Method for separating saccharomyces cerevisiae haploids in ultrahigh-throughput manner on basis of flow cytometry
A flux separation and haploid technology, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, methods using spores, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low separation efficiency, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and achieve the elimination of manual operations, The effect of avoiding diploid contamination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1 Preparation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae spore suspension
[0030] (1) Diploid yeast strains were activated in YPD liquid medium (yeast extract 10g / L, peptone 20g / L, glucose 20g / L) at 30°C and 220rpm for 18h, then transferred to 50mL fresh In YPD liquid medium, culture at 30°C, 220rpm for 24h. Centrifuge at 4000rpm for 5min, collect the cells, wash twice with saline, spread on solid sporulation medium (potassium acetate 20g / L, agar powder 20g / L), and culture at 26°C for 3 days. Collect the sludge on the solid spore-forming medium and resuspend in 5 mL of saline to obtain untreated spore suspension.
[0031] (2) Add 2.5% (w / w) helicase (Sangon Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., Cat. No. A600870-0001) to the untreated spore suspension in step (1), and incubate at 30° C. for 30 minutes with shaking. A spore suspension treated with helicase was obtained.
[0032] (3) Add 35-45% (v / v) glass beads of 425-600 nm to the spore suspension treated in step (2), and sh...
Embodiment 2
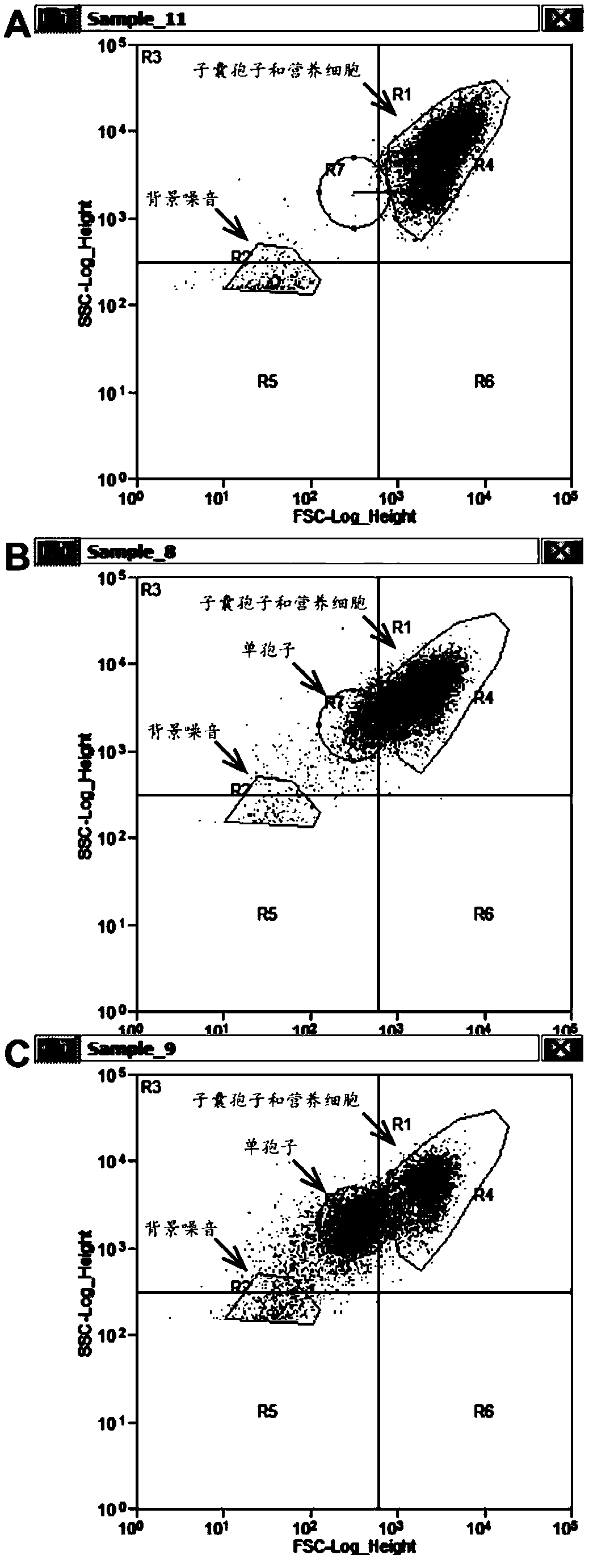
[0033] The determination of the position of embodiment 2 spore cell group
[0034] Utilizing the characteristics that ascospores and vegetative cells are smaller than haploid spores, the area where haploid spore cells are located is determined according to the forward scattered light signal (FSC) of the flow cytometer ( figure 1 ). Respectively to the untreated sporulation sample (prepared and obtained in embodiment 1 step (1)), only the spore suspension sample (prepared and obtained in embodiment 2 step (1)) and helicase treatment gained with only helicase The spore suspension sample prepared by bead oscillation (prepared and obtained in embodiment 1 step (3)) carries out flow cytometric analysis, and the results are as follows: figure 1 shown. figure 1 In A, the untreated sample cell population is in the upper right area of the figure; figure 1 In B, a part of haploid spores were isolated after the ascus wall was digested only by helicase treatment, and some cells were ...
