Detection method for radiosensitivity of solid tumor cell
A detection method and technology of tumor cells, applied in the field of detection of cell radiosensitivity of solid tumors, can solve problems such as complex operation, stability, and low success rate, and achieve the effect of deepening understanding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
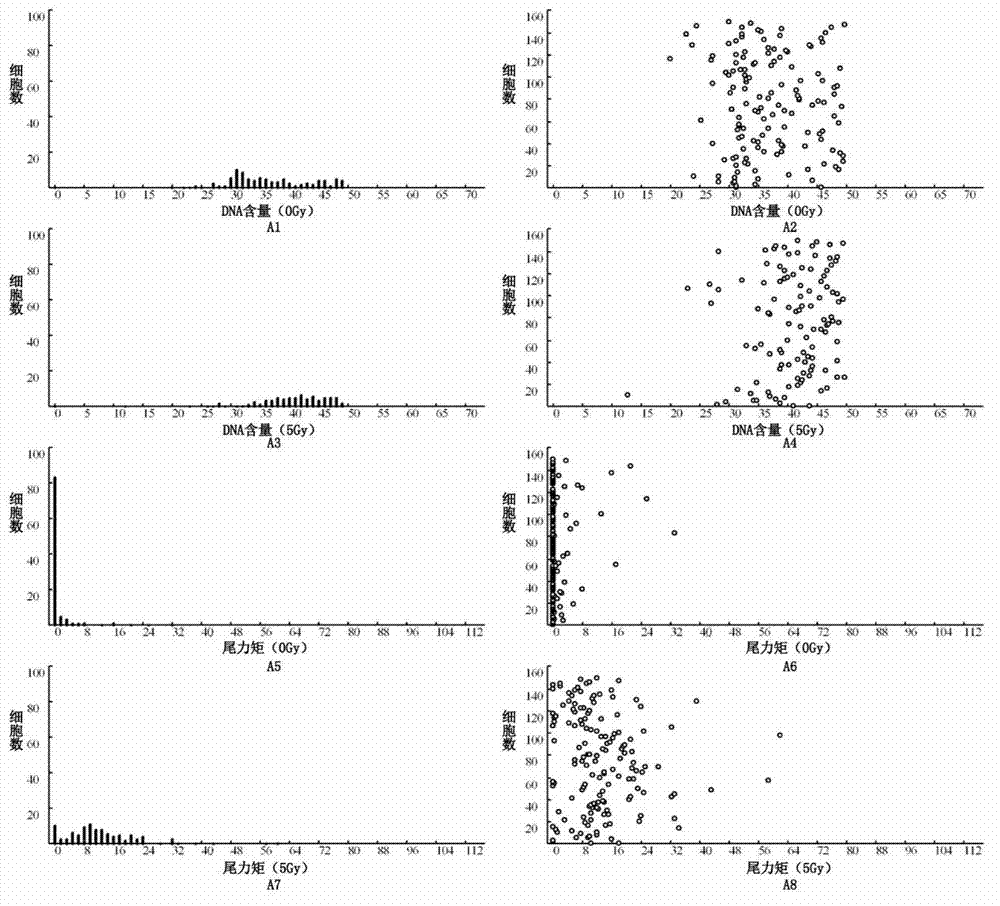
[0048] Figure 1 is a legend of the analysis report of the radiosensitivity of the cells of the nasopharyngeal carcinoma samples. 1A1-A8 are analysis reports of lymphoma cells cultured in vitro as external reference controls, which are used as positive references for system error correction and radiosensitivity assessment. From Figure 1A1 to Figure 1A8, the histogram and scatter diagram of the DNA content distribution of cells under 0 irradiation, the histogram and scatter diagram of the DNA content distribution of cells after 5Gy irradiation, and the distribution of tail moment (TM) of cells under 0 irradiation Histogram and scatter plot and the histogram and scatter plot of the distribution of cell tail moments after 5Gy irradiation. As shown in the figure, under the conditions of this experiment, the DNA content of lymphoma cells is mostly distributed on the right side of lane 35-40. And it can be seen from the TM distribution diagram that the TM value of the 5Gy irradiatio...
