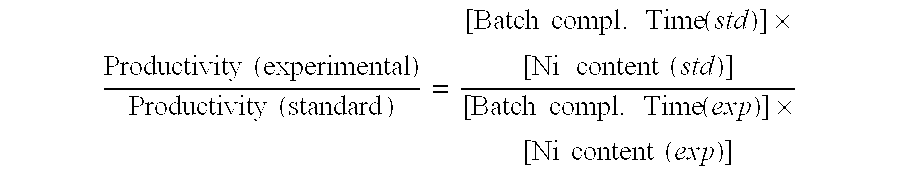
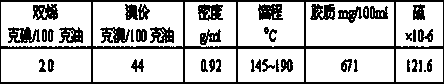Patents
Literature
172results about How to "Reduce nickel content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of preparing electronic grade nickel carbonate by sodium carbonate deposition
The invention discloses a manufacturing method of electron-grade nickel carbonate through sedimenting sodium carbonate, which is characterized by the following: adopting soluble nickel salt as nickel source and sodium carbonate as sediment; co-flowing nickel salt solution and sodium carbonate solution; controlling pH value, temperature and aging condition; washing; drying; washing again; drying again; grinding into product.
Owner:JINCHUAN GROUP LIMITED +1
Preparation method of concentration gradient distributed lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese and oxygen ternary lithium battery cathode material
InactiveCN103700845AImprove circulationIncrease battery capacityCell electrodesLithium carbonateCobaltous sulfate
The invention relates to a preparation method of a concentration gradient distributed lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese and oxygen ternary lithium battery cathode material. The method comprises the following steps: 1) preparing a solution from nickel sulfate, cobaltous sulfate and manganese sulfate according to different mole ratios, and numbering as 1, 2 and 3; 2) preparing three NaOH+NH3.H2O solutions with different ratios respectively, and numbering as I, II, and III respectively; 3) adding the No. I solution dropwise into the No.1 solution to react; 4) adding a No.2 solution, and adding the No.II solution dropwise to react; 5) adding the No.3 solution, and adding the No.III solution dropwise to react; 6) filtering, washing and drying after reacting and aging completely, thereby obtaining a ternary precursor; 7) mixing lithium carbonate and the ternary precursor, adding aluminum oxide powder, and carrying out ball milling; 8) sintering; and 9) crushing, thereby obtaining the concentration gradient distributed lithium, nickel, cobalt, manganese and oxygen ternary lithium battery cathode material. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the material cyclicity can be improved, and meanwhile the battery capacity of the material can be increased.
