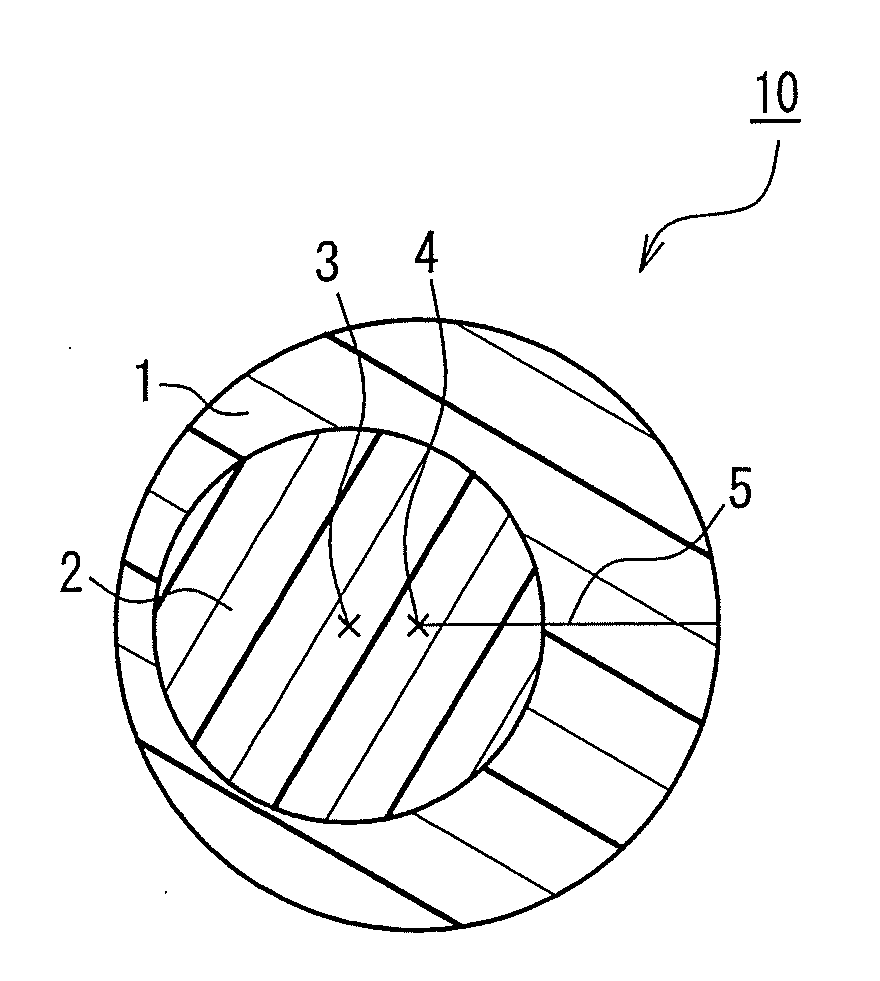
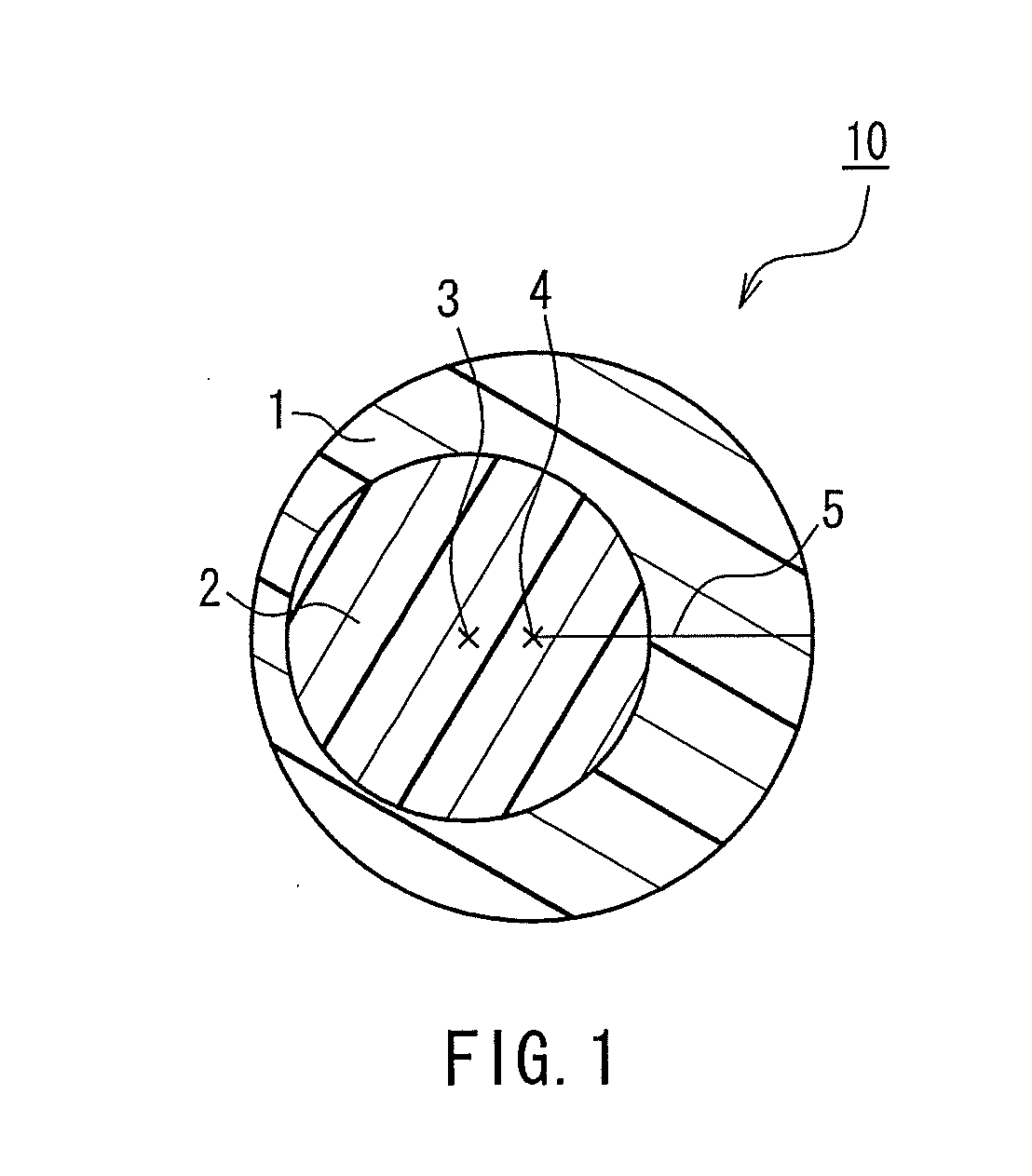
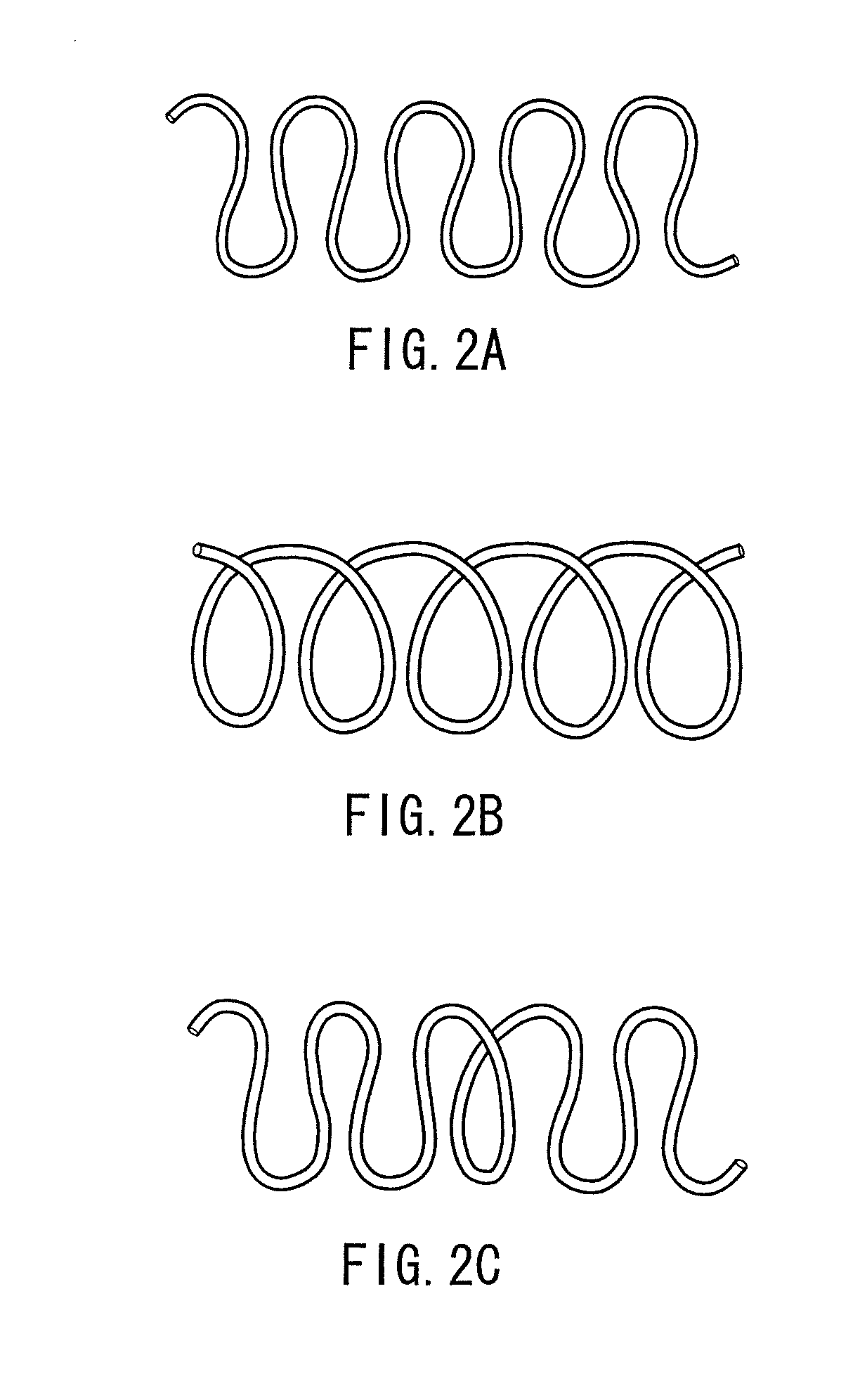
Crimped composite fiber, and fibrous mass and testile product using the same
a composite fiber and fiber technology, applied in the direction of yarn, filament/thread forming, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of nonwoven fabric bulk reduction, so-called sagging, nonwoven fabric, etc., and achieve the effect of limited application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Example 1
[0207]A crimped conjugate fiber was prepared under the above-described crimped conjugate fiber production conditions using only PP-A as the second component and a mixture of PB-1 and LLDPE-A having a mass ratio of PB-1 / LLDPE-A=92 / 8 as the first component. Next, a nonwoven fabric was prepared under the above-described nonwoven fabric production conditions using the resulting crimped conjugate fiber.
example 2
Example 2
[0208]A crimped conjugate fiber and a nonwoven fabric were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that a mixture of PP-A and PPR-1 having a mass ratio of PP-A / PPR-1=85 / 15 was used as the second component and a mixture of PB-1 and LLDPE-A having a mass ratio of PB-1 / LLDPE-A=97 / 3 was used as the first component.
example 3
Example 3
[0209]A crimped conjugate fiber and a nonwoven fabric were prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 except that a mixture of PP-A and PPR-1 having a mass ratio of PP-A / PPR-1=85 / 15 was used as the second component and a mixture of PB-1 and LLDPE-A having a mass ratio of PB-1 / LLDPE-A=95 / 5 was used as the first component.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting peak temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting peak temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com