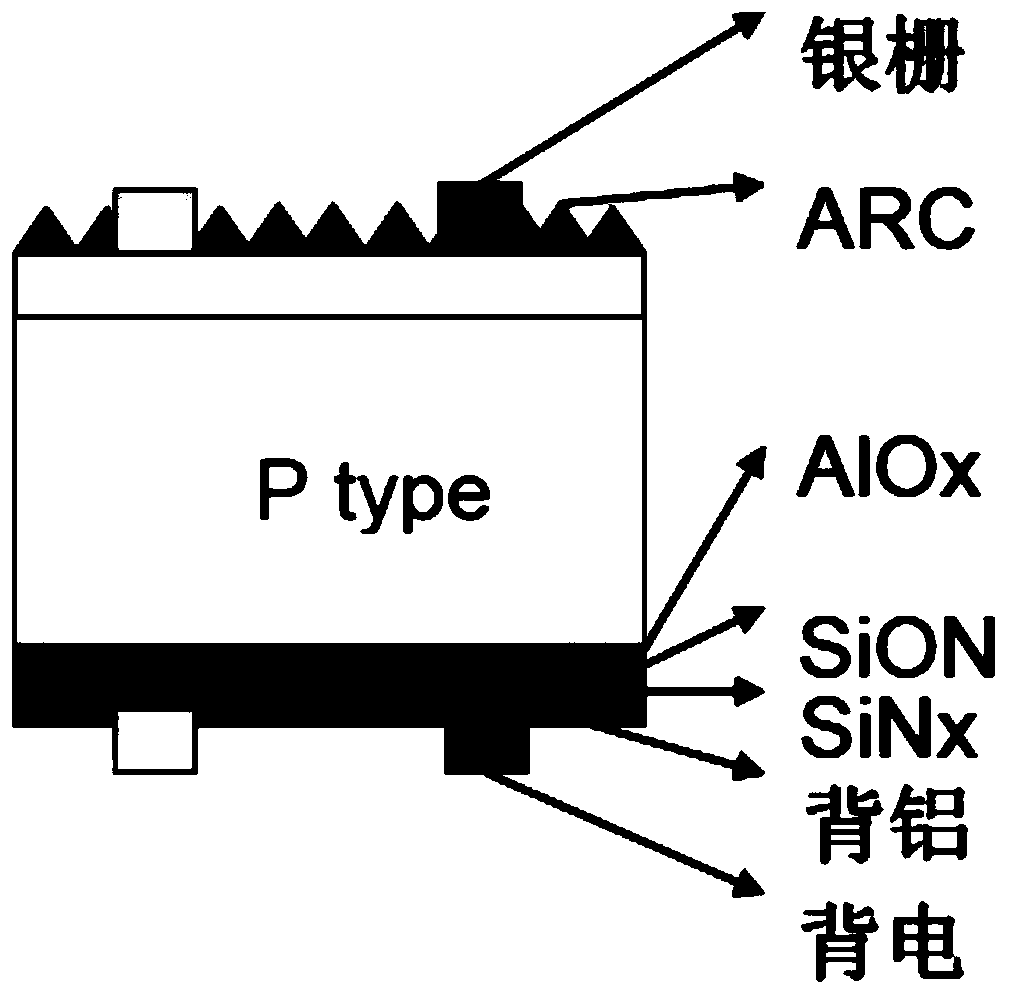
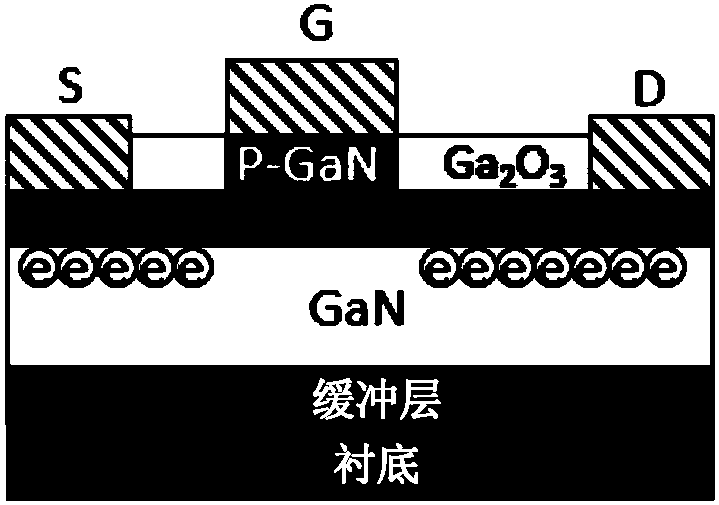
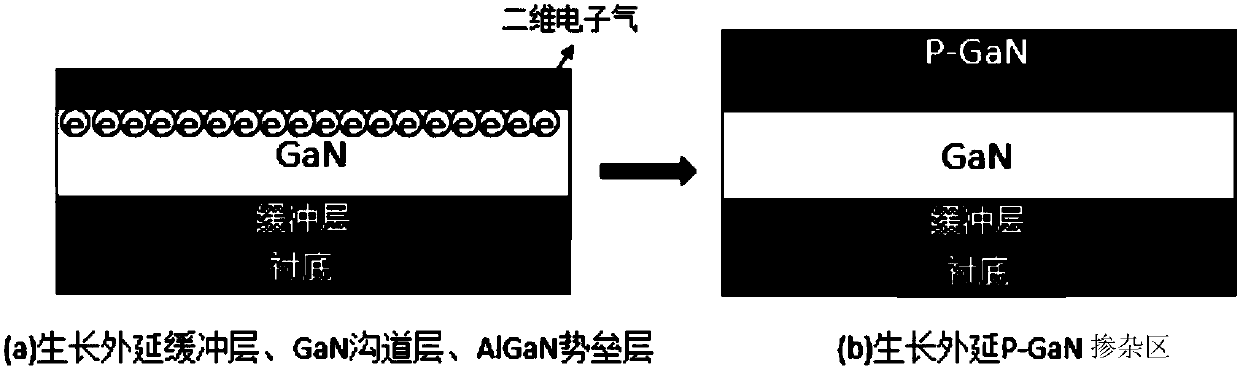
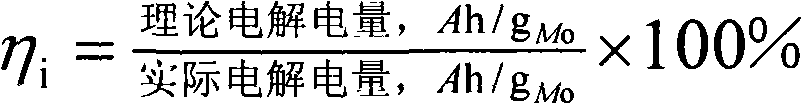Patents
Literature
102 results about "Oxide passivation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oxide passivation. Passivation of a semiconductor surface by producing a layer of an insulating oxide on the surface.
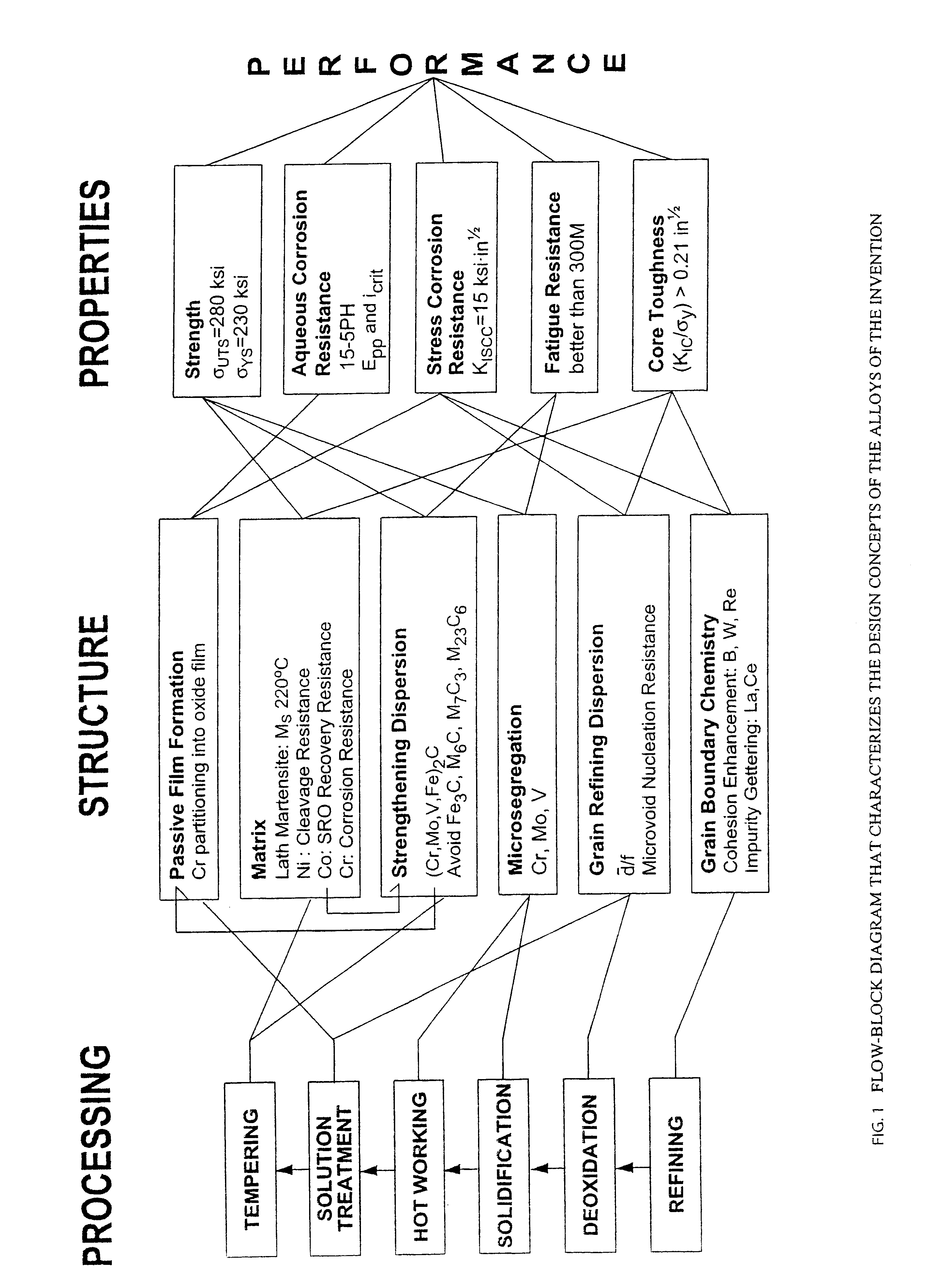
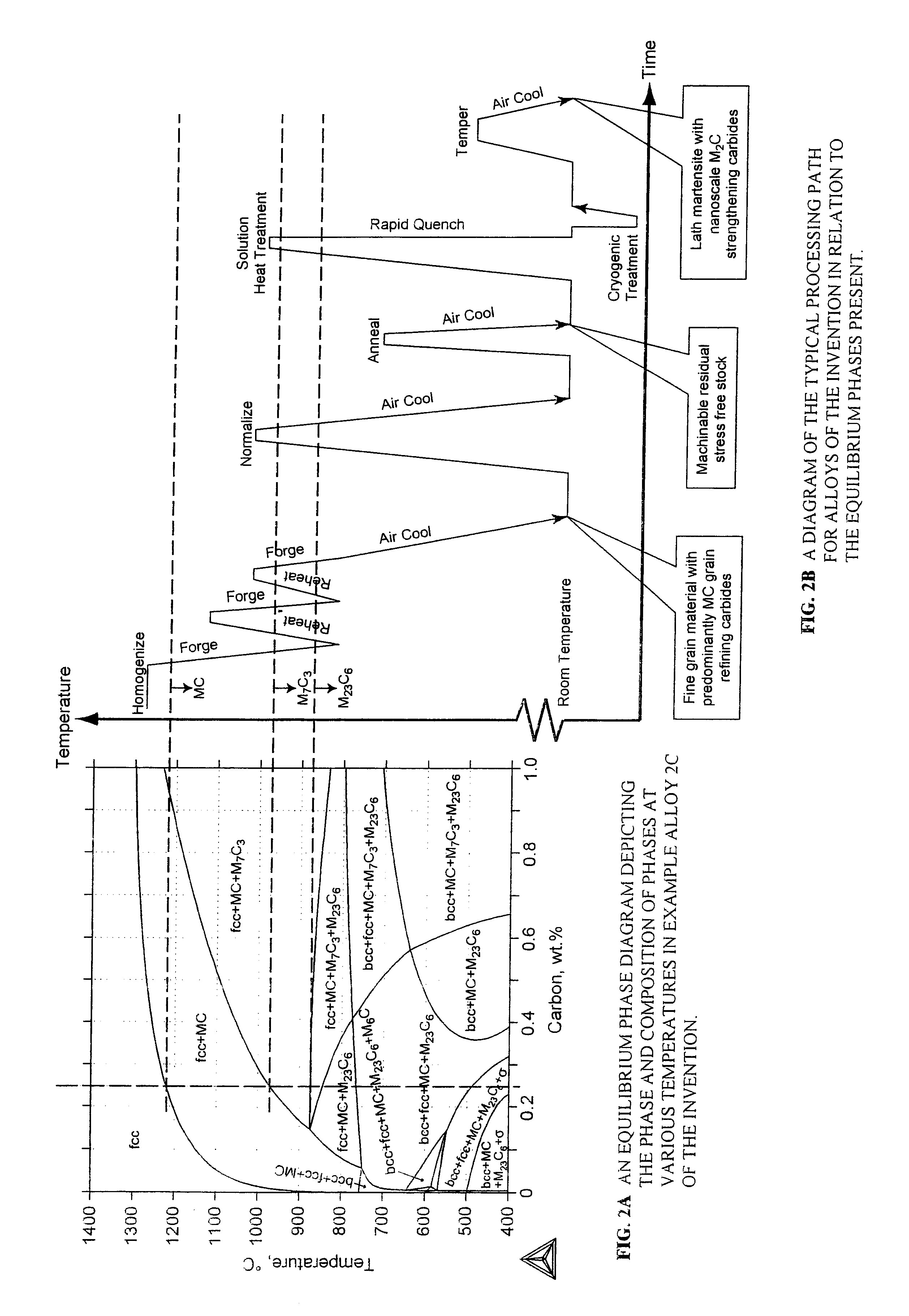
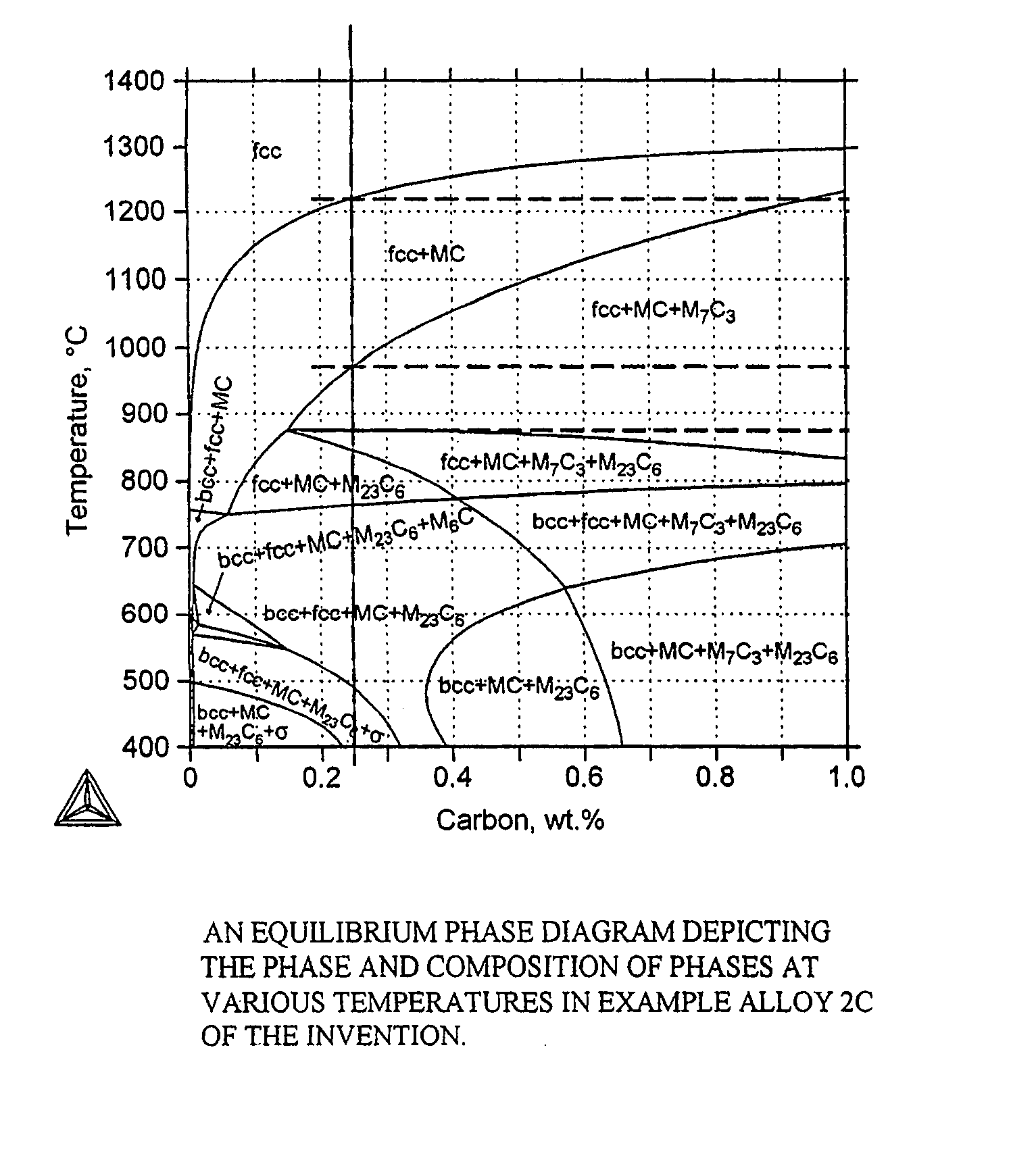
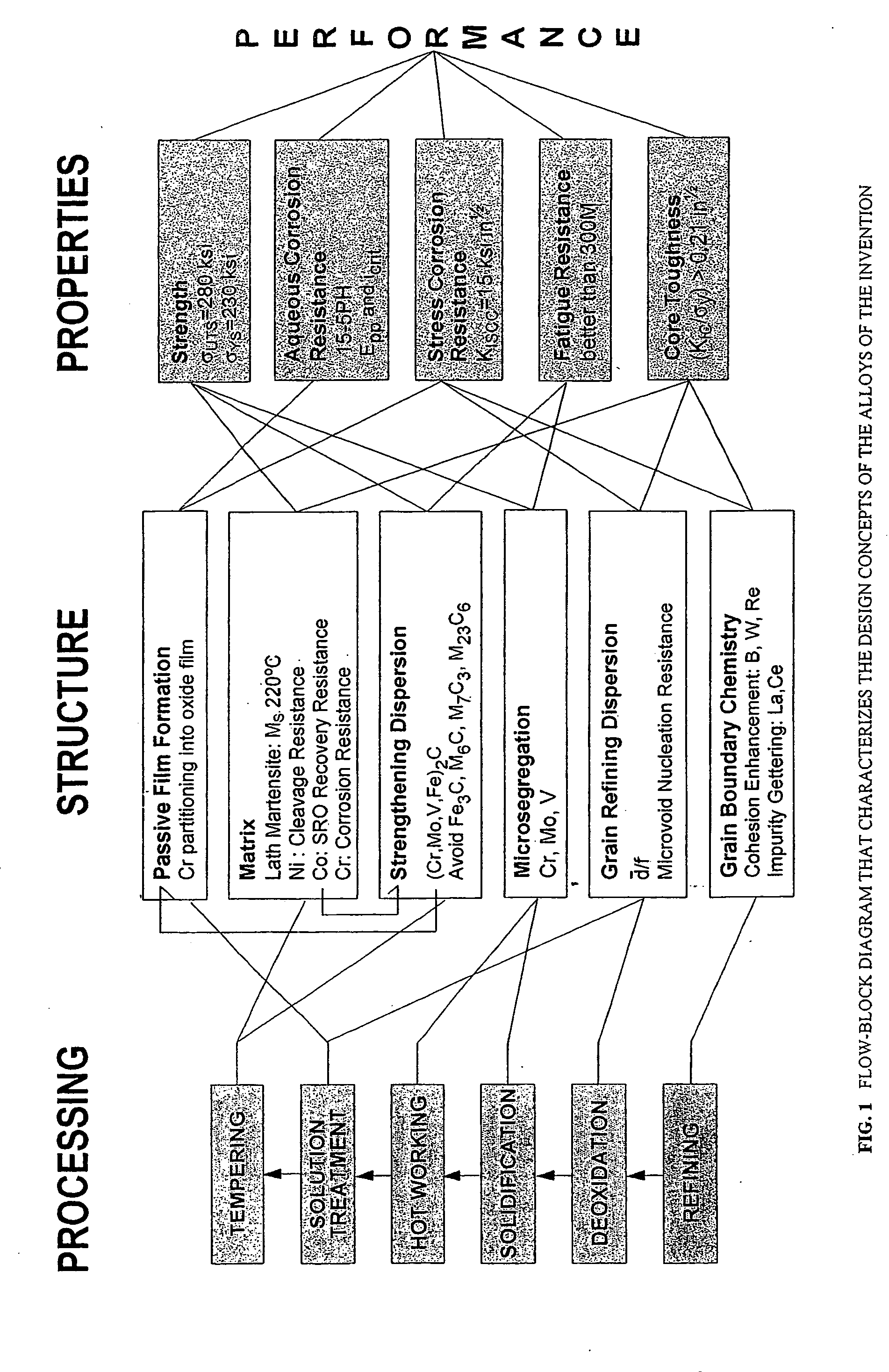
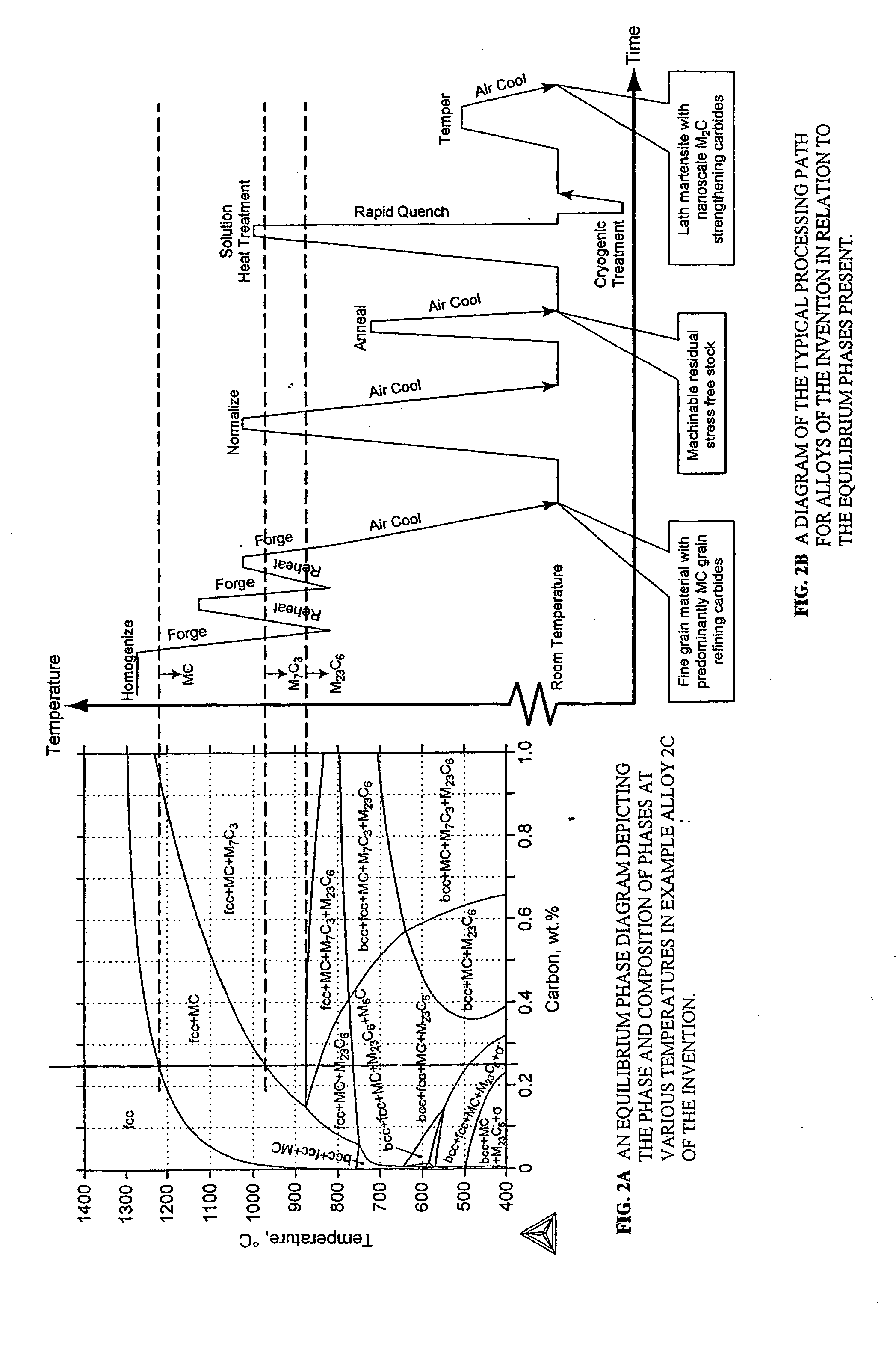
Nanocarbide precipitation strengthened ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steels
InactiveUS7160399B2Simple working processHigh strengthFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCobaltMaterials science
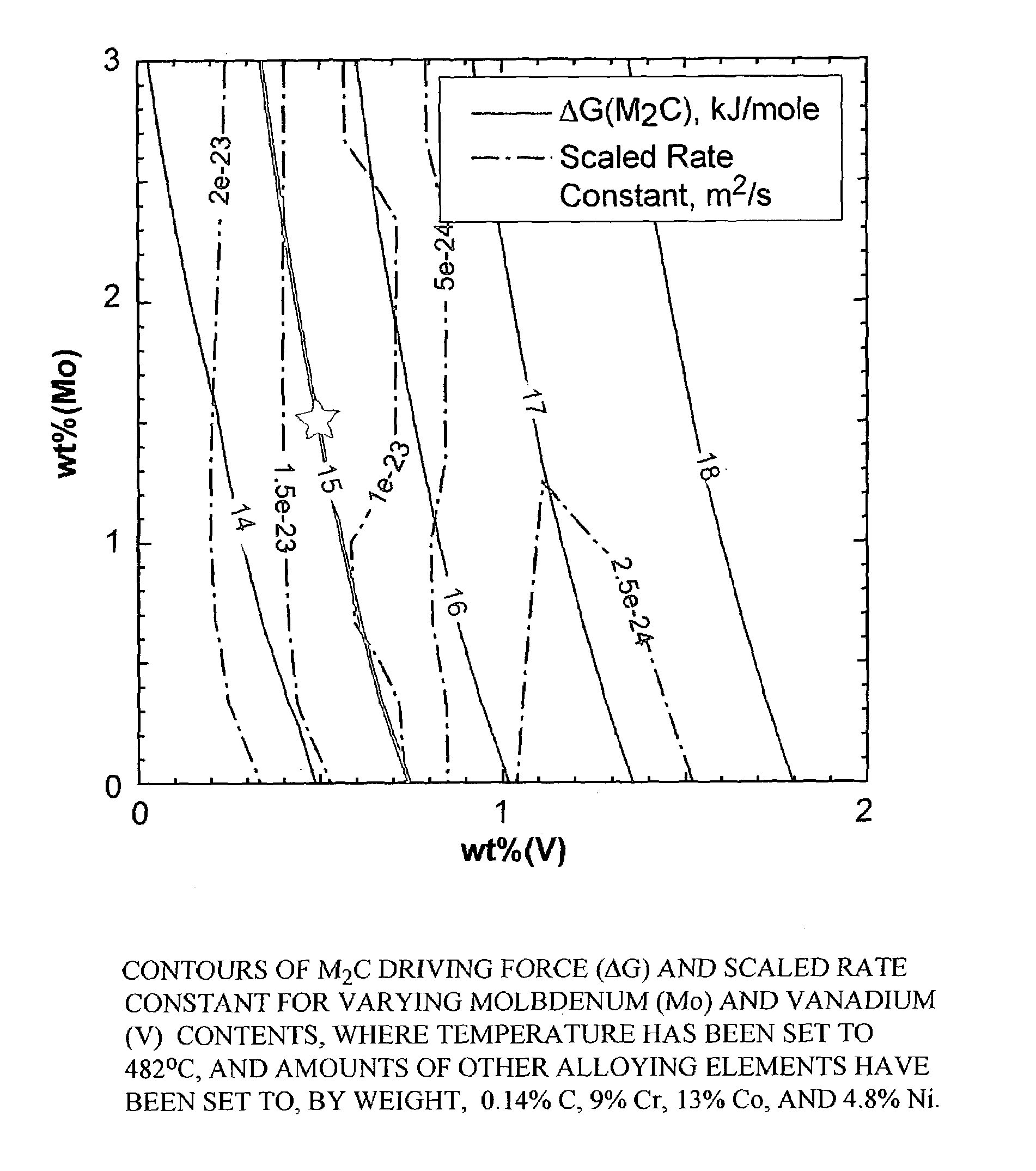
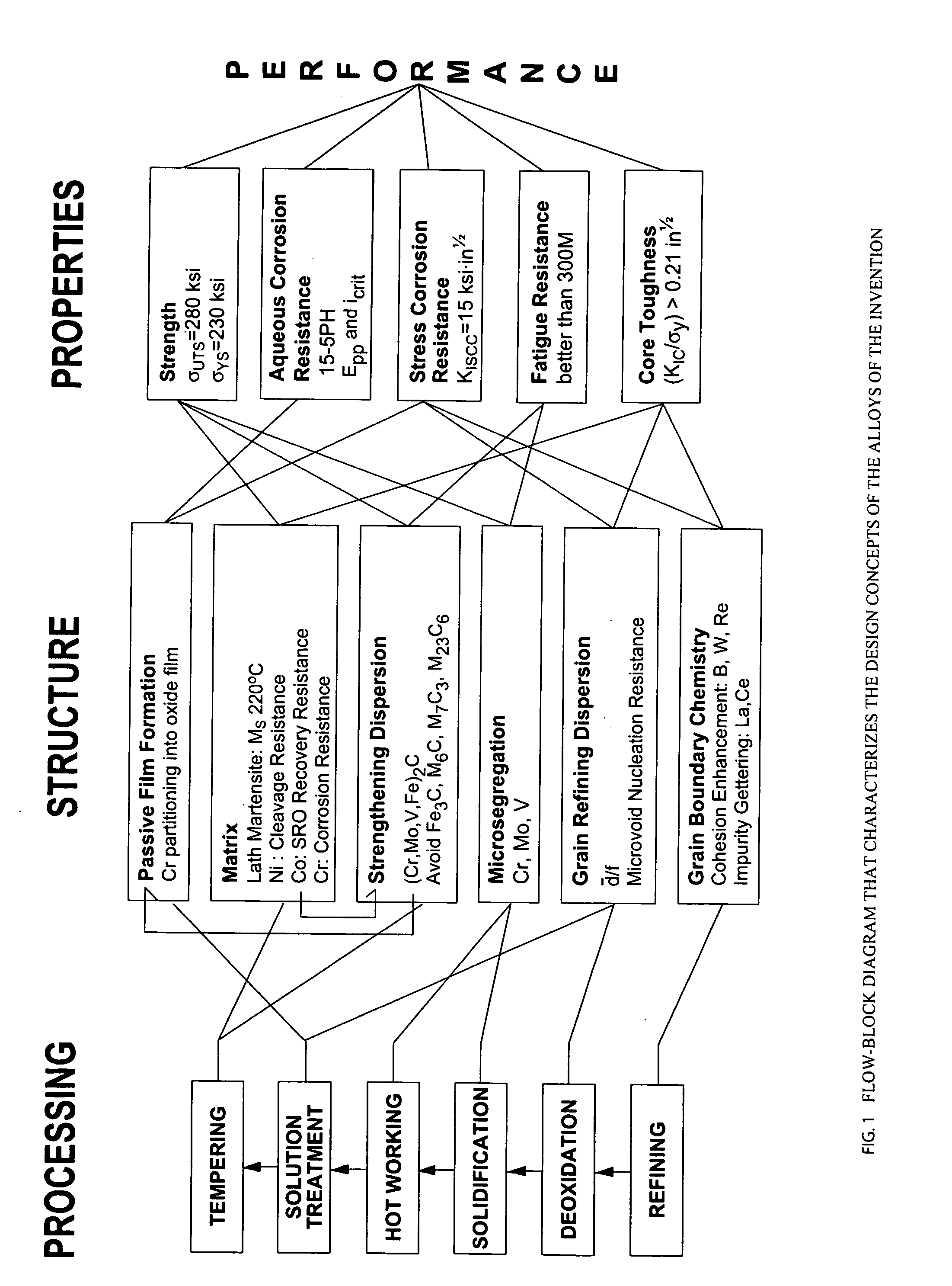
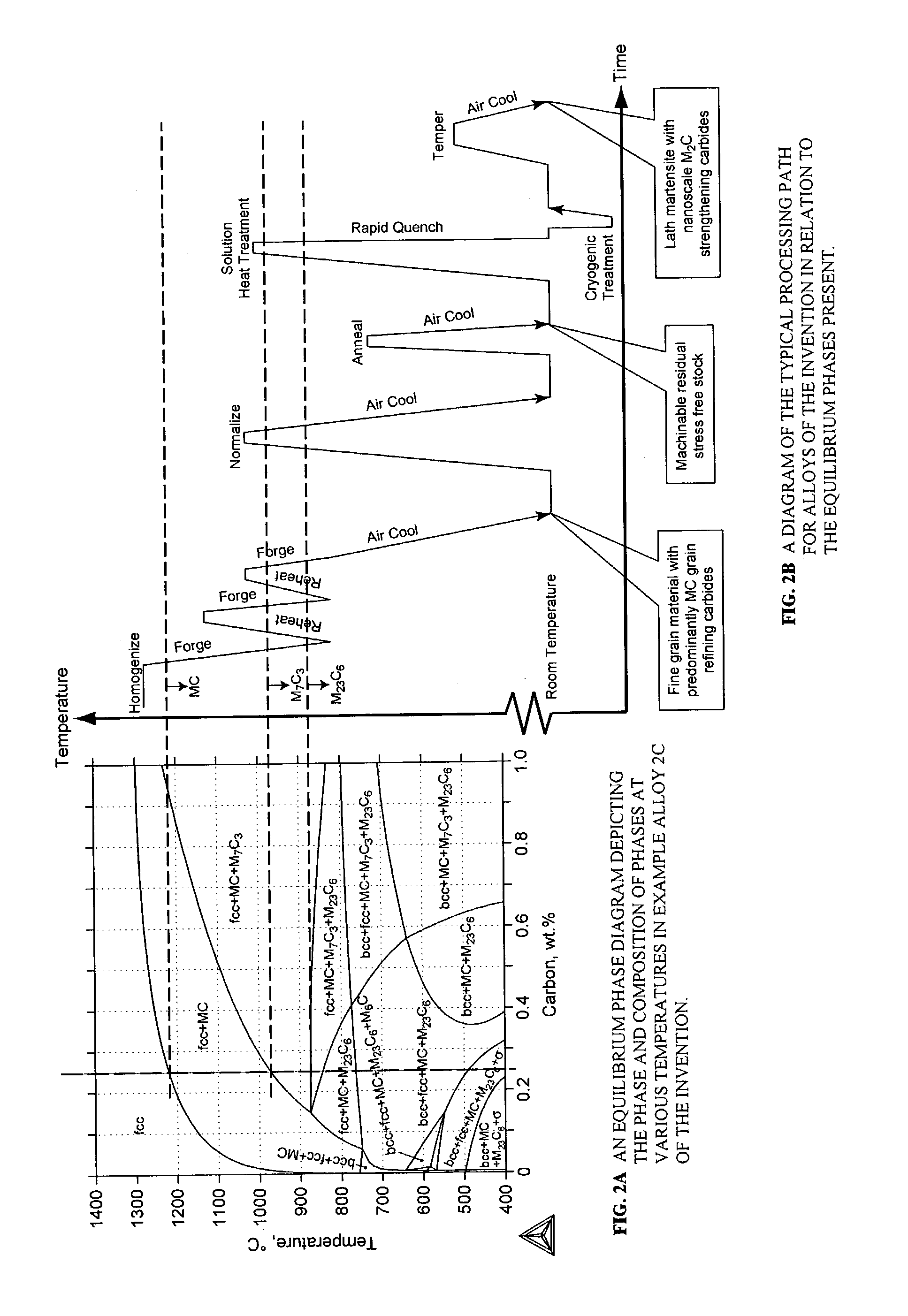
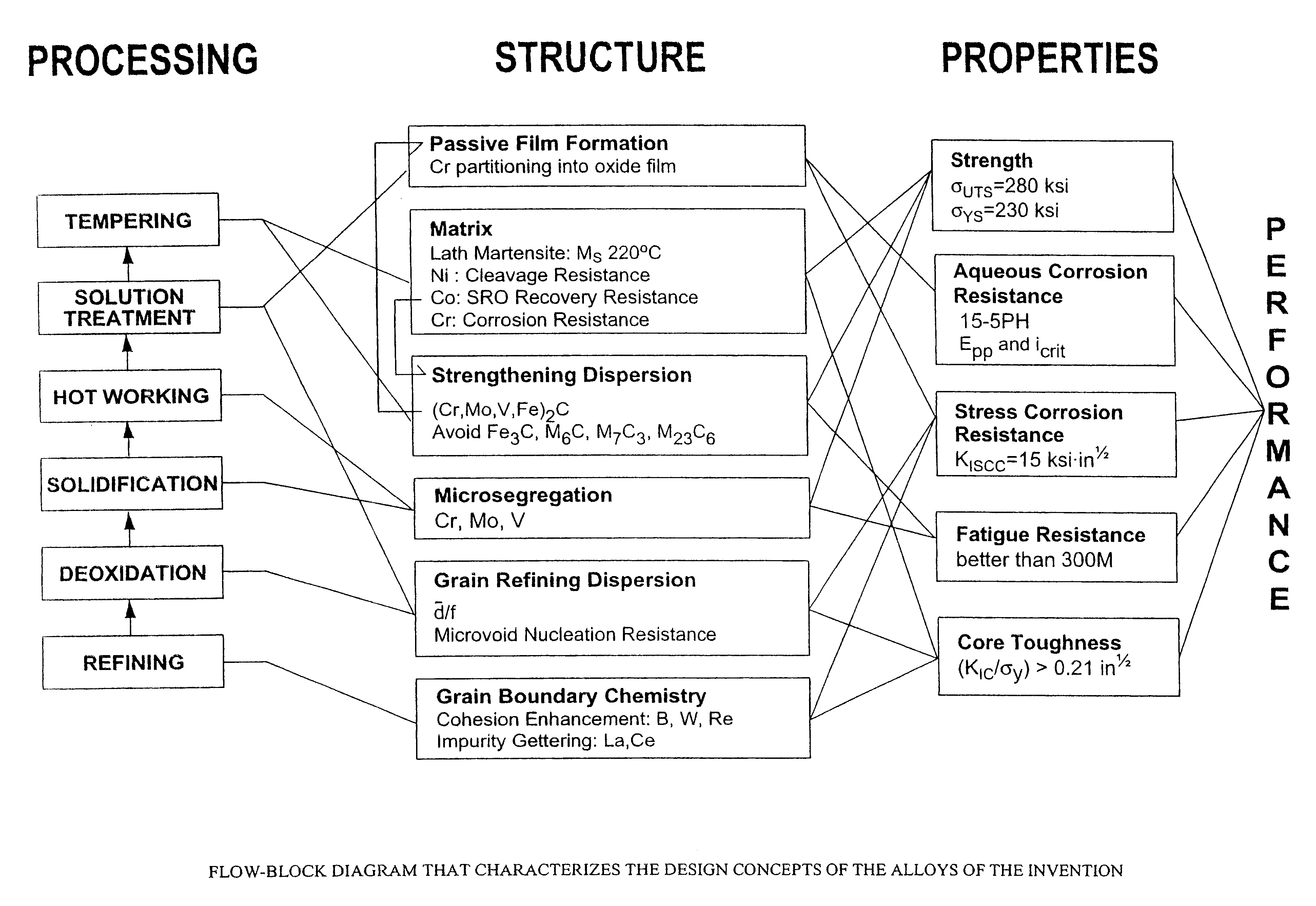
A nanocarbide precipitation strengthened ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steel possesses a combination of strength and corrosion resistance comprising in combination, by weight, about: 0.1 to 0.3% carbon (C), 8 to 17% cobalt (Co), 0 to 10% nickel (Ni), 6 to 12% chromium (Cr), less than 1% silicon (Si), less than 0.5% manganese (Mn), and less than 0.15% copper (Cu), with additives selected from the group comprising about: less than 3% molybdenum (Mo), less than 0.3% niobium (Nb), less than 0.8% vanadium (V), less than 0.2% tantalum (Ta), less than 3% tungsten (W), and combinations thereof, with additional additives selected from the group comprising about: less than 0.2% titanium (Ti), less than 0.2% lanthanum (La) or other rare earth elements, less than 0.15% zirconium (Zr), less than 0.005% boron (B), and combinations thereof, impurities of less than about: 0.02% sulfur (S), 0.012% phosphorus (P), 0.015% oxygen (O) and 0.015% nitrogen (N), the remainder substantially iron (Fe), incidental elements and other impurities. The alloy is strengthened by nanometer scale M2C carbides within a fine lath martensite matrix from which enhanced chemical partitioning of Cr to the surface provides a stable oxide passivating film for corrosion resistance. The alloy, with a UTS in excess of 280 ksi, is useful for applications such as aircraft landing gear, machinery and tools used in hostile environments, and other applications wherein ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steel alloys are desired.
