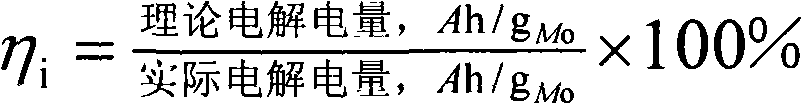Decomposition method for molybdenite by wet process
A technology of molybdenite and full wet method, which is applied in electrolysis process, electrolysis components, etc., can solve the problems of high production cost, high power consumption, and low current efficiency, and achieve high leaching rate, low energy consumption, and enhanced mass transfer Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] The molybdenite concentrate contains Mo47.40%, the particle size distribution is 10-100 μm, 87% is less than 45 μm, and the volume average particle size is 27.18 μm.
[0022] Add 2 parts of molybdenum concentrate, 0.25 parts of sodium carbonate, 5 parts of NaCl and 20 parts of water into an electrolytic cell without a diaphragm, and the electrolytic anode is a DSA anode (TiO 2 RuO plated on base 2 ), the cathode uses titanium mesh. After stirring and making pulp, energize and electrolytically oxidize at a temperature of 10°C, and control the anode current density to 700A / m during electrolysis 2 , energized and electrolyzed for 360 minutes, and stopped stirring. After washing the electrodes and filtering, the content of Mo in the filtrate was analyzed, and the leaching rate of Mo was 86.5%, the leaching rate of Re was 88.7%, and the electrolytic current efficiency was 72.2%.
[0023] Calculation of electrolysis current efficiency:
[0024]
[0025] Calculation of ...
Embodiment 2
[0028] A diaphragm-free electrolytic cell with an ultrasonic generating device is used (the ultrasonic probe is directly placed in the pulp), and the electrolytic anode is a DSA anode (TiO 2 RuO plated on base 2 ), the cathode adopts low carbon steel cathode (iron cathode).
[0029] 2 parts of molybdenum concentrate (Mo47.40%, the same as Example 1), 0.25 parts of sodium carbonate, 4.5 parts of KCl and 20 parts of water are added to the electrolytic cell, and after electrolytic stirring and slurrying, energized electrolytic oxidation at room temperature, electrolytic Control the anode current density at 750A / m 2 , continuous ultrasonic emission, energized electrolysis for 240 minutes, and stopped stirring. After washing the electrodes and filtering, the Mo content in the filtrate was analyzed, and the leaching rate of Mo was 99.4%, the leaching rate of Re was 100%, and the electrolytic current efficiency was 100.1%.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The test device is the same as in Example 2.
[0032] With 2 parts of molybdenum concentrate (Mo 47.40%, with embodiment 1), 0.25 parts of sodium hydroxide, 2.5 parts of NH 4 Cl and 15 parts of water are added into the electrolytic tank and stirred to make slurry. Control the electrolysis temperature to 45°C and the anode current density to 50A / m 2 , Ultrasonic waves are emitted for 3 minutes every 15 minutes, energized and electrolyzed for 600 minutes, and the stirring is stopped. After washing the electrodes and filtering, the content of Mo in the filtrate was analyzed, and it was found that the leaching rate of Mo was 94.8%, and the electrolytic current efficiency was 96.1%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com