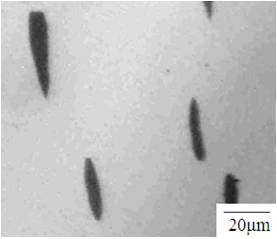
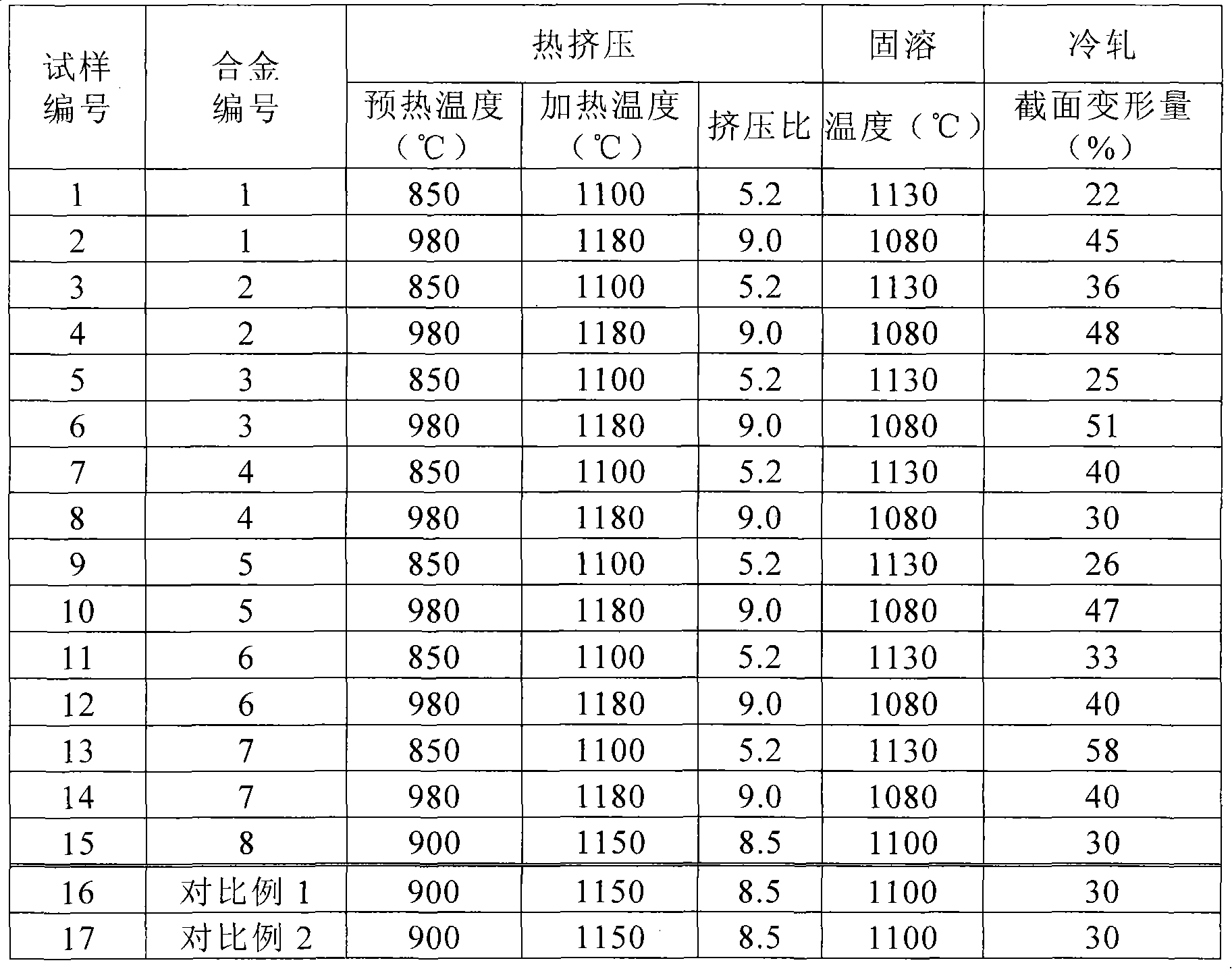
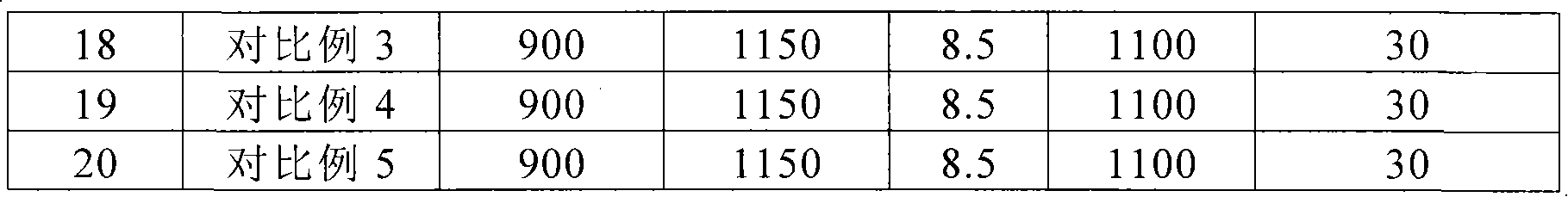
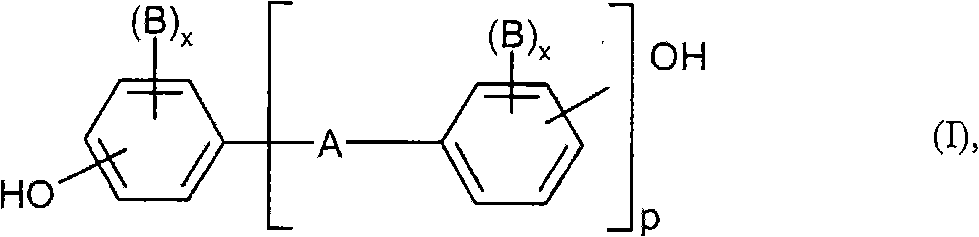
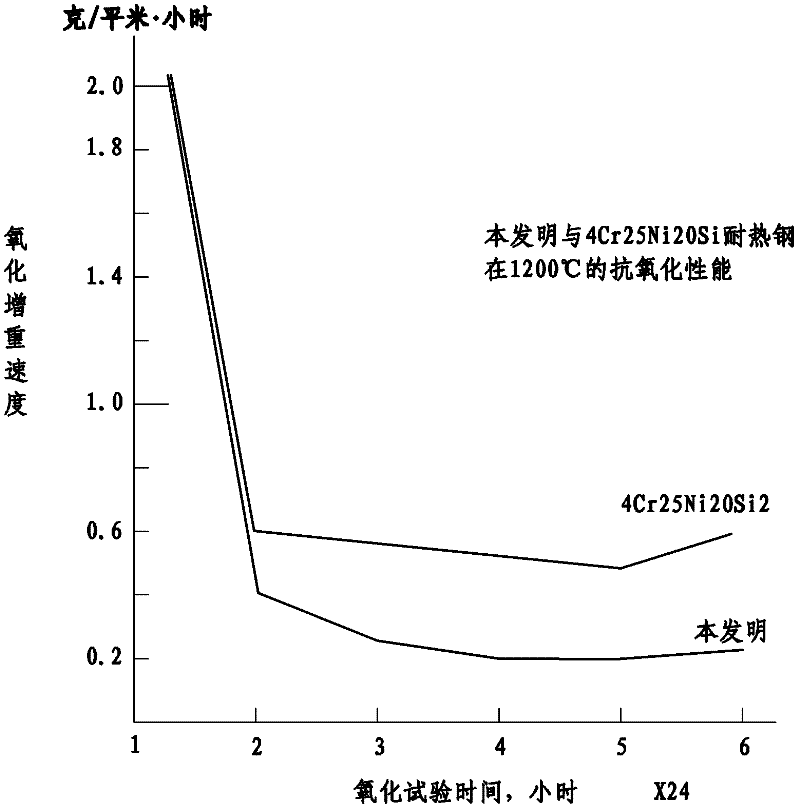
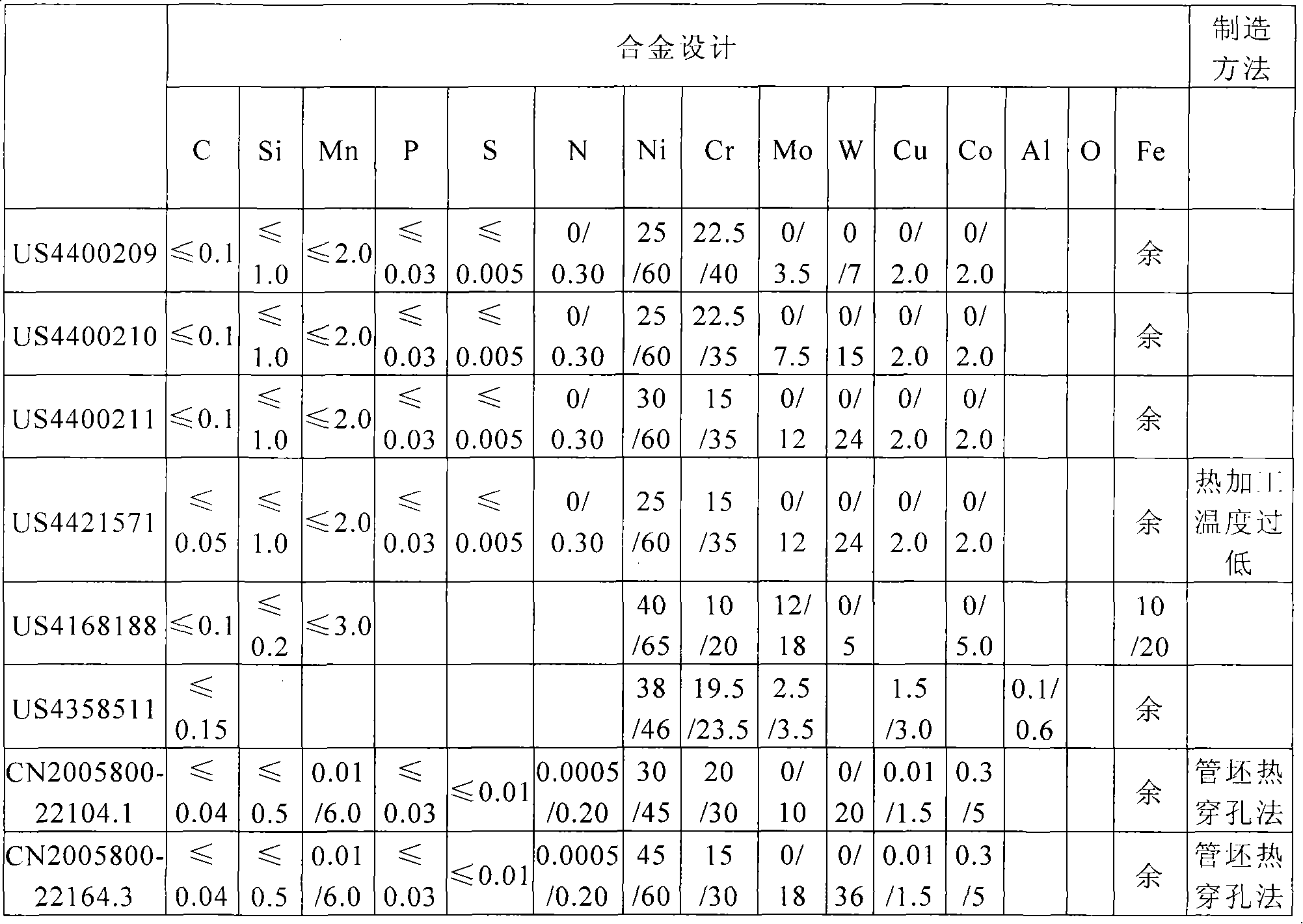Patents
Literature
477results about How to "Improve hot workability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Copper-based alloy and its manufacturing method
As a rawmaterial of a copper base alloy containing at least one of 0.2 to 12 wt% of tin and 8 to 45 wt% of zinc, at least one of a copper base alloy having a large surface area and containing carbon on the surface thereof, a copper base alloy having a liquidus line temperature of 1050 DEG C or less, a copper base alloy surface-treated with tin, and a copper base alloy containing 20 to 1000 ppm of carbon, is used for obtaining a copper base alloy having an excellent hot workability. If necessary, when the raw material of the copper base alloy is melted, the material of the copper base alloy may be coated with a solid material containing 70 wt% or more of carbon, or 0.005 to 0.5 wt% of a solid deoxidizer having a stronger affinity with O than C with respect to the weight of the molten metal may be added to the molten metal.
Owner:DOWA HLDG CO LTD
Highly processible compounds of high MW conventional block copolymers and controlled distribution block copolymers
The present invention provides a polymeric compound (e.g., a compounded polymeric composition) of highly improved processibility that includes a conventional block copolymer, a controlled distribution block copolymer, and optionally one or more components selected from the group consisting of olefin polymers, styrene polymers, tackifying resins, extending oils, waxes, fillers, and engineering thermoplastic resins. The controlled distribution block copolymer is used as a flow modifier to enhance processability of the conventional block copolymer compound. The polymeric compound of the present invention suffers no reduction in mechanic properties while exhibiting improved processability. One advantage of the present invention is that high performance rubber compounds can be made which can be more easily thermally processed relative to prior art compounds. As such, lower energy consumption, reduced cycle times, reduced part warpage, and / or increasing mold complexity can be achieved.
Owner:KRATON POLYMERS US LLC
Ni-base heat resistant alloy and welded joint thereof
InactiveUS20030005981A1Improve carburization resistanceImprove solubilityWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaUltimate tensile strengthEthylene