Owner:宁夏科捷锂电池股份有限公司
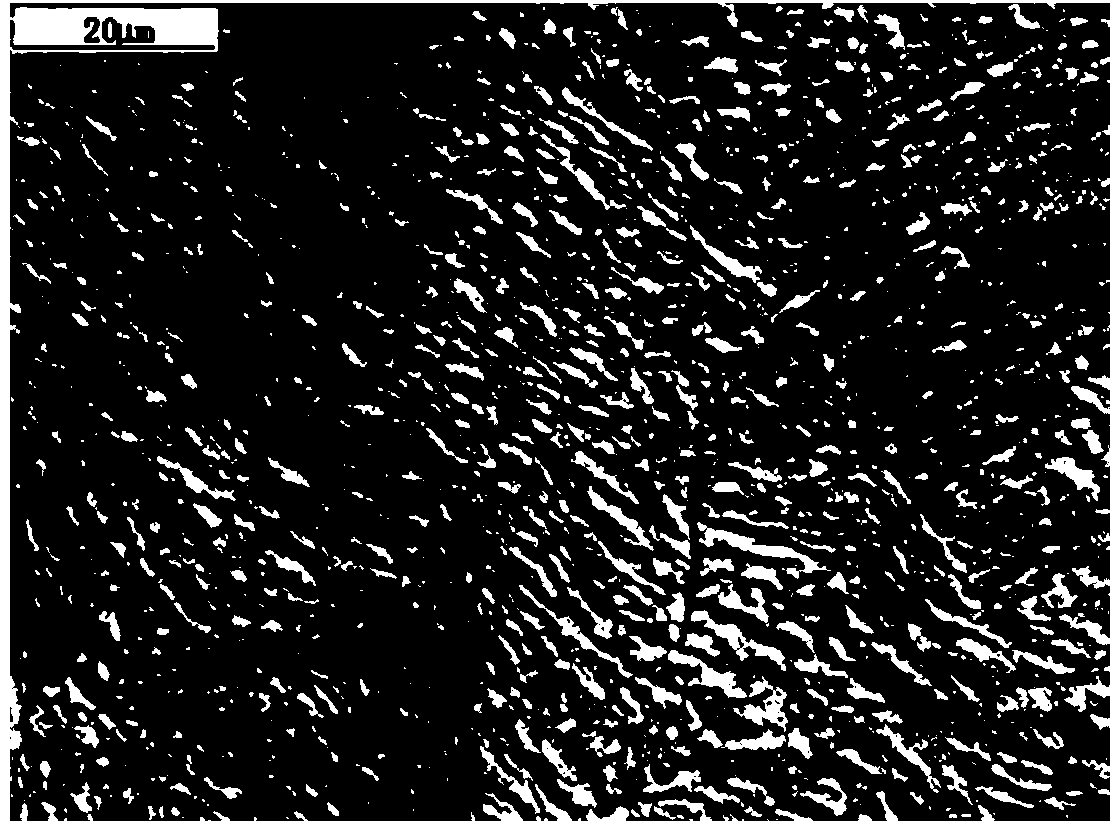
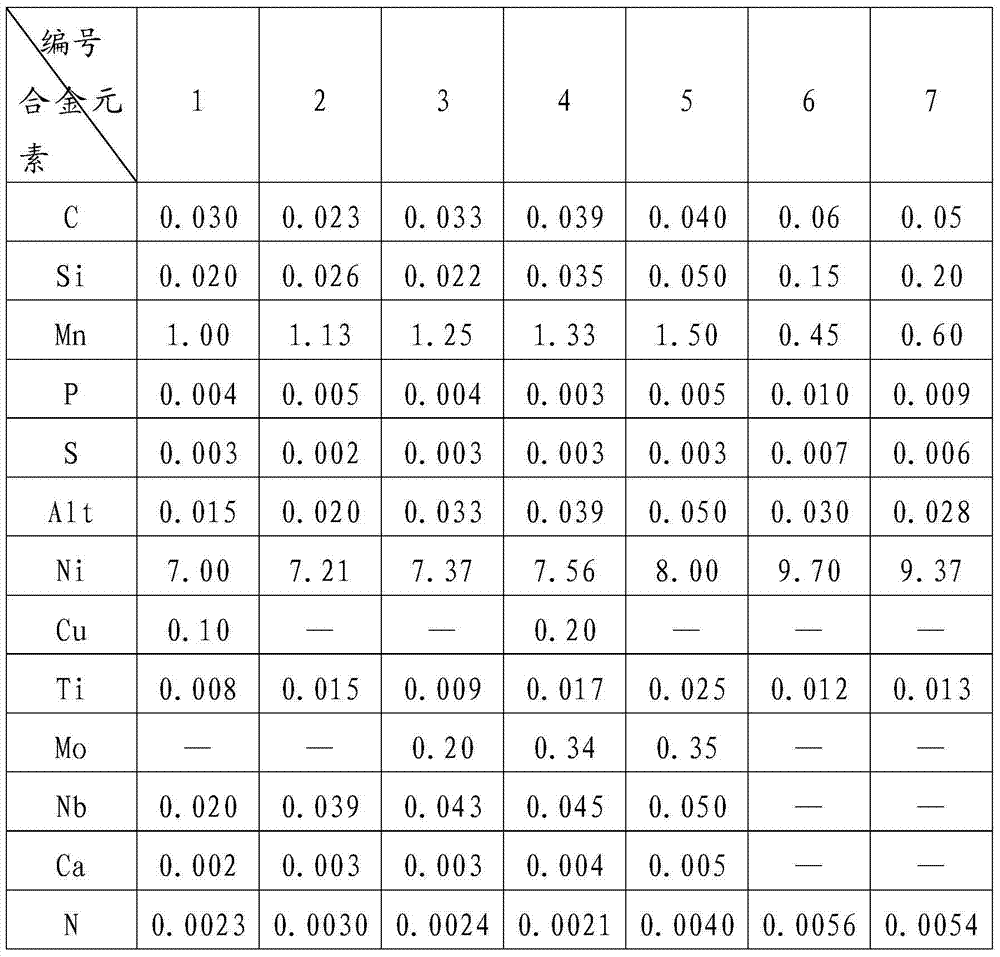
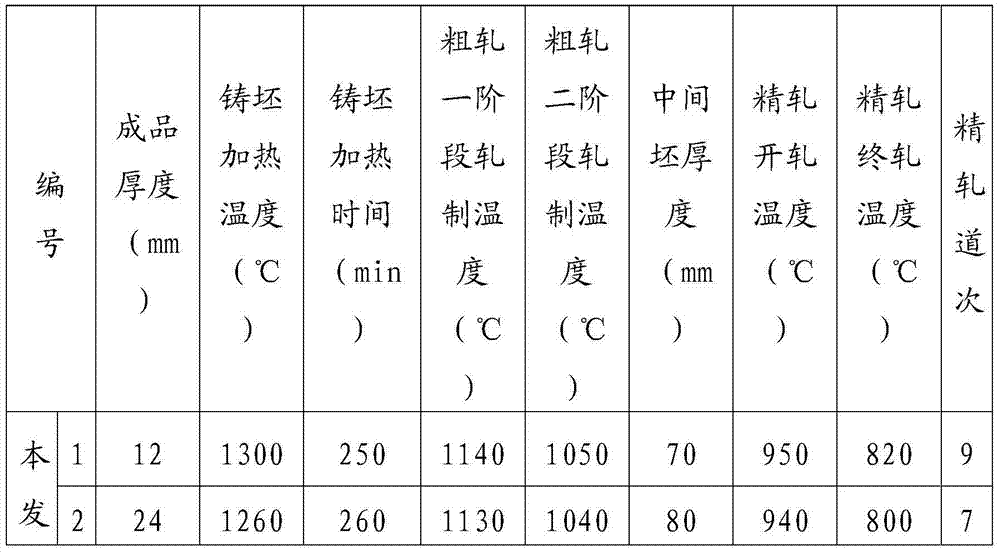
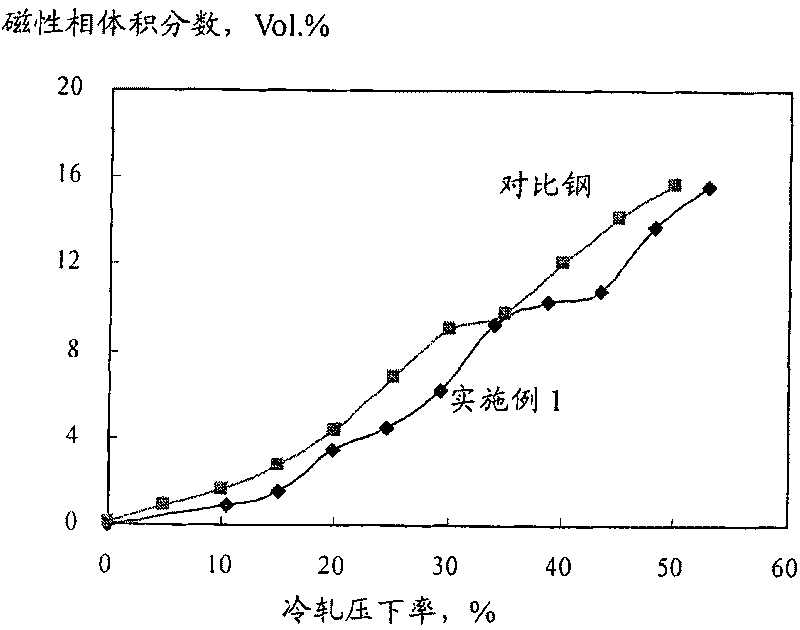
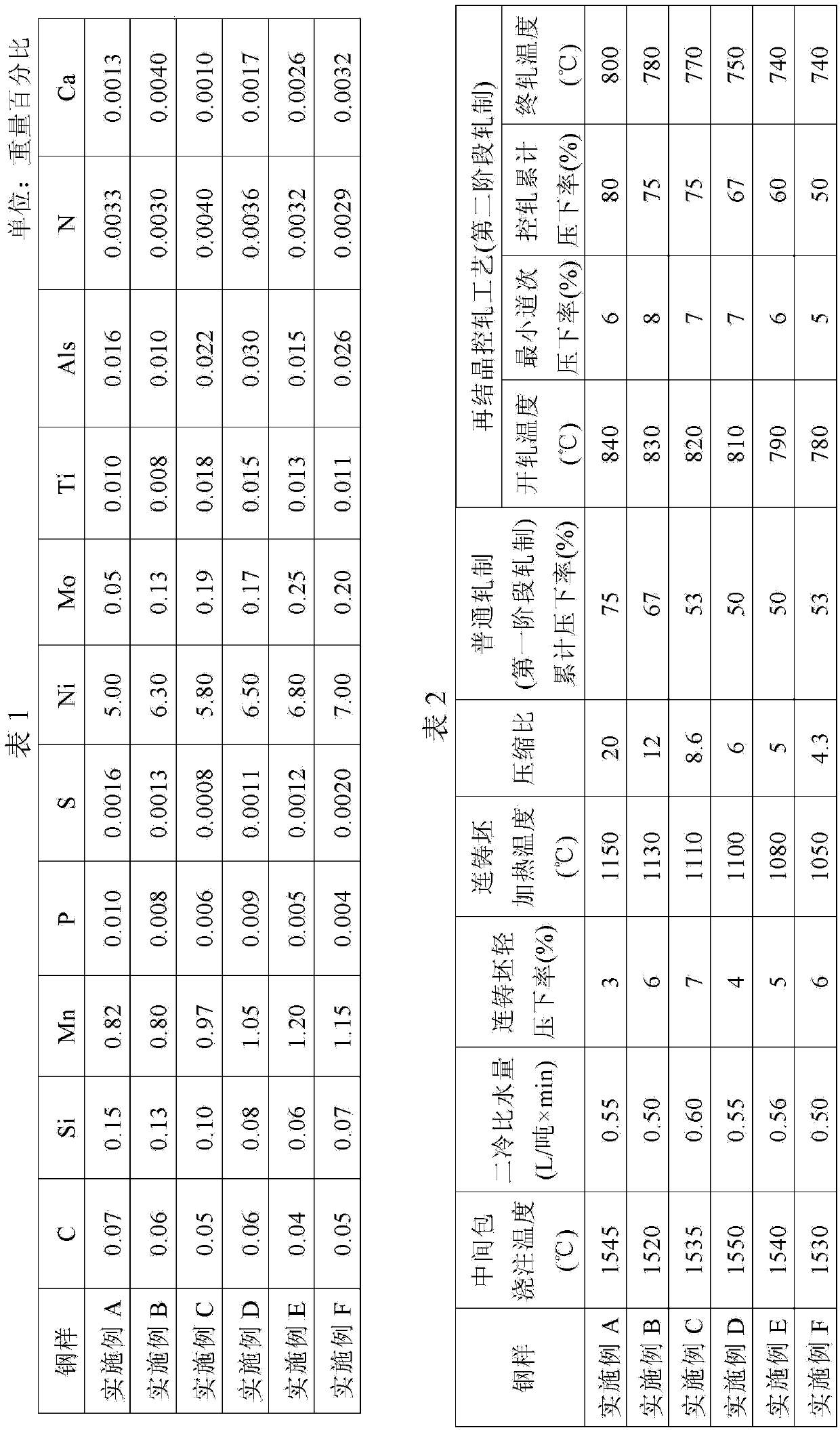
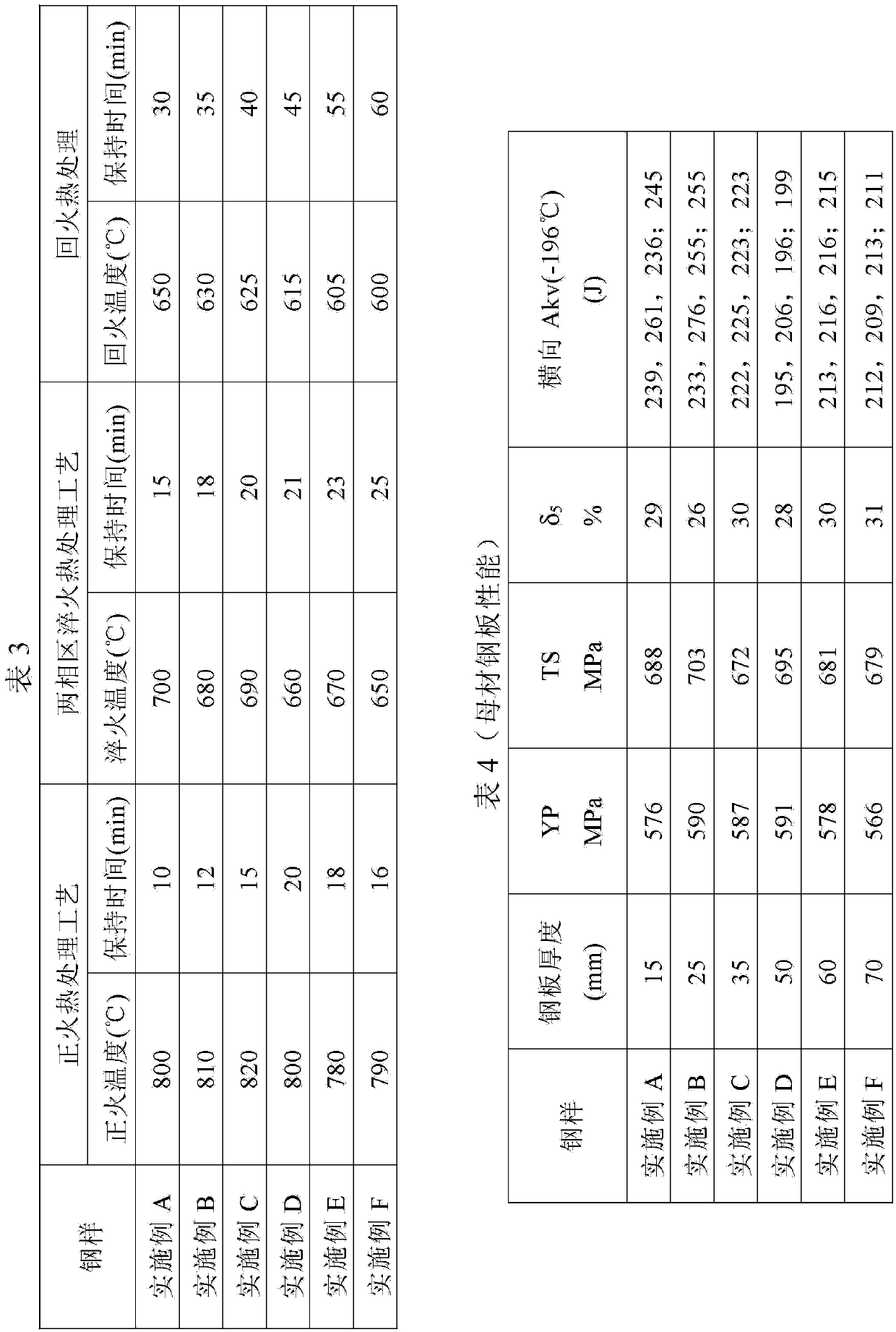
Low-Ni high-Mn economical low-temperature steel capable of being used at minus 196 DEG C and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103498100AReduce manufacturing costImprove low temperature toughnessChemical compositionToughness
The invention discloses low-Ni high-Mn economical low-temperature steel capable of being used at minus 196 DEG C and a preparing method thereof. The low-Ni high-Mn economical low-temperature steel capable of being used at minus 196 DEG C and the preparing method thereof solve the problem that existing low-temperature steel is high in technological difficulty and high in cost. The low-temperature steel comprises, by weight, C<=0.04, Si<=0.05, Mn:1.00-1.50, P<=0.005, S<=0.003, Alt:0.015-0.050, Ni:7.00-8.00, Nb:0.02-0.05, Ti:0.008-0.025, N<=0.004, at least one of Mo<=0.35, Cu<=0.20 and Ca<=0.005, and the balance Fe and inevitable impurities. The preparing method comprises the steps of smelting, rolling and drawing. The steel prepared with the method is good in toughness and welding performance after composition design, impurity control, rolling and heat treatment and can be used for manufacturing pressure vessel equipment requiring low-temperature usage in the LNG industry, and production difficulty and cost are effectively reduced.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
Low-nickel austenitic stainless steel and manufacturing method thereof
The invention relates to a low-nickel austenitic stainless steel, which comprises the following chemical components by weight percent: no less than 0.05% and no more than 0.15% of C, less than 1.00% of Si, more than 9.00% and less than 10.00% of Mn, no less than 14.00% and no more than 16.00% of Cr, no less than 0.50% and less than 1.00%, more than 0.15% and no more than 0.25% of N, more