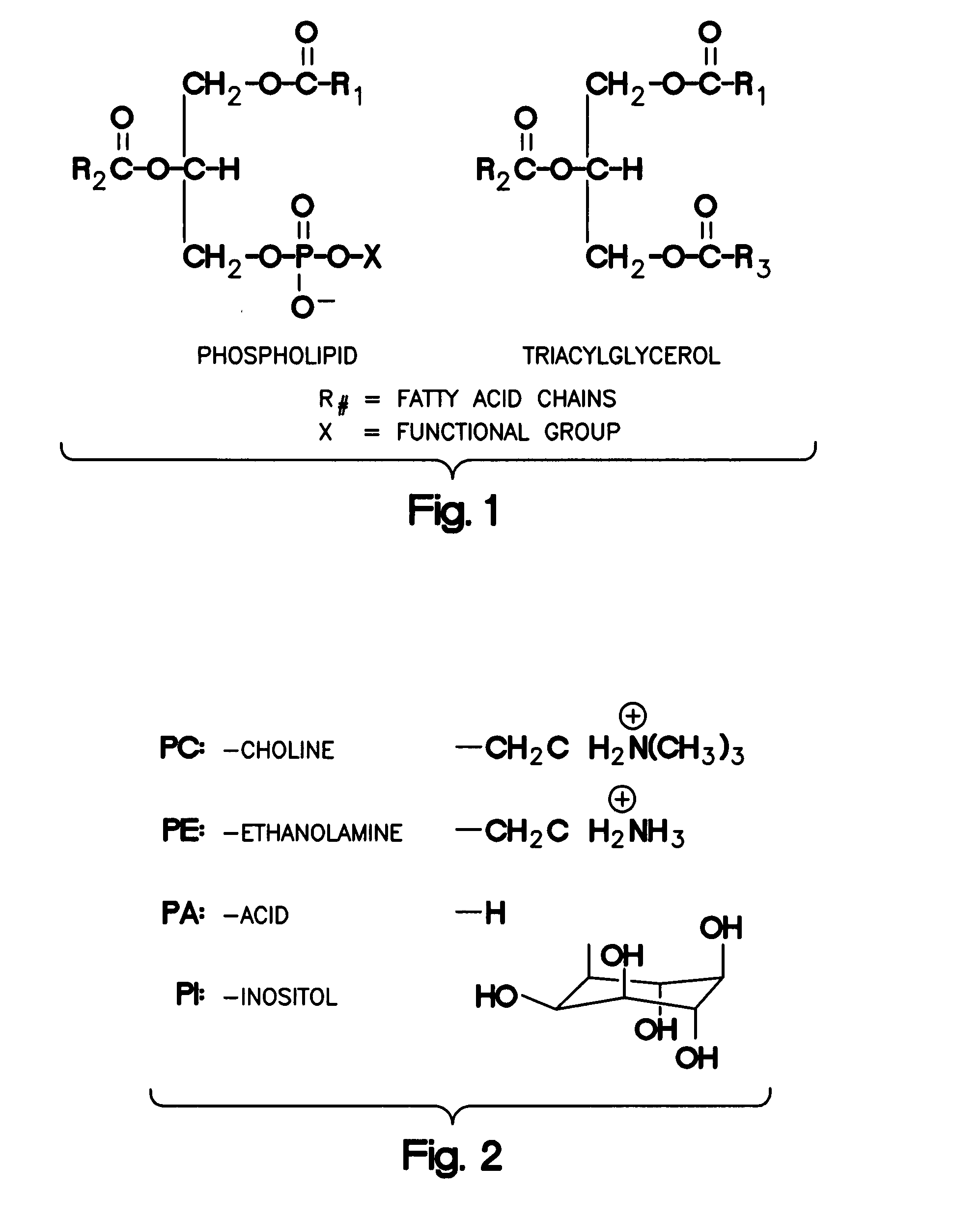
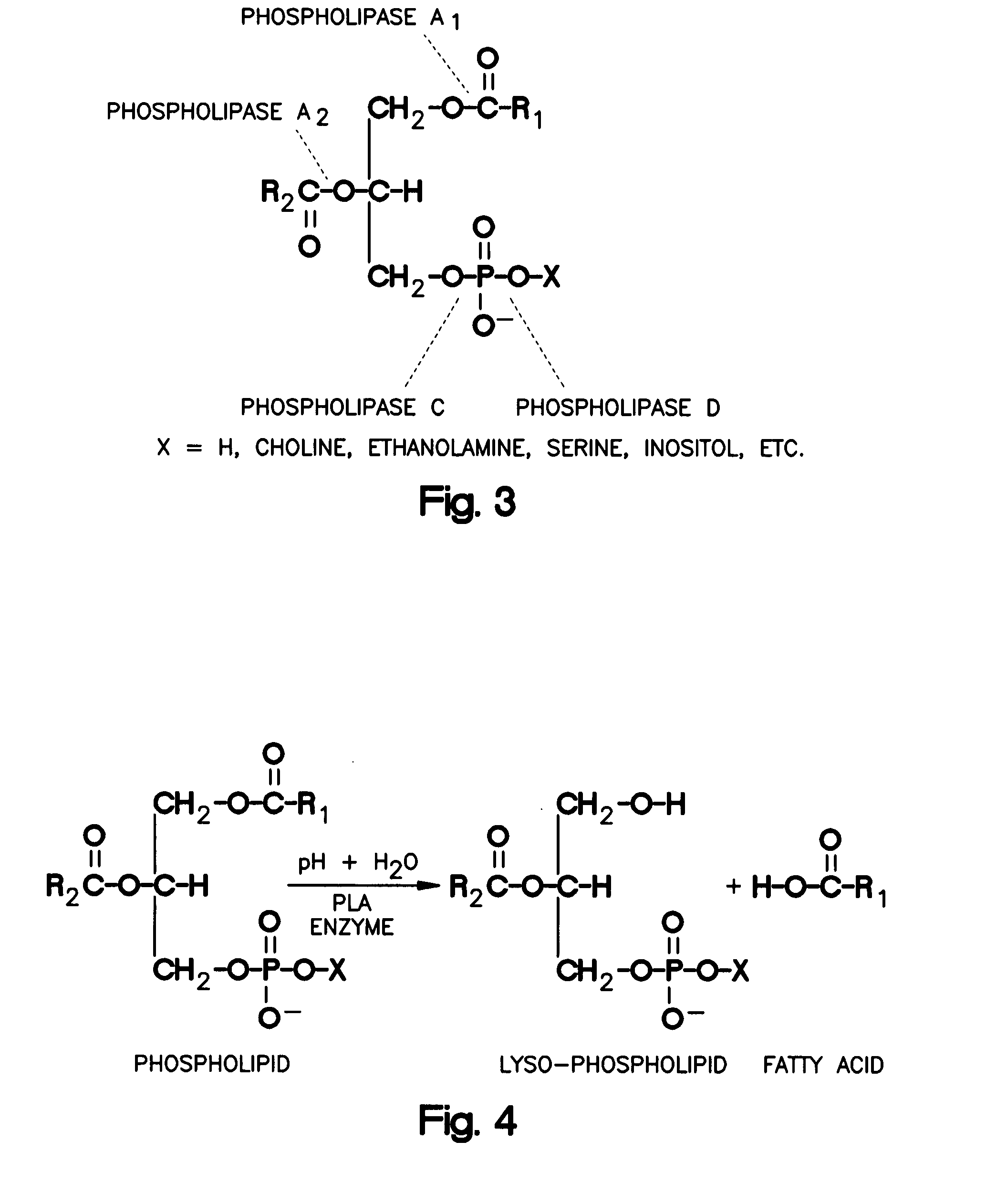
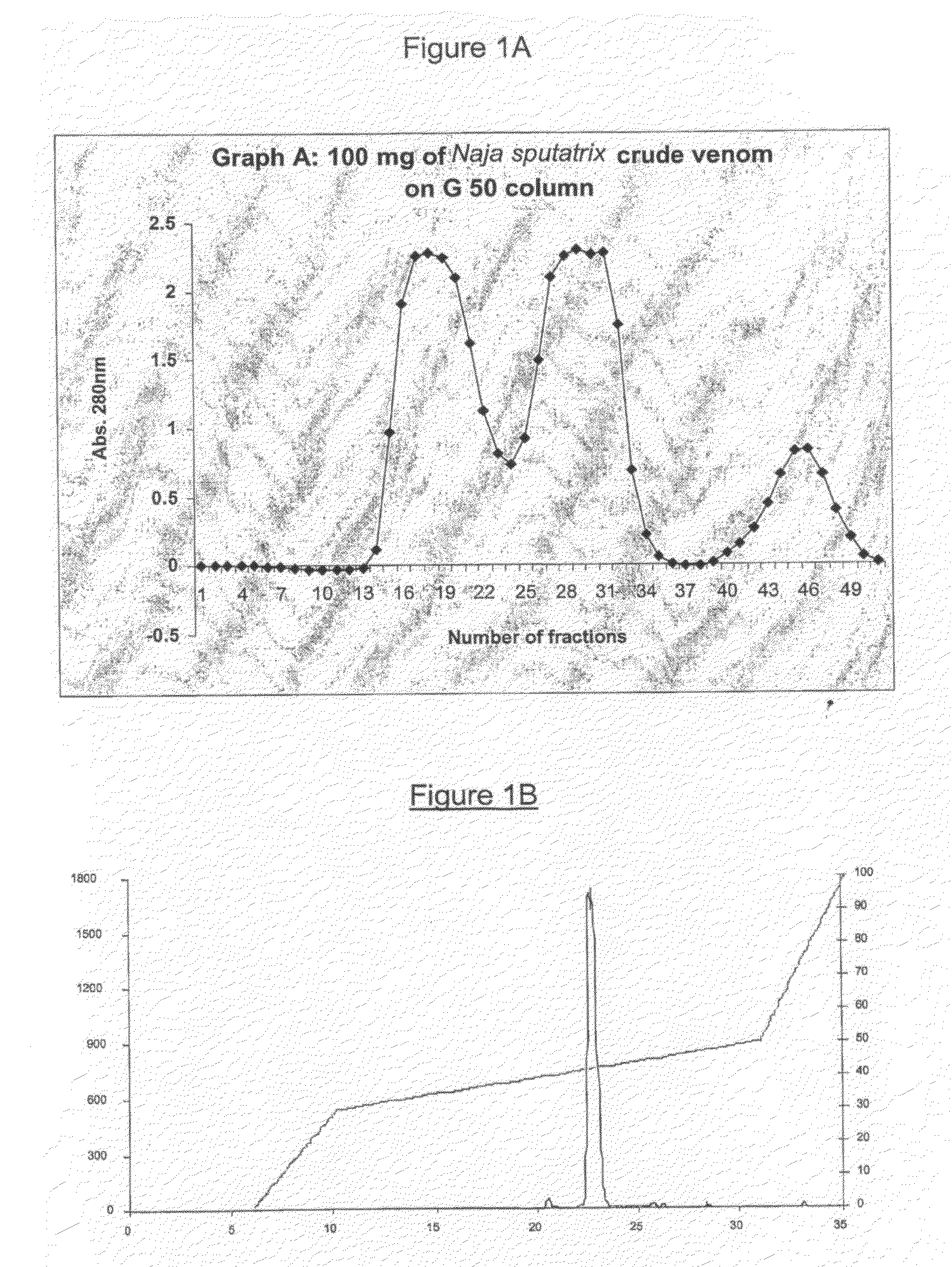
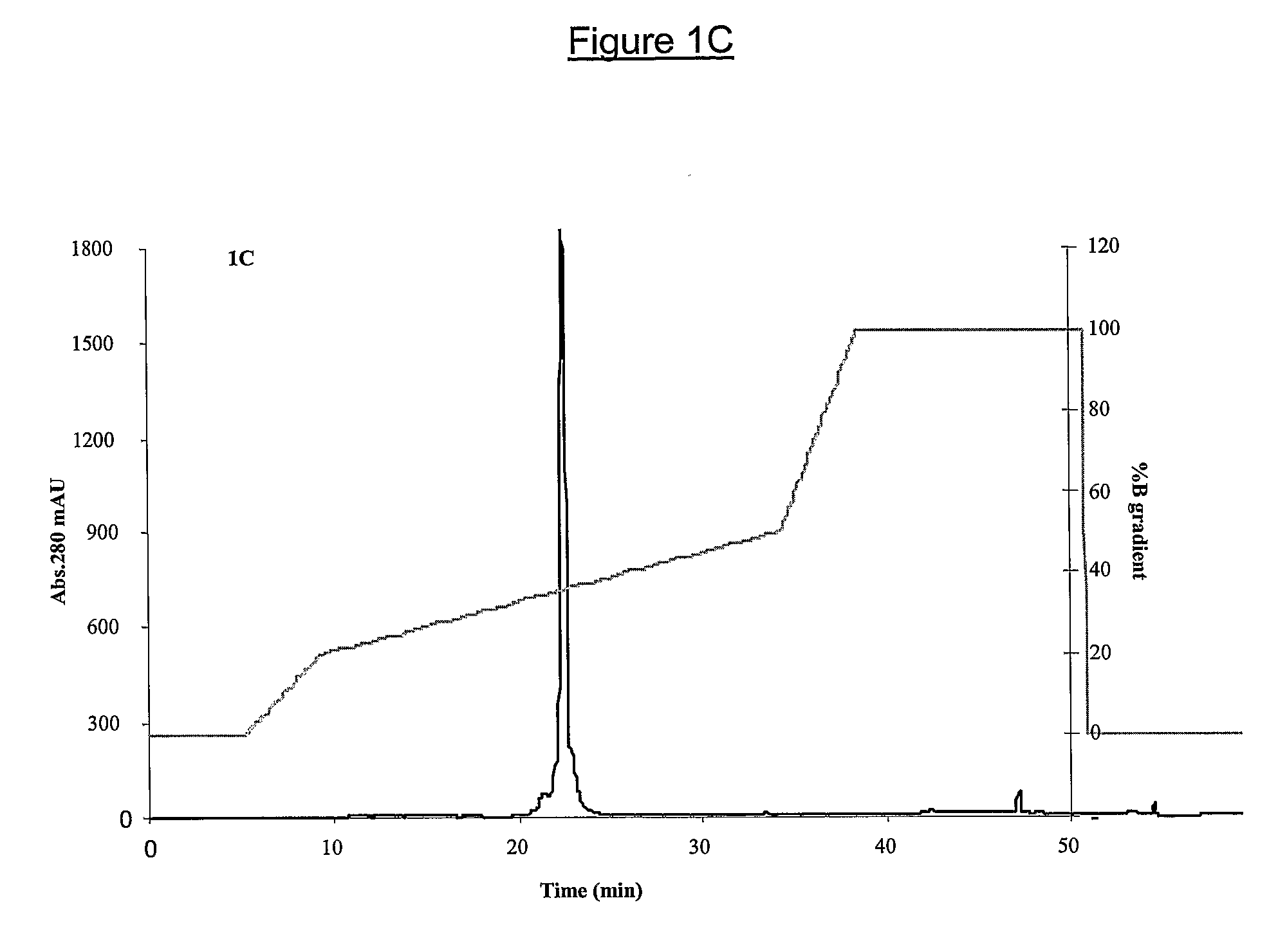
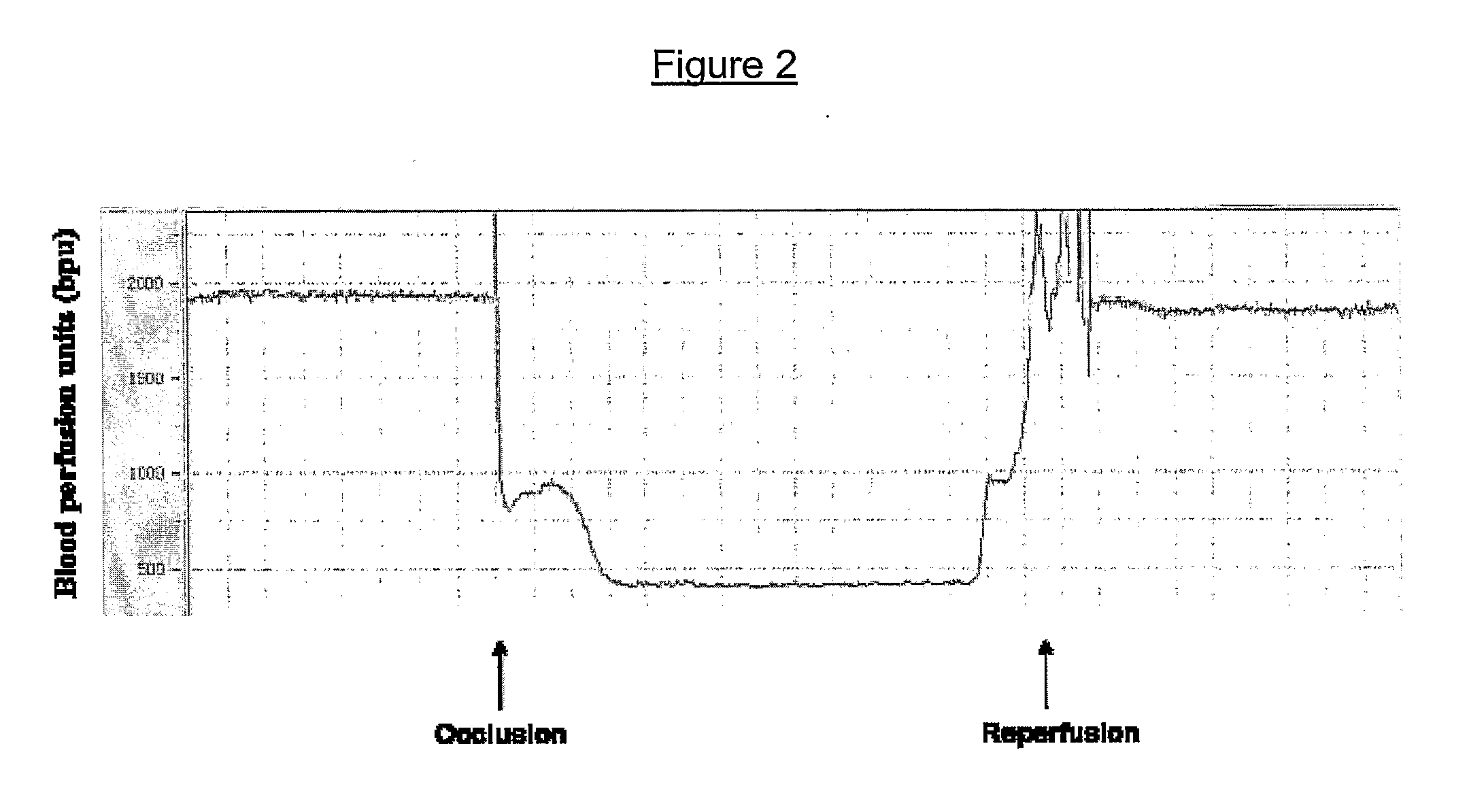
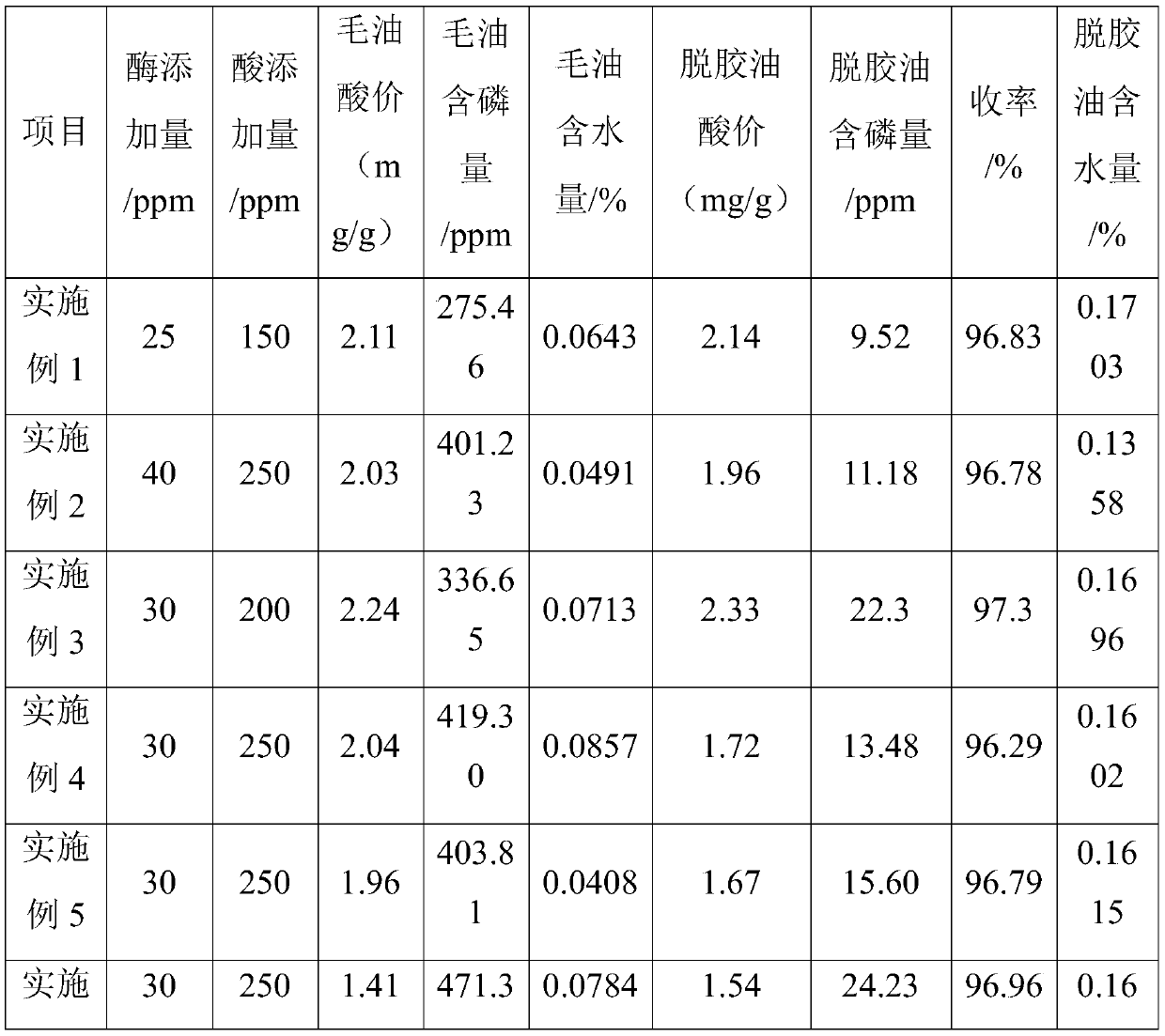
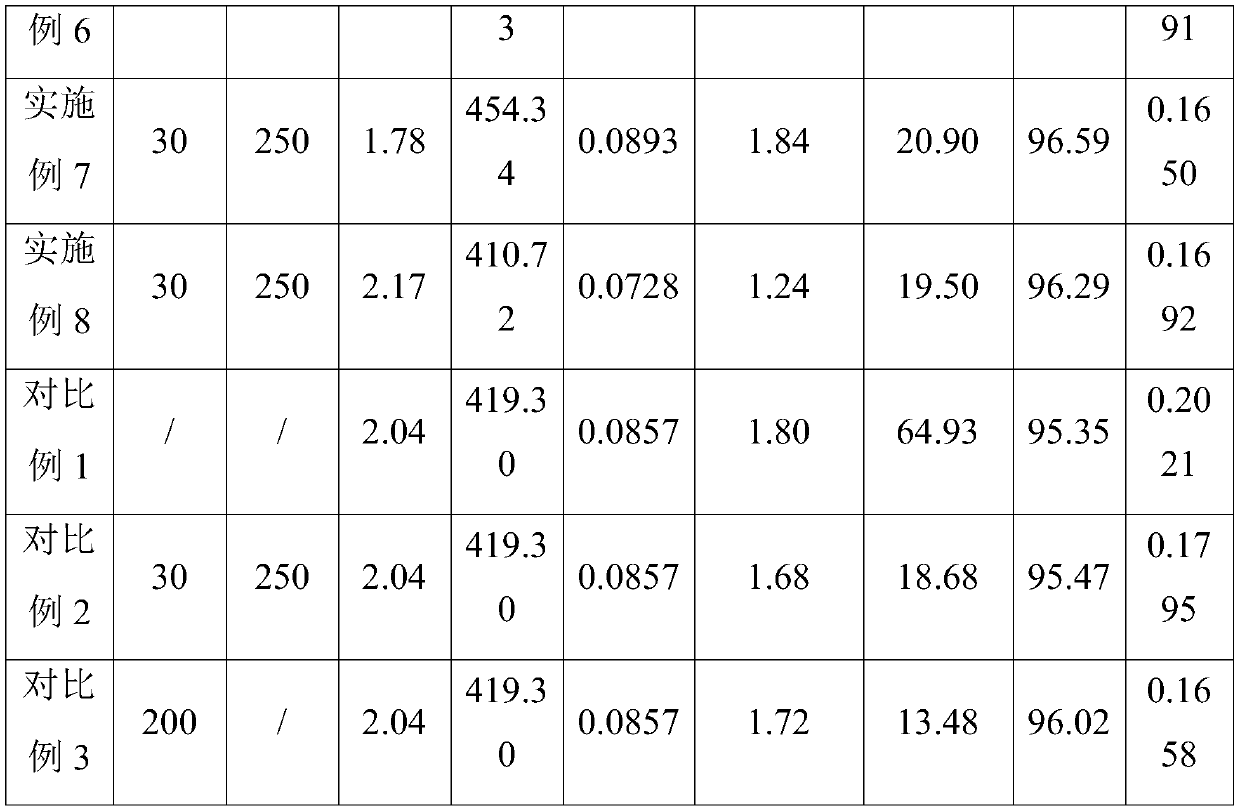
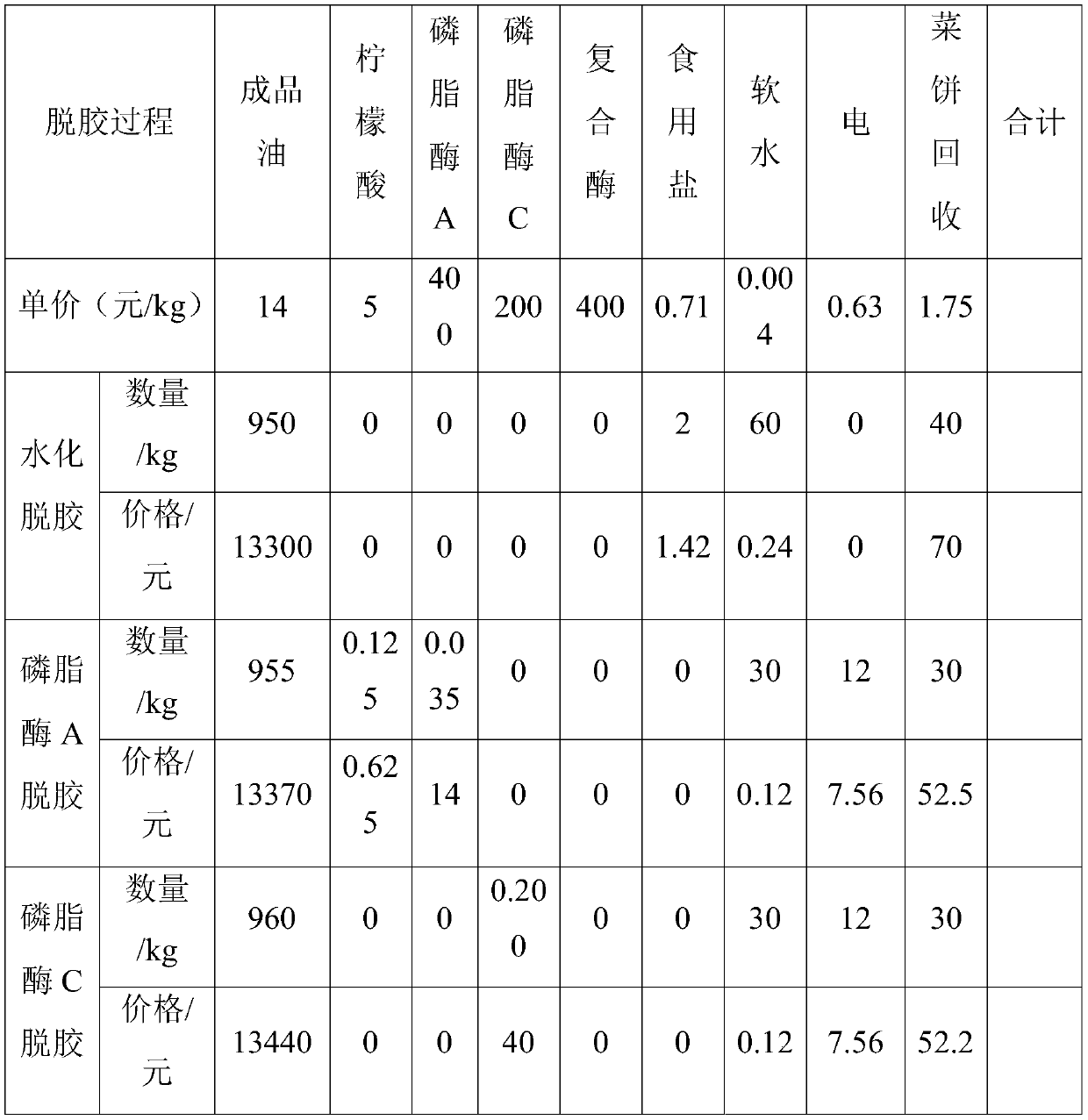
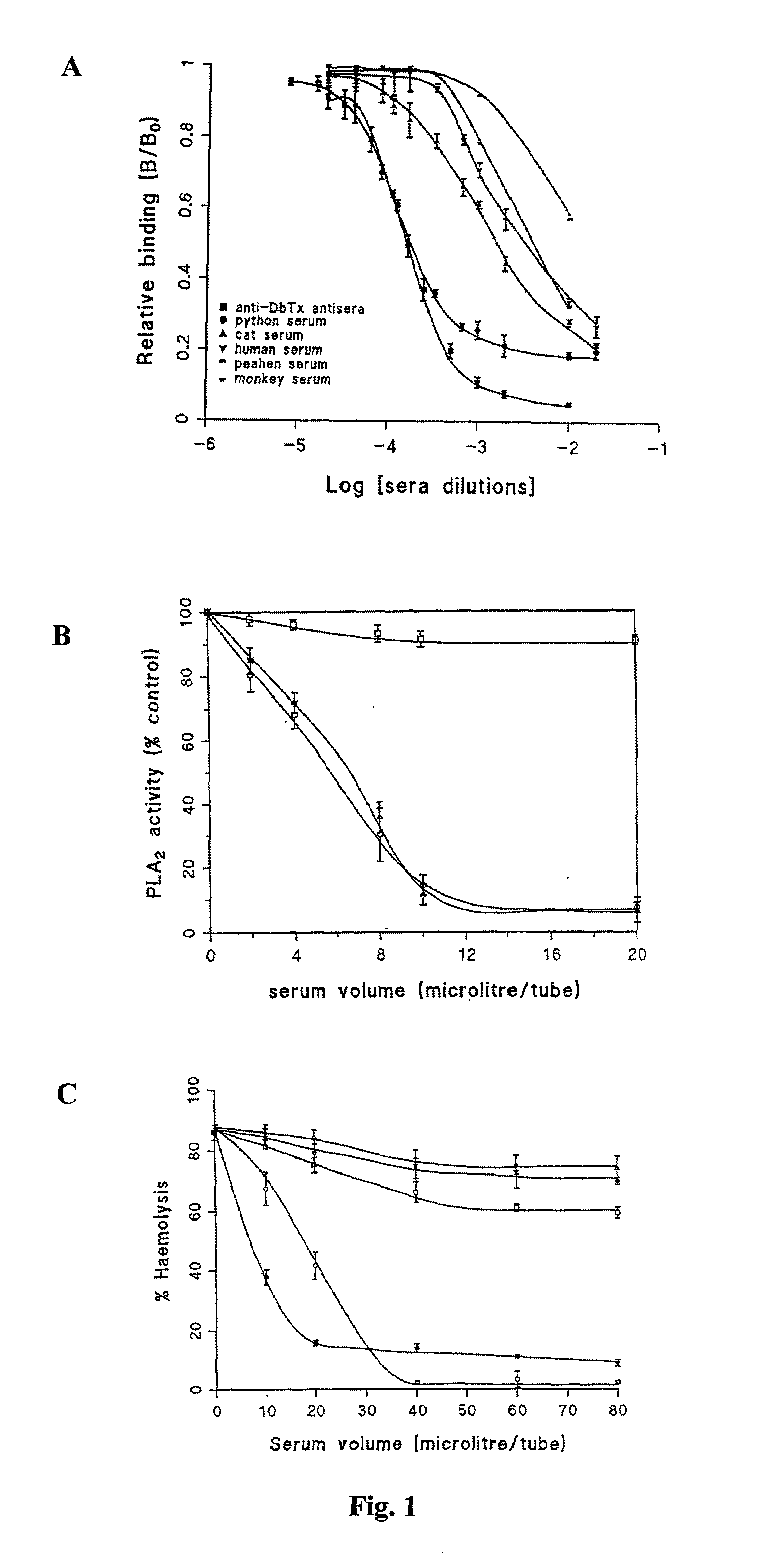
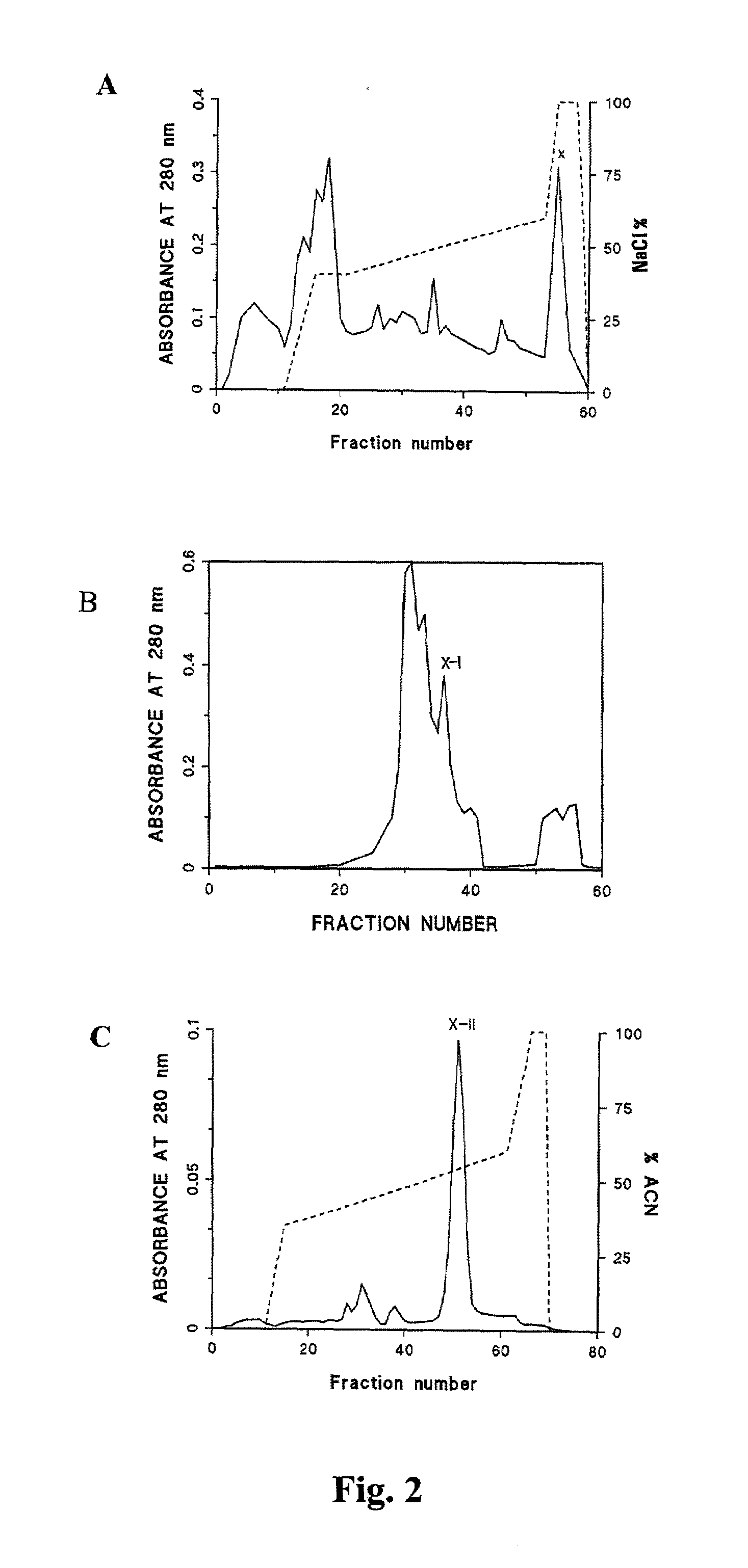
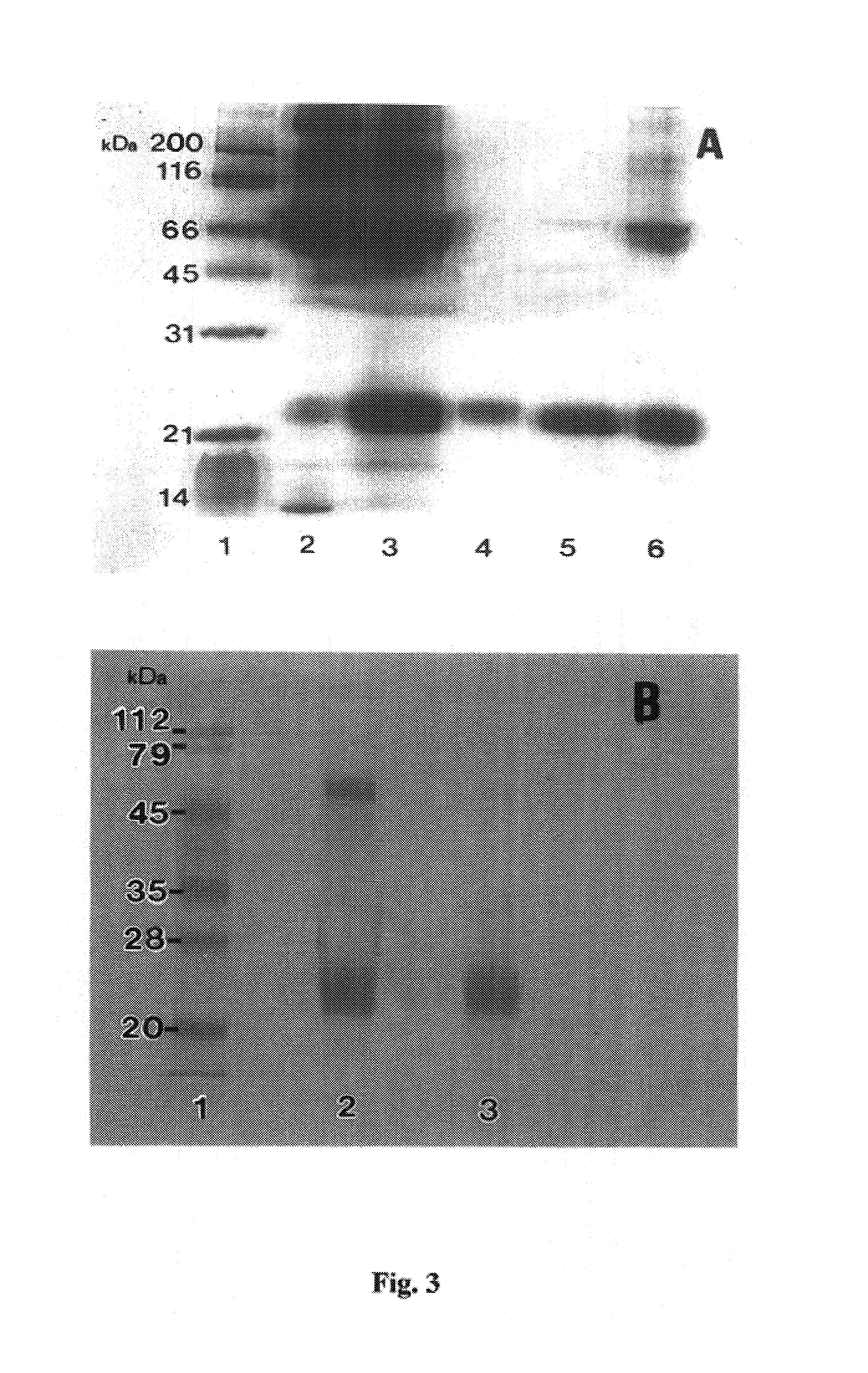
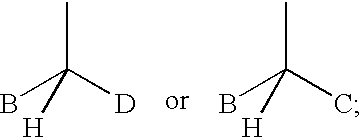Patents
Literature
48 results about "Phospholipases A" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
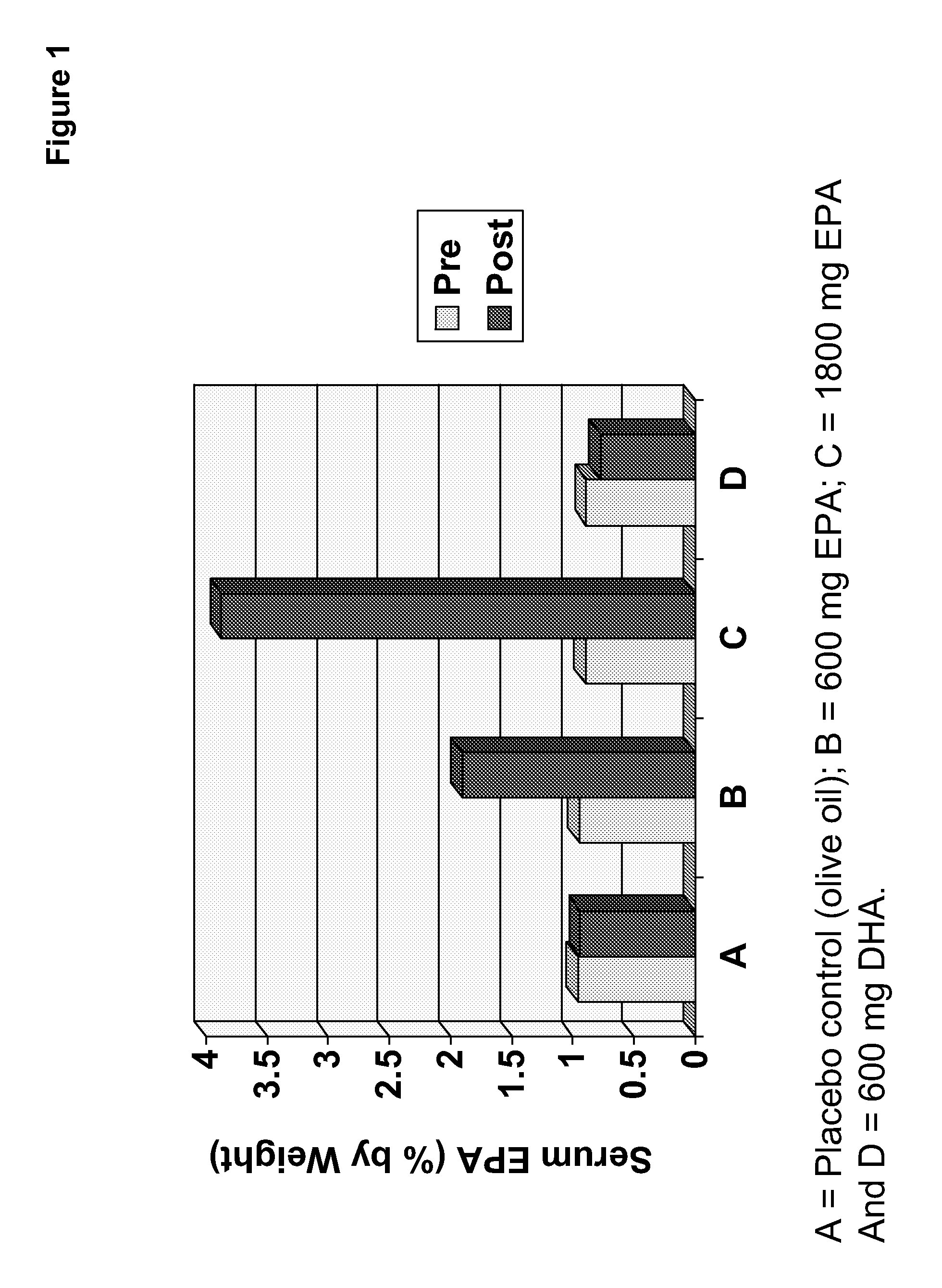
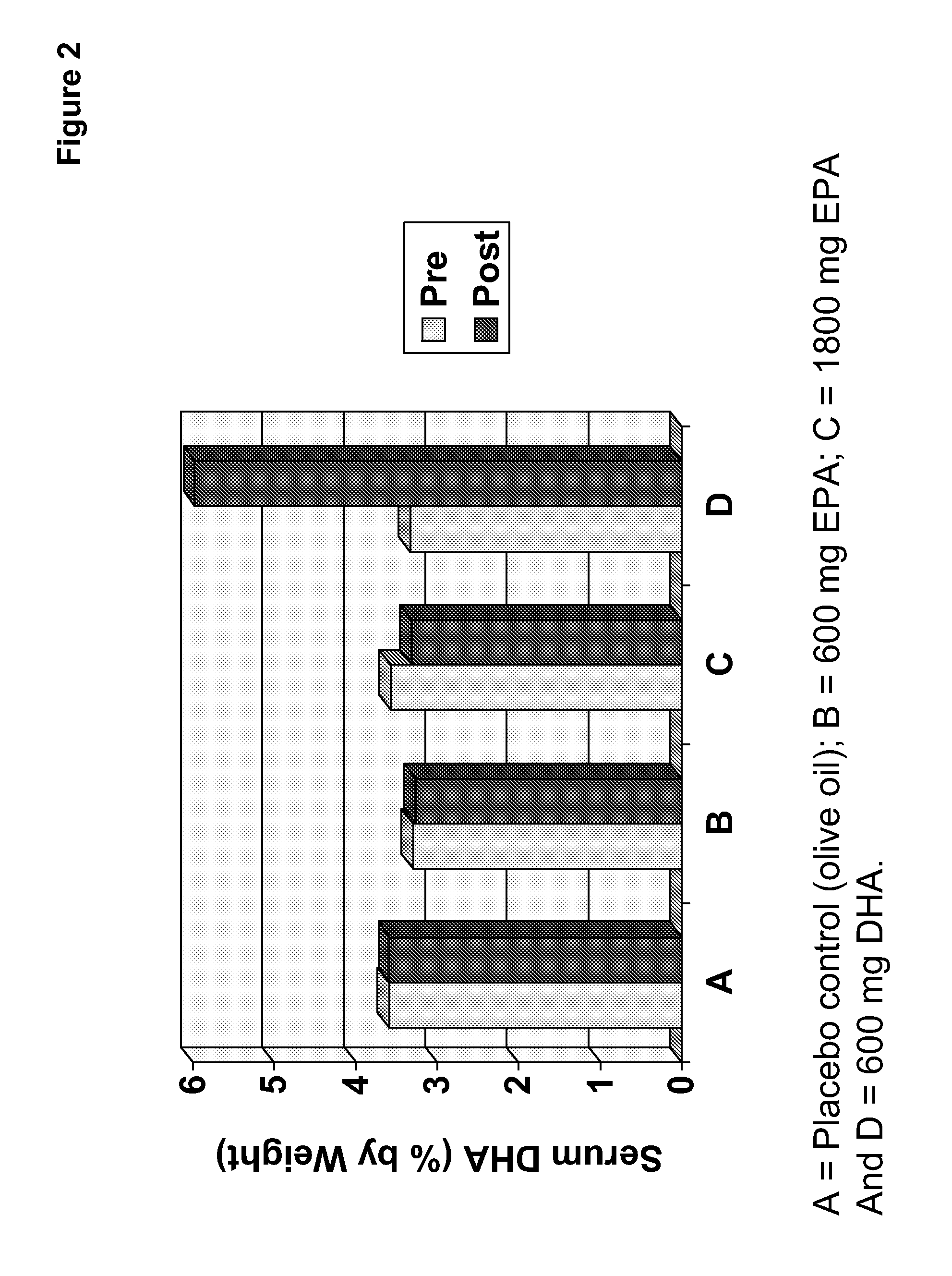
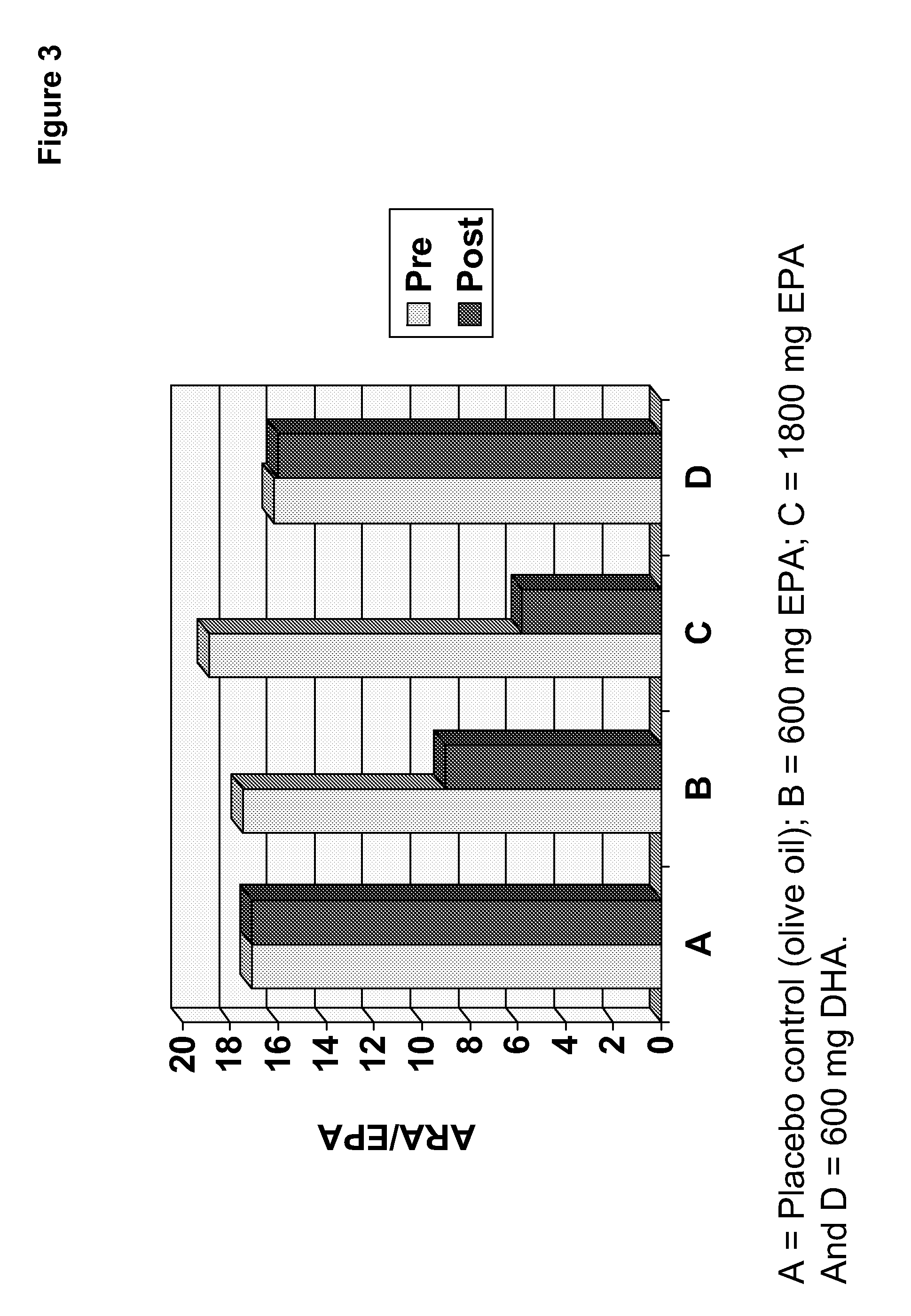
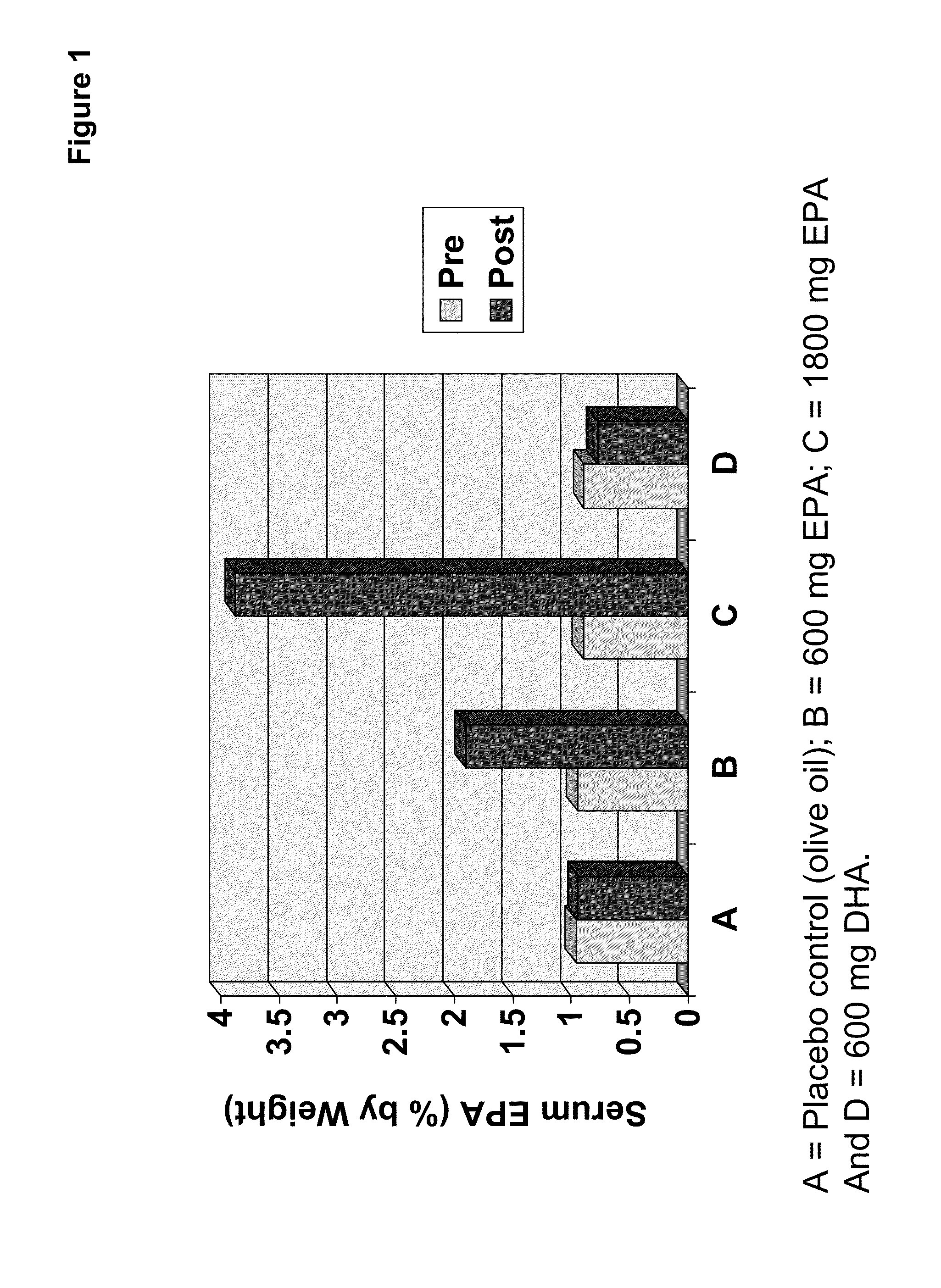
