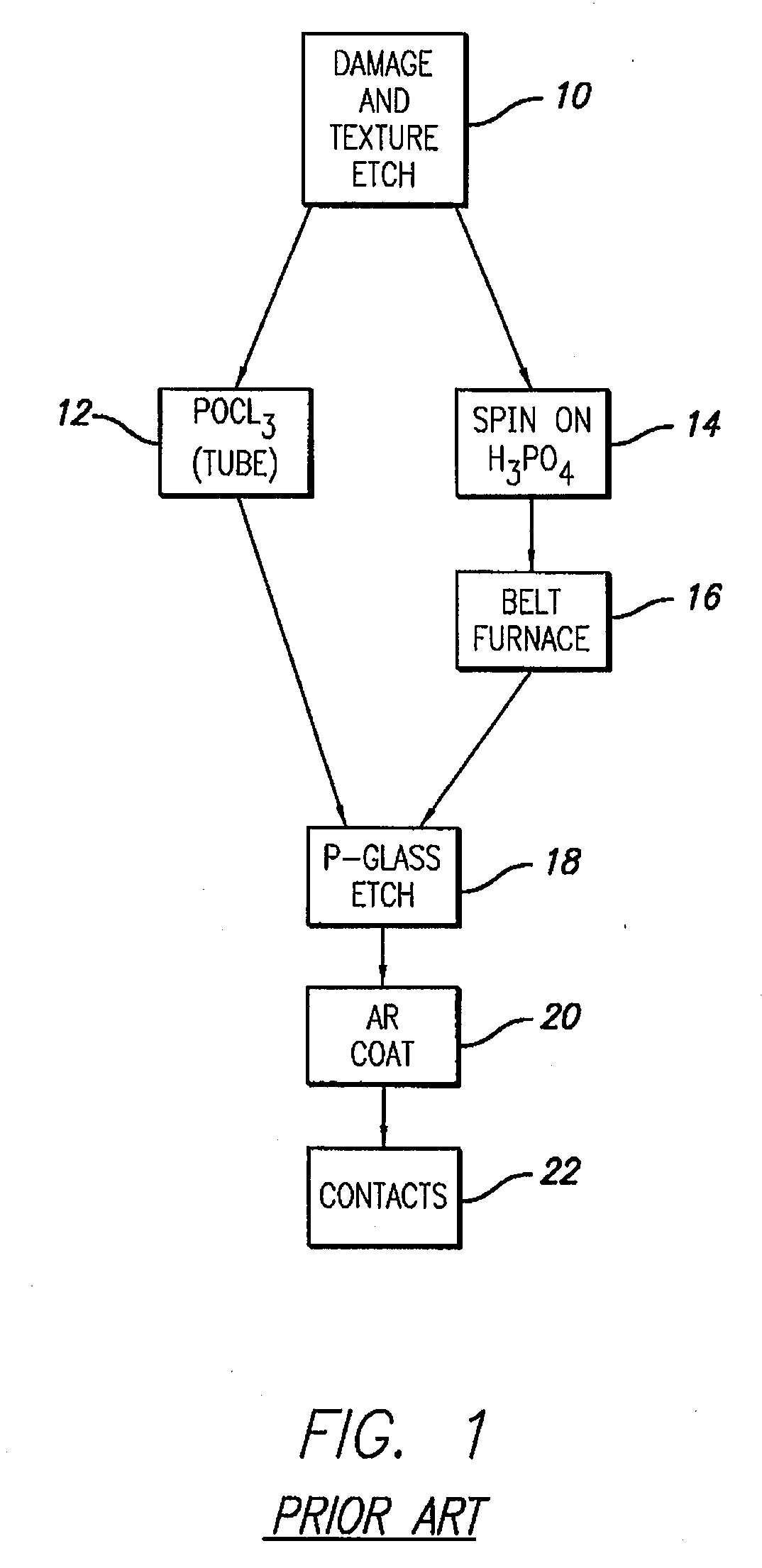
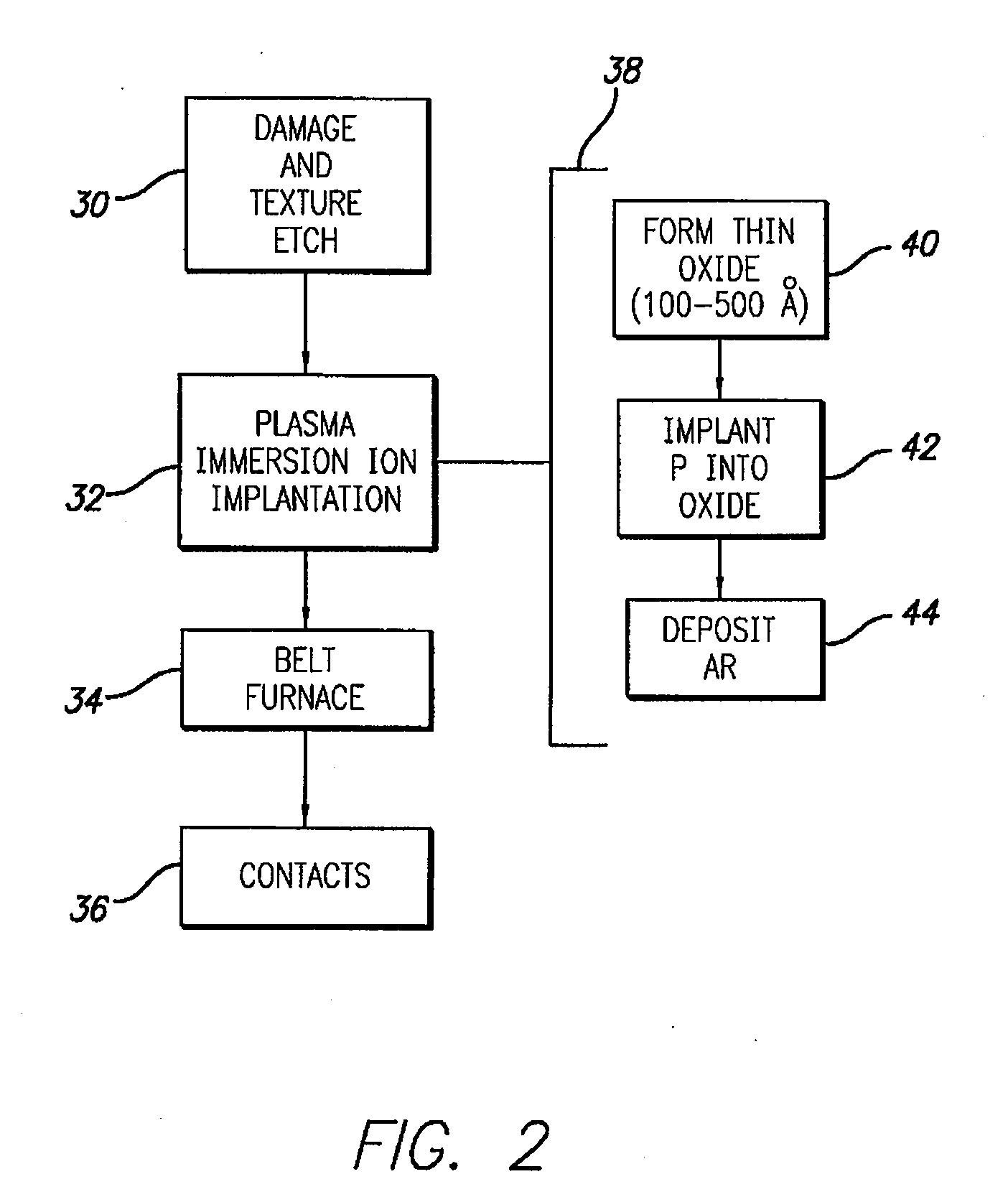
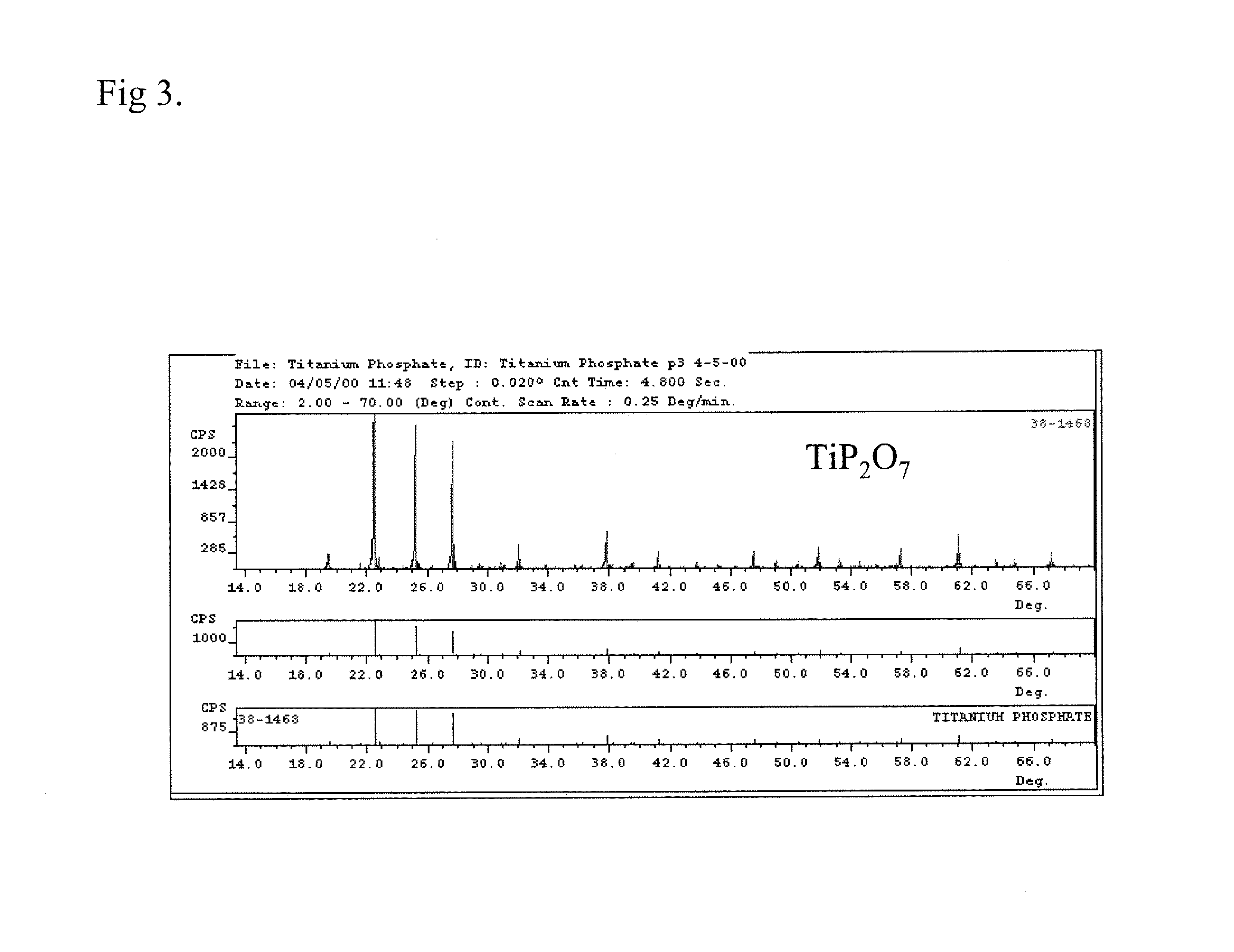
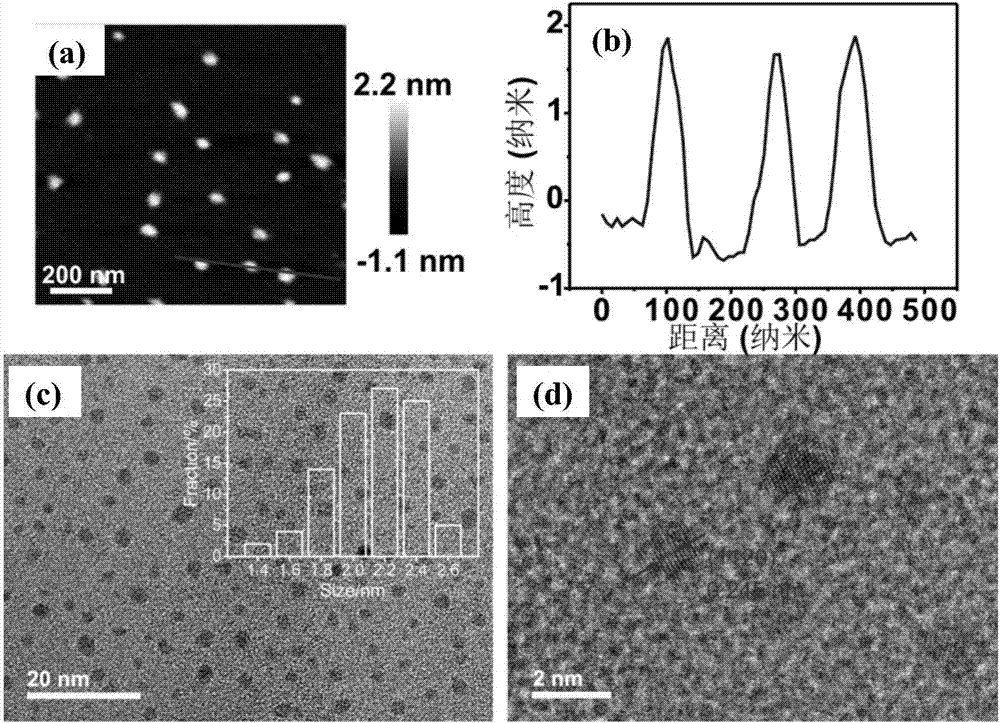
Patents
Literature
302 results about "Phosphorus doping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phosphorus atoms, which have five valence electrons, are used for doping n-type silicon (phosphorous provides its fifth, free, electron). A phosphorus atom occupies the same place in the crystal lattice that was occupied formerly by the silicon atom it replaced.