Owner:QUESTEK INNOVATIONS LLC
Nanocarbide precipitation strengthened ultrahigh strength, corrosion resistant, structural steels and method of making said steels
InactiveUS7235212B2Corrosion resistanceReduce contentFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesCobaltTa element
A nanocarbide precipitation strengthened ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steel possesses a combination of strength and corrosion resistance comprising in combination, by weight, about: 0.1 to 0.3% carbon (C), 8 to 17% cobalt (Co), 0 to 5% nickel (Ni), 6 to 12% chromium (Cr), less than 1% silicon (Si), less than 0.5% manganese (Mn), and less than 0.15% copper (Cu), with additives selected from the group comprising about: less than 3% molybdenum (Mo), less than 0.3% niobium (Nb), less than 0.8% vanadium (V), less than 0.2% tantalum (Ta), less than 3% tungsten (W), and combinations thereof, with additional additives selected from the group comprising about: less than 0.2% titanium (Ti), less than 0.2% lanthanum (La) or other rare earth elements, less than 0.15% zirconium (Zr), less than 0.005% boron (B), and combinations thereof, impurities of less than about: 0.02% sulfur (S), 0.012% phosphorus (P), 0.015% oxygen (O) and 0.015% nitrogen (N), the remainder substantially iron (Fe), incidental elements and other impurities. The alloy is strengthened by nanometer scale M2C carbides within a fine lath martensite matrix from which enhanced chemical partitioning of Cr to the surface provides a stable oxide passivating film for corrosion resistance. The alloy, with a UTS in excess of 280 ksi, is useful for applications such as aircraft landing gear, machinery and tools used in hostile environments, and other applications wherein ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steel alloys are desired.
Owner:QUESTEK INNOVATIONS LLC
Nanocarbide precipitation strengthened ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steels
A nanocarbide precipitation strengthened ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steel possesses a combination of strength and corrosion resistance comprising in combination, by weight, about: 0.1 to 0.3% carbon (C), 8 to 17% cobalt (Co), 0 to 10% nickel (Ni), 6 to 12% chromium (Cr), less than 1% silicon (Si), less than 0.5% manganese (Mn), and less than 0.15% copper (Cu), with additives selected from the group comprising about: less than 3% molybdenum (Mo), less than 0.3% niobium (Nb), less than 0.8% vanadium (V), less than 0.2% tantalum (Ta), less than 3% tungsten (W), and combinations thereof, with additional additives selected from the group comprising about: less than 0.2% titanium (Ti), less than 0.2% lanthanum (La) or other rare earth elements, less than 0.15% zirconium (Zr), less than 0.005% boron (B), and combinations thereof, impurities of less than about: 0.02% sulfur (S), 0.012% phosphorus (P), 0.015% oxygen (O) and 0.015% nitrogen (N), the remainder substantially iron (Fe), incidental elements and other impurities. The alloy is strengthened by nanometer scale MZC carbides within a fine lath martensite matrix from which enhanced chemical partitioning of Cr to the surface provides a stable oxide passivating film for corrosion resistance. The alloy, with a UTS in excess of 280 ksi, is useful for applications such as aircraft landing gear, machinery and tools used in hostile environments, and other applications wherein ultrahigh-strength, corrosion resistant, structural steel alloys are desired.
Owner:KUEHMANN CHARLES J +2
Fabrication method of P-type back-surface tunneling oxide passivation contact solar cell
InactiveCN110233180AAvoid secondary diffusionEasy to operateFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationOperabilitySilicon thin film
The invention provides a fabrication method of a P-type back-surface tunneling oxide passivation contact solar cell. The method comprises the steps of performing previous process processing on a frontsurface and a back surface of a P-type single-crystal silicon wafer; oxidizing the back surface to form an ultrathin tunneling oxide layer and fabricate a boron-doping silicon thin film layer; performing phosphorus diffusion on the front surface of the single-crystal silicon wafer, and fabricating a selective emitter; and printing metal electrodes on surfaces of a first passivation anti-reflection layer on the back surface and a second passivation anti-reflection layer on the front surface of the single-crystal silicon wafer, and forming favorable contact between the metal electrodes and thesingle-crystal silicon wafer, thereby obtaining P-type back-surface tunneling oxide passivation contact of the solar cell. The invention provides a complete and practical P-type tunneling oxide passivation contact solar fabrication process circuit, a process method of first back-surface boron-doping poly-silicon thin film and then front-surface phosphorus diffusion, secondary phosphorus diffusioncan be effectively prevented, so that a phenomenon that square resistance is not matched is generated, and the operability is high.
Owner:SUZHOU TALESUN SOLAR TECH CO LTD
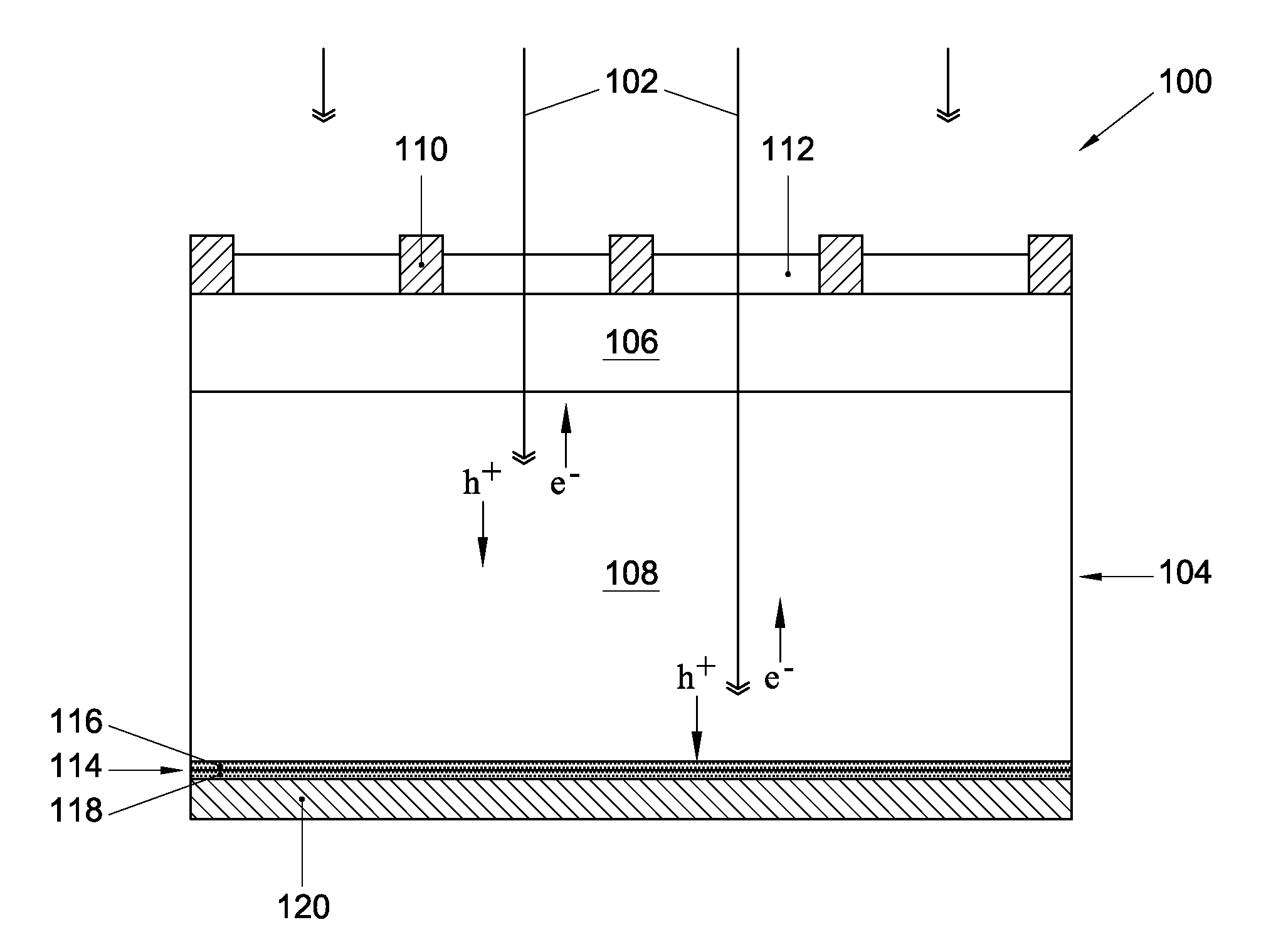
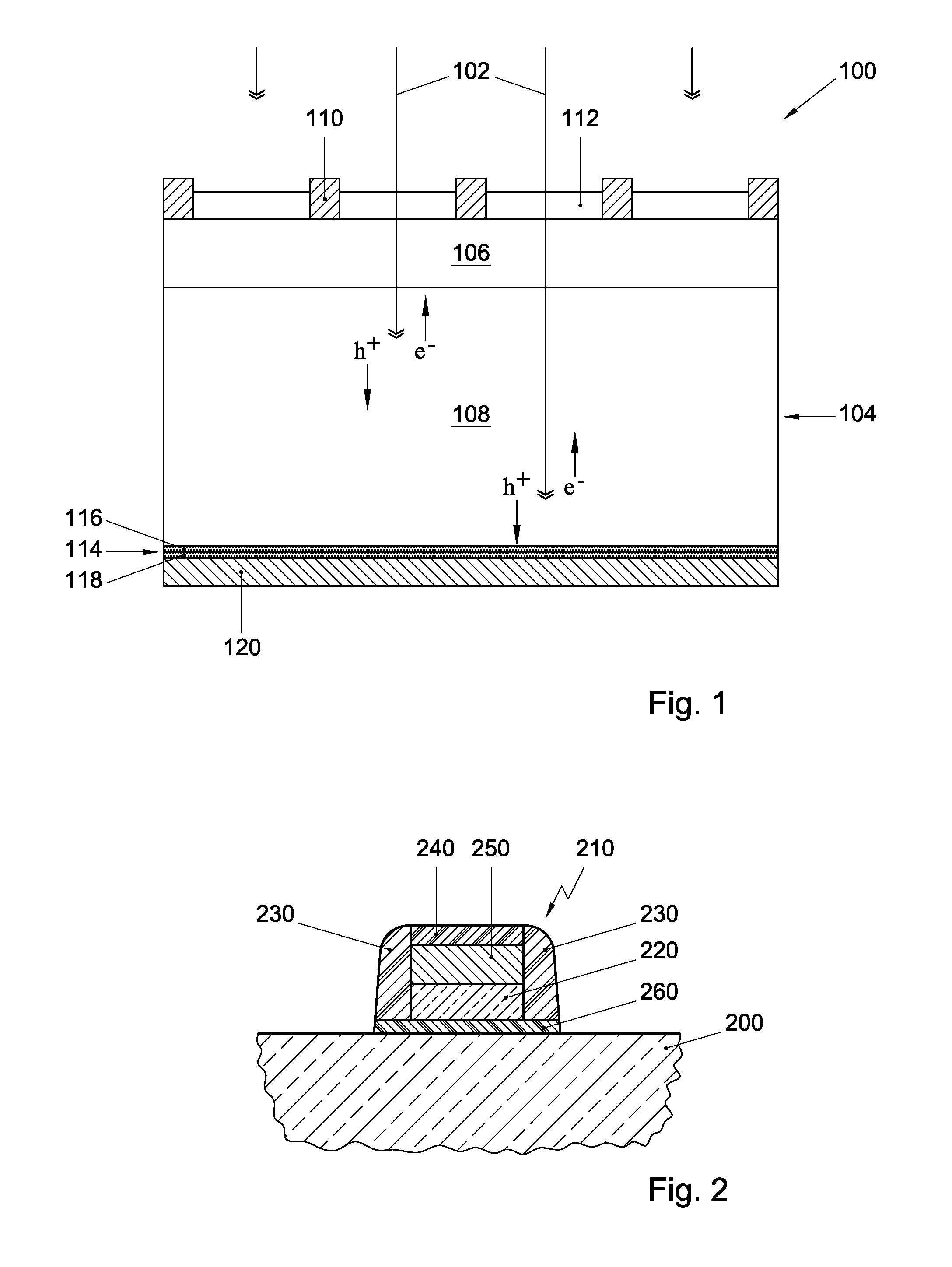
Ald of metal oxide film using precursor pairs with different oxidants
InactiveUS20120255612A1Improve featuresImprove efficiencyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThin metalOxygen plasma
Discloses is a method for depositing a thin metal oxide film on a substrate, comprising: providing a substrate (104); sequentially and alternatingly exposing a surface of said substrate to a first metal precursor and a first oxidant precursor, so as to deposit a first portion (116) of said metal oxide film (114) having a first thickness; and sequentially and alternatingly exposing the surface of the substrate to a second metal precursor and a second oxidant precursor, so as to deposit a second portion (118) of said metal oxide film (114) having a second thickness over said first portion of said metal oxide film, wherein the second oxidant precursor is ozone or oxygen plasma, while the first oxidant precursor is a milder oxidant than ozone. Also disclosed is a solar cell (100) including a metal oxide passivation film (114) deposited by said method.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
Photovoltaic cell, including a crystalline silicon oxide passivation thin film, and method for producing same
ActiveUS20120291861A1Good surface passivationEasy to implementFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionThin layer
A heterojunction photovoltaic cell includes at least one crystalline silicon oxide film directly placed onto one of the front or rear faces of a crystalline silicon substrate, between said substrate and a layer of amorphous or microcrystalline silicon. The thin film is intended to enable the passivation of said face of the substrate. The thin film is more particularly obtained by radically oxidizing a surface portion of the substrate, before depositing the layer of amorphous silicon. Moreover, a thin layer of intrinsic or microdoped amorphous silicon can be placed between said think film and the layer of amorphous or microcrystalline silicon.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Passivation contact solar cell with selective emitter structure and preparation method of passivation contact solar cell
InactiveCN111162145AImprove efficiencyEasy to prepareFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringSolar battery
The invention relates to a passivation contact solar cell with a selective emitter structure and a preparation method of the passivation contact solar cell. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing texturing surfaces on two surfaces of an N-type crystalline silicon substrate; (2) performing boron diffusion treatment on the texturing surface of the front surface of the substrate to form a lightly doped region layer; (3) performing local boron ion implantation on the lightly doped region layer by using a mask, and annealing to form a local heavily doped region; (4) preparing a tunneling oxide layer on the texturing surface of the back surface of the substrate, and preparing a phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon layer on the tunneling oxide layer; (5) preparing a silicon nitride antireflection layer on the phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon layer; preparing an aluminum oxide passivation layer on the lightly doped region layer on the front surface of the substrate, and preparing a silicon nitride antireflection layer on the aluminum oxide passivation layer; and (6) carrying out silk-screen printing of metallized slurry on the two surfaces of the substrate, andsintering. According to the invention, the composite current on the surface of the emitter can be remarkably reduced, so that the efficiency of the N-type passivation contact battery can be improvedby more than 0.2%.