Embodiment 2
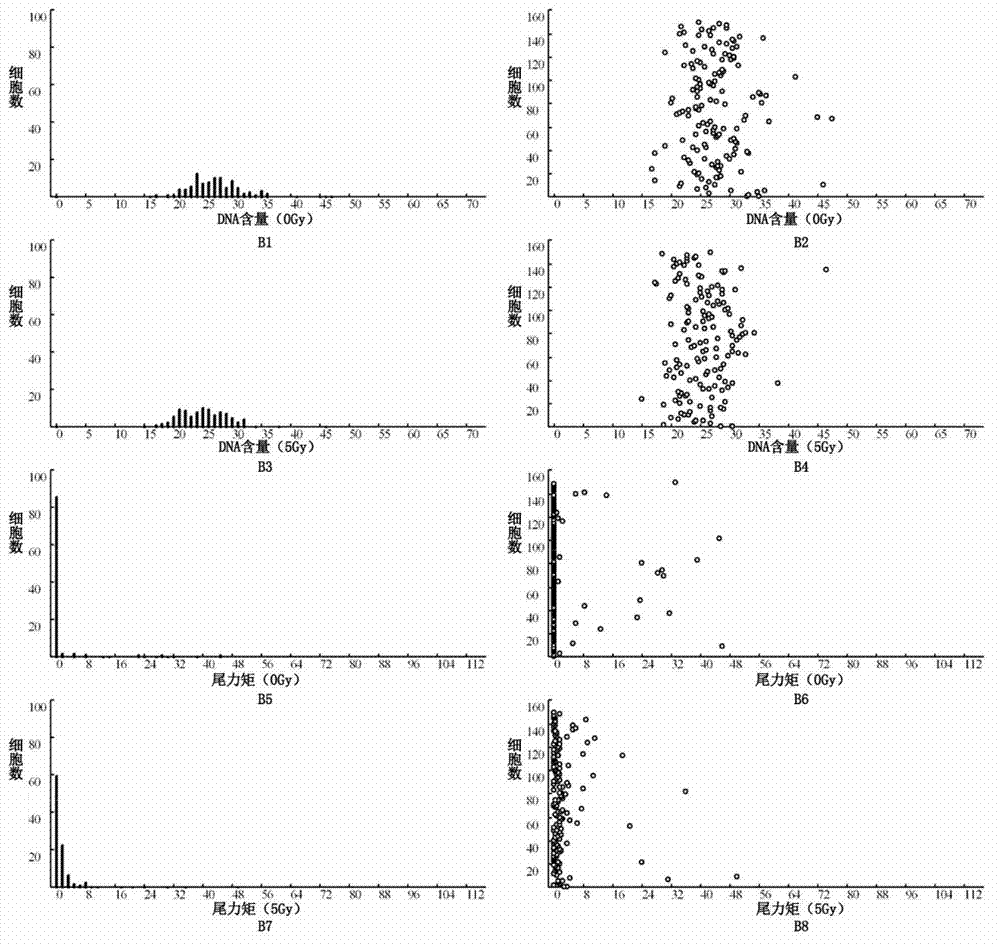
[0052] Figure 2 is a legend of the analysis report showing a typical high radiosensitivity (radiosensitive type) of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma sample after cell radiosensitivity testing. The analysis results showed that the TM values of most cells (including normal / tumor cells) in the tumor sample tissue after 5Gy irradiation were relatively large, even greater than that of the external reference control cells after 5Gy irradiation (shown as obvious under the microscope). "comet tail" formation). Fig. 2A1-A8, B1-B8 and C1-C8 are respectively the analysis reports of normal cells, tumor cells and external reference control lymphoma cells of test samples, as shown in the figure, the TM difference of external reference control lymphoma cells is 21.07, the TM difference of normal cells was 23.6, and the radiosensitivity was 1.12 (23.6 / 21.07), and the TM difference of tumor cells was 42.36, and the radiosensitivity was 2.01 (42.36 / 21.07).
[0053] The actual radioreactivity measu...
