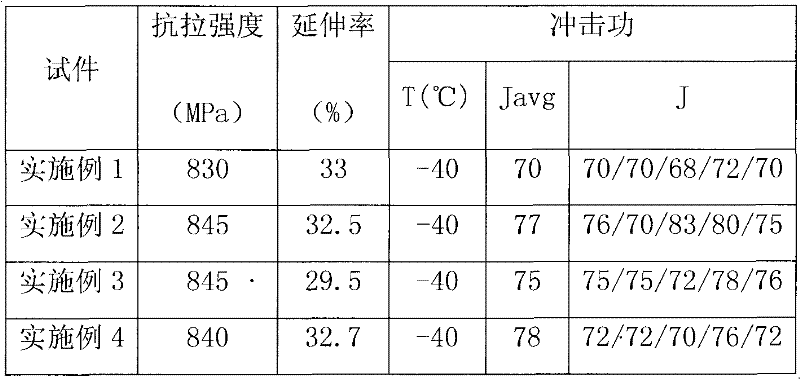
Patents
Literature
1366 results about "Slag (welding)" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Welding slag is a form of slag, or vitreous material produced as a byproduct of some arc welding processes, most specifically shielded metal arc welding (also known as stick welding), submerged arc welding, and flux-cored arc welding. Slag is formed when flux, the solid shielding material used in the welding process, melts in or on top of the weld zone. Slag is the solidified remaining flux after the weld area cools.
Technological process for producing super-thick plate
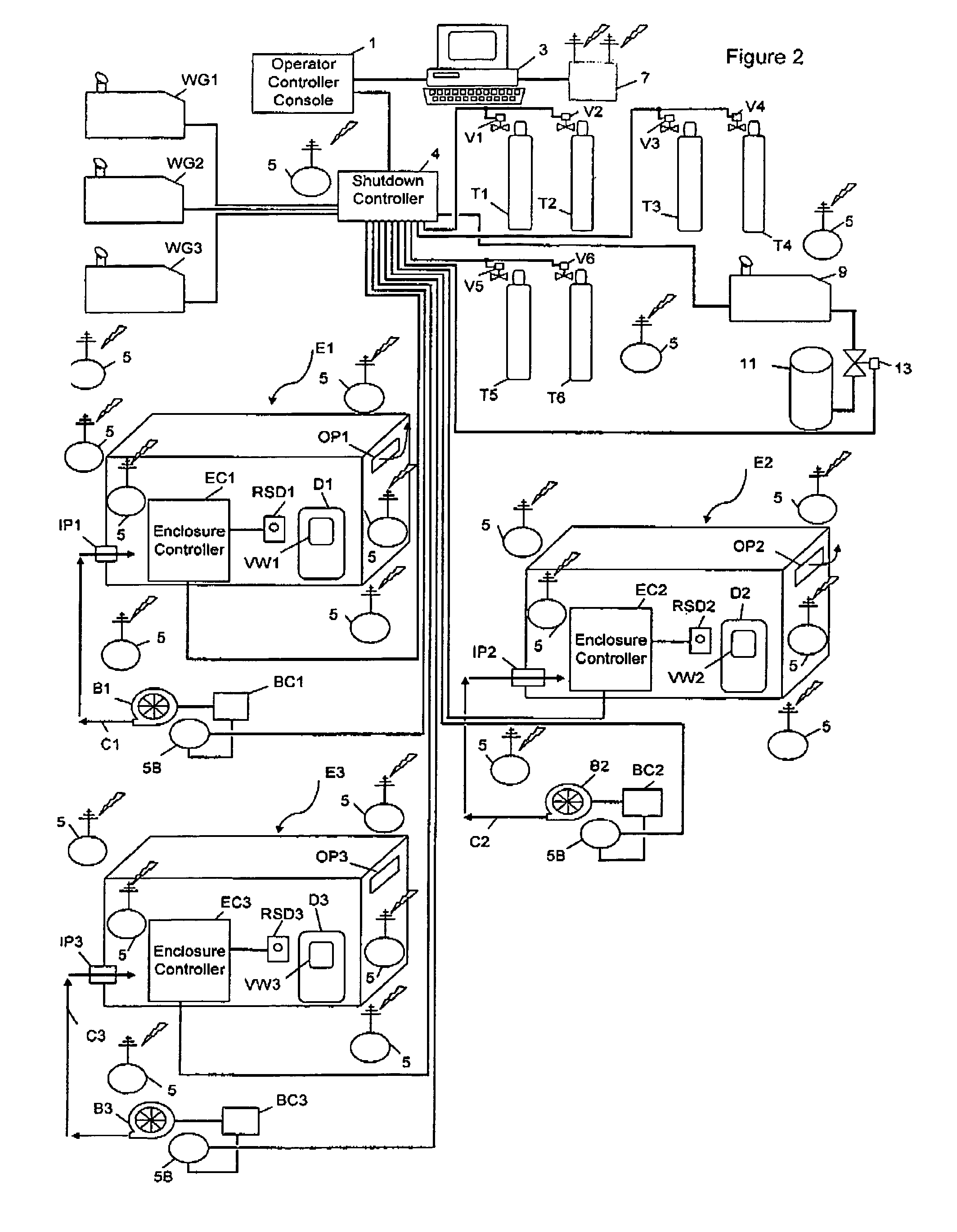
InactiveCN101439348AQuality improvementLow costTemperature control deviceElectron beam welding apparatusElectro-slag remeltingVacuum chamber
The invention relates to a process for producing an ultra-thick plate and belongs to the field of rolling and producing an ultra-thick steel plate in the metallurgical industry. The invention mainly overcome the defect of producing the ultra-thick steel plate by a traditional model casting manufacturing blank and an electro-slag remelting manufacturing blank. The method comprises the following steps: cutting and fixing lengths of the blanks, mechanically conditioning the blanks (eliminating, leveling and cleaning a single-surface oxide layer of a casting blank with a milling machine, a planer or a shot blast); clamping an assembly (relatively superposing the cleaning surfaces of the two blanks after processing, placing the two blanks oppositely and clamping the blanks); mounting the blanks in a vacuum chamber of an electronic beam welding machine for purpose of vacuuming; sewing the assembly on the electronic beam welding seal edge, heating the assembly in a furnace and rolling the assembly through temperature control; and then producing the ultra-thick steel plate. Compared with the traditional electro-slag remelting production process, the process has the advantages of high production efficiency, reduced electric power consumption, less investment of production devices and low production cost. Compared with the traditional die casting production process, the process solves the problem of segregation and looseness of a large-scale die casting ingot center part; the finished product ratio is high; and the finished product ratio of blank assembly is over 90 %.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Manufacturing method for box type pillar beam
ActiveCN102896472AAdvanced preparation technologyReasonable preparation processArc welding apparatusNumerical controlSlag (welding)
The invention relates to a manufacturing method for a pillar beam for the building field and especially relates to the manufacturing method for a box type pillar beam. The manufacturing method comprises the processes of steel check, line marking, cutting, material receiving, assembling, welding, finishing, coating, and marking. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps: splicing big plates and cutting the box type pillar beam under numerical control; adding lining strips and leaving gaps during the grouping process of four main welding seams of the box type pillar beam; welding the four main welding seams by adopting an automatic submerged arc welding method; welding box type separating plates by adopting non-melting nozzle electro-slag welding; keeping the welding seams of the non-melting nozzle electro-slag welding under an abreast state; machining after grouping the separating plates of the box type pillar beam; and end-milling the two ends of the box type pillar beam. According to the manufacturing method, during a manufacturing process of the box type pillar beam, an advanced box type separating plate non-melting nozzle electro-slag welding technology is adopted; the welding and the assembling are alternately performed; the welding sequence is scientific and reasonable; multiple measures are simultaneously taken for preventing welding deformation; the precise equipment is adopted for processing the end part, so that the manufacturing technology for the box type pillar beam is more advanced and reasonable; and the manufacturing method is suitable for the box type pillar beams in various cross section sizes and plate thicknesses.
