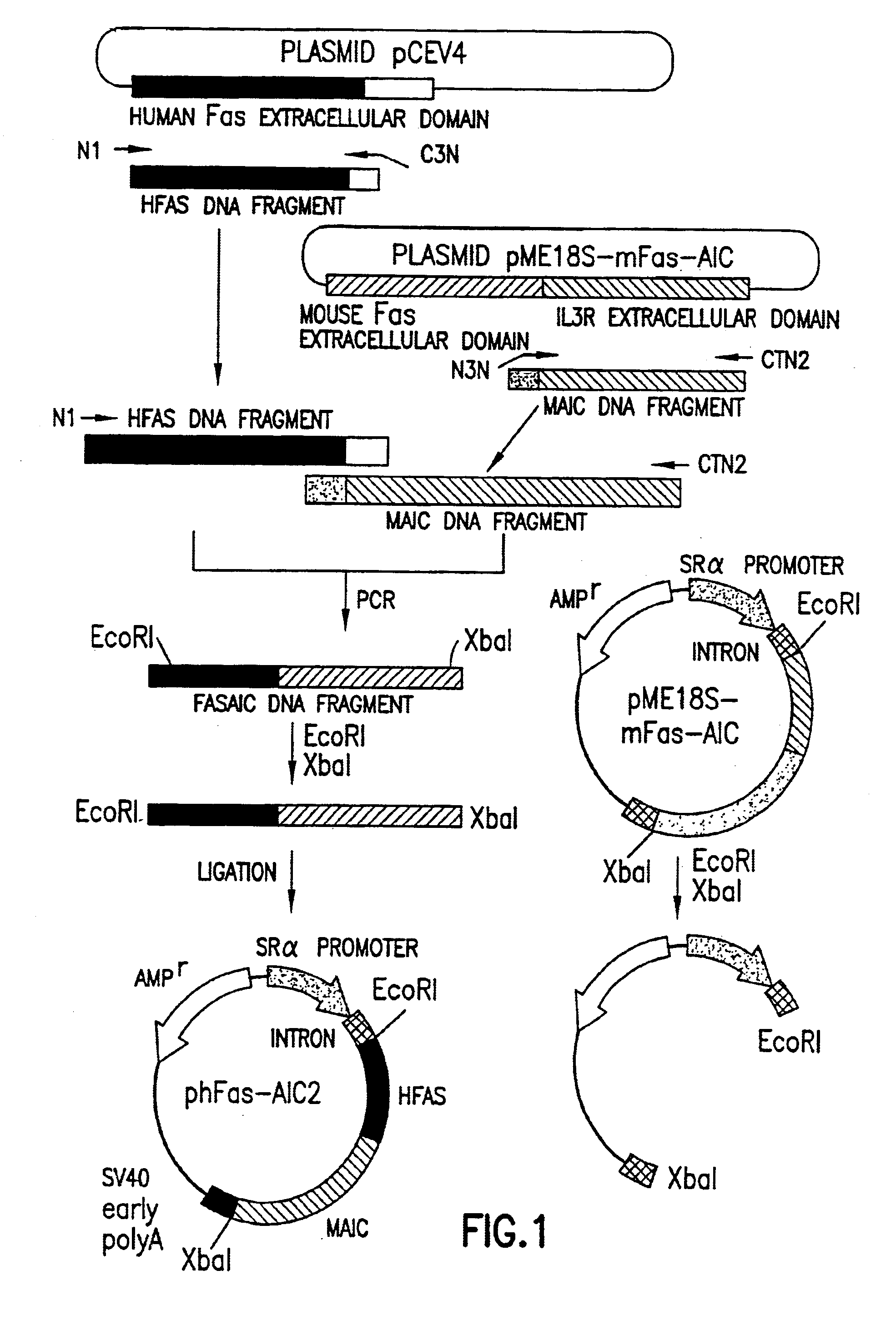
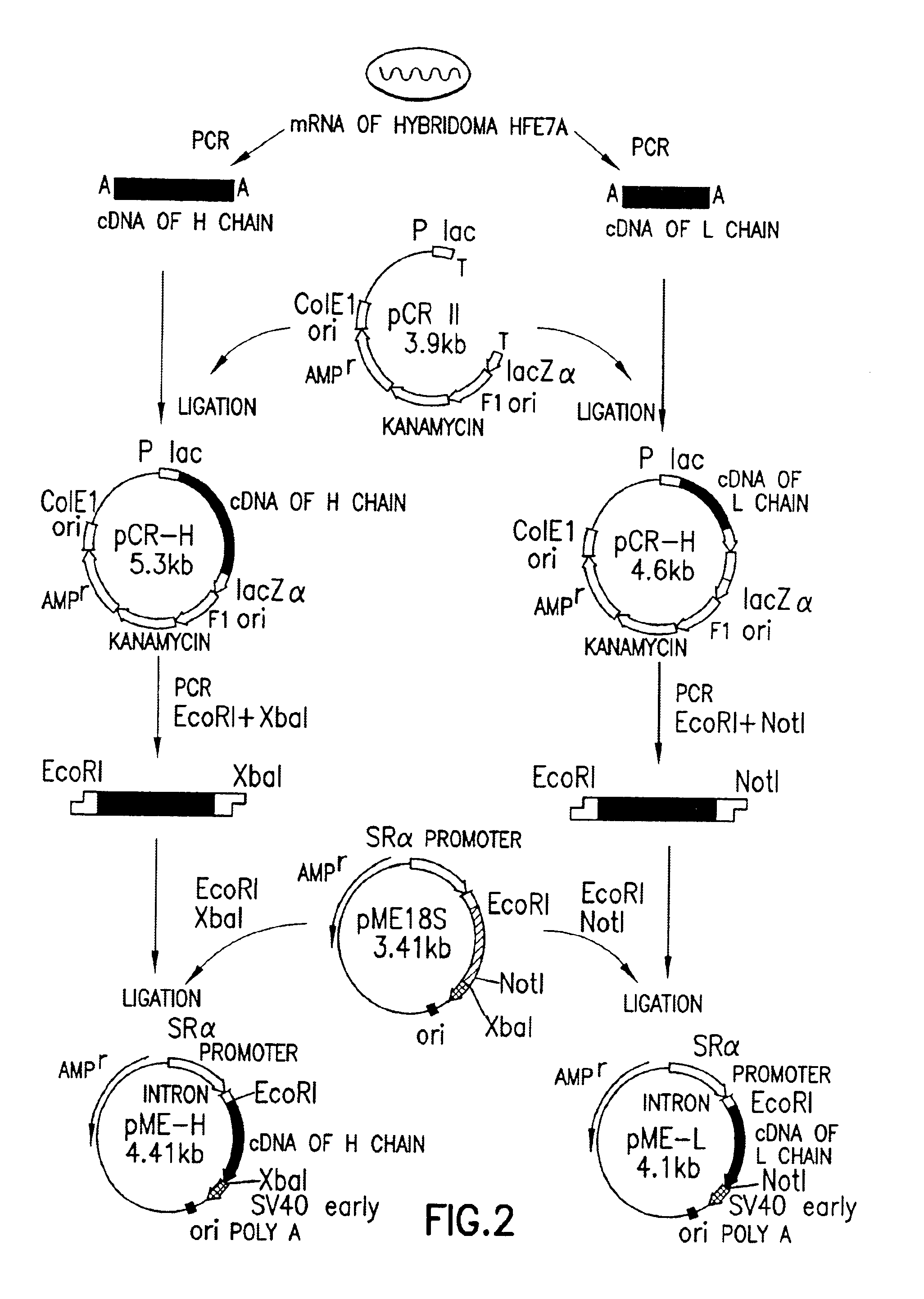
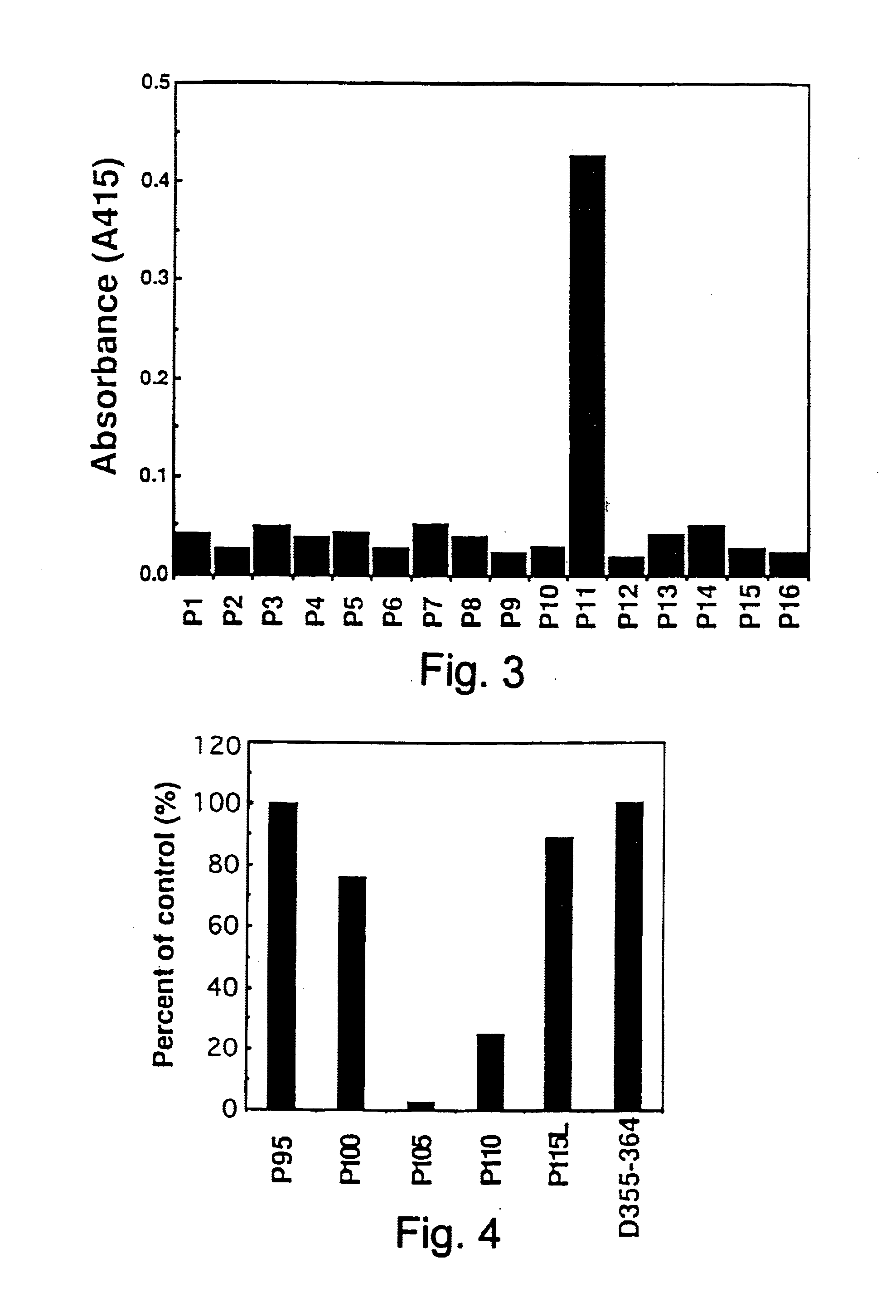
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Fas ligand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
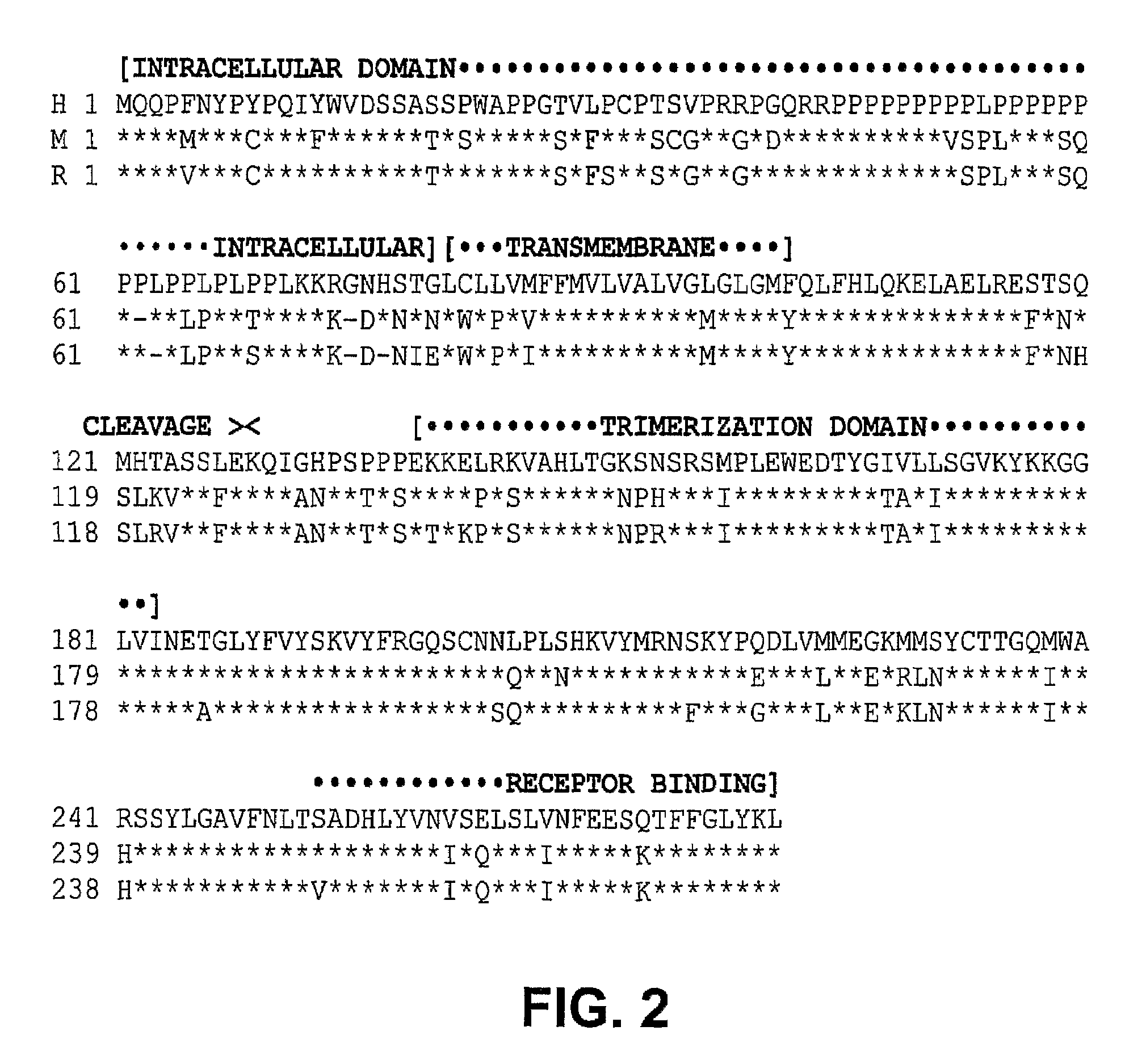
Fas ligand (FasL or CD95L or CD178) is a type-II transmembrane protein that belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) family. Its binding with its receptor induces apoptosis. Fas ligand/receptor interactions play an important role in the regulation of the immune system and the progression of cancer.
