Patents
Literature
46 results about "Atheromatous lesion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The shoulder of the atheromatous lesion - this is where the fibrous cap joins the arterial wall - is a site of continued active formation of foam cells as the atheromatous lesion progresses across the inner surface of the artery. The atheromatous plaque is weak at the shoulder of the lesion and it is this part of the cap that usually ruptures.
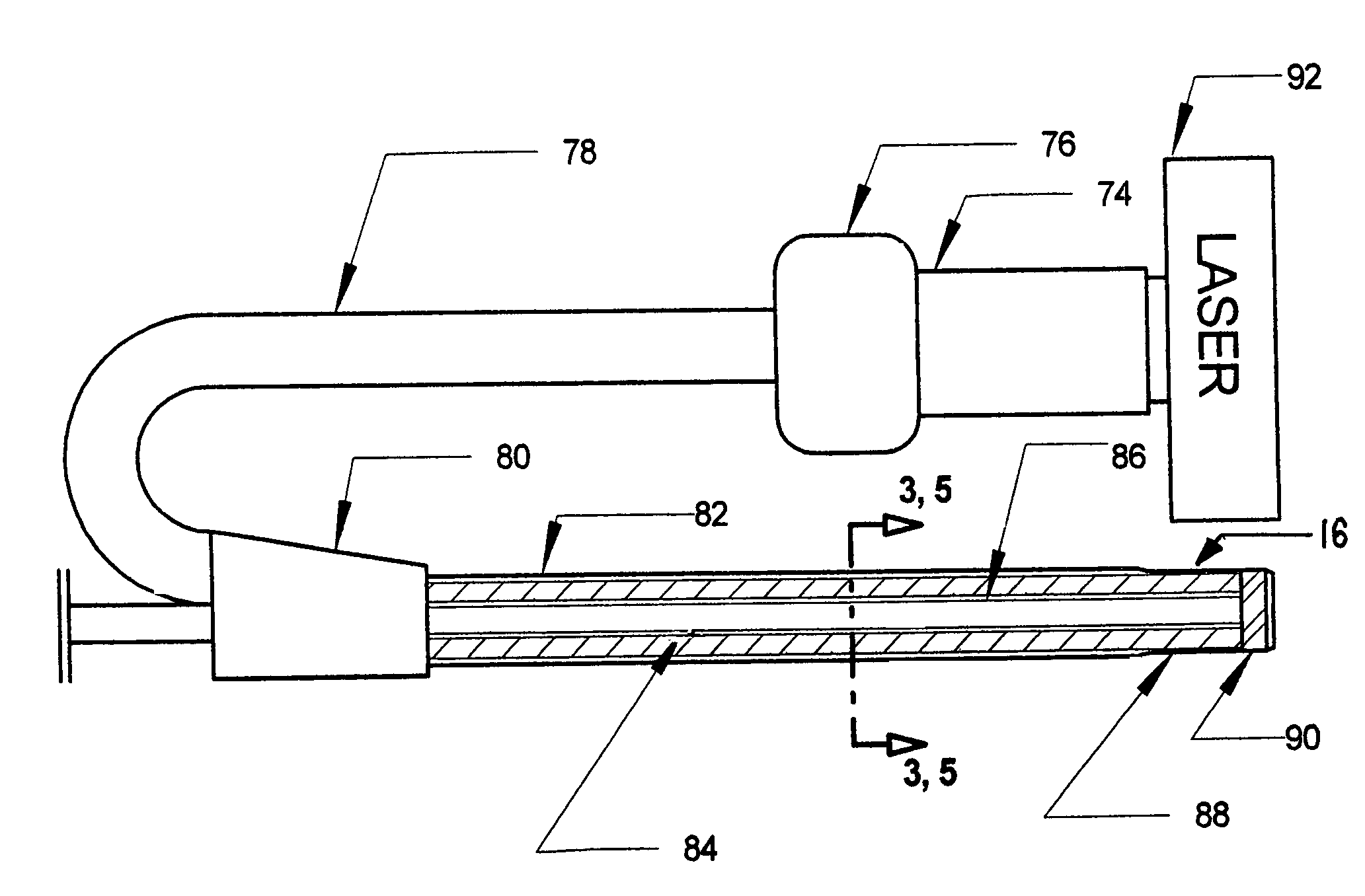
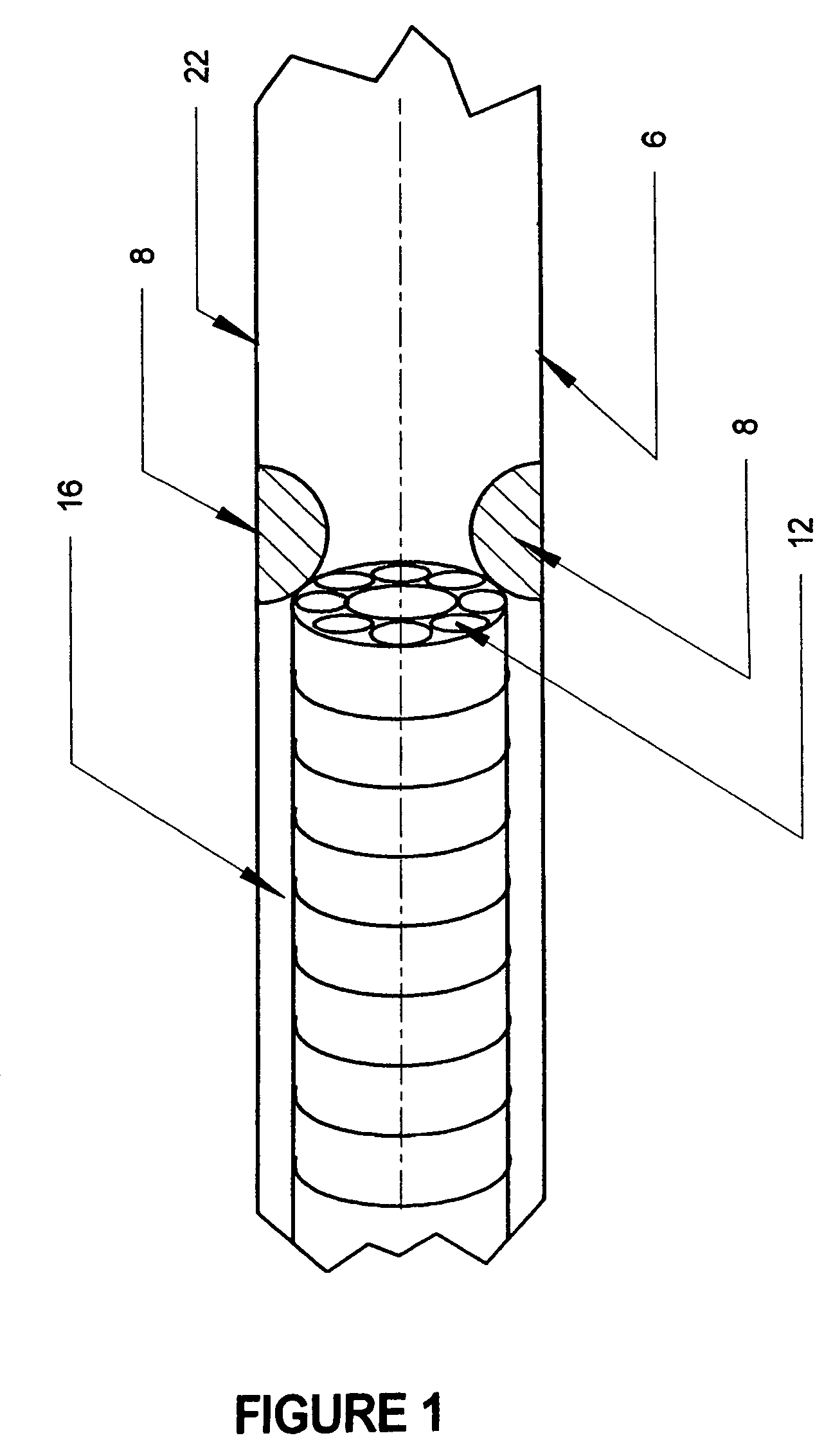
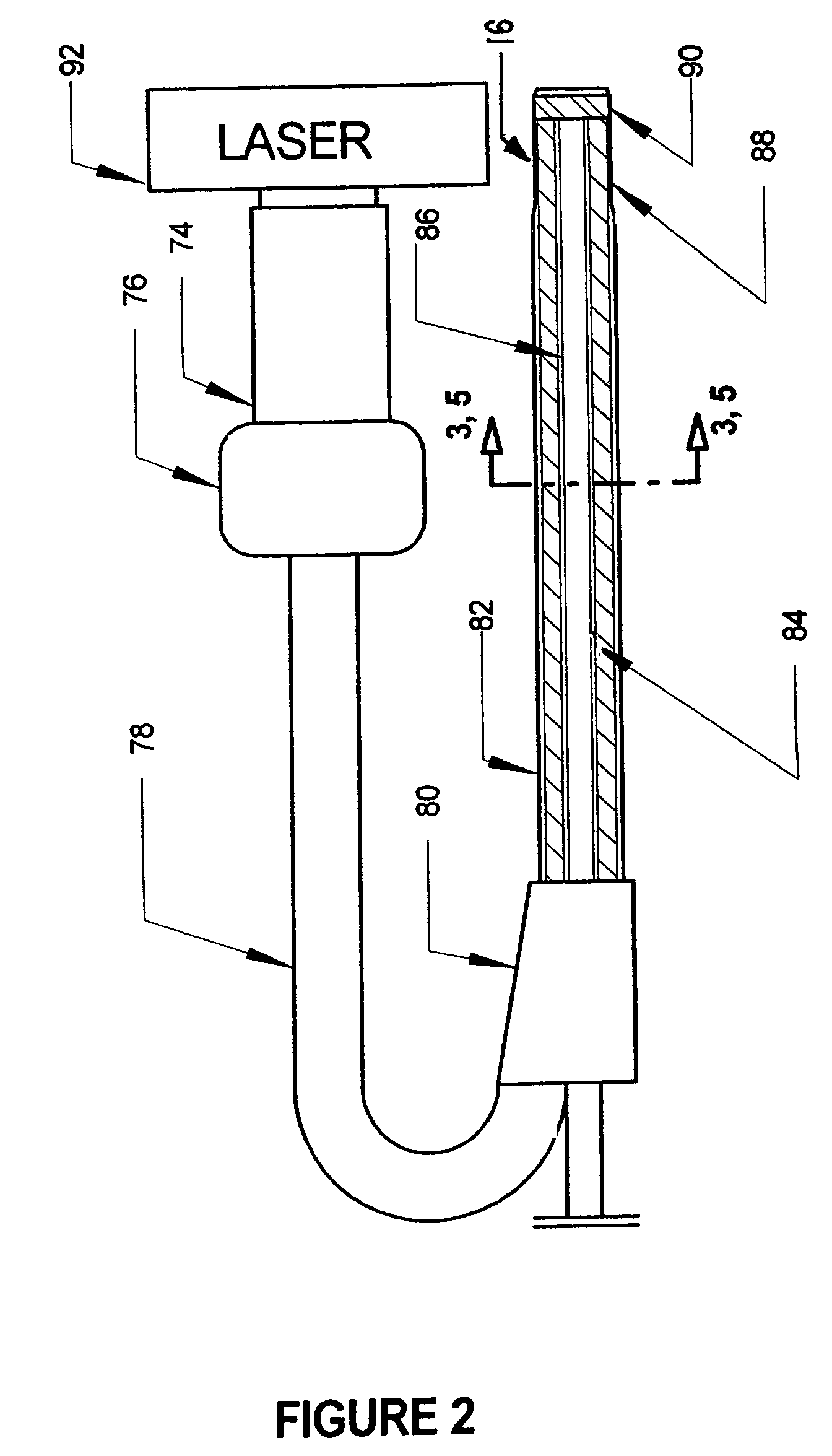
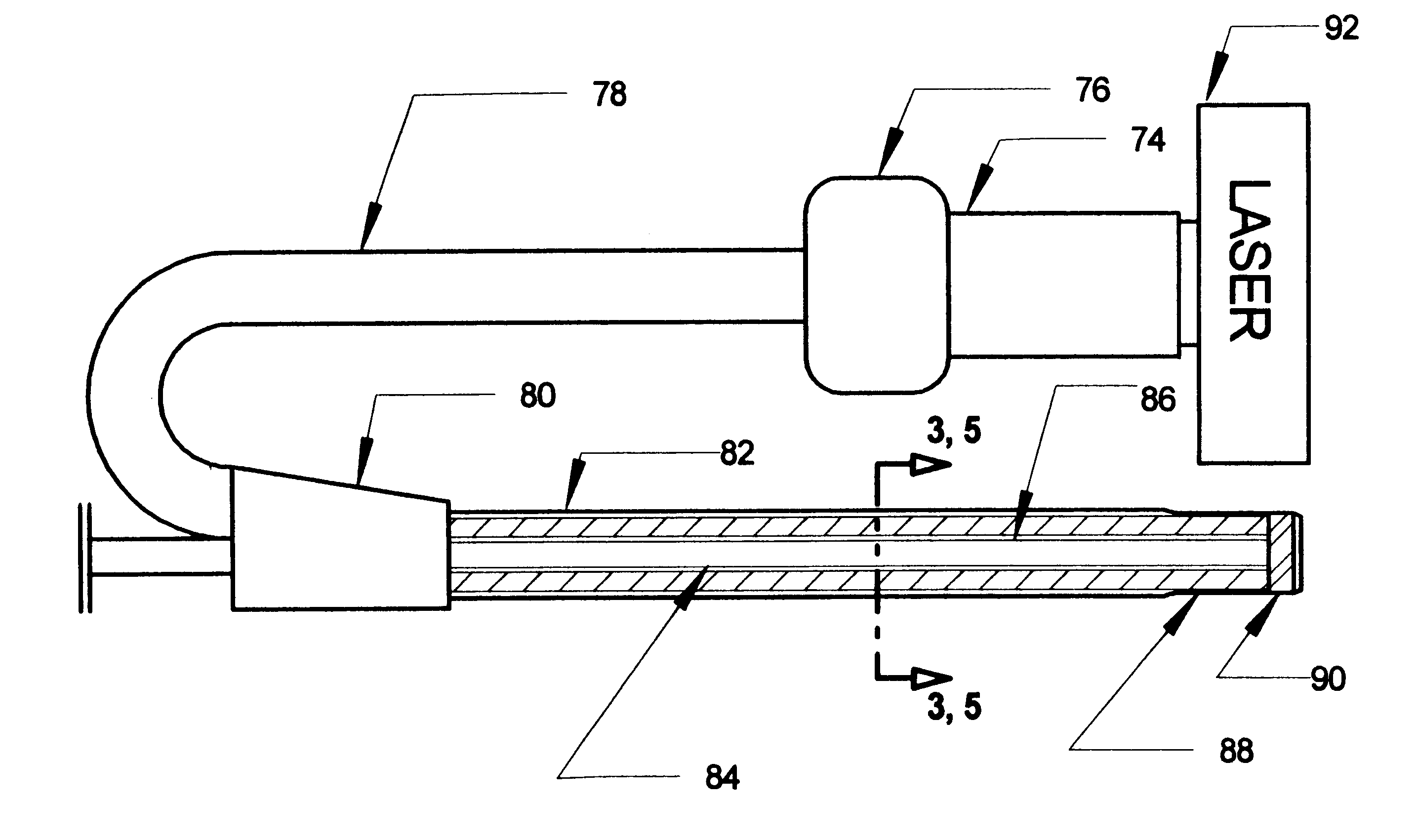
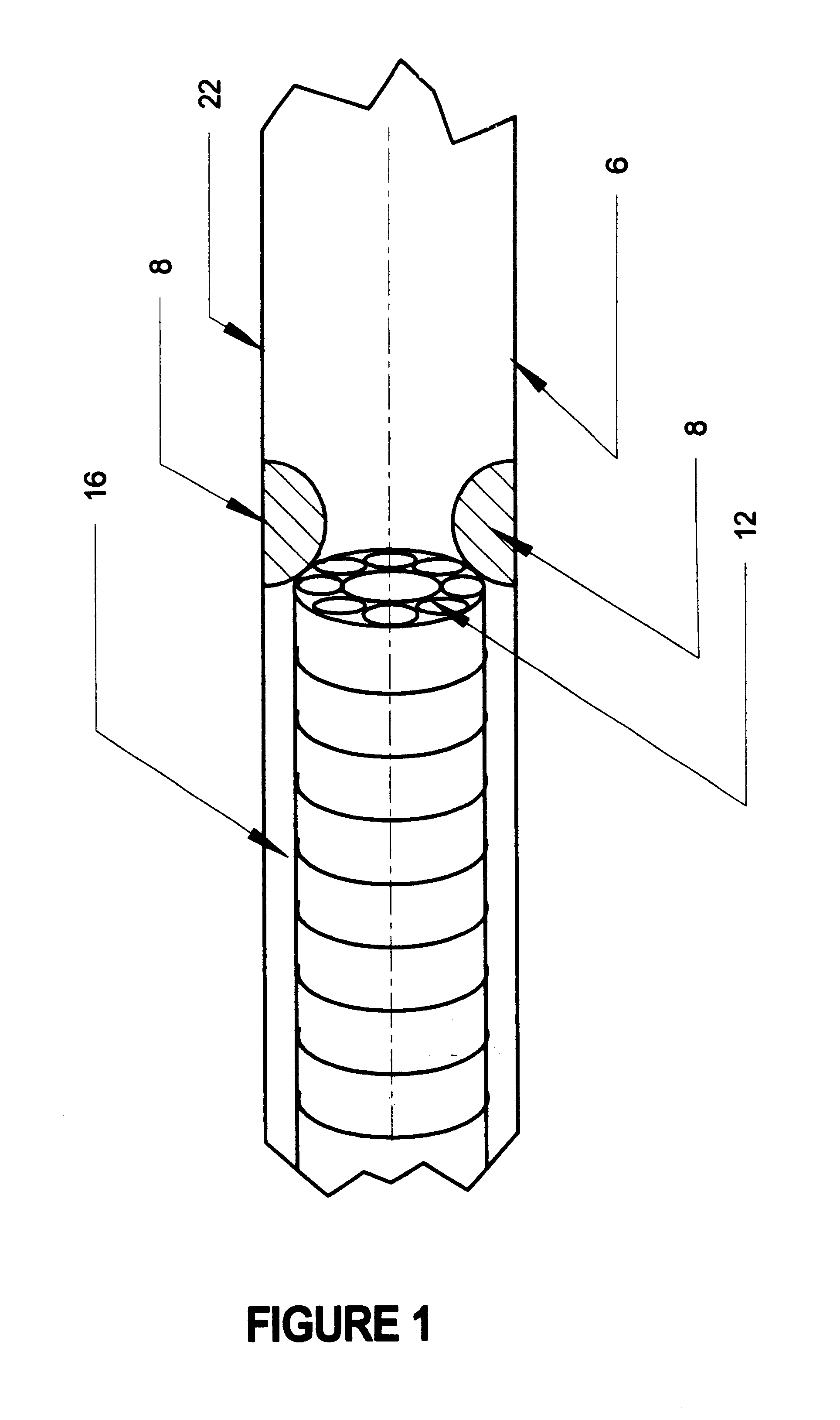
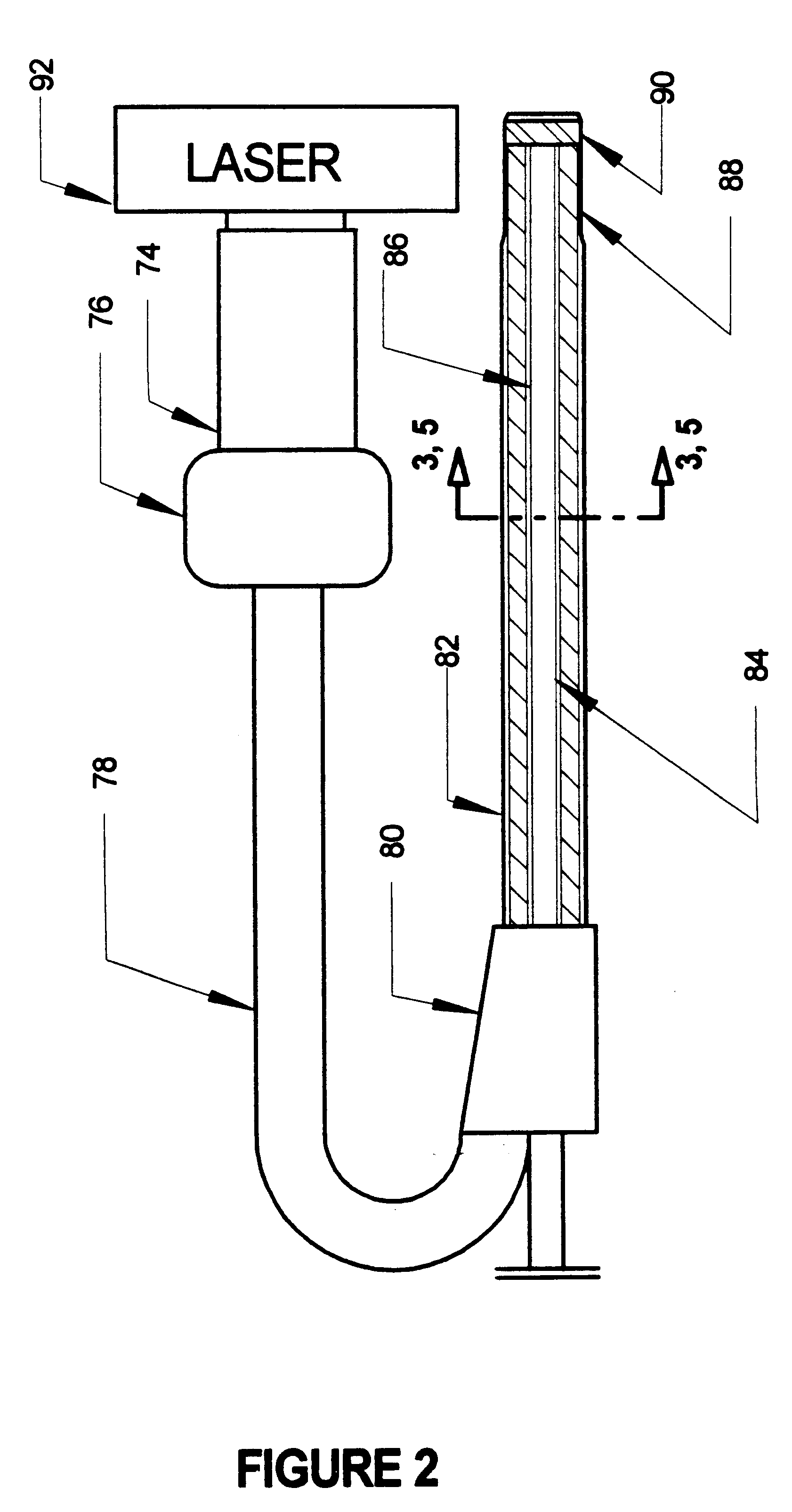
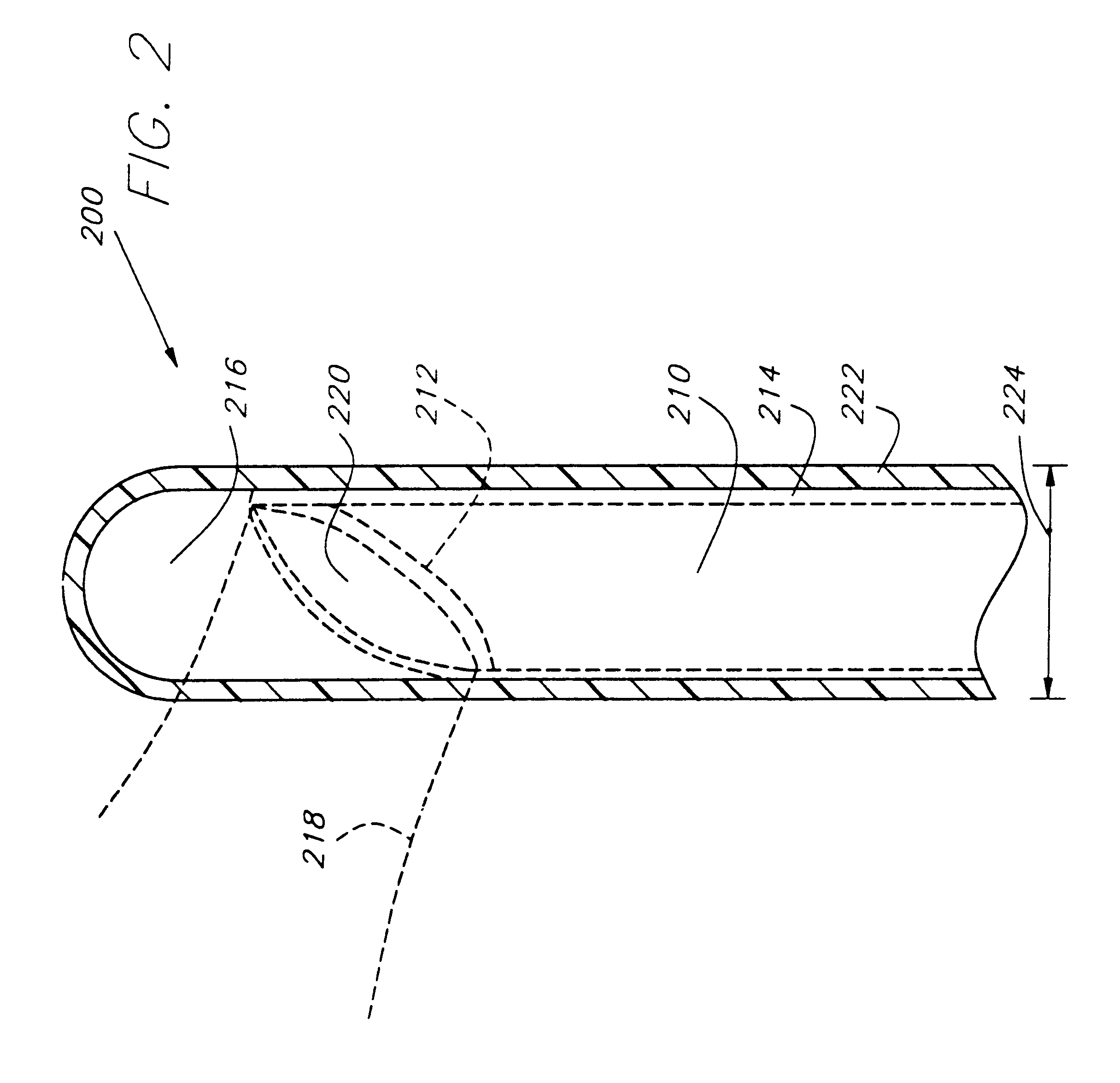
Excimer laser catheter
Owner:RENTROP PETER
Excimer laser catheter
InactiveUS6440125B1Reduce the possibilityHigh energy laserDiagnosticsCatheterEndovascular therapyAtheroma
A method and apparatus of providing endovascular therapy. The steps include arranging optical fibers within a catheter, the catheter having a tip whose length is at least 1 cm and whose diameter of less than 1 millimeter, connecting an excimer laser to the optical fibers; and delivering laser energy from the excimer laser in excess of 60 fluence at 40 Hertz through the optical fibers. The delivering of the laser energy may be to non-calcified or calcified deposits of an atherosclerotic lesion to ablate the same. The method also includes the step of inserting the catheter through an artery by pushing the same until the tip is in within laser energy striking distance of the atherosclerotic lesion.