than 1.50% and no more than 2.00% of Cu, no less than 10*10<-4>% and no more than 30*10<-4>% of B, no less than 1*10<-4> and no more than 50*10<-4>% of Ca, less than 0.030% of P, no less than 0.020% of S and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. For the stainless steel, heat processing performance of materials is improved through B alloying treatment on premise of further reducing the content of precious metal of nickel, and the purity of the liquid steel is enhanced through Ca treatment. The formability of stainless steel is enhanced through the reasonable alloy system design and a micro-alloy treatment method, the defects of sand buckle, sand holes, and the like are avoided in the forming process, the delayed rupture phenomenon is lightened, and the application scope of the festival nickel austenitic stainless steel is further broadened.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Ultralow temperature nickel steel with low cost and manufacturing method thereof
An ultralow temperature nickel steel with low cost and a manufacturing method thereof. The steel comprises the following components by weight: 0.04-0.070% of C, no more than 0.15% of Si, 0.80-1.20% of Mn, no more than 0.010% of P, 0.0020% of S, 5.00-7.00% of Ni, 0.05-0.25% of Mo, 0.010-0.030% of Als, 0.008-0.018% of Ti, no more than 0.0040% of N, 0.001-0.004% of Ca, and the balance of Fe and the inevitable inclusion. The invention uses a component system containing ultra low C, ultra low Si, middle Mn, low N and ultramicro Ti for treatment of low alloy steel, and controls the value of (%Mn)*[7.33 (%Si) + 5.16 (%Al)] at no more than 1.0, and the value of austenite stabilization index Au / intercritical quenching temperature T at no less than 0.007 and no more than 0.009; an optimized recrystallization controlled rolling and subsequent special heat treatment process endows the ultralow temperature nickel steel with ultrahigh ultralow temperature toughness, excellent weldability and bearing of high heat input welding, and the ultralow temperature nickel steel gains excellent anti-high tempering parameter SR embrittlement characteristics, and can be manufactured at a low cost.