Anti-Fas antibodies
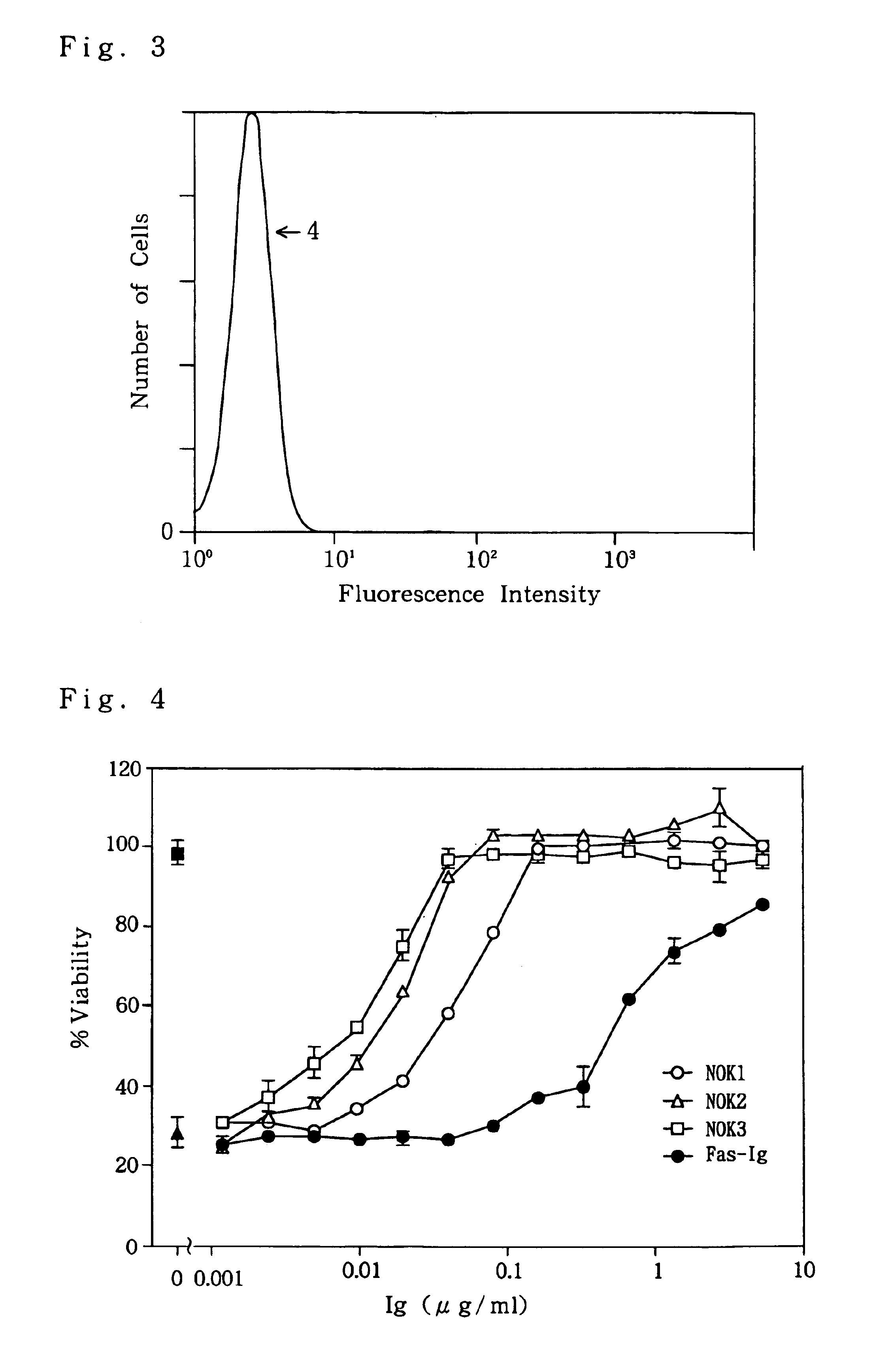
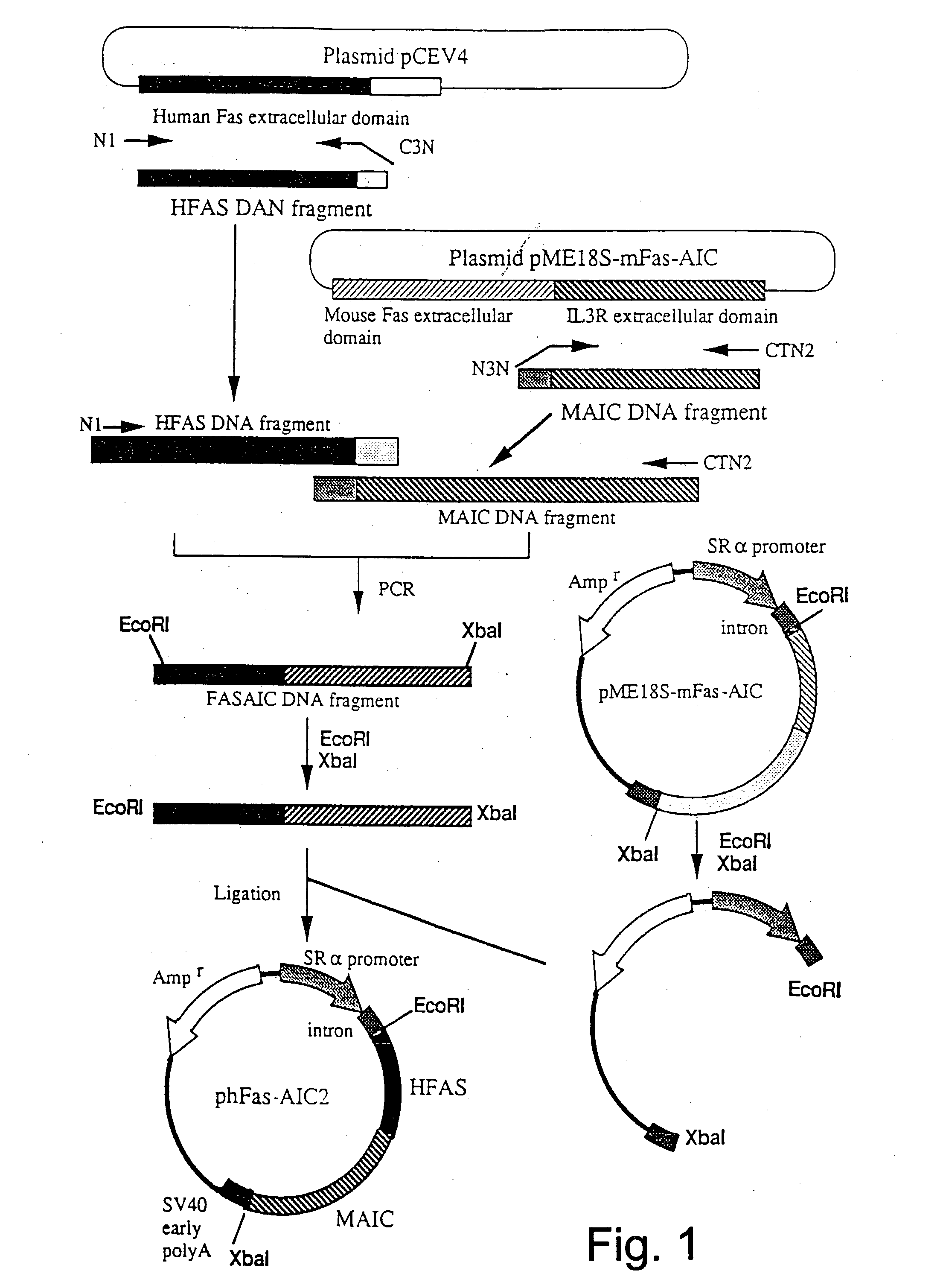
Anti-Fas antibodies which are cross-reactive with mouse and human Fas and are useful in the treatment of conditions attributable to abnormalities in the Fas / Fas ligand system.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
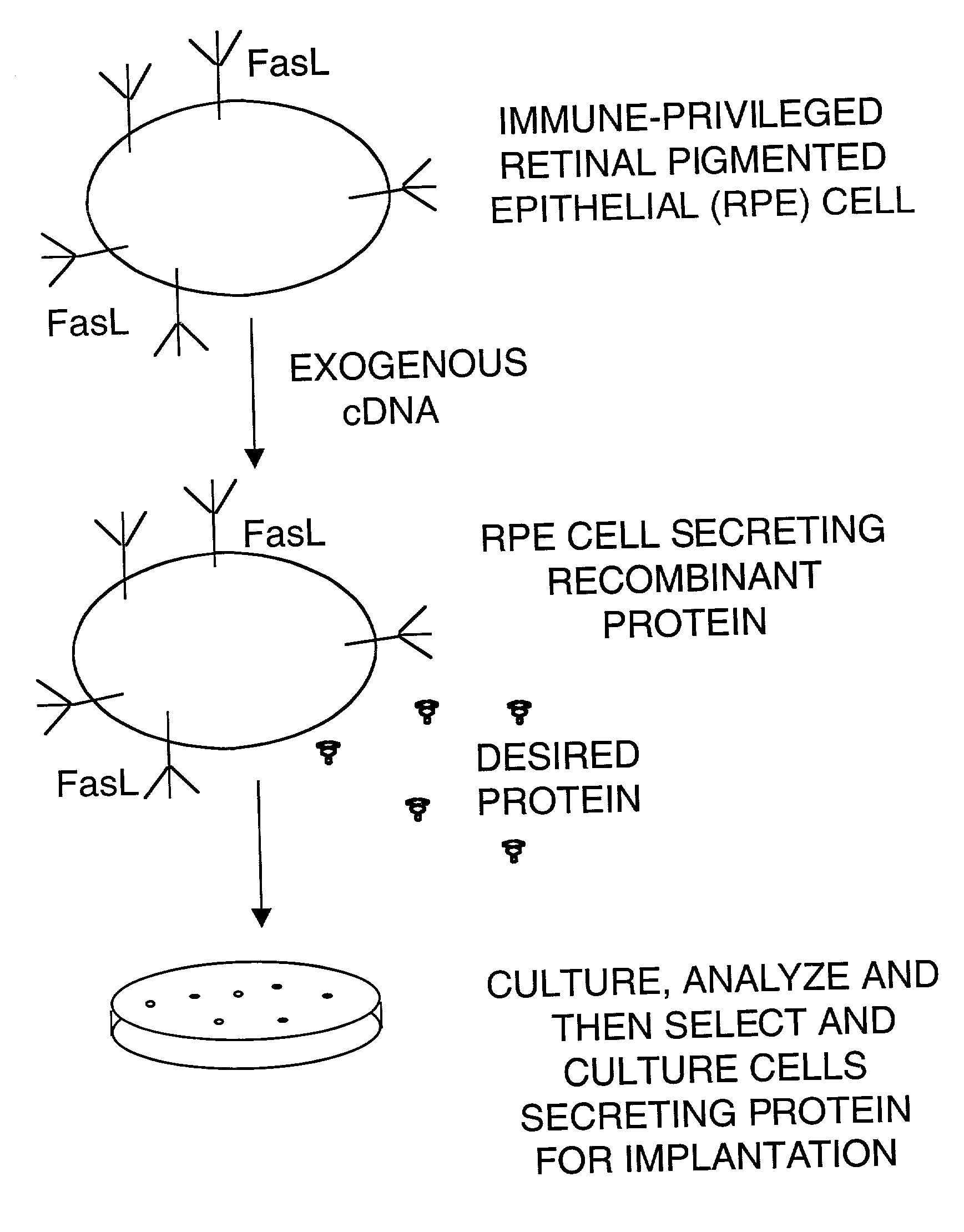
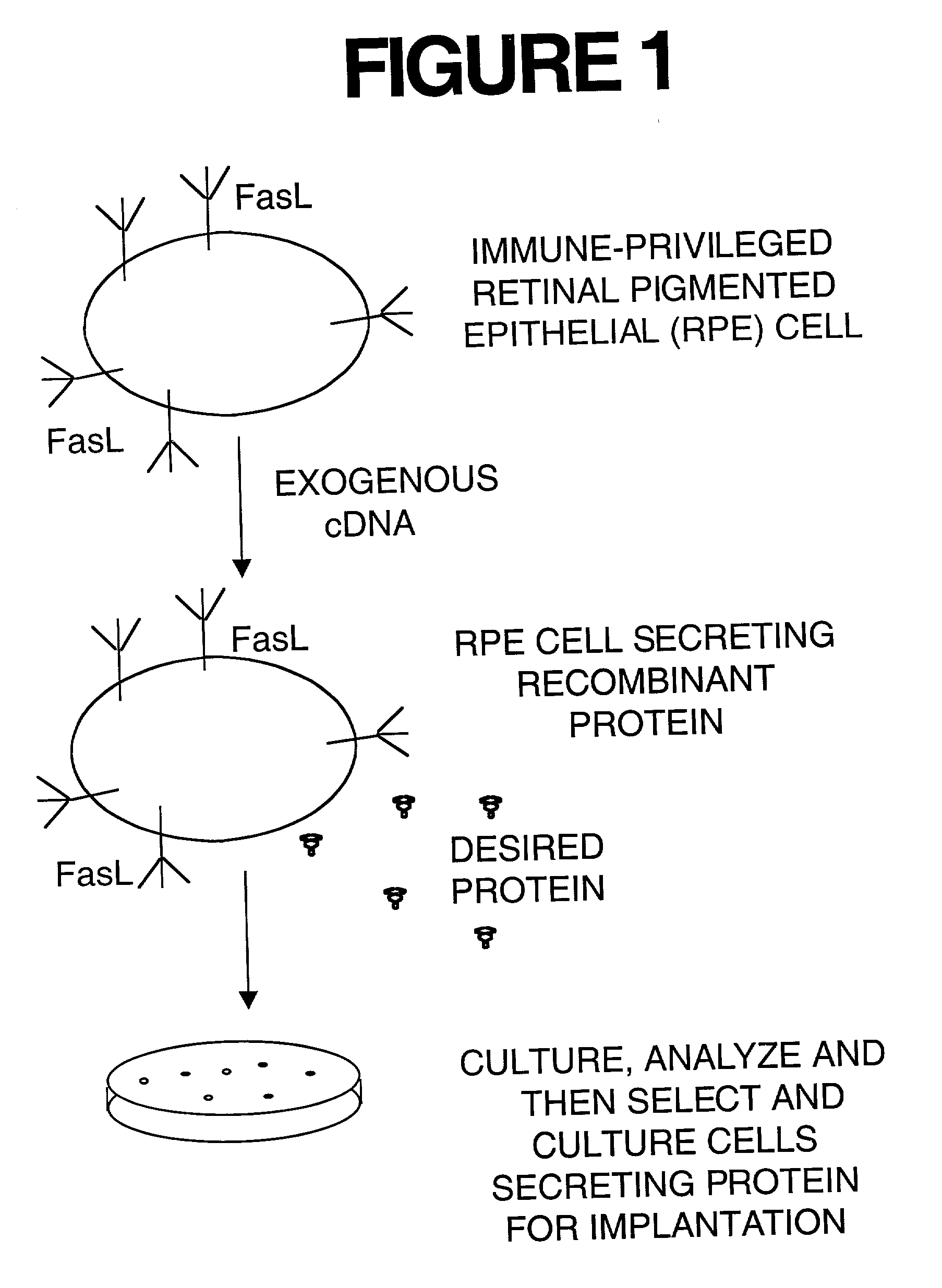
Immune privileged cells for delivery of proteins and peptides
InactiveUS20040086494A1Improve survivalAvoid reactionBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsFas ligandCell separation
Methods for sustained delivery of biologically active proteins or peptides to mammals are disclosed. Specific types of immune-privileged allogeneic or xenogenic donor cells that are naturally immune privileged are genetically modified in vitro to express or secrete the proteins or peptides. The genetically modified donor cells are subsequently implanted into host mammals and utilized for sustained delivery of biologically active proteins or peptides in vivo. The donor cells so utilized are those that inherently possess immune privilege due at least partly to the expression of Fas ligand. Methods for cell isolation, purification, tissue culture expansion, cryopreservation, gene transfer, transgene and Fas ligand expression, cell implantation, and measurement of immune responses of host animals are described.