Owner:CHINA 22MCC GROUP CORP
Method for melting nickel-base high temperature alloy with electro-slag furnace
The invention relates to a method for melting a nickel-base high temperature alloy with an electro-slag furnace. The method includes the following methods: loading materials, welding a high temperature alloy electrode and a false electrode to be smelted together, and placing slag materials at the bottom of a crystallizer; blowing the welded electrodes with inert gases, and closing a protection cover; protecting a smelting closing smoke exhaust valve, and feeding an Ar gas into the crystallizer and the protection cover; striking an arc and melting slag; cleaning smelting slag materials, starting a smelting period, and swinging a slag resistor for less than 0.5 m omega during the smelting process; adding oxidizing agents, and adding metal aluminum powder continuously or at intervals to serve as deoxidizing agents during an electro-slag re-melting process; adopting feeding thorough three stages, power feeding is decreased rapidly, power feeding is decreased slowly, and finally heat is preserved at constant power; and casting a die, cooling and demolding the die. According to the method for melting the nickel-base high temperature alloy with the electro-slag furnace, the surface of a nickel-base high temperature steel ingot has no slag groove defect, and the burning losses of Al and Ti are less than or equal to 5%.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Micro alloying SWRH87B hot rolled wire rod and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101597713AQuality improvementEasy to useTemperature control deviceManufacturing convertersTemperature controlWire rod
The invention provides a micro alloying SWRH87B hot rolled wire rod and a manufacturing method thereof, belonging to the technical field of hot rolled wire rod. In the invention, Cr and V micro alloying are adopted; double slag process high drawing carbon operation is used in a converter; end-point carbon is controlled at 0.40-0.60%, the steel tapping temperature is 1580-1620 DEG C, and the slag-blocked tapping is used; low nitrogen carburant is used for recarburization; Si-Ca-Ba is used for deoxidation; 600-800kg synthetic slag is added into each converter; oxygen activity is controlled below 10ppm by entering into an LF refining station, and the refined finishing slag sum of FeO and MnO is no more than 3%; inclusion modification treatment is carried out on the Ca-Si line; a billet in the size of 160mm*160mm is used, a casting mould is used for coordinating with final electromagnetic stirring (F-EMS); continuous casting machine whole protection, constant drawing speed casting and proper secondary cooling system are adopted; the initial rolling temperature is controlled at 1020-1150 DEG C which is conductive to welding the drawholes and increasing the probability of the drawholes welding; the water pre-cooling and phase transformation strengthening cooling technology is used to control the texture and the performance. The invention has the advantages that the aging time of the wire rod before the follow-up processing is shortened, the tensile strength thereof after aging time is larger than 1280MPa, and the area reduction rate is larger than 25%.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Method for producing cold-rolled steel strips
ActiveCN102416404AImprove pull performanceGood welding performanceMetal rolling arrangementsSlagLight treatment
The invention discloses a method for producing cold-rolled steel strips. The method comprises the following steps of: performing krypton (KR) desulfurization treatment, converter dephosphorization-less slag decarburization and relative humidity (RH) light treatment on molten iron, and performing continuous casting to obtain a high-purity plate blank; heating the plate blank, performing rough rolling and precision rolling to obtain a hot-rolled plate, cooling the hot-rolled plate and coiling the hot-rolled plate into a hot-rolled coil; and performing cold rolling, annealing and flattening on the hot-rolled coil, and coiling the hot-rolled coil into a finished product. By the method for producing the cold-rolled steel strips, the cold-rolled steel strips which have high drawing property and good welding performance and can be used for flux-cored wires can be produced, the production requirement of the flux-cored wires is met, splash in the welding process is reduced, seams with good welding quality are obtained, and the automation level of welding is improved.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Laser-CMT welding aluminum alloy additive manufacturing method and forming system
PendingCN107283061AImprove stabilityImprove interlayer bonding performanceWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser beam welding apparatusSlag (welding)Molten bath
The invention discloses a laser-CMT welding aluminum alloy additive manufacturing method and a forming system. A laser and an electric arc are adopted as a composite heat source, the cold metal short circuiting transfer manner is adopted, and additive manufacturing forming for an aluminum alloy component is achieved. According to the provided laser-CMT welding additive manufacturing method, the problems that in the process of aluminum alloy component manufacturing through laser additive, the required laser power is high, and forming is difficult are solved, the problems that in the traditional process of aluminum alloy manufacturing through electric arc additive, the heat input amount is large, deformation is serious, and a molten bath is prone to overflowing or webbing are solved, and the problem that in the process of aluminum alloy manufacturing through CMT welding additive, incomplete fusion or slag inclusion or the like is likely to happen is solved; and the additive manufacturing method based on the laser-electric arc composite heat source principle is provided for additive manufacturing forming for the aluminum alloy component.
Owner:NAT INST CORP OF ADDITIVE MFG XIAN +1
Method for brazing copper aluminum tubes without aid of brazing flux
InactiveCN102581414AReduce porosityImprove air tightnessSoldering apparatusWelding/soldering/cutting articlesSlag (welding)Weld seam
The invention discloses a method for brazing copper aluminum tubes without the aid of brazing flux. The method includes the steps: firstly, expanding one end of optional one of the copper aluminum tubes into a socket by a thermal expansion method, manufacturing a brazing alloy plate into a brazing thin tube by a stamping method, and placing the brazing thin tube into the socket; secondly, inserting one end of another welded tube into the brazing thin tube, and tightly abutting the end opening of the welded tube to the bottom of the socket to form close fit; and thirdly, assembling the brazing thin tube and the welded tube on a welding fixture, performing local induction heating for joints, and applying proper welding pressure and ultrasonic vibration. The method can be used for brazing the thin-wall copper aluminum tubes without the brazing flux, fusion lines are long, welding seams are compact, slag inclusion is avoided, the air tightness and the bonding strength of the joints are greatly improved, reliability is high, welding time is short, and great production and use values are achieved.
Owner:李明雨 +1
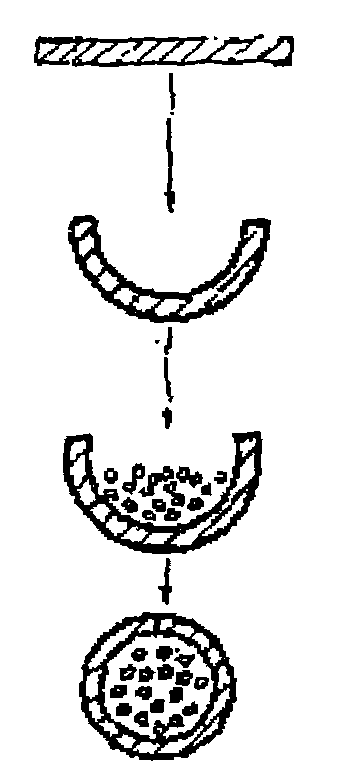
Surfacing electrode for repairing hot forged mould
InactiveCN101898284AExcellent welding performanceImprove yieldWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSolid componentSlag
The invention discloses a surfacing electrode for repairing a hot forged mould, which uses a low-carbon steel H08A core wire conforming to the GB / T3429 requirement. The solid component quality content of coating is as follows: 30-40% of marble, 12-20% of fluorite, 1.5-3% of zircon sand, 0-2% of soda ash, 2-5% of silicon epitaxy material, 1-3% of titanium white, 0-3% of flogopite, 1-2% of rare earth fluoride, 3-7% of manganese metal, 2-5% of ferrosilicon, 4-6% of ferrotitanium, 4-8% of chromium metal, 4-8% of ferromolybdenum, 6-12% of metallic nickel and 1-2% of aluminium magnesium alloy. The invention has favorable welding rod performance, smooth welding rod surface, high yield and stable eccentricity; electric arc is easy to ignite and is stable to burn; coating is even to melt, a welding line is attractive in shape, and slag is easy to clean; and a deposition metal weld metal buildup has moderate welding state hardness which reaches the requirements of the hot forged mould, thus improving the service life cycle of the hot forged mould.