A Ni-base heat resistant alloy excellent in weldability and strength at elevated temperatures and suited for use in manufacturing cracking furnace tubes and reformer furnace tubes to be used in ethylene plants as well as a welded joint therefor is provided. The alloy of the invention is a Ni-base heat-resistant alloy, which comprises C: not more than 0.1%, Si: not more than 2%, Mn: not more than 2%, P: not more than 0.025%, S: not more than 0.005%, N: not more than 0.04%, Cr: 10 to 30%, Al: 2.1 to less than 4.5%, and Mo: 2.5 to 15% or W: 2.5 to 9% or Mo and W: 2.5 to 15% in total, and satisfies the relation (1) given below:<paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>(104Si+1980P+1980S+9Al+15Ti+11Nb+1.8W+11600B)<={1.1(240-20000S-1900P-30Al-10Ti-9W+17000B) (1)< / in-line-formula>In the welded joint of the invention, both of the base metal and weld metal are made of the alloy having the above composition, and the ST value of the weld metal as calculated according to the following formula (2) or (3) is larger by not less than 3 than the ST value of the base metal:<paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>in the case of Ti<=4C; ST-Mo+1.5W+100Ti (2)< / in-line-formula><paragraph lvl="0"><in-line-formula>in the case of Ti>4C; ST=Mo+1.5W+400C (3).< / in-line-formula>
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Diphase stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses a diphase stainless steel, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: less than or equal to 0.05 percent of C, 0.2 to 1.0 percent of Si, 0 to 2.0 percent of Mn, 22 to 27 percent of Cr, 0 to 2.0 percent of W, less than or equal to 0.1 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of P, 0 to 0.003 percent of B, more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.2 percent rare earth of which the Ce content is more than 50 percent, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities, wherein a casting blank of the diphase stainless steel comprises over 60 percent of isometric crystal. A method for manufacturing the diphase stainless steel comprises the following steps of: performing smelting, die casting or continuous casting to form the casting blank, wherein the thickness of a steel die is more than 30 mm during the die casting to ensure that the cooling velocity of the steel is more than 10 DEG C per minute, and in the process of the continuous casting, the degree of superheating of the casting is between 30 and 100 DEG C, and the casting speed is over 1.2 meters per minute; putting the casting blank into a heating furnace, heating the casting blank to the temperature of between 1,100 and 1,250 DEG C, performing heat preservation on the casting blank, and then forging or hot-rolling the casting blank to a required thickness; and annealing and pickling a steel plate or a plate coil after forging or hot-rolling, and controlling the annealing temperature to be between 1,000 and 1,100 DEG C. The diphase stainless steel has high corrosion resistance and high hot-working performance, and can be widely applied in the fields of petroleum, chemical industry, papermaking, marine engineering and the like in rigorous corrosion environments.