Owner:RENTROP PETER
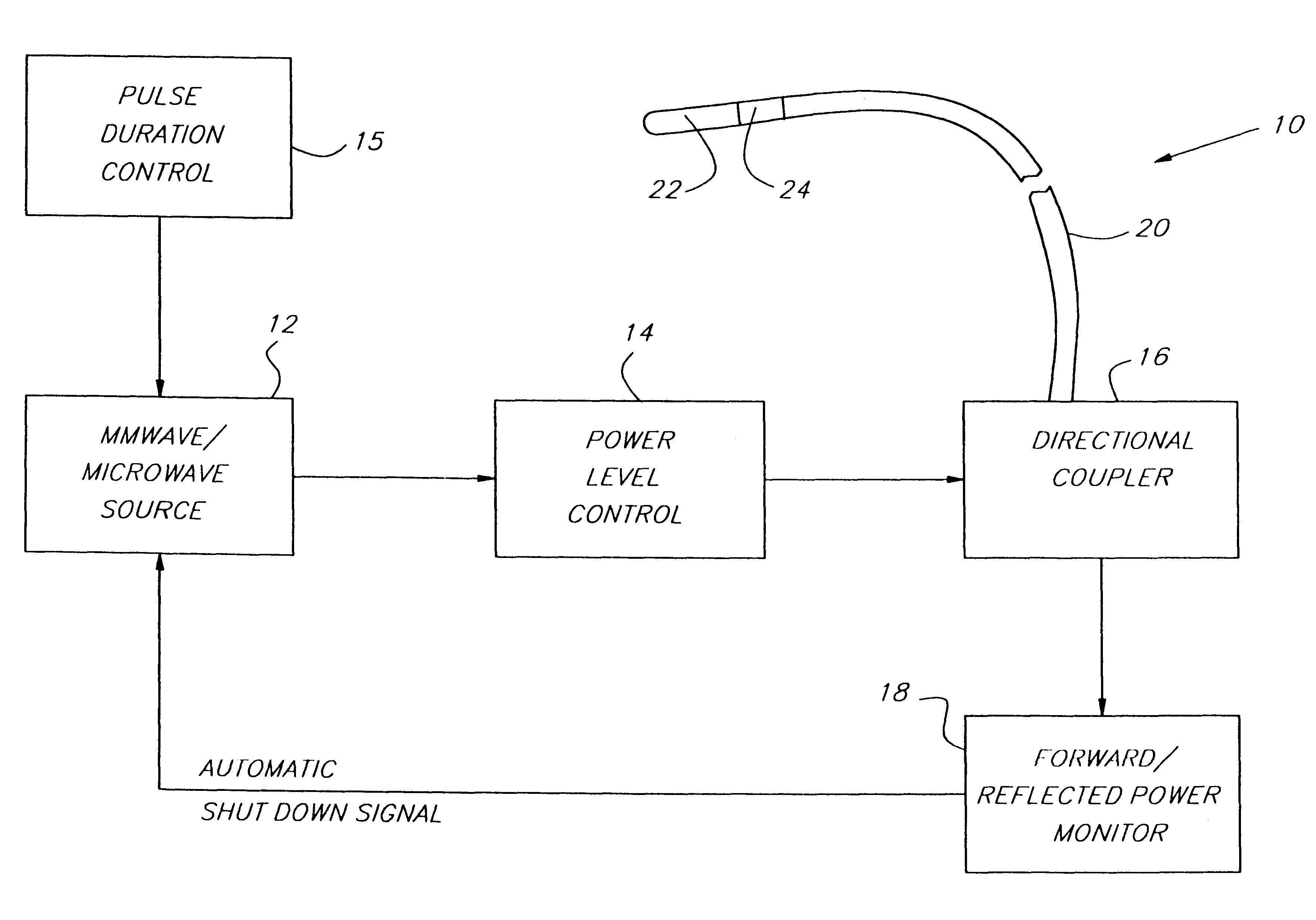
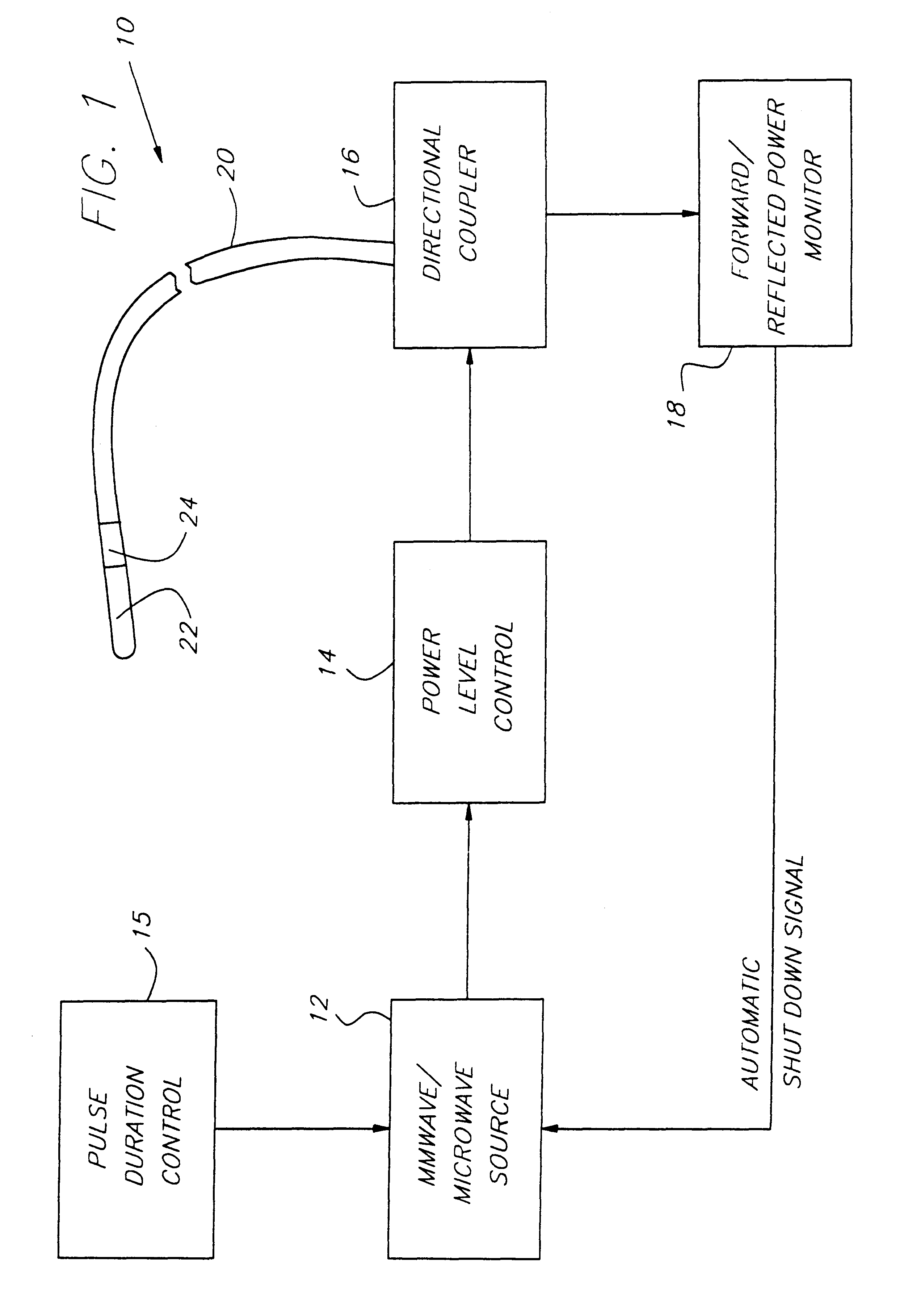
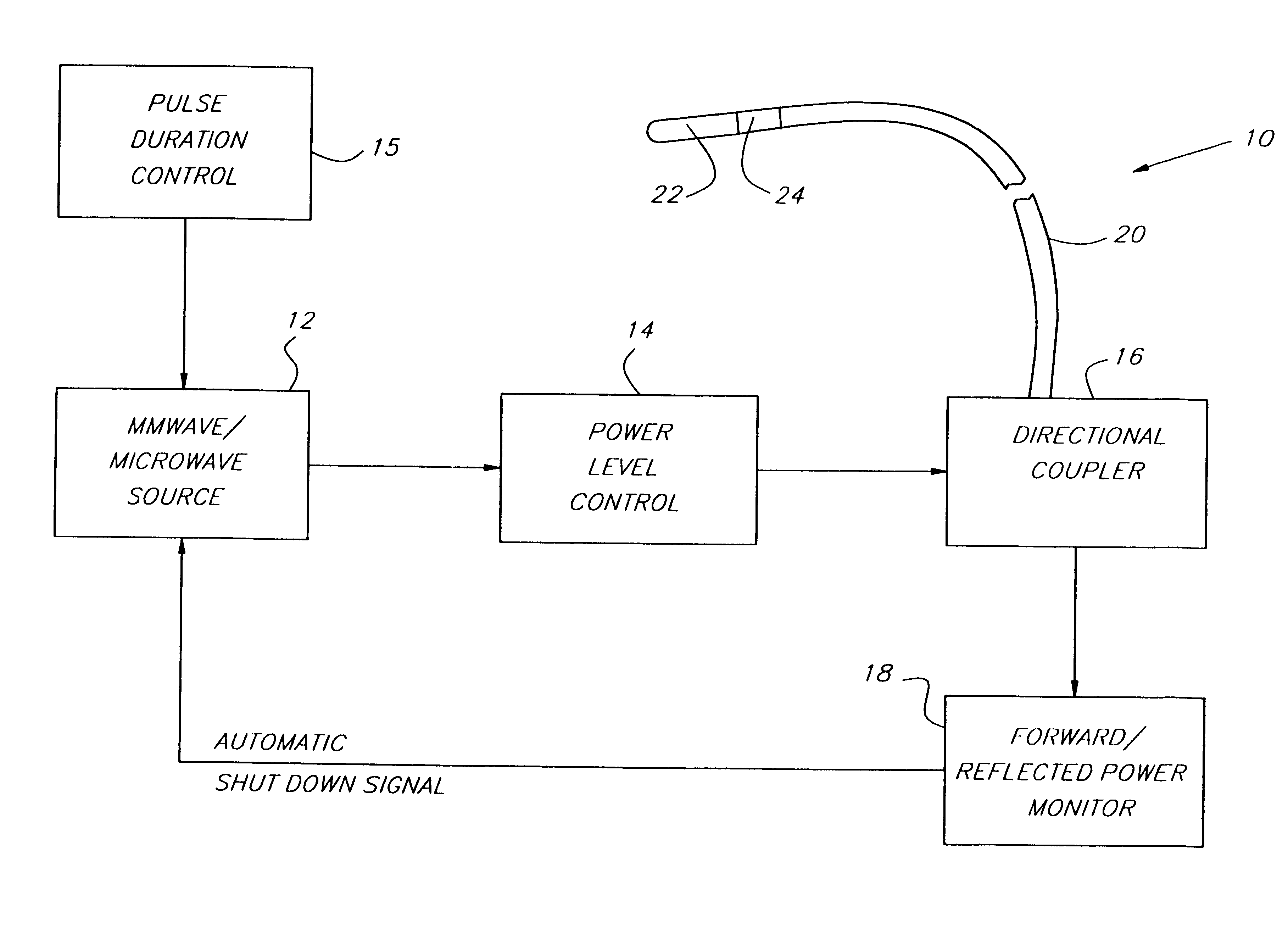
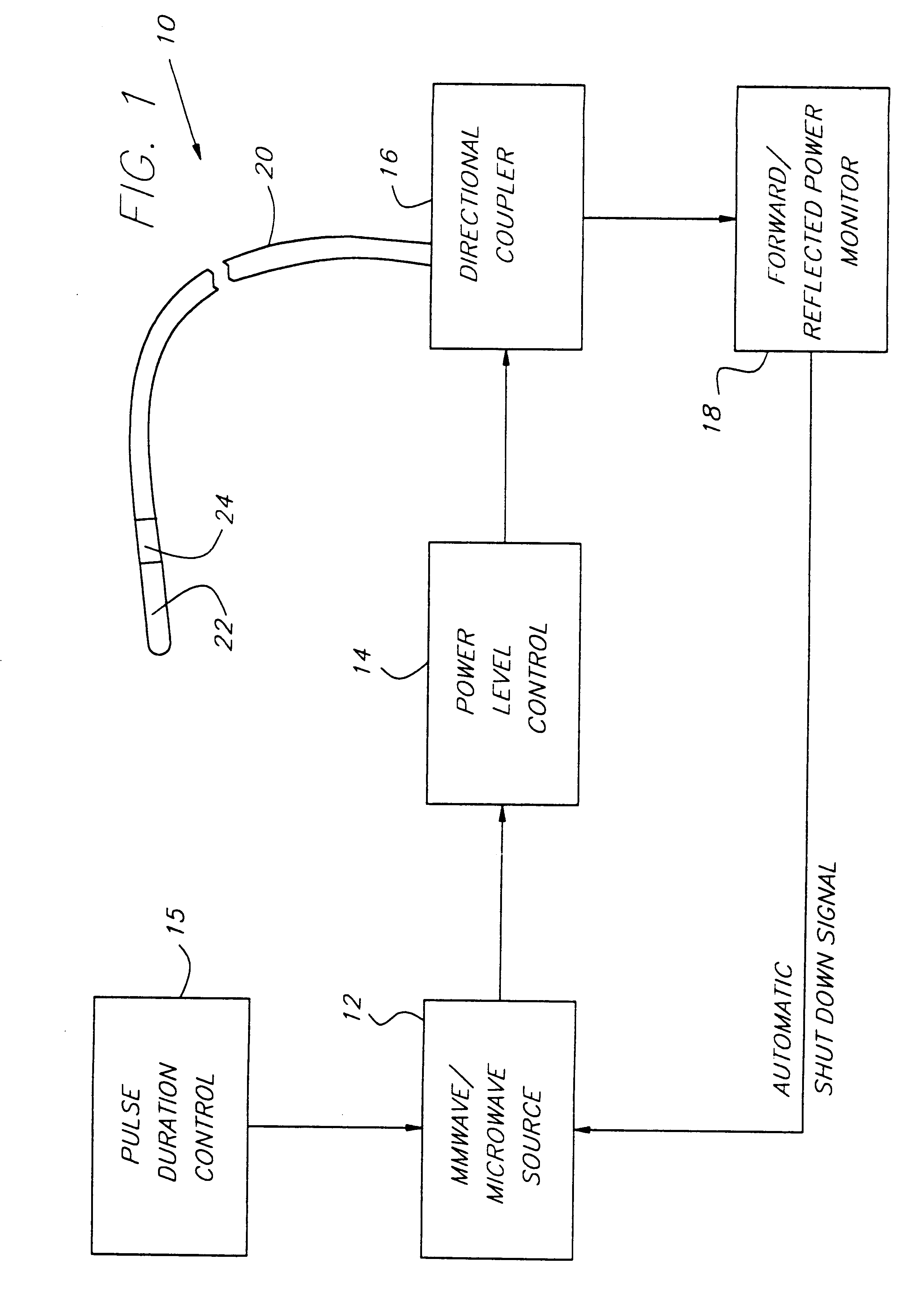
Endothelium preserving microwave treatment for atherosclerosis
Method and apparatus are provided to treat atherosclerosis wherein the artery is partially closed by dilating the artery while preserving the vital and sensitive endothelial layer thereof. Microwave energy having a frequency from 3 GHz to 300 GHz is propagated into the arterial wall to produce a desired temperature profile therein at tissue depths sufficient for thermally necrosing connective tissue and softening fatty and waxy plaque while limiting heating of surrounding tissues including the endothelial layer and / or other healthy tissue, organs, and blood. The heating period for raising the temperature a potentially desired amount, about 20° C. within the atherosclerotic lesion may be less than about one second. In one embodiment of the invention, a radically beveled waveguide antenna is used to deliver microwave energy at frequencies from 25 GHz or 30 GHz to about 300 GHz and is focused towards a particular radial sector of the artery. Because the atherosclerotic lesions are often asymmetrically disposed directable or focussed heating preserves healthy sectors of the artery and applies energy to the asymmetrically positioned lesion faster than a non-directed beam. A computer simulation predicts isothermic temperature profiles for the given conditions and may be used in selecting power, pulse duration, beam width, and frequency of operation to maximize energy deposition and control heat rise within the atherosclerotic lesion without harming healthy tissues or the sensitive endothelium cells.
