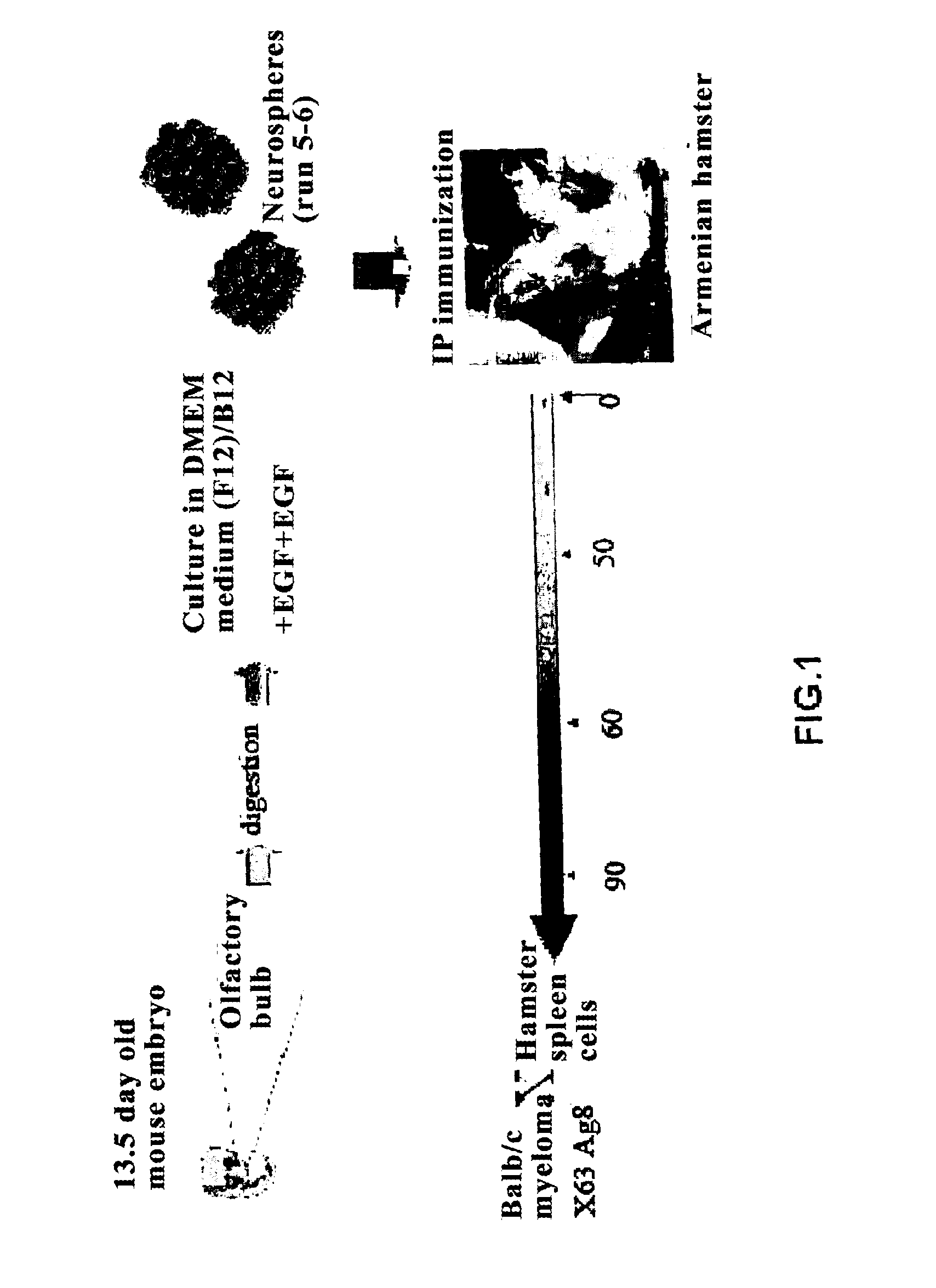
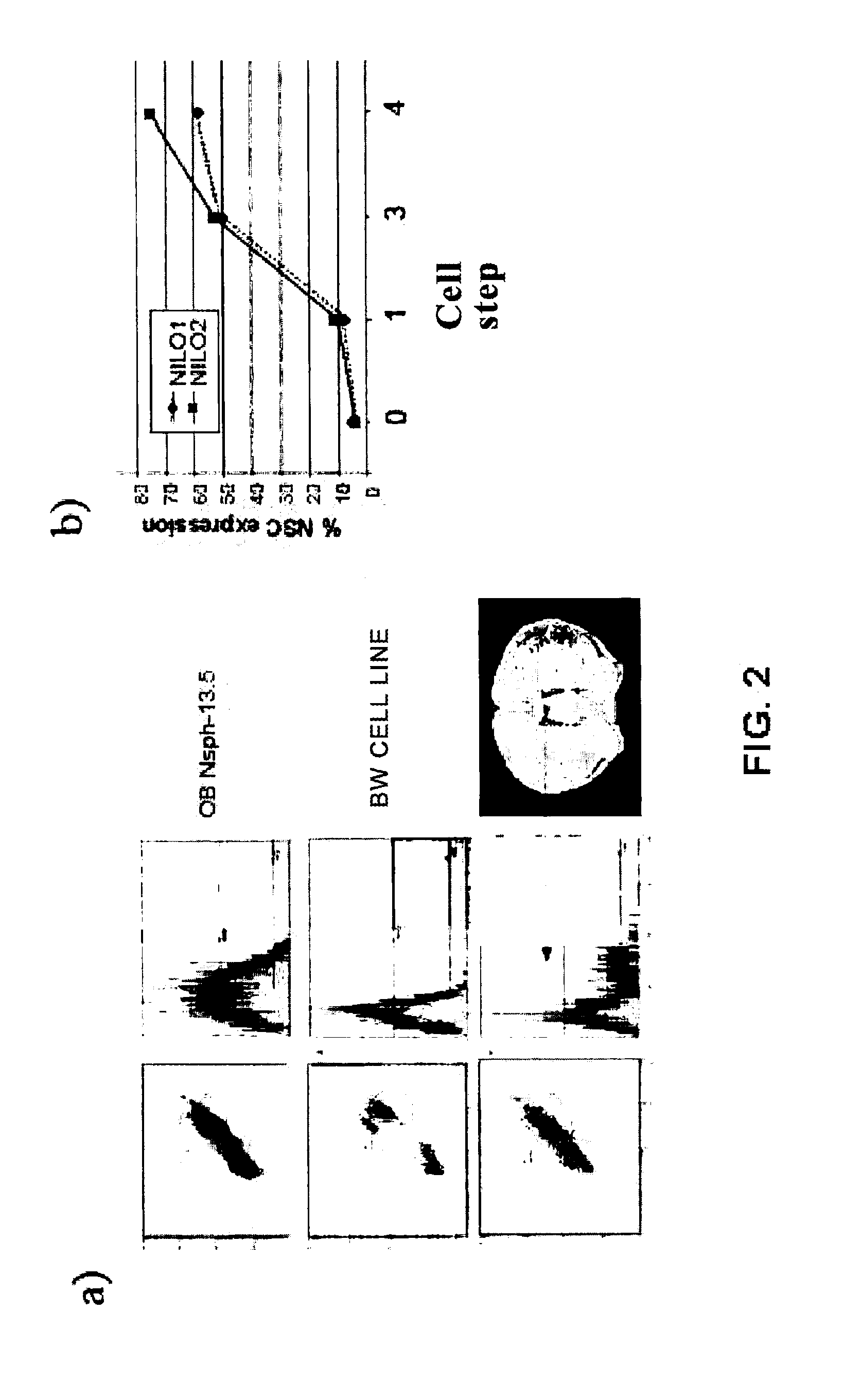
Method for generating monoclonal antibodies that recognize progenitor cells
Method for generating monoclonal antibodies that recognize progenitor cells. Said method comprises immunization of an Armenian hamster with neurospheres obtained from olfactory bulb cells from a 13.5-day mouse embryo and subsequent selection of the antibodies by means of neurosphere flow cytometry in the presence of propidium iodide. The antibodies thus obtained may be of use in the enrichment of cell cultures in progenitor cells, primarily neural progenitor cells.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
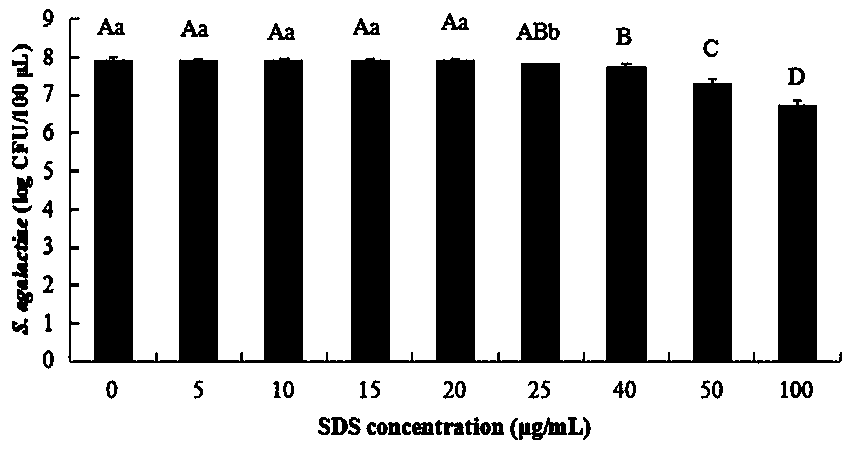
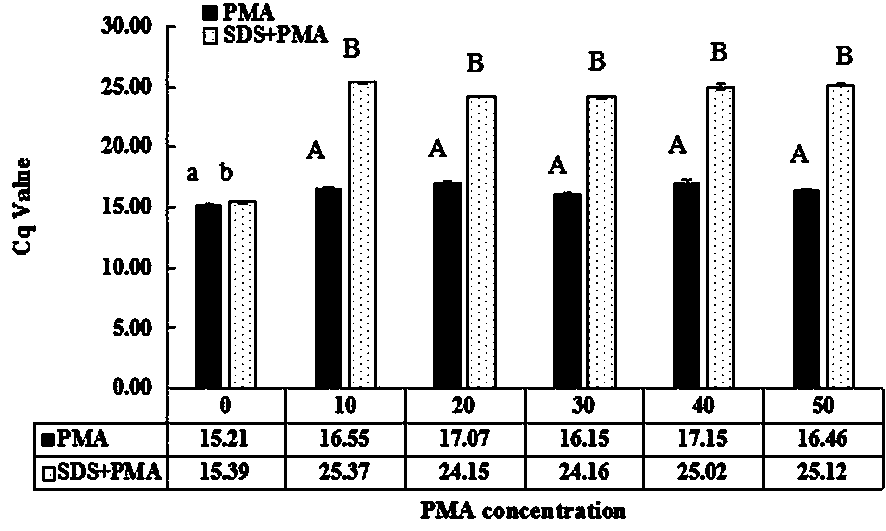
Method for detecting living streptococcus agalactiae in milk by SDS-PMA-qPCR (sodium dodecyl sulfate-propidium monoazide-quantitative polymerase chain reaction) method
InactiveCN109321666AEasy extractionImprove extraction efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPermeationFalse-positive result
The invention relates to the technical field of technology for detecting pathogenic bacteria in a milk sample, and in particular to a method for detecting living streptococcus agalactiae in milk by anSDS-PMA-qPCR (sodium dodecyl sulfate-propidium monoazide-quantitative polymerase chain reaction) method. The method is carried out according to the following steps: (Step 1) SDS-PMA treatment of a to-be-detected milk sample; (Step 2) extraction