Owner:LUOYANG SHUANGRUI SPECIAL ALLOY MATERIALS
Flux system to reduce copper cracking
InactiveUS20070051702A1Reduction of copper crackingReduces copper crackingArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsCopperMolten slag
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Carbon steel covered electrode for nuclear power carbon steel welding and preparation method
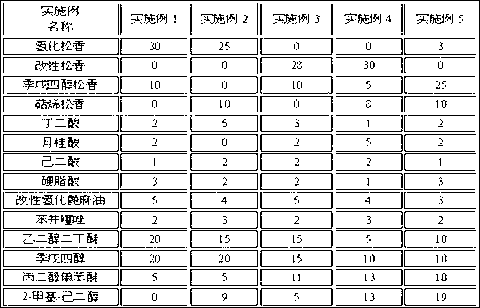
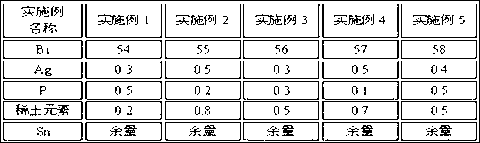
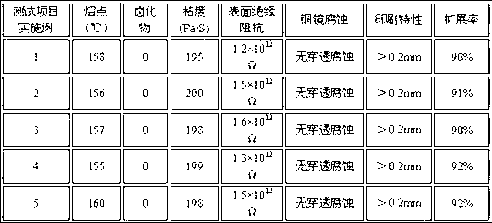
ActiveCN103551760ASimple processImprove mechanical propertiesWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlag (welding)Adhesive
The invention belongs to the technical field of a welding material and particularly relates to a carbon steel covered electrode for the third-generation nuclear power technical welding and a preparation method. The carbon steel covered electrode is characterized by comprising a core wire, a cover and an adhesive, wherein the mass ratio of powder to the covered electrode is (25 to 27):100 and the mass ratio of the powder to the adhesive is 100:(15 to 20). In the welding process of the covered electrode in the invention, electric arcs are stable and splashing is little; slag detachability is good; a postwelding slag crust in the flat welding process can be automatically upwarped; the covered electrode is well formed and has good whole-position operability; after welded deposited metal is subjected to heat preservation for 1h, 16h and 40h at a temperature of 595 to 625 DEG C, mechanical property in the three thermal treatment states meets the technical indexes and has high stability.
Owner:ATLANTIC CHINA WELDING CONSUMABLES +2
Low-temperature halogen-free lead-free solder paste
InactiveCN102990242AStir wellLow melting pointWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaRare-earth elementSlag (welding)
The invention relates to a low-temperature halogen-free lead-free solder paste. The solder paste is mixed by Sn-Ag-Bi-based lead-free solder powder added with P or rare earth elements and a rosin-based soldering flux. The soldering flux is basically composed of, by weight, 30-45% of rosin resin, 2-10% of an organic acid activator, 3-5% of a thixotropic agent, 2-5% of a corrosion inhibitor, 3-5% of a surfactant and the balance solvents. The solder paste has the advantages that the welding temperature is low, slag is reduced, and the solder paste is suitable for manual welding and printing welding with poor thermal shock resistance.
Owner:郴州金箭焊料有限公司
Sintered flux for two phase stainless steel
InactiveCN102039498AWelding specifications are stableEasy to remove slagWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlag (welding)SS - Stainless steel
The invention discloses a sintered flux for two phase stainless steel. The sintered flux comprises the dry powder components by weight percent: 24-32% of MgO, 12-23% of CaF2, 12-18% of ZrO2, 10-15% of Al2O3, 9-14% of SiO2, 2-10% of CaO, 1-3% of rare earth fluoride, 0.5-2% of sodium fluosilicate, 0.5-2% of chromium oxide green, 0.5-2% of deoxidier, 2-8% of alloying agent, and the balance chromium metal, wherein the deoxidier is Si-Fe in which the content of Si is not less than 70%, and the alloying agent contains 1.5-2.5% of ferromolybdenum in which the content of molybdenum is not less than 50%. The sintered flux disclosed by the invention is matched with ER2209 solder wires, is suitable for the welding and overlaying of two phase stainless steel containing 22% of Cr; the welding is ruled and stable, the slag detachability is excellent, and the weld pass is even in width, moderate in pile height, smooth in transition; the defects of gas pits, intermediate crystallization lines, slag bonding and the like are overcome; and the flux has high content of deposited metal ferrite, excellent mechanical property and corrosion resisting property.
Owner:LUOYANG SHUANGRUI SPECIAL ALLOY MATERIALS
High-hardness self-protecting cold roll build-up welding flux-cored wire
The invention discloses a high-hardness self-protecting cold roll build-up welding flux-cored wire, and belongs to the field of welding in material processing. The flux-cored wire is mainly applied to build-up welding repair of cold rolls of steel mills. The flux-cored wire is characterized in that: the outer surface of the powder cored wire is an H08A cold rolling steel strip; and the powder of the powder cored wire comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 25 to 45 percent of high carbon ferrochrome, 5 to 15 percent of chromium metal, 4 to 8 percent of ferromolybdenum, 5 to 10 percent of manganese metal, 4 to 8 percent of No.75 silicon iron, 4 to 10 percent of aluminum magnesium alloy, 6 to 12 percent of ferrocolumbium, 4 to 10 percent of ferrotungsten, 4 to 12 percent of nickel powder and 4 to 18 percent of iron powder. A coating prepared by build-up welding has high hardness (Rockwell hardness (HRC): 55 to 60) and excellent abrasion resistance; and a self-protecting build-up welding mode is adopted, namely a protective gas source and a flux are not needed in the build-up welding process, and slag knocking is not needed in the build-up welding process, so automatic production is easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING SURYEE SCI & TECH
Intergranular corrosion resistant high-strength full austenite welding rod
InactiveCN1927528ADoes not affect mechanical propertiesReduce manufacturing costWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlag (welding)Adhesive
The invention relates to an anti-inter-crystal-corrosion high-strength austenite welding bar. Wherein, it is formed by CaO-CaF2-SiO2 alkali coat slag and Cr-Ni-Mo-Mn-N alloy austenite coat, while its coat comprises marble at 45-55%, 45-55% at 16-25%, ferrotitanium at 8-12%, ferrosilicium at 1-5%, manganese metal at 2-8%, titanium dioxide at 1-6%, soda at 1-3% and fluoride rare earth at 0.5-2.0%; and the welding bar comprises C at 0.03-0.12%, Si at 0.2-0.7%, Mn at 2.0-7.0%, S and P<=0.030%, Cr at 15.0-19.5%, Ni at 20-25%, Mo at 4.0-7.0%, N at 0.15-0.25%, V at 0.15-0.3%, and the left is iron, then the mixed powder is coated on the welding core via soldium-water glass as adhesive.