Owner:NASA
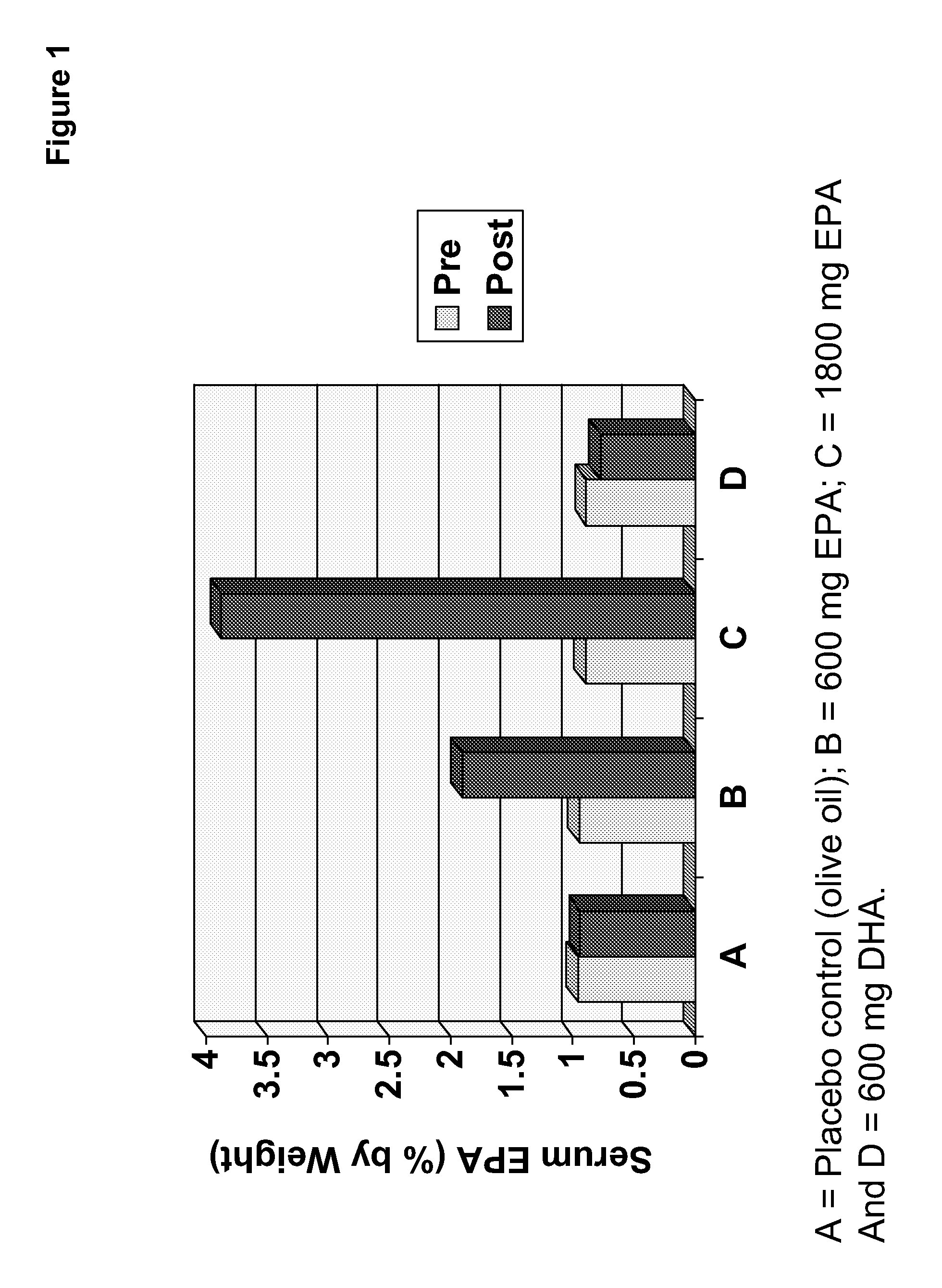
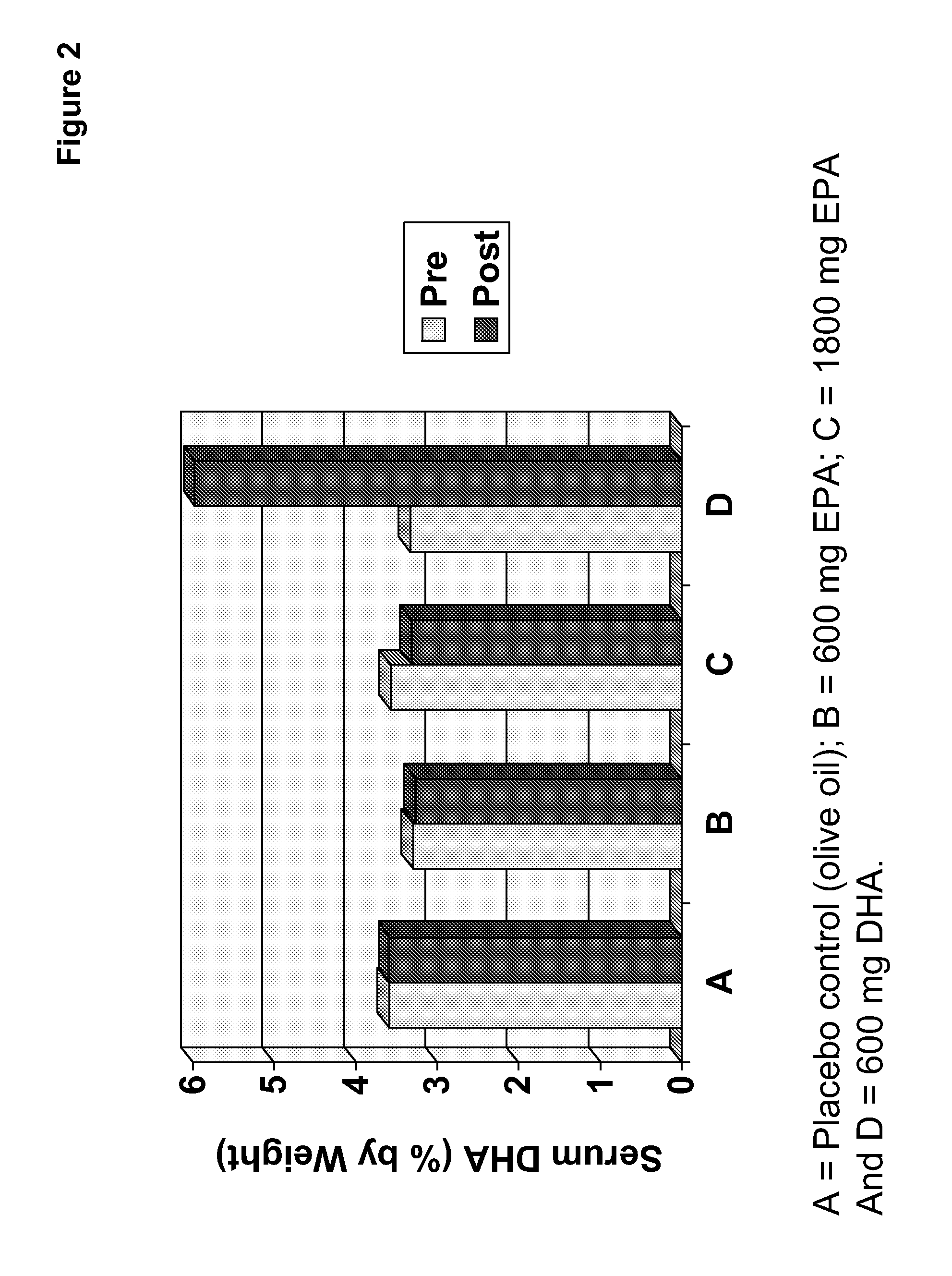
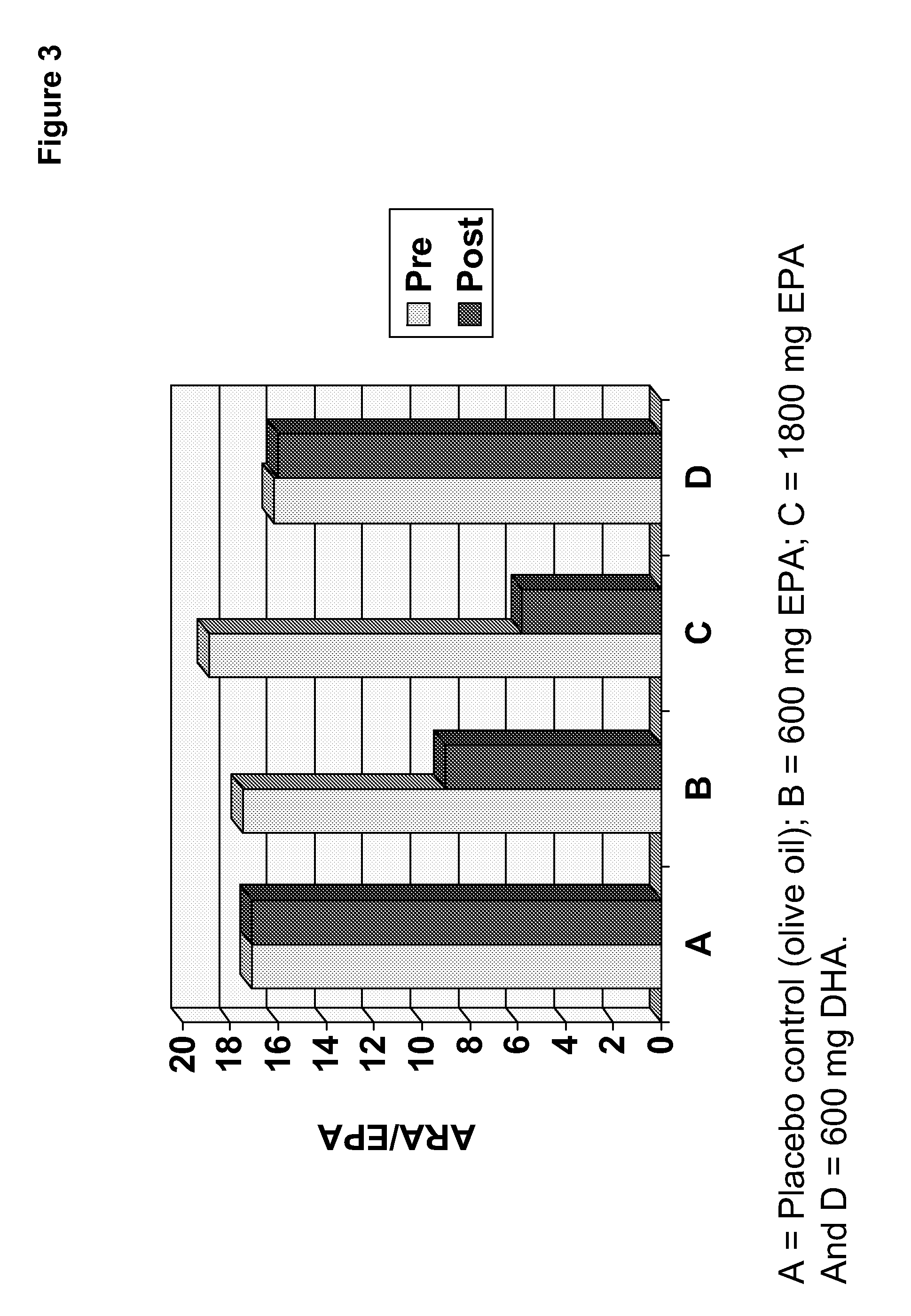
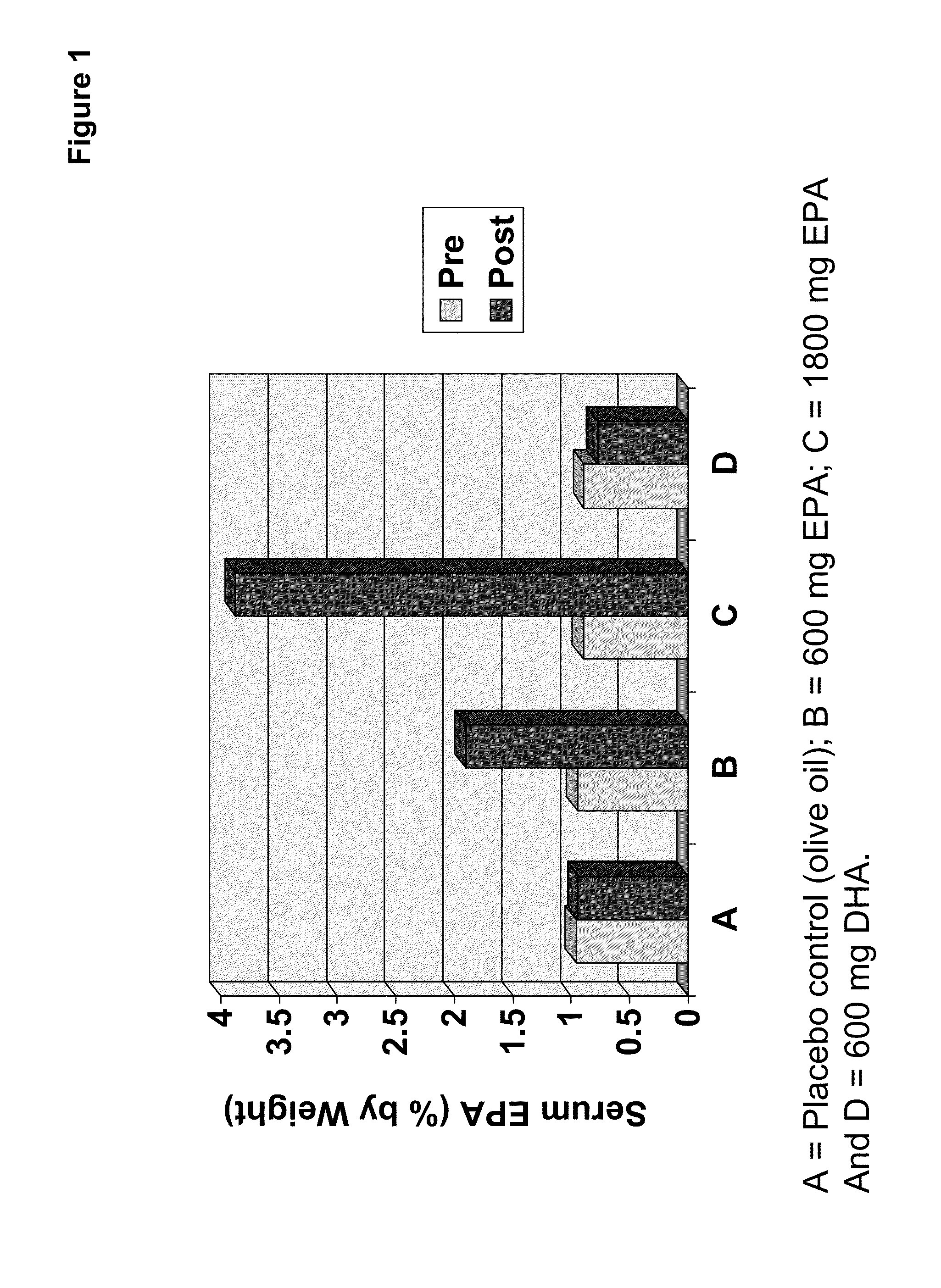
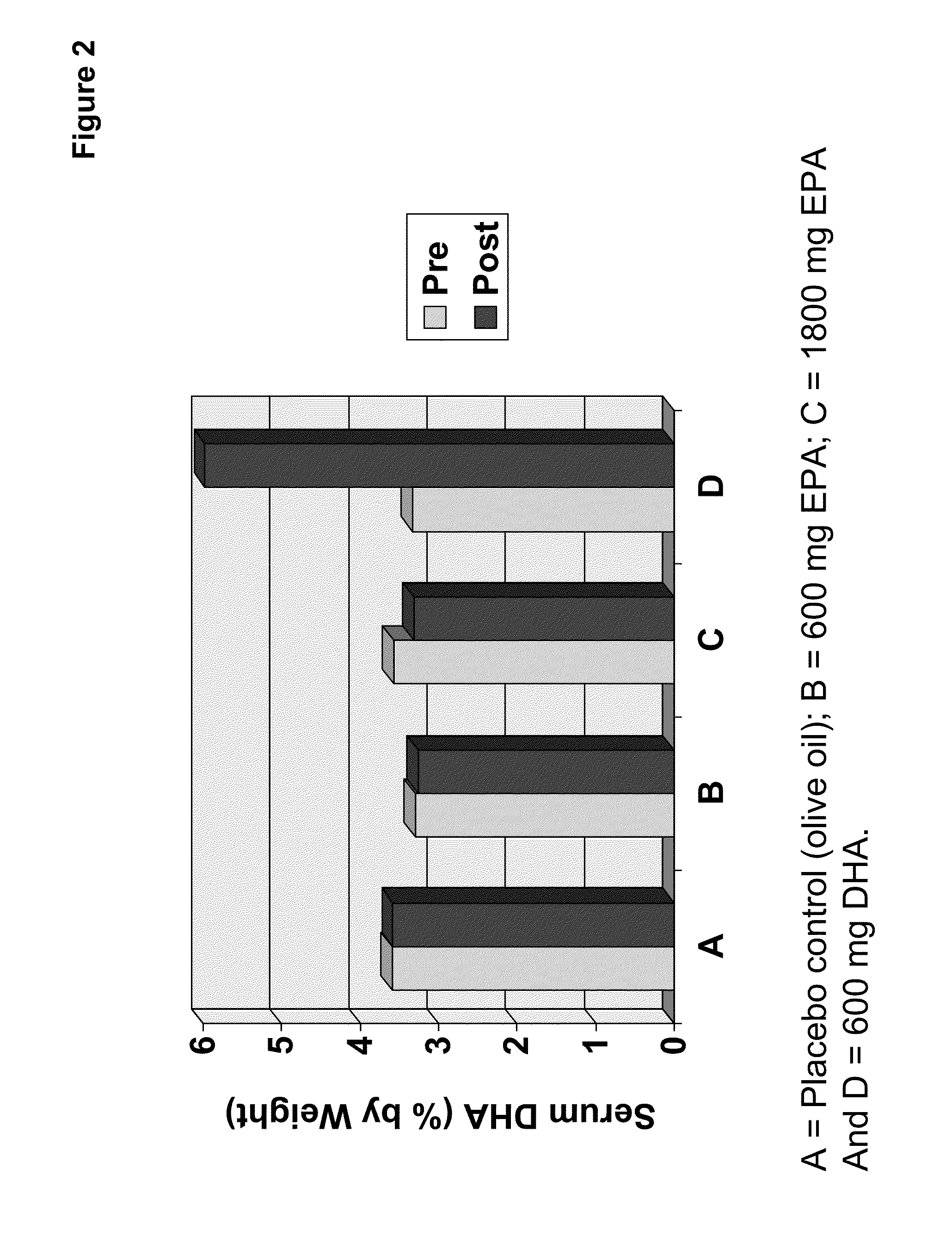
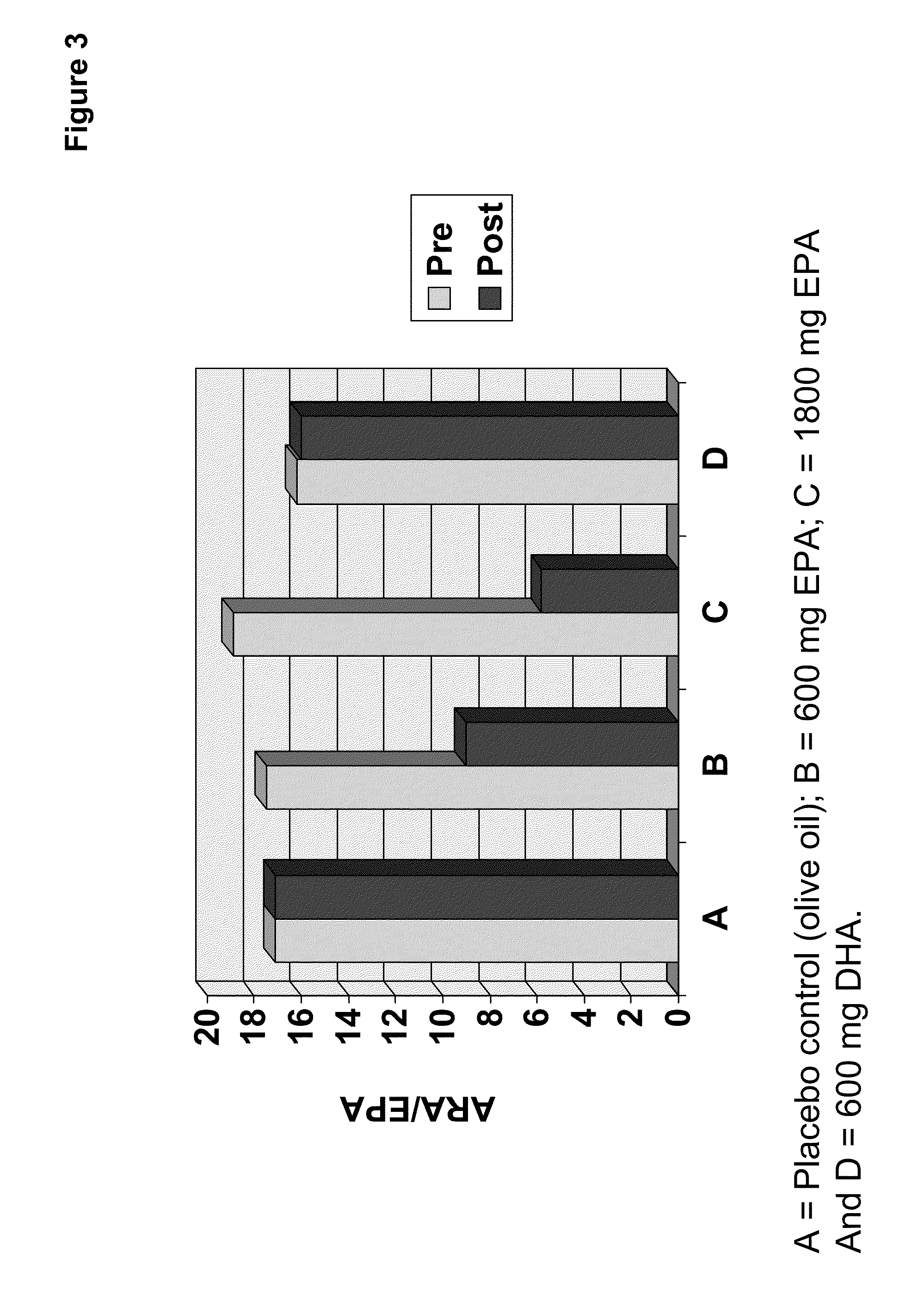
Clinical benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid in humans
InactiveUS20110178105A1Maintaining and lowering Lp-PLA levelWithout raising LDL cholesterol levelBiocideMetabolism disorderEicosapentaenoic acidOMEGA-3 POLYUNSATURATED FATTY ACIDS
Methods are provided for maintaining or lowering lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 [“Lp-PLA2”] levels, stabilizing rupture prone-atherosclerotic lesions, decreasing the Inflammatory Index and increasing Total Omega-3 Score™ in humans, by administering an effective amount of eicosapentaecnoic acid [“EPA”], an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”].
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Endothelium preserving microwave treatment for atherosclerois
Method and apparatus are provided to treat atherosclerosis wherein the artery is partially closed by dilating the artery while preserving the vital and sensitive endothelial layer thereof. Microwave energy having a frequency from 3 GHz to 300 GHz is propagated into the arterial wall to produce a desired temperature profile therein at tissue depths sufficient for thermally necrosing connective tissue and softening fatty and waxy plaque while limiting heating of surrounding tissues including the endothelial layer and / or other healthy tissue, organs, and blood. The heating period for raising the temperature a potentially desired amount about 20° C., within the atherosclerotic lesion may be less than about one second. In one embodiment of the invention, a radically beveled waveguide antenna is used to deliver microwave energy at frequencies from 25 GHz or 30 GHz to about 300 GHz and is focused towards a particular radial sector of the artery. Because the atherosclerotic lesions are often asymmetrically disposed, directable or focussed heating preserves healthy sectors of the artery and applies energy to the asymmetrically positioned lesion faster than a non-directed beam. A computer simulation predicts isothermic temperature profiles for the given conditions and may be used in selecting power, pulse duration, beam width, and frequency of operation to maximize energy deposition and control heat rise within the atherosclerotic lesion without harming healthy tissues or the sensitive endothelium cells.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTRATOR NAT AERONAUTICS & SPACE ADMINISTRATION
Clinical benefits of eicosapentaenoic acid in humans
Methods are provided for maintaining or lowering lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 [“Lp-PLA2”] levels, stabilizing rupture prone-atherosclerotic lesions, decreasing the Inflammatory Index and increasing Total Omega-3 Score™ in humans, by administering an effective amount of eicosapentaenoic acid [“EPA”], an omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”].