of DNA; (Step 3) qPCR amplification reaction; (Step 4) determination of result. Before DNA is extracted, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for extracting DNA better, and the sensitivity of the detection method is increased; before PMA is used for treating bacteria, SDS can be used for enhancing the permeability of PMA into the bacteria, moreover, an appropriate SDS concentration can effectively promote the permeation effect of PMA into dead bacteria, and the combination of both can accurately differentiate living and dead streptococcus agalactiae cells. To sum up, dead streptococcus agalactiae in the to-be-detected milk sample cannot interfere with the method disclosed by the invention, the method can accurately detect out thespecific content of streptococcus agalactiae in quantified milk, moreover, the specificity is high, and a false positive result can be prevented.
Owner:新疆农业科学院农业质量标准与检测技术研究所
Method for identifying gamma delta T cell killing
InactiveCN105424582ARapid detection of killing efficiencyDetection of killing efficiencyIndividual particle analysisPhosphateRadioactive agent
The invention discloses a killing method for identifying gamma delta T cells simply and rapidly. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, healthy volunteer peripheral blood is collected, separation is carried out by utilization of a human lymphocyte separating medium, mononuclear cells are obtained, phosphate antigens HMBPP with 10-30ng / ml and rhIL-2 factors with 500-1000 IU / ml are added, PBMC induction into gamma delta T cells is carried out and amplification culture is carried out; secondly, after culture is carried out for 8-10 days, gamma delta T cells are subjected to detection of destruction experiments, the living cell dye calcein-AM is employed to dye tumor cells, the cell density during dyeing is controlled at 10<5>-10<7> / ml; thirdly, the tumor cells after dyeing and the gamma delta T cells are cultured together for a period of time, the cells are collected, propidium iodide is added for dyeing before detection, finally, a flow cytometer is employed to detect cell death amount, and the cell killing rate is obtained. Through the method that the cell killing efficiency can be detected rapidly through a flow cytometer, limitation conditions of traditional 51Cr radioactive substance pollution and low sensitivity of MTT and LDH are overcome.
Owner:SHENZHEN HORNETCORN BIOTECH
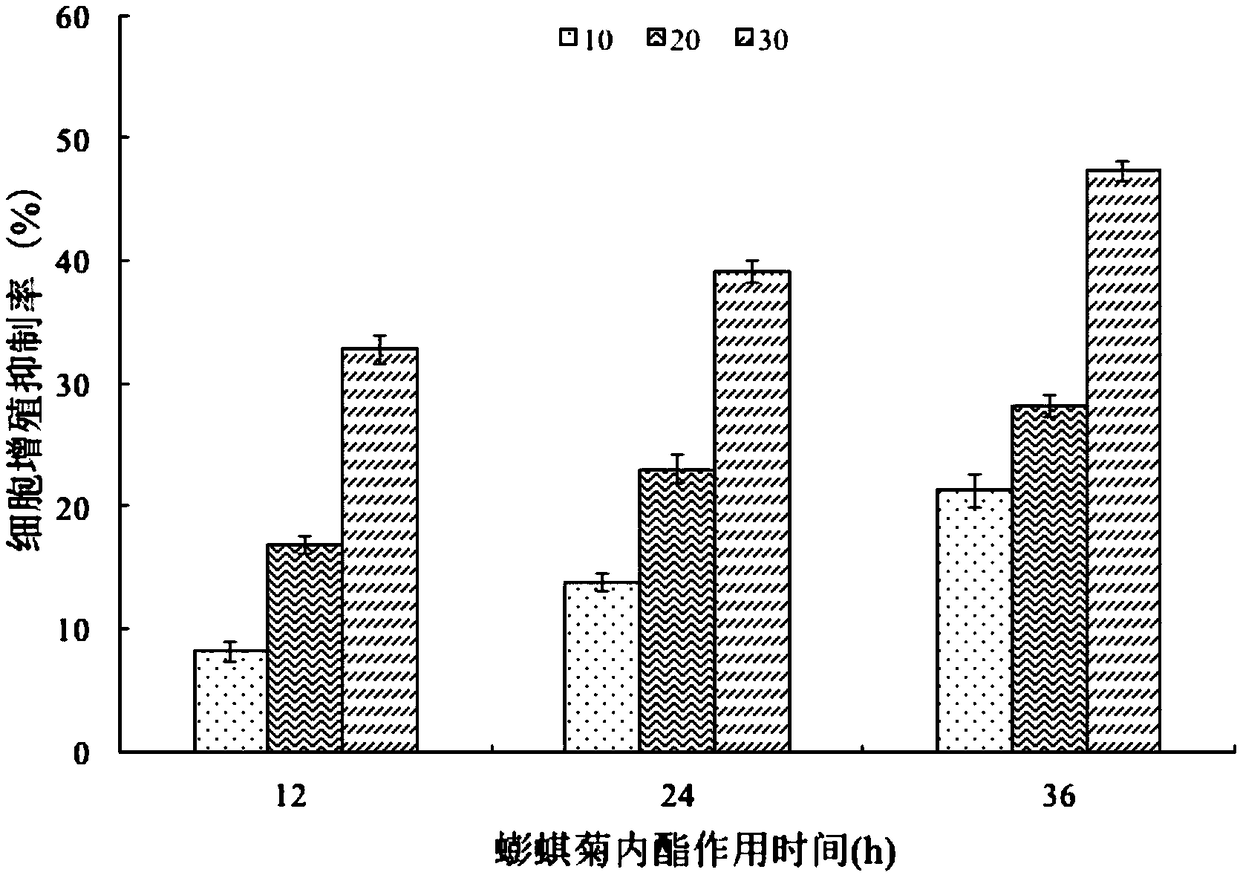
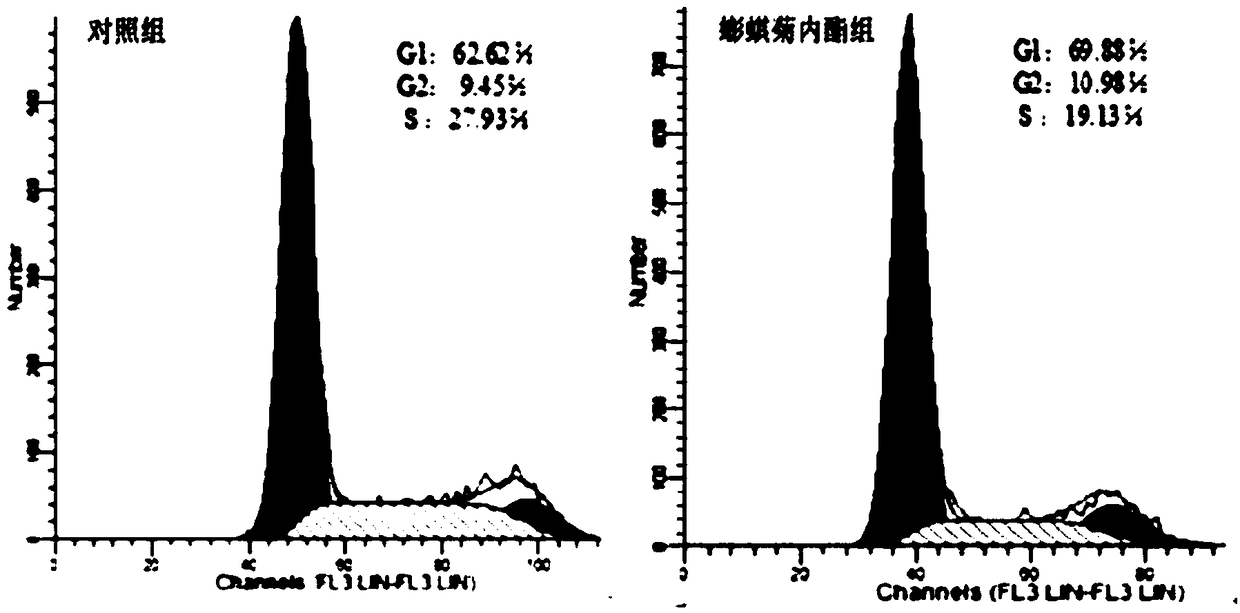
Research method of application of wedelolactone to preparation of lung cancer treating products
PendingCN108998415AMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processAbnormal tissue growthWedelolactone
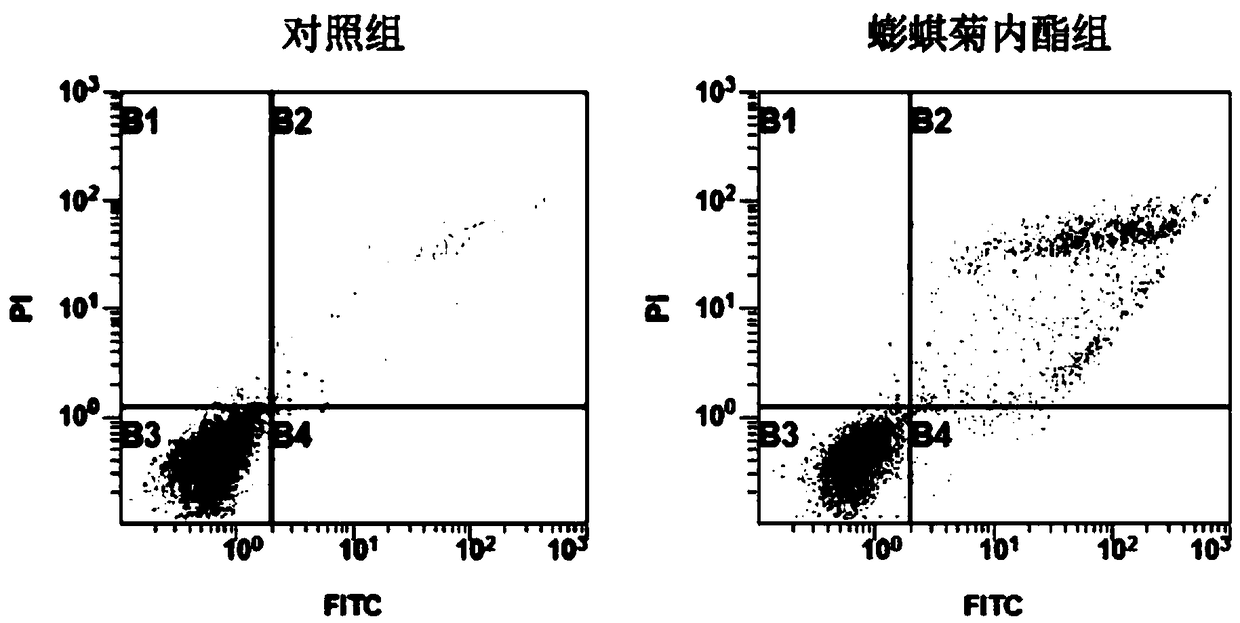
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to a research method of application of wedelolactone to preparation of lung cancer treating products. The invention researches influence of the wedelelactone on the activity, the cycles