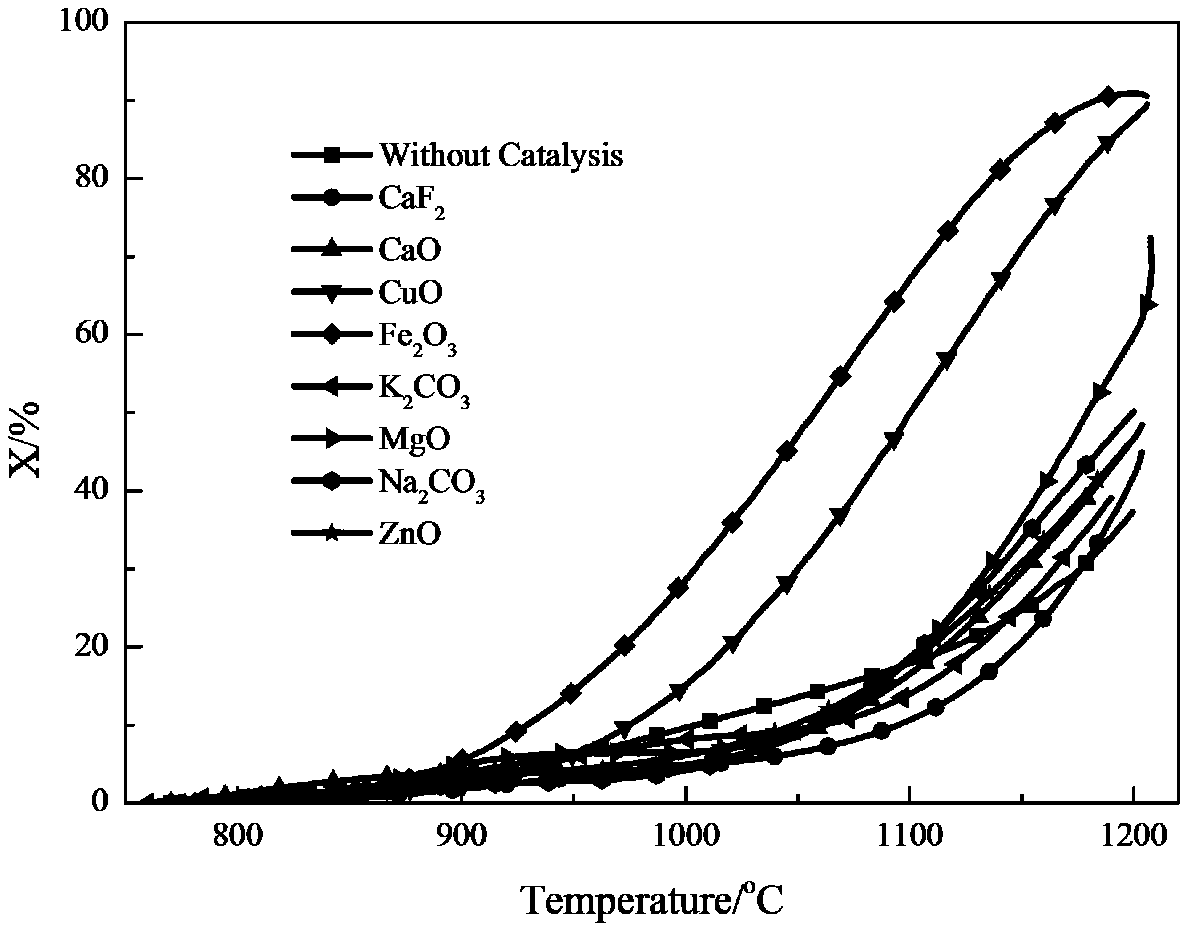
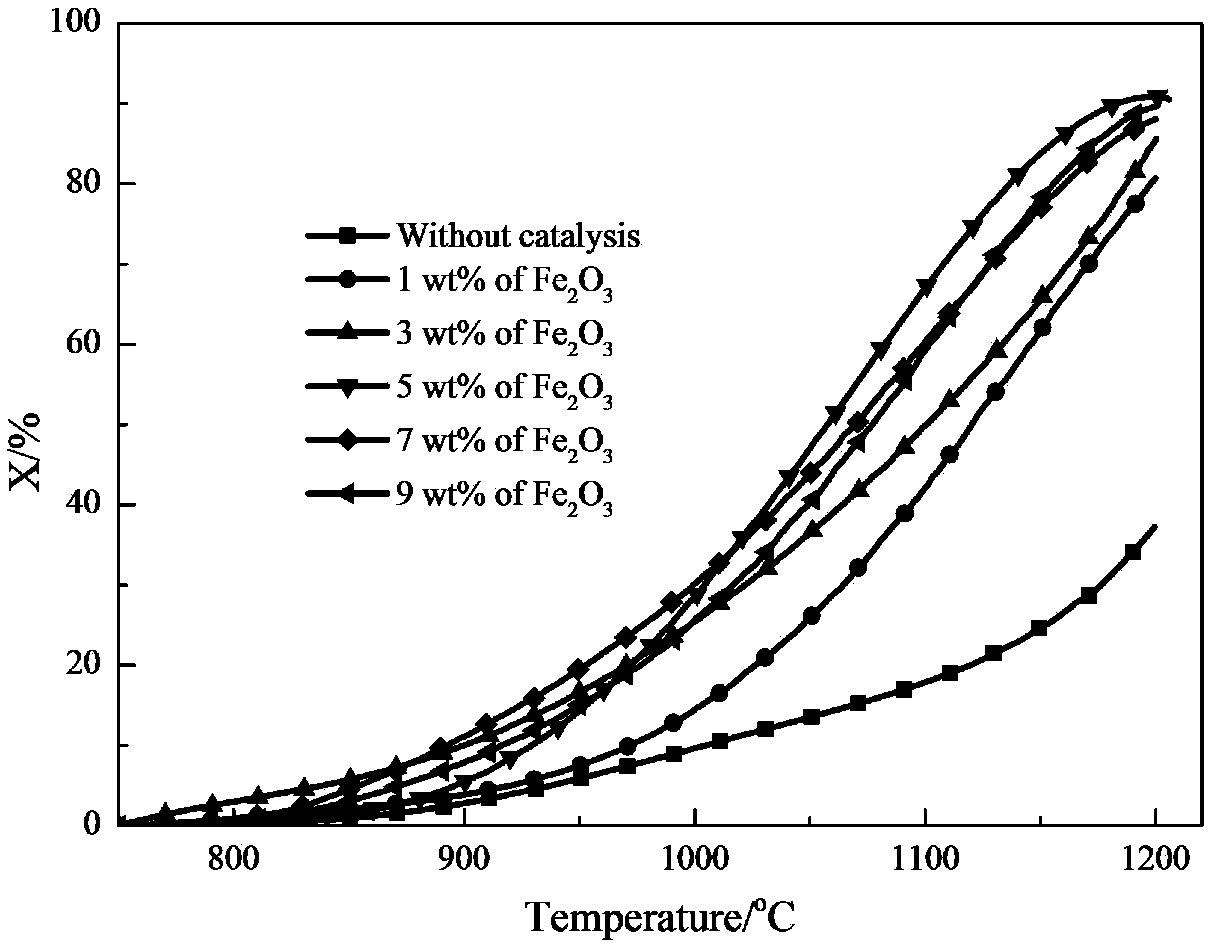
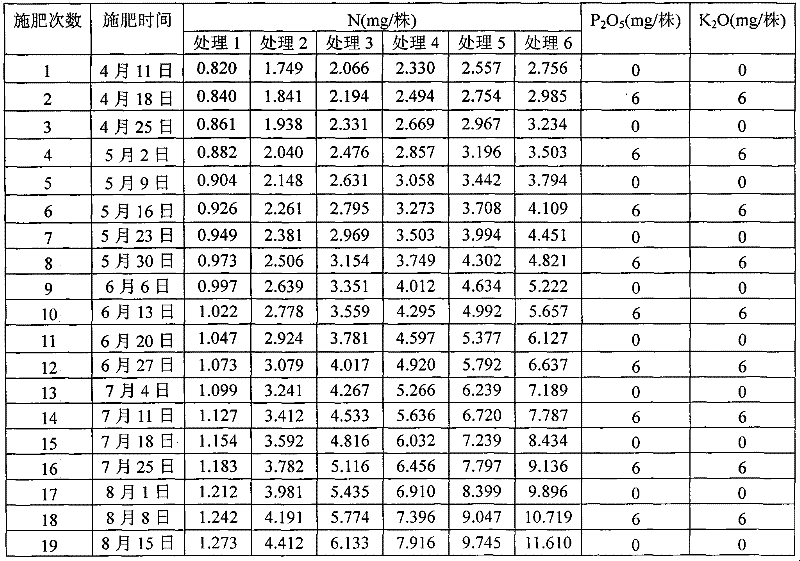
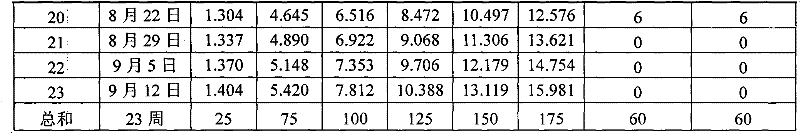
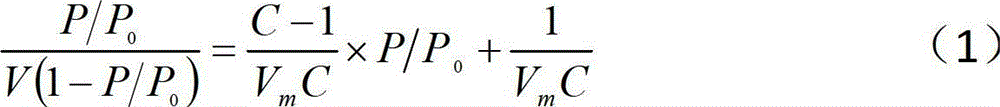Patents
Literature
231 results about "Nitrogen absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
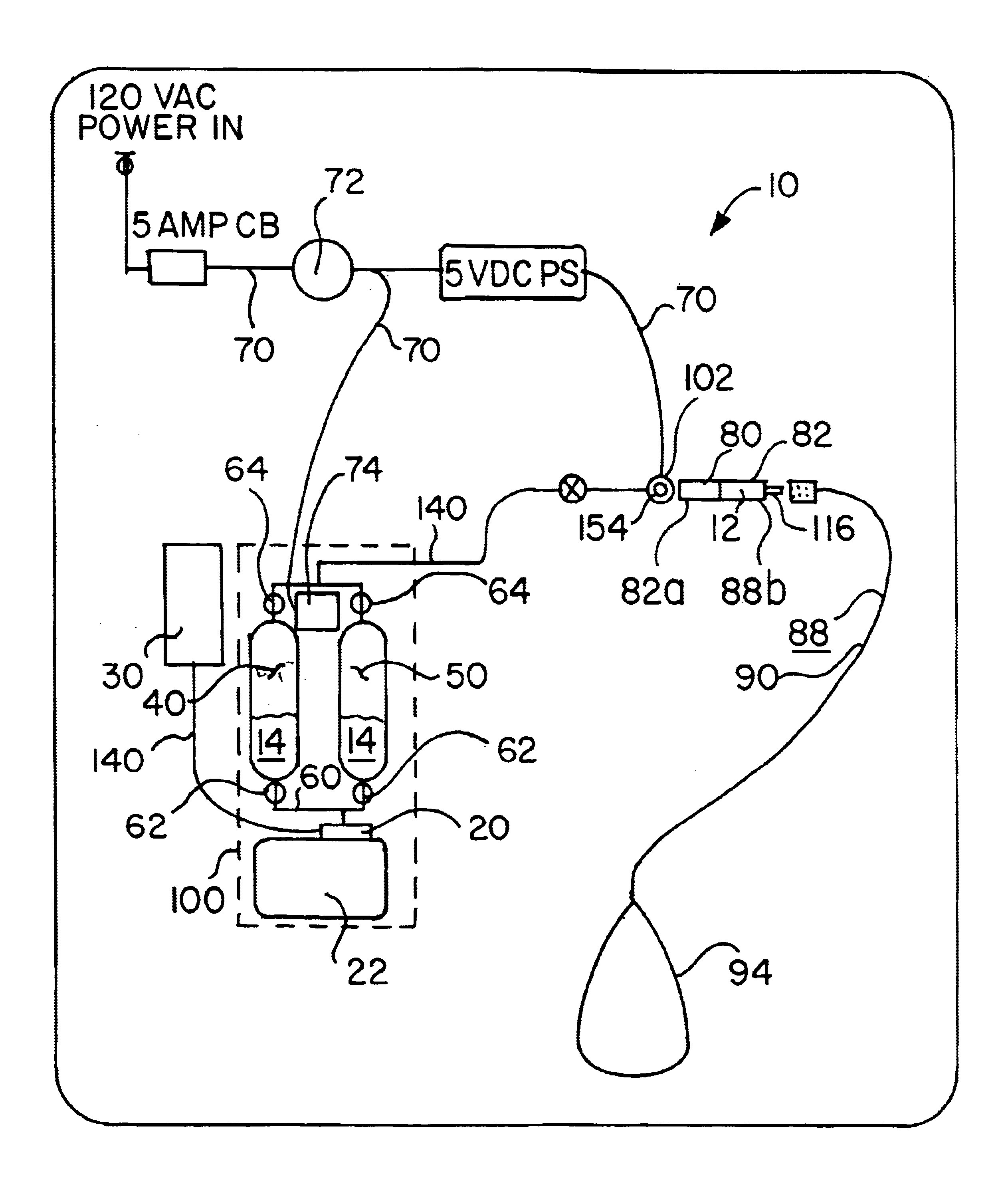
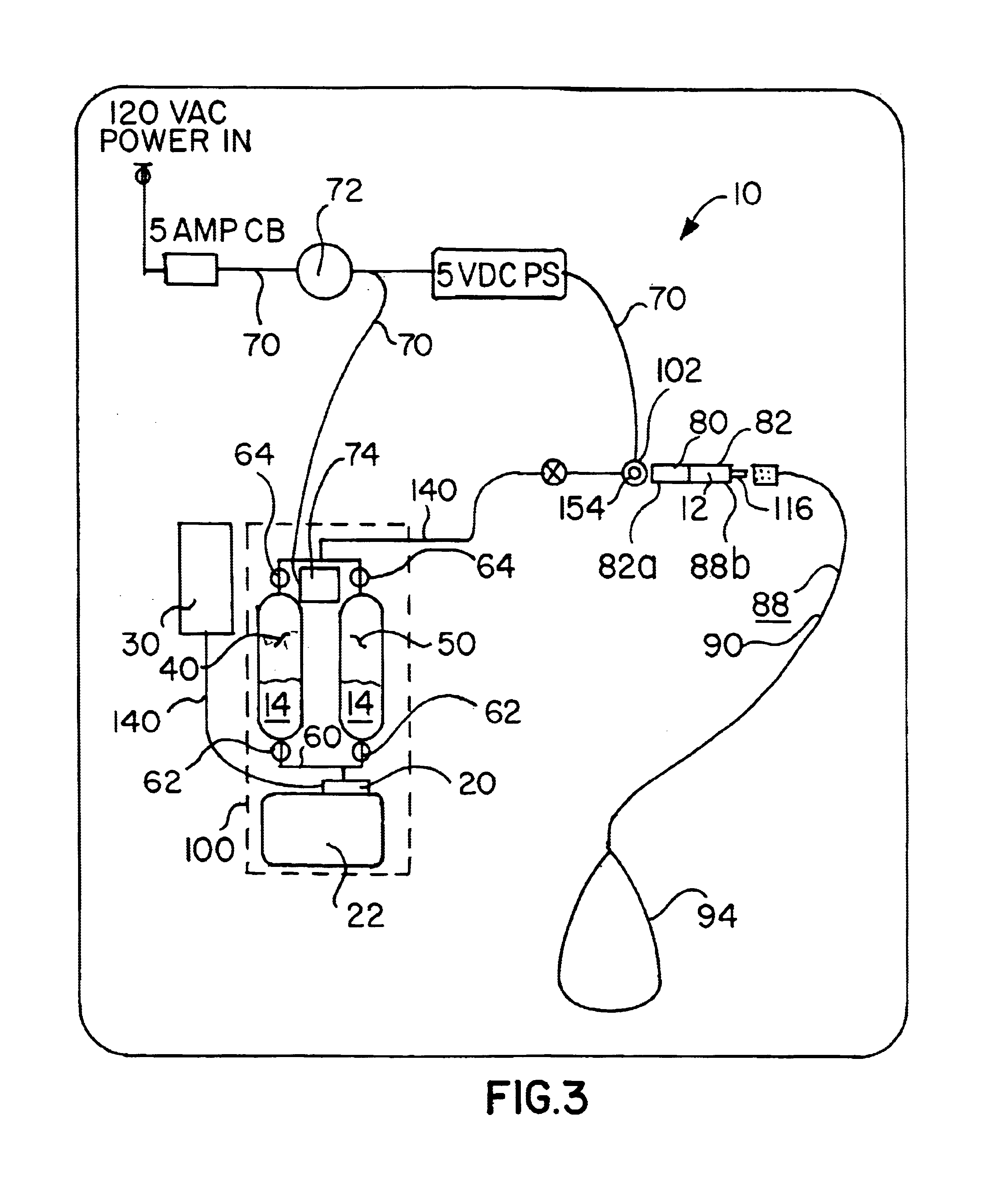
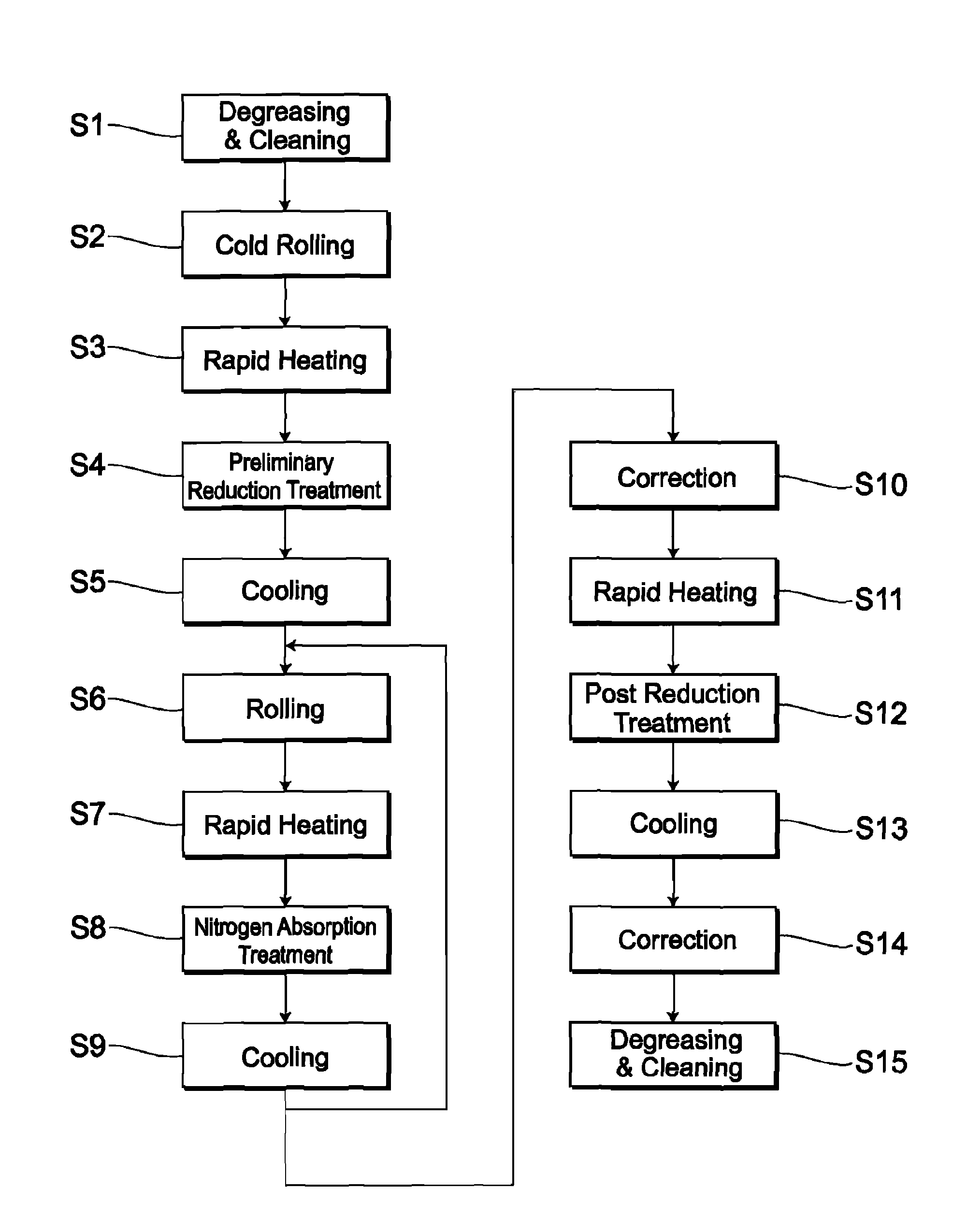
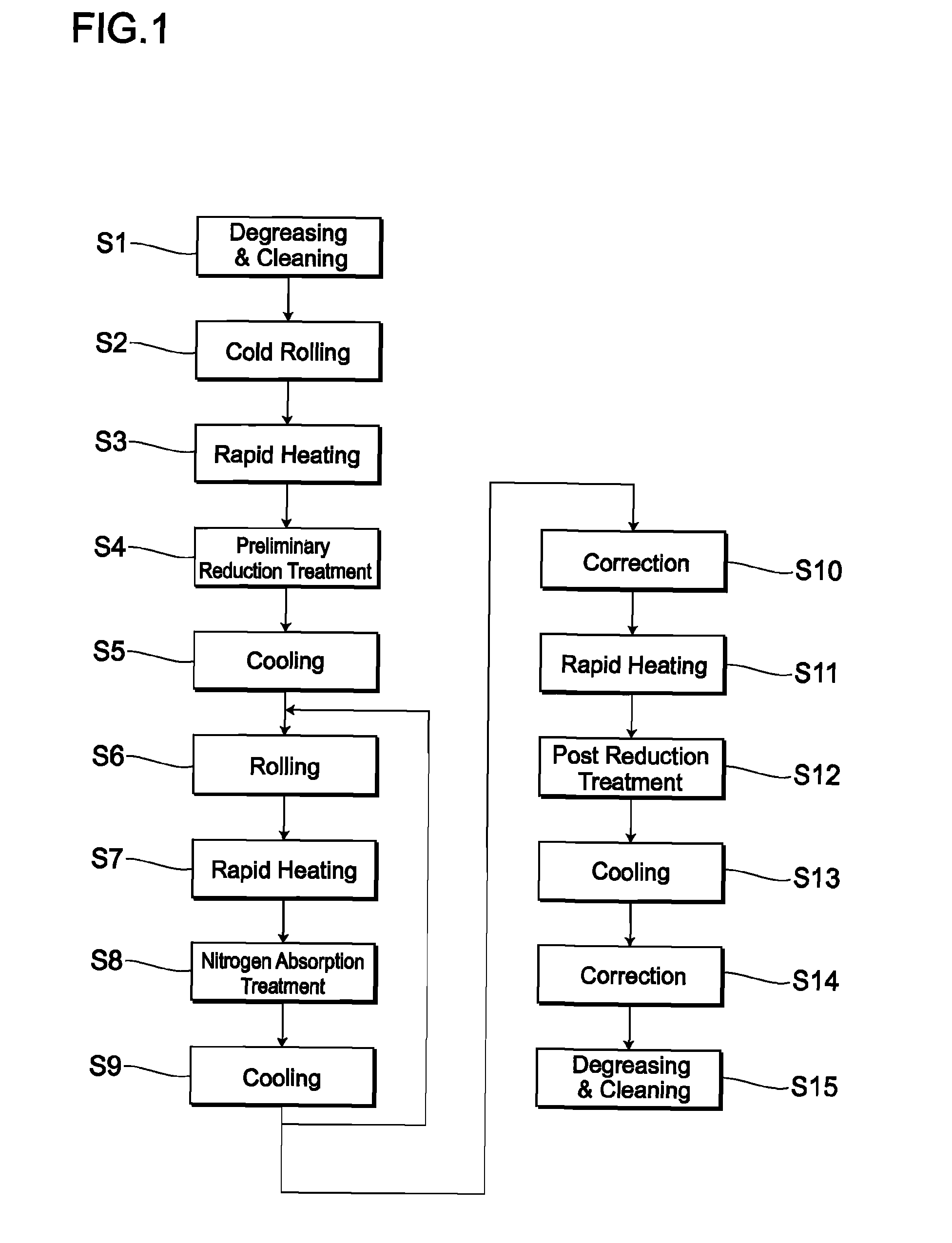
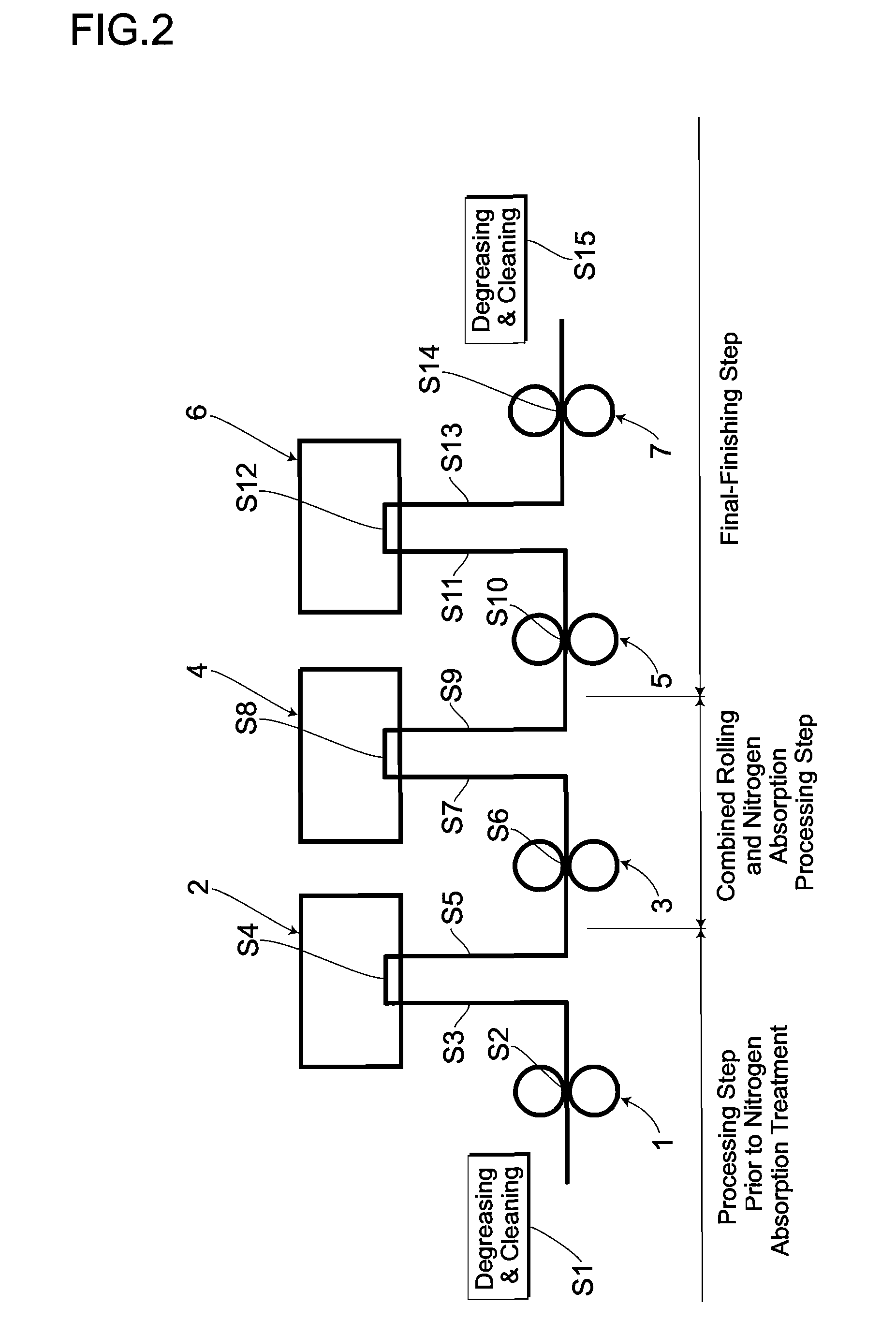
Oxygen concentrating aroma mixing breathable air delivery apparatus and method
InactiveUS6866041B2Operating means/releasing devices for valvesOther heat production devicesAtmospheric airAir compressor
An apparatus for concentrating the oxygen content of and injecting aroma into a stream of air and delivering the stream of air to the nostrils of a person includes an air intake filter in fluid communication with the air compressor for drawing a stream of air out of the surrounding atmosphere; a sieve bed in fluid communication with the air intake means, each sieve bed containing a quantity of nitrogen absorption material and having sieve bed input and output valve mechanism; so that the sieve bed extracts nitrogen from the air stream so that the proportion of oxygen exiting the sieve bed is elevated, and as the input valve mechanism closes, the sieve bed output valve mechanism opens and vents absorbed nitrogen from the sieve bed to the atmosphere; an aroma chamber containing aroma releasing material in fluid communication with the output valve mechanism.
Owner:EVOLUTION
Nodular Silica Sol and Method of Producing the Same
InactiveUS20100146864A1Easy to getImprove polishing effectPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesMaterials scienceNitrogen absorption
