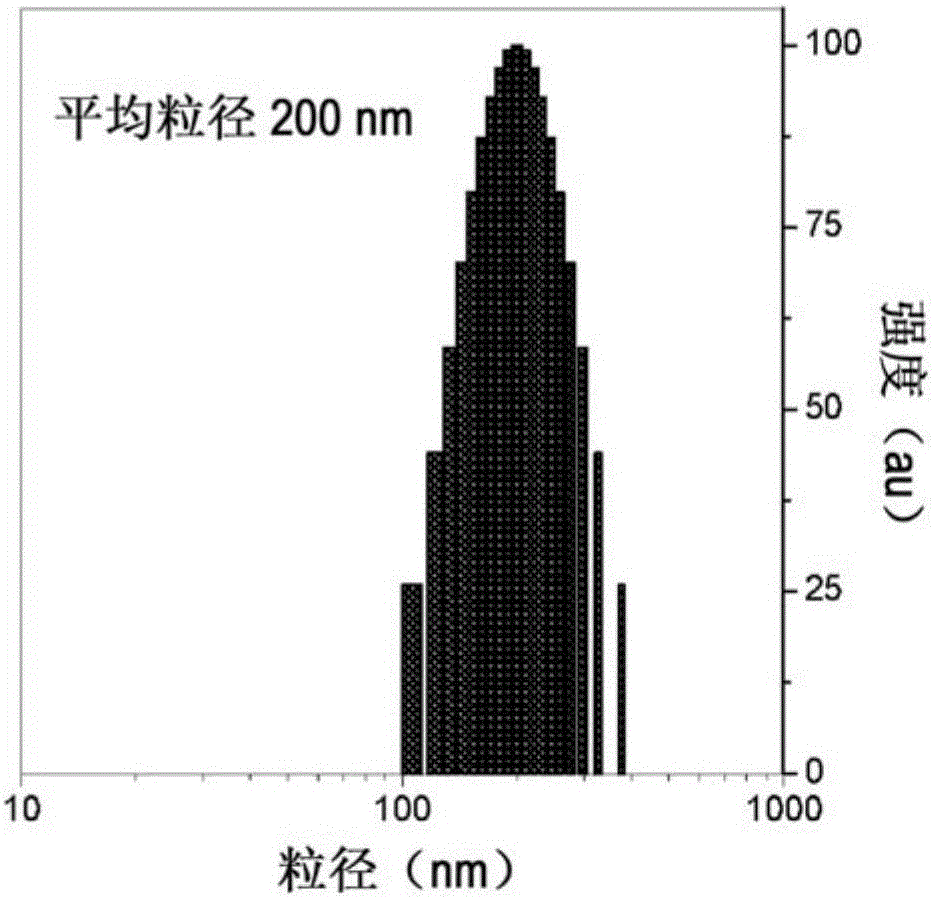
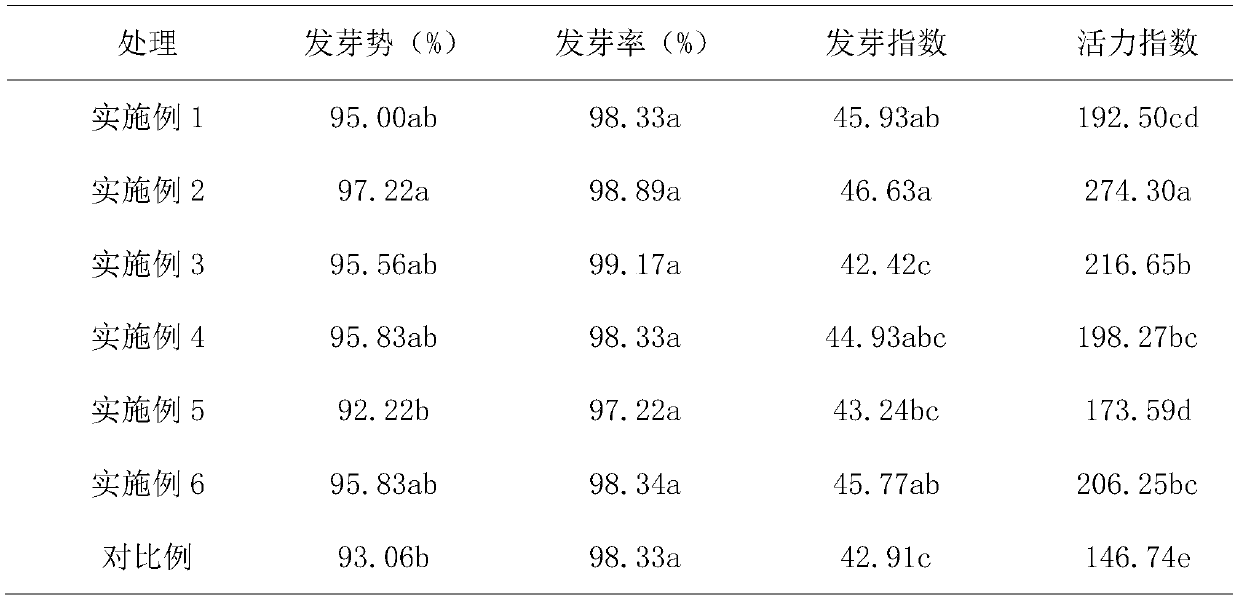
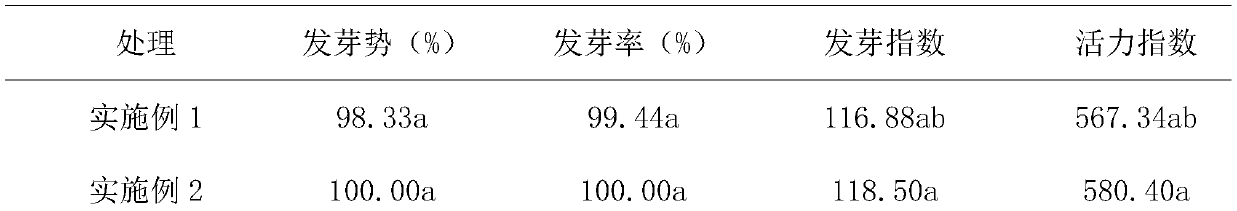
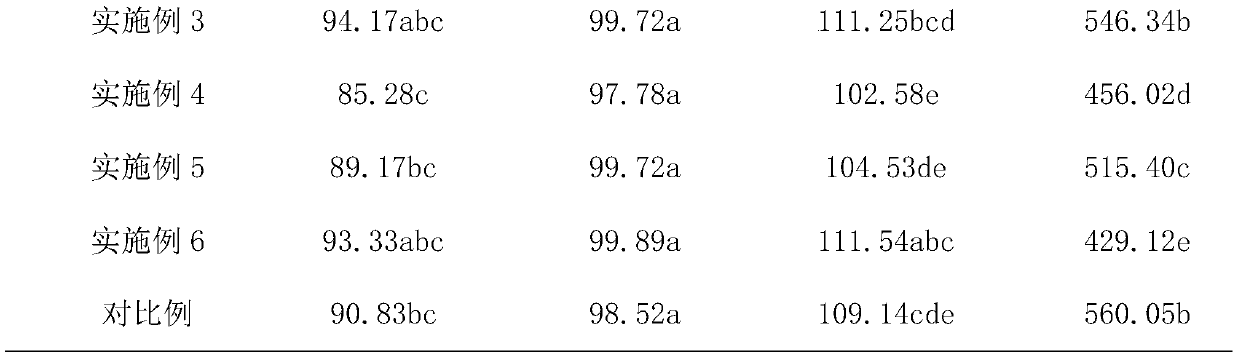
Patents
Literature
69 results about "Membrane lipids" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Membrane lipids are a group of compounds (structurally similar to fats and oils) which form the double-layered surface of all cells (lipid bilayer). The three major classes of membrane lipids are phospholipids, glycolipids, and cholesterol. Lipids are amphiphilic: they have one end that is soluble in water ('polar') and an ending that is soluble in fat ('nonpolar'). By forming a double layer with the polar ends pointing outwards and the nonpolar ends pointing inwards membrane lipids can form a 'lipid bilayer' which keeps the watery interior of the cell separate from the watery exterior. The arrangements of lipids and various proteins, acting as receptors and channel pores in the membrane, control the entry and exit of other molecules and ions as part of the cell's metabolism. In order to perform physiological functions, membrane proteins are facilitated to rotate and diffuse laterally in two dimensional expanse of lipid bilayer by the presence of a shell of lipids closely attached to protein surface, called annular lipid shell.
Pharmaceutical compositions and their use
InactiveUS6605298B1Improve bioavailabilityImprove consistencyOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiological bodyMembrane lipids
The invention provides a composition for delivering at least one biologically active compound to a living organism, said composition comprising at least one micelle-forming membrane lipid
Owner:PHARES PHARMA RES
Methods, immunoassays and devices for detection of anti-lipoidal antibodies
The present application describes compositions, methods and devices for detecting anti-lipid antibodies and diagnosing diseases such as syphilis. In particular, methods for immobilizing lipid antigens (including cardiolipin, lecithin, and cholesterol) on solid supports (eg, nitrocellulose membranes) are described. The ability to immobilize lipid antigens on membranes fulfills a long known need for a membrane-based assay for the detection of anti-lipid antibodies. An immunoassay device for simultaneous treponema pallidum and non-treponemal testing is also described.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
New use of sodium hydrosulfide for promoting wheat seeds sprouting under heavy metal stress
InactiveCN101385466APromote germinationGerminate fastBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAmylaseNormal growth
The invention discloses a new application of sodium hydrosulfide for promoting germination of wheat seeds under the stress of heavy metals, namely, the application is that the sodium hydrosulfide is taken as a sprout-promoting agent of germination in the soil polluted by heavy metals of Al<3+>, Cd<2+>, Cr<3+>, Cr<6+>, Pb<2+>, Hg<2> and the like. The invention can effectively improve the germinability of the wheat seeds under the stress of heavy metals, and induces the seeds to germinate fast and regularly. Research proves that the sodium hydrosulfide of the hydrogen sulfide donor is adopted to preprocess the wheat seeds, which can remarkably induce the activity expression of hydrolytic enzyme of amylase, protease, lipase and the like, in the seeds, enhances the oxygenolysis of storage matter, relieves the oxidative damage caused by the stress of the heavy metals in the seeds and maintains the lower membrane lipid overoxidation level in the seeds and the seedlings, thus being beneficial to the normal growth of embryo and radicle. The invention solves the key problem of restoring the production of the wheat in the areas polluted by heavy metals, has simple operation; the needed reagent is single and is easy to be obtained.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
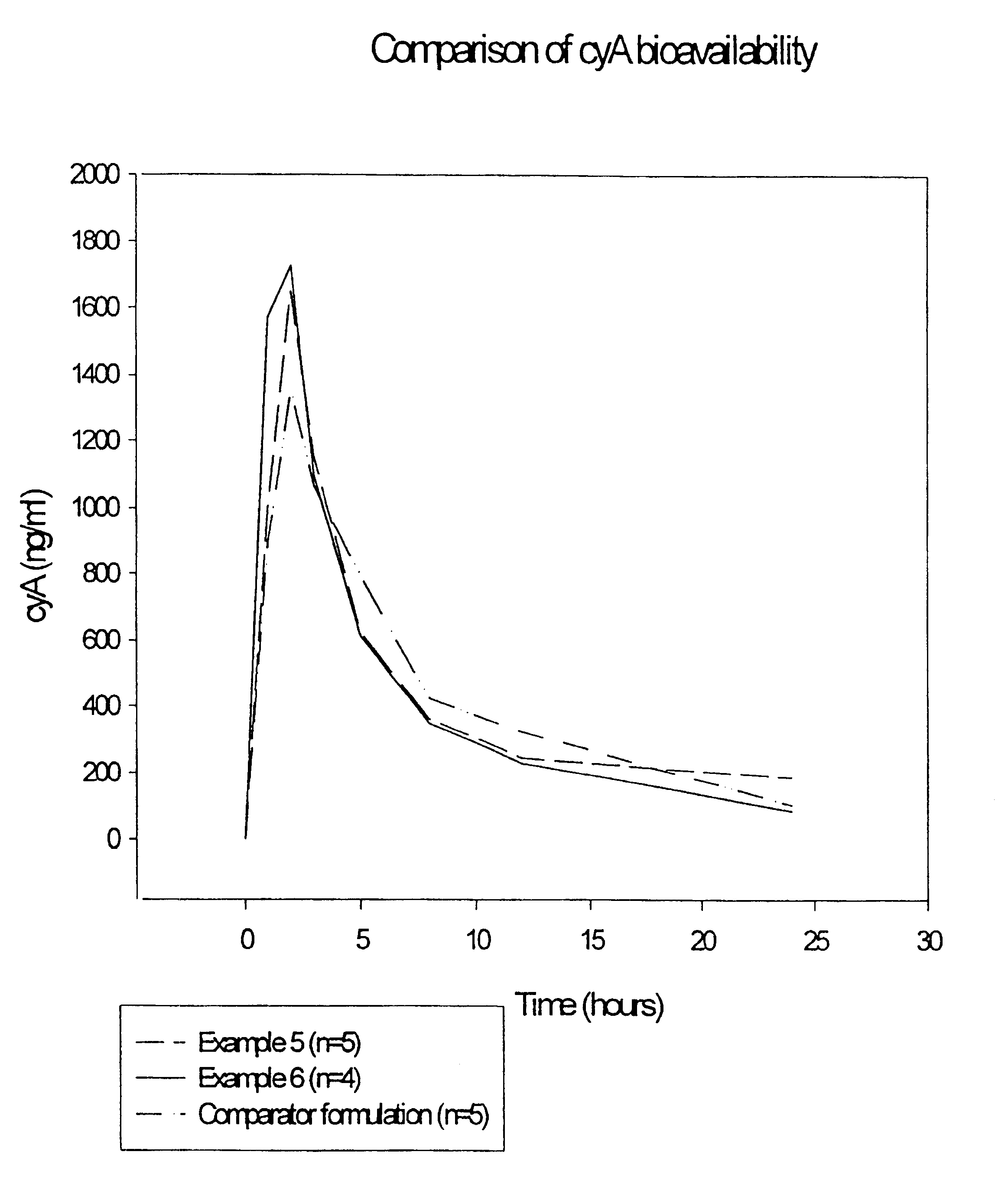
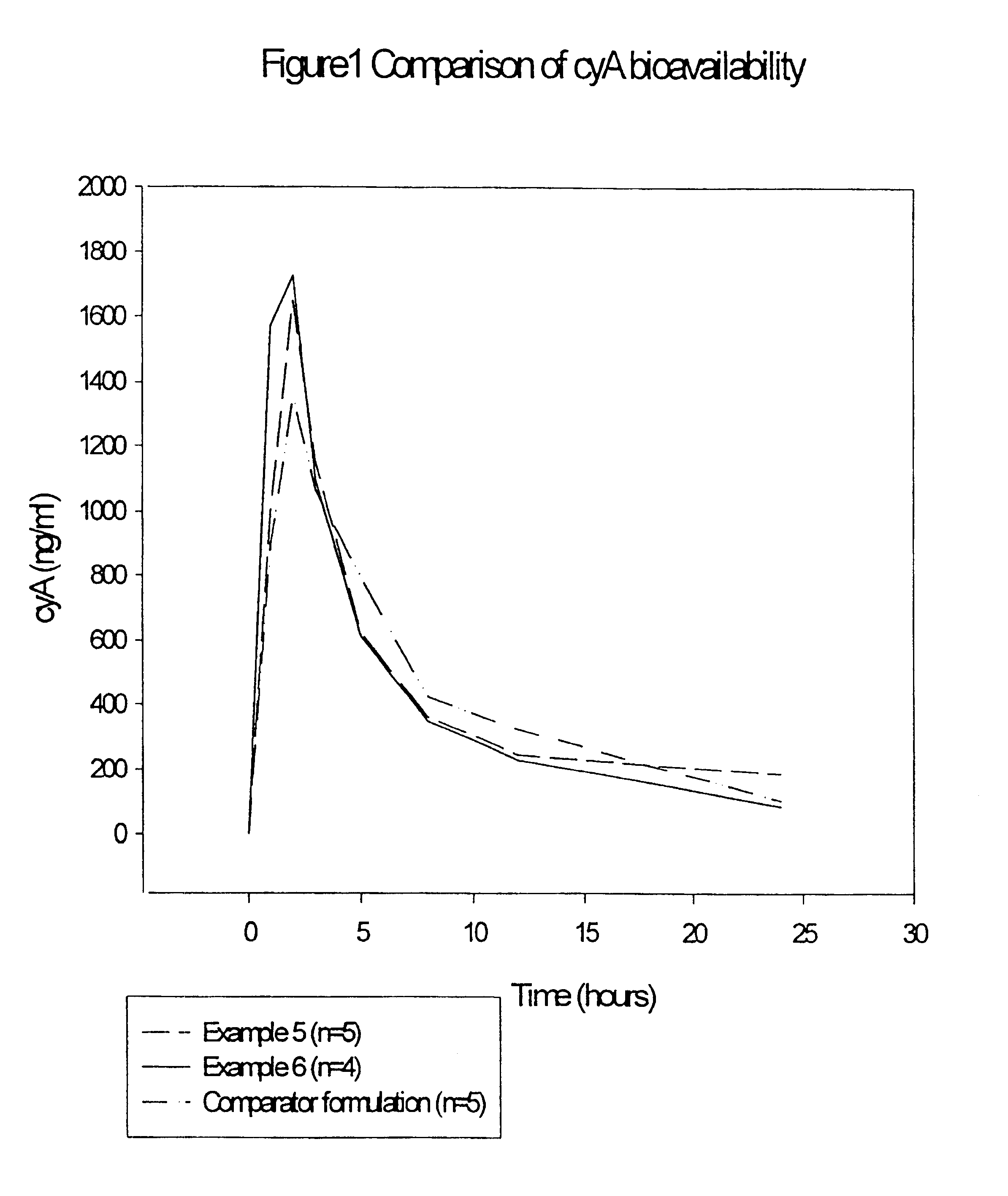
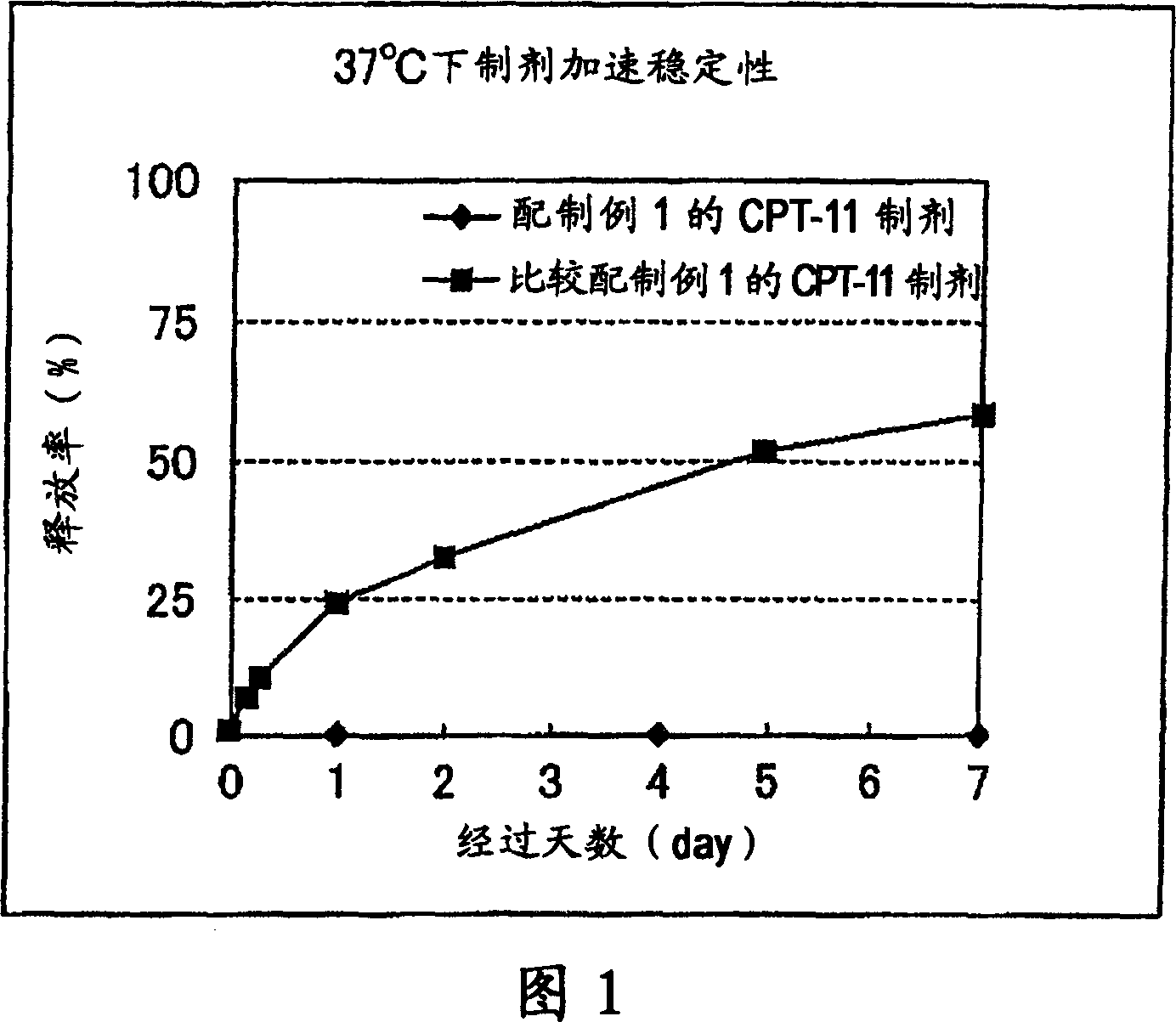
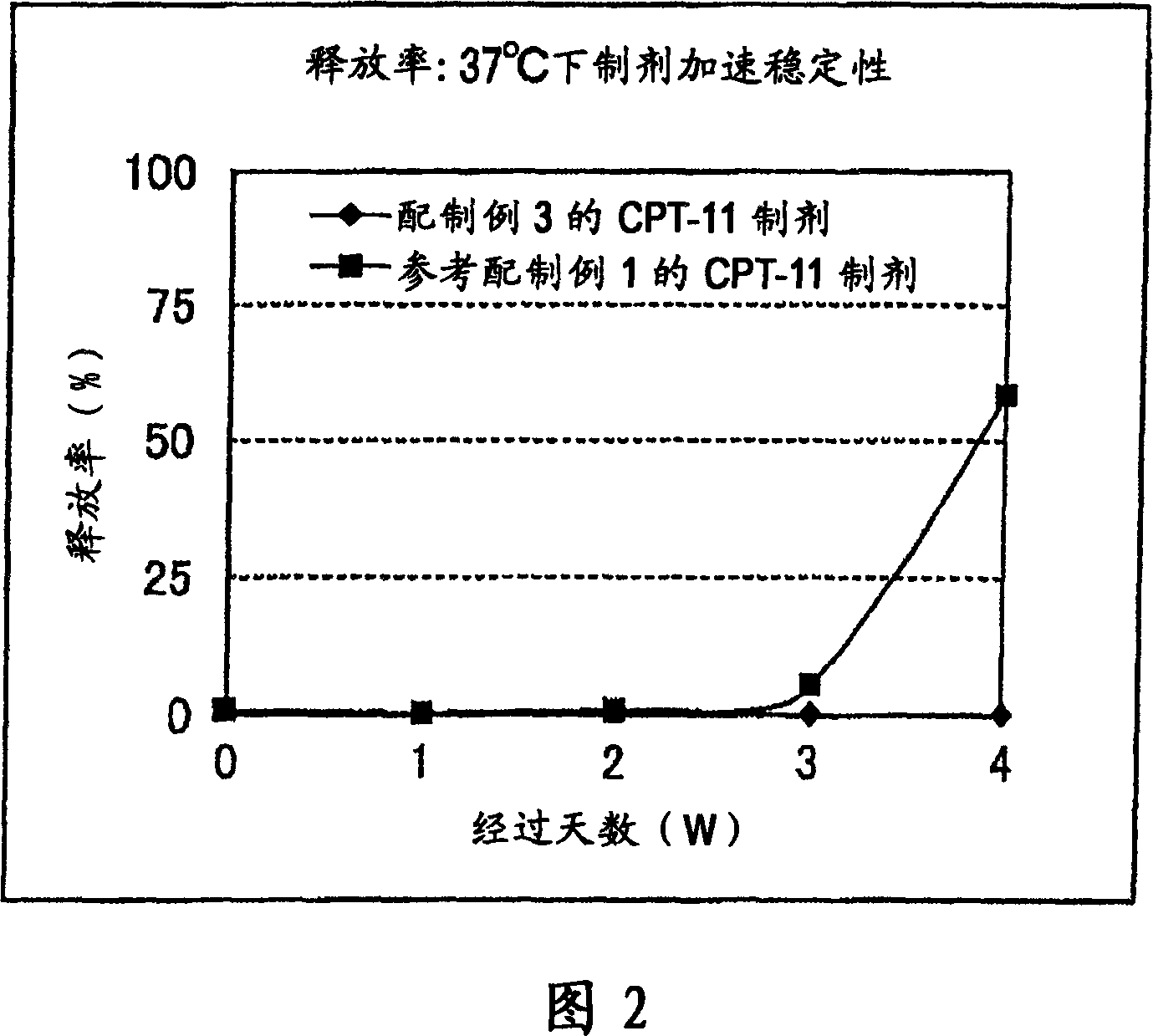
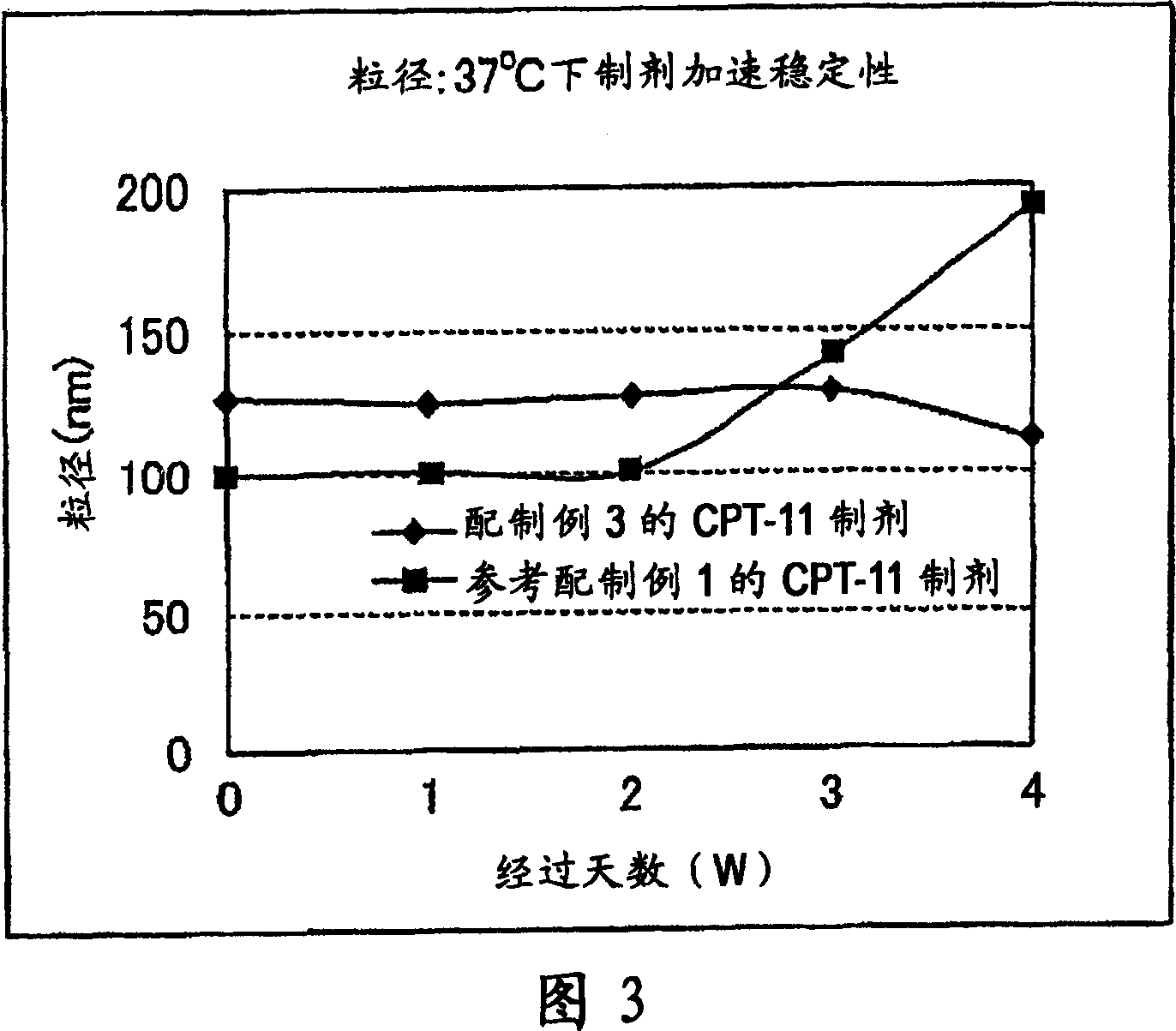
Irinotecan preparation
InactiveCN1960729AImprove stabilityImprove retentionOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsMembrane lipidsLipid formation
An irinotecan preparation having irinotecan and / or a salt thereof highly carried by a closed vesicle carrier, which exhibits a strikingly prolonged retention in blood as compared with that of conventional irinotecan liposome preparations and is capable of being present in blood for a prolonged period of time. There is provided an irinotecan preparation comprising closed vesicles formed of a lipid membrane wherein irinotecan and / or a salt thereof is sealed in a concentration of at least 0.07 mol / mol (medicine mol / total membrane lipid mol). The irinotecan preparation preferably has an ion gradient between an inner water phase and an outer water phase within the closed vesicles. The closed vesicles are preferably liposomes, and the liposomes preferably have only the external surface thereof modified with a surface modifier containing a hydrophilic polymer.
Owner:TERUMO KK +1
New use of sodium hydrosulfide for promoting plant root morphogenesis
InactiveCN101385465APromote seedlingsPromote growth and reproductionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideForest industryHypocotyl