Owner:BAOSTEEL SPECIAL STEEL CO LTD +1
Method for manufacturing high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy forge piece formed by spraying
The invention belongs to a manufacturing technology of aluminum alloy and relates to a method for manufacturing a high-strength 7055 aluminum alloy forge piece formed by spraying. The method sequentially comprises the following steps: (a) melting components of 7055 alloy in an intermediate frequency furnace; (b) degassing, deslagging, refining and filtering an aluminum alloy fusant; (c) forming the filtered fusant by spraying to obtain a columnar aluminum alloy ingot blank; (e) carrying out hot extrusion on the aluminum alloy ingot blank formed by spraying; (f) constantly cutting the extrusion ingot as required and then carrying out free forging; (g) carrying out blocker-type forging and / or stamp forging on the blank after the free forging to obtain a stamp forging piece; and (h) carrying out T6 heat treatment on the stamp forging piece. A large-specification and high-property 7055 product can be obtained by using the method which is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:JIANGSU HAORAN SPRAY FORMING ALLOY
Method for melting nickel-base high temperature alloy with electro-slag furnace
The invention relates to a method for melting a nickel-base high temperature alloy with an electro-slag furnace. The method includes the following methods: loading materials, welding a high temperature alloy electrode and a false electrode to be smelted together, and placing slag materials at the bottom of a crystallizer; blowing the welded electrodes with inert gases, and closing a protection cover; protecting a smelting closing smoke exhaust valve, and feeding an Ar gas into the crystallizer and the protection cover; striking an arc and melting slag; cleaning smelting slag materials, starting a smelting period, and swinging a slag resistor for less than 0.5 m omega during the smelting process; adding oxidizing agents, and adding metal aluminum powder continuously or at intervals to serve as deoxidizing agents during an electro-slag re-melting process; adopting feeding thorough three stages, power feeding is decreased rapidly, power feeding is decreased slowly, and finally heat is preserved at constant power; and casting a die, cooling and demolding the die. According to the method for melting the nickel-base high temperature alloy with the electro-slag furnace, the surface of a nickel-base high temperature steel ingot has no slag groove defect, and the burning losses of Al and Ti are less than or equal to 5%.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
High cobalt nickel-based high-temperature alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a high cobalt nickel-based high-temperature alloy used at 650 to 750 DEG C and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of high-temperature alloys. Thedifficult problem about improving the comprehensive performance of the nickel-based high-temperature alloy with the consideration of alloy performance and use cost in the prior art is solved by precisely controlling the component range of Co in the high-temperature alloy. The alloy is prepared from the components in percentage by mass: less than or equal to 0.1 percent of C, 12 to 20 percent of Cr, less than or equal to 4.0 percent of Mo, less than or equal to 6 percent of W, 12.01 to 25.00 percent of Co, less than or equal to 14 percent of Fe, 4.0 to 8.0 percent of Nb, 0.6 to 2.6 percent of Al, 0.4 to 1.4 percent of Ti, 0.003 to 0.03 percent of P, 0.003 to 0.015 percent of B, and the balance of Ni; the content of a gamma' phase is 15 to 30 mass percent; the content of eta-Ni3Al0.5Nb0.5 is0.5 to 10.0 mass percent. The preparation method of the nickel-based high-temperature alloy comprises the processes of smelting, forging and cogging, and performing heat treatment. According to the high cobalt nickel-based high-temperature alloy and the preparation method thereof, the high cobalt nickel-based high-temperature alloy can be used at the temperature of 650 to 750 DEG C.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
Austenitic stainless steels
InactiveCN1540026AHigh strengthImprove hot workabilityBook coversHeat exchange apparatusUltimate tensile strengthAustenite
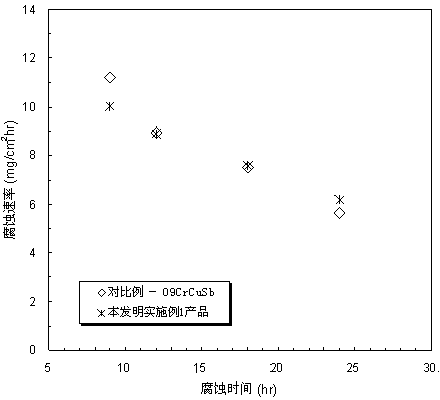
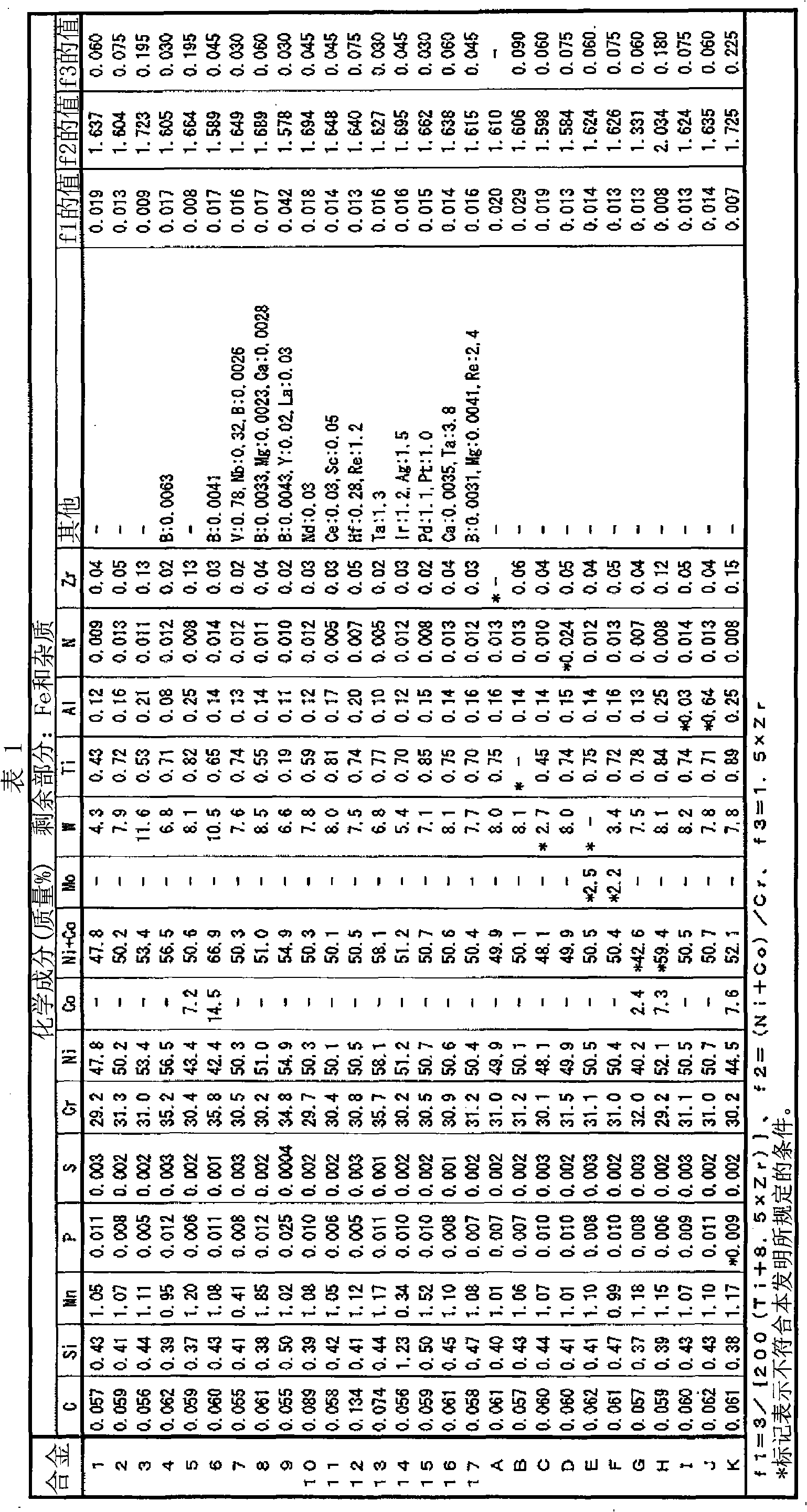
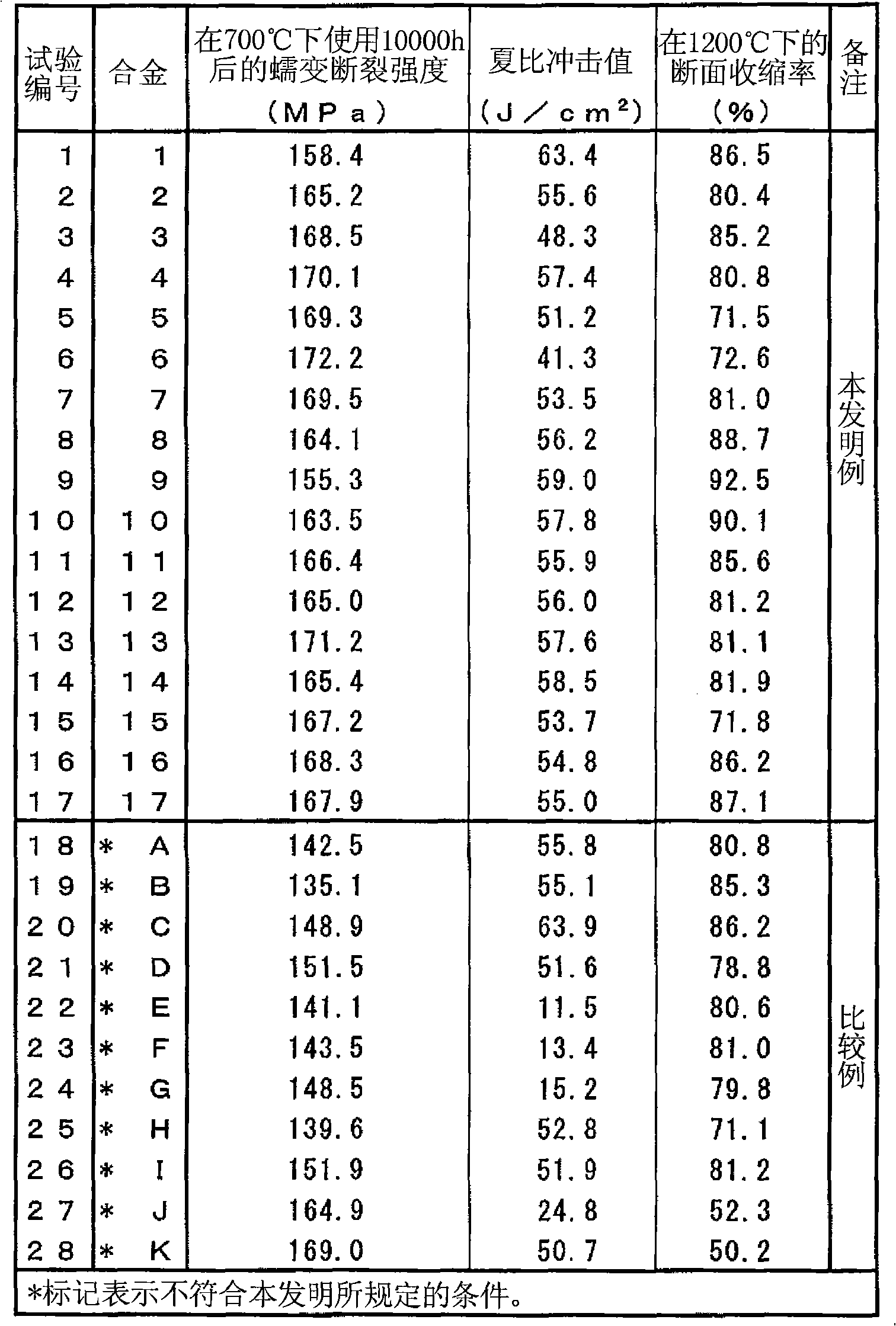