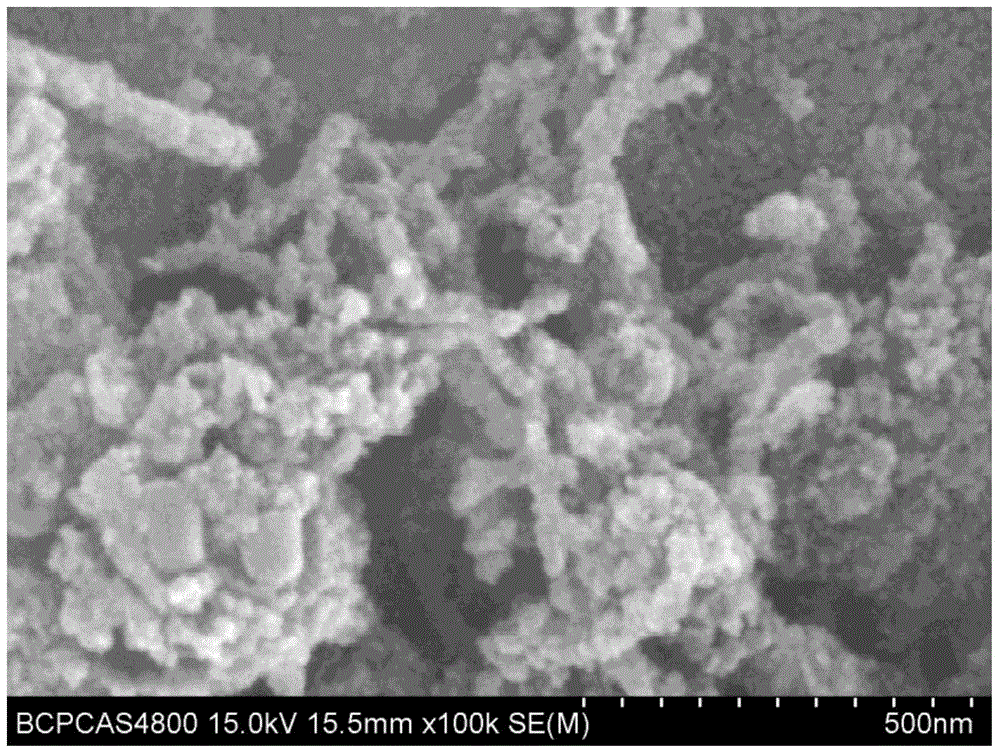
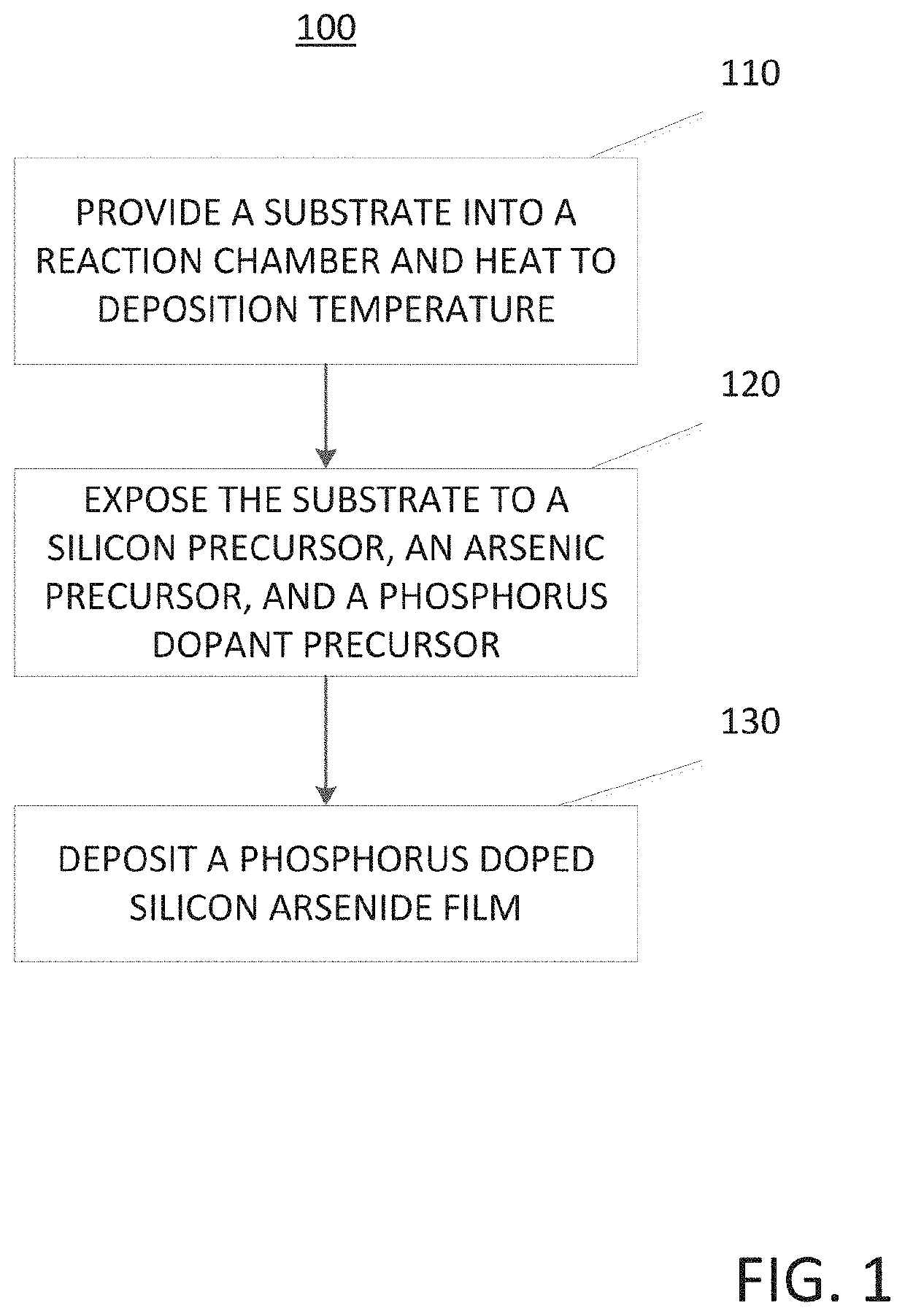
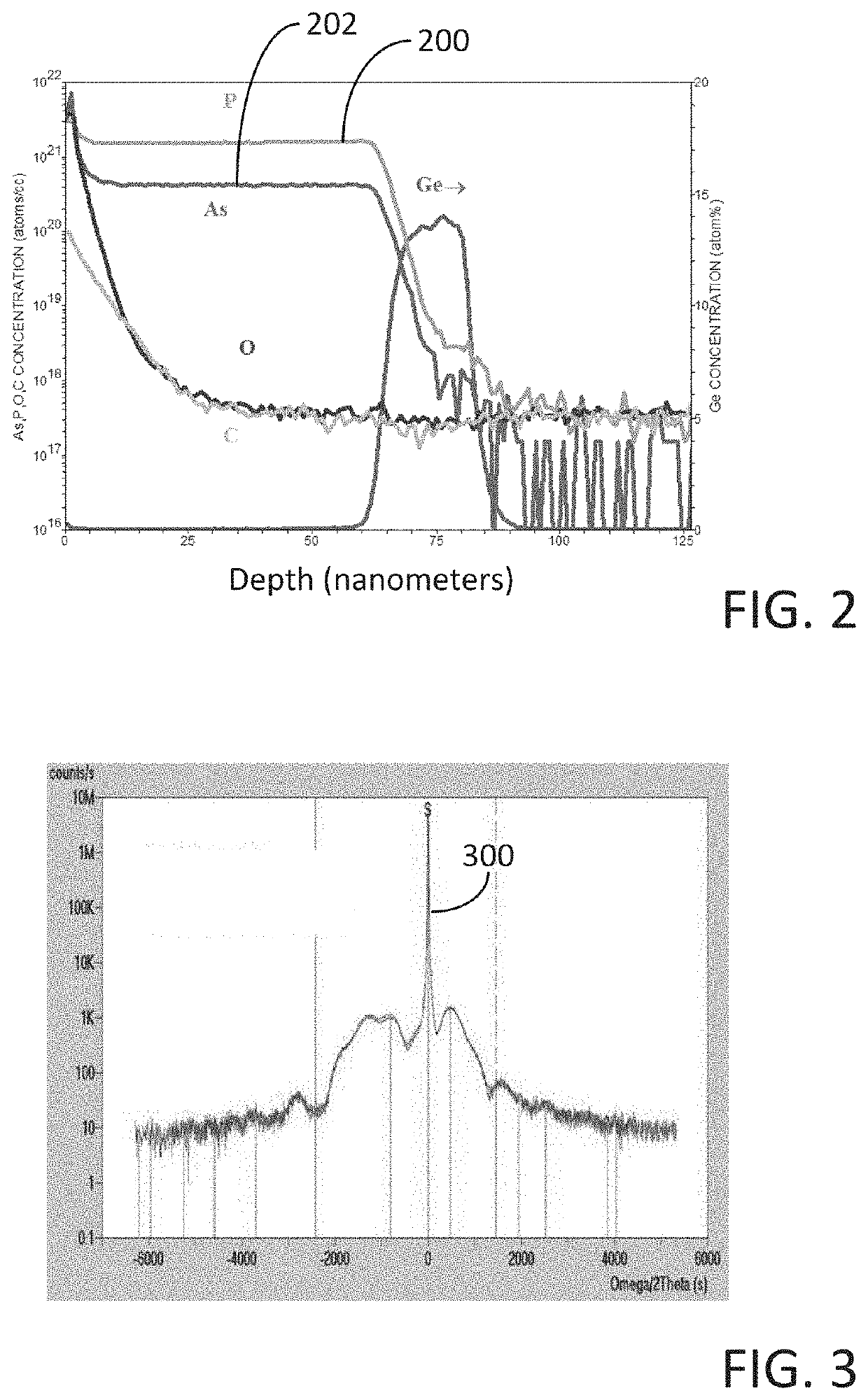
Method for depositing a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film and related semiconductor device structures
ActiveUS20200395444A1Inhibited DiffusionTransistorPolycrystalline material growthDevice materialSilicon thin film
A method for depositing a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film is disclosed. The method may include, providing a substrate within a reaction chamber, heating the substrate to a deposition temperature, exposing the substrate to a silicon precursor, an arsenic precursor, and a phosphorus dopant precursor, and depositing the phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film over a surface of the substrate. Semiconductor device structures including a phosphorus doped silicon arsenide film deposited by the methods of the disclosure are also provided.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of making an improved selective emitter for silicon solar cells
InactiveUS20090142875A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationPlasma-immersion ion implantationSilicon solar cell
A method for forming a selective emitter on a silicon solar cell is provided including forming an oxide layer on a surface of the P-type silicon substrate, implanting phosphorus doping atoms into the oxide layer on the substrate using plasma immersion ion implantation, patterning the oxide layer, annealing the substrate to provide heavily doped regions in the patterned regions and a lightly doped region between the patterned regions, and providing metal contacts to the heavily doped regions.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon catalyst and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105457666AAperture controllableImprove adsorption capacityPhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesPorous carbonAniline
The invention provides a preparation method and an application of a nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon catalyst and belongs to the field of oxygen reduction catalysts for a fuel cell cathode. Nitrogen and phosphorus are introduced with an in-situ doping method, and the nitrogen and phosphorus doping amount is changed by adjusting the content of a nitrogen and phosphorus precursor. Besides, nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon is prepared with a hard template method, and controllability of pore diameters of the porous carbon is realized by adjusting a hard template. The method comprises steps as follows: an earlier polymer of aniline monomers, a phosphorus precursor, a silica-based hard template and non-precious metal salt is prepared; the earlier polymer is calcined, and solids are obtained; the solids are etched, cleaned and dried, and the carbon material is obtained. More importantly, the prepared nitrogen and phosphorus co-doped porous carbon material has an excellent oxygen reduction electro-catalytic property under the acid condition and has huge application potential.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for controlling specific resistance of gallium-doped Czochralski silicon in crystal growth process
InactiveCN101654804AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costBy pulling from meltDopantPhotovoltaic industry
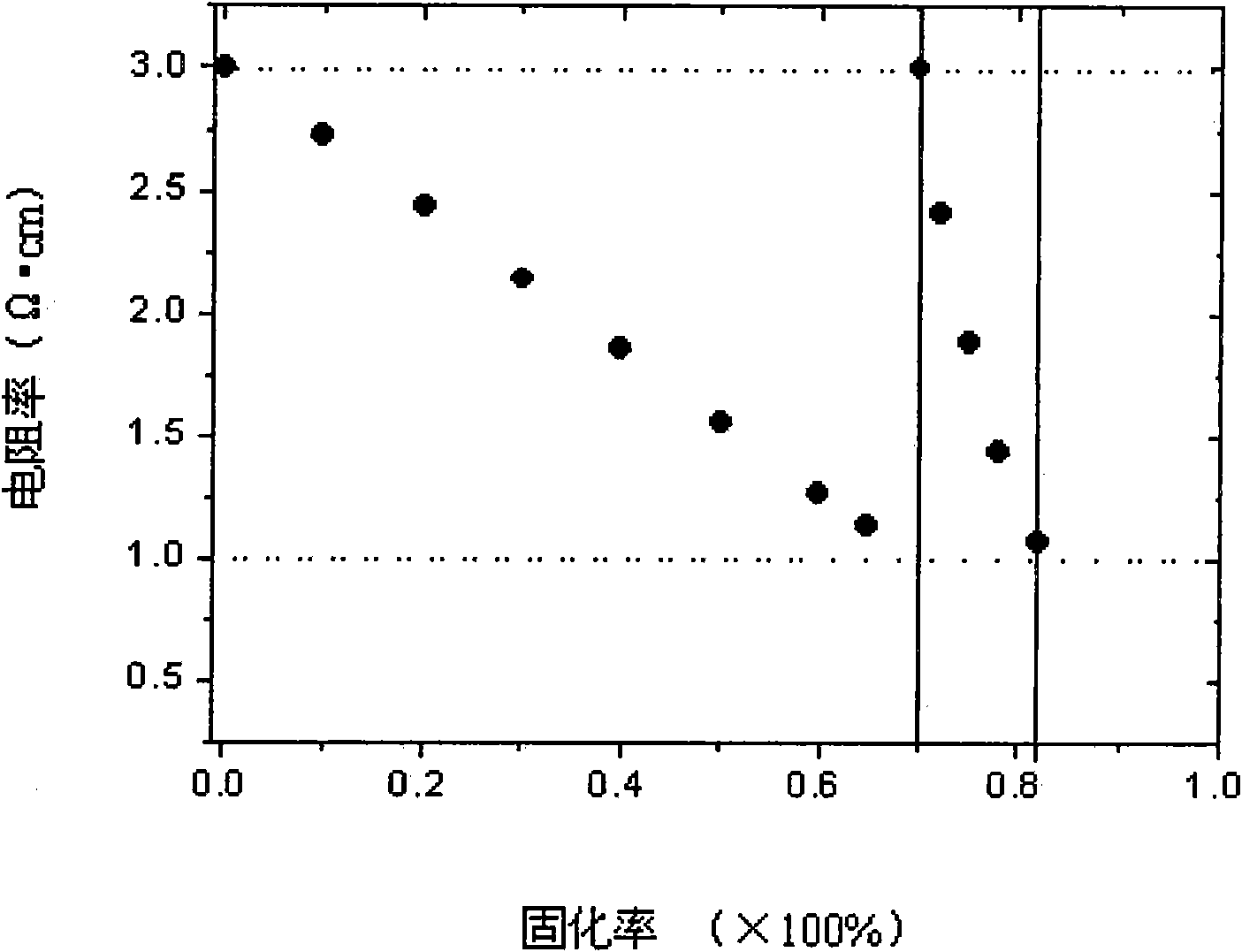
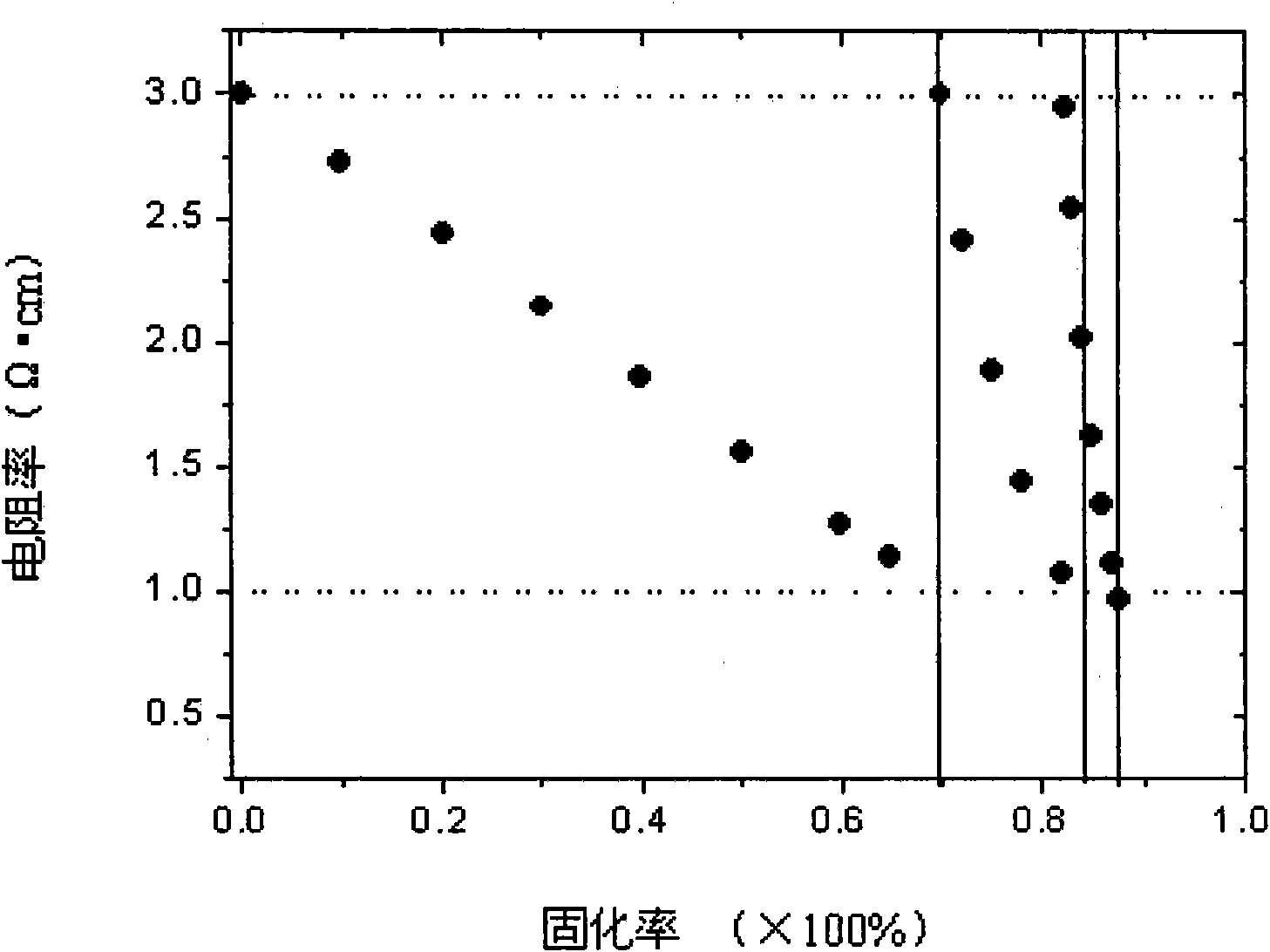
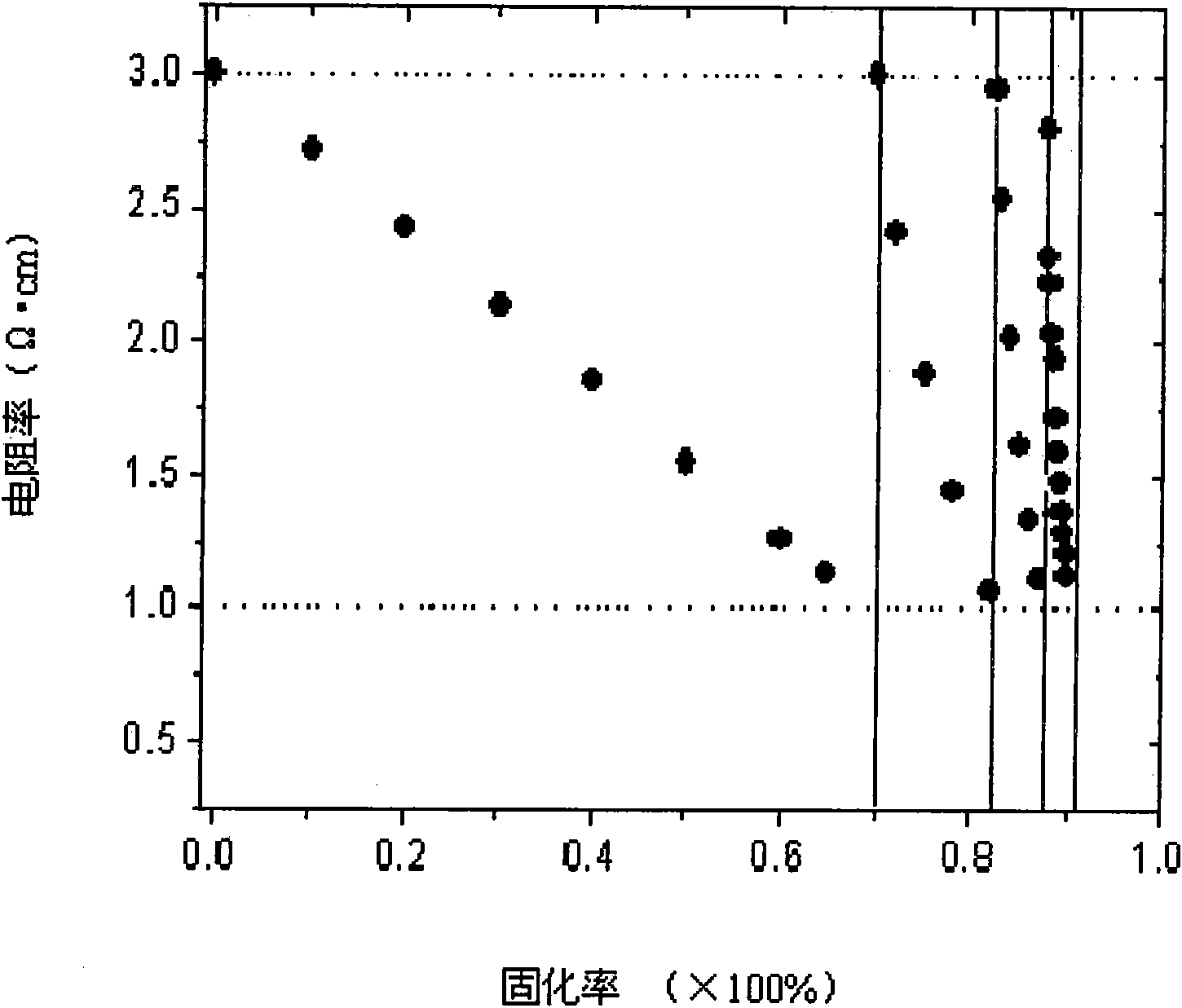
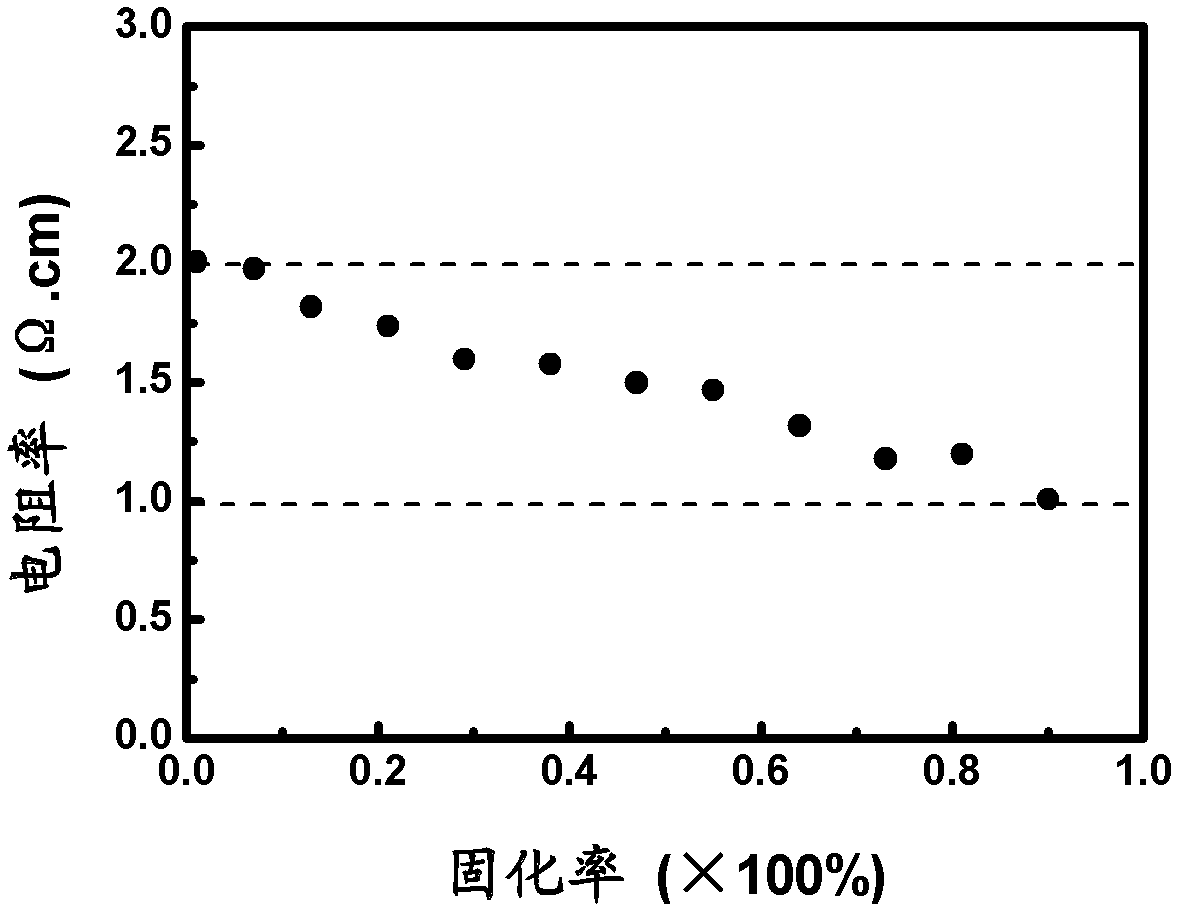
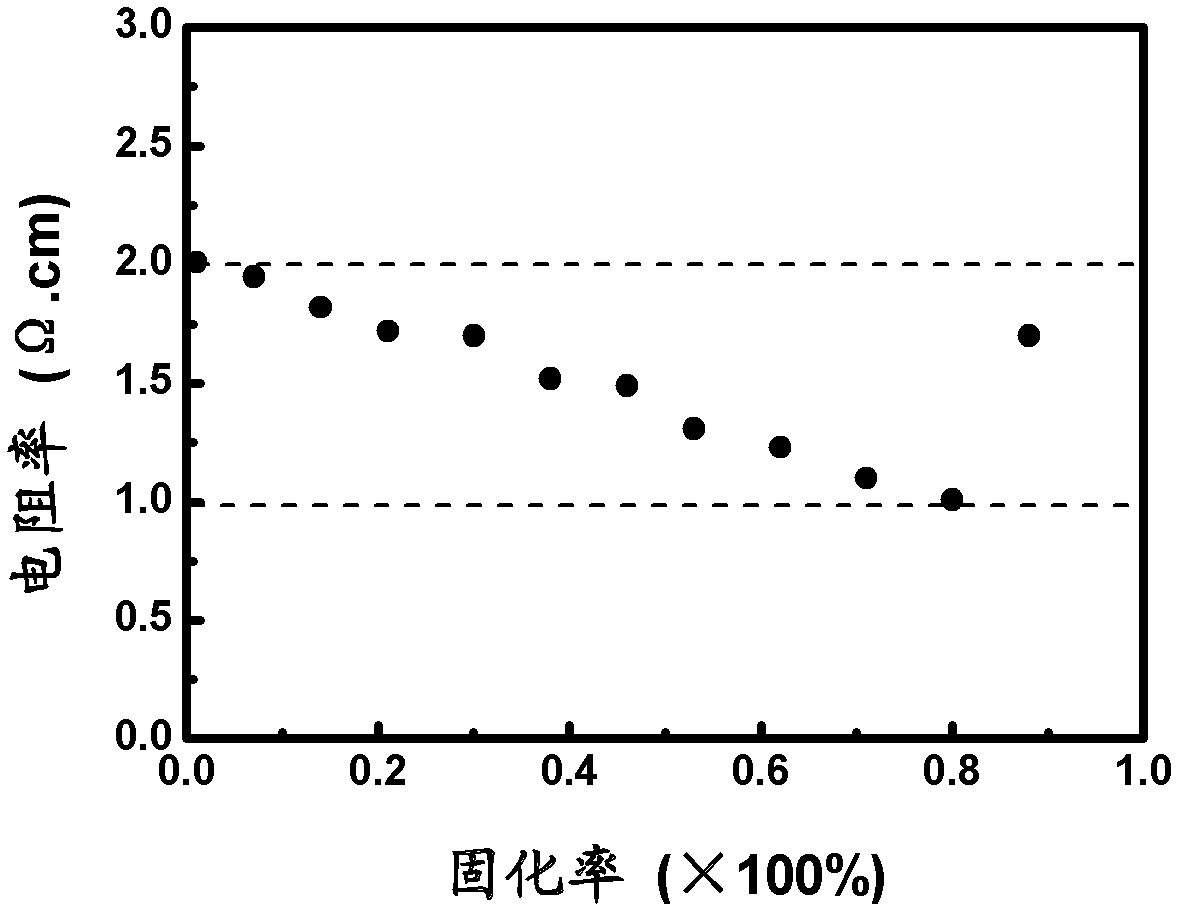
The invention discloses a method for controlling the specific resistance of gallium-doping Czochralski silicon in the crystal growth process, which comprises the following steps: melting multi-crystalsilicon in vacuum or under the protection of argon, melting gallium in the silicon solution to form a gallium-doping silicon solution, and growing the single crystal of the Czochralski silicon; in the crystal growth process, when the specific resistance of the crystal is 1.2-1.0 omega cm, doping the n type dopant-phosphorus with certain concentration in the residual gallium-doping silicon solution to form a phosphorus and gallium-doped silicon solution for continuously growing, and enabling the specific resistance of the crystal to be regulated to 3.0 omega cm again; and when the curing ratioof the crystal reaches 80-90%, stopping the growth. The phosphorus doping process in the residual gallium-doped silicon solution can be carried out many times. The invention can control the specificresistance of the back half part of the single crystal of the gallium-doped Czochralski silicon in the range of 1-3 omega cm to be favorable for increasing the utilization ratio of silicon materials in the process of preparing high-efficiency solar batteries, thus the manufacturing cost of the high-efficiency batteries is greatly reduced, and the method has simple operation and can be easily applied to the photovoltaic industry in a large scale.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Transition metal embedded porous nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN106807427ALarge specific surface areaFully contactedPhysical/chemical process catalystsCell electrodesPhosphoric acidMetal particle
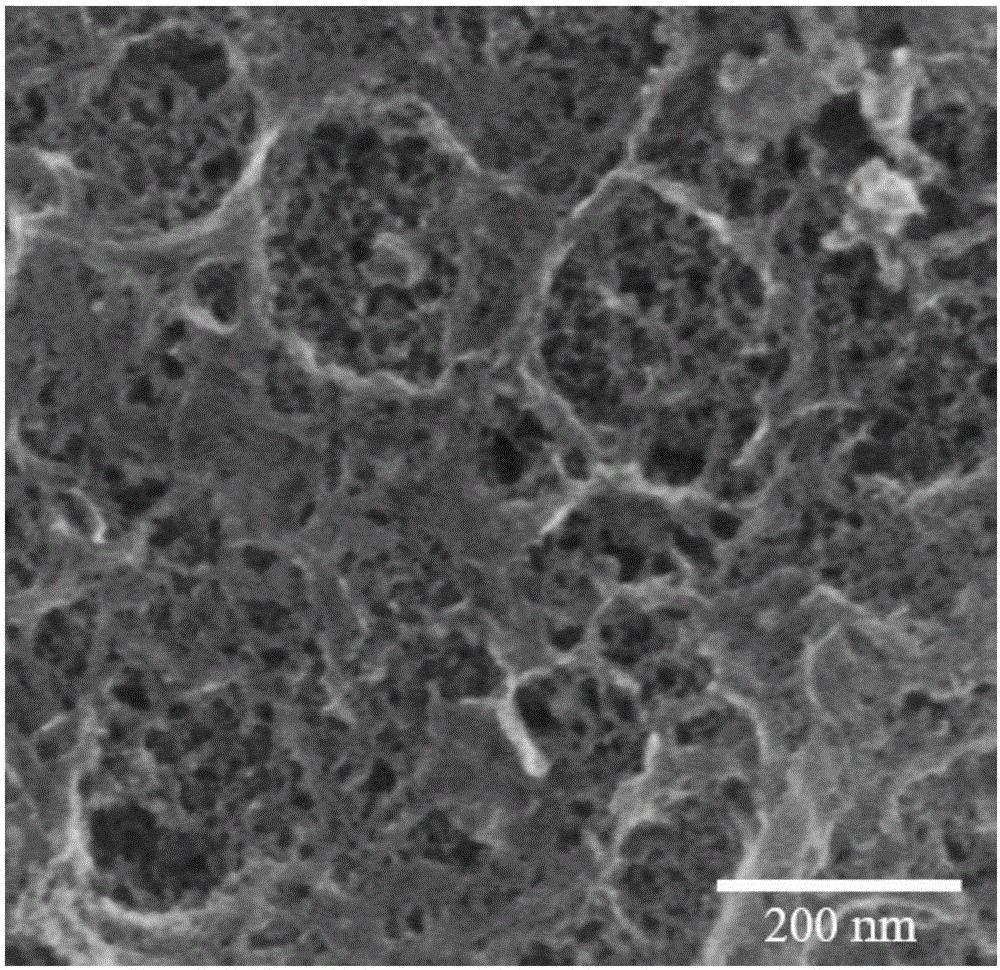
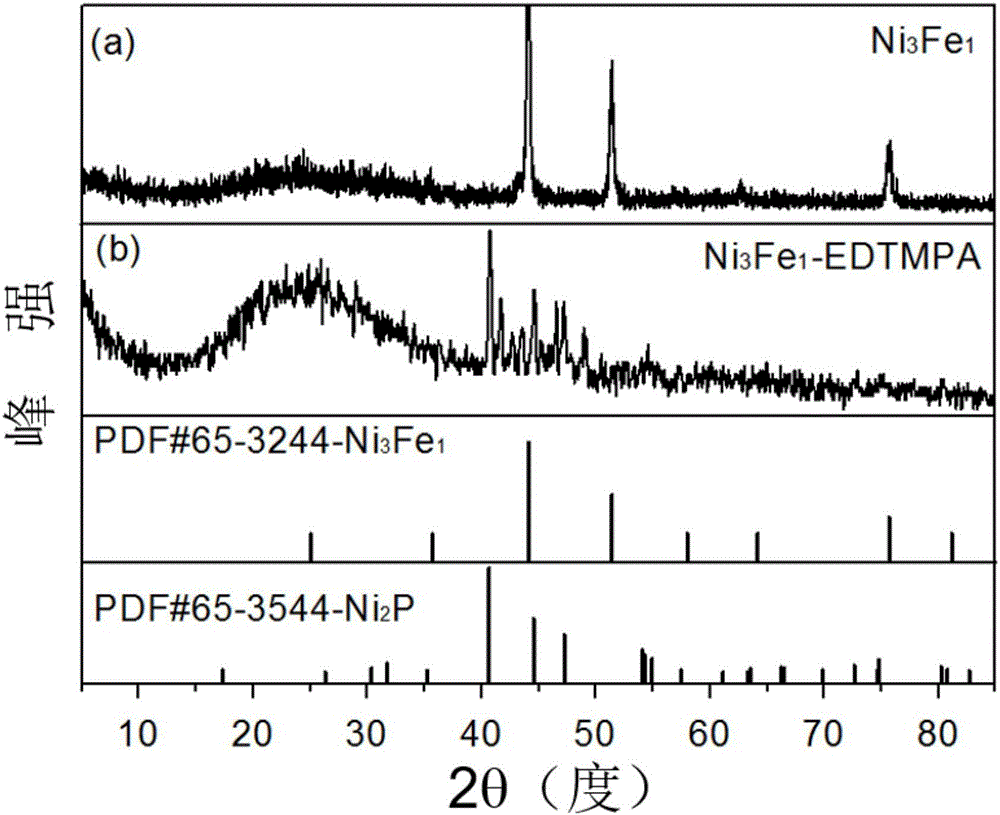