The invention relates to a new application of sodium hydrosulfide for promoting the morphogenesis of plant roots, namely, the application is that the sodium hydrosulfide is taken as root stimulate to promote the morphogenesis of side roots and adventitious roots of the seedling of the plant and the morphogenesis of the adventitious roots of cutting branches of the plant. The sodium hydrosulfide has obvious root-promoting effect to the seedlings of the plant such as rapes, mung beans, soybeans, cucumbers and the like, the hypocotyledonary axis of the cut segment thereof and the cutting branches of the plant such as willow branches, peach branches, grapes, batatas and the like, promotes the formation and growth of the side roots and the adventitious roots of the plant, enhances the water absorbing capacity of the plant, maintains the water balance in the body of the plant, reduces membrane lipid overoxidation damage of the hypocotyledonary axis of the cut segment and the cutting branches, maintains the relative stability of membrane structure of the explant and promotes the growth and propagation of the plant. The root-promoting agent can be used for growing roots of various plant seedlings, the hypocotyledonary axis of the cut segment and the cutting branches and is applicable to the root-promoting effect of promoting and culturing the seedlings of transplanting and cutting and the like, in the agriculture, forestry and gardening.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Multifunctional peanut growth inhibitor
InactiveCN101213964AEffective growth controlEasy to controlBiocidePlant growth regulatorsGrowth retardantSide effect
The invention relates to a multi-functional peanut growth inhibitor which is composed by the weight ratio of following components, paclobutrazol to prohexadione calcium to uniconazole is 3: 1.2-1.5: 0.8-1.2. The invention not only can effectively control the growth of the vegetative part of the peanut on the ground, can prevent the peanut from overgrowing and lodging, but also can effectively avoid the side effect brought by general growth inhibitor (e.g. paclobutrazol). At the same time, in the growth anaphase of the peanut, the invention can remarkably improve LAI (leaf area index), effective LAI, leaves membrane-lipid protective enzymatic activity (SOD, POD, CAT), Pr (soluble protein) content and so on, can reduce MDA content and can postpone the senescence rate of peanut leaves. More importantly, the invention can remarkably improve the output of pods. The production can be increased by 16.6 percent- 23.0 percent more than the production without spraying any inhibitor, and can be increased by 7.6 percent- 13.7 percent more than the production only spraying paclobutrazol. The invention solves the problem that the overgrowth and presenility can not be prevented synchronously in the production process of the peanuts.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Nutrient solution for preventing frost damage of plant and production method
InactiveCN101485340ANormal growthIncrease productionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsForest industryHydrolysate
The invention relates to a plant freezing injury resistant nutrient solution containing potassium hydroxide hydrolysate of plant seed dregs and peat, phosphoric acid, a microelement fertilizer and polyatomic alcohol and a preparation method thereof. The nutrient solution has the functions of promoting photosynthesis of plants, reducing the moisture in plant cells, preventing membrane lipid from being converted from liquid to gel at low temperature, has the advantages of reasonable formulation, low energy consumption in production, simple and convenient production technique, convenient use, increase of the crop output, reduction of the labor intensity, and the like, and has wide application in the fields of agriculture, forestry and the like.
Owner:宫玲玲
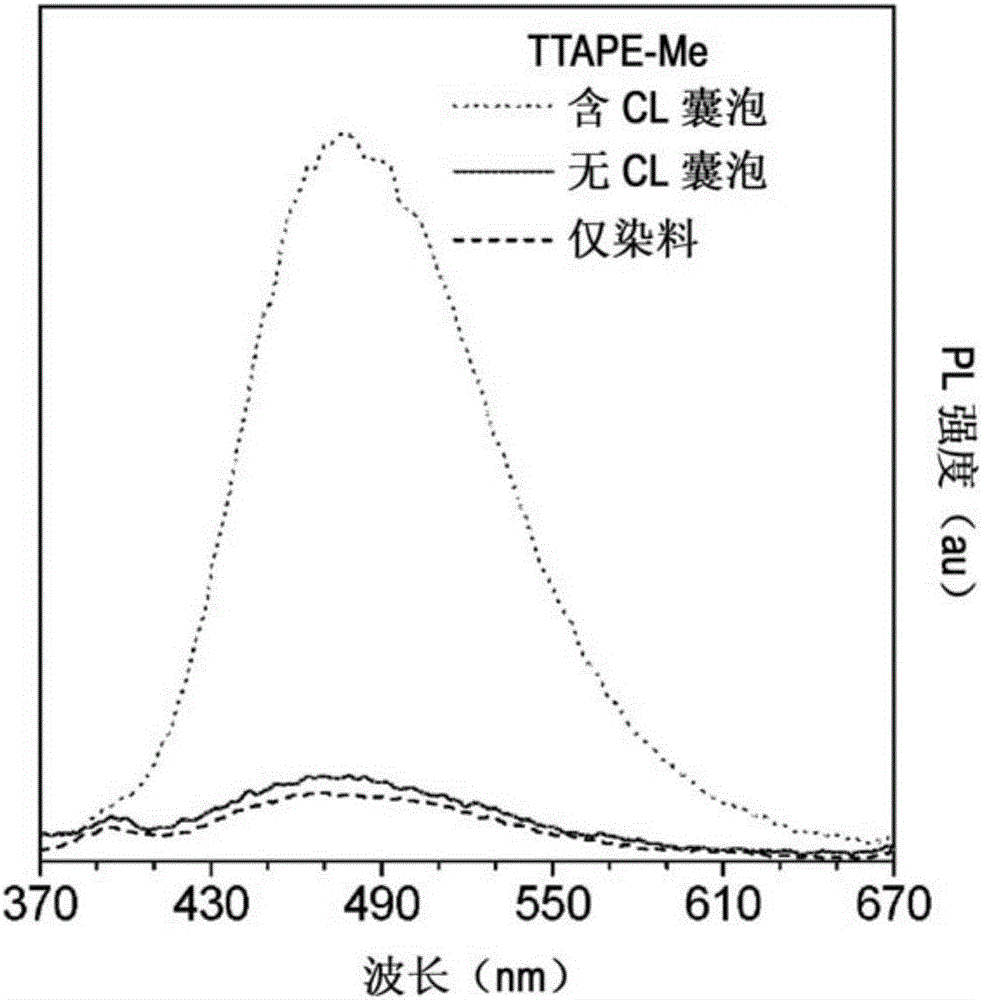
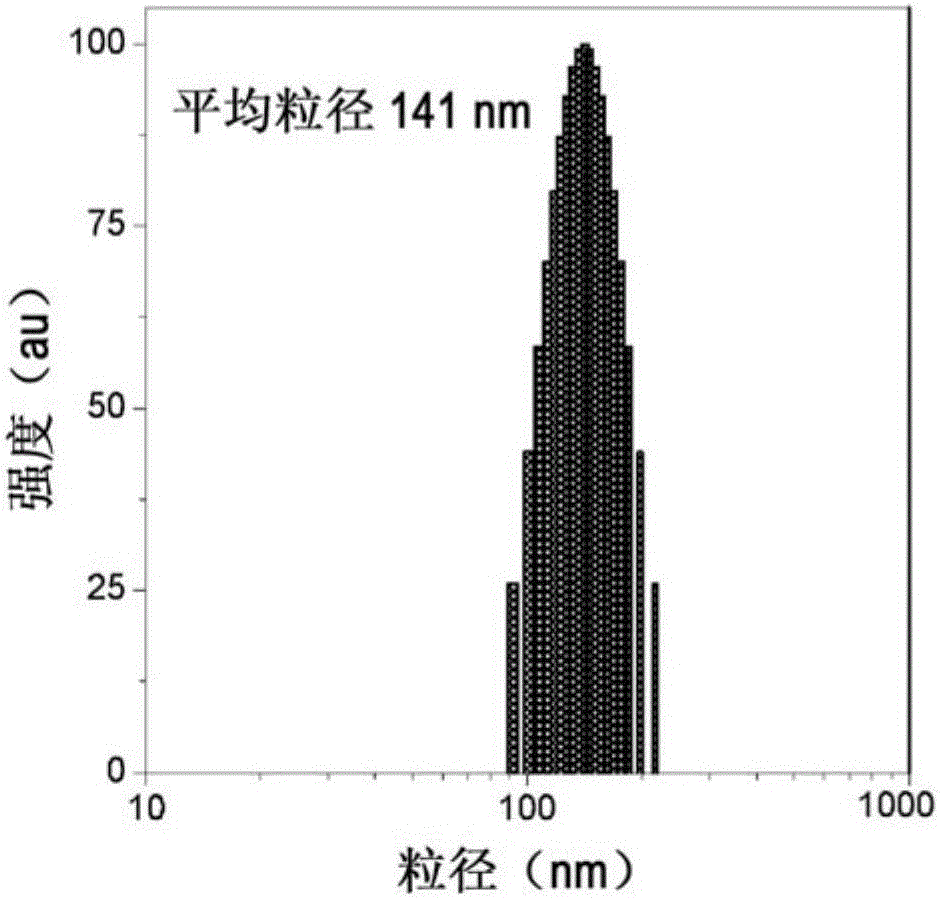
Specific detection and quantification of cardiolipin and isolated mitochondria by positively charged AIE fluorogens and method of manufacturing of AIE fluorogens
ActiveCN105874319AFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsMembrane lipidsIsolated mitochondria
The present subject matter relates to a one-step method of detecting and quantifying cardiolipin in a sample using a positively charged AIE luminogen by introducing the AIE luminogen to a solution containing the sample and measuring fluorescence intensity of the solution; a method of quantifying isolated mitochondria using a positively charged AIE luminogen by staining a sample containing isolated mitochondria with the AIE luminogen and measuring the fluorescence intensity; and a method of quantifying isolated mitochondria using a positively charged AIE luminogen by introducing the AIE luminogen to a sample containing isolated mitochondria, wherein the AIE luminogen stains the isolated mitochondria and identifying the stained isolated mitochondria under microscope. With improved sensitivity and excellent selectivity to CL over other major mitochondrial membrane lipids, an aggregation-induced emission-active fluorogen, TTAPE-Me, may serve as a valuable fluorescent sensor for CL detection and quantification and the quantification of isolated mitochondria.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Infant formula milk powder rich in milk fat globule membrane protein and phospholipid
The invention provides infant formula milk powder rich in milk fat globule membrane protein and phospholipid. By adding alpha-lactalbumin, milk fat globule membrane and a physiological activator, suchas bifidobacterium animalis Bb-12, milk fat globule membrane lipids and protein, N-acetylneuraminic acid (sialic acid), SN-2 structure lipid, human milk oligosaccharides (HMOs) and human milk oligose(HMO). By simultaneously adjusting the using amount ratio of all the components, especially sphingomyelin, gangliosides, the milk fat globule membrane protein, the human milk oligosaccharides, the human milk oligose, adiponectin and lysozyme, and the proportion between mucin, xanthine oxidoreductase, mucin 15, CD 36, butyrophilin, adipose differentiation-related protein and fatty acid binding proteins, the content of the active ingredients in the milk powder is closer to the content of active ingredients in human milk, the constitution of the infant formula milk powder is optimized, and the formula milk powder obtained by using the method is closer to the human milk.