Owner:MANDALMED
Mutant Forms of Fas Ligand and Uses Thereof
The invention provides for DNA encoding Fas ligand muteins and chimeras and the proteins encoded thereby. The invention further includes the use of DNA and vectors to produce transformed cells expressing the mutant or chimeric Fas ligand. When the Fas ligand of the invention is a non cleavable form, the cells expressing the Fas ligand are useful in vitro for identifying Fas expressing cells or in vivo for reducing populations of Fas expressing cells. Thus, in other embodiments, the present invention is also directed to a method for treating a patient, for example a mammal, for autoimmune disease or transplant rejection by administering a Fas ligand therapeutic agent. The therapeutic agent is a polypeptide, a polynucleotide encoding the polypeptide or a small molecule. The polypeptides include full-length Fas ligand polypeptide, or a biologically active variant, derivative, portion, fusion or peptide thereof.
Owner:CHU KETING
Humanized immunoglobulin reacting specifically with Fas ligand or active fragments thereof and region inducing apoptosis originating in Fas ligand
InactiveUS6777540B1Antibody mimetics/scaffoldsNGF/TNF-superfamilyDiagnostic agentMonoclonal antibody
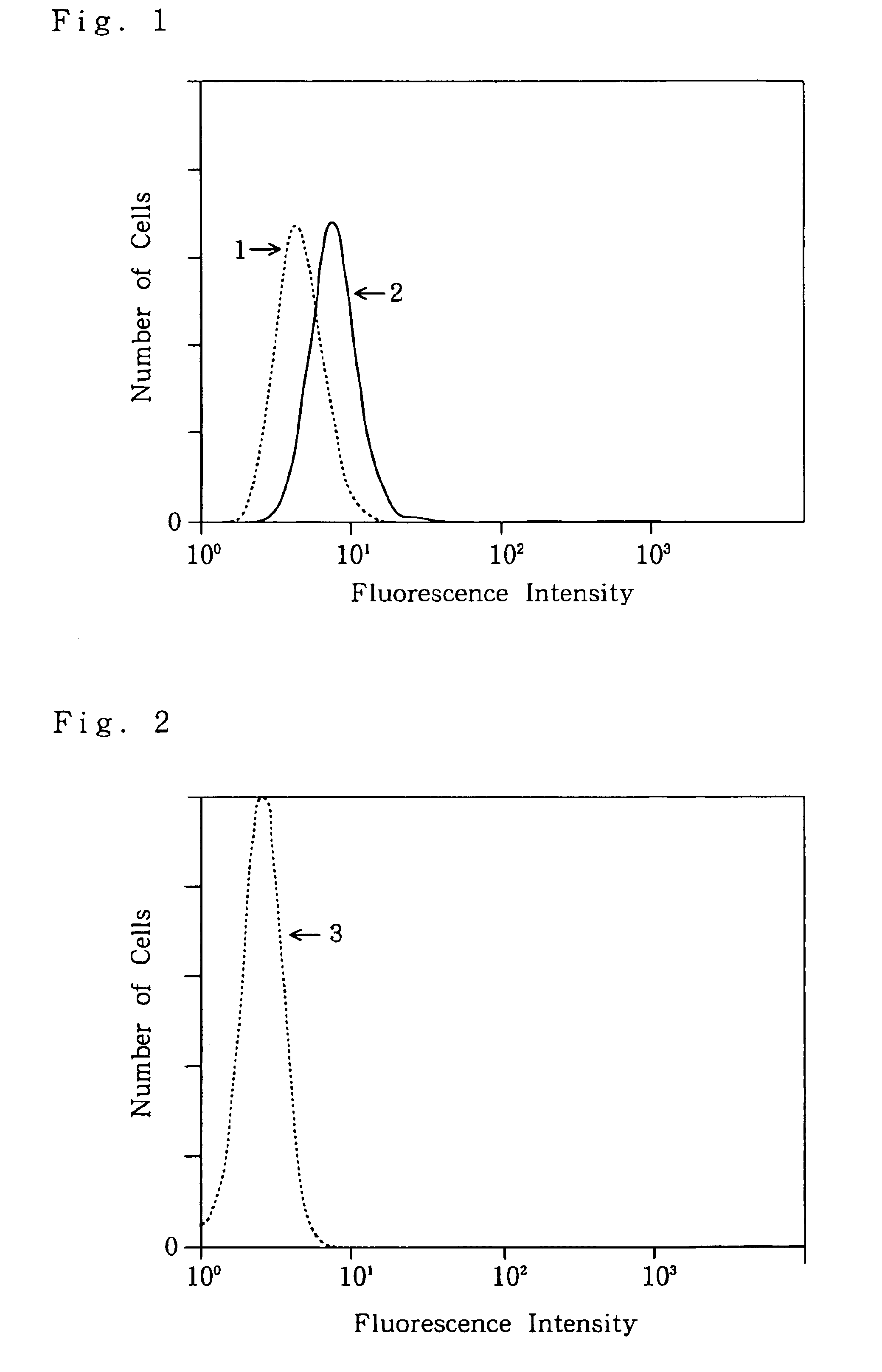
Novel humanized immunoglobulins and active fragments thereof which are specifically reactive to Fas ligand are provided, and a site on Fas ligand which is important to inhibit apoptosis induced by the Fas-Fas ligand interaction against Fas-expressing cells is demonstrated. The novel humanized immunoglobulins and active fragments thereof which are specifically reactive to Fas ligand are prepared from hybridomas which produce monoclonal antibodies specifically reactive to Fas ligand, via recombinant DNA techniques. The humanized immunoglobulins can inhibit the physiological reactions between Fas ligand and Fas such as apoptosis. Further, identification of the site which is on Fas ligand and responsible for apoptosis induction allows creation of recombinant proteins or peptides which are specifically reactive to the amino acids within the site so as to inhibit apoptosis, and to find new therapeutic or diagnostic agents.
Owner:OKUMURA KO
Use of certain drugs for treating nerve root injury
The present invention relates to a method and a pharmaceutical composition for treatment of nerve disorders comprising administration of a therapeutically effective dosage of at least two substances selected from the group consisting of TNF inhibitors, IL-1 inhibitors, IL-6 inhibitors, IL-8 inhibitors, FAS inhibitors, FAS ligand inhibitors, and IFN-gamma inhibitors. Preferably, at least one of the substances is a TNF inhibitor.
Owner:SCIATICON
Monoclonal antibody reacting specifically reacting with Fas ligand and production process thereof
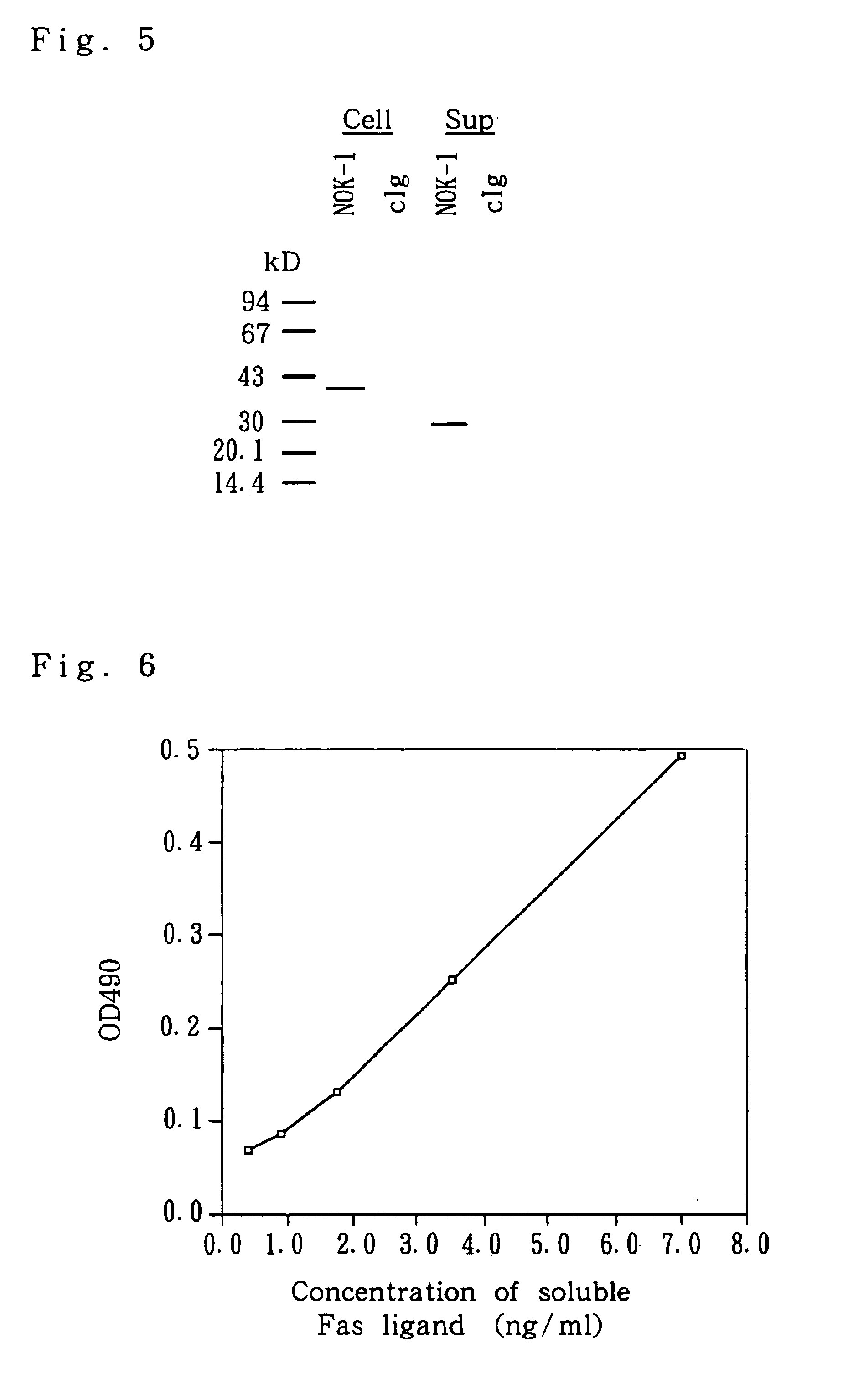
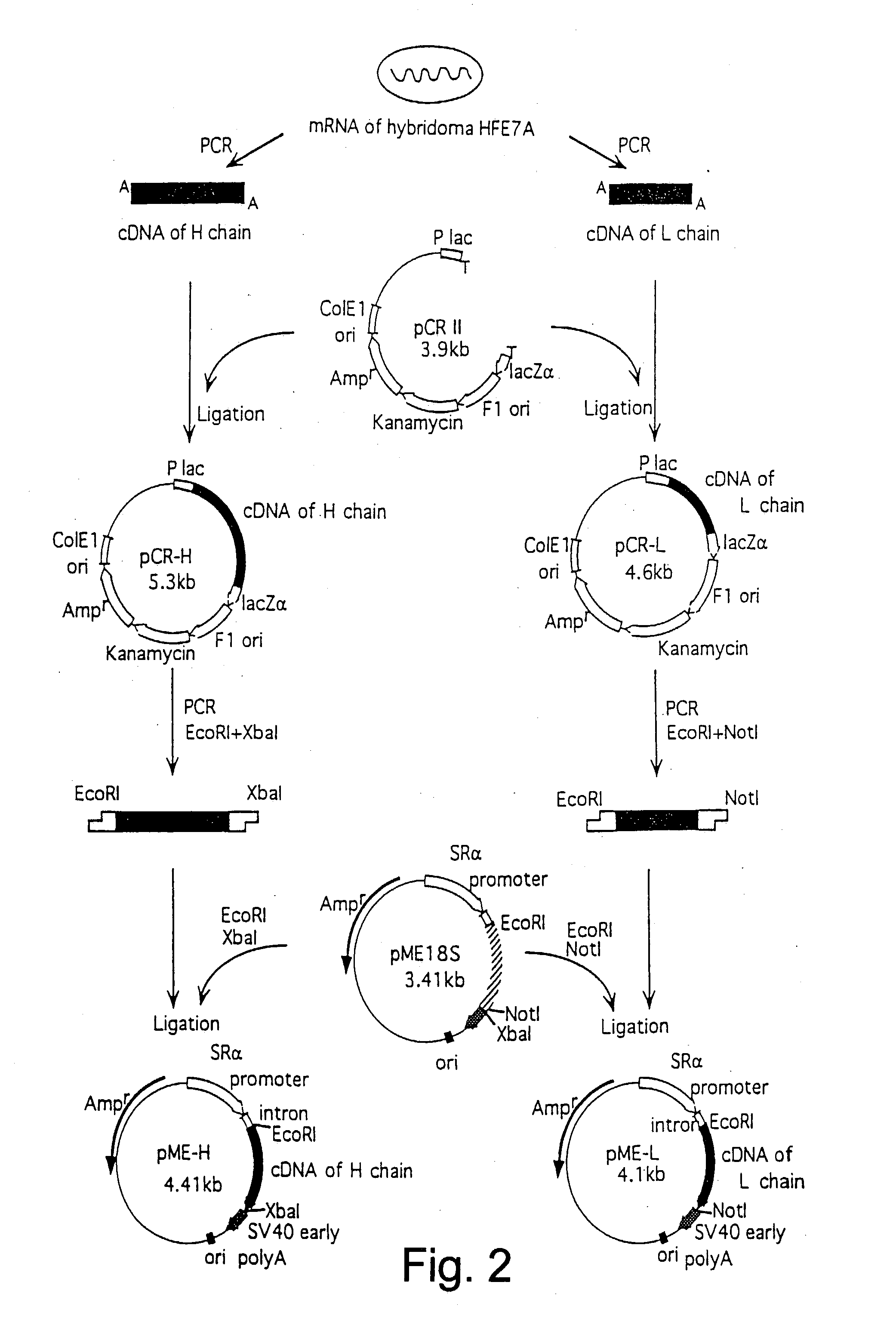
The invention provides monoclonal antibodies, which specifically react with a Fas ligand, or active fragments thereof, a production process of the monoclonal antibodies, which specifically react with a Fas ligand, hybridomas separately producing a monoclonal antibody, which specifically reacts with a Fas ligand present on a cell surface, a method of detecting a Fas ligand in a solution, and a kit for use in detecting a Fas ligand, comprising plurality of monoclonal antibodies against Fas ligand in combination.