A novel nodular silica sol adapted to use as a polishing material for polishing, for instance, CMP.The nodular silica sol has a ratio of an average particle diameter (r) measured by the dynamic light scattering method versus a particle diameter (r′) converted to that of an equivalent sphere computed from an average specific surface area measured by means of the nitrogen absorption method (r / r′, referred to as “association ratio”) in a range from 1.2 to 10, the particle diameter (r′) in a range from 5 to 200 nm, and the specific surface area in a range from 13 to 550 m2 / g. The nodular silica particles have heterogeneous forms, and contents of Ca and Mg contained in the nodular silica particles are below 1000 ppm against SiO2 respectively.
Owner:JGC CATALYSTS & CHEM LTD
Modified clay new material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102091609APhysical/chemical process catalystsOther chemical processesSilicon oxideAcid substances
The invention relates to a modified clay new material and a preparation method thereof. The new material is characterized in that the new material is a compound of dealuminated clay with large pore volume and high specific surface area and pseudo-boehmite or boehmite; the new material comprises the following main components: silicon oxide and aluminium oxide; the molar ratio of SiO2 to Al2O3 is (0.01-50):1; the BET specific surface area is 80-800m2 / g; and the low-temperature nitrogen absorption pore volume is 0.2-3.0ml / g. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly mixing the clay with certain amount of acids or alkalis to react at the temperature of 40-600 DEG C for 10 minutes to 48 hours to carry out dealuminizing to form a mixture of the clay and the aluminium salt, then adding 0-10% of pore-forming agents on dry basis to the mixture, mixing the mixture uniformly and carrying out a reaction on the mixture and alkaline substances or acidic substances, controlling the pH value to be 6-12, then raising the temperature to 50-200 DEG C for aging for 0.2-24 hours and drying the filter cake at the temperature of 60-500 DEG C after filtering and washing, thus obtaining the new material. The new material and the preparation method overcome the defects of poor viscosity of the modified clay, existence of waste residues in the production process and the like in the prior art.