The invention provides a transition metal embedded porous nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon material, employing agar as a carbon source, metal ions as a fixing agent, and EDTMPA (ethylene diamine tetramethylene phosphoric acid) as a nitrogen and phosphorus source; the porous nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon material prepared has co-existing microscopic and mesoscopic structures and metal particles evenly distributed in a carbon carrier. Compared with the prior art, the preparation method according to the invention is simple, the cost of raw materials is low, nitrogen and phosphorus doping efficiency can be improved effectively, the specific surface area of the catalyst nanoparticles can be enlarged effectively, and the prepared porous nitrogen-phosphorus-doped carbon material has high surface active area and high graphitizing degree, is capable of increasing current intensity when the catalyst engages in catalytic reaction, and has excellent electrocatalytic activity and fast dynamical progress.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of solar cell
InactiveCN101937945AOvercome defilementOvercome defectsFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesScreen printingSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: providing a plurality of polycrystalline silicon wafers for texturization; overlapping the textured silicon wafers, depositing a silicon nitride or silicon oxide masking film on the periphery of the silicon wafers, then diffusing a phosphorus doping layer on the front surface of the to-be-prepared positive electrode of the silicon wafers to form a PN junction, wherein the periphery of the silicon wafers can not form the diffusion PN junction owning to the existence of the masking film; removing the peripheral masking film and the surface phosphosilicate glass; preparing a passivation layer and an antireflection layer; and performing screen printing and sintering to form a back Ag electrode, a back Al-back surface and a front Ag electrode. In the preparation method of the solar cell provided by the invention, the masking film is formed before the impurity source diffusion used for preparing the PN junction; owning to the existence of the masking film, the periphery of the silicon wafers can not form the PN junction; and the silicon wafers after diffusion is washed with acid to remove the masking film on the periphery of the silicon wafers and the phosphosilicate glass on the diffusion surface, thus achieving the aim of replacing the etching step.
Owner:百力达太阳能股份有限公司
Growth process for N-type solar energy silicon single crystal with minority carrier service life of larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds
InactiveCN101724899ASolve the problem of low lifespanPractical growing methodPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCrystal orientationSingle crystal
The invention relates to a growth process for N-type solar energy silicon single crystal with minority carrier service life of larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds. The appearance is in 6-8 inches, the (100) crystal orientation resistivity range is between 1 omega.cm and 20 omega.cm, the minority carrier service life of the surface and the section is larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds, the clearance oxygen content [Oi] is smaller than or equal to 17.5ppma, and the substituted carbon content [Cs] is smaller than or equal to 0.5ppma. Phosphorus-doped block-shaped polycrystalline silicon is used as a raw material to prepare the N-type solar energy silicon single crystal. The process comprises the steps of: charging, heating, leading diameter, maintaining equal diameter, collecting, cooling, heating by a program, stably heating and melting the material; after a thermal field in melting silicon is stable, leading the thin diameter, lifting the tail part of a single crystal to the upper edge of a guide cylinder with the cooling time of not larger than three hours. The crystal growth process is practical, has high efficiency and low cost, can prepare the N-type single crystal silicon which is completely larger than or equal to 1,000 microseconds from the head part to the tail part by a CZ method, and creates an industrialized foundation for efficiency improvement of an efficient solar battery.
Owner:任丙彦 +1
Arsenic and phosphorus doped silicon wafer substrates having intrinsic gettering
ActiveUS7485928B2Improve uniformityLow resistivityPolycrystalline material growthAfter-treatment detailsWaferingPhysical chemistry
Owner:GLOBALWAFERS CO LTD
Method for boron doping of crystalline silicon solar battery
InactiveCN102437238ALow costFast coating speedFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesSilicon oxideOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a method for boron doping of a crystalline silicon solar battery, which comprises the following steps that: a first layer of film-boron doped silicon oxide film is deposited on the surface of a silicon chip after the wool making, a second layer of film-silicon oxide film is deposited on the first layer of the film to be used as a barrier layer, then the silicon chip is processed at high temperature, so boron atoms can be diffused into a silicon basic body to form a boron doped layer. Due to the adoption of the method, a boron transmission electrode (p+) can be prepared on an n-type silicon chip, or a boron back surface (p+) is formed on a p-type silicon chip. Through the barrier layer, single-faced boron doping can be realized, and a boron source is free from being sucked into a diffusion furnace tube, so the corrosion of the furnace tube can be reduced, and the service life can be prolonged; and if a phosphorus source is introduced during the high-temperature annealing process, the boron doping and phosphorus doping can be respectively realized on two sides of the silicon chip.
