Method for detecting living streptococcus agalactiae in milk by SDS-PMA-qPCR (sodium dodecyl sulfate-propidium monoazide-quantitative polymerase chain reaction) method
A technology of streptococcus lactis and live bacteria, which is applied in the field of detection of pathogenic bacteria in milk samples, can solve the problems of false positive and false negative results, achieve high specificity, improve sensitivity, and promote the effect of penetration
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
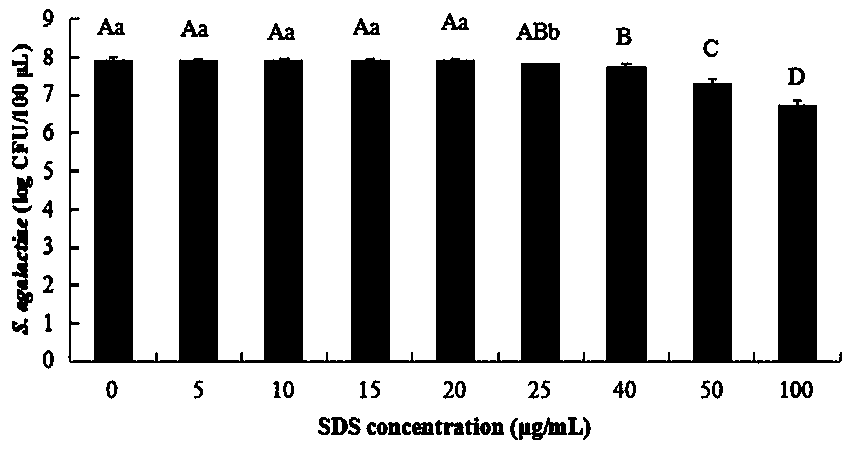
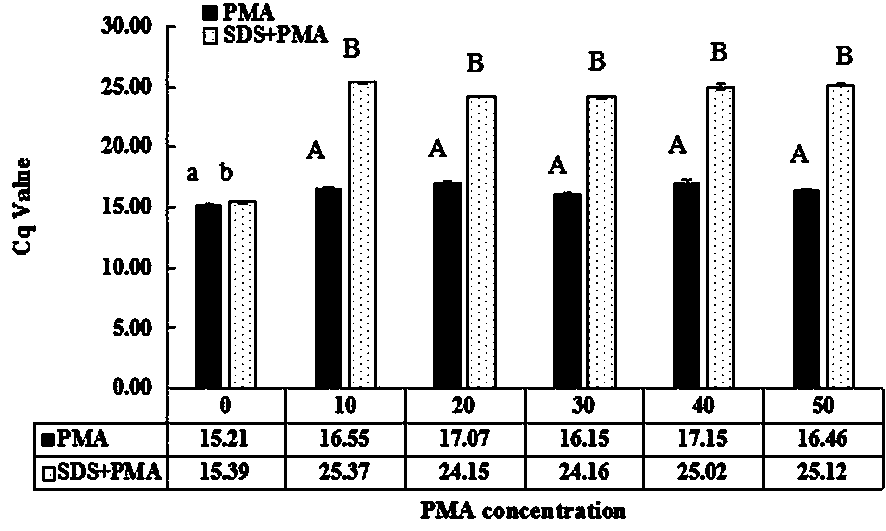
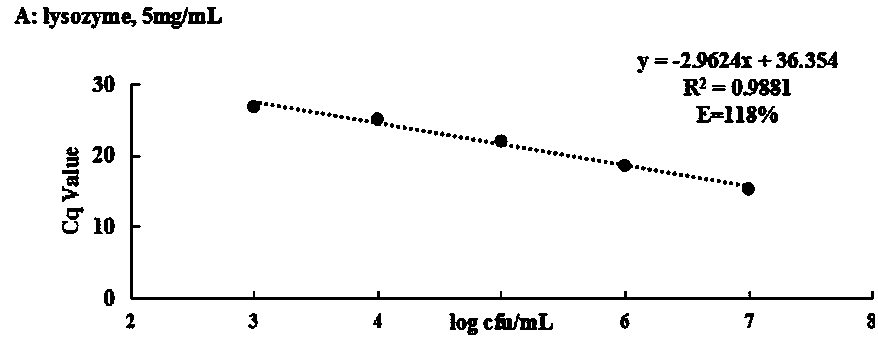
[0022] Example 1, the SDS-PMA-qPCR method for detecting viable Streptococcus agalactiae in milk was carried out according to the following steps: the first step, processing the milk sample to be tested: shake the milk sample to be tested, and take 2 mL of the milk sample in EP tube, then add SDS stock solution 10 to it 4 μg / mL 4 μL [the concentration of the SDS stock solution should be added to it is 20 μg / mL, but because the volume of SDS with a final concentration of 20 μg / mL added to the 2 mL milk sample is too small (only 0.008 μL), in practice, 0.008 μL It is very difficult to measure, it is easy to cause errors, and it is easy to cause distortion of the final test results. Therefore, using this concentration of SDS mother solution is not only easy to measure, but also the actual final addition amount is consistent with the addition amount of 20μg / mL SDS], adding the final concentration Mixture A was obtained for 2 μL of 10 mg / mL PMA, and then the mixture A was incubated ...
Embodiment 2
[0027] Example 2, as an optimization of the previous example, CTAB included 100 nM Tris-HCL pH 8, 1.4 M NaCl and 20 nM EDTA.
Embodiment 3
[0028] Embodiment 3, as an optimization of the above embodiment, the DNA extraction solution is prepared from phenol, chloroform and isopropanol, wherein the volume ratio of phenol:chloroform:isopropanol=25:24:1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com