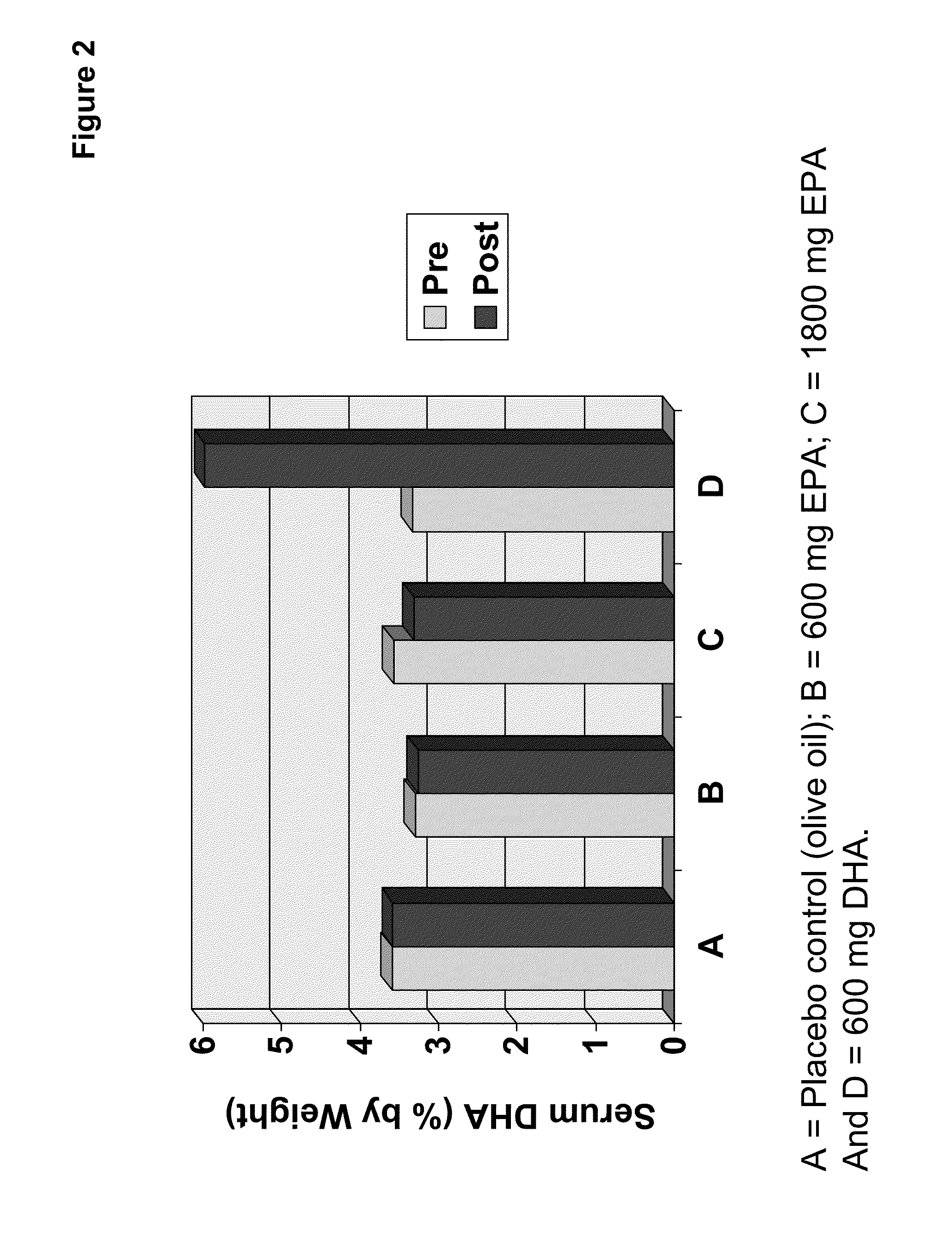
Clinical benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid in humans
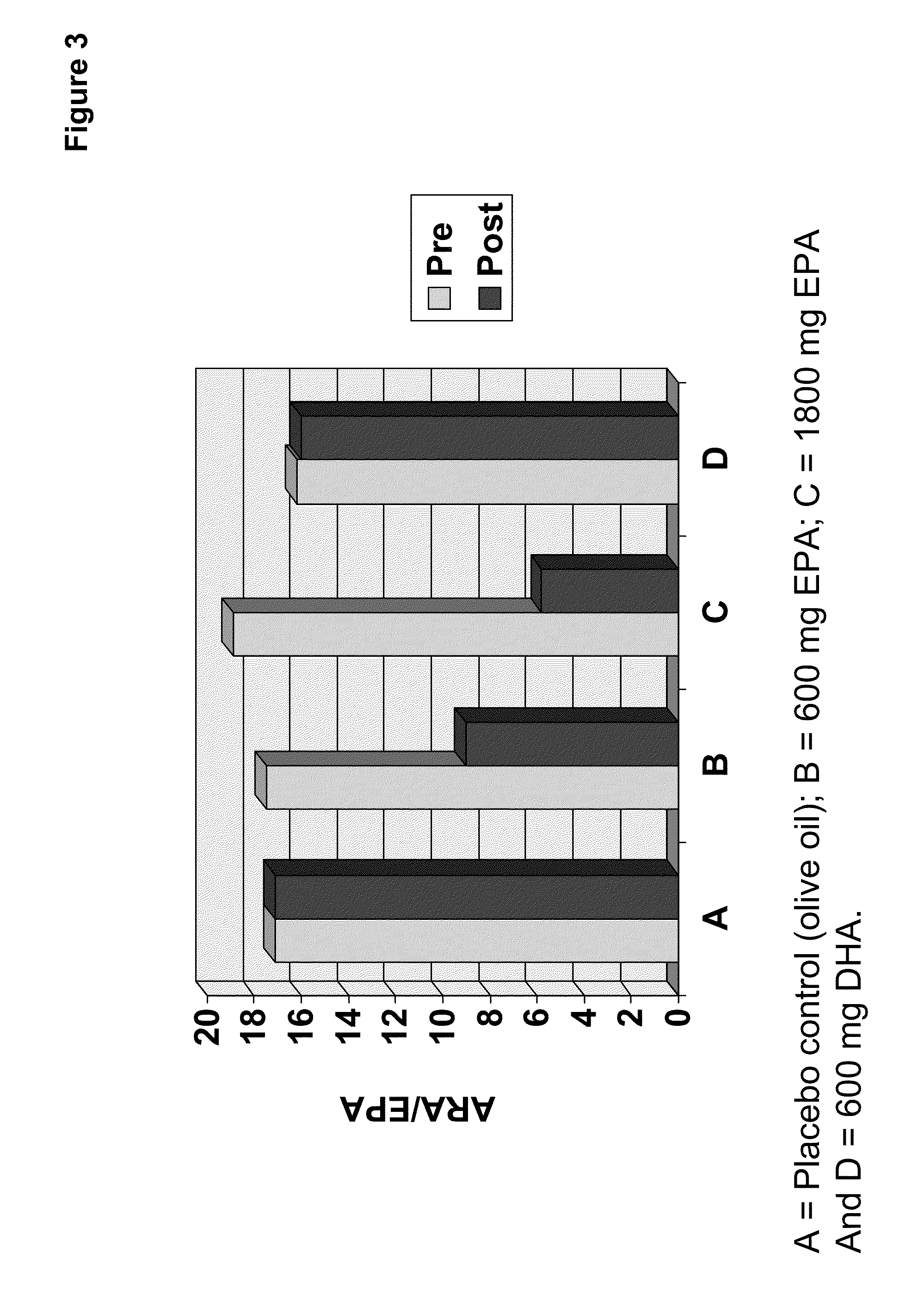
InactiveUS20110178105A1Maintaining and lowering Lp-PLA levelWithout raising LDL cholesterol levelBiocideMetabolism disorderEicosapentaenoic acidOMEGA-3 POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS
Methods are provided for maintaining or lowering lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 [“Lp-PLA2”] levels, stabilizing rupture prone-atherosclerotic lesions, decreasing the Inflammatory Index and increasing Total Omega-3 Score™ in humans, by administering an effective amount of eicosapentaecnoic acid [“EPA”], an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”].
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