Owner:KO OKUMURA
PD-L1 and PD-L2-based fusion proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS9657082B2Reduces severity of symptomIncrease frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseExtracellular Structure
Provided are fusion proteins comprising a first domain and a second domain, wherein the first domain comprises a polypeptide that binds to and triggers PD-1 and the second domain comprises a polypeptide that binds to and triggers a TRAIL receptor or Fas. In some embodiments, the polypeptide that binds to and triggers PD-1 comprises at least a portion of the extracellular domain of PD-L1 or PD-L2 and the second domain comprises at least a portion of the extracellular domain of TRAIL or Fas ligand. Also provided are methods for treating autoimmune, alloimmune or inflammatory diseases, and methods for treating cancer, using the fusion proteins.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Composition and method for clusterin-mediated stem cell therapy for treatment of atherosclerosis and heart failure
ActiveUS20060099194A1Reduce riskAvoid cell deathBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsOxysterolCytotoxicity
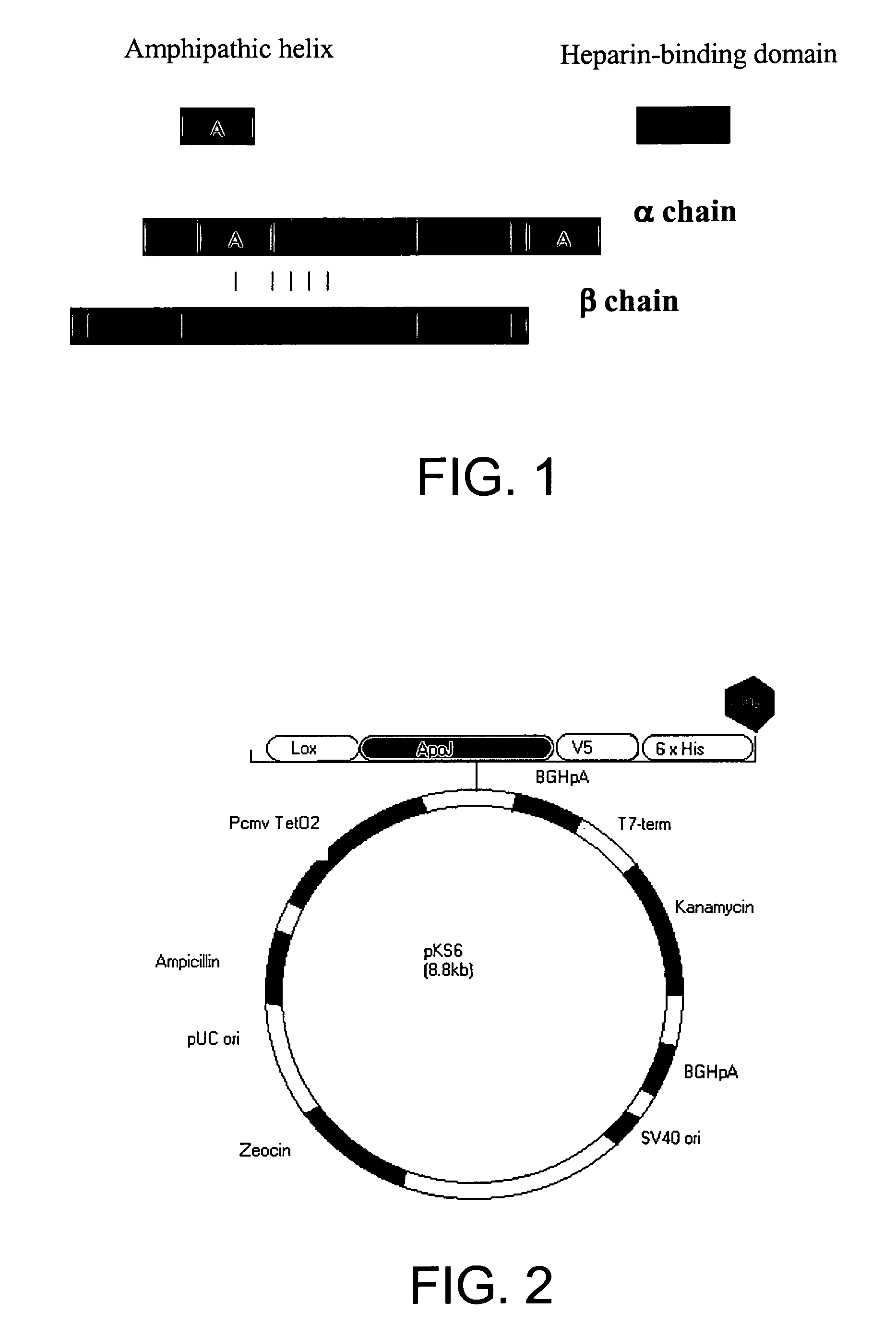
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting, deterring or preventing apoptosis of cardiac myocytes, transplanted stem cells, vascular stem cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells by means of expressing or synthesizing clusterin. Also disclosed are methods and compositions for producing recombinant clusterin, or its biologically active peptides, and for induction of clusterin-associated lipoproteins or enzymes for deterring or preventing inflammatory injury and apoptosis induced by oxLDL, oxysterols, cytokines, and Fas Ligand. Also disclosed is an induction method and composition for enhancing expression of ALDH and ALDH-associated enzymes or co-factors to prevent cytotoxicity or detoxification. Therapeutic methods providing new expression or overexpression of clusterin in vascular or cardiac tissue are expected to inhibit the formation of atherosclerotic lesions, stabilize existing atherosclerotic plaques, and repair failing or damaged cardiac tissue.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
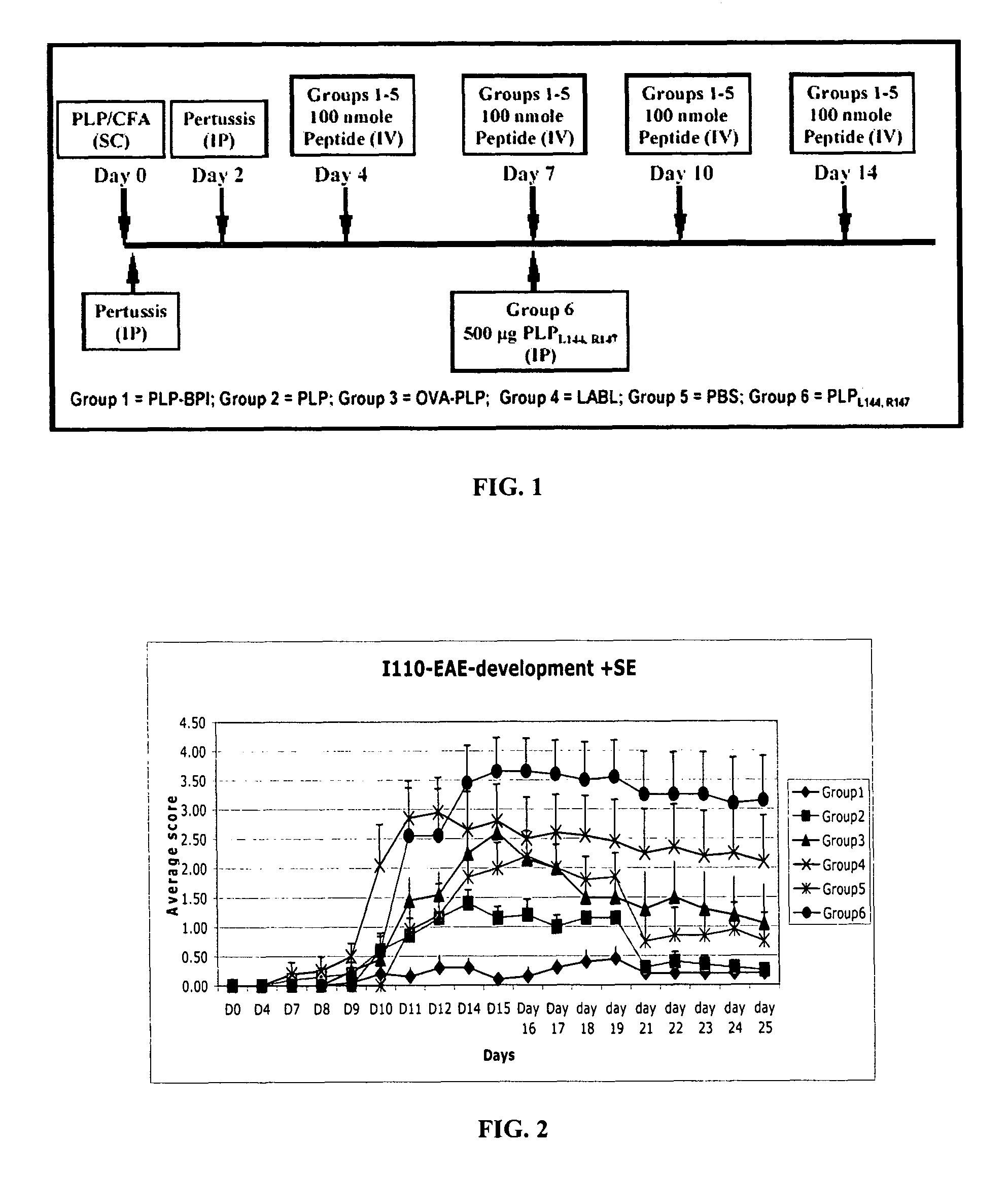
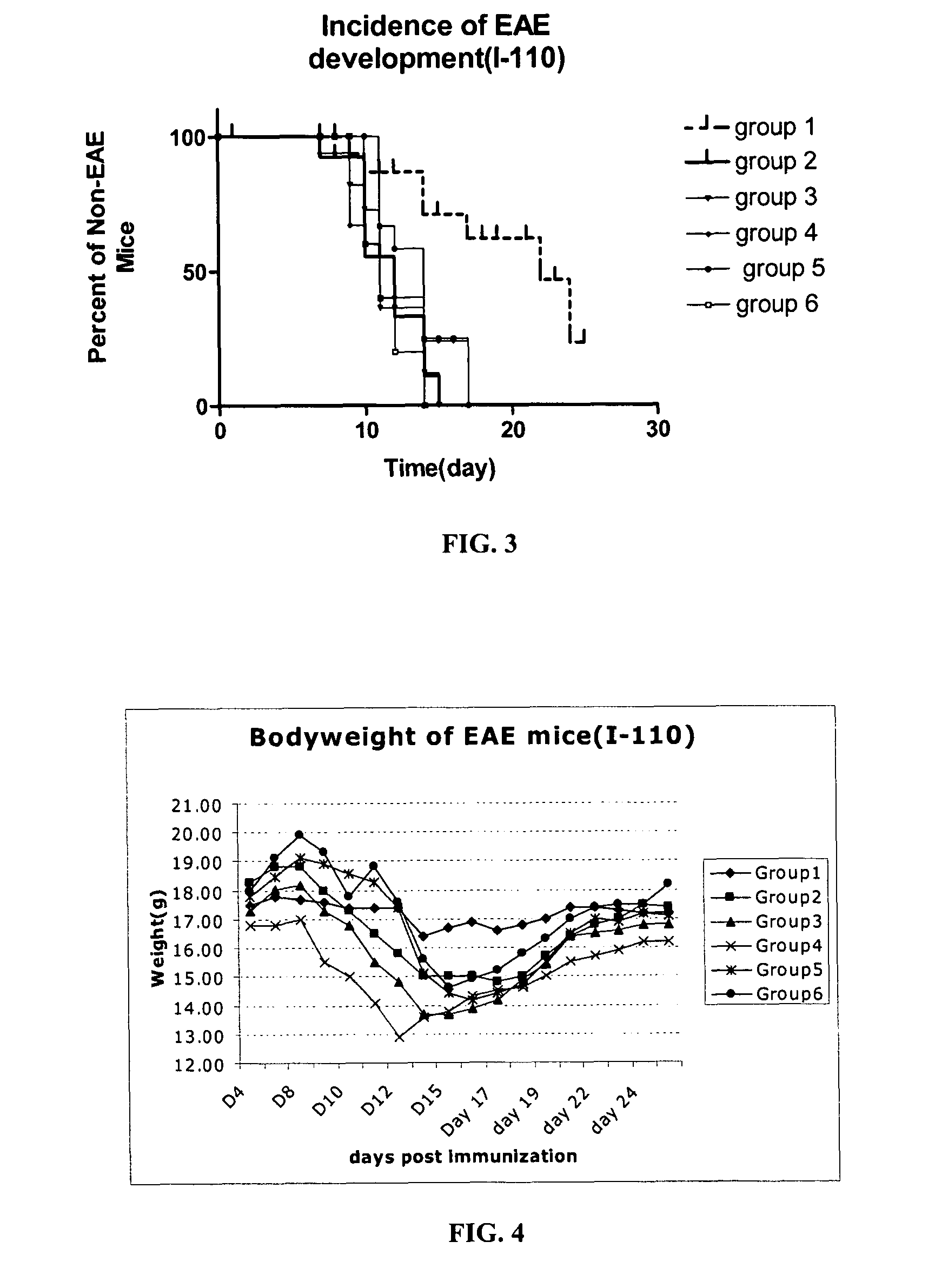
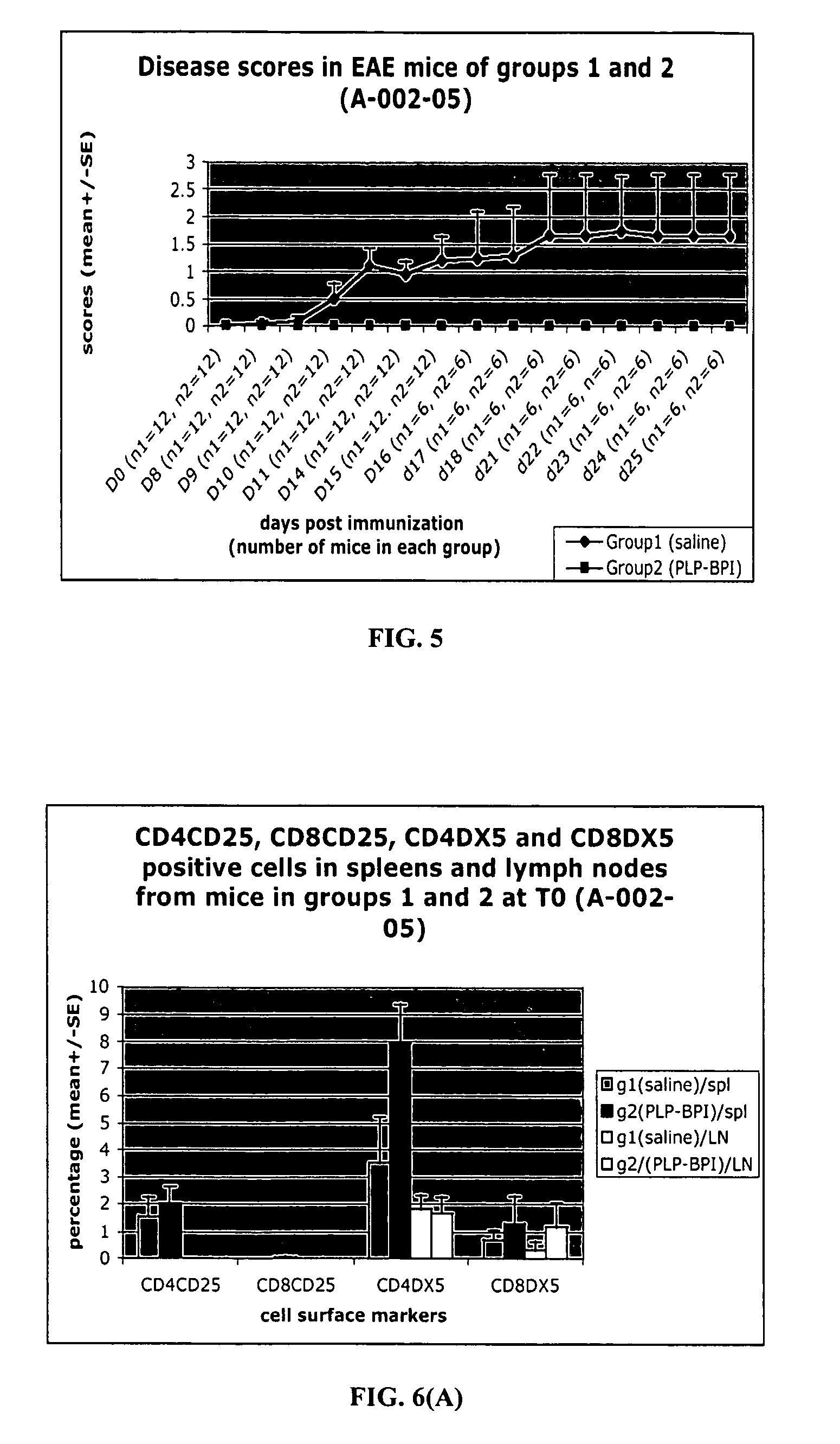
Bi-functional peptides for multiple sclerosis treatment and diagnosis
ActiveUS20080103091A1Lower immune responseReduced responseImmunoglobulin superfamilyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsBifunctionalCD11a
Novel bifunctional peptides useful in the treatment and / or diagnosis of EAE or MS. The peptides have a first peptide portion derived from an epitope of myelin proteolipid protein, myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein, or oligodendrocyte-specific peptide and a second peptide portion derived from CD11a (LFA-1 alpha subunit), CD18 (LFA-1 beta subunit), CD154 (CD40L), Fas-Ligand, or CTLA4. The carboxy and / or amino termini of the bifunctional peptides may be modified.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Fas ligand expressing hematopoietic cells for transplantation
InactiveUS20040131599A1Induced fastReduce the amount requiredBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHematopoietic cellDonor graft
The invention provides methods and compositions utilizing FasL armed donor graft cells to reduce or eliminate host allogeneic or xenogeneic graft rejection, and FasL armed host cells to reduce or eliminate graft versus host disease.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Composition of stem cells having highly expressed fas ligand
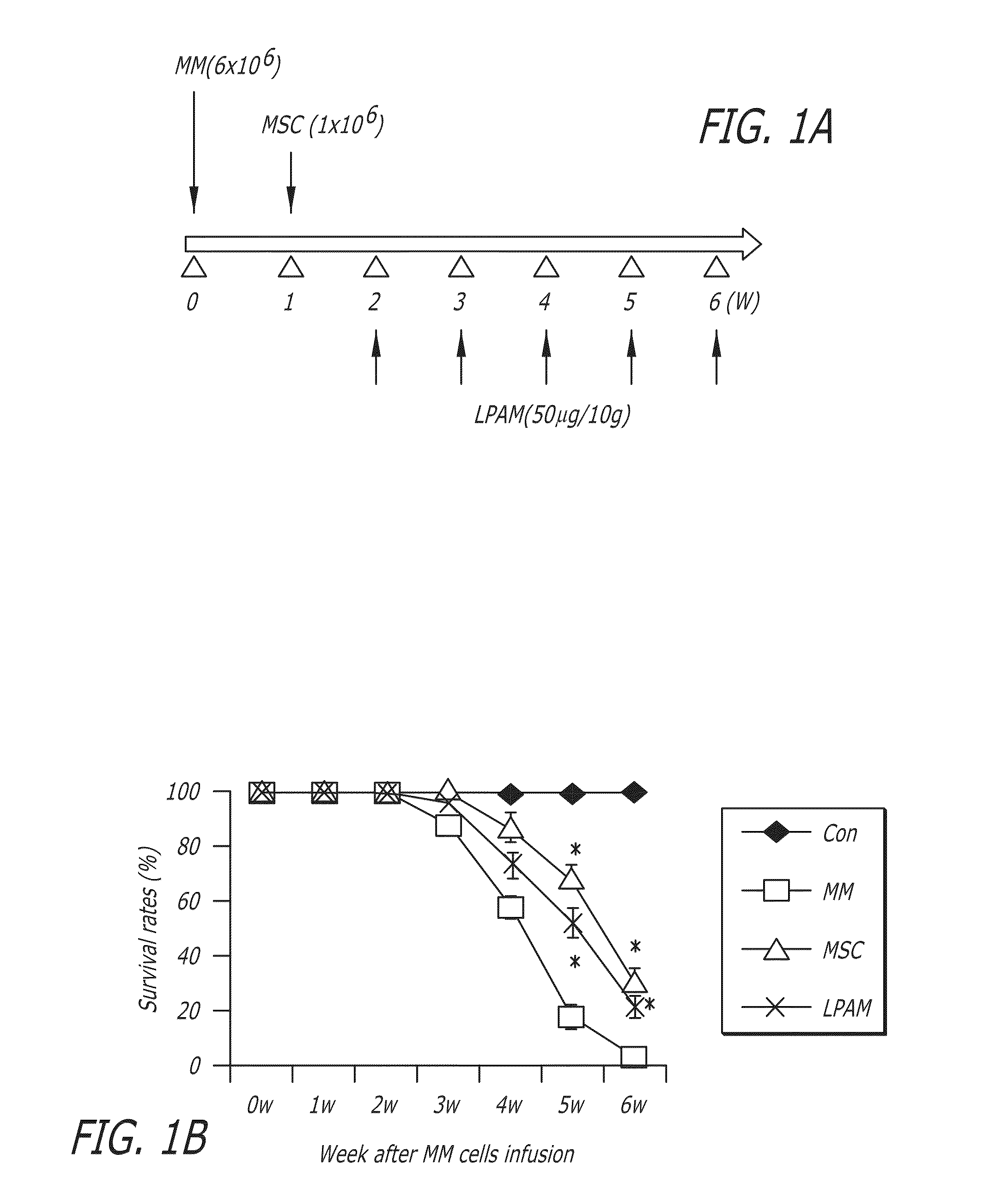
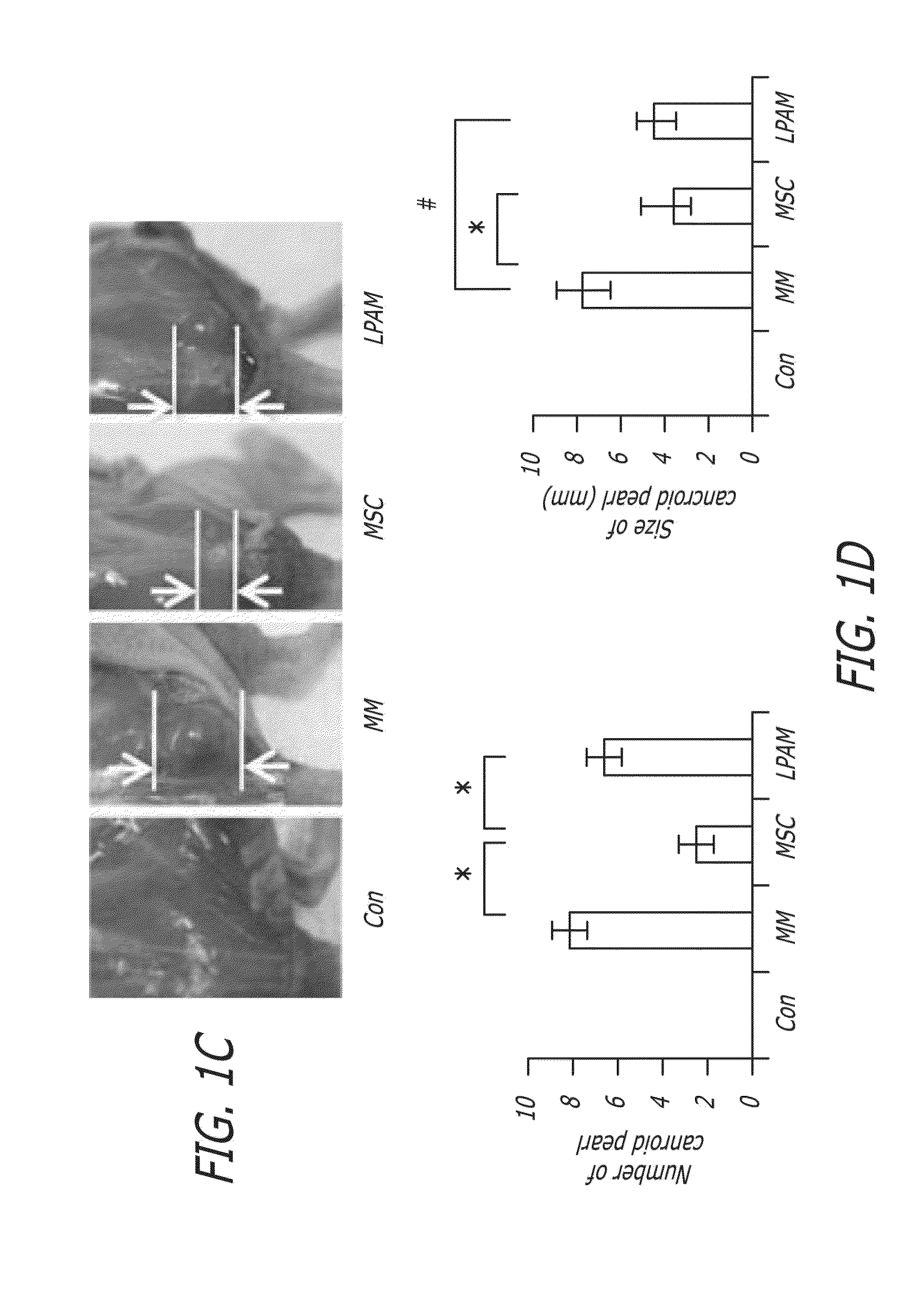
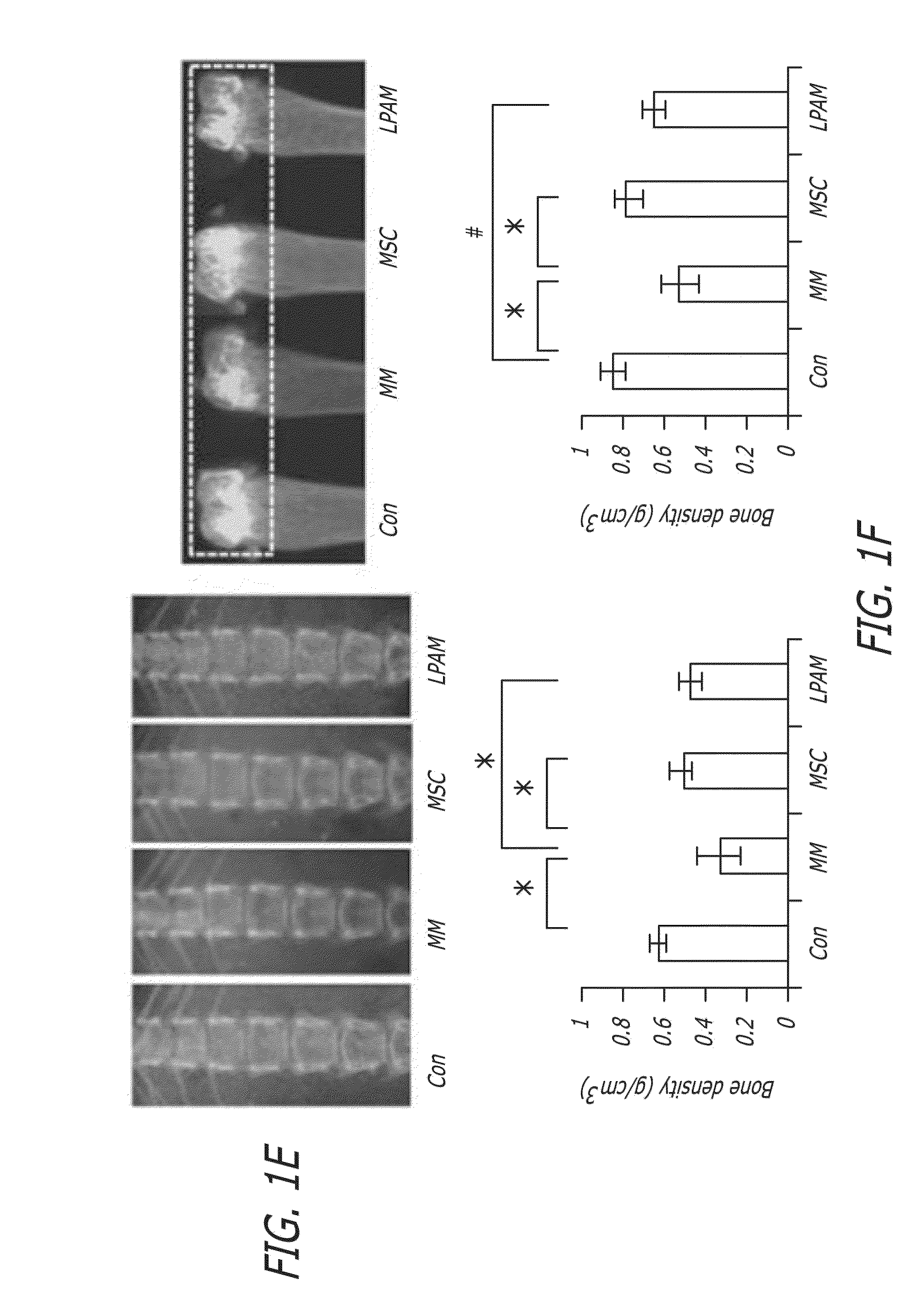
ActiveUS20160206660A1Inhibit tumor growthImprove survival rateBiocideSkeletal/connective tissue cellsDiseaseAspirin