Owner:TAIZHOU ZHONGLAI PHOTOELECTRIC TECH CO LTD
Metal member having a metal oxide film and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080164151A1Avoid crackingExcellent in resistance against exposureAnodisationCellsMetallic materialsRoom temperature
In a method of manufacturing a metal member, a metal material containing aluminum as a main component is anodized in an anodization solution having a pH of 4 to 10 and containing a nonaqueous solvent having a dielectric constant smaller than that of water and capable of dissolving water, thereby forming a nonporous amorphous aluminum oxide passivation film on a surface of the metal member. The method includes a step of controlling the viscosity of the anodization solution. In the step of controlling the viscosity, the viscosity of the anodization solution is lowered by elevating the temperature of the anodization solution above the room temperature or by adding to the anodization solution a substance having a dielectric constant smaller than that of water and a viscosity lower than that of the nonaqueous solvent.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP +1
High-nickel cathode material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109742376AReduce harmLower pHMaterial nanotechnologyCell electrodesInorganic saltsCrystal structure
The invention discloses a high-nickel cathode material and a preparation method thereof. A matrix material of the high-nickel cathode material is Lix(NiaCobMnc)O2 type NCM ternary material, wherein xis not less than 1.0 and not more than 1.06, a+b+c is equal to 1, and a is not less than 0.8. The preparation method is characterized by comprising a step of cladding a layer of surface-modified nano-crystalline metal oxide passivation layer on the matrix material, wherein the substance adopted by surface modification is low-melting point inorganic salt. A layer of nano-crystalline metal oxide passivation layer surface-modified through the low-melting point inorganic salt is covered on the matrix surface, the surface modification is accomplished by adopting twice annealing treatment in a ternary system for improving the nickel content, a crystal structure of the high-nickel cathode material is stabilized, and the material surface residual alkali content is reduced, the prepared high-nickelcathode material is high in capacity and good in circulation.
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Fuel cell with metal alloy contacts that form passivating conductive oxide surfaces
A metal alloy which when oxidized forms a highly conductive surface oxide layer. Alloy compositions such as, but not limited to, Ti—Nb, Ti—Ta, La—Sr—Cr, and La—Sr—Co are known to form oxide passivation layers which are highly conductive. Such alloys are useful in electrical contact apparatus. An electrical contact element formed of the alloy has a contact surface which when oxidized forms a highly conductive surface layer, thus maintaining electrical conductivity and continuity through the element. The oxide layer may be formed in situ after assembly of the electrical contact or may be provided in an oxidative step during manufacture. The electrical contact may be formed entirely of one or more of such alloys; or may be formed of an inexpensive substrate base metal, such as steel, having one or more of the alloys coated thereupon; or may be formed of a mixture of the base metal and the alloy.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD
P-type tunneling oxide passivated contact solar cell and preparation method thereof
PendingCN109980022AImprove interface passivation effectReduce composite speedFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationState of artSilicon thin film
The invention discloses a P-type tunneling oxide passivated contact solar cell and belongs to the technical field of crystalline silicon solar cells, aiming to solve the problem that the passivation effect of the back surface of the solar cell in the prior art is poor; the solar cell in the invention is characterized in that a silicon dioxide layer is formed on the front surface of a silicon wafer, and then an N-type heavily-doped polycrystalline silicon layer is formed on the silicon dioxide layer, so that the composite loss of a metal contact area is reduced; in addition, the tunneling oxideis combined with a heavily-doped silicon thin film to form a passivated contact structure, so that the original way of whole-face doping the back surface area is replaced, further, a high short-circuit current is kept, the open-circuit voltage is increased, the filling factor is improved, and the conversion efficiency of the battery is improved.
Owner:TONGWEI SOLAR ENERGY CHENGDU CO LID
P-type local back surface field passivation double-sided solar cell and preparation process thereof
PendingCN110828584AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyIncrease the duplex rateSemiconductor devicesPhotovoltaic energy generationMetallic electrodeOhmic contact
The invention discloses a p-type local back surface field passivation double-sided solar cell and a preparation process thereof, and relates to the technical field of solar cells. The solar cell comprises a p-type silicon substrate, wherein the bottom of the p-type silicon substrate is provided with a silicon oxide passivation layer, an aluminum oxide passivation layer and a back silicon nitride antireflection layer from top to bottom, the bottom of the p-type silicon substrate is embedded with a plurality of strips of a boron source doped layer, and the bottom of the boron source doping layeris connected with a back metal electrode layer which simultaneously penetrates through the silicon oxide passivation layer, the aluminum oxide passivation layer and the back silicon nitride antireflection layer. During the preparation, a plurality of local slots are formed in the lower surface of the back silicon nitride antireflection layer by using laser, the local slots are formed to the bottom of the p-type silicon substrate, the slotted area is printed with boron source slurry to form a high-low junction structure, the open-circuit voltage of the back cell of the double-sided solar cellis improved, the slotted boron source slurry heavily-doped area is in contact with a metal electrode to form ohmic contact, the series resistance is reduced, the filling factor is improved, and the double-sided rate of the cell is improved under the condition of not reducing the front efficiency.
Owner:TONGWEI SOLAR ENERGY (CHENGDU) CO LID
N-type crystalline silicon two-sided battery and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN103996721ASimple processImprove stabilityFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationIon implantationMaterials science
The invention discloses an N-type crystalline silicon two-sided battery and a preparing method thereof and belongs to the technical field of solar batteries. The N-type crystalline silicon two-sided battery comprises an N-type silicon substrate, a boron doping layer, an anode of the battery, an aluminum oxide passivation layer, silicon nitride antireflection layers, an ion implantation phosphor doping layer, a silicon nitride passivation and antireflection layer and a cathode of the battery. The invention further discloses the preparing method for the battery. The method specifically comprises the steps of (1) carrying out chemical cleaning; (2) adding a boron source; (3) injecting a phosphor source to the lower surface and carrying out annealing; (4) preparing the aluminum oxide passivation layer and the first silicon nitride antireflection layer on the upper surface; (5) preparing the second silicon nitride antireflection layer on the lower surface; (6) preparing the anode and the cathode of the battery; (7) carrying out sintering. According to the N-type crystalline silicon two-sided battery, the stability performance of the battery can be improved, absorption of short waves is reduced, blue ray response is improved, the short-circuit current density of the battery is improved, and the efficiency of the battery is improved; the method preparing the battery simplifies the manufacture procedure of the two-sided battery, and the battery has high practicality.
Owner:ALTUSVIA ENERGY TAICANG
Compound deoxygenation corrosion inhibitor for boiler water supply and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107352610AAvoid corrosionOvercome the disadvantage of low oxygen removal efficiencySpecific water treatment objectivesWater/sewage treatment by degassingLiquid productBoiler blowdown
The invention provides a compound deoxygenation corrosion inhibitor for boiler water supply. The deoxygenation corrosion inhibitor includes a variety of organic components, all the components cooperate and can achieve rapid and effective removal of dissolved oxygen from boiler water, and overcome the shortcoming of low deoxygenation efficiency of single deoxidant. The deoxygenation corrosion inhibitor obtained by adjusting the organic alkalizer content can be applied to ordinary pressure, medium-pressure and high-pressure boilers, and has wide application range. Oxime and hydrazide have strong reducibility, can quickly remove dissolved oxygen from boiler water, and at the same time can generate a layer of dense black ferroferric oxide passivation film on the boiler inner wall so as to prevent further corrosion of the boiler. The deoxygenation corrosion inhibitor provided by the invention has no need for ammonia water to serve as the pH regulator, and avoids ammonia corrosion. The deoxygenation corrosion inhibitor provided by the invention is composed of all-organic components, does not introduce inorganic impurities or reaction by-products, does not affect the boiler blowdown and steam quality, and is a liquid product, and has the advantages of no toxicity, no flash point, and safe and convenient use and operation.
Owner:SHENYANG DREAMLAND ENVIRONMENTS TECH
High-reliability PERC back silver conductive paste for crystalline silicon solar cell and preparation process for high-reliability PERC back silver conductive paste
ActiveCN109949966AImprove liquidityHigh mechanical strengthNon-conductive material with dispersed conductive materialCable/conductor manufactureCelluloseElectrical battery
The invention discloses high-reliability PERC back silver conductive paste for a crystalline silicon solar cell and a preparation process for the high-reliability PERC back silver conductive paste. The viscosity of the slurry is 20 to 80 Pa.S, and the paste contains the following components in percentage by mass: 0.1%-0.3% of an inorganic additive, 1%-5% of glass powder, 45%-65% of silver powder,2%-6% of ethyl cellulose, 1%-5% of terpilenol, 20%-35% of texanol ester alcohol and a proper amount of an organic additive, wherein the glass powder is formed by the mixing of glass powder I and glasspowder II. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing the organic additive, ethyl cellulose, terpilenol and texanol ester alcohol under the water bath condition to obtaina carrier; adding the mixed glass system and the inorganic additive into the carrier, and uniformly mixing the mixture; and adding the silver powder system into the system at the step 2, and performing uniform mixing, rolling and filtering to obtain the back conductive silver paste. According to the invention, the PERC back silver paste guarantees the characteristics of the traditional non-contactsilver paste, is fewer in damages to an aluminum oxide passivation layer, is high in welding reliability of a back silver paste sintered electrode due to the fact that a mixed glass system is adopted, and has excellent comprehensive performances under the condition that the actual temperature is 740 DEG C-780 DEG C.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GUANGDA ELECTRONICS TECH
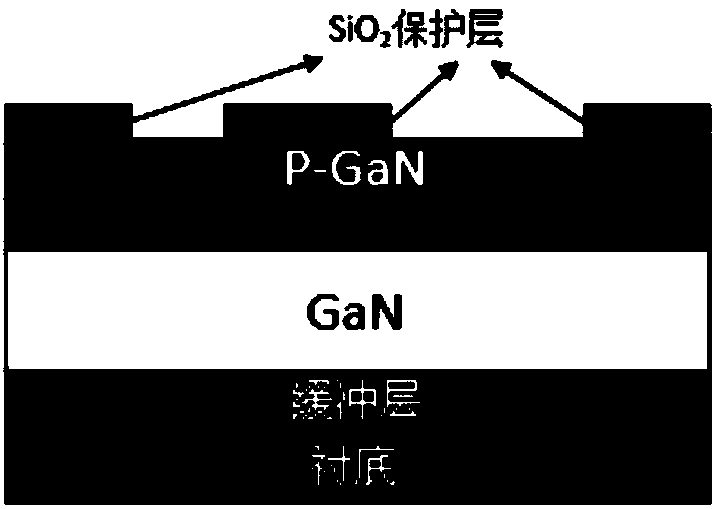
Enhanced transistor based on III oxide passivation and manufacturing method of enhanced transistor
InactiveCN109920850AHigh Electron Mobility EffectAvoid uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionHigh resistance
The invention discloses an enhanced transistor based on III oxide passivation and a manufacturing method of the enhanced transistor. The manufacturing method comprises the steps of growing and forminga heterojunction on a substrate, wherein the heterojunction comprises a first semiconductor and a second semiconductor formed on the first semiconductor, the second semiconductor has a band gap whichis wider than the first semiconductor, and two-dimensional electron gas is formed in the heterojunction; forming a cap layer on the second semiconductor, wherein the cap layer comprises a doping region and passivation regions, and the doping region is composed of a third semiconductor and is completely covered by the gate, the passivation regions are distributed between the gate and the drain andbetween the gate and the source, and the third semiconductor is used for exhausting the two-dimensional electron gas distributed in a gate lower region in the heterojunction; and making the source, the drain and the gate. According to the enhanced transistor disclosed by the invention, the uniformity, repeatability and introduction damage problems caused by etching the P-type doping region can beavoided, and the device reliability problem caused by the fact that a high-resistance layer formed by hydrogen plasma passivation is possibly re-activated at a high temperature can be avoided.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
Neodymium-iron-boron magnet surface composite corrosion-resistant coating and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110828099AExtended service lifeSimple preparation processPermanent magnetsTransformers/inductances corrosion protectionCoated surfaceAluminium powder
The invention discloses a neodymium-iron-boron magnet surface composite corrosion-resistant coating and a preparation method thereof. The composite corrosion-resistant coating sequentially comprises acold spraying aluminum coating, an aluminum oxide passivation layer obtained through surface passivation treatment and a hole sealing ceramic paint layer from the surface of a neodymium-iron-boron magnet to the outside. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) surface treatment of a neodymium-iron-boron substrate; (2) treatment of aluminum powder; (3) cold spraying of an aluminum coating; (4) passivation treatment to obtain an aluminum oxide passivation layer; and (5) hole sealing treatment to obtain a hole sealing ceramic paint layer. The prepared neodymium-iron-boron magnet surface composite corrosion-resistant coating has excellent local corrosion resistance, the corrosion-resistant coating is formed by well combining with the neodymium-iron-boron magnet, the defects that a pure aluminum coating is low in strength and hardness and micropores exist in the surface are overcome, and the service life of the corrosion-resistant coating is prolonged when the corrosion-resistant coating is used as a sintered neodymium-iron-boron magnetic material surface corrosion-resistant process.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF TECH
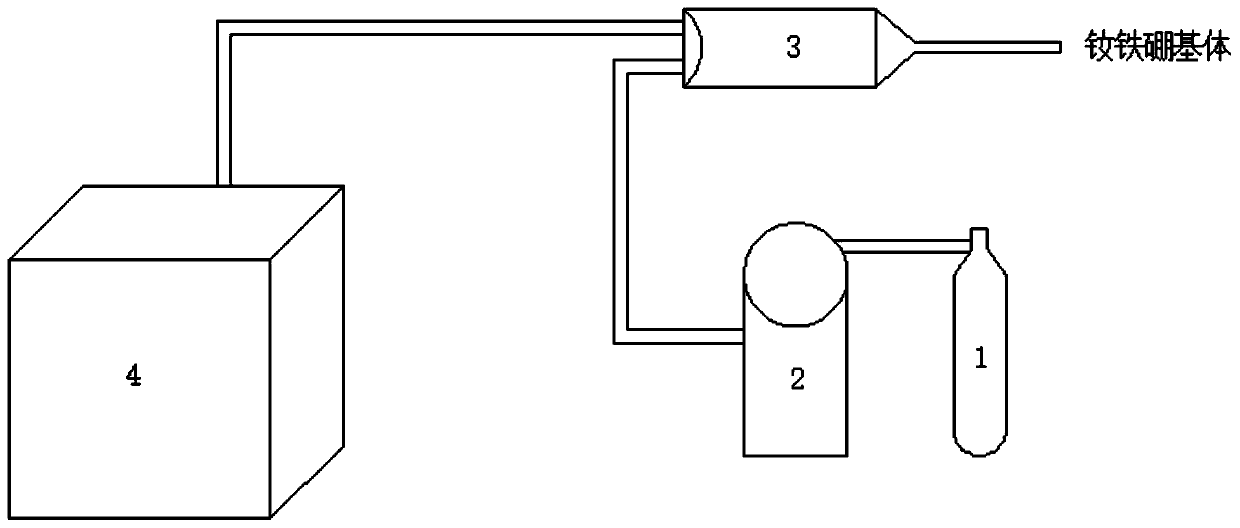
Decomposition method for molybdenite by wet process
InactiveCN101260461AImprove leaching rateReduce energy consumptionElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisUltrasound - action
The invention discloses a molybdenite whole-wet method decomposition method. The molybdenite, the chloride electrolyte and the water are added into a membraneless electrobath with an ultrasonic generator and are stirred to prepare the ore pulp with the ore pulp mass percentage ranging from 5 to 80 percent and the chloride electrolyte mass percentage ranging from 5 to 50 percent, the mixture is electrolyzed and oxidized under the action of ultrasonic and at a temperature ranging from 0 to 100 DEG C, in the electroanalysis process, the current density of the anode is controlled to be 50 to 1200 A / m<2>, the ultrasonic is emitted continuously or intermittently, the electrolyzed and oxidized molybdenite is converted into the molybdena or molybdate compound. By the ultrasonic field and the electric field coupling action, the method reinforces the wet method decomposition process of the molybdenite, overcomes the retardation of the oxide passive film generated in the oxidization leaching process of the conventional wet method, and improves the current efficiency and the Mo leaching rate of the prior membraneless electrooxidation leaching technique.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
P-type tunneling oxide passivation contact solar cell and preparation method thereof
PendingCN110690297AImprove interface passivation effectReduce composite speedFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionSolar battery
The invention discloses a P-type tunneling oxide passivation contact solar cell. The P-type tunneling oxide passivation contact solar cell comprises P-type silicon, an N-type heavily doped silicon layer and a front SiNx antireflection layer are sequentially deposited on the front surface of the P-type silicon from inside to outside, a silicon dioxide layer and an N-type heavily doped polycrystalline silicon layer which are in contact with each other are arranged in the N-type heavily doped silicon layer, the silicon dioxide layer is arranged on one side close to the P-type silicon, an Ag gatefinger electrode is arranged in the front SiNx antireflection layer, and the Ag gate finger electrode and the N-type heavily doped polycrystalline silicon layer correspond to each other and form ohmiccontact; and an aluminum oxide layer and a back SiNx antireflection layer are sequentially deposited on the back surface of the P-type silicon from inside to outside. The TOPCon solar cell structureprepared by the invention can combine the advantages of an existing heterojunction structure and a traditional polycrystalline silicon junction structure, namely, has high carrier selectivity, high temperature stability and excellent interface passivation effect, so that the solar cell with high conversion efficiency and high stability is achieved.