An austenitic stainless steel excellent in high temperature strength, high temperature ductility and hot workability, consisting of, by mass %, C: more than 0.05% to 0.15%, Si: 2% or less, Mn: 0.1 to 3%, P: 0.04% or less, S: 0.01% or less, Cr: more than 20% to less than 28%, Ni: more than 15% to 55%, Cu: more than 2% to 6%, Nb: 0.1 to 0.8%, V: 0.02 to 1.5%, sol. Al: 0.001 to 0.1%, but sol.Al<=0.4xN, N: more than 0.05% to 0.3% and O (Oxygen): 0.006% or less, but O<=1 / (60xCu), and the balance Fe and impurities. The austenitic stainless steel may contain at least one of Co, Mo, W, Ti, B, Zr, Hf, Ta, Re, Ir, Pd, Pt and Ag, and / or at least one of Mg, Ca, Y, La, Ce, Nd and Sc.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Duplex stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
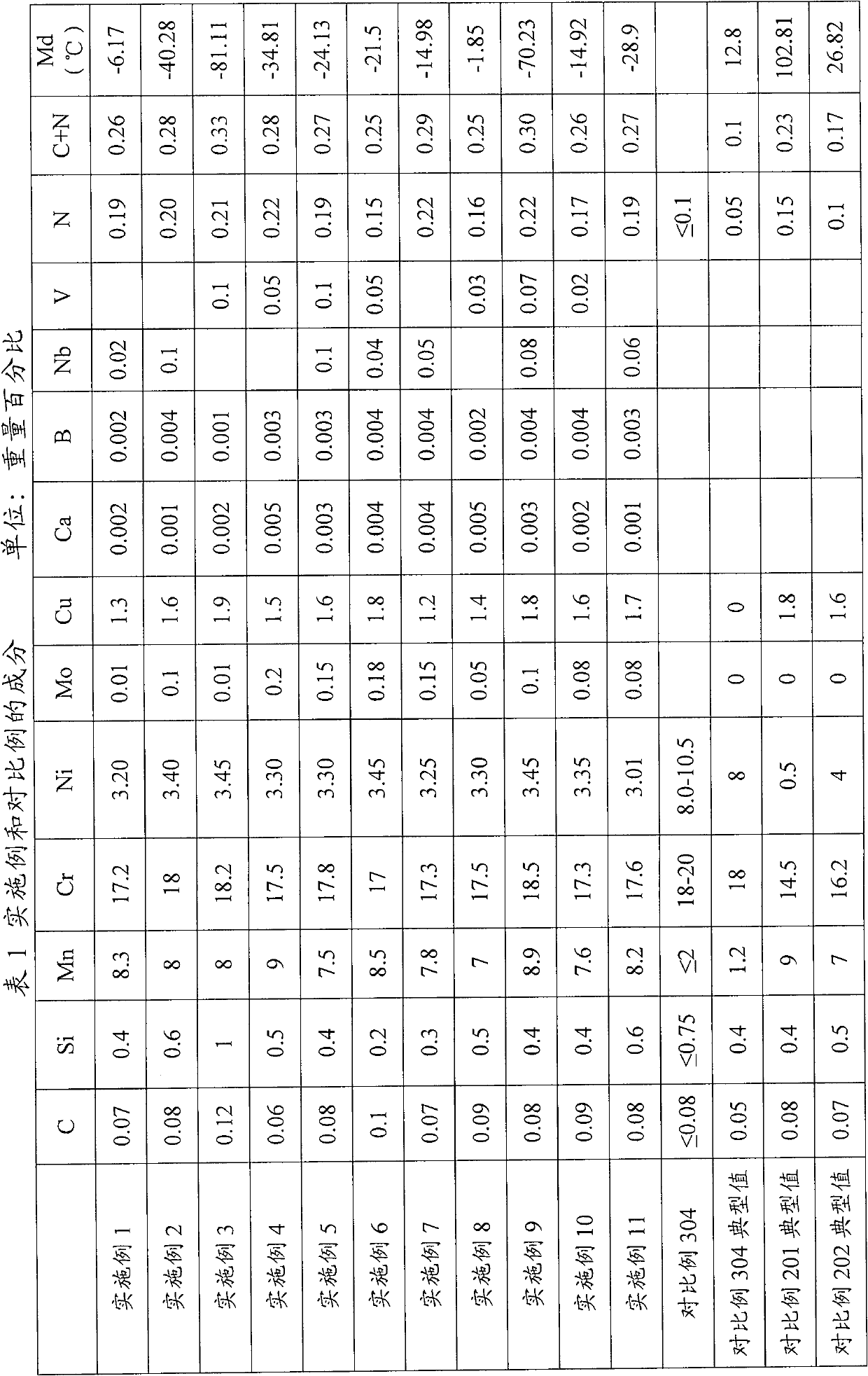
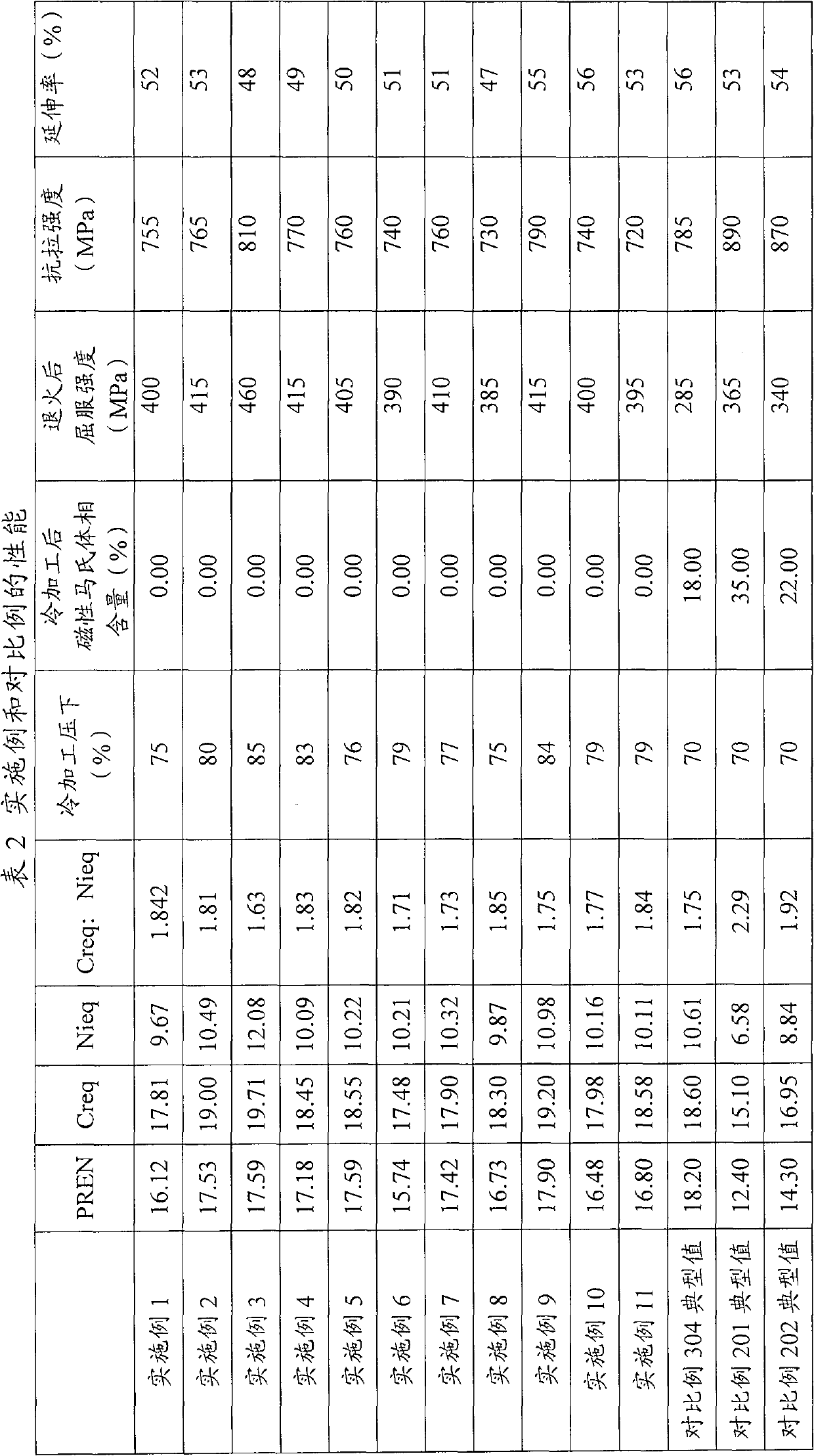
The invention relates to duplex stainless steel. The duplex stainless steel comprises the following chemical components in percent by weight: 0.01-0.08% of C, 0.2-1.0% of Si, 1.5-3.5% of Mn, 19.0-21.0% of Cr, 1.2-2.8% of Ni, 0.08-0.18% of N, less than or equal to 0.5% of Mo, less than or equal to 1.0% of W, less than or equal to 1.0% of Cu and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities; PREN (Pitting Resistance Equivalent Number) is 20-24, the martensitic temperature Md formed by strain induction is 60-130 DEG C. A manufacturing method comprises the following steps of: selecting vacuum induction smelting in an electric furnace, argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) or electric furnace, argon oxygen decarburization (AOD), external refining and LF (Ladle Furnace) smelting; carrying out die casting or continuous casting on molten steel, controlling the superheat degree to be 20-50 DEG C in die casting, matching with fast cooling, preventing nitrogen from escaping, and controlling the overheat degree to be 20-50 DEG C and the plate blank casting speed to be 0.8-2m / min; and putting a die-casting blank or a continuous casting blank into a heating furnace for heating to 1100-1250 DEG C, preserving the heat for 0.5-1.5 hours, processing the die-casting blank or the continuous casting blank on a forging production line or a hot-rolling mill group to the needed thickness, then carrying out annealing at the speed of 0.5-2.5min / mm and the temperature of 1030-1150 DEG C. The obtained duplex stainless steel has excellent corrosion resistance and TRIP effect.
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
Composite plate of intermetallic TiAl compound and Ti alloy and its production process
InactiveCN1672918AImprove hot workabilityImproved hot workabilityMetal layered productsHeat resistanceComposite plate
The present invention is composite plate of intermetallic TiAl compound and Ti alloy and its production process. The composite plate includes at least one layer of plate of intermetallic TiAl compound and at least one layer of plate of pure Ti or Ti alloy. The production process includes polishing plate or block of intermetallic TiAl compound and plate or block of pure Ti or Ti alloy; and subsequent canning rolling to produce the composite plate at the technological parameters of temperature 600-1400 deg.c, deformation 2-40 % each gate and total deformation of 5-95 %. The composite plate has the advantages of light weight, heat resistance, high strength and high plasticity.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Low-carbon high-sulfur free-cutting steel with excellent cutting performance and manufacturing method thereof
The invention discloses low-carbon high-sulfur free-cutting steel with excellent cutting performance and a manufacturing method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of free-cutting steel. the free-cutting steel contains the following ingredients by mass percentage composition: 0.05 to 0.2 percent of C, 0.6 to 2.0 percent of Mn, 0.04 to 0.1 percent of P, 0.2 to 0.45 percent of S, 0.005 to 0.02 percent of O, less than or equal to 0.02 percent of N, less than or equal to 0.005 percent of Si and less than or equal to 0.001 percent of Al. Generated MnS impurities have the following characteristics: (1) over 95 percent of MnS impurities in as cast steel are Class I MnS, and the proportion of single-phase MnS impurities is equal to or larger than 80 percent; (2) the length of at least 70 percent of MnS impurities in the rolling direction is equal to or larger than 5 micron, and the length-width ratio is lower than or equal to 6; and (3) the average area of MnS impurities in 1 square mm in the rolling direction is no less than 50 square micron. C is adopted for deoxygenation, the cooling rate of ingoting is controlled to range from 2 to 4 mm / min, the roll opening temperature is controlled to range from 1200 to 1250 DEG C, and the roll closing temperature is controlled to be equal to or larger than 1050 DEG C. The low-carbon high-sulfur free-cutting steel has excellent cutting performance. After cutting, the surface fineness of parts is improved. The low-carbon high-sulfur free-cutting steel is generally close to or matches the lead-containing low-carbon free-cutting steel, and is suitable for high-speed cutting.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Ni-based alloy oil sleeve and manufacturing method for high-acidity deep well