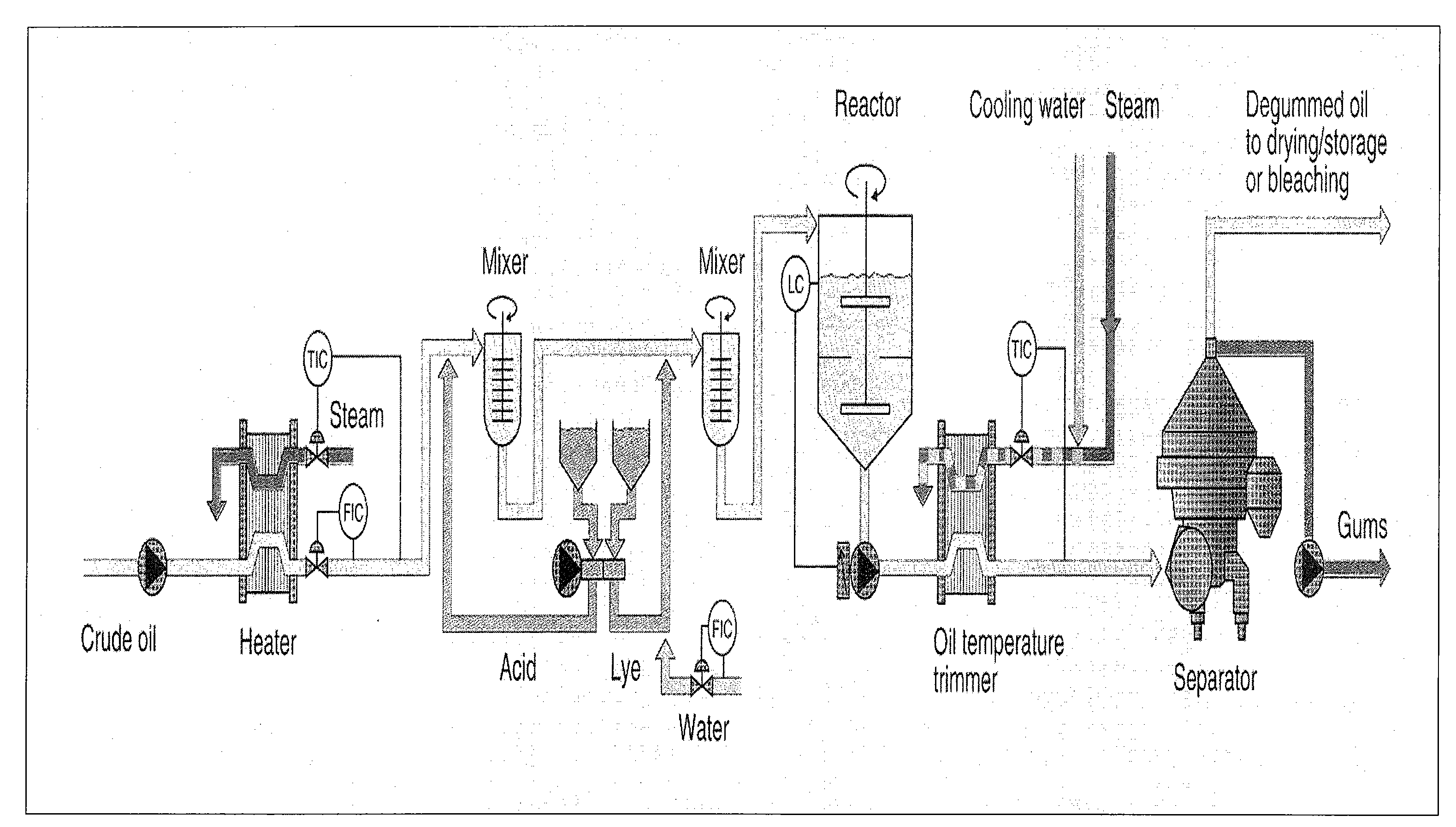
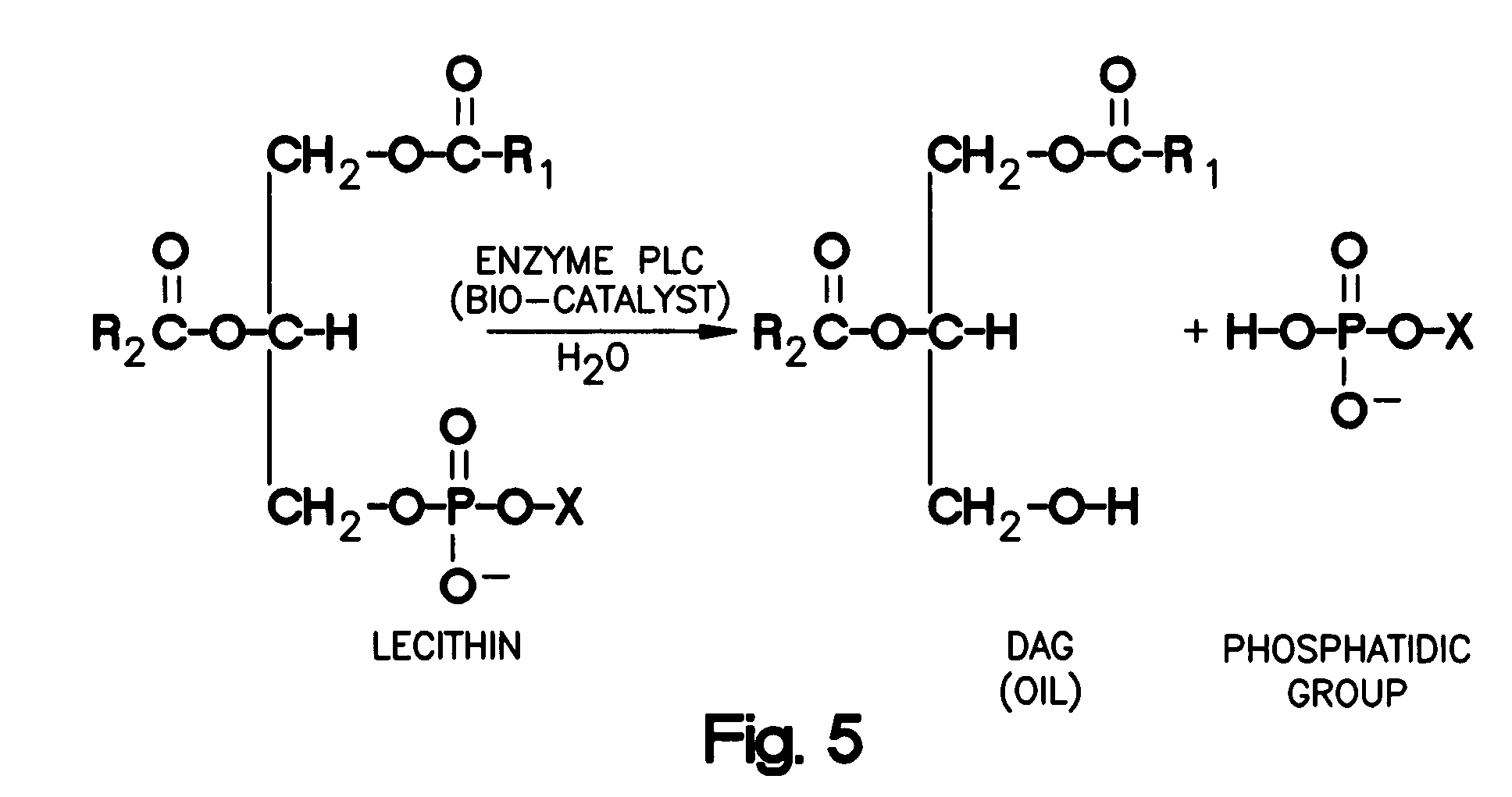
Enzymatic Degumming Utilizing a Mixture of PLA and PLC Phospholipases
ActiveUS20080182322A1Suitable for useLow in phospholipidsFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteFatty acids production/refiningPhospholipidPhospholipases C
A method for degumming an oil composition comprises the steps of (a) providing an oil composition containing a quantity of phospholipids, (b) contacting said oil composition simultaneously with one or more phospholipase A enzymes and one or more phospholipase C enzymes, under conditions sufficient for the enzymes to react with the phospholipids to create phospholipid reaction products, and (c) separating the phospholipids reaction products from the oil composition, the remaining oil composition after the separation being a degummed oil composition, whereby during step (b) the reaction of said one or more phospholipase A enzymes proceeds at a faster rate than it would in the absence of said one or more phospholipase C enzymes.
Owner:BUNGE OILS INC
Clinical benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid in humans
Methods are provided for maintaining or lowering lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 [“Lp-PLA2”] levels, stabilizing rupture prone-atherosclerotic lesions, decreasing the Inflammatory Index and increasing Total Omega-3 Score™ in humans, by administering an effective amount of eicosapentaenoic acid [“EPA”], an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”].