Owner:于向真
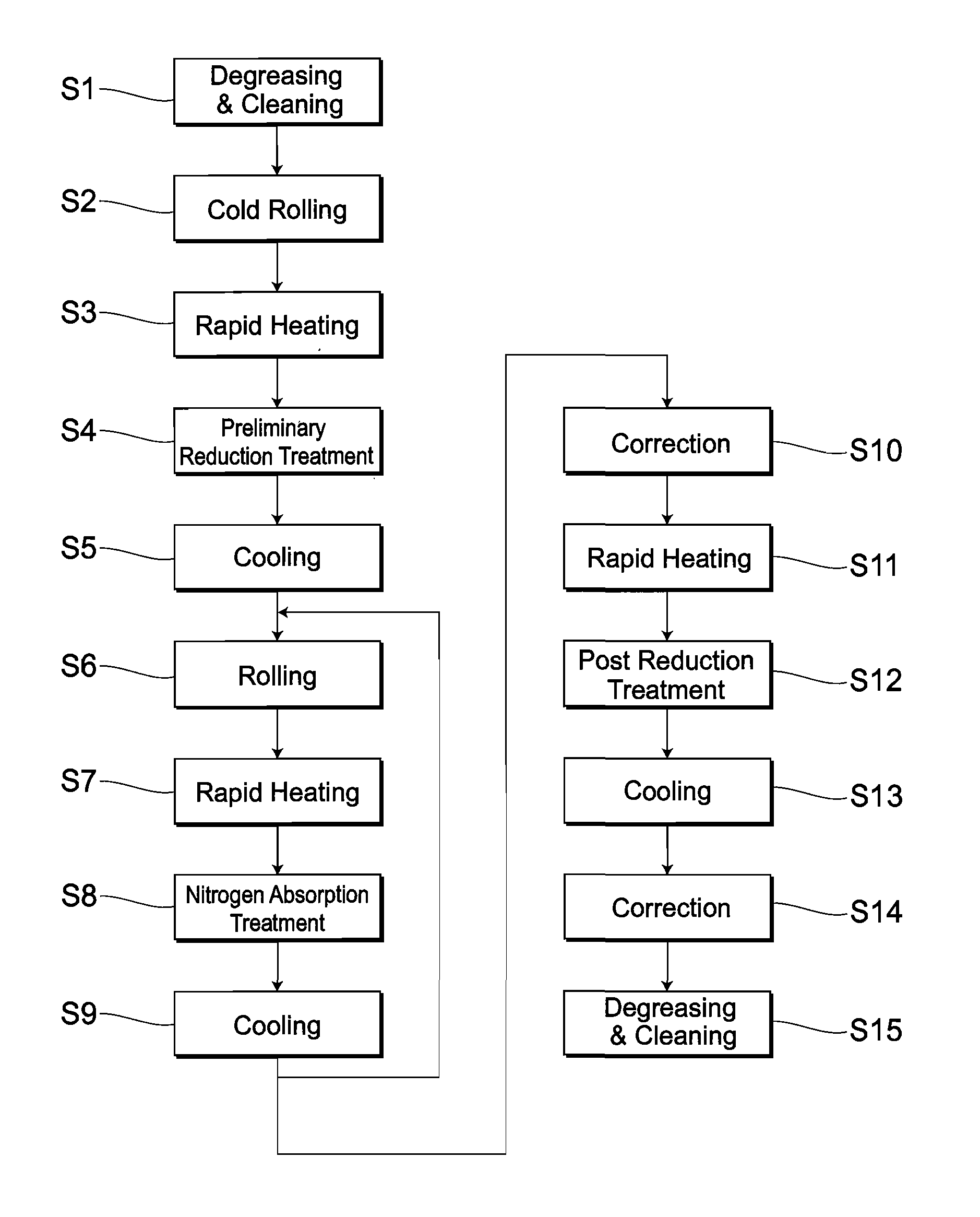
Method for manufacturing a stainless steel product and a stainless steel product manufactured by the method
InactiveUS20070186999A1Improve corrosion resistanceImprove workabilitySolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesNitrogen gasCorrosion
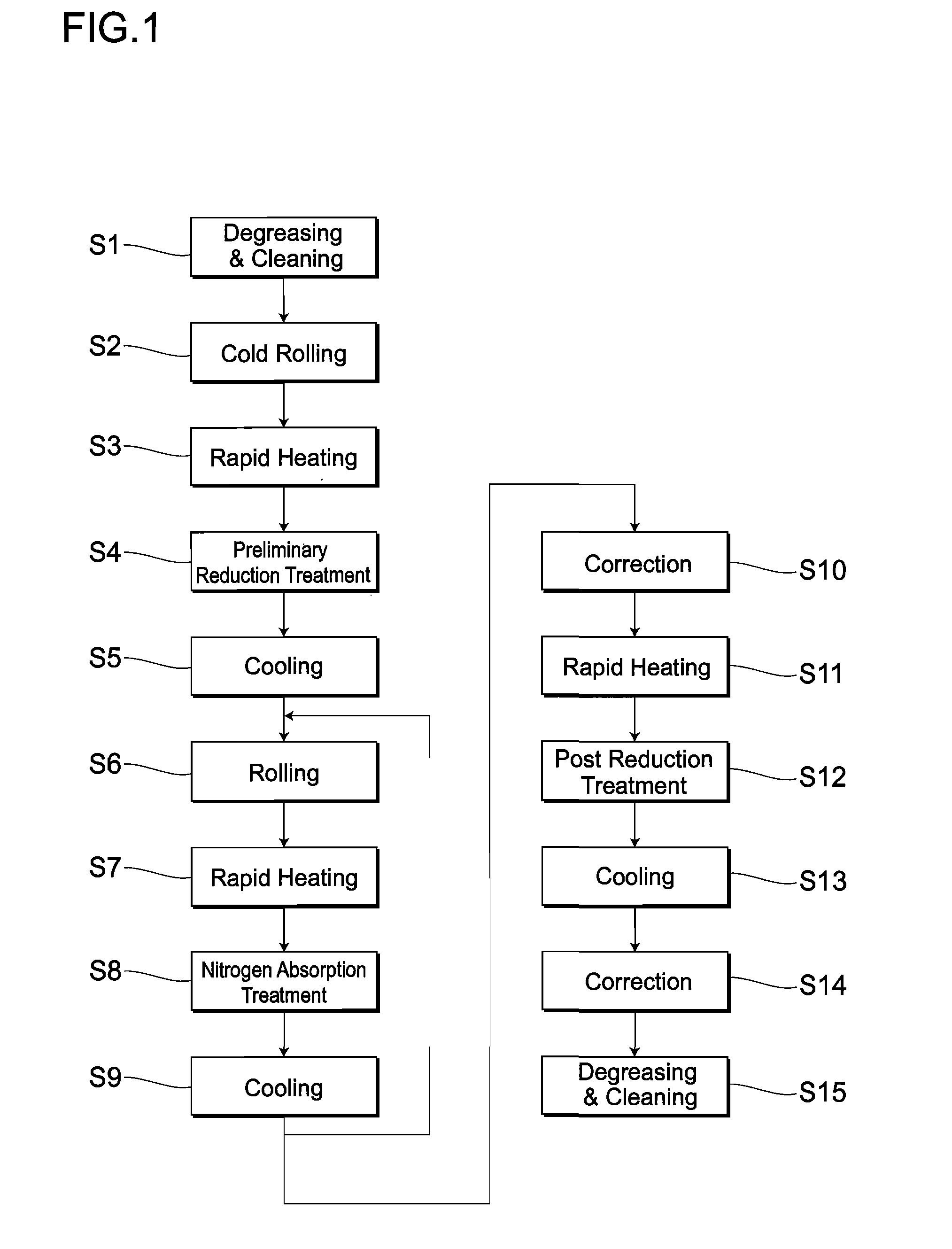
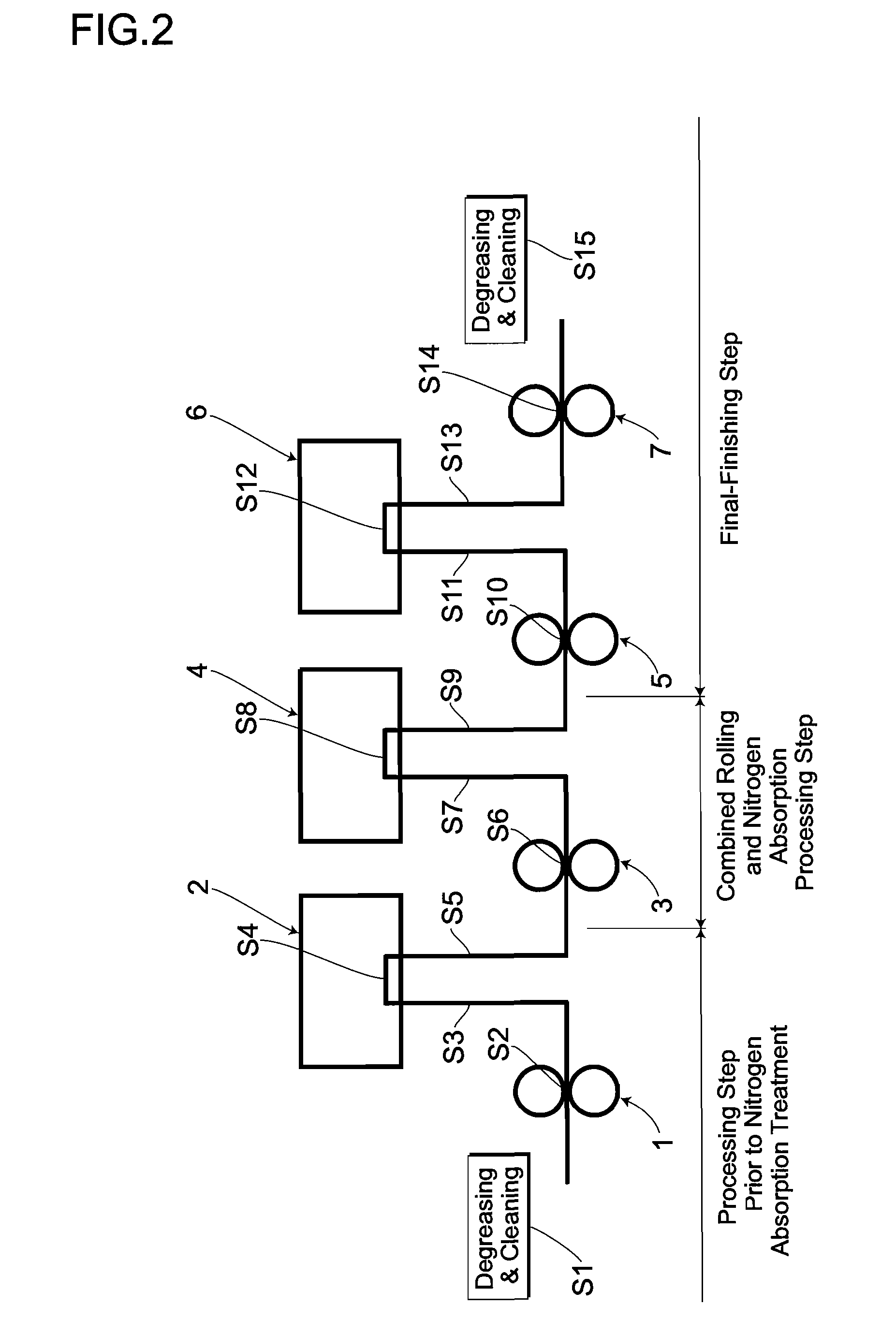
A Ni-free stainless steel product excellent in workability and corrosion resistance and a method for manufacturing such stainless steel product. A ferritic stainless steel product containing 18 to 24% by mass of Cr and 0 to 4% by mass of Mo is brought into contact with an inert gas containing a nitrogen gas at 800 degrees C. or above to subject it to nitrogen absorption treatment so that the product is austenitized partially or wholly to obtain such nickel-free product.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI +1
Electric heating element and method for its production
On the one hand is provided an electric heating element (15, 31) consisting of a semiconducting ceramic (28, 32) as well as a method for its production. The semiconducting ceramic material may be porous or foamed to thus contain pores (29, 34) open outwardly. The pores are attainable by admixing filler bodies, which dissolve during sintering, to the starting material or by impreganting a textile substrate material (36) with a ceramic material. Due to the porosity of the heating element (15, 31) an increased radiant surface area is attained. On the other hand is provided an electric heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) as well as a method for its production which consists of semiconducting ceramic and comprises a negative temperature coefficient of the electrical resistance. The temperature coefficient is negative throughout over the full operating temperature range. The material suitable for the heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) is doped silicon carbide or TiN. One such heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) may be put to use, for example, rod-shaped in a radiant heater body (111) or foil-shaped at the underside of a surface element (30) of a cooktop (31). The electric conductivity of the material of the heating element (115, 132, 145, 150, 158, 160, 162) can be adjusted by nitrogen absorption during annealing in a nitrogen atmosphere subsequent to the sintering process.
Owner:E G O ELEKTRO GERAETEBAU GMBH
Rubber composition for tread used for studless tire and studless tire having tread using thereof
InactiveUS20100184908A1Improve wear resistanceReduce hardnessSpecial tyresTyre tread bands/patternsPolymer sciencePolybutadiene
It is an object of the present invention to lessen strain dependency of hardness of a tread rubber used for a studless tire, have good performance on snow and ice while securing rigidity on non-snow roads, and improve abrasion resistance. The present invention provides a rubber composition for tread used for a studless tire comprising 30 to 150 parts by weight as a total of (1) silica with a nitrogen absorption specific surface area of at most 100 m2 / g and (2) silica with a nitrogen absorption specific surface area of at least 180 m2 / g based on 100 parts by weight of a rubber component in which a content of a natural rubber and / or a polybutadiene rubber is at least 80% by weight, wherein contents of silica (1) and silica (2) satisfy the formula below:[Content of silica (1)]×0.2≦[Content of silica (2)]≦[Content of silica (1)]×6.5,tan δ peak temperature Tg is at most −50° C., and rubber hardness at 0° C. is at most 64.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Gene OsPTR9 capable of improving nitrogen absorption efficiency and yield of rice and application thereof
InactiveCN102604962AEnhanced tillering abilityIncrease productionBacteriaClimate change adaptationGrowth plantMutant
The invention relates to the field of plant genetic engineering, and in particular relates to separation, cloning and application of a gene OsPTR9 which can improve nitrogen utilization efficiency and yield of rice. The OsPTR9 is one gene in a rice PTR (peptide transporter family) family, and an encoded protein is a nitrogenous organic matter transporter. In the invention, the OsPTR9 gene is excessively expressed, so that nitrogen fertilizer absorbing efficiency of normal rice is improved, tillering capacity is improved, ear length and thousand seed weight are increased, and functions of the OsPTR9 gene is verified in an OsPTR9 target gene mutant by adopting an RNAi (ribonucleic acid interference) technology. According to the invention, the expression quantity of the OsPTR9 gene is increased or reduced by adopting a genetic engineering technology, which sufficiently shows that the OsPTR9 gene can control the nitrogen absorption, plant tillering, ear length and thousand seed weight andthe like of the rice. The gene has important application values in the aspects of explaining influence of nitrogen on a plant growth and development process, efficiently utilizing nitrogen fertilizerfor the rice and improving the yield.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for catalytically oxidizing cyclohexane
ActiveCN102079695AIncrease the degree of mixingExtend your lifePreparation by oxidation reactionsMolecular sieve catalystsHysteresisDesorption
The invention discloses a method for catalytically oxidizing cyclohexane, which is characterized in that cyclohexane, hydrogen peroxide and a catalyst are in contact for reacting, the mol ratio of the cyclohexane to the hydrogen peroxide is 0.5-8, the concentration of the catalyst in a reaction system is 0.005-0.1g / min, the reaction temperature is 40-150 DEG C, the catalyst is a titanium-silicon molecular sieve with an MFI structure, a hysteresis loop exits between an adsorption isotherm and a desorption isotherm of low-temperature nitrogen absorption of the molecular sieve, a crystalline grain is a single hollow crystalline grain or an aggregated crystalline grain formed by the aggregation of a plurality of hollow crystalline grains, the radial length of the cavity part of the hollow crystalline grains is 5-300nm, and the benzene adsorption capacity of the sample of the molecular sieve, measured under the conditions that the absorption time is 1h, the temperature is 25 DEG C and P / P0 is equal to 0.10, is at least 70mg / g. The method has the advantages of high selectivity of a target product and environment protection.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery and process for producing positive electrode for use in non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20060292447A1Large capacityExcellent cycle characteristicsOrganic electrolyte cellsSecondary cellsLithium metalDesorption
A non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery in which a positive electrode formed of a graphite powder and an negative electrode formed of a material capable of absorption / desorption of a lithium metal or lithium are placed to face each other in an electrolyte containing lithium salt. The positive electrode of this battery where a Lc (112) which is the size of crystallite in a c axis direction which is calculated from a (112) diffraction line of a graphite crystal and determined by a powder X-ray diffraction method which is from 4 nm to 30 nm, and a charge capacity at the first cycle which is calculated on the basis of a total weight of the graphite material of the positive electrode filled in the battery is 20 to 50 (mAh / g). Preferably, the graphite powder of the positive electrode has an ratio (A / B) which is the ratio of a specific surface area A determined by a nitrogen absorption (BET) method to a surface area B determined on the basis of an area average diameter of 20 or less.
