Separation method for decidua basalis stem cells of placenta
A technology of placental decidua and separation method, which is applied in the field of regenerative medicine and biology, can solve the problems of large fluctuations in the number of extracted cells, large volume of digested tissue, unfavorable industrial production, etc., and achieve sufficient cell number and experimental operation The effect of short time and high activity rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
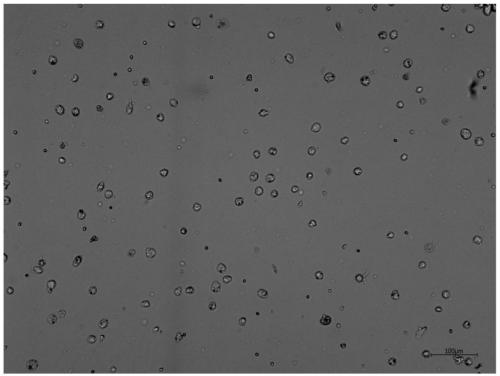
Embodiment 1
[0037] This embodiment is a method for separating placental stem cells according to the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0038] (1) Collect the placenta and soak it in the placenta preservation solution: soak the placenta obtained after delivery within 6 hours in PBS containing basal medium containing 1×-2× double antibody and volume concentration of 10% high-glucose DMEM solution, stored at 4°C for transportation;
[0039] (2) The placenta described in step (1) was peeled off to obtain the decidua basalis, and the placental decidua basalis was initially cleaned with 0°C PBS, and then the cleaning solution was sucked into the tissue with a 10mL disposable pipette until The decidua basalis blood is cleaned;
[0040] (3) Use scissors to cut up the decidua basalis treated in step (2), with an area of 3×3cm2 , the shredded decidua basalis was mixed with decidua basalis at 10: 1 volume ratio, 200R enzymatic hydrolysis for 0.5h, 1500rpm centrifugation for 5mi...
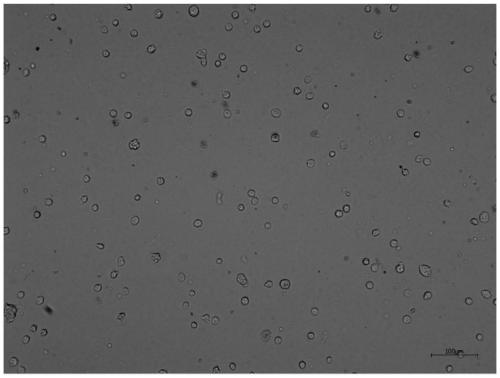
Embodiment 2
[0045] This embodiment is a method for separating placental stem cells according to the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0046] (1) Collect the placenta and soak it in the placenta preservation solution: Soak the placenta obtained after delivery in the PBS preservation solution containing the basal medium containing 1×-2× double antibody and 10% high-glucose DMEM within 6 hours , stored and transported at 4°C;
[0047] (2) The placenta described in step (1) was peeled off to obtain the decidua basalis, and the placental decidua basalis was initially cleaned with 4°C PBS, and then the cleaning solution was sucked into the tissue with a 10mL disposable pipette until The decidua basalis blood is cleaned;
[0048] (3) Use scissors to cut up the decidua basalis treated in step (2), with an area of 3×3cm 2 , the shredded decidua basalis was mixed with decidua basalis at 10: 1 volume ratio, 200R enzymatic hydrolysis for 0.5h, centrifugation at 1500rpm for 5mi...
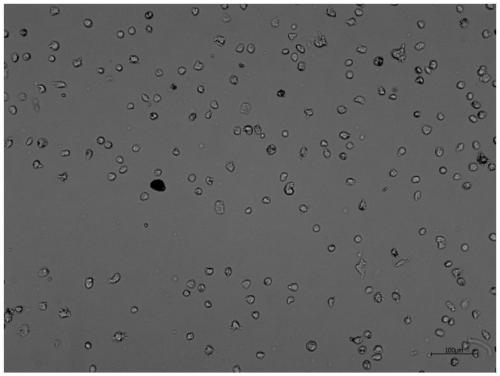
Embodiment 3
[0053] This embodiment is a method for separating placental stem cells according to the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0054] (1) Collect the placenta and soak it in the placenta preservation solution: soak the placenta obtained after delivery in PBS containing basal medium containing 1×-2× double antibody and 10% high-sugar DMEM within 6 hours. solution, stored at 4°C for transportation;
[0055] (2) The placenta described in step (1) was peeled off to obtain the decidua basalis, and the placental decidua basalis was initially cleaned with 2°C PBS, and then the cleaning solution was sucked into the tissue with a 10mL disposable pipette until The decidua basalis blood is cleaned;
[0056] (3) Use scissors to cut up the decidua basalis treated in step (2), with an area of 3×3cm 2 , the shredded decidua basalis was mixed with decidua basalis at 10: 1 volume ratio, 200R enzymatic hydrolysis for 0.5h, 1500rpm centrifugation for 5min; 15ng / ml survivin in...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com