Owner:李钟
No-heading Chinese cabbage seed initiator and application method thereof
InactiveCN109757489APromote germinationControl water absorptionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPolyethylene glycolCell membrane
The invention relates to the technical field of seed initiation, in particular to a no-heading Chinese cabbage seed initiator, which is prepared from ascorbic acid, calcium chloride, gibberellin, polyethylene glycol, buffer agents and sterilization agents, wherein the concentration of the ascorbic acid is 20 to 200mg / L; the two optimum concentrations of the ascorbic acid in the no-heading Chinesecabbage seed initiator are respectively 50 and 80 mg / L; the buffer agents are one or several kinds of materials of glucose and fumaric acid; the sterilization agents are tetra methylthiuram disulfide.The invention also discloses an application method of the no-heading Chinese cabbage seed initiator. Through the seepage initiation effect of the ascorbic acid, the seed cell water absorption is controlled; the seed gemmation power is favorably improved; the gemmation of the no-heading Chinese cabbage seeds is promoted; the functions of preventing membrane lipid peroxidation, clearing away free radicals and maintaining cytomembrane integrality are realized; the young seedling growth is more facilitated.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Membrane lipid compositions
InactiveUS6960354B1Convenient efficient meanGood storage stabilityPowder deliveryCosmetic preparationsLipid formationMembrane lipids
A composition in the form of a dry powder and which comprises: a) at least one membrane lipid, and b) at least one biologically active compound comprising a xanthine and / or a carboxylic acid, and which forms structured lipid assemblies when dispersed / dissolved in an aqueous medium. A method of preparing such a composition is also provided, together with a dispersion of structured lipid assemblies suspended in a solution of at least one biologically active compound and a method of preparing the same. The compositions and dispersions are suitable for use in creams and lotions for skin care.
Owner:LUCAS MEYER COSMETICS
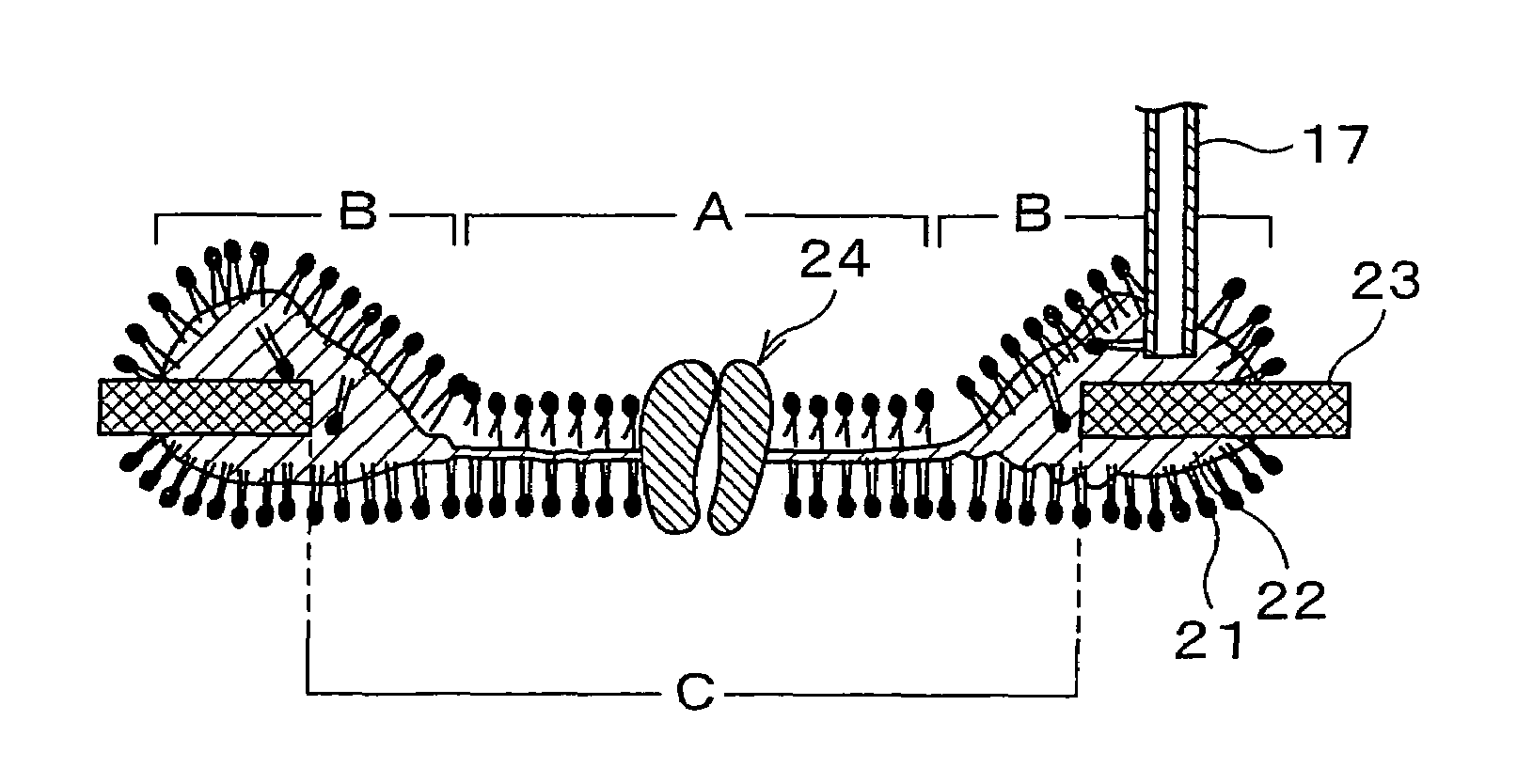
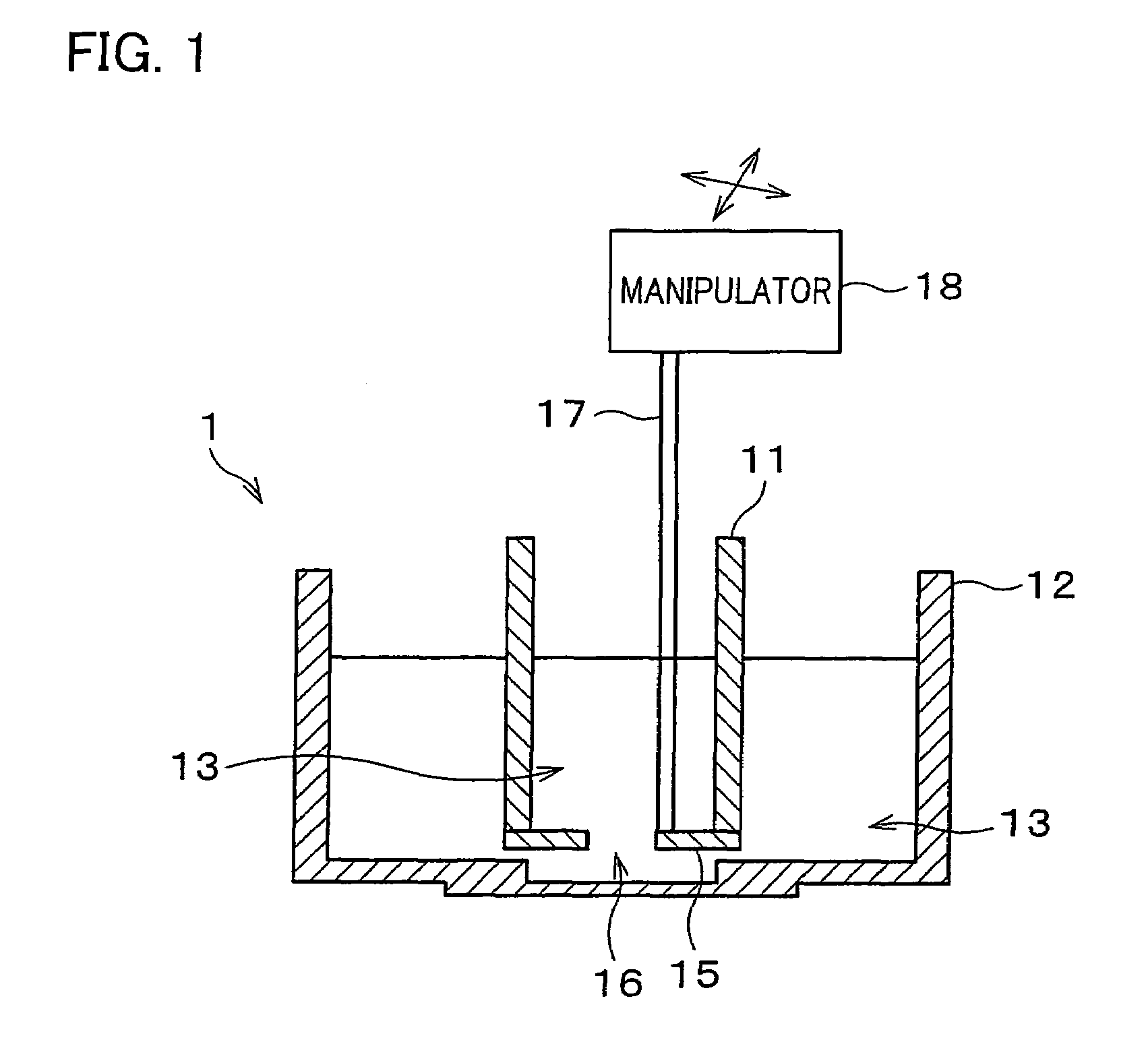
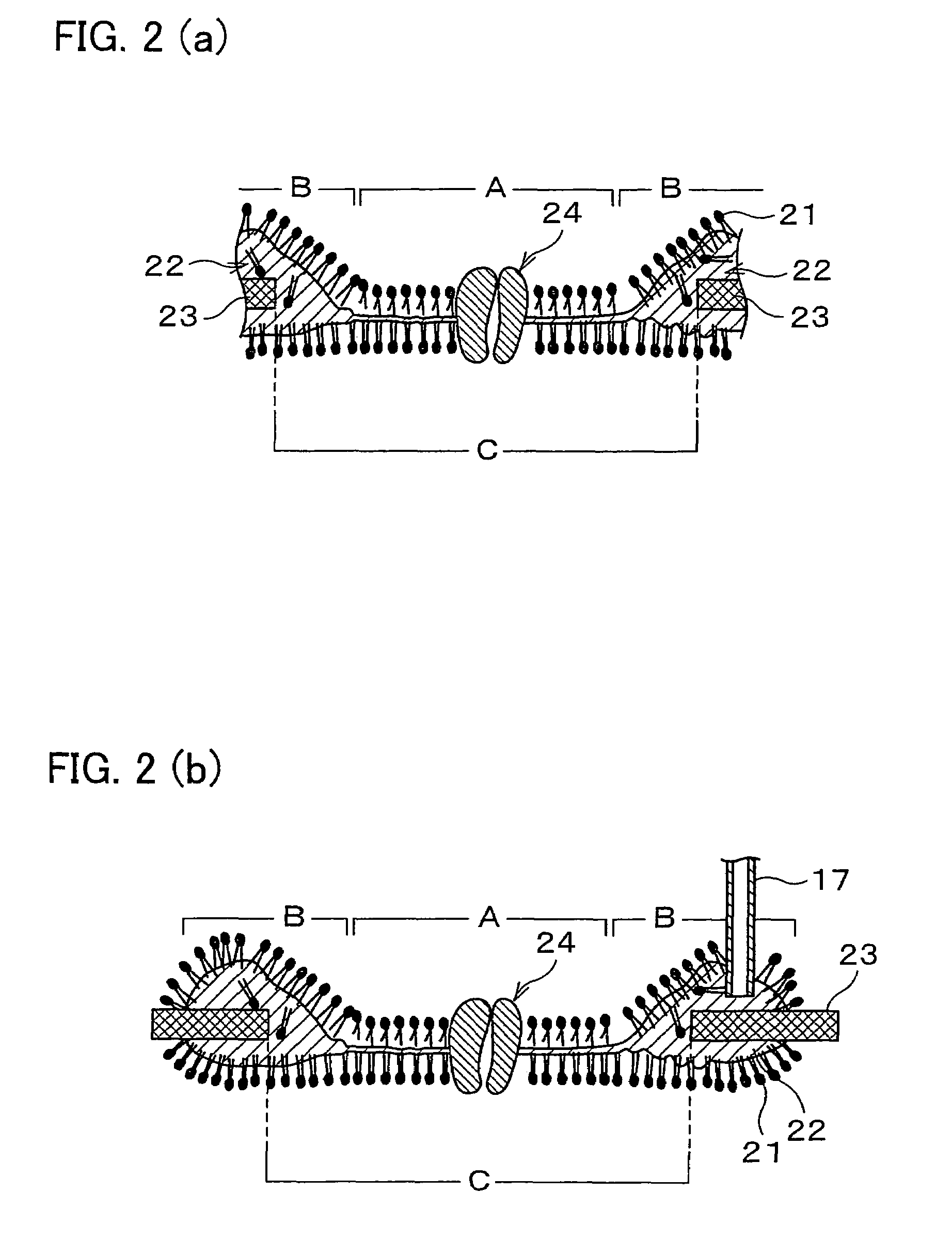
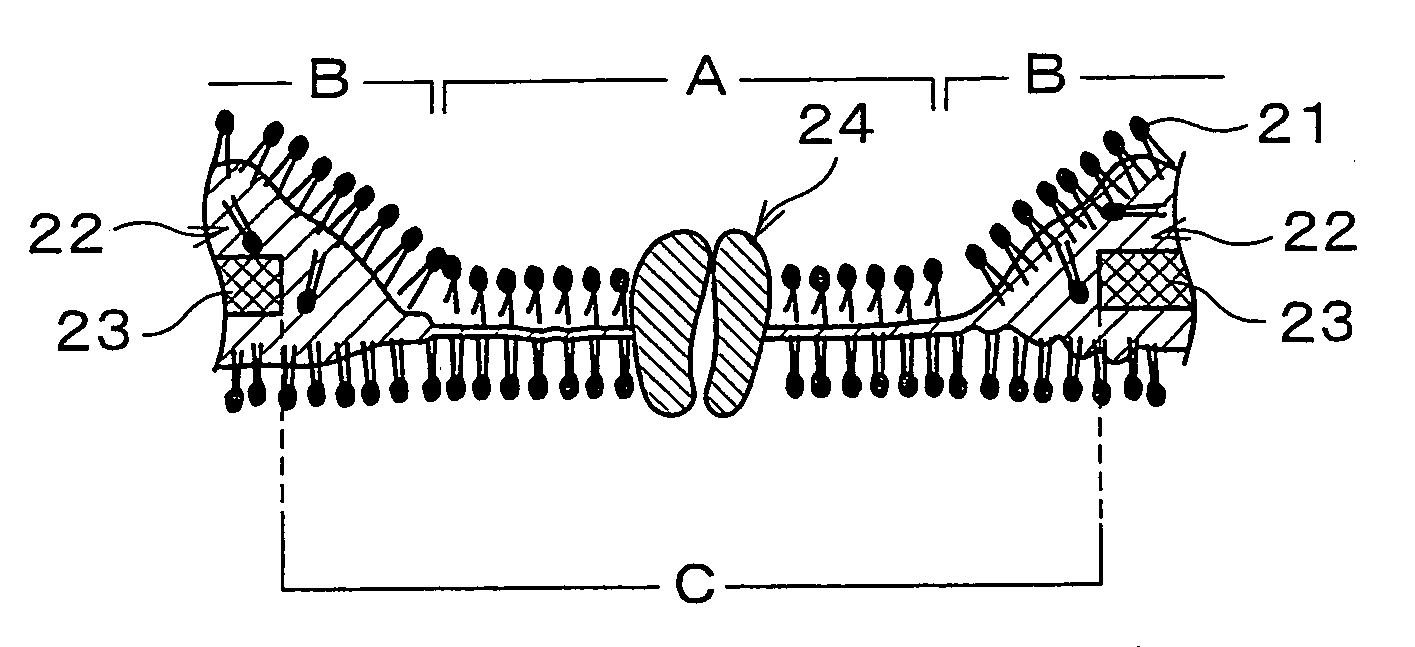
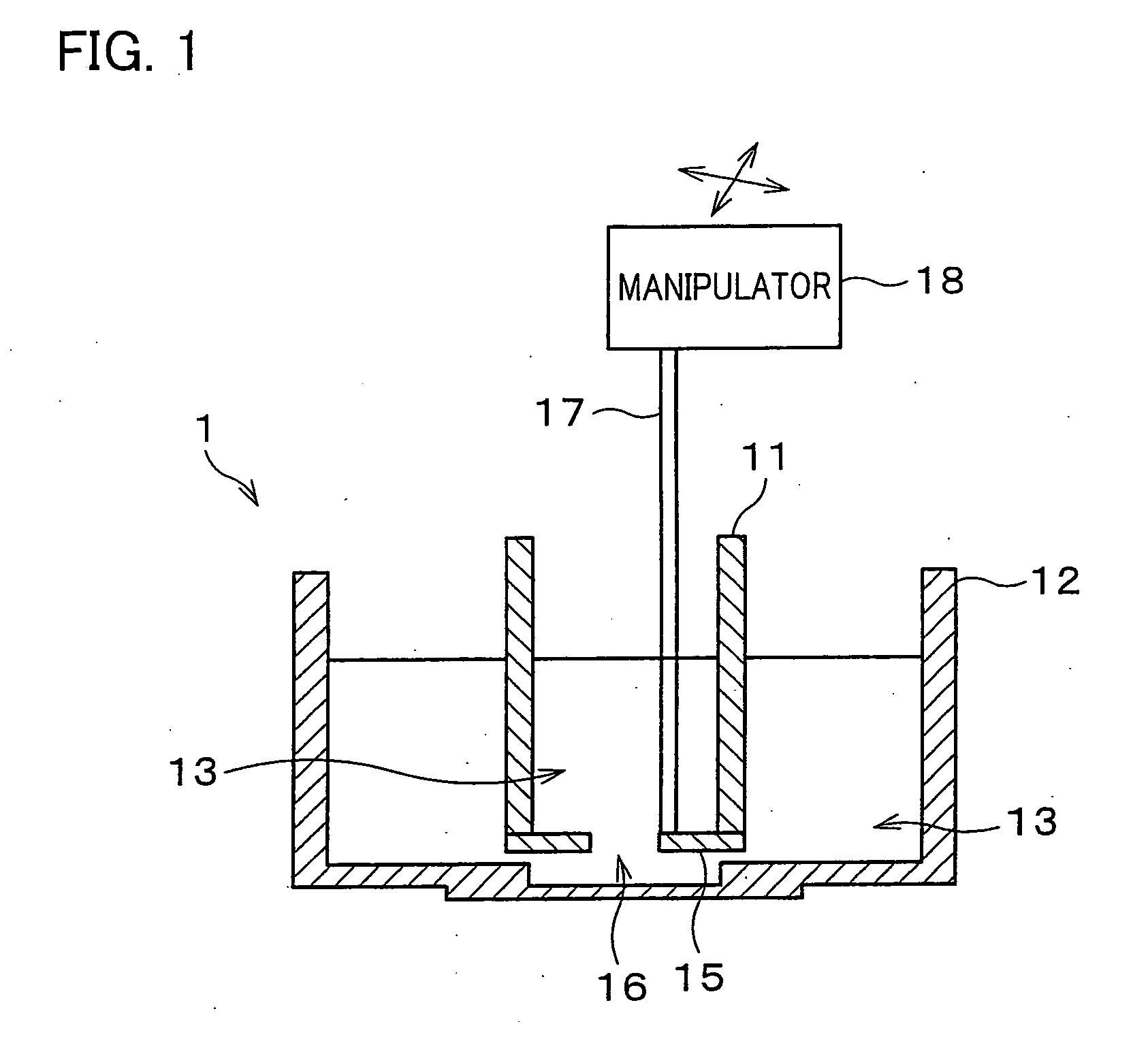
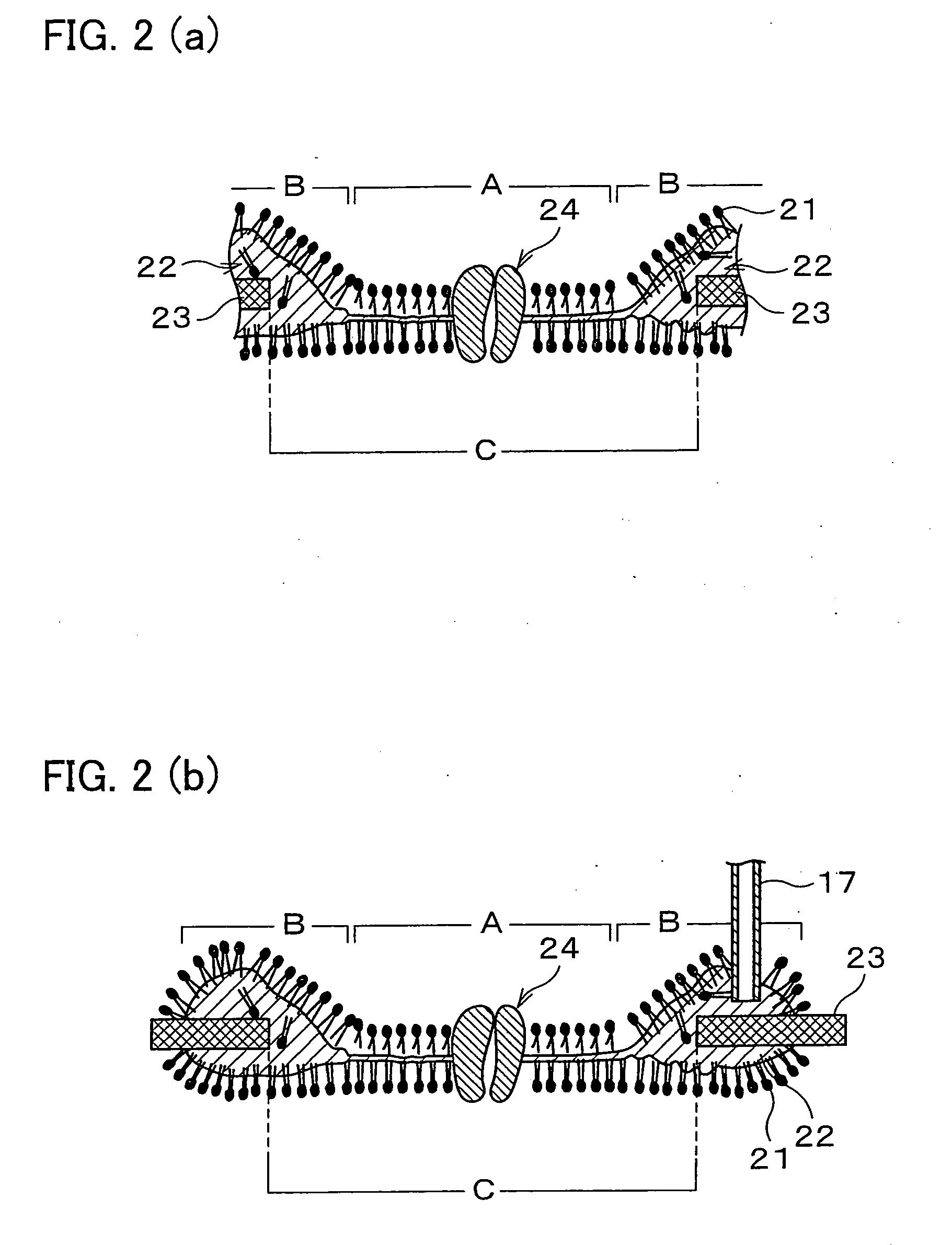
Artificial lipid bilayer membrane lipid substitution method, artificial lipid bilayer membrane obtained by using lipid substitution method, artificial lipid bilayer membrane formation device and ion permeation measuring device