Owner:TONGWEI SOLAR (ANHUI) CO LTD +1
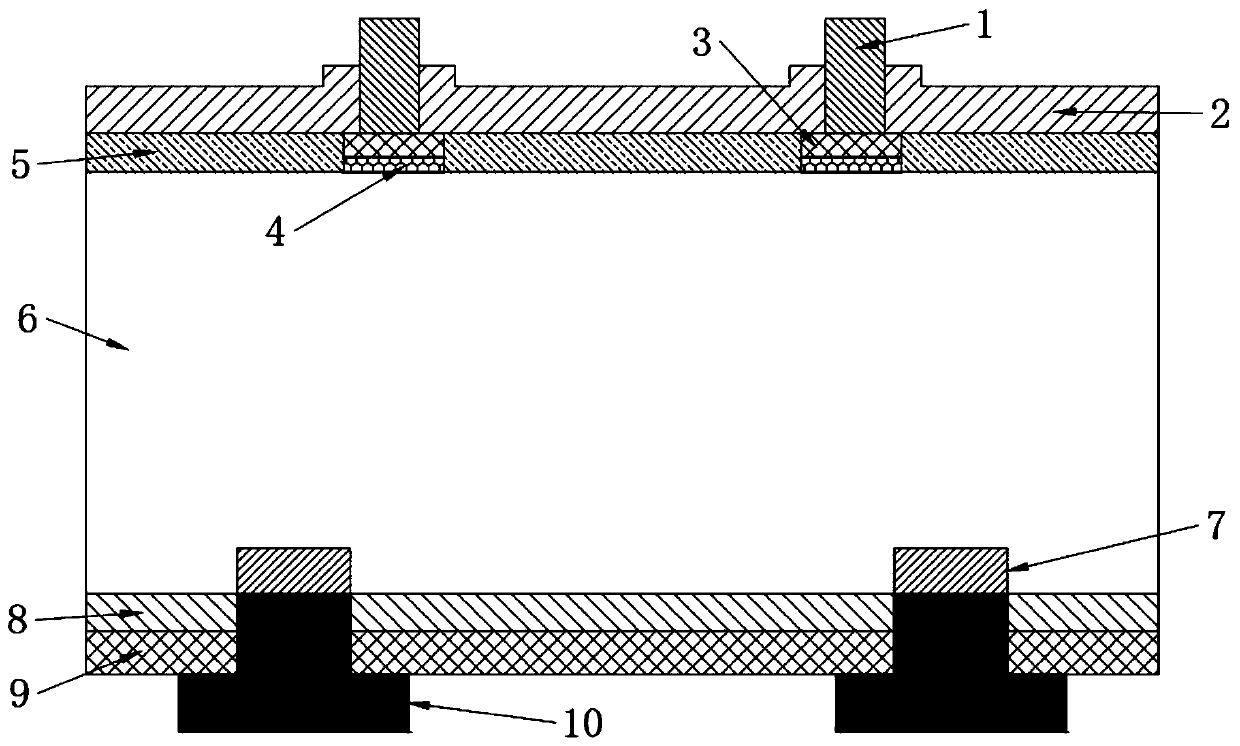
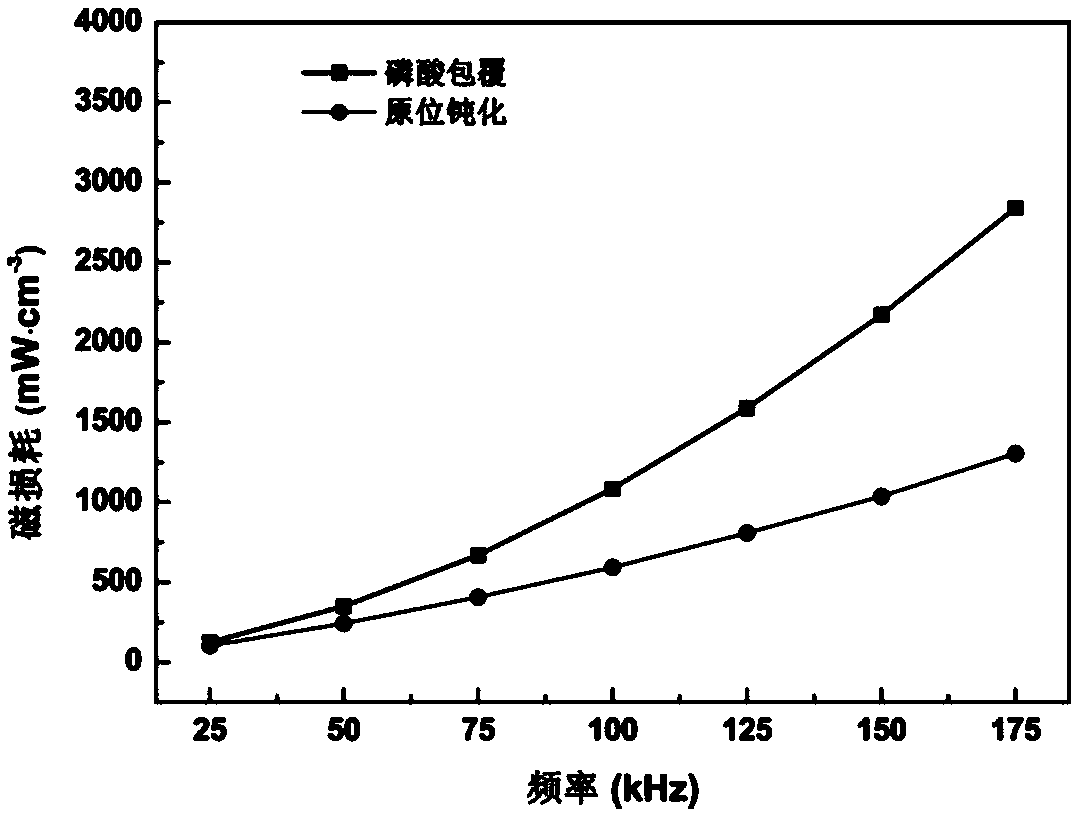
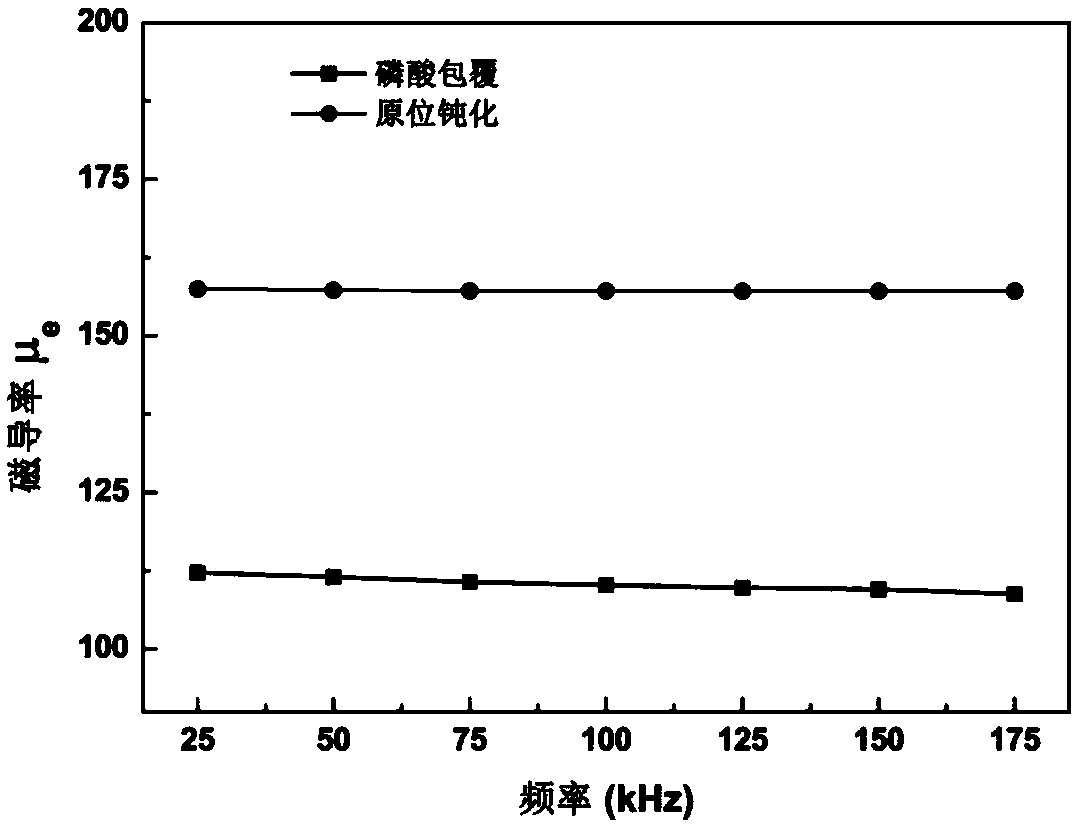
An in-situ passivation insulation coating treatment method of a metal soft magnetic composite material
InactiveCN109215924ASaturation magnetic flux density has little effectImprove bindingInorganic material magnetismThermal stabilityUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses an in-situ passivation coating treatment method of a metal soft magnetic composite material. In-situ passivation method was used to insulate the metal magnetic powder, and thenthe target product was obtained by bonding, pressing, heat treatment and spraying. A lay of dense passivation film is generated on that surface of the magnetic pow in situ by an in-situ passivation method, the passivation film is uniformly coated, the thickness is controllable, the resistivity is high, the thermal stability and the bonding strength are good, and the passivation film has excellentmagnetic and mechanical properties; In-situ passivation method was used to coat a layer of oxide passivation film on the surface of metal magnetic powder. The coating effect was better than that of the existing method, and it was easy to be operated and mass produced. The effective permeability of soft magnetic composites is greatly improved and the core loss is effectively reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Front grid line passivation contact-based PERC solar cell and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112186049AImprove efficiencyIncrease the open circuit voltageFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationSilicon oxideMaterials science
The invention belongs to the technical field of crystalline silicon solar cells, and relates to a front grid line passivation contact-basedPERC solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The solar cell comprises a P type monocrystalline silicon substrate; a back aluminum oxide passivation layer and a back silicon nitride passivation layer are sequentially arranged on the back surface of the P type monocrystalline silicon substrate from inside to outside. A front silicon oxide passivation layer and a front silicon nitride passivation layer are sequentially arranged on the front face of the Ptype monocrystalline silicon substrate from inside to outside; a front metal silver grid line penetrating through the front silicon oxide passivation layer and the front silicon nitride passivation layer is arranged on the front face of the P type monocrystalline silicon substrate. An ultrathin tunneling silicon oxide layer and a phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon layer are sequentially arranged on the front face of the P type monocrystalline silicon substrate and located below the front face metal silver grid line from inside to outside. According to the solar cell and preparation method thereof of the invention, the open-circuit voltage of the cell can be improved, the carrier recombination of a metal contact region can be reduced, the parasitic absorption of the doped polycrystalline silicon layer to light can be reduced, the current loss can be reduced, and the efficiency of the PERC cell can be improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD +1
An N-type crystalline silicon solar cell based on doped polysilicon germanium thin film and a preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109065643AImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyImplement selective collectionFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge carrier mobilityOxide passivation
The invention relates to an N-type crystalline silicon solar cell based on doped polycrystalline silicon germanium thin film and a preparation method thereof, wherein the N-type crystalline silicon wafer is velvet on both sides, Double-sided boron is then diffuse on that front surface to form an emitter, An oxide tunneling layer is prepared by alkali throwing on the back surface, Then N + polysilicon germanium thin films were prepared by reactive thermal CVD at low temperature below 350oC to form back tunneling oxide passivation contact structure. Then emitter passivation film and front and back antireflection film were prepared. Finally metal gate line electrodes were prepared in front and back of the cell. A low-temperature process is adopted to prepare that N + polycrystalline silicon germanium film on the back surface of the invention, which not only avoid the damage of the tunneling oxide layer caused by the high-temperature process, but also can obtain the polycrystalline silicongermanium film with higher crystalline quality, effectively improve the doping concentration and the carrier mobility of the film, and is beneficial to improving the filling factor and the conversionefficiency of the battery.
Owner:JIANGSU SHUNFENG PHOTOVOLTAIC TECH CO LTD
P-type crystalline silicon solar cell with tunneling passivation and preparation method thereof