Owner:BAOSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Nickel saving type metastable austenite stainless steel with excellent normal temperature mechanical property
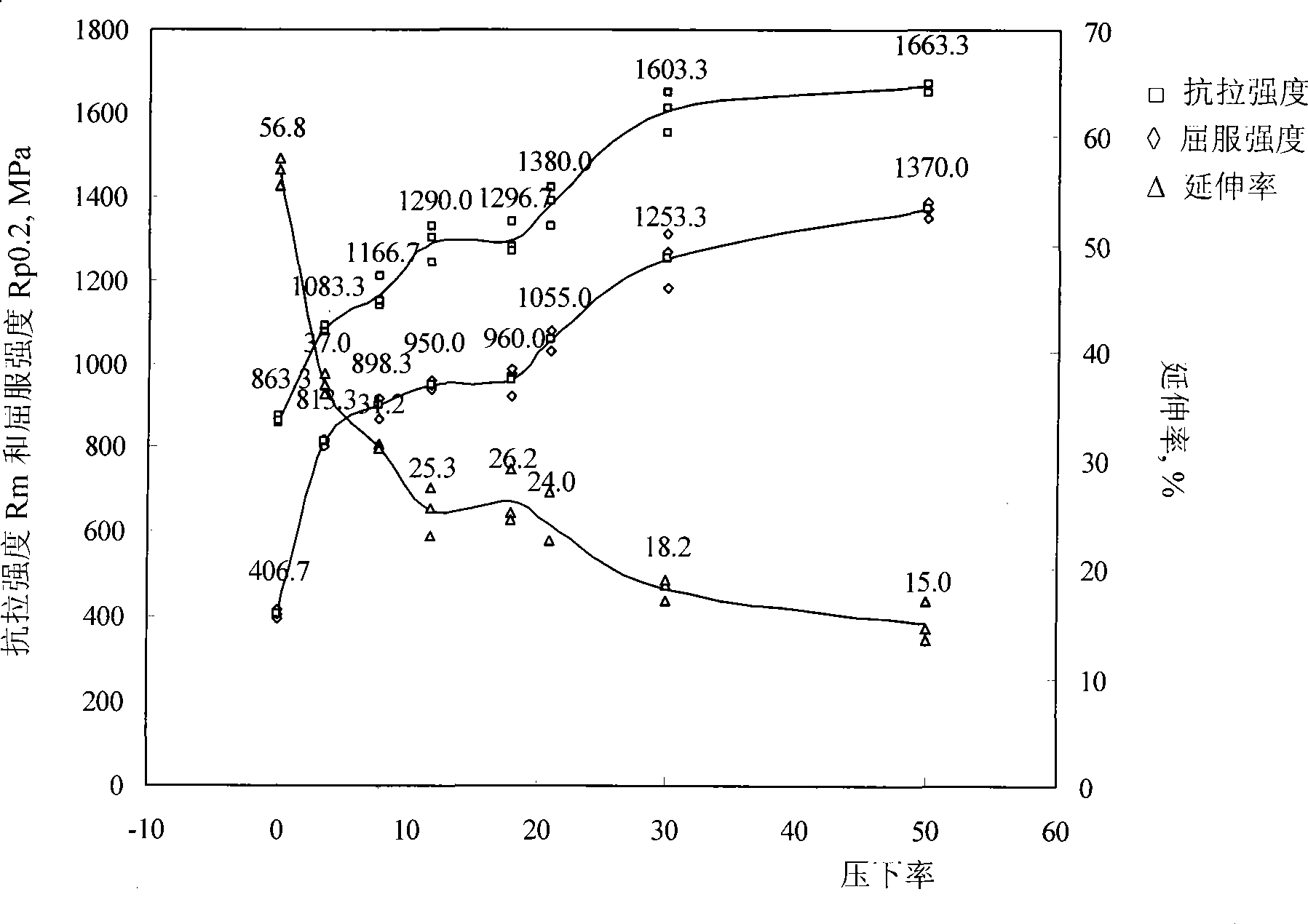
The invention provides a nickel saving type metastable austenite stainless steel with excellent normal temperature mechanical property. The stainless steel comprises the following chemical components by weight percentage: 0.06 to 0.15 percent of C, less than 1.00 percent of Si, 7.00 to 10.00 percent of Mn, 15.0 to 17.0 percent of Cr, 1.50 to 2.50 percent of Ni, 0.15 to 0.30 percent of N, less than 0.030 percent of P, less than 0.020 percent of s, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. In different states, the normal temperature yield strength of the raw material is 400 to 1,370 MPa, and the normal temperature tensile strength is 860 to 1,700 MPa, and the normal temperature expansion rate is 15 to 65 percent. The metastable austenite stainless steel of the invention is better than AISI304 in the normal temperature mechanical property, and has certain corrosion resistance, but the cost is obviously lower than that of the AISI304; the stainless steel can partially replace the AISI304 to be used in weak corrosive environments such as traffic, construction, hardware, and the like. The prepared precise strip steel can partially replace the metastable austenite stainless steel of the AISI301, AISI201, and the like which contains higher nickel, so that the precious metal nickel is saved.
Owner:BAOSTEEL DESHENG STAINLESS STEEL
Process for making nitriles
ActiveUS20130211126A1Reduce nickel contentOrganic compound preparationChemical recyclingMethyl groupHydrogen cyanide
Adiponitrile is made by reacting 3-pentenenitrile with hydrogen cyanide. The 3-pentenenitrile is made by reacting 1,3-butadiene with hydrogen cyanide and by isomerizing 2-methyl-3-butenenitrile. The reaction of 1,3-butadiene with hydrogen cyanide to produce 3-pentenenitrile also produces small amounts of dinitrile compounds, including adiponitrile (ADN) and methylglutaronitrile (MGN). Methylglutaronitrile is removed to provide an adiponitrile-enriched stream, which is used in a catalyst purification step.
Owner:INV NYLON CHEM AMERICAS LLC
Sea water corrosion resistant low-alloy cast iron
InactiveCN101225496AImproves corrosion resistance of cast ironReduce corrosion resistanceManganeseRare earth
The invention discloses a seawater corrosion-resistant low alloy cast iron, which is mainly used for manufacturing components in seawater hydraulic projects. Adopting the weight percentage as unit, the seawater corrosion-resistant low alloy cast iron comprises 0.6 to 1.6 Ni, 1.5 to 3.0 Cr, 1.8 to 2.8 Si, 2.8 to 3.6 C, 0.6 to 1.0 Mn, 1.5 to 3.0 Cu, 0.1 to 0.3 RE, less than or equal to 0.4 Al, less than or equal to 0.1 Sb, less than or equal to 0.12 P, less than or equal to 0.06 S, and remaining part of Fe. The seawater corrosion-resistant low alloy cast iron has the advantages of improving corrosion resistant performance due to joint action of the cast iron chromium, nickel, copper and other alloy elements, reducing nickel content and cost, and improving corrosion resistant performance of the seawater corrosion-resistant cast iron compared with the Ni-Cr alloy corrosion resistant cast iron.