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
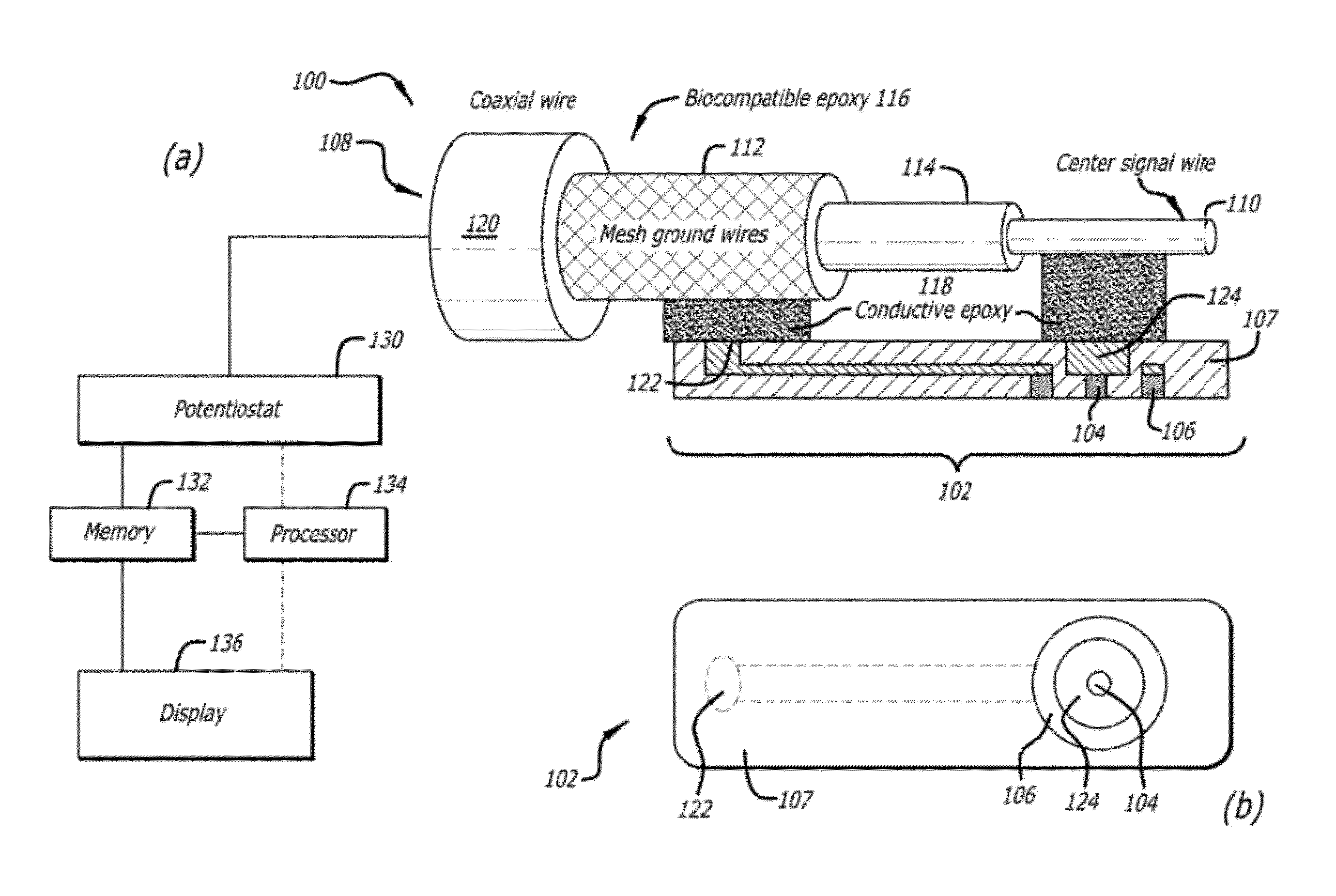
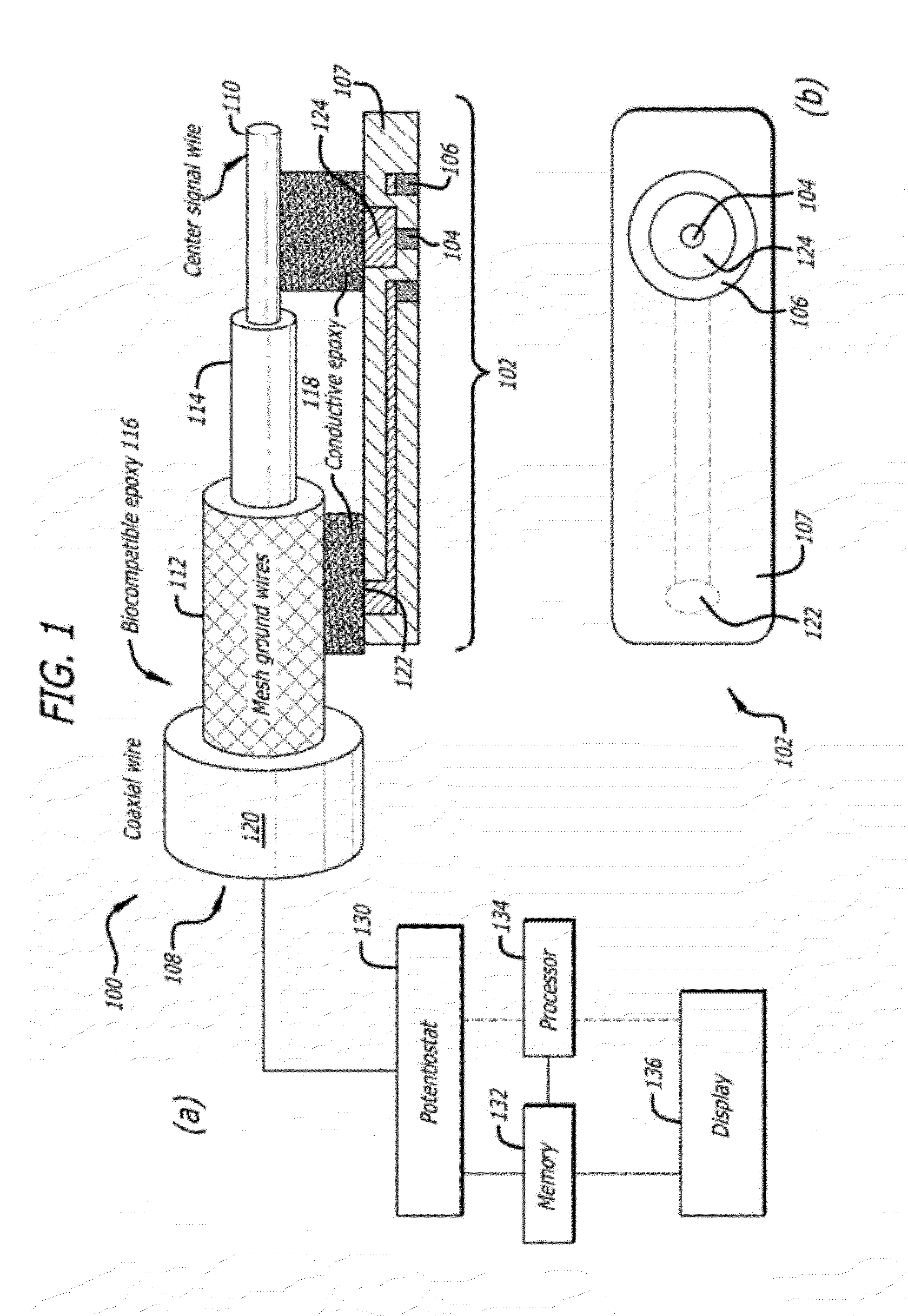
Concentric bipolar electrochemical impedance spectroscopy to assess vascular oxidative stress
InactiveUS20120061257A1Immobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsManufacturing technologySpectroscopy
Concentric bipolar electrode sensors and assemblies provide for and / or facilitate detection and diagnosis of the non-obstructive and pro-inflammatory atherosclerotic lesions in human arteries during catheterization using electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS). Fabrication techniques for concentric bipolar electrode sensors are also described.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Preventing and/or treating cardiovascular disease and/or associated heart failure
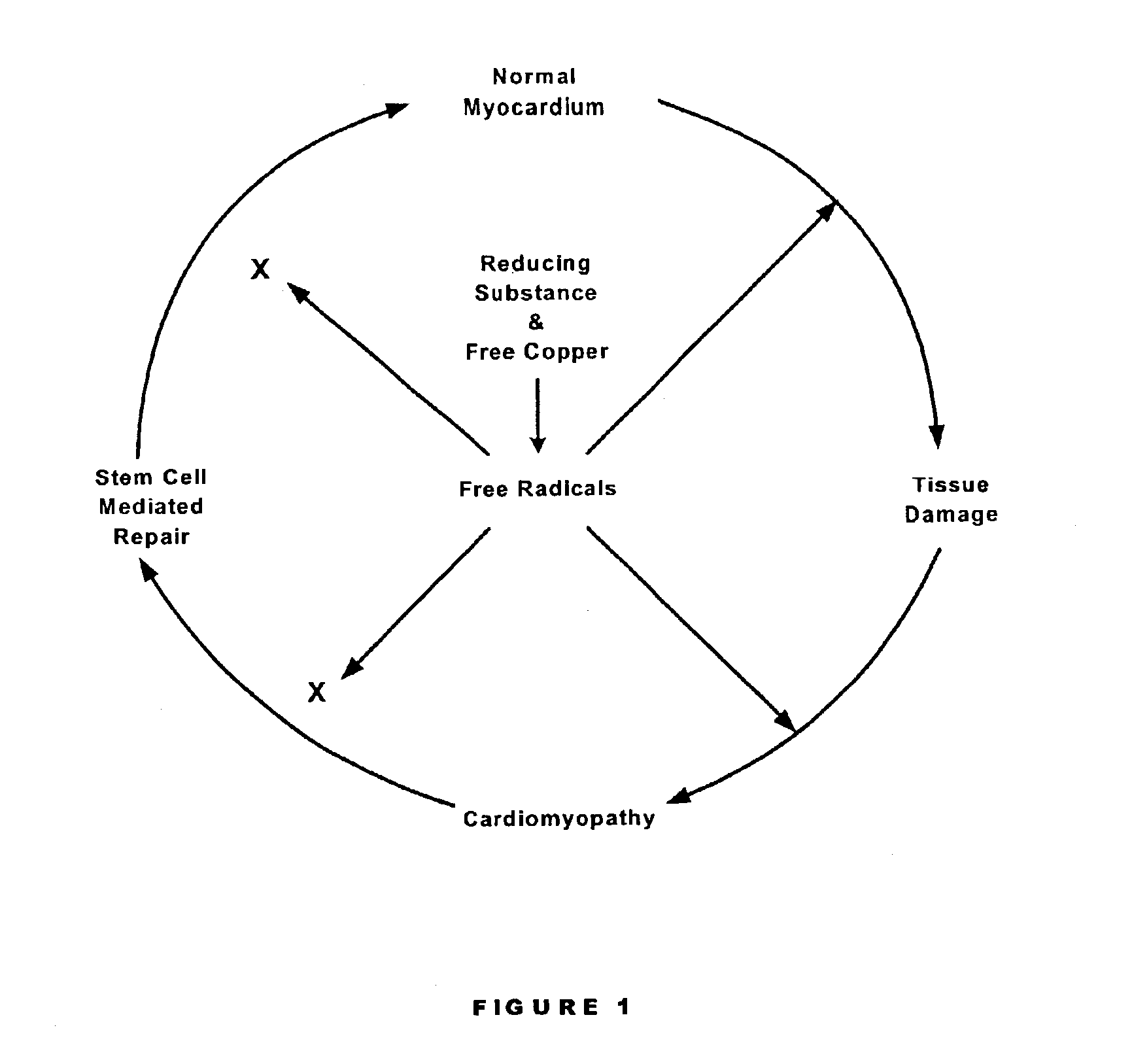
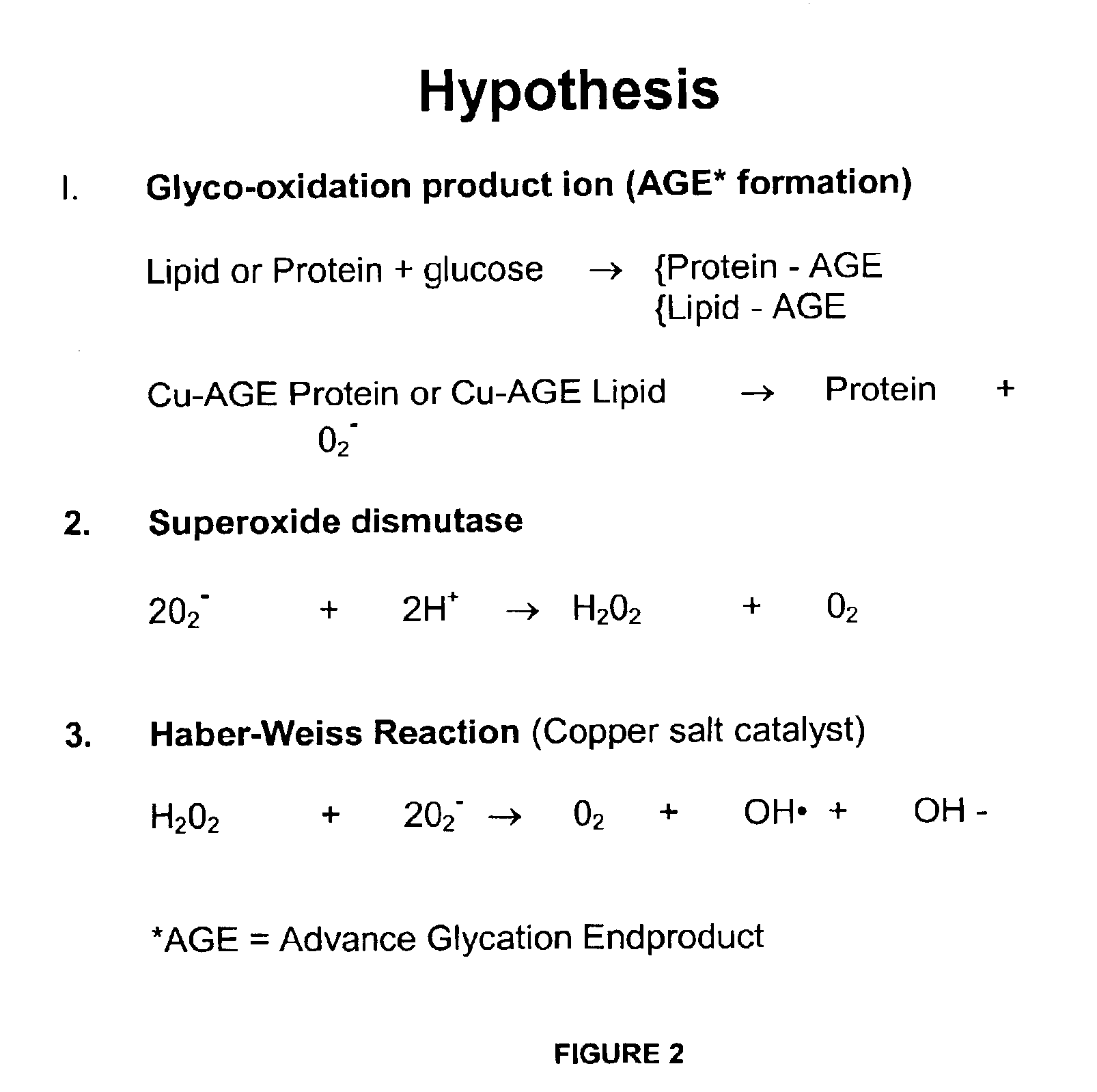
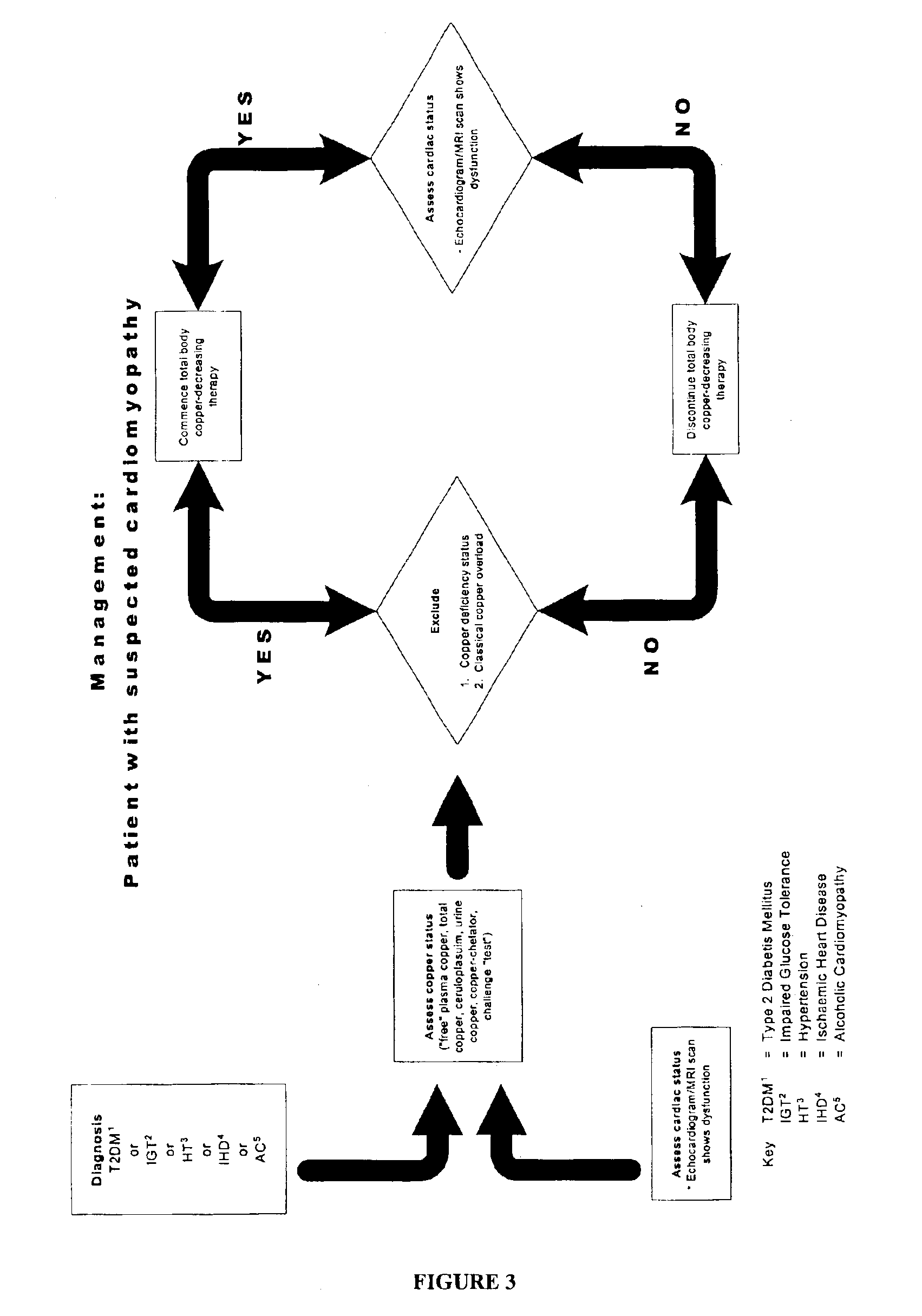
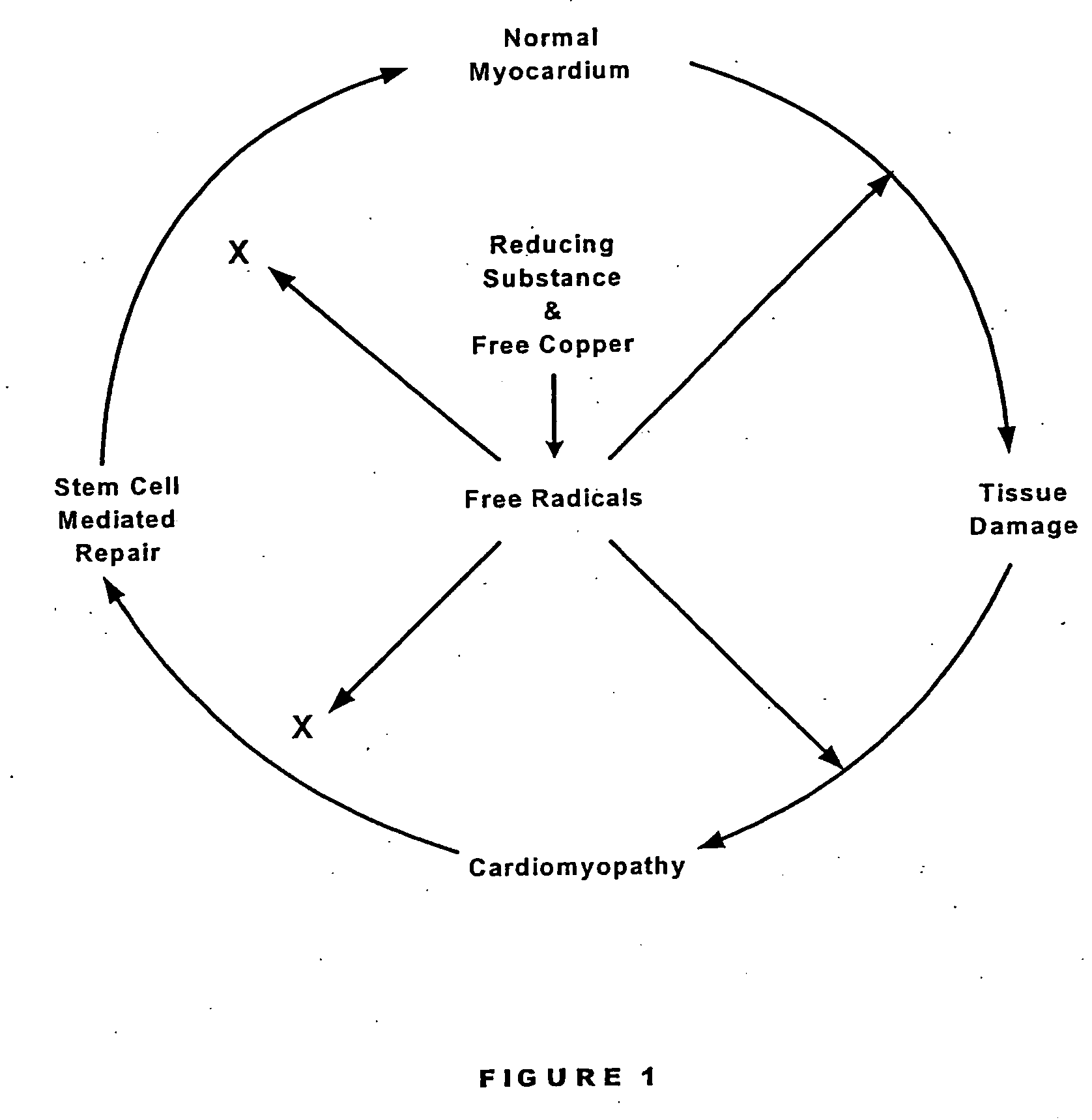
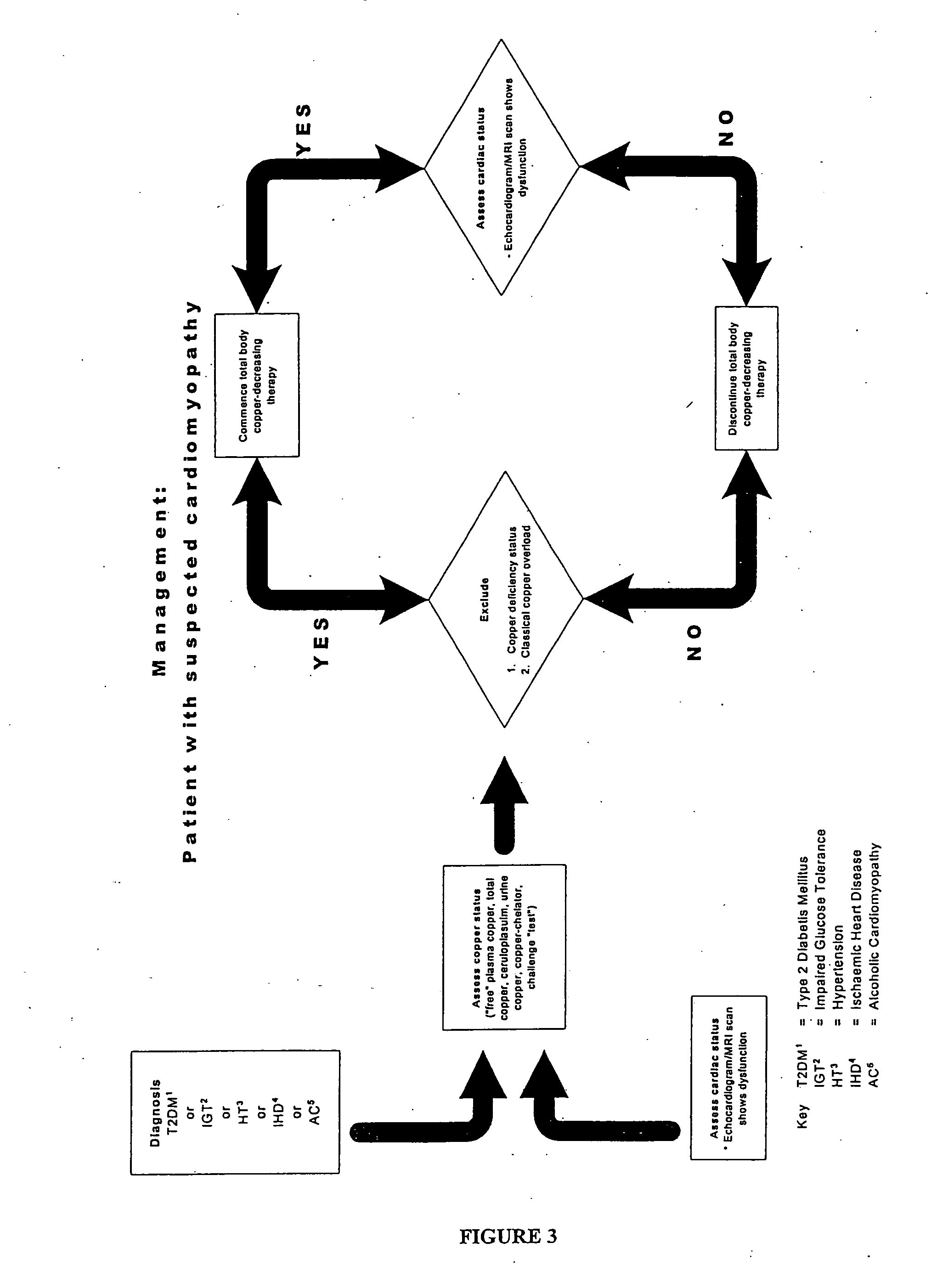
Methods are provided for reducing copper values for, by way of example, treating, preventing or ameliorating tissue damage such as, for example, tissue damage that may be caused by (i) disorders of the heart muscle (for example, cardiomyopathy or myocarditis) such as idiopathic cardiomyopathy, metabolic cardiomyopathy which includes diabetic cardiomyopathy, alcoholic cardiomyopathy, drug-induced cardiomyopathy, ischemic cardiomyopathy, and hypertensive cardiomyopathy, (ii) atheromatous disorders of the major blood vessels (macrovascular disease) such as the aorta, the coronary arteries, the carotid arteries, the cerebrovascular arteries, the renal arteries, the iliac arteries, the femoral arteries, and the popliteal arteries, (iii) toxic, drug-induced, and metabolic (including hypertensive and / or diabetic disorders of small blood vessels (microvascular disease) such as the retinal arterioles, the glomerular arterioles, the vasa nervorum, cardiac arterioles, and associated capillary beds of the eye, the kidney, the heart, and the central and peripheral nervous systems, (iv) plaque rupture of atheromatous lesions of major blood vessels such as the aorta, the coronary arteries, the carotid arteries, the cerebrovascular arteries, the renal arteries, the iliac arteries, the fermoral arteries and the popliteal arteries, (v) diabetes or the complications of diabetes.
Owner:PHILERA NEW ZEALAND +1
Expandable Prostheses for Treating Atherosclerotic Lesions Including Vulnerable Plaques
The invention provides expandable tubular prostheses that are designed for the treatment of atherosclerotic lesions, such as vulnerable plaques, and that are characterized by no foreshortening, optimal radial force and accuracy of deployment. In the treatment of vulnerable plaque, the device may be expanded in a blood vessel so that its central section at least partially contacts a vulnerable plaque lesion and / or the blood vessel wall in close proximity to the vulnerable plaque lesion. The invention also provides more general methods of treating atherosclerosis and promoting endothelialization using the prostheses of the invention.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
Differential delivery of nitric oxide
This invention relates to devices and methods for the local, differential delivery of nitric oxide within the body. The devices include devices having at least two differing nitric oxide donor compounds, such as nitric oxide donor compounds having differing half-lives and nitric oxide donor compounds having different release mechanisms. The devices also include devices having at least two chemically distinct compositions to which nitric oxide donor compounds are adsorbed or attached or within which the donor compounds are disposed. The devices are typically used to increase local nitric oxide concentration in the body upon placement of the medical article at a delivery position on or within a patient. The methods of the present invention include a method of treating an atherosclerotic lesion which comprises: exposing the lesion to a first higher concentration of nitric oxide effective to reduce the number of cells within the lesion; and subsequently exposing the lesion to a second lower concentration of nitric oxide effective to inhibit restenosis. The methods of the present invention also include methods for preferentially providing differing nitric oxide donor compounds within different tissues to effect therapy.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Methods for identifying stem cells based on nuclear morphotypes
ActiveUS7427502B2Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationCell specificAnticarcinogen
Methods for identifying stem cells and other cells specific to embryogenesis and carcinogenesis, classifying tissue samples, diagnosing precancerous and cancerous or atherosclerotic lesions, testing the value of anticancer agents, discovering macromolecules specifically expressed in particular cell types, using stem cells in restorative tissue therapy as well as methods for preparing tissue samples so heteromorphic nuclear morphotypes remain intact are disclosed.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Expandable vascular endoluminal prostheses
The invention provides expandable tubular endoluminal prostheses for the treatment of atherosclerotic lesions of blood vessels, including vulnerable plaque lesions, and methods of treatment using the prostheses. Various prostheses of the invention are characterized by hoop strength suitable for treating vulnerable plaque lesions, good conformability and good apposition to vessel walls, as well as minimal coverage areas in order to minimize the inflammatory response to the implanted prostheses.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
Composite endoluminal prostheses for treating vulnerable plaque
The invention provides expandable tubular endoluminal prostheses for the treatment of atherosclerotic lesions, such as vulnerable plaques, and methods for treating such lesions using the prostheses. The endoprostheses may include at least two expandable ring-like elements disposed on the inside or about the outer surface of an at least substantially tubular biodegradable element. The ring-like elements may be radio-opaque and may have a sinuate form. In use, a prosthesis according to the invention is expanded in a blood vessel so that the tubular biodegradable element at least partially covers an atherosclerotic lesion, such as a vulnerable plaque.