PendingCN112310231AReduce surface recombination rateImprove front passivationFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationMetallic aluminumEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of crystalline silicon solar cells, and relates to a P-type crystalline silicon solar cell with tunneling passivation and a preparation method thereof. Thesolar cell comprises a P-type substrate, and is characterized in that a selective emitter, an ultrathin tunneling silicon oxide layer, a phosphorus-doped polycrystalline silicon layer, a front silicon oxide passivation layer and a front silicon nitride passivation layer are sequentially arranged on the front face of the P-type substrate from inside to outside, and a back aluminum oxide passivation layer and a back silicon nitride silicification layer are sequentially arranged on the back face of the P-type substrate from inside to outside; A front metal silver grid line is arranged on the front silicon nitride passivation layer, a back metal aluminum grid line is arranged on the back face of the P-type substrate, and the back metal aluminum grid line penetrates through the back aluminum oxide passivation layer and the back silicon nitride silicification layer. The structure is very thin, the problem of light absorption of the silicon wafer is solved, the surface recombination rate ofthe cell is effectively reduced, the front passivation of the cell is improved, and the performance of the cell is improved.
Owner:TRINA SOLAR CO LTD +1
Oxide passivation contact solar cell and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110444611AReduce defect densityImprove passivation effectFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationMagnesium dopingElectrical battery
The invention discloses an oxide passivation contact solar cell and a preparation method thereof. The cell has the following structure from top to bottom: Ag / ITO / NiOx:Mg / SiOx / n-c-Si / SiOx / TiOx / Ag. Thepreparation method comprises the following steps of putting a cleaned silicon wafer into a HNO3 solution for thermal oxidation growth, growing a magnesium-doped nickel oxide thin film by utilizing a magnetron sputtering method, and growing a titanium oxide thin film by a magnetron sputtering method; dividing the silicon wafer into a sample with the area of 1.5*1.5cm2 by utilizing a laser scribingtechnology, and then growing an ITO transparent conductive thin film and a metal silver electrode by a magnetron sputtering method; and naturally cooling the manufactured cell to room temperature after annealing. The method does not need expensive thin film deposition equipment such as plasma chemical vapor deposition (PECVD) or atomic layer deposition (ALD), and has the characteristics of simpleprocess, low cost, environmental friendliness and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
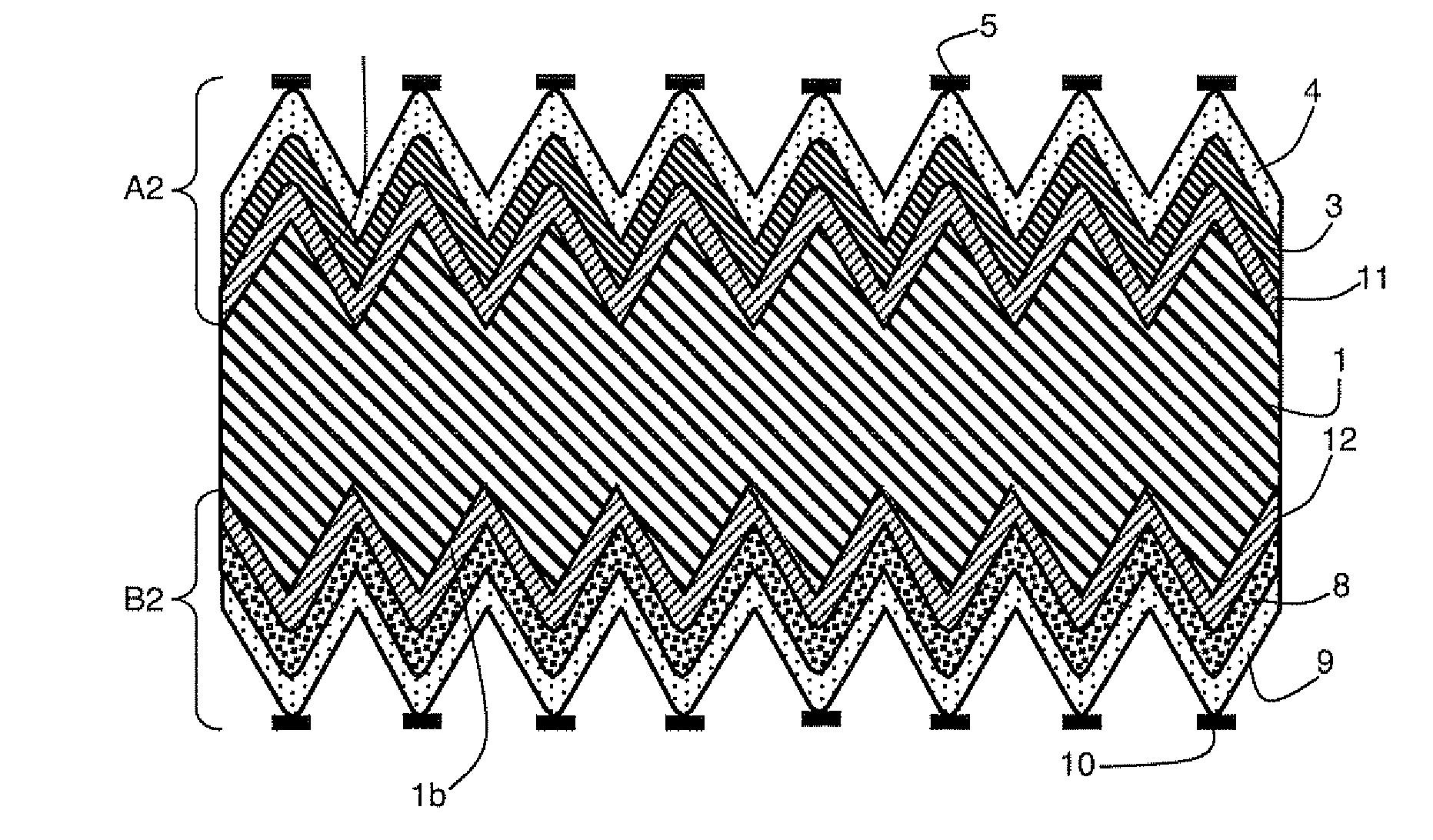
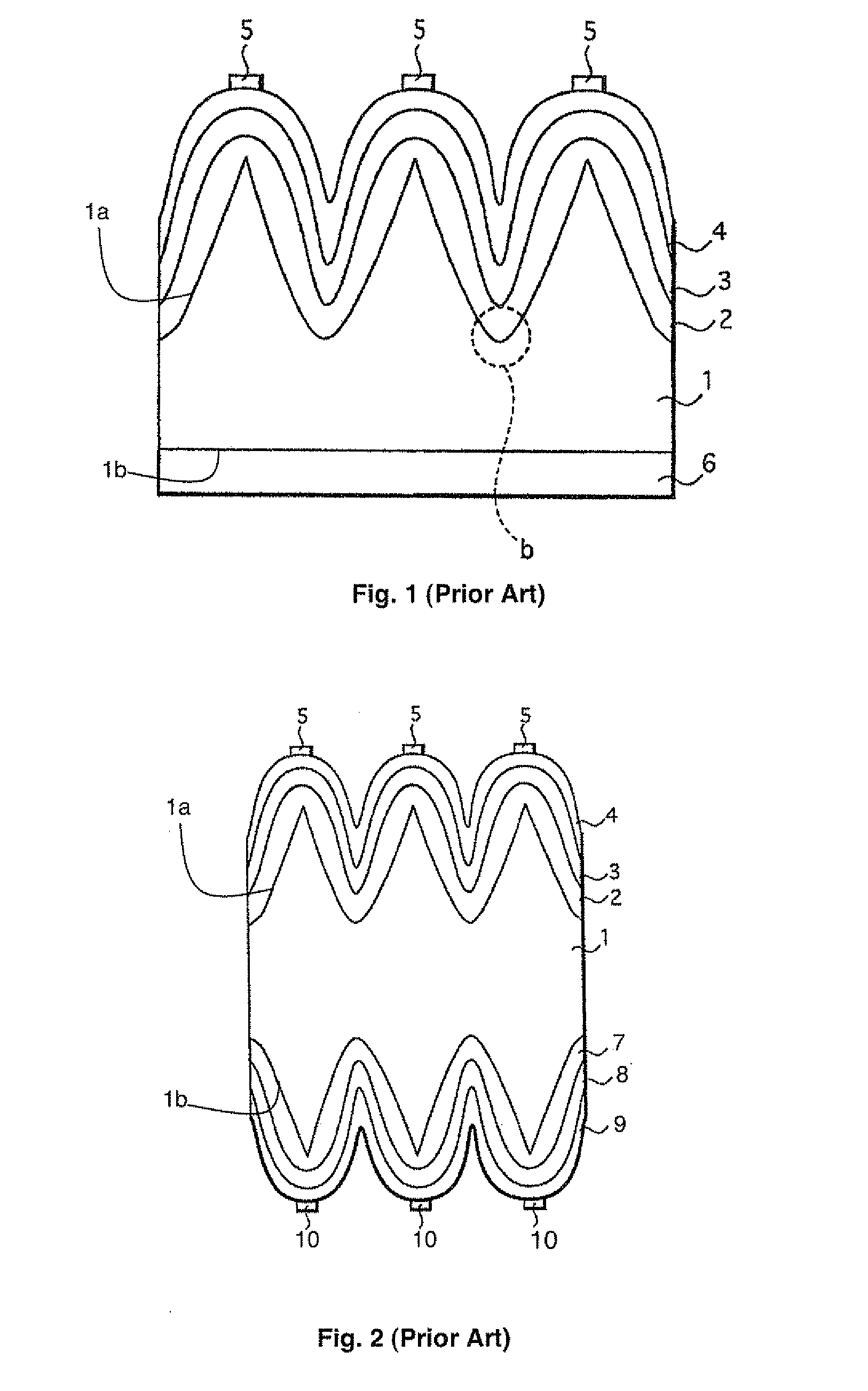
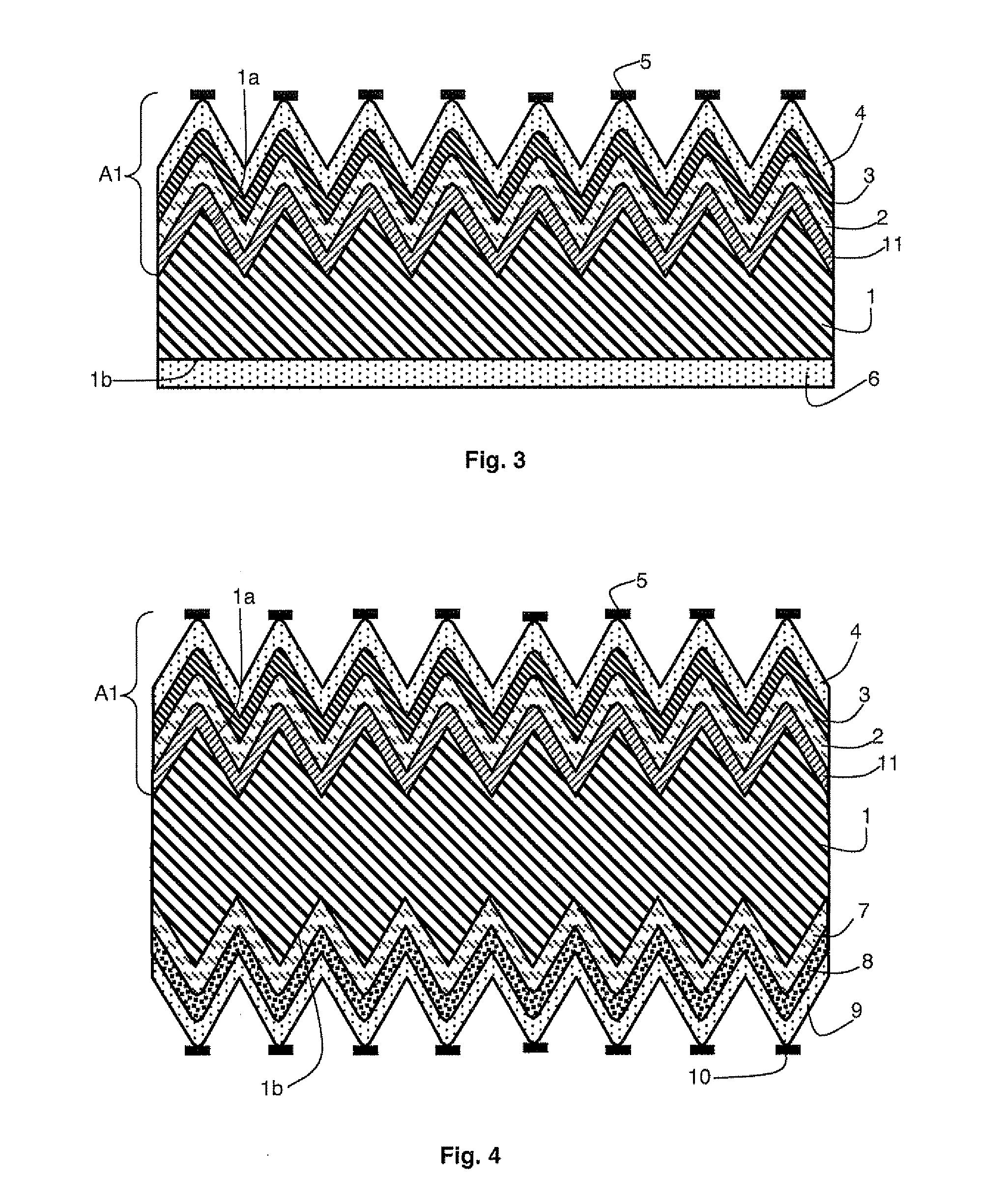
Electric double layer capacitor
InactiveUS20070228507A1Avoid corrosionLower internal resistanceHybrid capacitor electrodesDouble layer capacitorsInternal resistanceAlloy
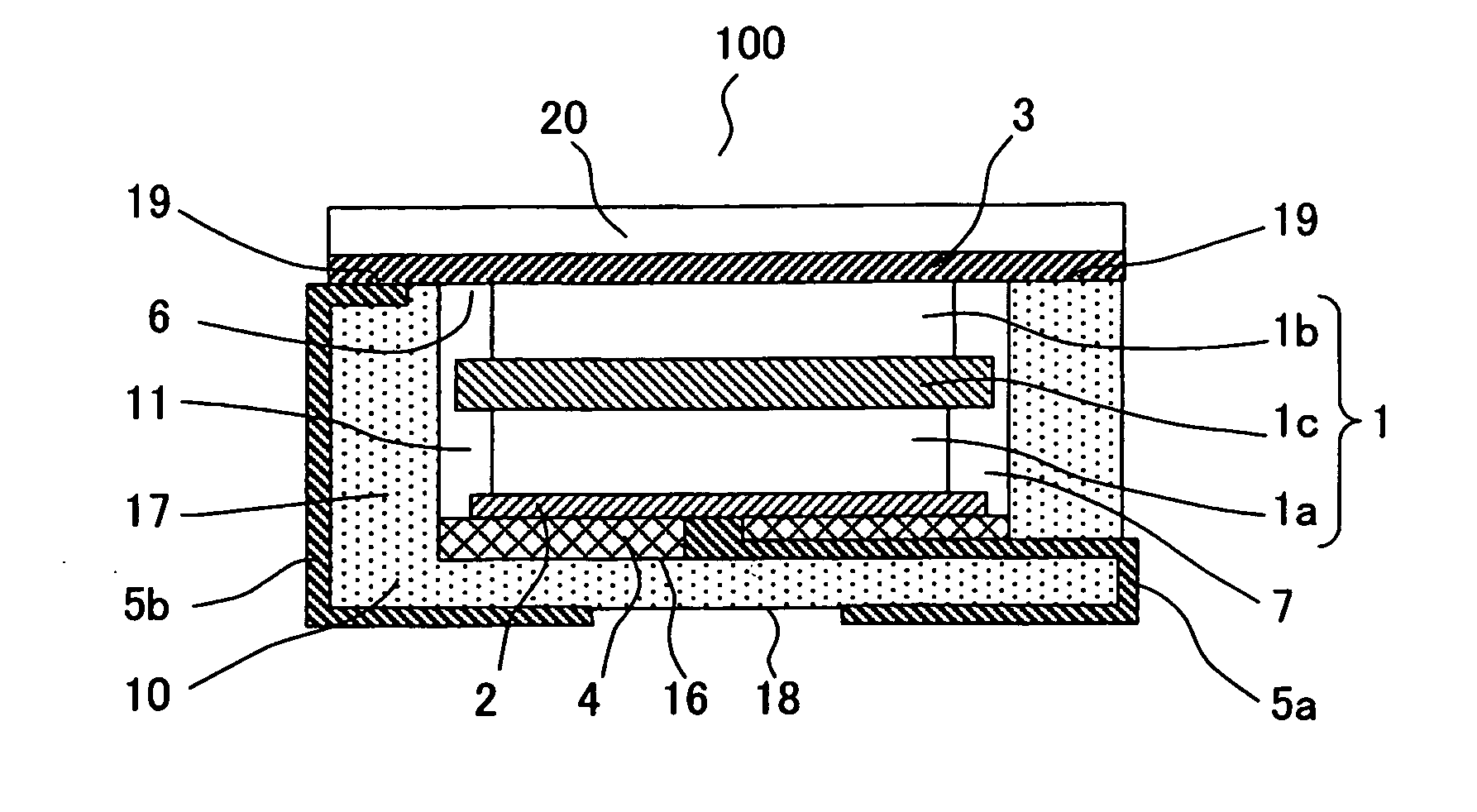
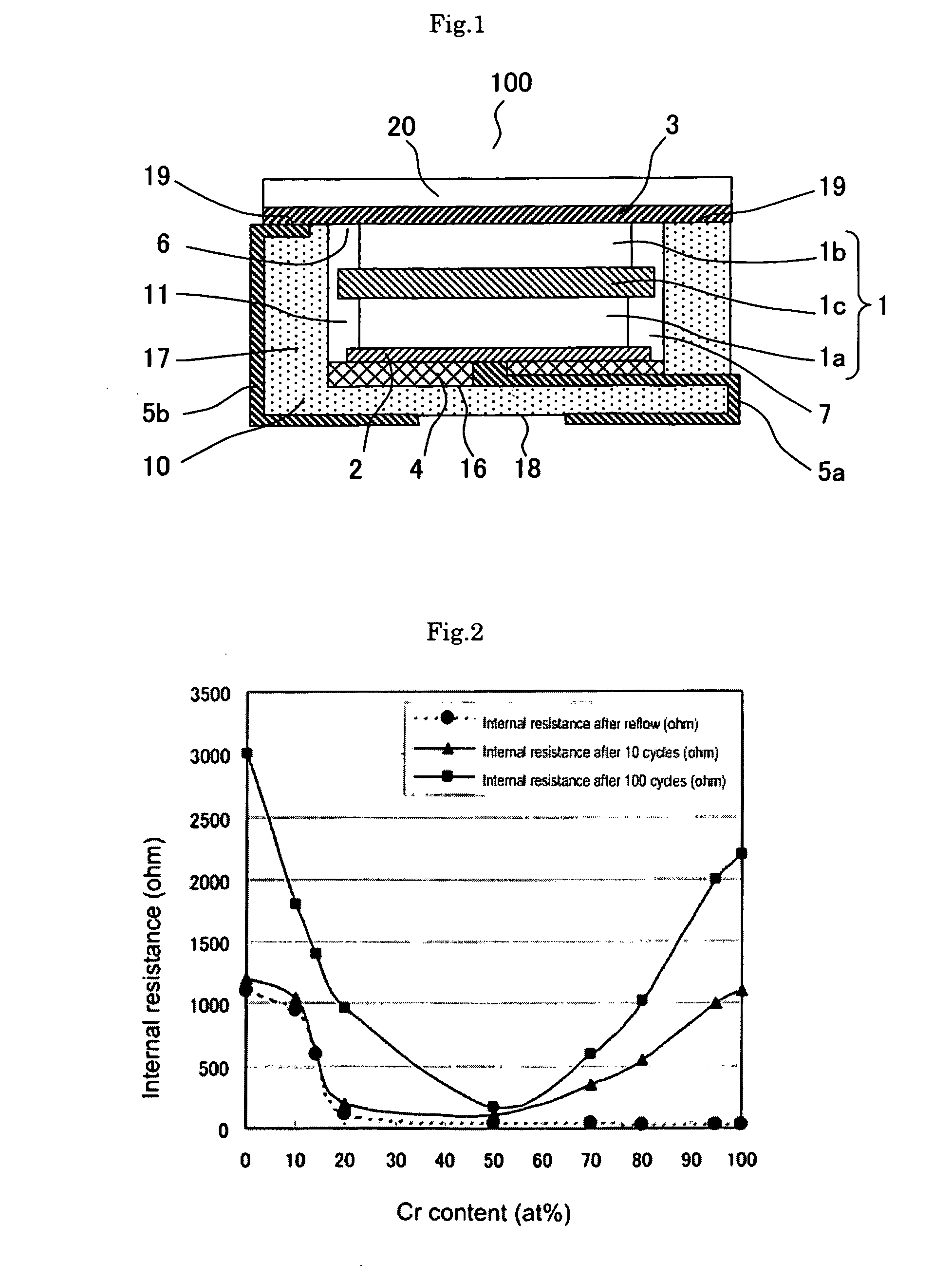
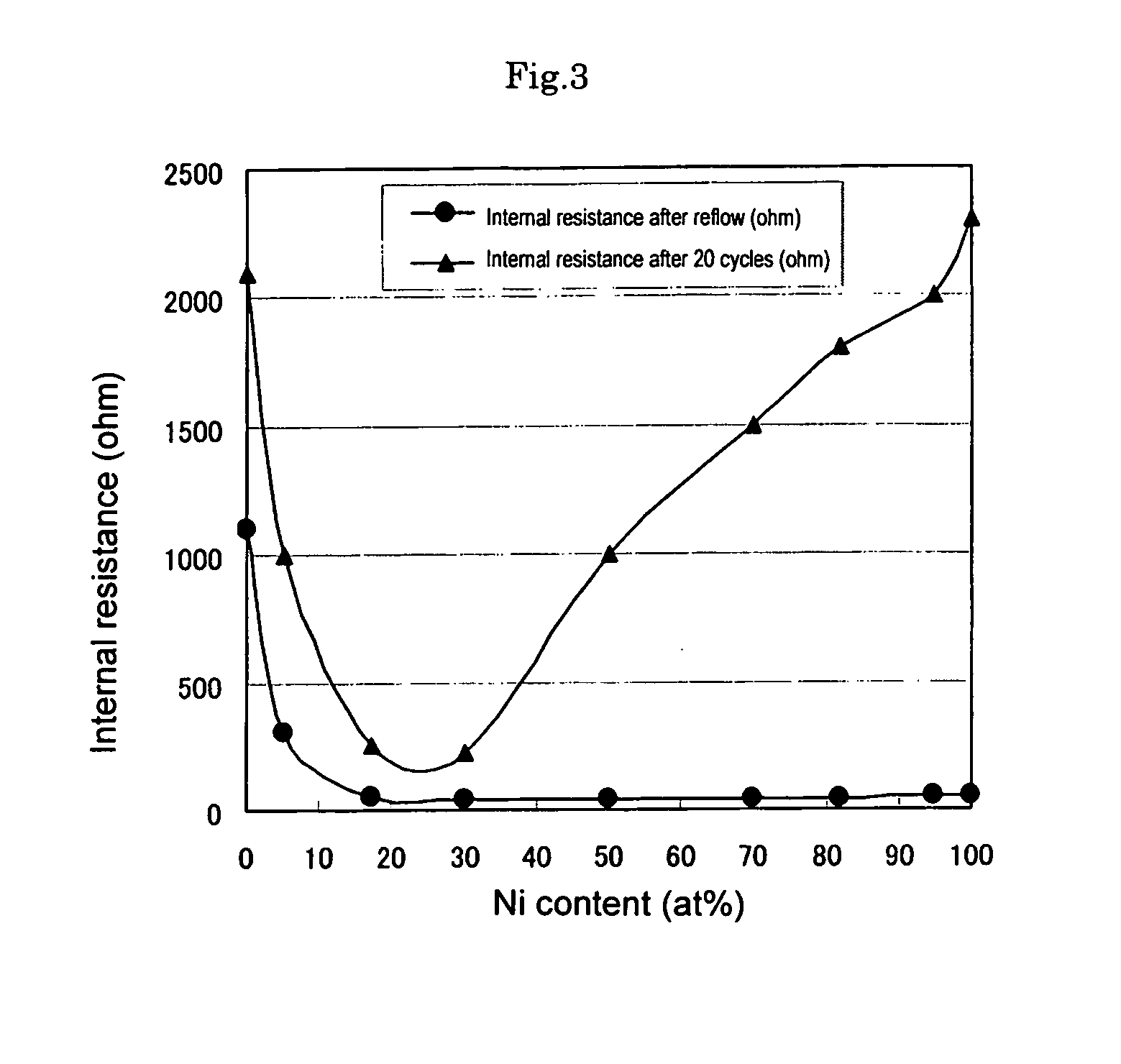
The current invention provides for an electric double layer capacitor which can be manufactured with low manufacturing cost, and an increase of internal resistance due to the damage of a cathode current collector by reflow is inhibited. For this reason, in the current invention, the electric double layer capacitor comprising a cathode 1a, anode 1b, a separator 1c to separate said cathode 1a and anode 1b, electrolytic solution 7 and a container 10 to house said cathode 1a, anode 1b, separator 1c and electrolytic solution 7, wherein said cathode 1a is electrically connected to cathode current collector 2, and said cathode current collector 2 is comprised of alloy of a metal element showing an oxide passivation phenomenon and aluminum.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Conductive coatings for PEM fuel cell electrodes
InactiveUS7037617B2Improve conductivityFuel cells groupingFinal product manufactureFuel cellsMetal alloy
Electrical contact surfaces of a bipolar plate for a fuel cell assembly are formed of metals or metal alloys which when oxidized form highly conductive oxide passivation layers, thus maintaining high electrical conductivity and continuity through the fuel cell and forestalling corrosion failure of a cell assembly. Alloy composition systems such as, but not limited to, Ti—Nb, Ti—Ta, La—Sr—Cr, and La—Sr—Co are known to form oxide passivation layers which are highly conductive. The passivation layers may be formed in situ after assembly of a fuel cell or may be provided in an oxidative step during manufacture. The bipolar plate may be formed entirely of one or more of such alloys or may be formed of an inexpensive substrate metal having the alloy layers coated thereupon.