Embodiment 3
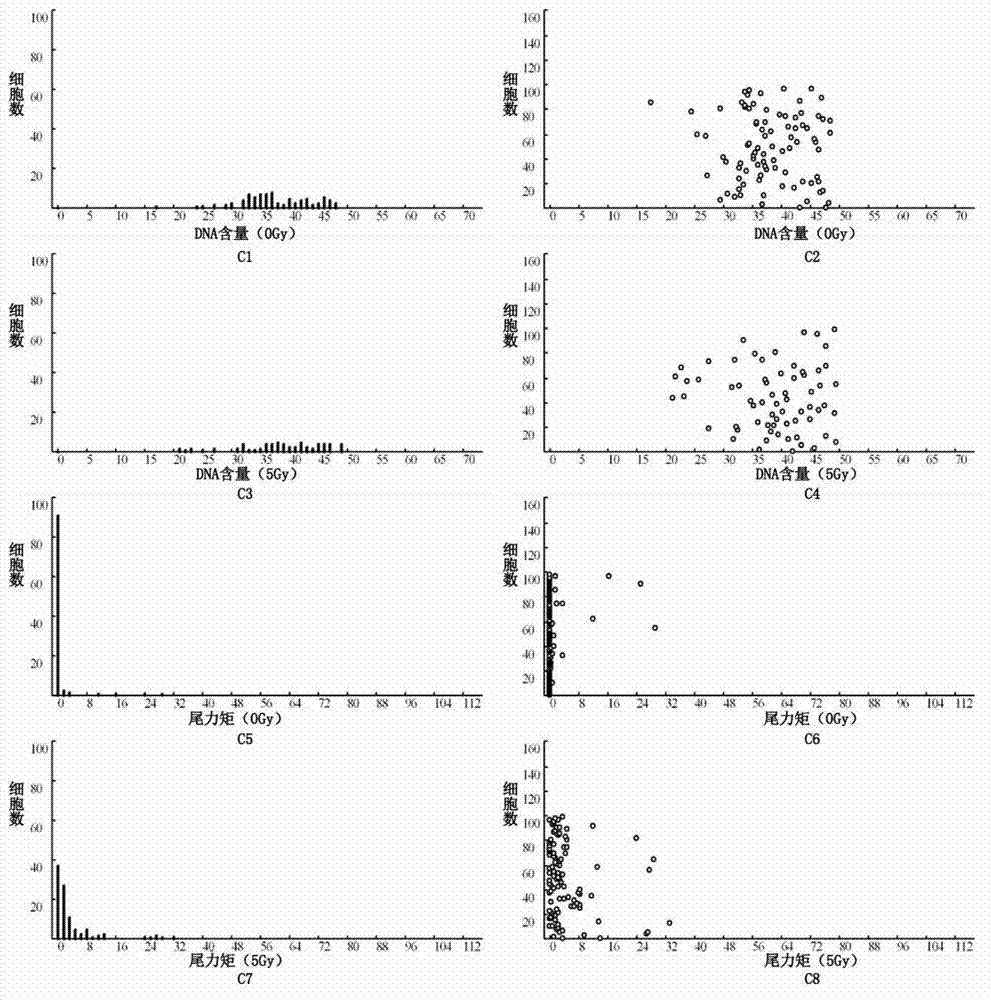
[0055] Figure 3 is a legend of the analysis report showing a typical low radiosensitivity (radiation insensitive type) of a nasopharyngeal carcinoma sample after cell radiosensitivity testing. The analysis results showed that the TM values of normal cells (lymphocytes, fibroblasts) and tumor cells in the tumor sample tissue after 5Gy irradiation were much smaller than those of the external reference control cells after 5Gy irradiation (shown as no obvious under the microscope). "comet tail" formation). Figure 3A1-A8, B1-B8, and C1-C8 are the analysis reports of normal cells, tumor cells, and lymphoma cells of the external reference control, respectively. As shown in the figure, the TM difference of the external reference control lymphoma cells is 73.24, The TM difference of normal cells was 1.13 and the radiosensitivity was 0.02 (1.13 / 73.24), while the TM difference of tumor cells was 13.03 and the sensitivity was 0.18 (13.03 / 73.24).
[0056] The actual radioreactivity meas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com