ActiveCN101613833ALow costImprove high temperature corrosion resistanceDrilling rodsRoll mill control devicesSolution treatmentImpurity
The invention relates to a Ni-based alloy oil sleeve for a high-acidity deep well, which comprises the following components in percentage by mass: less than or equal to 0.02 percent of C, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.5 percent of Si, less than or equal to 1.0 percent of Mn, 40 to 60 percent of Ni, 20 to 30 percent of Cr, 1 to 10 percent of Mo, 1 to 5 percent of W, 0 to 5 percent of Co, 0.1 to 3.0 percent of Cu, 0.01 to 0.5 percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of O, less than or equal to 1.5 percent of Ti, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. In the invention, the thermal extrusion processing performance and corrosion resisting performance of the alloy are effectively ensured by controlling the contents of the Al and O. The 90 to 140 ksi steel-grade Ni-based alloy oil sleeve meeting different well depth requirements of high-acidity oil fields and gas fields is manufactured by thermal extrusion, 1,050-1,150 DEG C of solution treatment and cold rolling of the smelted and forged blanks.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Preparation method for TiAl alloy plate of uniform structure
The invention provides a preparation method for a TiAl alloy plate of a uniform structure and relates to the preparation method for the TiAl alloy plate. The preparation method for the TiAl alloy plate of the uniform structure aims at solving the problems that the structure of an existing TiAl alloy plate is nonuniform, and the comprehensive performance is reduced. The preparation method comprises the steps that 1, blank preparing is conducted to obtain a cuboid TiAl alloy rolling blank; 2, sleeving is conducted to obtain a sleeved TiAl alloy blank; 3, double-step heat treatment is conducted before high-temperature rolling to obtain a TiAl alloy blank subjected to double-step heat treatment; 4, high-temperature rolling and heat preserving during passes are conducted to obtain a TiAl alloy plate subjected to high-temperature rolling; 5, stress relief annealing is conducted to obtain an annealed TiAl alloy plate; and 6, a sleeve is removed through machining, so that the TiAl alloy plate is obtained. The preparation method for the TiAl alloy plate of the uniform structure has the advantage that the TiAl alloy plate of the uniform structure is obtained by adopting double-step heat treatment before rolling. The preparation method is mainly used for preparing the TiAl alloy plate of the uniform structure.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Low-nickel austenitic stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a low-nickel austenitic stainless steel, which comprises the following chemical components by weight percent: no less than 0.05% and no more than 0.15% of C, less than 1.00% of Si, more than 9.00% and less than 10.00% of Mn, no less than 14.00% and no more than 16.00% of Cr, no less than 0.50% and less than 1.00%, more than 0.15% and no more than 0.25% of N, more than 1.50% and no more than 2.00% of Cu, no less than 10*10<-4>% and no more than 30*10<-4>% of B, no less than 1*10<-4> and no more than 50*10<-4>% of Ca, less than 0.030% of P, no less than 0.020% of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. For the stainless steel, heat processing performance of materials is improved through B alloying treatment on premise of further reducing the content of precious metal of nickel, and the purity of the liquid steel is enhanced through Ca treatment. The formability of stainless steel is enhanced through the reasonable alloy system design and a micro-alloy treatment method, the defects of sand buckle, sand holes, and the like are avoided in the forming process, the delayed rupture phenomenon is lightened, and the application scope of the festival nickel austenitic stainless steel is further broadened.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Austenitic stainless steel