Owner:JA SOLAR TECH YANGZHOU +1
N-type casting policrystalline silicon with uniform doping resistivity and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102560641AIncrease profitReduce manufacturing costPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsPhotovoltaic industryIngot
The invention discloses an N-type casting policrystalline silicon with a uniform doping resistivity and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: mixing a polycrystalline silicon material, a phosphorus doping agent and gallium; then fusing; and growing a polycrystalline silicon body by using a casting method. According to the N-type casting policrystalline silicon with the uniform doping resistivity, the resistivity of about 90% N-type phosphorus doping phosphorus doping cast ingots can be controlled in the range of 1.0-2.0 omega.cm, therefore, the utilization rate of the N-type polycrystalline silicon crystal in the process of manufacturing an efficient solar cell is beneficially improved, the manufacturing cost of the efficient solar cell is remarkably lowered, the preparation method is simple to operate and easy to popularize and use in the photovoltaic industry.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
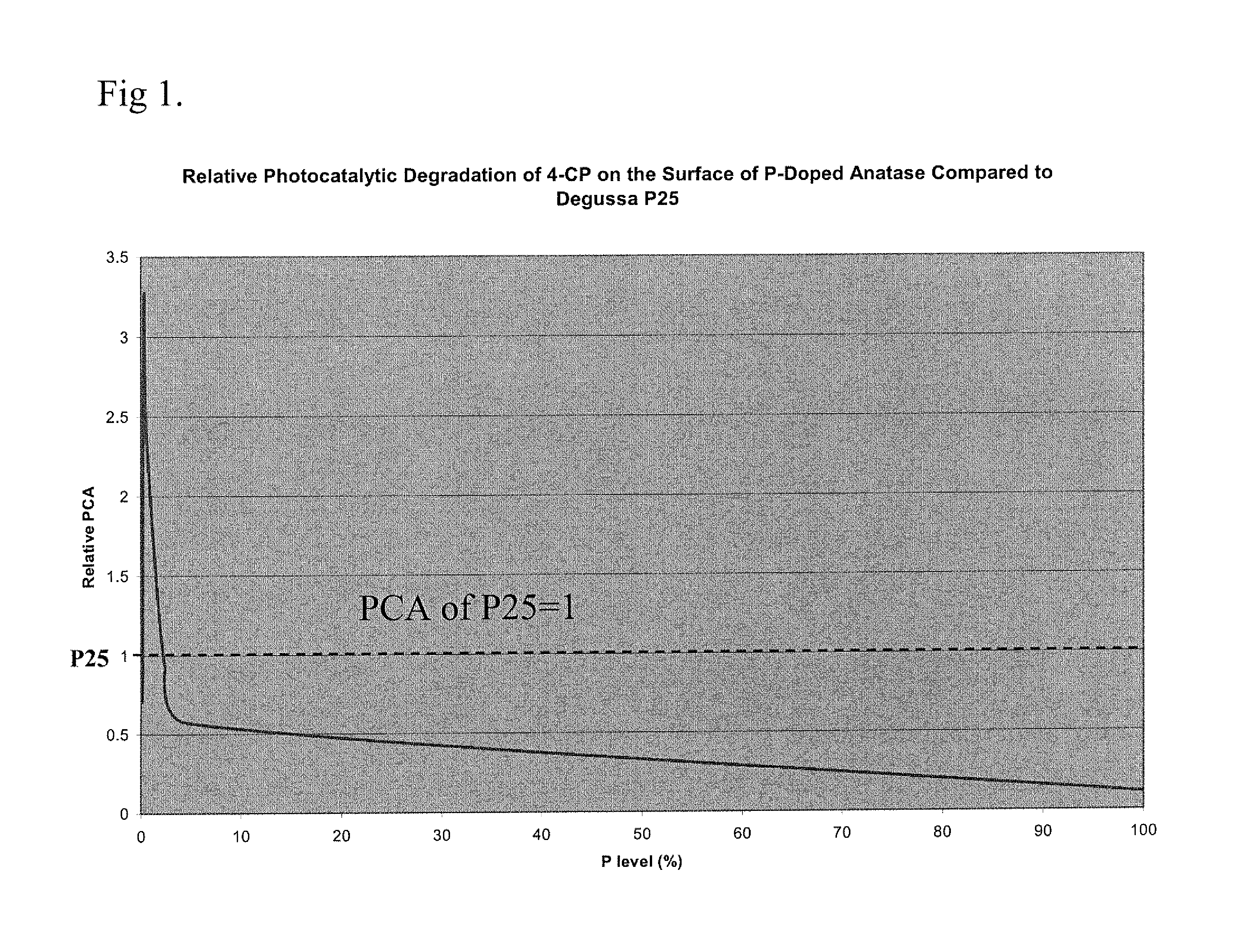
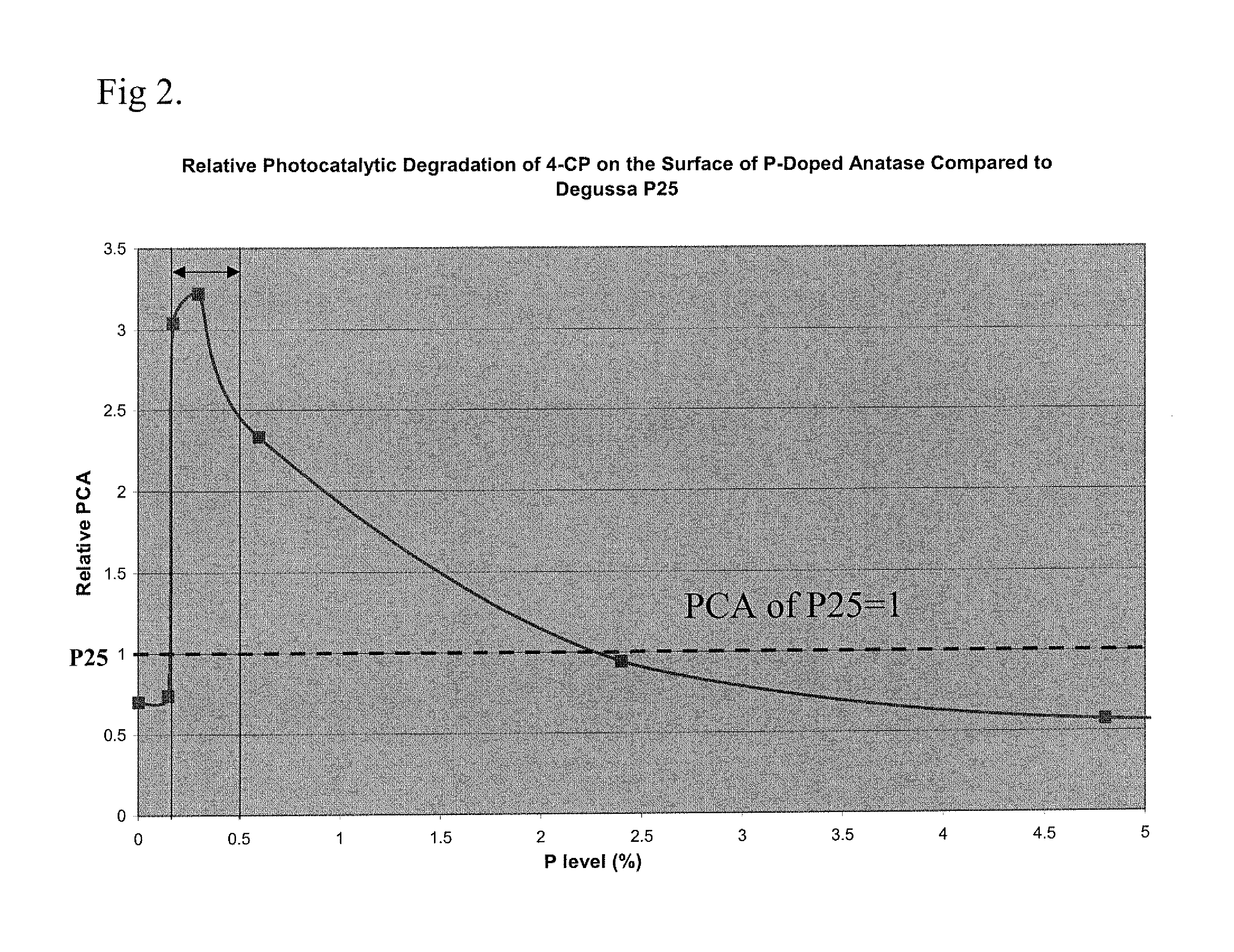
HIGHLY PHOTOCATALYTIC PHOSPHORUS-DOPED ANATASE-TiO2 COMPOSITION AND RELATED MANUFACTURING METHODS
InactiveUS20080045410A1Improve photocatalytic activityCatalyst activation/preparationTitanium dioxidePhosphorus dopedNanometre
The present invention is generally directed to doped anatase-TiO2 compositions that exhibit enhanced photocatalytic activity. In a composition aspect, the present invention provides a nanosized, anatase crystalline titanium dioxide composition. The composition is doped with phosphorus, and the doping level is between 0.10 and 0.55 weight percent.
Owner:ALTAIR NANOMATERIALS INC
Nitrogen-phosphorus-sulfur co-doping composite carbon material, preparation method of composite carbon material and lithium ion battery
ActiveCN108493424AReduce manufacturing costImprove cycle lifeCell electrodesSecondary cellsDischarge efficiencyBiological activation
The invention discloses a nitrogen-phosphorus-sulfur co-doping composite carbon material, a preparation method of the nitrogen-phosphorus-sulfur co-doping composite carbon material, and a lithium ionbattery. The nitrogen element of the composite carbon material is from a nitrogen-containing biomass carbon material; the phosphorus element is from a phosphorus doping graphene precursor. A method comprises the following steps of (1) mixing the nitrogen-containing biomass carbon material, the phosphorus doping graphene precursor, a sulfur source and an activating agent; water is added for soaking; then, drying is performed; (2) then, performing activation treatment at 600 to 1,000 DEG C to obtain the nitrogen-phosphorus-sulfur co-doping composite carbon material. The method provided by the invention achieves green and environment-friendly effects; the production cost is greatly reduced; when the composite carbon material is used for coating lithium iron phosphate, the power performance and circulation stability of the lithium iron phosphate positive electrode material can be obviously improved; the first time specific discharge capacity at the power of 0.1C is 161 mAh / g or higher; thecharging and discharging efficiency is 98 percent or higher; at the 8C power, the specific discharge capacity is 146 mAh / g or higher; after the circulation for 40 weeks, the volume is maintained at avalue being 98 percent or higher.
Owner:ZHONGKE LITHIUM BATTERY NEW ENERGY CO LTD +1
Double-sided selective emitter high-efficiency crystalline silicon cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111524983AAvoid the disadvantage of high surface concentrationPlay a passivation effectFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic industrySilicon oxide
The invention belongs to the field of solar photovoltaic industry and particularly provides a double-sided selective emitter efficient crystalline silicon cell and a preparation method thereof. The double-sided selective emitter efficient crystalline silicon cell is characterized in that a double-sided selective emitter structure is adopted, a boron-doped heavily-doped region is a polycrystallinesilicon structure in which aluminum oxide replaces silicon oxide to serve as a tunneling layer, a constant surface concentration increase fill factor (FF) exceeding 1E20atom / cm <3> can be achieved, alightly-expanded region is pure boron doping, a heavily-expanded boron doping process and a lightly-expanded boron doping process can be realized in one step, and the process is simplified. Silicon oxide is adopted as a tunneling layer for a phosphorus-doped region, a heavily-doped region is of a double-layer poly structure, the surface concentration is high, metallization contact is improved, a lightly-expanded region is of a single-layer lightly-doped poly structure, and then the open-circuit voltage (Voc) is increased. The formation of the double-sided selective emitter effectively utilizesa mask etching mode. The double-sided selective emitter efficient crystalline silicon cell is advantaged in that the structure can effectively improve battery efficiency, and is suitable for batch production.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +1
Preparation method of N-type crystalline silicon double-sided back contact solar cell
InactiveCN102683493AExcellent electrical performanceSimple preparation processFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesElectricityPhosphorus doped
The invention discloses a preparation method of an N-type crystalline silicon double-sided back contact solar cell, which comprises the following steps of: (1) cleaning and velvet-making; (2) carrying out local phosphorus doping on the back surface of a silicon chip; (3) carrying out boron diffusion on the front surface of the silicon chip; (4) etching a peripheral junction; (5) passivating the front surface and the back surface of the silicon chip or the front surface of the silicon chip; (6) arranging antireflective films on the front surface and the back surface of the silicon chip; (7) forming a hole on the silicon chip; (8) arranging a hole metal electrode in the hole; and printing metal electrodes on the double sides and sintering to obtain the N-type crystalline silicon double-sided back contact solar cell. The preparation method has the advantages that the local phosphorus doping is carried out on the back surface of the silicon chip, a non-phosphorus doping area on the back surface of the silicon chip is a peripheral area of a hole to be formed on the silicon chip, and the problems of short circuit and electricity leakage at the diffused junction are avoided in the solar cell obtained by the preparation method, so that the remarkable effect is obtained.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD +1
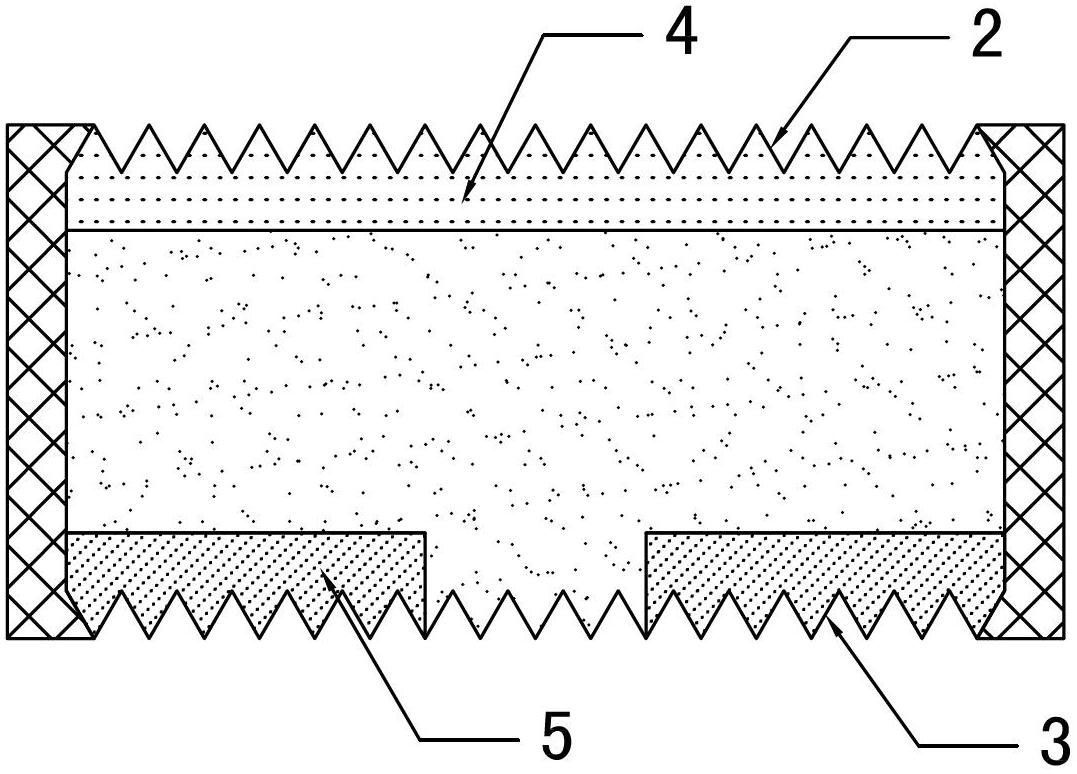
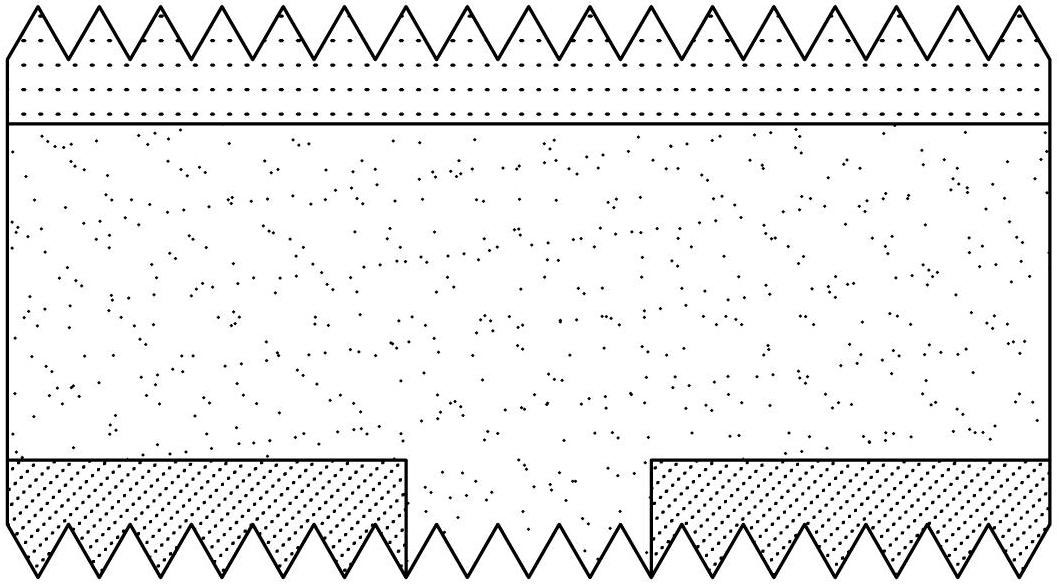
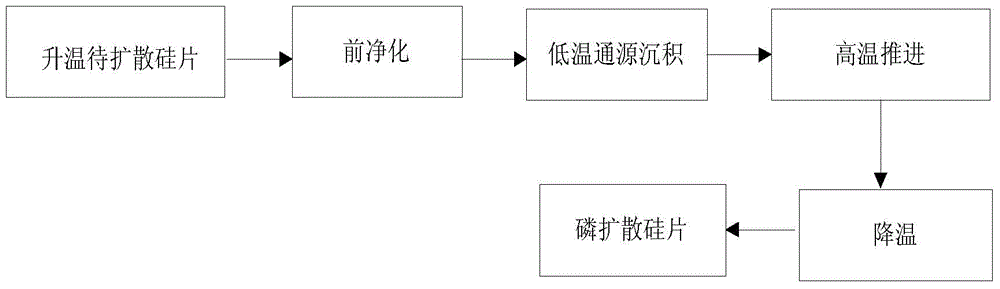
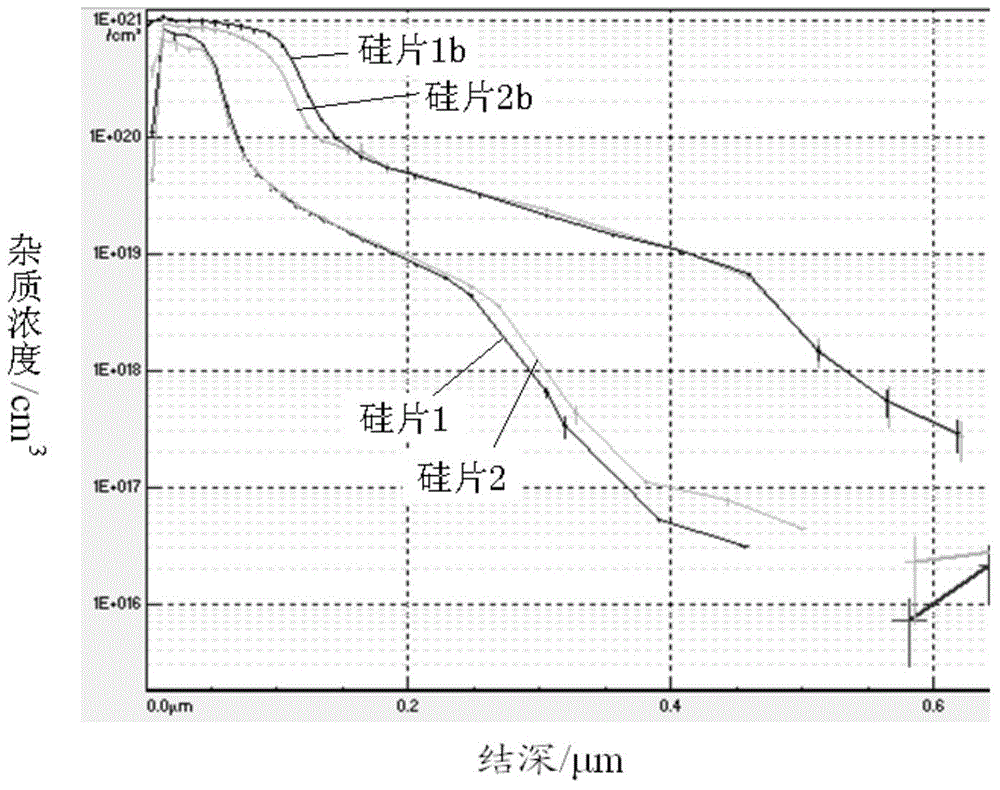
Phosphorus doping silicon wafer, manufacturing method of phosphorus doping silicon wafer, solar cell and manufacturing method of solar cell
ActiveCN103606596AGood electrical parametersImprove conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureDiffusion/dopingConcentration gradientSolar cell
The invention discloses a phosphorus doping silicon wafer, a manufacturing method of the phosphorus doping silicon wafer, a solar cell and a manufacturing method of the solar cell. The manufacturing method of the phosphorus doping silicon wafer includes the steps of warming of a silicon wafer to be doped, prepurification, phosphorus deposition and diffusion and cooling. In the phosphorus deposition and diffusion step, POC13 is used as a phosphorous source and reacts with O2 for step-by-step deposition diffusion, and in the step-by-step deposition and diffusion step, the volume ratio of POC13 to O2 is decreased progressively. By the adoption of the step-by-step deposition diffusion process, the diffusion speed is high in the initial stage, phosphorus on the surface of the silicon wafer diffused into the interior of a substrate of the silicon wafer, the concentration of phosphorus on the surface of the silicon wafer is gradually reduced, in the follow-up process, the amount of phosphorus deposited on the surface of the substrate of the silicon wafer is reduced along with reduction of the concentration of the phosphorous source, and the concentration of phosphorus distributed on the surface and the interior of the substrate of the silicon wafer is larger than the impurity concentration gradient under the condition that the phosphorous source POC13 with large concentration is continuously supplemented in the current deposition and diffusion process. Good electric parameters are acquired, and conversion efficiency of the solar cell is improved.