This disclosure relates in general to a stem cell treatment. This disclosure further relates to a stem cell treatment using a composition comprising stem cells having highly expressed Fas-L. This disclosure further relates to a stem cell treatment of multiple myeloma. This disclosure also relates to a composition comprising stem cells having highly expressed Fas-L. This disclosure also relates to preparation of a composition comprising stem cell having highly expressed Fas-L. This disclosure also relates to preparation of a composition comprising stem cells having highly expressed Fas-L by using a salicylate. An example of salicylate may be aspirin. This disclosure further relates to a stem cell treatment of multiple myeloma. This disclosure also relates to a stem cell treatment of an inflammatory disease and / or autoimmune disease.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Use of certain drugs for treating nerve root injury
Owner:SCIATICON
Molecules and chimeric molecules thereof
The present invention relates generally to the fields of proteins, diagnostics, therapeutics and nutrition. More particularly, the present invention provides an isolated protein molecule in or related to the tumour necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily such as TNF-a, Lymphotoxin-a (LT-a), TNFRI, TNFRII, OX40, BAFF, NGFR, Fas Ligand or chimeric molecules thereof comprising at least a portion of the protein molecule, such as TNF-a-Fc, LT-a-Fc, TNFRI-Fc, TNFRII-Fc, OX40-Fc, BAFF-Fc, NGFR-Fc, Fas Ligand-Fc; wherein the protein or chimeric molecule thereof has a profile of measurable physiochemical parameters, wherein the profile is indicative of, associated with or forms the basis of one or more pharmacological traits. The present invention further contemplates the use of the isolated protein or chimeric molecule thereof in a range of diagnostic, prophylactic, therapeutic, nutritional and / or research applications.
Owner:APOLLO LIFE SCI
Preventives and remedies for diffuse lung diseases
InactiveUS6905684B1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTherapeutic effectBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
Preventives and remedies for diffuse lung diseases whereby apoptosis can be inhibited and thus favorable preventive / therapeutic effects can be established.These drugs contain apoptosis-inhibiting substances as the active ingredient.The above apoptosis-inhibiting substances include Fas antagonists and Fas / Fas ligand binding inhibitors such as Fas derivatives and anti-Fas ligand antibodies.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Clusterin-mediated inhibition of apoptosis via stromal bone marrow cell delivery to a cardiac site
Methods and compositions are disclosed for inhibiting, deterring or preventing apoptosis of cardiac myocytes, transplanted stem cells, vascular stem cells, and vascular smooth muscle cells by means of expressing or synthesizing clusterin. Also disclosed are methods and compositions for producing recombinant clusterin, or its biologically active peptides, and for induction of clusterin-associated lipoproteins or enzymes for deterring or preventing inflammatory injury and apoptosis induced by oxLDL, oxysterols, cytokines, and Fas Ligand. Also disclosed is an induction method and composition for enhancing expression of ALDH and ALDH-associated enzymes or co-factors to prevent cytotoxicity or detoxification. Therapeutic methods providing new expression or overexpression of clusterin in vascular or cardiac tissue are expected to inhibit the formation of atherosclerotic lesions, stabilize existing atherosclerotic plaques, and repair failing or damaged cardiac tissue.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Antibodies to Fas-L for treatment of hepatitis
InactiveUS6068841AAvoid attackImprove the level ofCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsHepatitisBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 03089 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 27, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 27, 1998 PCT Filed Oct. 24, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 15326 PCT Pub. Date May 1, 1997The invention provides therapeutic agents for hepatitis, comprising an antibody against a human Fas ligand, or an active fragment thereof as an active ingredient. The therapeutic agents for hepatitis according to the invention are particularly effective for the treatment of hepatitis caused by the death of hepatocytes due to apoptosis among many kinds of hepatitis.