InactiveUS7638092B2Easy to changeEfficient use ofLaboratory glasswaresAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionLipid formationMembrane lipids
An artificial lipid bilayer membrane formation device is disclosed, which includes: an upper solution chamber (first solution chamber) and a lower solution chamber (second solution chamber), both of which are filled with aqueous solution. It further includes a partition wall disposed between the upper solution chamber and the lower solution chamber so as to part the upper and lower solution chambers from each other. The partition wall has an opening, and a first lipid solution is applied to a portion around the opening, thereby forming an artificial lipid bilayer membrane on the opening. Further, in the formation device, a tubule for lipid substitution is attached to the partition wall so as to be positioned on a bulk phase of the artificial lipid bilayer membrane. A second lipid solution is added via the tubule, thereby forming an artificial lipid bilayer membrane whose lipid composition is changed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Compound regulator for preventing premature senility and increasing yield of corn and application method thereof
InactiveCN102211965APromote germinationPromote growthFertilising methodsFertilizer mixturesPhosphatePotassium
The invention discloses a compound regulator for preventing premature senility and increasing yield of corn. Every kilogram of the compound regulator comprises 100-300 mg / kg of butane diacid, 1,000-3,000 mg / kg of chitin, 0.00001-0.00003 mg / kg of forchlorfenuron and 100,000-150,000 mg / kg of potassium dihydrogen phosphate (molecular formula: KH2PO4). The invention further discloses a method for applying the compound regulator. Due to the adoption of the compound regulator, the germination of corn seeds and the growth of seedlings can be promoted, the germination process of seeds is accelerated, the growth and the development of corn leaves and root systems are promoted, the leaf area and the root quantity of corn are increased, the chlorophyll content of leaves and the root system activity of corn are increased particularly at the middle and later periods of grain filling, the activities of anti-oxidases such as SOD (Superoxide Dismutase) and CAT (Catalase) and the like in the corn leaves and root systems are increased remarkably, the accumulation of active oxygen in the leaves and root systems is reduced, the peroxidation action of the membrane lipid is restrained, premature senility is prevented, and the yield of corn kernels is increased.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of guanidinated chitosan and application of guanidinated chitosan