An austenitic stainless steel, which comprises by mass %, C: 0.04 to 0.18%, Si≦1.5%, Mn≦2.0%, Ni: 6 to 30%, Cr: 15 to 30%, N: 0.03 to 0.35%, sol. Al≦0.03% and further contains one or more elements selected from Nb≦1.0%, V≦0.5% and Ti≦0.5%, with the balance being Fe and impurities, and among the impurities P≦0.04%, S≦0.03%, Sn≦0.1%, As≦0.01%, Zn≦0.01%, Pb≦0.01% and Sb≦0.01%, and satisfy the conditions P1=S+{(P+Sn) / 2}+{(As+Zn+Pb+Sb) / 5}≦0.06 and 0.2≦P2=Nb+2(V+Ti)≦1.7−10×P1 has high strength and excellent resistance to cracking due to grain boundary embrittlement in the welded portion during the use at high temperatures. Therefore, the said steel can be suitably used as materials for constructing machines and equipment, such as power plant boilers, which are to be used at high temperatures for a long period of time.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Production process of nuclear bolt
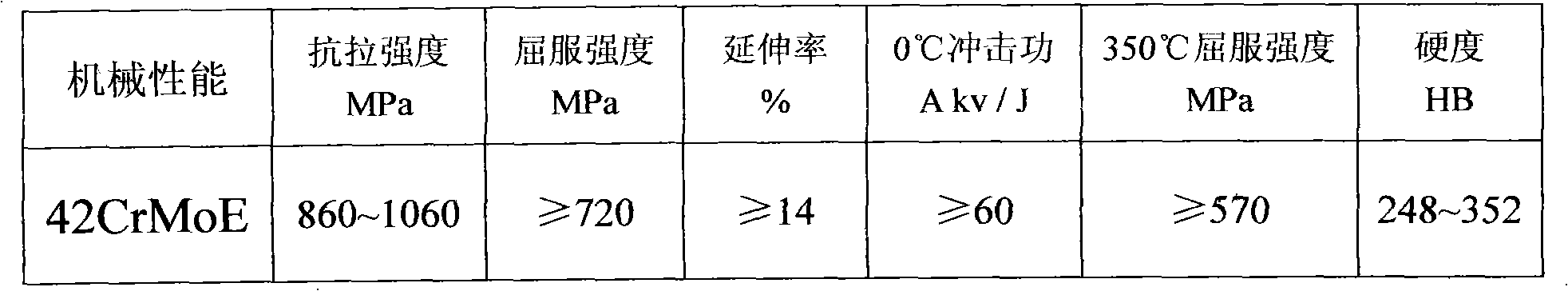
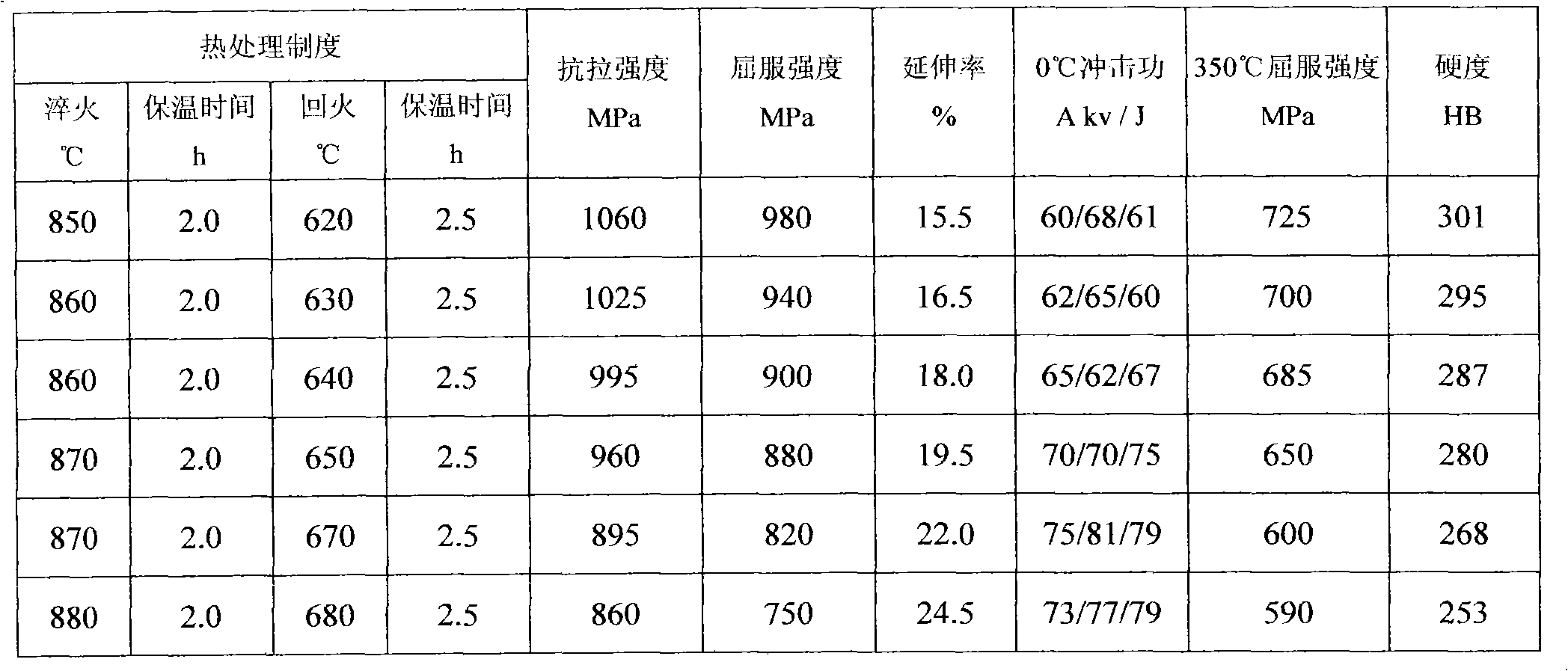
The invention mainly discloses a production process of a nuclear bolt. A 42CrMoE steel material is adopted as a raw material, and the nuclear bolt is produced by blank preparation, heat treatment, surface treatment and flaw detection, wherein the raw material of 42CrMoE comprises the following chemical components by mass percent: 0.38 to 0.48 of C, 0.10 to 0.40 of Si, 0.75 to 1.00 of Mn, no more than 0.025 of P, no more than 0.015 of S, 0.80 to 1.15 of Cr, 0.15 to 0.30 of Mo and the balance of Fe. The product obtained by production in the invention meets the requirements of nuclear 1-stage equipment, nuclear 2-stage equipment and nuclear 3-stage equipment, and the strength, the hardness and the impact resistance all reach standards.
Owner:浙江高强度紧固件有限公司
Steel plate resistant to sulfuric acid dew point corrosion and manufacturing method for steel plate
ActiveCN104357754AHigh yield strengthHigh strengthTemperature control deviceHigh pressure waterYield ratio
The invention discloses a strong-strength and low-yield ratio steel plate resistant to sulfuric acid dew point corrosion and a manufacturing method for the steel plate. The steel plate comprises the following chemical components in percentage by mass: 0.06 to 0.10 percent of C, 0.15 to 0.50 percent of Si, 0.90 to 1.20 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.012 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.008 percent of S, 0.40 to 0.70 percent of Cr, 0.15 to 0.45 percent of Ni, 0.20 to 0.50 percent of Cu, 0.02 to 0.04 percent of Al, 0.02 to 0.05 percent of V, 0.015 to 0.04 percent of Nb, 0.01 to 0.02 percent of Ti, 0.0005 to 0.005 percent of Ca, less than or equal to 0.007 percent of N and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurity elements. The steel plate resistant to sulfuric acid dew point corrosion is directly manufactured by a continuous casting billet of 150mm or more, and the manufacturing method comprises the following steps of heating the continuous casting billet to 1,180 to 1,230 DEG C, preserving heat for 2 to 3 hours, performing rolling after high-pressure water scale removal, cooling the continuous casting billet to 500 to 620 DEG C at the cooling speed of 7 to 15 DEG C / s, and performing straightening and cooling to obtain the steel plate resistant to sulfuric acid dew point corrosion. According to the steel plate and the manufacturing method, a trace amount of Ca, and Nb and V favorable for improving the toughness of steel are added on the basis of Cu-Cr-Ni-Ti anticorrosion, and the content of each element is reasonably set, so that the strength and toughness of the steel are improved on the basis of ensuring the resistance of the steel to the sulfuric acid dew point corrosion, and the yield ratio is lowered.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
Heat-resistant austenitic alloy, heat-resistant pressure-resistant member comprising the alloy, and process for producing the same
A heat-resistant austenitic alloy which contains 0.02-0.15%, excluding 0.02%, C, up to 2% Si, up to 3% Mn, up to 0.03% P, up to 0.01% S, 28-38% Cr, 40-60%, excluding 40%, Ni, up to 20% (including 0%) Co, 3-15%, excluding 3%, W, 0.05-1.0% Ti, 0.005-0.2% Zr, and 0.01-0.3% Al and has a N content up to 0.02% and a Mo content less than 0.5%, with the remainder being iron and impurities, and which satisfies relationships (1) to (3). The alloy has a high creep rupture strength, has satisfactory toughness even when used at a high temperature over long, and has excellent hot workability. This heat-resistant austenitic alloy may contain a specific amount of one or more elements selected from Nb, V, Hf, B, Mg, Ca, Y, La, Ce, Nd, Sc, Ta, Re, Ir, Pd, Pt, and Ag. P<=3 / {200(Ti+8.5Zr)} (1) 1.35Cr<=Ni+Co<=1.85Cr (2) Al>=1.5Zr (3).