Owner:OKUMURA KO
Bi-functional peptides for multiple sclerosis treatment and diagnosis
ActiveUS8188218B2Inhibition formationSuppresses disease progressionImmunoglobulin superfamilyIn-vivo radioactive preparationsEpitopeLFA-1 Alpha
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS
Peptides modulating caspase activation
InactiveCN1703428APeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansAutoimmune diseaseImmunodeficiency
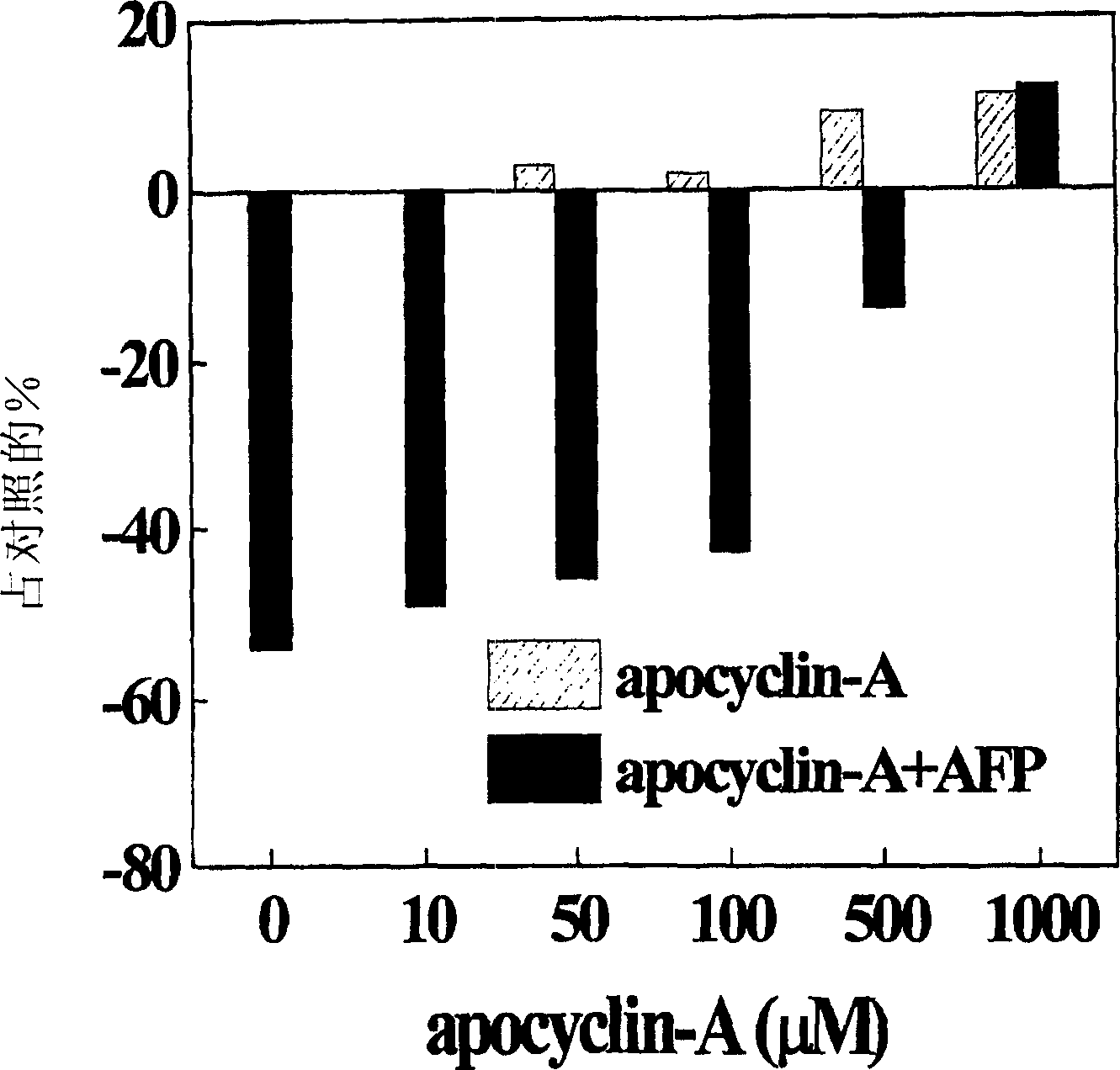
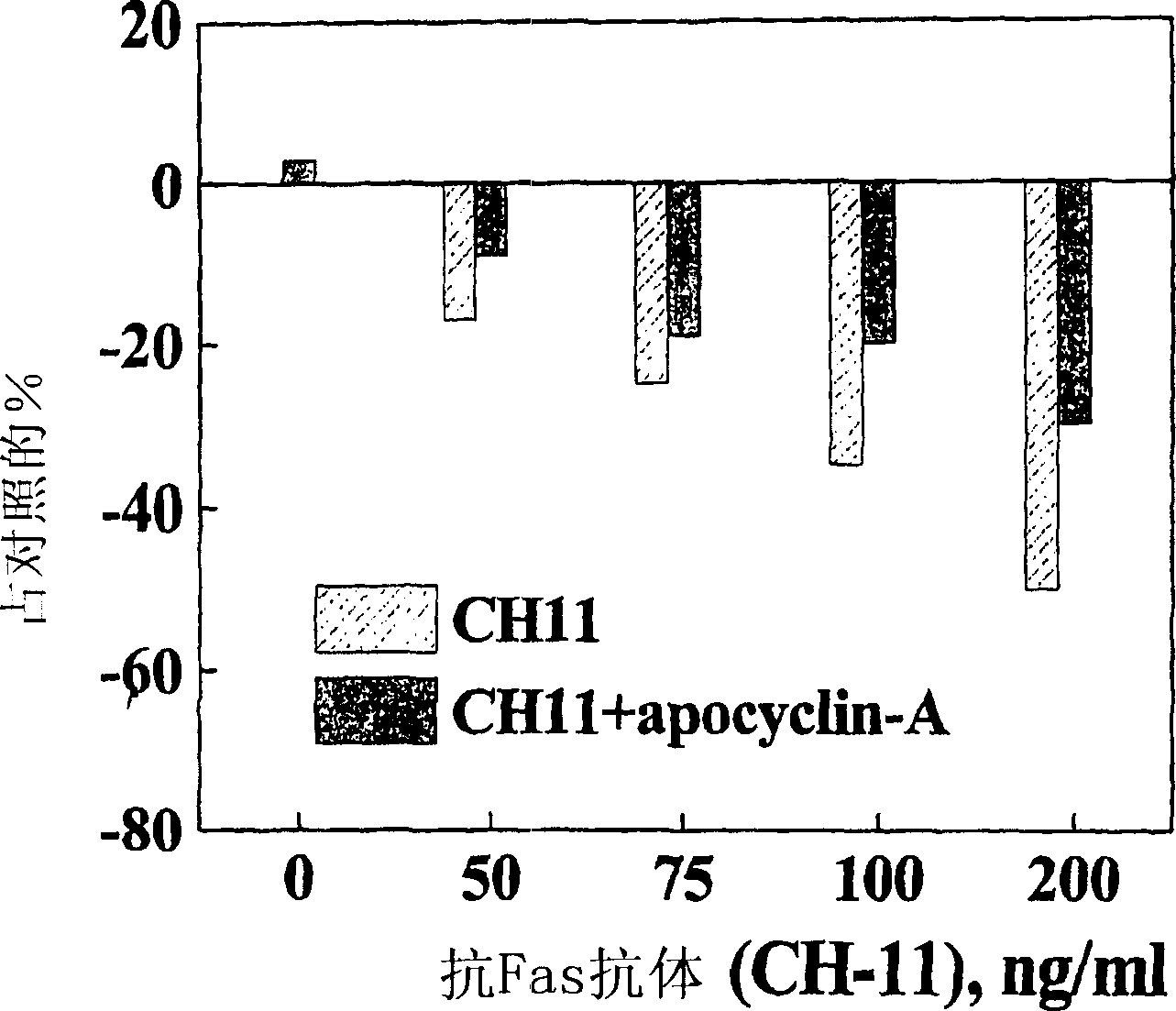
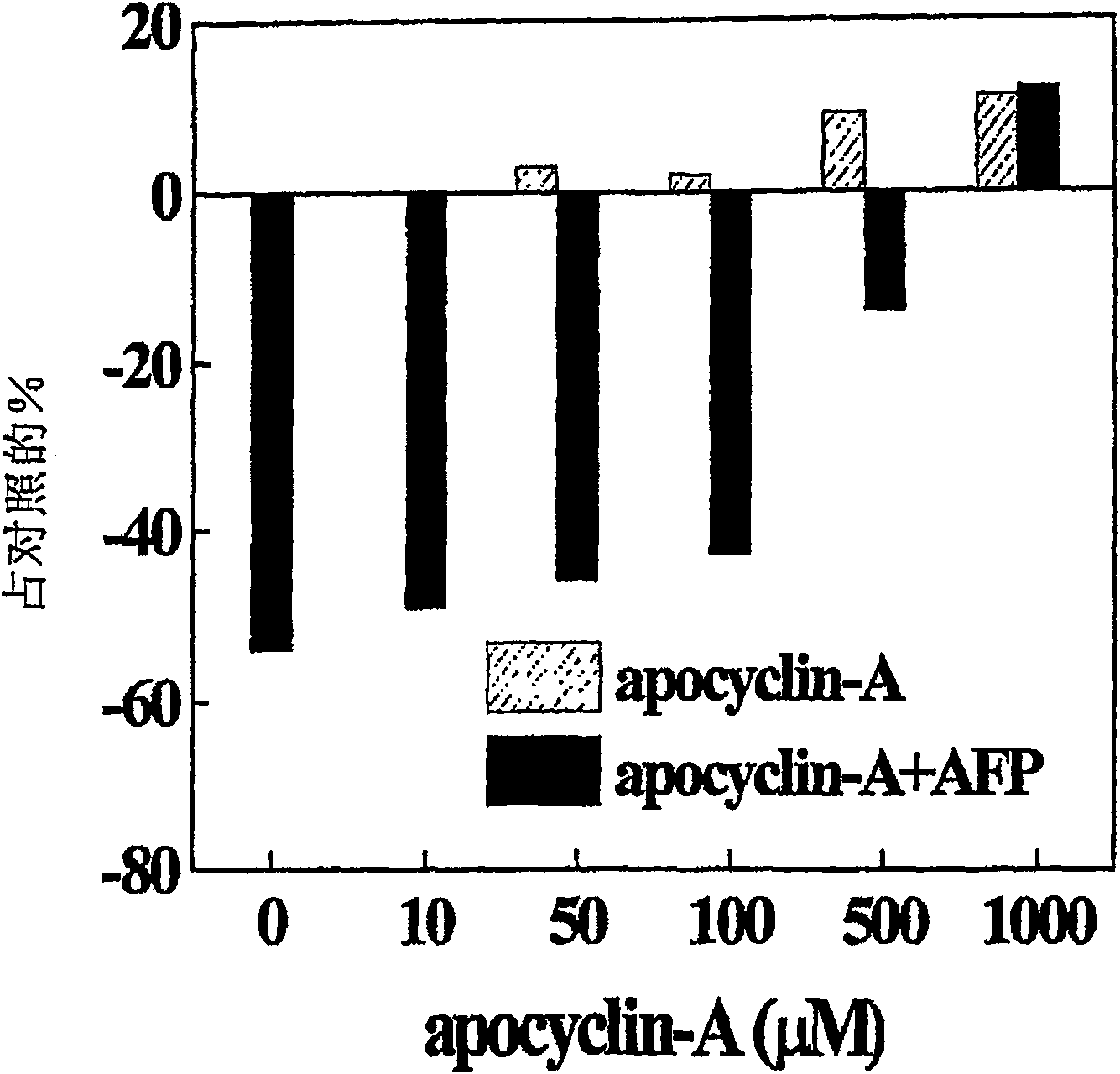
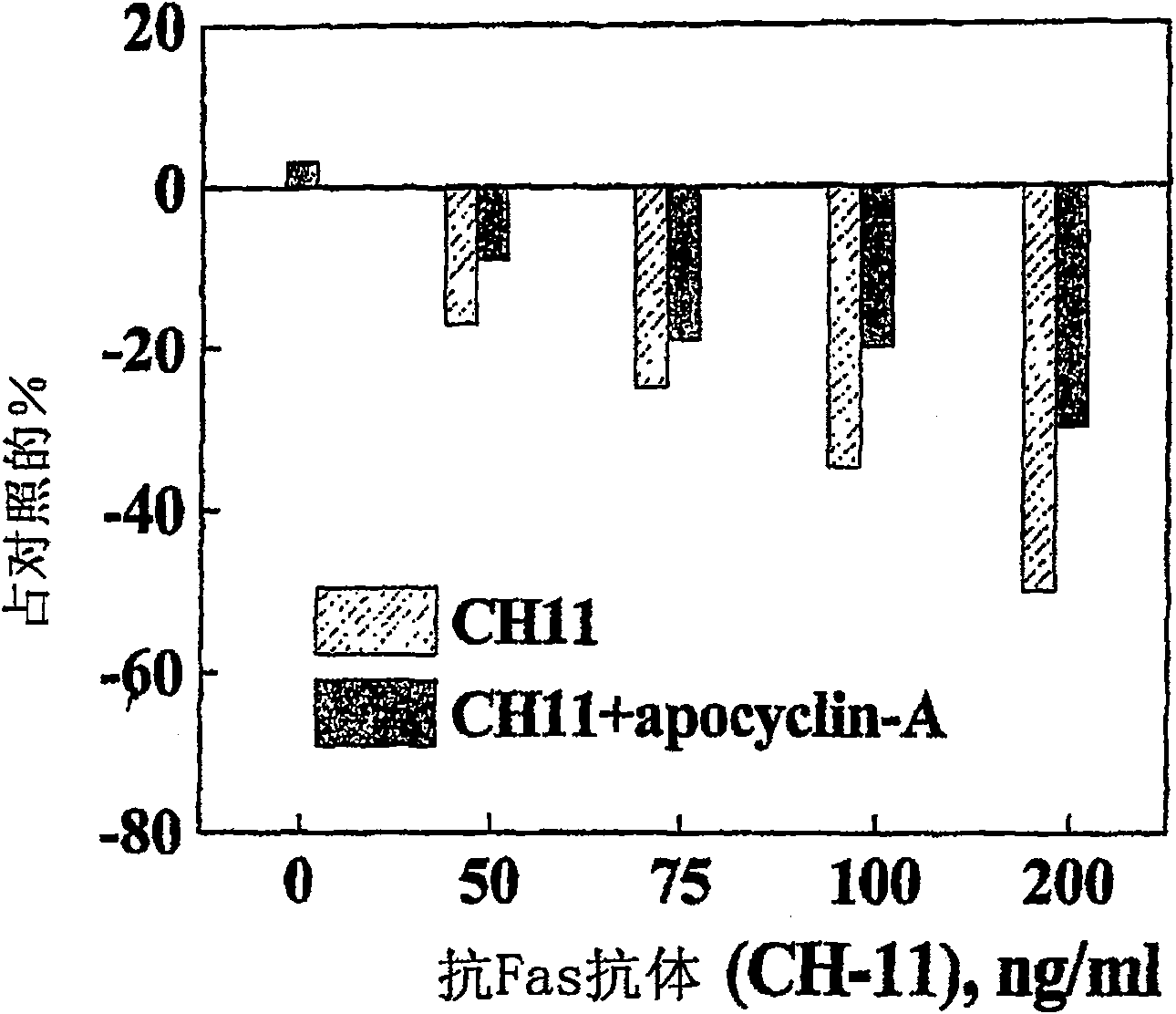
The present invention provides structures of small molecules capable of modulating apoptotic cell death. More specifically, the structures relate to the structures of apoptotic active sites of mammalian alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and albumin. Peptides mimicking the active site contain two sequences, Arg-Gly-Asp and Asp-X-X-Asp, wherein X means any amino acid. These sequences are needed in the same molecule for causing a wide range of biological activities. The peptides can be utilized to suppress apoptotic pathways by inhibiting the cytochrome c-mediated caspaseactivation. Thus, the peptides can be used to inhibit effects of apoptosis induced by oxidative stress, drugs, cytokines, Fas-ligand, alpha-fetoprotein, used to prevent apoptosis in culturing cells, in organ transplantation, in immunological autoimmune disorders and immunodeficiency syndrom induced by viral infection, or to diminish side cytotoxic effects after chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
Owner:鲍里斯·爱德华多维奇·塔图洛夫
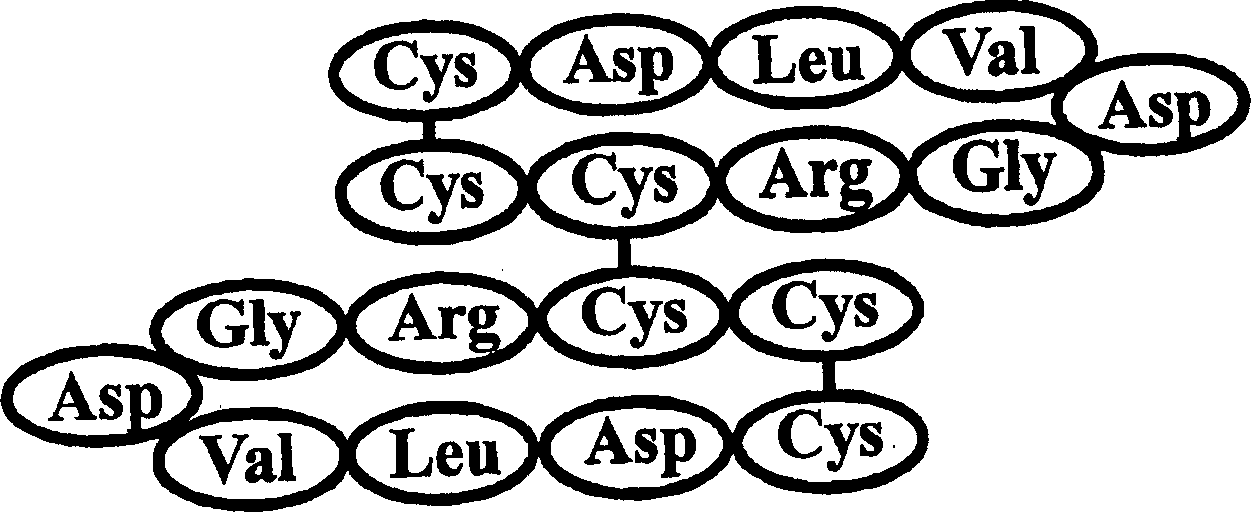
Tumor target and recombined human Fas ligand fusion protein and preparation method thereof
Tumor target and recombined human Fas ligand fusion protein and a preparation method thereof relate to a gene and provide construction, expression and purification of tumor target specific binding peptide and recombined human Fas ligand fusion protein gene as well as in vitro and vivo biology activity identification method. Fas ligand cDNA complete sequence is searched from GenBank, Arg-Lys-Arg is added by Linker(YNFPQQMLKCFC) at terminal N of the complete sequence to obtain original gene sequence for coding the tumor target specific binding peptide and recombined human Fas ligand fusion protein; nucleotide sequence of the tumor target specific binding peptide and recombined human Fas ligand fusion protein is modified according to degeneracy of codon and codon preference principle of colon bacillus; the modified fusion protein sequence is divided into twelve long primer segments, and BamH I and Xho I enzyme restriction sites are introduced; and the fusion protein gene is obtained by PCR reaction.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Fas ligand-fused proteins
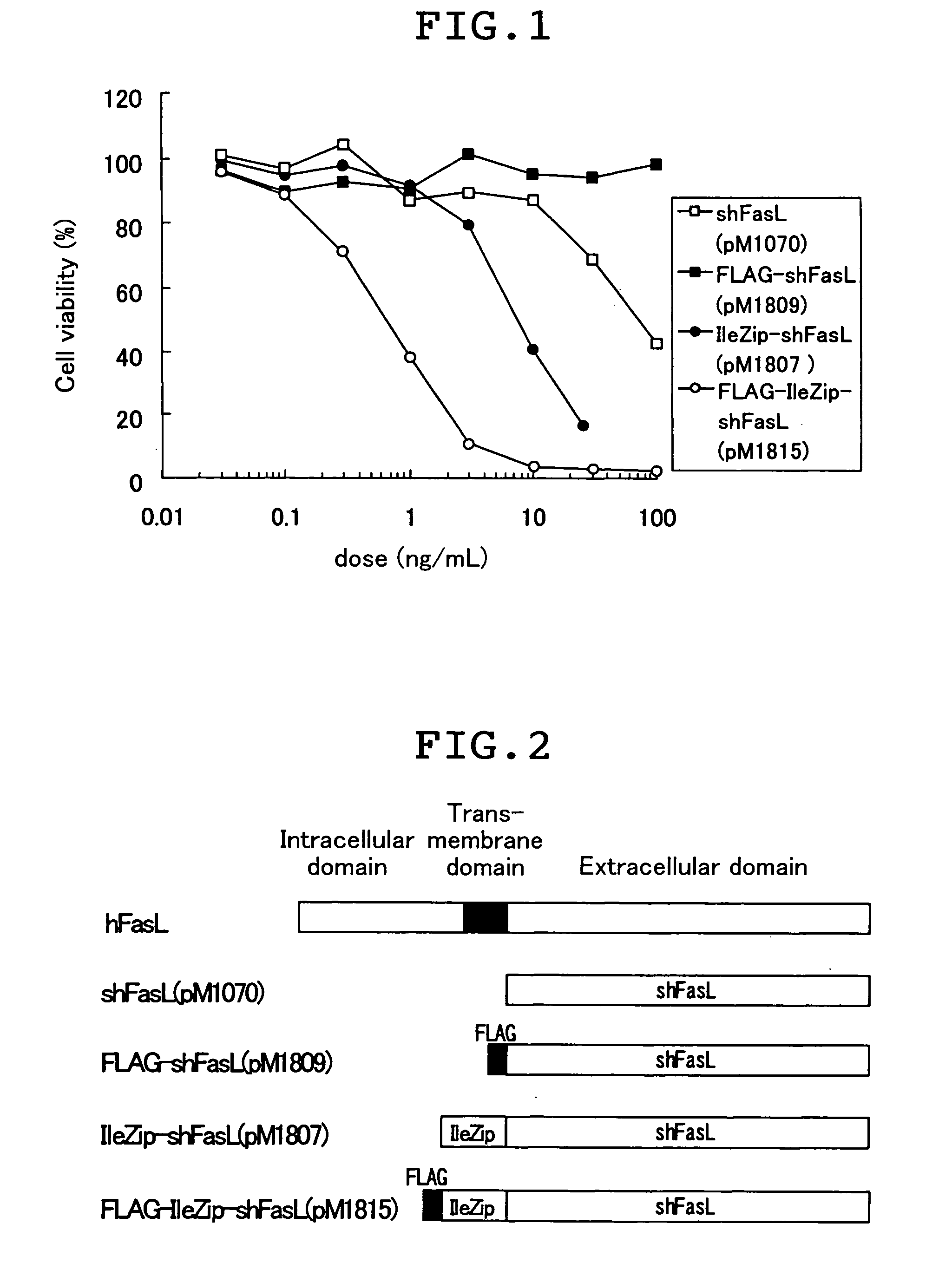
InactiveUS20040053249A1Improve biological activityIncrease productionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsTransmembrane proteinBiological organism
Provided by this invention is a fusion protein which is capable of binding to Fas, and which comprises a peptide comprising at least a part of the amino acid sequence of Fas ligand, a peptide having oligomerization ability, and a peptide which increases recombinant protein production. Also provided are a method for using the FLAG-like peptide for the purpose of increasing the production of the recombinant protein, and a method for using the FLAG-like peptide for the purpose of increasing the biological activity of the fusion protein of the leucine zipper and the transmembrane protein.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Method for inhibiting inflammation in immune privileged sites using Fas ligand fragments
InactiveUS20020127233A1Avoid developmentPeptide/protein ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsNervous systemPlacenta
The present invention is directed to a method of modulating inflammation within an immune privileged site in an animal by introducing an effective amount of a Fas ligand fragment comprising the extracellular domain of a full length Fas ligand, a derivative thereof, or a nucleic acid encoding the Fas ligand fragment, behind the blood-tissue barrier of the immune privileged site. In one embodiment the invention pertains to methods of modulating inflammation in the central nervous system generally, at specific lesions in the central nervous system, anterior chamber of the eye, testis, placenta and other immune privileged sites in a mammal. The FasL fragments used in the method of the present invention contain the extracellular domain of FasL and are soluble. The method of the present invention comprises the step of directly administering the FasL fragment, or derivative thereof, or a composition comprising the FasL fragment, or derivative thereof, behind the blood-tissue barrier of the immune privileged site.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Antagonistic anti-hFAS ligand human antibodies and fragments thereof