Owner:YINGLI GRP
Thin-film transistor structure
InactiveCN104576750ALower contact barrierReduce leakage currentTransistorInsulation layerElectrical conductor
The invention discloses a thin-film transistor structure. The thin-film transistor structure comprises a source, a drain, a semiconductor layer and a grid, wherein the drain and the source are arranged at an interval; the grid is arranged in an insulation manner relative to the semiconductor layer, the source and the drain through an insulation layer; an ohmic contact layer is further arranged between the semiconductor layer and the source and the drain, and the ohmic contact layer further comprises a first phosphorus-doped layer, a second phosphorus-doped layer and a third phosphorus-doped layer which are stacked, wherein the first phosphorus-doped layer is close to the semiconductor layer, the third phosphorus-doped layer is close to the source and the drain, the phosphorus doping concentration of the first phosphorus-doped layer is lower than that of the second phosphorus-doped layer, and the phosphorus doping concentration of the second phosphorus-doped layer is lower than that of the third phosphorus-doped layer. The thin-film transistor structure disclosed by the invention can reduce a contact potential barrier between a semiconductor and a metal to form good ohmic contact between the two and further effectively reduce the drain current of the amorphous silicon thin-film transistor without affecting the on-state current.
Owner:TRULY HUIZHOU SMART DISPLAY
Method for carrying out control over phosphorous doping concentration through combination of pre-oxidation mode and low temperature-high temperature-low temperature variable-temperature diffusion mode
ActiveCN103943719APrecise control of doping concentration gradientsImprove conversion efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical physicsPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for carrying out control over the phosphorous doping concentration through the combination of a pre-oxidation mode and a low temperature-high temperature-low temperature variable-temperature diffusion mode. According to the method, a pre-oxidation process and a low temperature-high temperature-low temperature three-step variable-temperature diffusion process are included; according to the processes, the phosphorous doping concentration gradient can be accurately controlled by optimizing the temperature gradient, a good PN junction can be obtained, high sheet resistance uniformity can be achieved, and conversion efficiency of a solar cell is improved.
Owner:JA SOLAR TECH YANGZHOU
Phosphorus diffusion method of crystalline silicon solar cell
ActiveCN106057980AControl concentrationConcentration Control Concurrent Reduction of Phosphorus Doping Concentration Gradients in the BodyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingConcentration gradientOxygen
The present invention discloses a phosphorus diffusion method of a crystalline silicon solar cell. The method comprises the steps of (1) entering into a boat, (2) adjusting temperature to be below 800 DEG C, introducing nitrogen carrying phosphorus source and dry oxygen, and forming a silicon dioxide layer containing phosphorus, (3) carrying out low temperature diffusion, (4) raising the temperature in a furnace and pushing with the rise of the temperature, (5) carrying out first time of high temperature diffusion, (6) raising the temperature in the furnace and pushing with the rise of the temperature, (7) carrying out second time of high temperature diffusion, (8) reducing the temperature in the furnace and pushing with the decrease of the temperature, and (9) reducing the temperature and going out of the boat, and completing a diffusion process. According to the method, an oxidation gettering effect is enhanced and the concentration gradient of the phosphorus doping is controlled, the separation and collection of carriers are facilitated, the open circuit voltage is raised, the temperature difference in a cooling process is controlled, and a crystal boundary gettering effect is enhanced.
Owner:CSI CELLS CO LTD +1
Preparation method and application of nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube loaded phosphorus-doped cobaltosic oxide composite material
ActiveCN111362254ABig spaceGood conductive pathMaterial nanotechnologySecondary cellsPtru catalystLithium sulfur
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube loaded phosphorus-doped cobaltosic oxide composite material, and belongs to the technical field of composite materials. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube, then adding a cobalt source to obtain a Co / NCNT material, oxidizing in an oxygen atmosphere to obtain the nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube loaded cobaltosic oxide composite material, and phosphatizing in an argon atmosphere to obtain the nitrogen-doped carbon nanotube loaded phosphorus-doped cobaltosic oxide composite material. According to the scheme, on one hand, a good conductive channel is provided, on the other hand, the phosphorus-doped cobaltosic oxide not only has relatively strong adsorbability to lithium polysulfide, but also can be used as a catalyst to effectively promote the redox process of the lithium-sulfur battery, so that the adsorption-diffusion-conversion processof the lithium polysulfide is accelerated to be carried out orderly, and the overall performance of the battery is improved.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Preparation method and application of phosphorus-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots
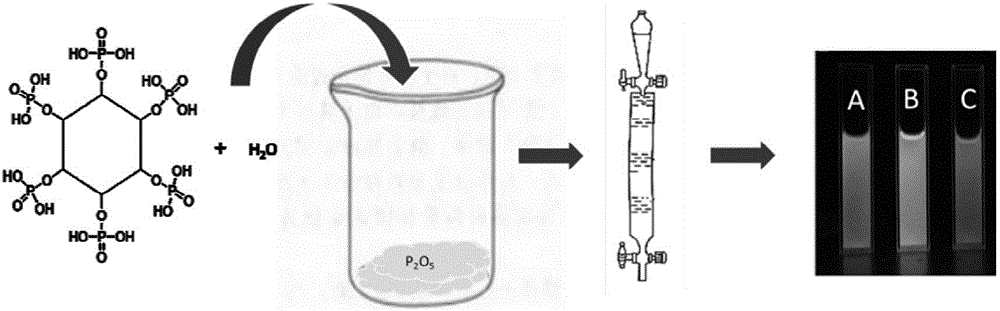
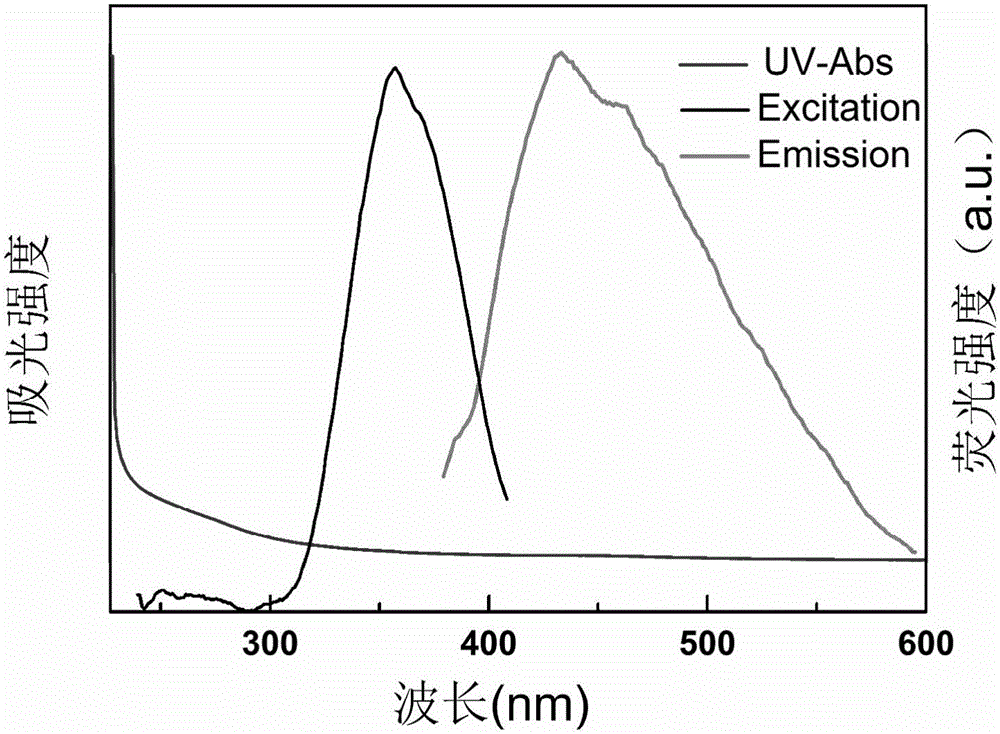
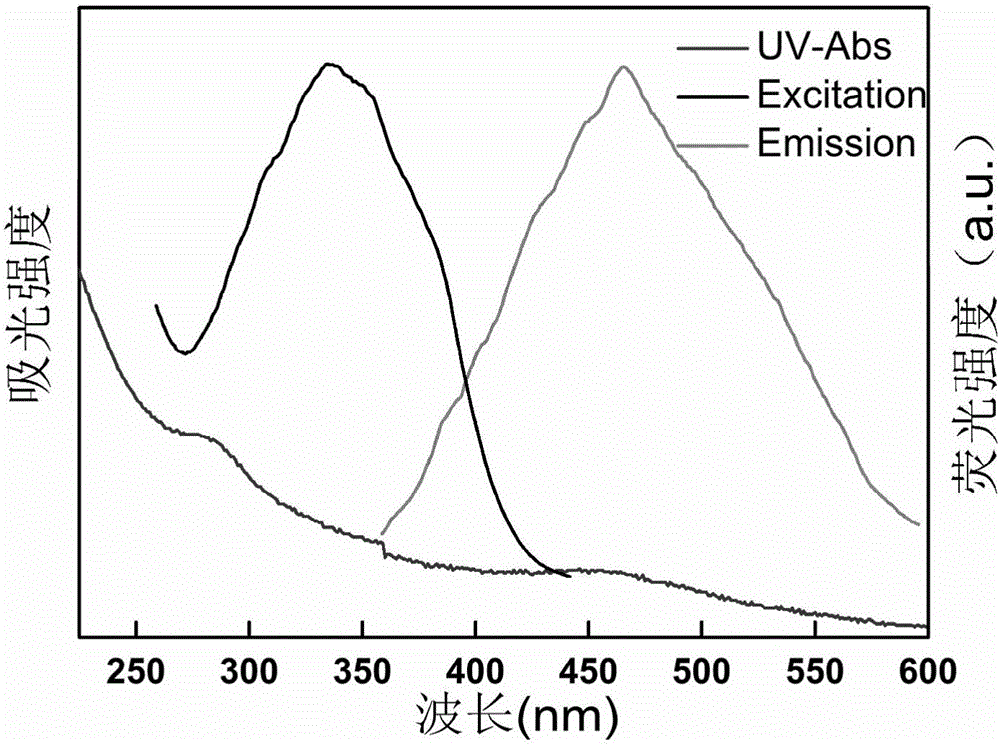
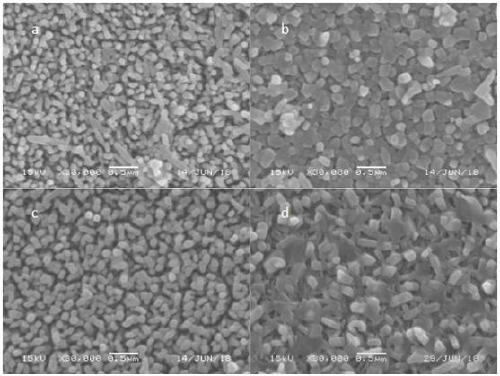
InactiveCN105950145AEasy to operateWide variety of sourcesFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsFreeze-dryingPhytic acid
The invention relates to a preparation method of phosphorus-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) adding phytic acid into a glass container, then adding secondary water, fully stirring, and carrying out ultrasonic treatment to obtain a clear solution; then, rapidly adding the clear solution into phosphorus pentoxide to obtain a dark brown solution; (2) after the glass container is naturally cooled, filtering the dark brown solution by using filter paper, and removing undissolved substance to obtain a clear dark brown solution; (3) separating by means of exclusion chromatography, wherein sephadex G-25 is taken as filler, and water is taken as a mobile phase, and separating according to time order to obtain three carbon quantum dot aqueous solutions; (4) respectively carrying out freeze drying on the three carbon quantum dot aqueous solutions to obtain three target products. The method is simple in operation technology, wide in source of raw materials, low in price of the raw materials, low in requirement for separation conditions and free from energy consumption; the obtained carbon quantum dots are stable in optical properties. The prepared phosphorus-doped fluorescent carbon quantum dots can be used for Fe<3+> ion detection, tetracycline detection and cell imaging.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Preparation method of cobalt-oxygen-oxygen-hydrogen-modified phosphorus-doped iron oxide photo-anode
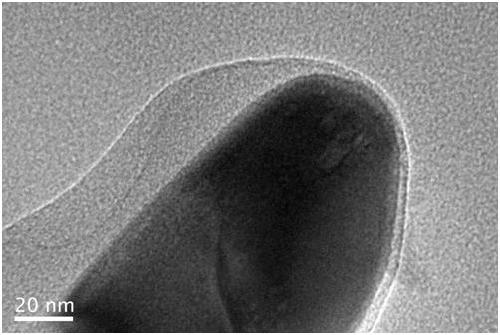
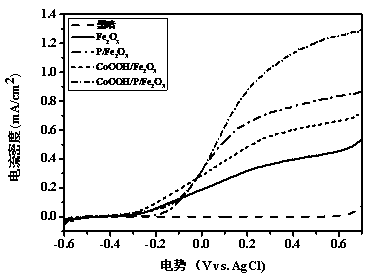
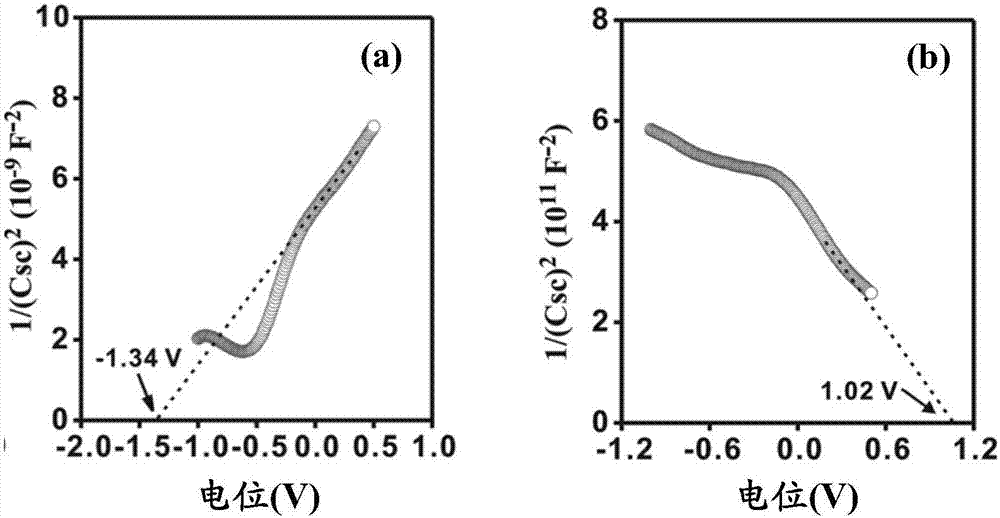
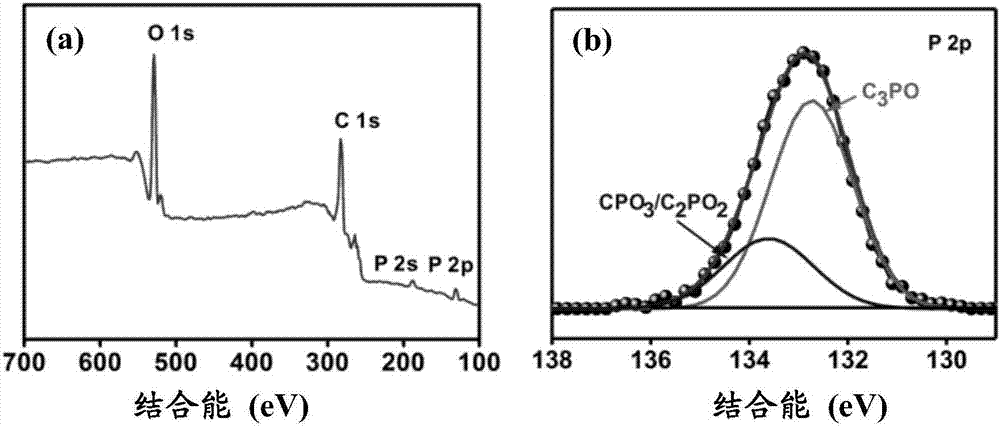
InactiveCN109504981AImprove performanceAchieve conversionSuperimposed coating processElectrodesTin dioxideNew energy
The invention relates to a preparation method of a cobalt-oxygen-oxygen-hydrogen-modified phosphorus-doped iron oxide photo-anode, and belongs to the technical field of new energy materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps that beta-FeOOH is generated on a F-doped tin oxide (FTO) conductive glass substrate through a hydrothermal method, then, the phosphorus-doped iron oxide photo-anode is generated by performing soaking in a phosphate solution and performing heat treatment, and finally, a layer of CoOOH is deposited on the surface of the phosphorus-doped iron oxide photo-anode by using a light-assisted electrodeposition method so as to obtain the cobalt-oxygen-oxygen-hydrogen-modified phosphorus-doped iron oxide photo-anode (CoOOH-P-Fe2O3). Due to phosphorus doping, the conductivity of the iron oxide photo-anode is improved; and furthermore, cobalt oxygen hydrogen is used as a catalyst for assistance in oxygen evolution, so that compared with basic iron oxide, thelight current density of the cobalt-oxygen-oxygen-hydrogen-modified phosphorus-doped iron oxide photo-anode prepared by using the method is improved by 200%.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dot-graphite phase carbon nitride p-n junction photocatalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107511161AUniform particle sizeUniform structurePhysical/chemical process catalystsWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSemiconductor materialsPhotocatalytic water splitting
The invention discloses a phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dot-graphite phase carbon nitride p-n junction photocatalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of dissolving 1,3,6-trinitropyrene and Na2HPO4.12H2O into water to obtain a mixed water solution, performing hydrothermal reaction under alkaline conditions to obtain phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dots, using Pi-Pi and hydrogen-bond interaction between the phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dots and graphite phase carbon nitride to form a stable composite material. The phosphorus-doped graphene quantum dot is a p-type semiconductor material, and forms a p-n junction composite material with n-type graphite phase carbon nitride; the p-n junction composite material has remarkably improved photogenerated charge separation rate and visible-light catalytic activity, and can be used for visible-light degradation of dye or organic pollutants as well as hydrogen production from photocatalytic water splitting.