Owner:SCHELLER PATRICIA
Side-viewing optical acoustic sensors and their use in intravascular diagnostic probes
One aspect of the invention provides side-sensing optical fiber-based optical acoustic sensors that are well suited to catheter-based intravascular diagnostic applications. Another aspect of the invention provides intravascular probes, such as catheters, that include a side-sensing optical acoustic sensor according to the invention and means for photoacoustically generating an acoustic signal, such as ultrasound, from a target tissue. Still another aspect of the invention provides a method for evaluating at least a section of a blood vessel, such as an artery, and in particular identifying, locating and / or characterizing atherosclerotic lesions within the blood vessel. A related embodiment provides a method for identifying, locating and / or characterizing lipid-rich atherosclerotic lesions such as vulnerable plaques.
Owner:PRESCIENT MEDICAL
Preventing and/or treating cardiovascular disease and/or associated heart failure
Owner:PHILERA NEW ZEALAND
Delivery systems and methods for diagnosing and treating cardiovascular diseases
InactiveUS20080138277A1Reduce developmentLower cholesterol levelsBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsVascular diseaseVulnerable plaque
The invention relates to the treatment and prevention of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases associated with atherosclerosis. The invention further relates to methods of diagnosing atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases associated with atherosclerosis. In certain embodiments, the invention provides biological systems and methods for delivering a therapeutic agent or an imaging agent to atherosclerotic lesions such as vulnerable plaques.
Owner:MEDSTAR HEATH INC +1
Methods of Treating Cardiovascular Disorders Associated with Atherosclerosis
InactiveUS20090186091A1Reduce accumulationPowder deliverySalicyclic acid active ingredientsBlood cholesterolCholesterol blood
Layered phyllosilicates are useful for adsorbing and / or binding to cholesterol and, thereby, reducing blood cholesterol in a patient. Accordingly, provided herein is a method of reducing hypercholesteremia in a mammal comprising administering to said mammal a protonated and at least partially exfoliated layered phyllosilicate material alone and in combination with other cholesterol-reducing agents in an amount effective to reduce hypercholesteremia in said mammal. Also provided are methods of treating a cardiovascular disorder associated with atherosclerosis in a mammalian subject comprising administering to the subject a layered phyllosilicate material in an amount effective to reduce atherosclerotic lesion formation in the subject.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
Dietary supplement derived from natural prodcuts by hot melt extrusion (HME) processing
ActiveUS20180271928A1Modify rate of releaseProlonged durationPowder deliveryAntinoxious agentsDietary supplementAdditive ingredient
The invention provides a composition rich in flavonoids based on natural extracts, comprising a flavonoid extract dispersed by melt mixing or extrusion and encapsulated in a polymer matrix. The invention is also a novel dietary supplement with the naturally occurring ingredient (−)-epicatechin, cacao extracted, that could potentially prevent or reduce the risk of Atherosclerotic pathology. The use of (−)-epicatechin is promising as a therapeutic agent due to its potential antioxidant activity and its diverse biological properties. (−)-Epicatechins are chemically unstable and extensively degraded in fluids of near neutral or greater pH, such as intestinal juice and bile. Current technologies used for taste masking and modified release as spray drying, liposome entrapment, co-crystallization, freeze drying, among others, suffer from numerous shortcomings, including poor repeatability and limitations on target delivery.
Owner:INST DE CAPACITACION E INVESTIGACION DEL PLASTICO & DEL CAUCHO - ICIPC +1
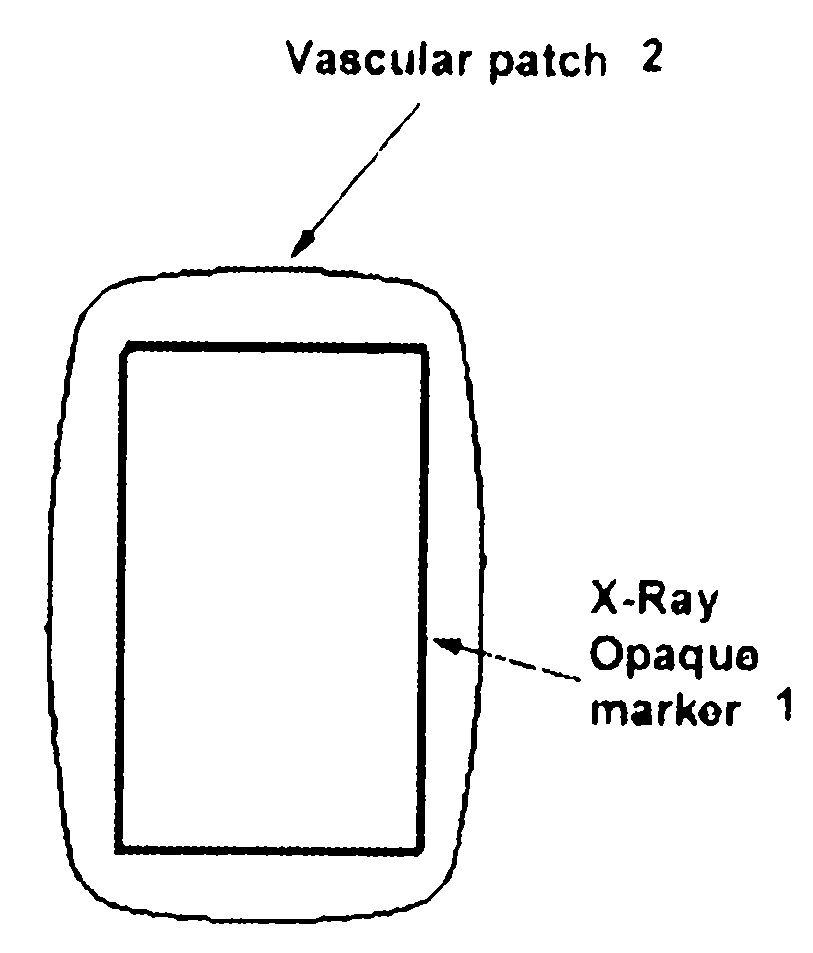
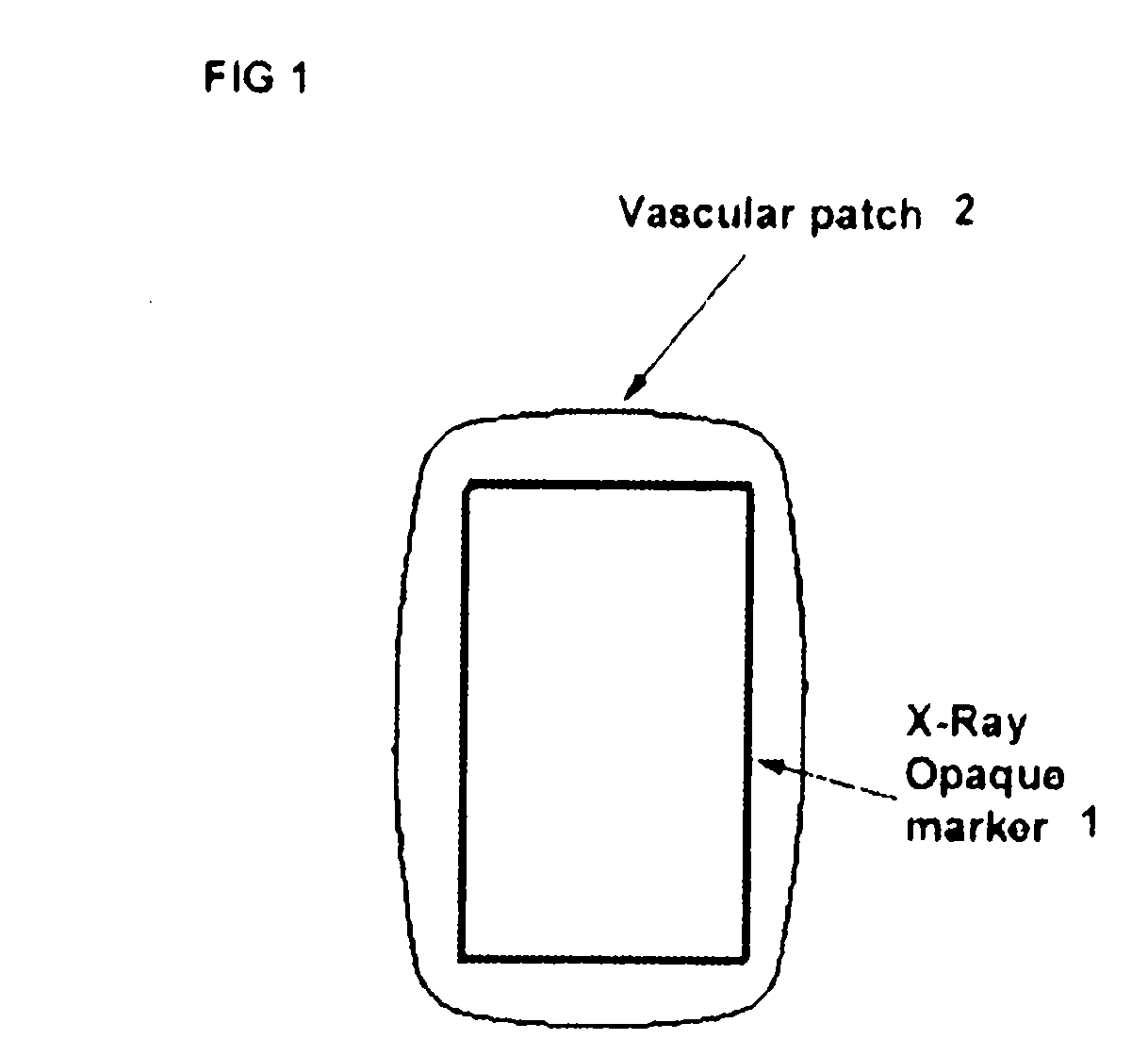
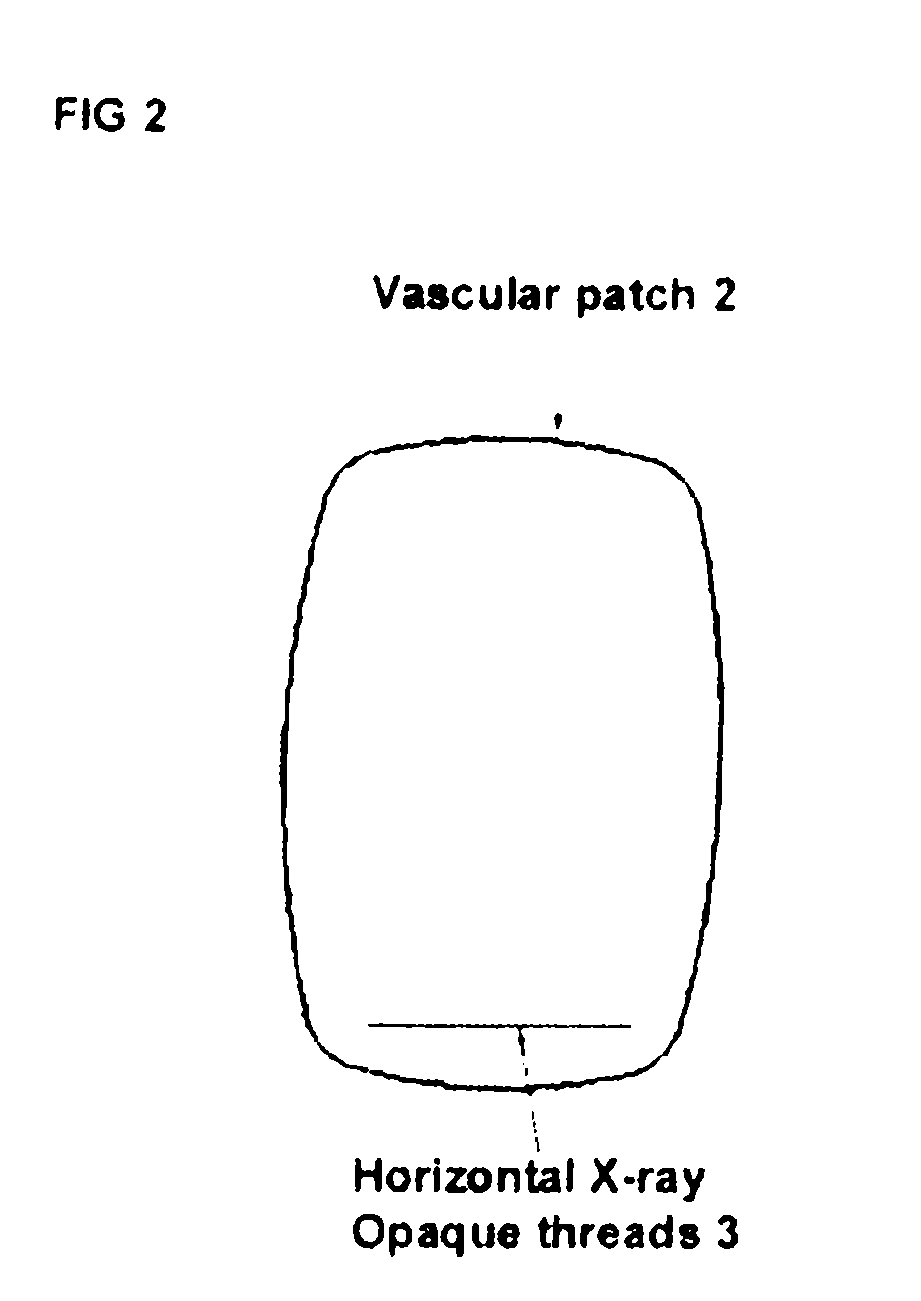
Labeled vascular patch
InactiveUS20080255609A1Impaired circulationNo damageDiagnostic markersSurgical veterinarySound energyLight energy
The present invention relates generally to a labeled vascular patch to be applied during surgical repair of blood vessels, which have become diseased by atherosclerosis or injured by trauma. More particularly, the present patch comprises a label, useful for locating the patch during post-operative recovery to assess the success of the surgery and / or during subsequent operations on the same portion of vasculature. The label can comprise any material useful for interacting with imaging energy including, but not limited to Radiation Energy (i.e. X-Rays) electromagnetic energy, sound energy, and light energy, and / or any other energy used for therapeutic imaging.
Owner:OPIE JOHN C
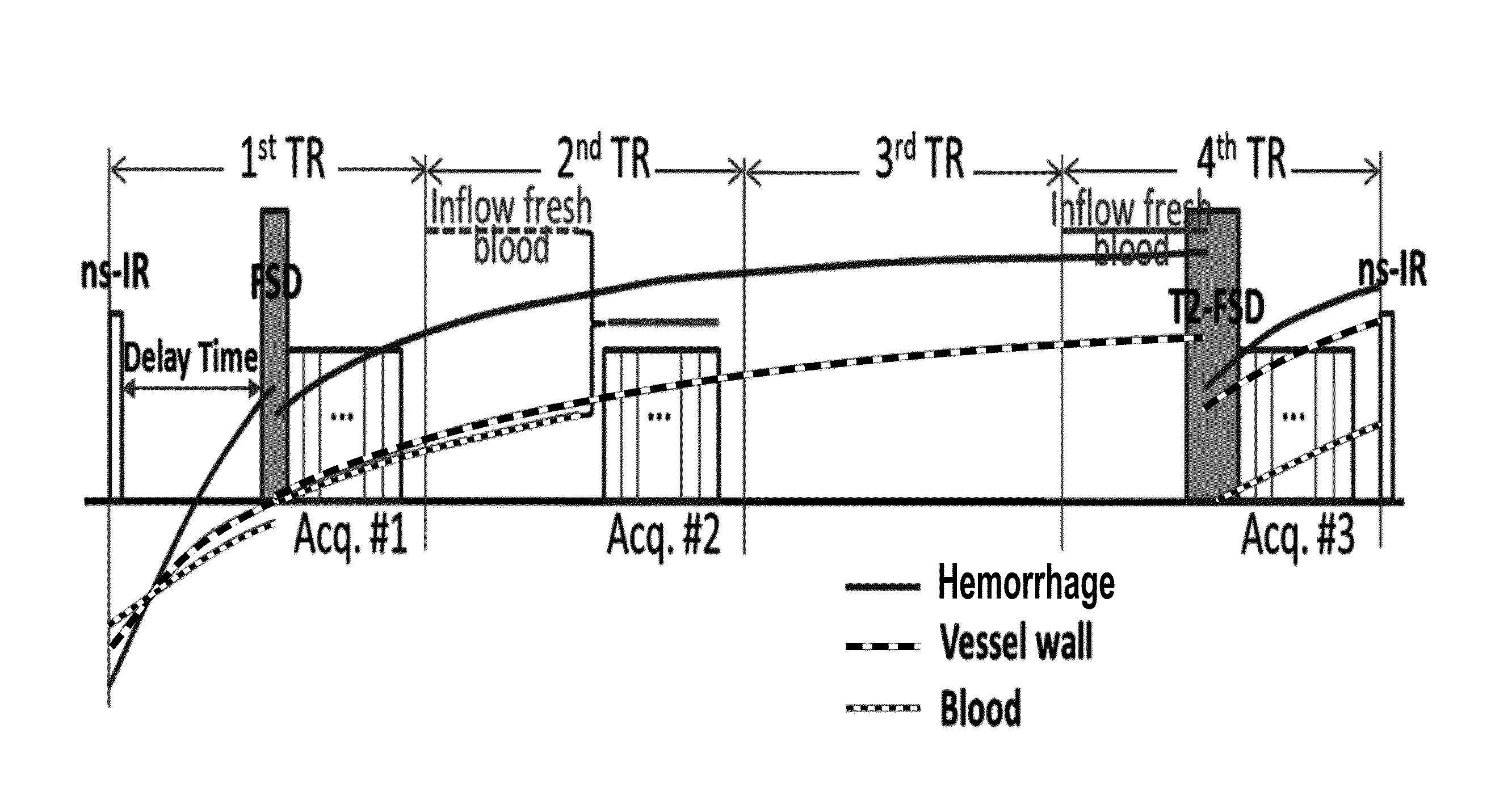
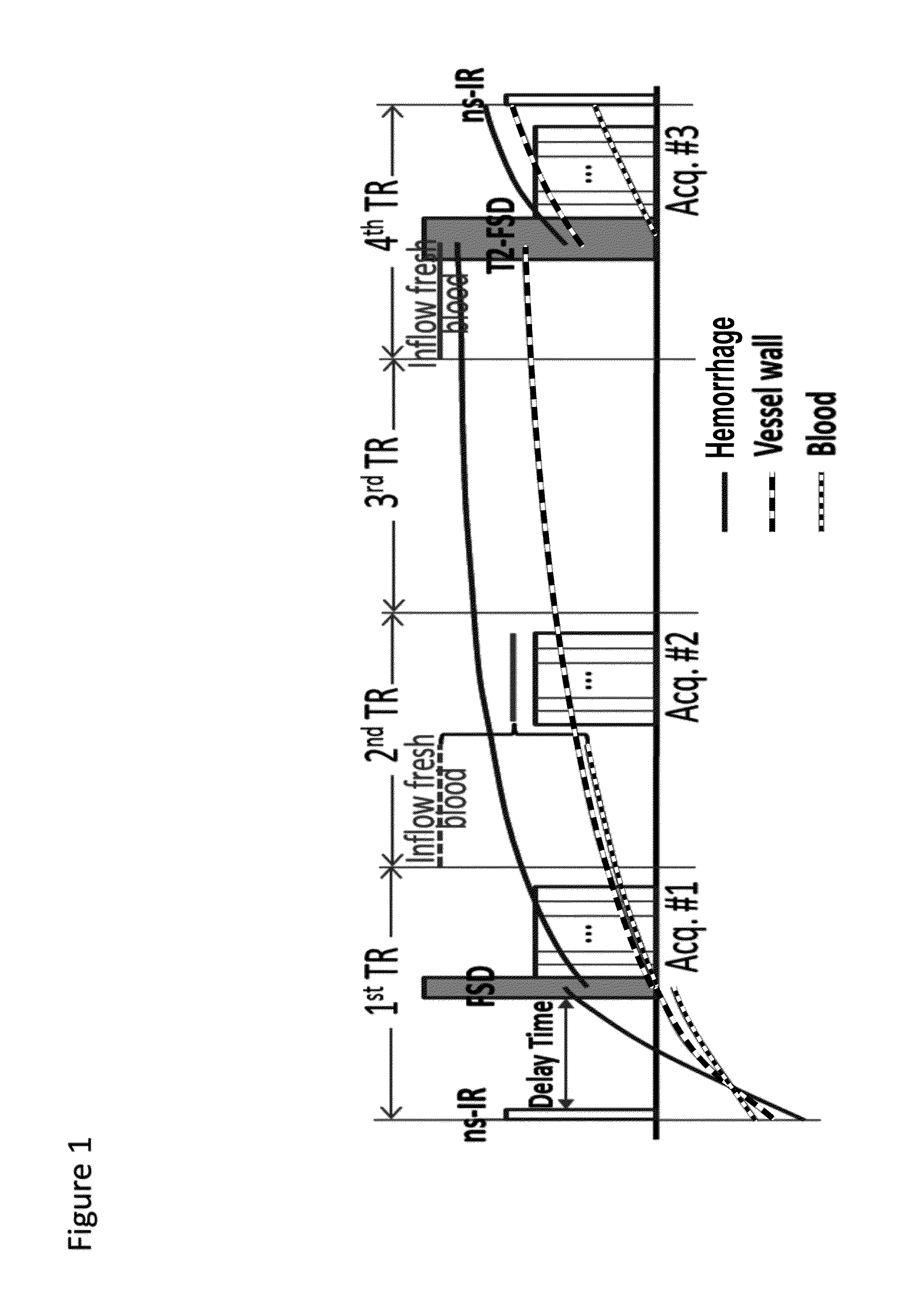
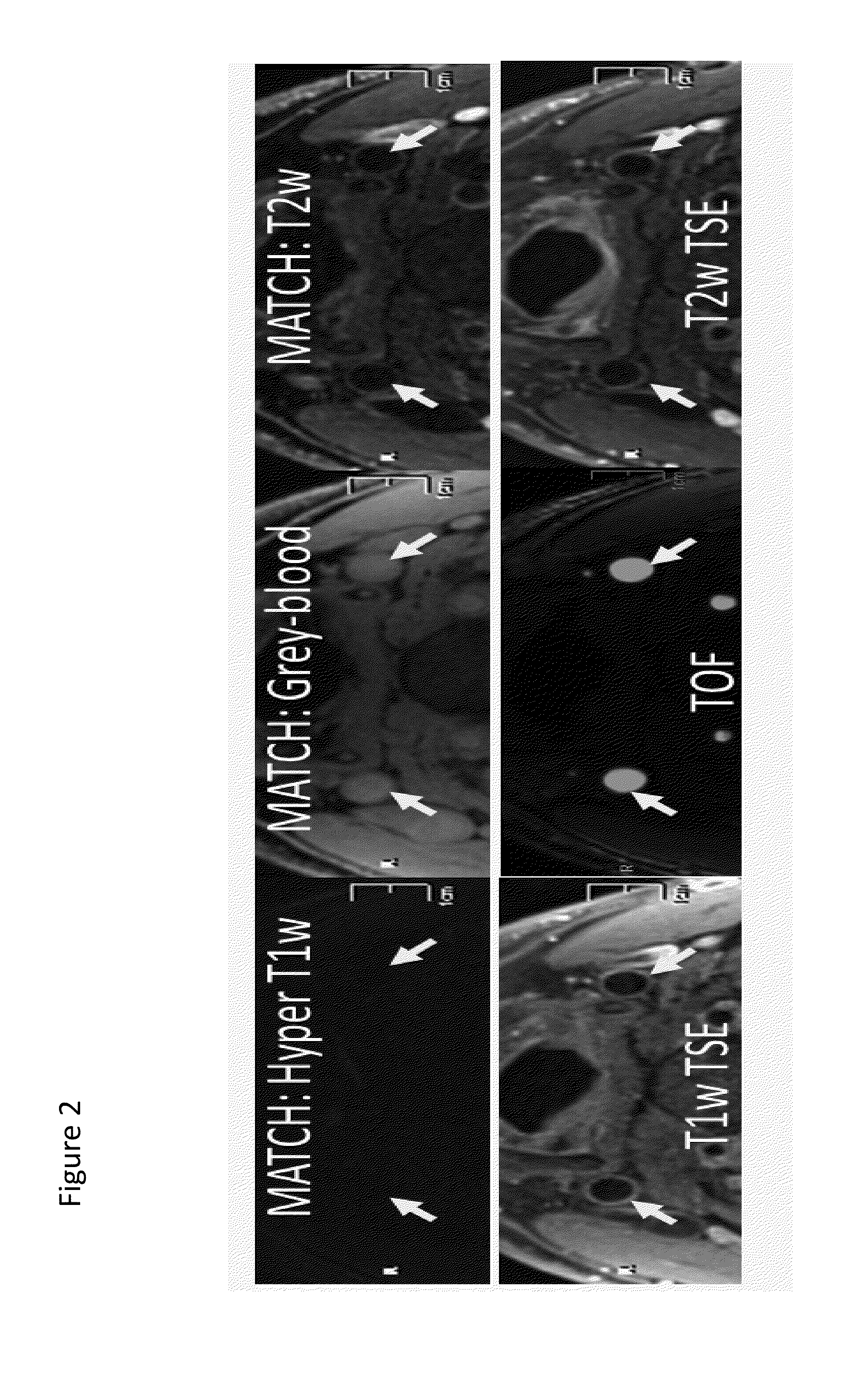
Atherosclerosis characterization using a multi-contrast MRI sequence
ActiveUS20150048821A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systems3d imageMagnetization
The present invention relates to imaging and characterizing atherosclerotic lesions. The invention utilizes a low-flip-angle gradient echo-based MRI acquisition technique combined with specialized magnetization preparative schemes (i.e. non-selective inversion and FSD), and multiple co-registered 3D image sets with different contrast weightings are collected in an interleaved fashion. Using the inventive method, a single scan allows for comprehensive assessment of atherosclerotic plaque within just a few minutes.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
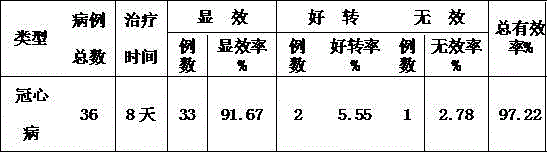
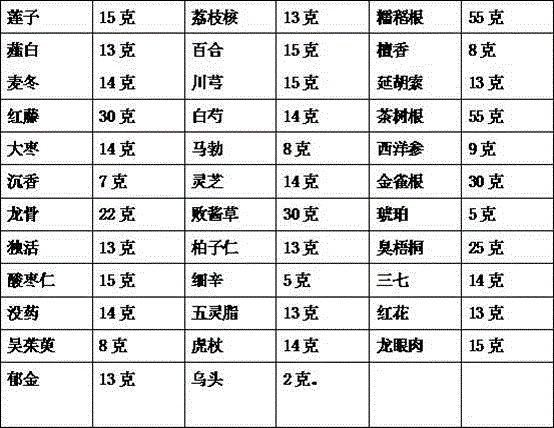
Medicine for treating coronary heart disease and preparation method of medicine
InactiveCN105596979AEffective treatmentFunctional sedationDispersion deliveryInanimate material medical ingredientsAconitum carmichaeliSargent gloryvine
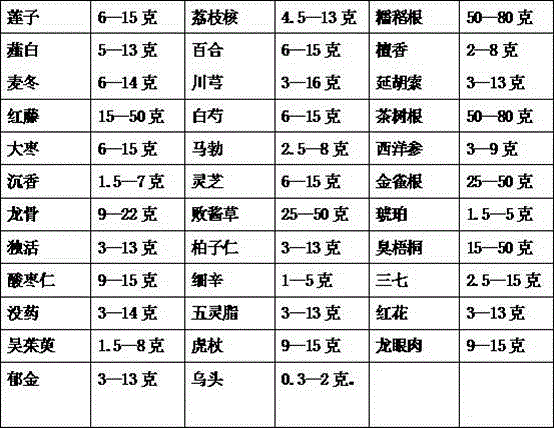
The coronary atherosclerotic heart disease is a heart disease of myocardial ischemia, anoxia or necrosis caused by vessel lomen stenosis or blocking resulted from atherosclerosis lesions of coronary artery blood vessels, and is often called as 'coronary disease'. The coronary disease further includes embolism stenosis or blocking caused by inflammation and embolism. The disease has remarkable regional difference, that is, the disease rates of northern provinces and cities are generally higher than those of southern provinces and cities. The medicine is prepared from medicines including lotus seeds, semen litchi, glutinous rice, allium macrostemon, lily, sandalwood, radix ophiopogonis, ligusticum wallichii, corydalis tuber, sargent gloryvine, radix paeoniae alba, tea tree roots, dates, puffball, American ginseng, aquilaria sinensis, lucid ganoderma, caragana sinica roots, dragon bone, patrinia scabiosaefolia, amber, radix angelicae pubescentis, platycladi seeds, harlequin glorybower leaves, spina date seeds, asarum, pseudo-ginseng, myrrh, trogopterus dung, carthamus tinctorius, fructus evodiae, polygonum cuspidatum, arillus longan, radix curcumae and aconitum carmichaeli. Due to the effects of the combined medicines, a synergistic effect can be achieved, and thus the coronary heart disease can be effectively treated.