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
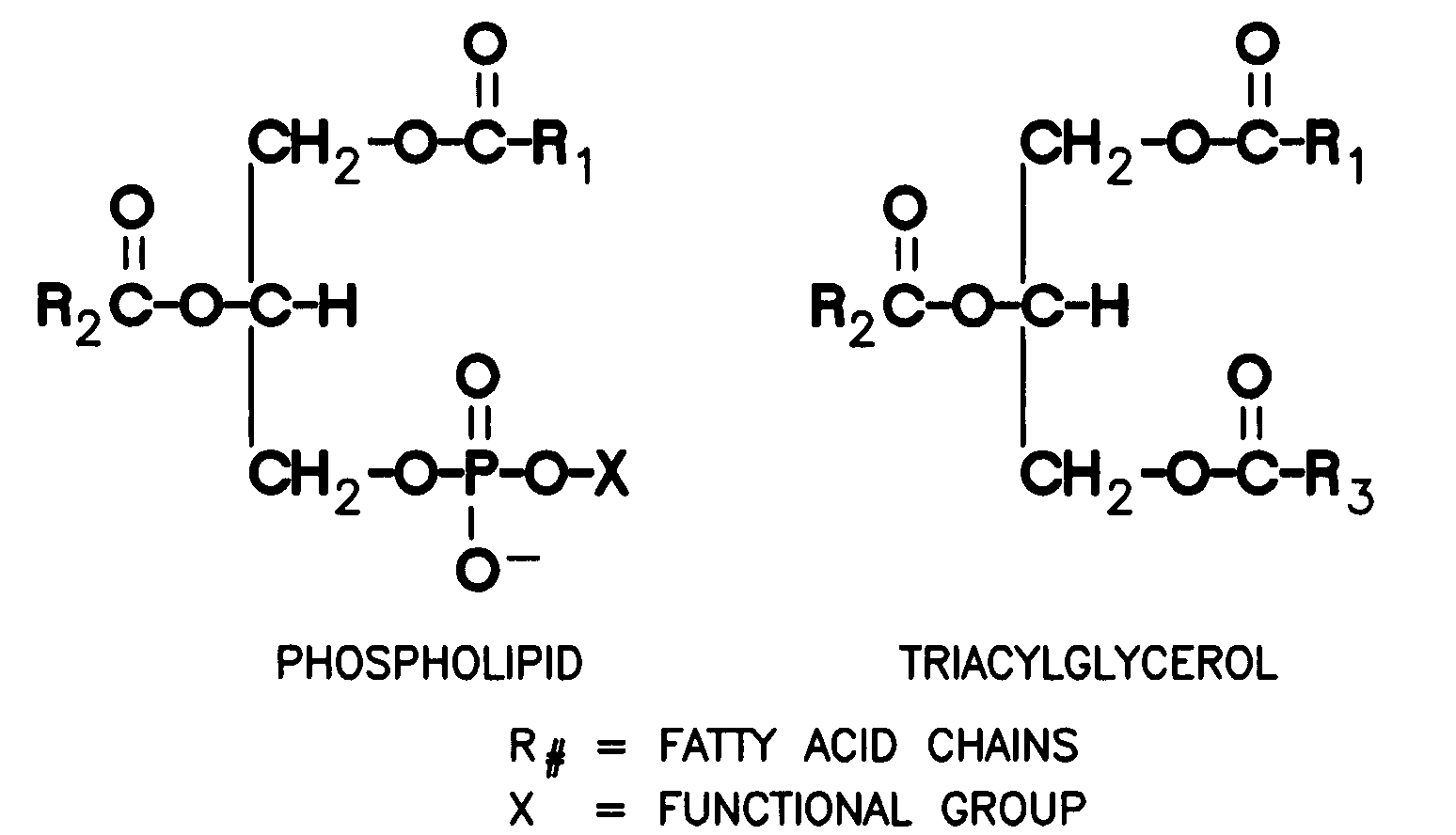
Phosholipases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
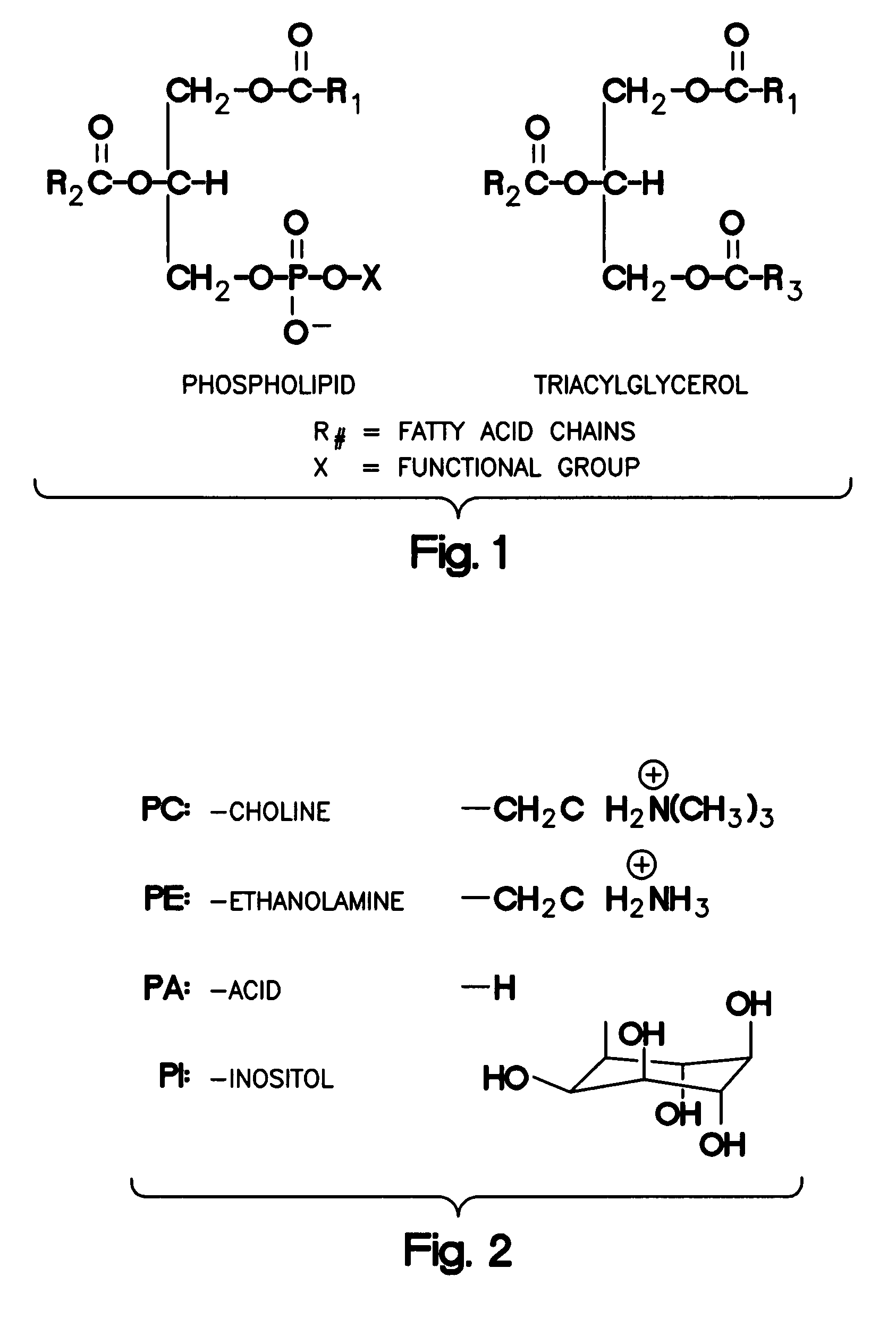
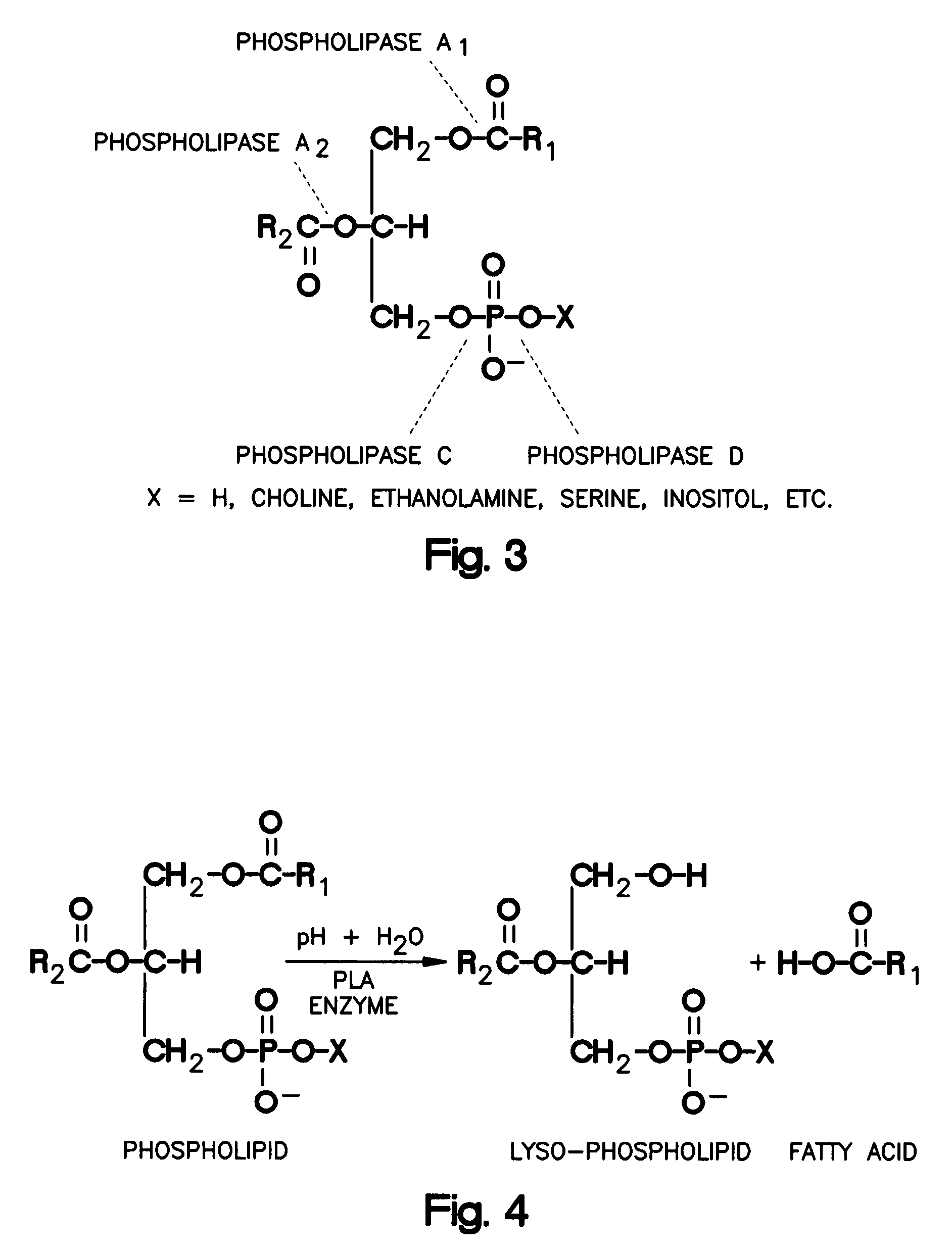
The invention provides novel polypeptides having phospholipase activity, including, e.g., phospholipase A, B, C and D activity, patatin activity, lipid acyl hydrolase (LAH) activity, nucleic acids encoding them and antibodies that bind to them. Industrial methods, e.g., oil degumming, and products comprising use of these phospholipases are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Inhibitors of phospholipase enzymes
Novel compounds are disclosed which inhibit the activity of phospholipase enzymes in a mammal, particularly cytosolic phospholipase A2. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds and methods of treatment using such compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
Methods for the use of inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2
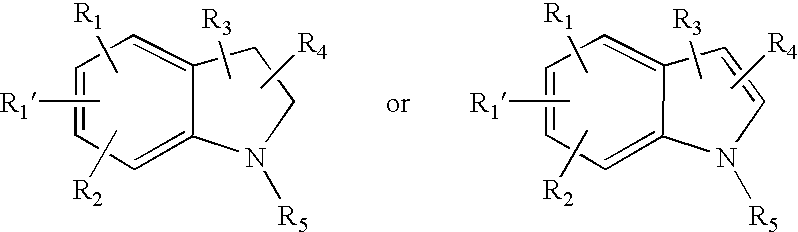
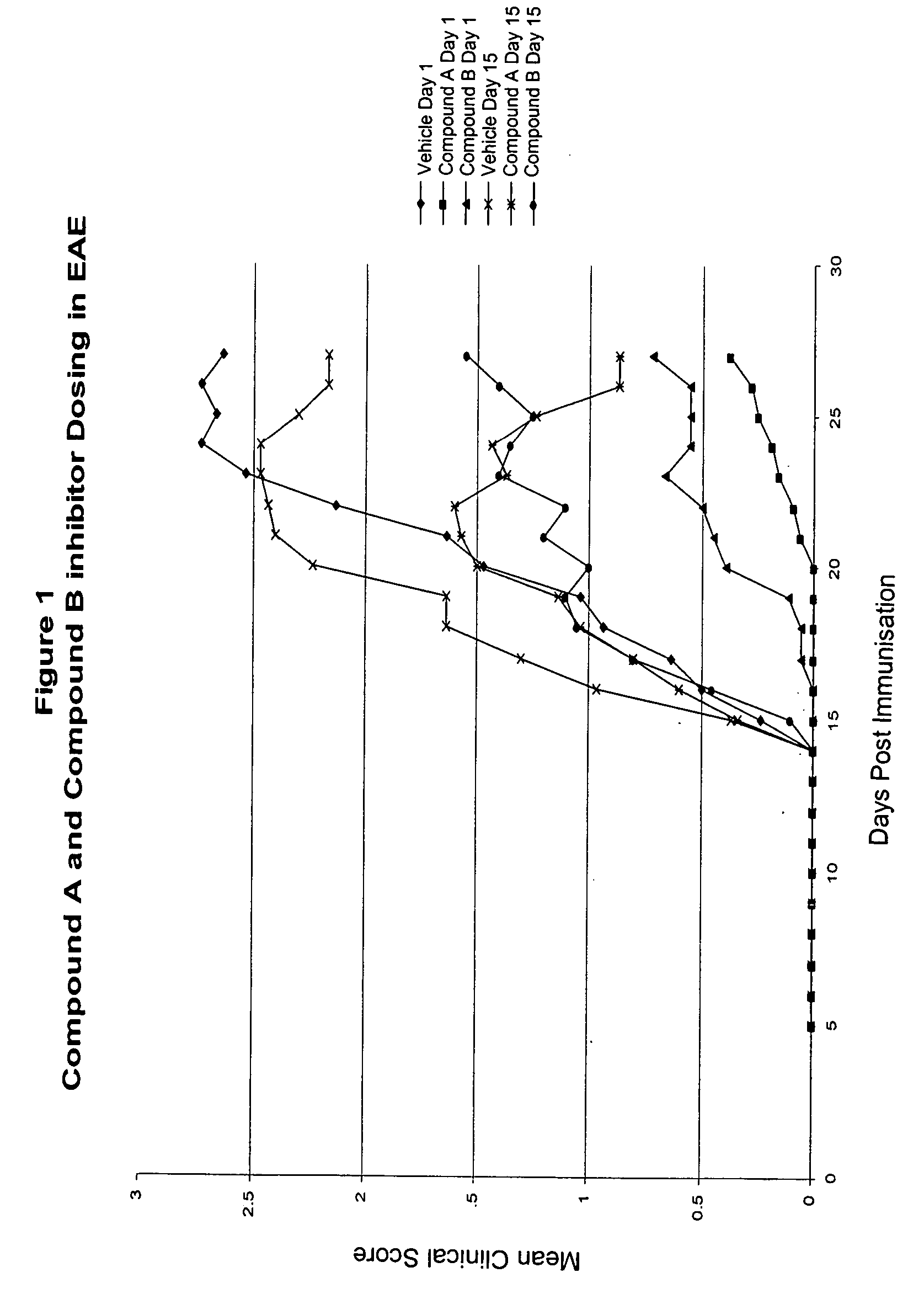
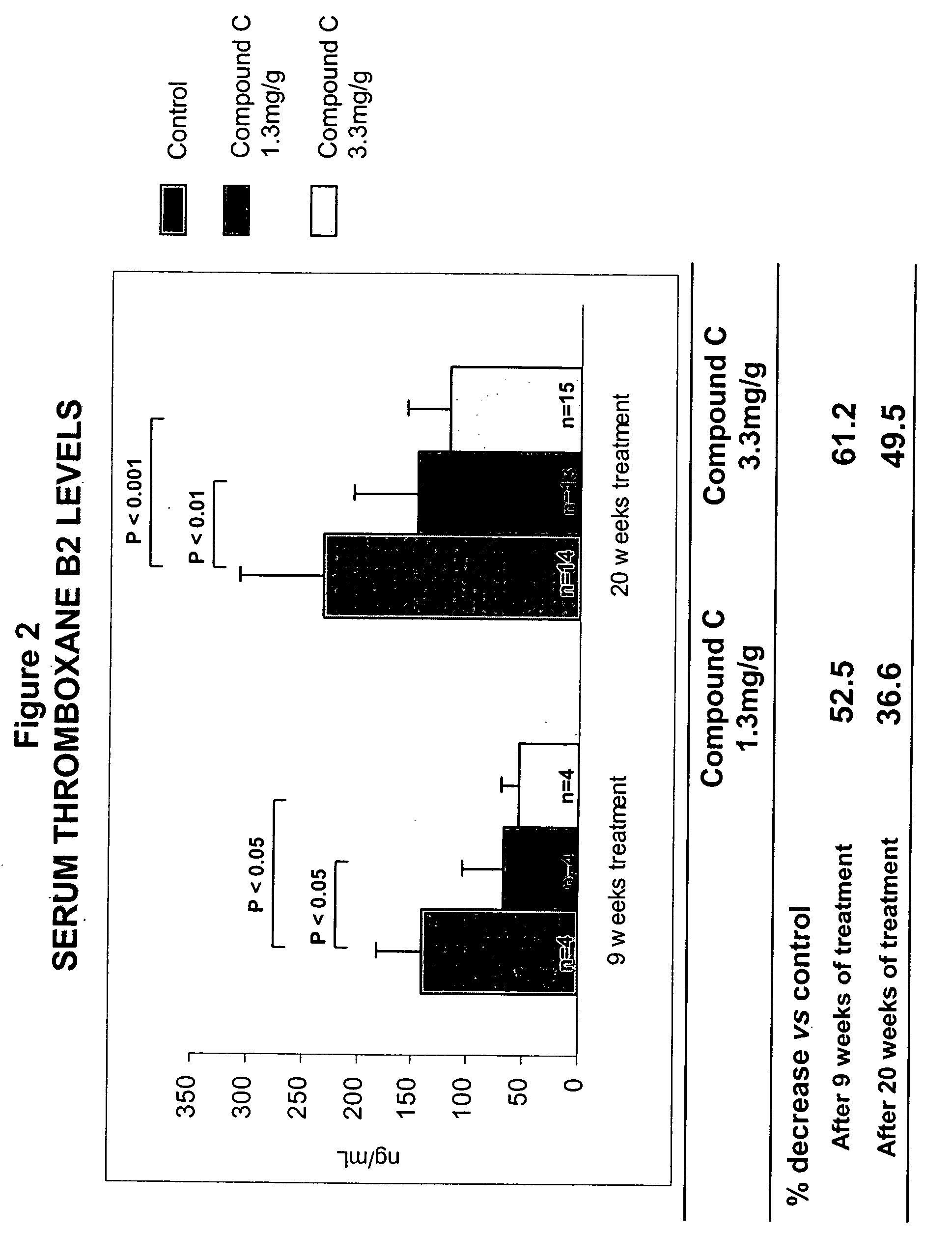
This invention provides methods for the use of substituted indole compounds of the general formula: and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof. The invention provides methods for the use of the compounds as inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly phospholipase A2 enzymes, and for the medical treatment, prevention and inhibition diseases and disorders including asthma, stroke, atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, arthritic disorders, rheumatic disorders, central nervous system damage resulting from stroke, central nervous system damage resulting from ischemia, central nervous system damage resulting from trauma, inflammation caused or potentiated by prostaglandins, inflammation caused or potentiated by leukotrienes, inflammation caused or potentiated by platelet activation factor, pain caused or potentiated by prostaglandins, pain caused or potentiated by leukotrienes, and pain caused or potentiated by platelet activation factor.
Owner:ZIARCO
Methods for treating arthritic disorders
This invention provides methods for treating in mammals arthritic or rheumatic disorders using substituted indole compounds of the general formula:and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof, and methods for using the compounds as inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly phospholipase A2 enzymes, and for the medical treatment, prevention and inhibition of pain and inflammation.