Owner:山东省耐磨耐蚀材料工程技术研究中心
Catalyst for use in preparation of paraphenyldimethylamine and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102029160AReduce nickel contentLow costOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationNickel catalystPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a catalyst for use in the preparation of paraphenyldimethylamine, which is a supported nickel catalyst. The carrier of the catalyst is gamma-Al2O3 type aluminum oxide, the specific surface area of the carrier is 170 to 200m<2> / g, the pore volume is 0.35 to 0.45cm<3> / g, and the aperture is 4.5 to 6.0nm, the carrier is loaded with nickel and an auxiliary catalyst which may be copper, cobalt, iron or zinc or one or two of copper, cobalt, iron or zinc, the loaded nickel accounts for 5 to 25 percent of the total mass of the catalyst, the auxiliary catalyst accounts for 3 to8 percent of the total mass, and the carrier aluminum oxide accounts for the balance. When the catalyst disclosed by the invention is used, paraphenyldimethylamine can be prepared by hydrogenation ofisophthalodinitrile under milder conditions, the conversion rate of isophthalonitrile is 100 percent, and the selectivity of the paraphenyldimethylamine can reach 98.8 percent. The invention also discloses the preparation method of the catalyst.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +2
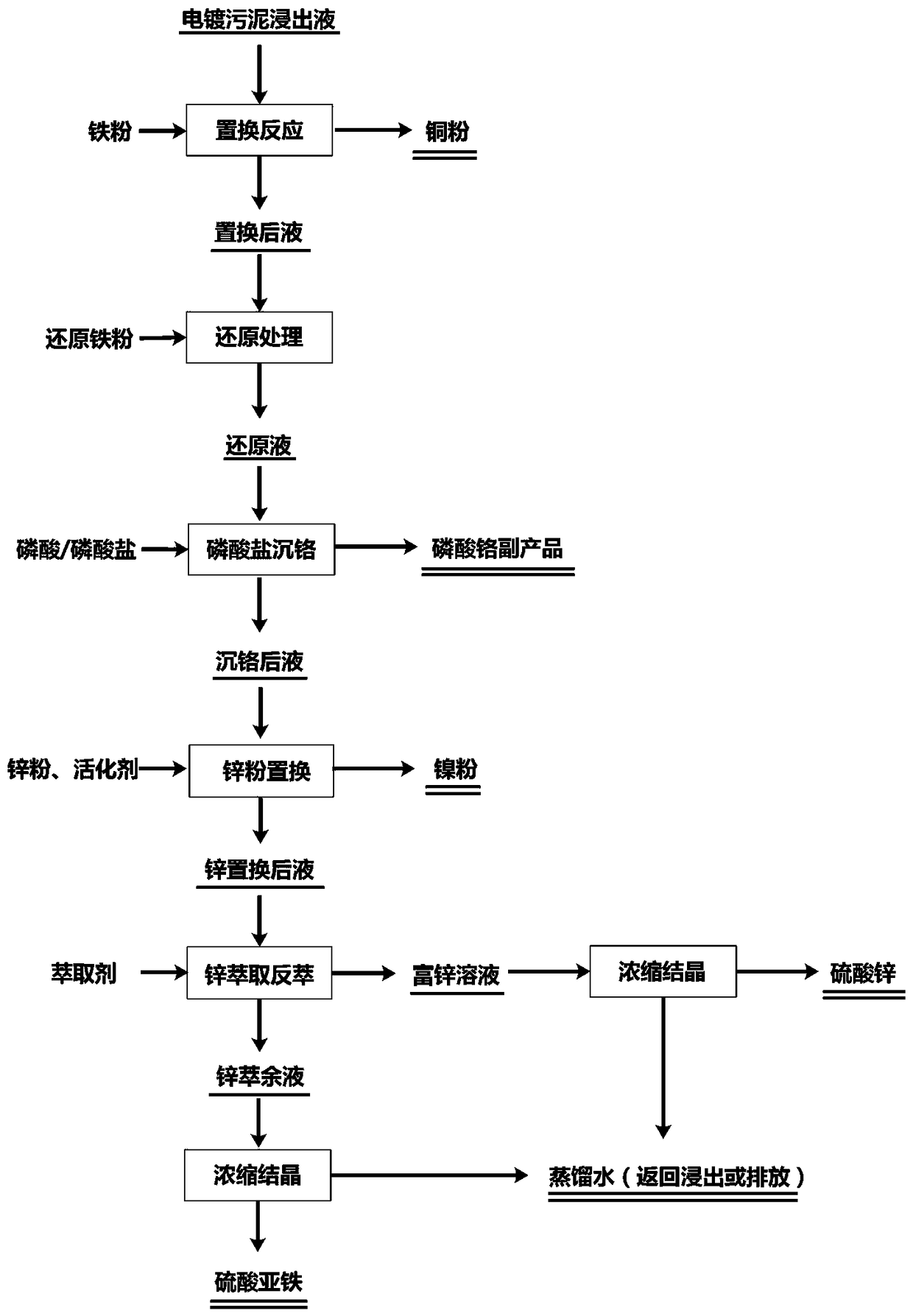
Method for separating iron, chromium, nickel, copper and zinc from high-iron high-chromium electroplating sludge leachate
The invention provides a method for separating iron, chromium, nickel, copper and zinc from high-iron high-chromium electroplating sludge leachate. The method comprises the following steps: (1) addingiron powder into the leachate to obtain a copper powder product and replaced liquid; 2) adding iron powder into the replaced liquid to obtain reduced liquid; (3) adding a chromium precipitating agentinto the reduced liquid, and carrying out filtering to obtain chromium-precipitated liquid and a chromium precipitate; (4) adding the activator antimony salt and zinc dust into the chromium-precipitated liquid, carrying out a reaction, and then carrying out filtering to obtain nickel powder and nickel-removed liquid; (5) adding an acidic phosphate extraction agent into the nickel-removed liquid to extract zinc, then carrying out reextraction by using dilute sulfuric acid, subjecting a zinc-rich solution to concentration and crystallization to prepare a zinc salt product, and subjecting zinc raffinate to subsequent treatment; and (6) subjecting the zinc raffinate to concentration and crystallization to prepare ferrous sulfate heptahydrate, and returning distilled water for leaching. The separation method of the invention has the advantages of short process and high efficiency, and can effectively solve the problem difficulties in separate separation of chromium, iron, nickel, copper and zinc metals in the high-iron high-chromium electroplating sludge leachate.
Owner:HUNAN AIGE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH CO LTD
Semi-steel roll and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101537428AReasonable compositionEasy to shapeFurnace typesRollsChemical compositionCarbide
The invention relates to a semi-steel roll and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of steel rolling. The semi-steel roll contains the following chemical components according to the mass percent: 1.65-1.90 of C, 0.80-1.15 of Cr, 0.35-0.65 of Si, 0.60-1.00 of Mn, 0.30-0.60 of Mo, 0.20-0.80 of Ni, 0.05-0.10 of K, 0.05-0.10 of Na, 0.05-0.15 of Ti, 0.05-0.15 of Nb, 0.08-0.15 of Y, 0.03-0.08 of Mg, 0.02-0.04 of Zn, 0.06-1.00 of Al, less than 0.04 of P, less than 0.03 of S, and the balance of Fe. The semi-steel roll has reasonable chemical component, prolonged service life, the hardness of 55-58 HS and the tensile strength of 900-950 MPa and the impact toughness of 10-12 J / cm2; the invention can save the nickel resource, reduce the cost, simplify the heat treatment, shorten the production period, improve the heat treatment efficiency, save the energy, thin the solidified organization, improve the forms and the distribution uniformity of carbides and inhibit the aliquation of alloy elements;.
Owner:江苏环立板带轧辊有限公司
Method for preparing molybdenum nickel alloy by directly reducing and smelting molybdenum nickel ore
The invention relates to a method for preparing molybdenum nickel alloy by directly reducing and smelting molybdenum nickel ore. The method comprises the following steps: grinding the molybdenum nickel ore into molybdenum nickel ore powder with the average particle size of less than or equal to 0.18 mm; adding a slag forming agent and a reducing agent with the average particle size of less than or equal to 0.18 mm into the molybdenum nickel ore powder to obtain furnace charge; mixing the furnace charge uniformly and pelletizing to obtain pellet; heating the pellet to 1,600 to 1,800 DEG C; smelting; and collecting liquid alloy, slag, smoke dust and furnace gas respectively, wherein the liquid alloy is crude molybdenum nickel alloy; the direct yield of the molybdenum and the nickel is 96 percent and 94 percent respectively; the molybdenum content of the smoke dust is less than 0.2 percent and the nickel content of the smoke dust is less than 0.2 percent; and the SO2 concentration of thefurnace gas is less than or equal to 400 mg / m<3>. The process method is simple and reasonable, and convenient to operate; the molybdenum nickel ore is not subjected to oxidizing roasting de-sulfuration; and the crude molybdenum nickel alloy is prepared by directly reducing and smelting the molybdenum nickel ore and by using the carbon of the molybdenum nickel ore as a reducing agent, so that indirect smelting is changed into direct smelting. The prepared molybdenum nickel alloy is low in sulfur content and phosphorus content, environment friendly and low in production cost; and the method is suitable for extraction of the molybdenum nickel ore.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV +2
Improved 40CrNiMo steel and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to improved 40CrNiMo steel and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of alloy steel. The improved 40CrNiMo steel comprises the following chemical elements in percentage by weight: 0.37 to 0.45 percent of C, 1.65 to 1.85 percent of Cr, 0.45 to 0.65 percent of Ni, 0.15 to 0.25 percent of Mo, 0.90 to 1.20 percent of Mn, 0.40 to 0.55 percent of Si, 0.0025 to 0.0045 percent of B, 0.22 to 0.28 percent of N, 0.007 to 0.012 percent of Ca, 0.002 to 0.005 percent of Mg, 0.03 to 0.06 percent of Nb, 0.04 to 0.08 percent of Ti, 0.02 to 0.06 percent of RE, less than or equal to 0.015 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.025 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.0008 percent of Al and the balance of Fe. The invention has the advantages that: the improved 40CrNiMo steel has low nickel content, so that cost can be reduced; the steel has a fine structure, the number of impurities is obviously reduced, and the impurities have a small size and are uniformly distributed, so that the performance of the steel is obviously improved; and a few process steps are performed in the preparation method, so that energy is saved, and the requirement of industrial scale-up production is met.