and the apoptosis of non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells as well as intervention to p-Caspase3, p53, p-STAT1 and STAT1 gene expressionof the cells, explores the anti-tumor effect of the wedelolactone on the A549 cells and the mechanism thereof, provides the research method of the application of the wedelolactone to the preparationof the lung cancer treating products, and provides a theoretical basis for future research on the non-small cell lung cancer treating mechanism of the traditional Chinese medicine. The research methodcomprise the following steps: performing cell culture, detecting the cell proliferation inhibiting rate by a CCK-8 method, detecting the cycles and the apoptosis of the cells through propidium iodideand Annexin-PI staining and detecting gene transcription and translation of the cells through RT-PCR and Western blot.
Owner:道赛尔生物科技(武汉)有限公司
Monoclonal antibodies that recognize neurospheres or neural progenitor cells
Method for generating monoclonal antibodies that recognize progenitor cells. Said method comprises immunization of an Armenian hamster with neurospheres obtained from olfactory bulb cells from a 13.5-day mouse embryo and subsequent selection of the antibodies by means of neurosphere flow cytometry in the presence of propidium iodide. The antibodies thus obtained may be of use in the enrichment of cell cultures in progenitor cells, primarily neural progenitor cells.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC)
Activity detection method for monilinia fructicola
InactiveCN110031438AImprove the efficiency of activity detectionGood repeatabilityPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSporeFluorescence
The invention discloses an activity detection method for monilinia fructicola. The activity detection method comprises the step of adopting a fluorescent dye to dye a monilinia fructicola spore, and judging the activity according to the dying conditions, wherein the fluorescent dye is propidium iodide and / or fluorescein diacetate, the dying condition of the propidium iodide is carrying out 4min lucifugal dying on the spore at a final concentration of 0.00025 mg / mL, and the dying condition of the fluorescein diacetate is carrying out 16min lucifugal dying on the spore at a final concentration of 0.0025 mg / mL. The activity detection method is capable of directly observing the life or death of the spores so that the operation is simple; and the whole detection process is within 30 min, so that the activity detection efficiency is improved. The activity detection method has the advantages of being rapid, correct, sensitive and good in repeatability, is capable of replacing the traditionalmorphological detection, and provides a novel rapid and effective detection method and way for the departments of port quarantine, agricultural production, plant protection and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
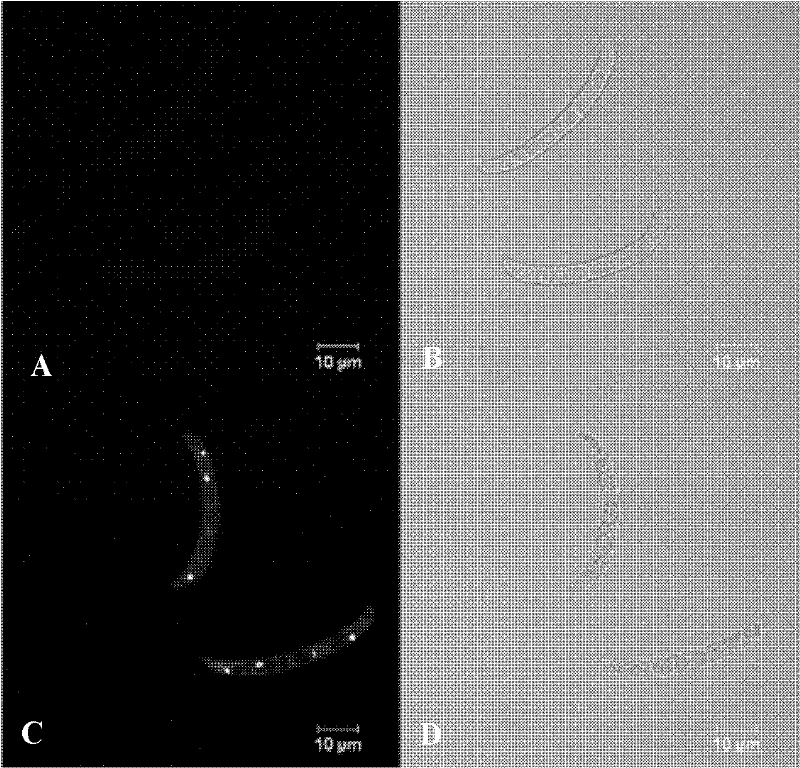
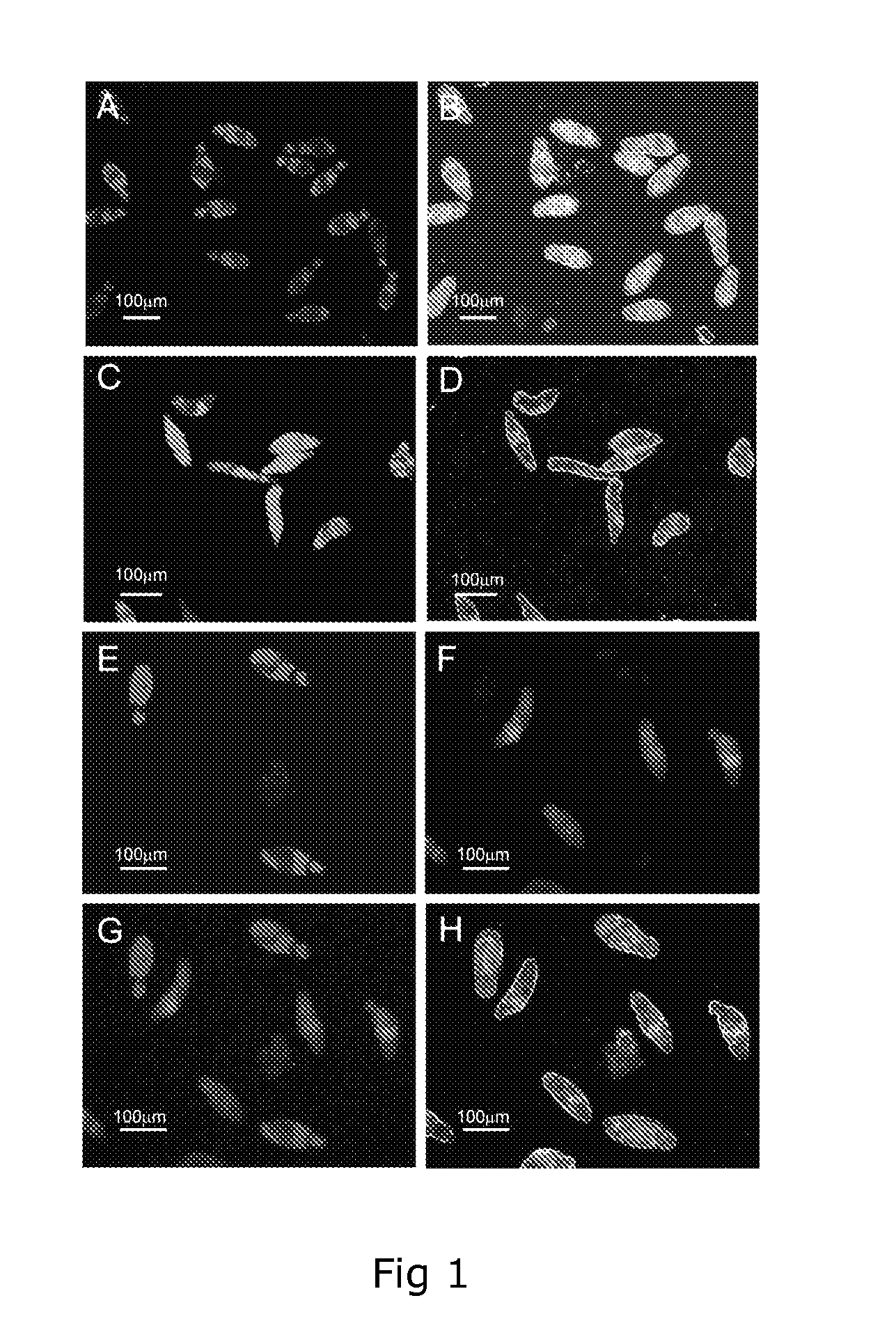