Owner:WYETH
Phospholipase(s) and Use(s) Thereof
InactiveUS20090252718A1Reduces ischemic infarct sizeReduces ischemic cell deathSugar derivativesHydrolasesMedicineMutant
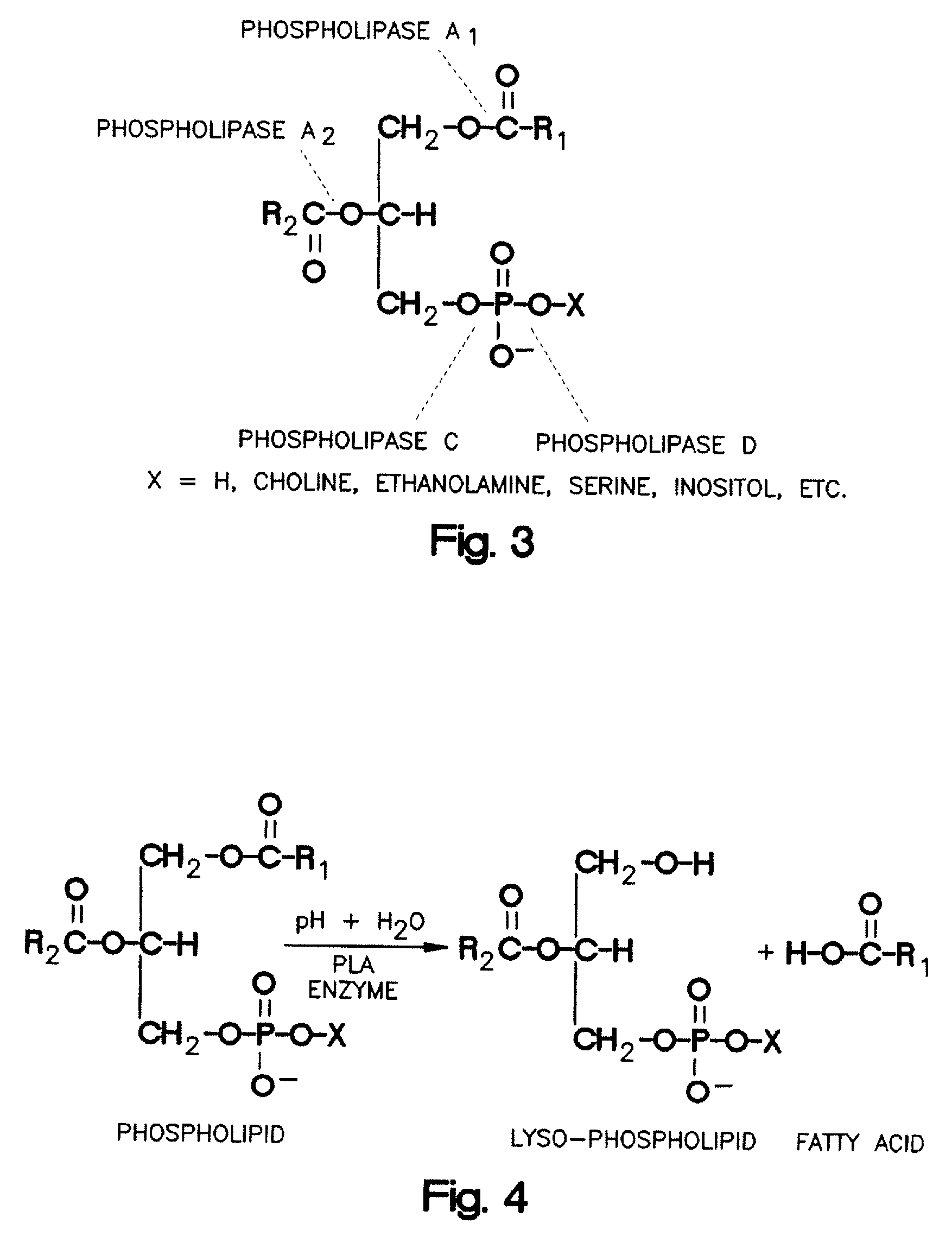
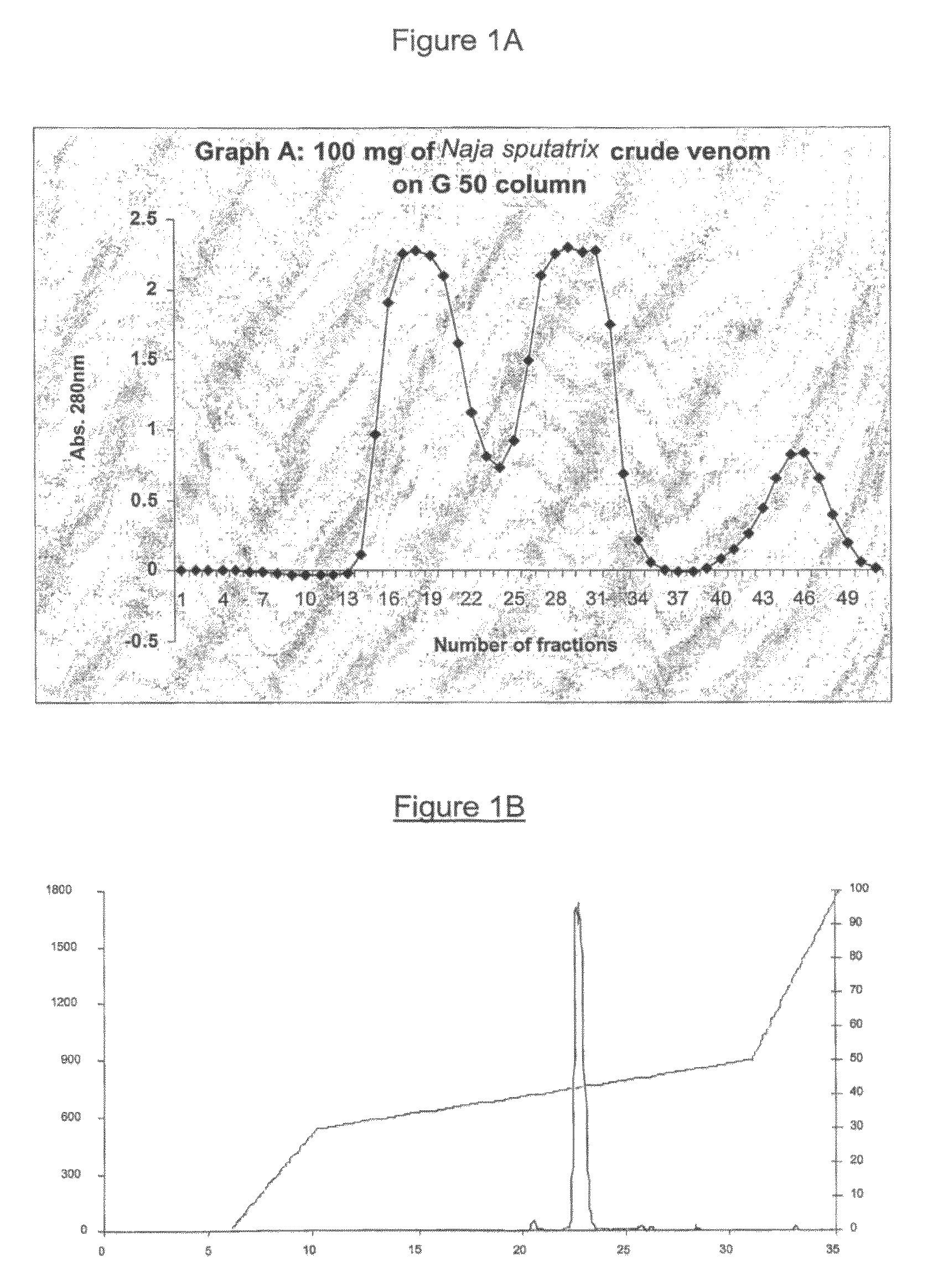
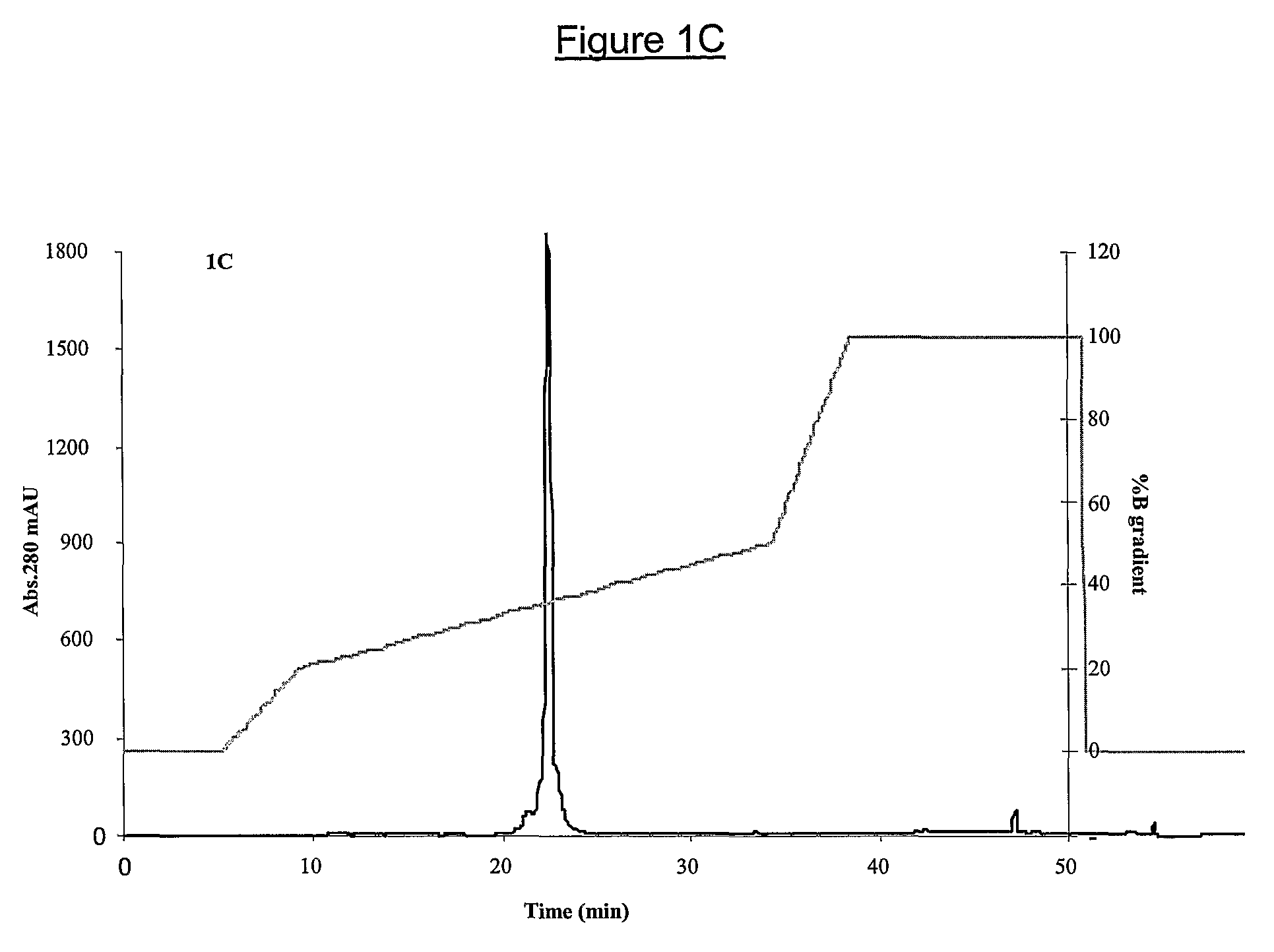
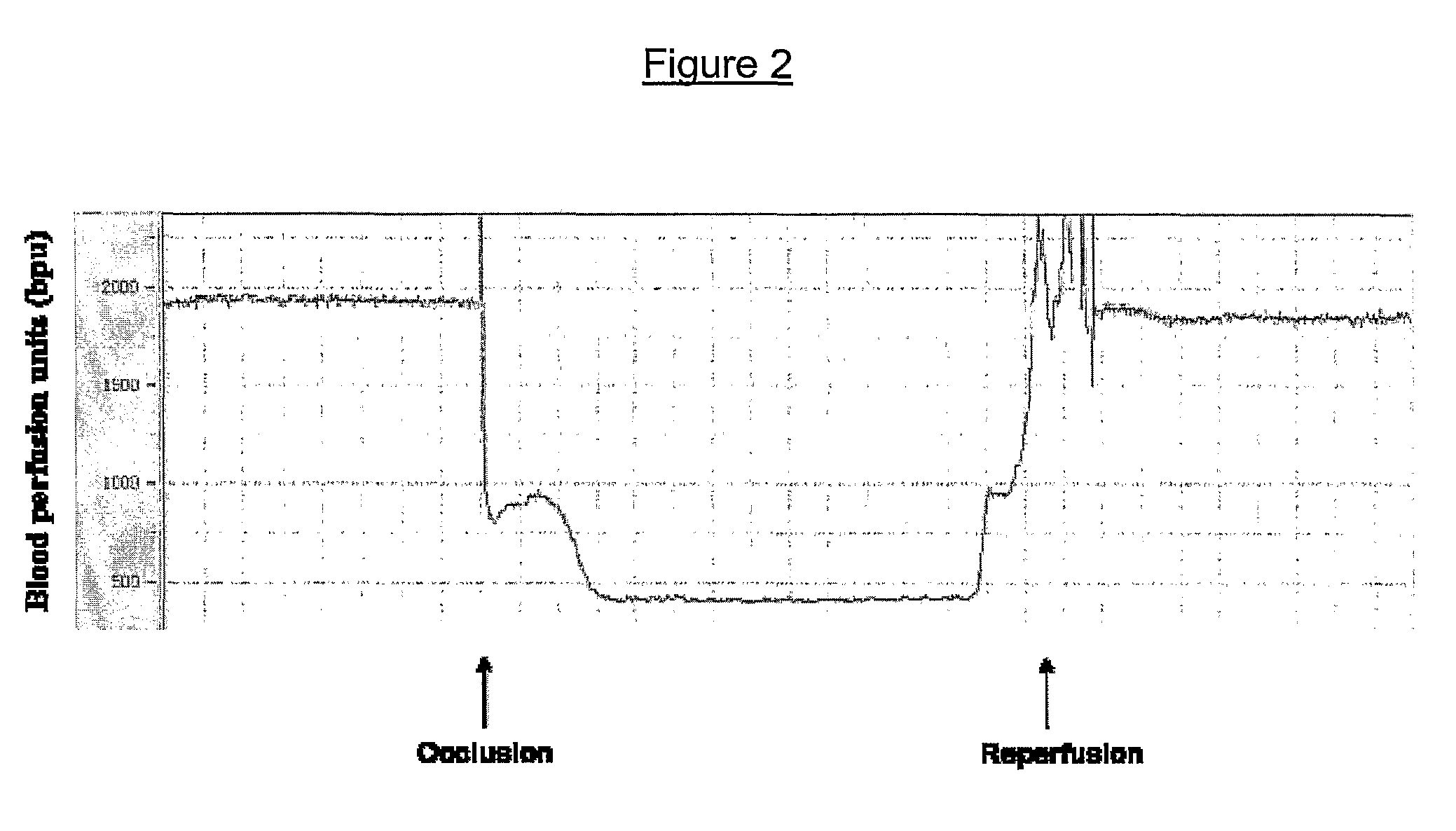
The invention relates to phospholipase(s), isoforms, derivatives, mutants and / or fragments thereof, for the preparation of a medicament for the treatment and / or prevention of ischemia. Preferred is the use of secretory phospholipase, particularly phospholipase A2, and even more particularly phospholipase A2 derived from the snake venom of Naja sputatrix
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2
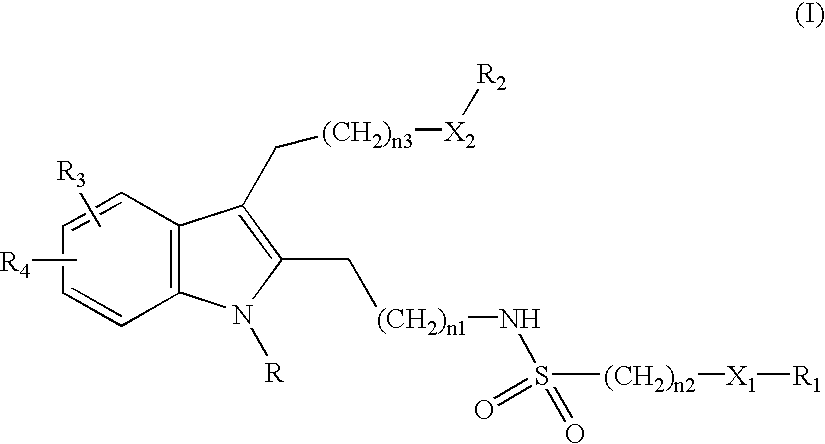
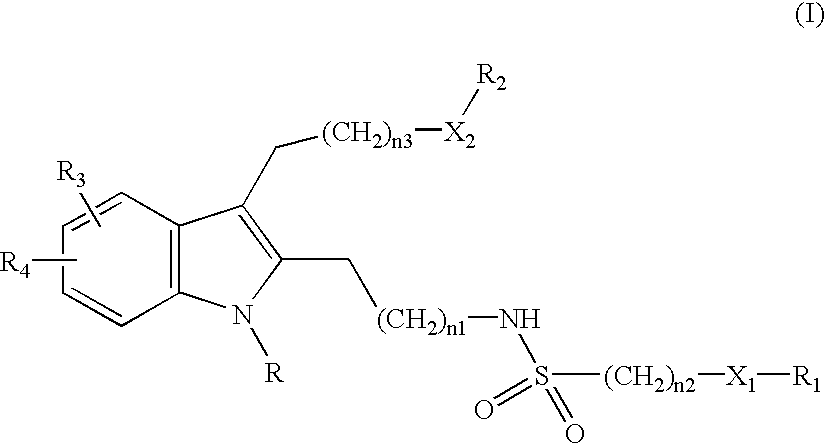
This invention provides chemical inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly cytosolic phospholipase A2 enzymes (cPLA2), more particularly including inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2 alpha enzymes (cPLA2α). In some embodiments, the inhibitors have the Formula I:wherein the constituent variables are as defined herein.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Phospholipases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
InactiveUS20120100581A1High activityYield maximizationFungiBacteriaAntiendomysial antibodiesAcyl group
The invention provides novel polypeptides having phospholipase activity, including, e.g., phospholipase A, B, C and D activity, patatin activity, phosphatidic acid phosphatases (PAP)) and / or lipid acyl hydrolase (LAH) activity, nucleic acids encoding them and antibodies that bind to them. Industrial methods, e.g., oil degumming, and products comprising use of these phospholipases are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Phospholipases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides novel polypeptides having phospholipase activity, including, e.g., phospholipase A, B, C and D activity, patatin activity, lipid acyl hydrolase (LAH) activity, nucleic acids encoding them and antibodies that bind to them. Industrial methods, e.g., oil degumming, and products comprising use of these phospholipases are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for degumming fragrant rap oil through enzymic process
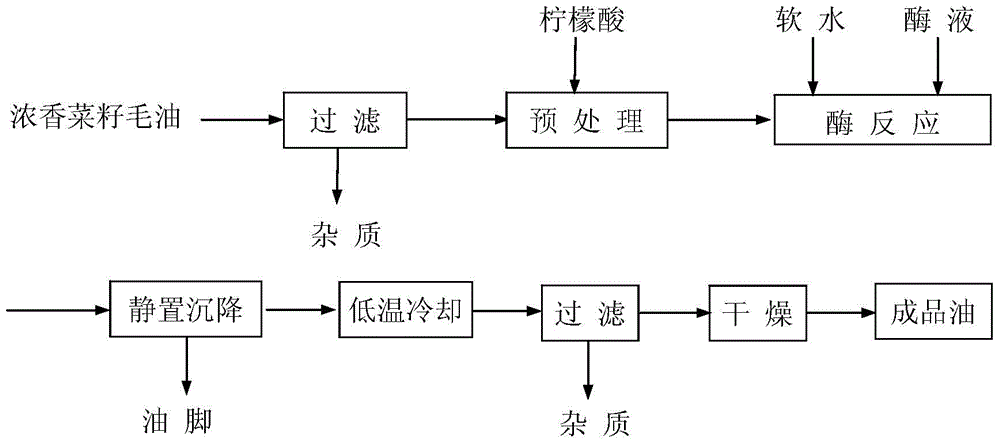
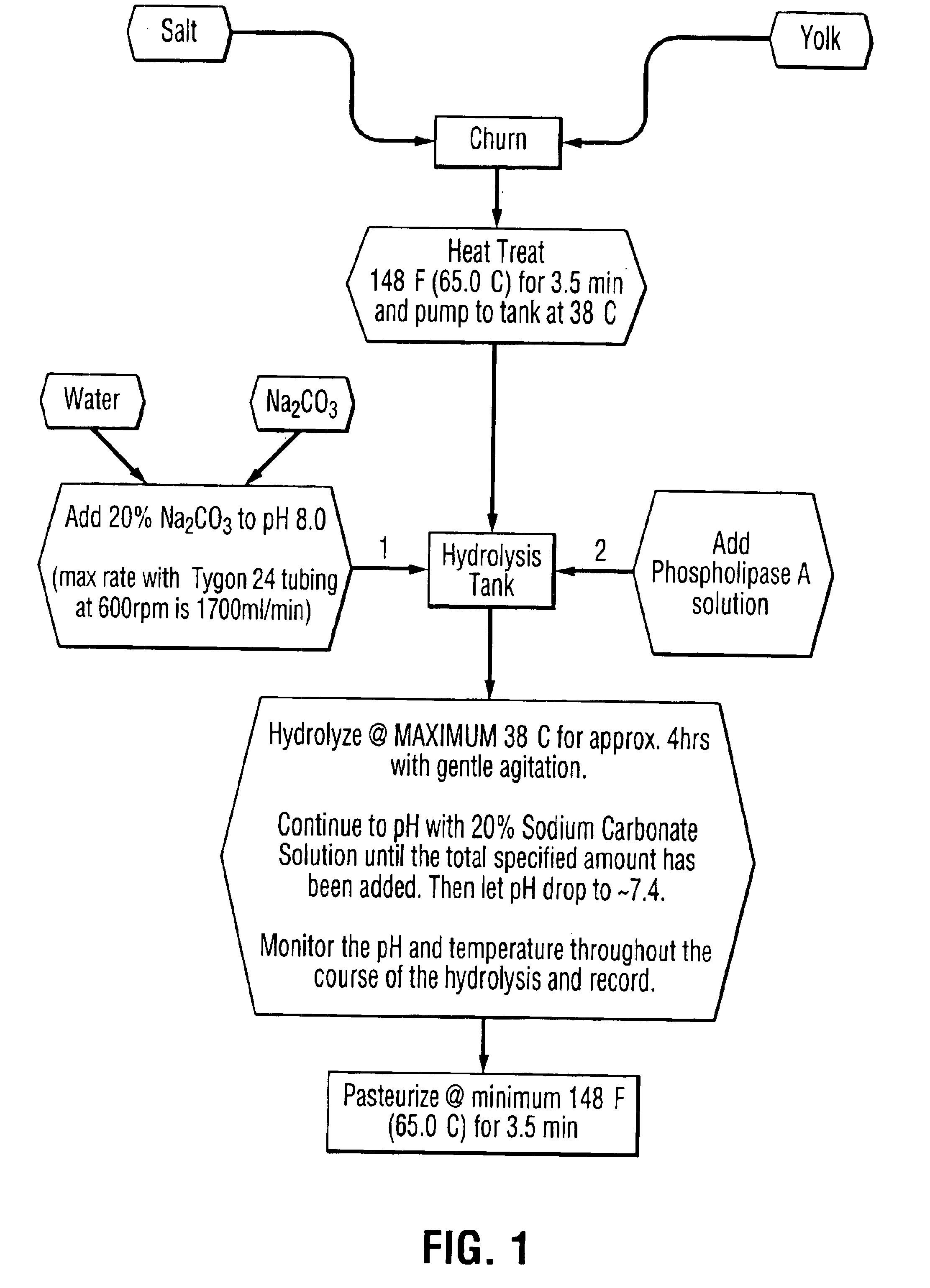
The invention discloses a method for degumming fragrant rap oil through an enzymic process. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: heating the squeezed fragrant crude rap oil without impurities to about 40 DEG C, adding a 50% citric acid aqueous solution according to 0.1% by weight of the oil, mixing the 50% citric acid aqueous solution with the fragrant crude rap oil, mixing and stirring at a rate of 50-60r / min, and stirring for one hour; adding soft water according to 1.8% by weight of the oil, adding a phospholipase A, phospholipase B or phospholipase C solution diluted to 100 times according to 0.13% of the total mass of oil and water, simultaneously stirring and reacting for 60 minutes at a rate of 40-50r / min under the temperature of 30-50 DEG C, filtering or centrifugally separating, and drying to obtain the finished product of the fragrant rap oil.
Owner:国粮武汉科学研究设计院有限公司
Enzymatic degumming utilizing a mixture of PLA and PLC phospholipases
ActiveUS8956853B2Suitable for useLow in phospholipidsFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteOrganic compound preparationPhospholipidPhospholipases A
A method for degumming an oil composition comprises the steps of (a) providing an oil composition containing a quantity of phospholipids, (b) contacting said oil composition simultaneously with one or more phospholipase A enzymes and one or more phospholipase C enzymes, under conditions sufficient for the enzymes to react with the phospholipids to create phospholipid reaction products, and (c) separating the phospholipids reaction products from the oil composition, the remaining oil composition after the separation being a degummed oil composition, whereby during step (b) the reaction of said one or more phospholipase A enzymes proceeds at a faster rate than it would in the absence of said one or more phospholipase C enzymes.
Owner:BUNGE OILS INC
Methods for the use of inhibitors of cytosolic phospholipase A2
This invention provides methods for the use of substituted indole compounds of the general formula:and pharmaceutically acceptable salt forms thereof. The invention provides methods for the use of the compounds as inhibitors of the activity of various phospholipase enzymes, particularly phospholipase A2 enzymes, and for the medical treatment, prevention and inhibition diseases and disorders including asthma, stroke, atherosclerosis, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, arthritic disorders, rheumatic disorders, central nervous system damage resulting from stroke, central nervous system damage resulting from ischemia, central nervous system damage resulting from trauma, inflammation caused or potentiated by prostaglandins, inflammation caused or potentiated by leukotrienes, inflammation caused or potentiated by platelet activation factor, pain caused or potentiated by prostaglandins, pain caused or potentiated by leukotrienes, and pain caused or potentiated by platelet activation factor.
Owner:ZIARCO
Phospholipases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides a separated, synthetic or recombinant nucleic acid, the polypeptide coded by the nucleic acid and the use thereof. The nucleic acid includes the nucleic acid sequence described by the invention for coding the polypeptide having the phosphatidase activity. The phospholipase activity includes, e.g., phospholipase A, B, C and D activity, patatin activity, lipid acyl hydrolase (LAH) activity. In one aspect, the nucleic acid codes the phospholipase lack of the natural precursor (signal) sequence. In the other aspect, the nucleic acid also includes the heterogenous nucleic acid sequence which codes the precursor (signal) sequence or the catalytic domain. The precursor (signal) sequence or the catalytic domain includes the phosphatidase precursor (signal) sequence or the catalytic domain or the non-phosphatidase precursor (signal) sequence or the catalytic domain of the yeast precursor (signal) sequence.
Owner:VERENIUM CORP (US)
Liquid egg yolk product comprising lysophospholipoprotein
Owner:M G WALDBAUM
Enzymatic degumming utilizing a mixture of PLA and PLC phospholipases with reduced reaction time
ActiveUS8460905B2Suitable for useLow in phospholipidsFatty oils/acids recovery from wasteBiocidePhospholipidPhospholipases C
A method for degumming an oil composition comprises the steps of (a) providing an oil composition containing a quantity of phospholipids, (b) contacting said oil composition simultaneously with one or more phospholipase A enzymes and one or more phospholipase C enzymes, under conditions sufficient for the enzymes to react with the phospholipids to create phospholipid reaction products, and (c) separating the phospholipids reaction products from the oil composition, the remaining oil composition after the separation being a degummed oil composition, whereby during step (b) the reaction of said one or more phospholipase A enzymes proceeds at a faster rate than it would in the absence of said one or more phospholipase C enzymes, and wherein the reaction of step (b) continues for a duration of less than about one hour.