Owner:DELPHI TECH INC
Substrate metallization and ball attach metallurgy with a novel dopant element
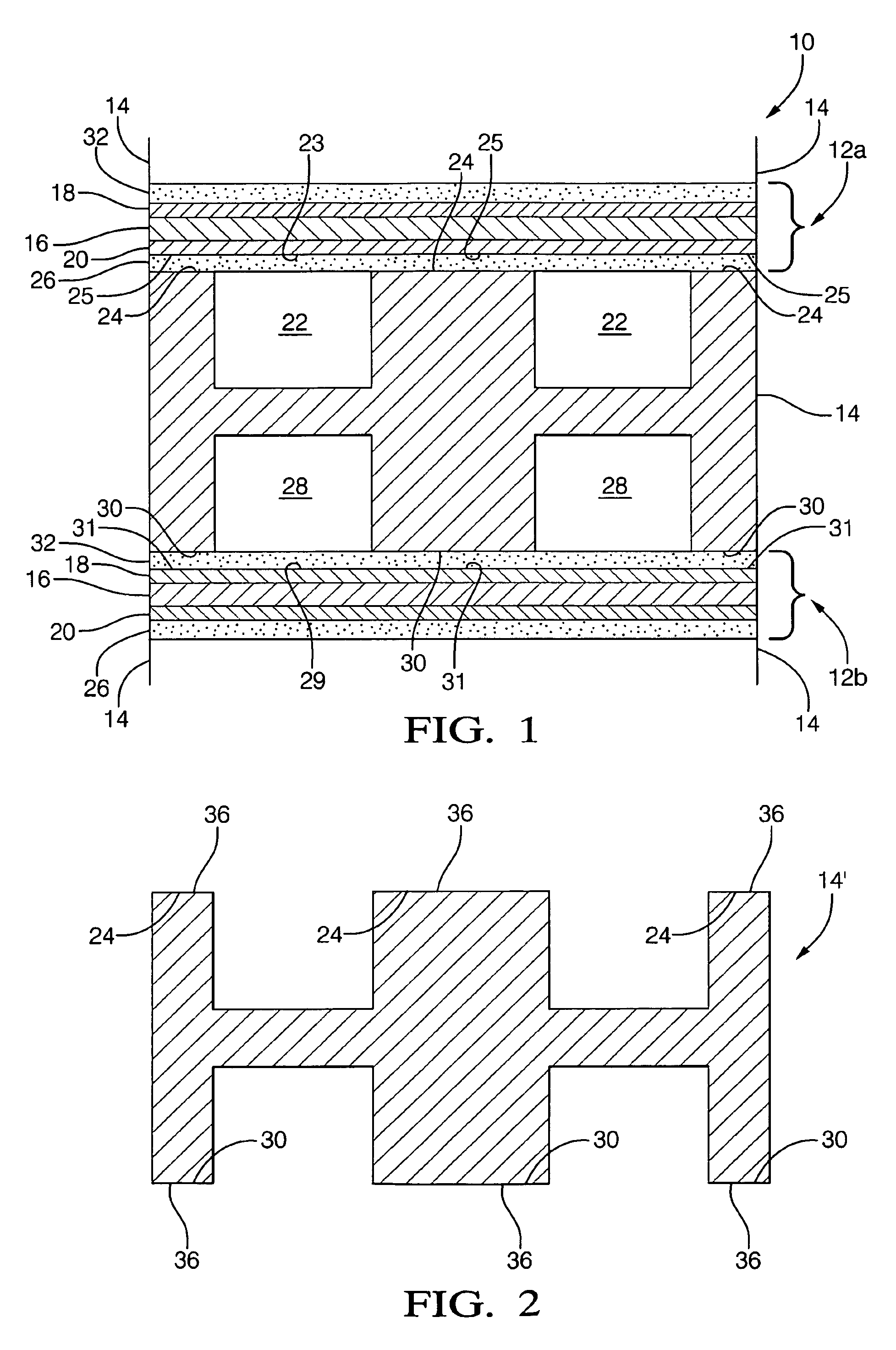
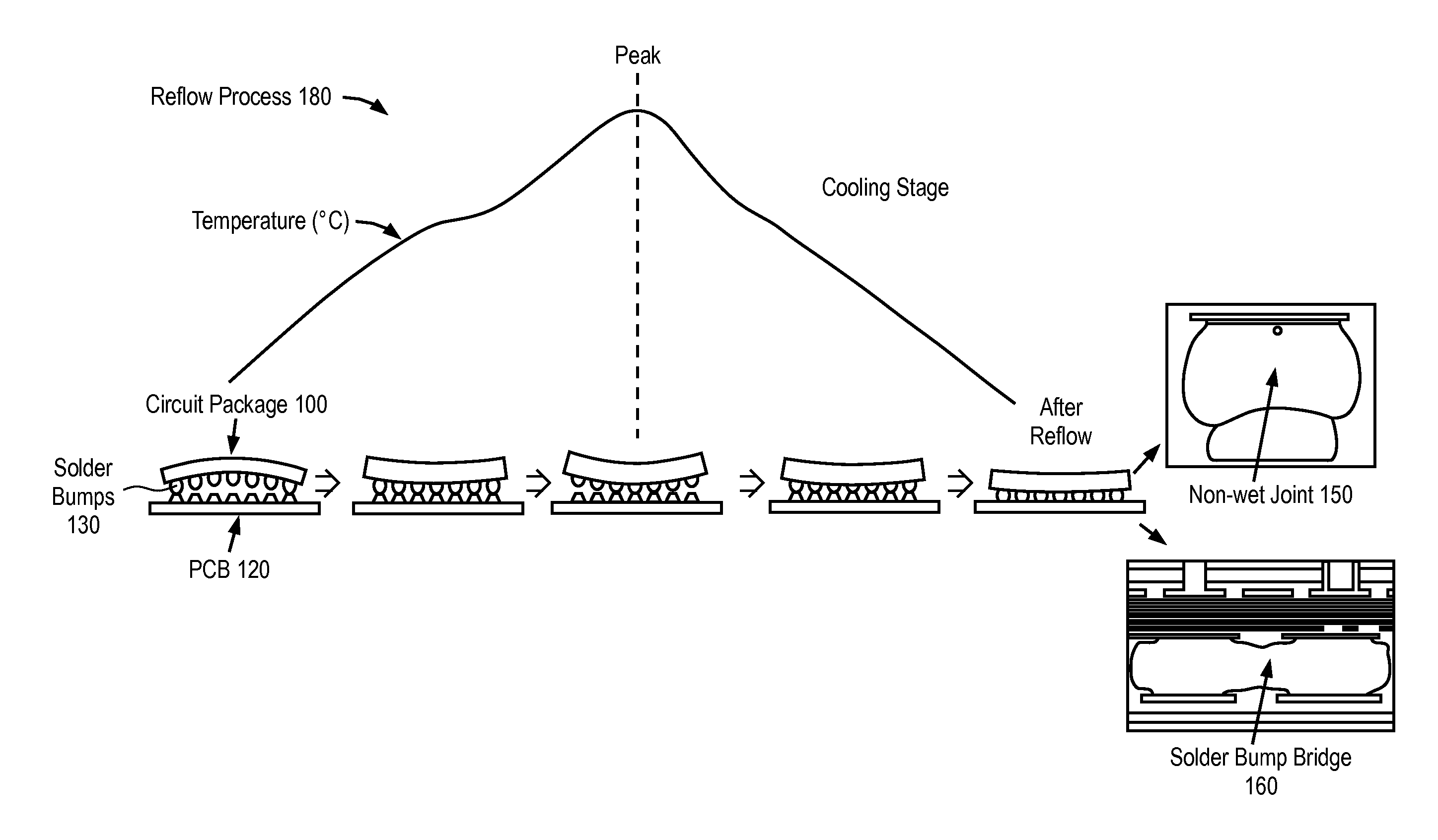
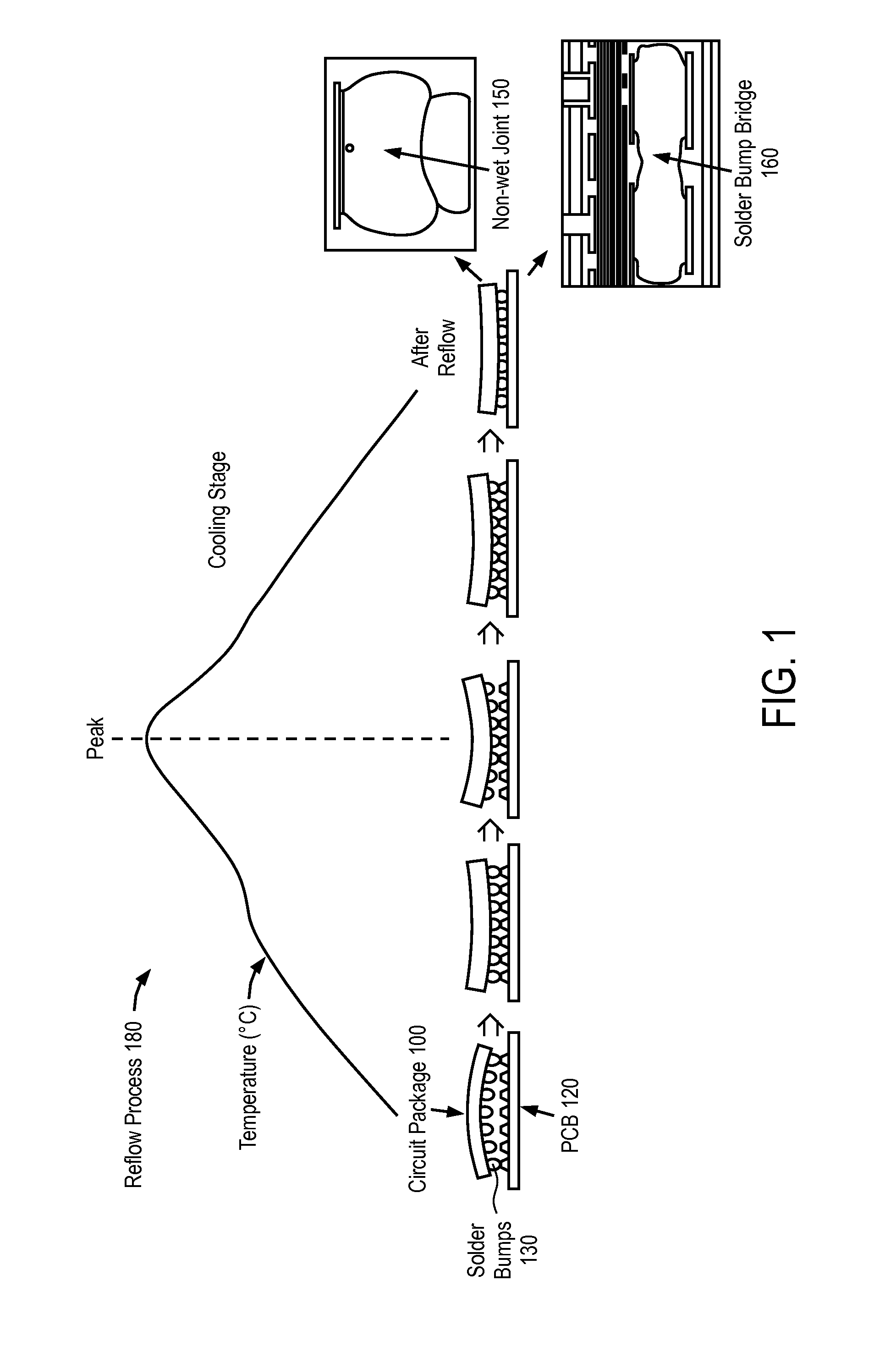
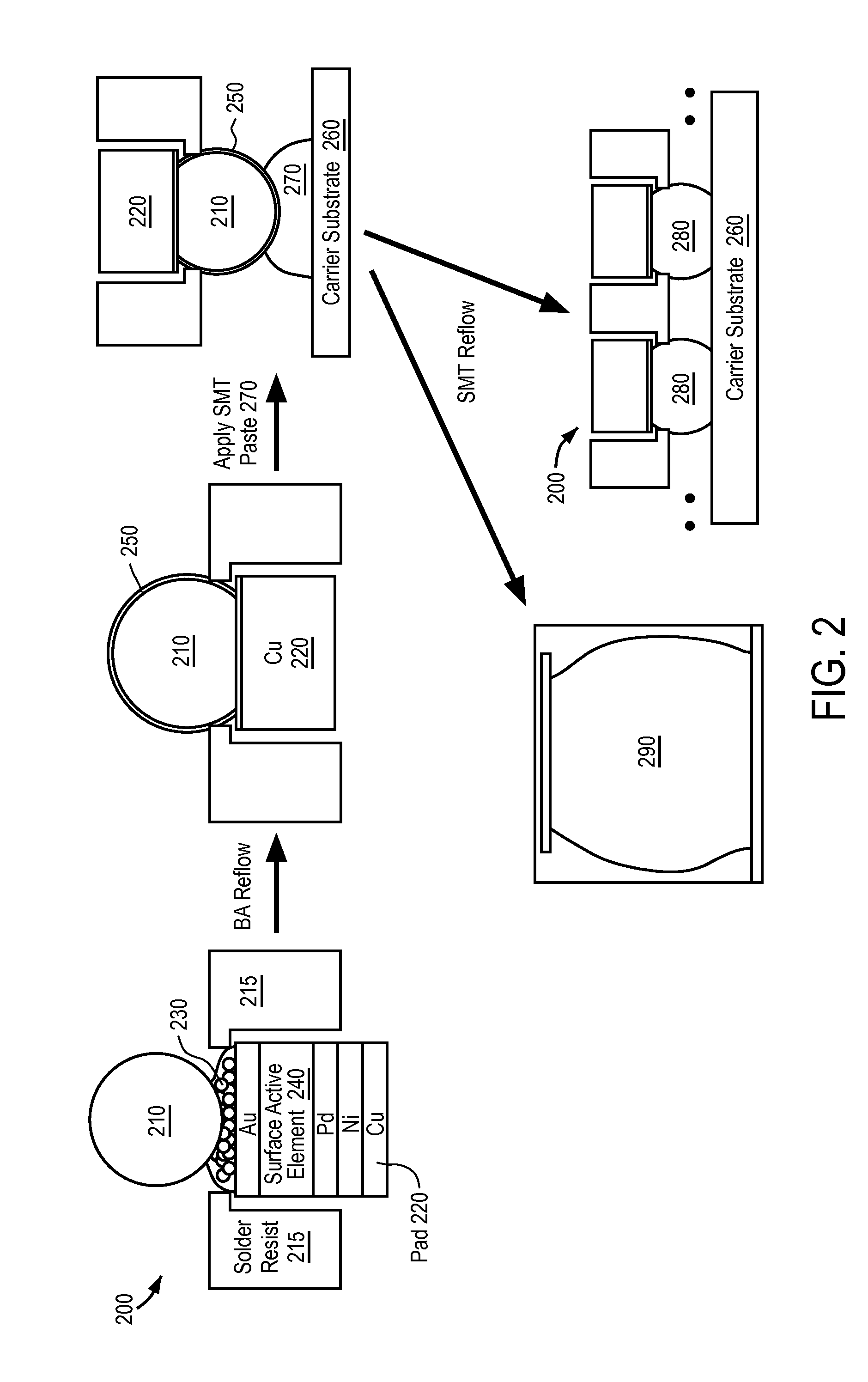
Surface-active dopants are added to a portion of a circuit package before a reflow process to promote wetting and reduce the formation of solder bump bridges. The circuit package has a solder element that electrically connects the circuit package to a substrate. A reflow process is performed to attach the solder element to a pad on the circuit package. During the reflow process, the surface-active dopants diffuse to the surface of the solder element and form an oxide passivation layer on the surface of the solder element.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Atomic layer etching 3D structures: si and sige and ge smoothness on horizontal and vertical surfaces
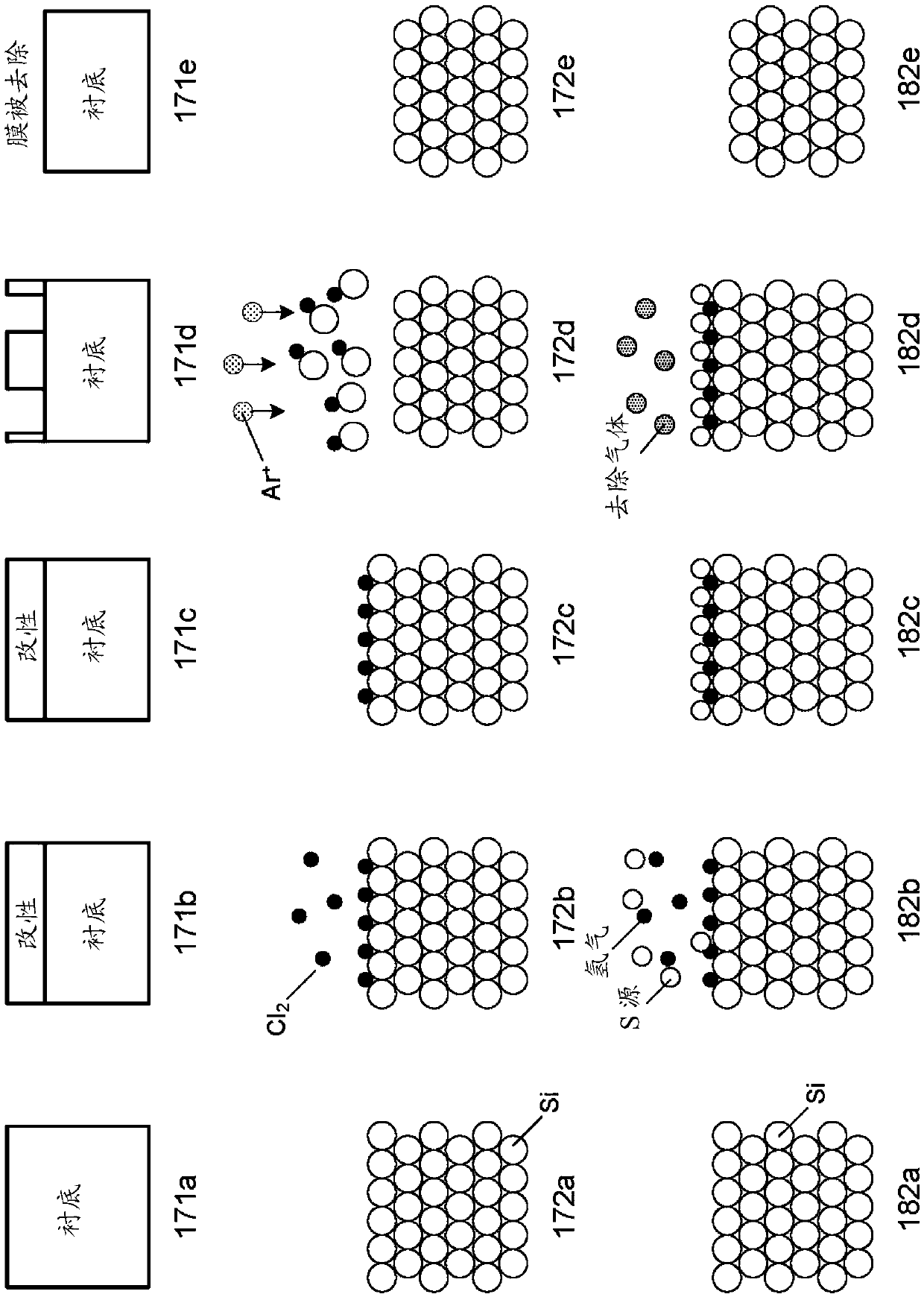
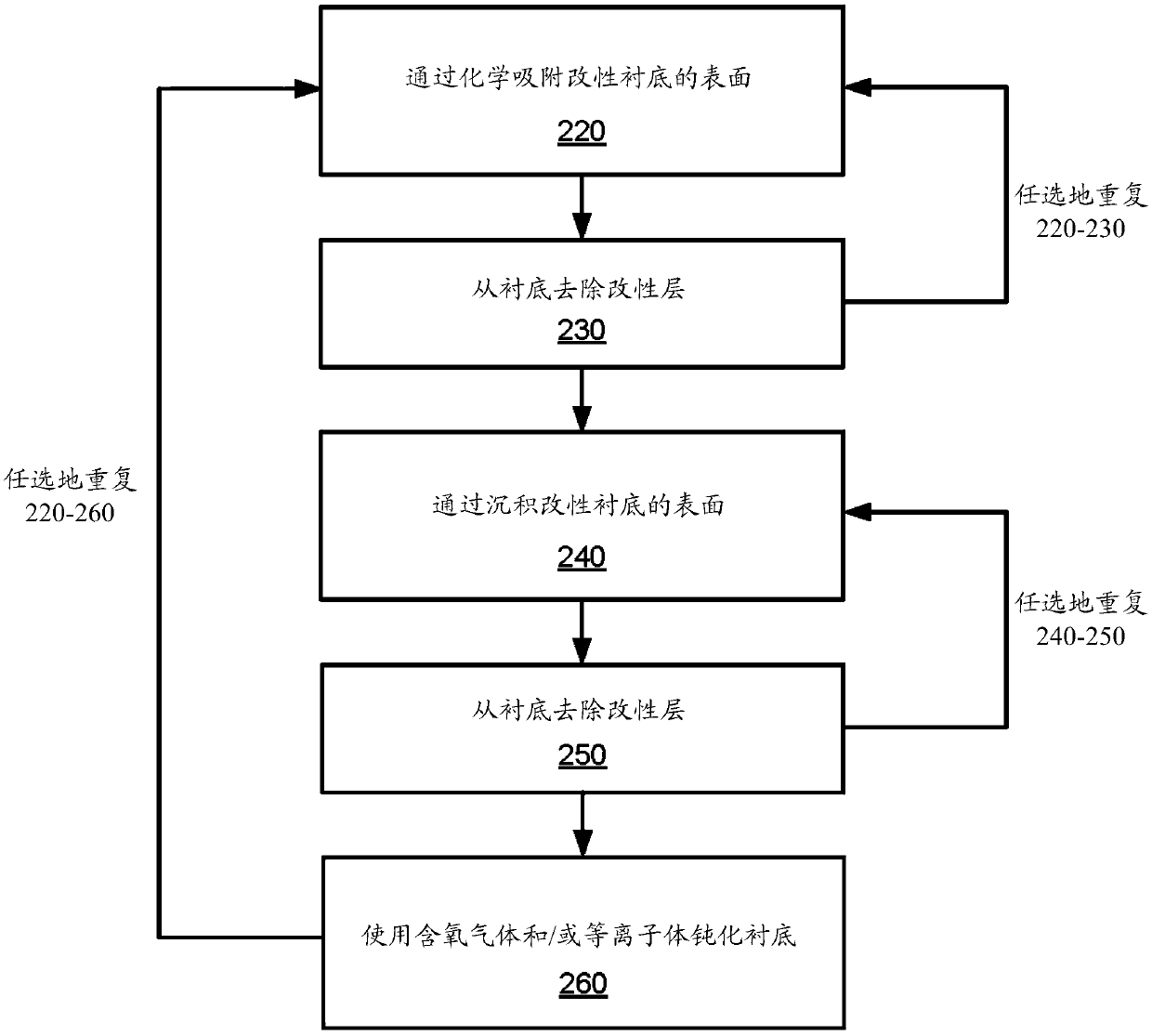
ActiveCN107068556AElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsHydrogen
The invention relates to atomic layer etching 3D structures: SI and SiGe and Ge smoothing on horizontal and vertical surfaces. Methods and apparatuses for etching semiconductor material on substrates using atomic layer etching by chemisorption, by deposition, or by both chemisorption and deposition mechanisms in combination with oxide passivation are described herein. Methods involving atomic layer etching using a chemisorption mechanism involve exposing the semiconductor material to chlorine to chemisorb chlorine onto the substrate surface and exposing the modified surface to argon to remove the modified surface. Methods involving atomic layer etching using a deposition mechanism involve exposing the semiconductor material to a sulfur-containing gas and hydrogen to deposit and thereby modify the substrate surface and removing the modified surface.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
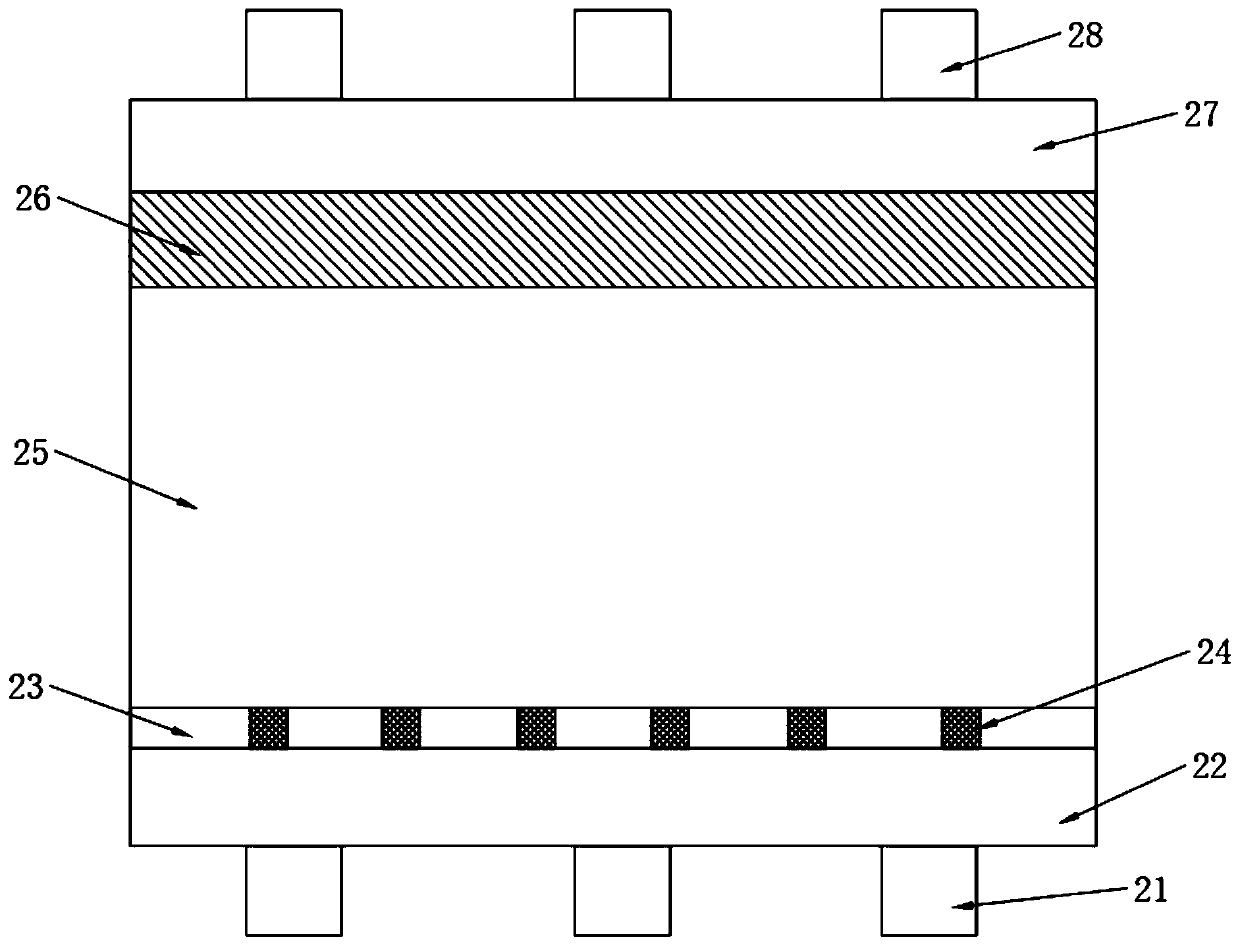
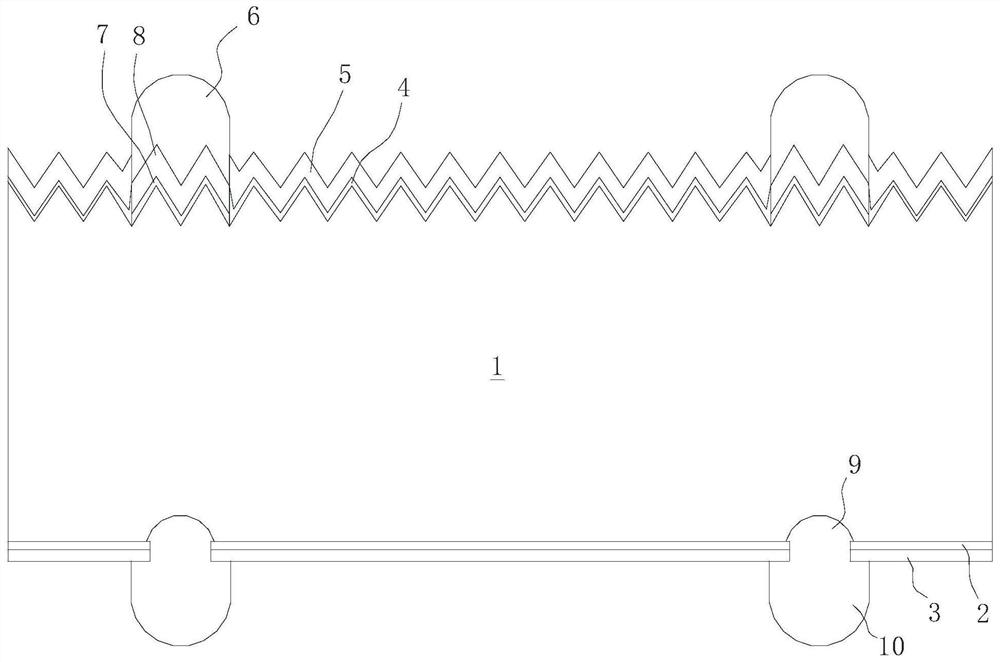
Wafer structure for reducing damage of wafer cutting stress and layout design method
ActiveCN103137567AGuaranteed widthAvoid stress crackingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh densityEngineering