Owner:725TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING INDAL CORP
Enclosure system for hot work within the vicinity of flammable or combustible material
Owner:ALFORD SAFETY SYST +1
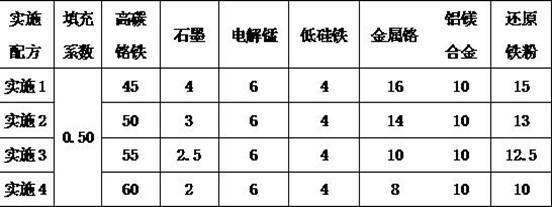
Flux-cored wire for visible arc overlaying of high-chromium cast iron
InactiveCN102513742AReduce construction costsReduce inconvenienceArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsFerrosiliconManganese
The invention relates to a flux-cored wire for the visible arc overlaying of high-chromium cast iron. According to the flux-cored wire, a flux core comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 40 to 60 percent of high-carbon ferrochromium, 1 to 6 percent of graphite, 4 to 8 percent of electrolytic manganese, 2 to 6 percent of low ferrosilicon, 10 to 30 percent of metal chromium, 8 to 15 percent of aluminum magnesium alloy and 10 to 20 percent of other alloys. When the flux-cored wire is used for welding, a dilution rate is low, an electric arc is stable, a weld joint does not have slag and has ultrahigh hardness and corrosion resistance, and the overlaying can be performed directly without addition of soldering fluxes and protective gas, so that the construction cost is reduced, and the inconvenience of the operation is reduced.
Owner:天津大桥金属焊丝有限公司
Smelting process of steel for high-titanium alloy welding wire
ActiveCN102586685AGood deoxygenationImprove purityElectric furnaceProcess efficiency improvementFerrosiliconTitanium alloy
The invention relates to a production process of steel, in particular to a smelting process of steel for a high-titanium alloy welding wire. The smelting process comprises the following steps of: in an electric furnace smelting step, adding molten iron and waste steel and tapping molten steel, wherein the molten iron accounts for 50-60% the total amount of the furnace charge, and the tapping temperature is not lower than 1630 DEG C; in a refining furnace refining step, adding silicon-aluminum-calcium deoxidant in a refining furnace for manufacturing white slag through diffusion deoxidization, and adding low-carbon ferromanganese and ferrosilicon according to steel grade component requirements and sampling component analysis to regulate components of the molten steel so as to reach temperature of 1630-1650 DEG C matching vacuum treatment; in a vacuum furnace degassing step, keeping the temperature for 10-15min under a low vacuum degree of 1 millibar, and carrying out secondary refining after vacuum breakage; and in a secondary refining step, adding low-aluminum ferrotitanium to regulate titanium content at the refining temperature of 1585-1600 DEG C, stirring for 1-2min, adding iron sulfide, stirring for 1-2min, taking a lollipop sample to analyze, continuously keeping static stirring, carrying out soft argon blowing for 15-40min after all components are qualified and carrying out continuous casting when the temperature is up to 1565-1585 DEG C. The smelting process disclosed by the invention can effectively control purification degree of the molten steel, ensures stability of titanium in the molten steel and improves the surface quality of a cast blank.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
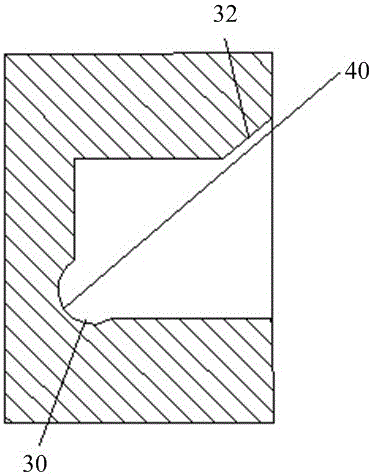
Method for welding box-shaped column
ActiveCN102240863ASimple process routeThe process route is accurateWelding apparatusSlag (welding)Electroslag welding
The invention discloses a method for welding a box-shaped column, which comprises a process for welding the box-shaped column and a method for welding a weld joint between a partition plate and a wing plate by electric slag welding. The box-shaped column comprises a web plate, the wing plate and the partition plate. The weld joint between the partition plate and the wing plate of the box-shaped column is welded by the electric slag welding method, and the overall welding process of the box-shaped column is analyzed and optimized based on the method. Thus, the process route is simple and accurate; and the method has the advantages of reducing manufacturing difficulty, improving processing precision, improving production efficiency and improving the quality of members.
Owner:BAOSTEEL CONSTR +1
Electro-slag remelting method of self-consumable electrode and electro-slag furnace
An electro-slag remelting method of a self-consumable electrode comprises the following steps: 1) welding a plurality of smelted castings in series into a whole, to form the self-consumable electrode; 2) slowly descending the self-consumable electrode and inserting into furnace slag of an electro-slag furnace, after energizing and arc striking, adjusting the remelting voltage and the remelting current; 3) slowly melting one end of the self-consumable electrode, gathering molten metal into metal molten droplets, falling off from the end of the self-consumable electrode, passing through a slag pool into a metal molten pool, and forming an ingot casting through forced cooling by a water-cooling crystallizer; 4) when melting the falling-off metal molten droplets, descending after pausing the non-molten self-consumable electrode for 10-20 s, and accelerating the descending speed by 10%-20%; and 5) after completion of electro-slag remelting, carrying out annealing treatment of the obtained ingot casting, and then carrying out mechanical processing to obtain the finished product. The invention also provides the electro-slag furnace for electro-slag remelting of the self-consumable electrode. Energy and raw materials are saved, the production efficiency is improved, the production time is shortened, and the high-purity ingot casting is obtained.
Owner:HUNAN LIFANG ROLLER +1
Manufacturing method of photovoltaic welding strip and tin coating machine thereof
ActiveCN102226259AAvoid pinholesQuality improvementHot-dipping/immersion processesFinal product manufactureSlagTransducer
The invention provides a manufacturing method of a photovoltaic welding strip and a tin coating machine thereof. The method comprises the following steps: A, carrying out a simple pretreatment on a copper strip; B, sending the pretreated copper strip into a plating solution of a tin furnace for tin coating, when tin coating, carrying out an ultrasonication to the copper strip with ultrasonic waveemitted by an ultrasonic wave transducer arranged above the tin furnace; C, blowing tin with inert gases, and D, receiving materials. According to the invention, by adding ultrasonic wave in the tin coating process, tin liquor can rapidly form an alloy layer of copper and tin on the surface of the copper strip by the sound pressure effect of the ultrasonic wave, the production efficiency of the photovoltaic welding strip is increased, the transporting speed of the copper strip reaches to 10-80m / min; by removing grease and oxide layer on the copper strip surface, reducing the usage of chemicalreagents, simplifying the pretreatment before coating, and utilizing the ultrasonic wave to crush clusters of tin oxide, the defects of pinhole and tin slag of the welding strip is prevented, the quality of the welding strip is improved, and the production efficiency is raised greatly.