Owner:FDK CORP
Lithium ion cell, anode therefor and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN1949561AGood dispersionImprove cycle performanceElectrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureLithiumAdhesive
The invention is an Li ion battery anode, comprising collector and coated and / or filled anode material on the collector, where the anode material comprises anode active matter, conducting agent and adhesive, the adhesive contains charcoal black which has a specific surface area above 500m2 / g obtained by nitrogen absorption, where the anode material also comprises dispersant. And a Li ion battery using the anode has good circulating performance and multiplying discharging performance.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Method for preparing epoxypropane
ActiveCN101397282ALow non-framework titanium contentIncrease the speed of diffusionOrganic chemistryMolecular sieve catalystsHysteresisMass ratio
The invention discloses a method used for preparing propylene oxide. The method is characterized in that propylene, oxygen, hydrogen, a solvent and a catalyst are mixed for contact reaction at the temperature of 0 to 8 DEG C and the pressure of 0.1 to 3.0 MPa; the molar ratio between the propylene, the oxygen and the hydrogen is 1:(0.1 to 10):(0.1 to 10) and the mass ratio between the propylene and the catalyst is (0.1 to 50):1 and the mass ratio between the solvent and the catalyst is (10 to 1000):1; the catalyst appears as a palladium-loaded hollow titanium-silicate molecular sieve with MFI structure, and the radial length of the grain hollow cavity on the molecular sieve is between 5 and 300 nanometers; and benzene absorption is measured to be at least 70 milligram / gram under the conditions that the temperature is 25 DEG C, the P / P0 is equal to 0.10 and the absorption time is one hour; and a hysteresis loop exists between an absorption isotherm for cryogenic nitrogen absorption and a desorption isotherm. The method has high propylene conversion rate and high propylene oxide selectivity; especially the effective availability of hydrogen is higher and the stability of activity is better.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Tire rubber composite and pneumatic tire
ActiveCN104245817AGood dispersionLow wear resistanceSpecial tyresRolling resistance optimizationRolling resistancePolymer science
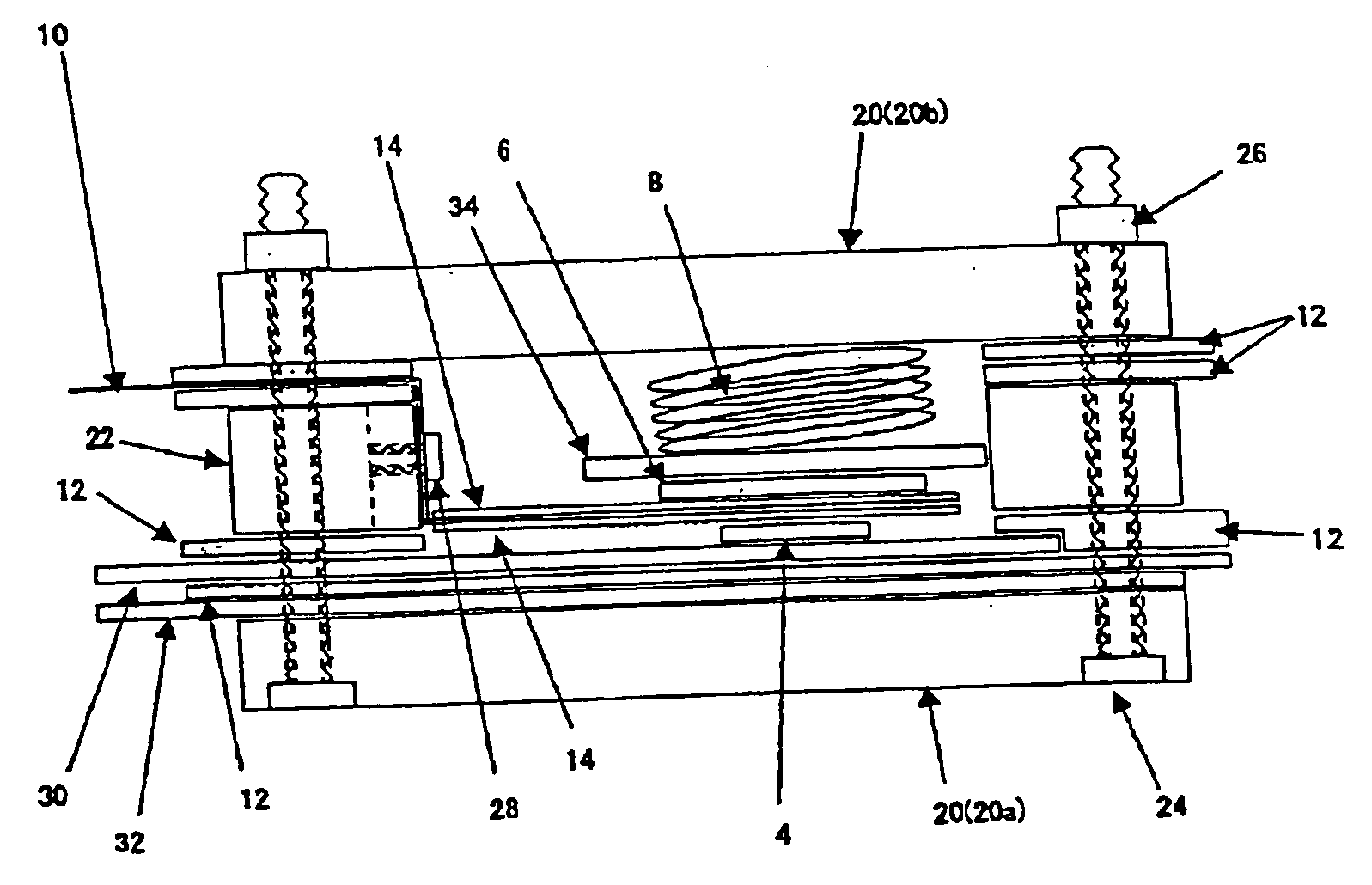
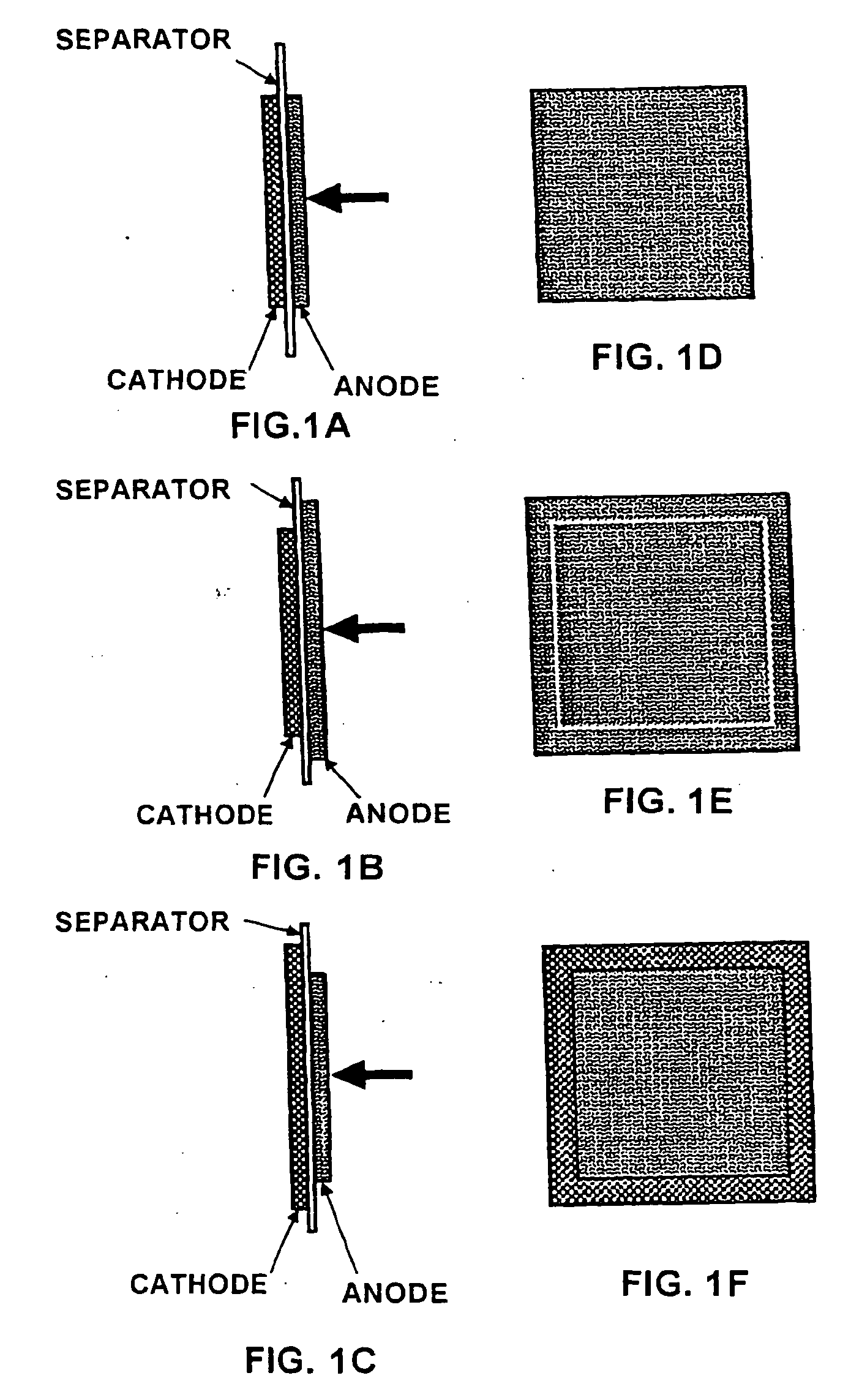
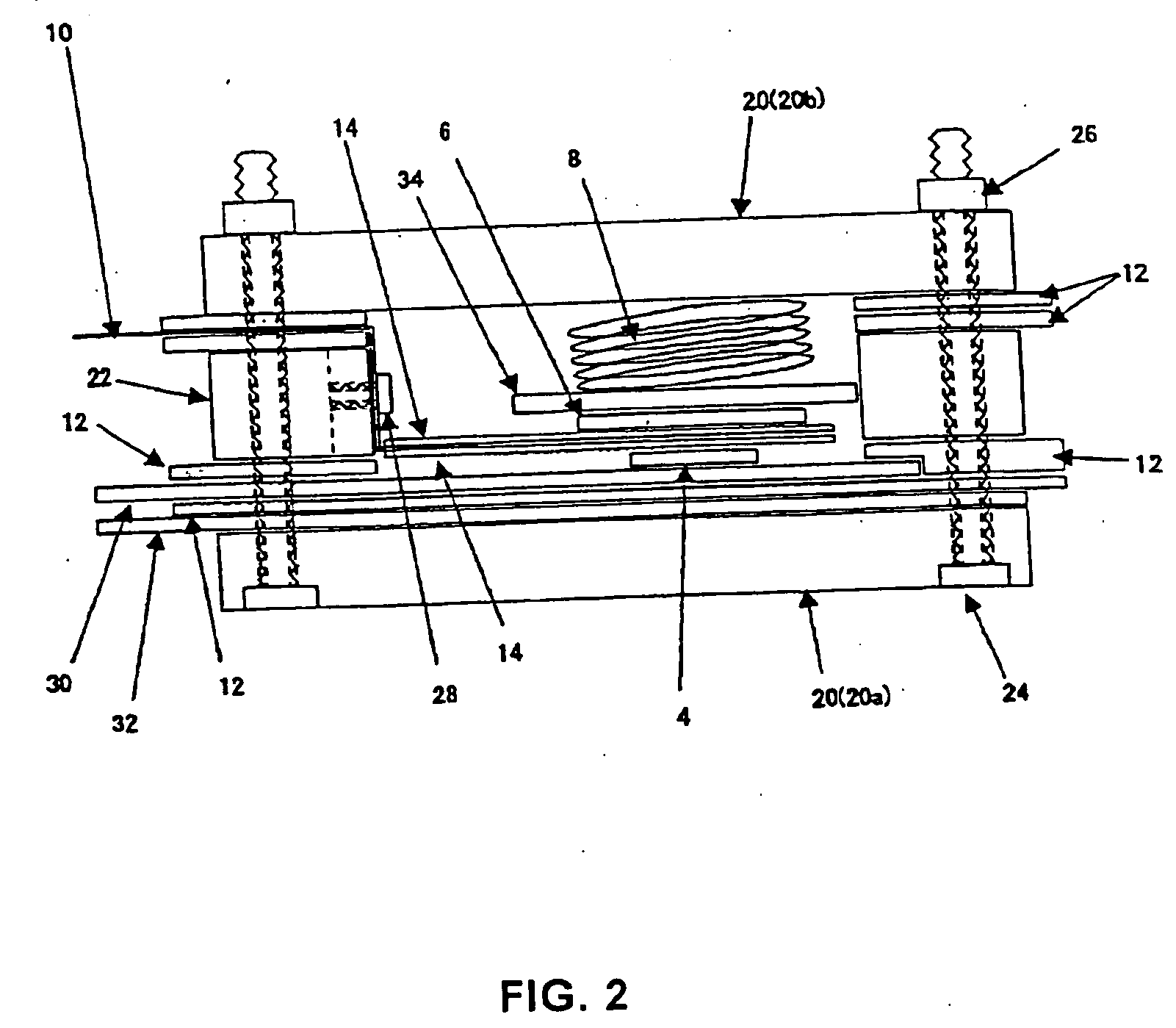
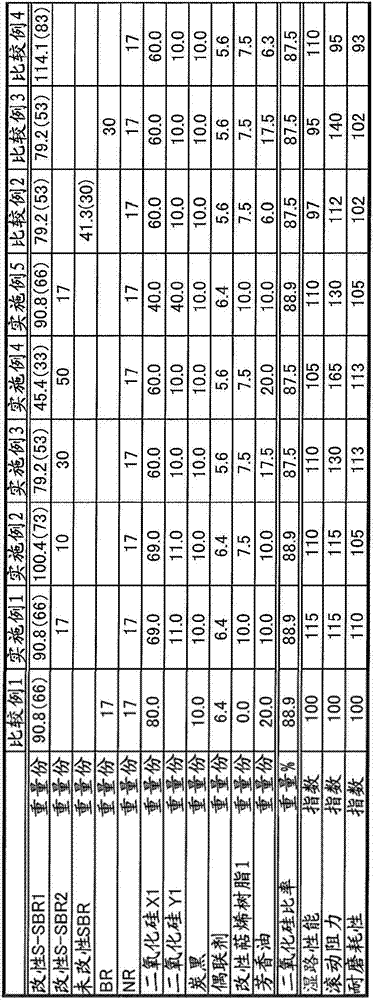
Provided is a tire rubber composition that has lower rolling resistance, and improved wet performance and abrasion resistance compared to conventional levels. The composition is characterized in that: 2-50 parts by weight of an aromatic modified terpene resin with a softening point of at least 100 DEG C and a total of 60-130 parts by weight of two types of silica, silica X and silica Y, are added to 100 parts by weight of a diene rubber that includes 5-50 wt% of a terminal-modified S-SBR having a vinyl unit content of at least 25 wt% and a glass transition temperature of - 50 DEG C or below; the functional group of the modified S-SBR is reactive with a silanol group; a reinforcing filler comprising of silica X, silica Y and optionally added carbon black includes the silica at a proportion of at least 85 wt%; the specific surface area of silica X as determined by nitrogen absorption is at least 140m<2> / g; the specific surface area of silica Y as determined by nitrogen absorption is 100-140m<2> / g exclusive; and if the respective masses of silica X and silica Y per 100 parts by weight of the diene rubber are expressed as x parts by weight and y parts by weight, the relationship x / 7 < y <=x is satisfied.
Owner:THE YOKOHAMA RUBBER CO LTD
Tire
The object is to improve both of low rolling resistance and strength of a tire. Disclosed is a tire comprising a side-wall, a case and an inner liner, wherein the side-wall comprises a rubber composition (A) for a side-wall which comprises 100 parts by weight of a specific rubber component (A1) and 20 to 45 parts by weight of a filler (A2), the case has a code coated with a rubber composition (B) for a case code which comprises 100 parts by weight of a specific rubber component (B1) and 20-45 parts by weight of a filler (B2), and the inner liner comprises a rubber composition (C) for an inner liner which comprises 100 parts by weight of a rubber component (C1) containing a butyl rubber at a content of 35-80 wt% and 15-45 parts by weight of a carbon black (C2) having a nitrogen-absorption specific surface area of 20-45 m2 / g.