The invention discloses a wafer structure for reducing damage of wafer cutting stress and a layout design method. The wafer structure comprises a high-density metal layer and an oxide passivation protection layer which is located above the high-density metal layer. The oxide passivation protection layer comprises a metal layer without graph connecting lines and a grinding cushion layer which is located above the metal layer without the graph connecting lines. The wafer structure further comprises an opening window and a metal fake component, wherein the opening window is arranged on the oxide passivation protection layer above characteristic graphs of the wafer structure, and the metal fake component is arranged on the metal layer without the graph connecting lines. According to the wafer structure for reducing the damage of the wafer cutting stress and the layout design method, large-energy stress crack is prevented from occurring when a wafer is cut, or a damage distance of the crack is shortened.
Owner:HEJIAN TECH SUZHOU
Method for preparing layered bimetallic hydroxide passivation film in situ
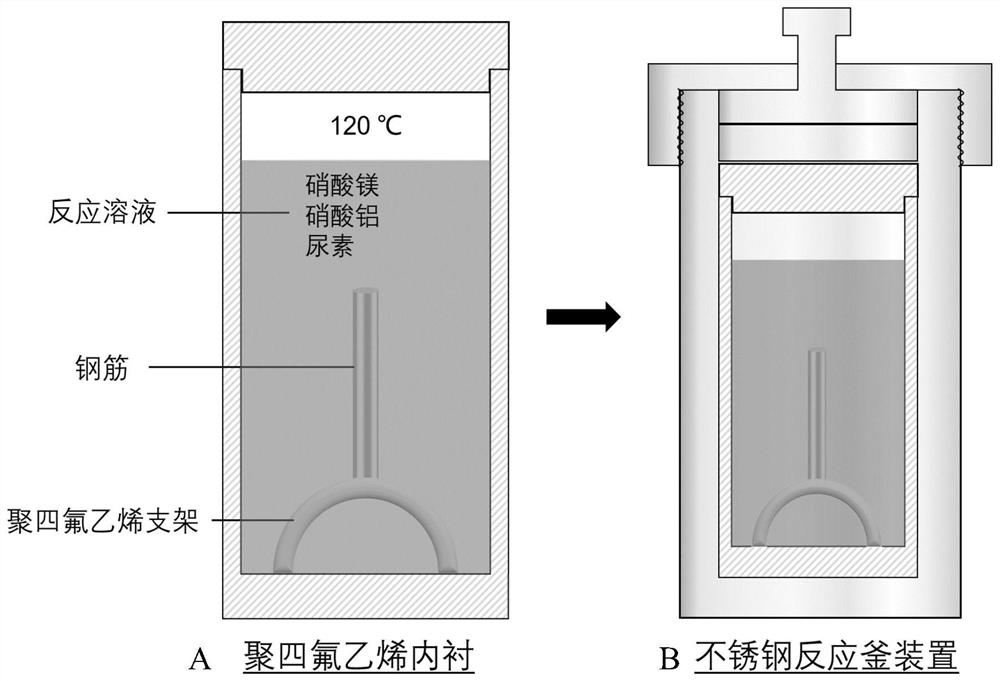
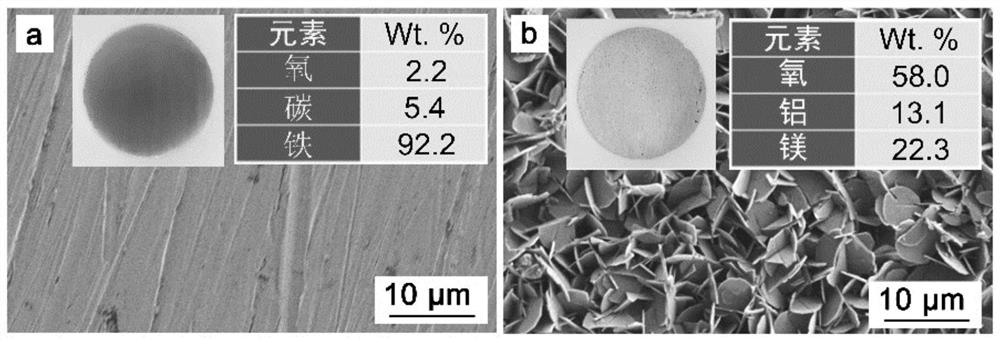
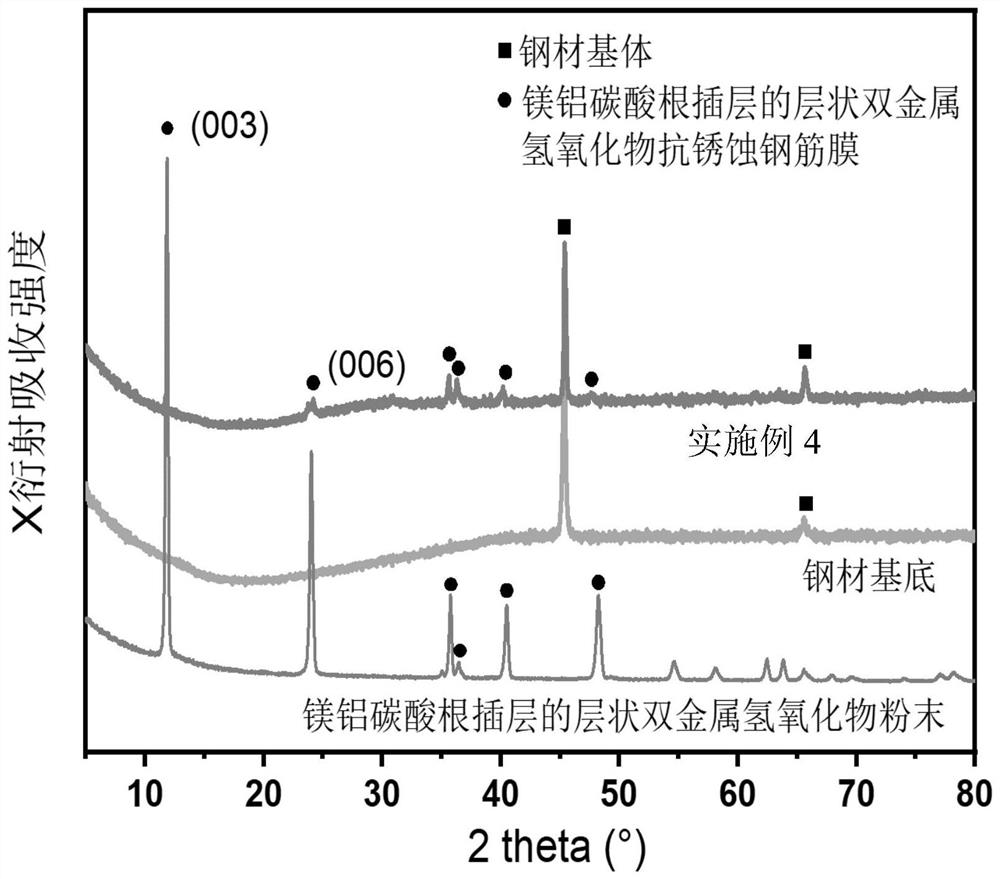
ActiveCN112301344ASimple processEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyMetallic material coating processesMetal nitrateDivalent metal
The application provides a method for preparing a layered bimetallic hydroxide passivation film in situ. According to the method, the layered bimetallic hydroxide passivation film grows on the surfaceof an iron-based substrate in situ in one step by utilizing a hydrothermal method and in combination with urea decomposition; a hydrothermal reaction is performed on the iron-based substrate obtainedby pretreatment and a reaction solution containing urea, a divalent metal nitrate, and a trivalent metal nitrate to grow the layered bimetallic hydroxide passivation film; the preparation method is simple in technology; further, the thickness of the passivation film can be controlled by controlling a reaction time and a reaction temperature; thus, the anti-corrosive protection of a reinforcing steel bar is achieved; the excessive pretreatment does not need to be performed on the reinforcing steel bar in a reaction process; the preparation of the layered bimetallic hydroxide passivation film can be easily realized by adopting a one-step in-situ synthesis urea decomposition hydrothermal method; and the method is simple, convenient, easy to operate, energy-saving, environment-friendly, further, low in cost, and suitable for wide industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com