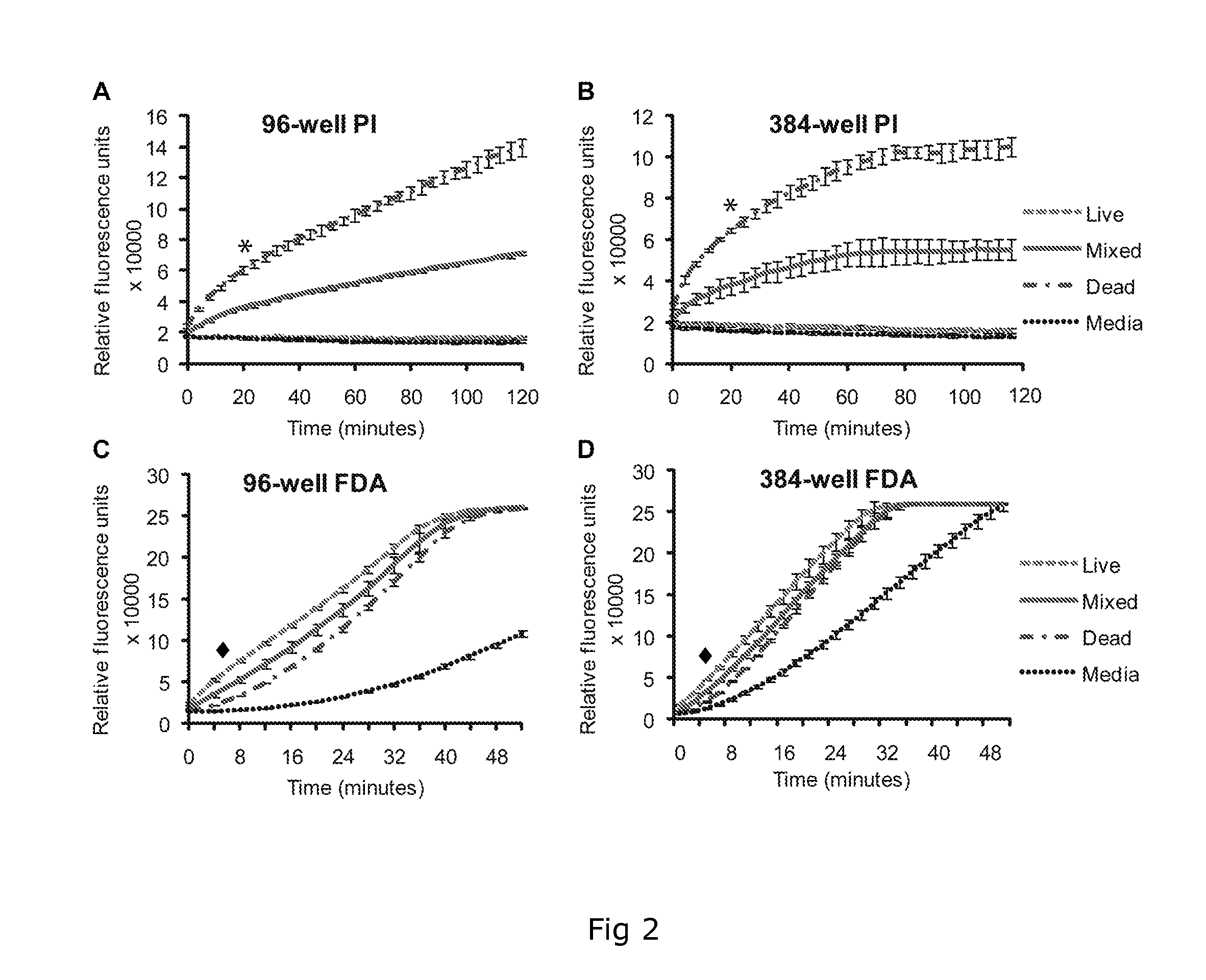
Dual Fluorescence Assay For Determining Viability Of Parasitic Or Non-Parasitic Worms
InactiveUS20120225019A1Enough timeGood fluorescenceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsChemical analysis using titrationMetaboliteSurvivability
A two colour fluorescent assay and a kit are described that permit the determination of live and dead parasitic or non-parasitic worms, for example helminths. The assay permits screening for the effect of one or more agents or an event on the viability of a parasitic or non-parasitic worm. In one example, the assay comprises (a) providing a sample comprising one or more parasitic or non-parasitic worms; (b) contacting the parasitic or non-parasitic worms with a concentration of fluorescein diacetate sufficient to yield detectable green fluorescence in any live parasitic or non-parasitic worms present in the sample and a concentration of propidium iodide sufficient to yield detectable red fluorescence in any dead parasitic or non-parasitic worms present in the sample; and (c) detecting the red and green fluorescence of the parasitic or non-parasitic worms. The assay further comprises contacting the parasitic or non-parasitic worms with one or more test agents, or subjecting the parasitic or non-parasitic worms to an event. The assay allows for a rapid and objective score of parasitic or non-parasitic worm death and survival and enables the performance of high- throughput screens for the identification of potential agents against diseases such as schistosomiasis. Also described are methods and kits for discriminatory analysis of parasitic or non-parasitic worm phenotype and / or metabolics using FTIR analysis.
Owner:ABERYSTWYTH UNIVERSITY
Methods and reaction mixture reagent for increasing the specificity and fidelity of polymerase reactions
InactiveUS7312054B2High selectivityImprove fidelitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAcridineSingle nucleotide mutation
A method for reducing the efficiency of primer extension by polymerase enzymes when the 3′ end of a primer or growing nucleic acid chain does not hybridize perfectly with the target, for increasing the selectivity of single nucleotide mutation or gene analyses, for suppressing false positive results and for enhancing the fidelity of the amplification of nucleic acid fragments by avoiding the incorporation of mispairs, the method comprising the steps of: (a) obtaining a nucleic acid sample; (b) hybridizing said nucleic acid sample to a primer; (c) subjecting said nucleic acid sample hybridized to a extension reaction by extending a primer with a polymerizing enzyme; and (d) detecting the presence of extension products; wherein the reaction extension mixture medium contains an intercalating agent such as ethidium bromide, dihydroethidium, ethidium homodimer-1, ethidium homodimer-2, acridine, propidium iodide, YOYO®-1 or TOTO®-1. When the intercalating agent is ethidium bromide the concentration is about 1 to 7 g / ml.