Owner:SUMITOMO RUBBER IND LTD
Nitrate transport protein of diatom and its coding gene and application
InactiveCN1887903ANormal growthImprove nitrogen absorption capacityAlgae/lichens peptidesFermentationNicotiana tabacumLow nitrogen
The present invention is kind of nitrate transport protein of diatom and its coding gene and application in transgenic plant. The nitrate transport protein has one of the following amino acid residue sequence: 1. SEQ ID No. 1 in the sequence list; and 2. the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No. 1 through substitution, deletion or addition of 1-10 amino acid residues and coding protein possessing nitrate transport function. The transgenic tobacco, rice or lawn grass with the gene of the present invention NAT3 can grow normally on the culture medium with nitrogen element content only 1 / 32 normal value, and this proves the capacity of NAT3 in raising the nitrogen absorption. The present invention may have wide application foreground in plant nitrogen fertilizer absorption and breeding low nitrogen resisting plant variety.
Owner:北京优利康生物农业技术有限公司
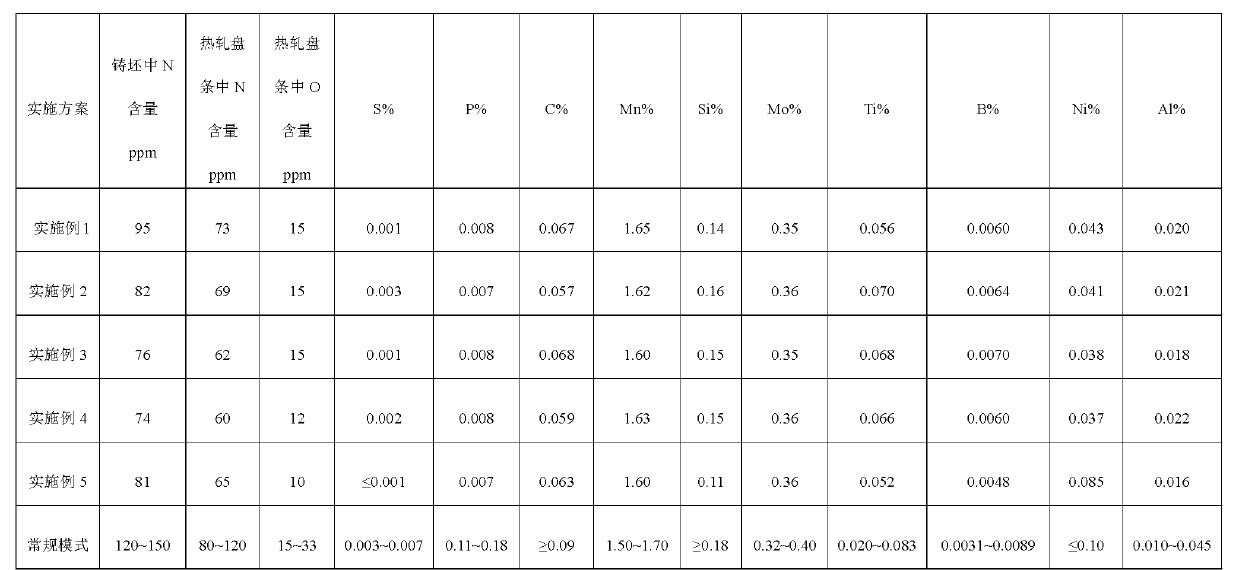
Method for reducing nitrogen content of welding steel wire rod
ActiveCN103276153AEasy to operateEasy to controlProcess efficiency improvementElectric furnaceFiberSlag (welding)
The invention discloses a method for reducing the nitrogen content of a welding steel wire rod. The method comprises the following steps of: treating the combination of molten iron and waste steel in a primary refining electric furnace, wherein the molten iron accounts for more than 70 percent; tapping at the temperature of between 1,620 and 1,650 DEG C; adding 10 to 20 kg / ton of metallic manganese and 4 to 10 kg / ton of ferromolybdenum into the molten steel after tapping, and delivering the mixture to a refining furnace; after the mixture is delivered to the low frequency (LF) refining furnace, sequentially adding a first batch of slag and a second batch of slag; after the slag becomes white, performing fine adjustment of alloy in the LF refining furnace to prevent nitrogen absorption caused by the naked molten steel in the ladle hoisting process, and finally adding 1 to 2 kg / ton of powdery carbon-free covering agent; and preventing the molten steel from absorbing nitrogen by using a fiber sealing ring during continuous casting. The method is simple in process route, strong in operability and easy to control.
Owner:WUHAN IRON & STEEL GRP ECHENG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
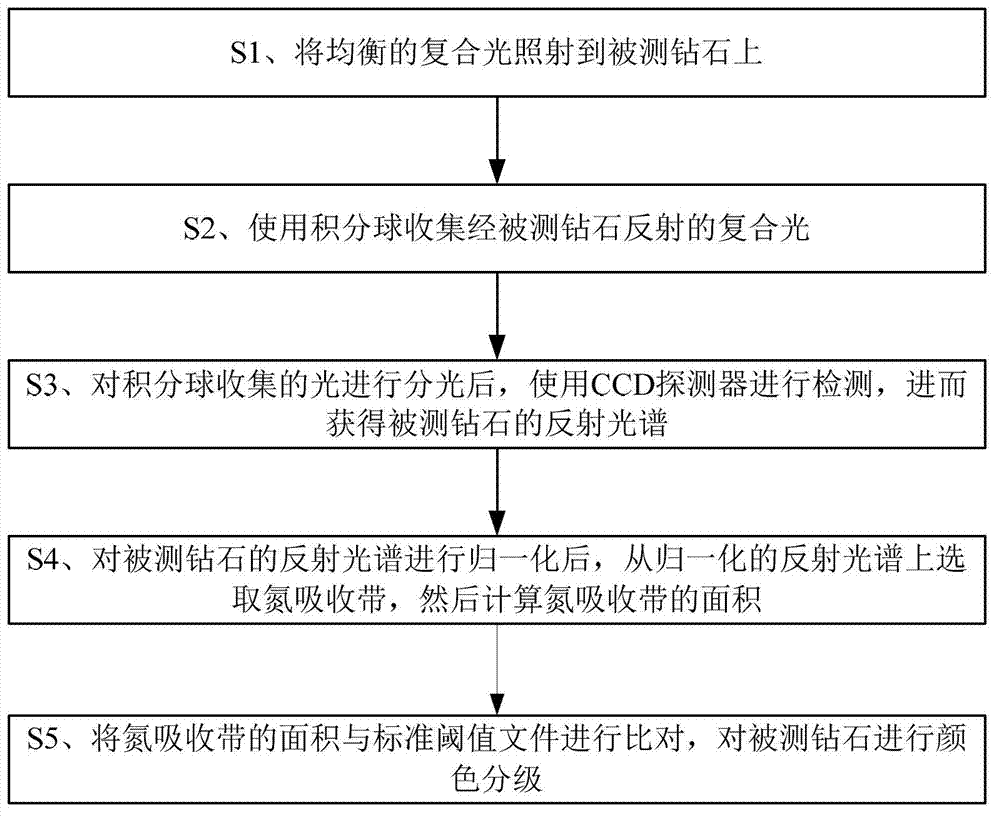
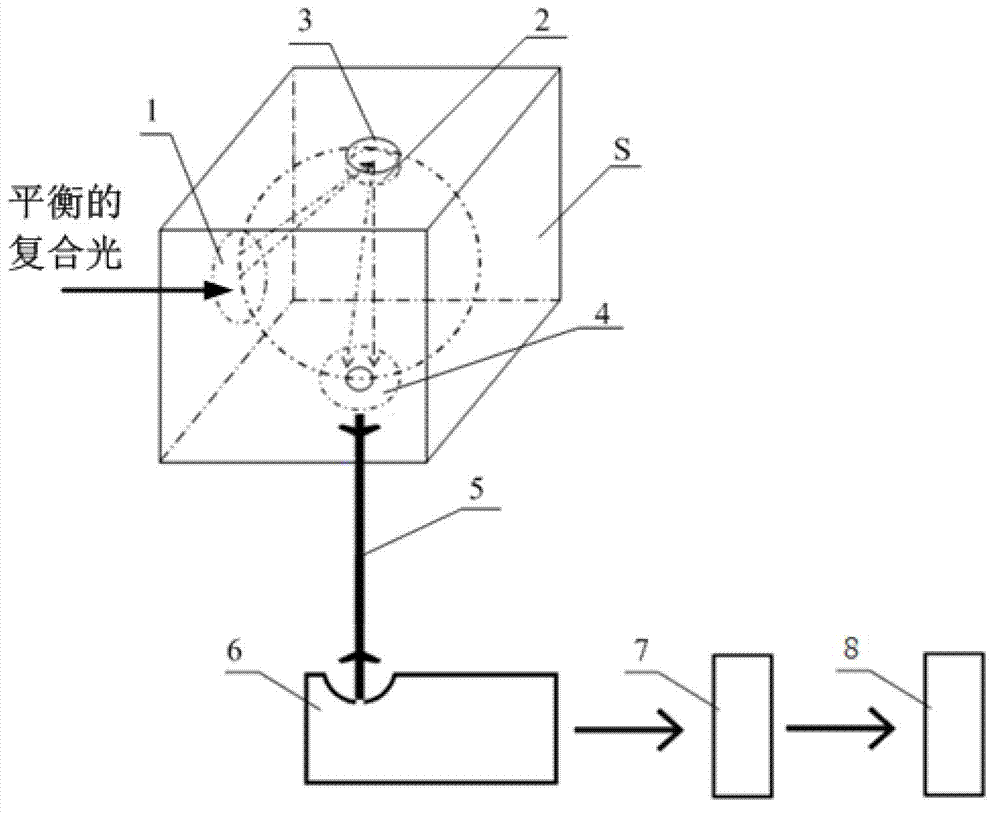
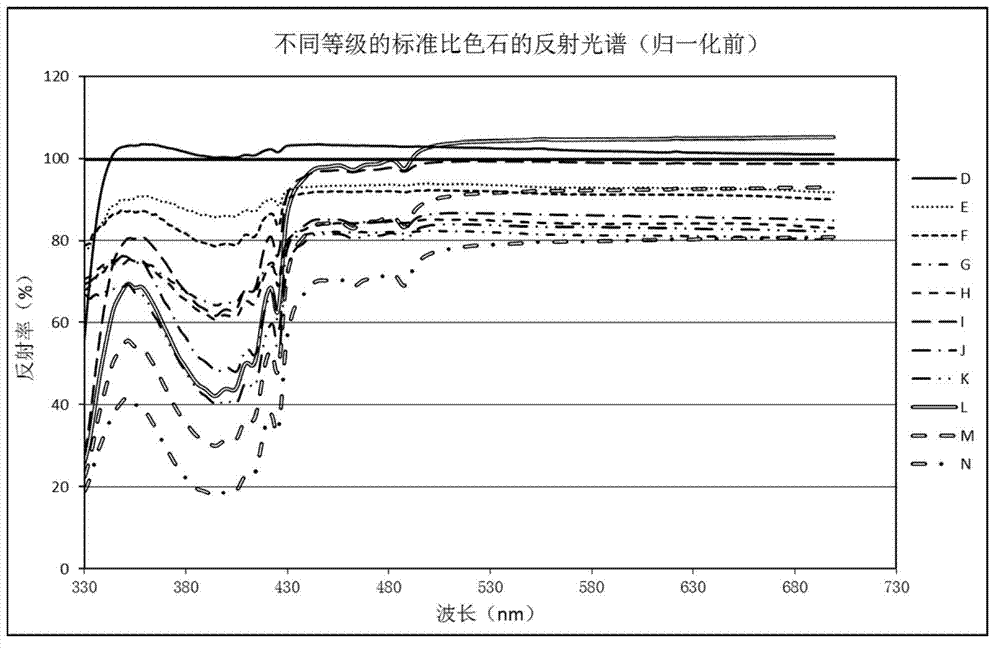
Ia type diamond color quick grading method based on spectrum
ActiveCN103090973AEasy to operateFast and Accurate TestingColor measuring devicesReflectance spectroscopyDiamond color
The invention discloses an Ia type diamond color quick grading method based on a spectrum. The Ia type diamond color quick grading method based on the spectrum comprises that balanced compound light is emitted on a to-be detected diamond, and the compound light which is reflected through the to-be detected diamond is collected through an integrating sphere. After the light collected by the integrating sphere is split, a charge coupled device (CCD) detector is used for detecting so as to obtain a reflectance spectrum of the to-be detected diamond. After the reflectance spectrum of the to-be detected diamond is uniformized, a nitrogen absorption band is selected from the uniformized reflectance spectrum, and then the area of the nitrogen absorption band is calculated. Compared the area of the nitrogen absorption band with a standard threshold value file, the color of the to-be detected diamond is graded. According to the Ia type diamond color quick grading method based on the spectrum, the nitrogen absorption band is selected from the reflectance spectrum of the collected to-be detected diamond and the area of the nitrogen absorption band is calculated, then the area of the nitrogen absorption band is compared with the standard threshold value file, and so that the grading of the color of the diamond is achieved. The Ia type diamond color quick grading method based on the spectrum is simple in operation, quick and accurate in testing, high in consistency and capable of being widely used in the jewelry identification industry.