Owner:江苏环立板带轧辊有限公司
Novel austenitic stainless steel for ultra (super) critical coal-fired unit
InactiveCN103774056AExcellent high temperature tensile strengthLow costUltimate tensile strengthAustenite
The invention relates to heat-resistant austenitic steel, and particularly relates to novel austenitic stainless steel for an ultra (super) critical coal-fired unit. The novel austenitic stainless steel is characterized by comprising the following raw materials by mass percent: no more than 0.1% of C, no more than 0.5% of Si, no more than 1% of Mn, 19-23% of Cr, 28-33% of Ni, 0.20-0.45% of Nb, 0.90-2.10% of Mo, 12.51-3.02% of Al, no more than 0.04% of P, no more than 0.01% of S, 0.010-0.15% of N, 0.001-0.010% of B and the balance of Fe. The high-temperature tensile strength (greater than or equal to 460MPa at 600 DEG C), the lasting creep properties (the lasting ultimate strength is greater than equal to 110MPa under the conditions at 600 DEG C and 100,000 hours), and the high-temperature oxidation resistance (the oxidation increase is smaller than or equal to 0.036mg / cm<2> under the conditions at 700 DEG C and100 hours) of the austenitic stainless steel disclosed by the invention are much better than these of the traditional Incoloy800 austenitic stainless steel; the novel austenitic stainless steel can be widely applied to the fields such as the ultra (super) critical coal-fired unit, agricultural engineering, chemical engineering, foods, livelihood appliances and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV +1
Hydrodeoxygenation catalyst for organic oxygen-containing compound of oil product as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN103028408AReduce nickel contentHas an ultrafine particle structureMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsRefining to eliminate hetero atomsNickel catalystPtru catalyst
The invention discloses a hydrodeoxygenation catalyst for an organic oxygen-containing compound of an oil product as well as a preparation method and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of oil product refinement. The preparation method for the low-nickel catalyst is a sol-gel method; the catalyst is a low-nickel-based catalyst; the loading amount of the active components of the catalyst is 5-25% (wt); the catalyst also comprises one or more of transition metal as an additive; a catalyst carrier is TiO2-SiO2 composite oxide; and the molar ratio of Ti to Si is 1:(1-20). The prepared catalyst is low in cost, high in activity and high in hydrodeoxygenation conversion rate.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
High-voltage lithium oil battery positive electrode material with spinel structure and preparation method of high-voltage lithium oil battery positive electrode material
InactiveCN105576231AUniform particlesImprove stabilityCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithiumRoom temperature
The invention relates to a high-voltage lithium oil battery positive electrode material with a spinel structure and a preparation method of the high-voltage lithium oil battery positive electrode material. The chemical general formula of the lithium oil battery positive electrode material is Li[M1aNibM2cMn1.5]O4, wherein a is larger than or equal to 0.025 and smaller than or equal to 0.05, b is larger than or equal to 0.4 and smaller than or equal to 0.45, c is larger than or equal to 0.025 and smaller than or equal to 0.05, and M1 and M2 are one or more of Mg, Zn, Fe, Li, Al, Cr and Co. During preparation, a soluble lithium source, a nickel source, a manganese source, M1 salt and M2 salt are weighed according to mole ratios firstly to prepare gel, the gel is then heated and dried, and the lithium oil battery positive electrode material is obtained after burning is conducted twice and the gel is cooled to the room temperature. The preparation method is simple, steps are easy to operate, the positive electrode material prepared from a lithium-enriched LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 positive electrode material formed by doping Li and other metal elements is uniform in particle, is of the spinel structure and is high in crystallinity, the material stability is improved, circulation and rate capability of the material can be effectively increased through the introduced doping elements, the nickel content is decreased, the production cost is reduced, and meanwhile pollution to the environment is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nickel base catalyst
ActiveCN103418384AReduce nickel contentIncreased nickel contentHydrocarbon oil crackingMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsComposite oxideOxide
The present invention relates to a nickel base catalyst, wherein problems of low nickel content and low active specific surface in the prior art are mainly solved with the present invention. The technical scheme comprises that the catalyst comprises the following components, by weight: a) 20-75 parts of metal nickel, and b) 25-80 parts of a composite oxide carrier comprising 20-40 parts by weight of aluminum oxide and 5-40% by weight of silicon oxide, wherein a specific surface area of the catalyst is 150-400 m<2> / g, a pore volume is 0.3-0.8 ml / g, and an average pore size is 5-15 nm. With the technical scheme, the problems in the prior art are well solved, and the catalyst can be widely used for industrial production of hydrotreating of light oil fractions, heavy oil fractions, unsaturated greases, cracking gasoline, and especially cracking C9 and hydrocarbons with a carbon atom number of more than 9.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Austenitic cast iron alloy used for piston ring carrier
The invention provides an austenite casting ferroalloy used in a piston ring carrier, belong to a casting ferroalloy. According to the weight percentage, the components of the alloy are 2.0 to 3.6 percent of carbon, 1.1 to 3.5 percent of silicon, 2.8 to 9.0 percent of manganese, 1.2 to 13.5 percent of nickel, less than or equal to 0.2 percent of phosphorus, less than or equal to 0.2 percent of sulfur, 1.1 to 8 percent of copper, less than or equal to 2.3 percent of chromium and the rest is iron. The austenite casting ferroalloy used in the piston ring carrier has the advantage of good wear resistance. Through experiments, the wear volume is only about one fifth of present austenite casting material. The nickel content is low, which lowers the production cost.
Owner:SHANDONG BINZHOU BOHAI PISTON
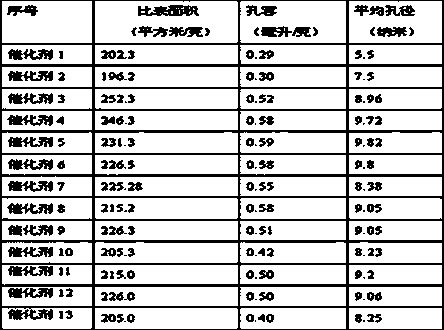
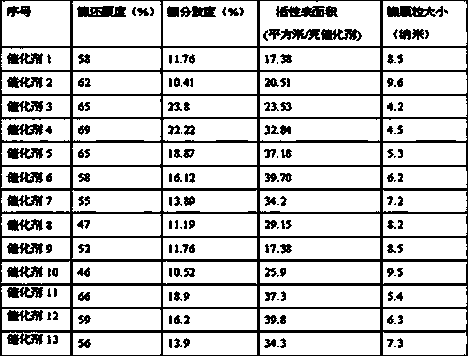
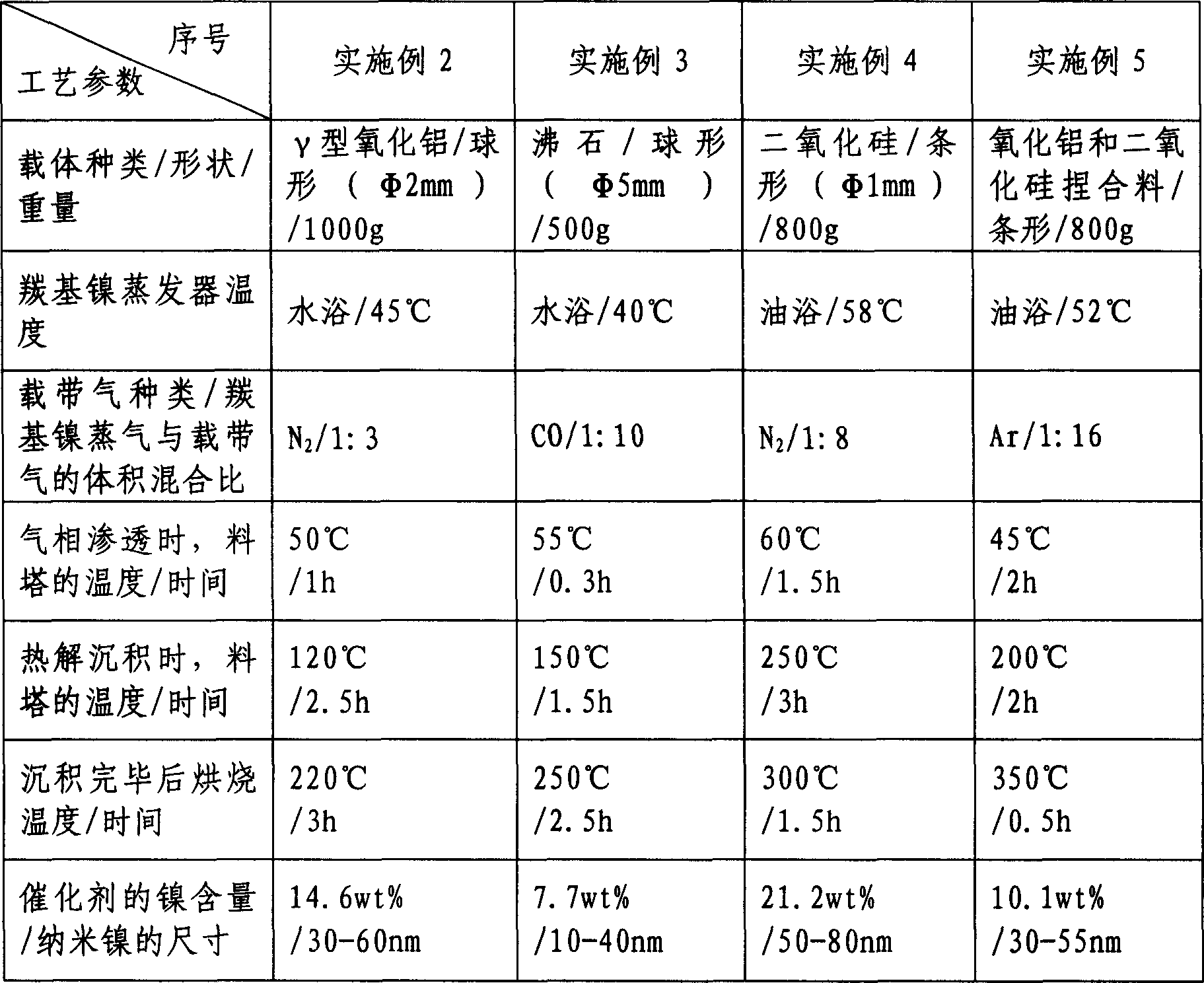
Gas phase permeation precipitation method for preparation of supported nanometer nickel hydrogenation catalyst
InactiveCN1806920ASimple processProcess conditions are easy to controlCatalyst carriersCatalyst activation/preparationNickel catalystGas phase