Human antibodies, preferably recombinant human antibodies that specifically bind to human Fas Ligand (hFasL) are disclosed. These antibodies have high affinity for hFasL, a slow off rate for hFasL dissociation and neutralize a Fas Ligand activity in vitro and in vivo. An antibody of the invention can be a full-length antibody or an antigen-binding portion thereof. The antibodies, or antigen-binding portions, of the invention are useful for neutralizing Fas Ligand activity, e.g., in a human subject suffering from a disorder in which hFas Ligand activity is detrimental. Nucleic acids, vectors and host cells for expressing the recombinant anti-hFasL human antibodies, and the methods for synthesizing the recombinant human antibodies are also encompassed by the invention.
Owner:ELI LILLY & CO
Modulators of the function of FAS/APO1 receptors
InactiveUS20020082401A1Improve efficiencyPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDna encodingIntracellular domain
The MORT-1 protein, analogs thereof and fragments thereof bind with the intracellular domain of the FAS ligand receptor. DNA encoding such protein, analogs and fragments, may be used to make vectors and host cells in order to produce such proteins, analogs and fragments. The peptides may be formulated into pharmaceutical compositions for use in modulation of the FAS-R ligand effect on cells carrying a FAS-R.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Peptides modulating caspase activation
Owner:鲍里斯·爱德华多维奇·塔图洛夫
Anti-Fas antibodies
InactiveUS20030170817A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsCancer researchFas ligand
Anti-Fas antibodies which are cross-reactive with mouse and human Fas and are useful in the treatment of conditions attributable to abnormalities in the Fas / Fas ligand system.
Owner:SANKYO CO LTD
Pd-l1 and pd-l2-based fusion proteins and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180057561A1Extended half-lifeIncrease frequencyPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseasePD-L1
Provided are fusion proteins comprising a first domain and a second domain, wherein the first domain comprises a polypeptide that binds to and triggers PD-1 and the second domain comprises a polypeptide that binds to and triggers a TRAIL receptor or Fas. In some embodiments, the polypeptide that binds to and triggers PD-1 comprises at least a portion of the extracellular domain of PD-L1 or PD-L2 and the second domain comprises at least a portion of the extracellular domain of TRAIL or Fas ligand. Also provided are methods for treating autoimmune, alloimmune or inflammatory diseases, and methods for treating cancer, using the fusion proteins.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Separation method for decidua basalis stem cells of placenta
ActiveCN111575229AReduced Chances of ContaminationEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsEmbryonic cellsHydrolysateHigh sugar
The invention relates to a separation method for decidua basalis stem cells of a placenta, and belongs to the technical field of regenerative medicine and biology. The separation method for the decidua basalis stem cells of the placenta comprises the following steps of collecting the placenta, and soaking the placenta in a placenta preservation solution which is a basic culture medium PBS containing 1x-2xdouble antibodies and 10% high-sugar DMEM; stripping the decidua basalis and carrying out cleaning; cutting the decidua basalis into pieces, carrying out enzymolysis by using enzymatic hydrolysate a which is a DMEM high-sugar basal culture medium containing 0.25% of pancreatin and 0.02% of EDTA, carrying out centrifuging, and discarding supernate, carrying out enzymolysis by using enzymatic hydrolysate b which is a DMEM high-sugar basic culture medium containing 0.1 to 0.2 mg / mL of collagenase IV, 0.01 to 0.05 mg / mL of neutral enzyme, 5 to 10 ng / ml of a Fas ligand inhibitor and 5 to 10ng / ml of a survivin inhibitor; and carrying out subpackaging, counting and inoculating. According to the separation method for the decidua basalis stem cells of the placenta, the decidua basalis stemcells of the placenta are extracted by adopting a double-enzymolysis method, and the method is simple in operation step, high in cell acquisition rate, sufficient in extracted cell number and high incell viability. In addition, the invention aims to comprehensively extract the decidua basalis stem cells of the placenta.