Owner:HUAWEI TEHCHNOLOGIES CO LTD
Passivation contact solar cell with selective emitter structure and preparation method of passivation contact solar cell
InactiveCN111162145AImprove efficiencyEasy to prepareFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar battery
The invention relates to a passivation contact solar cell with a selective emitter structure and a preparation method of the passivation contact solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing texturing surfaces on two surfaces of an N-type crystalline silicon substrate; (2) performing boron diffusion treatment on the texturing surface of the front surface of the substrate to form a lightly doped region layer; (3) performing local boron ion implantation on the lightly doped region layer by using a mask, and annealing to form a local heavily doped region; (4) preparing a tunneling oxide layer on the texturing surface of the back surface of the substrate, and preparing a phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon layer on the tunneling oxide layer; (5) preparing a silicon nitride antireflection layer on the phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon layer; preparing an aluminum oxide passivation layer on the lightly doped region layer on the front surface of the substrate, and preparing a silicon nitride antireflection layer on the aluminum oxide passivation layer; and (6) carrying out silk-screen printing of metallized slurry on the two surfaces of the substrate, andsintering. According to the invention, the composite current on the surface of the emitter can be remarkably reduced, so that the efficiency of the N-type passivation contact battery can be improvedby more than 0.2%.
Owner:TAIZHOU ZHONGLAI PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
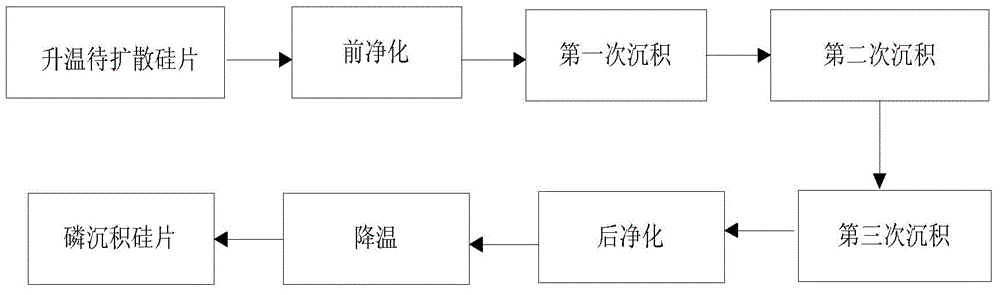
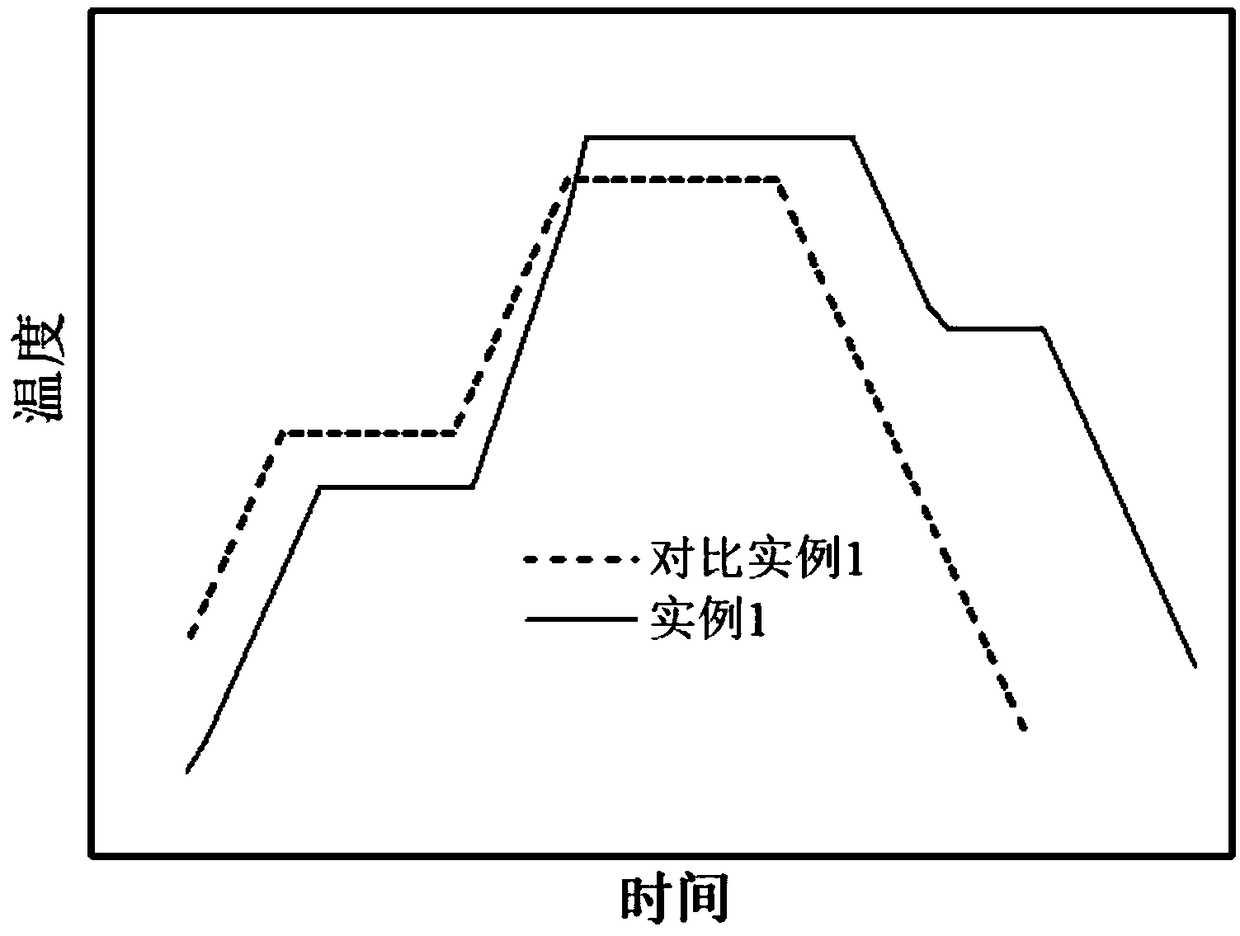
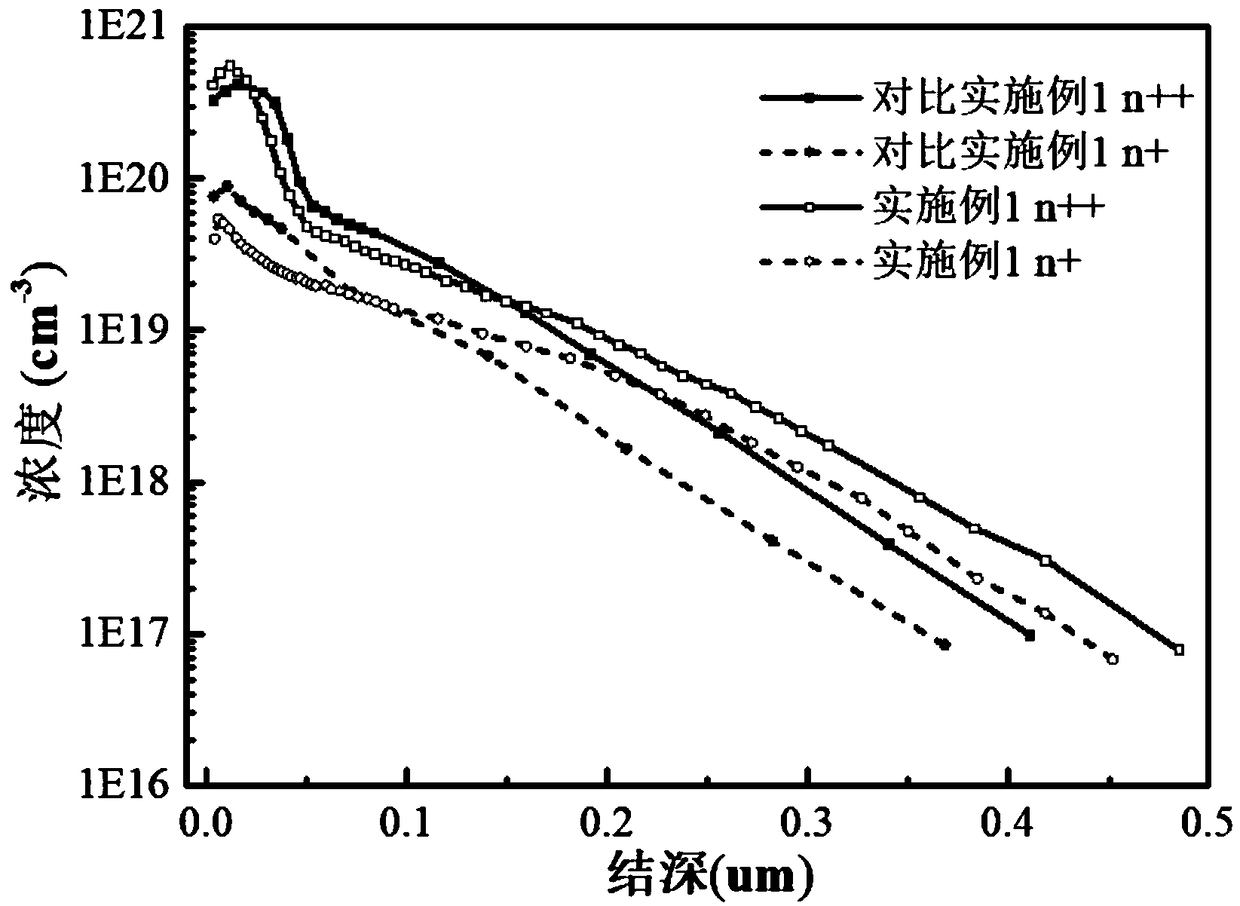
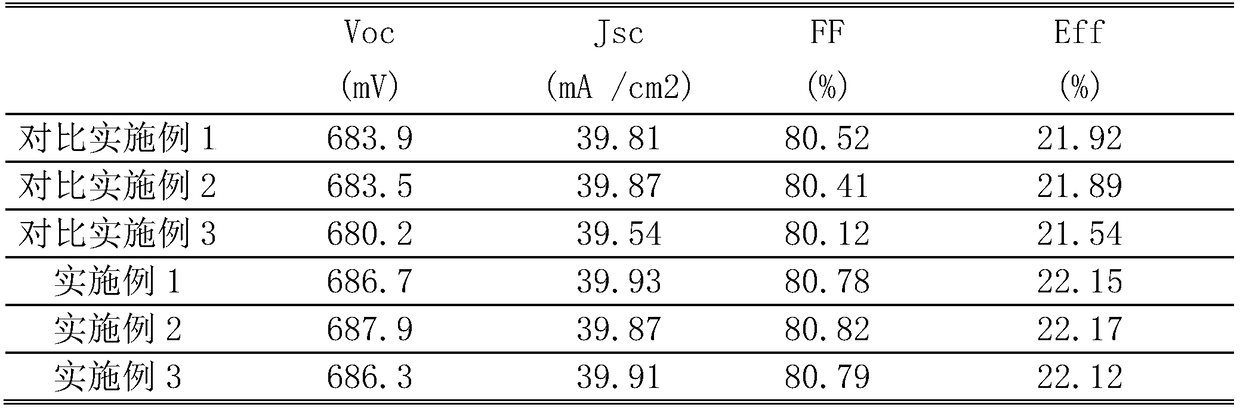
A step-by-step phosphorus doping method for high-efficiency and low-cost crystalline silicon batteries
ActiveCN109166794AIncrease the open circuit voltageReduce concentrationFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh concentrationHigh surface
The invention belongs to the technical field of solar cell manufacturing, and relates to a step-by-step phosphorus doping method of a high-efficiency and low-cost crystal silicon cell, namely a primary depletion diffusion combined with secondary high-concentration shallow layer diffusion and back etching method. By controlling the flow of oxygen, A low-temperature low-phosphorus source depositionis carry out for that first time on a p-type silicon substrate by nitrogen flow rate and phosphorus oxychloride flow rate, After a long time of high temperature propulsion, the phosphorus in the phosphor-silicate glass is exhausted, and the low surface concentration layer n + is realized. The second time, the phosphor-free glass is deposited on the phosphor-silicate glass, and the high surface concentration layer n + + is pushed to form a very thin high concentration layer, which can be quickly etched off by means of back etching. The method can accurately control the phosphorus doping distribution in different regions independently to ensure that the non-electrode region has low doping concentration and low recombination current so as to ensure higher open-circuit voltage. The electrode region has high doping concentration, which forms good ohmic contact with the metal electrode and ensures that the filling factor is not lost, so as to improve the photoelectric conversion performanceof the battery as a whole.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV +1
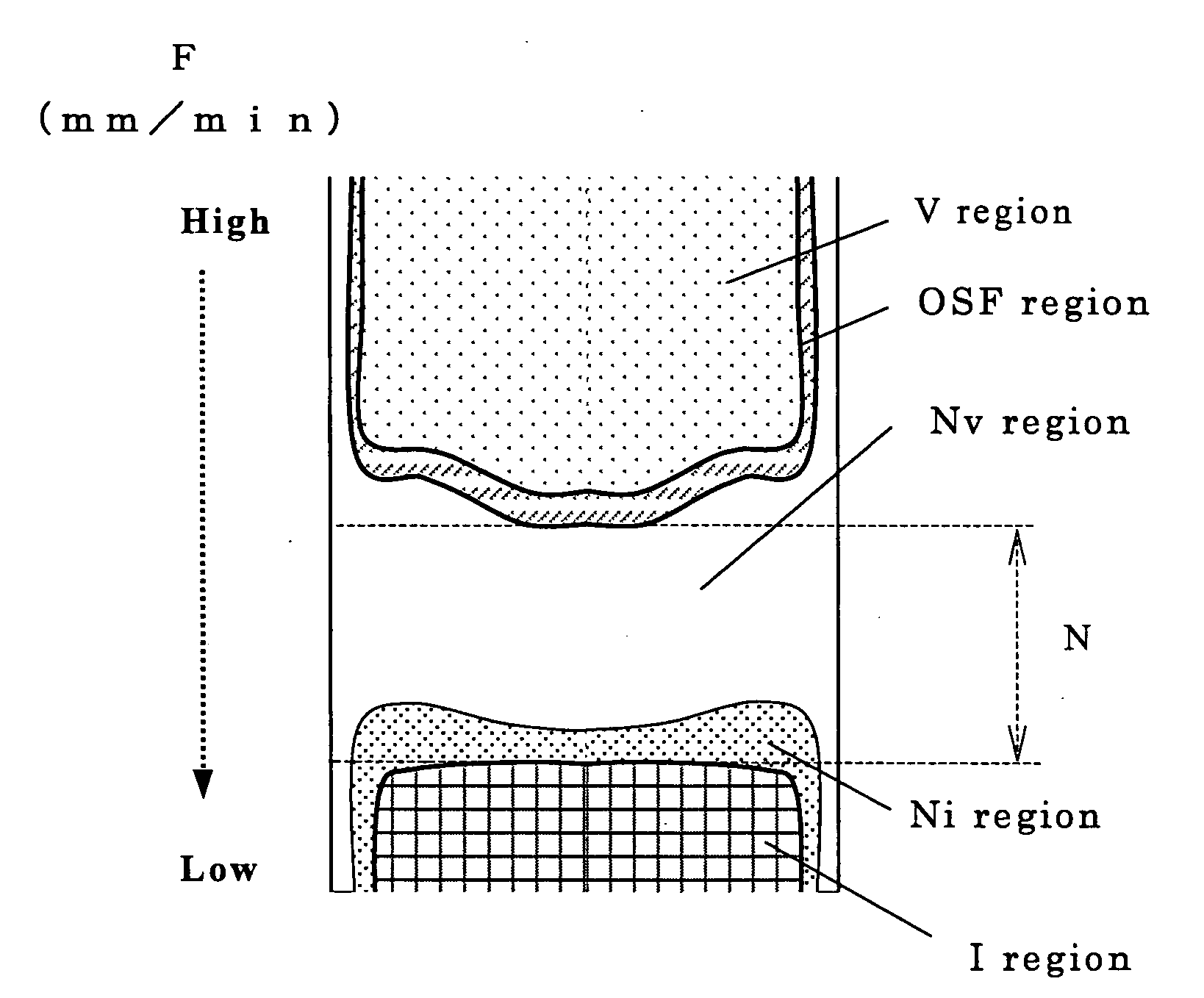
Process for producing p doped silicon single crystal and p doped n type silicon single crystal wafer
ActiveUS20060065184A1Easy and inexpensive to produceExcellent electrical propertiesPolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCzochralski methodSingle crystal
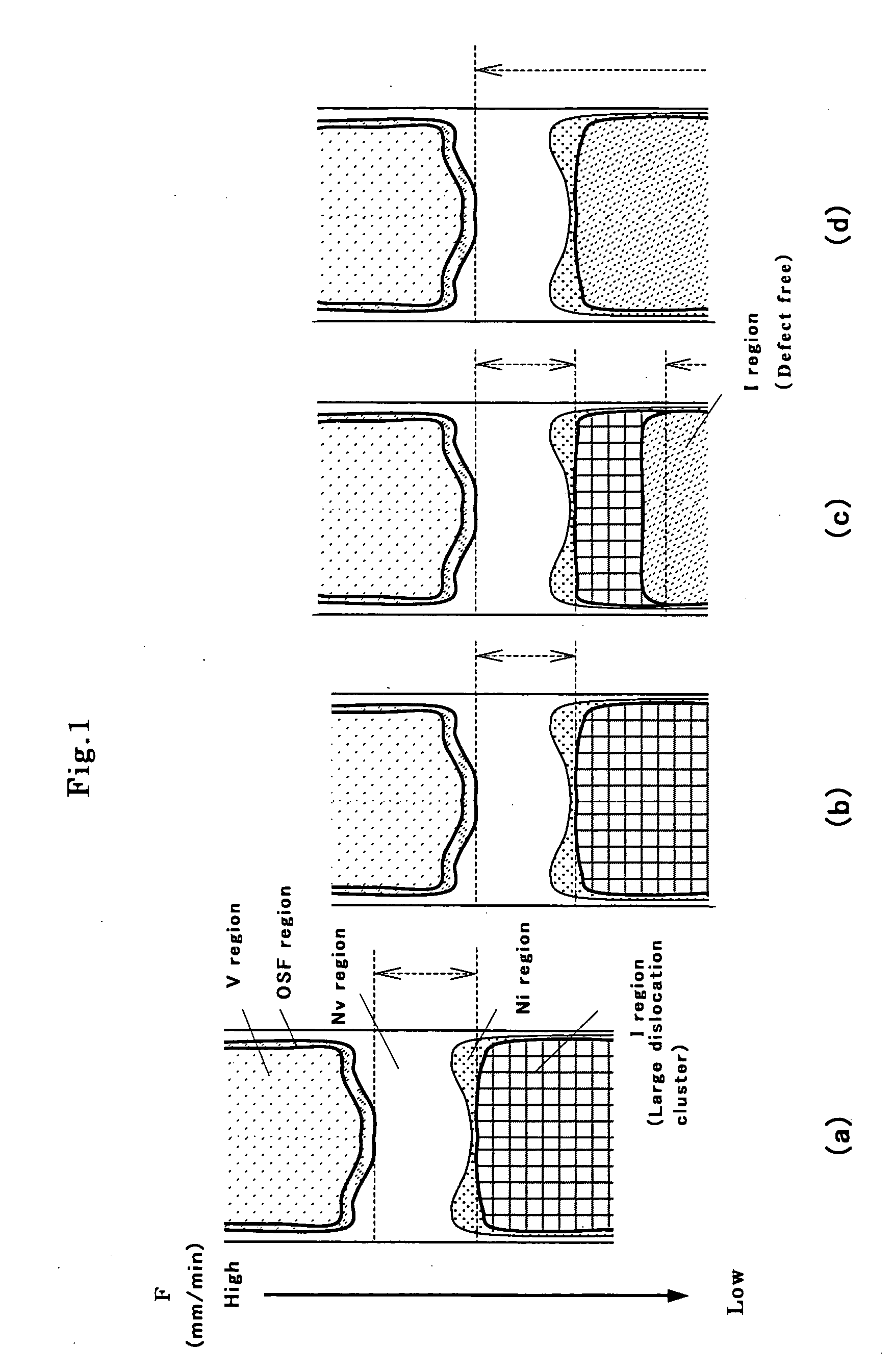