Owner:江苏威腾新材料科技有限公司
Two-phase stainless steel electrode
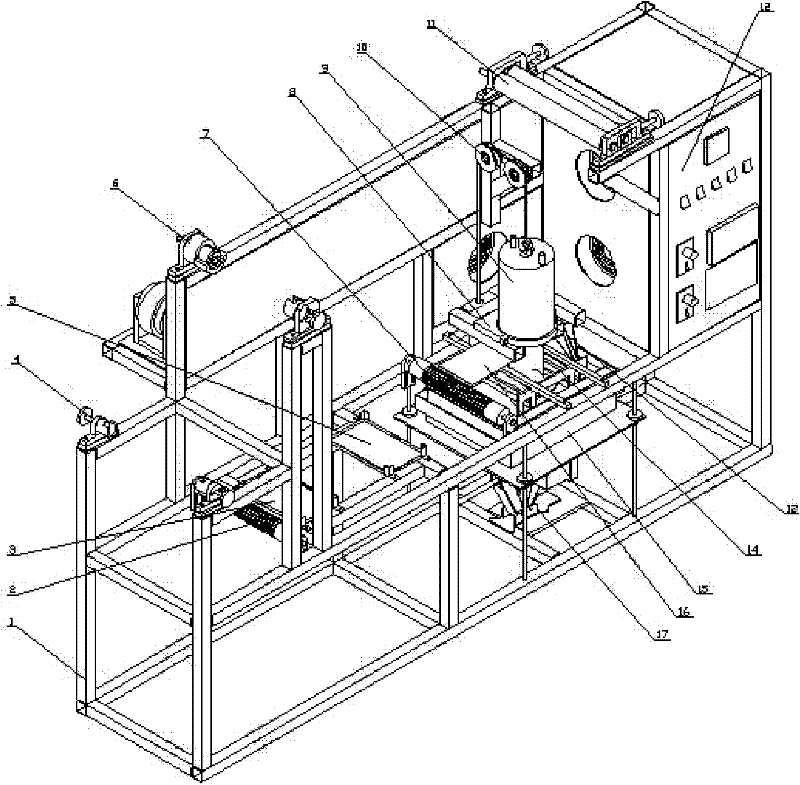
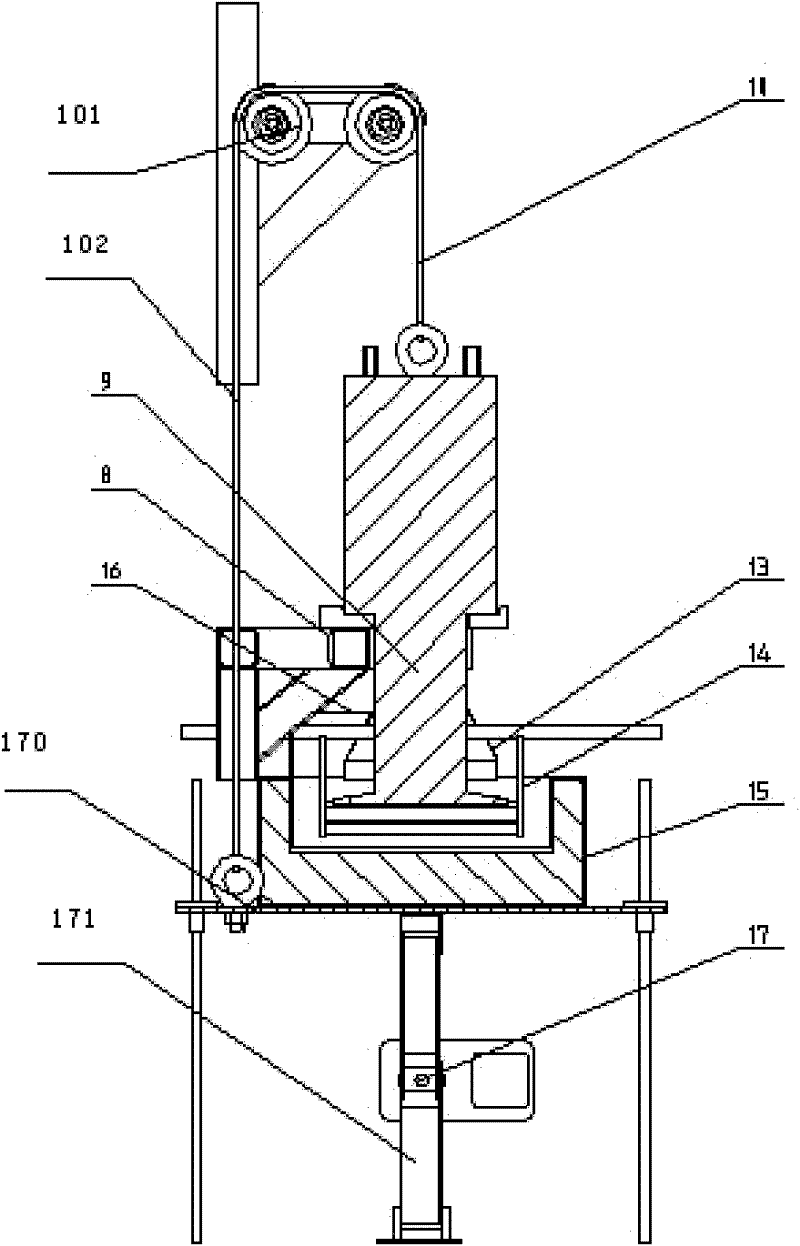
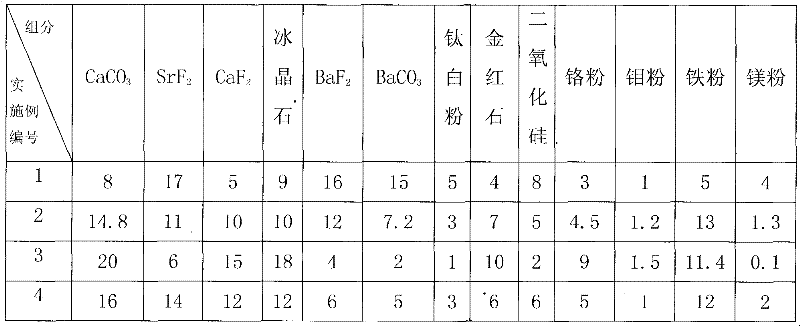
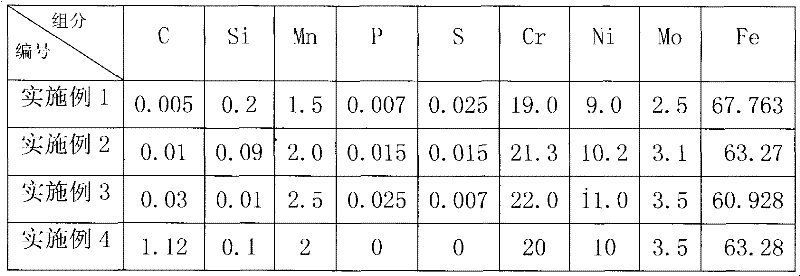
ActiveCN102233489AArc stabilizationReduce splashWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaSlagWeld seam
The invention discloses a two-phase stainless steel electrode, which comprises a core wire and a coating, wherein the coating is coated on the outer wall of the core wire and accounts for 0.4 to 0.5 percent of the total weight of the electrode. The core wire comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.005 to 0.030 percent of C, 0.01 to 0.20 percent of Si, 1.50 to 2.50 percent ofMn, 0 to 0.025 percent of P, 19.0 to 22.0 percent of Cr, 9.0 to 11.0 percent of Ni, 2.5 to 3.5 percent of Mo and the balance of Fe. The coating comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 8 to 20 percent of calcium carbonate, 2 to 15 percent of barium carbonate, 5 to 15 percent of calcium fluoride, 6 to 17 percent of strontium fluoride, 4 to 16 percent of barium fluoride, 9 to 18 percent of cryolite, 4 to 10 percent of rutile, 1 to 5 percent of titanium white, 2 to 8 percent of silicon dioxide, 3 to 9 percent of chromium powder, 1 to 1.5 percent of molybdenum powder, 0.1 to 4 percent of magnesium powder and 5 to 13 percent of iron powder. After the coating components are uniformly mixed, an adhesion agent is added into the mixture. The two-phase stainless steel electrode has high strength, high tenacity and intercrystalline corrosion resistance; and during welding, an electric arc is stable, splashing phenomena is reduced, a welding seam is well molded, slag is easy toremove, and the electrode has high operability.