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Blend of aromatic polycarbonate and polylactic acid, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101671476AImprove mechanical propertiesImprove hot workabilityTrans esterificationPolymer science
The invention relates to a blend of aromatic polycarbonate and polylactic acid, a preparation method and application thereof. According to the method, an ester exchange reaction catalyst is added in the process of preparing the blend of the aromatic polycarbonate and the polylactic acid so as to improve the compatibility of each composition in the blend. The blend of the aromatic polycarbonate and the polylactic acid has excellent mechanical performance, hot-working character and flame retardant property, and can be widely applied to mechanical products or parts, electrical and electronic products or parts, building materials and daily necessities.
Owner:COVESTRO POLYMERS CHINA CO LTD +1
High-intensity aluminum manganese alloy for heat exchanger and its manufacture method
ActiveCN101186986AHighlight substantive featuresSignificant progressHeat exchange apparatusManganeseHigh intensity
The invention provides an Al-Mn alloy for high strength heat exchanger and the process for preparing. The composition contents are as follows, including Si<=0.5wt%, Fe<=0.7wt%, Cu0.1-0.3wt%, Mn1.0-1.6wt%, Mg0.3-0.7wt%, Zn0.05-0.3wt%, and Cr0.05-0.15wt%. The method of manufacturing the alloy is to add Si, Fe, Cu, Mn, Mg, Cr and Zn into the industry pure aluminium ingot melt at different stage of temperature, after purifying treatment of the melt, control the cooling rate , cast and acquire Al-Mn line alloy ingot with large scale as-cast grain. After uniformly treatment, the allot ingot is hot rolled at a temperature of 470-510 DEG C and annealed at a temperature of 300-430 DEG C for 1-3h and then cold rough rolled and cold finish rolled, with the deformation of 30-70%, and at least acquire the manufactured product. The adopting states of O treatment state and H24 treatment state are achieved after the annealing of the manufactured product. The Al-Mn alloy has the advantages of good tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, hang-down resistance and low cost, thereby the Al-Mn alloy is the ideal productive material for the component of the heat exchanger.
Owner:CHINALCO MATERIALS APPL RES INST CO LTD
Austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel and processing method thereof
InactiveCN102230137AGood high temperature oxidation resistanceImprove carburization resistanceRare-earth elementManganese
The invention relates to austenitic stainless steel, and in particular relates to austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel and a processing method thereof. The austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel is characterized by comprising the following elements by mass percentage: 0.25-0.45% of carbon, 0.5-2% of silicon, 0.5-2% of manganese, 23-27% of chromium, 6-10% of nickel, 0.15-0.3% of nitrogen, 0.1-0.5% of rare-earth (RE) elements and the balance of iron. The austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel obtained by the processing method has the advantages of good high-temperature oxidation resistance, good carburizing resistance, good sulfurization corrosion resistance and lowered production cost.
Owner:XUANDA IND GRP
A kind of tin-containing ferritic stainless steel plate and its manufacturing method
The invention relates to a tin-containing ferrite stainless steel plate and a manufacturing method thereof. The stainless steel plate comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.001 to 0.02 percent of C, 0.001 to 0.02 percent of N, 0.001 to 1 percent of Al, 0.001 to 1.5 percent of Si, 0.001 to 0.5 percent of Mn, 11 to 30 percent of Cr, less than 0.05 percent of P, less than 0.1 percent of S, 0.001 to 5 percent of Ni, 0.001 to 1.5 percent of Cu, 0.001 to 5 percent of Mo, 0.01 to 2 percent of Sn, 0.001 to 2 percent of Ti, 0.001 to 2 percent of Nb, 0.001 to 0.5 percent of Ga, more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1 percent of RE, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. In the manufacturing method, pure tin, pure gallium and rare-earth alloy are added into molten steel after the molten steel is molten by a converter and refined by a vacuum oxygen blowing decarburization furnace and a smelting ladle furnace; and a plate blank is subjected to continuous casting, hot rolling, annealing, acid pickling, cold rolling and thermal treatment to prepare a steel plate. The tin-containing ferrite stainless steel plate manufactured by the method has the advantages of good hot workability, good corrosion resistance and good forming property.
Owner:SHANXI TAIGANG STAINLESS STEEL CO LTD
Easy-cutting lead-free brass alloy for forging and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses an easy-cutting lead-free brass alloy for forging and a preparation method thereof. The alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 55-68 percent of copper, 0.1-0.8 percent of bismuth, 0.05-0.3 percent of calcium, 0.05-0.3 percent of lithium, 0.05-0.15 percent of sulfur, 0.001-0.1 percent of aluminum, 0.001-0.05 percent of boron, 0.001-0.08 percent of mixed rare-earth elements (one or more lanthanum, cerium and neodymium) and the balance of zinc and unavoidable impurity. The preparation method comprises the following steps: smelting copper-zinc alloy at 1,150 DEG C-1,300 DEG C; after fusant sprays fire, sequentially adding bismuth and zinc rare-earth medium alloy; after the mixture stands and preserves the temperature for 10 minutes, sequentially adding zinc-calcium medium alloy, copper-sulfur medium alloy, the aluminum, copper-boron medium alloy, the zinc and zinc-lithium medium alloy; stirring and deslagging the mixture; preserving the mixture at 1100 DEG C for 15 minutes-20 minutes and casting the mixture at the casting temperature of 1,000 DEG C-1,050 DEG C; preparing an alloy casting blank; and finally casting and molding the obtained casting blank so as to obtain a part blank. An alloy product obtained by the invention has thin crystalline grain, high hot processing performance as well as favorable cutting performance and is suitable for forging.
Owner:XIAMEN LOTA INT CO LTD
Crimped composite fiber, and fibrous mass and testile product using the same
InactiveUS20120121882A1Good formabilityImprove spinnabilityFilament/thread formingAnimal housingFiberLinear low-density polyethylene
A crimped conjugate fiber of the present invention is a conjugate fiber containing a first component and a second component, the first component containing polybutene-1 and linear low density polyethylene, the linear low density polyethylene content being 2 to 25 mass %, the second component 2 containing a polymer having a melting peak temperature at least 20° C. higher than the melting peak temperature of polybutene-1 or a polymer having a melting initiation temperature of 120° C. or higher, when viewed from a fiber cross-section, the first component occupies at least 20% of the surface of the conjugate fiber 10 and the centroid position of the second component not overlapping the centroid position of the conjugate fiber, the conjugate fiber is an actualized crimping conjugate fiber in which three-dimensional crimps have been developed or a latently crimpable conjugate fiber in which three-dimensional crimps are developed by heating. Accordingly, a crimped conjugate fiber having high elasticity, a high level of bulk recovery properties, and high durability against repetitive compression as well as high elasticity, a high level of bulk recovery properties, and high durability when used at high temperatures, and a fiber assembly that uses the crimped conjugate fiber are provided.