Owner:BUNGE OILS INC
A method for immobilizing phospholipase with cellulose acetate/polypropylene composite membrane
InactiveCN102286453AGood chemical stabilityImprove adsorption capacityOn/in organic carrierPolypropylene compositesComposite film
The invention provides a cellulose acetate / polypropylene composite film prepared by using cellulose acetate and polypropylene film as materials, adopts an adsorption-crosslinking immobilization method, and uses the composite film to immobilize phospholipase. The effects of different immobilization conditions such as adsorption time, enzyme solution concentration, crosslinking agent concentration, crosslinking time and crosslinking temperature on the immobilization efficiency and catalytic effect of phospholipase were studied, and the enzymatic properties of the immobilized enzyme membrane were investigated. discuss. The advantage of using cellulose acetate / polypropylene composite membrane to immobilize phospholipase was further explained by the SEM images of the immobilized enzyme membrane. According to the adsorption characteristics of the composite membrane in the present invention, the immobilized phospholipase improves the activity and stability of the enzyme in the reaction system, regulates and controls the activity and selectivity of the enzyme, thereby facilitating the recovery of the enzyme and the production of the product, and finally obtains The immobilized enzyme activity is 4.6U / cm2.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Phospholipase(s) and use(s) thereof
InactiveUS7939064B2Reduce infarct sizeReduces ischemic infarct sizeSugar derivativesHydrolasesPhospholipaseMedicine
The invention relates to phospholipase(s), isoforms, derivatives, mutants and / or fragments thereof, for the preparation of a medicament for the treatment and / or prevention of ischemia. Preferred is the use of secretory phospholipase, particularly phospholipase A2, and even more particularly phospholipase A2 derived from the snake venom of Naja sputatrix.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Process for producing cheese
InactiveUS20050069607A1Improve propertiesIncrease productionMilk preparationHydrolasesBiotechnologyFat emulsions
The present invention relates to a process for producing cheese from enzyme-treated cheese milk, and the use of the resulting produced cheese as ingredient in food products. More particularly, the present invention relates to a process for producing cheese from cheese milk treated with a enzyme selected from the group of phospholipases, in particular phospholipase A1, A2 and B. Also, the present invention relates to a process for stabilizing the fat emulsion of a milk composition, e.g. cream, and the use of such stabilized milk composition, e.g. for the manufacturing of UHT-cream or cream liquor.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Process for producing cheese
InactiveUS6875454B2Improve propertiesIncrease productionMilk preparationHydrolasesFat emulsionAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to a process for producing cheese from enzyme-treated cheese milk, and the use of the resulting produced cheese as ingredient in food products. More particularly, the present invention relates to a process for producing cheese from cheese milk treated with a enzyme selected from the group of phospholipases, in particular phospholipase A1, A2 and B. Also, the present invention relates to a process for stabilizing the fat emulsion of a milk composition, e.g. cream, and the use of such stabilized milk composition, e.g. for the manufacturing of UHT-cream or cream liquor.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Microbial oil preparation method
InactiveCN105219812APromote fragmentationHigh yieldFermentationFatty-oils/fats productionMicroorganismMicrobial oil
Owner:CABIO BIOTECH WUHAN CO LTD
Method for preparing high purity L-alpha glycerylphosphorylcholine
Disclosed is a method for preparing L-α-Glycerylphosphorylcholine with high yields and purity. The method uses phospholipase A1-based enzymatic hydrolysis, ion-exchange resin purification and silica gel column chromatography to prepare L-α-glycerylphosphorylcholin with purity up to 99.8% and a final yield up to 78.4%. The method disclosed is simple, cost-effective, environmentally friendly, and adaptable to industrial applications.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Novel therapeutic and prophylactic agents and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20060078551A1Good anti-inflammatory activityGood potencyBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsPhospholipase inhibitorSnake bite venom
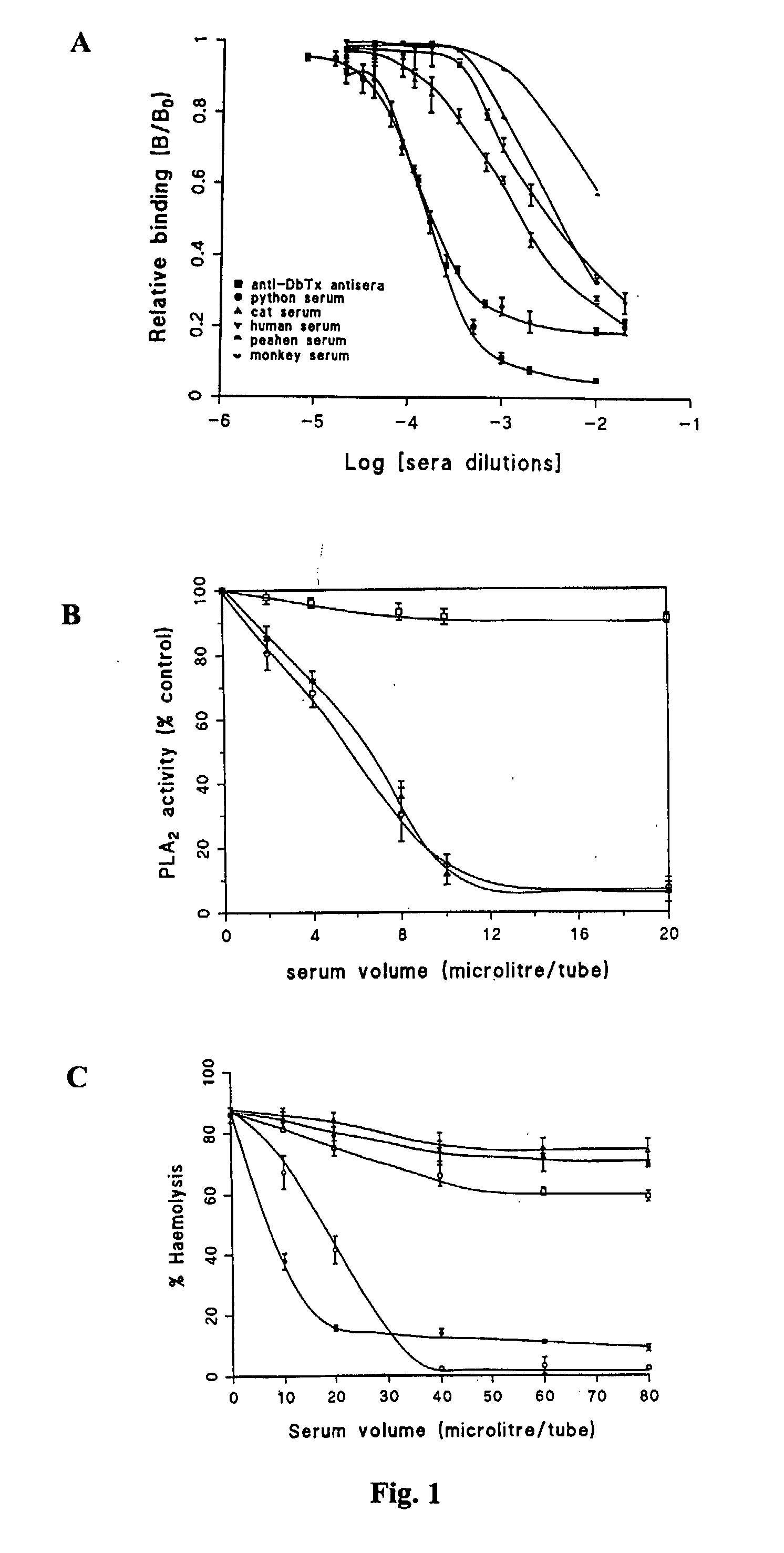
A phospholipase A2 inhibitor protein designated “Phospholipase Inhibitor from Python” (PIP)—formerly designated “Python Antitoxic Factor” (PAF)—is given by SEQ ID NO:2. The partial amino acid sequence for PIP was initially determined from the native protein purified from the blood serum of a non-venomous snake, Python reticulatus. The complete PIP polynucleotide sequence was obtained from a cDNA clone encoding PIP, given by SEQ ID NO:1, along with the full amino acid sequence deduced from it. Also disclosed is a recombinant protein PIP, which shows strong lethal toxin neutralizing activity similar to the native PIP, and has potent anti-inflammatory activity. Both the native and the functionally equivalent recombinant PIP are useful for the prevention or treatment of conditions such as snakebites, insect stings, and inflammatory diseases. Also, phospholipase A2 (PLA2) inhibitory polypeptides designated P-0029, P-0009, and P-0006, the sequences of which are given as SEQ ID NO:10, SEQ ID NO:11, and SEQ ID NO:12, respectively, are disclosed. Those polypeptides, and their synthetic chemical analogues and polypeptide variants that inhibit PLA2 activity and alleviate inflammation, may also be used in the diagnosis, study, prevention, and treatment of PLA2-related human inflammatory diseases.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Frozen foodstuff
InactiveUS20070259096A1Improve emulsion stabilityGood lookingEdible oils/fats with aqeous phaseEmulsionFreezing thawing
Phospholipo-proteins which have been enzyme modified may be used as an emulsifier to improve the emulsion stability of frozen products, e.g., during the freeze thaw and vacuum cool processes. Especially preferred is use of the enzyme phospholipase A to modify egg yolk and to use the modified egg yolk as an emulsifier in frozen products. Creation of a more stable emulsion can be expected to improve the overall appearance of the final product both in the frozen state and after the product has been reheated. Although egg yolk is preferred, examples of other phospholipo-protein containing substances include casein, skim milk, buttermilk, whey, cream, soybean, yeast, whole egg, blood serum and wheat proteins. Egg yolk and / or other sources of phopholipo-protein can be subjected to the action of phospholipase A or other enzyme, and then the modified product incorporated into the products of the invention. Alternatively, it is possible to isolate the phospholipo protein from its source and subject the isolated protein to the action of phospholipase A, after which the modified phopholipo-protein is incorporated into the frozen food products of the invention.