ActiveCN106905443AImprove the grafting rate of guanidinylationLow toxicityBiocideFungicidesSolubilityMicrosphere
The invention provides a preparation method of guanidinated chitosan. By guanidination modification for chitosan, the biological alkalinity and the water solubility of the chitosan are improved, and the action capacity of the chitosan to an electronegative cell membrane is enhanced; the provided preparation method of the guanidinated chitosan aims to increase the grafting rate of chitosan guanidination and avoid side reaction. The invention further provides a method for preparing antibacterial nano microspheres from the guanidinated chitosan. The method comprises the steps of by taking dextran sulfate as a crosslinking agent, preparing the lysozyme-coated guanidinated chitosan nano microspheres; by the use of the puncture action of the guanidinated chitosan to the cell membrane, the stability of the outer membrane lipid structure of gram negative bacteria (G-) is destroyed to expose peptidoglycan on the inner wall layer, and the peptidoglycan is hydrolyzed through lysozyme; under the synergistic action of the guanidinated chitosan and the lysozyme-coated guanidinated chitosan nano microspheres, the inhibition effect on G- is enhanced.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Antimicrobial compositions containing free fatty acids
ActiveUS20150157720A1Difficult to cultureImprove overall utilizationAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsMembrane lipidsMedicine
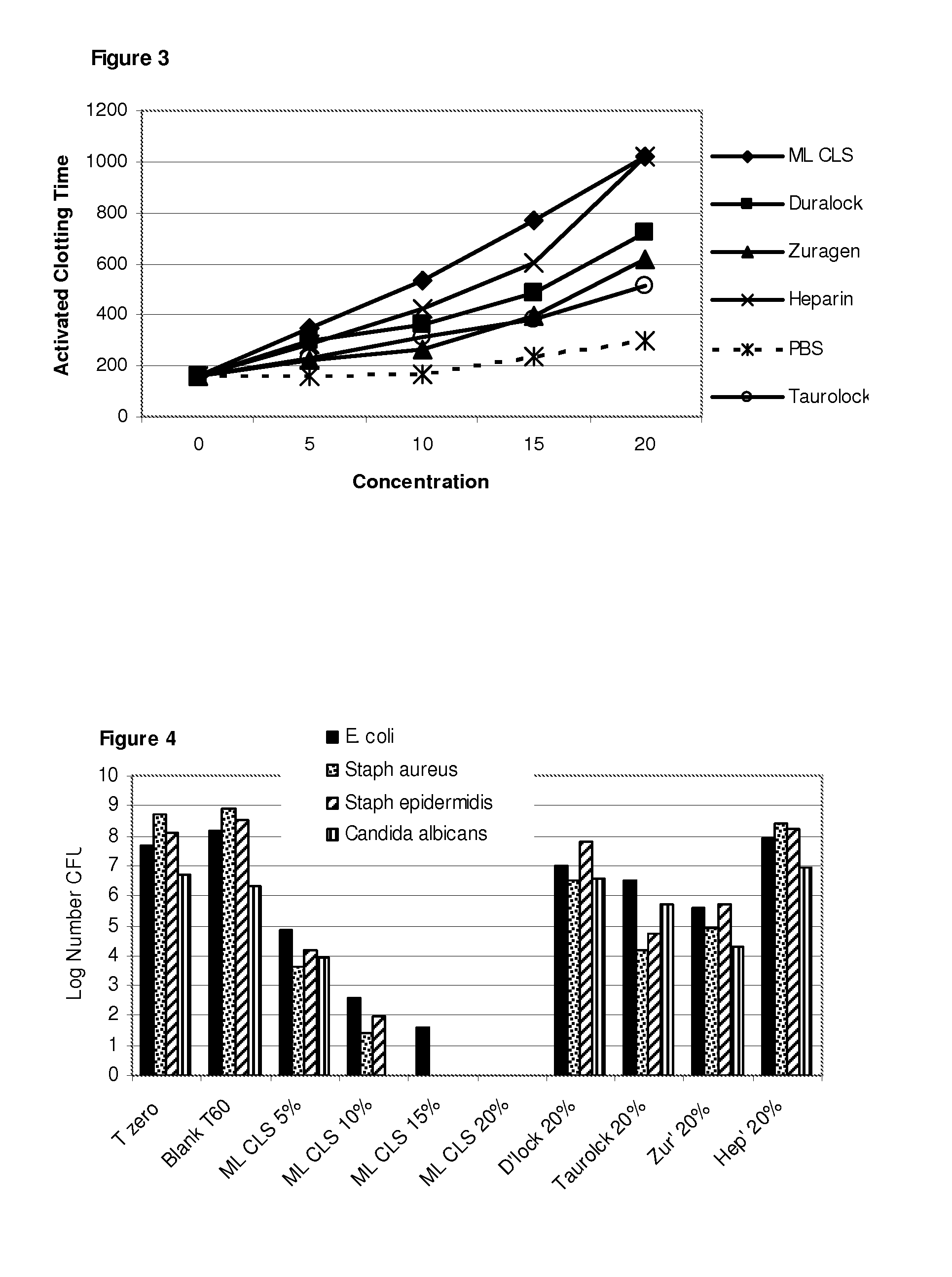
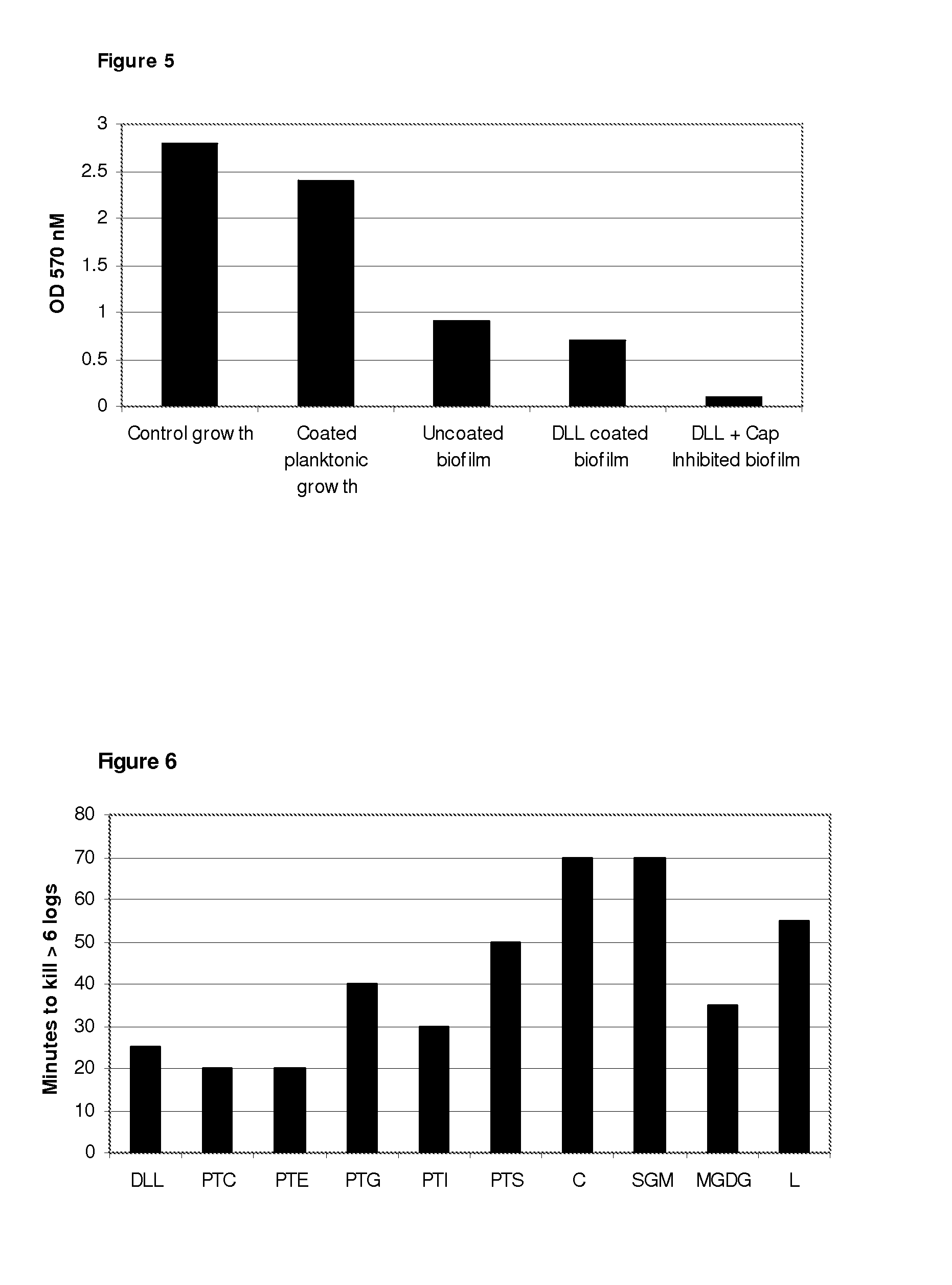
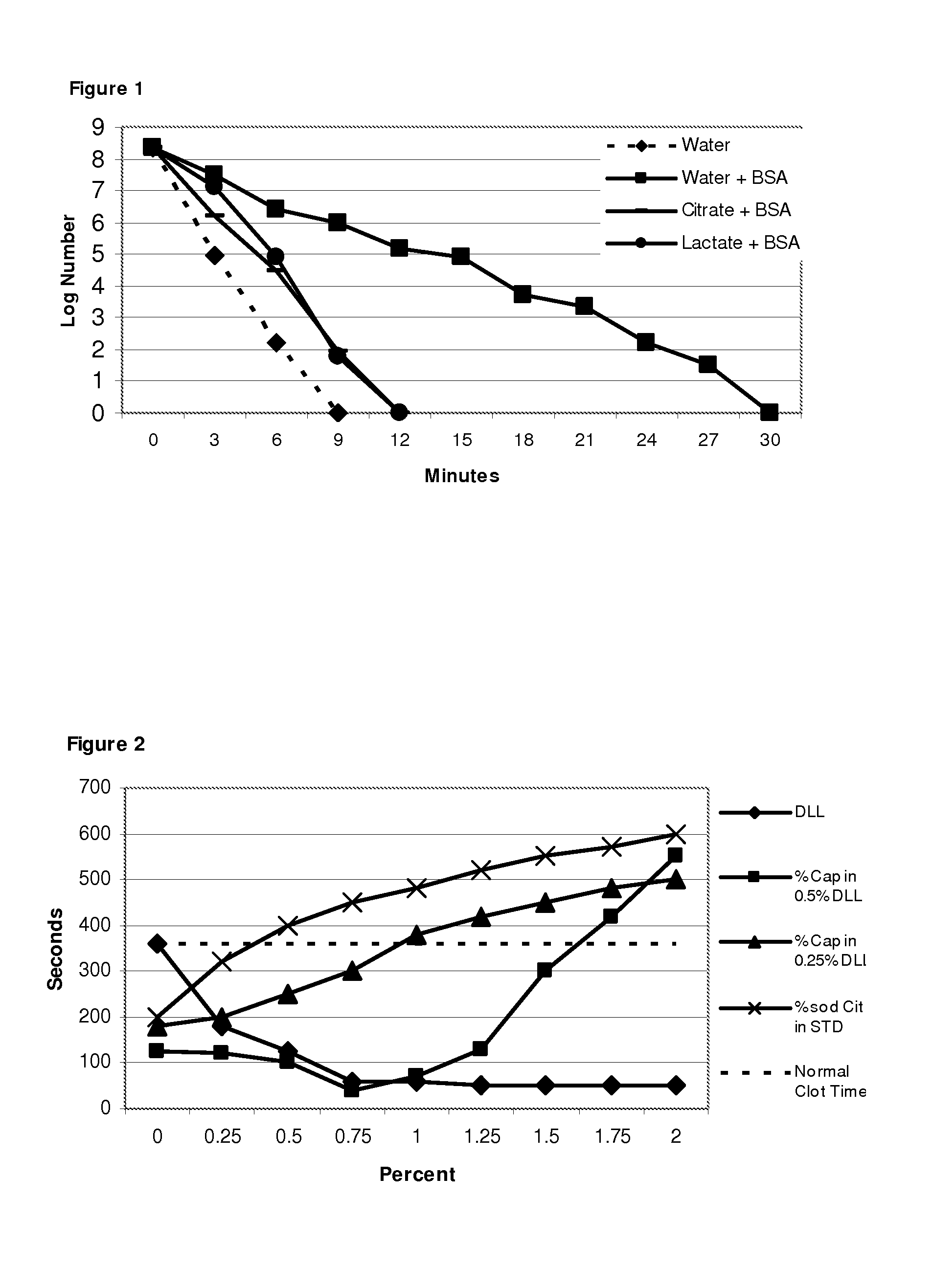
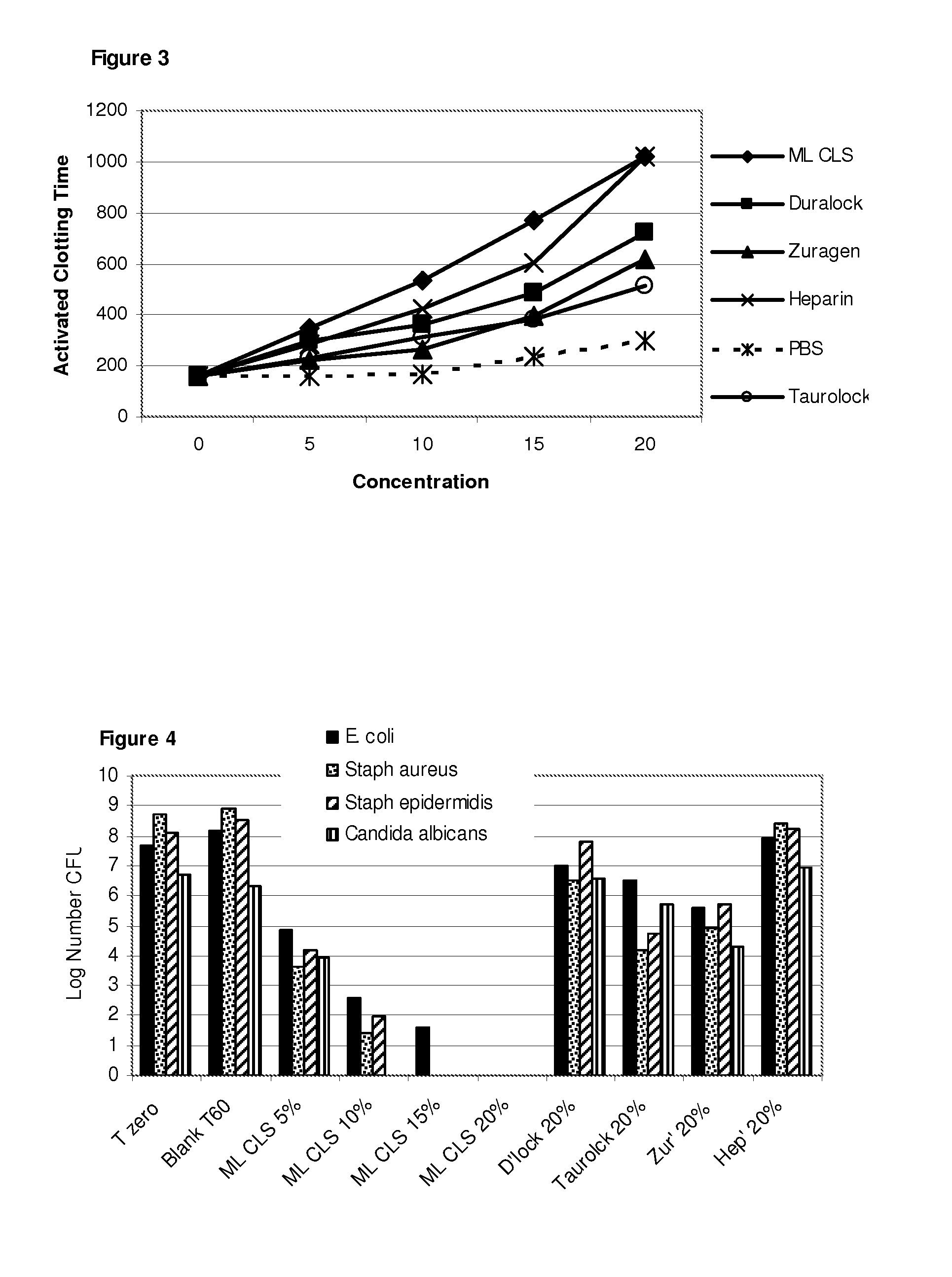
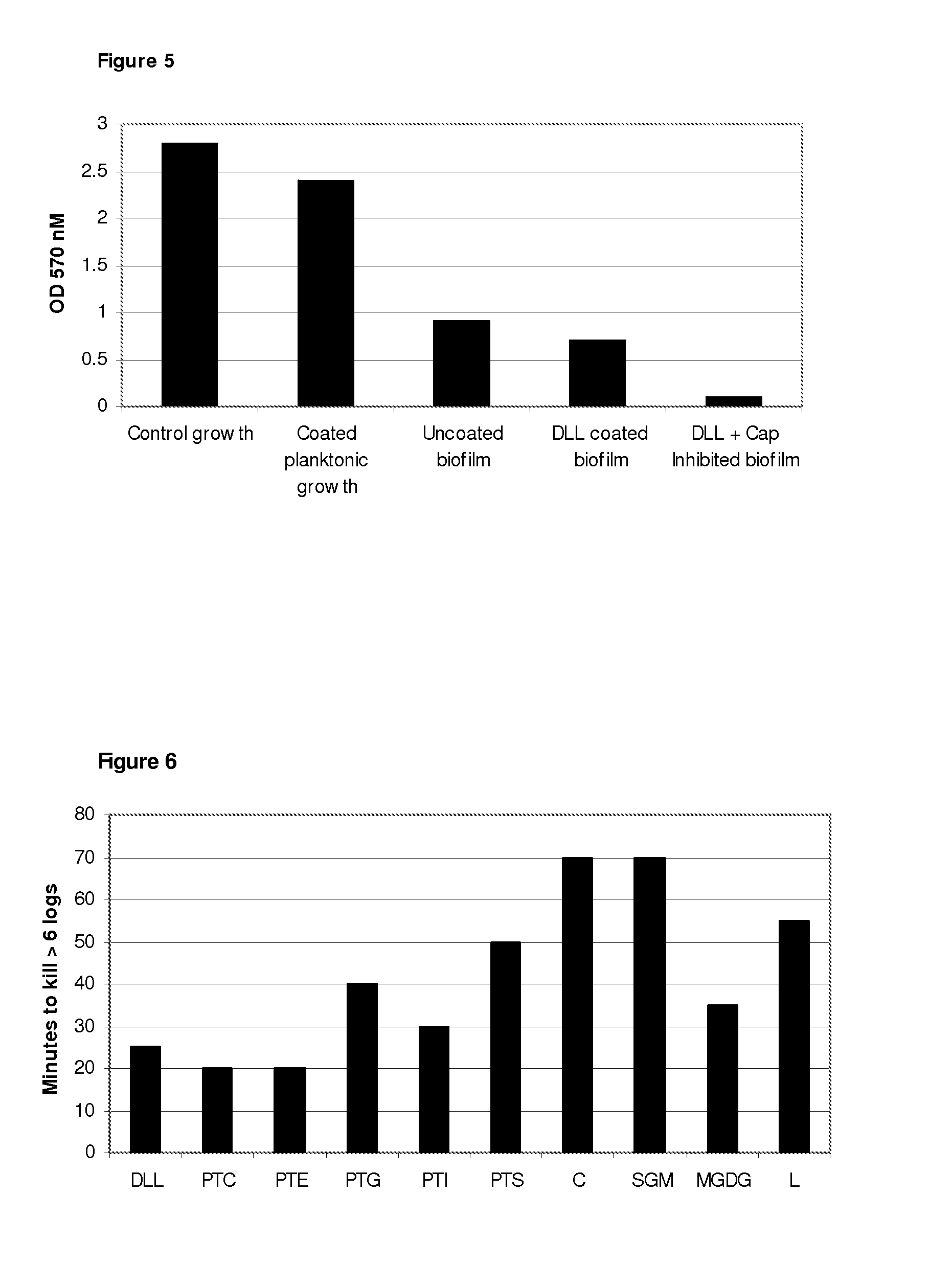
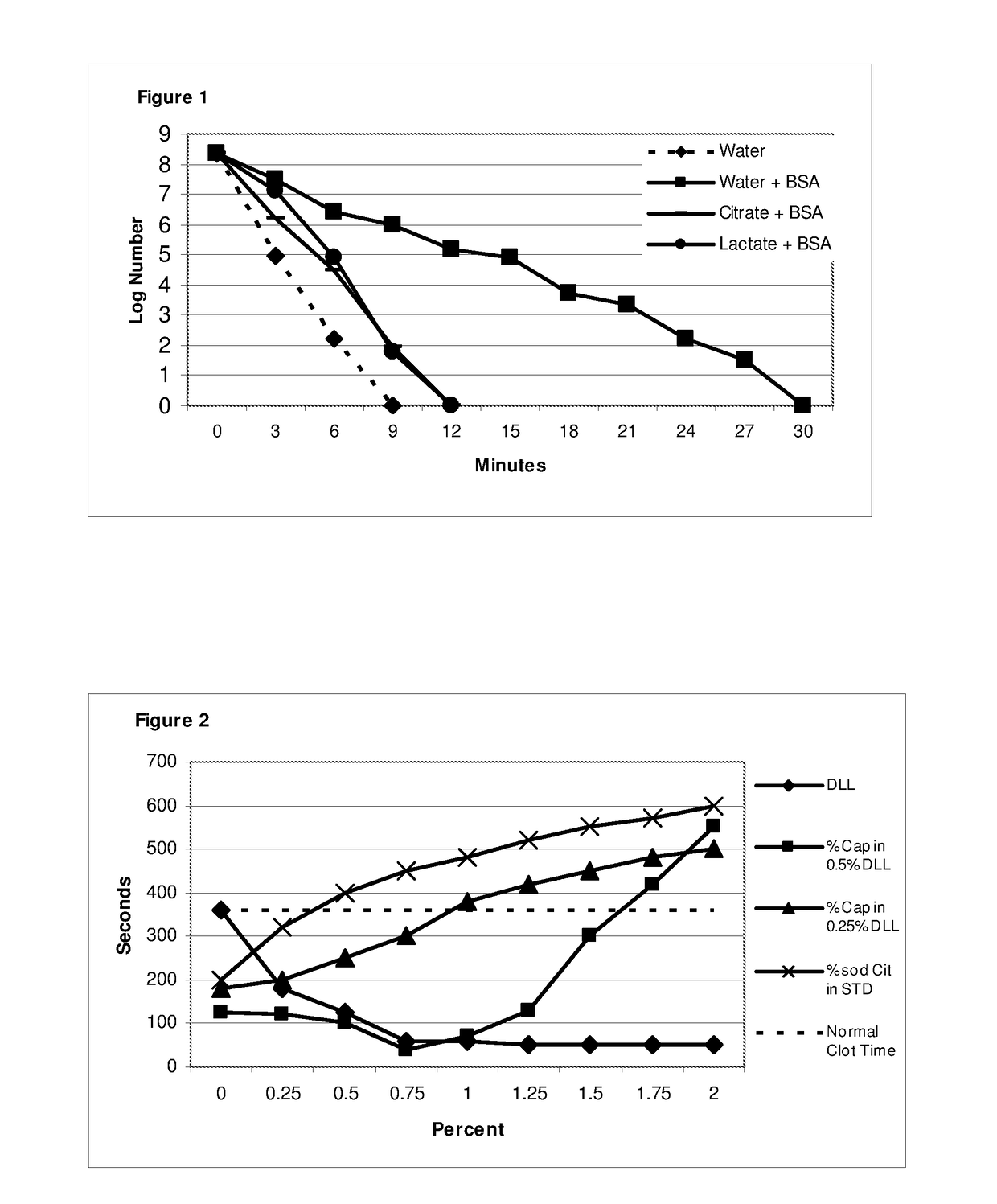
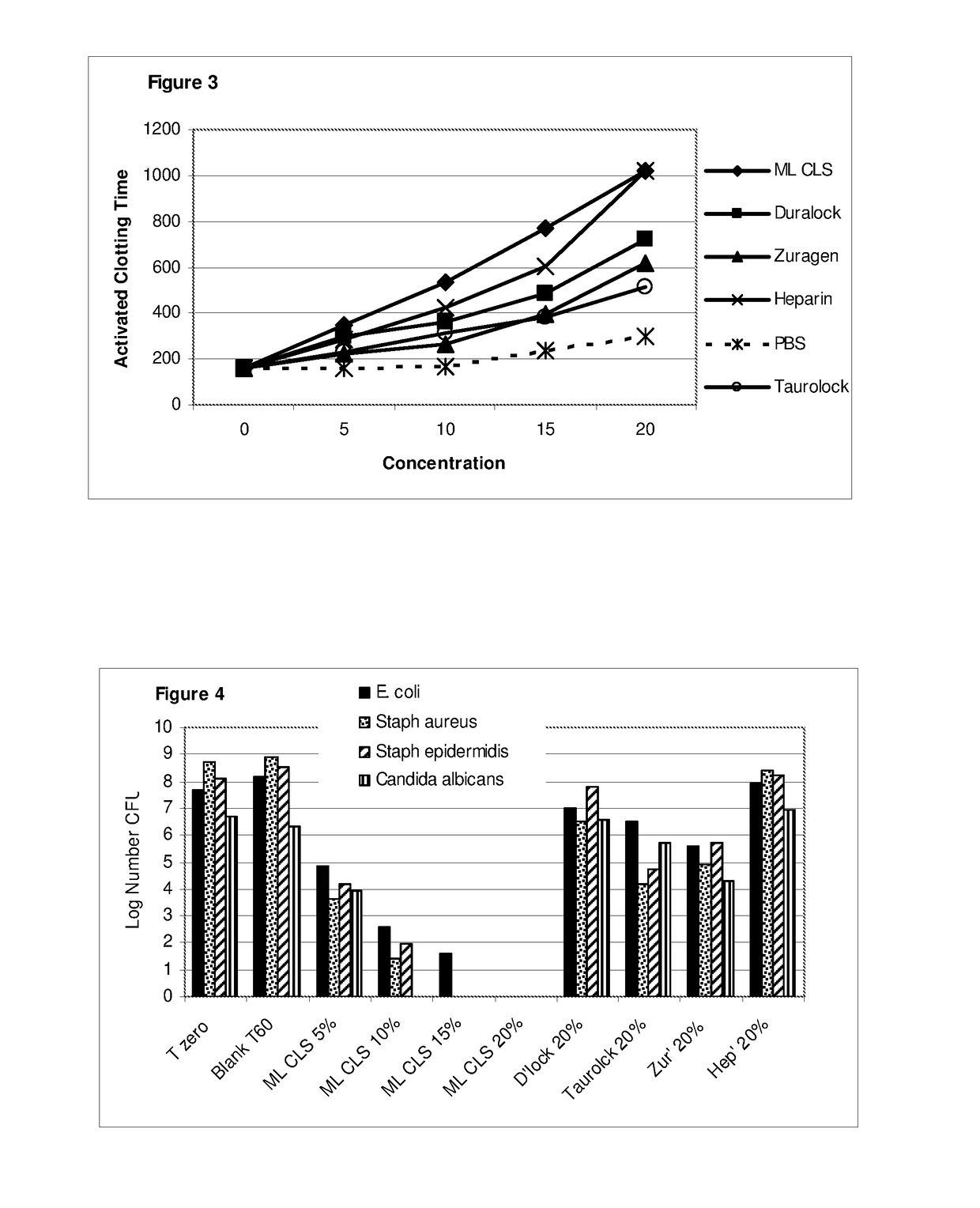
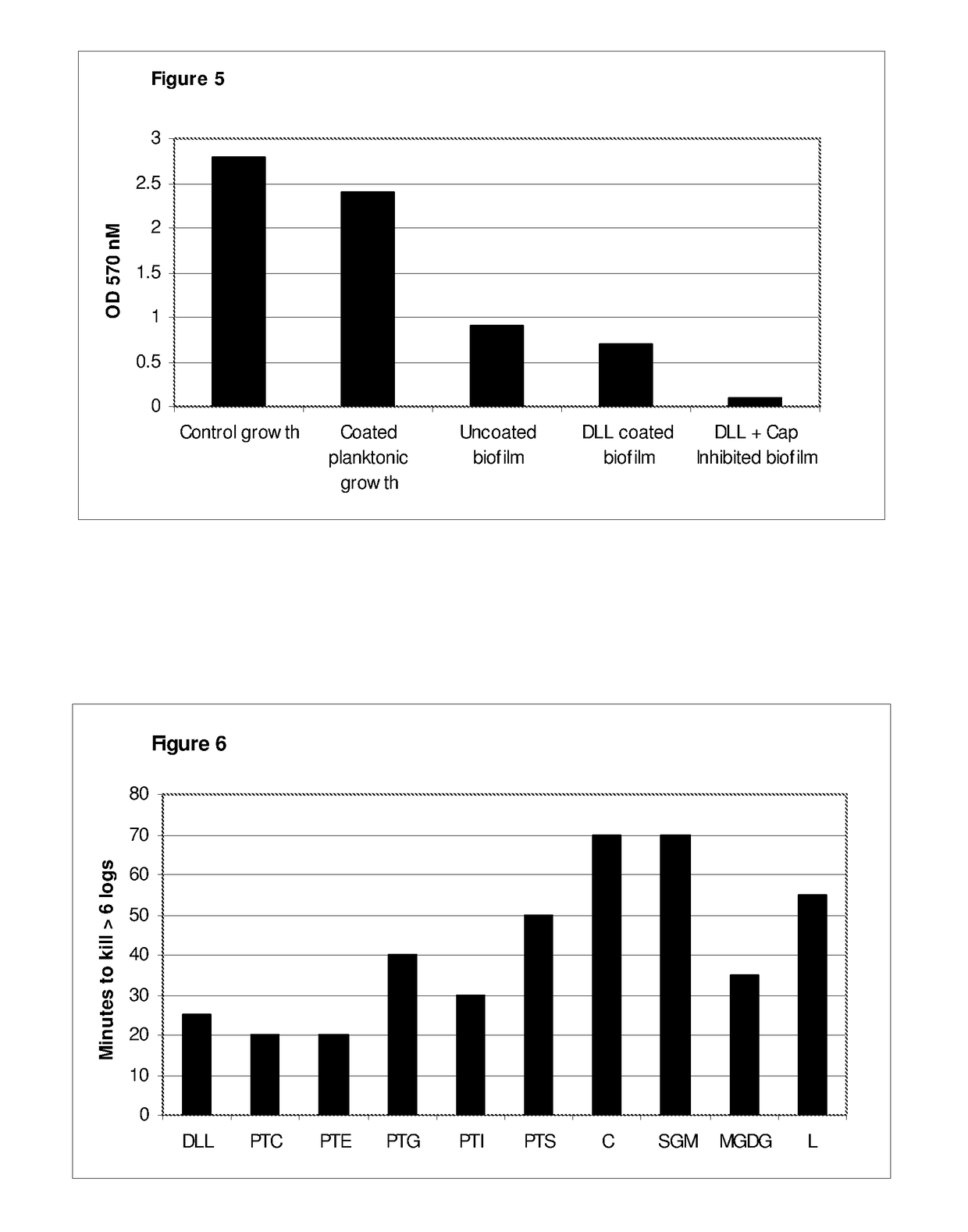
The invention concerns antimicrobial compositions comprising free fatty acids emulsified with membrane lipids or hydrolysed derivatives thereof, and pharmaceutical formulations comprising same. The compositions can be used in the treatment of prophylaxis of microbial infections. They can also regulate the rate of blood clotting rendering them suitable for incorporation in catheter locking solutions and for use in wound care.