Owner:薛学明
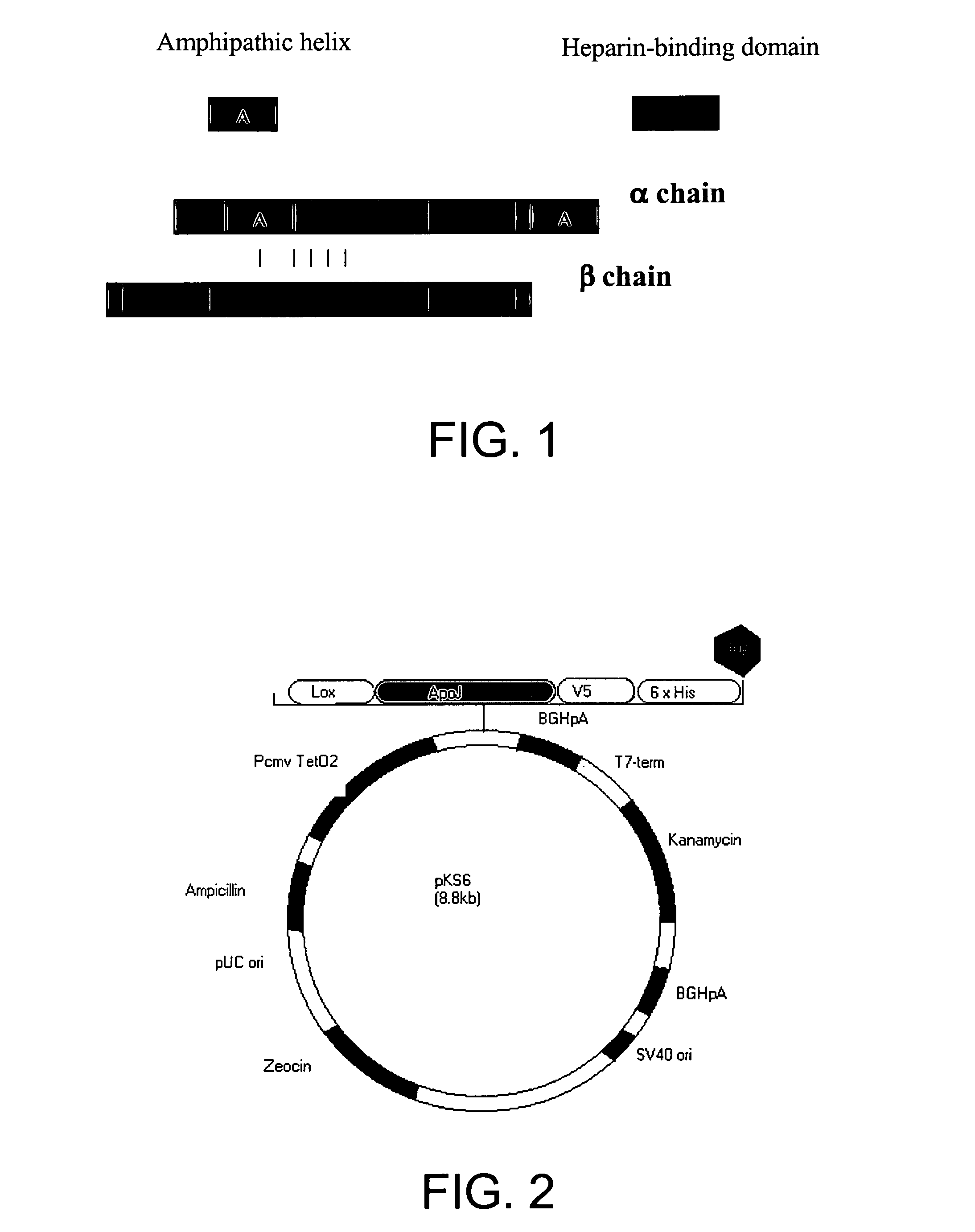
Clusterin-mediated inhibition of apoptosis via stromal bone marrow cell delivery to a cardiac site
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting, deterring or preventing apoptosis of cardiac myocytes, transplanted stem cells, vascular stem cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells by means of expressing or synthesizing clusterin. Also disclosed are methods and compositions for producing recombinant clusterin, or its biologically active peptides, and for induction of clusterin-associated lipoproteins or enzymes for deterring or preventing inflammatory injury and apoptosis induced by oxLDL, oxysterols, cytokines, and Fas Ligand. Also disclosed is an induction method and composition for enhancing expression of ALDH and ALDH-associated enzymes or co-factors to prevent cytotoxicity or detoxification. Therapeutic methods providing new expression or overexpression of clusterin in vascular or cardiac tissue are expected to inhibit the formation of atherosclerotic lesions, stabilize existing atherosclerotic plaques, and repair failing or damaged cardiac tissue.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods of Treating Cardiovascular Disorders Associated with Atherosclerosis
InactiveUS20120058157A1Reduce accumulationSalicyclic acid active ingredientsBiocideBlood cholesterolCholesterol blood
Layered phyllosilicates are useful for adsorbing and / or binding to cholesterol in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and, thereby, reducing blood cholesterol in a patient. Accordingly, provided herein is a method of reducing hypercholesteremia in a mammal comprising administering to said mammal a protonated and at least partially exfoliated layered phyllosilicate material alone and in combination with other cholesterol-reducing agents in an amount effective to reduce hypercholesteremia in said mammal. Also provided are methods of treating a cardiovascular disorder associated with atherosclerosis in a mammalian subject comprising administering to the subject a layered phyllosilicate material in an amount effective to reduce atherosclerotic lesion formation in the subject.
Owner:AMCOL INTERNATIONAL CORPORATION
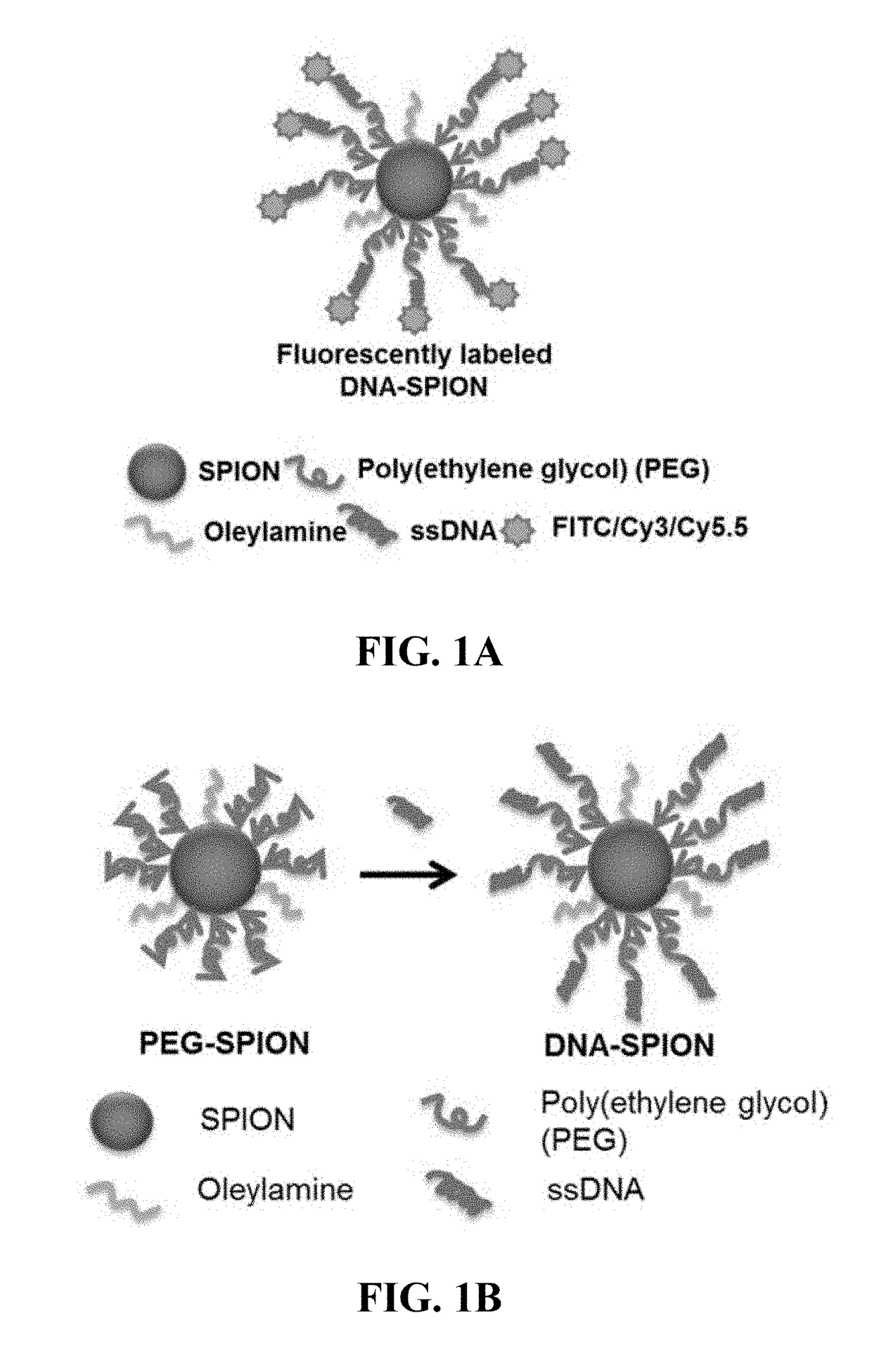
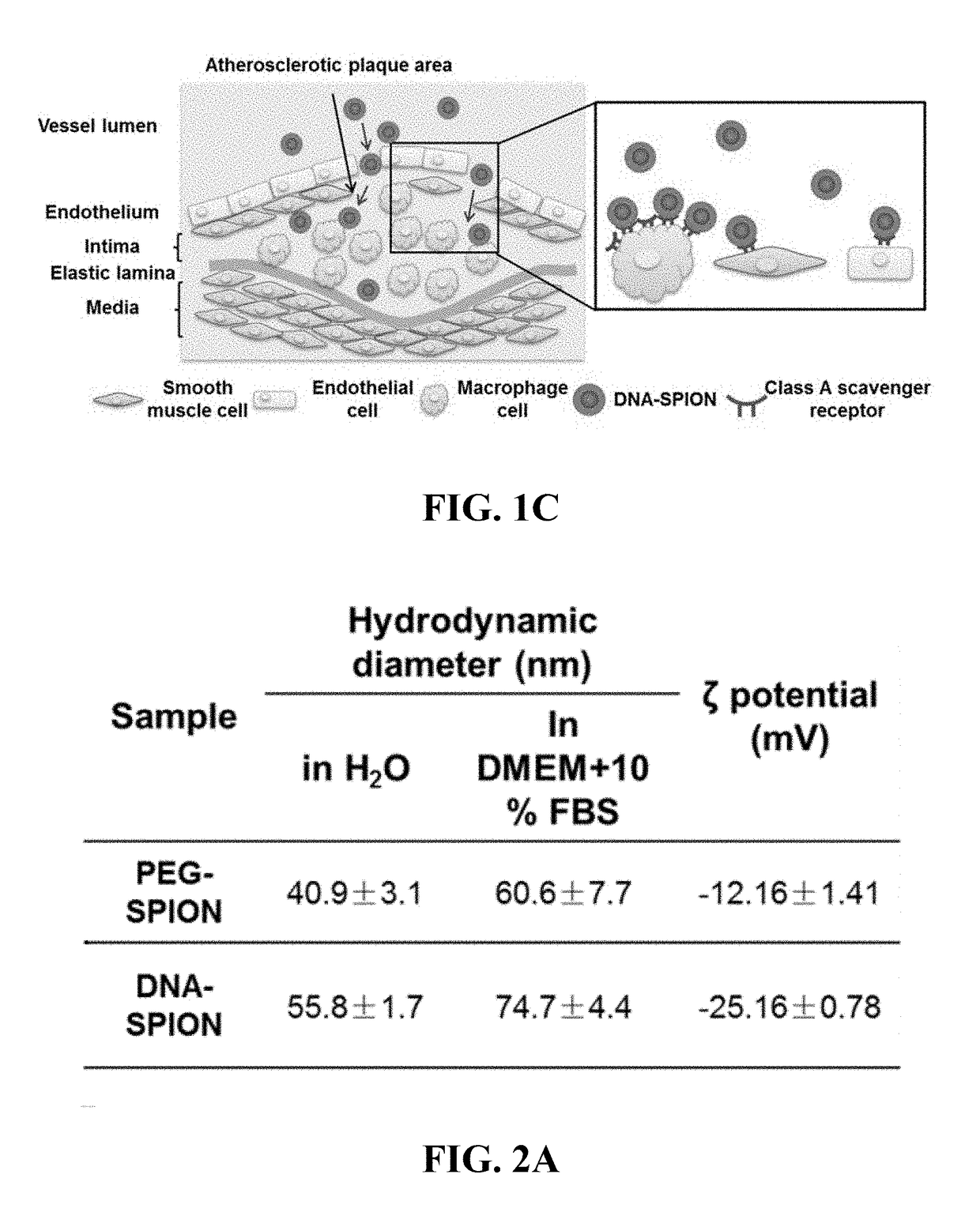
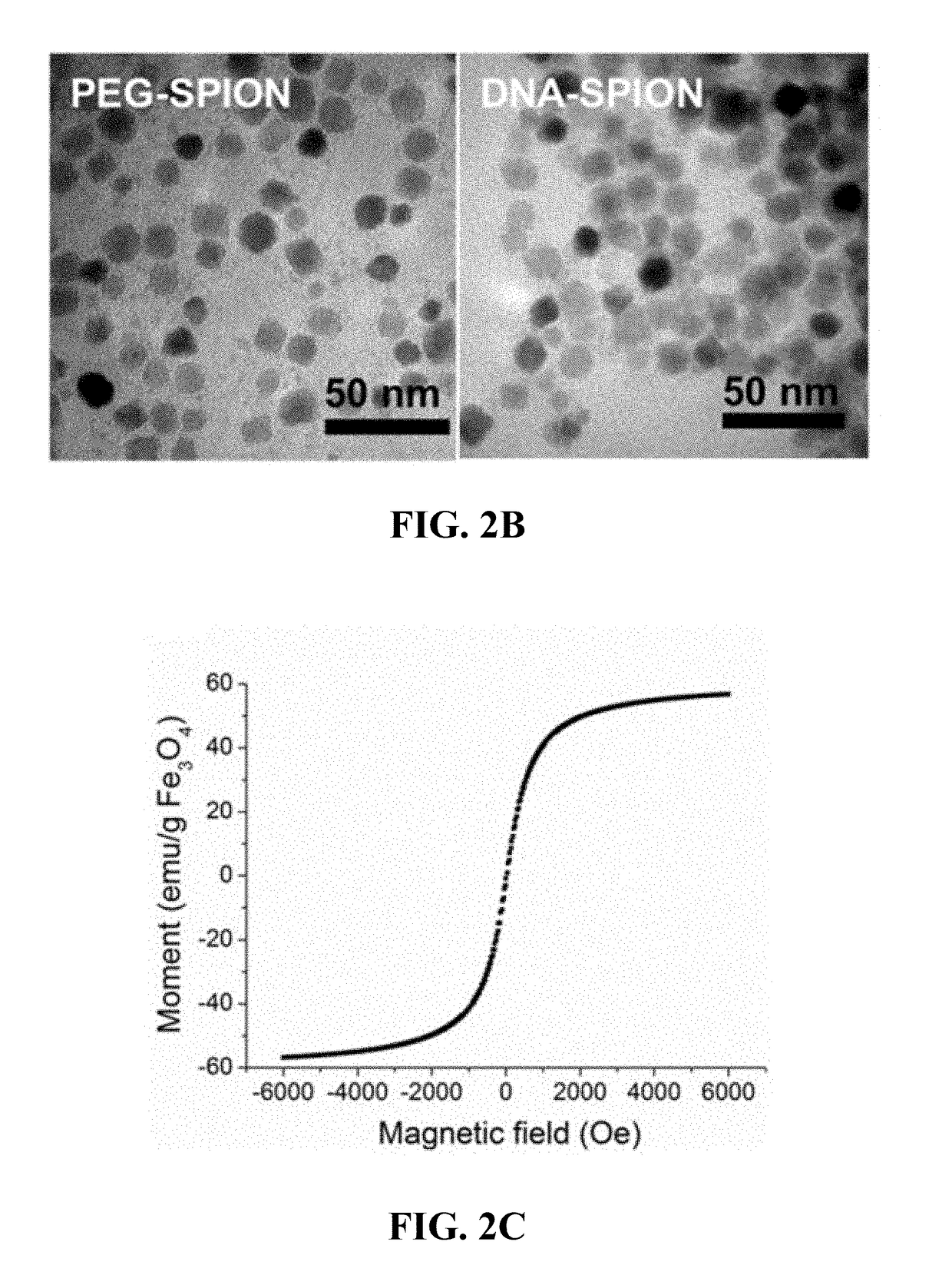
Materials and methods for effective in vivo delivery of DNA nanostructures to atherosclerotic plaques
ActiveUS20190060485A1Promote rapid accumulationPowder deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSuperparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticlesImaging agent
Provided are DNA-coated nanoparticles (DNA-NPS), superparamagnetic nanoparticles (DNA-SPNs), and superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (DNA-SPIONs) as efficient imaging agents for targeting and imaging atherosclerotic lesions and treating atherosclerotic disease. The DNA-NS, DNA-SPNs, and DNA-SPIONs can enter macrophage cells via the Class A scavenger receptor (SR-A)-mediated pathways and can be used to specifically target atheroscleortic plaques.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
Large Animal Model for Human-Like Advanced Atherosclerotic Plaque
An animal model for cardiovascular disease comprising one or more vascular plaque lesions formed at selected sites within a vascular segment of a nonhuman mammal. The vascular plaque lesion is formed by administering a hypercholesterolemic diet to the nonhuman mammal, inflicting an injury to the vascular wall at the selected site after a predetermined exposure to the hypercholesterolemic diet, and applying a hydrogel to the injured vascular wall. Another aspect of the invention provides a method for evaluating a test compound for an effect on atherosclerotic lesion formation comprising administering to a nonhuman mammal a hypercholesterolemic diet, and, after a defined period of time, isolating a segment of a blood vessel using a balloon catheter, inflicting an injury to the vascular wall within the isolated segment, and applying a hydrogel within the vascular segment. The method further comprises forming a vascular plaque lesion on the vascular wall at the site of the injury, delivering the test compound to the nonhuman mammal, and monitoring atherosclerotic lesion size and composition at the injured site after a defined period of exposure to the test compound.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Toxin-eliminating drug composition, drug preparation and preparation methods of drug composition and drug preparation
InactiveCN103272196AFacilitated releaseIncrease blood flowAntinoxious agentsPlant ingredientsDuodenal ulcerLung cancer
The invention provides a toxin-eliminating drug composition, a drug preparation and preparation methods of the drug composition and the drug preparation. The drug composition comprises the following components in parts by weight: 7-10 parts of dogbane, 15-18 parts of field sowthistle herb, 15-18 parts of dandelions and 3-5 parts of ginger, wherein dogbane has the functions of calming the liver, clearing heat, improving the eyesight and reducing internal heat and blood pressure; under the action of the drug dogbane, the content of nicotine in human bodies is reduced to some extent, thus reducing the harms of nicotine to human bodies; field sowthistle herb has the function of eliminating the toxicity of nicotine; the dandelions and ginger can be used for promoting the release of nicotine from the bodies and preventing and relieving such diseases caused by smoking as bronchitis, lung cancers, chronic obstructive lung diseases, atherosclerosis lesions and duodenal ulcer of smokers; therefore under the synergistic action of dogbane, field sowthistle herb, dandelions and ginger, the toxin-eliminating drug composition and drug preparation provided by the invention can be used for reducing the harms of nicotine to human bodies.