The present invention is a method of producing a P(phosphorus)-doped silicon single crystal by Czochralski method, wherein, at least, a growth of the single crystal is performed so that an Al (aluminum) concentration is 2×1012 atoms / cc or more. Thereby, there can be provided a method of easily and inexpensively producing a P(phosphorus)-doped silicon single crystal of defect-free region having an excellent capability of electrical characteristics to be high breakdown voltage, which contains neither, for example, V region, OSF region, nor large dislocation cluster (LSEPD, LFPD) region.
Owner:SHIN-ETSU HANDOTAI CO LTD
Prediction method of phase-transition temperature of VO2 materials in properties modified by nitrogen and phosphorus doping
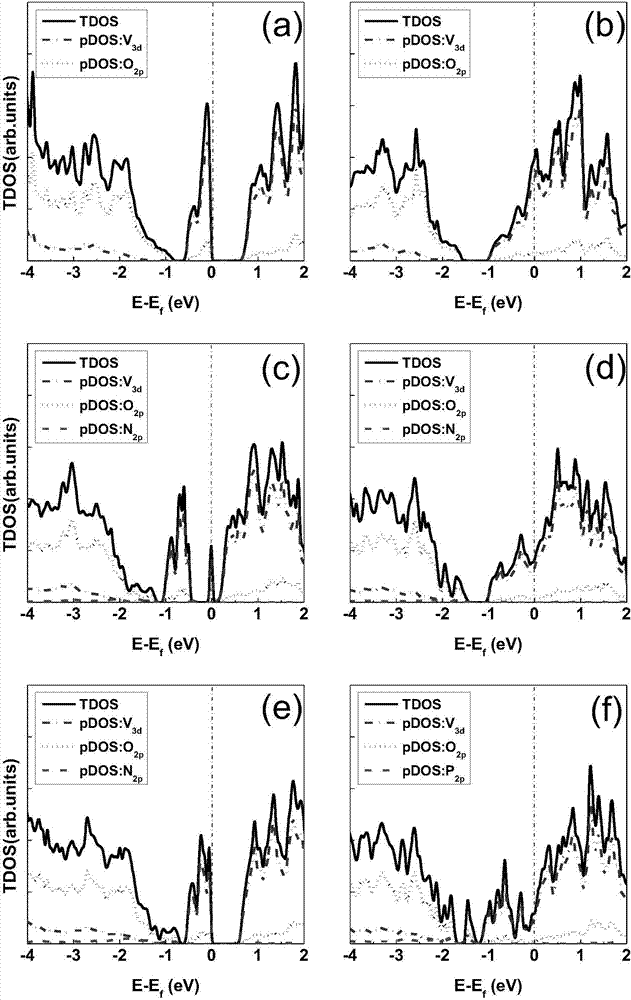
InactiveCN107133449AQuick calculationThe result is accurateMolecular entity identificationComputational theoretical chemistryNitrogenState density
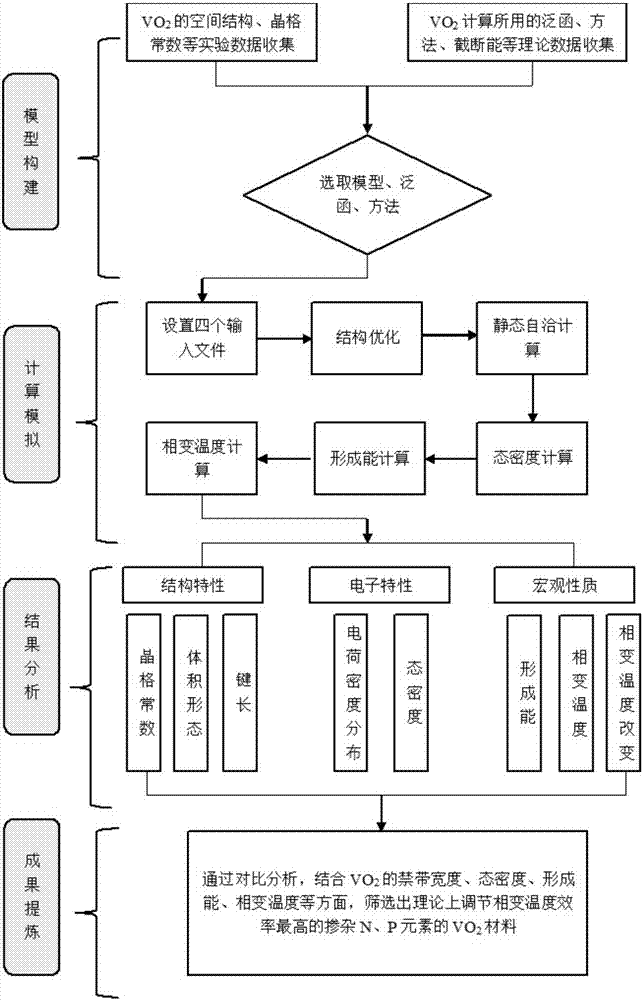
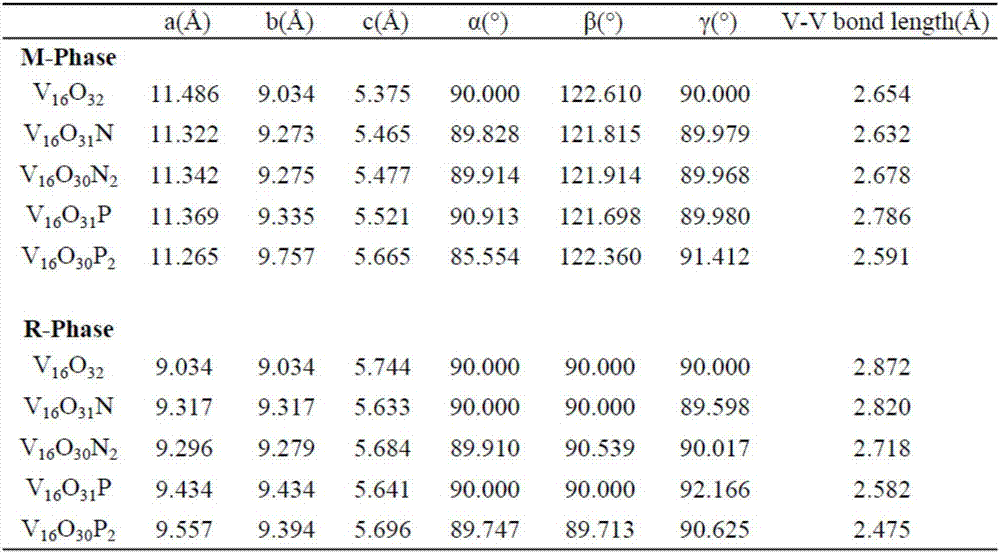
The invention discloses a prediction method of phase-transition temperature of VO2 materials in properties modified by nitrogen and phosphorus doping. The method comprises the steps of firstly, selecting nitrogen and phosphorus to mingle with VO2 materials and forming multiple VO2 element discrepancy models mingled with elements in different types and out-phase; secondly, by using optimization simulation software to conduct structural optimization on the VO2 element discrepancy models, obtaining the types of optimized doping elements according to formation energy of VO2 models of different elemental doping; thirdly, choosing different adulteration proportions of nitrogen and phosphorus in VO2 materials to form multiple VO2 proportion discrepancy models in different adulteration proportions; fourthly, by using optimization simulation software to conduct structural optimization on the VO2 proportion discrepancy models, forming variables by which phase-transition temperature can be calculated and combined with the state density map according to the formation energy of the VO2 element discrepancy models and the VO2 proportion discrepancy models, then obtaining an proportion of the optimized doping elements. The prediction method of phase-transition temperature of VO2 materials in properties modified by nitrogen and phosphorus doping has the advantages of providing fast calculation and accurate results, certifying and analyzing test results, and offering theoretical directions for selection and proportion of VO2 doping elements.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Method for realizing electron local passivation contact, and crystalline silicon solar cell and preparation method thereof
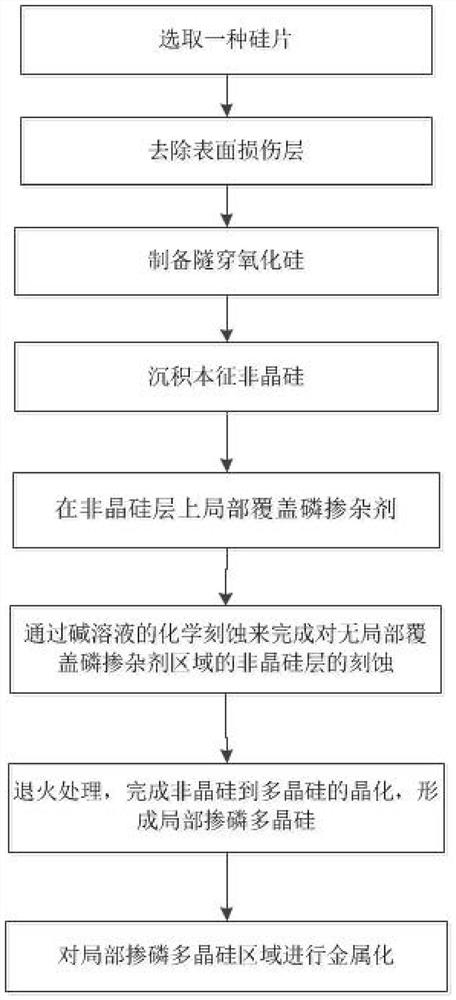
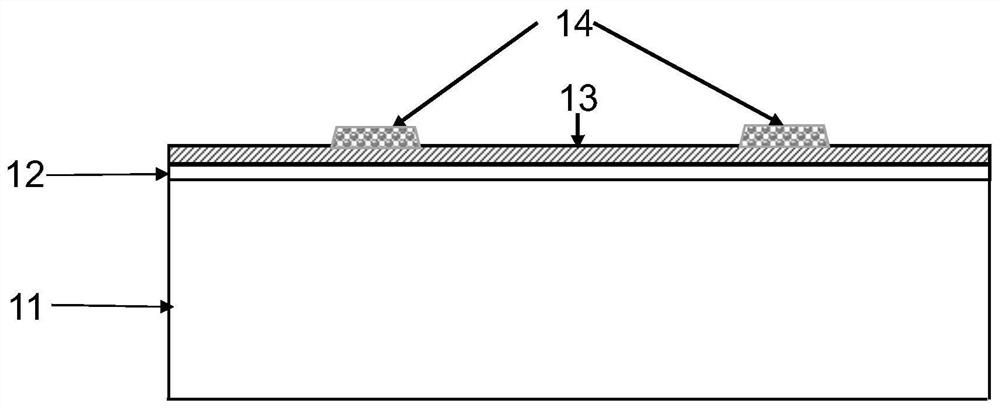
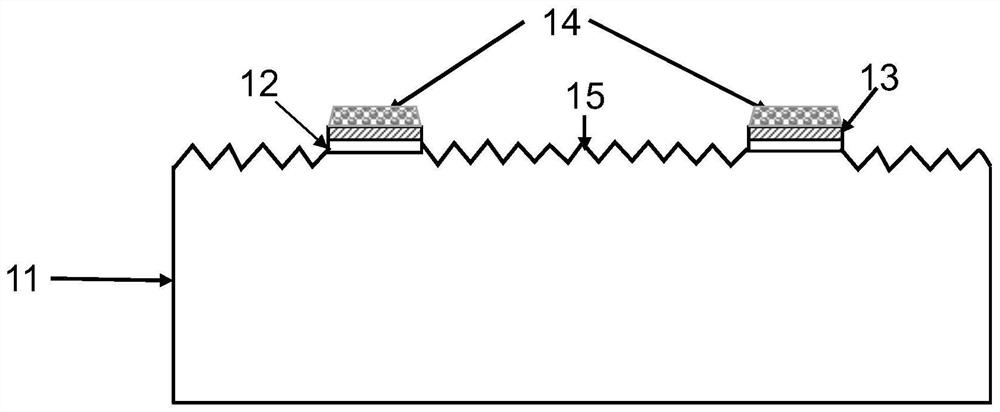
ActiveCN111628050ASimple processLow costFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon solar cellSilicon oxide
The invention discloses a method for realizing electron local passivation contact. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, preparing a tunneling silicon oxide layer and an amorphous siliconlayer on a crystalline silicon substrate of which a damage layer is removed; then locally covering the amorphous silicon thin film with a phosphorus doping agent; etching off an amorphous silicon thin film layer which does not partially cover a phosphorus dopant region through an alkaline solution, fully crystallizing amorphous silicon into polycrystalline silicon through annealing, activating aphosphorus dopant and finishing redistribution of the phosphorus dopant in the polycrystalline silicon thin film, and finally preparing a metallized layer on the partially phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon thin film. Furthermore, the invention also discloses a crystalline silicon solar cell with the electron local passivation contact structure and a corresponding cell preparation method. The method disclosed by the invention is simple in process and relatively low in cost, and has good industrial potential; and the cell provided by the invention is good in front optical performance andlow in metallization recombination, and can obtain higher photon-generated carrier collection probability and less photon-generated carrier transmission loss.