Owner:BIAOQI ELECTRONICS TECH
Sewage nitrogen and phosphorus removal method and device
InactiveCN104710081ATo achieve a large amount of degradationGuarantee the effect of water dischargeMultistage water/sewage treatmentAmmoniacal nitrogenWater flow
The invention discloses a sewage nitrogen and phosphorus removal method and device. The device comprises a water inlet tank (1), an anaerobic membrane bioreactor (2), an adsorption tank, a gas separation membrane device (11) and an ammonia nitrogen absorption tank (13) which are connected in sequence, wherein sewage enters the anaerobic membrane bioreactor (2) from the water inlet tank (1) for anaerobic hydration; a vacuum membrane pump (14) and a membrane surface washing device (19) conduct membrane surface washing on the anaerobic membrane bioreactor (2); the sewage after hydration enters the adsorption tank for adsorption phosphorus removal; the sewage after adsorption phosphorus removal and alkalinity medical liquid react; the sewage is separated into purified water and ammonia gas after the sewage enters the gas separation membrane device (11); the ammonia gas enters the ammonia nitrogen absorption cell (13) after the ammonia gas reacts with acidity medical liquid; purified water flows out from a water outlet. According to the invention, 99% of ammonia nitrogen (NH3-N) is removed and recovered; 98% of phosphorus (P) is removed and recovered; water outlet effect is good; new energy is provided; energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Electric Double Layer Capacitor
InactiveUS20100220429A1Increased durabilityImprove securityHybrid capacitor electrolytesProtecting/adjusting hybrid/EDL capacitorActivated carbonOptoelectronics
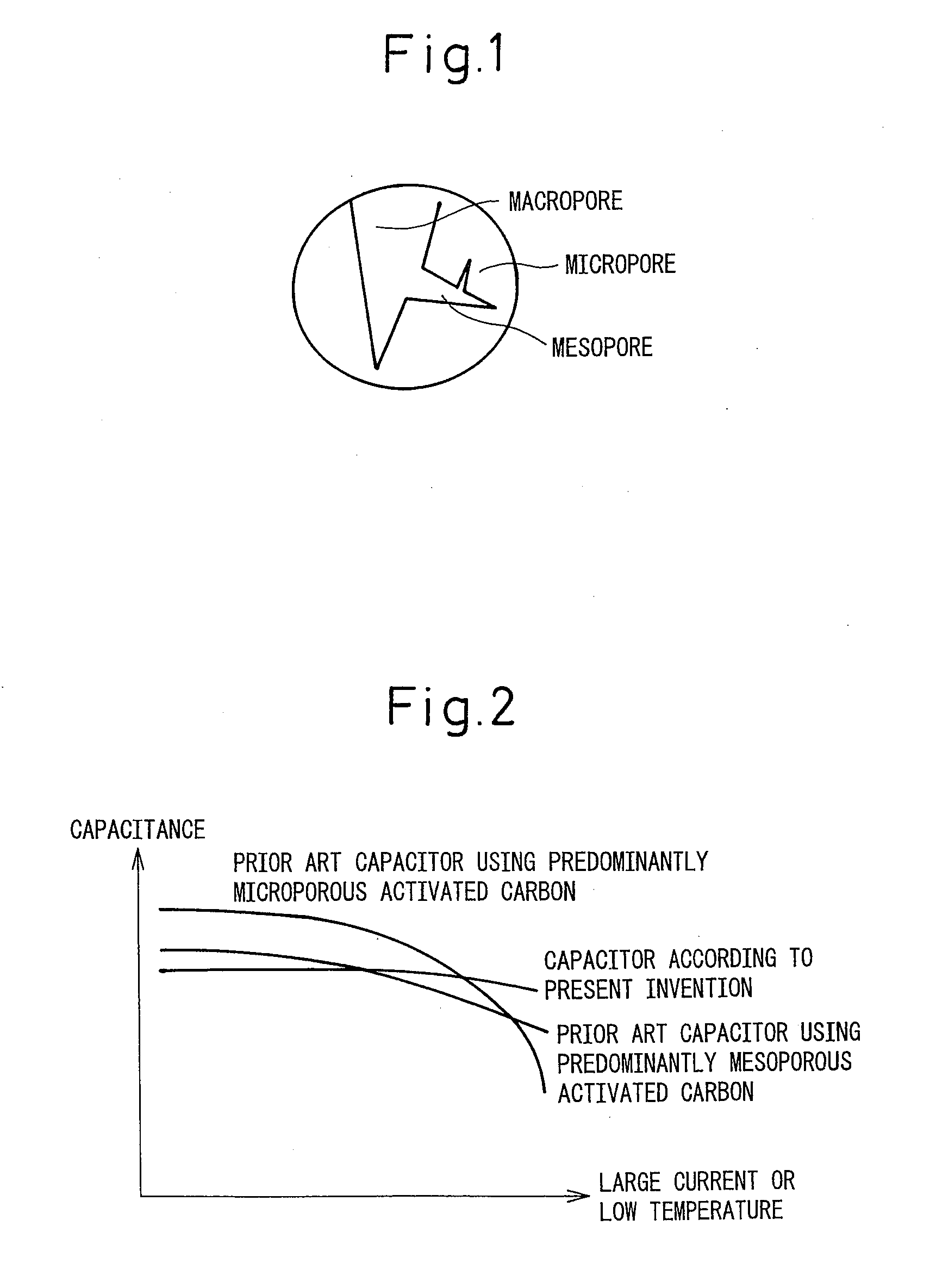
Disclosed is an electric double layer capacitor comprising a polarizable electrode layer that contains an activated carbon, a conductive agent, and a binder, wherein an external specific surface area of the activated carbon (defined as a specific surface area calculated from a nitrogen absorption isotherm by a t-plot method by excluding micropores of pore diameter smaller than 20 angstroms), per unit volume of the polarizable electrode layer, lies within a range of 450 to 800 m2 / cm3, and a volume based on inter-particle interstices per unit volume of the polarizable electrode layer lies within a range of 0.05 to 0.12 cm3 / cm3. The electric double layer capacitor according to the present invention is particularly suited to large current, quick discharge applications.
Owner:W L GORE & ASSOC GK
Microporous and mesoporous carbon xerogel having a characteristic mesopore size and precursors thereof and a process for producing these and their use
InactiveCN102083523APrevent collapseHigh porosityCarbon compoundsCell electrodesSupercritical dryingFreeze-drying
The invention relates to a microporous and mesoporous carbon xerogel and organic precursors thereof based on a phenol-formaldehyde xerogel. A characteristic parameter common to carbon xerogels is a peak in the mesopore size distribution determined by the BJH method (Barrett-Joyner-Halenda) from nitrogen absorption measurements at 77 K in the range from 3.5 nm to 4 nm. The production process is characterized firstly by the low starting material costs (use of phenol instead of resorcinol) and secondly by very simple and cost-effective processing; convective drying without solvent exchange instead of supercritical drying or freeze drying. The carbon xerogels and their organic phenol-formaldehyde xerogel precursors have densities of 0.20-1.20 g / cm3, corresponding to a porosity of up to 89%, and the xerogels can also have a relevant mesopore volume. The carbon xerogels obtained from the phenol-formaldehyde xerogels are also microporous.
Owner:EVONIK CARBON BLACK GMBH
Detection algorithm for pore structure of shale gas reservoir
InactiveCN104034645AAccurate valuationValuation validPermeability/surface area analysisRock coreRelative pressure
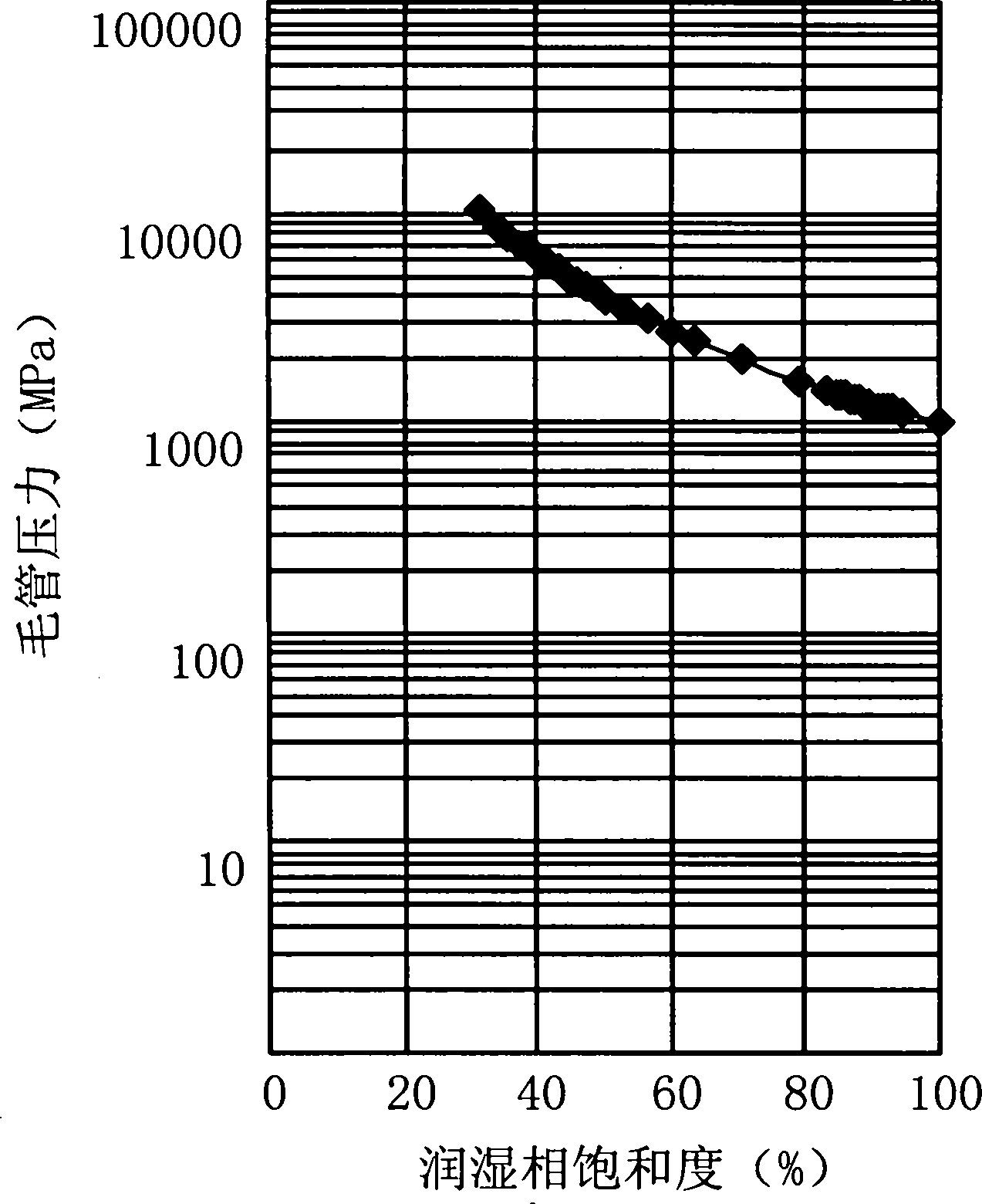
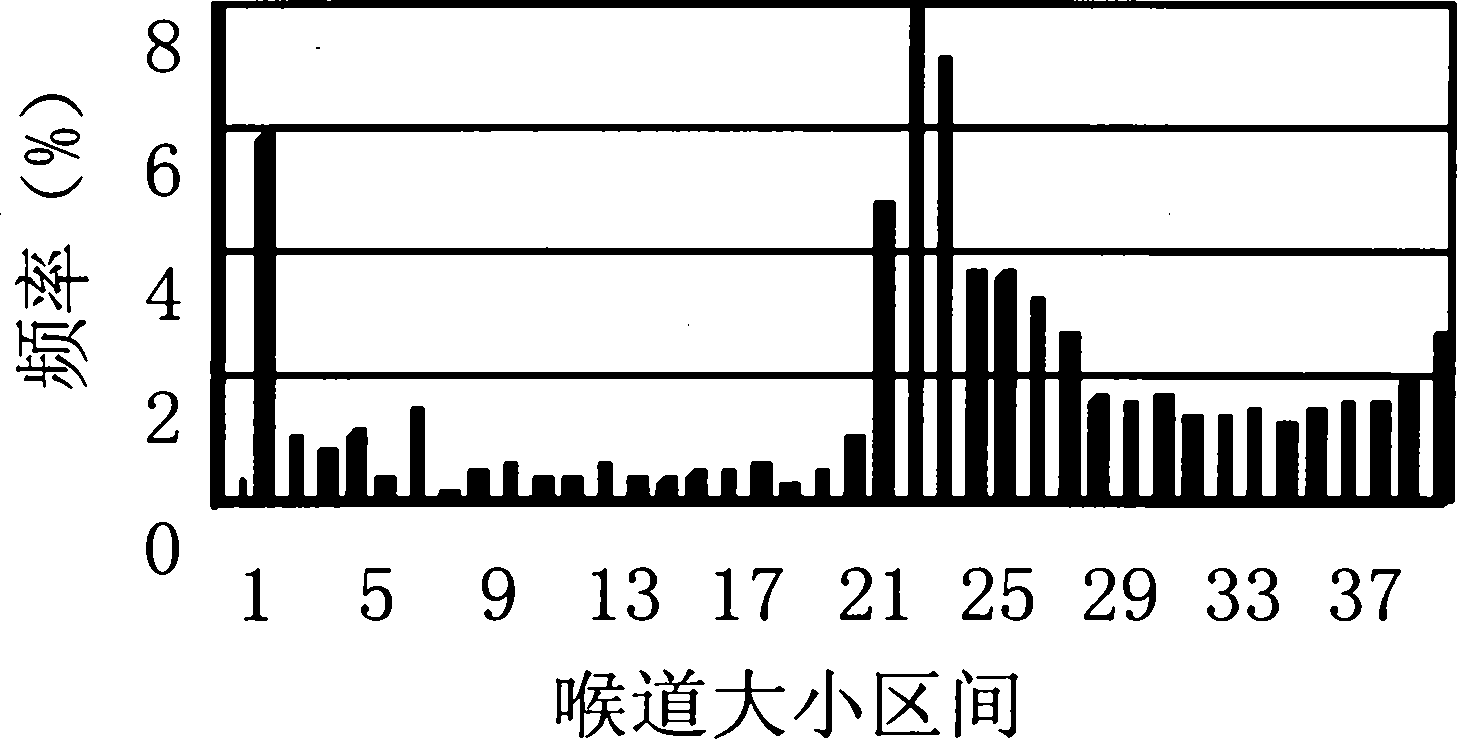
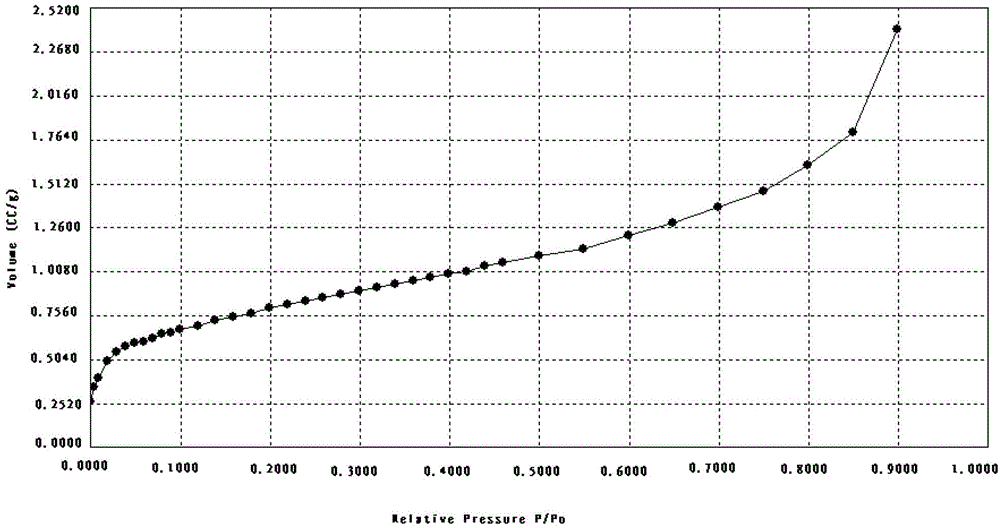
The invention discloses a detection algorithm for the pore structure of a shale gas reservoir. The detection algorithm comprises the step of carrying out specific surface analysis and detection to obtain partial data by adopting a nitrogen absorption method, and also comprises the following steps: (1) in the pressure reducing process after nitrogen is absorbed to maximum pressure, gradually and respectively converting staged desorbing amount of the nitrogen into the percent of the volume of a desorbed wetting phase at stages accounting for the volume of a rock-core pore and the percent of the volume of the desorbed nitrogen accounting for the total volume of the rock core; (2) calculating out the thickness of a wetting film in the process of staged desorption, namely, the throat radius of the process, by adopting a digital model for calculating the thickness of a water film according to the specific surface of nitrogen absorption and the density of the rock core; and (3) according to the relation of the capillary pressure theory, obtaining capillary pressure under the corresponding and relative pressure and a capillary pressure curve in the whole desorption process. The detection algorithm disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the characteristics of the pore structure of the shale gas reservoir and the characteristics of seepage and production of natural gas can be intuitively described, further the value of the shale gas reservoir is evaluated, the practical value is very high and the application prospect is very wide.