Owner:BIODYNAMICS
Semen energy quick detection reagent kit and its preparation and usage method
ActiveCN101055270BNo shynessShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisSemenTriton x100
The invention discloses a spermatozoon vigor fast detection kit and preparing and using method thereof. The kit includes a spermatozoon collecting box containing a plastic collecting box and spermatozoon liquefacient; triton X100 solution; propidium iodide solution; a standard color card, colors of which are color of adding triton solution with concentration of 0.05-0.2% and propidium iodide solution with concentration of 0.01-0.5% into spermatozoon sample with different concentration notarized by microscope; and a test board containing a shell and a basal plate, wherein two test pores are arranged on center of the shell, absorbent paper and filtering film are equipped on the basal plate. Advantages of the kit are: quantity of activated spermatozoon can be fast and accurately detected, more time can be saved than traditional diagnostic method, and usage is simple.
Owner:北京望升伟业科技发展有限公司 +1
Flow cytometry detection method for tetracycline resistance bacteria in drinking water
InactiveCN107121375AAccurate and reliable measurement resultsFully reflectIndividual particle analysisInjection volumePropidium iodide
The invention relates to a flow cytometry detection method for tetracycline resistance bacteria in drinking water. The method comprises the following steps of (1) adding a water sample to be detected into a brown test tube, adding tetracycline mother liquor, enabling the concentration of tetracycline in the water sample to be detected to be equal to an MIC value thereof, putting the water sample to be detected into a culture box, and culturing for 24h at 27 DEG C; (2) transferring the cultured water sample into a flow cytometry sample injection pipe, adding an SYBR Green I coloring agent and a propidium iodide coloring agent for coloring, and after fully vibrating, culturing in dark at 37 DEG C for 10 to 15min; (3) transferring the cultured flow cytometry sample injection pipe into a flow cytometry, starting to inject a sample, determining the number of the tetracycline resistance bacteria, and dividing by a sample injection volume so as to obtain the concentration of the tetracycline resistance bacteria in the drinking water. Compared with the prior art, the number of the tetracycline resistance bacteria is detected by utilizing the flow cytometry, so that the flow cytometry detection method has the advantages of quickness, accuracy and quantitation, overcomes the defect that the nonculturable resistance bacteria cannot be detected through a traditional culture method, and is more reliable in result.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for observing transferring of fusion protein to rice leafbud at long distance
InactiveCN103175810ASimple methodAccurate methodPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceConfocal microscopy
The invention discloses a method for observing the transferring of a fusion protein to a rice leafbud at long distance. The method comprises the following steps of: treating a root tip of rice by using a GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) fusion protein; then, freezing a leafbud of a rice plant with a treated root tip, and slicing; next, dyeing by using a PI (Propidium Iodide) fluorescent dye; and directly observing the transferring condition of the GFP fusion protein from the root tip to the rice leafbud by using a confocal microscopy. By using the method, the position, 0.5cm away from the root tip, of the rice is treated by using the GFP fusion protein, the leafbud is frozen and sliced and then dyed, and the transferring condition of the GFP fusion protein from the root tip to the rice leafbud is observed by using the confocal microscopy, so that the long-distance transferring condition of the GFP fusion protein in the rice plant can be directly and qualitatively known about. The position, 0.5cm away from the root tip of the rice, is directly treated by using the GFP fusion protein, the transferring of the GFP fusion protein to the leafbud is observed by using the confocal microscopy, and thus, a very powerful evidence can be further provided for the fact that an effect protein can induce the defensive reaction of a rice system. The method is simple, convenient, accurate and rapid.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for separating saccharomyces cerevisiae haploids in ultrahigh-throughput manner on basis of flow cytometry
InactiveCN109355245AQuantitatively examine the qualityImprove throughputMicroorganism based processesSpore processesSporeHigh-Throughput Screening Methods
The invention discloses a method for separating saccharomyces cerevisiae haploids in an ultrahigh-throughput manner on the basis of flow cytometry, and belongs to the technical field of high-throughput screening. The method has the advantages that ascospore treatment conditions are optimized, and accordingly the optimal saccharomyces cerevisiae spore suspension preparation conditions can be obtained; active spores and inactive cells in spore suspension are stained by PI (propidium iodide) and FDA (fluorescein diacetate) stain, stained samples are analyzed on the basis of flow cytometers, accordingly, the activity of saccharomyces cerevisiae spores can be distinguished, and the spores can be absolutely counted; the optimal spore suspension preparation conditions are established, and technologies for separating the saccharomyces cerevisiae haploids in the ultrahigh-throughput manner on the basis of the flow cytometers are created.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Activity detection method for fusarium virguliforme
InactiveCN102346107BGood repeatabilityPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSpore germinationStaining
The present invention discloses an activity detection method for fusarium virguliforme. According to the method, a propidium iodide staining method is adopted, a laser scanning confocal microscopy is adopted to detect, and the dead spores and the living spores of the fusarium virguliforme can be rapidly, accurately and sensitively distinguished. The method provided by the present invention can replace the traditional spore germination method, and is applicable for the departments of port inspection and quarantine, agricultural production, plant protection and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN AUDAQUE DATA TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com