Owner:李秋暑
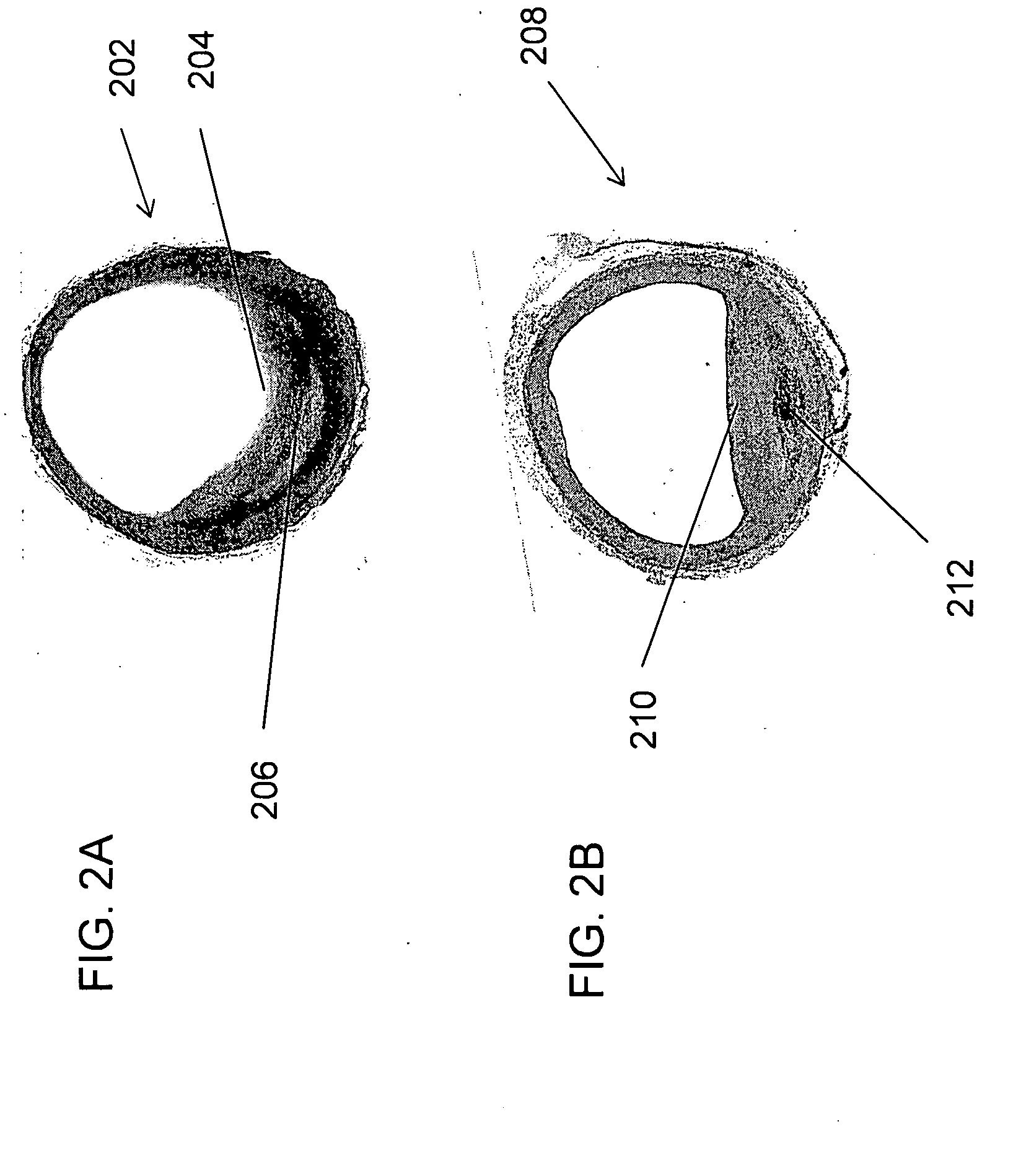
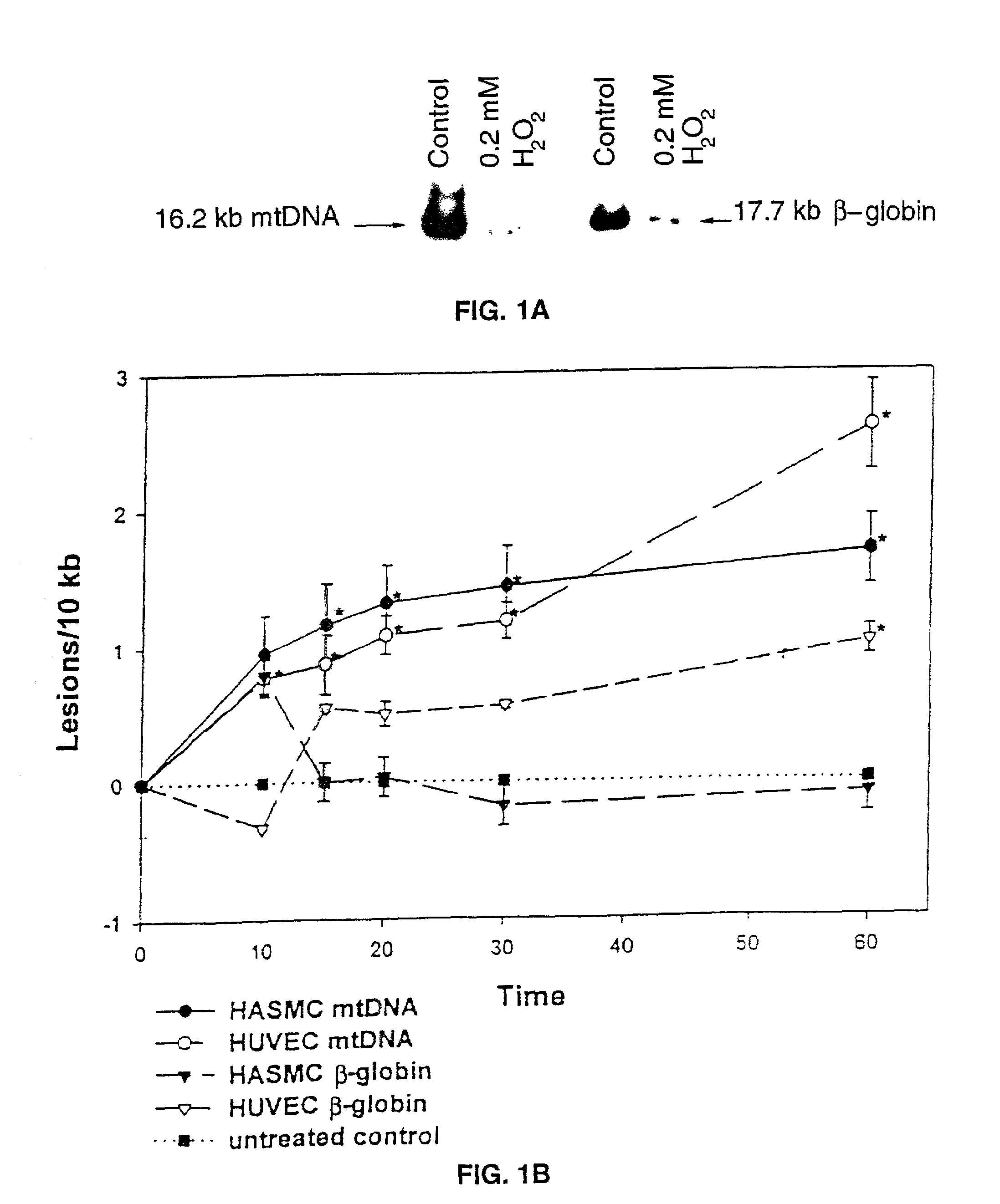
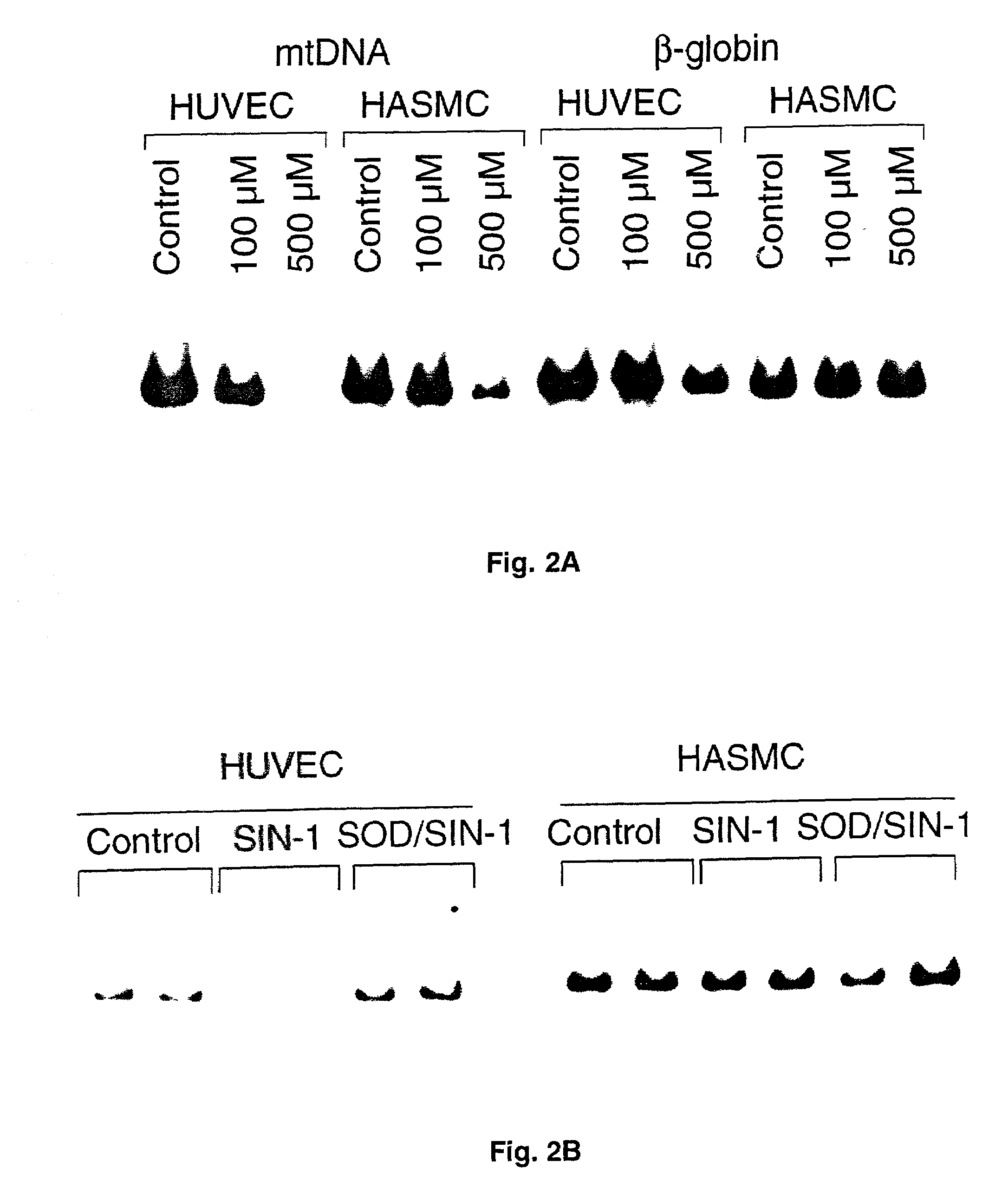
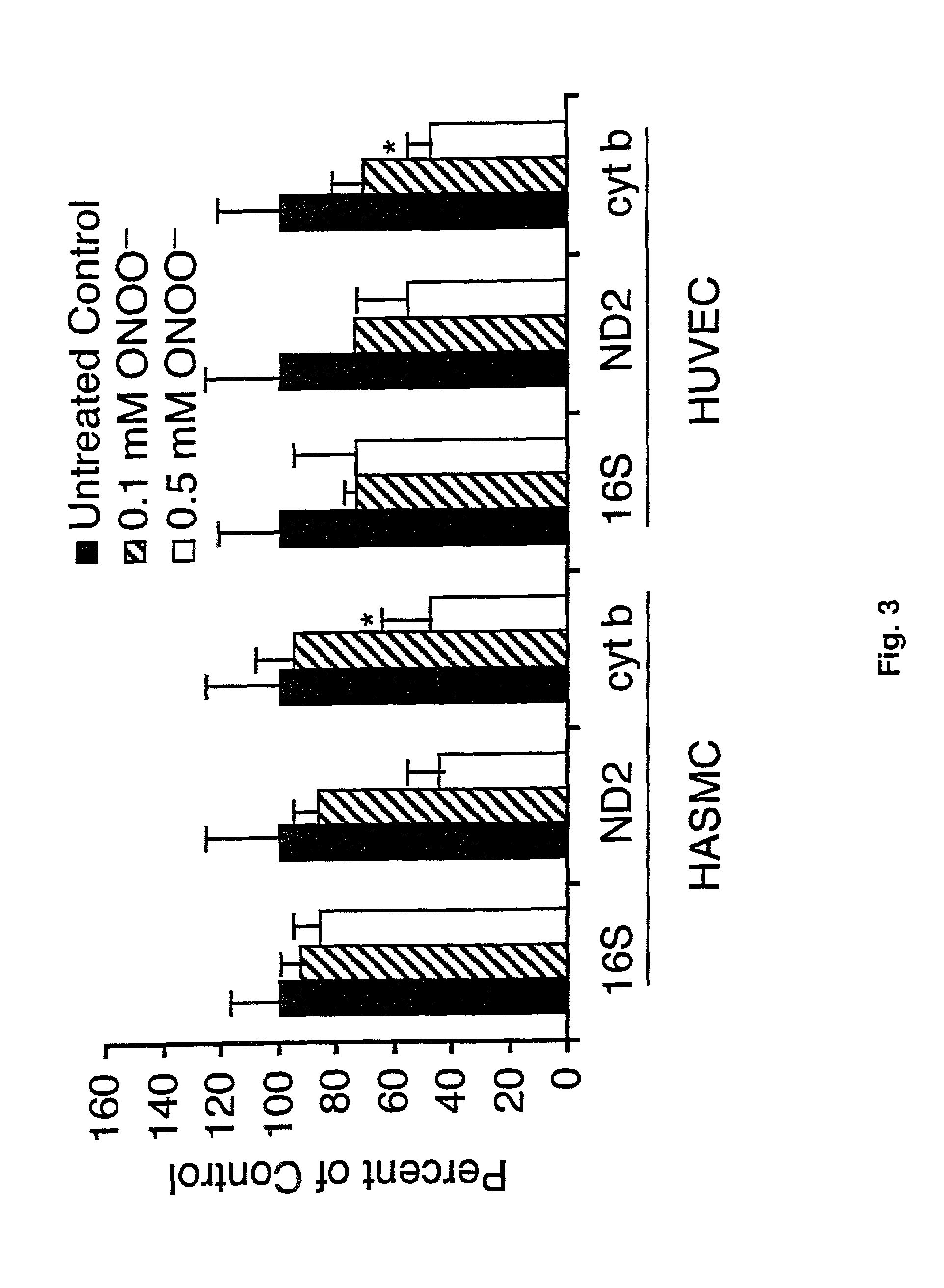
Mitochondrial DNA damage as a predictor of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease
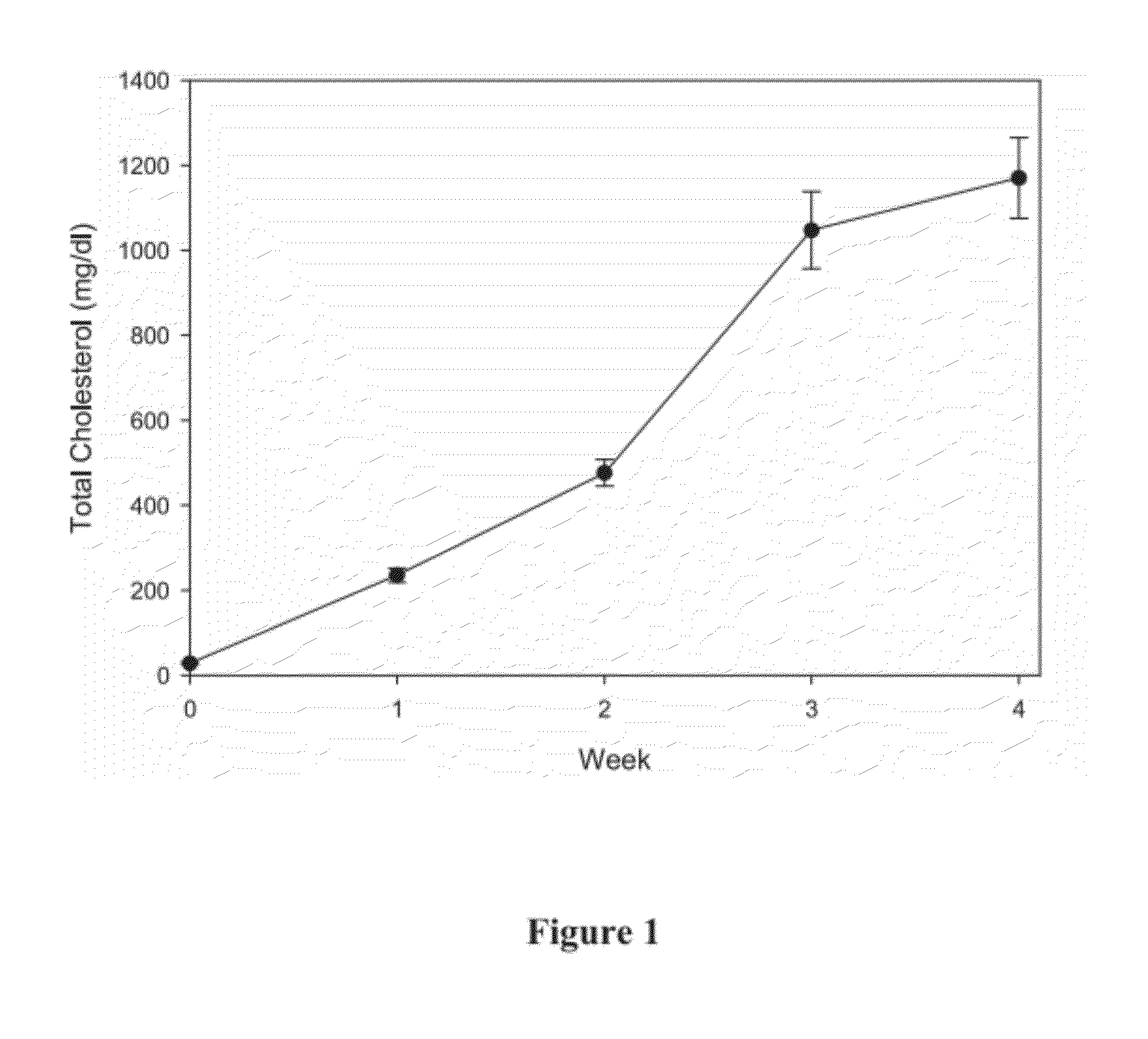
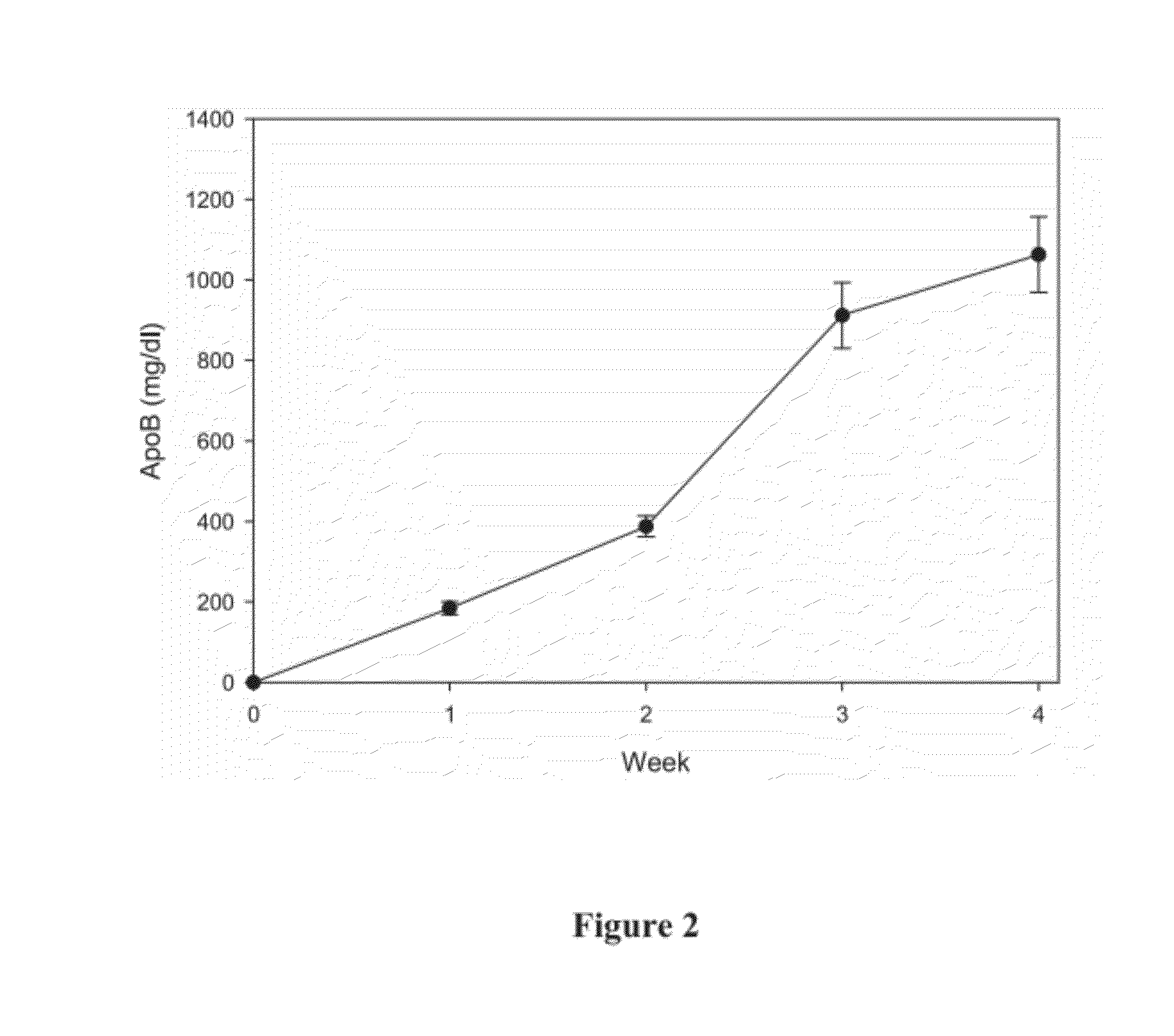
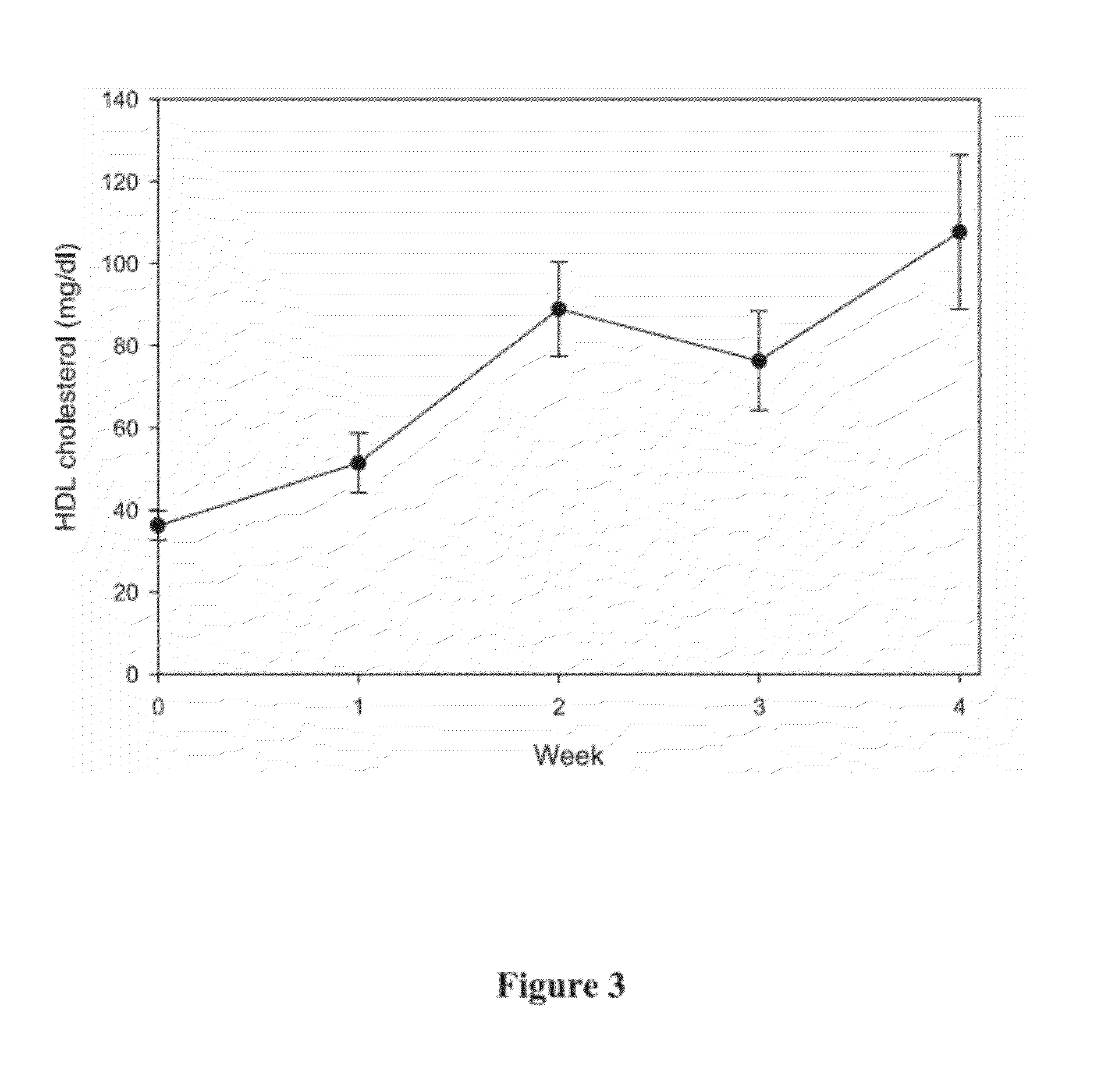
The present invention demonstrates that mitochondrial DNA damage occurs prior to, or simultaneous with, atherosclerotic lesion development, that aortic mitochondrial DNA damage increases with age, and that genotype and diet both influence the level of mitochondrial DNA damage. Hence, the present invention demonstrates that mitochondrial DNA damage occurs early in atherosclerosis, and may be an initiating event in atherogenesis, and provides methods to predict coronary atherosclerotic heart disease based upon the amount of mitochondrial DNA damage.