Owner:向丹
Method for producing ultralow-sulfur steel under high vacuum
InactiveCN102787209AImprove slag capacityImprove quality pass rateManufacturing convertersAlkalinityMolten steel
The invention provides a method for producing an ultralow-sulfur steel under high vacuum, the sulfur content of steel discharged by a converter can be controlled below 0.010%; during the LF furnace refine treatment process, the sulfur content can be controlled at 0.005-0.007%, the slag alkalinity in the later stage can be controlled between 2.0-4.5, thereby a CaO-MgO-Al2O3-CaF slag system is formed, the total slag amount can be controlled at 8.5-10kg / ton steel, the argon flow during the whole process is 150-250N1 / min; and a VD furnace high vacuum treatment is carried out by using argon with a flow of 450-550N1 / min for mixing. Thereby the molten slag equivalent of slag can be enhanced, great flip of a molten steel surface can be avoided, the addition of the molten steel nitrogen absorption and impurities can be minimized, rapid operation during desulphurization process can be promoted, the sulfur content of the finished product can be controlled below 0.005%, and nitrogen content of the finished product can be controlled below 25ppm, and the qualified rate of ultralow-sulfur steel production can be increased.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Method for detecting coke air hole characteristics
InactiveCN102980843AEasy to operateReduce volumePermeability/surface area analysisCapillary condensationUnit mass
The invention provides a method for detecting coke air hole characteristics. The method comprises the following step of: measuring the total volume of air holes contained in coke samples per unit mass by utilizing an automatic nitrogen absorption instrument, and then combining with real coke sample volumes, thereby obtaining the air hole rate of the coke samples. Capillary condensation phenomenon and volume equivalent exchange principle are utilized for determining pore diameter distribution by a gas absorption method, namely, liquid nitrogen amount filled in tested holes are equivalent to the volumes of holes. The method for detecting coke air hole characteristics provided by the invention is convenient to operate, is small in device volume, and has good repeatability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for adding nitrogen into steel ladle
The invention relates to a method for adding nitrogen into a steel ladle. The method includes the following steps in sequence: (I) a steel ladle loaded with molten steel suitable for ladle furnace (LF) smelting is moved to an LF station; (II) according to the low limit of nitrogen content in the steel grade, the nitrogen content difference in AOD (argon oxygen decarburization) tapping and the amount of tapped molten steel, nitrogen to be replenished is calculated by the formula: (NL-NA)*MA*1000=G; the flow of nitrogen per minute is set as V which is converted into weight M by the formula: V / 22.4*28=M; the nitrogen absorption of high-nitrogen molten steel is 95%+ / -4%, the time of bottom nitrogen blowing is not shorter than T which is calculated by the formula: G*1000 / M / (95%+ / -4%), and nitrogen blowing T is added by 3 to 4 minutes. NL is the lower limit of nitrogen content in the smelted high-nitrogen steel; NA is the nitrogen content in the tapping of an AOD furnace; MA is the weight of the molten steel; and M is the weight of bottom-blown nitrogen per minute; and (III) the nitrogen-blowing operation is finished, and sample is taken out of the steel ladle and analyzed. The amount of nitrogen added by the method for adding nitrogen into the steel ladle can meet the requirement of high-nitrogen steel grades, and the time of adding nitrogen can be easily controlled.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
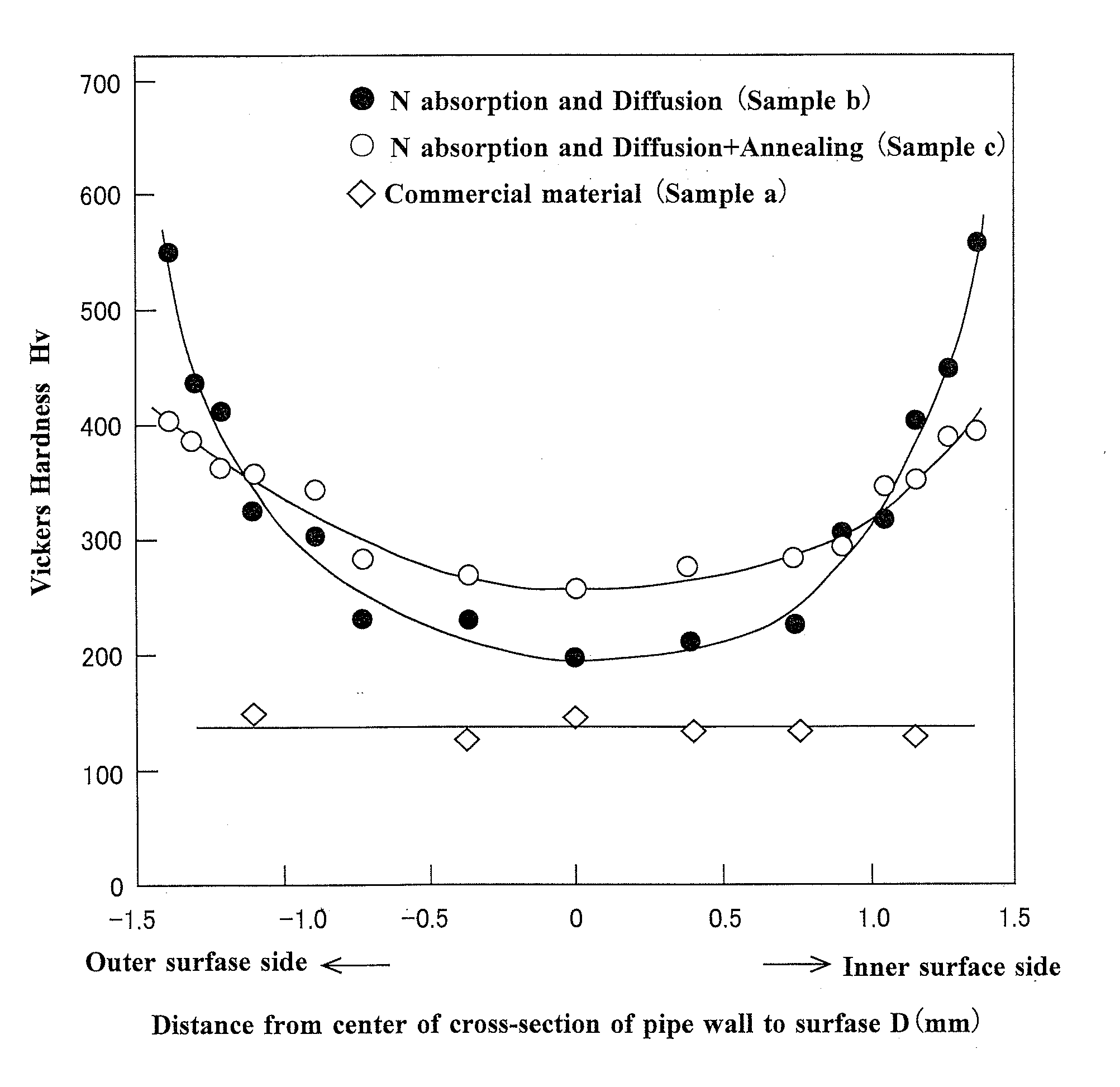
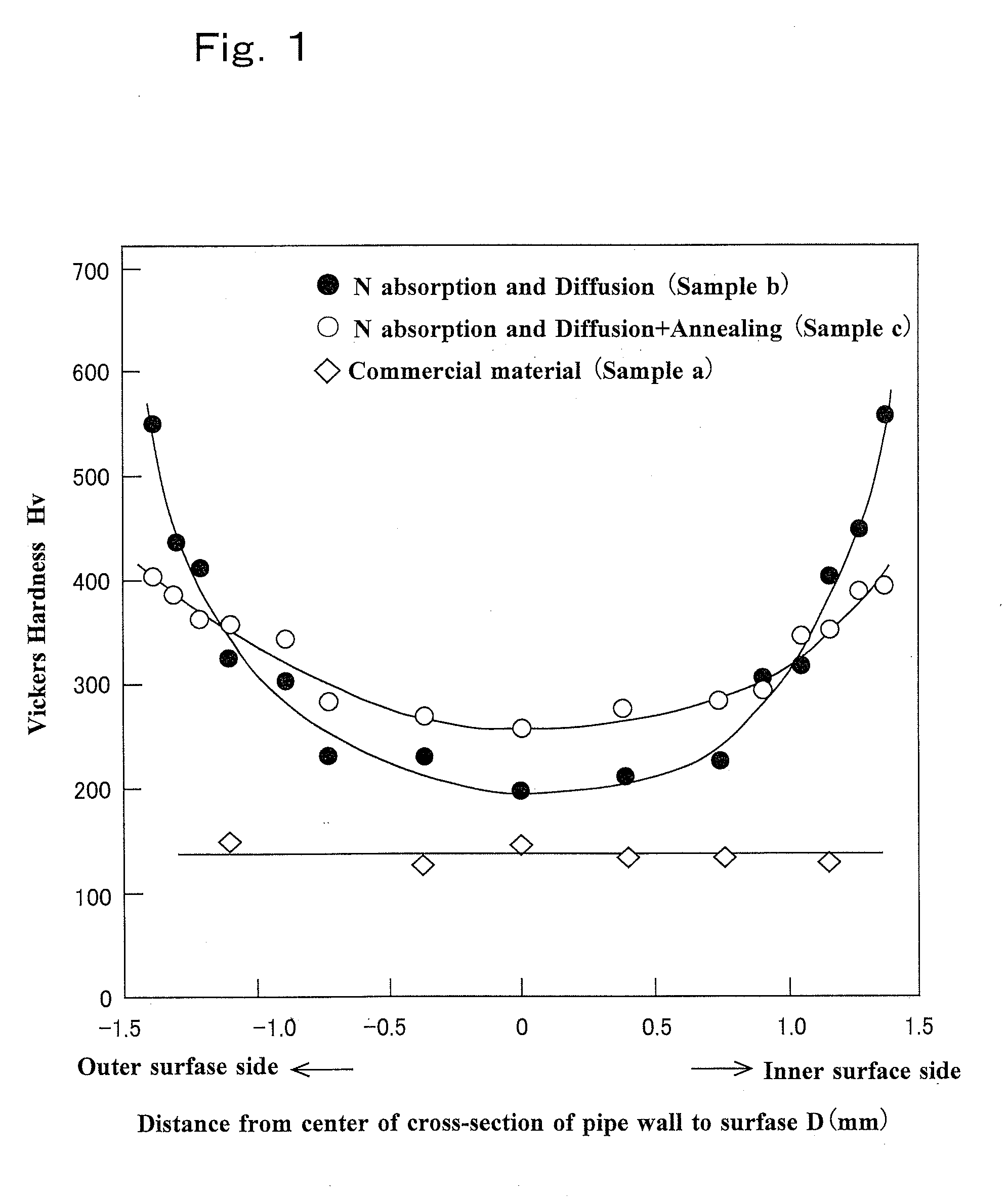
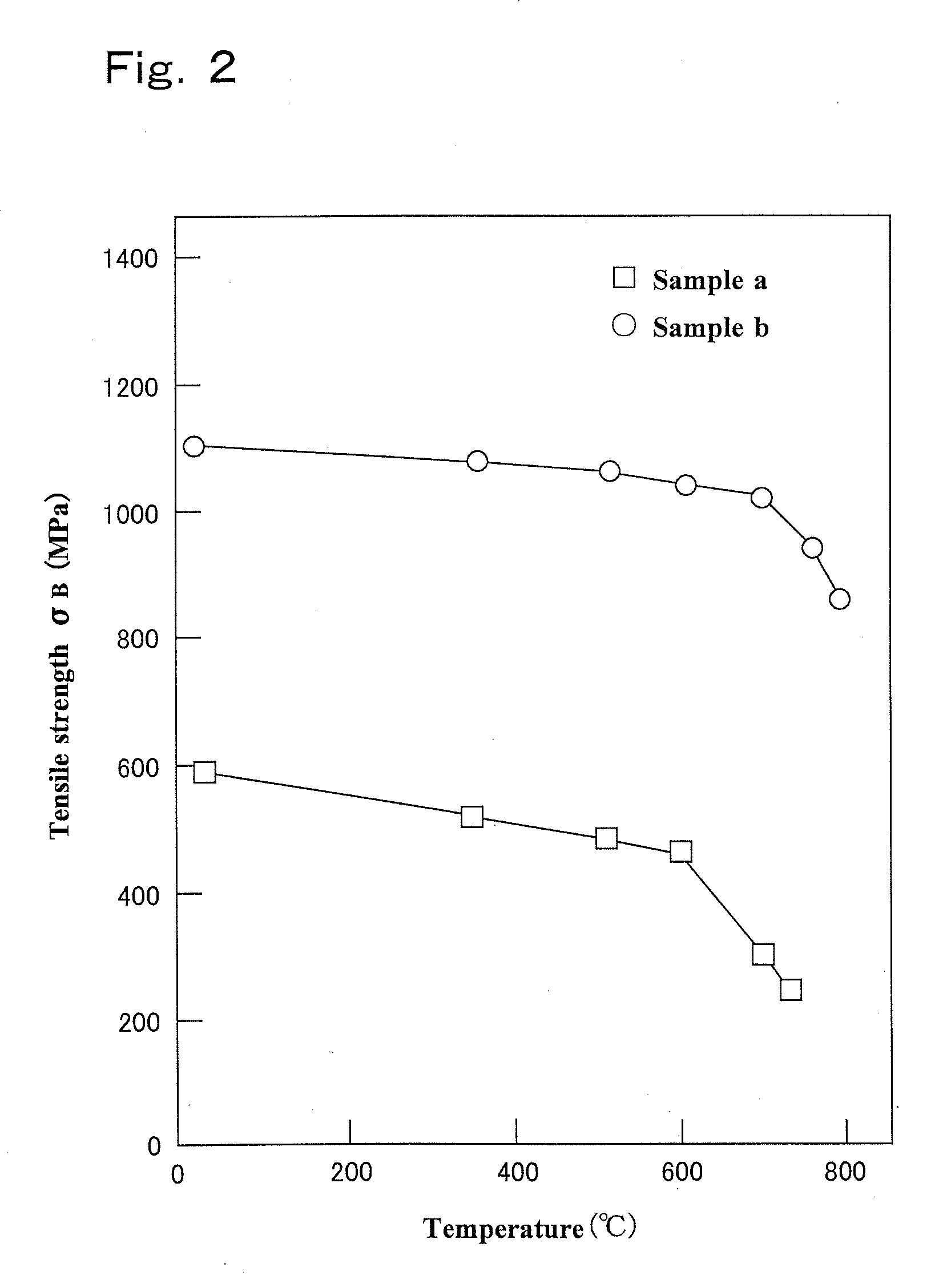
High-nitrogen stainless steel pipe with high strength, high ductility, and excellent corrosion and heat resistance and process for producing same
ActiveUS20130004883A1Easy to manufactureHighly strongReactant parameters controlFinal product manufactureHigh concentrationHigh pressure
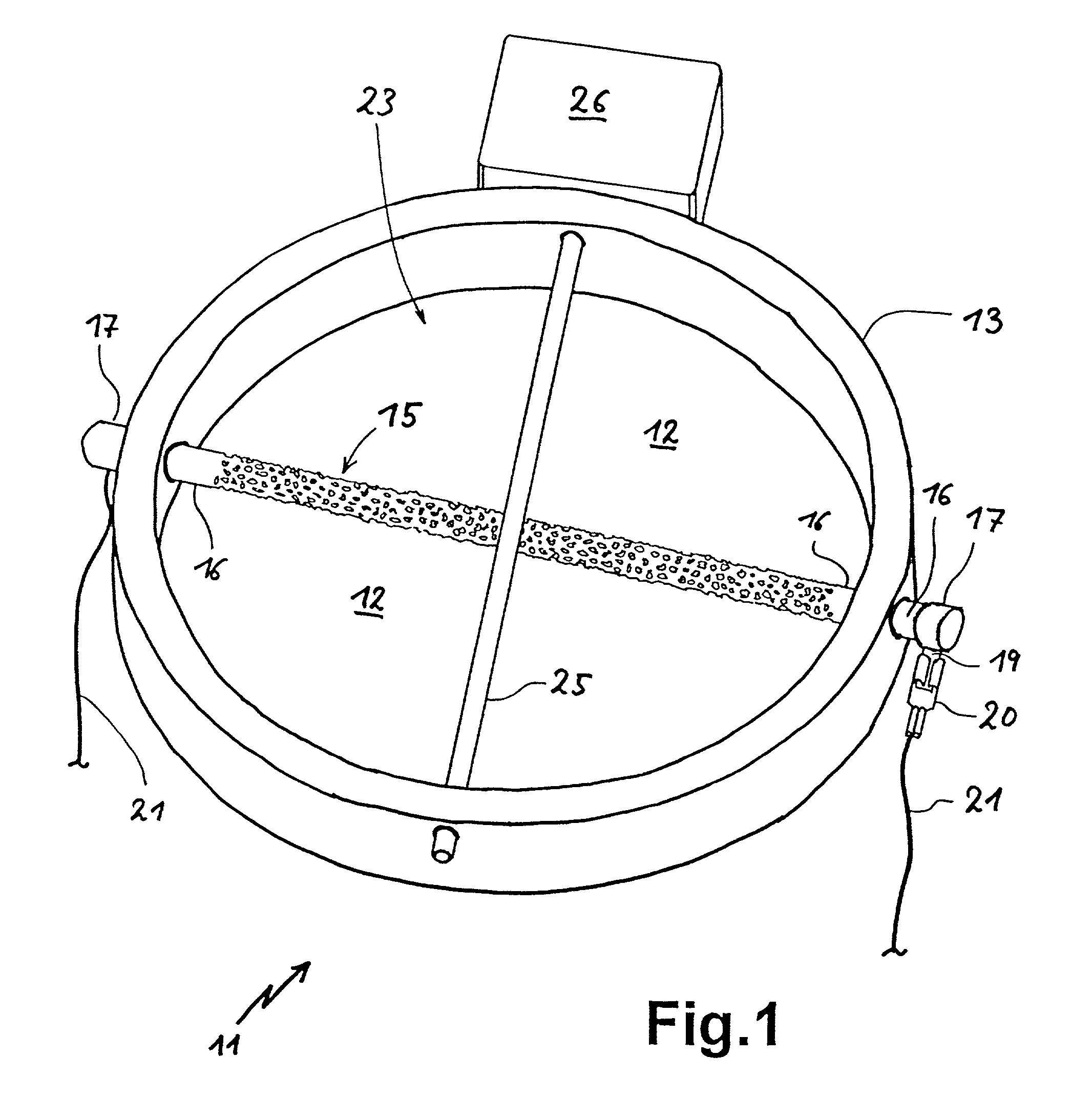
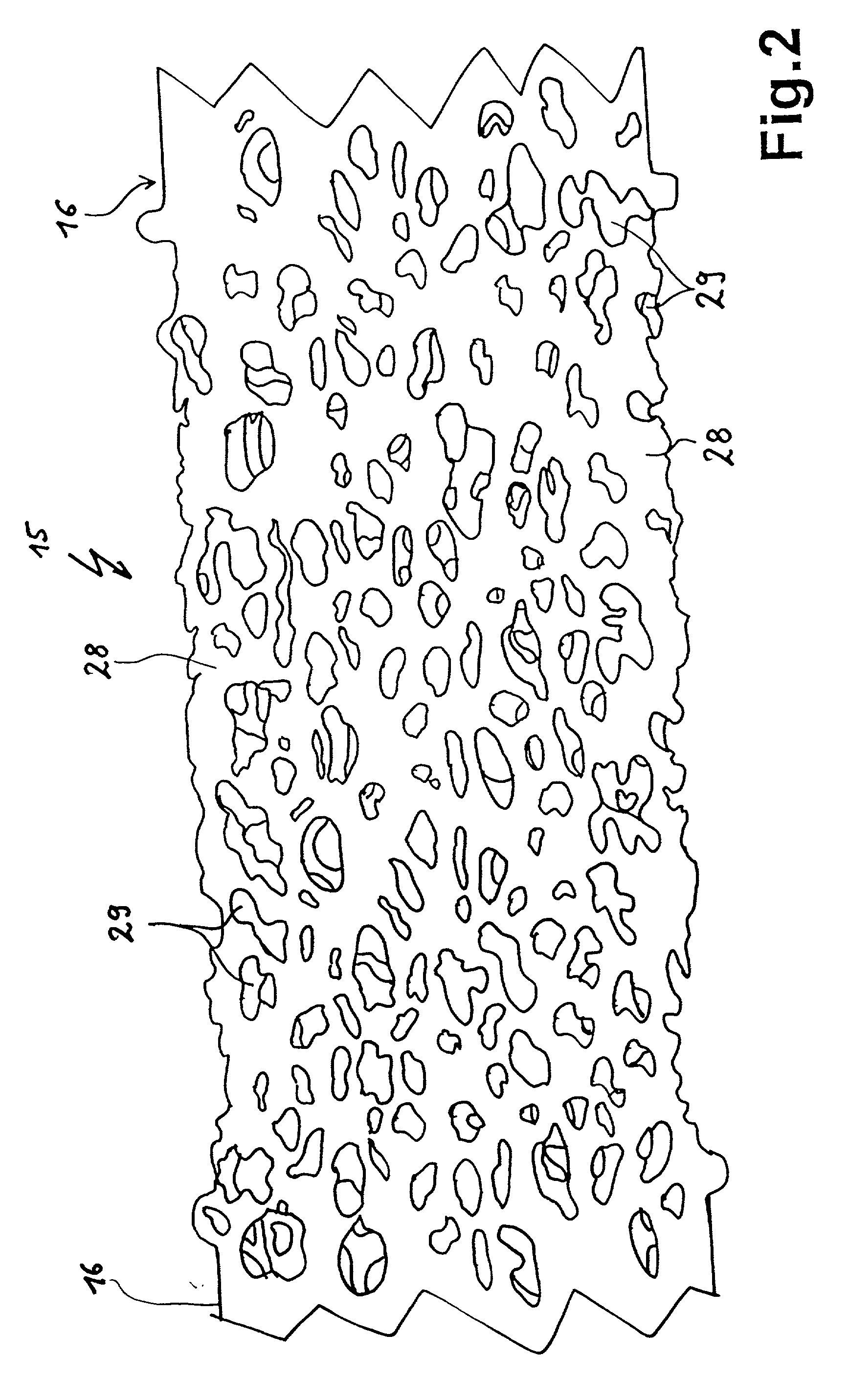
Provided is a novel high-nitrogen stainless-steel pipe which is not obtained with any conventional technique, the stainless-steel pipe having high strength, high ductility, and excellent corrosion and heat resistance and being obtained through size reduction of crystal grains and strengthening by slight plastic working besides formation of a gradient structure in which the concentration of solid-solution nitrogen continuously decreases gradually from the surface. Also provided are hollow materials of various shapes and sizes which are formed from the steel pipe and processes for producing the steel pipe and the hollow materials. An austenitic stainless-steel pipe is treated in a range of the temperatures not higher than the critical temperature for crystal grain enlargement of the steel pipe material to cause nitrogen (N) to be absorbed into the surface of the pipe and diffused into the solid phase, while minimizing the enlargement of crystal grains during the treatment. Thus, a gradient structure is formed, the structure including a part that is close to the surface part of the pipe and has been highly strengthened by the formation of a high-concentration solid solution of N and a part in which ductility gradually increases toward around the center of the cross-section of the pipe as the N concentration decreases. Thereafter, the pipe is subjected to size reduction of crystal grains by utilizing, for example, eutectoid transformation of the austenite phase, thereby greatly improving the elongation (ductility) of the steel pipe. Furthermore, the steel pipe is strengthened by slight plastic working to give a high-nitrogen austenitic stainless-steel pipe having high strength, high ductility, and excellent corrosion and heat resistance. A plurality of the thus-obtained high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel pipes of the same quality are disposed one over another so as to result in dimensions, e.g., diameter and wall thickness, according to the use or strength level, and this pipe arrangement is united by adhesion processing through hot drawing, hot rolling, or other method to give a high-nitrogen austenitic stainless-steel pipe or hollow material which has high strength, high ductility, and heat resistance and has repetitions of the gradient structure within the wall. This stainless-steel pipe or hollow material can have large or small sizes and be of various kinds, and examples thereof include a hollow material for use as a container for storing high-pressure hydrogen gas which is for fuel cell vehicles (FCVs) and which does not suffer hydrogen gas embrittlement (HGE) in the presence of high-pressure hydrogen gas.
Owner:MIURA HARUMATU +1
Method for manufacturing a stainless steel product and a stainless steel product manufactured by the method