Embodiment 3
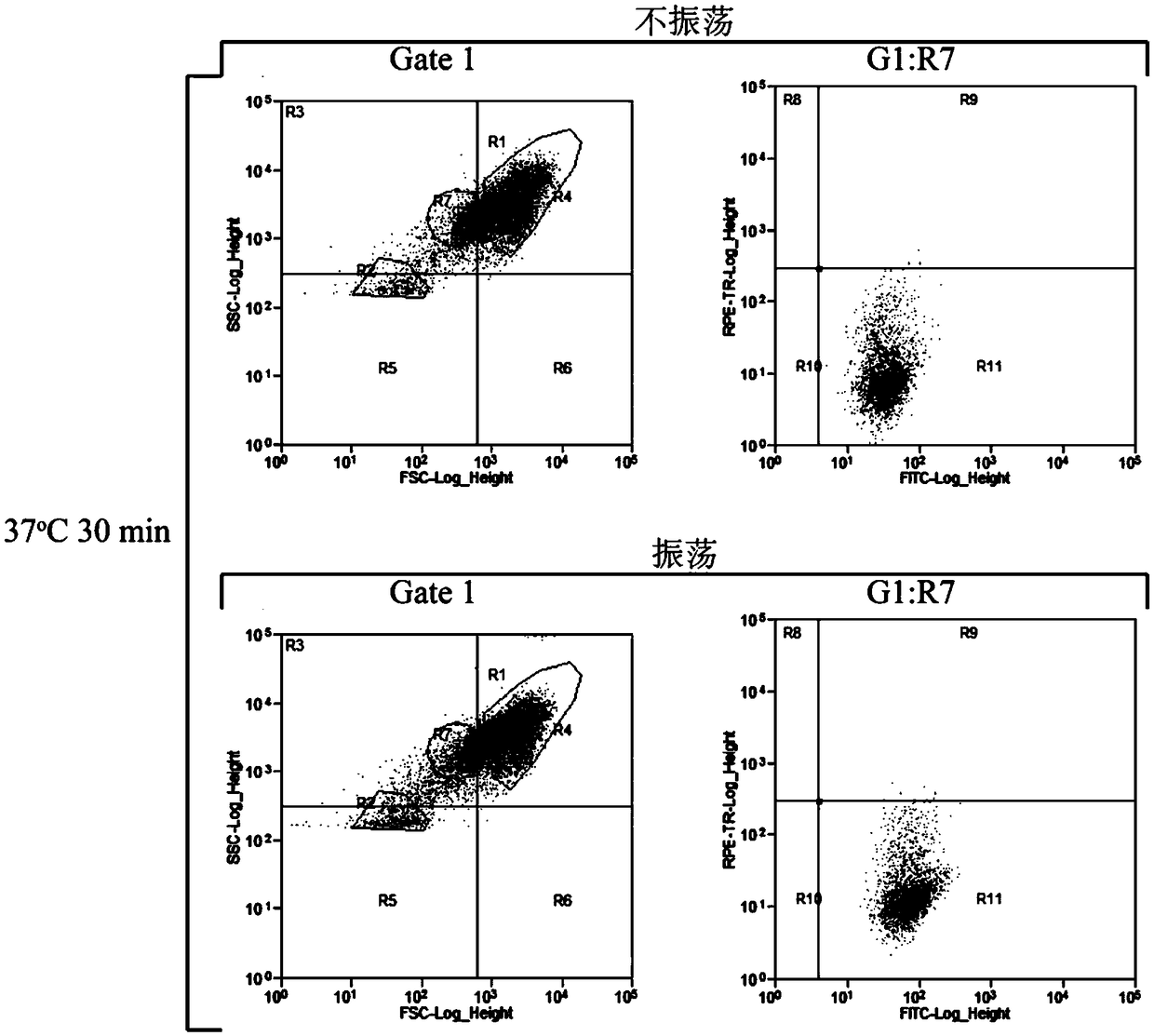
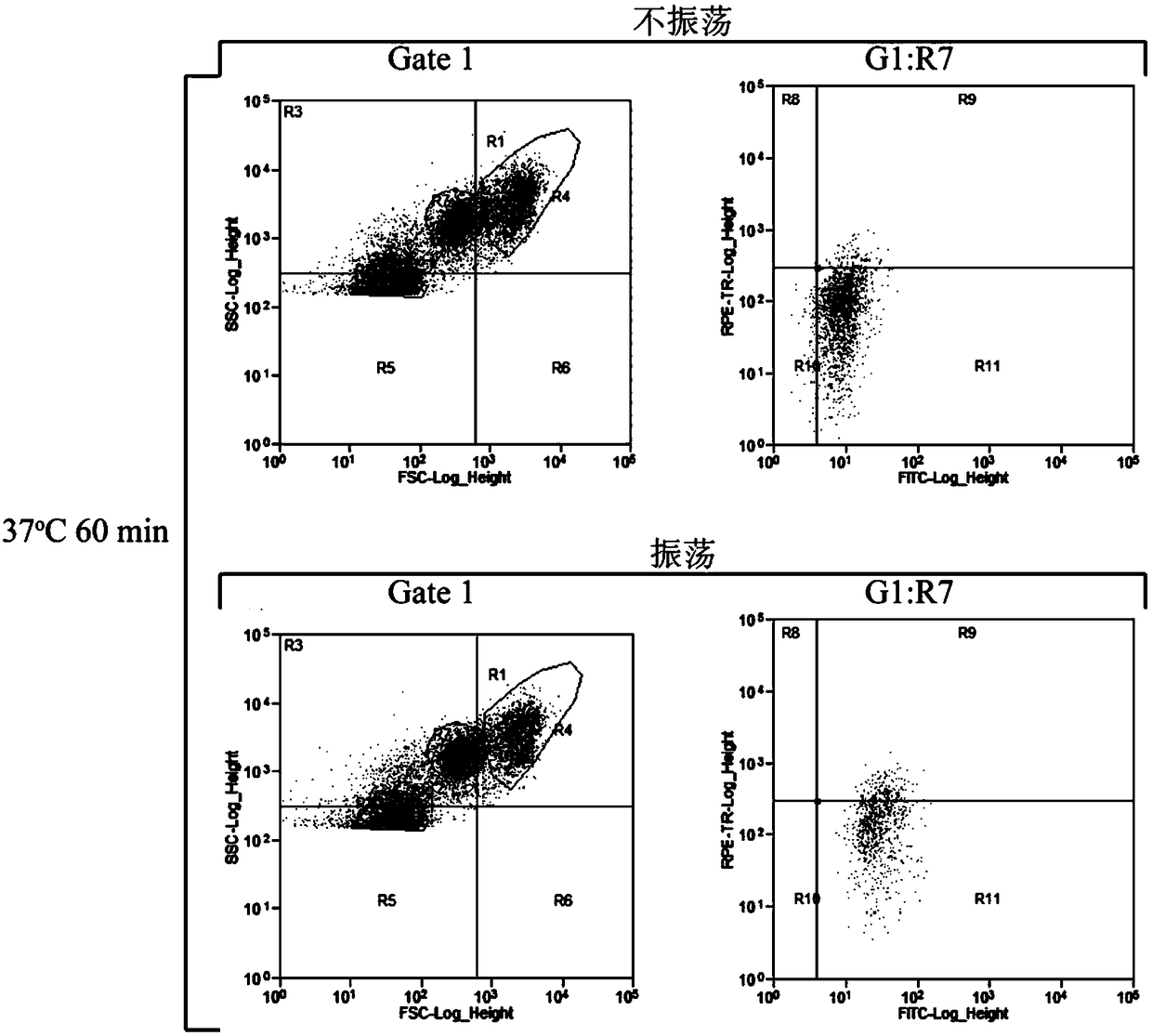
[0035] Example 3 PI and FDA dyes stain the Saccharomyces cerevisiae spore suspension
[0036] Weigh 0.01g PI, and dilute to 10mL with PBS (pH 7.4) buffer solution. Dilute to 10 μg / mL to obtain PI fluorescent dye. Store at 4°C protected from light. Weigh 0.01g FDA and dilute to 5mL with acetone. Dilute to 2 μg / mL with PBS (pH 7.4) buffer solution to obtain FDA fluorescent dye. Store at 4°C protected from light. The spore suspension prepared by embodiment 1 was diluted to 10 5 ~10 6 For each cell / mL, mix 2 mL of spore suspension with equal volumes of 8 μg / mL PI dye and 4 μg / mL FDA dye respectively, and incubate at 4°C for 20 min in the dark.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com