Owner:KUSN GINTUNE WELDING
Low-cost gas shielded flux-cored wire with recycled welding slag
InactiveUS20120241432A1Low costSave resourcesWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaIron powderSlag
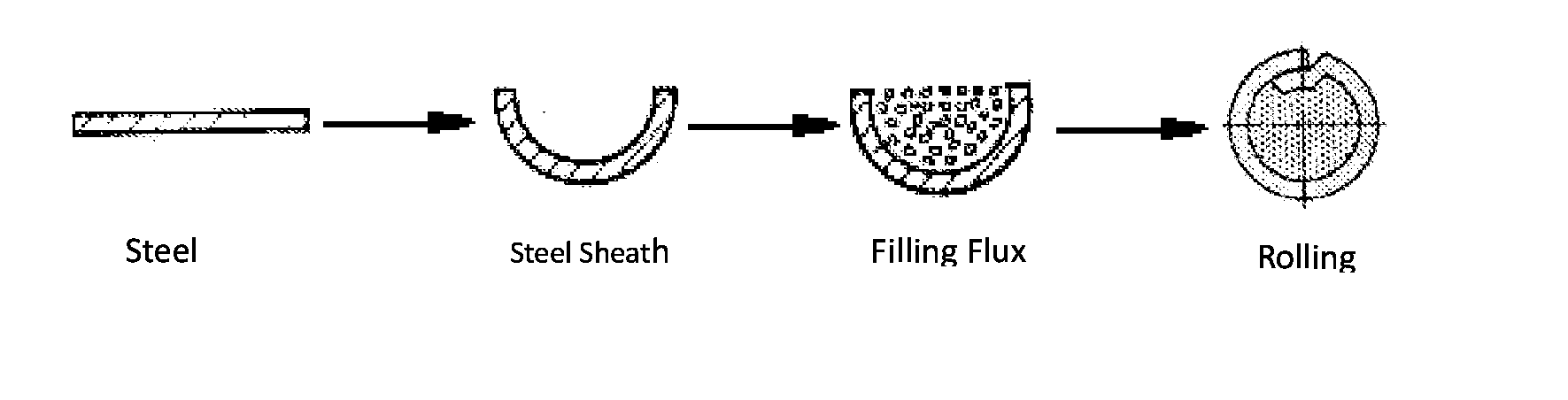
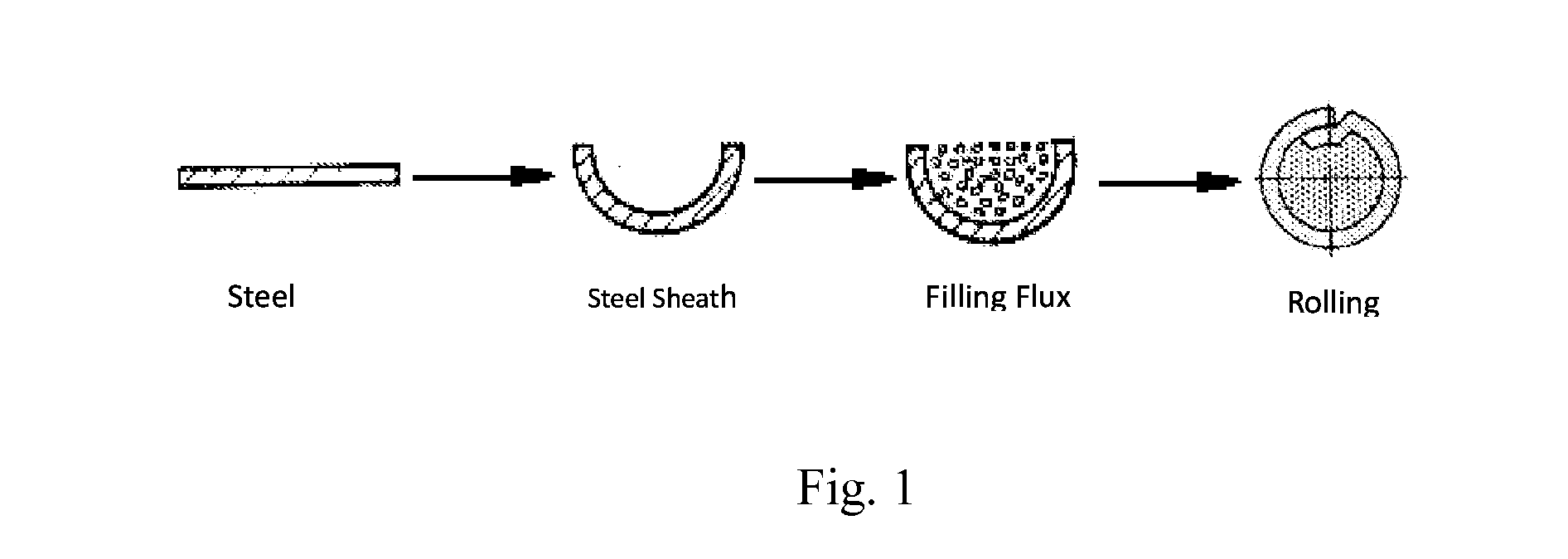
A gas shielded flux-cored wire (FCW) comprises s steel sheath and core flux, in which recycled welding slag powder is used to partially replace the natural rutile. The core flux contains (by weight): 10-50% recycling welding slag powder, 10-45% TiO2, 2-7% Si, 5-20% Mn, 0.5-5% Al—Mg (Al / Mg=1), 0-11.52% Na2CO3, 0-8.85% K2CO3, 0-10% MgO, 0.5-10% fluoride, and iron powder as balance. The recycling welding contains (by weight): TiO2: 20-65%, MnO: 5%-15%, MgO: 5%-15%, SiO2: 5%-15%, Fe2O3: 1%-10%, Al2O3: 1%-10%.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Metal powder type flux-cored wire and preparation and application thereof
InactiveCN102430877AGood welding process adaptabilityStable mechanical propertiesArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsSlag (welding)Sputtering
The invention discloses a metal powder type flux-cored wire comprising a carbon steel skin and powders filled inside it. The powders comprise the following components and percent thereof accounting total weight of the flux-cored wire: TiO2 0.20 to 1.5%, SiO2 0.1-0.5%, any one of Na2O or K2O or mixture with optimal mixing ratio 0.1-0.50%, SiO 0.15-0.65%, Mg 0.08-0.45%, Mn 0.9-2.4%, Cr 0.15-1.0%, Ni 1.5-4.5%, Ti 0.15-0.45%, B 0.004-0.012% and any one of NaF or CaF2 or mixture with optimal mixing ratio 0.5-1.5%. When the flux-cored wire is being welded, slag quantity on the welding seam surface is small, the deposition efficiency is high, the sputtering is few, the flux-cored wire has good low temperature impact toughness and anticracking ability, and diffusible hydrogen reaches the super low hydrogen level.