Owner:CONOPCO INC D B A UNILEVER
Phospholipases, nucleic acids encoding them and methods for making and using them
The invention provides novel polypeptides having phospholipase activity, including, e.g., phospholipase A, B, C and D activity, patatin activity, lipid acyl hydrolase (LAH) activity, nucleic acids encoding them and antibodies that bind to them. Industrial methods, e.g., oil degumming, and products comprising use of these phospholipases are also provided.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
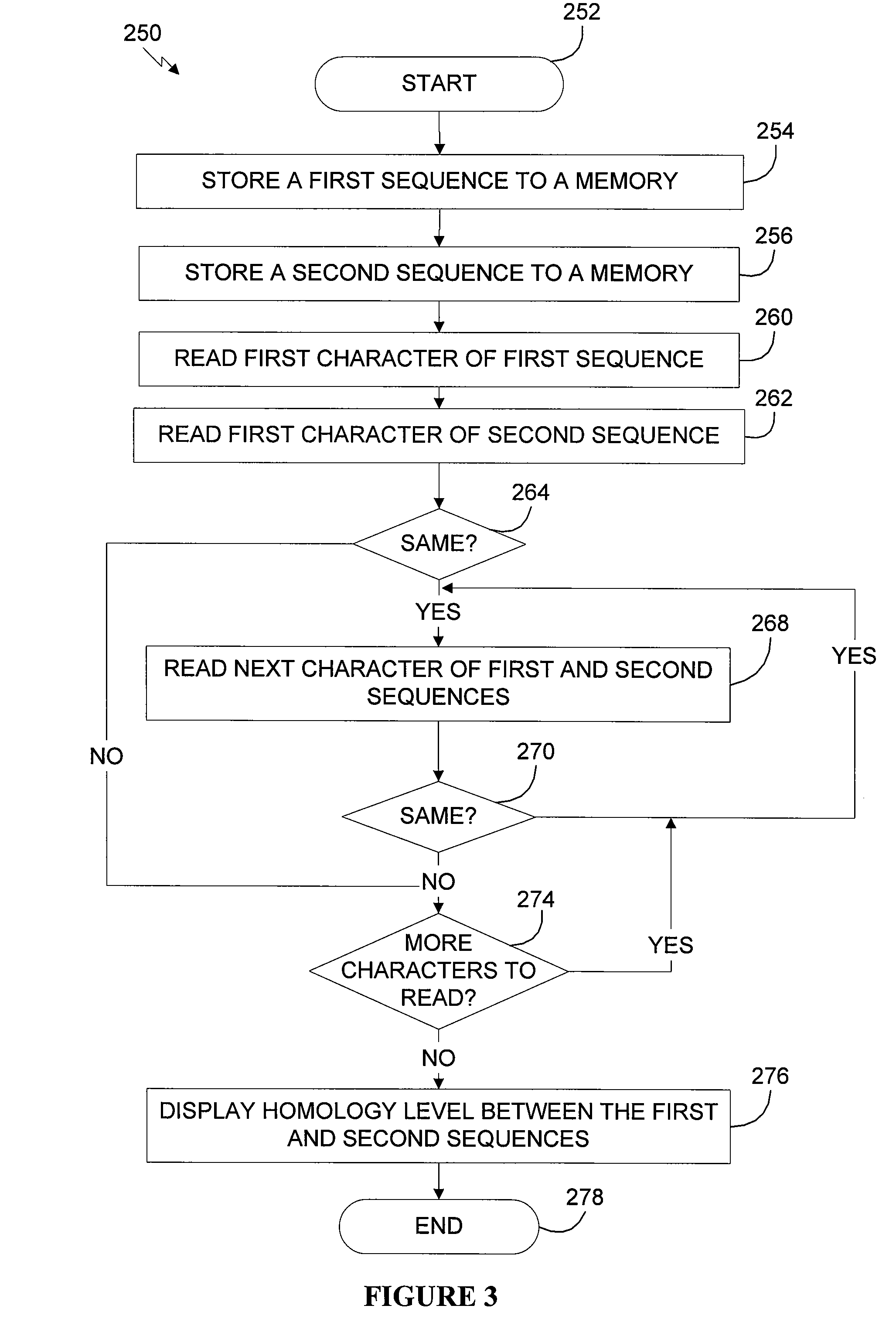
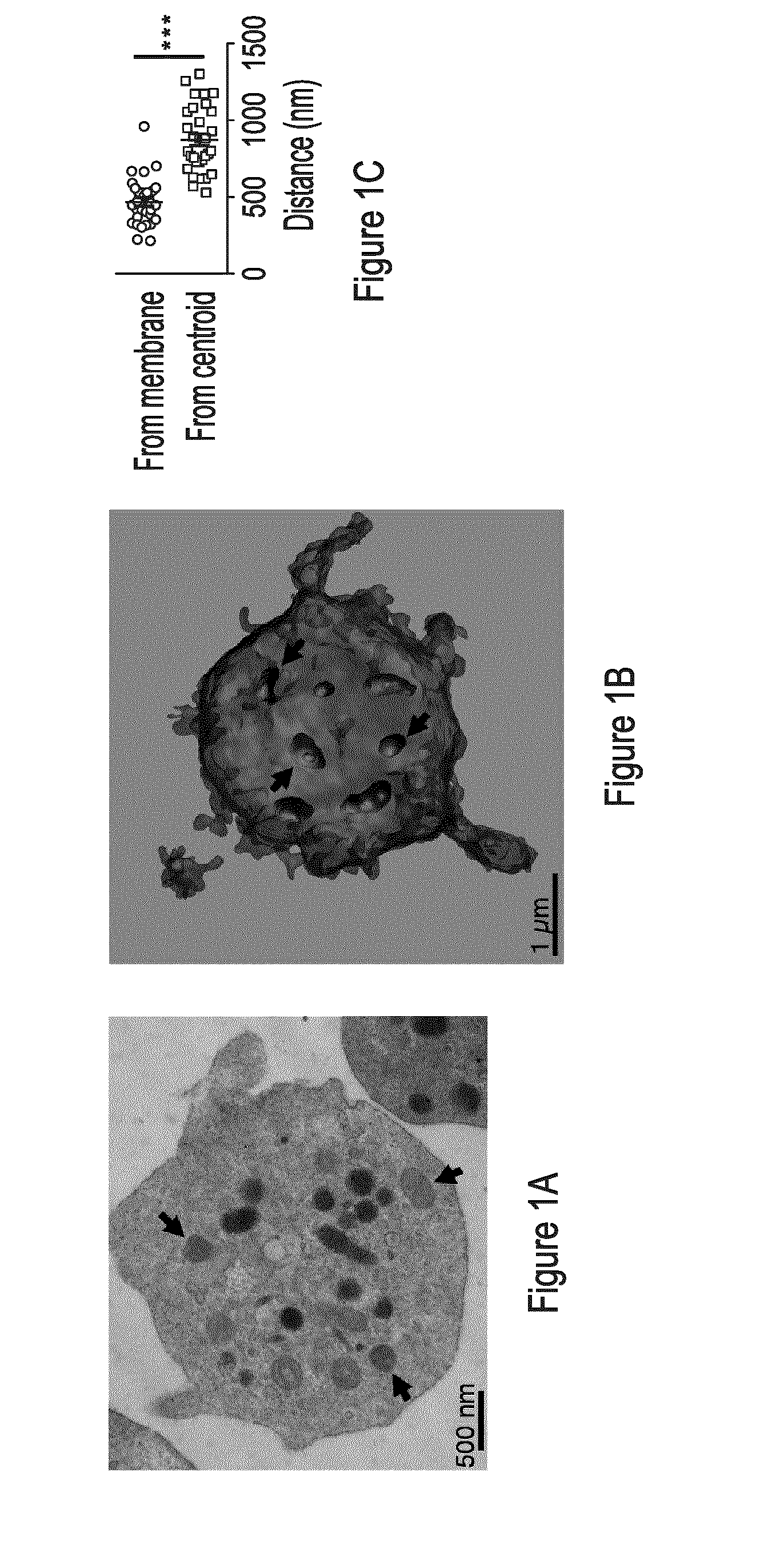
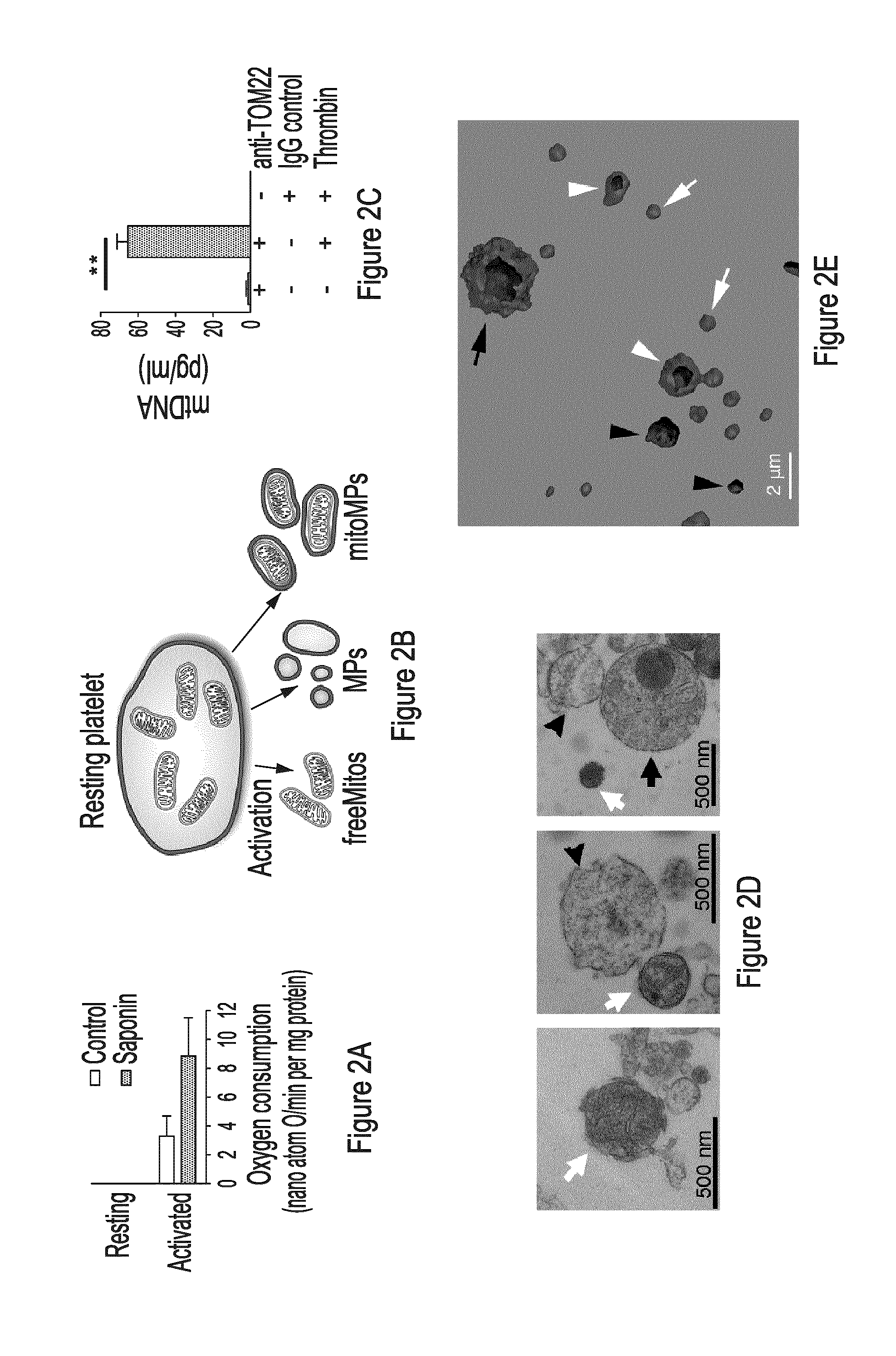
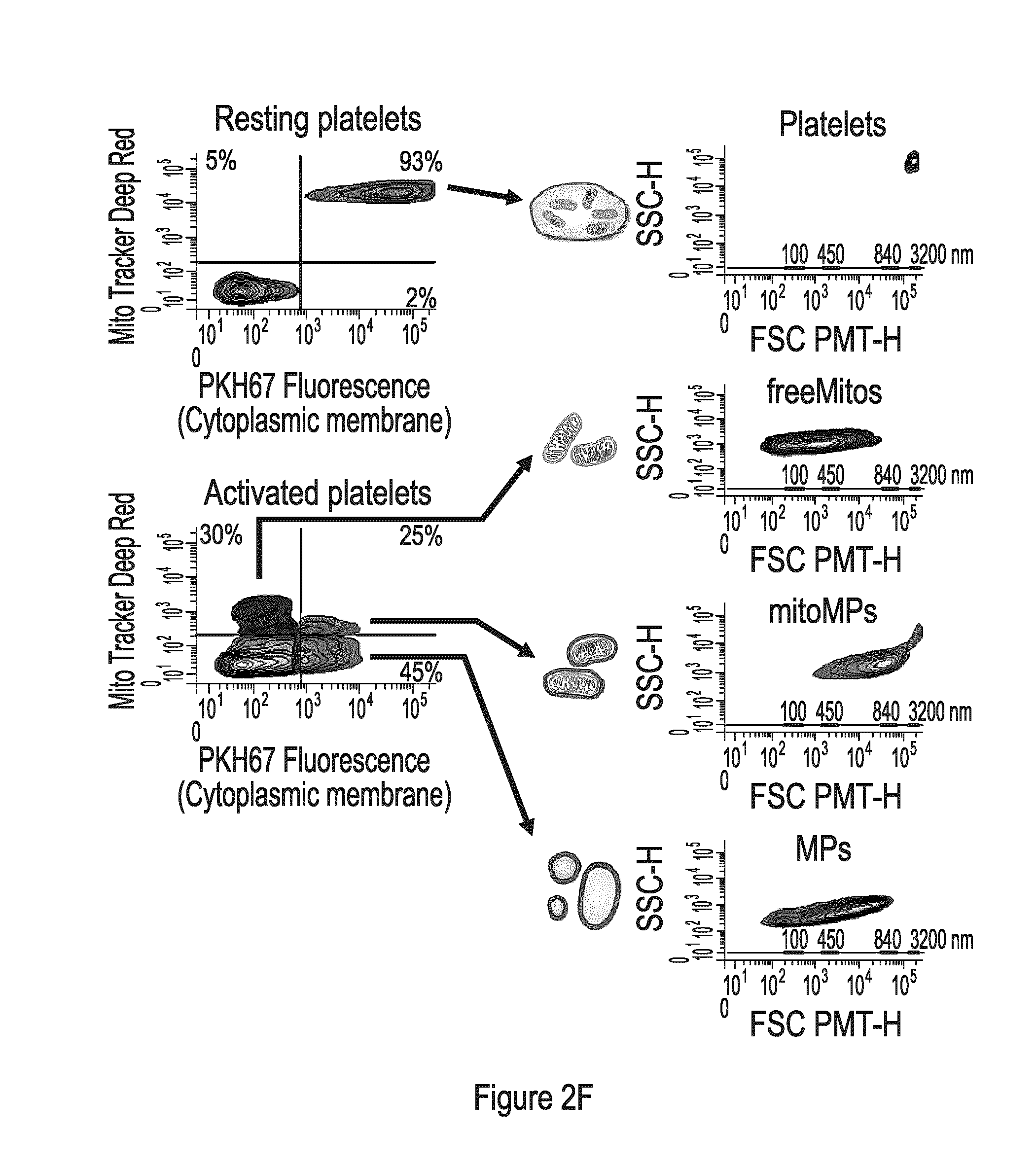
Extracellular Mitochondrial Components for Detecting Inflammatory Reactions and Conditions
InactiveUS20160258950A1Inhibition releaseCompound screeningApoptosis detectionIn vivoAutoantibody production
The present disclosure highlights the relationship between extracellular mitochondrial components, optionally in combination with the secreted phospholipase A2-IIA and / or an auto-antibody, and in vivo as well as in vitro and inflammatory reactions / conditions, especially those released as a result of the degradation of a platelet. The present disclosure provides methods for determining the presence of inflammatory mediators, for limiting inflammatory reactions / conditions, for the diagnosis inflammatory reactions / conditions, for screening therapeutics for the treatment and / or the alleviation of symptoms of inflammatory reactions / conditions based on the detection or modulation of the level of these extracellular mitochondrial components.
Owner:HEMA QUEBEC +2
Compound enzyme, highly-fragrant rapeseed oil processing method, highly-fragrant rapeseed oil and edible oil
InactiveCN110129132ALow in phospholipidsImprove qualityHydrolasesFatty-oils/fats refiningOil processingProteinase activity
The invention provides a compound enzyme, a highly-fragrant rapeseed oil processing method, highly-fragrant rapeseed oil and edible oil. Based on enzyme activity, the compound enzyme comprises 8092-8751 U / g of phospholipase A, 7317-7915 U / g of phospholipase C, 4154-4767 U / g of protease and 4047-4618 U / g of cellulase. The highly-fragrant rapeseed oil processing method comprises the following steps:mixing crude rapeseed oil with acid to be subjected to a first reaction to obtain an acid reaction liquid; mixing the acid reaction liquid with water and the compound enzyme to be subjected to a second reaction to obtain an enzyme reaction liquid; and carrying out inactivation treatment on the enzyme reaction liquid and then carrying out separation to obtain degummed oil. The highly-fragrant rapeseed oil is prepared by using the highly-fragrant rapeseed oil processing method. The edible oil comprises the highly-fragrant rapeseed oil. Through adoption of the compound enzyme and the highly-fragrant rapeseed oil processing method, the cost is low, the production efficiency is high, the yield is high, and the rapeseed oil has rich fragrance.
Owner:道道全粮油股份有限公司
Therapeutic and prophylactic agents and methods of using same
InactiveUS7094575B2Good potencyGood anti-inflammatory activityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticPhospholipase inhibitorSaxitoxin
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Novel method to produce cake
ActiveUS20100062106A1High viscosityDecreased batter viscosityDough treatmentHydrolasesEngineeringOrganic chemistry
The invention relates to a novel use of a phospholipase A in the production of cake to improve at least one of the properties selected from the group consisting of: (i) batter viscosity, (ii) specific density, (iii) initial crumb softness, (iv) crumb pore homogeneity, (v) crumb pore diameter, (vi) crumb softness upon storage, (vii) shelf life and / or (viii) cake volume. The invention also relates to a novel use of phospholipase A in the production of cake to enable reduction of the amount of eggs and / or fat used in the recipe.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com