The invention, belonging to hydrogenation catalyst, relates the method for preparation of loaded nanometer nickel catalyst. The method comprises the following steps: loading the nickel carbonoxide compound into feed tower with carrier gas, nickel carbonoxide penetrating and adsorbing on the carrier, then heating, nickel carbonoxide pyrolyzing and depositing on the carrier, finally calcining the carrier and getting the loaded nanometer nickel catalyst. The method has the advantages of simple technique, easy control, high productivity, low cost, non-pollution and wide applications.
Owner:BEIJING CISRI GAONA TECH
Gradient type monocrystal-like positive electrode material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109962233AImprove thermal stabilityImprove conductivityCell electrodesSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceChemistryNickel salt
The invention discloses a gradient type monocrystal-like positive electrode material and a preparation method thereof. The general chemical formula of the gradient type monocrystal-like positive electrode material is LiNixCoyMn (1-x-y) AnO2, wherein 0.5<=x<=0. 8, 0.1<=y<=0.2, 0<=n<=0. 3. The gradient type ternary precursor NixCoyMn (1-x-y) (OH)2 is prepared by the method. The change of the concentration of the added nickel salt solution, the cobalt salt solution and the manganese salt solution is controlled to gradually reduce the nickel content and gradually increase the cobalt and manganesecontent in the components from the core to the surface of the precursor, and the particle size of the precursor is controlled to be 2-5um. The step-by-step sintering mode is used and beneficial to theindustrial production and can reduce the inconsistency of the obtained product. Finally, the obtained gradient type monocrystal-like lithium nickel cobalt manganate positive electrode material has good discharge performance and cycle performance at the high voltage of 4.5V.
Owner:GEM WUXI ENERGY MATERIAL CO LTD +2
Catalyst for decomposition of hydrocarbons, process for producing the catalyst, and process for producing hydrogen using the catalyst
InactiveUS7196036B2Excellent anti-coking propertyReduce nickel contentHydrogenOther chemical processesHydrogenDecomposition
A catalyst for decomposition of hydrocarbons, comprises porous oxide particles containing magnesium and aluminum, and fine metallic nickel particles which are present in the vicinity of surface of the respective porous oxide particles, and have an average particle diameter of 1 to 10 nm, said catalyst having a nickel content of 0.15 to 12% by weight based on the weight of the catalyst and a molar ratio of nickel to a sum of magnesium, nickel and aluminum of 0.001 to 0.12 in which a molar ratio of magnesium to aluminum (Mg:Al) is 4:1 to 1.5:1. The catalyst for decomposition of hydrocarbons, is capable of maintaining as small a particle size of metallic nickel particles as not more than 10 nm at a considerably reduced nickel content, and exhibits an excellent anti-coking property even under a low steam atmosphere.
Owner:TODA IND
Low-nickel nitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel non-consumable electrode gas shielded welding wire and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111876680AReduce nickel contentReduce porosity defectsWelding/cutting media/materialsSoldering mediaHeat-affected zoneSS - Stainless steel
The invention discloses a low-nickel nitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel non-consumable electrode gas shielded welding wire and a preparation method thereof. The invention belongs to the technical field of welding material preparation and welding machining processes thereof. The low-nickel nitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel non-consumable electrode gas shielded welding wireand the preparation method solve the technical problems that when an existing austenitic stainless steel welding wire is used for conducting non-consumable electrode gas shielded welding on low-nickelnitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel, nitrogen loss, air holes, hot cracks in a weld joint area and nitride precipitation in a heat affected zone are prone to being generated in a welded joint, and consequently pitting corrosion is caused. The low-nickel nitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel non-consumable electrode gas shielded welding wire comprises the following chemical components including, by weight, 0.03% to 0.08% of C, 0.30% to 0.65% of Si, 6.50% to 8.50% of Mn, less than or equal to 0.05% of P, less than or equal to 0.01% of S, 17.50% to 18.50% of Cr, 2.20% to 2.90% of Ni, 0.03% to 0.10% of Mo, 1.00% to 2.00% of Cu, 0.15% to 0.35% of N, less than or equal to 0.05% of Co, less than or equal to 0.05% of the sum of Nb, Ti and V and the balance iron. The method comprises the steps of smelting, wire rod hot rolling and welding wire drawing, and finally the welding wire is obtained. According to the low-nickel nitrogen-containing austenitic stainless steel non-consumable electrode gas shielded welding wire and the preparation method, solid solution nitrogen is used for partially replacing nickel, and grain refinement can be promoted while nitrogen is effectively subjected to solid solution strengthening.
Owner:HARBIN WELDING INST LTD +2
Chromium-saved duplex stainless steel with phase-change plasticization effect and preparation method of chromium-saved duplex stainless steel with phase-change plasticization effect
The invention relates to a chromium-saved duplex stainless steel with a phase-change plasticization effect and a preparation method of the chromium-saved duplex stainless steel with the phase-change plasticization effect, and belongs to the technical field of steel alloy materials. The duplex stainless steel comprises components in percentage by mass as follows: more than 0 and less than or equal to 0.06% of C, less than or equal to 0.008% of S, less than or equal to 0.01% of P, 13.0-17.5% of Cr, 5-17% of Mn, 0.1-3.0% of Ni, 0.5-2.5% of Al or Si, 0.001-0.01% of B, 0.005-0.20% of rare earth Ce or Y, and the balance of Fe. A conventional melting process is adopted, rare-earth intermediate alloy is added before casting, which means that Fe-Ce intermediate alloy or Fe-Y intermediate alloy is prepared in advance and then cast and molded after comprehensive material blending and melting, and the duplex stainless steel with the phase-change plasticization effect is finally obtained after hot forging, cold rolling and appropriate solution treatment.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Nickel-copper alloy and preparation process for same
The invention belongs to the technical field of alloy materials, and particularly relates to a nickel-copper alloy and a preparation process for the same. The technical problems that in the prior art, manufacturing cost is high and the mechanical property is not enough are solved by the nickel-copper alloy and the preparation process for the same. The preparation process comprises the following steps of A, primary melting, B, standing and C, casting. Compared with the prior art, the nickel-copper alloy and the preparation process for the same have the advantages that the content of nickel is low, the material cost can be greatly reduced, and the cost is reduced; the mechanical property is good, and balance between the material cost and the mechanical property is achieved.