Owner:WUHAN TEMO WELDING CONSUMABLES CO LTD
Flux-cored wire having high abrasion resistance and application thereof
InactiveCN103240539AImprove wear resistanceReduce splashArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsNiobiumManganese
The invention discloses a flux-cored wire having high abrasion resistance and application thereof and belongs to the field of welding materials. The flux-cored wire comprises a skin and a flux core. The flux core comprises, by mass, 4.9-5.0% of tungsten carbide, 2.0-2.1% of boron powder, 1.9-2.1% of vanadium powder, 8-10% of manganese powder, 30-35% of chromium powder, 1-2% of niobium powder, 0.5-1% of cerium oxide, 0.8-1.3% of lanthanum oxide, yttrium oxide, 4.0-4.5% of quartz, 2.0-3.5% of magnesite, 3.5-4.0% of fluoride, and the balance rutile and carbon powder, wherein the total content of C in the flux core is 6.0-6.5%. The flux-cored wire has the advantages that the flux-cored wire splashes little, is good in stability, has easiness in deslagging and is good in abrasion resistance and toughness and slag is covered evenly. The flux-cored wire is particularly high in impact resistance and suitable for cutter welding having high requirements for abrasion resistance and toughness.
Owner:王井丽
High-strength aluminum alloy material applicable to motorcycle rim
The invention discloses a high-strength aluminum alloy material applicable to a motorcycle rim, which is characterized by comprising the following elements in mass percentage: not more than 0.15% of silicon, not more than 0.20% of ferrum, 0.40-1.4% of copper, 1.1-1.6% of magnesium, 0.10-0.30% of manganese, 5.6-6.8% of zinc, 0.02-0.08% of titanium, 0.10-0.30% of chromium, 0.05-0.20% of zirconium, and the balance of aluminum. The production process of the aluminum alloy material comprises the following steps of blending materials, charging, removing slag, adding magnesium, stirring, sampling, adjusting components, refining, removing slag, refining, keeping standing and casting. The high-strength aluminum alloy material has the advantages of high strength, good elongation percentage, good welding performance and good chemical polishing performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNISON ALUMINUM PRODS
Low-hydrogen alkaline electrode for online welding of X80 pipeline steel
InactiveCN102873473AImproved arc stabilityGood fluidity of molten poolWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaFerrosiliconFerrotitanium
The invention discloses a low-hydrogen alkaline electrode for online welding of X80 pipeline steel. The low-hydrogen alkaline electrode comprises a core wire and a coating. The coating comprises, by weight, from 40% to 45% of marble, from 15% to 20% of fluorite, from 2% to 4% of titanium dioxide, from 6% to 10% of rutile, from 7% to 10% of ferrotitanium, from 4% to 7% of low-carbon ferromanganese, from 2% to 5% of ferrosilicon, from 6% to 10% of iron powder, from 2.5% to 3% of synthetic mica, from 1.8% to 2.2% of rare earth and from 2% to 2.4% of microcrystal fibers, and the sum of the weight percents of the components is 100%. The electrode made from the coating is good in arc stabilization performance, a molten pool is good in flowability, splashing particles are tiny, post-welding slag detachability is good, slag coverage is uniform, and formed weld joints are delicate and attractive. Besides, the content of diffusible hydrogen in deposited metal of the manufactured electrode is effectively controlled.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Hydrogen-induced crack resisting high-ductility ultra-low hydrogen welding electrode
InactiveCN102528310AExcellent resistance to hydrogen crackingExcellent welding performance in all positionsWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaElectrolysisCrazing
The invention discloses a hydrogen-induced crack resisting high-ductility ultra-low hydrogen welding electrode which consists of a core welding wire and a coating, wherein the coating is coated on the outer wall of the core welding wire, the weight coefficient of the coating accounting for the total weight of the welding electrode is 0.4-0.5, the core welding wire comprises the following constituents in percentage by weight: 0.01-0.08% of C, 0.01-0.05% of Si, 0.30-0.55% of Mn, 0.005-0.20% of Cr, 0.005-0.20% of Ni, 0.001-0.006% of P, 0.001-0.005% of S and the balance of Fe; the coating adopts a basic slag system which comprises the following constituents: 30-50% of calcium carbonate, 1-2% of sodium carbonate, 15-30% of calcium fluoride, 3-8% of rutile, 1-5% of titanium pigment, 2-10% of silicon dioxide, 5-10% of electrolytic manganese, 2-5% of ferrosilicon and 0.1-1.5% of ferromolybdenum. When the welding electrode is adopted to weld, the tensile strength of a welding line is more than 500MPa, the striking energy is more than 170J at minus 30 DEG C, the content of diffusible hydrogen is between 2-3ml / 100g and the crack sensitivity is less than 0.11, and the hydrogen-induced crack resisting high-ductility ultra-low hydrogen welding electrode is used for welding of essential equipment in petrochemical industry and the like.