Owner:FOLAN MICHAEL ANTHONY
Antimicrobial compositions containing free fatty acids
ActiveUS9555116B2Improve overall utilizationAdhesion inhibitory propertyAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismMembrane lipids
The invention concerns antimicrobial compositions comprising free fatty acids emulsified with membrane lipids or hydrolyzed derivatives thereof, and pharmaceutical formulations comprising same. The compositions can be used in the treatment of prophylaxis of microbial infections. They can also regulate the rate of blood clotting rendering them suitable for incorporation in catheter locking solutions and for use in wound care.
Owner:FOLAN MICHAEL ANTHONY
Antimicrobial compositions containing free fatty acids
ActiveUS20170100357A1Improve overall utilizationAdhesion inhibitory propertyAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsMembrane lipidsMedicine
The invention concerns antimicrobial compositions comprising free fatty acids emulsified with membrane lipids or hydrolysed derivatives thereof, and pharmaceutical formulations comprising same. The compositions can be used in the treatment of prophylaxis of microbial infections. They can also regulate the rate of blood clotting rendering them suitable for incorporation in catheter locking solutions and for use in wound care.
Owner:WESTGATE BIOMEDICAL LTD
DSE (Dark Septate Endophyte) bacterium and application thereof in promoting growth and preventing drought of blueberry
ActiveCN107129935APromote seedling cultivationPromote seedling growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPeroxidaseOxygen
The invention discloses a DSE (Dark Septate Endophyte) bacterium and application thereof in promoting growth and preventing drought of blueberry, and belongs to the field of agricultural microorganisms. The invention provides the DSE bacterium R10, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.13882. When the DSE bacterium R10 is inoculated, the biomass of ground parts of blueberry, the photosynthetic rate of leaves, the protection enzyme activities such as SOD (Superoxide Dismutase) and POD (Peroxidase) are remarkably improved, and the contents of malondialdehyde and H2O2 in leaves are remarkably reduced, so that by adopting the strain, the accumulation of organic matters can be improved by increasing the photosynthetic rate of leave of host plants on one hand, on the other hand, reactive oxygen can be effectively eliminated by improving the activity of the protection enzymes, the peroxidation degree of drought degrees to membrane lipid is reduced, and the drought resistance of the blueberry is improved.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Cold-resistant agent for brassica rapa L. seedlings and application method of cold-resistant agent
InactiveCN104798788AImprove cold resistancePromote growthBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAridChemical control
The invention belongs to the technical field of agricultural production, and particularly relates to a cold-resistant agent for brassica rapa L. The cold-resistant agent for the brassica rapa L. seedlings is mainly characterized by comprising raw materials as follows: 15-25 mg / L of ABA (abscisic acid) and the balance of water, wherein the purity of the ABA (abscisic acid) is higher than or equal to 99.9%. The cold-resistant agent aims to solve the problem that the brassica rapa L. in the northern cold and arid regions is vulnerable to low-temperature freezing damage, growth of the overground part and the root system of the brassica rapa L. is promoted with chemical control means, especially the thickening growth of roots, the outstanding performance refers to increase of dry matter accumulation, and safe wintering of the brassica rapa L. is guaranteed; meanwhile, permeability (relative electrical conductivity) of leaf cell membranes as well as accumulation of membrane lipid peroxidation malonaldehyde can be reduced, so that the low-temperature freezing degree of leaves of the brassica rapa L. is reduced, the cold resistance of the brassica rapa L. is remarkably improved, and the cold-resistant agent has great practical significance on brassica rapa L. production.
Owner:GANSU AGRI UNIV
Brain tissue membrane protein extraction method
InactiveCN108383901AEfficient extractionSimple recipePeptide preparation methodsAnimals/human peptidesProtein structureReducing agent
The invention provides a brain tissue membrane protein extraction method, and relates to the technical field of biology. A used scale removal agent is very mild; in addition, the concentration is verylow; a reducing agent and a protein allosteric agent are not used; the protein structure and activity can be maintained. Membrane lipid surrounding the extracted protein is not completely lost; a tertiary structure of the protein can be effectively remained, so that the combination state of the protein with other protein can be stabilized. By using the extraction method provided by the invention,80 percent of membrane protein or more can be effectively dissolved. The formula of a used buffer solution system is simple; only conventional reagents and instrument equipment in a laboratory are needed; the result and the activity of the protein are not influenced at all by the used stain removal agent and the dosage; the extracted membrane protein can be used for biochemical tests with higherdifficulty in co-immunoprecipitation and the like and higher protein extraction requirements.
Owner:KUNMING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
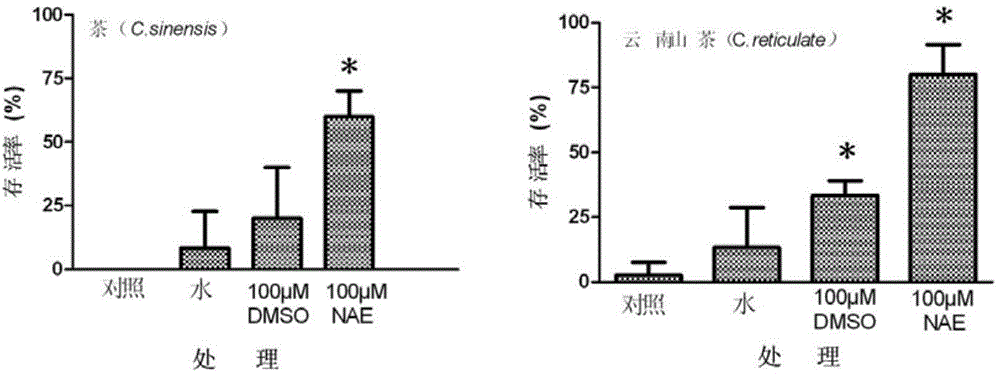
Method for improving survival rate of plant seeds by N-acylethanolamines after ultralow-temperature preservation and application of N-acylethanolamines
InactiveCN104365584AImprove survival rateWeighing by removing componentDead plant preservationMembrane lipidsGermination
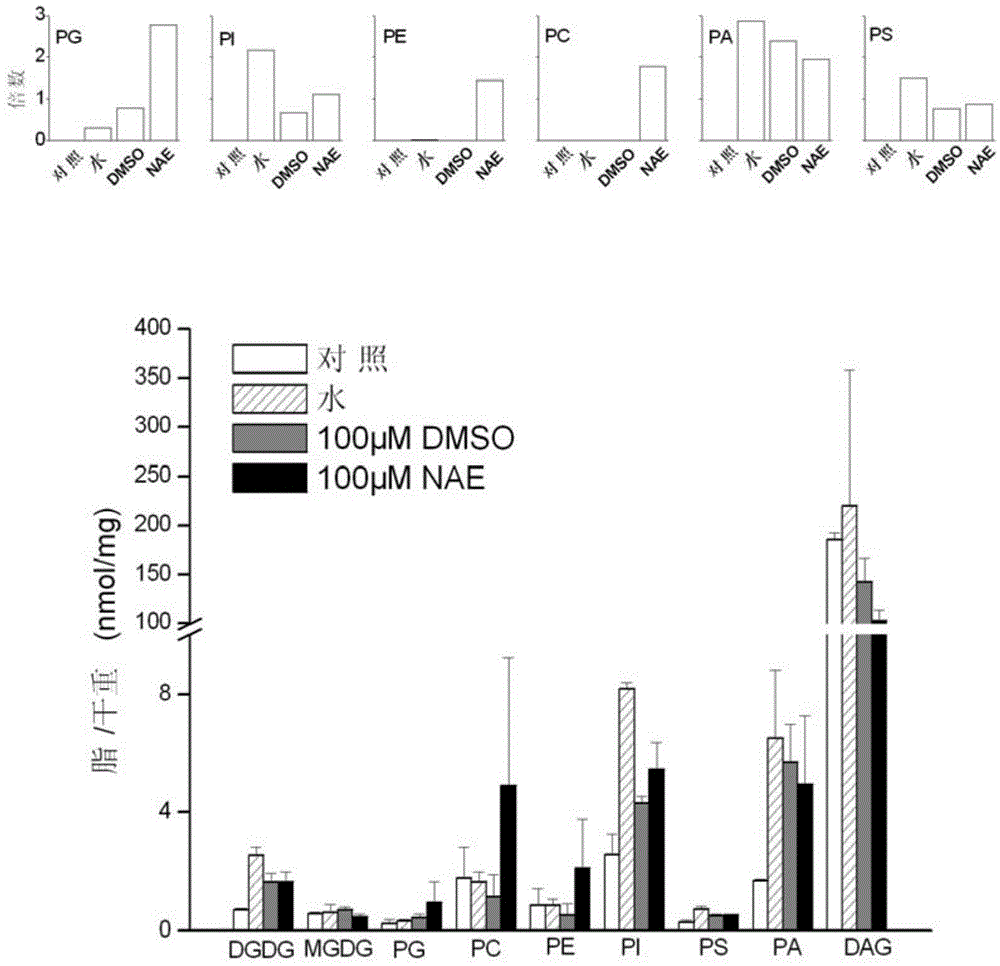
The invention provides a method for improving survival rate of plant seeds by N-acylethanolamines (NAE) after ultralow-temperature preservation and application of N-acylethanolamines. The method comprises the following steps: taking plumular axes of the plant seeds and applying the N-acylethanolamines to the plumular axes of the plant seeds; carrying out pretreatment and an ultralow-temperature preservation experiment; and carrying out a germination force experiment to detect the vitality. Meanwhile, the invention provides application of the N-acylethanolamines to the ultralow-temperature preservation of the plant seeds. Before the seeds with the plumular axes which are sensitive to dehydration are subjected to the ultralow-temperature preservation, the survival rate of the seeds can be remarkably improved if an inhibitor NAE (100 micromoles) of PLDalpha is exogenously applied;lipidomics analysis is carried out in a whole process and shows that in an ultralow-temperature preservation process of the plumular axis seeds treated with the NAE, substrate phospholipids (PG, PE and PC) for hydrolysis of PLD alpha are remarkably improved and the formation of membrane lipid is changed, so that the survival rate of the plumular axes after the ultralow-temperature preservation process is improved; and the method has a very good application prospect in the preservation of germplasm resources of the sensitive seeds.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
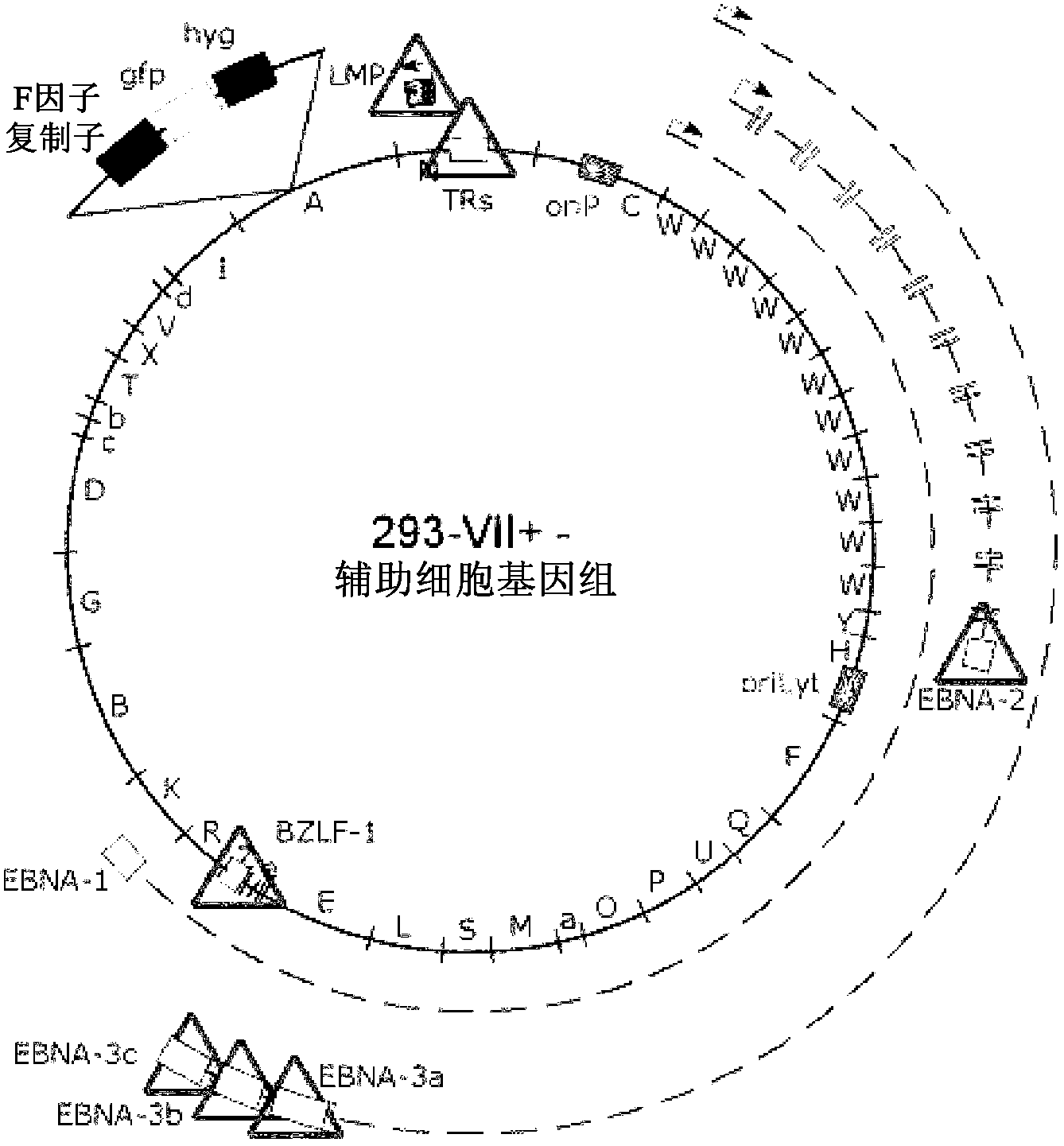
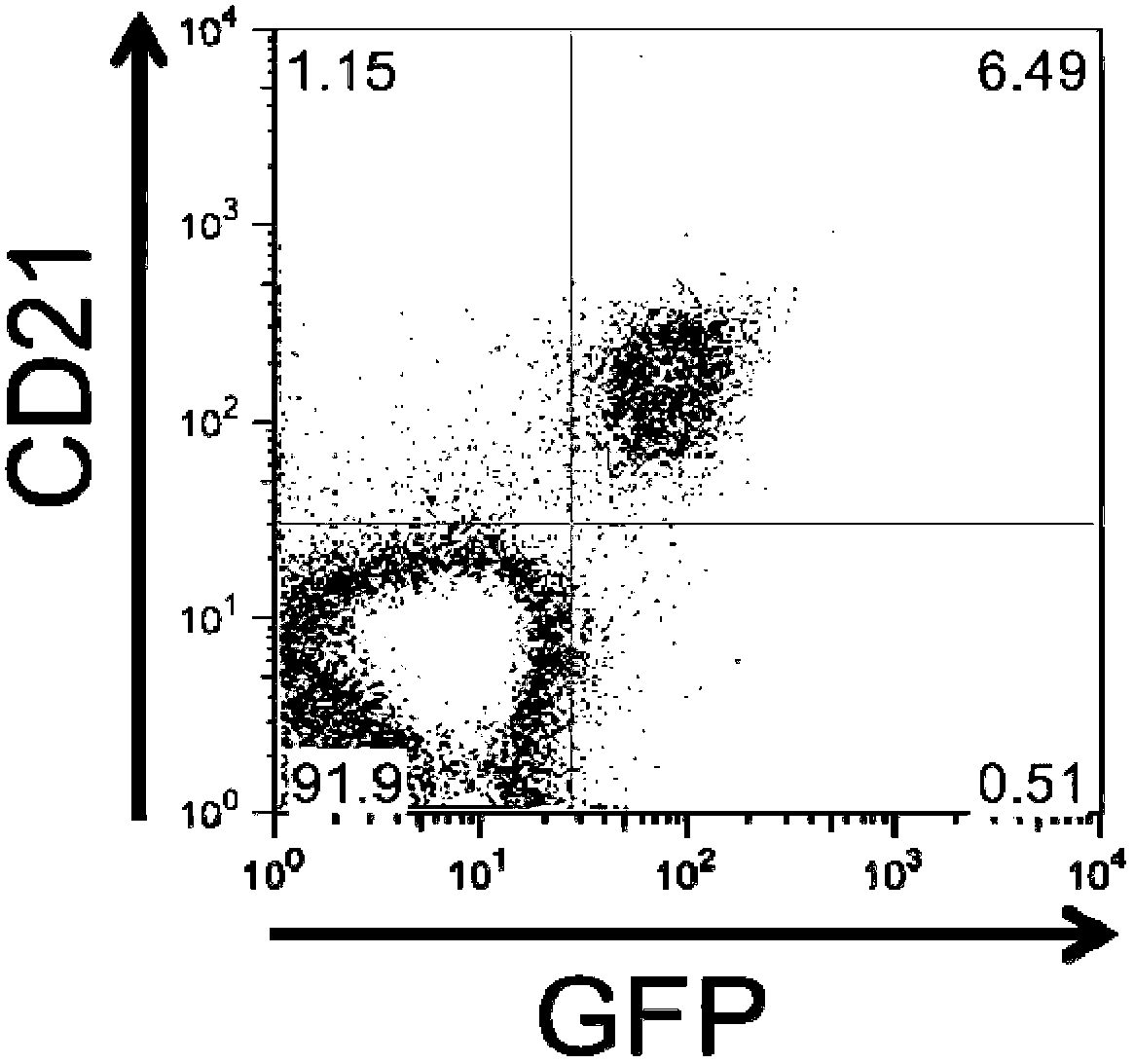
An epstein-barr-virus vaccine
InactiveCN103328003AViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesMembrane lipidsEpstein–Barr virus vaccine
The present invention relates to a vaccine comprising a particle, said particle comprising (i) at least one Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) structural polypeptide, (ii) at least one EBV lytic polypeptide, (iii) membrane lipids, said particle being devoid of EBV DNA, wherein (a) the B-cell transformation capacity of one or more EBV polypeptides required for B-cell transformation as comprised in said particle is disabled while their immunogenicity is maintained; and / or (b) said particle is devoid of one or more EBV polypeptides required for B-cell transformation. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for generating a particle, to a cell obtained in the method of the invention, a kit comprising the vaccine or the particle generated according to the method of the invention. Also, the invention relates to the use of the vaccine or the particle generated according to the method of the invention for generating CD8+ cells specific for an EBV antigen.