Owner:GUANGDONG CHINAHEALTH LIFE SCI CO LTD
Nitric oxide- and fas ligand- eluting compositions and devices and methods of treatment using same
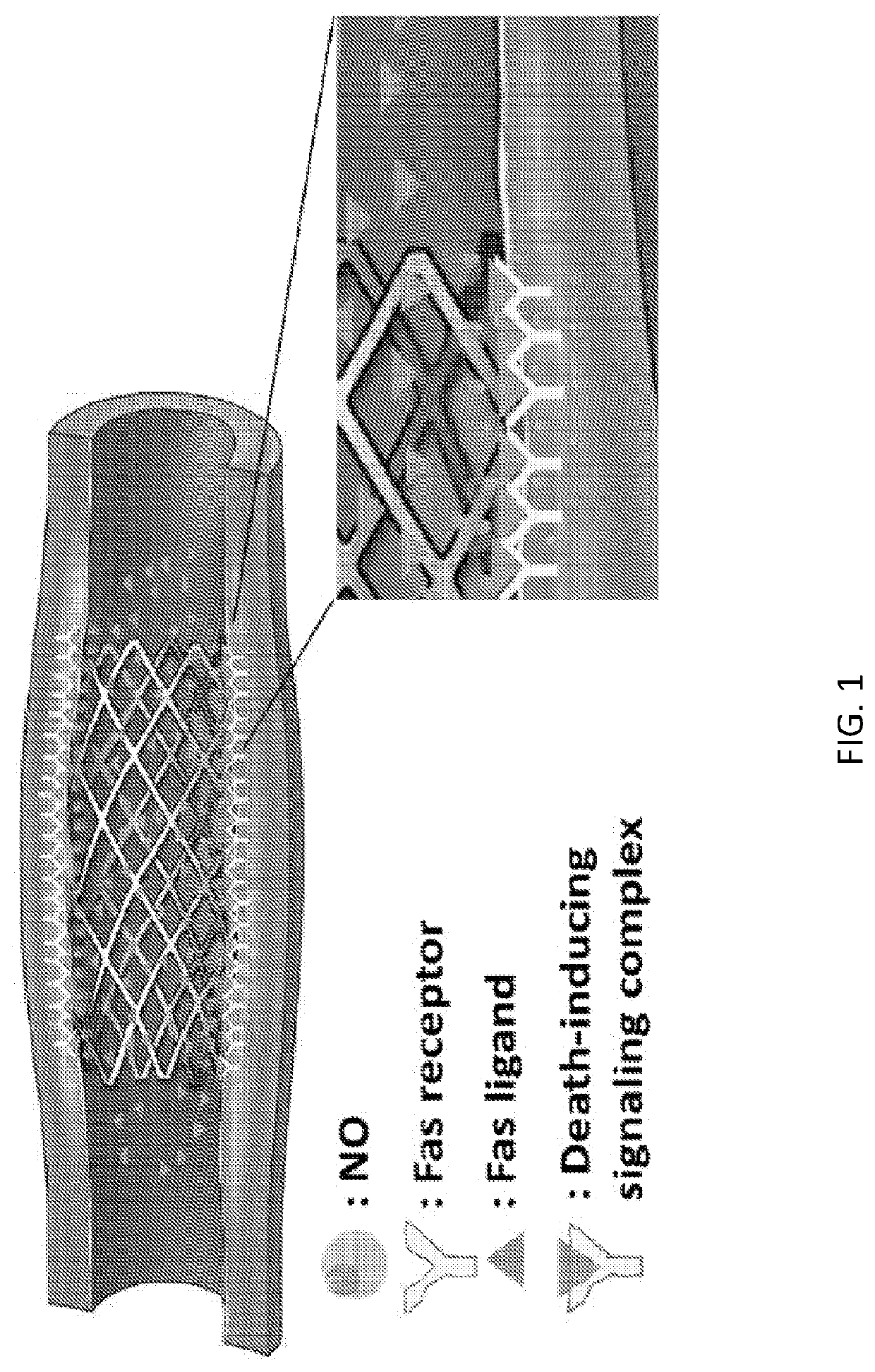
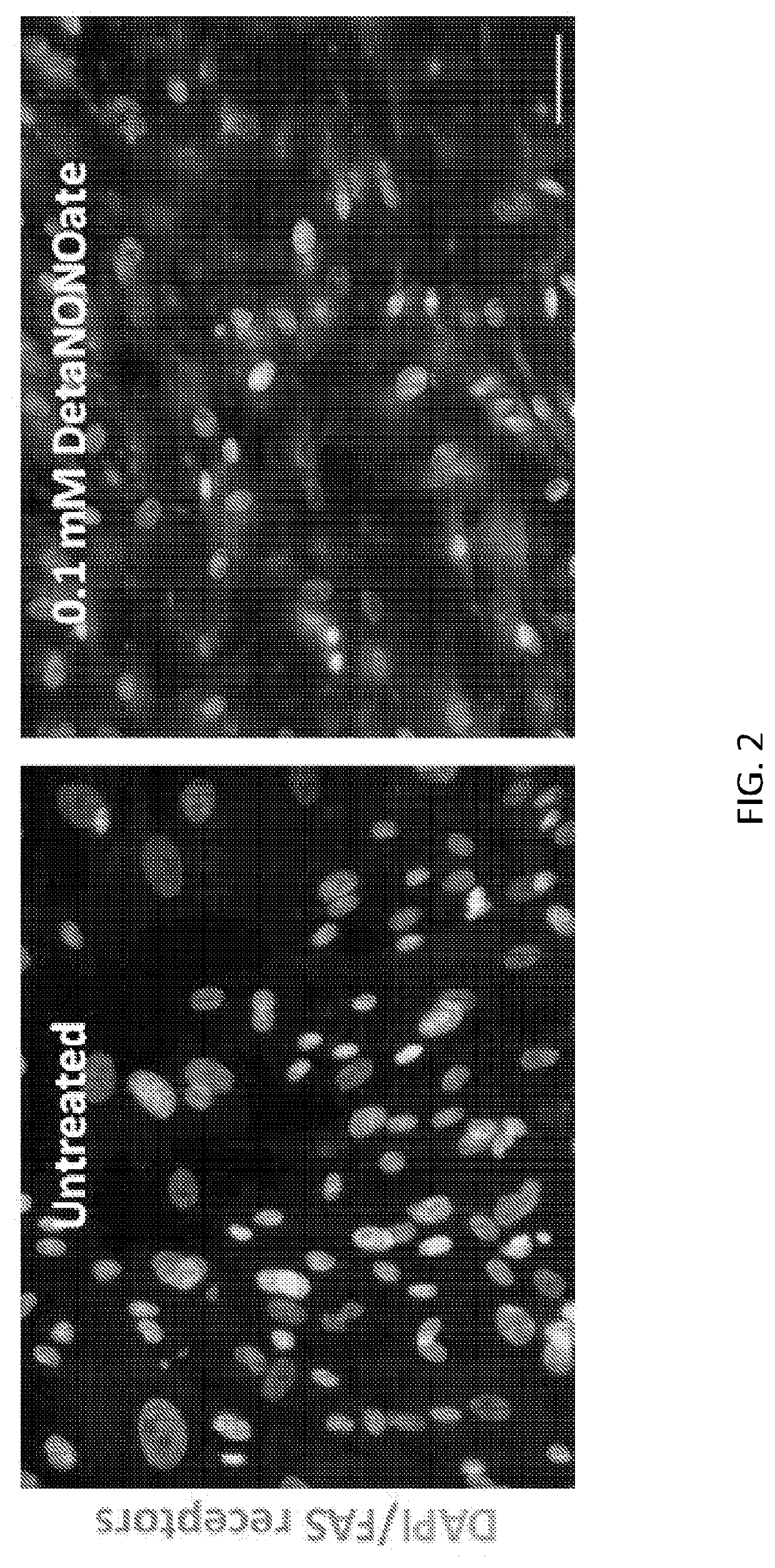
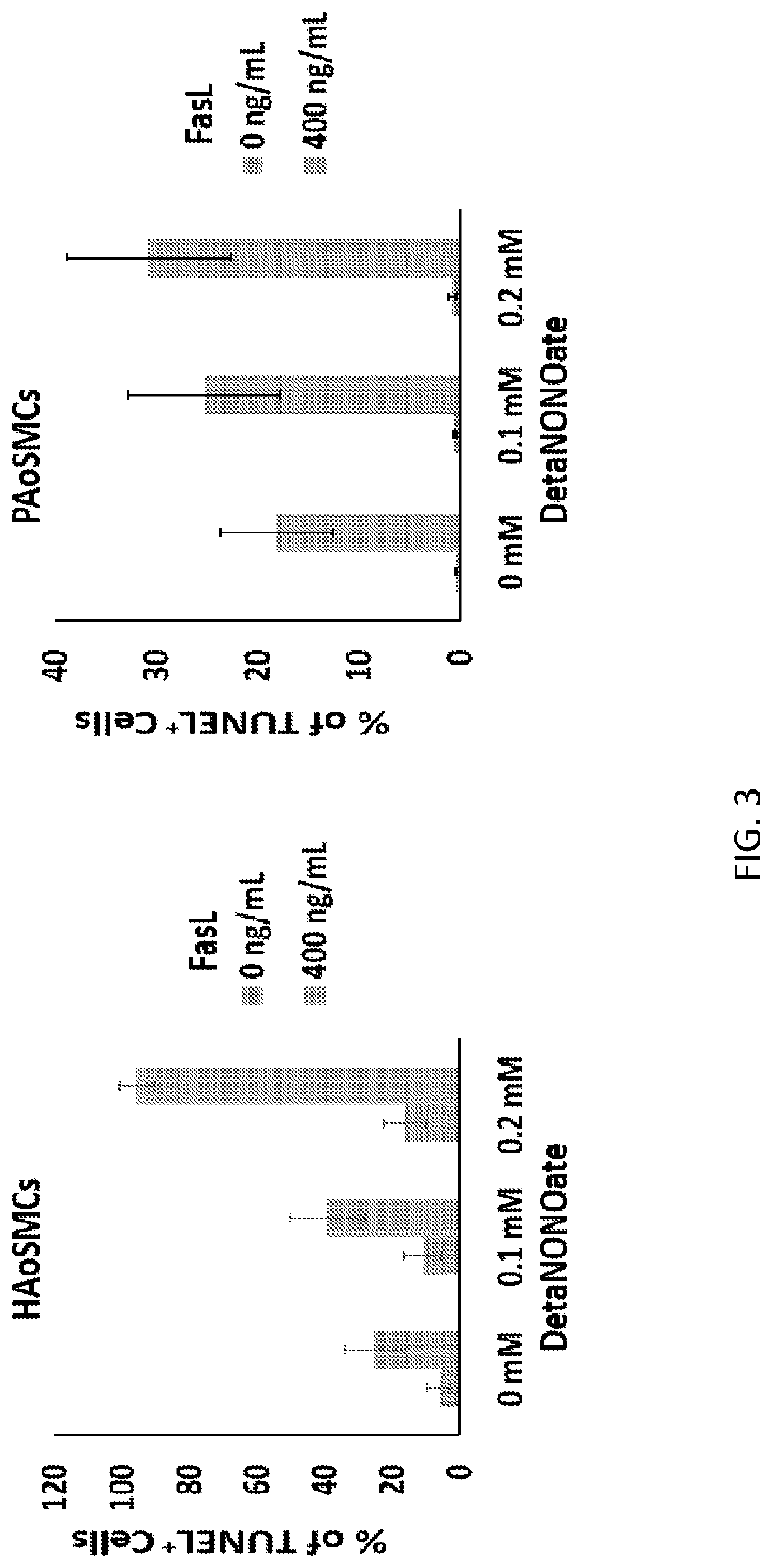
The present invention provides compositions and devices that release (a) a nitric oxide (NO) donor and / or NO, and (b) an agent that aggregates and / or trimerizes the Fas receptor, such as but not limited to a Fas-ligand (FasL). In certain embodiments, the invention includes a stent that elutes (a) a NO donor and / or NO, and (b) FasL. In other embodiments, the invention includes methods of treating a condition, such as intimal hyperplasia, in a subject by administering a stent that releases (a) a NO donor and / or NO, and (b) FasL.
Owner:YALE UNIV
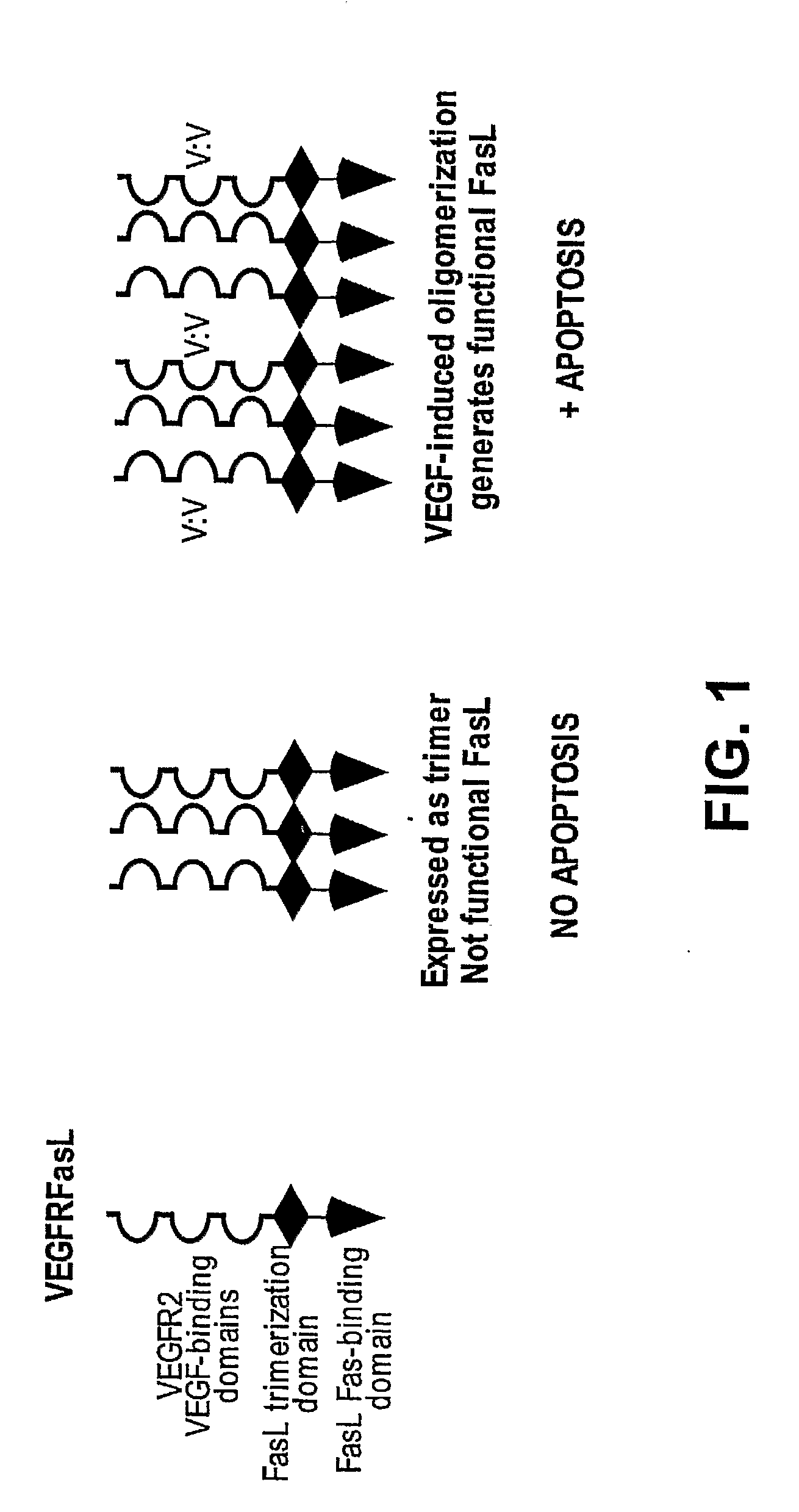
Vegf-activated fas ligands
The present invention provides fusion proteins comprising an extracellular domain of a VEGF receptor and a death ligand. The fusion proteins bind to VEGF and to death receptors on tumor cells thereby inhibiting VEGF activation of VEGF receptors and inducing apoptosis in the tumor cells. Fusion proteins of the present invention are useful for inducing apoptosis and cytotoxic effects in cells, treating cancer and diseases or disorders related to unregulated angiogenesis and / or vasculogenesis. Thus, this invention further provides methods for treating angiogenesis related diseases using the fusion proteins, polynucleotides encoding the fusion proteins, vectors containing the polynucleotides, pharmaceutical compositions and kits containing the fusion proteins or the polynucleotides encoding the fusion proteins.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
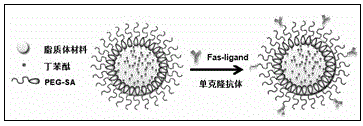
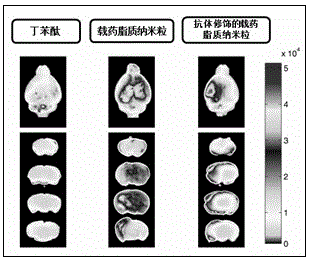
Death ligand antibody conjugated polyethylene glycol modified lipid nano drug delivery system and its application
ActiveCN103462933BGood brain targetingMuch distributionMacromolecular non-active ingredientsMicrocapsulesAntiendomysial antibodiesAntibody conjugate
The invention provides a death ligand antibody coupled polyethylene glycol modified lipid nano drug delivery system, which is delivered by preparing polyethylene glycol (PEG) modified and death ligand (Fas ligand) antibody coupled lipid nanoparticles Combined with the experimental animal model of ischemic brain injury, the pharmacodynamic indicators of the brain-targeted nano-drug delivery system coupled with Fas ligand antibody were evaluated from the whole animal level, which proved its good brain-targeting and brain-deficient drug delivery system. Targeting of the blood area. From the reduction of infarct size and the improvement of animal nerve function damage and other indicators, it is proved that the drug delivery system can reduce the drug dose and improve the efficacy of the drug, so as to provide a more efficient and low-toxic drug delivery system for the clinical treatment of ischemic stroke. .
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com