Owner:DAIWABO HOLDINGS CO LTD +1
High-strength high-corrosion-resistant nickel-based high-temperature alloy and solution and aging heat treatment method thereof
The invention provides a high-strength high-corrosion-resistant nickel-based high-temperature alloy and a solution and aging heat treatment method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a nickel-based high-temperature alloy. The alloy comprises the following chemical ingredients in percentage by weight: 40.0-44.0 percent of Ni, 19.5-22.5 percent of Cr, 2.5-3.5 percent of Mo, 1.5-3.0 percent of Cu, 0.10-0.50 percent of Al, 1.9-2.4 percent of Ti, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of C, less than or equal to 0.2 percent of Si, less than or equal to 1.0 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.02 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.015 percent of P, 0.001-0.005 percent of Mg, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The precipitates of a strengthening phase in tissues can be more uniform and fine by means of reasonable solution and subsequent aging treatment, the number of precipitated phases which are not beneficial to toughness and corrosion resistance can be remarkably reduced, and the obdurability and corrosion resistance in high-chlorine-ion marine environments and other severe environments of the alloy can be improved. On the basis of not influencing the structural stability, obdurability and corrosion resistance of the alloy, the content of Fe is increased as much as possible so as to improve the hot workability of the alloy and reduce the cost.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
High-strength and high-conductivity rare earth copper alloy for contact lines and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high-strength and high-conductivity rare earth copper alloy for contact lines and a preparation method thereof. The rare earth copper alloy is composed of chromium, zirconium, zinc, titanium, silver, copper, rare earth elements and inevitable impurity elements, wherein during preparation, a Cu-Zr intermediate alloy and a Cu-rare earth intermediate alloy are prepared at first, and then the Cu-Zr intermediate alloy and the Cu-rare earth intermediate alloy are smelted and subjected to mould casting with copper, zinc, silver and titanium to form a cast ingot, the cast ingot is subjected to hot extrusion to obtain a bar billet, the bar billet is subjected to solution treatment, the treated alloy is subjected to drawing deformation, and then subjected to aging treatment to prepare the high-strength and high-conductivity rare earth copper alloy. The conductivity, elongation, strength and softening temperature of the alloy disclosed by the invention can be greatly improved; the machining performances of the alloy are remarkably improved; the manufacturability of the alloy can be changed, thus benefiting refining, degassing and microalloying; and the requirements of a material for the industrial field of contact lines on the performances of copper alloys can be met well. The alloy disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation process, short in process flow, high in strength, good in conductivity and excellent in hot-working property.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Multi-catalyst system for olefin polymerization
ActiveUS6861485B2Improve hot workabilityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationOlefin polymerizationPolyolefin
A multi-catalyst system is disclosed. The catalyst system comprises catalyst A and catalyst B. Catalyst A comprises a supported bridged indenoindolyl transition metal complex. Catalyst B comprises a supported non-bridged indenoindolyl transition metal complex. The catalyst system of the invention produces polyolefins which have bi- or multi-modal molecular weight distribution.
Owner:EQUSR CHEM LP
Fe-based austenite alloy oil sleeve and manufacturing method for high-acidity deep well
InactiveCN101613834ALow head lifeIncrease production costDrilling rodsRoll mill control devicesSolution treatmentChemical composition
The invention relates to a Fe-based austenite alloy oil sleeve, which comprises the following components in percentage by mass: less than or equal to 0.03 percent of C, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.03 percent of S, 0.01 to 1.0 percent of Si, 0.01 to 3.0 percent of Mn, 25 to 40 percent of Ni, 20 to 35 percent of Cr, 1 to 5 percent of Mo, 0.1 to 1.5 percent of Cu, 0.01 to 0.5 percent of Al, less than or equal to 0.01 percent of O, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The 90 to 140 ksi steel-grade Fe-based alloy oil sleeve meeting different well depth requirements of high-acidity oil fields and gas fields is manufactured by thermal extrusion, 1,050-1,180 DEG C of solution treatment and cold rolling of the smelted and forged blanks.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Ni-saving austenitic stainless steel cold-rolled sheet with excellent processability and manufacturing method thereof
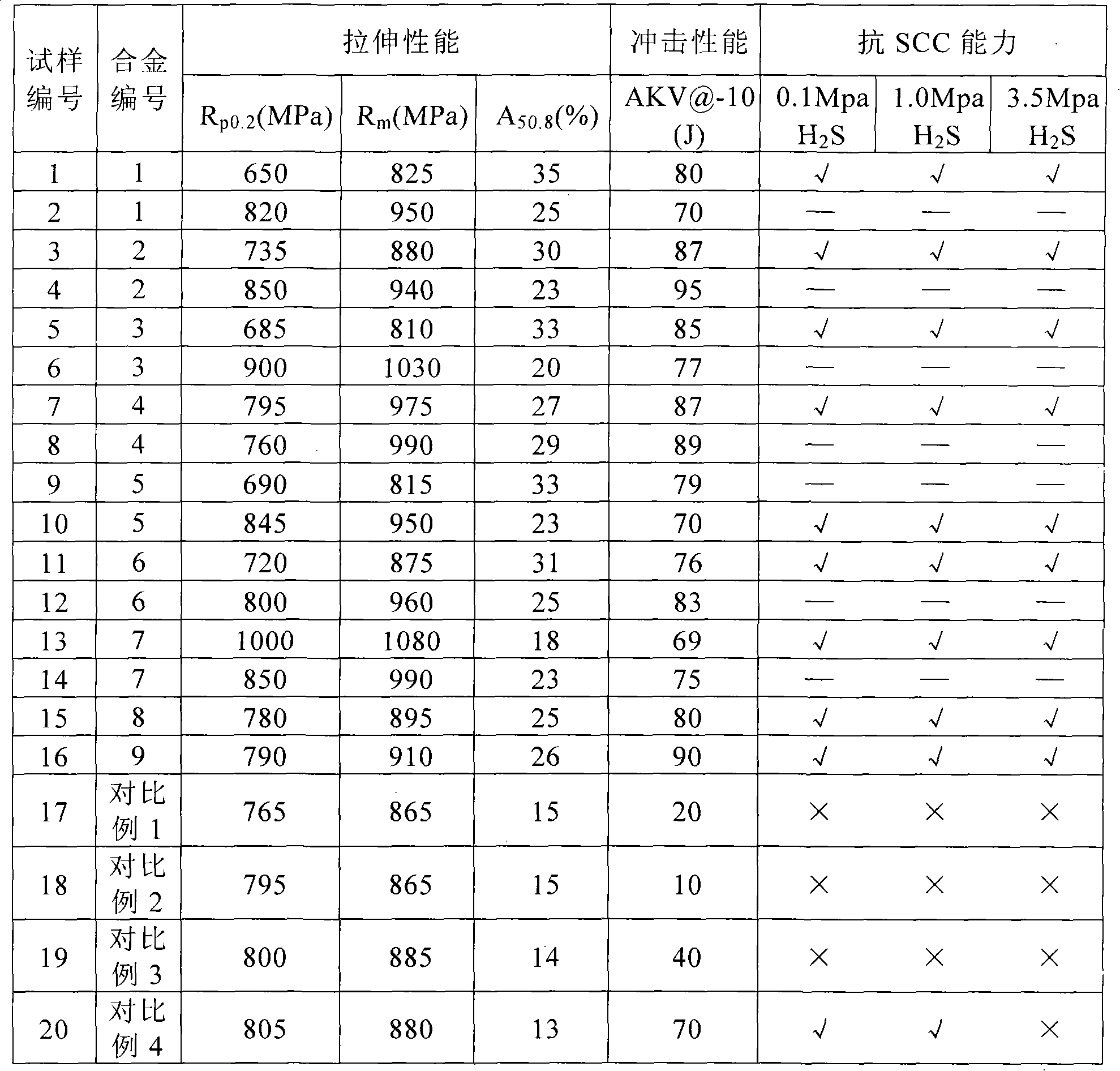
The invention relates to an Ni-saving austenitic stainless steel with excellent processability. The austenitic stainless steel comprises one or two of the following chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.06-0.12 of C, 0.2-1.0 of Si, 7.0-9.0 of Mn, 17.0-18.5 of Cr, 3.01-3.45 of Ni, 0.15-0.22 of N, 0.01-0.2 of Mo, 1.2-1.9 of Cu, B larger than or equal to 0.001% and smaller than or equal to 0.004%, Ca larger than or equal to 0.001% and smaller than or equal to 0.005%, V smaller than or equal to 0.1%, Nb smaller than or equal to 0.1%, and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities, wherein the sum of the percentage of C and the percentage of N is larger than or equal to 0.25%. The manufacturing method of the austenitic stainless steel comprises the following steps: heating a smelted and poured casting blank to 1100-1250 DEG C and preserving heat, performing hot working on the casting blank until a needed thickness is obtained, wherein the heat preserving time is more than 30min; after hot working, annealing at a controlled temperature of 980-1100 DEG C and washing the blank with any acid, and performing cold rolling, wherein when Md30 / 50 is larger than or equal to -30 DEG C and smaller than or equal to 0 DEG C, the maximum cold rolling deformation is 75-80%; or when Md30 / 50 is smaller than or equal to -30 DEG C, the maximum cold rolling deformation is 80-85%. According to the invention, the cold working performance of the Ni-saving austenitic stainless steel is improved; the corrosion resistance is close to that of type 304, and meanwhile the cost is lower than that of the type 304.
Owner:BAOSTEEL STAINLESS STEEL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com