Owner:RES DEVMENT FOUND
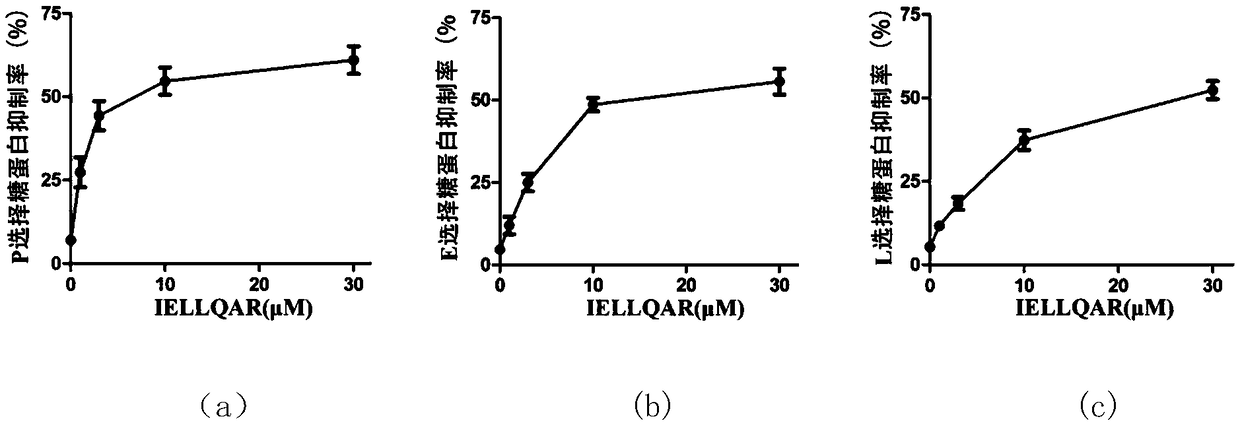
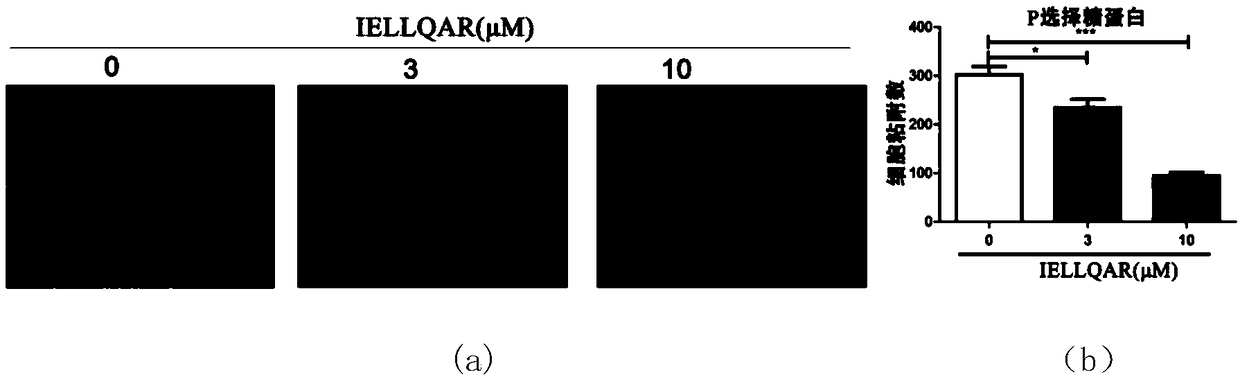
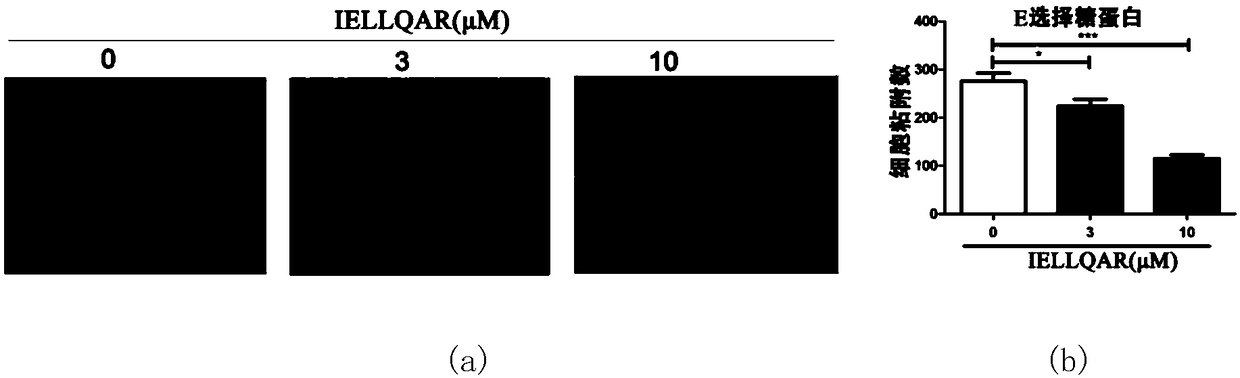
Application of IELLQAR as medicine for preventing and treating atherosclerosis diseases
ActiveCN109106940ADelay progressReduce infiltrationPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderInflammatory factorsAtheroma
Owner:FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF DALIAN MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and apparatus for localized administration of inhibitory moieties to a patient
Owner:ABBOTT LAB VASCULAR ENTERPRISE
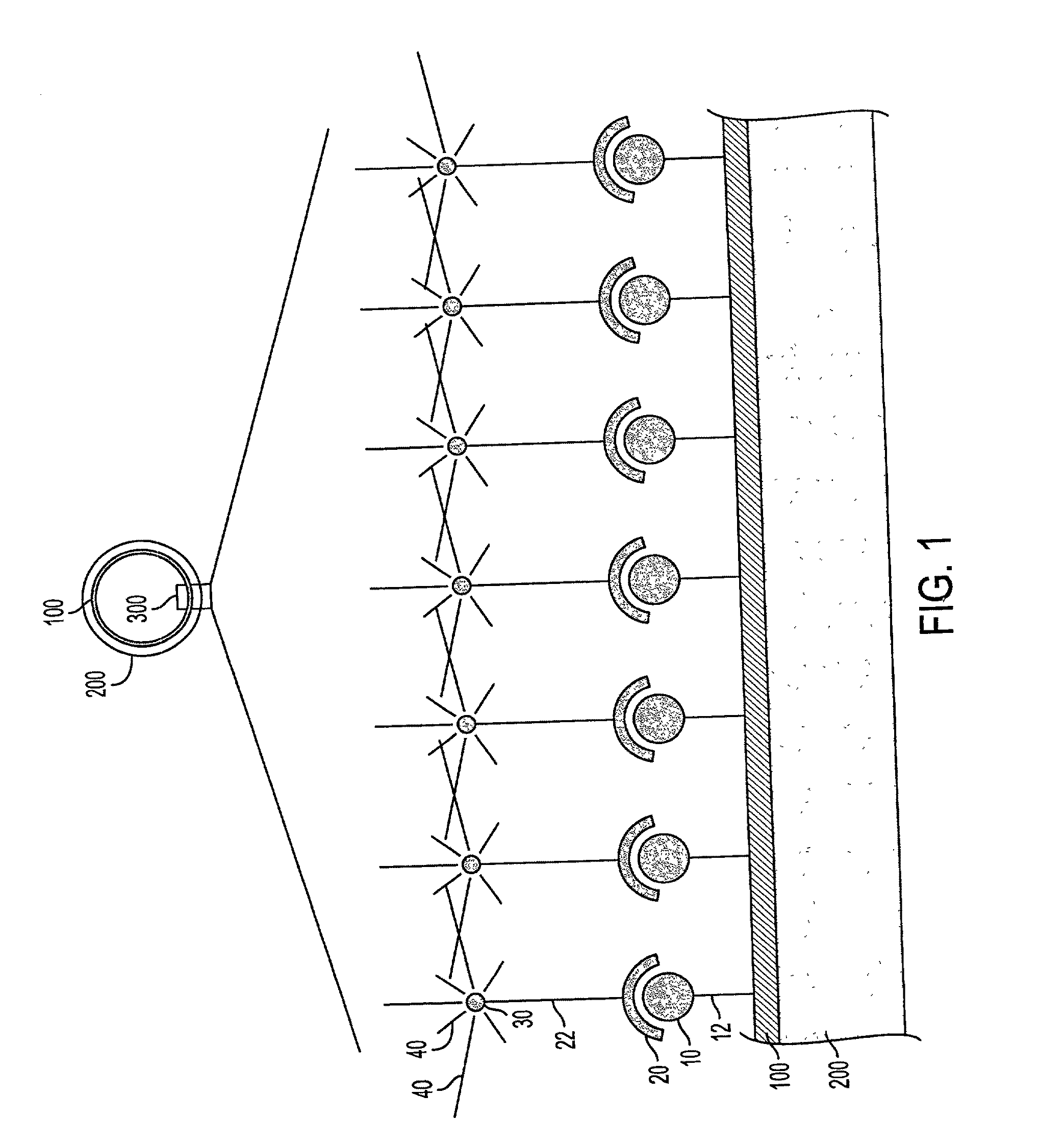
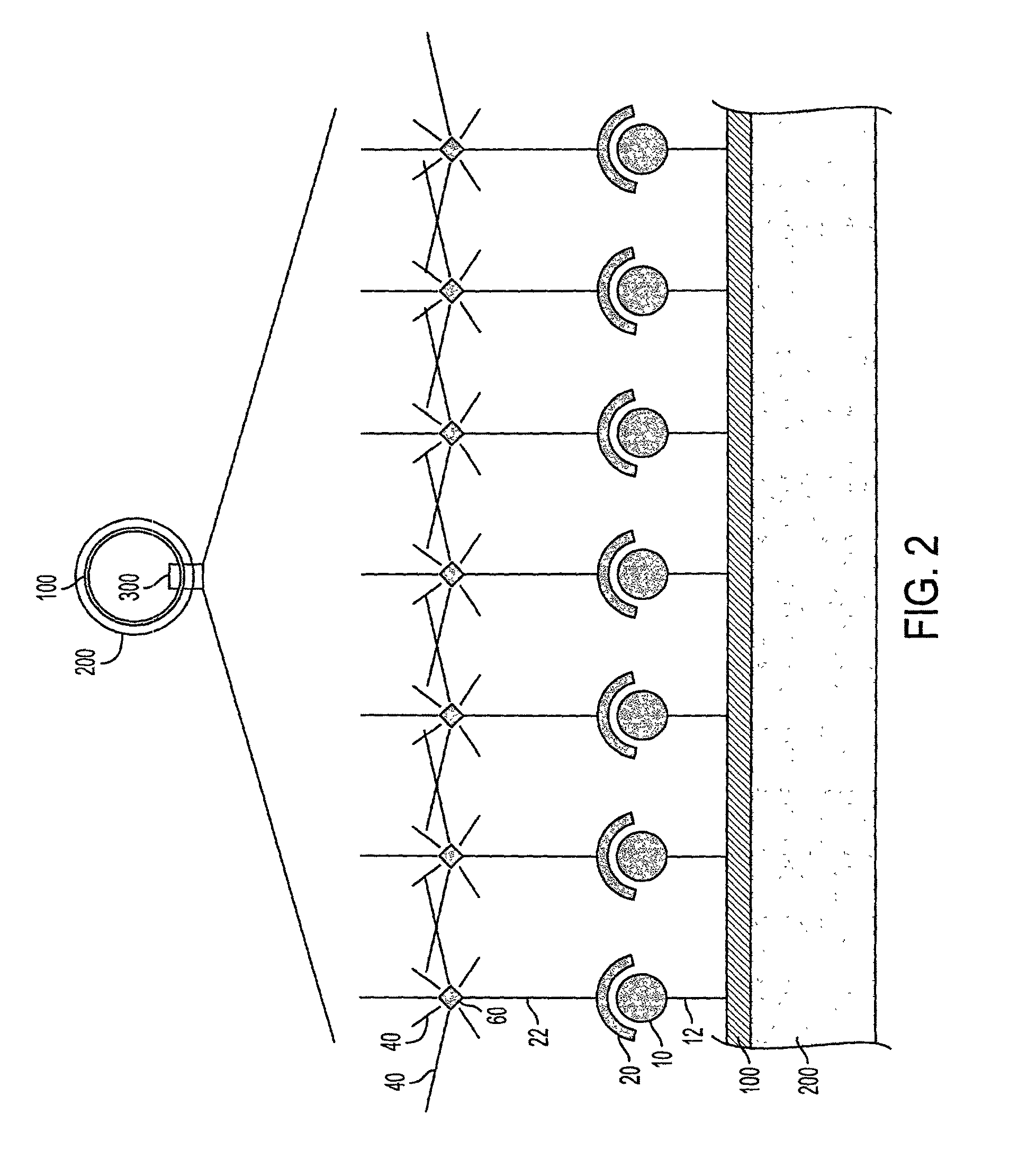
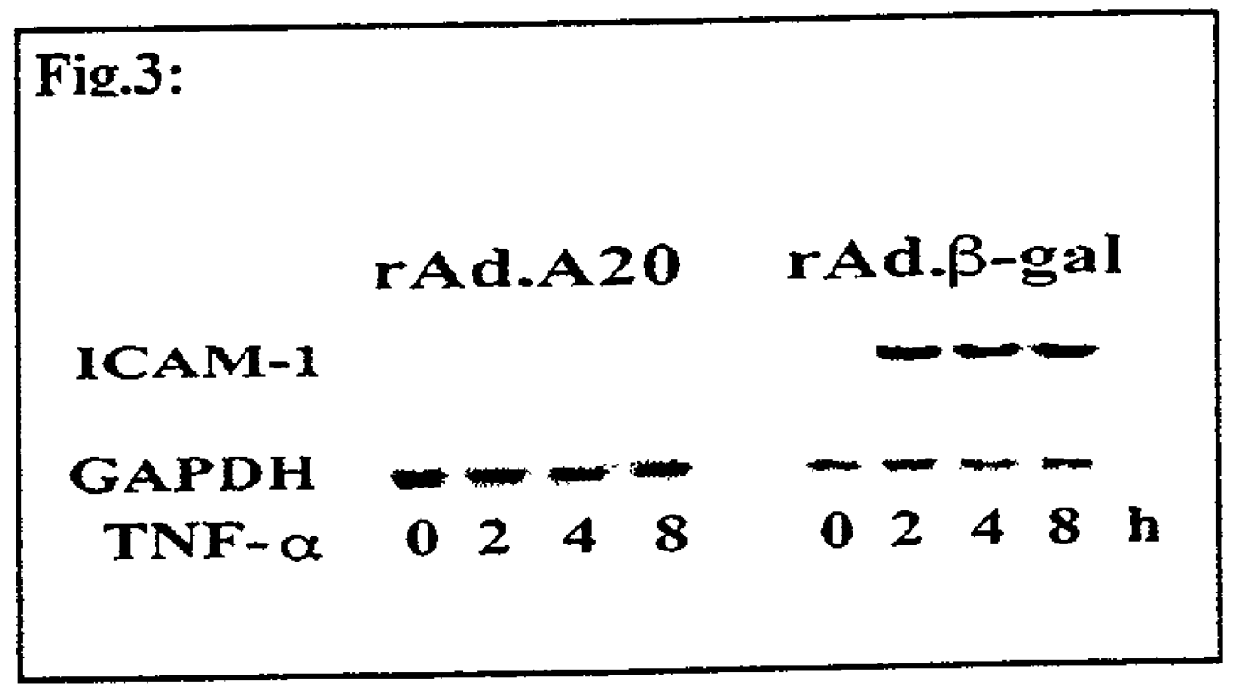
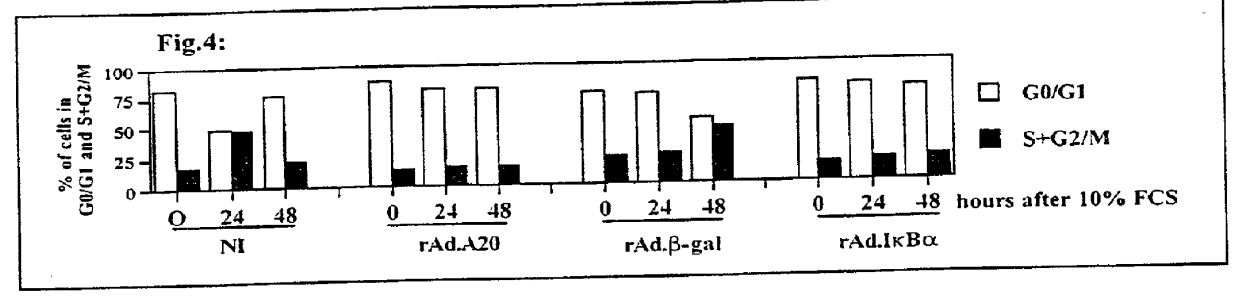
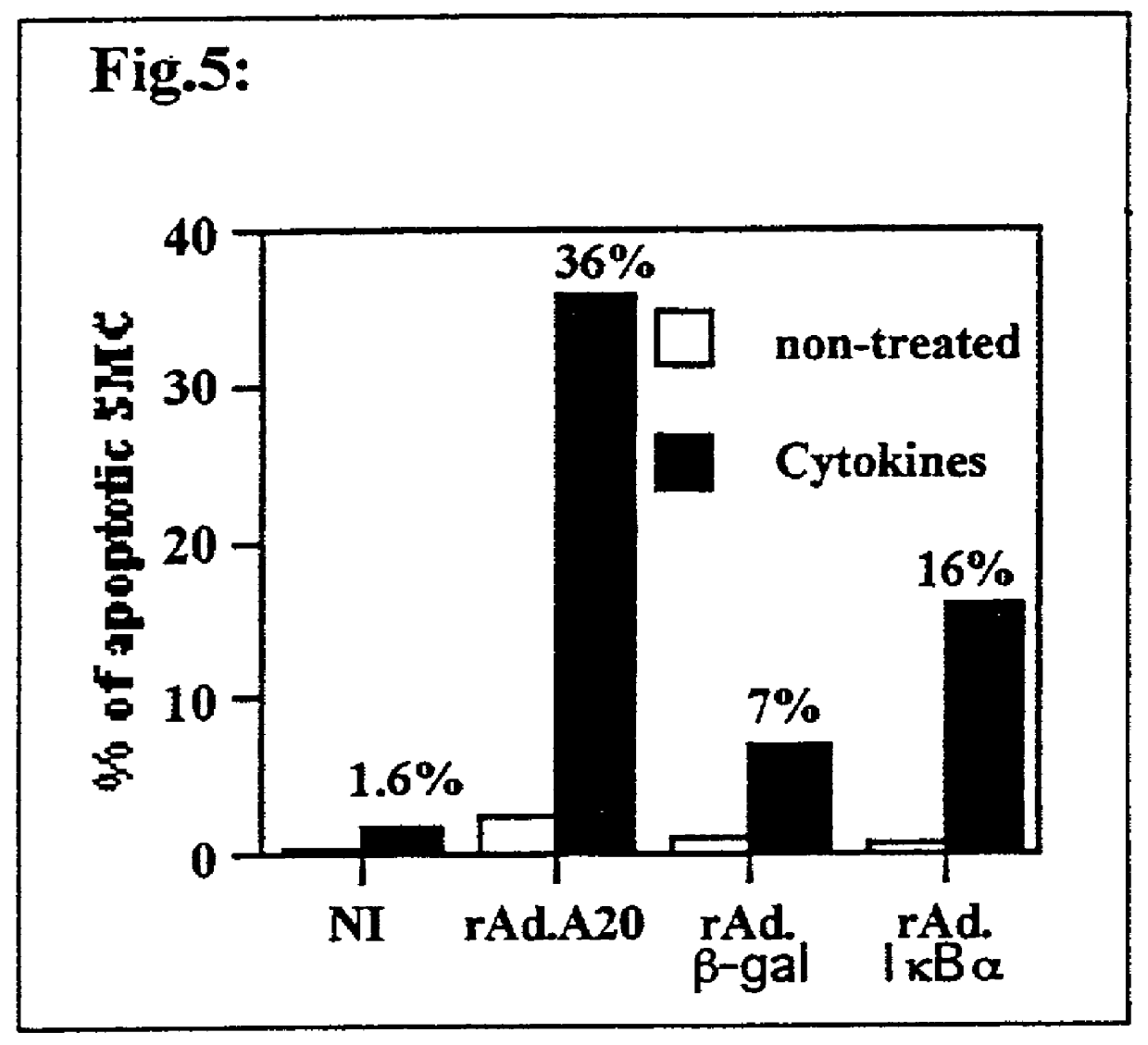
Use of pro-apoptotic factors in treatment of atherosclerosis
InactiveUS20010053769A1Reduce inflammationIncreased apoptosisBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAtheromaLesion
The present invention features a novel method of treating vascular disease that involves modifying smooth muscle cells to express a gene encoding a protein having both anti-inflammatory and pro-apoptotic activity. Preferably, the protein of the invention also has an anti-proliferative effect in smooth muscle cells. In general, the method is useful in preparing vascularized organs and vessels for transplant into a patient. Alternatively, the present invention can be applied to treat atherosclerotic lesions in damaged vessels.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com