Owner:CHANGZHOU SHICHUANG ENERGY CO LTD
Solar cell and preparation method thereof
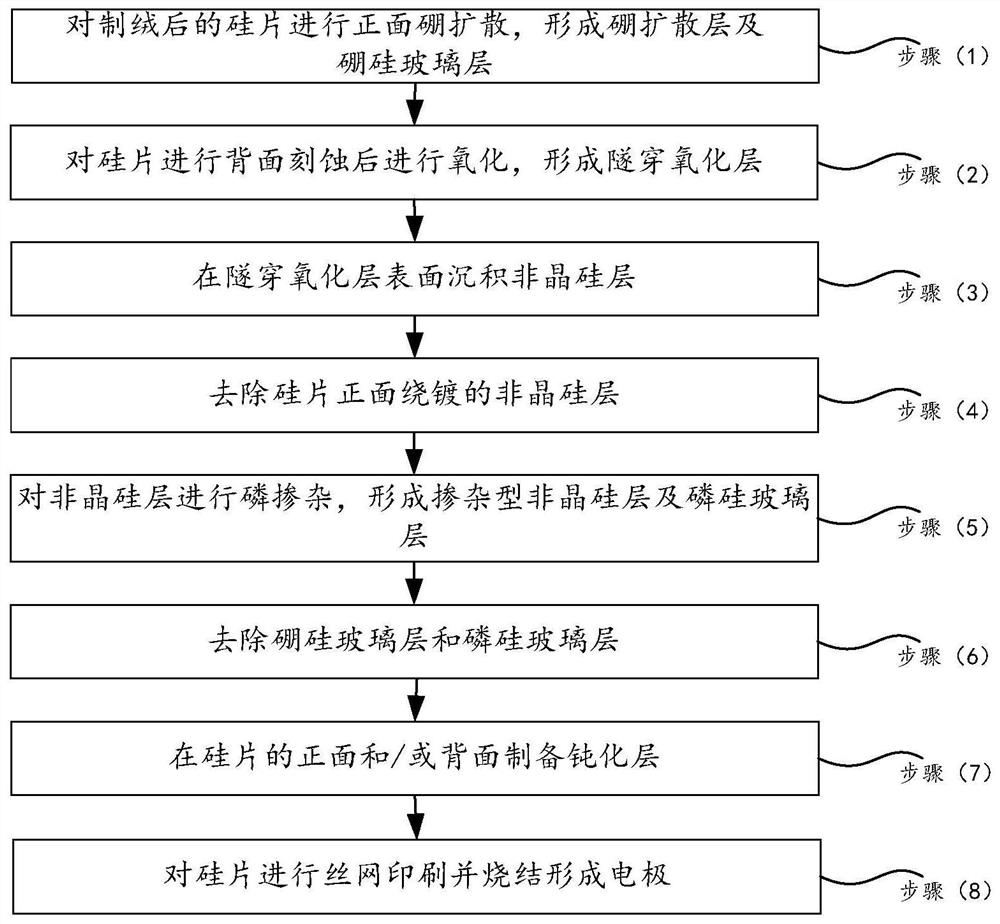
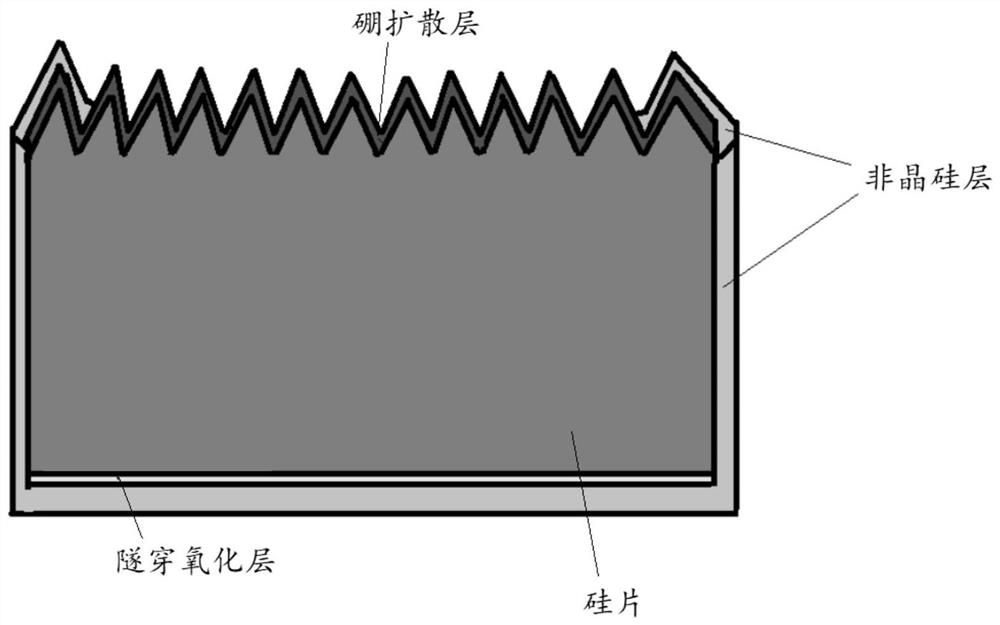
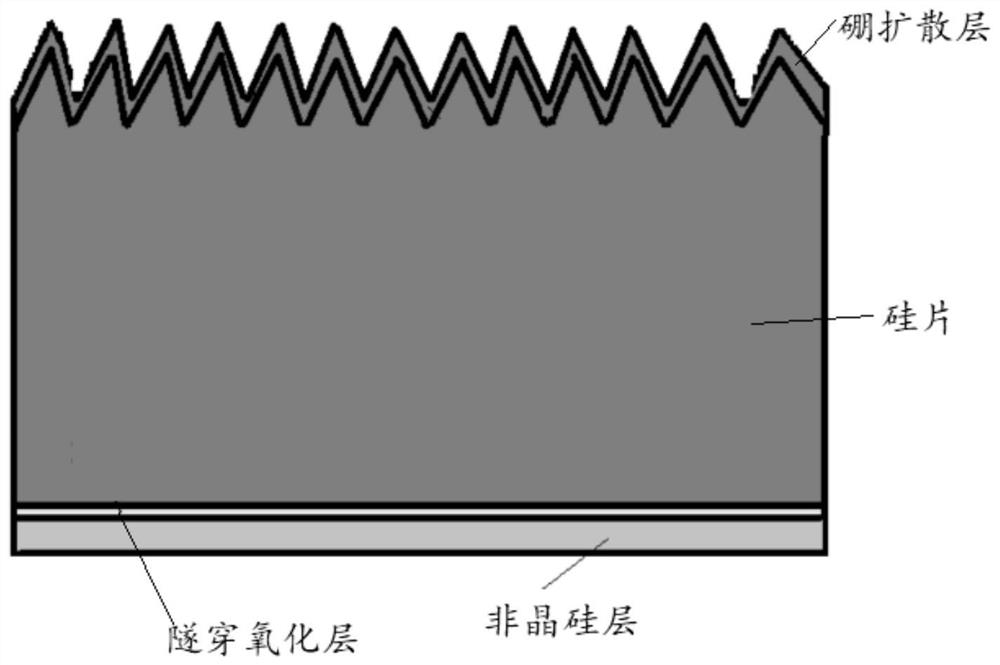
PendingCN111668345AGood removal effectTo achieve the purpose of dewinding and plating without overcutFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSolar cellMaterials science
The invention relates to the photovoltaic field and provides a solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out the front boron diffusion of a textured silicon wafer, and forming a boron diffusion layer and borosilicate glass; (2) etching the back surface of the silicon wafer and then oxidizing to form a tunneling oxide layer; (3) depositing an amorphous silicon layer on the surface of the tunneling oxide layer; (4) removing the amorphous silicon layer wound and plated on the front surface of the silicon wafer; (5) performing phosphorus doping on the amorphous silicon layer to form a doped amorphous silicon layer and a phosphorosilicate glass layer; and (6) removing the borosilicate glass layer and the phosphorosilicate glass layer. According to the solar cell and the preparation method thereof, the over-etching phenomenon generated by winding-plating removing treatment can be effectively reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINKO SOLAR CO LTD +1
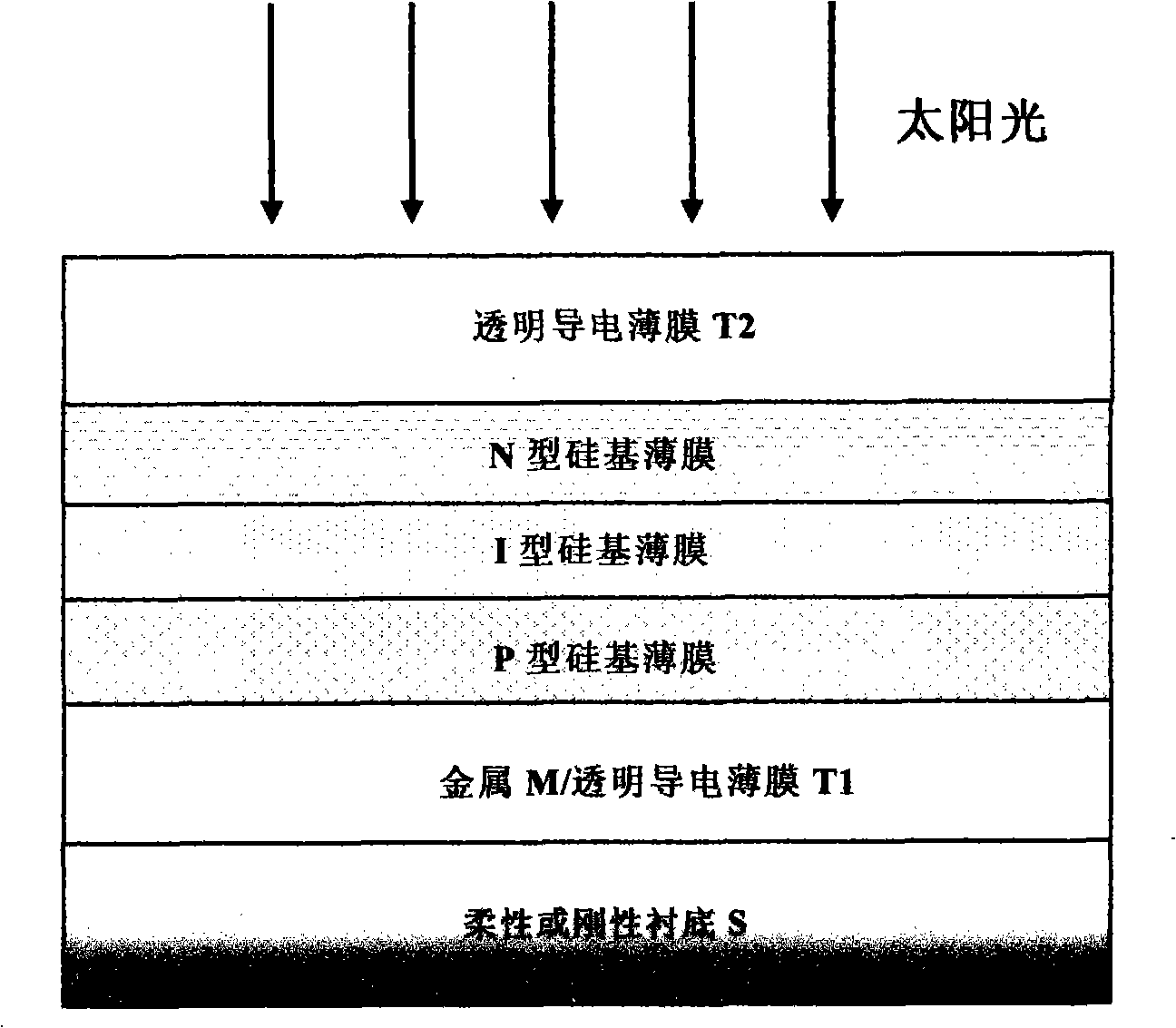
Window material for silicon based thin film solar battery and preparing method thereof
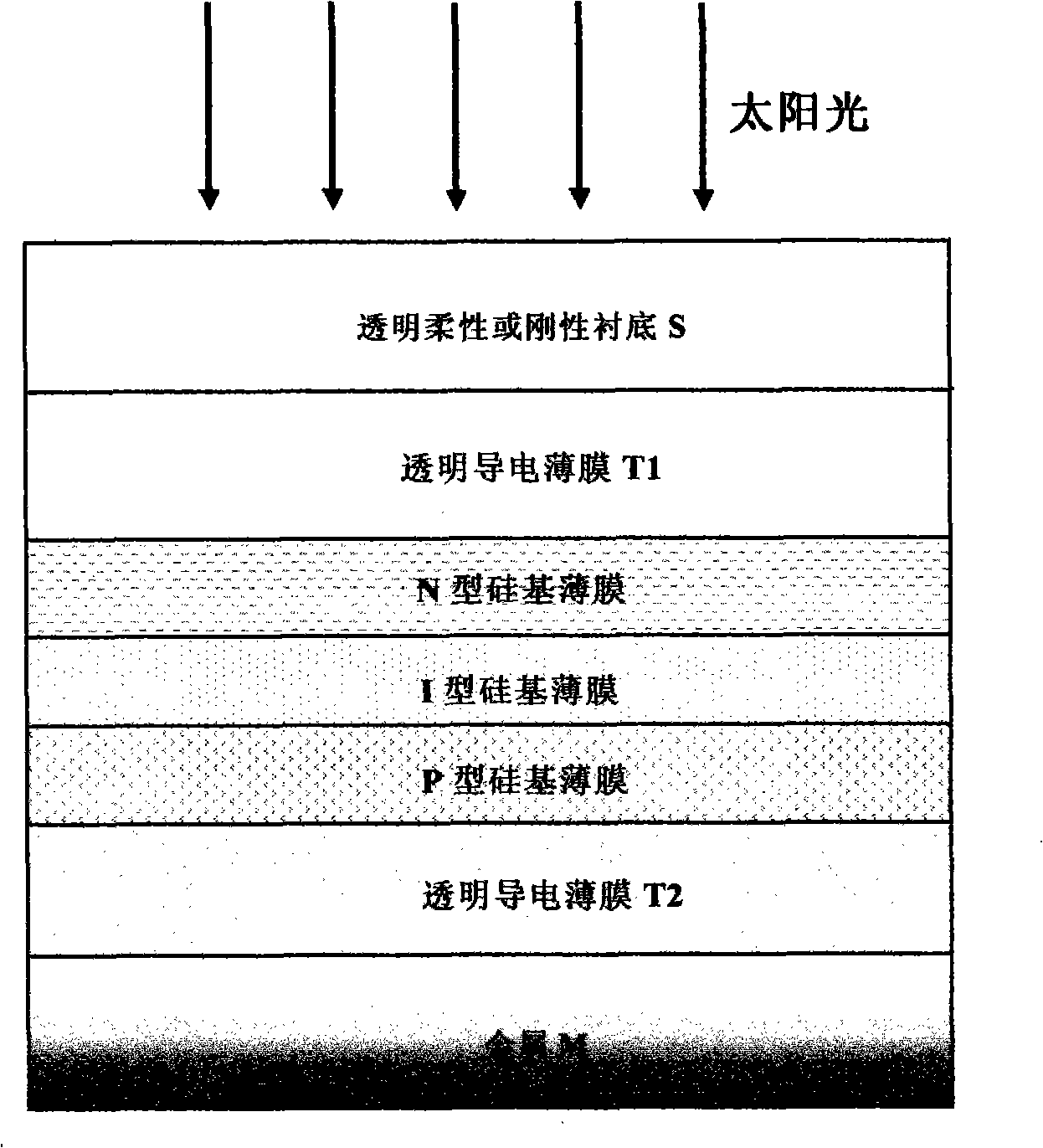
ActiveCN101257052AEasy transferIncreased processing flexibilityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSolar batteryPhosphorus doped
The present invention discloses windows material for silicone base thin film solar battery and manufacture method thereof. The windows material is phosphorus with silicone base thin film N, which includes phosphorus with N type micro crystal silica thin film, or phosphorus with N type nano silica. The preparing of the windows material is that put the sample to be processed in the deposition system, the deposition is taken as the phosphorus doped silicon base thin film N of the windows material for silicone base thin film solar cell on the intrinsic silicone base thin film I of the sample to be processed or the transparent conductive film T1. The present invention provides a windows layer material for the novel silicone base thin film solar cell novel silicone base thin film solar cell uses micro crystal silicone base or nano silicone base thin film material electric and hole mobility with the characteristic of same magnitude, provides a windows layer material for a novel silicone base thin film solar cell, producing the P / I / N type thin film solar cell on non-transparent or transparent substrate, can also produce N / I / P type thin film solar cell on the transparent substrate, the technique boost flexibly and obtain good battery efficiency more easily.
Owner:DONGJUN NEW ENERGY CO LTD
Preparation method of nitrogen-phosphorus co-doped carbon nanotube coated ferrocobalt bimetallic alloy in-situ electrode
The invention discloses an in-situ composite electrode of a nitrogen-phosphorus co-doped carbon nanotube coated ferrocobalt bimetallic alloy catalyst and preparation method thereof, and application ofin-situ composite electrode. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing an in-situ flaky MOF precursor on a carbon paper substrate; dipping the carbon paper on which the MOF precursor grows into a ferrous sulfate solution, and obtaining iron-containing MOF in the cation exchange process of the aqueous solution; after drying, putting the iron-containing MOF into a reactionkettle containing a phosphorus source, and performing heating to achieve gas-phase phosphorus doping; and in Ar gas flow or N2 gas flow, discharging urea for annealing and in-situ preparation of the carbon nanotubes. The product obtained by the technical scheme provided by the invention constructs a variety of high electrocatalytic active sites, and includes metal particles coated at the top end of a carbon nanotube and nitrogen-phosphorus co-doped carbon active sites. The in-situ composite electrode provided by the invention has the excellent and stable three-function catalytic activity of HER, OER and ORR.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com