Owner:KUSN GINTUNE WELDING
Defect mending method for martensite heat-resistant steel threaded hole
The invention discloses a defect mending method for a martensite heat-resistant steel threaded hole. The method comprises the steps of defect excavation, soldering preheating, soldering, roasting and secondary machining. The defects of conventional preheating welding techniques are overcome, and the mending method for the defects of the threaded hole and the problem of thread tooth breakage in the finishing machining process of martensite heat-resistant steel castings is provided specific to the problems of slag holes and sand holes occurring in the finish machining process of the threaded hole. Through strict welding process control, the welding process comprising the steps of soldering preheating, soldering and roasting is finely controlled to achieve the effect that post-welding heat treatment does not need to be conducted after completion of welding, and the effect that conditions such as cracking, deformation and scrapping do not occur to the welding repair parts can also be ensured.
Owner:KOCEL STEEL
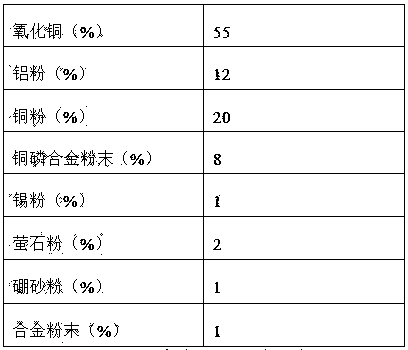
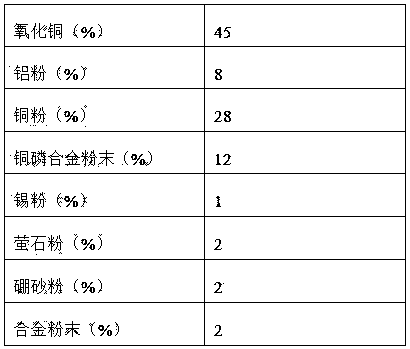
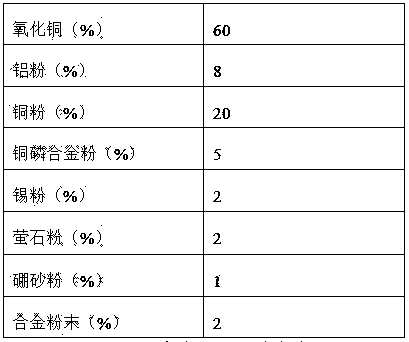
Exothermic welding powder for welding novel grounding grid materials
ActiveCN104043913AQuality improvementLower connection costsWelding/cutting media/materialsAlumino-thermic welding apparatusExothermic weldingAl powder
The invention discloses exothermic welding powder for welding novel grounding grid materials. The exothermic welding powder comprises, by weight, 45%-60% of copper oxide, 8%-13% of aluminum powder, 20%-30% of copper powder, 5%-15% of copper-phosphorus alloy powder, 1%-5% of tin powder, 2%-6% of fluorite powder, 1%-4% of borax powder and the balance alloy powder. The alloy powder comprises, by weight, 8%-12% of Ca, 40%-47% of Si, 28%-32% of Ba and the balance impurities. According to the exothermic welding powder, raw materials are low in price and easy to get, the problems that pores, slag inclusion, hot tear and the like can be easily generated in the welding process by using the exothermic welding powder are solved, the quality of welded joints is reliable, the connecting cost of the novel grounding grid materials is lowered, and the development of a grounding system in electric power engineering in China is facilitated.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Self-adaptive detection control system and method for narrow gap welding width
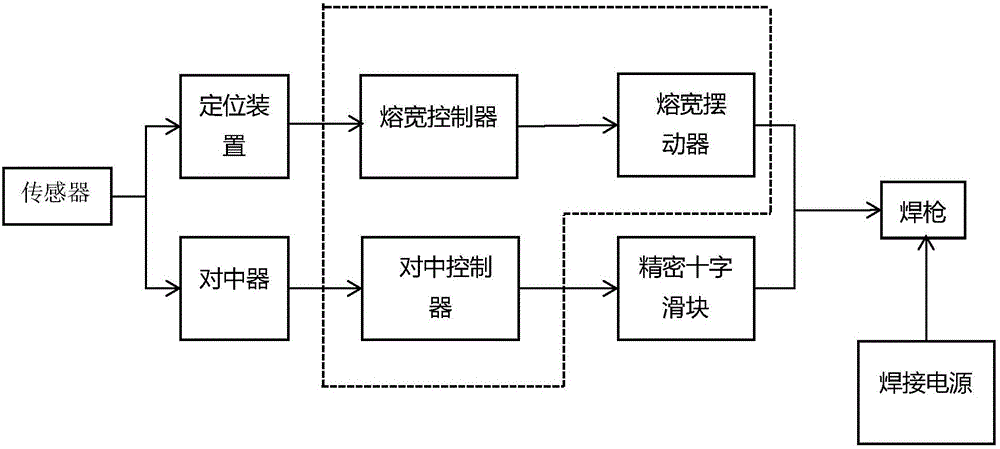
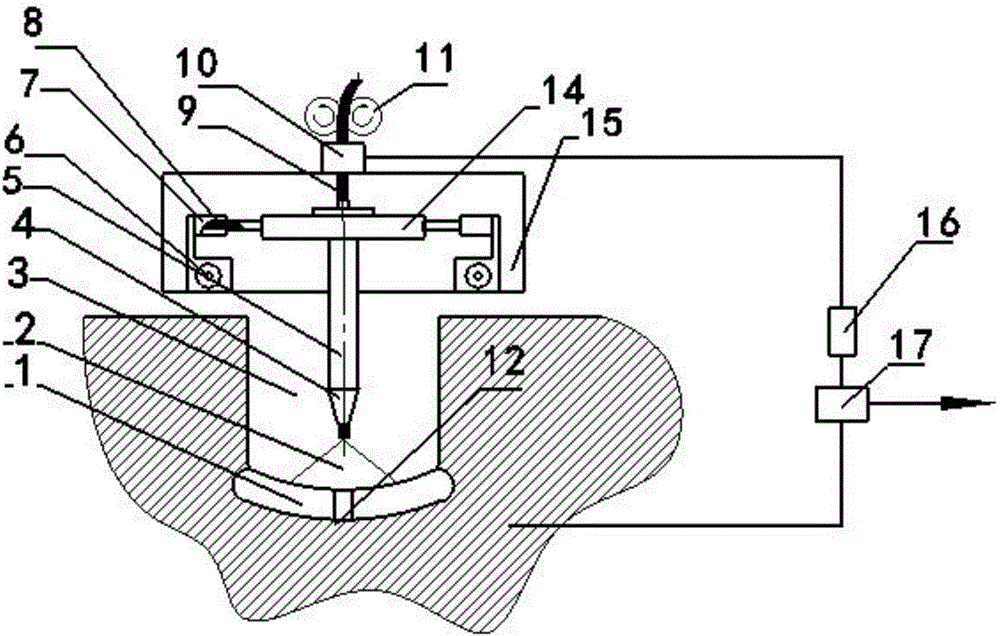
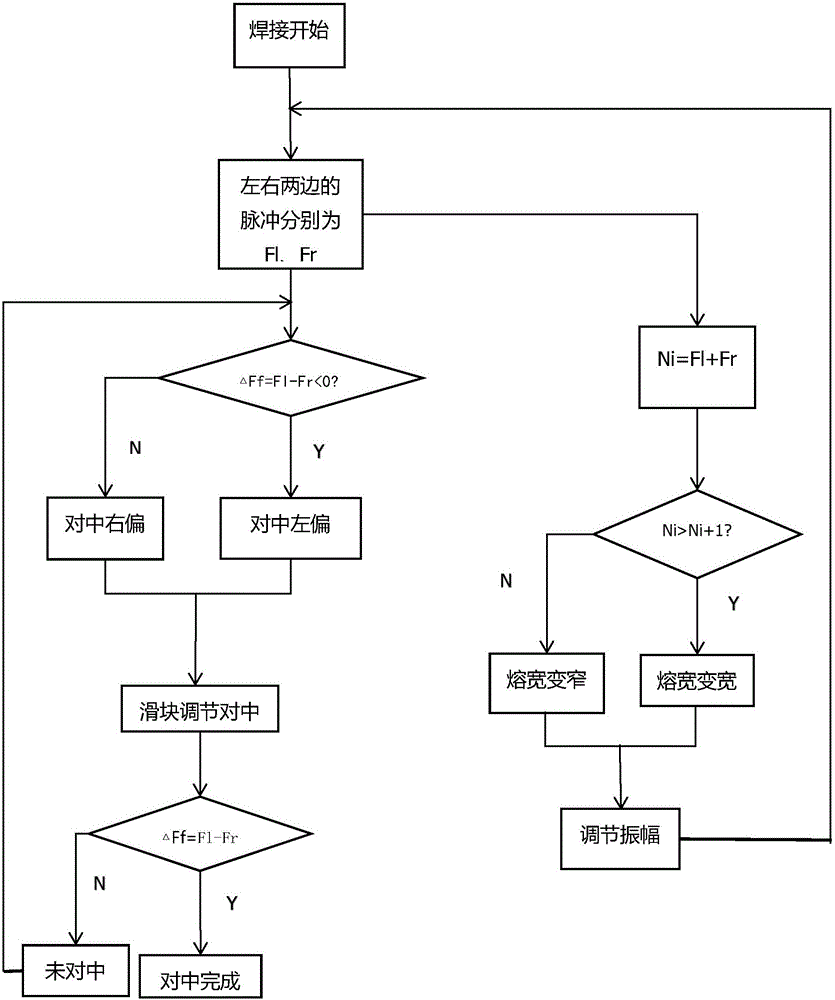
ActiveCN105834554AStrong applicabilityImprove detection accuracyArc welding apparatusPulse numberElectric arc
The invention discloses a self-adaptive detection control system and method for the narrow gap weaving arc welding width. By the adoption of the self-adaptive detection control system and method, the defects that when the existing narrow gap welding width is nonuniform, undercut, slag inclusion, nonuniform weld joints and the like are caused are overcome. According to the main points of the technical scheme, in the welding process, a weaving arc sensor controls an electric arc to swing so as to conduct scanning in the position of a slope, signals are collected by the sensor, the centering position deviation is determined by comprising the pulse number on the left side with the pulse number on the right side, the welding width change is judged by comparing the pulse sum, the swing amplitude of a welding torch is adjusted, and accordingly self-adaptive control and automatic centering of a welding gun are achieved. A detection algorithm is simple, the responds speed is high, the detection accuracy is high, the welding stability of the narrow gap weaving arc welding is improved, and welding defects are avoided.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com