InactiveUS7875128B2Increase resistanceImprove workabilitySolid state diffusion coatingFurnace typesSS - Stainless steelNitrogen gas
A Ni-free stainless steel product excellent in workability and corrosion resistance and a method for manufacturing such stainless steel product. A ferritic stainless steel product containing 18 to 24% by mass of Cr and 0 to 4% by mass of Mo is brought into contact with an inert gas containing a nitrogen gas at 800 degrees C. or above to subject it to nitrogen absorption treatment so that the product is austenitized partially or wholly to obtain such nickel-free product.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI +1
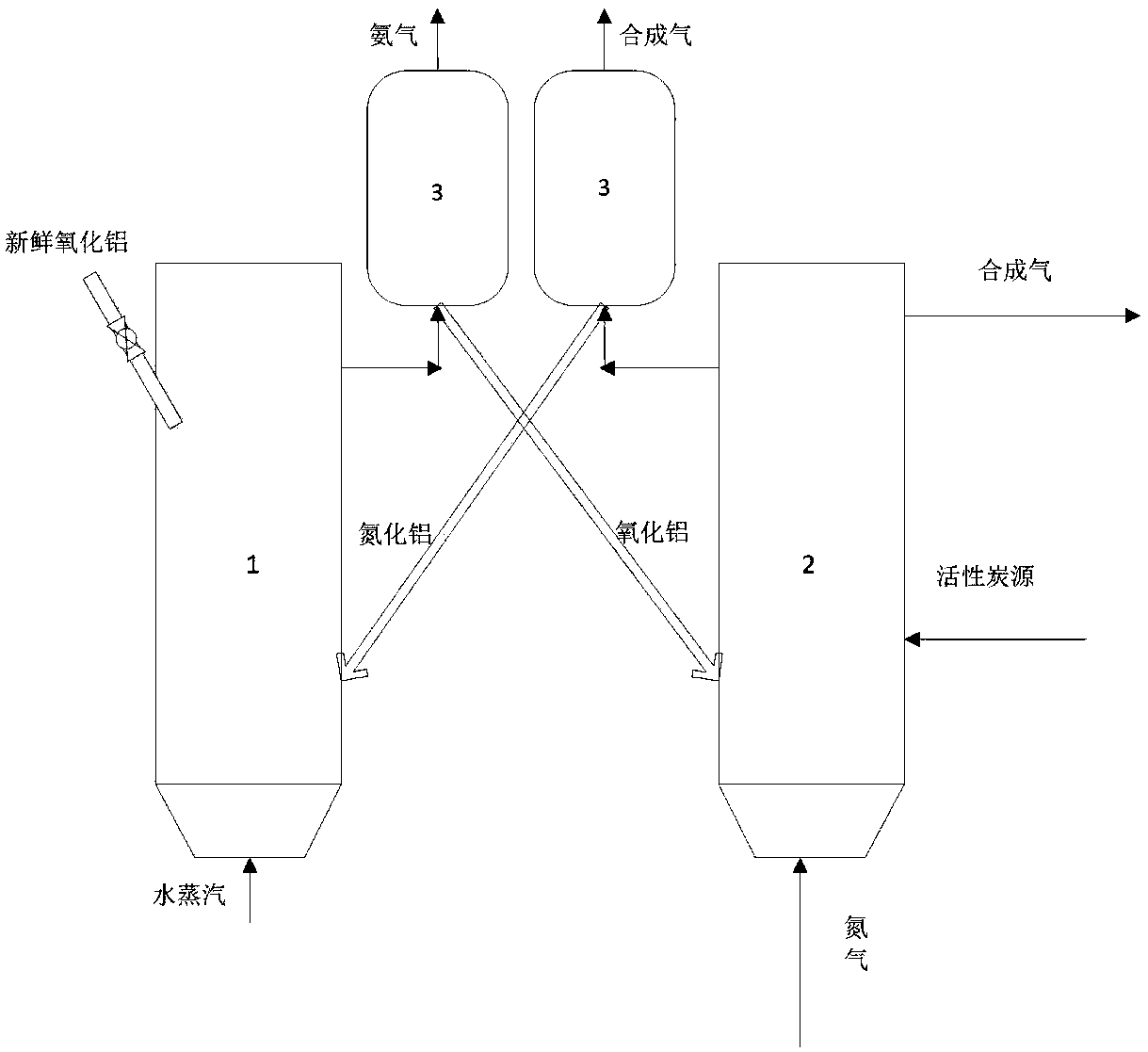
Method for preparing ammonia gas based on radical chain reaction
InactiveCN108217687AReduce energy consumptionImprove conversion rateHydrogen productionAmmonia preparation/separationWater vaporNitrogen gas
The invention provides a method for preparing ammonia gas based on radical chain reaction. The method mainly comprises the following steps: preparing aluminum nitride as a nitrogen carrier; uniformlymixing aluminum oxide, an activated carbon source and corresponding catalyst which is calcium fluoride based on the molar mass of 1: 3: 0.2 through a carbothermic method; transferring into nitrogen absorption reaction; increasing the temperature to reach 1200-1800 DEG C; charging nitrogen to generate aluminum nitride and synthesized gas; exhausting the synthesized gas which is separated through acyclone separator from the upper end; mixing aluminum nitride and the catalyst; feeding the mixture into nitrogen releasing reaction gas; maintaining the temperature to 900-1200 DEG C; charging watervapor to react with aluminum nitride so as to prepare ammonia gas and aluminum oxide; separating through the cyclone separator to obtain high-purity ammonia gas; and transferring the separated aluminum oxide into a nitrogen adsorption reactor for recycling. The method is high in ammonia gas preparation efficiency, and simple in equipment, and is an optimal scheme with low investment and low energyconsumption.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of nitrogen application method for cork oak container seedlings
InactiveCN102282930ARealize automatic fertilizationSeed and root treatmentFertilising methodsSeedlingNitrogen fertilization
The invention mainly relates to a nitrogen fertilization method for cork oak container seedlings, which belongs to the fertilization technology for forest tree container seedlings. Adopt the index fertilization method to apply nitrogen fertilizer to the cork oak container seedlings, start to apply nitrogen after the cork oak germinates, and end in mid-September, apply nitrogen once a week, and the nitrogen application amount increases exponentially each time, and the cumulative nitrogen application amount is 125mg / strain. The biomass and nitrogen content of the container seedlings of Quercus variabilis were 5.29g / plant and 73.14mg / plant respectively, and the nitrogen absorbed by the seedlings accounted for 58.5% of the amount of nitrogen applied; mm, reached the requirements of qualified seedlings. The present invention determines that the optimum nitrogen application rate for oak cork container seedlings is 125 mg / plant, adopts the exponential fertilization method, and the nitrogen application rate increases exponentially each time, and the amount of nutrients provided to the seedlings is synchronous with the growth and development requirements of the seedlings, thereby making the seedlings specifications and nitrogen content reached a maximum.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Application of PLD (phospholipase D) epsilon gene in increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of crops
InactiveCN103773798AEasy to transportEfficient reuseFermentationGenetic engineeringNutritionNucleotide
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant molecular breeding and biology, and discloses application of a PLD (phospholipase D) epsilon gene in increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of crops. The nucleotide sequence of the PLD epsilon gene is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, or has a similarity more than or equal to 60 percent as the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also discloses a method for increasing nitrogen nutrition effective utilization and seed yield of rape. Tests prove that growth and occurrence of lateral roots of rape can be promoted due to overexpression of AtPLD epsilon either in nitrogen starvation or nitrogen sufficiency condition, increase of rape leaf tissue cell growth and biological yield can be reinforced, absorption transportation and assimilation metabolism processes of rape plants can be promoted, which are particularly indicated in that the expression quantities of genes NTR1.1 and NTR2.1 related to overexpressed plant N transportation are remarkably higher than that of a wild type, and the nitrogen absorption rate is remarkably higher than that of the wild type.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Method for preparing alkynylated graphene supported nano-palladium catalyst compound hydrogen absorption material
ActiveCN108636449ARealize integrationSmall steric hindranceHydrogen separation using solid contactOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPalladium catalystIsotope
The invention discloses a method for preparing an alkynylated graphene supported nano-palladium catalyst compound hydrogen absorption material. The method comprises the steps of performing alkynylating modification for graphene and compounding the modified graphene with nano-palladium, so that the alkynylated graphene can be used as a hydrogenating reactant or a stabilizer and carrier of a nano-palladium catalyst, so that two-in-one of a solid organic reactant and a solid catalyst carrier in an inorganic two-dimensional material catalytic hydrogenation system can be realized, steric hindrancebetween the solid reactant and the catalyst can be reduced, the mutual contact probability can be increased, and a higher catalytic hydrogenation efficiency can be obtained; and after the material issaturated in hydrogen absorption, the barrier performance for hydrogen is superior to that of an organic hydrogen absorption material, and hydrogen and isotopes thereof can be well controlled to penetrate into the environment. The inorganic two-dimensional material serving as filler is added into a polymer, and can be used for improving the mechanical performance, thermal performance, barrier performance and the like of the polymer. The nitrogen absorption material belongs to an irreversible hydrogen absorption material, and can reduce the content of hydrogen to a relatively low level in a closed environment at normal temperature normal pressure.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for forecasting application amount of rice nitrogen fertilizer
InactiveCN103210727AReasonable recommended nitrogen application rateFertilising methodsLoss rateNitrogen fertilizer
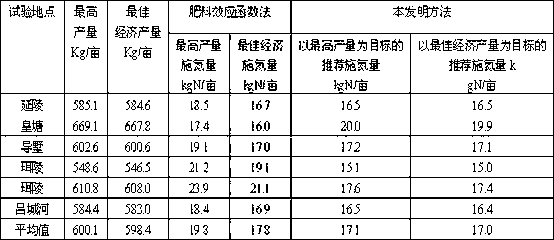
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com