Owner:亥姆霍兹慕尼黑中心德国研究健康与环境有限责任公司
Fresh-keeping method of toona sinensis sprouts based on ice-temperature storage
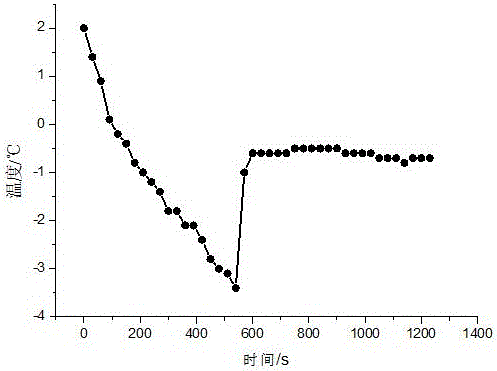
InactiveCN106472658AAvoid damageIncrease resistanceFruits/vegetable preservation by freezing/coolingMembrane lipidsAir conditioning
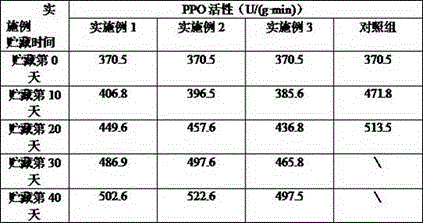
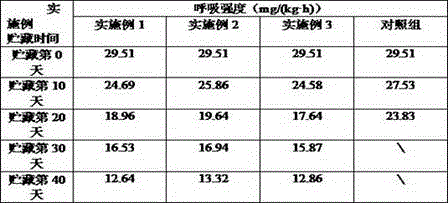
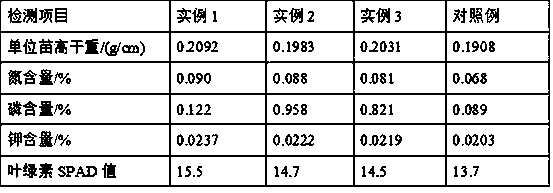
The invention relates to a fresh-keeping method of toona sinensis sprouts based on ice-temperature storage. The fresh-keeping method comprises the following steps of (1) collecting toona sinensis sprouts; (2) performing fresh keeping with a biological fresh-keeping agent and performing precooling; (3) performing spontaneous air-conditioning fresh-keeping packaging; (4) determining the temperature of ice temperature; and (5) performing ice-temperature preservation. According to the fresh-keeping method disclosed by the invention, internal nutrient components and external organoleptic quality of the toona sinensis sprouts are maintained to the great extent, and the breathe intensity and the lipid peroxidation degree of the toona sinensis sprouts are reduced. Besides, the activity of polyphenol oxidase PPO is restrained, the shelf life can be prolonged to about 40 days, and the purposes of storage and fresh keeping are achieved. The fresh-keeping technology is simple, convenient to operate, easy to implement, low in cost, environment-friendly, free from toxic effects on human bodies, and broad in market prospects.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Rice cold-resistant agent and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a rice cold-resistant agent and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of agriculture. According to the rice cold-resistant agent, plant endogenous cold-resistance substances in carex lanceolata boott and pyrola rotundifolia are extracted, and are compounded with allogenic materials to promote rice growth, improve rice disease resistance and stress and allelopathy resistance, improve tillering, height, accumulation of above-ground and underground biomass and improve cold resistance of rice; and the cytomembrane stability can be kept due to mineral ions in mineral liquid, normal functions of cytomembrane can be maintained, related enzyme systems, such as catalase, peroxidase and superoxide dismutase, are improved to reduce the oxidation effect of free radicals for membrane lipid, the cytomembrane functions can be kept, the cell ultrastructure is prevented from being destroyed, cold resistance of plants can be improved, plant cells are stimulated to secrete peroxidase into cell walls and improve the activity of cells, the firmness of cell walls can e reinforced, and cell collapse injury caused by extracellular freezing and dehydration can be prevented.
Owner:朱东洋
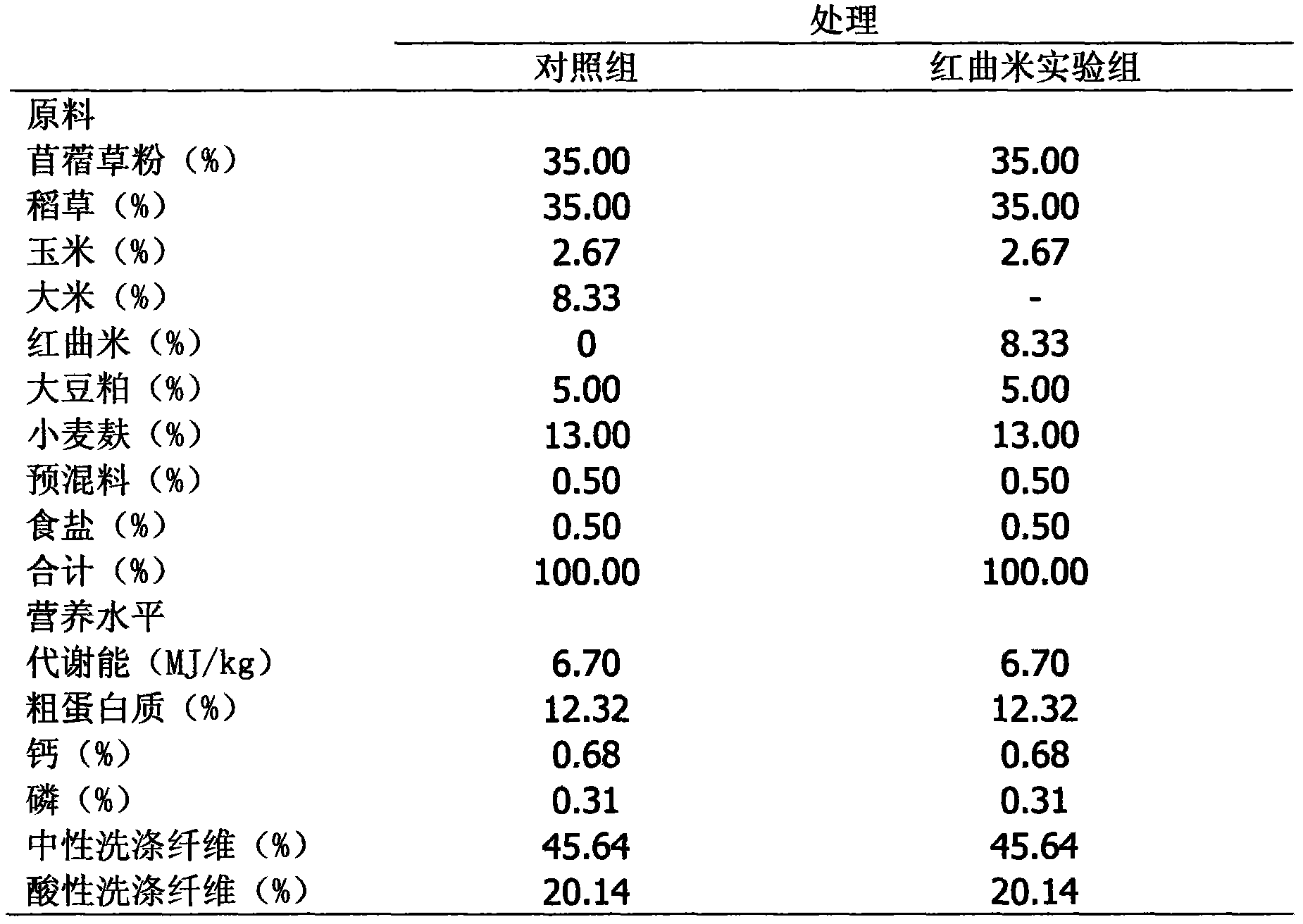
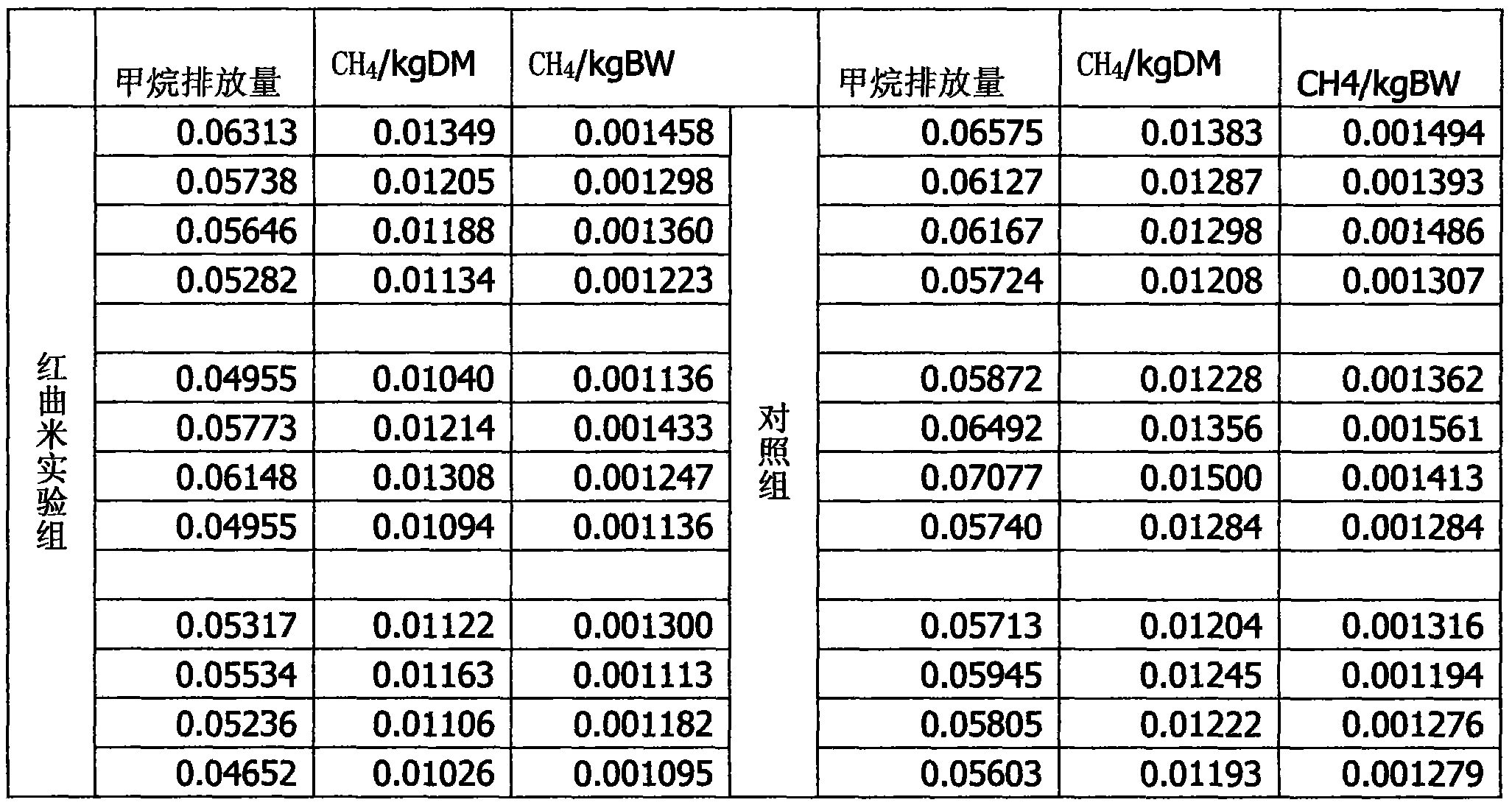
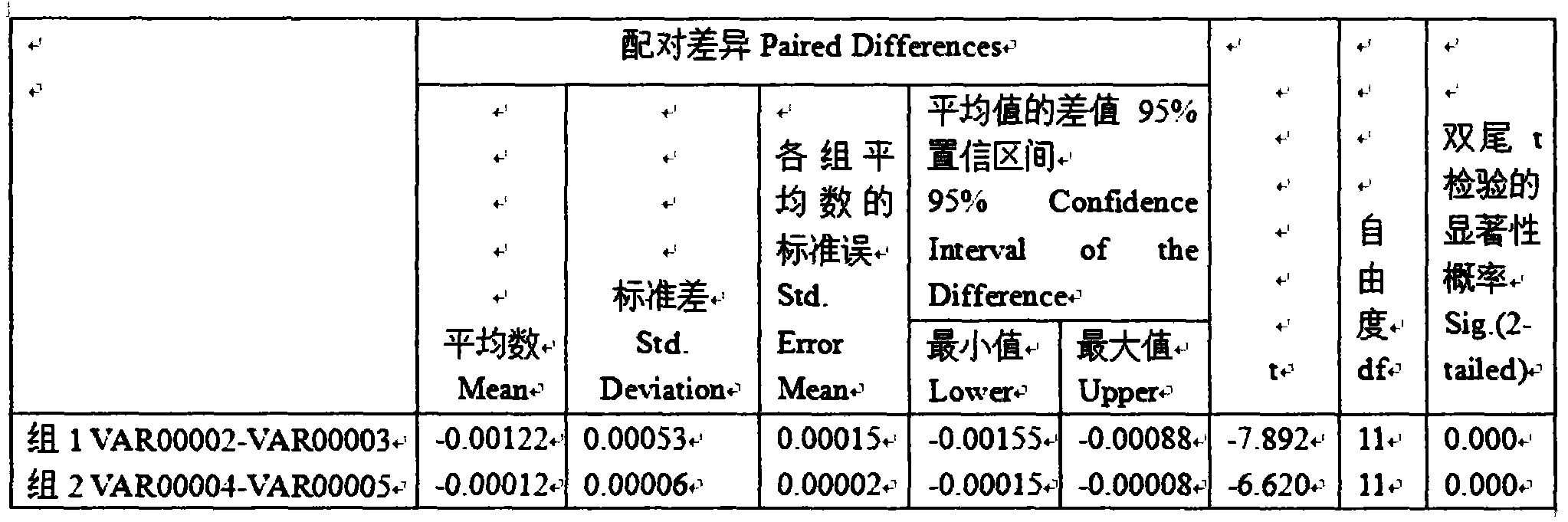
Application of red yeast rice to reduction of methane discharged by ruminant such as sheep
InactiveCN103829090AImprove nutrient utilizationGrowth inhibitionAnimal feeding stuffAgriculture gas emission reductionBiotechnologyRed yeast rice
The invention discloses application of red yeast rice to reduction of methane discharged by ruminant such as sheep. When the red yeast rice is added into ruminant feed to reduce methane discharged by ruminant, the additive amount of the red yeast rice in the daily ration of sheep depends on the average daily feed intake of the sheep, the content ratio of nutrients to lovastatin in the red yeast rice and the ratio of opening loops to closed loops of lovastatin. The red yeast rice is adopted for reducing methane discharged by sheep, and the added red yeast rice naturally containing lovastatin can competitively and powerfully inhibit 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase and cut off the passage for synthesizing methane bacteria membrane lipid, thereby effectively inhibiting the growth of methane bacteria and eventually reducing methane discharged by ruminant such as sheep.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Method for cultivating pomegranates