Owner:浙江海帆机械有限公司
Steel for boiler and method of producing the same
InactiveCN101368249AReduce nickel contentReduce alloy costTemperature control deviceFurnace typesSteel tubeElectric arc furnace
The invention discloses steel used for a boiler and a manufacture method thereof. The invention is mainly characterized by including the chemical elements with the following weight percentage: 0.04 to 0.10 percent of C, equal to or less than 0.50 percent of Si, equal to or less than 2.00 percent of Mn, 8.00 to 12.00 percent of Ni, 17.00 to 19.00 percent of Cr, 0.8 to 1.00 percent of Nb, equal to less than 0.25 percent of Cu, equal to or less than 0.015 percent of S, equal to or less than 0.040 percent of P, 0.005 to 0.040 percent of B, 0.10 to 0.20 percent of N, 0.005 to 0.100 percent of N and the rest is Fe as well as unavoidable impurities. The process flow of the invention is as follows: primary melting by an electric arc furnace, AOD refining, die casting, primary rolling, roughing or continuous casting, rolling a tube blank in a hot way and manufacturing a tube. The steel used for a boiler and a manufacture method thereof can solve the problems that steel tube used by the prior boiler is lower in intensity and is easy to generate a fatigue crack, and the like. Besides, the steel used for a boiler and a manufacture method thereof can further improve the comprehensive mechanical performances and the service life of the steel tube used for a boiler.
Owner:宝钢特钢有限公司
Mu90 iron, silicon and nickel magnetic powder core material and method for manufacturing same
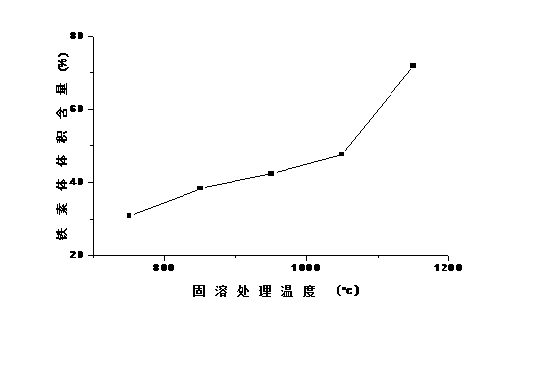
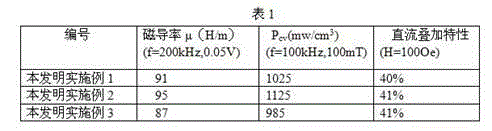
ActiveCN103824669AImprove solid solubilityLow coercivityInorganic material magnetismMetallic material coating processesThermal treatmentSilicon
The invention discloses a method for manufacturing a mu90 iron, silicon and nickel magnetic powder core material. The method includes steps of primarily melting 82-91wt% of iron and 4-8wt% of silicon to obtain a mixture; adding 5-10wt% of nickel powder into the mixture and secondarily melting the nickel powder and the mixture to form iron, silicon and nickel ternary alloy; spraying mist to manufacture powder; treating the surface of the powder; performing mold pressing on the powder and forming a material; performing heat treatment on the material and spraying paint on the surface of the material to obtain the iron, silicon and nickel magnetic powder core material. The invention further discloses the mu90 iron, silicon and nickel magnetic powder core material manufactured by the method. The method and the mu90 iron, silicon and nickel magnetic powder core material have the advantages that a magnetic core manufactured by the method is low in cost and consumption and high in direct-current superposition performance.
Owner:HENGDIAN GRP DMEGC MAGNETICS CO LTD
Nickel and Cobalt Plated Sponge Catalysts
InactiveUS20110011772A1Reduce cobalt contentReduce nickel contentRefining with metalsOrganic compound preparationChemistryOrganic compound
Novel nickel and / or cobalt plated sponge based catalysts are disclosed. The catalyst have an activity and / or selectivity comparable to conventional nickel and / or cobalt sponge catalysts, e.g., Raney® nickel or Raney® cobalt catalysts, but require a reduced content of nickel and / or cobalt. Catalysts in accordance with the invention comprise nickel and / or cobalt coated on at least a portion of the surface of a sponge support. Preferably, the sponge support comprises at least one metal other than or different from the metal(s) contained in the coating. The method of preparing the plated catalysts, and the method of using the catalysts in the preparation of organic compounds are also disclosed.
Owner:SCHMIDT STEPHEN RAYMOND
Phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode material, preparation method thereof and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN110713215AImprove cycle performanceExcellent rate performanceSecondary cellsPositive electrodesLithium-ion batteryPhosphorus doping
The invention provides a phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode material, a preparation method thereof and a lithium ion battery. The preparation method comprises the following steps:adding a nickel source, a cobalt source, a phosphorus source, an alkali source, an R source and a precursor Ni<1-x-y>CoxZy(OH)2 into water to obtain a mixed solution, and performing hydrothermal reaction to obtain a phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode precursor; and mixing the phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode precursor with a lithium source, and sintering the mixture in an oxygen atmosphere to obtain the phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode material. The phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode material is prepared by using the preparation method. The lithium ion battery is prepared from the phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode material. The phosphorus-doped core-shell ternary positive electrode material provided by the invention is stable in structure and good in cycle performance and rate capability.
Owner:SOUNDON NEW ENERGY TECH CO LTD
A preparation method for a vapor plating mask plate
InactiveCN103205784AReduce usageGood opening qualityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingAlloy coatingMetal anode
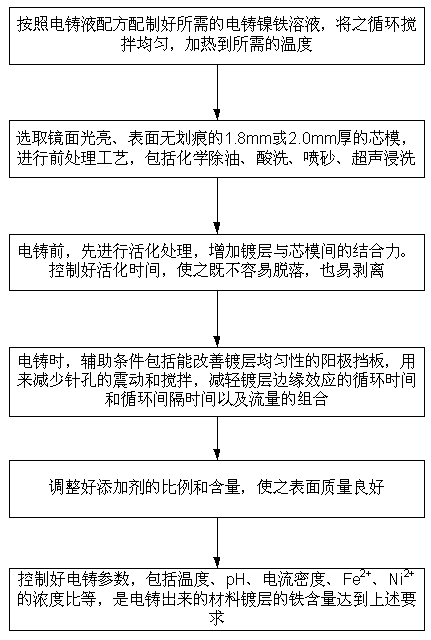
The invention discloses a preparation method for a vapor plating mask plate. The mask plate is produced from a nickel-iron alloy material by using an electroforming process. The nickel-iron alloy material comprises two elements of nickel and iron, with an iron content being 56%-62%. In a preparation method for the nickel-iron alloy material, an electroforming method is adopted, a sulfate system is used as an electroforming solution, a metal cathode and a metal anode are placed in the electroforming solution, and the nickel-iron alloy is deposited on the cathode; wherein the electroforming solution concretely comprises: 220-260g / L nickel sulfate, 30-50g / L nickel chloride, 40-50g / L boric acid, and 21-25g / L ferrous sulfate. According to the preparation method of the invention, the electroforming process is employed to replace an etching process, openings of obtained products are smooth, have good quality, no blurs, and high accuracy; by employing the process, the use amount of nickel is reduced, the cost is low, the three-waste management burden is alleviated, and an alloy coating with the iron content in the range of 56%-62% can be obtained, which means large flat surface metal mask coatings with different magnetisms can be obtained.
Owner:KUN SHAN POWER STENCIL
Process for making nitriles
ActiveUS20130211121A1Reduce nickel contentOrganic compound preparationChemical recyclingCatalyst degradationHydrogen cyanide
Owner:INV NYLON CHEM AMERICAS LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com