InactiveCN107691090AUniform sizeReduce pests and diseasesCultivating equipmentsPlant protectionMembrane lipidsFruit set
Owner:贺州佳成技术转移服务有限公司
Enhanced Triacylglycerol Accumulation in Vegetative Tissues of Plants
ActiveUS20160002651A1Fused cellsVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyMembrane lipids
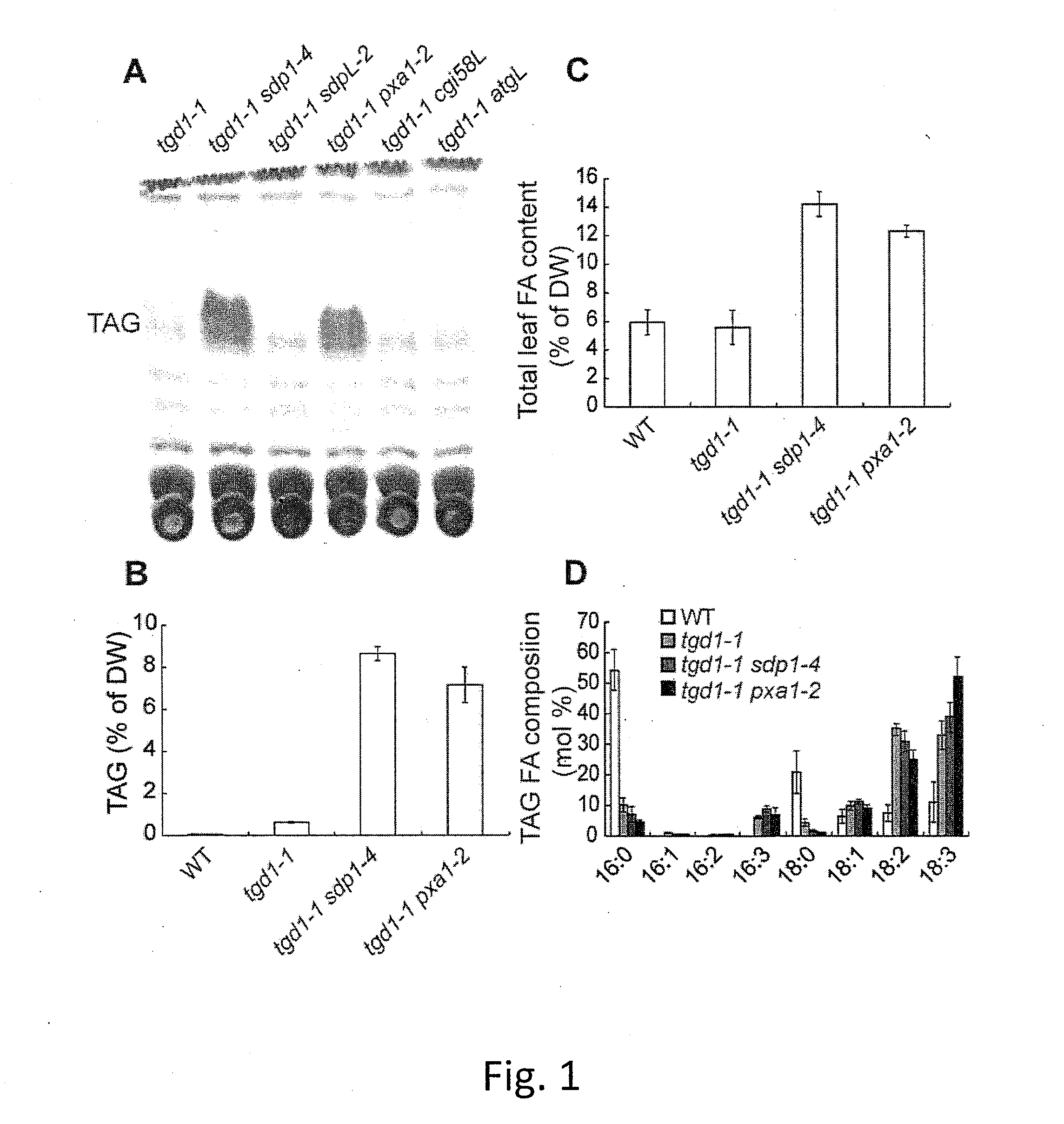
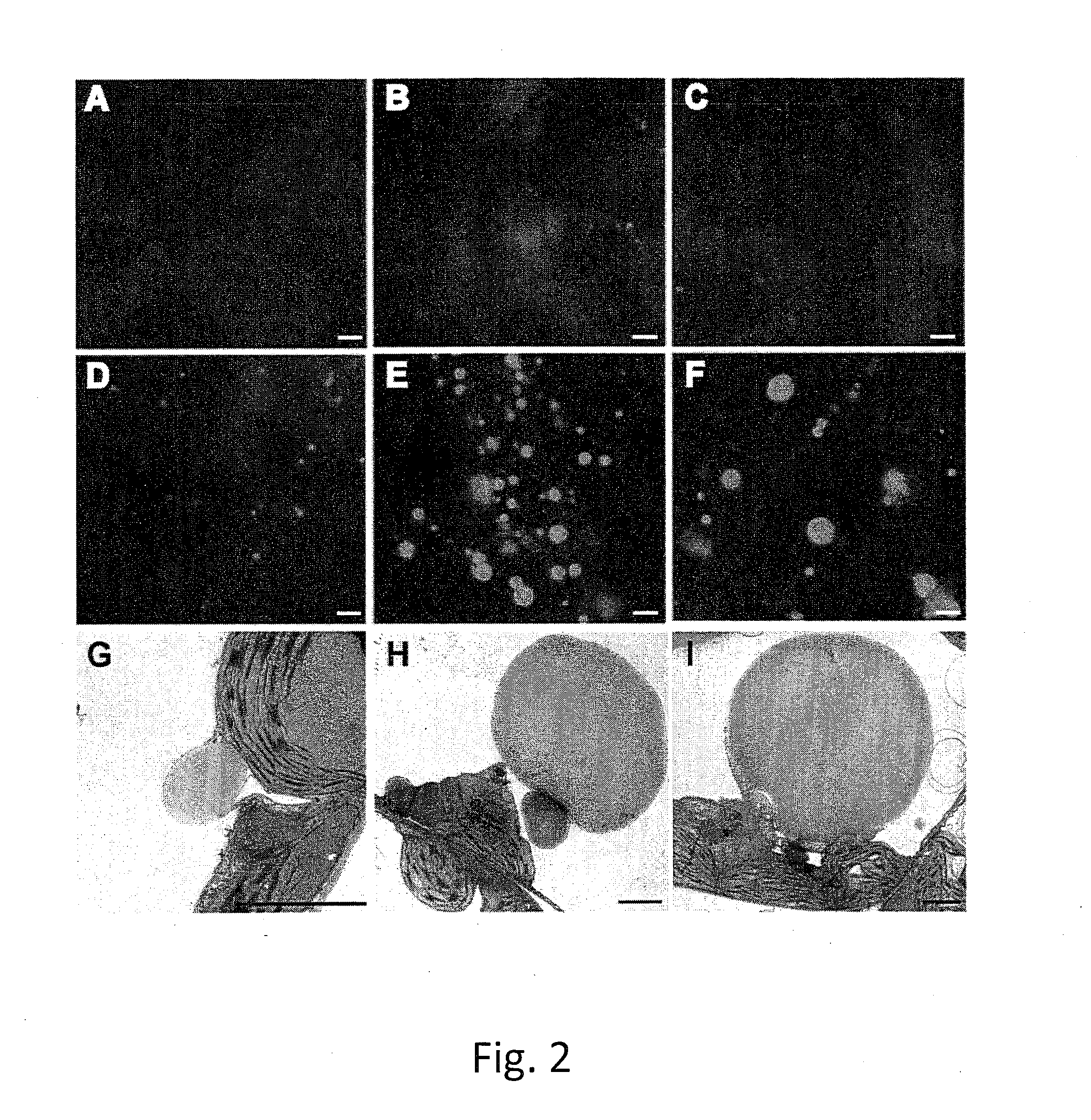
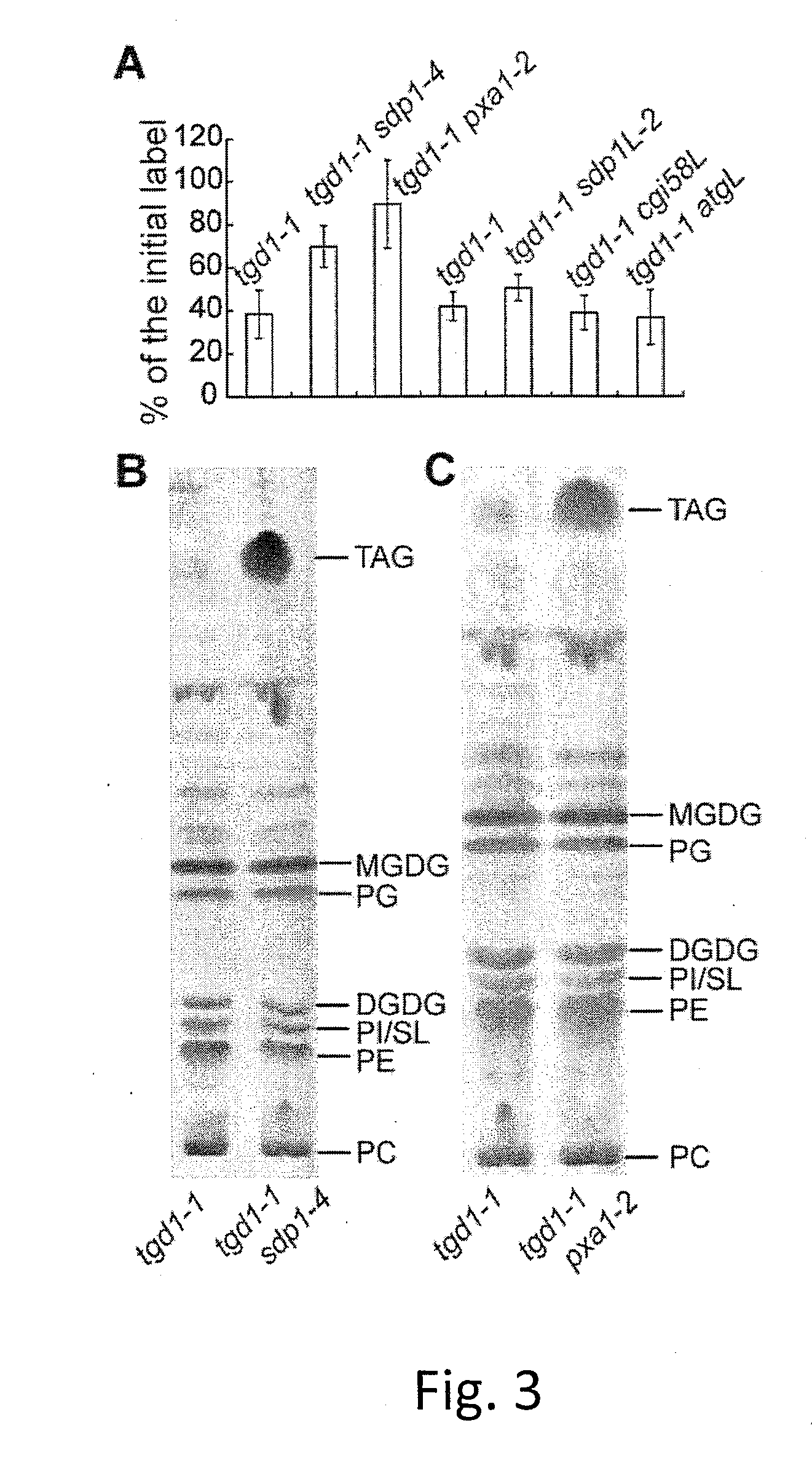
In the tgd1-1 mutant that displays substantially enhanced TAG synthesis and turnover, disruption of SUGAR-DEPENDENT1 (SDP1) TAG lipase or PEROXISOMAL TRANSPORTER1 (PXA1) severely decreases FA turnover, leading to an increase in leaf TAG content up to 9% of dry weight and total leaf lipid by three-fold. The membrane lipid content and composition of tgd1-1 sdp1-4 and tgd1-1 pxa1-2 double mutants are altered and they are compromised in growth and development and fertility.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Bifunctional agents possessing antioxidant and antiarrhythmic activity
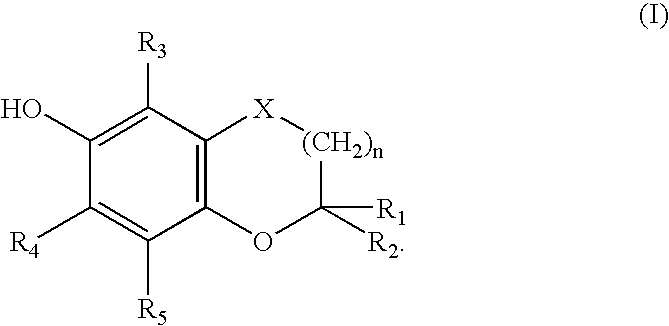
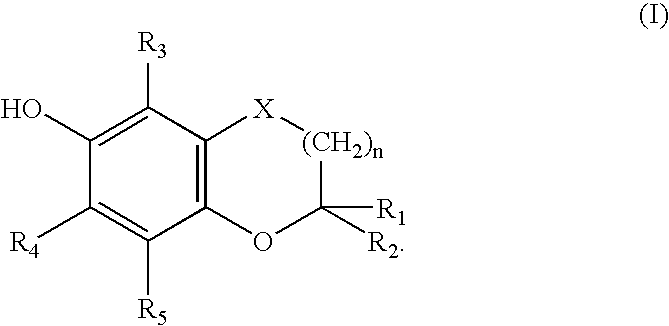
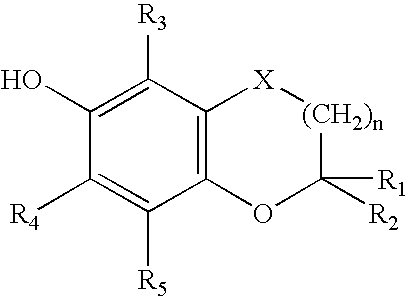
The present invention relates to novel bifunctional agents possessing antioxidant and antiarrhytmic activity, methods for the synthesis of the same and their applications in treating ischemia-reperfusion injury, as well as a variety of disorders related to free radicals and / or arrhythmias. These bifunctional drugs should preferentially segregate in the membrane and produce their antiarrhytmic effects while, at the same time, help in protecting the membrane lipids by scavenging free radicals. The present invention comprises compounds represented by Formula (I), wherein R1, R2, R3, R4, R5 are further defined
Owner:UNI PHARM KLEON TSETIS PHARM LAB SA
Artificial Lipid Bilayer Membrane Lipid Substitution Method, Artificial Lipid Bilayer Membrane Obtained by Using Lipid Substitution Method, Artificial Lipid Bilayer Membrane formation device and ion permeation measuring Device
InactiveUS20080290323A1Easy to changeEfficient use ofLaboratory glasswaresAnalysis by subjecting material to chemical reactionLipid formationMembrane lipids
An artificial lipid bilayer membrane formation device is disclosed, which includes: an upper solution chamber (first solution chamber) and a lower solution chamber (second solution chamber), both of which are filled with aqueous solution. It further includes a partition wall disposed between the upper solution chamber and the lower solution chamber so as to part the upper and lower solution chambers from each other. The partition wall has an opening, and a first lipid solution is applied to a portion around the opening, thereby forming an artificial lipid bilayer membrane on the opening. Further, in the formation device, a tubule for lipid substitution is attached to the partition wall so as to be positioned on a bulk phase of the artificial lipid bilayer membrane. A second lipid solution is added via the tubule, thereby forming an artificial lipid bilayer membrane whose lipid composition is changed.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
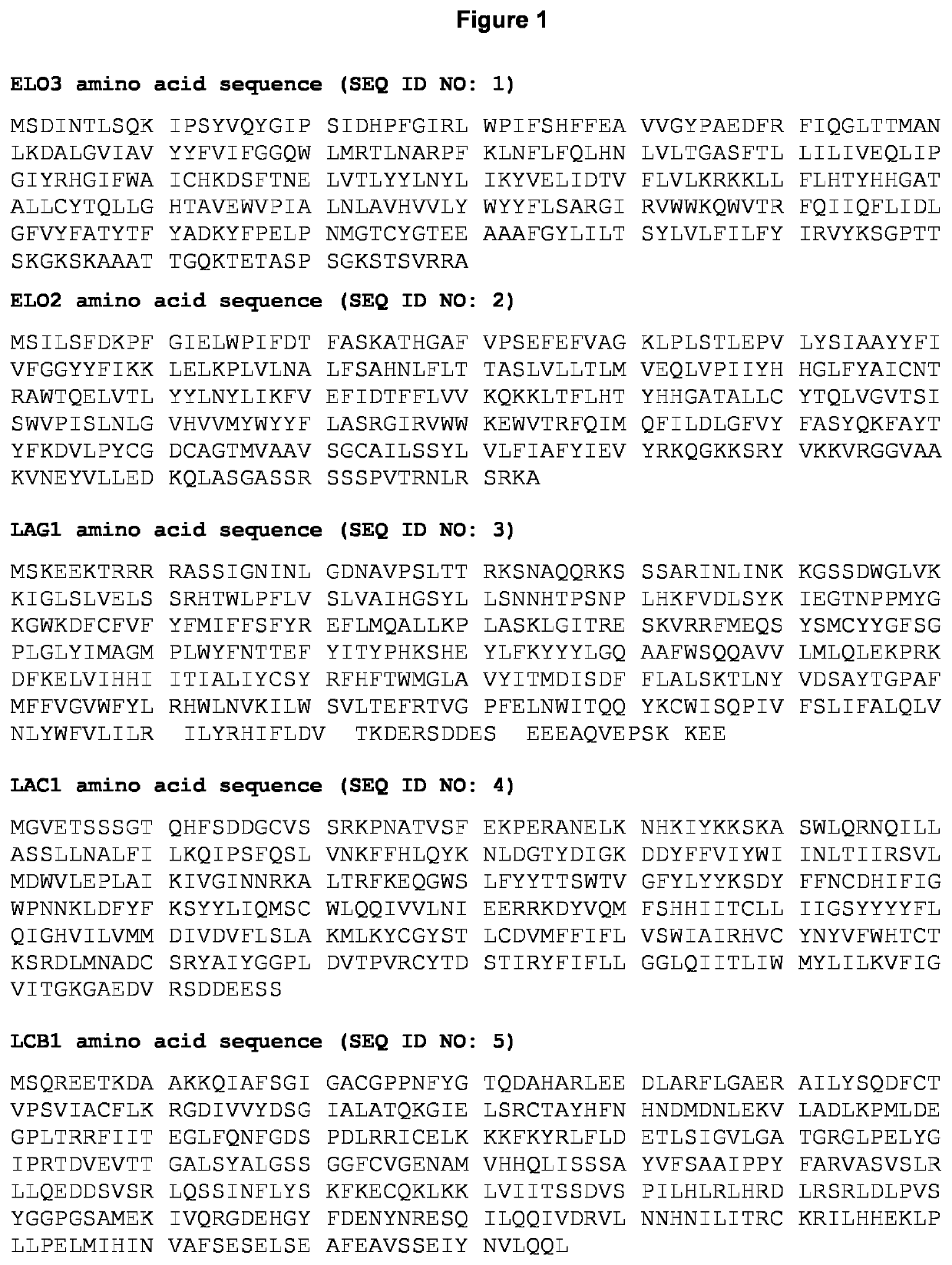
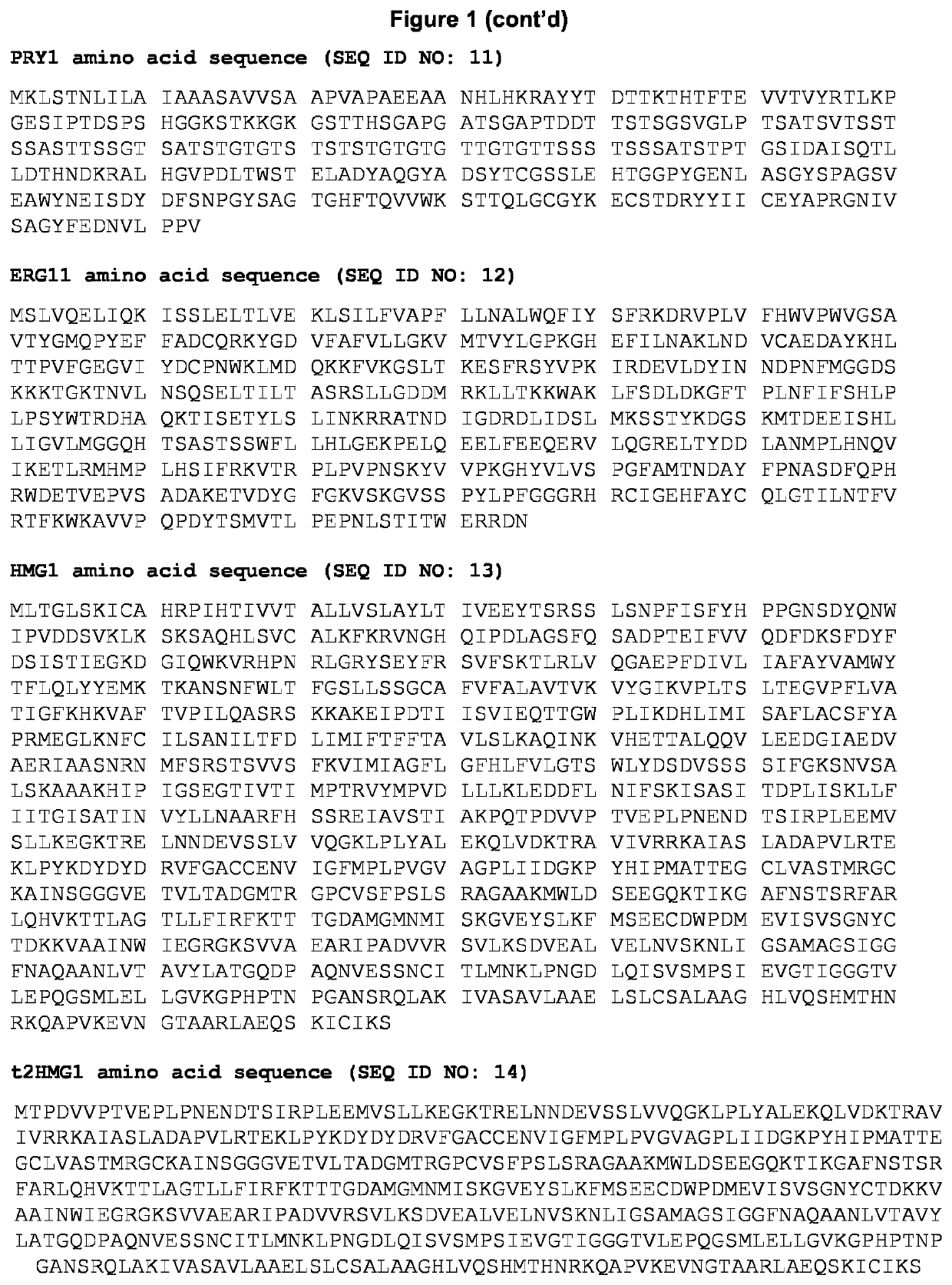
Recombinant host cell with altered membrane lipid composition
ActiveUS20210301313A1Increase productionHigh protein yieldImmunoglobulinsFermentationMembrane lipidsWAS PROTEIN
The present invention is in the field of recombinant biotechnology, in particular in the field of protein expression. The invention generally relates to a method of expressing a protein of interest (POI) from a host cell. The invention relates particularly to improving a host cell's capacity to express and / or secrete a protein of interest and use of the host cell for protein expression. The invention also relates to cell culture technology, and more specifically to culturing cells to produce desired molecules for medical purposes or food products.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM RCV GMBH & CO KG +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com